Page 1

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 1 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
Wireless LAN 802.11g USB Adapter
Adaptateur USB pour réseau local sans fil 802.11g
Adaptador USB para Red Inalambrica 802.11g mejorado
DX-WGUSB
USER GUIDE • GUIDE DE L’UTILISATEUR • GUÍA DEL USUARIO
Page 2

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 2 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
2
Dynex DX-WGUSB Wireless
LAN USB Adapter
Contents
Introduction..................................................................................... 2
Installing the software and hardware .............................................. 2
Configuring the wireless network .................................................... 4
Troubleshooting............................................................................... 6
FCC ................................................................................................... 7
Legal notices.................................................................................... 7
Français ....................................................... 8
Español ...................................................... 14
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing a Dynex Wireless LAN 802.11g USB adapter.
This package contains:
• A Wireless LAN 802.11g USB adapter
• A printed user guide
• A CD containing the wireless network adapter utility and drivers
and this user guide
If anything is missing, contact Dynex at (800) 305-2204.
Contents
8 If a warning box opens, click Continue Anyway. Your computer
copies files to your hard drive.
9 Click Finish.
To install wireless networking on a Windows 98, Windows 2000, or
Windows ME computer:
Caution : Do not connect the USB adapter until instructed to do so.
1 Install the access point. For more information, see the access point
documentation.
2 Turn on your computer.
3 Insert the included CD in the optical drive.
4 If the installation program does not start automatically, use
Windows Explorer to browse the CD and locate the file named
setup.exe, then double-click setup.exe to start installing the
software.
5 Follow the on-screen instructions to install the software.
6 Connect the USB adapter to a USB connector on your computer.
The Found New Hardware Wizard opens.
7 Right-click on the My Computer desktop icon, click Properties,
then click Hardware Device Manager. Make sure that the USB
adapter is listed as one of the devices in your computer.
Installing the software and
hardware
Use the following procedures to set up your wireless network.
To install wireless networking on a Windows XP computer:
Caution : Do not connect the USB adapter until instructed to do so.
1 Install the access point. For more information, see the access point
documentation.
2 Turn on your computer.
3 Insert the included CD in the optical drive.
4 If the installation program does not start automatically, use
Windows Explorer or My Computer to browse the CD and locate
the file named setup.exe, then double-click setup.exe to start
installing the software.
5 Follow the on-screen instructions to install the software.
6 Connect the USB adapter to a USB connector on your computer.
The Found New Hardware Wizard opens.
7 Click Install the software automatically (Recommended),
then click Next.
Page 3
DX-WGUSB.fm Page 3 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
Installing the software and hardware
8 If you are using Windows 98, right-click on the Network
Neighborhood desktop icon, then click Properties. The Lo cal
Area Connection Properties dialog box opens.
-ORIf you are using Windows ME and Windows 2000, right-click on
the Network Neighborhood desktop icon, click Properties,
then click Local Area Connection's properties. The Local Area
Connection Properties dialog box opens.
3
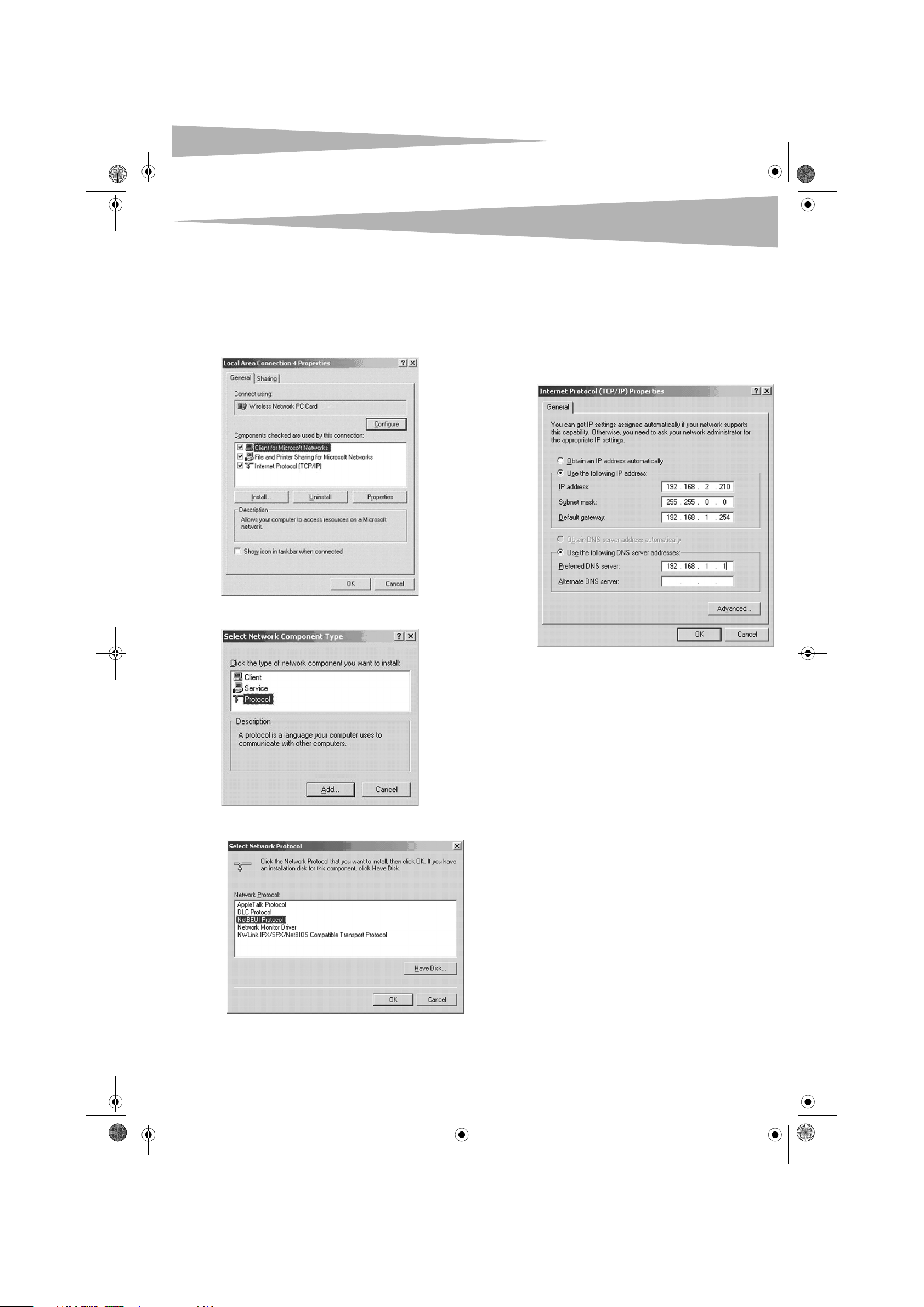
11 From the network protocols list, select NetBEUI, then click OK.
The NetBEUI protocol is installed.
12 Click OK to return to the Select Network Component Type dialog
box.
13 Repeat steps 10 through 12 to add the IPX/SPX protocol.
14 Click TCP/IP to set the IP address for your computer. Select either
Obtain an IP address automatically or Use the following IP
address setting. If you choose to specify an IP address, then enter
the IP value, subnet mask, DNS, Domain/ Workgroup name, and
Gateway Address values.
9 Click on the General tab, then click Install. The Select Network
Component Type dialog box opens.
10 Click Protocol, then click Add. The Select Net work Protocols dialog
box opens.
15 Click OK to return to Local Area Connection Properties dialog box.
16 Select the File and Printer Sharing options and sharing for your
computer’s resources, then click OK.
17 Click Yes when a pop up appears asking if you want to restart your
computer. Your computer turns off and turns on again.
Uninstalling the software and hardware
To uninstall the software and hardware:
1 Click Start, All Programs or Programs, Dynex DX-WGUSB
Wireless LAN Card Utility, then click Uninstall.
2 Remove the USB adapter.
3 Restart your computer.
Page 4

