Page 1

D-Link
DVG-G1402S
Wireless + 2Voice + 4SW VoIP Router
Manual
Building Networks for People
Version B.1
Page 2

Contents
Package Contents...........................................................................................................3
Introduction.....................................................................................................................4
Rear Panel Connections.................................................................................................5
Front Panel LEDs............................................................................................................6
Features...........................................................................................................................7
Installation.......................................................................................................................8
Using the Configuration Wizard....................................................................................9
Home > Wireless .........................................................................................................9
Home > Wireless .......................................................................................................10
Home > Wireless > Wireless LAN Authorization.......................................................11
Open Auth − Shared Key...........................................................................................12
WPA.........................................................................................................................13
WPA-PSK ................................................................................................................14
Home > WAN.............................................................................................................15
Home > WAN > Static IP Address.............................................................................17
Home > WAN > PPPoE.............................................................................................19
Home > LAN..............................................................................................................21
Home > VoIP .............................................................................................................22
Home > VoIP > Provisioning......................................................................................25
Home > VoIP > STUN Configuration.........................................................................26
Home > VoIP > User Agent.......................................................................................27
Home > VoIP > Peer to Peer..................................................................................... 28
Home > VoIP > Telephony ........................................................................................29
Page 3

Home > VoIP > Speed Dial........................................................................................30
Home > VoIP > Misc..................................................................................................31
Home > VoIP > Misc. > Ring Cadence......................................................................32
Home > VoIP > Misc. > Ring Default Rule ................................................................33
Home > VoIP > Misc. > Ring Rule.............................................................................34
Home > VoIP > Manage Features > Reject Incoming Call........................................35
Home > VoIP > Manage Features > Block Outgoing Call.........................................36
Home > DHCP...........................................................................................................37
Home > Proxy DNS................................................................................................... 39
Advanced > Virtual Server.........................................................................................40
Advanced > Filters.....................................................................................................42
Advanced > Filters > IP Filters...................................................................................43
Advanced > Filters > MAC Filters............................................................................45
Advanced > Firewall .................................................................................................. 46
Advanced > Routing > RIP Configuration..................................................................48
Advanced > Routing > Static Route ..........................................................................49
Advanced > NAT > NAT Configuration......................................................................50
Advanced > NAT > Dynamic NAT.............................................................................51
Advanced > NAT > Static NAT..................................................................................52
Tools > Admin............................................................................................................53
Tools > System..........................................................................................................54
Tools > Firmware.......................................................................................................55
Tools > SNMP............................................................................................................56
Tools > Time..............................................................................................................57
Status > Device Info...................................................................................................58
Status > Stats > Network...........................................................................................59
Status > Stats > Phone Call.......................................................................................60
Status > Diagnostics..................................................................................................61
Help............................................................................................................................62
2
Page 4

Package Contents
• D-Link DVG-G1402S Router
• Power Adapter - AC 12V, 1.2A
• Manual and Warranty on CD
• Quick Installation Guide
• Ethernet Cable (All the Ethernet ports on DVG-G1402S are
Auto-MDIX)
Note: Using a power supply with a different voltage rating than the one included with the
DVG-G1402S will cause damage and void the warranty for this product.
If any of the above items are missing, please contact your reseller.
• System Requirements for Configuration
• Ethernet-Based Cable or DSL Modem
• Computers with Windows, Macintosh, or Linux-based
operating systems with an installed Ethernet adapter
• Computers with Windows, Macintosh, or Linux-based
operating systems with an installed Ethernet adapter
• Internet Explorer Version 6.0 or Netscape Navigator Version
6.0 and Above
3
Page 5

Introduction
The D-Link DVG-G1402S High-Speed VoIP Router Links traditional telephony netwo rks
to IP networks with conventional telephony devices such as analog phones or fax
machines. It can reduce long distance phone charges and deliver toll-quality voice
communication over the IP network. This gateway provides two loop start Foreign
Exchange Subscriber (FXS) ports and four LAN ports. One Ethernet port for a
DSL/Cable Modem or other WAN devices, and the other for connection to create a
home or small office LAN networks. The built-in DHCP server/client and Network
Address Translation (NAT) function automatically assign IP address for LAN use rs,
allowing multiple users to share a single Internet connection. It can be
configured/monitored via the Console, Web browser, Telnet and HTTPS provisioning is
also supported.
4
Page 6
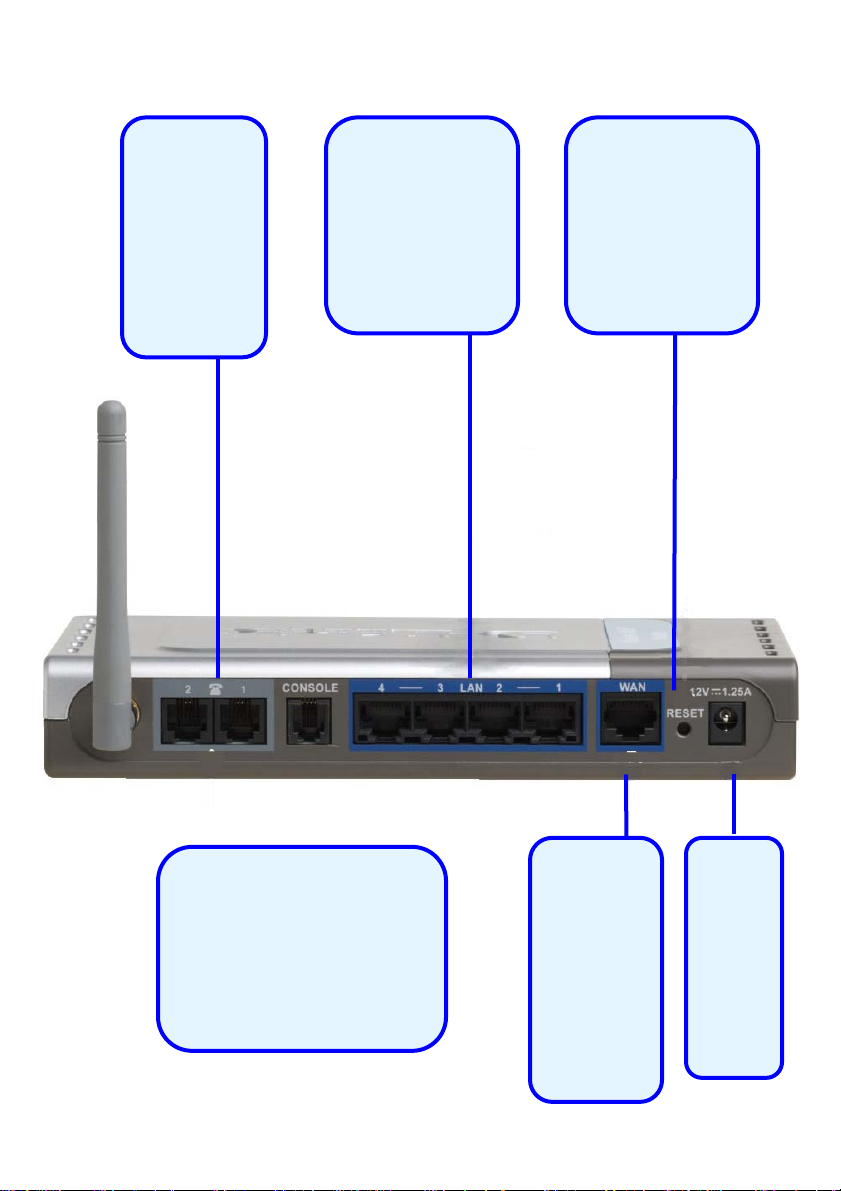
Rear Panel Connections
Phone
Connections
Connect to
your phones
using
standard
phone
cabling.
Auto MDI/MDIX
LAN Ports
Connect the
Ethernet cable
from computers
on your LAN to
these ports.
Factory Reset
Button
Pressing this
button will
restore the router
to its factory
default settings.
All Ethernet Ports (WAN
and LAN) are auto
MDI/MDIX, meaning you
can use either a
straight-through or a
crossover Ethernet
WAN Port
Connect
the
Ethernet
cable from
your
ADSL
modem to
Power
Adapter
Connect
your 12V
1.25A
power
adapter
here.
this port.
5
Page 7
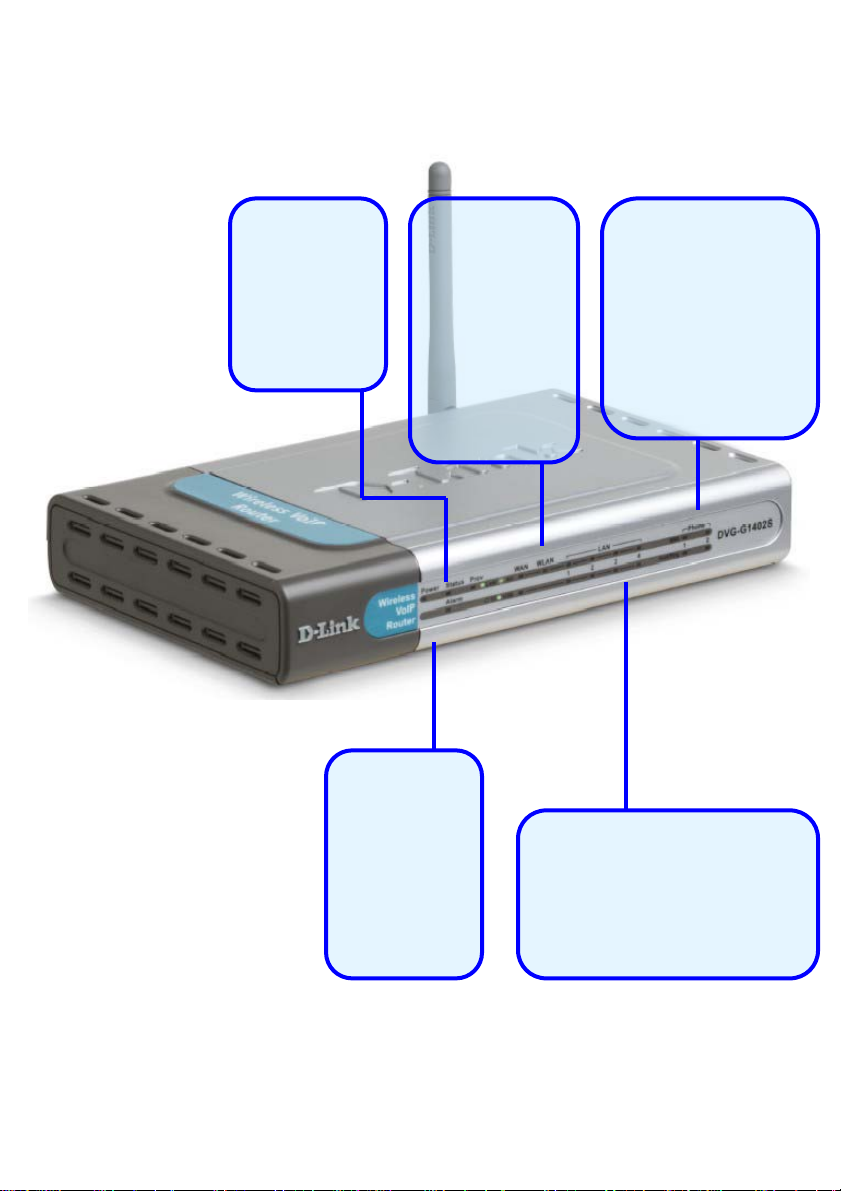
Front Panel LEDs
Status LED
A blinking LED
indicates the
DVG-G1402S
is functioning
properly.
Power LED
WAN LED
An active LED
indicates a link
has been
established. A
blinking LED
indicates
activity on the
WAN port.
Phone LEDs
The Hook LED will
light when a
telephone is off the
hook. A blinking LED
indicates an
incoming call is
detected.
A solid light
indicates a
valid
connection
to the power
supply.
6
An active LED indicates a
link has been established.
A blinking LED indicates
activity on the LAN port.
LAN LEDs
Page 8

