D-Link DSL-560I User Manual

DSL-560I
ADSL Router
User’s Guide
(September 2002)
651SL560I015

DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise
1. Bitte lesen Sie sich diese Hinweise sorgfältig durch.
2. Heben Sie diese Anleitung für den spätern Gebrauch auf.
3. Vor jedem Reinigen ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen. Vervenden Sie keine Flüssig- oder Aerosolreiniger. Am
besten dient ein angefeuchtetes Tuch zur Reinigung.
4. Um eine Beschädigung des Gerätes zu vermeiden sollten Sie nur Zubehörteile verwenden, die vom Hersteller zugelassen
sind.
5. Das Gerät is vor Feuchtigkeit zu schützen.
6. Bei der Aufstellung des Gerätes ist auf sichern Stand zu achten. Ein Kippen oder Fallen könnte Verletzungen
hervorrufen. Verwenden Sie nur sichere Standorte und beachten Sie die Aufstellhinweise des Herstellers.
7. Die Belüftungsöffnungen dienen zur Luftzirkulation die das Gerät vor Überhitzung schützt. Sorgen Sie dafür, daß diese
Öffnungen nicht abgedeckt werden.
8. Beachten Sie beim Anschluß an das Stromnetz die Anschlußwerte.
9. Die Netzanschlußsteckdose muß aus Gründen der elektrischen Sicherheit einen Schutzleiterkontakt haben.
10. Verlegen Sie die Netzanschlußleitung so, daß niemand darüber fallen kann. Es sollete auch nichts auf der Leitung
abgestellt werden.
11. Alle Hinweise und Warnungen die sich am Geräten befinden sind zu beachten.
12. Wird das Gerät über einen längeren Zeitraum nicht benutzt, sollten Sie es vom Stromnetz trennen. Somit wird im Falle
einer Überspannung eine Beschädigung vermieden.
13. Durch die Lüftungsöffnungen dürfen niemals Gegenstände oder Flüssigkeiten in das Gerät gelangen. Dies könnte einen
Brand bzw. Elektrischen Schlag auslösen.
14. Öffnen Sie niemals das Gerät. Das Gerät darf aus Gründen der elektrischen Sicherheit nur von authorisiertem
Servicepersonal geöffnet werden.
15. Wenn folgende Situationen auftreten ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen und von einer qualifizierten Servicestelle zu
überprüfen:
a – Netzkabel oder Netzstecker sint beschädigt.
b – Flüssigkeit ist in das Gerät eingedrungen.
c – Das Gerät war Feuchtigkeit ausgesetzt.
d – Wenn das Gerät nicht der Bedienungsanleitung ensprechend funktioniert oder Sie mit Hilfe dieser Anleitung keine
Verbesserung erzielen.
e – Das Gerät ist gefallen und/oder das Gehäuse ist beschädigt.
f – Wenn das Gerät deutliche Anzeichen eines Defektes aufweist.
16. Bei Reparaturen dürfen nur Orginalersatzteile bzw. den Orginalteilen entsprechende Teile verwendet werden. Der
Einsatz von ungeeigneten Ersatzteilen kann eine weitere Beschädigung hervorrufen.
17. Wenden Sie sich mit allen Fragen die Service und Repartur betreffen an Ihren Servicepartner. Somit stellen Sie die
Betriebssicherheit des Gerätes sicher.
18. Zum Netzanschluß dieses Gerätes ist eine geprüfte Leitung zu verwenden, Für einen Nennstrom bis 6A und einem
Gerätegewicht großer 3kg ist eine Leitung nicht leichter als H05VV-F, 3G, 0.75mm2 einzusetzen
Limited Warranty
Hardware:
D-LINK WARRANTS EACH OF ITS HARDWARE PRODUCTS TO BE FREE FROM DEFECTS IN WORKMANSHIP AND
MATERIALS UNDER NORMAL USE AND SERVICE FOR A PERIOD COMMENCING ON THE DATE OF PURCHASE FROM
D-LINK OR ITS AUTHORIZED RESELLER AND EXTENDING FOR THE LENGTH OF TIME STIPULATED BY THE
AUTHORIZED RESELLER OR D-LINK BRANCH OFFICE NEAREST TO THE PLACE OF PURCHASE.
THIS WARRANTY APPLIES ON THE CONDITION THAT THE PRODUCT REGISTRATION CARD IS FILLED OUT AND
RETURNED TO A D-LINK OFFICE WITHIN NIN ETY (90) D AYS O F PURCHASE. A LI ST OF D-LIN K OFF ICES IS PRO VIDED AT
THE BACK OF THIS MANUAL, TOGETHER WITH A COPY OF THE REGISTRATION CARD.
IF THE PRODUCT PROVES DEFECTIVE WITHIN THE APPLICABLE WARRANTY PERIOD, D-LINK WILL PROVIDE REPAIR
OR REPLACEMENT OF THE PRODUCT. D-LINK SHALL HAVE T HE SOLE D ISCR ETION WHETH ER TO REP AIR O R REPLAC E,
AND REPLACEMENT PRODUCT MAY BE NEW OR RECONDITIONED. REPLACEMENT PRODUCT SHALL BE OF
EQUIVALENT OR BETTER SPECIFICATIONS, RELATIVE TO THE DEFECTIVE PRODUCT, BUT NEED NO T BE IDENTICAL.
ANY PRODUCT OR PART REPAIRED BY D-LINK PURSUANT TO THIS WARRANT Y SHALL H AVE A WARR ANT Y PERIOD OF
NOT LESS THAN 90 DAYS, FROM DATE OF SUCH RE PAIR, IRRESPECTIVE OF ANY EARLIER EXPIRATION OF ORIGINAL
WARRANTY PERIOD. WHEN D-LINK PROVIDES REPLACEMENT, THEN THE DEFECTIVE PRODUCT BECOMES THE
PROPERTY OF D-LINK.
ii

DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
WARRANTY SERVICE MAY BE OBTAINED BY CONTACTING A D-L INK OFFICE WITHIN THE APPLICABLE WARRANTY
PERIOD, AND REQUESTING A RETURN MATERIAL AUTHORIZATION (RMA) NUMBER. IF A REGISTRATION CARD FOR
THE PRODUCT IN QUESTION HAS NOT BEEN RETURNED TO D-LINK, THEN A PROOF OF PURCHASE (SUCH AS A COPY OF
THE DATED PURCHASE INVOICE) MUST BE PROVIDED. IF PURCHASER'S CIRCUMSTANCES REQUIRE SPECIAL
HANDLING OF WARRANTY CORRECTION, THEN AT THE TIME OF REQUESTI NG RMA NUMBER, PURCH ASER MAY ALSO
PROPOSE SPECIAL PROCEDURE AS MAY BE SUITABLE TO THE CASE.
AFTER AN RMA NUMBER IS ISSUED, THE DEFECTIV E PRODUCT MUST BE PAC KAGED SECURELY IN THE ORIGINAL OR
OTHER SUITABLE SHIPPING PACKAGE TO ENSURE THAT IT WILL NOT BE DAMAGED IN TRANSIT, AND THE RMA
NUMBER MUST BE PROMINENTLY MARKED ON THE OUTS IDE OF THE PACKAGE. TH E PACKAGE MUST BE MAILED OR
OTHERWISE SHIPPED TO D-LINK WITH ALL C OSTS OF MAILING/SHIPPING/ INSURANCE PREPAID. D-LINK SHA LL NEVER
BE RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY SOFTWARE, FIRMWARE, INFORMA TION, OR MEMO RY DATA OF P URCHASER C ONTAINE D IN,
STORED ON, OR INTEGRATED WITH ANY PRODUCT RETURNED TO D-LINK PURSUANT TO THIS WARRANTY.
ANY PACKAGE RETURNED TO D-LINK WITHOUT AN RMA NUMBER WILL BE REJECTED AND SHIPPED BACK TO
PURCHASER AT PURCHASER'S EXPENSE, AND D-LINK RES ERVES THE RI GHT IN SUCH A CASE TO LEVY A RE ASONAB LE
HANDLING CHARGE IN ADDITION MAILING OR SHIPPING COSTS.
Software:
WARRANTY SERVICE FOR SOFTWARE PRODUCTS MAY BE OBTAINED BY CONTACTIN G A D-LINK OFFICE WI THIN THE
APPLICABLE WARRANTY PERIOD. A LIST OF D-LINK OFFICES IS PROVIDED AT THE BACK OF THIS MANUAL,
TOGETHER WITH A COPY OF THE REGISTRATION CARD. IF A REGISTRATION CARD FOR THE PRODUCT IN QUESTION
HAS NOT BEEN RETURNED TO A D-LINK OFFICE, THEN A PROOF OF PURC HASE (SUCH AS A COPY OF THE DATED
PURCHASE INVOICE) MUST BE PROVIDED WHEN REQUESTING WARRANTY SERVICE. THE TERM "PURCHASE" IN THIS
SOFTWARE WARRANTY REFERS TO THE PURCHASE TRANSACTION AND RESULTING LICENSE TO USE SUCH
SOFTWARE.
D-LINK WARRANTS THAT ITS SOFTWARE PRODUCTS WILL PERFORM IN SUBSTANTIAL CONFORMANCE WITH THE
APPLICABLE PRODUCT DOCUMENTATION PROVIDED BY D-LINK WITH SUCH SOFTWARE PR ODUCT, FOR A PERIOD OF
NINETY (90) DAYS FROM THE DATE OF PURCHASE FROM D-LINK OR ITS AUTHORIZED RESELLER. D-LINK WARRANTS
THE MAGNETIC MEDIA, ON WHICH D-LINK PROVIDES ITS S OFTWAR E PRODUCT, AGAINS T FAILURE DURING THE SAME
WARRANTY PERIOD. THIS WARRANTY APPLIES TO PURCHASED SOFTWARE, AND TO REPLACEMENT SOFTWARE
PROVIDED BY D-LINK PURSUANT TO THIS WARRANTY, BUT SHALL NOT APPLY T O ANY UPDATE OR REPLACEMENT
WHICH MAY BE PROVIDED FOR DOWNLOAD VIA THE INTER NET, OR TO ANY UPDATE WHICH MAY OTHERWISE BE
PROVIDED FREE OF CHARGE.
D-LINK'S SOLE OBLIGATION UNDER THIS SOFTWARE WARRANTY SHALL BE TO REPLACE ANY DEFEC TIVE SOFTWARE
PRODUCT WITH PRODUCT WHICH SUBSTANTIALLY CONFORMS TO D-L INK'S APPLICABLE P RODUCT DOCU MENTATION .
PURCHASER ASSUMES RESPONSIBILITY FOR THE SELECTION OF APPROPRIATE APPLICATION AND SYSTEM/PLATFORM
SOFTWARE AND ASSOCIATED REFERENCE MATERIALS. D-LINK MAKES NO WARRANTY THAT ITS SOFTWARE
PRODUCTS WILL WORK IN COMBINATION WITH ANY HARDWARE, OR ANY APPLICATION OR SYSTEM/PLATFORM
SOFTWARE PRODUCT PROVIDED BY ANY THIRD PARTY, EXCEPTING ONLY SUCH PRODUCTS AS ARE EXPRESSLY
REPRESENTED, IN D-LINK'S APPLICABLE PRODUCT DOCUMENTAT ION AS BEING COMPATIBLE. D-LINK'S OB LIGATION
UNDER THIS WARRANTY SHALL BE A REASONABLE E FFORT TO PROVIDE COMPATIBILITY, BUT D- LINK SHALL HAVE
NO OBLIGATION TO PROVIDE COMPATIBILITY WHEN THERE IS FAULT IN THE THIRD-PARTY HARDWARE OR
SOFTWARE. D-LINK MAKES NO WARRANTY THAT OPERATION OF ITS SOFTWARE PRODUCTS WILL BE
UNINTERRUPTED OR ABSOLUTELY ERROR-FREE, AND NO WARRANTY THAT ALL DEFECTS IN THE SOFTWARE
PRODUCT, WITHIN OR WITHOUT THE SCOPE OF D-LINK'S APPLICABLE PRODUCT DOCUMENTATION, WILL BE
CORRECTED.
D-Link Offices for Registration and Warranty Service
THE PRODUCT'S REGISTRATION CARD, PROVIDED AT THE BACK OF THIS MANUAL, MUST BE SENT TO A D-LINK OFFICE.
TO OBTAIN AN RMA NUMBER FOR WARRANTY SERVICE AS TO A HARDWA RE PRODUCT, OR TO OBTAIN WARRANTY
SERVICE AS TO A SOFTWARE PRODUCT, CONTACT THE D-LINK OFFICE NEAREST YOU. AN
ADDRESS/TELEPHONE/FAX/E-MAIL/WEB SITE LIST OF D-LINK OFFICES IS PROVIDED IN THE BACK OF THIS MANUAL.
LIMITATION OF WARRANTIES
IF THE D-LINK PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS WARRANTE D ABOVE, THE CUSTOMER'S S OLE REMEDY S HALL BE, AT
D-LINK'S OPTION, REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT. THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND
ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW,
STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. D-LINK NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER
LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION MAINTENANCE OR USE OF D-LINK'S PRODUCTS
D-LINK SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THAT THE
ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT EXIST OR WA S CAUSED BY THE CUSTOMER' S OR ANY THIRD PERSON'S
MISUSE, NEGLECT, IMPROPER INSTALLATIO N OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR, OR ANY OTHER
CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED USE, OR BY ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING OR OTHER HAZARD.
iii

DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
IN NO EVENT WILL D-LINK BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAG ES, INCLUDING LOSS OF DATA, LOSS OF PROFITS, COST OF
COVER OR OTHER INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INDIRECT DAMAGES ARISING OUT THE INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE OR INTERRUPTION OF A D- LINK PRODUCT, HOWEVER CAUSED AND
ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY. THIS LIMITATION WILL APPLY EVEN IF D-LINK HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
IF YOU PURCHASED A D-LINK PRODUCT IN THE UNITED STATES, SOM E STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE LIMITATIO N OR
EXCLUSION OF LIABILITY FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIA L DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT
APPLY TO YOU.
Trademarks
Copyright 2000 D-Link Corporati o n.
Contents subject to change without prior notice.
D-Link is a registered trademark of D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc.
All other trademarks belong to their respective proprietors.
Copyright Statement
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any
derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without permission from D-Link
Corporation/D-Link Systems Inc., as stipulated by the United States Copyright Act of 1976
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference in
which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
iv

TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS USER’S GUIDE................................................................................. VII
Guide Overview............................................................................................................................................ vii
Before You Start ...............................................................................................................................................vii
Requirements ....................................................................................................................................................vii
Web Browser................................................................................................................................................viii
Ethernet Port (NIC Adapter)........................................................................................................................ viii
About Bridged Ethernet Connections (RFC 1483) ......................................................................................viii
About IPoA Connections (RFC 1577)...........................................................................................................ix
Additional PVC Settings................................................................................................................................ ix
Packing List.......................................................................................................................................................... ix
INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................ 1
What is ADSL?............................................................................................................................................... 1
Router Description and Operation...................................................................................................................... 1
Router Features..................................................................................................................................................... 2
Front Panel.......................................................................................................................................................... 3
Rear Panel........................................................................................................................................................... 4
LED Indicators.................................................................................................................................................... 5
HARDWARE INSTALLATION................................................................................... 7
Connect ADSL Line.............................................................................................................................................. 7
Compuer to Router Connection........................................................................................................................... 7
Connect Ethernet LAN to Router........................................................................................................................ 8
Hub or Switch to Router Connection.................................................................................................................. 8
Power On Router .................................................................................................................................................. 9
CONFIGURING THE ROUTER FOR THE FIRST TIME ...........................................10
Configuring IP Settings on Your Computer...................................................................................................... 10
Access the Configuration Manager................................................................................................................... 17
Configure the Router......................................................................................................................................... 17
WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT .................................................................................20
Accessing the Web Manager............................................................................................................................. 20
Folders and Menus........................................................................................................................................ 21
BASIC .......................................................................................................................21
Router Configuration ......................................................................................................................................... 21
Configuring the WAN Connection ................................................................................................................... 22
Additional Virtual Connections (PVCs) ........................................................................................................... 23

