Page 1
MAVIC 2 PRO/ZOOM
User Manual
2018.08
v1.0
Page 2
Searching for Keywords
Search for keywords such as “battery” and “install” to find a topic. If you are using Adobe Acrobat
Reader to read this document, press Ctrl+F on Windows or Command+F on Mac to begin a search.
Navigating to a Topic
View a complete list of topics in the table of contents. Click on a topic to navigate to that section.
Printing this Document
This document supports high resolution printing.
Using This Manual
Legend
Warning Important Hints and Tips Reference
Read Before the First Flight
Read the following documents before using the MAVICTM 2 Pro/Zoom:
1. Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom In the Box
2. Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
3. Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom Quick Start Guide
4. Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom Disclaimer and Safety Guidelines
5. Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom Intelligent Flight Battery Safety Guidelines
TM
It is recommend to watch all tutorial videos on the ocial DJI
Disclaimer and Safety Guidelines before rst time use. Prepare for your rst ight by reviewing the Mavic
2 Pro/Zoom Quick Start Guide and refer to this Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual for more details.
website and read the Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom
Video Tutorials
Go to the address below or scan the QR code on the right to watch the Mavic 2 Pro/
Zoom tutorial videos, which demonstrate how to use the Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom safely:
http://www.dji.com/mavic-2/info#video
Download the DJI GO 4 App
Be sure to use the DJI GOTM 4 app during ight. * Scan the QR code on the right to
download the latest version. The Android version of DJI GO 4 is compatible with Android
v4.4 and later. The iOS version of DJI GO 4 is compatible with iOS v9.0 and later.
* For increased safety, flight is restricted to a height of 98.4 ft (30 m) and range of 164 ft (50 m) when not connected
or logged into the app during flight. This applies to DJI GO 4 and all apps compatible with DJI aircraft.
Download DJI Assistant 2
Download DJI Assistant 2 at http://www.dji.com/mavic-2/info#downloads.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
2
©
Page 3

Contents
Using This Manual
Legend
Read Before the First Flight
Video Tutorials
Download the DJI GO 4 App
Download DJI Assistant 2
Product Prole
Introduction
Preparing the Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom
Preparing the Remote Controller
Aircraft Diagram
Activation
Aircraft
Flight Modes
Aircraft LEDs and Status Indicator
Return to Home
Vision Systems and Infrared Sensing Systems
Intelligent Flight Modes
Advanced Pilot Assistance Systems
Flight Recorder
Attaching and Detaching the Propellers
Intelligent Flight Battery
Gimbal and Camera
Remote Controller
Using the Remote Controller
Dual Remote Controller Mode (Coming soon)
Linking the Remote Controller
DJI GO 4 App
Equipment
Editor
SkyPixel
Me
2
2
2
2
2
2
6
6
6
8
9
11
13
13
14
15
20
23
32
32
33
34
37
40
40
46
47
49
49
52
52
52
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
3
Page 4

Flight
Flight Environment Requirements
Flight Limits and GEO Zones
Pre-Flight Checklist
Auto Takeoff/Landing
Starting/Stopping the Motors
Test Flight
Appendix
Specications
Calibrating the Compass
Firmware Updates
Remote Controller LCD Screen Menu Information
After-Sales Information
55
55
55
57
57
58
58
61
61
64
65
66
68
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
4
©
Page 5

Product Prole
This section introduces
and lists the components of the
Zoom
aircraft and remote controller.
Mavic 2 Pro/
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
5
Page 6

Product Prole
Introduction
The DJI Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom features omnidirectional Vision Systems and Infrared Sensing Systems.
Effortlessly capture complex shots using signature DJI technologies such as Obstacle Sensing and
Intelligent Flight Modes like Hyperlapse, Point of Interest, ActiveTrackTM 2.0, TapFly, QuickShots, and
Advanced Pilot Assistance Systems (APAS).
The Mavic 2 Pro features a fully stabilized 3-axis gimbal with a 1" CMOS sensor camera (jointly
developed by DJI and Hasselblad) that shoots 4K video, 20-megapixel photos, and supports lters.
The Mavic 2 Zoom features a fully stabilized 3-axis gimbal camera that shoots 4K video, 12-megapixel
photos, supports 2x optical zoom, and 24-48 mm lens, and supports lters.
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom uses the latest technology to increase stability and footage quality, reducing the
Mavic 2 Zoom angle vibration range to within ±0.005° and Mavic 2 Pro angle vibration range to within
±0.01°.