Features
• 1 NWay 10/100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet port for
WAN-connection
• 4 NWay 10/100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet port for
LAN-connection
• 2 Foreign Exchange Subscriber (FXS) POTS ports (RJ-11
Jacks)
• Voice Activity Detection (VAD) /Comfort Noise Generation
(CNG)
• Silence suppression to reduce bandwidth consumption.
• Adaptive jitter buffer for a smooth voice reception
• Lost packet recovery ability for improved voice quality
• Support QoS (Quality of Service) for voice quality guarantee.
• Build-in PPPoE function to support dial-up connection for
broadband technology.
• IP address assignment using DHCP or static configuration
• RIP1/RIP2 and static routing support
• Support IP sharing to allow multiple users to access the
Internet via a single IP address
• Support Caller ID function
• Configuration download using HTTPS and SSL/TLS client
certificate encryption and authentication
• Support VPN Pass-Through
• MAC and Packet filter support
• Remote configuration and management over the Internet
using web browsers
• Firmware backup support
• Support configuration backup and restore
7
Page 9

Installation
For a typical setup at home, please do the following:
1. You will need broadband Internet access (a Cable or DSL-subscriber line
into your home or office)
2. Consult with your Cable or DSL provider for proper installation of the
modem
3. Connect the Cable or DSL modem to the DVG-G1402S VoIP Router (see
the printed Quick Installation Guide included with your router.)
4. Install the D-Link DFE-530TX+ adapter into a desktop computer. The four
Ethernet LAN ports of the DVG-G1402S are Auto MDI/MDIX and will work
with both Straight-Through and Cross-over cables.
(See the printed Quick Installation Guide included with the DFE-530TX+.)
8
Page 10
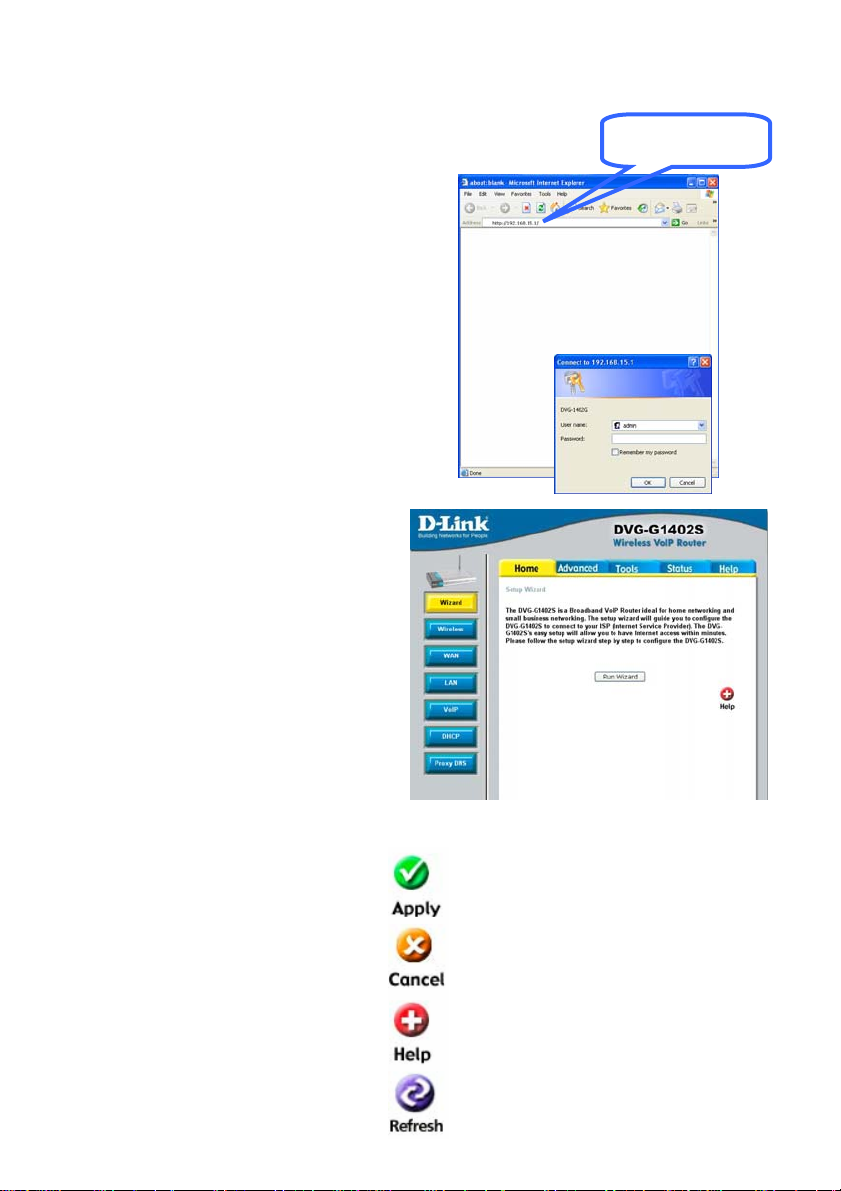
Using the Configuration Wizard
Whenever you want to configure
your network or the DVG-G1402S,
you can access the Configuration
Menu by opening the web-browser
and typing in the IP Address of the
DVG-G1402S. The DVG-G1402S
default IP Address is shown to the
right:
• Open the web browser
• Type in the IP Address of the
The Home > Wizard screen will appear.
Please refer to the Quick Installation
Guide for more information regarding the
Setup Wizard.
These buttons appear on most of the
configuration screens in this section.
Please click on the appropriate button at
the bottom of each screen after you have
made a configuration change.
Note: if you have changed the default IP
Address assigned to the DVG-G1402S,
make sure to enter the correct IP
Address.
Router (http://192.168.15.1)
• Type admin in the User Name
field