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 4 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
4
Configuring the wireless network
Your Wireless LAN 802.11g USB adapter uses its own management
software. All functions are controlled by this utility. To make it easier to
move from one network environment to another, the utility uses profiles
that you create.
To use the wireless utility:
1 Click Start, All Programs or Programs, Dynex DX-WGUSB
Wireless LAN Card Utility, then Dynex DX-WGUSB Wireless
LAN Card Utility.
Note: The wireless utility icon should appear in your icon tray. If the
icon is red, it means that the Wireless LAN 802.11g NIC configuration is
invalid or incomplete.
Configuring the wireless network
Connected To Network—This field displays the current status of the
connection. Possible status messages include:
• Connected to Network—Indicates normal flow of operation in
Infrastructure mode. The computer is connected to an access point
and networking is available.
• Scanning—Indicates the computer is searching for an available
access point within range.
Note: This field also displays error messages if the driver fails to initialize.
Network Type—Possible network types include:
• Infrastructure Mode—The driver scans all available channels
continuously until it finds one or more access points that match its
SSID (network name). At that point it tries to authenticate and
associate with the access point.
• Peer to Peer Mode—The driver scans for five seconds looking
for an existing Ad Hoc network using the same SSID.
Channel—Displays the channel the network is on.
Encryption—Displays Off when encryption is turned off, WEP when
either 64-bit or 128-bit is turned on, or WPA when WPA is turned on.
Link Speed—Displays the current connection data rate.
Signal Strength—The Signal Strength bar graph is only active when
the network is in infrastructure mode. The bar graph displays normalized
signal strength as reported by the radio, averaged over all frames over
100 bytes long that are received from the access point.
Link Quality—The Link Quality bar graph is only active when the
network is in infrastructure mode. The bar graph displays the quality of
the link between the computer and access point.
2 Select the profile you want to use for your network connection.
-ORClick on the following:
• The tabs to navigate through the different settings.
•The X button to minimize the window.
•The More… button to get more information.
Link Information tab
Available Networks tab
The Available Networks tab shows the current status of available access
points within the network and lets you select which access point you
want to connect to.
To connect to an access point:
1 Select an access point from list.
2 Click Connect to connect to the access point.
If the access point you want to connect to is not listed, click Refresh to
rescan the network and list all available access points within network.
Fields on the Link Information tab include:
Page 5

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 5 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
Configuring the wireless network
Connecting to a network
To connect to a network:
1 Click Connect on the Available Networks tab. The following screen
opens.
2 Set the values of the following fields:
• Network Name—Type a name for the new profile.
• Network Type —Select from the list of supported network
types. Supported types include:
• Peer to Peer—This is the 802.11g peer-to-peer mode (also
known as Ad Hoc). Only one wireless cell is supported for each
different SSID. All communication is done from client to client
without the use of an access point. 802.11g Ad Hoc
networking uses the same SSID for establishing the wireless
connection.
• Access Point—This mode requires an 802.11g or 802.11b
access point. All communication is done through the access
point, which relays packets of information to other wireless
computers as well as to computers on a wired network (such
as Ethernet).
• Transfer Rate —The transmission rate at which the access point
transmits the data packets. You may set this to:
• fixed 1 Mbps, fixed 2 Mbps, fixed 5.5 Mbps, fixed 11 Mbps, or
Automatic if you are using an 802.11b access point.
• fixed 6 Mbps, fixed 9 Mbps, fixed 12 Mbps, fixed 18 Mbps,
fixed 24Mbps, fixed 36 Mbps, fixed 48 Mbps, fixed 54 Mbps,
or Automatic if you are using an 802.11g access point.
3 Click Next. The following screen opens.
5
5 Click Next. The following screen opens.
When encrypted information is received it is only accepted if it
decrypts correctly. This happens only if the computer has the WEP
Key used by the access point. This screen lets you enter the WEP
key.
6 Set the values of the following fields:
• Input Method—Select the input method that matches the
input method used by the access point.
• Key—Enter the WEP Key. This key must be the same as the key
used by the access point. It must be between 8 and 63 characters
long.
Note: Use only the digits 0-9 and letters A-F for the key.
• Key Index—Select the key index that matches the key index
used by the access point.
7 Click Next. The following screen opens.
4 Set the values of the following fields:
• Authentication Mode—Use the default authentication mode.
• Encryption—Use the default encryption.
8 If you want to set the IP setting, click Enable, then go to step 9.
-ORIf you want the IP setting to be set up automatica lly, click Disable,
then click Complete. You are finished.
Page 6

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 6 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
6
9 Click Next. The following screen opens.
The purpose of this screen is to configure the TCP/IP setting of
each wireless connection. You must define if the current profile’s IP
setting is assigned by a DHCP server or assigned by a fixed IP that
is determinate by the Network Administrator.
10 Set the values of the following fields:
• DHCP Status—Select Enable if the TCP/IP information is
assigned by a DHCP Server. Select Disable if you would like to
specify the IP address manually.
• IP Address—Enter the IP address for the network card.
• Subnet Mask—Enter the subnet mask for the network card. The
default is 255.255.255.0
• Default Gateway—Enter your network’s default gateway’s IP
address.
• DNS Server—Enter the domain name system server’s address.
11 Click Complete. You are finished.
Profile Setting tab
The Profile Setting tab lets you create profiles for different network
environments.
Troubleshooting
About tab
The About tab shows the product version including details of the driver,
application, and firmware versions. You must use this version number
when reporting problems to Dynex.
Troubleshooting
Windows 98
To make sure that the WLAN 802.11g device is installed properly:
1 Click Start, Settings, Control Panel, then Network. Click the
Configuration tab. If you find the WLAN 802.11g USB adapter
listed, it means the USB adapter is installed properly. If you see a
yellow question mark, it means there is a resource conflict.
-ORRight-click on the My Computer desktop icon, then select
Properties. Click Device Manager, then click on Network
Adapter. If you find the WLAN 802.11g USB adapter listed, it
means the USB adapter is installed properly. If you see a yellow
question mark, it means there is a resource conflict.
2 Click on the USB adapter and then on the adapter service. You will
see the status of the USB adapter. If there is a yellow sign on the
USB adapter, check the following:
• Check to see if your computer has a free IRQ. Free an IRQ by
assigning the same IRQ to some devices. For example COM 1
and COM 2 can be assigned the same IRQ values.
• Make sure that you have connected the correct USB adapter
and have installed the correct driver.
On this tab, you can click the following buttons:
• Add to create new profile.
• Edit to edit the currently highlighted profile.
• Delete to delete the currently highlighted profile.
• Connect to connect to a network using the currently highlighted
profile.
Windows 2000
To make sure that the WLAN 802.11g device is installed properly:
1 Use Windows 2000 Diagnostics to see if there is any conflict in the
resource allocation of the I/O Address or IRQ allocations. If you find
that the IRQ or I/O Addresses are already assigned to other devices,
you must change that value. The I/O Address must be 40h bytes
long.
2 Go to the Control Panel. Double-click on the USB adapter and view
the WLAN adapter. Double-clicking on the USB adapter shows you
the USB adapter information, driver name, and the driver file. If
you do not find the names, there are some problems and the
driver is not installed correctly. Reinstall the driver.
3 Check the PnP BIOS setup menu, then click No.
Page 7

