DYNEX MP04HBT490-26, MP04HBP490-28, MP04HBP490-24, MP04HBP490-26, MP04HBN490-28 Datasheet
...
MP04---490
1/9
www.dynexsemi.com
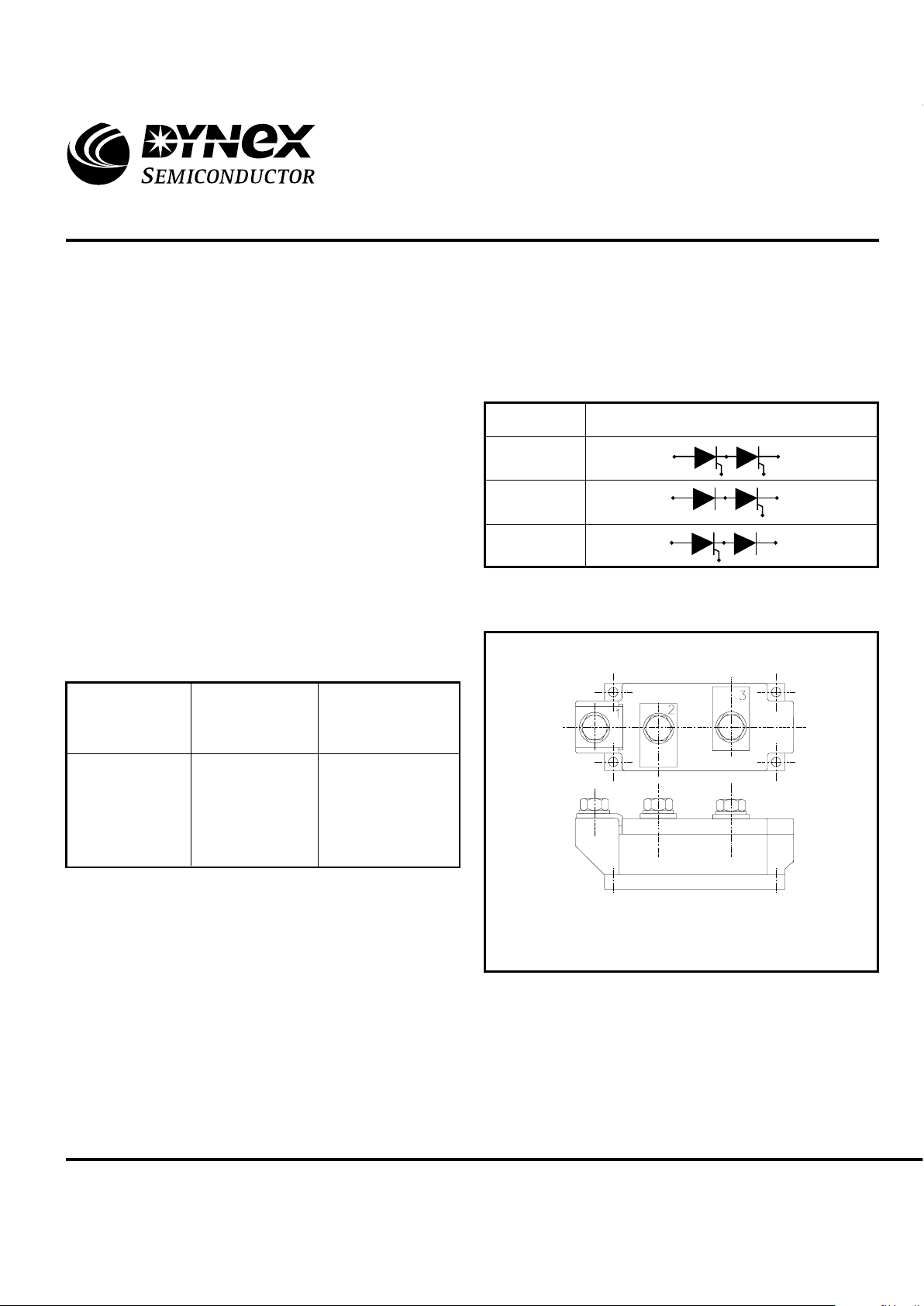
Code
Circuit
HBT
HBP
HBN
FEATURES
■ Dual Device Module
■ Electrically Isolated Package
■ Pressure Contact Construction
■ International Standard Footprint
■ Alumina (Non Toxic) Isolation Medium
■ Integral Water Cooled Heatsink
APPLICATIONS
■ Motor Control
■ Controlled Rectifier Bridges
■ Heater Control
■ AC Phase Control
VOLTAGE RATINGS
ORDERING INFORMATION
Order As:
MP04HBT490-28 or MP04HBT490-26 or MP04HBT490-24
MP04HBP490-28 or MP04HBP490-26 or MP04HBP490-24
MP04HBN490-28 or MP04HBN490-26 or MP04HBN490-24
Note: When ordering, please use the whole part number.
