Page 1

DVX-7090 VoIP Router
User's Guide
© 2006 D-Link Computer Corp.
Page 2

D-Link Voice System DVX-7090
VoIP Router for organizations
Document №: 1
Document type: User's Guide
Document status: Version 1.2.0.0
Date of issue: 10.10.2006
TRADEMARKS
Trademarks used in this text: D-Link and the D-LINK logo are trademarks of DLink Computer Corporation; Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either
the entities claiming the marks and names or their products. D-Link Computer
Corporation disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names
other than its own.
COPYRIGHT STATEMENT
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2006 D-Link Computer Corporation. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means or
used to make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation
without permission from D-Link Computer Corporation.
Page 3

Contents
1 INTRODUCTION ......................................................................................................................................5
1.1 DOCUMENT PROFILE ..............................................................................................................................5
1.2 AUDIENCE..............................................................................................................................................5
1.3 TYPOGRAPHICAL CONVENTIONS ............................................................................................................5
1.4 DOCUMENT STRUCTURE ........................................................................................................................5
2 PRODUCT OVERVIEW...........................................................................................................................6
2.1 HARDWARE ...........................................................................................................................................6
2.2 SOFTWARE.............................................................................................................................................7
2.3 ROUTER FEATURES................................................................................................................................8
2.4 PROTOCOLS AND STANDARDS ...............................................................................................................8
3 INSTALLATION AND CONNECTION..................................................................................................9
4 CONFIGURATION .................................................................................................................................10
4.1 CONFIGURING NETWORKING PROPERTIES ............................................................................................10
4.2 CONFIGURING USER ENDPOINTS...........................................................................................................14
4.2.1 User basic settings.......................................................................................................................17
4.2.2 Registration settings....................................................................................................................18
4.2.3 User NAT-, fax-related and signaling-dependent settings...........................................................18
4.2.4 Call forward dialog.....................................................................................................................20
4.2.5 Codec capability settings.............................................................................................................21
4.2.6 Default user.................................................................................................................................23
4.3 CONFIGURING GATEWAYS ...................................................................................................................23
4.3.1 Basic gateway settings.................................................................................................................25
4.3.2 Registration settings....................................................................................................................25
4.3.3 D-Link DVX-7090 Router registration settings...........................................................................26
4.3.4 Gateway NAT-, fax-related and type-of-signaling properties......................................................27
4.3.5 Gateway codec capability settings...............................................................................................27
4.4 CONFIGURING DVX-7090 SERVICES....................................................................................................27
4.4.1 Commands that invoke services...................................................................................................30
4.5 CONFIGURING THE ROUTING TABLE .....................................................................................................31
4.5.1 Commands executed during routing............................................................................................32
4.5.2 Why position of routing rules in the table is important...............................................................33
4.6 GROUPS AND GROUPING ......................................................................................................................34
4.6.1 General........................................................................................................................................34
4.6.2 Configuring groups......................................................................................................................34
4.7 MANAGING VOICE PROMPTS ................................................................................................................36
4.8 CDRS AND LOGS .................................................................................................................................38
4.8.1 Call detail records (CDRs)..........................................................................................................38
4.8.2 Viewing CDRs .............................................................................................................................38
4.8.3 Logs.............................................................................................................................................42
4.8.4 Viewing Logs...............................................................................................................................44
4.9 SOFTWARE VERSION MANAGEMENT.....................................................................................................45
5 CONFIGURATION HOW-TO'S............................................................................................................49
5.1 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO VOICE TO EMAIL ....................................................................49
5.2 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO DIRECT INWARD SYSTEM ACCESS .........................................51
5.3 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO EXTENSION NUMBERS ............................................................54
5.4 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH FOR OUTBOUND CALLS................................................................55
5.5 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO CALL PICKUP .........................................................................56
5.6 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO IMPERSONATE FUNCTION .......................................................58
5.7 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO GROUP CALL SERVICE ...........................................................60
5.8 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO AUTO REDIAL .........................................................................62
5.9 HOW TO USE MATCH AND PATTERN FIELDS IN THE ROUTING TABLE ...................................................63
5.10 HOW TO CREATE A NETWORKING ALIAS FOR SUBNET 192.168.224.0...................................................67
Page 4

Contents
USER INTERFACE .................................................................................................................................72
6
6.1 CONFIGURING USER’S DATA ................................................................................................................72
6.2 VIEWING STATISTICS ...........................................................................................................................74
6.3 MANAGING VOICE PROMPTS ...............................................................................................................75
7 USAGE HOW-TO’S.................................................................................................................................77
7.1 HOW TO USE CALL TRANSFER ..............................................................................................................77
7.2 HOW TO MAKE CONFERENCE CALLS.....................................................................................................77
APPENDIX A ACRONYMS..........................................................................................................................79
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 4 of 83
Page 5

1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 DOCUMENT PROFILE
This manual describes the D-Link DVX-7090 VoIP Router and explains how to configure
and operate it.
1.2 AUDIENCE
This document is intended for computer systems specialists tasked with deployment and
configuration of the DVX-7090 VoIP Router. The readers of this document are assumed to
be familiar with the concepts of IP telephony and principles of networking. The system
administrator who configures the VoIP Router must have a working knowledge of regular
expression.
1.3 TYPOGRAPHICAL CONVENTIONS
The conventions used in this document are described in the table below.
Table 1: Conventions
Introduction
Convention Description
Note: text Important information requiring special attention
NAT
0011
.wav
Words highlighted by grey background represent names of
configuration parameters when they appear in the text of the document
Digits in bold italics denote numbers of a dialing sequence
Column title of a tabular form
Bold face letters are used to indicate names of programs, directories
and files
1.4 DOCUMENT STRUCTURE
Here is a brief synopsis of the chapters in this document:
Chapter 1 describes the purpose and structure of the document
Chapter 2 gives an overview of the product hardware and software components, details the
product’s features and specifications.
Chapter 3 describes how to install and connect the DVX-7090 VoIP Router.
Chapter 4 shows you how the system administrator can use the Router’s web interface for
the purposes of configuration
Chapter 5 introduces some configuration tips
Chapter 6 describes the application interface accessible to extension subscribers
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 5 of 83
Page 6

2 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The DVX-7090 VoIP Router is a packet telephony switching system with a full range of features
typical for traditional PBXs and a number of additional capabilities.
The DVX-7090 VoIP Router is an affordable branch exchange solution for geographically
distributed organizations that eliminates the need to have two separate networks for voice and
data and allows telephone communications over the same line that subscribers use for Internet
access.
Product overview
Fig. 1 DVX-7090 deployment in a geographically distributed organization
2.1 HARDWARE
The hardware specifications of DVX-7090 are as follows:
Form Factor: Standard industrial 19” 1U rackmount
Processor: VIA C3 1 GHz
System Memory: 1 144-pin SODIMM, up to 256MB
Storage: 1 CompactFlash type II 512 MB card
4 10/100Base-TX Ethernet ports
.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 6 of 83
Page 7

2.2 SOFTWARE
The DVX-7090 software has a modular structure that includes five functional components:
Control Unit (CU),
Switching Unit (SU),
Database server (DBS) and
Web-interface (WI).
Fig. 2 presents a block diagram of the D-Link VoIP Router software
Product overview
Fig. 2 Block diagram of D-Link VoIP Router software modules
The CU is the Router’s backbone element that functions as a server intended for user
authentication and authorization, control of the SU, and interaction with the database server
(DBS).
The SU is an integration of:
a stateful softswitch that transparently supports the SIP and H.323 signaling protocol
an RTP/RTCP proxy for conversion and reassembly of IP packets without
modification of their contents (i.e. without codec conversion)
a media proxy for full conversion of media streams
an audio file recording and playback utility (.wav format)
a SIP registrar
a SIP client for registering to remote SIP registrars/proxy servers
an H.323 gatekeeper
a RAS client for registering to H.323 gatekeepers/proxy servers
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 7 of 83
Page 8

The DBS is a suite of XML files. The DBS is a repository of data used to store and provide
access to user records, the routing table, information about gateways and the system
configuration.
2.3 ROUTER FEATURES
The DVX-7090 VoIP Router allows:
Call holds
Call transfer
Conditional and unconditional call forwarding
Conference calls (max. 3 participants in the current version of the software)
Voice to email delivery
Direct Inward System Access (DISA)
Call pick up
Call waiting
Impersonate function
Product overview
Group calls
Codec conversion
2.4 PROTOCOLS AND STANDARDS
VoIP protocols:
H.323 v.2
SIP
H.245 v.7
H.225 v.4
RTP/RTCP
T.38
SDP
Supported voice encoding algorithms (codecs):
G.729
G.729A
G.723.1 5.3 kBit/s
G.723.1 6.4 kBit/s
G.711 mU-Law
G.711 A-Law
GSM 06.10-FR
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 8 of 83
Page 9

3 INSTALLATION AND CONNECTION
Prepare a Windows workstation connected to the local area network. You will need the
workstation to access the newly installed Router.
To install and power on your DVX-7090 VoIP Router, proceed as follows:
1. Unpack the supplied Router and install the box at a location of your choice
2. Connect the DVX-7090 VoIP Router to the LAN switch through the Ethernet port (port
2 in Fig. 3)
Installation and connection
Fig. 3 DVX-7090 front panel
3. The Windows workstation that you have prepared and the VoIP Router box must be on
the same network. To ensure this, create a network alias for subnet 192.168.224.0 on the
Windows workstation (see section 5.10 for details).
4. Switch on the Router. It takes some 30-40 seconds to load and start the VoIP Router
applications.
5. Start the Internet Explorer web browser on the Windows workstation and enter the URL
http://192.168.224.226
6. To log in with the administrator’s permissions, enter the default login and password –
admin, qwerty.
7. Configure the system as described in Ch. 4 and Ch. 5 of this guide
8. When through with the configuration, reboot the VoIP Router by clicking the
button on the page ‘Configuration’ of the Web interface.
9. Switch off the VoIP Router box and unplug the networking cable from the Ethernet port
(see port 2 in Fig. 3)
10. Plug in the networking cable into the WAN port (port 1 in Fig. 3) to make the VoIP
Router accessible at URL http://<WAN_IP> where <WAN_IP> is the assigned IP
entered in the field IP address of the WAN settings dialog.
to access the Router’s logon page.
Now you can use any web browser to access the DVX-7090 Router and configure the system
working remotely.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 9 of 83
Page 10

