Page 1

RTK
User Manual
2020.03
v2.2
Page 2
Searching for Keywords
Search for keywords such as “battery” and “install” to find a topic. If you are using Adobe
Acrobat Reader to read this document, press Ctrl+F on Windows or Command+F on Mac to
begin a search.
Navigating to a Topic
View a complete list of topics in the table of contents. Click on a topic to navigate to that
section.
Printing this Document
This document supports high resolution printing.
Page 3
Information
There are two kinds of altitudes displayed in the DJI GS RTK app, absolute altitude and relative altitude.
Absolute altitude: The geographical attribute, in relation to longitude and latitude.
Relative altitude: The altitude data of the operation tasks relative to the Home Point. In the same operation,
the absolute altitude for the same point during the operation will vary when taking o from locations with different elevations.
Using this manual
Legends
Warning Important Hints and Tips Reference
Read Before the First Flight
Read the following documents before using the PHANTOMTM 4 RTK:
1. In the Box
2. User Manual
3. Quick Start Guide
4. Disclaimer and Safety Guidelines
5. Intelligent Flight Battery Safety Guidelines
We recommend that you watch all tutorial videos on the ocial DJITM website and read the Disclaimer and
Safety Guidelines before you y. Prepare for your rst ight by reviewing the Quick Start Guide and refer to
the User Manual for more details.
Watch the Tutorial Videos
Please watch the tutorial videos at the link below, which demonstrates how to use the
Phantom 4 RTK safely: http://www.dji.com/product/phantom-4-rtk/info#video
Download the DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom
Download DJI ASSISTANTTM 2 for Phantom from: http://www.dji.com/phantom-4-rtk/info#downloads
The operating temperature of this product is 0° to 40° C. It does not meet the standard operating
temperature for military grade application (-55° to 125° C), which is required to endure greater
environmental variability. Operate the product appropriately and only for applications that it meets the
operating temperature range requirements of that grade.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
2
©
Page 4

Contents
Information
Using this manual
Legends
Read Before the First Flight
Watch the Tutorial Videos
Download the DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom
Product Prole
Introduction
Features Highlights
Installation
Aircraft Overview
Remote Controller Overview
Aircraft
Prole
Flight Modes
Aircraft Status Indicators
Return to Home (RTH)
Industrial Applications
Vision System and Infrared Sensing System
RTK Functions
Flight Recorder
Attaching and Detaching the Propellers
DJI Intelligent Flight Battery
Remote Controller
Prole
Using the Remote Controller
Remote Controller Status LED
Linking the Remote Controlle
Multi-Aircraft Control Function
Gimbal and Camera
Camera
Gimbal
2
2
2
2
2
2
6
6
6
6
9
10
13
13
13
14
15
20
27
30
31
31
32
38
38
38
42
43
44
47
47
49
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
3
Page 5

DJI GS RTK App
Main Screen
Planning View
Camera View
Cloud PPK Service
Flight
Flight Environment Requirements
GEO (Geospatial Environment Online) System
Flight Restrictions
GEO Unlocking
Calibrating the Compass
PreightChecklist
Starting/Stopping the Motors
StoppingMotorsMid-ight
Flight Test
DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom
Installation and Launching
Using DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom
Appendix
Specications
Updating the Firmware 73
51
51
52
54
56
60
60
60
61
63
64
64
65
65
66
68
68
68
70
70
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
4
©
Page 6

Product Prole
This section introduces the Phantom
4 RTK and lists the components of the
aircraft and remote controller.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
5
Page 7

Product Prole
Introduction
The Phantom 4 RTK is a smart mapping and imaging drone capable of highly accurate mapping functions.
The aircraft has a built-in DJI Onboard D-RTKTM, which provides precision data for centimeter-level
positioning accuracy*. Multi-directional obstacle sensing achieved through vision and infrared sensors
enables intelligent obstacle avoidance during flight and indoor hovering and flight. The Phantom 4 RTK
records videos at 4K and captures 20 megapixel photos. The OCUSYNCTM HD video downlink built into
both the aircraft and remote controller ensures a reliable and stable transmission.
Features Highlights
The Phantom 4 RTK aircraft has a built-in DJI Onboard D-RTK, providing high-precision data for centimeterlevel positioning when used with Network RTK service or a DJI D-RTK 2. Raw satellite observations and
exposure event records can be used for post-processed kinematic (PPK) dierential corrections.
The Phantom 4 RTK can hover and y in extremely low altitude and indoor environments, and provides
multi-directional obstacle sensing and vision positioning functions. Obstacles detection and avoidance in
large range and landing protection enhance ight safety.
The Phantom 4 RTK is equipped with a 24 mm (35 mm format equivalent) wide angle camera, high-
precision and anti-shake gimbal, 1-inch CMOS sensor, mechanical shutter to oer the best in aerial photo
analysis.
Built into the remote controller is the latest DJI OcuSync technology with enhanced anti-interference
capability to deliver a more stable and smoother video downlink. When combined with the receiver in the
aircraft, the remote controller has a transmission range up to 4.3 mi / 7 km (FCC-compliant version). The
remote controller is equipped with a 5.5-inch high luminance monitor, and an integrated DJI GS RTK App
for real-time HD display. Users can plan ight paths and perform ight operations in the app for operation
types of Photogrammetry, Waypoint Flight, Linear Flight, Terrain Awareness Mode, and Block Segmentation.
For Photogrammetry, Linear Flight, Terrain Awareness Mode, and Block Segmentation operations, simply
tap on the map in the app or import les to set a ight area. For waypoint operations, y the aircraft to set
waypoints and congure waypoint actions, then the aircraft will be able to perform automated operations.
The remote controller’s Multi-Aircraft Control mode can be used to coordinate the operation of up to ve
aircraft at the same time, enabling pilots to work very eciently.
Image data from the Phantom 4 RTK can be used to generate maps for eld planning when operating a DJI
AGRASTM aircraft. Users can also import photos to the DJI PC GS Pro application or third-party mapping
software to composite highly accurate maps for dierent applications.
Installation
Preparing the Aircraft
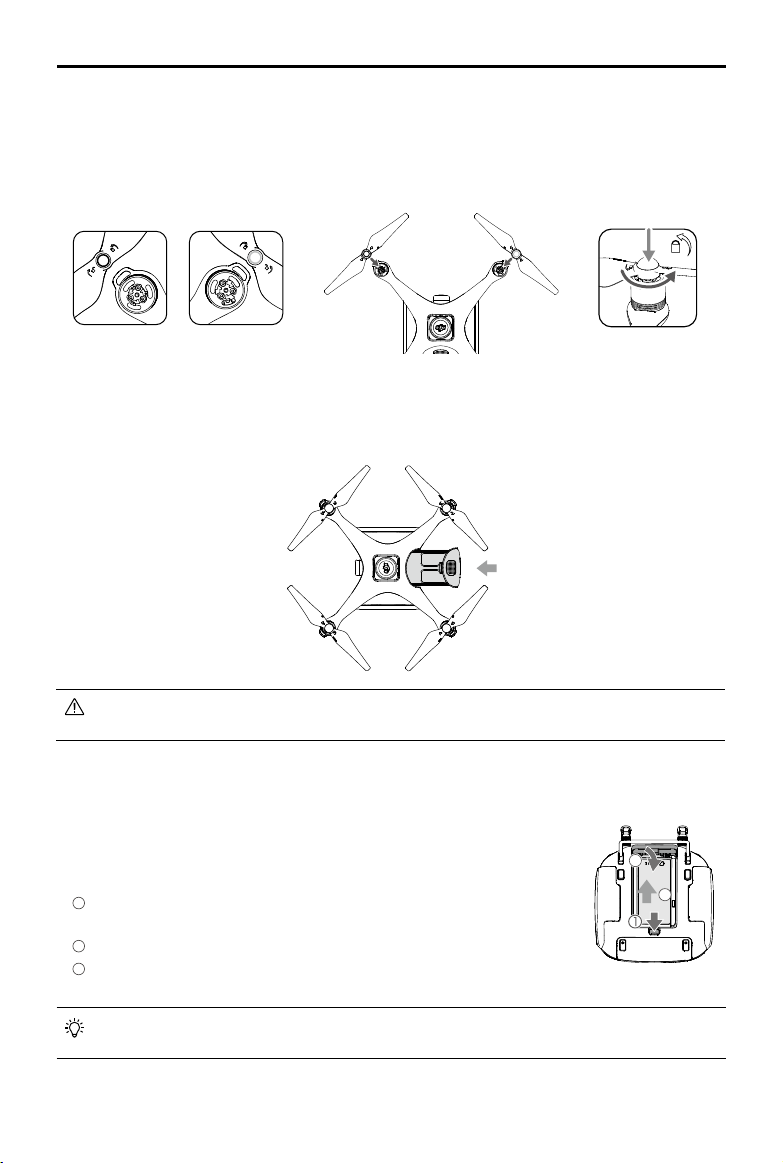
1. Remove the gimbal clamp from the camera as shown below:
* This should be used with Network RTK service, a DJI D-RTK 2 High-Precision GNSS Mobile Station (purchased
additionally) or post-processed kinematic (PPK) data (recommended when RTK signal is weak during operation).
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
6
©
Page 8
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
2. Attaching the Propellers
Mount the propellers with black propeller rings to the motors with black dots. Mount the propellers with
sliver propeller rings to the motors without black dots. Press the propeller down onto the mounting plate
and rotate in the lock direction until it is secured.
3. Battery Installation
Slide battery into the battery compartment according to the arrow’s direction as shown below.
When the upper and lower buckles on the battery are in place, a click sound indicates the battery is
securely installed. Failure to do so may aect the ight safety of your aircraft.
Preparing the Remote Controller
1. Mounting the Remote Controller Battery
The remote controller uses an easily removable interchangeable Intelligent
Battery for long-term operation.
1
Slide the battery compartment cover lock on the back of the remote
controller down to open the cover.
2
Insert the Intelligent Battery into the compartment and push it to the top.
3
Close the cover.
To remove the Intelligent Battery, open the cover, press and hold the battery release button, then
push the battery downward.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
3
2
7
Page 9
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
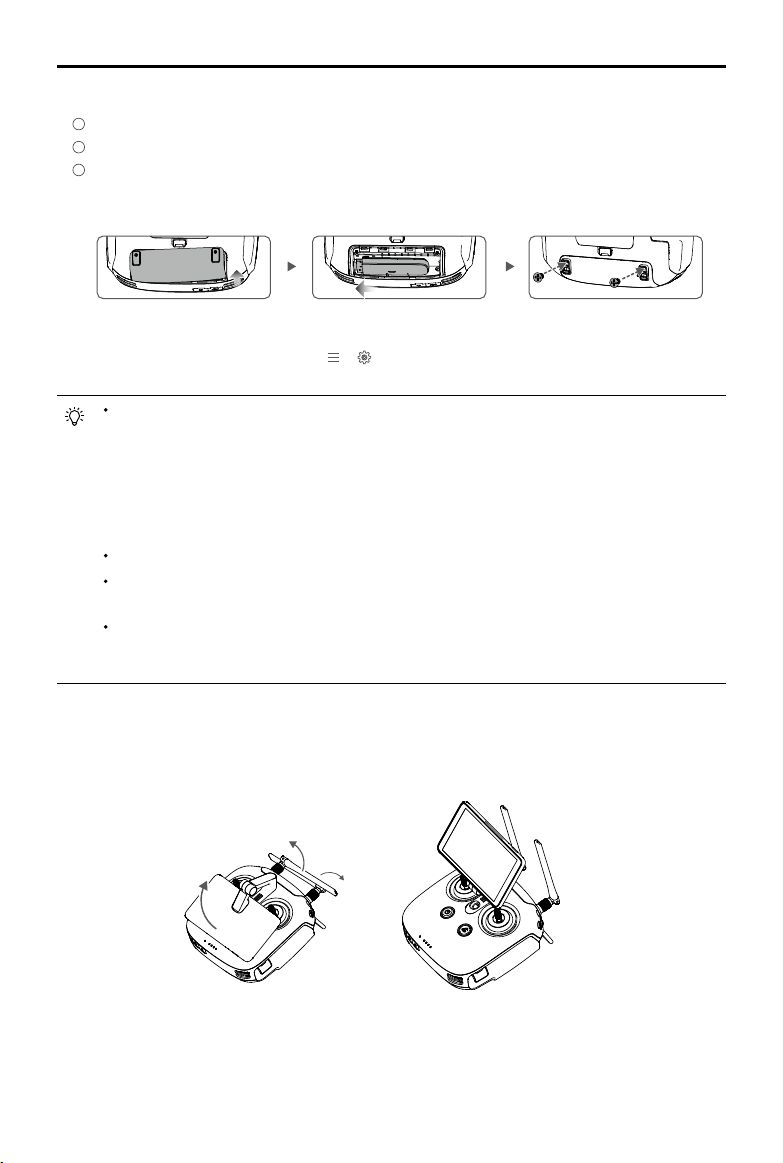
2. Mounting the Dongle and SIM Card
1
Lift the dongle compartment cover at the gap at its lower right corner, then remove it.
2
Insert the dongle into the USB port with the SIM card inserted into the dongle and test. *
3
Re-mount the cover. To secure the cover, open the silicone protectors on it, insert and tighten two
Phillips screws, then close the protectors.
* Test procedure: Press the remote controller power button once, then press again and hold to turn the remote
controller on. In the DJI GS RTK app tap > and select Network Diagnostics. If the statuses of all the
devices in the network chain are shown in green the dongle and SIM card are functioning properly.
The Phantom 4 RTK remote controller can access the Internet using a 4G dongle with SIM card or
Wi-Fi signal. For UK, EU, ACUK, or ACEU versions, a Network RTK server can only be accessed
using a 4G dongle with SIM card. For NA, AU or AFUS versions, using a 4G dongle with SIM card is
recommended, but a Wi-Fi signal can also be used. To conrm the version of your unit, please view
the version code after the product name on the label on the product packaging. When uploading or
downloading system logs or operation data, using a Wi-Fi signal for Internet access is recommended.
Only use a DJI approved dongle.
The dongle supports various network standards. Use a SIM card that is compatible with the chosen
mobile network provider and select a mobile data plan according to the planned level of usage.
The dongle and SIM card are used to enable the remote controller to access to specic networks
and platforms, such as the DJI AG platform. Be sure to mount them correctly, or else network access will not be available.
3. Unfolding the Remote Controller
Tilt the display device on the remote controller to the desired position, then adjust the antennas so they
are facing outward.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
8
©
Page 10
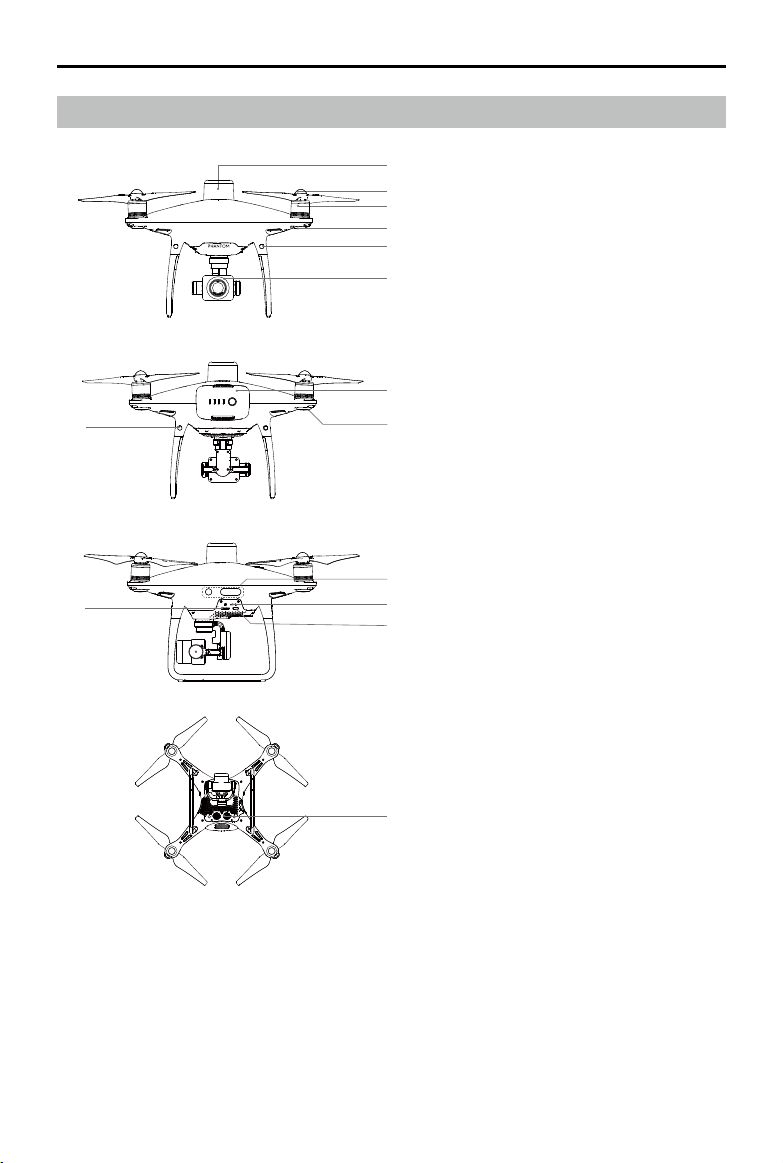
Aircraft Overview
9
13
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
1
2
3
4
5
6
1. Onboard D-RTK Antenna
2. Propellers
3. Motors
4. Front LEDs
5. Forward Vision System
6. Gimbal and Camera
7. Intelligent Flight Battery
7
8
8. Aircraft Status Indicator
9. Rear Vision System
10. Infrared Sensing System
11. Camera / Linking Status Indicator and
Link Button
12. Micro USB Port
13. Camera microSD Card Slot
10
11
12
14. Downward Vision System
14
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
9
Page 11
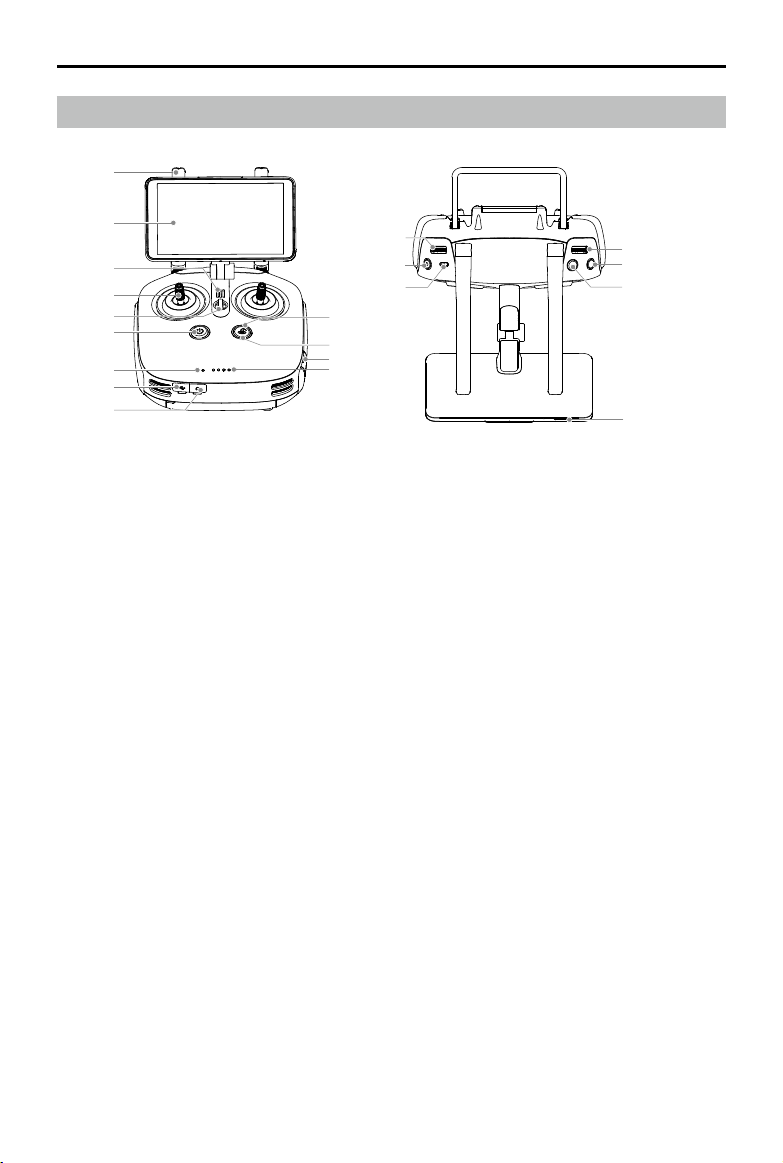
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Remote Controller Overview
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1. Antennas
Relays aircraft control signals.
2. Display Device
Android-based to run the DJI MG app.
3. Speaker
Audio output.
4. Control Sticks
Controls aircraft movement. Can be set to
Mode 1, Mode 2, or a custom mode.
5. Lanyard Attachment
Used to attach the remote controller lanyard.
6. Power Button
Used to turn the remote controller on and o.
7. Status LED
Indicates whether the remote controller is linked
to the aircraft.
8. USB-C Port
Connects to a computer via a USB-C cable
for conguration. Connects to the aircraft via a
USB-C OTG cable and a Micro USB cable for
aircraft rmware update.
9. 3.5 mm Audio Jack
Used to connect audio input/output devices.
10. Battery Level LEDs
Displays current battery level.
11. MicroSD Card Slot
Provides display device with up to 128 GB of
extra storage.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
10
©
14
15
16
13
12
11
10
20
19
18
17
12. RTH Status LED
Circular LED around the RTH button. Displays
RTH status.
13. RTH Button
Press and hold this button to initiate Return to
Home (RTH).
14. Gimbal Dial
Use this dial to control the tilt of the gimbal.
15. Video Recording Button
Press to start recording video. Press again to
stop recording.
16. Pause Switch
During a Photogrammetry or Waypoint operation,
toggle to pause the operation.
During RTH, toggle to pause RTH.
17. Sleep/Wake Button
Press to sleep/wake the screen; press and hold
to restart.
18. Shutter Button
Press to take a photo.
19. Reserved Button
20. Aircraft Control Switch Dial
Turn and press the dial to switch among
the aircraft when using Multi-Aircraft Control
function.
Page 12
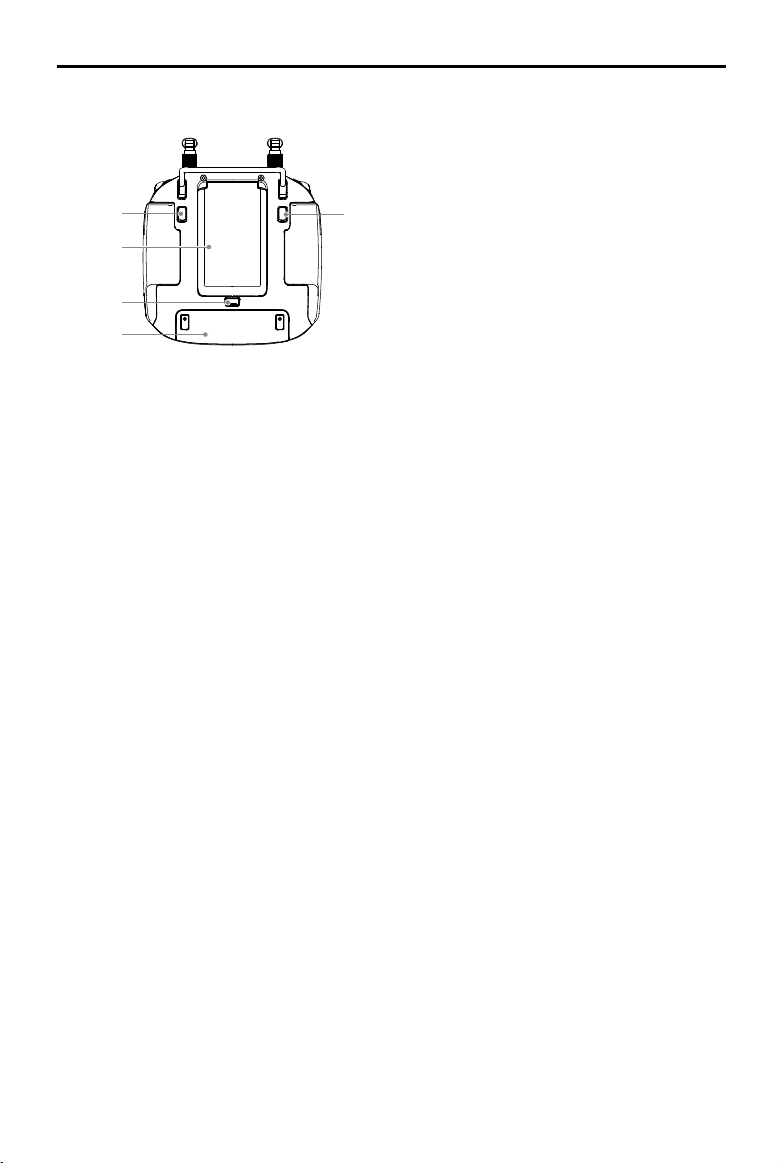
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
21. Button C1
Press Button C1 to switch between Map View
and Camera View.
22. Button C2
When you are planning a Waypoint Flight
22
23
21
operation, it adds a waypoint. The button is
disabled in any other operations.
23. Battery Compartment Cover
24
25
Open the cover to mount or remove the Intelligent
Battery from the remote controller.
24. Battery Compartment Cover Lock
Slide the lock down to open the cover.
25. Dongle Compartment Cover
Open the cover to mount or remove the dongle.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
11
Page 13