• Type admin in the Password
field
• Click OK
Clicking this button will save configured
settings to the router.
Clicking Cancel will clear changes made to
the current page.
Clicking Help will provide the user with
helpful information about the current
window.
192.168.15.1
Click refresh will refresh the statistics of the
9
Page 11
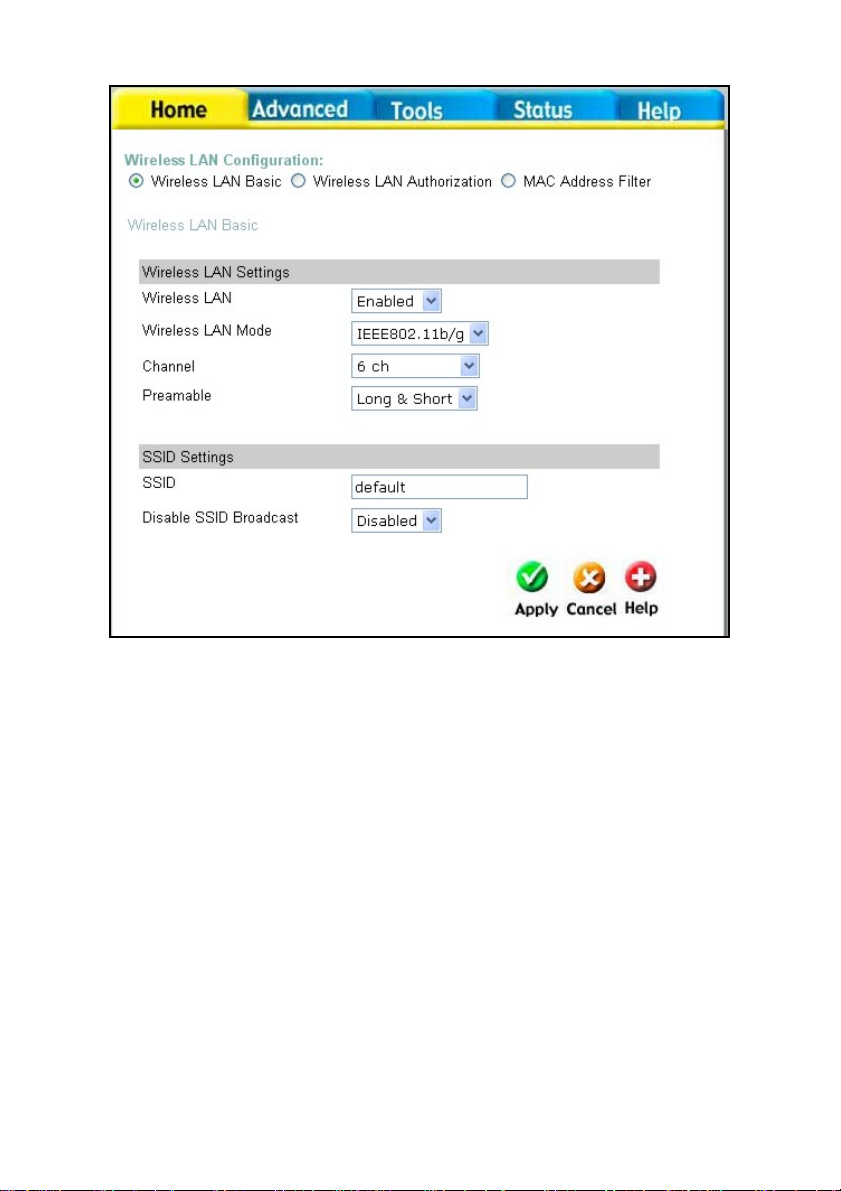
Home > Wireless
Wireless LAN Usage This drop-down menu allows you to enable or disable the
Wireless LAN feature on the DVG-G1402S.
Wireless LAN Mode
Channel
Rate Config You can select between Long, Short, and Long and Short.
SSID Service Set Identifier (SSID) is the name designated for a specific
Hidden SSID Enabling this feature will prevent the DVG-G1402S from
You can select between three IEEE WLAN standards − 802.11b/g,
802.11g, and 802.11b − depending upon which type of Wireless LAN
devices you have.
What channels are available for use by the access point depends on
the local regulatory environment. Remember that all devices
communicating with the device must use the same channel (and use
the same SSID). Use the drop down menu to select the channel used
for your 802.11b wireless LAN.
wireless local area network (WLAN). The SSID’s factory default setting
is default. The SSID can be easily changed to connect to an existing
wireless network or to establish a new wireless network.
broadcasting it’s SSID. Remote stations will have to have the
router’s SSID manually entered to connect.
10
Page 12
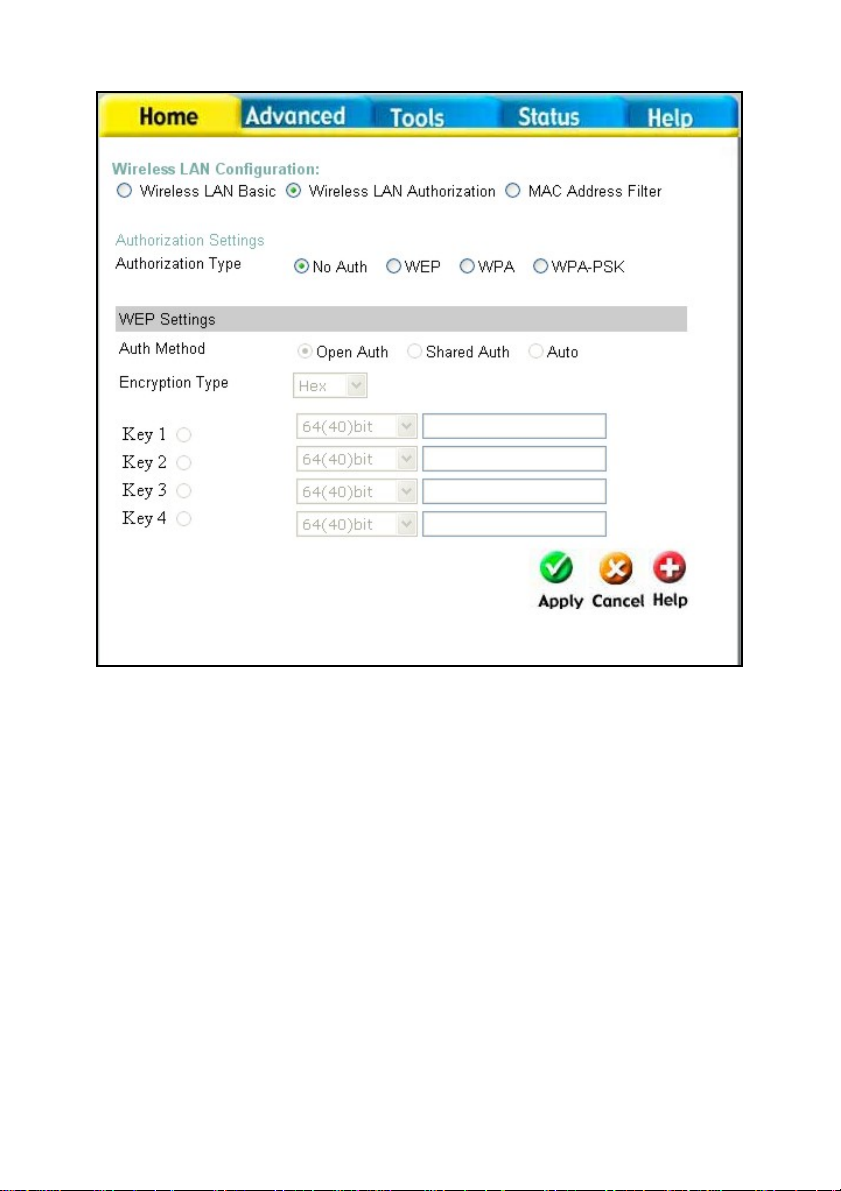
Home > Wireless > Wireless LAN Authorization
Authentication This router employs three basic types of Authentication for
access to the router’s wireless network, WEP, WPA, and
WPA-PSK, which can be selected by clicking the corresponding
radio button. No Auth will disable Wireless LAN authentication.
Each selection will alter the window to accommodate the entry
of the necessary keys. See the explanation below for more
information.
11
Page 13
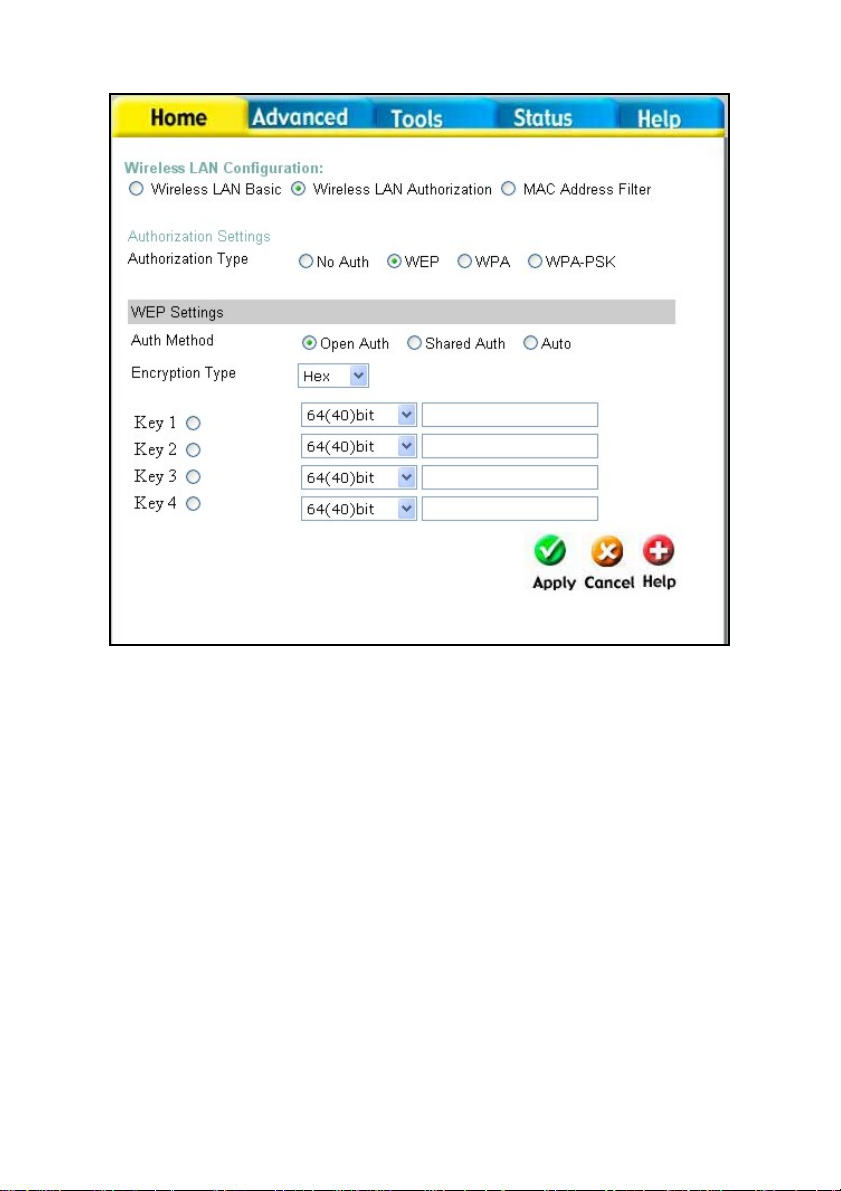
Open Auth − Shared Key
The Open Auth − Shared Key choice for Authentication will produce the screen shown above for
the user’s configuration. The Open Auth choice is for general use and utilizes basic WEP
encryption. The Shared Key choice is used bet ween cooperating devices that share a common
encryption key. WEP (Wireless Encryption Protocol or Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption can
be enabled for security and privacy. WEP encrypts the data portion of each frame transmitted
from the wireless adapter using one of the predefined keys. Decr yption of the data contained in
each packet can only be done if the both the receiver and transmitter have the correct shared key.