4 CONFIGURATION
Start your web browser and enter http://192.168.224.226 on the address line to access the logon
page of the Router’s web interface.
The initial logon credentials that provide access to the administration interface of your system
are admin, qwerty. If the entered login name and password are correct, you will be displayed
with the main page of the Web interface.
Configuration
Fig. 4 DVX-7090 logon page
Make sure that the change of the initial access password is the first procedure that you perform.
Note: The no-activity timeout for the web interface is 20 min. On timeout expiration the user
is returned to the logon page.
4.1 CONFIGURING NETWORKING PROPERTIES
The page with the Router’s networking properties is the first page displayed on entry to the
system.
To access the page with the Router’s global settings from anywhere else in the web interface,
click the tab
Fig. 5
. The DVX-7090 VoIP Router entry page is shown in
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 10 of 83
Page 11

Configuration
Fig. 5 Networking configuration page
The configuration box WAN Settings allows you to configure the Router’s WAN properties and
define the following parameters:
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 11 of 83
Page 12

Configuration
Fig. 6 WAN settings dialog box
Use DHCP select this checkbox if you wish to engage dynamic IP address assigning
and enable DHCP
IP address – IP address of the WAN interface in the common dot-separated format
Netmask – subnet mask of the WAN interface
Default Gateway – IP address of the LAN’s border router
Hostname – the name of the host
Domain – domain name
DNS – IP address of the DNS server
SSL is a combo box that allows you to choose between encrypted and unencrypted
connections with the VoIP Router. In case of remote system administration select Yes
for encrypted connection. If you administer the system locally, you connection may
be unencrypted and you may wish to select No.
Note: Remember selecting Yes in the SSL combo box slows down operation of the web
interface
The configuration form SMTP Server allows you to configure the e-mail defining the following
parameters:
IP address – IP address (or DNS name) of the SMTP server
Port – SMTP server connection port
Source – email address of the DVX-7090 Router that will appear on the From: line of
email letters with sound files
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 12 of 83
Page 13

Configuration
Fig. 7 SMTP server settings box
Note: It is assumed that the configured SMTP Server does not require authorization.
The date-time dialog box allows you to set the current date and time.
Fig. 8 Date and time setting box
Use NTP. Select the checkbox Use NTP if you wish to use automatic time synchronization and
configure NTP time servers. Deselect the checkbox when you plan to make manual date-time
setting. A deselected Use NTP checkbox makes the NTP servers list, the entry line and Timezone
combo box dimmed and inaccessible.
Note: If your system is very slow or too fast in time (about one hour and more) it advisable
that you set the time manually before selecting the Use NTP checkbox.
Timezone. Use the Timezone combo box to select the time zone where the DVX-7090 Router
resides.
To add an NTP server to the list of time synchronization servers, type the server name in the edit
box above the Timezone combo box and click the add button
box. Click
Note: After clicking the button
to validate the newly made entry.
you will be alerted to pending system restart
located to the right of the edit
inevitably caused by date/time modifications.
Click , to remove the latest erroneous entry from the list of NTP servers.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 13 of 83
Page 14

When setting the date and time manually, enter the current date and time in the respective boxes
Configuration
and click
remove an erroneous entry.
The purpose of the dialog Change password is self-explanatory. A change of the access
credentials set by the manufacturer (admin, qwerty) should be the first procedure you perform on
your newly deployed system.
The configuration boxes SIP registrar and H.323 Gatekeeper allow you to specify the name of
the SIP registrar and H.323 gatekeeper correspondingly and configure unicast and multicast ports
for receipt of user registration requests.
. Click whenever you want to update the date-time setting or
Fig. 9 Change password dialog
Fig. 10 SIP registrar and H.323 gatekeeper configuration boxes
Fill the edit boxes with the necessary data and click
When through with changing the access password, click
4.2 CONFIGURING USER ENDPOINTS
Click the tab to access the page that displays the table of configured users.
to accept the changes.
to restart the system.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 14 of 83
Page 15

Configuration
Fig. 11 Table of configured user extensions
You can change the quantity of records displayed simultaneously by entering the desired number
of records in the text box Show users per page above the table and clicking .
You can skip directly to any portion of the records or page through the displayed listing
successively by clicking the page numbers on the blue bar under the table.
The table columns present the following data and control elements:
shows a dimmed checkbox that indicates the active or inactive status of the
user record
contains , the Edit button. Click this button to edit the record.
shows the phone number of the user
presents the user’s name in the system
displays the user’s IP
includes , the button that invokes the groups dialog
sshows the registration status of registering endpoints. The valid values are:
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 15 of 83
Page 16

Configuration
- Registered – the endpoint is successfully registered with the system;
- Unregistered – the endpoint is unregistered;
- In-call – the endpoint has established a connection with a remote party;
- Failed – unsuccessful endpoint registration.
- empty field - no successful endpoint registration has occurred
includes two buttons – and .
is the button that you click to make a duplicate of the record
is the delete button used to remove the record.
You may wish to use the filter located on top of the Users table (see Fig. 12) to display selective
listings of configured extensions. User records can be filtered by the phone number, subscriber’s
name or the group the user belongs to and by any combination thereof.
Fig. 12 Search filter of Users page
When you intend to have displayed only those user records where the extension number starts
with 5, enter 5 in the field Phone and click . When it is necessary to further narrow
the search and display only user records that have phone numbers starting with 509, enter 509 in
the field Phone and click .
You can perform search by a digit or digits the phone number starts with and cannot search by
digits occurring in the middle or in the end of the number. You cannot enter regular expressions
in the filter field Phone either.
The search argument entered in the field Name is an alphabetic character or several characters
that can be found as a substring occurrence within a name string. The performed exact-match
search is case insensitive. For example, if you enter the letter A in the Name field and click
the search will return all user records where the user name includes characters A
and a, regardless of their number and position within the name string.
The search argument in the filter field Group is one selected from the drop-down list.
While using the filter you can define any single search argument, any combination of two
arguments (phone and name, phone and group, name and group) and all three arguments
simultaneously.
Click to bring up the user configuration form and configure the endpoint
properties. The user configuration form is shown in Fig. 13
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 16 of 83
Page 17

Configuration
The configuration form comprises five types of configuration parameters:
Basic settings (User name, Phone number, Signaling, IP address, IP Port ,E-mail Pin-
code, and Web password)
Registration settings (Login, Password, Web password)
General options (NAT, Fax T.38, Convert etc.)
SIP options (Ringback Tone, Allow SIP Redirect, Allow noproxy)
H.323 options (Tunneling, Fast Start, Multiple Fast Start, Ext, T.38 compatibility,
Start H.245)
Codec capabilities (Codec, FPP)
The checkbox Enabled in the upper left corner of the form can be selected or deselected to make
the record active or inactive. You may wish to make the user record inactive to temporarily
disable the extension and avoid the necessity to configure the user record anew when need be.
The DVX-7090 Router ignores disabled user records.
4.2.1 USER BASIC SETTINGS
To configure the user basic attributes:
Fig. 13 User configuration form
1. Type the user’s name in the text field User name
2. Enter the user’s extension number in the edit box Phone number
3. Select the signaling standard that the endpoint supports (h.323 or sip) from the drop-down
list of the combo box Signaling
4. Enter the IP address of the user’s terminal in the text field IP address
5. Enter a signaling port in the edit field IP port
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 17 of 83
Page 18

Note: You may skip entering an IP address and port if the checkbox Registration is selected,
meaning that the endpoint being configured is a registering entity
6. Type the user’s email address in the E-mail edit field as the destination for voice messages
delivered by the DVX-7090 Router Voice-to-email mechanism.
7. Enter the user’s PIN-code in the edit field Pin code to grant the user access to the
Impersonate functionality.
8. Enter the user’s personal password in the Web password field to provide for remote access
to the User’s Interface.
Fig. 14 presents an example of completed basic user settings.
Configuration
Fig. 14 User basic settings
4.2.2 REGISTRATION SETTINGS
Select the checkbox Registration if you wish to configure the user’s terminal as a registering
endpoint. With the checkbox selected, enter a registration login and password in the appropriate
fields. Use the field TTL to configure time-to-live for the endpoint registrations.
Note: With the Registration checkbox selected you need to fill t he field Password only if the
registering endpoint is capable of secure authentication..
Fig. 15 Endpoint registration data
4.2.3 USER NAT-, FAX-RELATED AND SIGNALING-DEP END ENT SETTINGS
If necessary, configure other user endpoint properties that include the parameters shown in Fig.
16:
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 18 of 83
Page 19

Configuration
Fig. 16 NAT- , fax-related and protocol-specific settings
The combo box NAT serves to select a NAT traversal policy and offers triple choice:
- direct means that call packets will go direct without enabling NAT traversal
- forced stands for the NAT traversal function enabled
- detect denotes automatic detection of NAT presence
Select direct when you are positive that communication with the endpoint you are
configuring does not involve network address translation (NAT). Select the option forced
when it is known that the endpoint sits behind a NAT router. Select detect when unsure
about the situation with NAT.
FAX T.38 allows you to enable/disable T.38 fax support.
The Convert combo box offers three options:
– none (no codec conversion is performed even if the call originator and terminator
have a common codec capability)
– adaptive (the DVX-7090 Router performs codec conversion when necessary, i.e.
when the calling and called endpoints feature no common codec capabilities)
– forced (the DVX-7090 Router always performs conversion of media even when a
common capability exists)
Note: The use of codec conversion should be judicious as codec conversion is very
demanding in terms of the system computing power and takes toll on voice quality. The option
adaptive is the best choice as with adaptive selected the Router tries to put the call through
without conversion and automatically engages the codec converter when the call is impossible
otherwise. The option forced is for extraordinary cases when two endpoints cannot communicate
otherwise even with a common codec capability.
The Repacketize control allows you to manage repacketization of media streams that may be
necessary to improve the quality of speech and remedy possible silence suppression
incompatibility occurring occasionally in terminal equipment. The options of the Repacketize
drop-down list include:
– none disables repacketization of media streams
– incoming (enables repacketization of ingress media)
– outgoing (enables repacketization of egress media)
– both (enables repacketization of ingress and egress streams)
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 19 of 83
Page 20