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 7 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
FCC
FCC
Federal Communication Commission Interference
Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for
a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged
to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to
operate this equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Important Note (for DX-WGUSB)
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for
an uncontrolled environment. End users must follow the specific
operating instructions for satisfying RF exposure compliance. This
transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter. This equipment has been SAR-evaluated
for use in laptops (notebooks) with side slot configuration.
Dynex declares that DX-WGUSB (FCC ID: MXF-U950731G) is limited in
CH1~CH11 for 2.4 GHz by specified firmware controlled in U.S.A.
IC statement (for DX-WGUSB)
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may
not cause interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference,
including interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
Important Note
IC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with IC radiation exposure limits set forth for
an uncontrolled environment. End users must follow the specific
operating instructions for satisfying RF exposure compliance. This
transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.
7
Legal notices
© 2006 Dynex. DYNEX and the DYNEX logo are trademarks of Best Buy
Enterprise Services, Inc. Other brands and product names are trademarks
or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Specifications and
features are subject to change without notice or obligation.
Page 8

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 8 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
8
Adaptateur USB pour
réseau local sans fil Dynex
DX-WGUSB
Table des matières
Introduction..................................................................................... 8
Installation du logiciel et du matériel............................................... 8
Configuration du réseau sans fil ..................................................... 10
Problèmes et solutions................................................................... 13
FCC ................................................................................................. 13
Avis juridiques................................................................................ 13
Introduction
Merci d’avoir acheté cet adaptateur pour réseau local sans fil 802.11g
Dynex. Cet ensemble contient :
• Un adaptateur USB pour réseau local sans fil 802.11g
• Un guide de l’utilisateur (format papier)
• Un CD contenant l’utilitaires et les pilotes de l’adaptateur réseau
sans fil et ce guide de l’utilisateur
Si un article manque, contacter Dynex au (800) 305-2204.
Table des matières
7 Cliquer sur Install the software automatically
(Recommended) (Installer le logiciel automatiquement
[recommandé]), puis sur Next (Suivant).
8 Si une boîte d’alerte s’ouvre, cliquer sur Continue Anyway
(Continuer). L’ordinateur copie les fichiers sur le disque dur.
9 Cliquer sur Finish (Terminer).
Pour installer l’adaptateur de réseau sans fil sur un ordinateur sous
Windows 98, Windows 2000 ou Windows ME :
Attention : Ne pas connecter l’adaptateur USB tant que ce n’est pas requis
par l’application d’installation.
1 Installer le point d’accès. Pour plus d’informations, voir la
documentation sur le point d’accès.
2 Mettre l'ordinateur sous tension.
3 Insérer le CD fourni dans le lecteur optique.
4 Si l’application d’installation ne démarre pas automatiquement,
utiliser l’explorateur Windows pour parcourir le CD et localiser le
fichier setup.exe, puis double-cliquer sur setup.exe pour
installer le logiciel.
5 Suivre les instructions d'installation à l'écran pour installer les
logiciels.
6 Connecter l’adaptateur USB à un connecteur USB de l’ordinateur.
La fenêtre Found New Hardware Wizard (Assistant Ajout de
nouveau matériel détecté) s’affiche.
Installation du logiciel et du
matériel
Utiliser les procédures suivantes pour l’installation du réseau sans fil.
Pour installer le réseau sans fil sur un ordinateur sous Windows XP :
Attention : Ne pas connecter l’adaptateur USB tant que ce n’est pas requis
par l’application d’installation.
1 Installer le point d’accès. Pour plus d’informations, voir la
documentation sur le point d’accès.
2 Mettre l'ordinateur sous tension.
3 Insérer le CD fourni dans le lecteur optique.
4 Si l’application d’installation ne démarre pas automatiquement,
utiliser l’explorateur Windows ou My Computer (Poste de travail)
pour parcourir le CD et localiser le fichier setup.exe, puis
double-cliquer sur setup.exe pour installer le logiciel.
5 Suivre les instructions d'installation à l'écran pour installer les
logiciels.
6 Connecter l’adaptateur USB à un connecteur USB de l’ordinateur.
La fenêtre Found New Hardware Wizard (Assistant Ajout de
nouveau matériel détecté) s’affiche.
7 Cliquer à l’aide du bouton droit de la souris sur l’icône du bureau
My Computer (Poste de travail), cliquer sur Properties
(Propriétés), puis cliquer sur Hardware Device Manager
(Gestionnaire de périphériques matériels). Vérifier que
l'adaptateur USB est listé parmi les périphériques de l’ordinateur.
Page 9

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 9 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
Installation du logiciel et du matériel
8 Sous Windows 98, cliquer à l’aide du bouton droit de la souris sur
l’icône du bureau Network Neighborhood (Voisinage réseau),
puis cliquer sur Properties (Propriétés). La boîte de dialogue
Local Area Connections Properties (Propriétés des connexions au
réseau local) s’ouvre.
- OU Sous Windows ME et Windows 2000, cliquer à l’aide du bouton
droit de la souris sur l’icône du bureau Network Neighborhood
(Voisinage réseau), puis cliquer sur Properties (Propriétés), puis
cliquer sur Local Area Connection's properties (Propriétés des
connexions au réseau local). La boîte de dialogue Local Area
Connections Properties (Propriétés des connexions au réseau local)
s’ouvre.
9
10 Cliquer sur Protocol(Protocole), puis sur Add(Ajouter). La boîte
de dialogueSelect Network Protocols (Sélection des protocoles
réseau) s’ouvre.
11 Dans la liste des protocoles réseau, sélectionner NetBEUI, puis
cliquer sur OK. Le protocole NetBEUI est installé.
12 Cliquer sur OK pour retourner à la boîte de dialogue Select Network
Component Type (Sélection du type de composant réseau).
13 Répéter les étapes 10 à 12 pour ajouter le protocole IPX/SPX.
14 Cliquer sur TC P/IP pour configurer l’adresse IP de l’ordinateur.
Sélectionner l’une des options Obtain an IP address
automatically (Obtenir une adresse IP automatiquement) ou
Use the following IP address (Utiliser l’adresse IP suivante).
Pour spécifier une adresse IP, saisir alors la valeur IP, le masque de
sous-réseau (subnet mask) et les valeurs DNS, nom de Domaine/
Groupe de travail (Domain/ Workgroup) et passerelle (Gateway).
9 Cliquer sur l’onglet General (Général) puis sur Install (Installer).
La boîte de dialogue Select Network Component Type (Sélection du
type de composant réseau) s’ouvre.
15 Cliquer sur OK pour retourner à la boîte de dialogue Local Area
Connection Properties (Propriétés des connexions au réseau local).
16 Sélectionner les options File and Printer Sharing (Partage de
fichier et d’imprimante) et le partage des ressources de
l’ordinateur, puis cliquer sur OK.
17 Cliquer sur Ye s (Oui) quand une fenêtre contextuelle s'affiche
proposant de redémarrer l'ordinateur. L’ordinateur s’arrête et
redém arre.
Page 10