Built into the remote controller is the DJI’s long-range transmission technology OCUSYNCTM 2.0, oering
a maximum transmission range of 5 mi (8 km) and displaying video from the aircraft on to DJI GO 4 on
your mobile device at up to 1080p. The remote controller works at both 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz, and it
can select the best transmission channel automatically without any latency. The aircraft and camera can
easily be controlled using the onboard buttons. An onboard LCD screen gives real-time aircraft data
information, and the detachable control sticks make the remote controller easier to store. The maximum
run time is 2 hours and 15 minutes. The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom boasts a maximum ight speed of 44.7 mph
(72 kph) and a maximum ight time of 31 minutes.
The major difference between the Mavic 2 Pro and Mavic 2 Zoom is the camera. The general
descriptions in this manual apply to both Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom.
Maximum flight time was tested in an environment with no wind while flying at a consistent 15.5
mph (25 kph) and the maximum flight speed was tested at sea level altitude with no wind. These
values are for reference only.
The remote controller reaches its maximum transmission distance (FCC) in a wide-open area
with no electromagnetic interference at an altitude of about 400 ft (120 m). The maximum
runtime was tested in a laboratory environment. This value is for reference only.
5.8 GHz is not supported in some regions. Please observe the local laws and regulations.
Preparing the Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom
Preparing the Aircraft
All aircraft arms are folded before the aircraft is packaged at the factory. Follow the steps below to
unfold the aircraft.
1. Remove the gimbal cover from the camera.
2. Unfold the front arms, and then unfold the rear arms.
2
1
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
6
©
3
Page 7
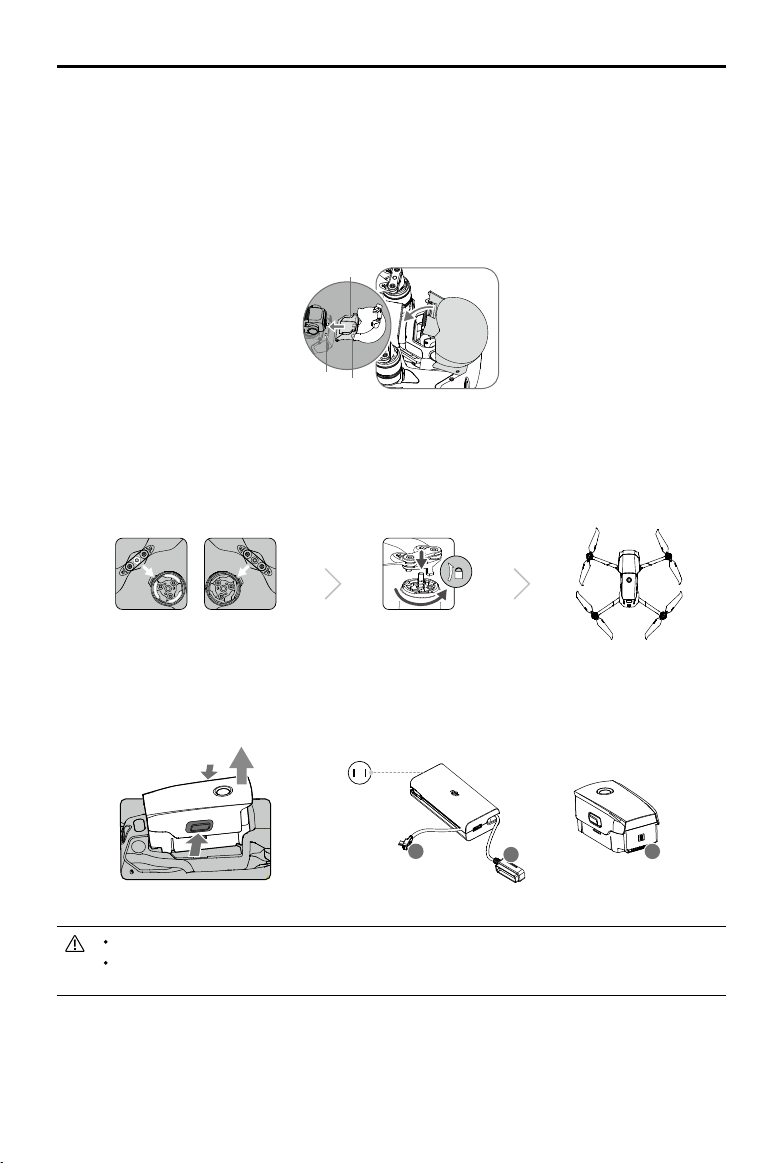
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
*Attach the gimbal cover when not in use.
1)Hold the gimbal in place and insert gimbal clamp between the aircraft and the gimbal.
2) Make sure the hooks on the Gimbal Protector are locked in the grooves of the aircraft, then lower
the Gimbal Protector over the gimbal and secure with the buckle. The buckle will click when it is
securely attached.