Configuration
DTMF Options the DTMF Options combo box is used to select a type of DTMF digits payload.
The available options include:
1. RFC2833 for all terminal equipment types
2. INFO V.1 for CISCO SIP terminals
3. INFO V.2 for Nortel SIP terminals
Dealing with H.323 Options:
Tunneling enables/disables encapsulation of H.245 messages
Fast Start enables/disables FastStart
Multiple FastStart. With Multiple FastStart set to ‘true’ the system includes FastStart in every
packet
Ext T.38 compatibility
This parameter is intended to overcome slight incompatibilities that frequently exist in vendorspecific implementations of the H.323 standard. For example, setting Ext T.38 compatibility to
true ensures trouble-free interoperation of Vocaltec endpoints with the DVX-7090 Router.
Start H.245 has three options:
- callproceeding
- connect
- alerting
that help you define which of the above H.225 messages will trigger establishment of the
H.245 control channel
Early Connect – this flag is used to ensure smooth interoperation with endpoints that do not
exchange capabilities (codecs etc.) until the arrival of CONNECT. Select true to provide for an
early CONNECT message.
Dealing with SIP Options:
Ringback Tone is used to configure the RBT capability for the endpoint. If the terminal you are
configuring is capable of generating RBT, select local, otherwise select emulate.
Allow SIP Redirect allows/disallows SIP redirection
Allow noproxy when set to true enables signaling proxy only and direct flow of media streams.
The value false enables full proxy, which involves proxy operation for both signaling and media
packets.
Note: Remember that the setting of the parameter Allow noproxy must be the same for both
the calling and the called endpoint
4.2.4 CALL FORWARD DIALOG
Fig. 17 Call forward configuration form
To configure conditional and unconditional call forwarding:
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 20 of 83
Page 21

Configuration
1. Click
2. Select a condition (Busy, No answer, Unreachable, Unconditional) that will cause call
forward using the combo box in the column Fwd Condition
3. If the forward rule being configured applies to a particular calling number only, type the
necessary calling number in the edit box Source. Alternatively, you can write a regular
expression that covers a series of numbers.
Leave the edit box intact if the calling number is of no importance for the call forward
you are configuring.
4. When necessary, you can limit call forward to a particular time period and day or days
of week.
To define a call forwarding period, select the checkbox Time (in the column Activity
Schedule) and specify the period start and end time in the edit boxes From and To
respectively. To specify on what days call forwarding will take place, select the
checkbox Days and select call forward days on the drop-down menu invoked by a click
on the appearing down-arrow button.
5. Type in the forward number in the text box Fwd Number of the form and click
to validate the changes you have made to the record.
4.2.5 CODEC CAPABILITY SETTINGS
The add-new-user dialog appears with all codecs in place and frame-per-packet settings done
(see Fig. 18.) If you wish to delete unnecessary codecs, click the delete button
To add to the codec capability of the user’s terminal, click
required codec from the drop-down list of codec options.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 21 of 83
.
and select the
Page 22

Configuration
Fig. 18 Codeсs options
Enter a number of frames per packet in the neighboring edit box FPP with due regard to the
endpoint capability and buffer size. Information about codec frame sizes is given in the table
below.
Table 2 Frame sizes by codecs
Codec Frame size
G.729 10 ms
G.729A 10 ms
G.723 30 ms
G.711-aLaw 1 ms
G.711-uLaw 1 ms
GSM 06.01 20 ms
Therefore, if an endpoint can accept no more than, say, 60ms worth of audio per packet, for
G.711 you can enter the value 60; for G.723 it will be 2 (60/30 = 2); for G.729 it would be 6
(60/10 = 6).
Note: Please, remember that for G.711 codecs it makes sense to enter “frames per packet”
values in multiples of ten only.
You can increase/decrease codec precedence in the table by clicking up- and down-arrow
buttons.
Click
to move the codec record up one line and increase the codec precedence.
Click
Click
To add the new user record to the population of configured users, click
to move the codec record down one line thus decreasing the codec precedence.
to delete the codec record.
. Click
, to cancel the made changes.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 22 of 83
Page 23

4.2.6 DEFAULT USER
The Default user account is the only preconfigured user account that exists in the system at the
time of the first startup.
Configuration
Fig. 19 Users table on first start
The existence of the Default user record is a must therefore you cannot delete this record. The
system uses the Default user account whenever a call comes originated by a user not registered
with the system.
4.3 CONFIGURING GATEWAYS
To access the page Gateways, press . The page presents a table of configured
gateways as shown in Fig. 20
Fig. 20 Table of gateways
The columns in the gateways table present the following information:
or inactive
contains , the Edit button. Click this button to edit the record.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 23 of 83
contains a dimmed checkbox that shows if the gateway record is activated
Page 24

Configuration
shows the name the gateway is assigned in the system
includes , the button that invokes the groups dialog
shows the gateway’s current registration status. Possible values include:
- Registered – the gateway is successfully registered with the DVX-7090 Router
- In Call – the gateway is handling calls
- External – the DVX-7090 Router is registered to the gateway
- Both – combination of Registered and External
incorporates the button that you click to delete the record.
The parameters on the gateway configuration form are similar to those on the user configuration
page. The gateway configuration form is presented in Fig. 21
Fig. 21 Gateway properties form
The parameters on the gateway configuration form fall under five categories:
- Basic gateway settings (Gateway name, Signaling, IP Address, IP Port)
- Gateway registration settings (Login, Password and TTL)
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 24 of 83
Page 25

- Parameters for DVX-7090 Router registrations with external registrars (Login,
Password, Port, TTL, Security type, Endpoint type)
- NAT-, fax-related and signaling-dependent settings
- Codec capability settings
4.3.1 BASIC GATEWAY SETTINGS
Basic gateway settings include the following configuration parameters:
Configuration
Fig. 22 Basic gateway attributes
Note: The name entered in the field Gateway name is u sed as the gateway’s identifier in
registrations to a remote gatekeeper/SIP registrar. So, make sure the configured gateway name
matches the registration name on the remote GK/SIP registrar.
The checkbox Enabled activates/deactivates the gateway record in the system.
Gateway name is a text box for entering the gateway’s identifier.
Signaling is a combo box used to select the gateway’s signaling standard.
Use the IP Address edit box to enter the gateway’s IP.
Enter a listening port number in the IP Port edit field.
The checkboxes under the name Caller IDs have the following intent:
Use a selected checkbox Relay Incoming to indicate the call source gateway from which
the Router may accept the caller’s ID for further relay to destination.
Use a selected checkbox Trust Incoming to indicate a gateway as a trusted source from
which caller’s IDs are acceptable for the purposes of the Impersonate function.
Use a selected checkbox Send for gateways on the outgoing call leg to allow them to
pass the caller’s ID further to the destination.
4.3.2 REGISTRATION SETTINGS
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 25 of 83
Page 26

Fig. 23 Gateway registration panel
This category of settings is used to configure the registration parameters of the gateway that
include:
- the checkbox Registration. A selected checkbox means that the gateway being
configured will register to the DVX-7090 Router.
- Login is a text box for the gateway’s registration name
- Password is an edit field for password entries.
- TTL is a box for registration time-to-live data.
4.3.3 D-LINK DVX-7090 ROUTER REGISTRATION SETTINGS
Configuration
Fig. 24 DVX-7090 Router registrations dialog
Use this category of settings to configure the Router registration parameters that enable the
system to register to remote gatekeepers and SIP registrars.
The registration parameters include:
- checkbox Register with GK/registrar. The checkbox allows/disallows the DVX-7090
Router registration to external servers. Select this checkbox to activate the sub-form and
configure the Router’s external registration data.
- Server name. Use this edit field to enter the name of the gatekeeper or SIP registrar
server the Router is expected to register to.
- Address is a box for entering the IP address where the Router should send registration
requests
- Login provides a text box for the Router’s registration name
- Password is an edit field for registration password entries
- Port is a field for entering a port number for registration exchange
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 26 of 83
Page 27

- TTL provides an edit box for entering a time-to-live registration period in seconds
- Security type is a combo box with types of logon credentials encryption:
o H323Alias – login and password are transmitted unencrypted as plain text
o CRYPTO-TOKEN – encrypt the logon credentials using the MD5 algorithm
o CHAP – CHAP encryption of data
- Endpoint type is a combo box used to define how the DVX-7090 Router will register to
the remote registrar/gatekeeper, as a terminal or as a gateway
Configuration
4.3.4 GATEWAY NAT-, FAX-RELATED AND TYPE-OF-SIGNALING PRO PERTIES
The area of the form that serves to configure the gateway NAT- and fax-related options as well
as pertinent signaling protocol parameters is illustrated in Fig. 25
Note: Actually the web interface displays either the H.323 options form or the SIP options
form in accordance with the type of signaling selected in the combo box Signaling (see Fig. 22)
Fig. 25 Gateway NAT, fax and signaling options
The gateway settings shown in Fig. 25 are identical to the similar parameters appearing on the
User configuration form. Refer to 4.2.3 for a detailed explanation of the configuration
parameters.
4.3.5 GATEWAY CODEC CAPABILITY SETTINGS
The gateway codec capability parameters are identical to those described for the User
configuration page (see 4.2.5)
4.4 CONFIGURING DVX-7090 SERVICES
To access the services page, click the tab . The page presents a table view similar to
that illustrated in Fig. 26
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 27 of 83
Page 28

Configuration
Fig. 26 Table of services
The intent of the table columns is as follows:
contains the checkbox Enabled that shows if the service is available in the
system.
contains the edit button . Click this button to change the voice prompt or
prompts associated with the service.
shows a descriptive name of the service
presents the command associated with the service
contains the delete button
To add a new service, click
.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 28 of 83
Page 29

Configuration
Fig. 27 New service dialog
The displayed new-service configuration form is shown in Fig. 27.
Note: The way the invoked new-service configuration form looks depends on what service
you are configuring. The Prompts configuration dialog is displayed only when DISA and
Impersonate commands are selected in the combo box Command. The dialog Forward options
appears only when configuring DISA and Group call services.
1. Select the checkbox Enabled to make the newly created record active
2. Type in the service name in the text box Service name overwriting the default name New
Service
3. Use the combo box Command to select a command that the DVX-7090 Router will execute
when the service you are configuring is addressed. The drop-down list includes the
following commands:
- Group Call
- Voice Mail
- DISA
- Auto redial
- Pick Up
- Impersonate
Refer to 4.4.1for more information about the commands
4. When dealing with configuration of DISA and Group call you may wish to arrange for call
forward selecting the attendant forwarding condition for DISA and unconditional or no reply
for the Group call service.
5. When through with configuring the service record click
to add the service record
to the table.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 29 of 83
Page 30

Configuration
Whenever necessary click
Click
to remove unneeded records only. Whenever it is required to disable a service record
to refresh the view.
for some time, deselect the checkbox Enabled to save the trouble of configuring the service
anew.
4.4.1 COMMANDS THAT INVOKE SERVICES
The items that populate the drop-down list of the combo box Command are actually command
options that cause execution of a certain algorithm.
Table 3 Commands and invoked algorithms (services)
Command What the system does in response
Group Call generates simultaneous calls to all group members
Voice to eMail 1. plays a voice prompt inviting the caller to leave a message after the tone
2. records the message
3. convert the recorded message into a .wav sound file and
4. sends the file to the callees’s email address
DISA allows access to a set of functions and services configured for this
particular type of the inward system access
Auto redial keeps dialing the required number until the call is answered
Pick Up Connects the line to the member user who dialed the Pick Up number
Impersonate 1. prompts the caller to dial Pin code
2. authenticates the caller
3. gives the caller access to the system according to the rights and
privileges characteristic of the user’s account
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 30 of 83
Page 31