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 10 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
10
Désinstallation des logiciels et du matériel
Pour désinstaller les logiciels et le matériel :
1 Cliquer sur Start (Démarrer), All Programs (Tous les
programmes) ou Programs (Programmes), Dynex DX-WGUSB
Wireless L AN Card Utility (Utilitaire pour l’adaptateur de réseau
local sans fil Dynex DX-WGUSB), puis cliquer surUninstall
(Désinstaller).
2 Retirer l'adaptateur USB.
3 Redémarrer l'ordinateur.
Configuration du réseau sans fil
L’adaptateur USB pour réseau local sans fil 802.11g utilise son propre
logiciel de gestion. Toutes les fonctions sont contrôlées par cet utilitaire.
Pour faciliter le déplacement d’un environnement réseau à l’autre,
l’utilitaire utilise les profils créés par l’utilisateur.
Pour utiliser l’utilitaire pour sans fil :
1 Cliquer sur Start (Démarrer), All Programs (Tous les
programmes) ou Programs (Programmes), Dynex DX-WGUSB
Wireless L AN Card Utility (Utilitaire pour l’adaptateur de réseau
local sans fil Dynex DX-WGUSB), puis cliquer surDynex
DX-WGUSB Wireless LAN Card Utility.
Remarque : L’icône de l’utilitaire pour l'adaptateur de réseau sans fil
doit s’afficher dans la barre d’état. Si l’icône est rouge, cela signifie que
la configuration de l’adaptateur du réseau local sans fil 802.11g est non
valide ou incomplète.
Configuration du réseau sans fil
Onglet Link Information (Information de
liaison)
2 Sélectionner le profil à utiliser pour la connexion au réseau.
- OU Cliquer sur ce qui suit :
• Les onglets permettant de parcourir les différents paramètres.
• Le bouton X pour minimiser la fenêtre.
• Le bouton More… (Plus…) pour obtenir plus d’information.
Les champs dans l’onglet Link Information (Information de liaison),
incluent :
Connected To Network (Connecté au réseau) — Ce champ affiche
l’état actuel de la connexion. Les messages d’état potentiels incluent :
• Connected to Network (Connecté au réseau) — Indique un flux
normal de fonctionnement en mode d’infrastructure. L’ordinateur
est connecté à un point d’accès et le réseau est disponible.
• Scanning (Balayage) — Indique que l’ordinateur recherche un
point d’accès disponible à portée.
Remarque : Ce champ affiche également les messages d’erreur si le pilote
échoue dans sa tentative d’initialisation.
Network Type (Type de réseau) — Les types de réseaux possible sont :
• Infrastruc ture Mode (Mode d’infrastructure) — Le pilote balaie
tous les canaux disponibles en continu jusqu’à détecter un ou
plusieurs points d’accès correspondant à son SSID (nom réseau). À
ce stade il tente d’authentifier et d’associer le point d’accès.
• Peer to Peer Mode (Mode d’égal à égal) — Le pilote balaie
pendant cinq secondes à la recherche d’un réseau existant ad hoc
utilisant le même SSID.
Channel (Canal) — Affiche le canal sur lequel est le réseau.
Encryption (Cryptage) — Affiche Offquand le cryptage est désactivé,
WEP quand soit 64 bits soit 128 bits est activé ou quand WPA est activé.
Link Speed (Vitesse de la connexion) — Affiche le débit de données
actuel de la connexion.
Signal Strength (Puissance du signal) — Le graphique à barres de la
puissance du signal n’est actif qu’en mode d’infrastructure. Le graphique
à barres affiche la puissance du signal normalisée détectée par le
récepteur, basée sur la moyenne des trames de 100 octets qui sont reçues
du point d’accès.
Link Quality (Qualité du lien) — Le graphique à barres de la qualité du
lien n’est actif qu’en mode d’infrastructure. Le graphique à barres affiche
la qualité du lien entre l’ordinateur et le point d’accès.
Page 11

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 11 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
Configuration du réseau sans fil
Onglet Available Networks (Réseaux
disponibles)
L’onglet Available Networks affiche l’état actuel des points d’accès
disponibles sur le réseau et permet à l’utilisateur de sélectionner le point
d’accès auquel il souhaite se connecter.
Pour le raccordement à un point d’accès :
1 Sélectionner un point d’accès dans la liste.
2 Cliquer sur Connect (Connexion) pour se connecter au point
d’accès.
Si le point d’accès souhaité n’est pas listé, cliquer sur Refresh
(Actualiser) pour balayer de nouveau le réseau et lister les points d’accès
disponibles sur le réseau.
Connexion à un réseau
Pour se connecter à un réseau
1 Cliquer sur Connect (Connexion) dans l’onglet Available Networks
(Réseaux disponibles). L’écran suivant s’affiche.
11
• Access Point (Point d’accès) — Ce mode nécessite un point
d’accès 802.11g ou 802.11b. La communication est
entièrement faite à travers le point d’accès qui retransmet les
paquets d’information aux autres ordinateurs sans fil ainsi
qu’aux ordinateurs du réseau par câble (réseau Ethernet par
exemple).
• Transfer Rate (Vitesse de transfert) — C’est la vitesse de
transmission à laquelle le point d’accès transmet les paquets de
données. Ce paramètre peut être réglé sur :
• fixé à 1 Mbps, fixé à 2 Mbps, fixé à 5,5 Mbps, fixé à 11 Mbps ou
Automatic (Automatique) en cas d’utilisation d’un point
d’accès 802.11b.
• fixé à 6 Mbps, fixé à 9 Mbps, fixé à 12 Mbps, fixé à 18 Mbps,
fixé à 24 Mbps, fixé à 36 Mbps, fixé à 48 Mbps, fixé à 54 Mbps
ou Automatic (Automatique) en cas d’utilisation d’un point
d’accès 802.11g.
3 Cliquer sur Next (Suivant). L’écran suivant s’affiche.
4 Régler les valeurs des champs suivants :
• Authentication Mode (Mode d’authentification) — Pour
utiliser le mode d’authentification par défaut.
• Encryption (Cryptage) — Pour utiliser le cryptage par défaut.
5 Cliquer sur Next (Suivant). L’écran suivant s’affiche.
2 Régler les valeurs des champs suivants :
• Network Name (Nom du réseau) — Saisir un nom pour le
nouveau profil.
• Network Type (Type de réseau) — Sélectionner dans la liste les
types de réseaux pris en charge. Les types pris en charge
comprennent :
• Peer to Peer (D’égal à égal) — Il s’agit du mode d’égal à
égal 802.11g (connu aussi sous le nom ad hoc). Une seule
cellule sans fil est prise en charge pour chaque SSID différent.
La communication est entièrement faite de client à client sans
utilisation d’un point d’accès. Les réseaux Ad Hoc 802.11g
utilisent le même SSID pour l’établissement d'une connexion
sans fil.
L’information cryptée reçue n’est acceptée que si elle se décrypte
correctement. Cela ne se produit que si l’ordinateur a une clé WEP
utilisée par le point d’accès. Cet écran permet la saisie de la clé
WEP.
Page 12