WEP – Click the Enabled radio button to employ WEP encryption on the router.
Auth Method – Select Open Auth, Shared Auth, or Auto.
Encryption Type – Use the pull-down menu to select the type of Key t o be used for encryption.
The user may choose HEX (Hexadecimal) or ASCII (American Standard Code for Information
Interchange). Both will require the user to enter a key in the following field.
Key field drop-down menu - Use the drop down menu to select the type of WEP encryption.
Select 64 Bit to enable 64 bit Hexadecimal encryption, 128 Bit to enable 128 bit Hexadecimal
encryption, 152 Bit to enable 152 bit Hexadecimal encryption.
Key – The user may enter up to four keys to be used for encryption. Only the key selected using
the corresponding radio button will be used for encryption.
12
Page 14
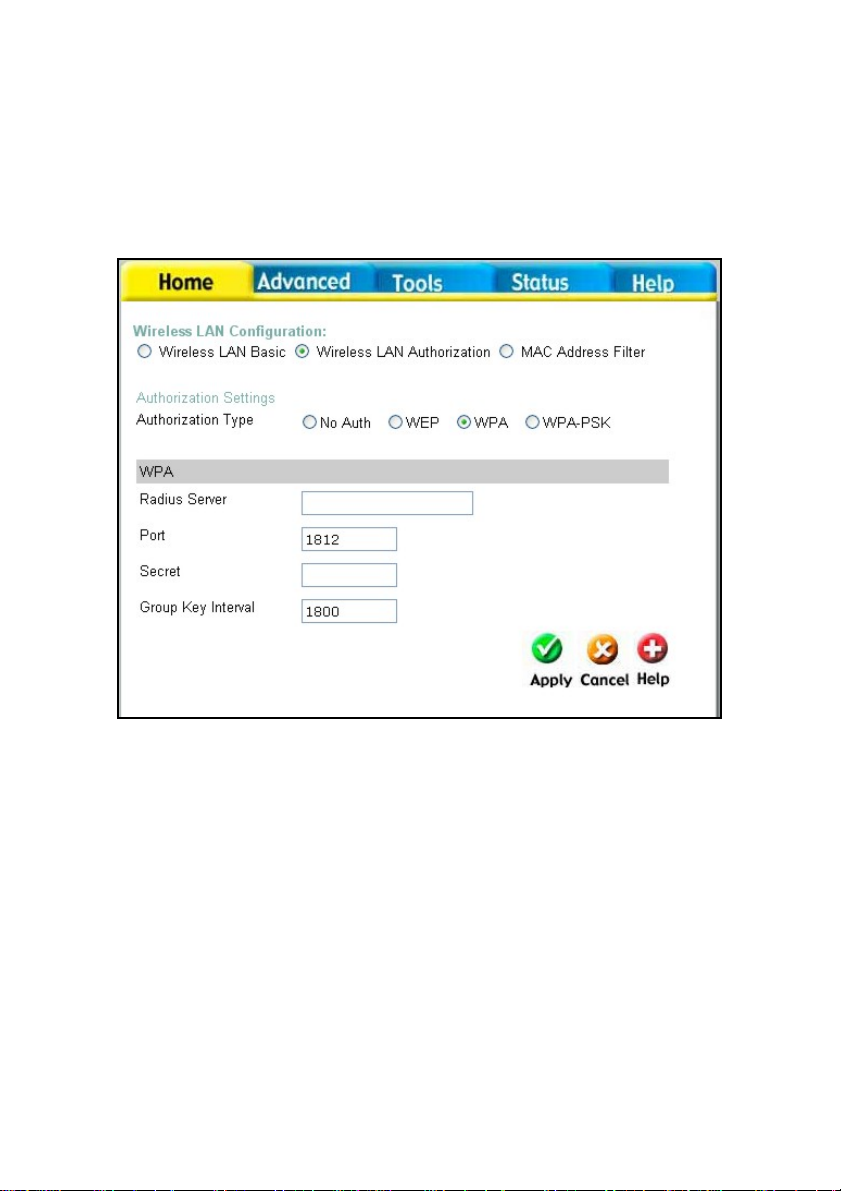
Click Apply to set the information in the router’s memory. You will be prompted to restart the
router to make the settings current.
WPA
WPA or Wireless Protection Access is a new an improved standard of wireless security. WPA
offers encryption keys of up to 256-bits that automatically change frequently. On this router, the
WPA utilizes the RADIUS protocol, which utilizes a server to authorize the user by matching a
Shared Secret password listed in its RADIUS database. There are three choices for the user to
choose from. WPA, WPA2 which uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), and WPA-Auto
which will authorize clients using either WPA or WPA2. See the explanation below.
RADIUS Server IP – Enter the IP address of the remote RADIUS server you will use to be
authenticated through.
Port – Enter the virtual port number to which to connect through the RADIUS server. Common
port numbers for RADIUS are 1812 and 1813.
Secret – Enter the password which will be used to authenticate you on the wireless network. This
password must be on the RADIUS server in order for you to be authorized.
Group Key Interval – Enter the time period, in seconds, that group keys will be exchanged.
13
Page 15
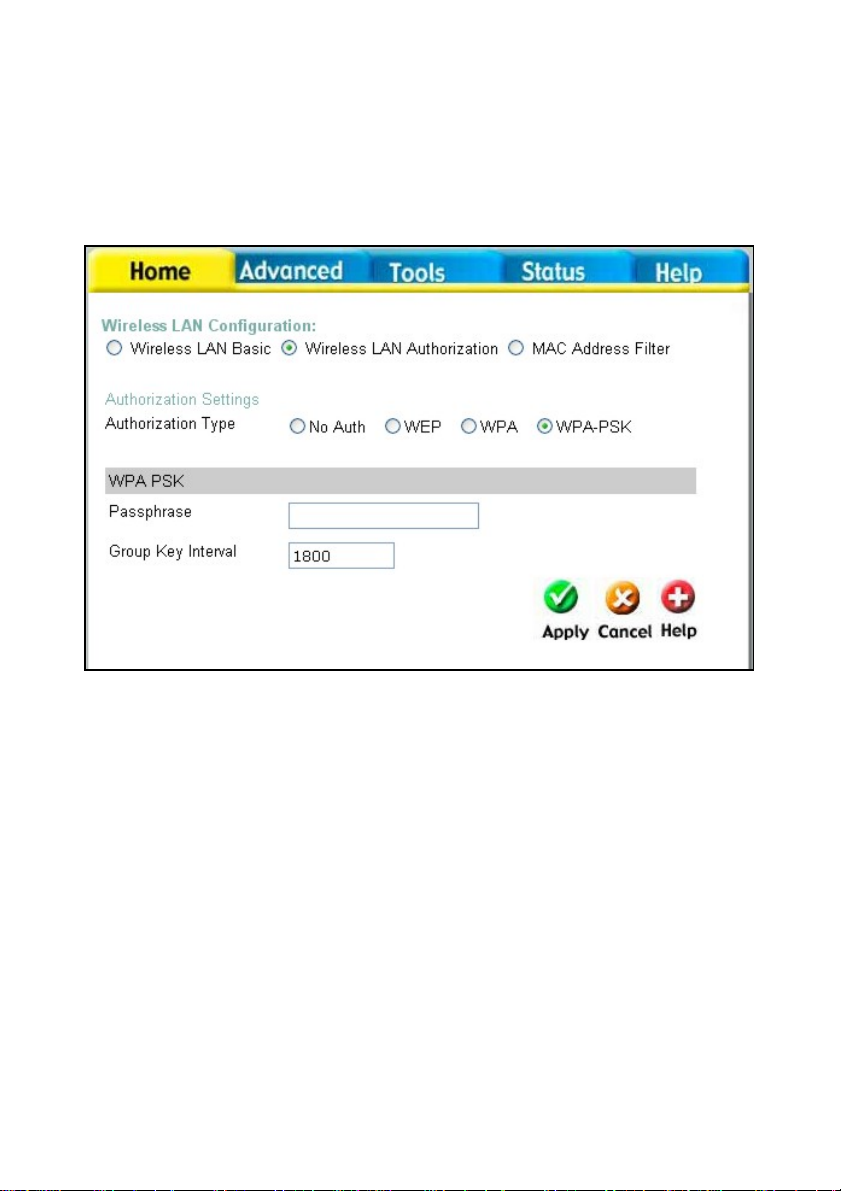
WPA-PSK
WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key) uses the same encryption as the WPA but is implemented
differently. All devices on the wireless network share the same key (Passphrase) to
activate the WPA security. There are three choices for the user to choose from.
WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK which uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), and
WPA-PSK-Auto which will authorize clients using either WPA or WPA2. To utilize, select
one of the previous choices, enter the Passphrase, confirm it in the second field and
click Apply.
14
Page 16