Aircraft
This section introduces the aircraft components,
features and functions.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
12
©
Page 14

Aircraft
Profile
The Phantom 4 RTK aircraft includes a flight controller, a communication system, a positioning system,
a propulsion system and an Intelligent Flight Battery. This section describes the functions of these
components.
Flight Modes
The Phantom 4 RTK uses a DJI dedicated ight controller, which provides the ight modes below:
P-mode (Positioning): P-mode works best when the GNSS signal is strong. The aircraft utilizes the GNSS /
RTK module and Vision System to automatically stabilize itself, navigate between obstacles, and perform a
Photogrammetry or Waypoint Flight operation.
When the GNSS signal is strong, the aircraft uses GNSS for positioning. When RTK module is enabled and
the dierential data transmission is good, it provides centimeter-level positioning. When the GNSS signal is
weak and the lighting conditions are sucient, the aircraft uses Vision System for positioning.
When the forward obstacle sensing is enabled and lighting conditions are sucient, the maximum ight
attitude angle is 25° with a maximum ight speed of 31 mph (50 kph). When forward obstacle sensing is
disabled, the maximum ight attitude angle is 35° and the maximum ight speed is 36 mph (58 kph).
A-mode (Attitude): GNSS and Vision System are NOT used for positioning and aircraft can only maintain
altitude using the barometer. It enters A-mode only when there is weak GNSS signal or when the compass
experiences interference where the Vision System is unavailable.
Attitude Mode Warning
The aircraft will y in P-mode by default. It enters A-mode only when there is weak GNSS signal or when the
compass experiences interference where the Vision System is unavailable.
In A-mode, the Vision System and some advanced features are disabled. Therefore, the aircraft cannot
position or auto-brake in this mode and is easily aected by its surroundings, which may result in horizontal
shifting. Use the remote controller to position the aircraft.
Maneuvering the aircraft in A-mode can be dicult. Avoid ying in areas where GNSS signal is weak, or
in conned spaces. The aircraft will otherwise be forced to enter A-mode, leading to potential ight risks,
please land it in a safe place as soon as possible.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
13
Page 15
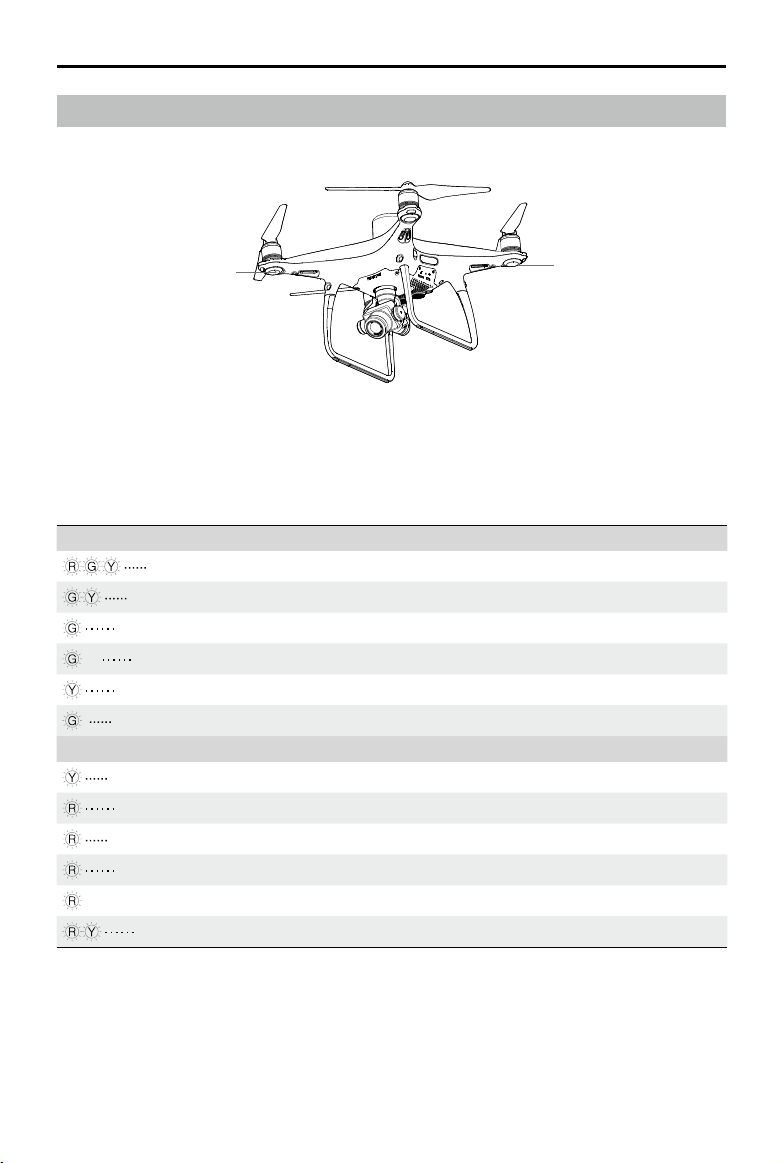
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Aircraft Status Indicators
The Phantom 4 RTK has Front LEDs and Aircraft Status Indicators. The positions of these LEDs are shown
in the gure below:
Front LEDs
The Front LEDs show the orientation of the aircraft. The Front LEDs glow solid red when the aircraft is turned
on to indicate the front (or nose) of the aircraft. The Aircraft Status Indicators communicate the system sta-
tus of the ight controller. Refer to the table below for more information about the Aircraft Status Indicators.
Aircraft Status Indicators
Aircraft Status Indicator Description
Normal
Alternate red, green and yellow ashing Turning On and Self Diagnostic Testing
Alternate green and yellow ashing Warming Up
Slow green ashing P-mode with GNSS or RTK
×2 Two green ashes P-mode with Vision System
Slow yellow ashing A-mode but No GNSS or Vision System
Fast green ashing Braking
Warning
Fast yellow ashing Remote Controller Signal Lost
Slow red ashing Low Battery Warning
Fast red ashing Critical Battery Warning
Red ashing Uneven Placement or Large Sensors Bias
— Solid red Critical Error
Alternate red and yellow ashing Compass Calibration Required
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
14
©
Page 16