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 12 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
12
6 Régler les valeurs des champs suivants :
• Input Method (Méthode d’entrée) — Sélectionner la méthode
d’entrée qui correspond à celle du point d'accès.
• Key (Clé) — Entrer la clé WEP. Cette clé doit être la même que
celle utilisée par le point d’accès. Elle doit comporter entre 8 et 63
caractères.
Remarque : N’utiliser que les chiffres de 0 à 9 et les lettres de A à F pour la
clé.
• Key Index (Index de la clé) — Sélectionner l’index de la clé qui
correspond à celui utilisé par le point d’accès.
7 Cliquer sur Next (Suivant). L’écran suivant s’affiche.
Configuration du réseau sans fil
• Subnet Mask (Masque de sous-réseau) — Saisir le masque de
sous-réseau pour l’adaptateur réseau. Le paramètre par défaut est
255.255.255.0
• Default Gateway (Passerelle par défaut) — Saisir l’adresse IP de
la passerelle par défaut du réseau.
• DNS Server (Serveur DNS) — Saisir l’adresse du système DNS.
11 Cliquer sur Complete (Terminer). La configuration est terminée.
Onglet de paramétrage du profil (Profile)
L’onglet de Profile Setting (Paramétrage du profil) permet de créer des
profiles pour des environnements réseaux différents.
8 Pour la configuration du paramétrage IP, cliquer sur Enable
(Activer), puis aller à l’étape 9.
- OU Pour régler la configuration IP automatiquement, cliquer sur
Disable (Désactiver), puis cliquer sur Complete (Terminer). La
configuration est terminée.
9 Cliquer sur Next (Suivant). L’écran suivant s’affiche.
L’objet de cet écran est de configurer les paramètres TCP/IP pour
chaque connexion sans fil. Il est nécessaire de définir si le
paramétrage IP du profil actuel est affecté par un serveur ou par
une IP statique, ce qui est déterminé par l’administrateur du
réseau.
10 Régler les valeurs des champs suivants :
• DHCP Status (État DHCP) — Sélectionner Enable (Activé) si
l’information TCP/IP est affec tée par un serveur DHCP. Sélectionner
Disable (Désactivé) si l’adresse IP est spécifiée manuellement.
• IP Address (Adresse IP) — Saisir l’adresse IP pour l’adaptateur
réseau.
Dans cet onglet il est possible de cliquer sur les boutons suivants :
• Add (Ajouter) pour créer un nouveau profil.
• Edit (Édition) pour éditer le profil mis en surbrillance.
• Delete (Supprimer) pour supprimer le profil mis en surbrillance.
• Connect (Connexion) pour se connecter à un réseau en utilisant le
profil mis en surbrillance.
Onglet About (À propos de)
L’onglet About (À propos de) affiche la version du produit y compris les
détails sur les versions du pilote, de l’application et du microprogramme.
Si Dynex est contacté pour des problèmes, ce numéro de version devra
être fourni.
Page 13

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 13 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
Problèmes et solutions
Problèmes et solutions
Windows 98
Pour vérifier que l’adaptateur WLAN 802.11g est installé correctement :
1 Cliquer sur Start (Démarrer), Settings (Paramètres), Control
Panel (Panneau de configuration), puis sur Network(Réseau).
Cliquer sur l’onglet Configuration . Si l'adaptateur USB WLAN
802.11g est listé, cela signifie qu’il est installé correctement. Si un
point d’interrogation jaune est affiché, cela signifie qu’il existe un
conflit de ressources.
- OU Cliquer à l’aide du bouton droit de la souris sur l’icône du bureau
My Computer (Poste de travail), puis sélectionner Properties
(Propriétés). Cliquer sur Device Manager (Gestionnaire de
périphériques) puis cliquer sur Network Adapter (Adaptateur
réseau). Si l'adaptateur USB WLAN 802.11g est listé, cela signifie
qu’il est installé correctement. Si un point d’interrogation jaune est
affiché, cela signifie qu’il existe un conflit de ressources.
2 Cliquer sur l’adaptateur USB puis sur le service de l’adaptateur.
Cela permet de voir l’état de l’adaptateur USB. Si un point
d’interrogation jaune est affiché sur l’adaptateur USB, vérifier ce
qui suit :
• Vérifier si l’ordinateur dispose d’une Interruption (IRQ )
disponible. Libérer une interruption (IRQ) en affectant la
même interruption à plusieurs services. Par exemple COM 1 et
COM 2 peuvent utiliser la même valeur d’interruption (IRQ).
• Vérifier que l’adaptateur USB correct a été inséré et que le
pilote adapté a été installé.
Windows 2000
Pour vérifier que l’adaptateur WLAN 802.11g est installé correctement :
1 Utiliser les diagnostics de Windows 2000 pour détecter tout conflit
d'allocation de ressources de l’adresse Entrée/Sortie (I/O) ou de
l’interruption (IRQ). Si les adresses de l’interruption (IRQ) ou de
l’Entrée/Sortie (I/O) sont déjà attribuées à d’autres périphériques,
cette valeur doit être modifiée. L’adresse I/O doit être de 40 octets.
2 Aller au Panneau de configuration (Control Panel). Double-cliquer
sur l’adaptateur USB pour accéder à l'adaptateur WLAN.
Double-cliquer sur l’adaptateur USB permet d’accéder à
l’information le concernant, au nom du pilote et au fichier du
pilote. Si les noms n’apparaissent pas, c'est un signe de problème
et que le pilote n'est pas installé correctement. Réinstaller le
pilote.
3 Vérifier le menu de configuration du BIOS PnP, puis cliquer sur No
(Non).
FCC
Déclaration de la Federal Communications
Commission - FCC (Commission fédérale des
communications des États-Unis)
Cet équipement a été testé et déclaré conforme aux limitations prévues
dans le cadre de la catégorie B des appareils numériques, définie par
l’article 15 du règlement de la FCC. Ces limites ont été établies pour
fournir une protection raisonnable contre les interférences indésirables
lors d’une installation résidentielle. Cet équipement génère, utilise et
diffuse des ondes radio et s’il n’est pas installé ni utilisé en conformité
avec les instructions dont il fait l’objet, il peut provoquer des
interférences indésirables avec les communications radio. Cependant, il
n’est pas possible de garantir qu’aucune interférence ne se produira pour
une installation particulière. Si cet équipement cause des interférences
gênant la réception d'ondes radio ou télévisées (déterminé en éteignant
13
et en rallumant l’équipement), il est recommandé que l’utilisateur tente
de corriger le problème en suivant au moins l'une des mesures suivantes
:
• Réorienter ou déplacer l’antenne réceptrice.
• Augmenter la distance entre l’équipement et le récepteur.
• Brancher l’équipement sur la prise électrique d’un circuit différent
de celui auquel le récepteur est relié.
• Contacter le revendeur ou un technicien radio/télévision qualifié
pour toute assistance.
Avertissement FCC : Tout changement ou modification non expressément
approuvé par la partie responsable de la conformité pourrait annuler
l’autorisation pour l’utilisateur de faire fonctionner cet équipement.
Cet appareil est conforme à l’article 15 du règlement de la FCC. Son
fonctionnement est soumis aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) Ce
dispositif ne doit pas causer d’interférences indésirables et (2) ce
dispositif doit accepter toutes interférences reçues, y compris celles
risquant d'entraîner un fonctionnement indésirable du dispositif.
Remarque importante (pour le modèle
DX-WGUSB)
Déclaration de la FCC sur l’exposition aux irradiations :
Cet équipement est conforme aux limitations prévues par la FCC pour
l’exposition aux irradiations dans le cadre d’un environnement d’accès
libre. Les utilisateurs doivent se conformer aux instructions spécifiques
d'utilisation pour satisfaire à la norme d'exposition aux radiofréquences.
Cet émetteur ne doit pas être situé à proximité ou fonctionner
simultanément avec une autre antenne ou émetteur. Cet équipement a
été évalué SAR pour être utilisé sur les ordinateurs portatifs avec un
connecteur latéral.
Dynex déclare que le modèle DX-WGUSB (Identification FCC :
MXF-U950731G) est limité aux canaux CH1 à CH11 à 2,4 GHz par
microprogramme spécifique contrôlé aux États-Unis.
Déclaration d’IC (pour le modèle DX-WGUSB)
Son fonctionnement est soumis aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) Ce
dispositif ne doit pas provoquer d’interférence et (2) doit accepter toutes
interférences reçues, y compris celles risquant d’entraîner un
fonctionnement indésirable dudit dispositif.
Remarque importante
Déclaration d’IC sur l’exposition aux irradiations :
Cet équipement est conforme aux limitations prévues par IC pour
l’exposition aux irradiations dans le cadre d’un environnement d’accès
libre. Les utilisateurs doivent se conformer aux instructions spécifiques
d'utilisation pour satisfaire à la norme d'exposition aux radiofréquences.
Cet émetteur ne doit pas être situé à proximité ou fonctionner
simultanément avec une autre antenne ou émetteur.
Avis juridiques
©2006 Dynex. DYNEX et le logo de DYNEX sont des marques de
commerce de Best Buy Enterprise Services, Inc. Les autres noms de
marques et de produits sont des marques de commerce ou des marques
de commerce déposées de leurs propriétaires respectifs. Les
spécifications et caractéristiques sont susceptibles d’être modifiées sans
préavis.
Page 14