Home > WAN
Dynamic
Host Name
MAC Address
Clone MAC Address The default MAC address is set to the WAN’s physical interface
Choose Dynamic IP Address to obtain IP Address information
automatically from your ISP. This option should be selected if
your ISP has not supplied you with an IP address. This option is
commonly used for Cable modem services.
The Host Name is optional but may be required by some ISPs.
The default host name is the device name of the Router and
may be changed.
The default MAC Address is set to the WAN ’s physical interfac e
MAC address on the Broadband Router. It is not recommended
that you change the default MAC address unless required by
your ISP.
MAC address on the Broadband Router. You can use the “Clone
15
Page 17

MAC Address” button to copy the MAC address of the Ethernet
Card installed by your ISP and replace the WAN MAC address
with the MAC address of the router. It is not recommended that
you change the default MAC address unless required by your
ISP.
Enter a DNS Address if you wish not to use the address
provided by your ISP.
The upstream bandwidth can be set for the data traffic. The
Upstream Bandwidth
bandwidth can be maximized for voice packets and limited for
data that requires less throughput.
16
Page 18

Home > WAN > Static IP Address
Static IP Address Choose Static IP Address if all WAN IP information is provided
to you by your ISP. You will need to enter in the IP address,
subnet mask, gateway address, and DNS address(es) provided
to you by your ISP. Each IP address entered in the fields must
be in the appropriate IP form, which are four octets separated
by a dot (x.x.x.x). The Router will not accept the IP address if it
is not in this format.
IP Address
Subnet Mask Input your Subnet ma sk. (All devices in the network must have
IP Gateway
Input the public IP address of the ISP to which you are
Address
Primary DNS
Address
Secondary DNS
This is an optional DNS Address entry to be used if the primary
Address
Input the public IP Address provided by your ISP.
the same subnet mask.)
connecting.
Input the primary DNS (Domain Name Server) IP address
provided by your ISP
17
Page 19

DNS Fails.
Upstream Bandwidth The upstream bandwidth can be set for the type of packets that
the will be sent. The bandwidth can be maximized for voice
packets and limited for data that requires less throughput.
18
Page 20
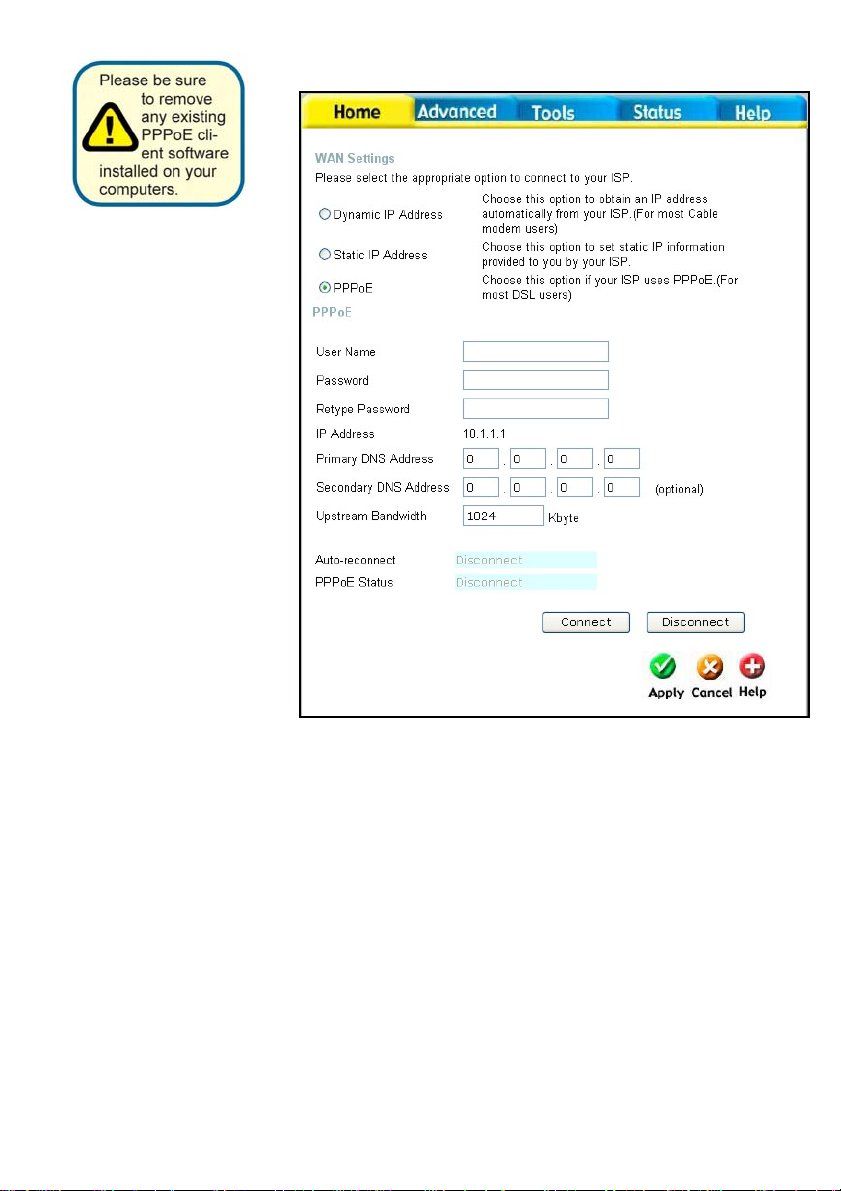
Choose PPPoE (Point to
Point Protocol over Ethernet)
if your ISP uses a PPPoE
connection. Your ISP will
provide you with a username
and password. This option is
typically used for DSL
services.
Home > WAN > PPPoE
PPPoE Choose this option if your ISP uses PPPoE. (Most DSL users
will select this option.)
Password
Enter The PPPoE user name provided to you by your ISP.
Retype Password Retype the password entered in the previous field.
Service Name Enter the Service Name provided by your ISP (optional).
IP Address This option is only available for Static PPPoE. Enter the s tatic
IP Address for the PPPoE connection.
MAC Address The default MAC Address is set to the WAN’s physical interface
MAC address on the Broadband Router. It is not recommended
that you change the default MAC address unless required by
your ISP.
19
Page 21

Primary DNS
Input the primary DNS (Domain Name Server) IP address
Address
provided by your ISP
Secondary DNS
This is an optional DNS Address entry to be used if the primary
Address
The upstream bandwidth can be set to suit the type of packets
Upstream
Bandwidth
DNS fails.
that the connection will be sending. The bandwidth can be
maximized for voice packets and limited for data that requires
less throughput.
20
Page 22

Home > LAN
LAN is short for Local Area Network. This is considered your internal network. These
are the IP settings of the LAN interface for the DVG-G1402S and may be referred to as
Private settings. You may change the LAN IP address if needed. The LAN IP address is
private to your internal network and cannot be seen on the Internet.
IP Address The IP address of the LAN interface. The default IP address is
192.168.15.1.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask of the LAN interface. The default subnet
mask is 255.255.255.0.
21
Page 23

Home > VoIP
All of the screens necessary to setup and configure the router to handle VoIP traffic are
accessed from the screen shown below.
To access any of the individual configuration screens, click on the corresponding
radio-button and that screen will appear.
22
Page 24