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Return to Home (RTH)
Return to Home (RTH) function brings the aircraft back to the last recorded Home Point. There are three
types of RTH: Smart RTH, Low Battery RTH, and Failsafe RTH. This section describes these three scenarios
in detail.
GNSS
If a strong GNSS signal was acquired before takeo, the Home Point is the location
Home Point
The aircraft can sense and avoid obstacles when the Forward Vision System is enabled and lighting
conditions are sufficient. The aircraft will automatically climb up to avoid obstacles and descend
slowly as it returns to the Home Point. To ensure the aircraft returns home forwards, it cannot rotate
or y left and right during RTH while the Forward Vision System is enabled.
from which the aircraft launched. The GNSS signal strength is indicated by the GNSS
icon ( Less than 4 bars is considered a weak GNSS signal). The aircraft status
indicators will blink rapidly when the home point is recorded.
Description
Updating the Home Point
You can update the Home Point in the DJI GS RTK app during ight. There are two options for setting the Home
Point:
1. Set the aircraft’s current coordinates as the Home Point.
2. Set the remote controller’s current coordinates as the Home Point.
Ensure the space above the remote controller’s GNSS module (located beneath the DJI logo) is not
obstructed and that there are no tall buildings around when updating the Home Point.
Follow the instructions below to update the Home Point:
1. Go to DJI GS RTK > Fly.
2. Tap > , select in Home Point settings to set the aircraft's current coordinates as the
Home Point.
3. Tap > , select in Home Point settings to set the remote controller's current coordinates
as the Home Point.
4. The Aircraft Status Indicator will blink green to indicate that the new Home Point has successfully
been set.
Failsafe RTH
The Forward Vision System allows the aircraft to create a real-time map of its ight route as it ies. If the
Home Point was successfully recorded and the compass is functioning normally, Failsafe RTH will be
automatically activated if the remote controller signal is lost for more than three seconds. The aircraft will
plan its return route and retrace its original ight route home. During RTH, if the remote controller signal is
recovered, users can control the aircraft altitude and speed. Press the RTH button once to cancel RTH.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
15
Page 17
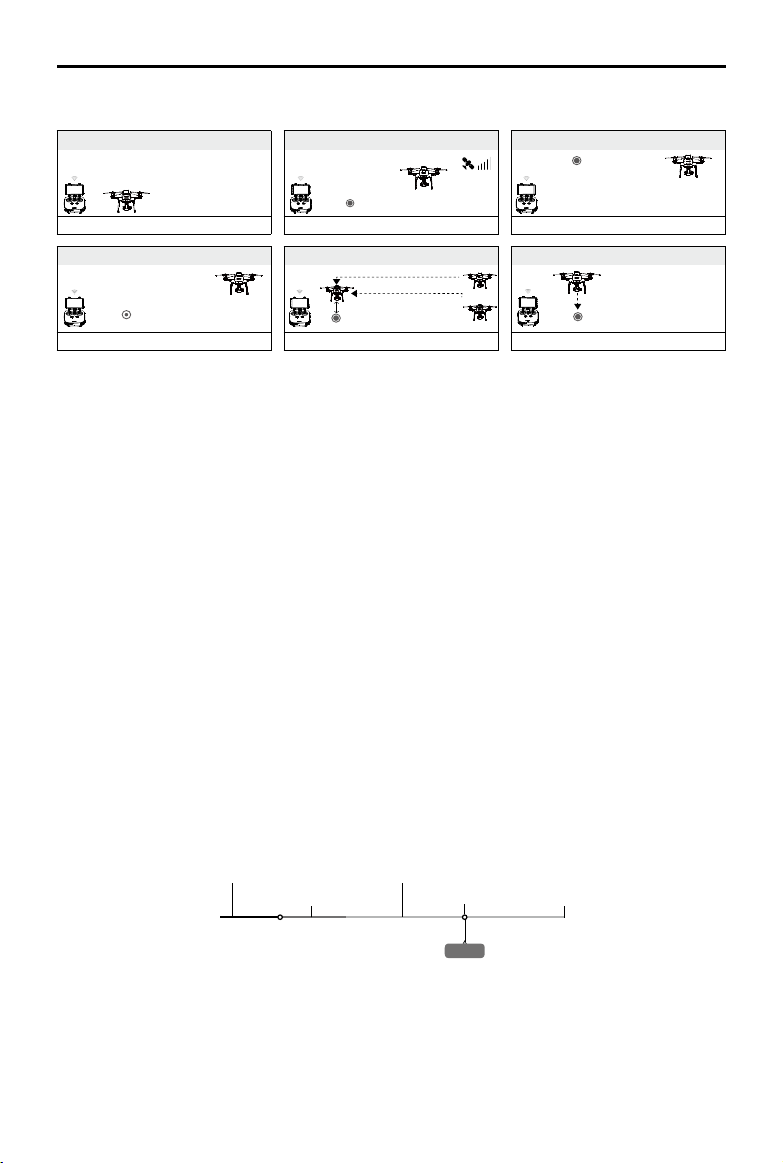
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Failsafe Illustration
1 Record Home Point
Blinking Green
4
Signal Lost Lasts (after 3 sec.)
>3S
× ×
Fast Blinking Yellow
2 Conrming Home Point
Blinking Green
5
RTH (adjustable altitude)
Height over HP>Failsafe Altitude
Elevate to Failsafe Altitude
Failsafe Altitude
Fast Blinking Yellow
Height over HP<=Failsafe Altitude
3 Remote Controller Signal Lost
×
Fast Blinking Yellow
6 Landing (after ho vering for 5 secs)
×
Fast Blinking Yellow
Smart RTH
Use the RTH button on the remote controller when GNSS is available to initiate Smart RTH. The aircraft will
then automatically return to the last recorded Home Point. Use the remote controller to control the aircraft’s
speed or altitude to avoid a collision during the Smart RTH process. As the aircraft returns, it will use the
primary camera to identify obstacles as far as 300m in front, allowing it to plan a safe route home. Press and
hold the Smart RTH button once to start the process, and press the Smart RTH button again to terminate
the procedure and regain full control of the aircraft.
Low Battery RTH
The low battery level failsafe is triggered when the DJI Intelligent Flight Battery is depleted to a point that
may aect the safe return of the aircraft. The user can cancel the RTH procedure by pressing the RTH
button on the remote controller. The thresholds for these warnings are automatically determined based on
the aircraft’s current altitude and distance from the Home Point. The Low Battery RTH will only be triggered
once during the same ight.
The aircraft will land automatically if the current battery level can only support the aircraft long enough to
descend from its current altitude. The user cannot cancel the auto landing but can use the remote controller
to alter the aircraft’s orientation during the landing process.
The Battery Level Indicator is displayed in the DJI GS RTK app, and is described below:
Critical Low battery level warning
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
16
©
(Red)
Low battery
level warning (Yellow)
Power requires to return home
Sucient battery
level (Green)
Remaining ight time
12:29
Battery level Indicator
Page 18
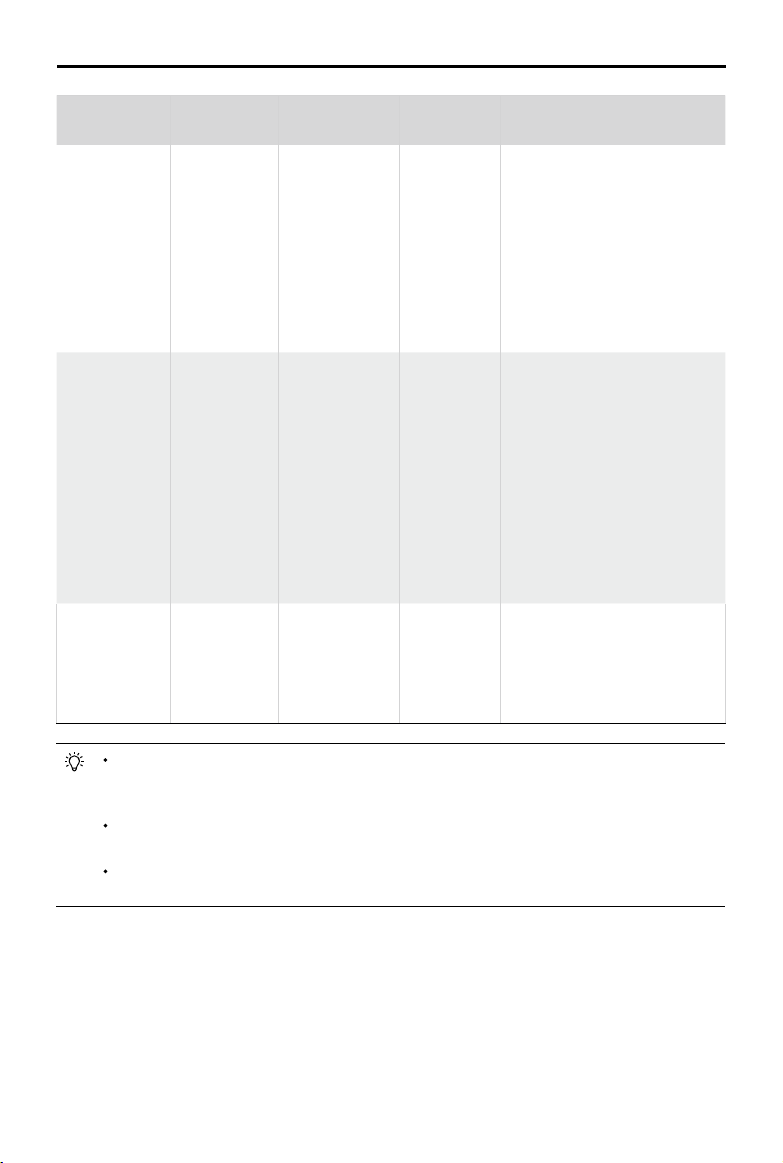
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Battery Level
Warning
Low battery
level warning
Critical Low
battery level
warning
Estimated
remaining ight
time
Remark
Battery power
is low. Fly the
aircraft back.
The aircraft
must land
immediately.
Estimated
remaining
ight based on
current battery
level.
Aircraft Status
Indicator
Aircraft status
indicator blinks
RED slowly.
Aircraft status
indicator blinks
RED quickly.
N/A N/A N/A
DJI GS RTK
App
N/A
The DJI GS
RTK app
display will
ash red and
the aircraft
will start to
descend.
The remote
controller will
sound an
alarm.
The aircraft will return to the
Home Point automatically and
hover at 2 meters above the
Home Point. Users can also
cancel the RTH process and land
manually. Note: The Low Battery
Level Warning will not prompt
after users cancel RTH and
regain control.
Allow the aircraft to descend and
land automatically.
Flight Instructions
When the Critical low battery level warning is triggered and the aircraft begins to land automatically,
push the left stick upward to make the aircraft hover at its current altitude, giving you an opportunity
to navigate to a more appropriate landing location.
The colored zones and markers on the battery level indicator bar reect the estimated remaining
ight time. They are automatically adjusted according to the aircraft’s current location and status.
The Low Battery Warning threshold set in the Aircraft Battery settings page in the app is only for an
alert and will not trigger RTH.
Precision Landing
The aircraft automatically scans and attempts to match the terrain features underneath during Return to
Home. When current terrain matches home point terrain, the aircraft will start landing immediately to achieve
precision landing.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
17
Page 19
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
5m
H
Landing Protection is active during precision landing.
Precision Landing performance is subject to the following conditions:
a) Home point is recorded upon take o, and cannot not be refreshed during ight.
b) Aircraft must take o vertically. Take o altitude must be greater than 7 meters.
c) Home point terrain features remain largely unchanged.
d) Home point terrain with no distinctive features will aect the performance.
e) Lighting conditions cannot be too light nor too dark.
The following actions are available during landing:
a) Pull throttle down to accelerate landing.
b) Moving the control sticks in any other direction will stop Precision Landing. The aircraft will descend
vertically and Landing Protection will remain active.
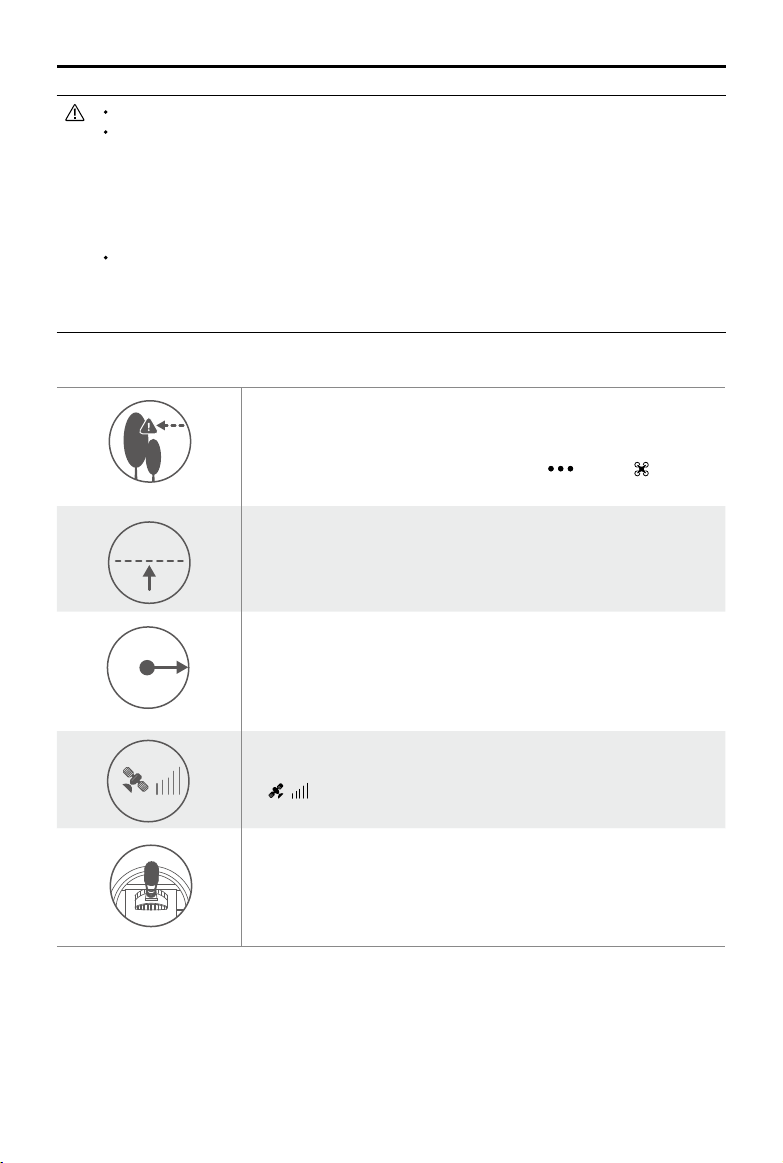
RTH Safety Notices
The aircraft cannot avoid obstruction during RTH when the Forward Vision
System is disabled. Users can use the remote controller to control aircraft
altitude and speed. It is important to set a suitable Failsafe altitude before
20m
each flight. Launch the DJI GS RTK app, tap
Failsafe Altitude.
If the aircraft is ying under 65 feet (20 meters) and RTH (including Smart
RTH, Low Battery RTH and Failsafe RTH) is triggered, the aircraft will rst
automatically ascend to 65 feet (20 meters) from the current altitude. You
can only cancel the ascending by exiting the RTH.
and tap to set the
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
18
©
5m
H
The aircraft will automatically descend and land if RTH is triggered when the
aircraft ies within a 16-feet (5 meters) radius of the Home Point and when
the aircraft altitude is under 98 feet (30 meters), or if the obstacle sensing
function is disabled. The aircraft will not ascend, and will land immediately
at the current location.
Aircraft cannot return to the Home Point when GNSS signal is weak
( [ ] displays grey) or the module is unavailable.
If you move the throttle stick after the aircraft rises above 65 feet (20
meters) but below the pre-set Failsafe RTH altitude, the aircraft will stop
ascending and immediately return to the Home Point.
Page 20
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
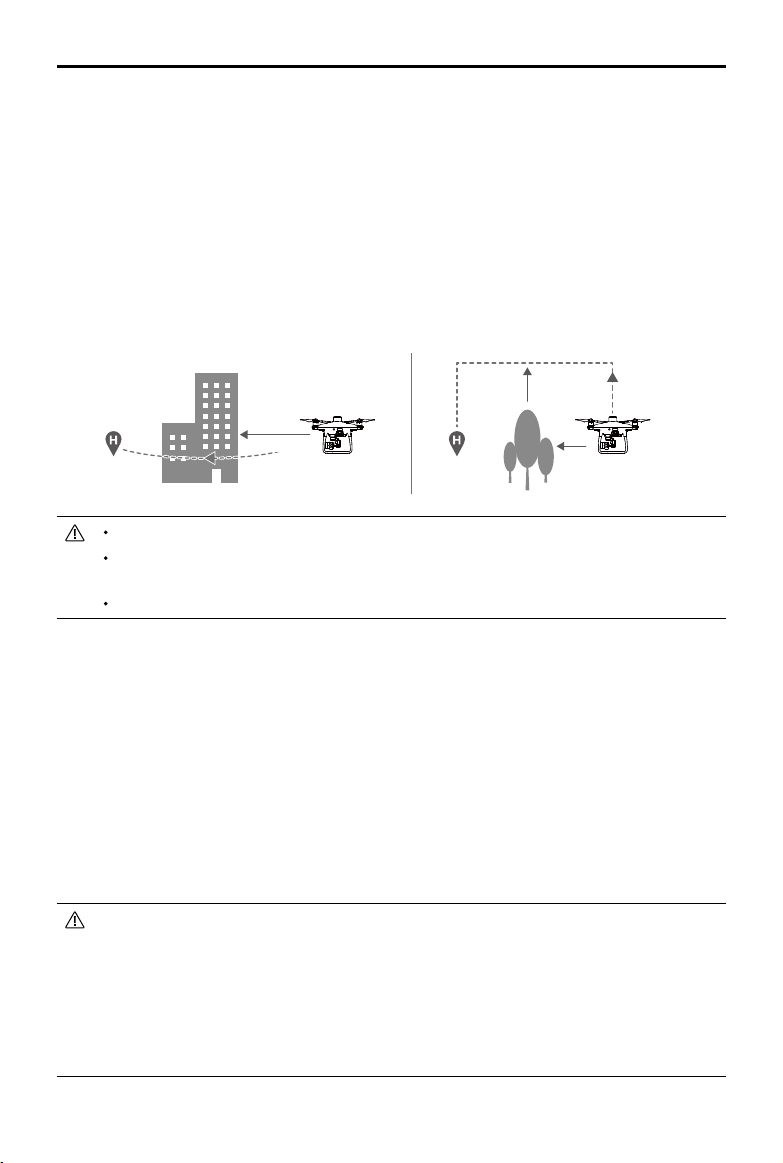
Obstacle Avoidance During RTH
Aircraft can now sense and actively attempt to avoid obstacles during RTH, provided that the lighting
conditions are adequate for the Forward Vision System. Upon detecting an obstacle, the aircraft will act as
follows:
1. The aircraft will use the primary camera to identify obstacles as far as 984 feet (300 meters) in front,
allowing it to plan a safe route home.
2. The aircraft decelerates when an obstacle is sensed at 49 feet (15 meters) ahead.
3. The aircraft stops and hovers then starts ascending vertically to avoid the obstacle. Eventually, the
aircraft will stop climbing when it is at least 16 feet (5 meters) above the detected obstacle.
4. Failsafe RTH procedure resumes, the aircraft will continue ying to the Home Point at the current altitude.
5 meters
300 meters
15 meters
The Obstacle Sensing function is disabled during RTH descent. Operate with care.
To ensure the aircraft returns home forwards, it cannot rotate during RTH while the Forward Vision
System is enabled.
The aircraft cannot avoid obstacles above, beside, or behind the aircraft.
Landing Protection Function
Landing Protection will activate during auto landing.
1. Landing Protection determines whether the ground is suitable for landing. If so, the aircraft will land
gently.
2. If Landing Protection determines that the ground is not suitable for landing, the aircraft will hover and
wait for pilot conrmation. The aircraft will hover if it detects the ground is not appropriate for landing
even with a critically low battery warning. Only when the battery level decreases to 0% will the aircraft
land. Users retain control of aircraft ight orientation.
3. If Landing Protection is inactive, the DJI GS RTK app will display a landing prompt when the aircraft
descends below 0.3 meters. Tap to conrm or pull down the control stick for 2 seconds to land when
the environment is appropriate for landing.
Landing Protection will not be active in the following circumstances:
•
a) When the user is controlling the pitch/roll/throttle sticks (Landing ground detection will re-activate
when control sticks are not in use)
b) When the positioning system is not fully functional (e.g. drift position error)
c) When the Downward Vision System needs re-calibration
d) When light conditions are not sucient for the Downward Vision System
• If an obstacle is within 1-meter of the aircraft, the aircraft will descend to 0.3m above the ground
and hover. The aircraft will land upon with user conrmation.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
19
Page 21
Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Industrial Applications
The Phantom 4 RTK can be used for industrial applications including but not limited to, photogrammetry and
power line inspections. Select Photogrammetry, Waypoint Flight, Linear Flight, Terrain Awareness, or Block
Segmentation, plan ight paths, set parameters, and then the aircraft will perform automated operations.
Operation resumption and obstacle avoidance are available. Users can import images to the DJI PC GS Pro
application or a third-party mapping software to composite highly accurate maps for dierent applications.
KML/KMZ les can be imported into the DJI GS RTK app to help plan operations.
KML/KMZ File Import
To plan operations, insert the microSD card with the KML/KMZ les into the microSD card slot on the remote
controller to import the les into DJI GS RTK. For les including polygons, users can view the data on the
map and use it to plan ight areas. For les including line strings, users can only view the data on the map,
but cannot use it for planning.
Preparing Files
1. Create a folder named “DJI” in the root directory of the microSD card. Then create a folder named “KML”
under this folder. (The letters are not case sensitive.)
2. Store the KML/KMZ les into the “KML” folder created above.
Importing Files
1. Insert the microSD card into the microSD card slot on the remote controller. There will be a pop-up
window on the main screen in the DJI GS RTK app then. If not, tap , then tap .
2. Tap the le in the window to select it. To delete the le, swipe to the left and tap . Select les and then
tap to import the les. Wait until the app indicates successful import.
Viewing Files
1. Go DJI GS RTK main screen > > , select KML Files in the drop-down menu on the top to view the
les. They are sort by time. KML le names displayed in the app are the original names of the les. KMZ
les will be named in sequence: doc, doc(1), doc(2), etc.
2. Tap the icon on the right of each le to enter Map View and view the data on the map.
Users can also tap on the left in Camera View or Map View, and then select KML File in the
drop-down menu to enter the le list page.
3. Tap Edit to edit the waypoints for photogrammetry operation planning if the waypoint number is fewer
than 125. Refer to the Photogrammetry section below for details on operation planning. If the waypoint
number is more than 125, users have to reimport KML/KMZ les that meet the requirements.
Photogrammetry
After the operation area has been set, and settings have been congured, the DJI GS RTK app produces
a flight route based on the user’s input. After planning, the aircraft can carry out automated operations
following the ight route. There are three types of Photogrammetry operations: 2D, 3D (Double Grid) and 3D
(Multi-oriented). The 2D ight route is s-shaped and can be used for digital orthophoto map (DOM). The 3D
(Double Grid) ight route consists of s-shaped routes that are crisscrossed to create 3D models. The default
values of the gimbal pitch angle for the two types are dierent. The 3D (Multi-oriented) ight routes consist of
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
20
©
Page 22