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 14 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
14
Adaptador USB para LAN
Inalámbrica Dynex
DX-WGUSB
Contenido
Introducción................................................................................... 14
Instalación del software y del hardware......................................... 14
Configuración de la red inalámbrica............................................... 16
Localización y corrección de fallas .................................................. 19
FCC ................................................................................................. 19
Avisos legales................................................................................. 19
Introducción
Gracias por comprar un adaptador USB Dynex para LAN Inalámbrica
802.11g. El paquete contiene:
• Un adaptador USB para LAN Inalámbrica 802.11g
• Una guía del usuario impresa
• Un CD que contiene la utilidad para el adaptador de la red
inalámbrica, los controladores y está guía del usuario
Si falta algo, póngase en contacto con Dynex al (800) 305-2204.
Contenido
7 Haga clic en Install the software automatically
(Recommended) (Instalar el software automáticamente
[Recomendado]), luego haga clic en Next (Siguiente).
8 Si se abre un cuadro de advertencia, haga clic en Continue
Anyway (Continuar de todos modos). Su computadora copia
archivos a su disco duro.
9 Haga clic en Finish (Finalizar).
Para instalar equipo de red inalámbrica en una computadora con
Windows 98, Windows 2000, o Windows ME:
Precaución: No conecte el adaptador USB hasta que se le pida que lo
haga.
1 Instale el punto de acceso. Para obtener más información,
refiérase a la documentación del punto de acceso.
2 Encienda la computadora.
3 Inserte el CD incluido en la unidad óptica.
4 Si el programa de instalación no inicia automáticamente, use el
Explorador de Windows para examinar el CD y ubicar el archivo
llamado setup.exe, luego haga doble clic en setup.exe para
iniciar la instalación del software.
5 Siga las instrucciones de pantalla para instalar el software.
6 Conecte el adaptador USB a un puerto USB en su computadora. Se
abre la ventana del Found New Hardware Wizard (Asistente para
hardware nuevo encontrado).
Instalación del software y del
hardware
Siga los procedimientos a continuación para configurar su red
inalámbrica.
Para instalar la red inalámbrica en una computadora con Windows XP:
Precaución: No conecte el adaptador USB hasta que se le pida que lo
haga.
1 Instale el punto de acceso. Para obtener más información,
refiérase a la documentación del punto de acceso.
2 Encienda la computadora.
3 Inserte el CD incluido en la unidad óptica.
4 Si el programa de instalación no inicia automáticamente, use el
Explorador de Windows o My Computer (Mi PC) para examinar el
CD y ubicar el archivo llamado setup.exe, luego haga doble clic
en setup.exe para iniciar la instalación del software.
5 Siga las instrucciones de pantalla para instalar el software.
6 Conecte el adaptador USB a un puerto USB en su computadora. Se
abre la ventana del Found New Hardware Wizard (Asistente para
hardware nuevo encontrado).
7 Haga clic con el botón secundario en el icono de My Computer
(Mi PC) en el escritorio, haga clic en Properties (Propiedades) y
luego haga clic en Hardware Device Manager (Administrador
de Dispositivos de Hardware). Verifique que el adaptador USB esté
listado cómo uno de los dispositivos en su computadora.
Page 15

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 15 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
Instalación del software y del hardware
8 Si está usando Windows 98, haga clic con el botón secundario en
el icono Network Neighborhood (Entorno de Red) en su
escritorio y luego haga clic en Properties (Propiedades). Se abre
el cuadro de diálogo Local Area Connections Properties
(Propiedades de Conexiones de Área Local).
- O Si está usando Windows ME y Windows 2000, haga clic con el
botón secundario en el icono Network Neighborhood (Entorno
de Red) en su escritorio, luego haga clic en Properties
(Propiedades) y finalmente en Local Area Connection's
properties (Propiedades de la Conexión de Área Local) Se abre el
cuadro de diálogo Local Area Connections Properties (Propiedades
de Conexiones de Área Local).
15
10 Haga clic en Protocol (Protocolo) luego en Add (Agregar). Se
abrirá el cuadro de dialogo Select Network Protocols (Seleccionar
Protocolos de Red).
11 En la lista de protocolos, seleccione NetBEUI, luego haga clic en
OK (Aceptar). El protocolo NetBEUI estará instalado.
12 Haga clic en OK (Aceptar) para regresar al cuadro de diálogo Select
Network Component Type (Seleccionar el Tipo de Componente de
Red).
13 Repita los pasos 10 al 12 para agregar el protocolo IPX/SPX.
14 Haga clic en TCP/IP para establecer las direcciones para su
computadora. Seleccione ya sea Obtain an IP address
automatically (Obtener una dirección IP automáticamente) o
Use the following IP address (Usar la siguiente dirección IP). Si
decide especificar una dirección IP, ingrese el valor IP y los valores
de la máscara de subred, DNS, Dominio/Nombre de grupo de
trabajo y la dirección de la puerta de enlace.
9 Haga clic en la ficha General y luego en Install (Instalar). Se
abrirá el cuadro de dialogo Select Network Component Type
(Seleccionar el Tipo de Componente de Red).
15 Haga clic en OK (Aceptar) para regresar al cuadro de diálogo Local
Area Connection Proper ties (Propiedades de la Conexión de Área
Local) .
16 Seleccione las opciones de “File and Printer Sharing” (Compartir
Archivos e Impresoras) para los recursos de su computadora, luego
haga clic en OK (Aceptar).
17 Haga clic en Yes (Sí) cuando aparezca una ventana emergente
solicitándole que reinicie su computadora. Su computadora se
apagará y encenderá de nuevo.
Page 16