Home > VoIP > Server Configuration
The Router can be
configured to handle voice
signals over the Internet
Protocol (Voice over IP −
VoIP). The screen shown
to the right, along with those
on the following pages are
used to configure your router
to communicate with the
devices that will send and
receive telephone calls over
the Internet.
23
Page 25

Server FQDN Use this drop-down menu to Enable or Disable the Server
Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) function. This is
disabled when the SIP URL domain name is different from
the SIP proxy server domain name. The phone will then use
the domain name in Domain Name field as part of SIP URL
but send and receive SIP messages through the SIP proxy
server defined in the Service Domain field.
IP Address Enter the IP address of the SIP Server in this field.
Domain Name Enter the domain name corresponding to the IP address
entered above in this field.
Port Enter the SIP server’s listening port for the SIP in this field.
Leave this field set to the default if your VoIP service
provider did not give you a server port number for SIP.
Secondary SIP Server The Secondary Features (FQDN, IP address, domain name
and port), act as a backup for the initial connections’ settings.
In the event that the connection with the SIP server is lost,
the backup settings will be used.
Outbound Proxy
The Outbound Proxy is a normal SIP proxy. If instructed to do so
by your ISP, enable the Outbound Proxy, and enter its IP address,
Domain Name and Port Number in the appropriate fields.
Service Domain Enter the SIP service domain name in this field.
URL Format Select SIP-URL to have the router include the domain name
with the SIP number in the SIP messages that it sends.
Select TEL-URL to have the router use the SIP number
without a domain name in the SIP messages that it sends.
User Parameter You can set this to phone or none. This determines
whether or not the phone number is appended to the
information forwarded to your SIP server. Your VoIP
service provider will instruct you which setting to use.
Caller ID Delivery Use this pull-down menu to initiate the delivery of the
inbound caller ID.
Display CID Use this pull-down menu to enable or disable the display of
the Caller ID.
Timer T2 Set the timer to 4, 8, 16 or 32.
Initial Unregister Enable or disable the initial unregister.
Register Expiration
Use this field to set how long the router will wait before
sending a repeat registration request if a registration attempt
fails or there is no response from the registration server.
24
Page 26

Home > VoIP > Provisioning
Provisioning is a
function that
automatically updates
your DVG-G1402S’s
VoIP configuration by
using a TFTP server
located on the
Internet. If you have
accesses to such a
service, you will need
to know the URL and
Proxy Address of the
Provisioning Server.
Provisioning Function Use this drop-down menu to Enable or Disable the Provisioning
Function on the router.
Server URL Enter the URL of the Provisioning Server in this field.
Proxy Address Enter the IP address of the Proxy Server in this field.
Proxy Port Number Enter the port number the Proxy Server will use to make the
connection in this field.
25
Page 27

Home > VoIP > STUN Configuration
Simple Traversal of UDP
over NAT (STUN) − is a
protocol which enables a
VoIP device, such as this
router or an IP phone, to
detect the presence and
type of NAT behind which
the phone is placed. This
router supports STUN
and can intelligently
modify the private IP
address and port in its
SIP/SDP message by
using the NAT mapped
public IP address and port
through a series of STUN
queries against a STUN
server located on the
public Internet. This will
allow SIP signaling and
RTP media to
successfully traverse a
NAT without requiring any
configuration changes on
the NAT.
STUN is useful if you need to use the DVG-G1402S behind a modem or router that
provides the connection to your ISP and then to the Internet and does not support
symetric NAT. You will need access to a STUN server on the Internet and its IP
address to use STUN on the DVG-G1402S.
STUN State Use this drop-down menu to Enable or Disable STUN on the
router.
STUN Server IP Address Enter the IP address of a STUN server in this field.
STUN Server Port Enter the port number the STUN server will use in this field.
If you do not have any information as to the proper port
number, leave the default setting here.
STUN ReqInterval This determines the amount of time, in seconds, between
STUN requests. If you do not have any information as to the
26
Page 28

proper interval, leave the default setting here.
STUN NAT Type Displays the result of the STUN NAT examination.
Home > VoIP > User Agent
The Router can be
configured to handle
voice signals over the
Internet Protocol (Voice
Over IP − VOIP).
Same Phone Number Use this field to Enable or Disable the use of the same
telephone number for the User Agent as for the Server Agent.
Index Use this field to assign line 1 or line 2 telephone sockets (on
the back of the router) to the information entered in the User
Agent.
Phone Number The telephone number assigned to the User Agent.
Domain Name The name that will be displayed when the User Agent is in use.
User Agent Port This selects the port number the router will listen to when
determining when calls are being made.
Authentication Name The Username used to access your SIP server and your VoIP
service provider.
Password The Password used to access your SIP server and your VoIP
service provider.
Retype Password Retype your password to confirm.
To query the registration state of click Query. When the server responds you have the
option to register or unregister.
27
Page 29

Home > VoIP > Peer to Peer
The Router can
be configured to
handle voice
signals over the
Internet Protocol
(Voice Over IP −
VOIP).
Phone Number The telephone number assigned to this entry
User IP Address Enter the IP address of the remote peer in this field.
Port Enter the UDP port number the remote peer will use to make
the connection in this field
. If you do not have any information
as to the proper port number, leave the default setting here.
.
28
Page 30

Home > VoIP > Telephony
The Router can be
configured to handle
voice signals over
the Internet Protocol
(Voice Over IP −
VoIP).
Index Use this field to assign line 1 or line 2 telephone sockets (on
the back of the router) to the information entered in the User
Agent.
DTMF Method Out-of band Dual Tone Multi-frequency -The Dual Tone
Multi-frequency (DTMF) mode sets how the router will handle
the tones that your telephone makes when you push its buttons.
It is recommended that you use the same mode that your VoIP
service provider uses. Select RFC 2833 to send the DTMF
tones in RTP packets. Select Inband to include the DTMF
tones in the voice data stream. This method works best when
you are using a codec that does not use compression (like
G.711).
Select INFO to transmit DTMF tones out-of-band.
Payload Type
A payload type is a number from 96 through 127 that identifies
the type of payload carried in the packet. For example, a
payload type of 122 denotes a fax payload. This field is only
active when the DTMF method is set to RFC 2833.
VAD Voice Activity Detection (VAD) -detects whether or not speech
is present. This reduces the bandwidth that a call uses by not
transmitting “silent Packets” when you are not speaking.
29
Page 31

Home > VoIP > Speed Dial
The Router can be
configured to dial a
specified telephone
number when you
enter a numerical dial
code. For example,
you could assign 22 to
the telephone number
555-1234. Then you
can dial that
telephone number by
entering 22.
Index A number used to identify the current speed dial table entry.
Dial Code A numerical code that will correspond to the phone number
entered in the field below. You will dial this number, and the
router will dial the corresponding telephone number.
Phone Number Enter the telephone number you want the router to dial when
you dial the Dial Code entered in the field above.
30
Page 32

Home > VoIP > Misc.
Instead of adding additional lines to handle different telephone numbers, distinctive
rings can be set to allow more than one telephone number to reach the same line.
Calls coming in on different numbers on the same line can be identified by their
distinctive ring pattern. For example, you could set a “short-short” ring for the sales
department number, and a regular ring for the technical support number. Use the radio
button to select Ring Cadence, Ring Default Rule, or Ring Rule. These three features
allow the user to set distinctive rings. To configure distinctive rings, see the descriptions
of the three features below.
31
Page 33

Home > VoIP > Misc. > Ring Cadence
By using the Ring
Cadence window, you can
set up to 8 distinct ring
patterns. The ring pattern
of each distinct ring can
be configured by setting
the On and Off time. The
amount of times that the
ring pattern will repeat
itself can also be set.
Duration This field is used to limit the amount of times that the ring
pattern will repeat itself. For example, if a ring pattern is set for
16 seconds and the duration is set for 60000 ms, then the ring
pattern will repeat itself 3 times; then, 3 quarters of the way
through the fourth repetition, the ringing will stop. The default
value is 180000 ms.
Ring on Ring off One ring pattern is comprised of four rings and four periods of
silence. The On field refers to the time of 1 ring. The Off time
refers to the period of silence between rings. One unit of time in
the On and Off fields is equal to 50 ms; so a value of 40 in the
On field sets a 2000 ms ring (2 seconds). The sum of all the
fields must be less than or equal to 320 ms and must be a
multiple of 8. However, individual On and Off times don’t
necessarily have to be multiples of 8. A ring pattern could be
32
Page 34

set at 12, 12, 8, 4, 10, 50, 0, 0. While some of the On and Off
times are not multiples of 8, their sum of 96 meets the
requirement so this would be a valid ring pattern.
Home > VoIP > Misc. > Ring Default Rule
The Ring Default Rule
is set for inbound
callers that are not
defined by the Ring
Rule. One Ring
Default Rule can be
set for each VoIP port.
Use this pull-down menu to select a Ring Cadence for the Ring
Ring Cadence
Profile ID
Default Rule. The 8 different Ring Cadences can be configured
on the Ring Cadence window.
33
Page 35