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
a single nadir view ight path and four oblique ight paths to create more accurate 3D models.
Planning a Flight Route
1. Add edge points of the operation area through the two methods below:
View the imported KML/KMZ file, and then tap Edit. The vertices of the polygon in the file will be
converted to the edge points of the operation area.
Go to the main screen in the DJI GS RTK app, tap Plan, and select Photogrammetry to enter Planning
View. Then tap on the map to add edge points.
2. Edit edge points
Move: Drag the point to move.
Fine Tuning: Tap the point to show Fine Tuning buttons. Tap to adjust.
Delete: Tap twice to delete a point.
3. Settings: After points are added, there will be a settings list on the right screen. Congure the settings
and the app will produce a corresponding ight route.
4. Adjust the route direction: Tap and drag the icon near the route to adjust the ight direction of the
produced route.
5. Tap Save, name the operation, and then tap OK.
Waypoint Flight
Fly the aircraft to desired positions, add waypoints and congure settings and actions for each waypoint.
The waypoints will produce a flight route in sequence. After the operation is started, the aircraft will fly
alongside the route and perform pre-set actions at each waypoint.
Planning Route
1. Go to the main screen in the DJI GS RTK app, tap Plan, and select Waypoint Flight to enter Planning View.
2. Fly the aircraft to the desired position, and short press the C2 Button on the remote controller once to
add a waypoint.
The position of the added waypoints cannot be adjusted. Users can edit the waypoint for other
congurations. See details below.
3. Edit waypoints
Tap the added waypoint on the map and there will be a settings list on the screen. Tap < / > to switch
among the waypoints to edit each waypoint.
Altitude: The relative altitude between the aircraft and the Home Point at the selected waypoint. The
aircraft will ascend or descend gradually to the altitude pre-set at the next waypoint if the values at the
two consecutive waypoints are dierent. Tap the button, and then slide up or down anywhere on the
screen to adjust the value.
Heading: The aircraft heading at the selected waypoint. North is 0°, with a positive value indicating
clockwise and a negative value indicating counter clockwise. The aircraft will rotate gradually to the
heading pre-set at the next waypoint if the values at the two consecutive waypoints are dierent. Tap the
button, and then slide up or down anywhere on the screen to adjust the value.
Pitch: The gimbal pitch angle at the selected waypoint. Pitch angle can range from -90° to 0°, with
downward represented by -90° and forward represented by 0°. The gimbal will tilt to the angle pre-set
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
21
Page 23

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
after reaching the selected waypoint. Tap the button, and then slide up or down anywhere on the screen
to adjust the value.
Action: Waypoint actions include: single shot, 3 continuous shots and none.
: Tap to delete the selected waypoint.
Users cannot add waypoints during Edit Mode. Waypoints can be added after tapping Save or
Cancel in the settings list.
4. Route settings: After waypoints are added, tap the route settings button on the lower right corner to
set an ending action for a task, action for when RC signal is lost, aircraft heading, cruising speed, and
route recording. (Note that if route recording is enabled, shooting actions set for all the waypoints will be
disabled, and the raw satellite observations will not be recorded.) Close the menu after conguration.
5. Tap Save, name the operation, and then tap OK.
Linear Flight Mission
The DJI GS RTK app automatically generates linear ight area and several independent ight paths after the
user has set the linear ight points, expansion distance, and linear ight cutting distance. Users perform the
operation, and the aircraft will automatically y alongside the selected ight paths in the linear ight area.
Planning a Flight Route
1. Add linear ight points by:
●
Viewing the imported KML/KMZ le, and then tapping Edit to convert points in the le to points in a
linear ight mission.
●
Going to the main screen in the DJI GS RTK app, tapping Plan, and selecting Linear Flight to enter
Planning View. Then tap on the map to add linear ight points.
2. Edit linear ight points
Move: Drag the point to move.
Delete: Tap twice to delete a point.
3. After points are added, there will be a settings list on the right side of the screen. Congure the settings
accordingly.
Expansion Distance to Left or Right: Adjusts the expansion distance to the left or right of the linear ight
area, where the front is dened by the line that any point on the linear ight path makes with the previous
point.
Linear Flight Cutting Distance: Divides linear ight areas with a long center line into multiple segments
according to this setting.
4. Tap Generate Flight Route. The app will generate the corresponding ight route. Each segment will have
a sub-mission with an independent ight route if the linear ight area is divided. Users can select the
desired ight route before performing the operation. Tap Back to edit the linear ight points and settings
mentioned above if needed.
5. After the ight route is generated, there will be a settings list on the right side of the screen. Congure the
settings accordingly. If sub-missions are created, the settings will apply to all of them.
Height: The altitude of the aircraft during the operation.
Speed: The ight speed during the operation.
Working Mode: The area where images are collected and the ight route generated will vary in dierent
working modes. If Full Coverage is selected, the ight route will include an extra path on both sides of the
linear ight area. If Eciency is selected, the ight route will just cover the linear ight area.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
22
©
Page 24

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Shooting Mode: Select between Timed Shooting and Distance Shooting.
Finish: Aircraft action after the operation is completed. Users can choose from RTH, hovering, landing,
and returning to the rst ight point.
Flight route generated along center line: Select whether the ight route generated will include the center
line. The center line refers to the line made by connecting the linear ight points added when planning the
ight route.
Camera Settings: Includes photo ratio, white balance, gimbal angle, shutter priority and distortion
correction.
If distortion correction is enabled, the image quality may be lower due to processing. It is
recommended to disable this option when original images are need for post processing.
Advanced Settings: Includes horizontal overlapping rate and vertical overlapping rate. The vertical
overlapping rate is the overlapping rate of two pictures captured consecutively in the same heading
along the ight path. The horizontal overlapping rate is the overlapping rate of two pictures taken on two
parallel paths.
6. Tap Save, name the operation, and then tap OK.
Terrain Awareness Mode
Import DSM les including altitude information to plan a Terrain Awareness Mode operation and perform
precise terrain follow ight.
Preparing Files
1. Create a folder named “DJI” in the root directory of the microSD card. Then create a folder named “DSM”
under this folder. (The letters are not case sensitive.)
2. In the DSM folder created in the previous step, create a folder for each DSM data set, and then put the
TIF and TFW les or a TIF le including TFW strings in the folder.
Make sure that there is only one TIF le and one TFW le in each folder. Otherwise, the les
may not be identied when importing.
Importing Files
1. Insert the microSD card into the microSD card slot on the remote controller. A window will pop up on the
main screen in the DJI GS RTK app. If not, tap , then tap .
2. Tap the le in the window to select it. Once selected, swipe to the left and tap to delete the le, or tap
Import to import the les. Wait until the app indicates a successful import.
Planning a Flight Route
1. Go to the main screen in the DJI GS RTK app, tap Plan, and select Terrain Awareness Mode to enter
Planning View. There will be a list of imported DSM les on the right side of the screen.
2. Tap the desired DSM le, and then tap Plan Task.
3. A white dotted box on the center of the map will indicate the area covered by the DSM le. Add and edit
edge points of the operation area in the white dotted box by:
●
Tapping the KML icon on the top of the screen, select the KML/KMZ le, and then tap Import. The
points in the le will be converted to the edge points for the operation area.
●
Tapping on the map to add edge points.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
23
Page 25

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Edit the edge points to adjust the location and shape of the operation area. The instructions are similar to
those for Photogrammetry operations.
If the points imported through the KML/KMZ le are outside of the dotted box, edit them to
make sure they are in the white dotted box so the operation can be performed.
4. After the edge points are added, the app will produce the ight route automatically. The curve of the
altitude of the whole ight route will be displayed at the bottom of the screen. Tap the point on the curve
to show the altitude of this point and the corresponding waypoint on the ight route will turn blue.
5. Congure other settings accordingly.
6. Tap Save, name the operation, and then tap OK.
Performing Operations
An operation can be performed directly after planning. Follow the instructions below if the operation was not
used immediately.
1. Power on the remote controller, and then power on the aircraft.
2. Go to the main screen in the DJI GS RTK app, and then tap Fly.
3. Tap in the Camera View for camera settings. Tap
and then select an operation route. Tap the map to enter Edit Status to edit the waypoints and adjust
operation settings, and then save.
4. Tap Invoke, and then tap Start. Wait for the ight route uploaded to the aircraft.
5. Takeo and perform the operation.
If you y the aircraft manually, slide to start the operation.
①
If the aircraft is on the ground, slide to takeo and start the operation.
②
on the left, select Plan in the drop-down menu,
Block Segmentation
Block Segmentation operations can be used to divide the operation area into several small blocks when the
operation area is large. Users can then y one aircraft to cover each block or y several aircraft using the
Multi-Aircraft Control function to cover dierent blocks.
Planning a Flight Route
1. Add edge points of the operation area by:
●
Viewing the imported KML/KMZ le, and then tapping Edit. The points in the le will be converted to the
edge points of the operation area.
●
Going to the main screen in the DJI GS RTK app, tapping Plan, and selecting Block Segmentation to
enter Planning View. Then tap on the map to add edge points.
2. Edit edge points
Move: Drag the point to move.
Fine Tuning: Tap the point to show Fine Tuning buttons. Tap to adjust.
Delete: Tap twice to delete a point.
3. A segmentation grid will be displayed on the map. Congure the grid as follows:
Set the area for segmentation: The size of the grid will change according to the area value for
segmentation.
Move the grid: Drag the grid to move.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
24
©
Page 26

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Adjust the direction of the grid lines: Tap and drag the icon near the grid to adjust the direction of the
grid lines. Tap -/+ for ne tuning.
4. Tap Next to divide the operation area into smaller blocks. Each block is a sub-mission. Tap the block to
select it and split the block or merge blocks. Tap Back to adjust the grid again if needed.
5. Tap Save, name the operation, and then tap OK.
6. Tap Edit to adjust the grid again. Tap Parameter Conguration to set the height, speed, shooting mode,
ending action, camera settings, overlapping rates, and enable altitude optimization. Tap and drag the
icon near the route to adjust the ight direction of the route. These settings will apply to all of the sub-
missions.
7. Tap Save, name the operation, and then tap OK.
Mission Assignment
When only one aircraft is used to perform operations, assign the desired blocks to the aircraft after selecting
the operation in the operation list.
When multiple aircraft are used to perform operations, link all the aircraft to one remote controller following
instructions for the Multi-Aircraft Control function, and then select the operation in the operation list. In this
case, bind an aircraft to each block in the aircraft list to assign the corresponding mission.
Important instructions for performing Block Segmentation operations with multiple aircraft:
Operate the remote controller at a location central to all the aircraft that will perform the
sub-missions to ensure optimal transmission.
Switch between aircraft to check all their status to ensure ight safety.
Make sure that the distance between each aircraft is more than 5 m. The distance
should be further if you want all aircraft to take off at the same time.
Performing Operations
1. Tap Start, and then wait for the ight routes to be uploaded to the aircraft.
2. Slide the slider for each aircraft to perform the mission bound to the aircraft.
3. Slide the slider at the bottom to take o all of the aircraft and perform all of the missions simultaneously.
You cannot have all aircraft take o at the same time if the number of linked aircraft exceeds the
number of blocks.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
25
Page 27

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Operation Safety Notices
Only take o in open areas.
The operation will be automatically cancelled if the motors are started before beginning the operation. You will need to recall the operation in the operation list.
During a Photogrammetry operation, the aircraft heading will follow the ight route. However, users
can control the heading (not recommended), and y forward or backward using the control sticks.
During a Waypoint Flight operation, the aircraft heading can be set to follow the ight route or the
customized angle pre-set for each waypoint in Route Settings. However, users cannot control the
heading with the control stick, but they can control the direction of ight (forward or backward).
During the operation, tap Pause on the screen and the aircraft will hover. Users can y the aircraft
forward or backward along the ight route. Tap Resume and the operation will resume from the cur-
rent position.
An operation can be paused by toggling the Pause switch. The aircraft will hover and record the
breakpoint, and then the aircraft can be controlled manually. To continue the operation, select it from
the list again and then resume. The aircraft will automatically return to the breakpoint and resume the
operation.
The aircraft will hover at the end point automatically once the operation is complete. Instead of RTH,
the aircraft can also be set to perform other ight actions within the app.
Operation Resumption
When exiting an operation, the aircraft will record a breakpoint. The Operation Resumption function allows
you to pause an operation temporarily (e.g., to change battery, and avoid obstacles manually) and then
resume operation at the breakpoint.
Recording a Breakpoint
Exit an operation through one of the following methods and the aircraft will record its location as a breakpoint
if GNSS signal is strong:
1. Tap the End button on the lower right corner of the screen.
2. Initialize the RTH procedure.
3. Toggle the Pause switch.
4. If the GNSS signal is weak, the aircraft enters Attitude mode and exits the current operation. The last
position where there was a strong GNSS signal is recorded as a breakpoint.
Ensure that GNSS signal is strong when using the Operation Resumption function. Otherwise, the
aircraft cannot record and return to the breakpoint.
The breakpoint is updated as long as it meets one of the above conditions.
Resuming Operation
1. Exit an operation through one of the above methods. The aircraft will record the current location as the
breakpoint.
2. The aircraft will end the current operation and record the operation progress. Users can control the
aircraft manually.
3. Select the operation in the Executing tag of the operation list again. The aircraft will automatically return
to the breakpoint and resume the operation.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
26
©
Page 28