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 16 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
16
Desinstalar el software y el hardware
Para desinstalar el software y el hardware:
1 Haga clic en Start (Inicio), All Programs (Todos los Programas) o
Programs (Programas), Dynex DX-WGUSB Wireless LAN Card
Utility (Utilidad de la Tarjeta de LAN Inalámbrica Dynex
DX-WGUSB), y luego haga clic en Uninstall (Desinstalar).
2 Remueva el adaptador USB.
3 Reinicie la computadora.
Configuración de la red
inalámbrica
Su adaptador USB para LAN Inalámbrica 802.11g usa su propio software
de administración. Todas las funciones se controlan con esta utilidad.
Para moverse fácilmente de un entorno de red a otro, la utilidad utiliza
perfiles que usted creará.
Para usar la utilidad inalámbrica:
1 Haga clic en Start (Inicio), All Programs (Todos los Programas) o
Programs (Programas), Dynex DX-WGUSB Wireless LAN Card
Utility (Utilidad de la Tarjeta de LAN Inalámbrica Dynex
DX-WGUSB) y luego haga clic en Dynex DX-WGUSB Wireless
LAN Card Utility.
Nota: El icono de la utilidad inalámbrica deberá aparecer en su
bandeja de iconos. Si el icono está color rojo, significa que la
configuración de la tarjeta de red inalámbrica 802.11g no es válida o
está incompleta.
2 Seleccione el perfil que desea usar con su conexión de red.
- O Haga clic en los siguientes:
• Las fichas para navegar a través de los diferentes ajustes.
• El botón X para minimizar la ventana.
• El botón More… (Más…) para obtener más información.
Configuración de la red inalámbrica
La ficha Link Information (Información del
Enlace)
Los campos en la ficha Link Information (Información del Enlace)
incluyen:
Connected To Network (Conectado a la Red) — Este campo muestra
el estado actual de la conexión. Los posibles mensajes de estado
incluyen:
• Connected to Network (Conectado a la Red) — Indica el flujo
de operación normal en el modo de Infraestructura. La
computadora estará conectada a un punto de acceso y la conexión
de red estará disponible.
• Scanning (Escaneando) — Indica que la computadora está
buscando un punto de acceso disponible dentro del rango.
Nota: Este campo también muestra mensajes de error si el controlador no
se puede inicializar.
Network Type (Tipo de Red) — Los tipos de red posibles incluyen:
• Infrastructure Mode (Modo de Infraestructura) — El
controlador escanea continuamente todos los canales disponibles
hasta que encuentra uno o más puntos de acceso que tengan su
mismo SSID (nombre de red). En ese momento intentará
autenticarse y asociarse con el punto de acceso.
• Peer to Peer Mode (Modo Equipo a Equipo) — El controlador
escanea por cinco segundos buscando una red ad hoc existente
que use el mismo SSID.
Channel (Canal) — Muestra el canal en que se encuentra la red.
Encryption (Codificación) — Muestra Off (Desactivada) cuando la
codificación está desactivada, WEP cuando se ha activado la codificación
de 64 bits o de 128 bits, o WPA cuando se ha activado la codificación
WPA.
Link Speed (Velocidad del Enlace) — Muestra la velocidad de datos de
la conexión actual.
Signal Strength (Intensidad de la Señal) — El gráfico de barras de la
intensidad de la señal sólo se activa cuando la red se encuentra en el
modo de infraestructura. El gráfico de barras muestra la intensidad de la
señal normalizada según la reporta el radio, calculando el promedio de
todos los marcos con un tamaño de más de 100 bytes que se reciben
desde el punto de acceso.
Page 17

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 17 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
Configuración de la red inalámbrica
Link Quality (Calidad del Enlace) — El gráfico de barras de la calidad
del enlace sólo se activa cuando la red se encuentra en el modo de
infraestructura. El gráfico de barras muestra la calidad del enlace entre la
computadora y el punto de acceso.
Ficha Available Networks (Redes
Disponibles)
La ficha Available Networks (Redes Disponibles) muestra el estado actual
de los puntos de acceso disponibles dentro de la red y le permite
seleccionar a cual punto de acceso se quiere conectar.
17
• Peer to Peer (De equipo a Equipo) — Este es el tipo de
modo equipo a equipo de 802.11g (también conocido como
Ad Hoc). Sólo una celda inalámbrica se soporta para cada SSID
diferente. Toda la comunicación es hecha de cliente a cliente
sin usar un punto de acceso. La red Ad Hoc 802.11g usa el
mismo SSID para establecer la conexión inalámbrica.
• Access Point (Punto de Acceso) — Este modo requiere un
punto de acceso 802.11g o 802.11b. Toda la comunicación se
hace a través del punto de acceso, el cual retransmite los
paquetes de información a otras computadoras inalámbricas
así como a computadoras en una red cableada (cómo
Ethernet).
• Transfer Rate (Velocidad de Transmisión) — La velocidad de
transmisión a la cual el punto de acceso transmite los paquetes de
datos. Puede configurarlo cómo:
• fixed (fijo) 1 Mbps, fixed (fijo) 2Mbps, fixed (fijo) 5.5 Mbps,
fixed (fijo) 11 Mbps, o Automático si está usando un punto de
acceso 802.11b.
• fixed (fijo) 6 Mbps, fixed (fijo) 9Mbps, fixed (fijo) 12 Mbps,
fixed (fijo) 18 Mbps, fixed (fijo) 24 Mbps, fixed (fijo) 36 Mbps,
fixed (fijo) 48 Mbps, fixed (fijo) 54 Mbps, o Automático si está
usando un punto de acceso 802.11g.
3 Haga clic en Next (Siguiente). Se abrirá la siguiente pantalla.
Para conectarse a un punto de acceso:
1 Seleccione un punto de acceso de la lista.
2 Haga clic en Connect (Conectar) para conectarse al punto de
acceso.
Si el punto de acceso al que se quiere conectar no está en la lista, haga
clic en Refresh (Actualizar) para re-escanear la red y listar todos los
puntos de acceso disponibles en su red.
Conexión a una red
Para conectarse a una red:
1 Haga clic en Connect (Conectar) en la ficha Available Networks
(Redes Disponibles). Se abrirá la siguiente pantalla.
4 Ajuste los valores de los siguientes campos:
• Authentication Mode (Modo de Autenticación) — Use el modo
de autenticación automático.
• Encryption (Codificación) — Use la codificación por omisión.
5 Haga clic en Next (Siguiente). Se abrirá la siguiente pantalla.
2 Ajuste los valores de los siguientes campos:
• Network Name (Nombre de Red) — Ingrese un nombre para el
perfil nuevo.
• Network Type (Tipo de Red) — Seleccione en la lista de tipos de
redes soportadas. Los tipos soportados incluyen:
Page 18

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 18 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
18
Cuando se recibe información codificada, sólo se aceptará si se
decodifica correctamente. Esto sucede sólo si la computadora
tiene la clave WEP usada por el punto de acceso. Esta pantalla le
permite ingresar la clave WEP.
6 Ajuste los valores de los siguientes campos:
• Input Method (Método de Entrada) — Seleccione el método de
entrada que coincide con el método de entrada usado por el punto
de acceso.
• Key (Clave) — Ingrese la clave WEP. La clave debe ser la misma
que usa el punto de acceso. Debe estar entre 8 y 63 caracteres de
longitud.
Nota: Solamente use los dígitos 0-9 y letras A-F para la clave.
• Key Index (Índice de clave) — Seleccione el índice de claves que
coincide con el índice de claves usado por el punto de acceso.
7 Haga clic en Next (Siguiente). Se abrirá la siguiente pantalla.
Configuración de la red inalámbrica
10 Ajuste los valores de los siguientes campos:
• DHCP Status (Estado de DHCP) — Seleccione Enable (Habilitar)
si la información de TCP/IP es asignada por un servidor DHCP.
Seleccione Disable (Deshabilitar) si desea especificar la dirección
IP manualmente.
• IP Address (Dirección IP) — Ingrese la dirección IP para la tarjeta
de red.
• Subnet Mask (Máscara de Subred) — Ingrese la máscara de
subred para la tarjeta de red. El valor por omisión es
255.255.255.0
• Default Gateway (Puerta de Enlace Predeterminada) — Ingrese
la dirección IP de la puerta de enlace predeterminada de su red.
• DNS Server (Servidor DNS) — Ingrese la dirección del servidor
del sistema de nombres de dominio.
11 Haga clic en Complete (Completar). Ha terminado.
Ficha de Ajustes de Perfil
La ficha Profile Setting (Ajustes de Perfil) le permite crear perfiles para
diferentes entornos de red.
8 Si desea ajustar la configuración IP, haga clic Enable (Habilitar) y
luego vaya al paso 9.
- O Si desea que la configuración IP sea automática, haga clic en
Disable (Deshabilitar) y luego haga clic en Complete
(Completar). Ha terminado.
9 Haga clic en Next (Siguiente). Se abrirá la siguiente pantalla.
El propósito de esta pantalla es configurar los ajustes de TCP/IP de
cada conexión inalámbrica. Debe definir si la configuración IP del
perfil actual está asignada por un servidor DHCP o por una
dirección IP fija que el administrador de la red determina.
En esta ficha, puede hacer clic en los siguientes botones:
• Add (Agregar) para crear un perfil nuevo.
• Edit (Editar) para editar el perfil resaltado actualmente.
• Delete (Eliminar) para eliminar el perfil seleccionado
actualmente.
• Connect (Conectar) para conectarse a una red usando el perfil
resaltado actualmente.
Ficha About (Acerca de)
La ficha About (Acerca de) muestra la versión del producto incluyendo
detalles del controlador, la aplicación y las versiones del firmware.
Deberá usar este número de versión cuando reporte problemas a Dynex.
Page 19