Home > VoIP > Misc. > Ring Rule
You can use the Ring
Rule window to assign
Caller IDs to
frequently received
inbound calls. Any call
that has been
assigned a caller ID
will have its ID
number displayed on
the receiver’s caller
display. This way, the
receiver knows which
department the
inbound call is
attempting to reach by
the ring cadence, and
who the caller is by
the caller ID.
From Use the From field to select either VoIP or PSTN.
Port Use the Port field to select either Port 1 or Port 2. You can also
choose both ports 1 and 2.
Use this pull-down menu to select a Ring Cadence for the Ring
Ring Cadence
Profile ID
Caller ID Set a numerical Caller ID of up 32 digits. 32 caller IDs can be
Rule. The 8 different Ring Cadences can be configured on the
Ring Cadence window.
created and will be listed below the Ring Rule Configuration
area. To edit or delete an entry that has already been created,
find the entry in the list and click on the appropriate icon.
34
Page 36

Home > VoIP > Manage Features > Reject Incoming Call
You can configure the router to reject incoming calls from particular telephone numbers
by entering the telephone number in the screen shown below.
Name Enter a name to identify the current entry.
PhoneNum Enter the telephone number you want to block incoming calls
from.
35
Page 37

Home > VoIP > Manage Features > Block Outgoing Call
You can configure the router to reject outgoing calls from particular telephone numbers
by entering the telephone number in the screen shown below.
Name Enter a name to identify the current entry.
PhoneNum Enter the telephone number you want to block outgoing calls to.
36
Page 38

Home > DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) allows the
gateway to automatically
obtain the IP address from a
DHCP server on the service
provider’s network. The
service provider assigns a
global IP address from a
pool of addresses available
to the service provider.
Typically the IP address
assigned has a long lease
time, so it will likely be the
same address each time the
Router requests an IP
address. If DHCP is not
enabled on the Router, it is
necessary for the user to
assign a static IP address to
each computer on your LAN.
To setup DHCP for your
LAN, first enable the Router
as a DHCP server by clicking
the corresponding Enabled
radio button in the window
above.
The next step is to set a range of IP addresses that you wish to allot to the devices on
your LAN by entering a Starting IP Address and an Ending IP Address. This may be
in a range from 2 to 254 (192.168.1.2 – 192.168.1.254). Computers on your LAN will
have an IP address within this range then automatically assigned to them. Finally, enter
the Lease Time, which is the time the Server will set for devices using DHCP to
re-request an IP Address. Clients authorized for DHCP will be listed in the table at the
bottom of the page. Click Apply to implement information set in this table. The DHCP
Server is enabled by default.
DHCP may also be statically configured as well. This method allows the router to assign
the same IP address information to a specific computer on the network, defined by its
MAC address. This computer will get the same DHCP implemented IP address
information every time the computer is turned on and this IP address will be specific to
that computer’s IP address on the local network. No other computer can be assigned
this address. This is useful for computers on the LAN that are hosting applications such
as HTTP or FTP. First, the user must enable the Static DHCP function by clicking the
37
Page 39

corresponding Enabled radio button. Next the user must enter the host name and the IP
address for that computer by entering the last numbers into the space provided in the IP
Address field. Next, the user is to enter the MAC address of the computer into the
space provided. Click Apply to implement these static settings. The DHCP Client field
will allow users to Clone the settings from their computer that were learned from the
DHCP server. Simply use the pull down menu to select the MAC address of the
computer to be cloned and then click the Clone button. The settings from this computer
will be implemented in the Static DHCP configuration area. Click Apply to implement
these static settings. The lower portion of the window contains the Static DHCP
Configuration List. Click on the
entry.
icon to edit an entry and on the icon to delete an
38
Page 40

Home > Proxy DNS
State Use this drop down menu to enable or disable the Proxy DNS.
Proxy DNS IP Address Enter the IP Address of the Proxy DNS.
39
Page 41

Advanced > Virtual Server
To view the following window, click on the Advanced tab at the top of the window and
then click the Virtual Server button to the left. The Virtual Server will allow remote
users access to various services outside of their LAN through a public IP addres s, such
as FTP (File Transfer Protocol) or HTTPS (Secure Web). After configuring the Router
for these features, the Router will redirect these external services to an appropriate
server on the user’s LAN.
These external services may be modified by clicking its corresponding edit icon, or they
may be deleted by clicking the corresponding delete icon. Though there are seven fields
available to configure the Virtual Server, in most cases, only the IP address of the
Virtual Server will be needed for implementation. To enable an already existing Virtual
Server, click its corresponding edit button, configure the appropriate fields listed below
40
Page 42

and set the Status fields to Enabled by clicking the radio button. To configure other
virtual servers for the Router, configure the following fields and click Apply.
Index This is an index number used to identify the Virtual Server
entry.
Private IP Enter the IP address of the Virtual Server.
Protocol Type The protocol type used for the Virtual Server. The user may
select TCP, UDP or Both, depending on the type of Virtual
Server implemented.
Start/End Global Port Enter a range of ports on the device on the WAN side of the
network that will be accessing the Virtual Server currently being
configured. Commonly, this range of ports is identical to the
local range of ports. Existing Virtual Servers may already have
their well-known port ranges listed but this may need to be
changed in certain circumstances.
Start/End Local Port Enter the range of ports of the Virtual Server’s computer.
Existing Virtual Servers may already have their well-known port
ranges listed but this may need to be changed in certain
circumstances.
41
Page 43

Advanced > Filters
Packet filtering is a basic security measure that should be used on any network that is
exposed to a security risk. A packet filter system examines data packets and scrutinizes
them in order to control network access. Filtering rules determine whether packets are
42
Page 44

passed through the Router from either side of the gateway. The rules are created and
controlled by the network administrator and can be precisely defined. These rules are
used to block access to the LAN from outside the network and/or to deny access to the
WAN from within the network. The Router uses filtering rules to examine data packet
headers for specific information. Packets passing through the Router that do not meet
the criteria specified by the rule set are dropped.
Effective implementation of packet filtering requires detailed knowledge of network
services and communication protocols. An overly complicated filtering scheme can
adversely affect the Router’s performance, while an inadequate set of rules may
needlessly compromise security.
This Router has two fields to configure for filtering which are IP Filters and MAC Filters.
Advanced > Filters > IP Filters
43
Page 45

This window will aid
the use in configuring
filters for IP
addresses. This will
deny specified LAN
IP addresses or
specific ports
associated with these
LAN IP address from
accessing the
Internet. Well known
ports have already
been previously set
in the IP Filters List
and can be modified
by clicking their
corresponding edit
icon, and simple
adding an IP address
to the configuration.
To access this screen, click the Advanced tab along the top of the configuration window
and then the Filters tab to the left hand side.
Protocol The protocol associated with this IP filter. The user may choose
between TCP, UDP or Both.
IP Address
An IP address or range of IP addresses that will be denied
access to the Internet.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask that corresponds to the IP address above.
Start Port/End Port A port or range of ports that will be denied access to the
44
Page 46

Internet. If no port is entered, all ports in this IP range will be
denied access to the Internet.
All computers are
uniquely identified by their
MAC (Media Access
Control) address. The
following window will allow
users to deny computers
access to the Internet or
only allow certain
computers access to the
Internet, based on their
MAC address. To access
this screen, click the
Advanced tab along the
top of the configuration
window, then the Filters
tab to the left hand side
and finally click the
corresponding radio
button for MAC Filters.
Advanced > Filters > MAC Filters
Index A number used to identify this MAC address filter setting.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address to be filtered.
State This field allows you to enable or disable this MAC address
filter setting.
45
Page 47

This Router comes equipped
with a firewall. The Firewall
configuration screen allows
the Router to enforce specific
predefined policies intended
to protect against certain
common types of attacks. To
configure the Router’s firewall,
click the Advanced tab at the
top of the screen and then the
Firewall tab to the left.
Advanced > Firewall
Pass or Block Select the action you want the filter to take when it finds a
packet that meets the criteria entered below.
Protocol The protocol associated with this IP filter. The user may choose
between TCP, UDP or Both.
Source
Enter the IP address or range of IP addresses that you wish to
block or allow to pass through the router. The Source may be
identified on the LAN side, the WAN side or both by using the
pull-down menu for the Interface heading.
Destination
Enter the IP address or range of IP addresses that you wish to
deny or allow access to the Internet. The Destination may be
identified on the LAN side, the WAN side or Both by using the
pull-down menu for the Interface heading. The type of protocol
46
Page 48

may also be chosen by using the pull-down menu. The user
may choose between TCP, UDP, ICMP or (*) Any. The user
may also select a range of ports of the destination IP addresses
by entering the range under the Port Range heading.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask that corresp onds to the IP address above.
47
Page 49

Advanced > Routing > RIP Configuration
RIP − Routing
Information Protocol −
specifies how routers
exchange information.
With RIP, routers
occasionally exchange
entire routing tables.
You can select RIPv1 or
RIPv2 by clicking the
radio button under the
Version heading, and
then select On or Off by
clicking the radio button
under the State heading.
LAN RIPv1
LAN RIPv2 Select RIPv1 or RIPv2 for use by the router on your LAN.
WAN RIPv1 Select RIPv1 or RIPv2 for use by the router on the WAN.
WAN RIPv2 Select RIPv1 or RIPv2 for use by the router on the WAN.
State Select On or Off to enable or disable RIP on either the LAN or the
Select RIPv1 or RIPv2 for use by the router on your LAN.
WAN
48
Page 50