Configuring LAN IP Settings............................................................................................................................ 26
Access Control.............................................................................................................................................. 27
ADSL Link Status......................................................................................................................................... 29
Routing Setup................................................................................................................................................ 30
Save and Reboot............................................................................................................................................ 30
Erase and Reboot .......................................................................................................................................... 31
ADVANCED..............................................................................................................32
ADSL Mode.................................................................................................................................................. 33
Redirect Port ................................................................................................................................................. 33
NAT .............................................................................................................................................................. 34
DHCP Server................................................................................................................................................. 35
SNMP............................................................................................................................................................ 36
Interface ........................................................................................................................................................ 37
VCC .............................................................................................................................................................. 39
PPPoE ........................................................................................................................................................... 41
PPPoA........................................................................................................................................................... 42
IGMP Proxy.................................................................................................................................................. 42
Bridge............................................................................................................................................................ 43
Spanning Tree............................................................................................................................................... 44
Filter.............................................................................................................................................................. 46
Interface ........................................................................................................................................................ 47
TCP-IP .......................................................................................................................................................... 48
DHCP-Lease................................................................................................................................................. 49
AAL5 ............................................................................................................................................................ 49
SNDCP.......................................................................................................................................................... 50
Loopback....................................................................................................................................................... 50
Ping............................................................................................................................................................... 51
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS...............................................................................52
LAN IP SETUP..........................................................................................................54
Assigning Network IP Addresses....................................................................................................................... 54
Using the Default IP Address............................................................................................................................ 54
Manual IP Address Assignment.................................................................................................................... 54
Using DHCP ................................................................................................................................................. 55
Changing the IP Address of the Router............................................................................................................. 55
IP CONCEPTS..........................................................................................................56
IP Addresses........................................................................................................................................................ 56
Subnet Mask........................................................................................................................................................ 58
MICROFILTERS AND SPLITTERS..........................................................................59
Microfilters ................................................................................................................................................... 59
Line Splitter .................................................................................................................................................. 60

DSL-560I ADSL Ethernet Router User’s Guide
About This User’s Guide
This user’s guide provides instructions on how to install the DSL-560I ADSL Router and use it to connect a
computer or Ethernet LAN to the Internet.
If you are using a computer with a functioning Ethernet port, you can use the Quick Installation Guide to quickly
establish your ADSL connection and access the Internet.
Guide Overview
Introduction – Describes the Router and its key features. Provides an introduction to ADSL. Lists
standards to which the Router complies. Contains a packing list.
Hardware Installation – Discusses how to connect the Router to an Ethernet LAN.
Configuring the Router for the First Time – Provides information on how to configure the Router and
establish the WAN connection using the web-based manager.
Web-based Configuration – Describes how to use the web-based manager to change Router settings and
configure additional virtual connections (PVCs).
Appendix A - Technical Specifications – Lists the technical specifications of the Router, including
standards compliance.
Appendix B - Low Pass Filters – Illustrated examples of how to use low pass filters.
Before You Start
Please read and make sure you understand all the prerequisites for proper installation of your new Modem. Have
all the necessary information and equipment on hand before beginning the installation.
Installation Overview
The procedure to install the Router can be described in general terms in the following steps:
1. Gather information and equipment needed to install the device. Before you begin th e actual installation
make sure you have all the necessary information and equipment.
2. Install the hardware, that is, connect the cables (Ethernet and telephone) to the device and connect the
power adapter.
3. Check the IP settings on your computer and change them if necessary so the computer can access the
web-based software built into the Router.
4. Use the web-based management software to configure the device to suit the requirements of your ADSL
account.
Requirements
To install and use the Router you need a computer equipped with an Ethernet port (such as an Ethernet NIC) and
a web browser. You may also need to use information given to you by your ISP. This information is stored in th e
Router’s memory and used to establish the WAN connection and confirm your identity. Read the next page for
more details about these requirements.
Low Pass Filters
Since ADSL and telephone services share the same copper wiring to carry their respective signals, a filtering
mechanism may be necessary to avoid mutual interference. A low pass filter device can be installed for each
telephone that shares the line with the ADSL line. These filters are easy to install passive devices that connect to
the ADSL device and/or telephone using standard telephone cable. Ask your service provider for more
information about the use of low pass filters with your installation. Appendix B provides illustrated examples of
how to install two common styles of low pass filters.
vii
DSL-560I ADSL Ethernet Router User’s Guide
Operating System
The DSL-560I uses a HTML-based web interface for setup and management. The web configuration manager
may be accessed using any operating system capable of running web browser software.
Web Browser
Any common web browser can be used to configure the Router by accessing its web configuration management
software. The program is designed to work best with more recently released browsers such as Microsoft Internet
Explorer® version 5.0, Netscape Navigator® version 4.7, or later versions. The web browser must have
JavaScript enabled. JavaScript is enabled by default on many browsers. Make sure JavaScript has not been
disabled by other software (such as virus protection or web user security packages) that may be running on your
computer.
Ethernet Port (NIC Adapter)
Any computer that uses the Router must be able to connect to it through the Ethernet port on the Router. This
connection is an Ethernet connection and therefore requires that your computer be equipped with an Ethernet
port as well. Nowadays, most notebook computers ar e alread y sold with the installed Ethernet adap ter. Likewise,
most fully assembled desktop computers come with an Ethernet NIC card as standard equipment. If your
computer does not have an Ethernet port, you must install an Ethernet NIC adapter before you can access the
Router. If you must install an adapter, follow the installation instructions that come with the Ethernet NIC
adapter.
Additional Software
It may be necessary to install software on your computer that enables the computer to access the Internet.
Additional software must be installed if you are using what is called a “bridged” connection. For a bridged
connection, the information needed to make and maintain the Internet connection is stored on your co mputer, not
in the Router. This type of connection is similar to the arrangement used for analog dial-up mode ms, but the
connection speed is much faster. Various terms are to describe a bridged ADSL connection including the term
“RFC 1483 Bridge” which is also used in this guide.
If your ADSL service is delivered through a PPP (Point to Point Protocol) connection, the information needed to
establish and maintain the Internet connection can be stored in the Router. In this case, it is not necessary to
install any PPP software on your computer.
Account Information (User Name and Password)
Most users will need to supply a user name and password used to access the service provider’s network (and
ultimately, the Internet). This information is stored either in the Router’s memory or on your computer
depending on the type of ADSL connection you have.
ACCOUNT INFORMATION (PPP Connections Only)
User Name:
Password:
About Bridged Ethernet Connections (RFC 1483)
Using this method, the DSL-560I acts as a transparent bridge, and is invisible to other devices on both the WAN
and LAN side of the bridge. It is therefore necessary to provide some means of acquiring global IP settings for
your account.
All connections to the Internet require a unique global IP address. For bridged conn ections, the glob al IP settings
must reside in a TCP/IP enabled device on the LAN side of the bridge, such as a PC, server or firewall hardware.
The IP address can be assigned in a number of ways. Your network service provider will give you in structions
about any additional connection software or NIC configuration that may be required.
viii