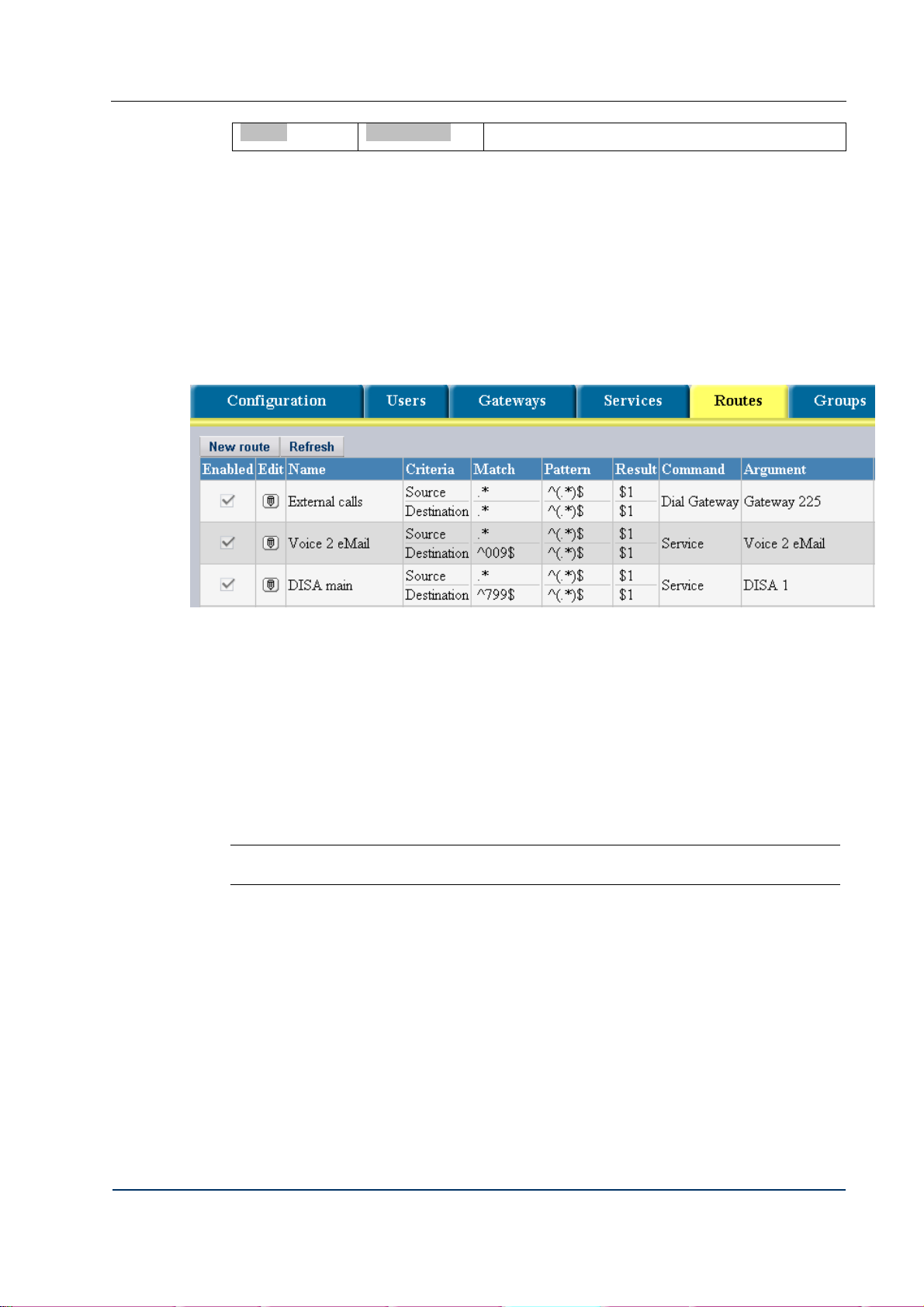
4.5 CONFIGURING THE ROUTING TABLE
Preparation of the routing table essentially means creation of call handling rules. Click the tab
to access the configuration page illustrated in Fig. 28
Configuration
Fig. 28 Routing table
The columns of the routing table have the following meaning:
currently in effect. A deselected checkbox disallows the DVX-7090 Router to apply
the rule.
contains , the Edit button. Click this button to edit the record
shows the descriptive name of the routing rule.
indicates two rule application criteria – the source and destination number.
displays match regular expressions for the source and destination number.
includes cells for regular expressions that set the number transformation
pattern.
is a box for a regular expression defining the number translation result.
of the routing rule. The list of possible commands includes:
contains a checkbox. A selected checkbox identifies a call handling rule
presents the command that the System executes during implementation
- Continue
- Restart
- Reject
- Dial user
- Dial gateway
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 31 of 83
Page 32

Configuration
- Service
shows the name of the invoked service (when the command is Service )
or the name of the target gateway (when the command is Dial gateway).
includes the button that invokes the groups dialog. To include
the rule you are configuring into a group, select the necessary checkbox in the
displayed groups dialog box and click .
Note: The configured rule will apply only if the call originator and the rule belong
to the same access group.
The column displays the following buttons:
-
– move the record one line up (see 4.5.2)
-
– move the record down one line (see 4.5.2)
-
– duplicate the record.
-
– delete the record.
To add a new rule to the routing table, click
To update the table view, click
click
click
to delete the record
to duplicate the record
.
The DVX-7090 Router processes call handling rules in the table in the order of precedence;
therefore, the rule that is higher in the table takes precedence of the rule located closer to the
table bottom.
4.5.1 COMMANDS EXECUTED DURING ROUTING
The items on the drop-down list of the combo box Command on the routing rule form fall under
two categories – the commands pertaining to the routing process and call handling commands
Table 4 Commands executed during call routing
Routing control commands
Command What the system does in response
Continue Goes to the next routing rule. The command Continue is commonly used to
resume routing after number transformation.
Restart Goes to the first rule in the table
Call handling commands
.
Command Argument What the system does in response
Reject Rejects the call
Dial User 1. Compares the destination number against the
database of configured extensions
2. if the matching number is found, dials the
extension number, otherwise
3. executes Continue
Dial Gateway GW name Sends the call to the specified gateway
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 32 of 83
Page 33
Service Service name Provides the specified service
4.5.2 WHY POSITION OF ROUTING RULES IN THE TABLE IS IMPORTANT
The Router picks rules in the routing table one by one starting from the topmost.
The Router applies (executes) the routing rule only if all of the below conditions are met:
• The routing rule is enabled;
• The source and destination numbers of the call match the respective numbers specified
in the routing rule
• The rule and the calling party belong to the same group
The Router goes to the next record in the table, if at least one of the above conditions is not met.
Configuration
Fig. 29 Why position of routing rule in the table matters
Consider the case when the routing rule for egress calls is positioned on the topmost line of the
table (see Fig. 29.) As the destination number condition is always met the Router will send all
calls regardless of the destination number to the gateway intended for traffic leaving the system.
Actually, it will never come to comparing the call destination number against the numbers
defined in the routing records positioned under the rule for outgoing calls.
By this means a routing rule that allows any source and any destination number placed ahead of
all other routing rules in the table makes all other destination numbers, i.e. extensions and
services, unreachable.
Note: Always position the routing rule based on the regular expressio n ‘*.’ for the source
and destination numbers on the bottom lin e of the t abl e .
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 33 of 83
Page 34

4.6 GROUPS AND GROUPING
4.6.1 GENERAL
In the DVX-7090 Router you can do grouping based on access to the Router’s features and an
organizational principle.
Grouping allows you to economize on the configuration effort, and is a prerequisite to some of
the Router functions and services (for example, pick up and group calls.)
You need to specify groups when you configure users, services and routes.
Users. By including the user into this or that group you define what Router features and functions
will be accessible to the user and what incoming calls the user can answer (from the standpoint
of the pick up capacity and group calls.)
When you configure services (e.g. DISA and Group call) you need groups to indicate the target
for second leg calls that the Router generates
When you configure routes for the routing plan you need groups to define what users are allowed
to send calls along the configured routing path.
The two types of groups currently available in the DVX-7090 Router are access and pickup. A
group of the type access allows access to the selected DVX-7090 Router service. A group of the
type pickup allows members to pick up calls intended for other members of the group.
Additionally, group calls are possible only with groups of the type pickup.
Configuration
4.6.2 CONFIGURING GROUPS
To configure groups, go to the Groups page by clicking the tab .
The Groups page displays a table of configured groups similar to that presented in Fig. 30
You can use the table for adding new groups and editing the existing ones.
The purpose of the table columns is as follows:
contains the checkbox Enabled that shows if the group record is active in
the DVX-7090 Router. Deselect the checkbox to deactivate the group record.
is the group’s name that describes either the nature of grouping or the group
make up. For example, the group name Only Transfer in the table presented in Fig. 30
describes the services accessible to the group members. Another possible name is
Marketing and Sales (see Fig. 30) indicating the organization unit the members of
which can use the Pick up functionality etc.
Fig. 30 Table of existing groups
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 34 of 83
is a combo box with a list of existing group categories.
- access. Groups of the type ‘access’ categorize users by accessibility of services
Page 35

Configuration
- pick up. Groups of the type ‘pickup’ include members with the capability to
perform call pick up and group call recipients.
contains a checkbox selection/deselection of which allows/disallows
access to the call transfer service.
contains a checkbox selection/deselection of which allows/disallows
access to the call forwarding service
contains a checkbox selection/deselection of which allows/disallows
access to the conferencing service.
contains a checkbox selection/deselection of which allows/disallows
access to the call waiting service. Call Waiting is a feature that allows the user to be
notified of an incoming call during a call session already in progress, and gives the
user the ability to answer the second call with the first call placed on hold.
Note: The Conference service is accessible only to users with access to call transfers.
contains the button (Delete)
Click
to refresh the table view.
To configure a new group:
1. Click
to add an empty group record to the table (see Fig. 31)
Fig. 31 Adding a group
2. Type in the group name in the column replacing the default name Group #... with a name
string of your choice.
3. Select the group type in the combo box
4. Select the necessary checkboxes that allow the services and function of the System.
5. Click
to confirm the changes you have made
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 35 of 83
Page 36