Advanced > Routing > Static Route
The Routing table, shown to
the right, allows you to enter
static routes between
computers on both the WAN
(Internet) and your LAN.
IP Address Enter the IP Address of the subnet or device where packets are
to be routed.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask corresponding to the IP address entered
.
above
Gateway Enter the IP address of the gateway used for packets that are
to be routed to the IP address entered above.
Interface Select the WAN (Internet) or LAN interface.
Metric Enter the number of hops (the number of routers) that packets
will be allowed to cross when being routed to the IP address
entered above.
State Use this drop-down menu to Enable or Disable this route.
49
Page 51

Advanced > NAT > NAT Configuration
Network Address
Translation (NAT) is a
method by which the
router translates
between the IP address
your ISP assigns to your
account and the IP
addresses assigned to
the PCs on your LAN.
NAT Interface IP Address
NAT Interface Netmask This field displays the subnet mask corresponding to the IP
NAT Function Use this pull-down menu to enable or disable NAT on the
This field displays the current IP address of the LAN side of
the router. All IP address that are translated by the router
will be in the same range as this IP address.
address displayed above
.
router
.
50
Page 52

Advanced > NAT > Dynamic NAT
Network Address
Translation (NAT) is a
method by which the
router translates
between the IP address
your ISP assigns to
your account and the
IP addresses assigned
to the PCs on your
LAN. The Dynamic
NAT entries are
displayed below the
Dynamic NAT
configuration fields.
To edit or delete an
entry, find it on the list
and click either the edit
or delete icon.
This is an index number used to identify this NAT table entry.
Index
Global IP Start/End Enter the range of IP addresses that will be assigned to your
Internet account by your ISP
.
Local IP Start/End Enter the range of IP addresses that you will assign to PCs on
your LAN
.
51
Page 53

Advanced > NAT > Static NAT
Network Address
Translation (NAT) is a
method by which the router
translates between the IP
address your ISP assigns
to your account and the IP
addresses assigned to the
PCs on your LAN.
Index
This is an index number that will be used to identify this NAT
table entry
.
Local IP Address Enter the IP address of the PC on your LAN.
Global IP Address Enter the IP address assigned to your Internet account by your
ISP
.
52
Page 54

Tools > Admin
At this page, the
DVG-G1402S administrator
can change the system
password. There are two
accounts that can access the
Broadband Router’s
Web-Management interface.
They are admin and user.
Admin has read/write access
while user has read-only
access. User can only view
the settings but cannot make
any changes.
Web Port Number The port number used to access the Broadband Router. The
default port number for web management is 80.
WAN Access Control
Enter the password, admin, here and the same password in the
Administrator
Password
WAN access control allows remote management via the DI-624
to be configured from the Internet by a web browser. A
username and password are still required to access the
Web-Management interface. In general, only a member of your
network can browse the built-in web pages to perform
Administrator tasks. This feature enables you to perform
Administrator tasks from the remote (Internet) host. Click the
radio button to Enabled to activate this feature.
Confirm Password field. This will be the password that the
administrator will use to gain access to the configuration menu
of the device. There is no default password for this device.
53
Page 55

Tools > System
Backup
Restore Configuration
To restore the configuration file click on Browse to search the
File
Click Backup to backup the configuration file to your local hard
drive.
local hard drive and locate the configuration file to be used for
the configuration restoration. Once the file has been located,
click Open in the browser window and then Upload on the
System window.
Click Reset Factory Default Settings to restore the factory
Restore Factory
Default Settings
default settings.
54
Page 56

Tools > Firmware
You can update both the software and firmware of the Router. Please check the
D-Link Support site for firmware updates at
firmware upgrades to your hard drive from the D-Link support site.
http://support.dlink.com. You can download
Software Update Enter the TFTP server address.
Firmware Update Click Enabled to begin the firmware update.
File Name Enter the firmware file name and DOS path in this field. For
example, C:\firmware.had
55
Page 57

Tools > SNMP
This menu can be accessed
directly by clicking on the
SNMP button or hyperlink in
the Tools setup menu. Simple
Network Management
Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI
Layer 7 Application designed
specifically for managing and
monitoring network devices.
SNMP enables network
management stations to read
and modify the settings of
gateways, routers, switches,
and other network devices.
Use SNMP to configure system features for proper operation, performance monitoring,
and detection of potential problems in the Router or network.
The SNMP IP Management Address is the address of the PC
SNMP IP
Management Address
Traps are messages that alert network personnel of events that
SNMP Trap
Management
running the SNMP software from the DVG-G1402S device. A
defined set of variables (managed objects) is maintained by the
SNMP agent and used to manage the device. Enter the IP
address of PC that you want to use to manage the network.
You may also enter a backup address of another PC that can
manage the network.
occur on the Switch. The events can be as serious as a reboot
(someone accidentally turned OFF the Switch), or less serious
like a port status change. The Router generates traps and
sends them to the trap management server. Typical traps
include trap messages for Authentication Failure, Topology
Change and Broadcast/Multicast Storms. Use the pull-down
menu to enable or disable the SNMP on the device. Enter the
Trap Manager IP and Trap Community Name of the trap
management server.
56
Page 58

The system time is the time
used by the DVG-G1402S
for scheduling services.
You can manually set the
time, connect to a NTP
(network time protocol)
server or synchronize the
time on the router with your
PC. If an NTP server is set,
you will only need to set the
time zone (in the set up
wizard).
Tools > Time
57
Page 59

Status > Device Info
This page displays the
current information for the
DVG-G1402S. It will display
the LAN, WAN, Disk
Information statistics.
This window will show the
DVG-G1402S’s working
status:
WAN IP Address: WAN/Public IP Address
Subnet Mask: WAN/Public Subnet Mask
Default Gateway: WAN/Public Gateway IP Address
LAN LAN MAC Address: MAC address of the DVG-G1402S
IP Address: LAN/Private IP Address of the DVG-G1402S
Subnet Mask: LAN/Private Subnet Mask of the DVG-G1402S
58
Page 60

Status > Stats > Network
The Broadband Router keeps a running log of events and activities occurring on the
Router. If the device is rebooted, the logs are automatically cleared. You may save the log
files under Log Settings. The screen above displays the Network Statistics. Here you can
view th e a mo u nt o f p a ck ets that pass through the DVG-G1402S on both the WAN and
the LAN ports. The traffic counter will reset if the device is rebooted or can be reset by
clicking the Reset button. To refresh current statistics, click the Refresh button.
59
Page 61

Status > Stats > Phone Call
60
Page 62

The Broadband Router keeps a running log of events and activities occurring on the
Router. If the device is rebooted, the logs are automatically cleared. You may save the log
files under Log Settings. The screen above displays the Phone Statistics. Here you can
view th e a mo u nt o f p a ck ets that pass through the DVG-G1402S on both Phone 1 and
Phone 2 ports. The traffic counter will reset if the device is rebooted or can be reset by
clicking the Reset button. To refresh current statistics, click the Refresh button.
Status > Diagnostics
The Diagnostics window allows users to test the functionality of the router by executing
a ping test. Enter the IP address of the Ping Target and then click Test.
61
Page 63

Help
The Help tab will give basic information referring to various screens locted in the Router.
To view a specific section, click on its hyperlinked name. A new window of information
will appear.
62
Page 64

Technical Specifications
Standards
IEEE 802.3
IEEE 802.3u
VPN Pass Through/ Multi-Sessions
PPTP
L2TP
I PSec
Device Management
Web-Based- Internet Explorer v6 or later; Netscape Navigator v6 or
later; or other Java-enabled browsers
DHCP Server and Client
Advanced Firewall Features
NAT with VPN Passthrough (Network Address Translation)
MAC Filtering
IP Filtering
URL Filtering
Domain Blocking
Scheduling
Operating Temperature
º
32
Humidity:
95% maximum (non-condensing)
FCC
F to 131 ºF (0ºC to 55ºC)
Safety and Emissions:
63
63
Page 65

Technical Specifications
LEDs:
Power
WAN
LAN (10/100)
Phone
Status
Physical
Dimensions:
L = 7.56 inches (192mm)
W = 4.65 inches (118mm)
H = 1.22 inches (31 mm)
Power Input:
Ext. Power Supply DC 12V, 1.5A
Weight: 10.8 oz. (0.3kg)
Warranty:
3 year (depends on D-Link global warranty policy)
64
63
Page 66

Technical Support
You can find software updates and user documentation on the D-Link website.
D-Link provides free technical support for customers within the United States
and within Canada for the duration of the warranty period on this product.
U.S. and Canadian customers can contact D-Link technical support through our
website, or by phone.
Tech Support for customers within the United States:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(877) 453-5465
24 hours a day, seven days a week
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.com
email:support@dlink.com
Tech Support for customers within Canada:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(800) 361-5265
Monday to Friday 7:30am to 12:00 am EST
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.ca
email:support@dlink.ca
65
 Loading...
Loading...