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
System Data Protection
During an operation, the System Data Protection feature enables the DJI GS RTK app to retain vital system
data (e.g. operation progress, breakpoint) after the aircraft is powered o for battery replacement. Follow the
instructions in Operation Resumption to resume the operation after restarting the aircraft.
Vision System and Infrared Sensing System
The main components of the Vision System are located on the front, rear and bottom of the aircraft,
including [1] [2] [4] three stereo vision sensors and [3] two ultrasonic sensors. The Vision System uses
ultrasound and image data to help the aircraft maintain its current position, enabling precision hovering
indoors or in environments where a GNSS signal is not available. The Vision System constantly scans for
obstacles, allowing the aircraft to avoid them by going over, around, or hovering.
The Infrared Sensing System consists [5] of two 3D infrared modules on both sides of the aircraft. These
scan for obstacles on both sides of the aircraft and is active in certain ight modes.
[5]
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
Detection Range
The detection range of the Vision System and Infrared Sensing System are depicted as follow. Note that the
aircraft cannot sense and avoid the obstacles that are not within the detection range.
0.7m
13.1cm
6.8m
7m
0.7m
In P-mode, both the forward and the rear Vision Systems work if the speed is within 13mph (22kph).
At higher speeds, only the vision system facing the direction of travel is active.
6.8m
7m
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
27
Page 29

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Calibrating Sensors
Vision Systems cameras installed on the aircraft are calibrated on delivery. However these cameras are
vulnerable to excessive impact and will require occasional calibration via DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom. Follow
the steps below to calibrate the sensors.
01
02
Align the boxes
03
Pan and tilt the aircraft
Using Vision Positioning
Vision Positioning is activated automatically when the aircraft is turned on. No further action is required. Vision
Positioning is typically used in indoor environments, where GNSS is unavailable. Using the sensors that are
built into the Vision System, the aircraft can hover precisely even without GNSS. The Downward Vision System
works best when the aircraft is at altitudes of under 33 ft (10 m). Operate the aircraft with great caution when
ying at high speeds at low altitudes (under 0.5 m).
Follow the steps below to use Vision Positioning:
1. Turn on the aircraft. The aircraft status indicator will ash green two times, which indicates the Vision Po-
sitioning is ready.
2. Gently push the left stick up to lift o and the aircraft will hover in place.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
28
©
Page 30

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Assisted Braking from Obstacle Sensing
Powered by the Obstacle Sensing, the aircraft will now be able to actively brake when obstacles are
detected around the aircraft. Note that Obstacle Sensing function works best when lighting is adequate
and the obstacle is clearly marked or textured. The aircraft must y at no more than 31mph (50kph) to allow
sucient braking distance.
The 3D Infrared Sensing System is only active in Beginner mode* and Tripod mode*. Fly with
caution.
The performance of your Vision System and Infrared Sensing System are aected by the surface being
own over. Ultrasonic sensors may not be able to accurately measure distances when operating above
sound-absorbing materials and the camera may not function correctly in suboptimal environments.
The aircraft will switch from P-mode to A-mode automatically if neither vision sensors nor ultrasonic
sensors and Infrared Sensing System are available. Operate the aircraft with great caution in the following
situations:
a) Flying over monochrome surfaces (e.g. pure black, pure white, pure red, pure green).
b) Flying over a highly reective surfaces.
c) Flying at high speeds of over 31mph (50kph) at 2 meters or over 11mph (18kph) at 1 meter.
d) Flying over water or transparent surfaces.
e) Flying over moving surfaces or objects.
f) Flying in an area where the lighting changes frequently or drastically.
g) Flying over extremely dark (lux < 10) or bright (lux > 100,000) surfaces.
h) Flying over surfaces that can absorb sound waves (e.g. thick carpet).
i) Flying over surfaces without clear patterns or texture.
j) Flying over surfaces with identical repeating patterns or textures (e.g. tiling).
k) Flying over inclined surfaces that will deect sound waves away from the aircraft.
l) Flying over obstacles with too small eective infrared reective surface.
m) DO NOT position the sides of two aircraft toward each other to avoid interference between
the 3D infrared modules.
n) DO NOT cover the protective glass of the infrared module. Keep it clean and undamaged.
o) Flying at high speed at low altitude (under 0.5 m).
Keep sensors clean at all times. Dirt or other debris may adversely aect their eectiveness.
Vision Positioning is only eective when the aircraft is at altitudes of 0.3 to 10 meters.
The Vision Positioning may not function properly when the aircraft is ying over water.
The Vision System may not be able to recognize pattern on the ground in low light conditions (less
than 100 lux).
Do not use other ultrasonic devices with frequency of 40 kHz when Vision System is in operation.
* This mode will be supported later.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
29
Page 31

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
RTK Functions
The Phantom 4 RTK has a built-in DJI Onboard D-RTK, which provides more accurate data for centimeterlevel positioning to improve operation precision when using with the DJI D-RTK 2 High-Precision GNSS
Mobile Station or Network RTK service. The onboard D-RTK, providing precision position and speed
information combined with optimized algorithms, is more accurate than a standard compass sensor and
functions even with magnetic interference from metal structures, ensuring stable ight. If the RTK signal is
weak and dierential data cannot be transmitted during a Photogrammetry or Waypoint Flight operation,
users can read the raw satellite observations* recorded in the microSD card in the aircraft after the ight, and
then use PPK technology to achieve centimeter-level positioning.
Enable/Disable RTK
Ensure that the “RTK Function” is enabled and RTK service type is correctly set (D-RTK 2 Mobile Station or
Network RTK service) before each use. Go to Camera View in the DJI GS RTK app > > RTK to view and
set.
Make sure to disable RTK function if not in use. Otherwise, the aircraft will not be able to take o when there
is no dierential data.
Using with the DJI D-RTK 2 Mobile Station
1. Refer to the D-RTK 2 Mobile Station User Guide to complete linking between the aircraft and the mobile
station and setup of the mobile station.
2. Power on the mobile station and wait for the system to start searching for satellites. The RTK status icon
on top of the Camera View in the DJI GS RTK app will show to indicate that the aircraft has obtained
and used the dierential data from the mobile station.
After enabling the RTK function and connecting to a data source, be sure to wait for the aircraft’s
RTK module to nish initializing and the RTK / GNSS signal strength icon in the app shows FIX so
that the aircraft can take o.
Using with the Network RTK Service
The Network RTK service uses the remote controller instead of the base station to connect to an approved
Network RTK server for dierential data. Keep the remote controller on and connected to the Internet when
using this function.
1. Ensure that the remote controller is connected to the aircraft and has access to the Internet.
2. Go to Camera View in the DJI GS RTK app > > RTK, select the RTK service type to custom network
RTK, and then input the network information.
3. Wait for the remote controller to be connected with the Network RTK server. The RTK status icon on top
of the Camera View in the DJI GS RTK app will show to indicate that the aircraft has obtained and
used the RTK data from the server.
* The raw satellite observations are stored in the same directory as the aerial photos. They will only be recorded
during Photogrammetry or Waypoint Flight operations. For Waypoint Flight operations, route recording
should be disabled in Route Settings. Otherwise, the raw satellite observations cannot be recorded. In other
situations, such as ying the aircraft and shooting manually, the data will not be recorded.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
30
©
Page 32

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Flight Recorder
Flight data is automatically recorded to the internal storage of the aircraft. To access this data, connect the
aircraft to the PC through the Micro USB port and launch the DJI Assistant 2.
Attaching and Detaching the Propellers
Use only DJI approved propellers with your aircraft. The grey and black ring on the propeller indicate where
they should be attached and in which direction whey should spin.
Propellers Silver Ring Black Ring
Figure
Attach On Motors without black dots Motors with black dots
Legends
Lock : Turn the propellers in the indicated direction to mount and tighten.
Unlock : Turn the propellers in the indicated direction to loosen and remove.
Attaching the Propellers
1. Be sure to remove the warning stickers from the motors before attaching the propellers.
2. Mount the propellers with black propeller rings to the motors with black dots. Mount the propellers with
sliver propeller rings to the motors without black dots. Press the propeller down onto the mounting plate
and rotate in the lock direction until it is secured in its position.
Detaching the Propellers
Press the propellers down into the motor mount and rotate in the unlock direction.
Be aware of the sharp edges of the propellers. Handle with care.
Use only the DJI approved propellers. Do not mix propeller types.
Check that the propellers and motors are installed correctly and rmly before every ight.
Ensure that all propellers are in good condition before each ight. DO NOT use aged, chipped, or
broken propellers.
To avoid injury, STAND CLEAR of and DO NOT touch propellers or motors when they are spinning.
ONLY use original DJI propellers for a better and safer ight experience.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
31
Page 33

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
DJI Intelligent Flight Battery
The DJI Intelligent Flight Battery has a capacity of 5870 mAh, a voltage of 15.2 V, and a smart charge/
discharge functionality. It should only be charged using an appropriate DJI approved power adapter and
charging hub.
Intelligent Flight Battery AC Power Adapter Charging Hub
The Intelligent Flight Battery must be fully charged before using it for the rst time.
Never insert or remove the battery when it is turned on.
Ensure the battery is mounted rmly. The aircraft will not take o if the battery is mounted
incorrectly.
DJI Intelligent Flight Battery Functions
1. Battery Level Display: The LED indicators display the current battery level.
2. Auto-Discharging Function: To prevent swelling, the battery automatically discharges to below 65% of
total power when it is idle for more than ten days. It takes around two days to discharge the battery to
65%. It is normal to feel moderate heat being emitted from the battery during the discharge process.
3. Balanced Charging: Automatically balances the voltage of each battery cell when charging.
4. Overcharge Protection: Charging automatically stops when the battery is fully charged.
5. Temperature Detection: The battery will only charge when the temperature is between 5°C (41°F) and
40°C (104°F).
6. Over Current Protection: The battery stops charging when a high amperage (more than 8 A) is detected.
7. Over Discharge Protection: To prevent over-discharge damage, discharging automatically stops when
the battery voltage reaches 12 V.
8. Short Circuit Protection: Automatically cuts the power supply when a short circuit is detected.
9. Battery Cell Damage Protection: The DJI GS RTK app displays a warning message when a damaged
battery cell is detected.
10. Sleep Mode: To save power, the battery enter sleep mode after 20 minutes of inactivity.
11. Communication: Information pertaining to the battery’s voltage, capacity, current, etc. is transmitted to
the aircraft’s main controller.
Refer to Phantom 4 Series Intelligent Flight Battery Safety Guidelines before use. Users take full
responsibility for all operations and usage.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
32
©
Page 34

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Using the Battery
LED1
LED2
LED3
LED4
Power Button (Built-in LED)
Battery Level Indicators
Turning ON/OFF
Turning On:
Turning
Press the Power Button once, then press again and hold for 2 seconds to turn on. The Power
LED will turn green and the Battery Level Indicators will display the current battery level.
Press the Power Button once, then press again and hold for 2 seconds to turn o. The battery
Off:
power LED will flash when powering off the Phantom to allow automatically stopping of a
recording during the event recording wasn’t stopped.
Low Temperature Notice:
1. Battery capacity is signicantly reduced when ying in low temperature (< 0°C) environments.
2. It is not recommended that the battery be used in extremely low temperature (< -10°C) environments.
Battery voltage should reach the appropriate level when operating environment with temperatures
between -10°C and 5°C.
3. End the flight as soon as the DJI GS RTK app displays the “Low Battery Level Warning” in low
temperature environments.
4. Keep the battery indoors to warm it before ying in low temperature environments.
5. To ensure optimal performance of the battery, keep the battery temperature above 20°C.
6. The charger will stop charging the battery if the battery cell’s temperature is not within the operating
range (0°C ~ 40°C ).
In cold environments, insert the battery into the battery compartment and turn on the aircraft for
approximately 1-2 minutes to warm up before taking o.
Checking the Battery Level
The Battery Level Indicators display how much power remains. When the battery is turned o, press the
Power Button once. The Battery Level Indicators will light up to display the current battery level. See below
for details.
The Battery Level Indicators will also show the current battery level during charging and discharging.
The indicators are dened below.
: LED is on. : LED is ashing.
: LED is o.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
33
Page 35

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Battery Level Indicators
LED1 LED2 LED3 LED4 Battery Level
87.5%~100%
75%~87.5%
62.5%~75%
50%~62.5%
37.5%~50%
25%~37.5%
12.5%~25%
0%~12.5%
=0%
Charging the Intelligent Flight Battery
Air cool the Intelligent Flight Battery after each ight. Allow its temperature to drop to room
temperature before charging.
The charging temperature range is 5° to 40° C. The battery management system will stop the
battery from charging when the battery cell temperature is out of range.
Always turn o the battery before inserting it or removing it from the aircraft. Never insert or
remove a battery when it is turned on.
Using only the Power Adapter for Charging
1. Connect the AC power adapter to a power source (100-240 V 50/60 Hz).
2. Connect the Intelligent Flight Battery to the power adapter to start charging. If the battery level is above
95%, turn on the battery before charging.
3. The Battery Level Indicator will display the current battery level as it is charging.
4. The Intelligent Flight Battery is fully charged when the Battery Level Indicators are all o.
AC Power Adapter
Intelligent Flight Battery
Battery Level Indicators While Charging
LED1 LED2 LED3 LED4 Battery Level
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
34
©
Power Outlet
0%~25%
25%~50%
50%~75%
75%~100%
Fully Charged
Page 36

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Using the Power Adapter and Charging Hub for Charging
1. Connecting to a Power Source
Connect the power adapter to a power outlet (100-240V, 50/60Hz), then connect the charging bub to
the power adapter.
Charging Hub
AC Power Adapter
Power Outle
2. Connecting Batteries
Charging Mode:
Align the grooves on the Intelligent Flight Battery with the battery slot tracks to insert the battery and
begin charging. The Intelligent Flight Battery with the highest power level will be charged rst. Other
batteries will be charged in sequence according to their power levels.
If the Status LED Indicator of the charging hub is solid green and the LED lights on the Intelligent Flight
Battery turn o, charging is complete and the Intelligent Flight Battery can be disconnected from the
charging hub.
Storage Mode:
The charging hub will discharge batteries with more than 50% power to reduce the charge to 50%.
Meanwhile batteries with less than 50% charge will be charged to 50%.
Battery
Slot Track
Be sure to align the grooves on the Intelligent Flight Battery with the battery slot tracks. The Status
LED Indicator will turn solid yellow if the battery is properly inserted.
In storage mode, you can power on the Intelligent Flight Batteries to discharge them without having to
connect to a power source if all batteries have more than 50% power.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
35
Page 37

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Status LED Indicator Description
Status LED Indicator Description
Charging Mode
—
Solid Yellow
......
Blinking Green
—
Solid Green
—
Solid Red
......
All Blinking Red
Queuing to charge
Charging
Fully charged
No battery detected
Power supply error, please check the connection to the Battery Charger
Storage Mode
—
Solid Yellow
......
Blinking Blue
—
Solid Blue
—
Solid Red
......
All Blinking Red
Ready to charge or discharge
Charging or discharging
The battery’s power level is 50%
No battery detected
Power supply error, please check the connection to the Battery Charger
Battery Protection LED Display
The table below shows battery protection mechanisms and corresponding LED patterns.
Battery Level Indicators while Charging
LED1 LED2 LED3 LED4 Blinking Pattern Battery Protection Item
After these issues are resolved, press the Power Button to turn o the Battery Level Indicator. Unplug the
Intelligent Flight Battery from the charger and plug it back in to resume charging. Note that you do not need
to unplug and plug in the charger in the event of a room temperature error; the charger will resume charging
when the temperature is within the allowable range.
LED2 blinks twice per second Over current detected
LED2 blinks three times per second Short circuit detected
LED3 blinks twice per second Over charge detected
LED3 blinks three times per second Over-voltage charger detected
LED4 blinks twice per second Charging temperature is too low
LED4 blinks three times per second Charging temperature is too high
DJI does not take any responsibility for damage caused by third-party chargers.
If the battery level is above 95%, turn on the battery before charging.
How to discharge your Intelligent Flight Battery:
Place the Intelligent Flight Battery into the battery compartment and turn it on. Fly the aircraft out
doors until the battery level is low (such as 20% of power left).
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
36
©
Page 38

Remote Controller
This section describes the features
of the remote controller and includes
instructions for controlling the aircraft
and the camera.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
37
Page 39

Remote Controller
Profile
The Phantom 4 RTK remote controller has a transmission range of up to 4.3 mi / 7 km (FCC-compliant
version) with controls for camera tilt and photo capture. Built into the remote controller is the latest DJI
OcuSync to enhance anti-interference ability for more stable and smoother video downlink. The remote
controller includes a 5.5-inch high luminance monitor with integrated DJI GS RTK app for HD display. Users
can plan ight paths and perform both Photogrammetry and Waypoint Flight operations in the app. The
remote controller’s Multi-Aircraft Control mode can be used to coordinate the operation of up to ve aircraft
at the same time, enabling pilots to work more eciently.
Compliance Version: The remote controller is compliant with local compliance and regulations.
Stick Mode: Control can be set to Mode 1 or Mode 2, or to a custom mode.
Mode 1: The right stick serves as the throttle.
Mode 2: The left stick serves as the throttle.
Using the Remote Controller
Turning the Remote Controller On and O
The remote controller uses a removable, interchangeable Intelligent Battery. The battery level is indicated via
the Battery Level LEDs on the front panel after the battery is mounted. Follow the steps below to turn on
your remote controller:
1. When the remote controller is turned o, press the Power button once to check the current battery level,
indicated by the Battery Level LEDs. If the battery level is too low, recharge before use.
2. Press the Power button once. Then press and hold to turn on the remote controller.
3. The remote controller will beep when turned on. The Status LED will rapidly blink green, indicating that
the remote controller is linking to the aircraft. They will glow solid green when linking is complete.
4. Repeat Step 2 to turn o the remote controller.
The remote controller internal backup battery allows users to insert and remove the external Intelligent
Battery while the remote controller is still on and in use. The device will enter Sleep Mode to save
power. Users are then required to replace the Intelligent Battery within three minutes, or the remote
controller will power o.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
38
©
Page 40