DSL-560I ADSL Ethernet Router User’s Guide
About IPoA Connections (RFC 1577)
IP over ATM connections may require global IP settings for the device. Your service provider will give you IP
settings information if needed. Some IPoA connections function like peer-to-peer connections and therefore do
not require IP settings on the WAN interface.
Additional PVC Settings
If you are using multiple virtual connections it will be necessary to provide additional VPI and VCI values for
the device. These numbers define a unique route used on the ATM backbone of the WAN. Chapter 5 contains
instruction on how to set up additional PVCs for accounts using more than one virtual connection.
Packing List
Open the shipping carton and carefully remove all items. In addition to this User's Guide, ascertain that you have:
1. One DSL-560I ADSL Ethernet Router
2. One User’s Guide
3. One twisted-pair telephone cable used for ADSL connection
4. One straight-through Ethernet cable
5. One AC power adapter suitable for your electric service
ix


DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
Introduction
This section provides a brief description of the Router, its associated technologies and a list of Router features.
What is ADSL?
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) is an access technology that utilizes ordinary copper telephone
lines to enable broadband high-speed digital data transmission and interactive multimedia applications for
business and residential customers. For ADSL services, it is not necessary to use expensive new cabling or
condition the line in any way.
ADSL greatly increases the signal carrying capacity of copper telephone lines withou t interfering with regular
telephone services. For the ADSL user, this means faster downloads and more reliable connectivity. ADSL
devices make it possible to enjoy benefits such as high-speed Internet access without experiencing any loss of
quality or disruption of voice/fax telephone capabilities.
ADSL provides a dedicated service over a single telephone line operating at speeds of up to 8 Mbps downstream
and up to 640 Kbps upstream, depending on local telephone line conditions. A secure point-to-point conn ection
is established between the user and the central office of the service provider.
D-Link ADSL devices incorporate the recommendations of the ADSL Forum regarding framing, data format,
and upper layer protocols.
Router Description and Operation
The DSL-560I ADSL Router is designed to provide a simple, cost-effective and secure ADSL Internet
connection for your small- to medium-sized private network. The DSL-560I combines the benefits of high-speed
ADSL connection technology and TCP/IP routing with a conventional Ethernet interface in one compact and
convenient package. ADSL connection techno logy enables many interactive multi-media applications such as
video conferencing and collaborative computing.
The Router is easy to install and use. The DSL-560I connects to an Ethernet LAN via a standard Ethernet
100BASE-T interface using RJ-45 connectors. The ADSL connection is made using ordinary twisted-pair
telephone line with standard RJ-11 connectors. This arrangement means that several PCs can be networked and
connected to the Internet using a single WAN interface and IP address.
The Router supports transparent bridging and can be used for IP packet routing over the Internet. Cost saving
features of the Router such as NAT (Network Address Translator) and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol) improve administration efficiency and improve security. The advanced security enhancements, packet
filtering and port redirection, can help protect your network from potentially devastating intrusions by malicious
agents from outside your network.
1

DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
Router Features
The DSL-560I ADSL Ethernet Router utilizes the latest ADSL enhancements to provide a reliable Internet portal
suitable for most small to medium sized offices. DSL-560I advantages include:
• PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) Security The DSL-560I ADSL Router supports PAP (Password
Authentication Protocol) and CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) for PPP connections.
• DHCP Support Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol automatically and dynamically assigns al LAN IP
settings to each host on your n etwork. This eli minates the need to reconfigure ever y host when ever ch anges
in network topology occur.
• Network Address Translation (NAT) For small office environments, the DSL-560I allows multiple users
on the LAN to access the Internet concurrently through a single Internet account. This provides Internet
access to everyone in the office for the price of a single user.
NAT improves network security in effect by hiding the private network behind one global and visible IP
address. NAT address mapping can also be used to link two IP domains via a LAN-to-LAN connection.
• TCP/IP (Transfer Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) The DSL-560I supports TCP/IP protocol, the
language used for the Internet. It is compatible with access servers manufactured by major vendors.
• RIP-1/RIP-2 The DSL-560I supports both RIP-1 and RIP-2 exchanges with other routers. Using both
versions lets the Router to communicate with all RIP enabled devices.
• Static Routing This allows you to select a data path to a particular network destin ation that will remain in
the routing table and never “age out”. If you wish to define a specific route that will always be used for data
traffic from your LAN to a specific destination within your LAN (for example to another router or a server)
or outside your network (to a ISP defined default gateway for instance).
• Default Routing This allows you to choose a default path for incoming data packets for which the
destination address is unknown. This is particularly useful when if the Router functions as the sole
connection to the Internet.
• ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) The DSL-560I supports Bridged Ethernet over ATM (RFC1483), IP
over ATM (RFC1577) and PPP over ATM (RFC 2364).
• Precise ATM Traffic Shaping Traffic shaping is a method of controlling the flow rate of ATM data cells.
This function helps to establish the Quality of Service for ATM data transfer.
• G.hs (Auto-handshake) This allows the Router to automatically choose either the G.lite or G.dmt ADSL
connection standards.
• High Performance Very high rates of data transfer are possible with the Router. Up to 8 Mbps downstream
bit rate using the G.dmt.
• Full Network Management The DSL-560I incorporates SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
support for web-based management and text-based network management via an RS-232 or Telnet
connection.
• Telnet Connection The Telnet enables a network manager to access the Router’s management software
remotely.
• Easy Installation The DSL-560I uses a web-based graphical user interface program for convenient
management access and easy set up. Any common web browser software can be used to manage the Router.
• Multiple PVC Support Up to eight PVCs can be assigned for use by the Modem. This can be useful to
ADSL clients who wish to dedicate a PVC for a specific application, LAN or server.
2

DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
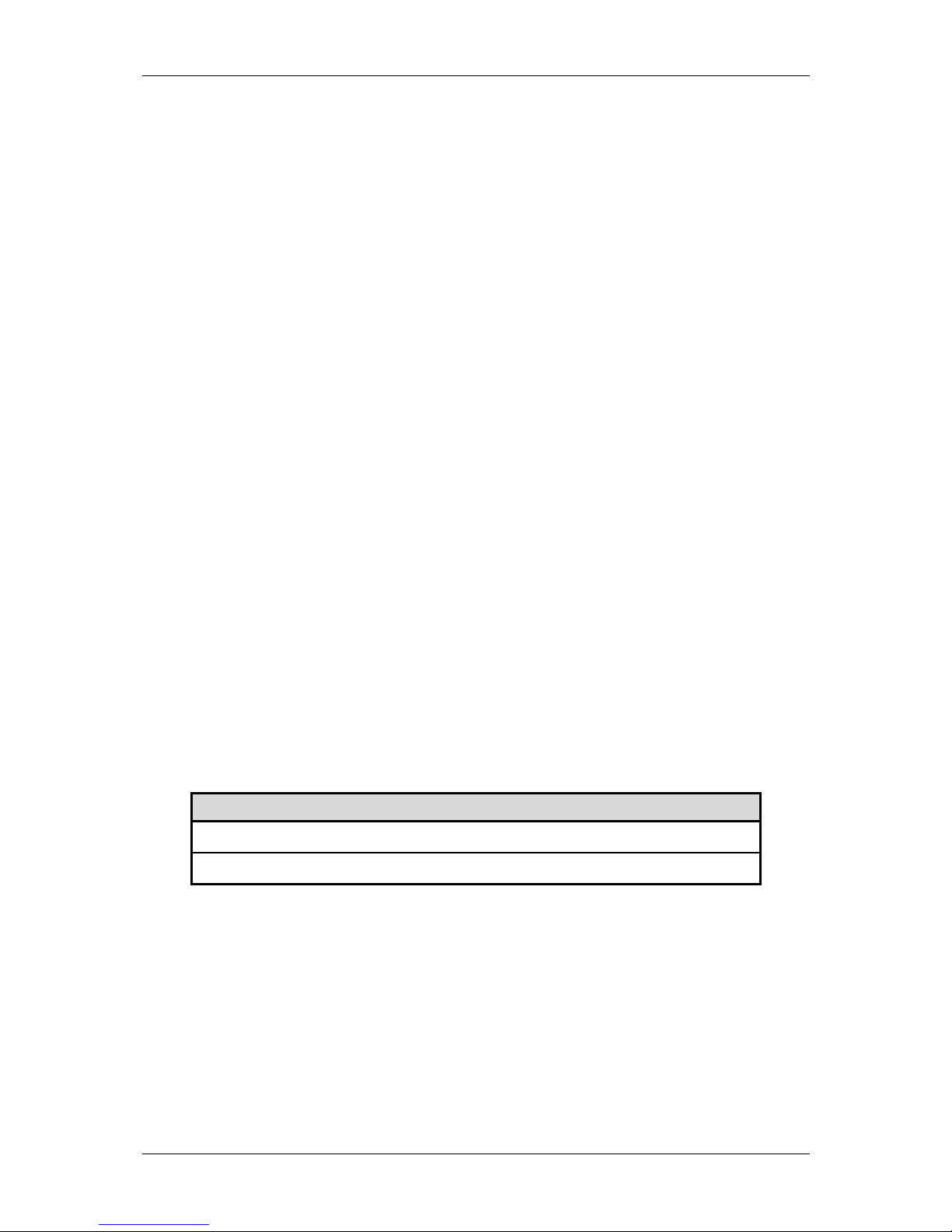
Front Panel
Place the Router in a location that allows a view of the LED indicators on the front panel.
3
DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
Rear Panel
All cable connections to the Router are made at the rear panel. The power switch and factory reset button is
located here as well.
Power Cord
connects here.
Ethernet port,
connect
thernet cable E
here
The factory rese
t
b
utton is locate
d
here.
ADSL port,
connect ADSL
cable here
4

DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
LED Indicators
Power
Status
Ethernet
Link/Activity
ADSL
Link/Activity
The LED Indicators read as follows:
Power Steady green light indicates the unit is powered on.
Status Blinking light indicates a normal state. Off or steady On means the device is malfunction.
ADSL: Link Steady green light indicates a valid ADSL connection. This will light after the ADSL
negotiation process has been settled.
ADSL: Act Blinking green light indicates an active WAN session.
5

DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
Ethernet: Link Steady green light indicates a valid Ethernet connection.
Ethernet: Act Blinking green indicates an active Ethernet session.
6
DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
Hardware Installation
In this chapter you will learn about the various connections you will need to make in order to use the Router.
When selecting the location for the Router, make sure to allow room to access the connections on the rear panel.
You will want to place the Router so that you will be able to see the LED indicators on the front panel. Allow
some space above the Router for ventilation to avoid problems with overheating.
It may be convenient for you by placing the Router near the PC which you intend to use for initial Router
configuration.
Connect ADSL Line
Use the standard phone cable that comes with the Router to connect it to your telephone outlet. Simply plug one
end of the cable into the Router’s ADSL port (RJ-11 receptacle) on its rear panel, and insert the other end into
the wall jack. The ADSL connection is the WAN interface. It links the Router to the network serv ice provider’s
backbone infrastructure. This is the Router’s access point to the Internet.
The Router must undergo a negotiation process to establish the terms of the ADSL connection. During this
negotiation the ADSL Link/Activity LED will flash in a steady interval, after the line is established which it will
become steadily On. When the ADSL line traffic starts, it will then begin flashing according to the traffic
activities. If the ADSL line is disconnected, the whole ADSL negotiation process will repeat itself again.
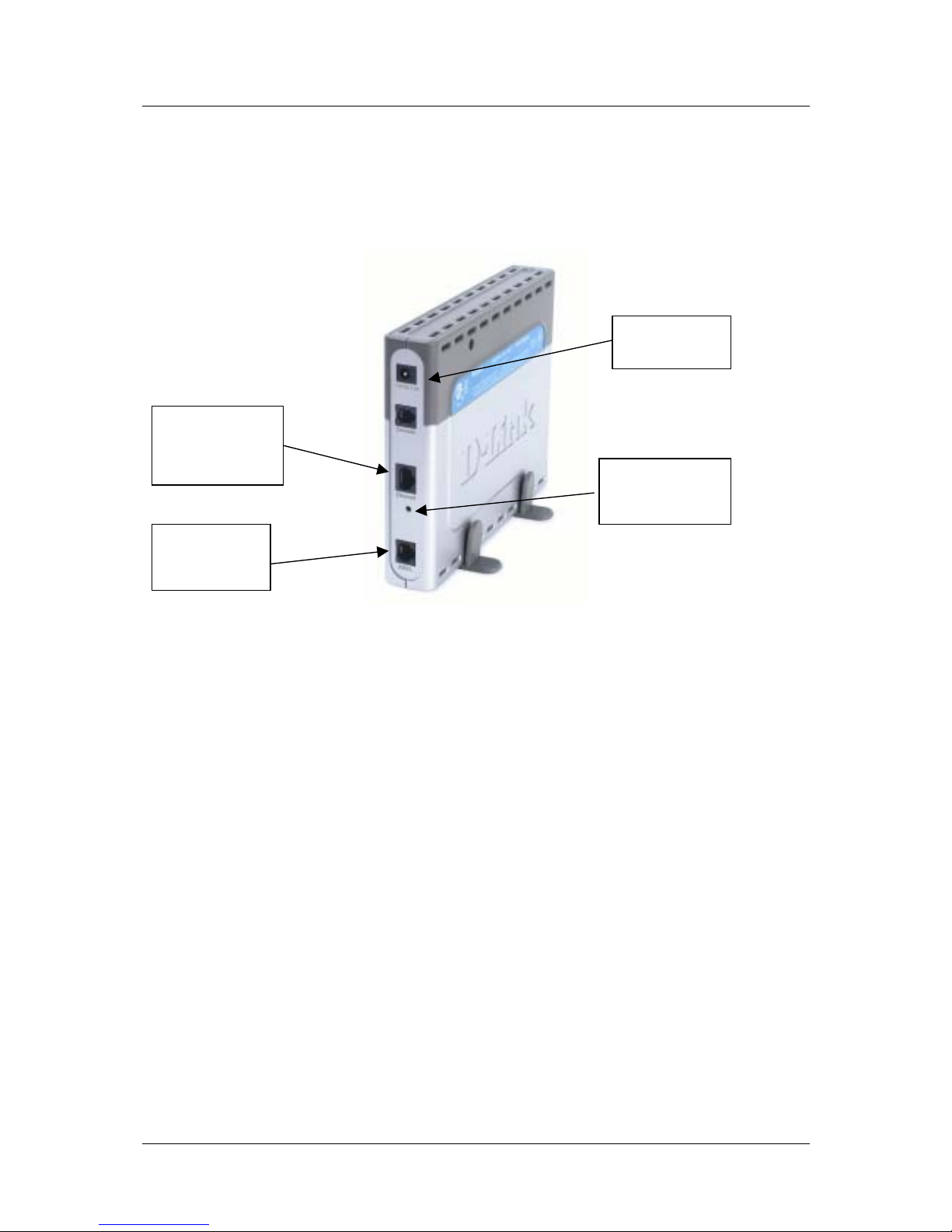
Compuer to Router Connection
You can connect the Router
directly to a 10/100BASETX Ethernet adapter card
(NIC) installed on a PC
using the Ethernet cable
provided as shown in this
diagram.
7
DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
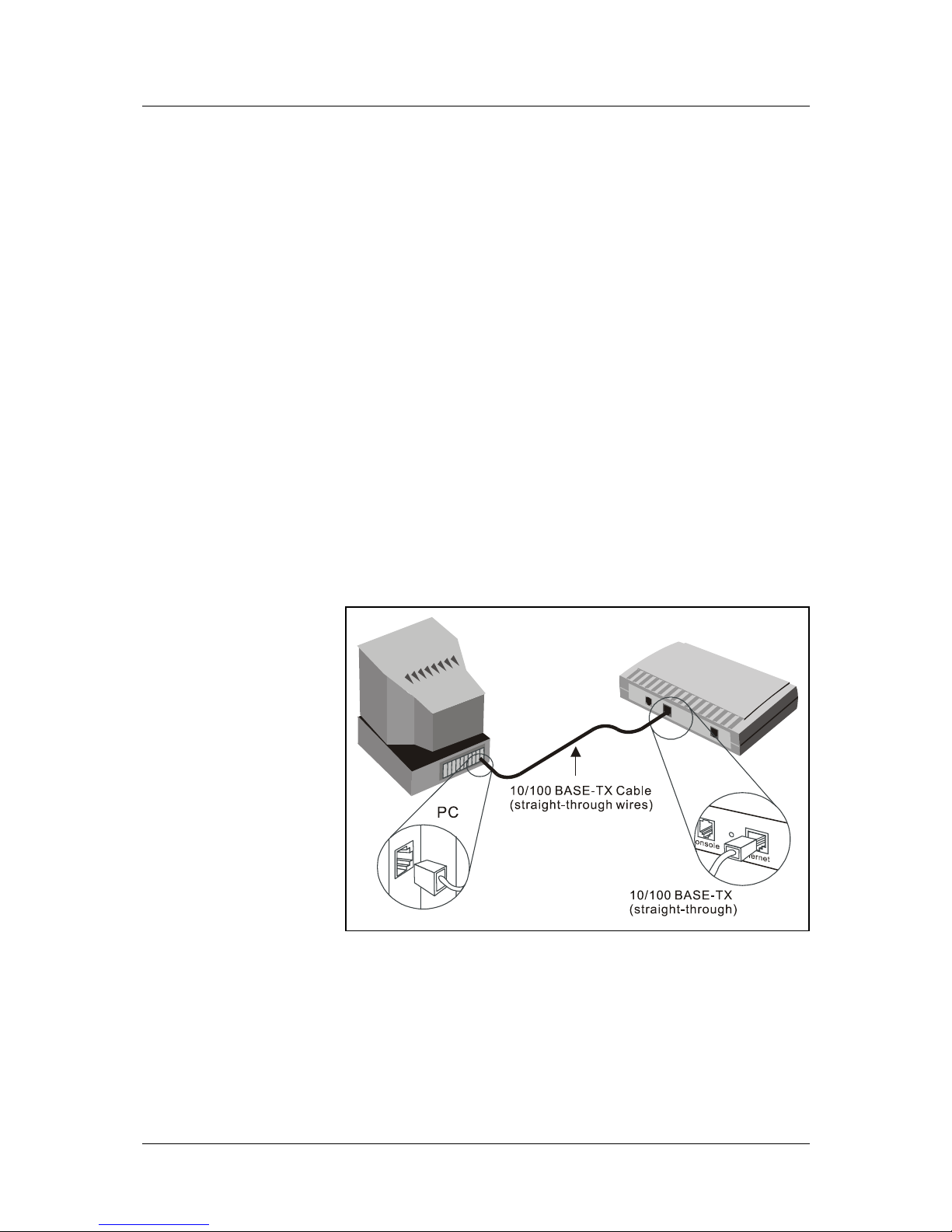
Connect Ethernet LAN to Router
The Router may be connected to any 10/100BASE-TX Ethernet LAN. Any connection to an Ethernet
concentrating device such as a switch or hub can operate at a speed of 10/100 Mbps. When connecting the
Router to any Ethernet device that is capable of operating at speeds higher than 10Mbps, be sure that the
Ethernet device has auto-negotiation (NWay) enabled for the connecting port.
Use standard CAT-5 cable with RJ-45 connectors. The RJ-45 port on the Router is a crossed port (MDI-X).
Follow standard Ethernet guidelines when deciding what type of cable to use to make this connection. When
connecting the Router directly to a PC or server use a normal straight-throug h cable. You should use a crossed
cable when connecting the Router to a normal (MDI-X) port on a switch or hub. Use a normal straight-through
cable when connecting it to an uplink (MDI-II) port on a hub or switch. The Ethernet Link LED indicator will
indicate a valid connection.
The rules governing Ethernet cable lengths apply to the LAN to Router connection. Be sure that the cable
connecting the LAN to the Router does not exceed 100 meters.
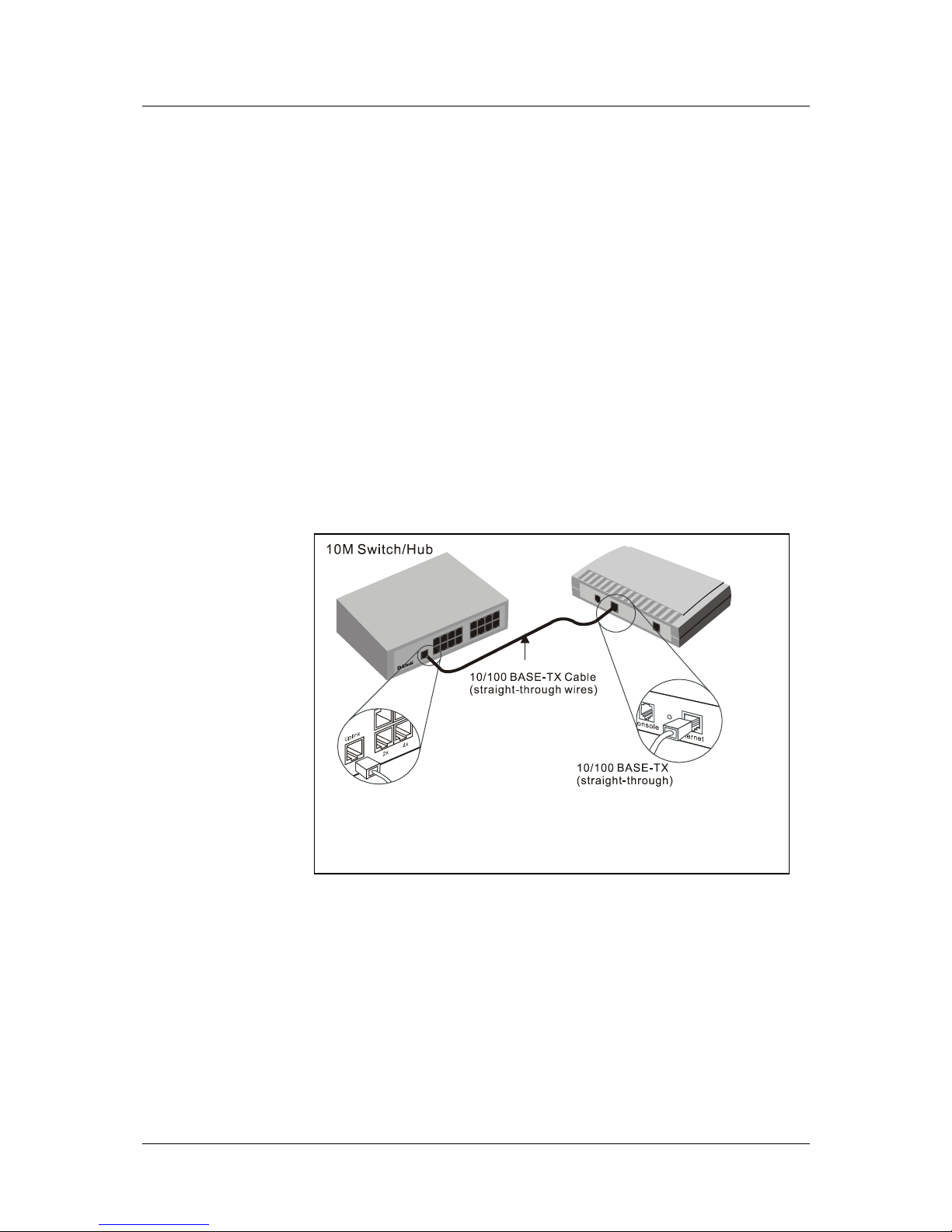
Hub or Switch to Router Connection
Connect the Router to an uplink port (MDI-II) on an Ethernet hub or switch with a straight-through CAT-5
networking twisted pair cable as shown in the diagram below:
If you wish to reserve
the uplink port on the
switch or hub for
another device, connect
to any on the other MDIX ports (1x, 2x, etc.)
with a crossed cable.
8

DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
Power On Router
To power on the device:
1. Insert the AC Power Adapter cord into the power receptacle located on the Router’s back panel, and plug
the adapter into a nearby power source.
2. You should see the Power LED indicator light up and remain lit.
9

DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
4
Configuring the Router for the First Time
The first time you setup the Router, it is recommended that you configure the Rou ter’s WAN connection by
using a single stand-alone computer that only connects to the Router’s Ethernet port. Once the WAN port is
properly setup and its connection is fully functional, you may continue making changes to its other
configurations including the IP settings and/or its DHCP server options. This chapter will focus on how to
properly setup your Router’s WAN connection. The following chapter describes the various menus used to
configure and monitor the Router including how to change IP settings and DHCP server options.
WAN Configuration Summary
1. Connect to the Router To configure the Router’s WAN connection, it is necessary to communicate
with the Router through its management interface, which is HTML-based, and it can be accessed using
a web browser. To access the management software, your computer must be able to “see” the Router.
Your computer can see the Router if it is in the same “neighborhood” or subnet as the Router’s. This is
accomplished by making sure that your computer has the correct IP settings which place it in the same
subnet as the Router’s. The easiest way to make sure your computer has the correct IP settings is to
enable your PC’s DHCP client option, and to automatically get the assigned IP addresses from the
default Router’s DHCP server operation. The next section describes how to change the IP configuration
for a computer running a Windows OS to be a DHCP client.
2. Configure the WAN Connection Once you have successfully logged-in the Router’s Web
configuration menu, you can proceed to change the settings for the ADSL connection and the Service
Provider’s signing-on process. There are different methods used to establish the connection to the
service provider’s network and ultimately to the Internet. You should know what Encapsulation and