4.7 MANAGING VOICE PROMPTS
Voice prompts management consists in an authorized person (system administrator or user)
replacing the default prompts with customized ones.
Prompt management rights of users vary with the type of the user account in the system. The
system administrator has access to all prompts and can replace default prompts with
customized ones. After replacement the prompts newly added by the administrator become
default.
In the D-Link DVX-7090 Router extension subscribers have access to and can customize
only some of the system prompts, i.e. those essential for and connected with operating their
own extensions (the Line busy prompt, the No answer prompt, the Voice to email greeting
etc.). User-customized prompts remain operational only as long as the user needs them. A
user can always revert to default prompts configured by the system administrator.
Configuration
Click
available in the system (see Fig. 32 )
The table of current prompts shows the name of the event or digit the prompt refers to and
displays two buttons in the column Action.
to access the Prompts page that displays the table of prompts currently
Fig. 32 Table of available prompts
The right-arrow button
With MIME type associations properly set in the web browser the selected .wav prompt file
will be played, otherwise the file dialog will be displayed inviting you to save the sound file.
If you wish to replace a prompt with one of your own click
intend to change.
The upload dialog will appear above the Prompts table (see Fig. 33.)
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 36 of 83
serves to play the prompt or display the name of the prompt file.
on the line of the prompt you
Page 37

Configuration
Fig. 33 Prompt upload dialog
Click
click
to open the file dialog, find the .wav file with the necessary prompt and
.
The prompt file must be a valid .wav file with voice encoded using the PCM codec (PCM –
16 bits mono, 8 KHz). PCM encoding can be done with the help of the standard Microsoft
recorder utility that comes with the operating system.
Note: The uploaded custom prompt overwrites the current sound file and becomes the
default prompt in the system. You can revert to the default prompt supplied by your system
manufacturer only if you saved the prompt file before replacing it with a prompt of your own.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 37 of 83
Page 38

4.8 CDRS AND LOGS
4.8.1 CALL DETAIL RECORDS (CDRS)
The DVX-7090 Router writes information about calls to files comprised of CDRs (Call
Detail Records). The system generates two types of CDRs:
• User CDRs that contain information about calls involving the user extension. A user
CDR provides data about the call originator and destination, date and time of the
call session start and end, call disconnect reason etc. Each new call entails creation
of a new record with call details.
• Administrator CDRs. Administrator CDRs include summarized call data for all
users configured in the system. The files with CDR summaries are kept for a month.
At the end of the month period the system starts a new file, archives the current
CDR file and sends it to the email address, specified in the Email CDR to field.
4.8.2 VIEWING CDRS
The administrator can view CDRs on the CDRs page of the administrator’s web-interface.
Click the CDRs tab to access the CDRs page.
Configuration
Fig. 34 CDRs look up page
The CDRs page includes two elements, a drop-down list of CDR files (CDR files list ) and a
table of records of the CDR file currently open (Current file CDRs).
The table Current file CDRs displays CDRs of the currently open file only and disappears
whenever any CDR file other than the currently open is selected from the drop-down list.
The column names of the table Current file CDRs have the following intent:
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 38 of 83
Page 39

Configuration
shows the date and time of the call.
presents the caller’s number
displays the number of the called party
provides information about the in-call time in the hh:mm:ss notation
shows the disconnect reason for the call. The disconnect reason is output as a
verbal interpretation of a Q931 disconnect cause code or SIP disconnect response where no
applicable Q931 code is found.
The underlined column name is an indication that you can click the name to sort the table
records accordingly. For example, by clicking the name you have the table
records sorted by dates.
If you wish to view call detail records from any other CDR file you must download it first.
Click the download button
next to the selected CDR file to download it to your
workstation. CDR files are plain text files that can be viewed in any text editor.
An individual call detail record consists of a number of semicolon-delimited fields that
provide the following data:
1. SETUP Time
2. CONNECT Time
3. Disconnect Time
4. Calling Number
5. Caller’s name
6. Called number
7. Callee’s name
8. Call type (incoming/outgoing)
9. Disconnect Cause Code
10. Disconnect cause description
Below is an example of a CDR extracted from a CDR file:
128000314450000000;128000314480000000;128000314650000000;50399;DPH120s;124;PBX-SIP;outgoing;16;Normal call termination
The time data (fields 1 through 3) is presented as the Windows File Time
Note: Windows file time is a 64-bit value that represents the number of 100-nanosecond
intervals that have elapsed since 12:00 midnight, January 1, 1601 A.D. (C.E.) Coordinated
Universal Time (UTC). Windows uses a file time to record when an application creates,
accesses, or writes to a file.
Any user configured in the system can view CDRs pertaining to the user’s extension number
by clicking
on the User’s personal page (for more information see ch. 6 User
Interface):
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 39 of 83
Page 40

Configuration
Fig. 35 User CDRs
User CDRs are call detail records that include information about the date and time of the call,
call direction (incoming or outgoing), the other call party’s name and number, and the call’s
disconnect reason.
You can view downloaded CDR data in Microsoft Excel. To view a downloaded CDR file in
Microsoft Excel:
1. Start Excel
2. Click File –> Open
3. Find the downloaded CDR file you wish to inspect
4. As the CDR file is in plain text format, Excel will automatically start the text import
wizard
5. In the text-import wizard select the Delimited radio button to indicate that the CDR
file has delimited contents
6. Click Next to display the next dialog of the wizard and select the checkbox
Semicolon. Additionally deselect the checkbox Tab if it is selected. This done, click Next
again.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 40 of 83
Page 41

Configuration
7. The text-import wizard will display the next dialog where you may wish to specify
the type of data column-wise. It is advisable to leave the type of data General as it appears in
all the columns of the table, though.
8. Click Finish to complete the data import procedure.
The result of the import is shown in Fig. 36
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 41 of 83
Page 42

Configuration
Note: The function for calculating the duration of a call session is =(Cn-Bn)/10,000,000
(seconds), where n denotes the number of a row of cells. For example, the duration of the
call session shown in the first row of the table in Fig. 36 is (C1-B1)/10,000,000 = 19 sec.
4.8.3 LOGS
In addition to CDR files the DVX-7090 Router writes log files designed to keep track of the
system operation and events.. A log is a runtime journal with a listing of all events that occur
on the server during operation of the DVX-7090 Router. The log files are necessary for
debugging purposes.
The Router generates four types of logs:
• Control unit log is a file containing messages generated by the CU during operation.
• CU protocol log is a file of messages exchanged by the CU and SU during
• Switching unit log includes event messages generated by the SU during operation.
Fig. 36 CDR file data imported to Excel
The file name format is Logic-<YYYY-MM-DD>-<hh-mm-ss>.log, where
YYYY-MM-DD is the year, month and date of the file creation, hh-mm-ss is the
hour, minute and second of the file creation, .log is the filename suffix.
operation. The file name format is Protocol-<YYYY-MM-DD>-<hh-mm-ss>.log.
The file name format is trace-<YYYY-MM-DD>-<hh-mm-ss>.log.
• SU protocol log comprises signaling messages exchanged by the SU and H.323 or
SIP endpoints. The file name format is log-<YYYY-MM-DD>-<hh-mm-ss>.log.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 42 of 83
Page 43

Configuration
When addressing the customer support service, attach the pertinent four log files to the bug
report.
Note: CDR and log files take up quite a large amount of disk space. So, at the expiry of a
certain period of time the system archives the logs and saves the archive to the Router flash
drive.
Click
to access the Logs page (see Fig. 37):
Fig. 37 Logs page
The Logs page consists of two parts: the CDRs and logs management form and the table of
log files.
To configure a rotation period for CDR and log files fill in the following fields of the CDRs
and logs management form:
Keep Logs for is an edit box for setting a rotation period for log files. The recommended
value for this parameter is 7.
Keep User CDRs for provides a box for entering a rotation period for files with user CDRs.
Keep Administrator CDRs for is a field for setting storage time for administrator CDR files.
Email CDR to is an edit field for the destination e-mail address to which the system will send
administrator CDRs archives after the expiry of the keeping time configured in the Keep
Administrator CDRs field.
The table of files is designed for viewing log file listings. The table is comprised of the
following columns:
– the column of file creation time stamps in the YYYY.MM.DD hh:mm:ss format.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 43 of 83
Page 44
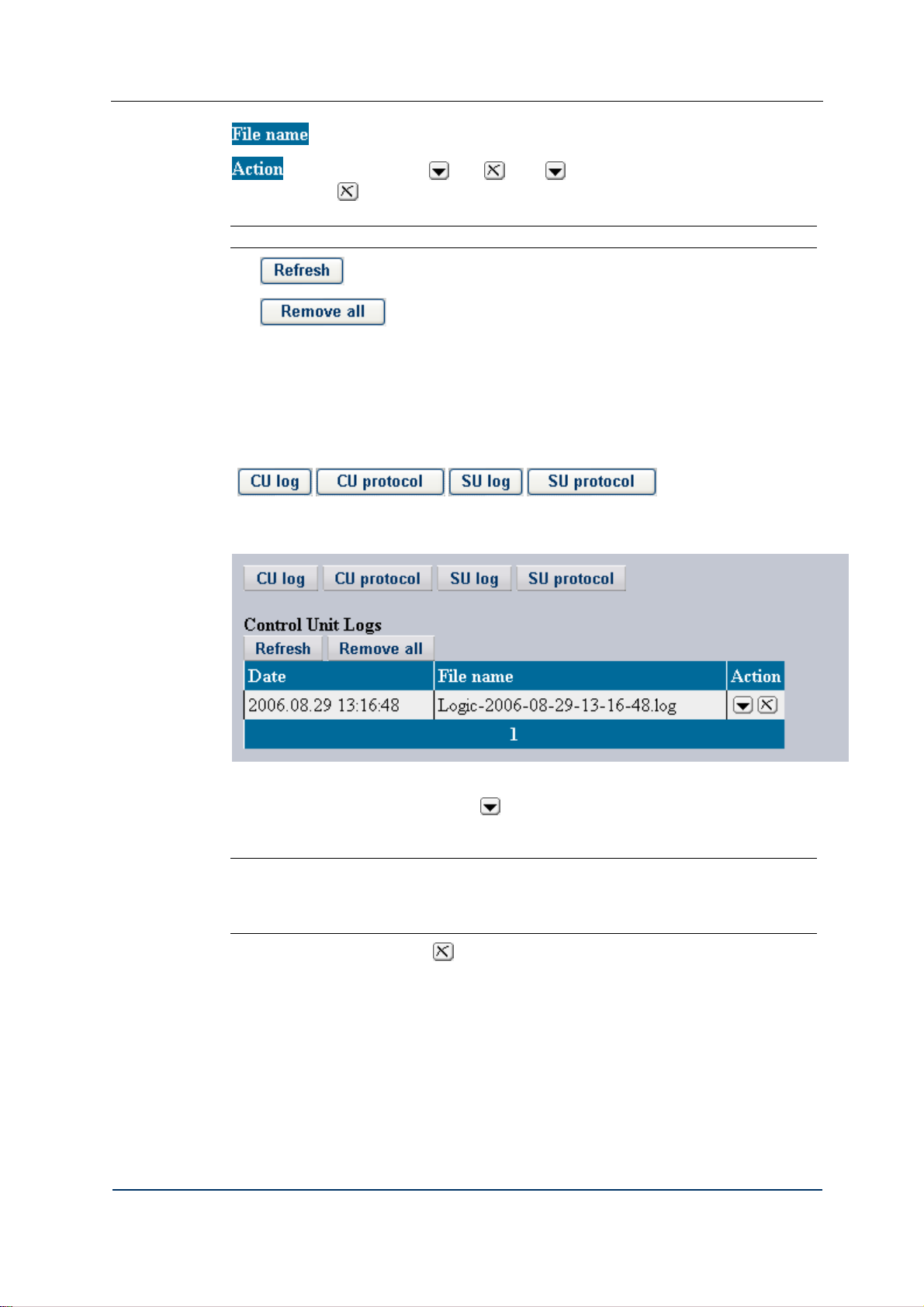
Configuration
– the column for log file names.
contains two buttons and . Use to download the selected file to your
workstation, use
to delete the selected file.
Note: Deletion of the currently open log file is impossible.
The button refreshes the table view.
The
4.8.4 VIEWING LOGS
Log files are necessary for debugging purposes. In case of a addressing to the customer
support service you can attach a log file to the bug report.
To view a list of the desired log files click the respective button
(
shows a list of CU protocol logs:
, , , ). For example, Fig. 38
button deletes all files from the table.
Fig. 38 A list of control unit protocol logs
To download a file from the table click
, specify the destination directory and save the file
to your computer. Now you can view the downloaded log file in any plain text editor.
Note: CDR and log files are written in UNIX format and have UNIX end- of-line
characters, so some text editors (such as Notepad) may display them incorrectly. Use either
the Windows WordPad or Unix text editors (for example, vi or emacs) to view the
downloaded files.
To delete the selected file, click .
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 44 of 83
Page 45