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Charging the Remote Controller
Charge the remote controller Intelligent Battery using the included AC power adapter and Charging Hub.
1. Place the battery into the Charging Hub, connect the AC power adapter to the Charging Hub, and then
connect the charger to a power outlet (100-240V, 50/60Hz).
2. The Charging Hub will intelligently charge batteries in sequence according to battery power levels from
high to low.
3. The Status LED blinks green when charging and turns solid green when fully charged. The buzzer will
begin beeping when charging is complete. Remove the battery or turn o the buzzer to stop it.
Power Outlet
Charging Hub
AC Power Adapter
DO NOT charge the Intelligent Flight Battery together with the Intelligent Battery.
USB power supply port can be used to charge the mobile device of 5V/2A.
Status LED Description
Blinks Green Charging
Solid Green Fully charged
—
Blinks Red Battery Charger Error. Retry with an ocial battery charger.
Solid Red Battery error
—
Blinks Yellow
Solid Yellow Ready to charge
—
Alternating Green Blinks Intelligent Battery not detected
Battery temperature too high/low. Temperature must be within operating
range (5°-40℃)
Controlling the Camera
Shoot videos/photos, and adjust gimbal pitch
angle via the Shutter Button, Record Button,
and Gimbal Dial on the remote controller.
1. Gimbal Dial
Control the tilt of the gimbal. Turn left to tilt the gimbal upward and right to tilt the gimbal downward.
2. Video Recording Button
Press once to start recording video, then press again to stop recording.
3. Shutter Button
Press to take a photo.
1
2
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
3
39
Page 41

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Controlling the Aircraft
This section explains how to control the orientation of the aircraft through the remote controller. Control can
be set to Mode 1 , Mode 2 or Mode 3, or to a custom mode.
Mode 1
Mode 2
Mode 3
Left Stick
Forward
Backward
Turn RightTurn Left
Right Stick
Right StickLeft Stick
Up
Down
Turn RightTurn Left
Left Stick Right Stick
Forward
Up
Down
RightLeft
Forward
Backward
RightLeft
Up
Backward
RightLeft
The Remote Control is set to Mode 2 by default.
Stick Neutral/Mid-Point: Control sticks are in the center position.
Moving the Control Stick: The control stick is pushed away from the center position.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
40
©
Down
Turn RightTurn Left
Page 42

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Remote
Controller
(Mode 2)
( Indicates Nose Direction)
Aircraft
Remarks
Moving the left stick up and down changes the
aircraft’s elevation.
Push the stick up to ascend and down to descend.
When both sticks are centered, the aircraft will hover
in place.
The more the stick is pushed away from the center
position, the faster the aircraft will change elevation.
Always push the stick gently to prevent sudden and
unexpected elevation changes.
Moving the left stick to the left or right controls the
rudder and rotation of the aircraft.
Push the stick left to rotate the aircraft counterclockwise, push the stick right to rotate the aircraft
clockwise. If the stick is centered, the aircraft will
maintain its current orientation.
The more the stick is pushed away from the center
position, the faster the aircraft will rotate.
Moving the right stick up and down changes the
aircraft’s forward and backward pitch.
Push the stick up to fly forward and down to fly
backward. The aircraft will hover in place if the stick is
centered.
Push the stick further away from the center position
for a larger pitch angle (maximum 30˚) and faster ight.
Moving the right stick control left and right changes
the aircraft’s left and right pitch.
Push left to y left and right to y right. The aircraft
will hover in place if the stick is centered.
During an automatic ight, toggle the Pause Switch
to exit from the automatic ight. The aircraft will hover
at the current position.
Adjusting Controller Sticks
Hold and twist the controller sticks clockwise or counter clockwise to adjust the
length of the controller sticks. A proper length of controller sticks can improve
the controlling accuracy.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
41
Page 43

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
RTH Button
Press and hold the RTH button to start the Return to Home (RTH) procedure. The LED ring around the RTH Button
will blink white to indicate that the aircraft is entering RTH mode. The aircraft will then return to the last recorded
Home Point. Press this button again to cancel the RTH procedure and regain control of the aircraft.
Optimal Transmission Range
The transmission signal between the aircraft and the remote controller is most reliable within the area that
depicted below:
Optimal Transmission RangeStrong Weak
Ensure that the aircraft is ying within the optimal transmission zone. To achieve the best transmission performance, maintain the appropriate relationship between the operator and the aircraft.
Remote Controller Status LED
The Status LED reects the strength of the connection between the remote controller and the aircraft. The
RTH LED indicates the RTH status of the aircraft. The table below contains more information about these
indicators.
RTH LED
Status LED
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
42
©
Page 44

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Status LED Alarm Remote Controller Status
— Solid Red Chime The remote controller is disconnected from the aircraft.
— Solid Green Chime The remote controller is connected to the aircraft.
Slow Blinking Red D-D-D
/
Red and Green/ Red and
......
Remote controller error.
None HD downlink is disrupted.
Yellow Alternate Blinks
RTH LED Sound Remote Controller Status
— Solid White Chime Aircraft is returning home.
Blinking White D
Blinking White DD
. . .
.. .. ..
Sending RTH command to the aircraft.
RTH procedure in progress.
The Remote Controller Status Indicator will blink red and sound an alert, when the battery level is critically low.
Linking the Remote Controlle
The remote controller is linked to your aircraft by default. Linking is only required when using a new remote
controller for the rst time. If using Multi-Aircraft Control function, linking all the aircraft to the same remote
controller is required.
1. Power on the remote controller and open the DJI GS RTK app. Power on the aircraft.
2. Tap Fly to enter Camera View and tap > . Select Aircraft as the linking device, tap Single Linking
or Multi Linking (if Multi-Aircraft Control is in use), and then tap Pairing. The Status LED blinks blue and
the remote controller sounds double beep repeatedly, indicating that the remote controller is ready for
linking.
Linking
Press the aircraft’s linking button to
continue
End linking
3. Press the Link button on the aircraft. Then release and wait for a few seconds.
4. The Status and Link LED will glow solid green if linking is successful. If the Link LED does not glow solid
green, linking failure occurred. Enter linking status again and retry.
5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 to complete linking between all the aircraft (up to ve) and the remote controller, if
Multi Linking is selected. Then tap End linking.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
43
Page 45

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Multi-Aircraft Control Function
The remote controller features Multi-Aircraft Control function which can be used to coordinate the operation
of up to ve aircraft at the same time, enabling pilots to work very eciently. Turn the Aircraft Control Switch
Dial on the remote controller to switch between dierent aircraft for single control of the desired aircraft.
When using the Multi-Aircraft Control function, to avoid interference among operation groups, do not
operate more than three groups within a 50-meter radius. Unless using the Phantom 4 RTK with a DJI
D-RTK 2 Mobile Station, it is necessary to manually congure each remote controller’s serial number in
the DJI GS RTK app.
Enter Multi-Aircraft Control Mode
1. Link all the aircraft (up to five) to the same remote controller according to the steps in “Linking the
Remote Controller”.
2. Close the settings menu after linking. The linked aircraft will be listed on the left of the screen sorted by
number.
Switch Control
Users can switch control among dierent aircraft via the aircraft status box on the left screen in the app or
the Aircraft Control Switch Dial on the remote controller. The Front LEDs of the selected aircraft will be solid
red while the Front LEDs of other aircraft will be solid yellow.
Switch in the App
Tap the status box of the corresponding number in the app. The side of the box will turn blue and the Front
LEDs of the aircraft will blink red quickly, indicating the corresponding aircraft has been selected.
Switch by the Dial
1. Turn the Aircraft Control Switch Dial on the remote controller. There will be an arrow near the
corresponding status box in the app, and the Front LEDs of the aircraft will blink yellow quickly, indicating
the corresponding aircraft is in pre-selected status.
2. Press the dial once. The side of the box in the app will turn blue and the Front LEDs of the aircraft will
blink red quickly for a few seconds and then turn to solid red, indicating the corresponding aircraft has
been selected.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
44
©
Page 46

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Multi-Aircraft Operations
1. Select the desired aircraft by switching control.
2. Tap the status box of the selected aircraft, then tap on the left of the screen, or tap on top of the
screen to select and use an operation in the Plan tag. Perform the operation after setting operation
parameters. The selected ight routes data will be uploaded to the aircraft.
3. Use an operation to each aircraft. Tap to show the status boxes of all the aircraft and tap another
status box to switch to the corresponding aircraft.
4. Tap Start after using operations for all the aircraft. Users can slide the sliders for each aircraft in the
prompted window or slide the slider for all aircraft at the bottom position to take o all the aircraft and
start operations at the same time.
5. If there is any emergency during operation, toggle the Pause Switch on the remote controller to brake all
the aircraft. Then all operations will be paused and the aircraft will hover in place and can be controlled
manually. To continue the operation, users should use the operation again in Executing tag in icon.
During multi-aircraft operations, aircraft will automatically avoid each other based on positioning
information. When the distance between aircraft is 15 m, they will slow down, and when the distance
is 5 m, the aircraft will not be able to get any closer to each other.
Exit from Multi-Aircraft Control Mode
Users can exit from the mode through the following three methods.
Method 1: Link the remote controller to the only one desired aircraft according to the previous instructions
(Single-Machine Pairing should be selected).
Method 2: Delete other aircraft and remain the only one aircraft in the Linked Aircraft list. So the remote
controller can control this aircraft only.
Method 3: Power o the other aircraft that don’t need control and power on the only one desired aircraft.
So the remote controller can control this aircraft only. Note: if power on the other aircraft again, the remote
controller and the linked aircraft will enter Multi-Aircraft Control mode automatically. Exit from this mode
completely through method 1 or 2 if needed.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
45
Page 47

Gimbal and Camera
This section provides the technical
specications of the camera and
explains the gimbal’s operation modes.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
46
©
Page 48

Gimbal and Camera
Camera
Prole
The Phantom 4 RTK camera uses a 1-inch CMOS sensor with eective pixels of 20 M and a 24 mm (35 mm
format equivalent) wide-angle lens. It is equipped with a blue glass lter to deliver enhanced picture quality
and a UV lens for additional protection. An ND lter can be used when the operating environment is too
bright.
The Phantom 4 RTK supports the capture of 4K at 30fps and a maximum video bitrate of 100 Mbps.
The 20 megapixel photos taken by Phantom 4 RTK is the result of the application of advanced image
processing technique. A mechanical shutter with a 1/2000 max speed eliminates rolling shutter distortion
when capturing stills of fast moving objects.
Camera Micro SD Card Slot
To store your photos and videos, insert the microSD card into the slot as shown below before turning on the
aircraft. The Phantom 4 RTK comes with a 16 GB microSD card and supports microSD cards up to 128 GB.
A UHS-1 and above microSD card is recommended due to their fast read and write speeds that support
high-resolution video data. Users can read the photos and videos, and the raw satellite observations during
Photogrammetry and Waypoint Flight operations from the microSD card.
Do not remove the microSD card from the aircraft when it is shooting.
To ensure the stability of the camera system, single video recordings are capped at 30 minutes.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
47
Page 49

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Micro USB Port
Turn on the aircraft and connect a Micro USB cable to the Micro USB Port to update rmware,
read the photos and videos, and the raw satellite observations during Photogrammetry and
Waypoint Flight operations.
Camera Operation
Use the Shutter and Video Recording buttons on the remote controller or in the DJI GS RTK app to shoot
the photos or videos.
Camera Status LED Indicator Descriptions
The Camera LED Indicator lights up after the ight battery is powered on. It provides information on the
working status of the camera.
Camera LED Indicator Camera status
Green Fast Blink System is warming up
— Solid Green
Slow Red Blink Recording
×2 Double Red Blink Overheated Camera
—— Solid Red System error
Green and Red Blink Firmware Upgrading
Green Blink Once Taking a single picture
Fast Red Blink microSD card error
The system is warmed up, the microSD card is inserted and
working properly
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
48
©
Page 50

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Gimbal
Prole
The 3-axis gimbal provides a steady platform for the attached camera, allowing you to capture clear, stable
images and video. Turn the dial to adjust the gimbal pitch angle.
Controllable range of the pitch angel is -90° to +30°. The default range is -90° to 0°. This can be adjusted in
the DJI GS RTK app.
30°
0°
-90°
Gimbal Operation Modes
Two gimbal operation modes are available. Switch between the different operation modes on the gimbal
settings page of the DJI GS RTK app. Refer to the table below for details:
Follow Mode
FPV Mode
A gimbal motor error may occur in these situations:
(1) the aircraft is placed on uneven ground or the gimbal’s motion is obstructed.
(2) the gimbal has been subjected to an excessive external force, such as a collision. Please take
o from at, open ground and protect the gimbal at all times.
Flying in heavy fog or clouds may make the gimbal wet, leading to temporary failure. The gimbal
will recover full functionality after it dries.
It is normal for the gimbal to produce a short beeping tone upon initialization.
In the case of less exposure time (no more than 1/200 second) or ight in S-mode with full
remote controller stick movement, the aerodynamic vibration of the aircraft may increase due
to aerodynamic forces. This can make the gimbal more susceptible to wind, causing photos
to show a noticeable dynamic deformation (i.e., the “rolling shutter" eect). In such cases, it is
suggested to increase the exposure time by using the lter or reducing the lens aperture, or
reduce ying with smaller remote controller stick movement for better picture performance.
The angle between the gimbal’s orientation and aircraft’s nose remains
constant at all times.
The gimbal will synchronize with the movement of the aircraft to provide a
rst-person perspective ying experience.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
49
Page 51

DJI GS RTK App
This section introduces the main
functions of the DJI GS RTK app.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
50
©
Page 52

DJI GS RTK App
The DJI GS RTK app is designed for mapping applications. It can be used to plan operation areas and ight
routes, set various parameters, and view the status of the operations in real time.
Main Screen
3
PHANTOM4
RTK
Broad Vision
Precision Targeting
2
1
Aircraft connected
Plan Fly
1. Plan a Field | Execute Operation
Plan: Tap the button and then select Photogrammetry or Waypoint Flight operation, and then enter
Planning View for planning.
Fly: Tap to enter Camera View or Map View to view the aircraft status, congure the settings and perform
operations.
2. Aircraft Connection Status
: Shows whether the aircraft is connected to the remote controller.
3. Menu
Tap to manage tasks, view user information, aircraft information, and congure general settings.
: Task Management — View the progress of operations, planned operations and imported KML les.
: User Info — View user information of the account logged in.
: Aircraft Info — View the information of the connected aircraft.
: General Settings — Tap for settings such as units of measurement, network diagnosis, and Android
system settings
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
51
Page 53

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Planning View
Photogrammetry
1 2 4
3
Photogrammetry
Mapping Area Estimated Flight Time Photos/SD Card
Height(M)(GSD 2.74 cm/pixel)
Speed (M/s)
Finish
RETURN-TO-HOME
Camera Settings
Advanced Settings
Cancel
5
100
9.0
Save
6
7
89
1. Main Screen
: Tap this icon to return to the main screen.
2. Operation Type
Photogrammetry
: Shows the current type of operation being planned.
3. Planning Information
Shows the mapping area, estimated ight time, and number of photos.
4. More Settings
Tap to enter the extended menu to view and adjust the parameters of all other settings. Refer to the
introduction for Camera View.
5. Location
: Tap to center the map around the aircraft’s location or the latest recorded Home Point.
6. Map Mode
: Tap to switch among Standard, Satellite, or Night modes.
7. Operation Parameters Settings
This settings list will pop-up after edge points added by tapping on the map.
Height: The altitude of the aircraft during the operation.
Speed: The ight speed during the operation. The preset ight speed cannot exceed the maximum speed
displayed above the Speed setting. The maximum speed is the ight speed at which images meeting
mapping requirements can be captured and is calculated by the app according to current settings.
Relative Altitude: The relative height between the takeoff point and the operation area. The actual
operation height is the aircraft height minus the relative height. NOTE: Make sure to set the correct
relative height to ensure the results contain appropriate overlap rates.
Finish: The aircraft action after the operation is completed. Choose from RTH, hovering, landing, and
back to the start point.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
52
©
Page 54