connection type you are required to use for your ADSL service. It is also possible that you must change
the PVC settings used for the ADSL connection. Your service provider should provide all the
information you need to configure the WAN connection.
Configuring IP Settings on Your Computer
In order to configure your system to receive IP addresses from the Router, it must first have the TCP/IP protocol
installed. If you have an Ethernet port on your computer, it probably already has TCP/IP protocol installed. If
you are using Windows XP, the TCP/IP is enabled by default for the standard installations. Below is an
illustrated example of how to configure a Windows XP system to automatically ob tain the IP addresses fro m the
Router. Following this example is a step-by-step description of the procedures used with other Windows
operating systems. No matter what OS you have loaded on the PC, you will need to check first to see if its
TCP/IP protocol has been installed. If the TCP/IP protocol is not installed, you will need to go through the PC’s
network protocol installation process (provided in the later session) to properly install the TCP/IP protocol. Once
the protocol has been installed you can configure the PC to receive IP addresses from the Router.
10
DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
Configure Windows XP for DHCP
Use the following steps to configure a computer running Windows XP to be a DHCP client.
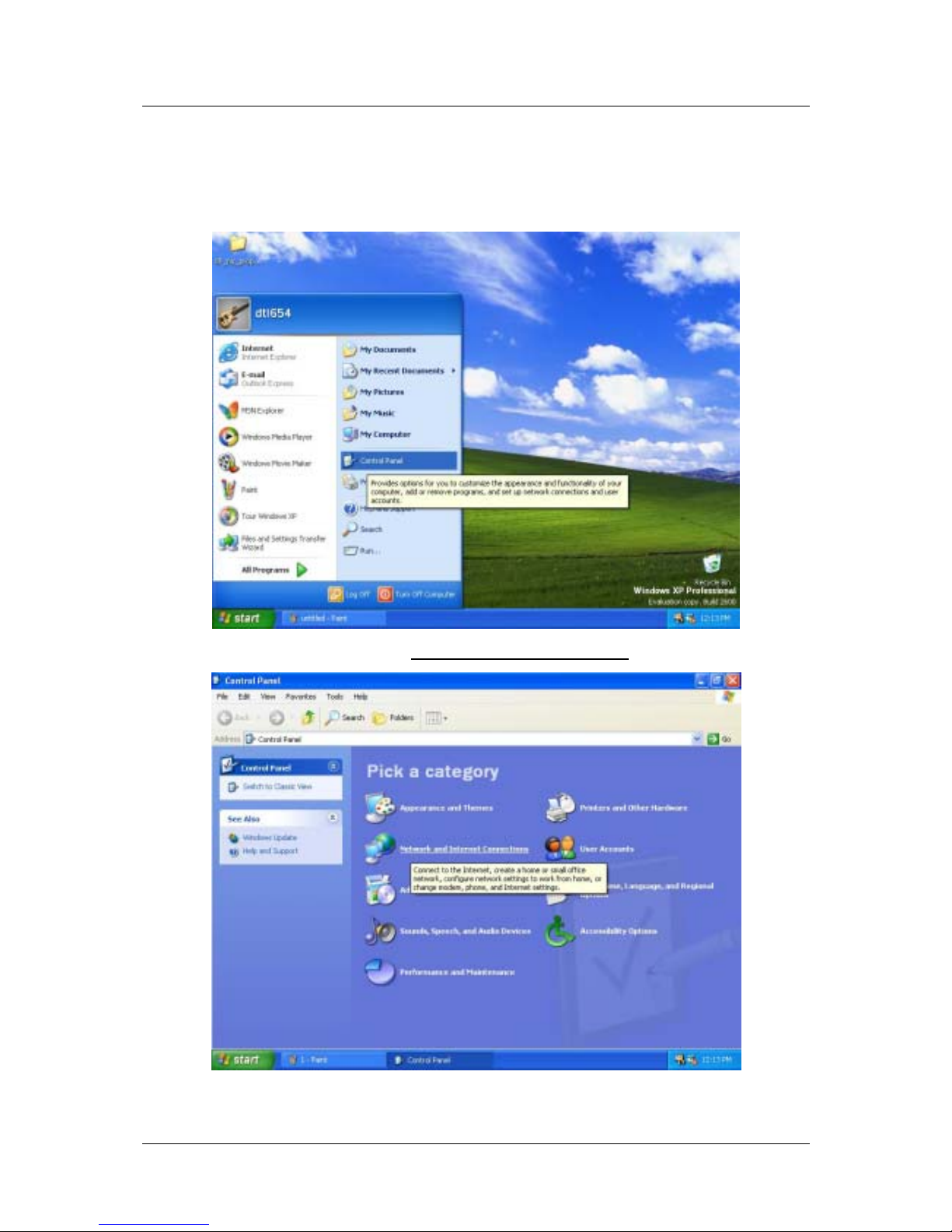
1. From the Start menu on your desktop, go to click on Control Panel.
2. In the Control Panel folder, click on Network and Internet Connections
.
11
DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
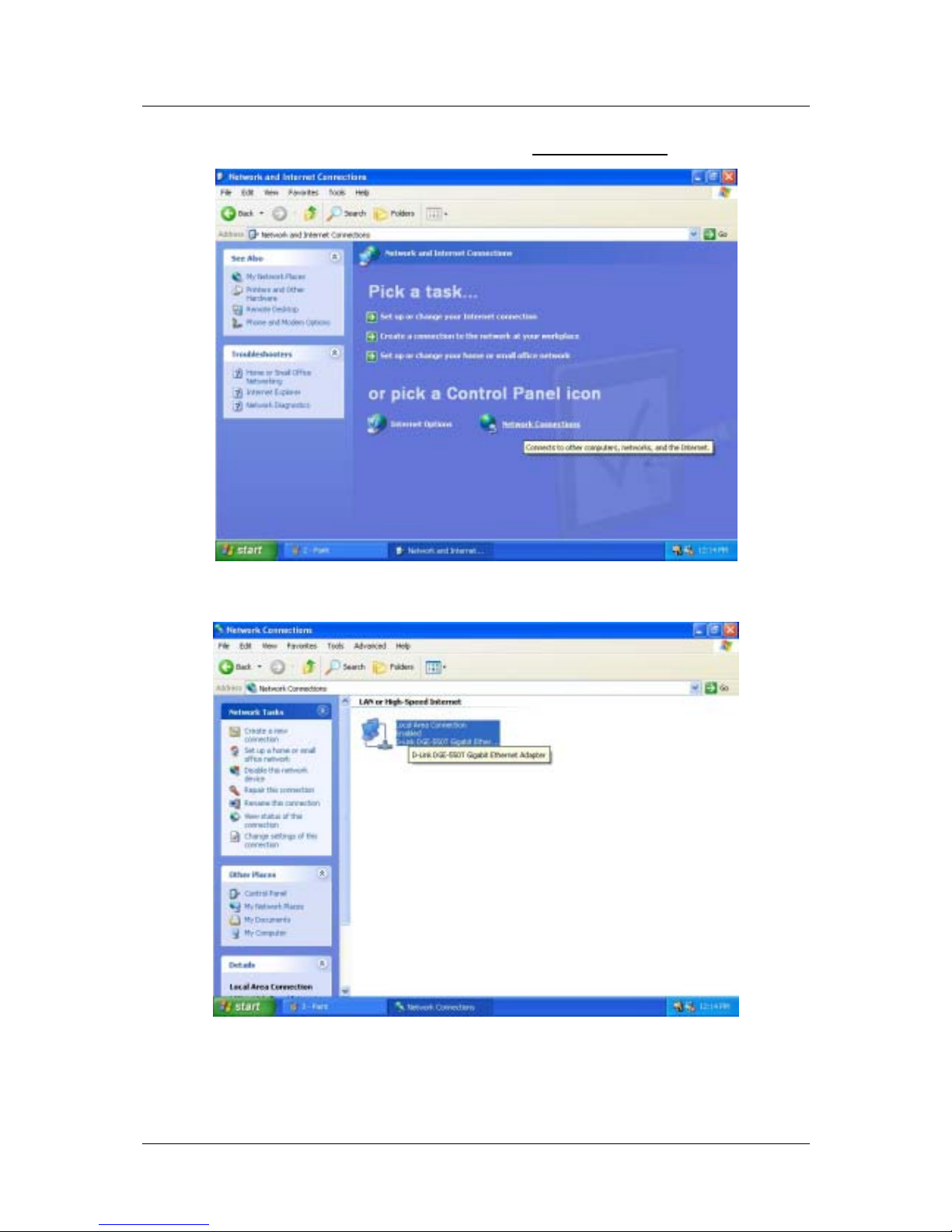
3. In the Network and Internet Connections folder, click on Network Connections
.
4. In the Network Connections folder, highlight the Local Area Connection icon by clicking on it once.
A new option is revealed under Network Tabs in the left side panel.
12
DSL-560I ADSL Router User’s Guide
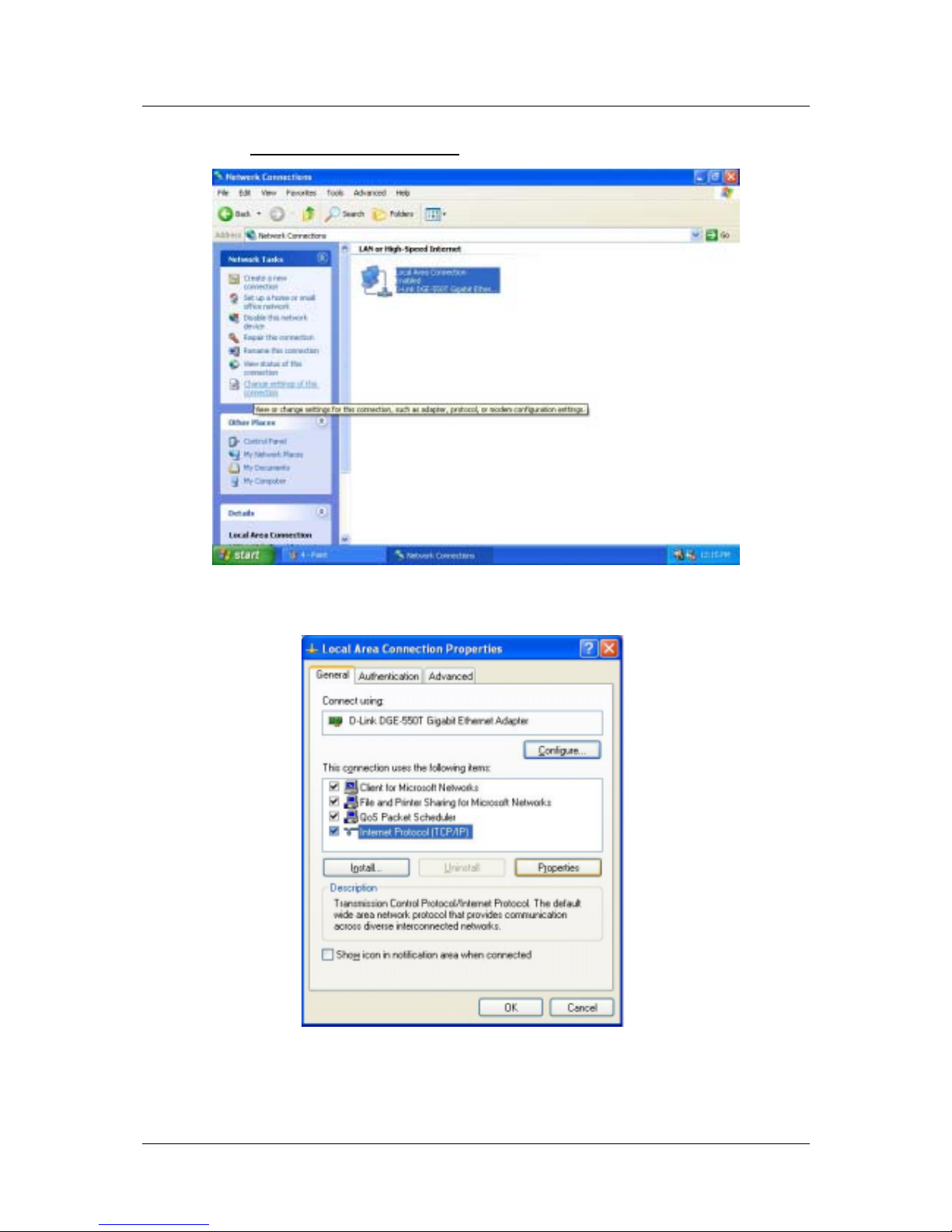
5. Click on Change settings of the connection
under Network Tabs.
6. In the General Tab of the Local Area Connection Properties menu, highlight Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) under “This connection uses the following items:” by clicking on it once. Click on the
Properties button.
13
 Loading...
Loading...