4.9 SOFTWARE VERSION MANAGEMENT
The DVX-7090 Router features a flexible software version management mechanism that
allows you to:
upload SW upgrades obtained from the manufacturer’s site
preserve preferred SW versions
remove obsolete and unused application releases
select a version that most suits you operational needs at the moment
switch between the application releases whenever you find it opportune
You can have up to 4 software versions on the system simultaneously.
Configuration How-to’s
To add another SW version (an upgrade or a steady, proven release) click
the SW management page (see Fig. 39).
to access
Fig. 39 Software management page
The SW release that you plan to add to your current population of the DVX-7090 Router
versions must be on the workstation you are using for administration at the moment.
You can have no more than 4 Router software versions on the system. For this reason, if you
already have 4 SW versions on the DVX-7090 Router host you need to remove at least one
before you can add another.
Click
You cannot delete the current and the previous version, this is why the delete button is
present on topmost lines of the table.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 45 of 83
on the line of the version you wish to remove.
Page 46

Configuration How-to’s
Click
to bring up the upload dialog (see Fig. 40).
Fig. 40 Version upload dialog box
Click
to display the file dialog and find the SW update on the host you are
using to access the Router.
Click
to upload the update to the Router host server.
If there is not enough free disk space, an error message appears above the table of versions:
Delete one of the earlier versions to be able to add a new one.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 46 of 83
Page 47

Configuration How-to’s
When the newly uploaded version appears in the table of versions, chose a version selected to
be operational at the moment and click
The button
allows you to make backups of the current
for the made changes to take effect.
configuration database and save them to your computer.
The
button allows you to upload the saved version of the
configuration database to the Router host.
The
button allows you to cancel all the application settings and revert to
the ‘ex-works’ configuration. Current settings will be removed from the database.
To update the operating system:
1. download an update OS image from the site of the DVX-7090 Router manufacturer
2. logon to the DVX-7090 Router and click the tab
to access the
software management page
3. Click
to invoke the SW upload dialog, and you will be displayed
with the warning as shown in Fig. 41
Fig. 41 System restart warning
4. Click the OK button to go on with the OS update procedure, and the Router will
produce the OS update upload dialog (see Fig. 42)
Fig. 42 OS image upload dialog
5. Click
to bring up the file dialog and select the OS image you intend to
upload
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 47 of 83
Page 48

Configuration How-to’s
6. The OS image selected, click
to upload the image to the DVX-7090
Router host.
The uploaded OS installs automatically and becomes current. The newly installed and current
OS version is displayed on the bottom line of the table ‘Operating system updates’
The button
allows you to roll back to the previous version of the OS. It is
strongly recommended that you use this button only when it is absolutely necessary.
When you click the rollback button, the system reverts to the previous OS version and the
table ‘Operating system updates’ displays one line less than the number of lines before the
rollback.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 48 of 83
Page 49

Configuration How-to’s
5 CONFIGURATION HOW-TO'S
5.1 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO VOICE TO EMAIL
When started, the Voice-to-email service prompts the caller to leave a message after the tone,
records the caller’s message, converts it into a .wav sound file and sends the file to the user’s
email address.
To configure a routing path to the Voice-to-email service:
1. Click
2. Click
3. Replace the default name Route #... with a descriptive name of your choice (Voice Mail
Route, for example)
4. Use the drop-down list of the combo box Command to select the option Service
5. Use the appearing combo box Argument to select the option Voice to eMail
6. In the edit box Match on the Destination line of entry boxes enter the destination number
009 for the service
7. Suppose you need to make this service available on weekends only. Click
title Activity Schedule and select the checkbox Time to enter the start and end time for the
Voice to eMail tool. Further, select the checkbox Days and select Saturday and Sunday on
the drop-down list of weekdays.
to access the routing table page.
to add a new record.
under the
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 49 of 83
Page 50

Configuration How-to’s
8. Click
to add the newly configured record to the table of configured routes. This
done, you will return to the Routes page again. This step completes the Voice-to-eMail route
configuration procedure.
Note: Remember, to benefit from the voice-to-email service, the called user must have
the destination e-mail address and call forward to voice-to-email number configured
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 50 of 83
Page 51

Configuration How-to’s
5.2 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO DIRECT INWARD SYSTEM ACCESS
To enable an authorized user to access all or some of the D-Link DVX-7090 Router services
from a remote location, create the DISA service with the required range of accessible
features.
Suppose your objective is to create two routes to two different DISA services – the main one
with unlimited access to all of the DVX-7090 Router features and customized DISA with
access to conference calls only. The main DISA service will be accessed by dialing 799
while the customized one by 798.
To configure DISA:
1. Click
2. Click
3. In the text box Service name of the add-new-route dialog replace the default name New
service entering some descriptive name, for example DISA 1.
4. Select the option DISA in the drop-down list of the combo box Command and make sure
the checkbox Enabled is selected or the routing rule will remain inactive.
to access the Services page.
to add a new record.
5. You don’t have to configure the prompt as the DISA prompt is assigned by default.
6. Click
Services page again.
7. Click
All. Members of the access group All have access to all services.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 51 of 83
to add the newly configured record, and you will be back to the
in the column and in the pop-up menu select the checkbox
Page 52

Configuration How-to’s
8. Click
9. Click
to confirm your choice
to add another record
10. Give the new DISA service some other name (say, DISA limited)
11. Repeat steps 4 through 6 of the configuration sequence.
12. Click
in the column and in the pop-up menu select the checkbox
Conferences only.
13. Click
14. Click
15. Click
to confirm your choice
to access the routing table page
to bring up the add-new-route dialog
16. Make sure the checkbox Enabled is selected or the routing rule will remain inactive
17. Replace the default name Route #... with a descriptive name of your choice (DISA main,
for example)
18. Use the drop-down list of the combo box Command to select the option Service
19. Use the appearing combo box Argument to select the option DISA 1
20. In the edit box Match on the Destination line of entry boxes enter the destination
number 799 for the main DISA service
21. Click
to add the newly configured record to the table of configured routes.
This done, you will return to the Routes page again. This step completes the DISA route
configuration procedure.
To add a routing record for the limited DISA service (destination number 798)
1. Click
to duplicate the newly created DISA record, and you will be
displayed with the clone editing form
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 52 of 83
Page 53

Configuration How-to’s
2. Replace the default route name DISA main clone with the name you have
chosen for the limited DISA (DISA_conferences, for example)
3. Select the option DISA limited in the combo box Argument
4. Replace the destination number 799 with the destination number 798 in the
Match entry box on the line Destination
5. Click
to add the newly configured record to the table of
configured routes. This done, you will return to the Routes page again. This
step completes the configuration procedure for alternate DISA routes.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 53 of 83
Page 54

Configuration How-to’s
5.3 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO EXTENSION NUMBERS
To configure call routing to DVX-7090 Router extensions:
1. Click
2. Click
3. In the text box Route name of the add-new-route dialog replace the default name Route
#... entering some descriptive name, for example Route to local users.
4. Make sure the checkbox Enabled is selected or the routing rule will remain inactive
5. Select the option Dial User in the combo box Command
6. Leave the fields for the source and destination numbers unchanged
7. Click
The resulting call handling record is shown in Fig. 43
to access the routing table page.
to add a new call handling rule.
to confirm your choice.
Fig. 43 Call routing rule for extension numbers
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 54 of 83
Page 55

Configuration How-to’s
5.4 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH FOR OUTBOUND CALLS
To create a rule for calls leaving the system do the following:
1. Click
2. Click
3. In the text box Route name of the add-new-route dialog replace the default name Route
#... entering a descriptive name to your liking, for example Outgoing calls.
4. Select the option Dial Gateway in the combo box Command
5. Select the gateway that handles outward calls from the drop-down list of configured
gateways of the combo box Argument.
6. If neither source nor destination number transformation is necessary, leave the Source
and Destination number edit boxes as they are.
to access the routing table page.
to add a call handling rule.
Fig. 44 Routing rule for outbound calls
7. Make sure the checkbox Enabled is selected or the routing rule will remain inactive
8. Click
the routing table page.
Refer to section 5.9 for tips on configuring a technical prefix for calls placed outside the
system.
to submit the newly configured call handling rule, and you will return to
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 55 of 83
Page 56