KEY PARAMETERS
V
DRM
2800V
I
T(AV)
490A
I
TSM(per arm)
11250A
V
isol
3000V
MP04---490
Dual Thyristor, Thyristor/Diode Module
Advance Information
Replaces Jun3 2000 version, DS5204-1.2 DS5204-2.1 April 2001
Fig. 2 Electrical connections - (not to scale)
2800
2600
2400
MP04---490-28
MP04---490-26
MP04---490-24
Conditions
T
vj
= 0˚ to 125˚C,
I
DRM
= I
RRM
= 50mA
V
DSM
= V
RSM
=
V
DRM
= V
RRM
+ 100V
respectively
Lower voltage grades available.
Type Number Repetitive Peak
Voltages
V
DRM VRRM
V
Fig.1 Circuit diagrams
Module type code: MP04.
For further information see Package Details.
MP04---490
2/9
www.dynexsemi.com
Test Conditions
Half wave resistive load T
case
= 75˚C
T
case
= 85˚C
T
case
= 75˚C
10ms half sine, T
j
= 125˚C
V
R
= 0
10ms half sine, T
j
= 125˚C
V
R
= 50% V
DRM
Commoned terminals to base plate.
AC RMS, 1 min, 50Hz
Symbol
I
T(AV)
I
T(RMS
I
TSM
I2t
I
TSM
I2t
V
isol
Units
A
A
A
kA
A
2
s
kA
A
2
s
V
Max.
490
420
770
11.25
633 x 10
3
9
506 x 10
3
3000
Test Conditions
dc, 4.5 Ltr/min
Half wave, 4.5 Ltr/min
3 Phase, 4.5 Ltr/min
Mounting torque = 5Nm
with mounting compound
Reverse (blocking)
-
Mounting - M6
Electrical connections - M10
-
Parameter
Thermal resistance - junction to water
(per thyristor or diode)
Thermal resistance - case to heatsink
(per thyristor or diode)
Virtual junction temperature
Storage temperature range
Screw torque
Weight (nominal)
THERMAL AND MECHANICAL RATINGS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS - PER ARM
Stresses above those listed under 'Absolute Maximum Ratings' may cause permanent damage to the device. In extreme
conditions, as with all semiconductors, this may include potentially hazardous rupture of the package. Appropriate safety
precautions should always be followed. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Ratings may affect device reliability.
Parameter
Mean on-state current
RMS value
Surge (non-repetitive) on-current
I
2
t for fusing
Surge (non-repetitive) on-current
I
2
t for fusing
Isolation voltage
Symbol
R
th(j-c)
R
th(c-hs)
T
vj
T
stg
-
-
Units
˚C/kW
˚C/kW
˚C/kW
˚C/kW
˚C
˚C
Nm (lb.ins)
Nm (lb.ins)
g
Max.
0.056
0.060
0.066
0.02
125
130
6 (35)
12 (106)
1580
Min.
-
-
-
-
-
–40
-
-
-
MP04---490
3/9
www.dynexsemi.com
Units
mA
V/µs
A/µs
V
mΩ
Test Conditions
At V
RRM/VDRM
, Tj = 125˚C
To 67% V
DRM
, Tj = 125˚C
From 67% V
DRM
to 1500A, gate source 1.5A,
t
r
= 0.5µs, Tj = 125˚C
At T
vj
= 125˚C. See note 1
At T
vj
= 125˚C. See note 1
Parameter
Peak reverse and off-state current
Linear rate of rise of off-state voltage
Rate of rise of on-state current
Threshold voltage
On-state slope resistance
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS - THYRISTOR
Symbol
I
RRM/IDRM
dV/dt
dI/dt
V
T(TO)
r
T
Max.
50
1000
500
0.91
0.65
Min.
-
-
-
-
-
Parameter
Gate trigger voltage
Gate trigger current
Gate non-trigger voltage
Peak forward gate voltage
Peak forward gate voltage
Peak reverse gate voltage
Peak forward gate current
Peak gate power
Mean gate power
Test Conditions
V
DRM
= 5V, T
case
= 25oC
V
DRM
= 5V, T
case
= 25oC
At V
DRM Tcase
= 125oC
Anode positive with respect to cathode
Anode negative with respect to cathode
-
Anode positive with respect to cathode
See table fig. 5
-
Symbol
V
GT
I
GT
V
GD
V
FGM
V
FGN
V
RGM
I
FGM
P
GM
P
G(AV)
GATE TRIGGER CHARACTERISTICS AND RATINGS
Max.
3.5
200
0.25
30
0.25
5
10
150
10
Units
V
mA
V
V
V
V
A
W
W
Note 1: The data given in this datasheet with regard to forward voltage drop is for calculation of the power dissipation in the
semiconductor elements only. Forward voltage drops measured at the power terminals of the module will be in excess of these
figures due to the impedance of the busbar from the terminal to the semiconductor.
 Loading...
Loading...