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Camera Settings: Includes photo ratio, white balance, metering mode, gimbal angle, shutter priority
and distortion correction.
The default metering mode is average metering as it best serves mapping applications.
If distortion correction is enabled, the image quality may be lower due to processing. It is
recommended to disable this option when original images are need for post processing.
Advanced Settings: Includes horizontal overlapping rate, vertical overlapping rate and margin. The vertical
overlapping rate indicates the overlapping rate of two pictures captured consecutively along the same
path. The horizontal overlapping rate indicates the overlapping rate of two pictures on two parallel paths.
8. Map Zoom In/Out
: Tap to show the slider, and then slide it to zoom in or out.
9. Route Direction
: The system automatically produces ight routes after adding edge points and setting parameters.
Tap and drag this icon to adjust the ight direction of the produced route. Tap the icon for ne tuning in
the pop-up menu.
The descriptions above use Photogrammetry operations as an example. Operations such as Terrain
Awareness Mode, Block Segmentation and others have similar interfaces with Photogrammetry operations.
For 3D Photogrammetry (Multi-oriented) operations, click the numbers 1 to 5 in the map view to preview
each flight path. 1 refers to the nadir view flight path, and 2 to 5 refer to the four oblique flight paths
respectively.
Waypoint Flight
1
Route Length
In Flight (RTK)
12
RTK
D 10.0M/SH 10.0M
V.S: 0.0M/S H.S: 3.3M/S
Estimated Flight Time SD Card
1
93 m
99%
2
H
Route Settings Save
7
1. Planning Information
Shows the planned route length, estimated ight time, and microSD card capacity.
2. Map Mode
: Tap to switch among Standard, Satellite, or Night modes.
3. Location Follow
: Tap to center the map around the aircraft’s location at all times, following its location update.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
2
3
4
5
6
53
Page 55

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
SHUTTEREVWB
F
4. Location
: Tap to center the map around the aircraft’s location or the latest recorded Home Point.
5. Clear Screen
: Tap to clear the ight path currently shown on the map.
6. Waypoints
2
: The waypoints added by pressing the C2 Button on the remote controller. Tap to set the ight altitude,
heading, speed, gimbal angle and waypoint actions of each waypoint, switch among waypoints, and
delete the waypoint.
7. Route Settings | Save
Route Settings: Tap to enter the route settings menu to set task ending action, remote controller signal
loss action, aircraft heading in relevance to the ight route, cruising speed and route recording.
Other elements in this view are the same as the ones in Camera View.
Camera View
After tapping Fly in the main screen, users can switch between Camera View and Map View. The
descriptions below use the Camera View as an example.
1. Main Screen
: Tap this icon to return to the main screen.
2. Aircraft Status
In Flight (RTK)
3. Battery Level Indicator
on the battery level indicator represent the power levels needed to carry out dierent functions.
4. RTK / GNSS Signal Strength
12
RTK
: This icon is displayed once the RTK is enabled and begins working properly. The number on
the upper right corner indicates the number of satellites connected. The RTK status below includes
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
54
©
21 4 5 6 7 8 9
In Flight (RTK)
1
%
21
89
2
%
67
20
3
12
RTK
19:29
5.6
10米
19
0.3 Auto
78%
112
99%
10
AE
11
12
13
14
15
D 10.0MH 10.0M
V.S: 0.0M/S H.S: 3.3M/S
End Pause
161718
: Indicates current ight modes and warning messages.
: The battery level indicator provides a dynamic display of the battery level. The colored zones
Page 56

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
two statuses: FIX indicates that dierential data analysis is completed and RTK can be used for aircraft
positioning. Only under this status can the aircraft take o. FLOAT indicates that dierential data is in
analysis. Waiting for it to be FIX is required.
: This icon is displayed if the RTK is disabled, indicating the current GNSS signal strength and
number of satellites connected.
5. RTK Data Source Status
Icons displayed when using RTK data. The display varies when using the D-RTK 2 or Network RTK
Service.
: Displays RTK signal strength when using the D-RTK 2.
: Indicates that the connection with the D-RTK 2 is abnormal. Refer to the prompts in the app.
: Displays RTK signal strength when using the Network RTK Service.
: Indicates that the connection with the Network RTK server is abnormal. Refer to the prompts in the
app.
6. Control and HD Video Link Signal Strength
: Shows the signal strength of the control and HD video downlink connection between the aircraft and
the remote controller.
7. Obstacle Sensing Function Status
: Tap into this button to enable or disable features provided by the Vision System.
8. Camera Parameters
Displays camera settings parameters and capacity of the microSD card.
9. Battery Level
: Shows the current battery level. Tap to set the Low Battery Warning threshold and view battery
information.
10. More Settings
Tap to enter the extended menu to view and adjust the parameters of all other settings.
: Aircraft Settings — Includes Home Point settings, Return to Home Altitude, maximum altitude,
distance limit, remote controller signal lost action, advanced settings, etc.
RTK: RTK Settings — Includes RTK function switch, RTK service type and their corresponding settings.
: Sensor Settings — Includes enabling obstacle avoidance, radar map display, advanced vision
settings, etc.
: Remote Controller Settings — Includes remote controller calibration, stick mode, linking, etc.
: Image Transmission Settings — Includes channel mode and sweep frequency chart selection.
: Aircraft Battery Settings — Includes low battery warning thresholds, battery information, etc. When
a high discharge current, a short circuit, high or low discharge temperatures or battery cells damage is
detected, there will be an on-screen prompt.
: Gimbal Settings — Includes gimbal mode, advanced settings, gimbal roll adjustment, and auto
gimbal calibration.
: General Settings — Includes map settings, ight route display, to nd aircraft, etc.
11. Auto Exposure Lock
: Tap to lock the exposure value.
AE
12. Photo/Video Button
: Tap to switch between photo and video recording modes.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
55
Page 57

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
13. Shutter / Record Button
/ : Tap to shoot photos or start/stop recording. When recording, the time code below the button
indicates the length of the recording. Users can also press the Shutter or Video Recording button on the
remote controller to shoot photos or record video.
14. Operation Progress
78%
: Shows the progress of the Photogrammetry operation and number of photos taken.
112
15. Camera Settings
: Tap to set ISO, shutter, exposure values, OSD information, continuous auto focus (available for
manual ying and shooting), etc.
16. Operation Control Buttons
Buttons to control during dierent operation types, including invoke, start, pause, or end an operation,
etc.
17. Flight Parameters
: Vertical distance from the aircraft o the Home Point.
: Horizontal distance from the aircraft to the Home Point.
: Movement speed across a vertical distance.
: Movement speed across a horizontal distance.
18. Map
Tap the mini map to switch between Camera View and Map View. The icons in Map View
are the same as those in Planning View.
19. Operation List
: Tap to view the planned operations, operations in progress and the imported KML les. Select Plan
or Executing in the drop-down menu on top to use the operations. Select KML File to view and edit the
data and use the data to plan the Photogrammetry operation area.
20. Obstacle Detection Status
Shows information on the detected obstacles when the obstacle avoidance function is enabled. Front
obstacle information appears on the upper screen, and rear obstacle information appears on the lower
screen. Red, orange, yellow, and green bars indicate the distance of obstacles in succession. The value
indicates the distance between the aircraft and the nearest obstacle.
21. Aircraft Status Box in Multi-Aircraft Control Mode
Displays the status of all the connected aircraft sorted by number when using Multi-Aircraft Control
function. Tap to switch the selected aircraft and the left side of the box will turn blue.
Cloud PPK Service
PPK is a post-processing dierential correction technique that produces results with centimeter-level positioning
accuracy. Unlike RTK (real-time kinematic), PPK records rover data and base station data separately to
conduct post-process calculations and is therefore not restricted by the real-time communication link and
protocols between the base station and the rover. In addition, PPK has a longer baseline distance than RTK,
improving reliability. The DJI GS RTK app’s Cloud PPK Service (premium add-on) supports multiple base
station data sources, enabling users to connect to the cloud server for PPK calculations.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
56
©
Page 58

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Purchase
Once purchased, the Cloud PPK Service will be bound to the aircraft SN. The app can only recognize
operation data that corresponds to an aircraft SN with Cloud PPK Service activated.
Contact your local DJI authorized dealer to purchase an activation code for Cloud PPK Service.
In-app purchase is only supported in Mainland China. Users in other countries or regions can
purchase the activation code of Cloud PPK Service from a dealer.
Activation
1. Connect the aircraft for which Cloud PPK Service has been purchased, or insert the microSD card that
contains the operation data of the aircraft into the remote controller, so that the app can recognize the
unique aircraft SN.
2. Go to the main screen of the app, tap on the upper left corner, then , and select Cloud PPK
Service to enter the settings menu, and tap Activate.
3. Read the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy carefully, and check the box to agree.
4. Input the activation code from the dealer.
5. Cloud PPK Service is available once activated.
Users can use Cloud PPK Service to calculate data collected before the activation if the
rmware of the aircraft is v02.02.0312 or later.
Usage
Go to the Cloud PPK Service settings page. First, enable PPK Data Upload, and then tap START USING
NOW to enter the Cloud PPK Service page. The page includes Account Information, Create Task, Current
Tasks, and Past Tasks. In the Account Information tab, view the activated aircraft SN. In the Create Task tab,
create tasks for PPK calculations. In Current Tasks and Past Tasks, view task progress and download PPK
calculation results. The process is as follows:
1. Access PPK data from the aircraft:
Data storage path: The folder that contains the PPK data and signature le is the same folder where
images of the ight tasks are stored. Make sure that the name of the folder is same as the task code of
the data, for example, microSD card\DCIM\SURVEY\100_0005.
To import data: Insert the microSD card that contains the data into the remote controller. The app will
recognize the folders in the card. Users can select data from one or multiple ight tasks in the app.
Users can select the desired data in the Submitted tab if the aircraft PPK data has already
been uploaded to the server.
When users want to use aircraft PPK data with base station data from a RINEX base station,
the RINEX base station data must be stored in: microSD card\third_base.
2. Make sure that the remote controller has access to the internet via a 4G dongle or Wi-Fi. In the Network
Diagnostics page, check the status of the links and make sure the remote controller is connected to the
DJI AG platform.
3. Go to the Cloud PPK Service page in the app.
4. Tap Create Task, and select one or more aircraft PPK source datasets. View details on the right side of
the screen.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
57
Page 59

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
5. Tap Select Base Station Data to select the required base station data from the sources below.
DJI Base Station: Set up the D-RTK 2 Mobile Station near the operation area to record the base station
data when the aircraft performs operations. When nished, connect it to the remote controller using a
USB-C OTG cable and a USB-C cable to access the data from it.
If the latitude, longitude, and altitude of the base station was manually entered when setting up
the D-RTK 2 Mobile Station, the input values will be used as the reference position. If the D-RTK
2 Mobile Station loses power during the operation but, once restarted, is within 5 m from the
initial position, the initial position will be used. If it moves further than 5 m, the single point
positioning (SPP) location of the D-RTK 2 Mobile Station will be used as the reference point.
If no coordinates are entered, the D-RTK 2 Mobile Station will use the SPP location as the
reference point.
RINEX base station: Insert the microSD card with the RINEX base station data stored in the path “microSD
card\third_base” into the remote controller. Select datasets in the app, and manually input the base
station coordinates or select the single point positioning (SPP) as the reference point.
6. Tap Start Calculations, and then wait for the calculations to nish.
7. Tap Current Tasks to view the data processing progress.
8. Tap Past Tasks to view and download the results of completed tasks. The downloaded data will be
stored in the corresponding ight mission folder.
Users can import the PPK result file to DJI Terra for 2D or 3D reconstructions to improve
accuracy. Refer to the DJI Terra User Manual for more details.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
58
©
Page 60

Flight
This section describes safe ight
practices and ight restrictions.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
59
Page 61

Flight
Once the pre-ight preparation is complete, it is recommended to hone your ight skills through training and
practice ying safely. The altitude limit is 1, 640 feet (500 meters). Avoid ying at any altitudes higher. It is
important to understand basic ight guidelines for the safety of both you and those around you. Refer to the
Disclaimer and Safety Guidelines for more information.
Flight Environment Requirements
1. Do not use the aircraft in severe weather conditions. These include wind speeds exceeding 10 m/s,
snow, rain and fog.
2. Only y in open areas. Tall structures and large metal structures may aect the accuracy of the on-board
compass and GNSS system.
3. Avoid obstacles, crowds, high voltage power lines, trees, and bodies of water.
4. Minimize interference by avoiding areas with high levels of electromagnetism, including base stations and
radio transmission towers.
5. Aircraft and battery performance is subject to environmental factors such as air density and temperature.
Be very careful when ying at altitudes greater than 19, 685 feet (6000 meters) above sea level, as the
performance of the battery and aircraft may be aected.
6. In the Earth’s polar regions the aircraft can only operate in Attitude mode or using vision positioning.
GEO (Geospatial Environment Online) System
Introduction
DJI’s Geospatial Environment Online (GEO) System is a global information system committed to
providing real-time airspace information within the scope of international laws and regulations.
GEO provides flight information, flight times and location information to assist Unmanned Aerial
Vehicle (UAV) users in making the best decisions related to their personal UAV use. It also includes
a unique Regional Flight Restrictions feature which provides real-time ight safety and restriction
updates and blocks UAVs from ying in restricted airspace. While safety and obeying air trafc
control laws is a paramount concern, DJI recognizes the need for exceptions to be made under
special circumstances. To meet this need, GEO also includes an Unlocking feature that enables
users to unlock flights within restricted areas. Prior to making their flight, users must submit an
unlock request based on the current level of restrictions in their area.
GEO Zones
DJI’s GEO System designates safe flight locations, provides risk levels and safety concerns for
individual ights, and offers restricted airspace information, which can be viewed by users in real
time on the DJI GS RTK app. The locations designated by GEO are called GEO Zones. GEO Zones
are specic ight areas that are categorized by ight regulations and restrictions. GEO Zones that
prohibit ight are implemented around locations such as airports, power plants, and prisons. They
can also be temporarily implemented around major stadium events, forest res, or other emergency
situations. Certain GEO Zones do not prohibit flight but do trigger warnings informing users of
potential risks. All restricted ight areas are referred to as GEO Zones, and are further divided into
Warning Zones, Enhanced Warning Zones, Authorization Zones, Altitude Zones, and Restricted
Zones. By default, GEO limits flights into or taking off within zones that may result in safety or
security concerns. There is a GEO Zone Map, which contains comprehensive global GEO Zone
information on the ofcial DJI website: https://www.dji.com/ysafe.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
60
©
Page 62

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
The GEO System is for advisory purposes only. Individual users are responsible for checking ofcial
sources and determining which laws or regulations may apply to their ight. In some instances,
DJI has selected widely-recommended general parameters (such as a 1.5-mile radius at airports)
without making any determination as to whether these guidelines match regulations that apply to
specic users.
GEO Zone Denitions
Warning Zones:
Enhanced Warning Zones:
are required to submit an unlock request to y in the zone, for which they must conrm their ight
path.
Authorization Zones:
Authorization Zones can be unlocked by authorized users with a DJI-verified account. SelfUnlocking privileges must be applied for online.
Altitude Zones:
Restricted Zones:
obtained permission to y in a Restricted Zone, please go to https://www.dji.com/ysafe or contact
ysafe@dji.com to unlock the zone.
DJI GEO Zones aim to ensure the user’s flight safety, but it cannot be guaranteed to be in full
compliance with local laws and regulations. Users should check local laws, regulations, and
regulatory requirements before each ight and are responsible for the ight safety.
All intelligent ight features will be affected when DJI aircraft y nearby or into GEO Zones. Such
interference includes, but is not limited to, decreased speed, takeoff failure, and ight termination.
Users receive a warning message with information relevant to their ight.
Users receive a prompt from the GEO System at the time of ight. They
Users receive a warning message and the flight is prohibited by default.
Flights are limited to a specic altitude.
Flights are completely prohibited. UAVs cannot y in these zones. If you have
Flight Restrictions
Introduction
UAV operators should abide by all ight regulations established by the relevant government and
regulatory agencies, including the ICAO and the FAA. For safety reasons, flights are restricted
by default, which helps users operate DJI products safely and legally. Flight restrictions include
altitude and distance limits, and GEO Zones.
When Global Navigation Satellite Service (GNSS) is available, altitude limits, distance limits, and
GEO Zones are all taken into account to ensure ight safety. Otherwise, only altitude limits take
effect.
Maximum Altitude & Radius Restrictions
Maximum flight altitude restricts an aircraft’s flight altitude, while maximum radius restricts its
distance. These limits can be set using the DJI GS RTK app.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
61
Page 63

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Maximum Flight Altitude
Max Radius
Home Point
Height of aircraft when turned on
Strong GNSS Signal
Restriction Description DJI GS RTK App Message
Maximum Flight Altitude reached. Adjust
your altitude using Aircraft Settings if
required.
Maximum Flight Distance reached. Adjust
your distance using Aircraft Settings if
required.
Max Altitude
Max Radius
Aircraft's altitude cannot exceed
the specied value.
Flight distance cannot exceed
the specied value.
Weak GNSS Signal
Restriction Description DJI GS RTK App Message
Max Altitude
Altitude is restricted to 26 ft (8 m) when
GNSS signal is weak and the Vision
System is activated. Altitude is restricted
to 98 ft (30 m) when GNSS signal is weak
and the Vision System is deactivated.
Maximum Flight Altitude
reached. Adjust your altitude
using Aircraft Settings if
required.
Max Radius No limit. N/A
When an aircraft exceeds a specied limit, the pilot can still control the aircraft but it will be unable
to y any farther.
When an aircraft exceeds the max radius it automatically ies back within range when GNSS
signal is strong.
For safety reasons, do not y near airports, highways, railway stations, railway lines, city centers,
or other sensitive areas. Only y aircraft in areas that are within your direct line of sight.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
62
©
Page 64