Configuration How-to’s
5.5 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO CALL PICKUP
The DVX-7090 Router provides for two types of call pickup:
1. group call pickup and
2. directed call pickup
Group call pickup allows you to answer any ringing phone that is in the same pickup group
with you simply by dialing the pickup number.
In directed call pickup you must enter the call pickup key sequence and dial the extension
number of the ringing phone to answer the call. You do not have to be in the same group with
the user of the ringing phone to use directed call pickup.
Suppose the administrator assigns key sequence 888 for the call pickup rule.
To configure call pickup:
1. Click
2. Click
3. In the text box Route name of the add-new-route dialog replace the default name Route
#... entering a descriptive name to your liking, for example Pick Up.
4. Select the option Service in the combo box Command
5. Select the name of the service that ensures pick up from the drop-down list of service
names of the combo box Argument.
6. As the source number is of no importance here, leave the edit boxes on the line Source
unchanged. Enter the Pick up service destination number 888 in the edit box Match and
edit box Pattern followed by a regular expression for whatever number that may be
dialed after 888, to allow for directional pick up.
to access the routing table page.
to add a call handling rule.
Fig. 45 Routing rule for group and directional pick up
7. Make sure the checkbox Enabled is selected or the routing rule will remain inactive.
8. Click
the routing table page
9. Click
groups), the members of which will be eligible to use the service.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 56 of 83
to submit the newly configured call handling rule, and you will return to
in the column and in the pop-up menu select a group (or
Page 57

Configuration How-to’s
Note: To make call pick up possible the owner of the ringing phone and the configured
rule must belong to the same access group.
10. Click to confirm your choice.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 57 of 83
Page 58

Configuration How-to’s
5.6 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO IMPERSONATE FUNCTION
The Impersonate function allows a caller who enters a specific PIN code to access the
Router‘s services and features configured for the account of the user to which the entered
PIN code belongs.
Suppose, the administrator assigns the Impersonate function key sequence 777. To use the
office phone from a remote location, the user must:
• Dial into the Router
When outside the system
To configure a routing rule for the Impersonate service invoked by dialing 777 followed by
the user’s office phone number or number of some other service:
• Dial the DISA number and get the dial tone
• Enter the Impersonate key sequence 777
• Enter the user’s telephone number
• Enter the user’s pin-code and get the dial tone
• Now the user can make calls from the remote location as if being in the
office
1. Click
2. Click
3. In the text box Route name of the add-new-route dialog replace the default name Route
#... entering a descriptive name to your liking, for example Impersonate.
4. Select the option Service in the combo box Command
5. Select the name of the service that ensures the Impersonate function from the drop-down
list of service names of the combo box Argument.
6. The source number being of no importance here, leave the edit boxes on the line Source
unchanged. Enter the Impersonate service destination number 777 in the edit box Match
and edit box Pattern followed by a regular expression for whatever number that may be
dialed after 777, i.e. (.*).
to access the routing table page.
to invoke the rule configuration form
7. If necessary, click on the Activity Schedule form and enter time restrictions for
the service accessibility.
8. Click
9. Click
groups, the members of which will be eligible to use the Impersonate service:
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 58 of 83
to add the rule to the routing table.
in the column and select in the pop-up menu a group or
Page 59

Configuration How-to’s
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 59 of 83
Page 60

Configuration How-to’s
5.7 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO GROUP CALL SERVICE
A group call is a call intended for a particular group of DVX-7090 Router subscribers. When
a group call comes, telephone sets of all the group members start ringing simultaneously.
When one of the group members answers the call, all other telephones stop ringing.
Suppose the administrator has assigned the Group call service key sequence 444. To make a
group call, the caller is expected to:
When outside the system
To configure a Group call rule, do the following:
1. Click
2. Click
3. In the text box Route name of the add-new-route dialog replace the default name Route
#... entering a descriptive name to your liking, for example Call whoever answers.
4. Select the option Service in the combo box Command
5. Select Group call from the drop-down list of service names of the combo box Argument.
6. The source number being of no importance here, leave the edit boxes on the line Source
unchanged. Enter the Group call service destination number 444 in the edit box Match
on the Destination row of edit boxes.
• Dial into the DVX-7090 Router
• Dial the DISA number and get the dial tone
• Dial Group call service number 444 and get RBT
• Wait till one of the group extensions answers
to access the routing table page.
to invoke the rule configuration form
7. If necessary, click on the Activity Schedule form and enter time restrictions for
the service accessibility.
10. Click
11. Click
the appearing pop-up menu.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 60 of 83
to add the rule to the routing table.
in the column and select a target group for Group calls in
Page 61

Configuration How-to’s
Note: Remember that the configured rule and the dialing user must belong to the same
access group.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 61 of 83
Page 62

Configuration How-to’s
5.8 HOW TO CONFIGURE ROUTING PATH TO AUTO REDIAL
The Auto Redial function saves the user the trouble of repeated dialing when the called
number is busy or unreachable for some reason.
Suppose, the administrator assigns the Auto Redial function key sequence 003. To use Auto
Redial, the user must:
• Dial into the Router
When outside the system
To configure a routing rule for the Auto Redial service invoked by dialing 003 followed by
the target phone number:
• Dial the DISA number and get the dial tone
• Enter the Auto Redial key sequence 003 followed by 1 (for line busy) or 0
(for any other cause making the number unreachable)
• Enter the target telephone number
• Wait until the call is answered
1. Click
2. Click
3. In the text box Route name of the add-new-route dialog replace the default name Route
#... entering a descriptive name to your liking, for example Auto Redial.
4. Select the option Service in the combo box Command
5. Select the option Auto Dial from the drop-down list of service names of the combo box
Argument.
6. The source number being of no importance, leave the edit boxes on the line Source
unchanged. Enter destination number 003 for the Auto Redial function in the edit box
Match and edit box Pattern followed by a regular expression for whatever number that
may be dialed after 003, i.e. (.*).
to access the routing table page.
to display the rule configuration form
7. Click
8. Click
groups, the members of which will be eligible to use Auto Redial.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 62 of 83
to add the rule to the routing table.
in the column and select in the pop-up menu a group or
Page 63

Configuration How-to’s
5.9 HOW TO USE MATCH AND PATTERN FIELDS IN THE ROUTING
TABLE
Regular expressions are character strings used to build search patterns. Regular expressions
also provide a powerful string handling tool. Regular expressions may include both
alphanumeric characters, i.e. letters and digits normally used in writing and the so-called
metacharacters. Metacharacters are symbols that have special meaning and use.
In this application you use regular expressions to define match (
(
The
destination number search.
The most instrumental and frequent metacharacters that you may need to use in match
patterns include:
) strings.
field is for regular expressions that define a match pattern for the source or
^ denotes the beginning of the match string. For example, ^56 matches a string
starting with “56”.
$ stands for the end of a string. For example, 88$ corresponds to any set of
characters ending with “88”.
) and pattern
. signifies any character
\d means any decimal digit.
When the number of symbols in the sought string is unknown, use special metacharacters
called quantifiers. The most commonly used quantifiers are as follows:
– * denotes any number of something, for example, X* means any number of X’s;
– ? stands for zero or 1 entry of a character, for example, X? means none or one X;
– + is used to express one or more entries of a character, for example you type X+
to signify 1 or more entries of X, and finally
– X{n} denotes exactly n number of Xs.
The field
The need to transform the source or destination number often arises before passing the
number to a particular service. If no changes are required, use the following regular
expression
When number transformation is necessary without passing it to any particular service
afterwards, select one of the following commands from the list:
• Continue – the modified number is passed to the next rule in the Routing table;
• Restart – the modified number is passed to the first rule of the Routing table.
Brackets are used to mark parts of the number extracted during call handling, for example
^(56.*). In the field
represents a positive integer (greater than or equal to one) that identifies the number of the
brackets occurrence (e.g. $1 denotes the first set of brackets, $2 means the second set of
brackets etc).
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 63 of 83
is designed for entering source and destination number translation rules.
.*.
the marked parts are referred to as $n. In the expression $n n
Page 64

Configuration How-to’s
For example, to give local users whose extension numbers start with 56 the capability to
make outgoing calls through dialing technical prefix 0, configure source and destination
number transformation as shown in the table below:
Match Pattern Result
Source ^56.* ^(56.*) $1
Destination ^0.* ^0(.*) $1
According to this rule prefix 0 will be cut off from the destination number because the
internal prefix used in the system is of no relevance to the gateway sending calls outside the
system.
The syntax of regular expressions appearing in the field
regular expressions entered in the field
.
is identical to that of
The table below contains a list of regular expression constructs applicable in configuring the
system.
Table 5 Summary of regular expression constructs
Construct Matches
Characters
x The character x
\0n The character with octal value 0n (0 <= n <= 7)
\0nn The character with octal value 0nn (0 <= n <= 7)
\0mnn The character with octal value 0mnn (0 <= m <= 3,
0 <= n <= 7)
\xhh The character with hexadecimal value 0xhh
\uhhhh The character with hexadecimal value 0xhhhh
\t
\n
The tab character ('\u0009')
The newline (line feed) character ('\u000A')
Character classes
[abc]
[^abc]
[a-zA-Z]
[a-d[m-p]]
[a-z&&[def]]
[a-z&&[^bc]]
[a-z&&[^m-p]]
a, b, or c (simple class)
Any character except a, b, or c (negation)
a through z or A through Z, inclusive (range)
a through d, or m through p: [a-dm-p] (union)
d, e, or f (intersection)
a through z, except for b and c: [ad-z] (subtraction)
a through z, and not m through p: [a-lq-z](subtraction)
Predefined character classes
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 64 of 83
Page 65

.
Any character (may or may not match line terminators)
Configuration How-to’s
\d
\D
\s
\S
\w
\W
^
$
\b
\B
\A
\G
\Z
\z
A digit: [0-9]
A non-digit: [^0-9]
A whitespace character: [ \t\n\x0B\f\r]
A non-whitespace character: [^\s]
A word character: [a-zA-Z_0-9]
A non-word character: [^\w]
Boundary matchers
The beginning of a line
The end of a line
A word boundary
A non-word boundary
The beginning of the input
The end of the previous match
The end of the input but for the final terminator, if any
The end of the input
Greedy quantifiers
X? X, once or not at all
X* X, zero or more times
X+ X, one or more times
X{n} X, exactly n times
X{n,} X, at least n times
X{n,m} X, at least n but not more than m times
Reluctant quantifiers
X?? X, once or not at all
X*? X, zero or more times
X+? X, one or more times
X{n}? X, exactly n times
X{n,}? X, at least n times
X{n,m}? X, at least n but not more than m times
Possessive quantifiers
X?+ X, once or not at all
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 65 of 83
Page 66

Configuration How-to’s
X*+
X, zero or more times
X++ X, one or more times
X{n}+ X, exactly n times
X{n,}+ X, at least n times
X{n,m}+ X, at least n but not more than m times
Logical operators
XY X followed by Y
X|Y Either X or Y
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 66 of 83
Page 67