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 19 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
Localización y corrección de fallas
Localización y corrección de
fallas
Windows 98
Para verificar que el dispositivo WLAN 802.11g está instalado
adecuadamente:
1 Haga clic en Start (Inicio), Settings (Configuración), Control
Panel (Panel de Control) y luego en Network (Red). Haga clic en
la ficha Configuration (Configuración). Si encuentra el adaptador
USB WLAN 802.11g listado significa que el adaptador USB está
instalado adecuadamente. Si ve un símbolo de interrogación
amarillo, significa que hay un conflicto de recursos.
- O Haga clic con el botón secundario en el icono My Computer (Mi
PC) en el escritorio y luego seleccione Properties (Propiedades).
Haga clic en Device Manager (Administrador de Dispositivos) y
luego haga clic en Network Adapter (Adaptador de Red). Si
encuentra el adaptador USB WLAN 802.11g listado significa que
el adaptador USB está instalado adecuadamente. Si ve un símbolo
de interrogación amarillo, significa que hay un conflicto de
recursos.
2 Haga clic en adaptador USB y luego en el servicio del adaptador.
Verá el estado del adaptador USB. Si hay un símbolo amarillo en el
adaptador USB, verifique lo siguiente:
• Verifique que su computadora tiene un IRQ disponible. Liberé
un IRQ asignando el mismo IRQ a unos dispositivos. Por
ejemplo, COM 1 y COM 2 pueden tener asignados los mismos
valores de IRQ.
• Verifique que ha insertado el adaptador USB correcto y que ha
instalado el controlador correcto.
Windows 2000
Para verificar que el dispositivo WLAN 802.11g está instalado
adecuadamente:
1 Use los diagnósticos de Windows 2000 para ver si hay un conflicto
en la asignación de recursos de la dirección de entrada/salida o la
asignación de IRQ. Si encuentra que el IRQ o las direcciones de
entrada/salida ya están asignadas a otros dispositivos, deberá
cambiar ese valor. La dirección de entrada/salida debe ser de 40h
(hexadecimal) bytes.
2 Vaya al Panel de Control. Haga doble clic en el adaptador USB y vea
el adaptador de WLAN. Hacer doble clic en el adaptador USB le
muestra información del adaptador USB, el número del
controlador y el archivo del controlador. Si no encuentra los
nombres, hay algunos problemas y el controlador no está
instalado correctamente. Reinstale el controlador.
3 Revise el menú de configuración del BIOS PnP y luego haga clic en
No.
FCC
19
particular. Si el equipo causa interferencias perjudiciales en la recepción
de la señal de radio o televisión, lo cual puede comprobarse
encendiéndolo y apagánd olo alternativamente, se recomienda al usuario
corregir la interferencia mediante uno de los siguientes procedimientos:
• Cambie la orientación o la ubicación de la antena receptora.
• Aumente la distancia entre el equipo y el receptor.
• Conecte el equipo a un tomacorriente de un circuito distinto de
aquél al que está conectado el receptor.
• Solicite consejo al distribuidor o a un técnico experto en radio/TV
para obtener ayuda.
Advertencia de la FCC: Cualquier cambio o modificación no aprobada
expresamente por la parte responsable del cumplimiento normativo
puede anular la autoridad del usuario para operar este equipo.
Este dispositivo satisface la parte 15 del reglamento FCC. Su operación
está sujeta a las dos condiciones siguientes: (1) Este dispositivo no puede
causar interferencia dañina, y (2) este dispositivo debe aceptar cualquier
interferencia recibida incluyendo interferencias que puedan causar una
operación no deseada.
Nota Importante (para DX-WGUSB)
Declaración de Exposición a la Radiación de la FCC:
Este equipo cumple con los limites de exposición a la radiación de la FCC
especificados para un ambiente sin control. Los usuarios finales deben
seguir las instrucciones de operación específicas para satisfacer el
cumplimiento con la exposición RF. Este transmisor no debe estar
compartiendo lugar u operando en conjunto con cualquier otra antena o
transmisor. Este equipo ha sido evaluado por SAR para se usado en
notebooks con una configuración de ranura lateral.
Dynex declara que DX-WGUSB (FCC ID: MXF-U950731G) está limitado en
CH1~CH11 para 2.4 GHz por un firmware especificado que es controlado
en EE.UU.
Declaración del IC (para DX-WGUSB)
Su operación está sujeta a las dos condiciones siguientes: (1) Este
dispositivo no puede causar interferencia dañina, y (2) este dispositivo
debe aceptar cualquier interferencia recibida incluyendo interferencias
que puedan causar una operación no deseada.
Nota Importante
Declaración de Exposición a la Radiación de la IC:
Este equipo cumple con los límites de exposición a la radiación de la IC
especificados para un ambiente sin control. Los usuarios finales deben
seguir las instrucciones de operación específicas para satisfacer el
cumplimiento con la exposición RF. Este transmisor no debe estar
compartiendo lugar u operando en conjunto con cualquier otra antena o
transmisor.
Avisos legales
© 2006 Dynex. DYNEX y el logotipo de DYNEX son marcas comerciales de
Best Buy Enterprise Services, Inc. Otras marcas y nombres de productos
son marcas comerciales o marcas registradas de sus respectivos dueños.
Las especificaciones y características están sujetas a cambio sin aviso
previo u obligación.
Declaración de Interferencia de la Comisión
Federal de Comunicaciones (FCC)
Este equipo ha sido sometido a pruebas y se ha determinado que
satisface los límites establecidos para clasificarlo cómo dispositivo digital
de Clase B de acuerdo con la Parte 15 del reglamento FCC. Estos límites se
han establecido para proporcionar una protección razonable contra
interferencias perjudiciales en una instalación residencial. Este equipo
genera, utiliza y puede irradiar energía de radiofrecuencia y, si no es
instalado y utilizado de acuerdo a las instrucciones, puede causar
interferencias perjudiciales en las comunicaciones de radio. Sin embargo,
no se garantiza que no ocurrirá interferencia en una instalación
Page 20

DX-WGUSB.fm Page 20 Monday, August 21, 2006 3:20 PM
www.dynexproducts.com (800) 305-2204
Distributed by Best Buy Purchasing, LLC
7601 Penn Ave. South, Richfield, MN 55423 U.S.A.
Distribué par Best Buy Purchasing, LLC
7601 Penn Ave. South, Richfield, MN 55423 É.-U.
Distribuido por Best Buy Purchasing, LLC
7601 Penn Ave. South, Richfield, MN 55423 U.S.A.
R1
 Loading...
Loading...