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
GEO Zone Flight Restrictions
GEO Zone Description
Takeoff: The aircraft’s motors cannot be started.
In-ight: When GNSS signal changes from weak to strong, DJI GS RTK
starts a 20-second countdown. Once the countdown is over, the aircraft
Restricted Zone
Authorization Zone
Enhanced Warning Zone
Warning Zone The aircraft ies normally but the user receives warning messages.
Altitude Zone
Free Zone The aircraft ies normally with no restrictions.
immediately lands in semi-automatic descent mode and turns off its
motors after landing.
In-ight: When the aircraft approaches the boundary of the Restricted
Zone, it automatically decelerates and hovers.
Takeoff: The aircraft’s motors cannot be started. Takeoff is only available
after submitting an unlock request with the user’s phone number.
In-ight: When GNSS signal changes from weak to strong, DJI GS RTK
starts a 20-second countdown. Once the countdown is over, the aircraft
immediately lands in semi-automatic descent mode and turns off its
motors after landing.
The aircraft ies normally but the user is required to conrm the ight
path.
When GNSS signal is strong, the aircraft cannot exceed the specied
altitude.
In-ight: When GNSS signal changes from weak to strong, the aircraft
will descend and hover below the altitude limit.
When the GNSS signal is strong, the aircraft approaches the boundary
of the Altitude Zone. If it is higher than the altitude limit, the aircraft
decelerates and hovers in place.
When the GNSS signal changes from weak to strong, DJI GS RTK app
starts a 20-second countdown. Once the countdown is over, the aircraft
will descend and hover below the altitude limit.
GEO Unlocking
Due to differing laws and regulations between countries and regions, and differing ight restrictions
between GEO Zones, DJI provides users with two methods for unlocking GEO Zones: Self-Unlocking
and Custom Unlocking.
Self-Unlocking is used for Authorization Zones, where the user is required to submit an unlock request by authenticating their phone number for a registered DJI account. This feature is only available in certain countries. Users can choose whether to submit their unlock request via the website
at https://www.dji.com/ysafe (Scheduled Self-Unlocking), or through the DJI GS RTK app (Live
Self-Unlocking).
Custom Unlocking is based on special requirements for individual users. It sets a special ight
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
63
Page 65

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
area that users can unlock by providing ight permission les according to their specic GEO
Zone and other requirements. It is available in all countries and can be applied for on the website:
https://www.dji.com/ysafe.
For more information about unlocking, please visit https://www.dji.com/ysafe or contact ysafe@
dji.com.
Preflight Checklist
1. Remote controller, Intelligent Flight Battery are fully charged.
2. Propellers are mounted correctly and rmly.
3. MicroSD card has been inserted.
4. Gimbal and camera are functioning normally.
5. Motors can start and are functioning normally.
6. The DJI GS RTK app is successfully connected to the aircraft.
7. Ensure that the sensors for the Vision System and Infrared Sensing System are clean.
Calibrating the Compass
Only calibrate the compass when the DJI GS RTK app or the status indicator prompt you to do so. Observe
the following rules when calibrating your compass:
DO NOT calibrate your compass where there is a chance of strong magnetic interference, such as
magnetite, parking structures, and steel reinforcements underground.
DO NOT carry ferromagnetic materials with you during calibration such as cellular phones.
The DJI GS RTK app will prompt you to resolve the compass issue if the compass is aected by
strong interference after calibration is complete. Follow the prompted instructions to resolve the
compass issue.
Calibration Procedures
Choose an open area to carry out the following procedures.
1. Tap the Aircraft Status Bar in the app and select “Calibrate”, then follow the on-screen instructions.
2. Hold the aircraft horizontally and rotate 360 degrees. The Aircraft Status Indicators will display a solid
green light.
3. Hold the aircraft vertically, with nose pointing downward, and rotate it 360 degrees around the center
axis.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
64
©
Page 66

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
4. Re-calibrate the aircraft if the aircraft status indicators glows blinking red.
If the Aircraft Status Indicator blinks red and yellow after the calibration procedure, move your
aircraft to a dierent location and try again.
DO NOT calibrate the compass near metal objects such as a metal bridge, cars, scaolding.
If the aircraft status indicators are blinking red and yellow alternately after placing the aircraft on
the ground, the compass has detected magnetic interference. Change your location.
Starting/Stopping the Motors
Starting the Motors
A Combination Stick Command (CSC) is used to start the motors. Push both sticks to the bottom inner or
outer corners to start the motors. Once the motors have started spinning, release both sticks simultaneously.
OR
Stopping the Motors
There are two methods to stop the motors.
Method 1: When the aircraft has landed, push the left stick down , then conduct the same CSC that was
used to start the motors, as described below . Motors will stop immediately. Release both sticks once
motors stop.
Method 2: When the aircraft has landed, push and hold the left stick down. The motors will stop after three
seconds.
OR
Method 1 Method 2
Stopping Motors Mid-flight
Perform the CSC to stop the motors. It can be enabled in the app. Go to Camera View > > > Ad-
vanced Settings to set the Urgent Stop Mode. Only stop motors mid-ight in emergency situations when
doing so can reduce the risk of damage or injury.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
65
Page 67

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Flight Test
Takeo/Landing Procedures
1. Place the aircraft in an open, at area with the battery level indicators facing towards you.
2. Turn on the remote controller and then turn on the Intelligent Flight Battery.
3. Launch the DJI GS RTK app and tap Fly.
4. Wait until the Aircraft Status Indicators start to blink green slowly, which indicates that GNSS or RTK is in
use. If using RTK, ensure that the RTK function is enabled and that the RTK/GNSS signal strength icon
shows FIX. Then perform CSC to start motors.
5. Push the left stick up slowly to take o.
6. To land, hover over a level surface and gently pull down on the left stick to descend.
7. After landing, hold the left stick at its lowest position until the motors stop.
8. Turn o the Intelligent Flight Battery rst, then the remote controller.
When the Aircraft Status Indicators blink yellow rapidly during ight, the aircraft has entered Failsafe
mode.
A low battery level warning is indicated by the Aircraft Status Indicators blinking red slowly or rapidly
during ight.
Watch our video tutorials for more ight information.
Video Suggestions and Tips
1. Go through the full pre-ight checklist before each ight.
2. Select the desired gimbal operation mode in the app.
3. Only shoot photos or record videos when ying in P-mode.
4. Always y in good weather conditions and avoid ying in rain or heavy wind. An ND lter can be used
when the operating environment is too bright.
5. Choose the camera settings that suit your needs. Settings include ISO, exposure values, etc.
6. Perform ight tests to establish ight routes and preview scenes.
7. Push the control sticks gently to keep the aircraft’s movement smooth and stable.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
66
©
It is important to understand basic ight guidelines, for the safety of both you and
those around you. Do not forget to read the Disclaimer and Safety Guidelines.
Page 68

DJI Assistant 2 for
Phantom
This section introduces the usage of the
DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom software.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
67
Page 69

DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom
Update rmware, copy ight records and calibrate the Vision System in the DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom
software. For users that own DJI Agras aircraft, the DJI Assistant 2 for MG can also be used for the functions
above.
Installation and Launching
1. Download the software installation le from the Phantom 4 RTK download page:
http://www.dji.com/phantom-4-rtk/info#downloads
2. Install the software.
3. Launch DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom.
Using DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom
Connecting the Aircraft
Connect the Micro USB port of the aircraft to your computer with a Micro USB cable. Then power on the
aircraft.
Be sure to remove the propellers before using DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom.
Firmware Update
A DJI account is required for rmware updates. Login with your DJI account or register for one.
Data Upload
Save the ight data recorded by the ight controller or the system logs to a local path or upload them.
Flight Data
Click Open Data Viewer to view ight data. Data Viewer is used to view and analyze the ight data les of the
aircraft for performance analysis and troubleshooting.
Calibration
Calibrate the Vision System here when the app prompts for calibration.
Connecting the Remote Controller
Connect the USB-C port of the remote controller to your computer with a USB-C cable. Then power on the
remote controller.
Firmware Update
A DJI account is required for rmware updates. Login with your DJI account or register for one.
DO NOT power o the remote controller during the update.
DO NOT perform the rmware update while the aircraft is in the air. Only carry out the rmware
update when the aircraft is on the ground.
The remote controller may become unlinked from the aircraft after the rmware update. Relink the
remote controller and aircraft if necessary.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
68
©
Page 70

Appendix
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
69
Page 71

Appendix
Specifications
Aircraft
Weight (Battery &
Propellers Included)
Diagonal Size
(Excluding Propellers)
Max Ascent Speed 6 m/s (automatic ight); 5 m/s (manual control)
Max Descent Speed 3 m/s
Max Speed 31 mph (50 kph) (P-mode); 36 mph (58 kph) (A-mode)
Max Tilt Angle 25° (P- mode); 35° (A-mode)
Max Angular Speed 150°/s (A-mode)
Max Service Ceiling
Above Sea Level
Max Wind Speed
Resistance
Max Flight Time Approx. 30 minutes
Operating
Temperature
Operating Frequency
EIRP
Hover Accuracy
Range
Image Position Oset
GNSS
Single-Frequency
High-Sensitivity GNSS
1391 g
350 mm
19685 ft (6000 m)
10 m/s
32° to 104° F (0° to 40° C)
2.400 GHz to 2.483 GHz (Europe, Japan, Korea)
5.725 GHz to 5.850 GHz (United States, China)
2.4 GHz
CE (Europe) / MIC (Japan) / KCC (Korea): < 20 dBm
5.8 GHz
FCC (United States) / SRRC (Mainland China) / NCC (Taiwan, China): < 26 dBm
RTK enabled and functioning properly:
Vertical: ±0.1 m; Horizontal: ±0.1 m
RTK disabled:
Vertical: ±0.1 m (with vision positioning); ±0.5 m (with GNSS positioning)
Horizontal: ±0.3 m (with vision positioning); ±1.5 m (with GNSS positioning)
The position of the camera center is relative to the phase center of the onboard
D-RTK antenna under the aircraft body’s axis: (36, 0, and 192 mm) already
applied to the image coordinates in Exif data. The positive x, y, and z axes of
the aircraft body point to the forward, rightward, and downward of the aircraft,
respectively.
GPS + BeiDou + Galileo* (Asia); GPS + GLONASS + Galileo* (other regions)
* Supported later.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
70
©
Page 72

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Frequency Used
GPS: L1/L2; GLONASS: L1/L2; BeiDou: B1/B2; Galileo*: E1/E5
Multi-Frequency MultiSystem High-Precision
RTK GNSS
Mapping Functions
Mapping Accuracy**
Ground Sample
Distance (GSD)
Acquisition Eciency
Gimbal
Stabilization 3-axis (pitch, roll, yaw)
Controllable Range Pitch: -90° to +30°
Max Controllable
Angular Speed
Angular Vibration
Range
Vision System
Velocity Range ≤ 31 mph (50 kph) at 6.6 ft (2 m) above ground with adequate lighting
Altitude Range 0 - 33 ft (0 - 10 m)
Operating Range 0 - 33 ft (0 - 10 m)
Obstacle Sensory
Range
FOV
Measuring Frequency Forward/Rear: 10 Hz; Downward: 20 Hz
Operating
Environment
Infrared Sensing System
Obstacle Sensory
Range
FOV 70°(Horizontal), ±10°(Vertical)
Measuring Frequency 10 Hz
Operating
Environment
Camera
Sensor 1’’ CMOS; Eective pixels: 20M
First-Fixed Time: < 50 s
Positioning Accuracy: Vertical 1.5 cm + 1 ppm (RMS); Horizontal 1 cm + 1 ppm
(RMS).
1 ppm indicates error with a 1 mm increase over 1 km of movement.
Velocity Accuracy: 0.03 m/s
Mapping accuracy meets the requirements of the ASPRS Accuracy Standards
for Digital Orthophotos Class III.
(H/36.5) cm/pixel, H indicates the aircraft altitude relative to the shooting scene
(unit: m)
Max operating area of approx. 1 km2 for a single ight (at an altitude of 182 m, i.e.,
GSD is approx. 5 cm/pixel, meeting the requirements of the ASPRS Accuracy
Standards for Digital Orthophotos Class III).
Pitch: 90°/s
±0.02°
2 - 98 ft (0.7 - 30 m)
Forward/Rear: 60° (horizontal), ±27° (vertical)
Downward: 70° (front and rear), 50° (left and right)
Surfaces with clear patterns and adequate lighting (> 15 lux)
0.6 - 23 ft (0.2 - 7 m)
Surface with diuse reection material, and reectivity > 8% (such as wall, trees,
humans, etc.)
* Supported later.
** The actual accuracy depends on surrounding lighting and patterns, aircraft altitude, mapping software used,
and other factors when shooting.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
71
Page 73

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Lens
ISO Range
Mechanical Shutter 8 - 1/2000 s
Electronic Shutter 8 - 1/8000 s
Max Image Size 4864×3648 (4:3); 5472×3648 (3:2)
Still Photography
Modes
Video Recording
Modes
Max. Bitrate Of Video 100 Mbps
Photo JPEG
Video MOV
Supported File
Systems
Operating
Temperature
Remote Controller
Operating Frequency
EIRP
Max Transmission
Distance
Power Consumption 16 W (typical value)
Display Device 5.5 inch screen, 1920×1080, 1000 cd/m2, Android system, 4G RAM + 16G ROM
Operating
Temperature
Intelligent Flight Battery (PH4-5870mAh-15.2V)
Capacity
Voltage
Battery Type
Energy
Net Weight
Operating
Temperature
Max Charging Power
Intelligent Flight Battery Charging Hub (P4CH)
Voltage 17.5 V
Operating Temperature 41° to 104° F (5° to 40° C)
FOV (Field of View) 84°, 8.8 mm (35 mm format equivalent: 24 mm), f/2.8 - f/11,
auto focus at 1 m - ∞
Video: 100 - 3200 (Auto), 100 - 6400 (Manual)
Photo: 100 - 3200 (Auto), 100 - 12800 (Manual)
Single shot
H.264, 4K: 3840×2160 30p
FAT32 (≤ 32 GB); exFAT (> 32 GB)
32° to 104° F (0° to 40° C)
2.400 GHz to 2.483 GHz (Europe, Japan, Korea)
5.725 GHz to 5.850 GHz (United States, China)
2.4 GHz
CE / MIC / KCC: < 20 dBm
5.8 GHz
SRRC / NCC / FCC: < 26 dBm
FCC / NCC: 4.3 mi (7 km); CE / MIC / KCC / SRRC: 3.1 mi (5 km)
(Unobstructed, free of interference)
32° to 104° F (0° to 40° C)
5870 mAh
15.2 V
LiPo 4S
89.2 Wh
468 g
14° to 104° F (-10° to 40° C)
160 W
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
72
©
Page 74

Phantom 4 RTK User Manual
Remote Controller Intelligent Battery (WB37-4920mAh-7.6V)
Capacity 4920 mAh
Voltage 7.6 V
Battery Type LiPo 2S
Energy 37.39 Wh
Operating Temperature -4° to 104° F (-20° to 40° C)
Intelligent Battery Charging Hub (WCH2)
Input Voltage 17.3 to 26.2 V
Output Voltage and
Current
Operating
Temperature
AC Power Adapter (PH4C160)
Voltage 17.4 V
Rated Power 160 W
8.7 V, 6 A; 5 V, 2 A
41° to 104° F (5° to 40° C)
Updating the Firmware
Users can update the rmware in the DJI Assistant 2 for Phantom. The DJI GS RTK app can also be used
to update the rmware of both the aircraft and remote controller, if using a rmware version of 01.04.0330 or
above. Follow the instructions below.
1. Power on the remote controller and the aircraft. Ensure that the remote controller has access to the
Internet.
2. Connect the USB-C port on the remote controller to the Micro USB port on the aircraft via a USB-C OTG
cable and a Micro USB cable.
3. There will be a prompt on the lower right corner in the DJI GS RTK app if there is new rmware. Tap the
text to enter rmware page.
4. Select the desired rmware and tap Update to enter rmware information page.
5. Tap Download XXX (XXX indicates the rmware version) to download the rmware package for all the
devices.
6. When the download is complete, tap Update XXX under each device to enter the update page for the
corresponding device, then tap Install and wait for the update complete.
7. After successfully completing the update, restart the remote controller and the aircraft manually.
The battery level should be above 30% for the rmware update.
The remote controller and the aircraft will restart automatically during rmware update. Be sure to
keep the connection between the remote controller and the aircraft. DO NOT operate them manually
until the app indicates installation is completed.
The remote controller may become unlinked from the aircraft after the rmware update. Relink the
remote controller and aircraft if necessary.
2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
73
Page 75

DJI Support
http://www.dji.com/support
This content is subject to change.
Download the latest version from
http://www.dji.com/phantom-4-rtk
If you have any questions about this document, please contact
DJI by sending a message to
is a trademark of DJI.
PHANTOM
Copyright © 2020 DJI All Rights Reserved.
DocSupport@dji.com
.
 Loading...
Loading...