Configuration How-to’s
5.10 HOW TO CREATE A NETWORKING ALIAS FOR SUBN ET
192.168.224.0
On a PC with the Windows OS click Start → Control Panel and double click the Network
Connections option in the displayed Control Panel window.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 67 of 83
Page 68

User’s Interface
Double-click Local Area Connection and press the Properties button on the tab sheet
General.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 68 of 83
Page 69

User’s Interface
In the appearing LocalArea Connection Properties window select the item Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP) and click the Properties button.
In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties view, click the button Advanced...
Click the Add button in the Advanced TCP/IP Settings window
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 69 of 83
Page 70

User’s Interface
Type 192.168.224.n in the appearing TCP/IP Address dialog. n can be any number in the 0-
255 range. Click the Add button to finalize the procedure.
The newly configured address should appear in the Advanced TCP/IP Settings window
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 70 of 83
Page 71

User’s Interface
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 71 of 83
Page 72

6 USER INTERFACE
To access the logon page of the Web interface the user must start a Web browser and point it
to http://ROUTER_IP
the IP address field of the WAN Settings box.
The login name and password that allow access to the user’s personal interface are usually
the user’s telephone number configured in the DVX-7090 Router.
6.1 CONFIGURING USER’S DATA
A Router user can access the page with the user’s personal settings only. Of all the personal
settings presented on the page the user can edit E-mail, Web access password and call
forwarding settings.
, where ROUTER_IP is the IP specified by the system administrator in
User’s Interface
Fig. 46 User personal settings
To be able to receive email messages with sound files attached, type your email address in
the E-mail edit field.
Specify a password for access to this page in the Web access password field.
To configure conditional and unconditional call forwarding:
1. Click to add a line to the table Forward options
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 72 of 83
Page 73

User’s Interface
2. Select a condition (Busy, No answer, Unreachable, Unconditional) that will
cause call forward using the combo box in the column Fwd Condition
3. If the forward rule being configured applies to a particular calling number only,
type the necessary calling number in the edit box Source. Leave the field intact
if the calling number does not matter.
4. When necessary, you can limit call forward to a particular time period and day
or days of week.
To define a call forwarding period, select the checkbox Time (in the column
Activity Schedule) and specify the period start and end time in the edit boxes From
and To respectively. To specify on what days call forwarding will take place, select
the checkbox Days and select call forward days on the drop-down menu invoked by
a click on the appearing down-arrow button.
5. Type in the forward number in the text box Fwd Number of the form and click
to validate the changes you have made to the record.
You may add as many lines with call forward settings as you deem appropriate.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 73 of 83
Page 74

6.2 VIEWING STATISTICS
To access the Statistics page, click . The page presents call statistics for the user
endpoint.
User’s Interface
Fig. 47 User’s endpoint call statistics
The delete button
Click
Click
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 74 of 83
allows removal of the selected record.
to repaint the statistics view.
to remove all the records from the table.
Page 75

6.3 MANAGING VOICE PROMPTS
To access the Prompts page, click the tab :
Fig. 48 The Prompts page of the user’s interface
User’s Interface
You can play or save the prompts on your computer using the button
You can upload new prompts from your computer with the help of the
button, to invoke the Upload Prompt dialog box that appears above the prompts table:
Fig. 49 “Upload prompt” dialog
.
button. Click this
Click
.
Lines with customized prompts are easily identified by the ‘roll-back’ button
50)
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 75 of 83
to invoke the file dialog, select the .wav file you need and click
(see Fig.
Page 76

User’s Interface
Fig. 50 Table of prompts with customized line-busy prompt
Prompt files added by users do not overwrite the default sound files, and users can always
revert to the default prompt using the “roll-back” button
in the column
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 76 of 83
Page 77

7 USAGE HOW-TO’S
7.1 HOW TO USE CALL TRANSFER
The DVX-7090 Router provides for 2 types of transfer:
• Attended (consultative) transfer when the transferor first contacts the transfer target
before leaving the call, and
• Blind (unsupervised) transfer when the transferor just transfers the call to the called
extension and hangs up.
To use the transfer service the user should belong to a group authorized to use the Transfer
service (See the Configuring groups
A common transfer scenario unfolds as follows:
1. User A calls user B
2. User B answers the call
3. User B wishes to transfer the call to user C (the sequence of events when user A
does the transfer to user C is the same).
section for details).
Usage how-to’s
4. User B presses the Flash button to place user A on hold. (Note: If there is no Flash
button hitting the Flash key can be emulated by sequentially pressing * and # within
one second time.)
5. User B dials user C (Note: The majority of phones require pressing # to comp lete
dialing).
Further steps vary with the type of transfer (attended or blind.)
In case of a blind transfer:
6. User B hangs up.
7. User A becomes the calling party for user C and hears the ringback tone.
8. When/if user C answers the call, a call session between A and C is established.
During an attended transfer:
6. User B establishes a connection with user C
7. User B is able to switch between user A and C by pressing the Flash button if any (if
there is no Flash button hitting the Flash key can be emulated by sequentially
pressing * and # within one second time.) User A and C do not hear each other.
Note: If user B’s group has Conference permissions users A and C will b e able to hear
each other.
8. When user B hangs up, a call session between A and C becomes established.
7.2 HOW TO MAKE CONFERENCE CALLS
The DVX-7090 Router supports 3 party conference calls only.
As setting up a conference involves the call transfer service, the user who is the conference
initiator must belong to a group with both Transfer and Conference permissions.
The 3-party conference scenario unfolds as follows:
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 77 of 83
Page 78

Usage how-to’s
1. User A calls user B
2. User B answers the call
3. User B wishes to transfer the call to user C (the procedure when user A does the
transfer to user C is the same).
4. User B presses the Flash button to place user A on hold. (Note: If there is no Flash
button hitting the Flash key can be emulated by sequentially pressing * and # within
one second time.)
5. User B dials user C.
6. User C answers the call
7. User B presses the Flash key. From this moment on all call parties can hear and talk
to each other. (Note: If there is no Flash button hitting the Flash key can be
emulated by sequentially pressing * and # within one second time.)
8. Any user can leave the conference at any time. When one of the conference
participants leaves the conference turns to a regular phone call.
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 78 of 83
Page 79

APPENDIX A ACRONYMS
Table 6 List of acronyms used in this manual
Acronym Expansion
Appendix A
CDR
CHAP
DB
DHCP
DISA
DNS server
DTMF
LAN
MIME
NAT
PBX
RAS
RBT
RTP/RTCP
SIP
SMTP
SSL
Call Details Record
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
Database
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Direct Inward System Access
Domain Name Server
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency
Local Area Network
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension
Network Address Translation
Private Branch Exchange
Remote Access Service
Ring-Back Tone
Real-Time Protocol/Real-Time Transmission Protocol
Session Initiation Protocol
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Secure Socket Layer
SW
TTL
VoIP
WAN
Software
Time-To-Live period
Voice Over IP
Wide Area Network
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 79 of 83
Page 80

List of illustrations
Illustrations
Fig. 1 DVX-7090 deployment in a geographically distributed organization.........................................................6
Fig. 2 Block diagram of D-Link VoIP Router software modules..........................................................................7
Fig. 3 DVX-7090 front panel ................................................................................................................................9
Fig. 4 DVX-7090 logon page..............................................................................................................................10
Fig. 5 Networking configuration page.................................................................................................................11
Fig. 6 WAN settings dialog box..........................................................................................................................12
Fig. 7 SMTP server settings box .........................................................................................................................13
Fig. 8 Date and time setting box..........................................................................................................................13
Fig. 9 Change password dialog ...........................................................................................................................14
Fig. 10 SIP registrar and H.323 gatekeeper configuration boxes........................................................................14
Fig. 11 Table of configured user extensions........................................................................................................15
Fig. 12 Search filter of Users page ......................................................................................................................16
Fig. 13 User configuration form..........................................................................................................................17
Fig. 14 User basic settings...................................................................................................................................18
Fig. 15 Endpoint registration data .......................................................................................................................18
Fig. 16 NAT- , fax-related and protocol-specific settings ...................................................................................19
Fig. 17 Call forward configuration form .............................................................................................................20
Fig. 18 Codeсs options........................................................................................................................................22
Fig. 19 Users table on first start...........................................................................................................................23
Fig. 20 Table of gateways ...................................................................................................................................23
Fig. 21 Gateway properties form.........................................................................................................................24
Fig. 22 Basic gateway attributes..........................................................................................................................25
Fig. 23 Gateway registration form.......................................................................................................................26
Fig. 24 DVX-7090 Router registrations dialog ...................................................................................................26
Fig. 25 Gateway NAT, fax and signaling options ...............................................................................................27
Fig. 26 Table of services .....................................................................................................................................28
Fig. 27 New service dialog..................................................................................................................................29
Fig. 28 Routing table...........................................................................................................................................31
Fig. 29 Why position of routing rule in the table matters....................................................................................33
Fig. 30 Table of existing groups..........................................................................................................................34
Fig. 31 Adding a group........................................................................................................................................35
Fig. 32 Table of available prompts......................................................................................................................36
Fig. 33 Prompt upload dialog..............................................................................................................................37
Fig. 34 CDRs look up page .................................................................................................................................38
Fig. 35 User CDRs ..............................................................................................................................................40
Fig. 36 CDR file data imported to Excel.............................................................................................................42
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 80 of 83
Page 81

List of illustrations
Fig. 37 Logs page................................................................................................................................................43
Fig. 38 A list of control unit protocol logs ..........................................................................................................44
Fig. 39 Software management page ....................................................................................................................45
Fig. 40 Version upload dialog box ......................................................................................................................46
Fig. 41 System restart warning............................................................................................................................47
Fig. 42 OS image upload dialog..........................................................................................................................47
Fig. 43 Call routing rule for extension numbers..................................................................................................54
Fig. 44 Routing rule for outbound calls...............................................................................................................55
Fig. 45 Routing rule for group and directional pick up .......................................................................................56
Fig. 46 User personal settings .............................................................................................................................72
Fig. 47 User’s endpoint call statistics..................................................................................................................74
Fig. 48 The Prompts page of the user’s interface................................................................................................75
Fig. 49 “Upload prompt” dialog..........................................................................................................................75
Fig. 50 Table of prompts with customized line-busy prompt..............................................................................76
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 81 of 83
Page 82

List of tables
Tables
Table 1: Conventions.............................................................................................................................................5
Table 2 Frame sizes by codecs............................................................................................................................22
Table 3 Commands and invoked algorithms (services).......................................................................................30
Table 4 Commands executed during call routing................................................................................................32
Table 5 Summary of regular expression constructs.............................................................................................64
Table 6 List of acronyms used in this manual.....................................................................................................79
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 82 of 83
Page 83

Document history
List of tables
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 83 of 83
 Loading...
Loading...