Gimbal clamp
Grooves Hooks
3. Attaching the propellers.
Attach the propellers marked white to the motors with white marks. Press the propeller down onto
the motors and turn until it is secure. Attach the other propellers to the unmarked motors. Unfold all
the propeller blades.
4. All Intelligent Flight Batteries are in Hibernation mode before shipment to ensure safety. Use the
provided AC power adapter to charge and activate Intelligent Flight Batteries for the rst time. To
charge an Intelligent Flight Battery after ight, remove it from the aircraft and attach it to the AC
power adapter.
Power Outlet
100-240 V
B
Unfold the front arms and propellers before unfolding the rear arms.
Be sure the gimbal cover is removed and all arms and propellers are unfolded before powering
on the aircraft. Otherwise, it may affect the aircraft self-diagnostics.
A
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
~1 hour 30 minutes
A
Charging Time:
7
Page 8
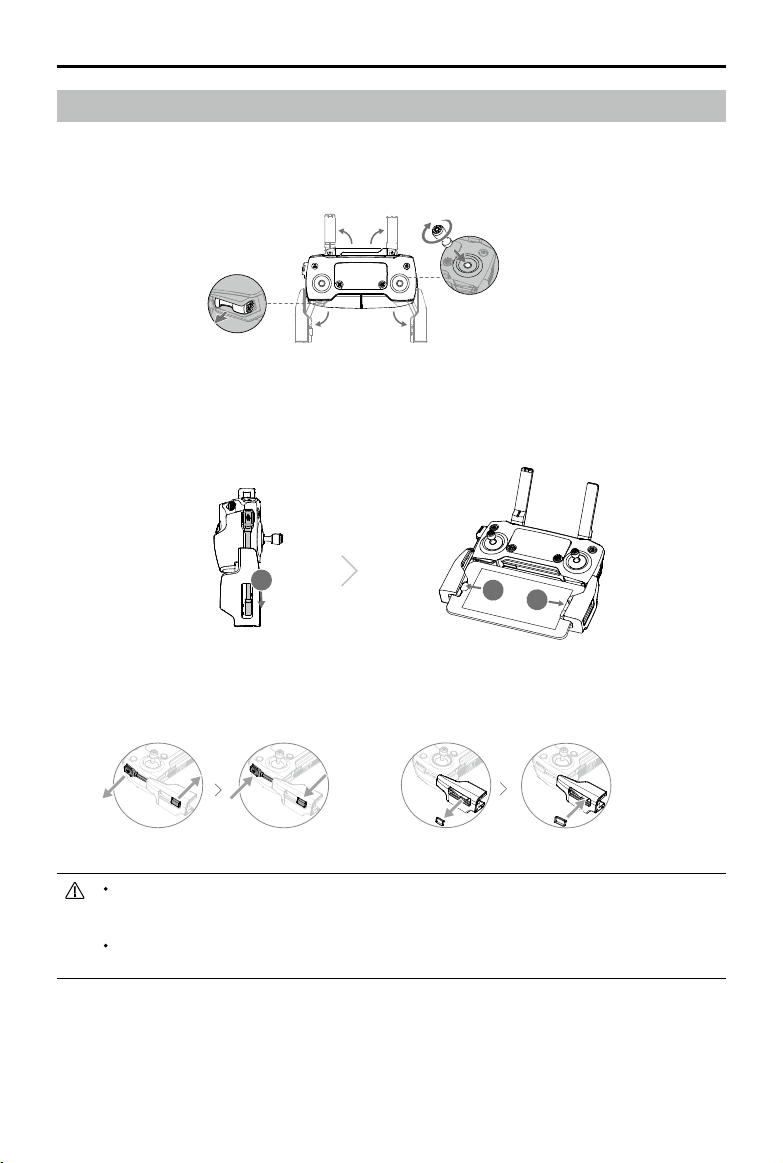
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Preparing the Remote Controller
1. Unfold the mobile device clamps and the antennas.
2. Remove the control sticks from their storage slots on the remote controller and screw them into
place.
3. Choose an appropriate RC cable based on the type of mobile device. A cable with a Lightning
connector is connected by default to the cable slider. Micro USB and USB-C cables are also
included in the packaging. Connect the end of the RC cable to your mobile device. Secure your
mobile device by pushing both clamps inward.
1
2
3
Refer to the gure below for how to replace the RC cable. The RC cable slider must be replaced if using
a USB -C RC cable.
You can also connect your mobile device to the remote controller using a USB cable if the
mobile device is too big to place into the clamps. Plug one end of the cable into your mobile
device and the other end into the USB port on the bottom of the remote controller.
Do not use the Micro USB and USB ports simultaneously for video linking. Remove the cable
from one port before connecting a device to the other port for video linking.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
8
©
Page 9
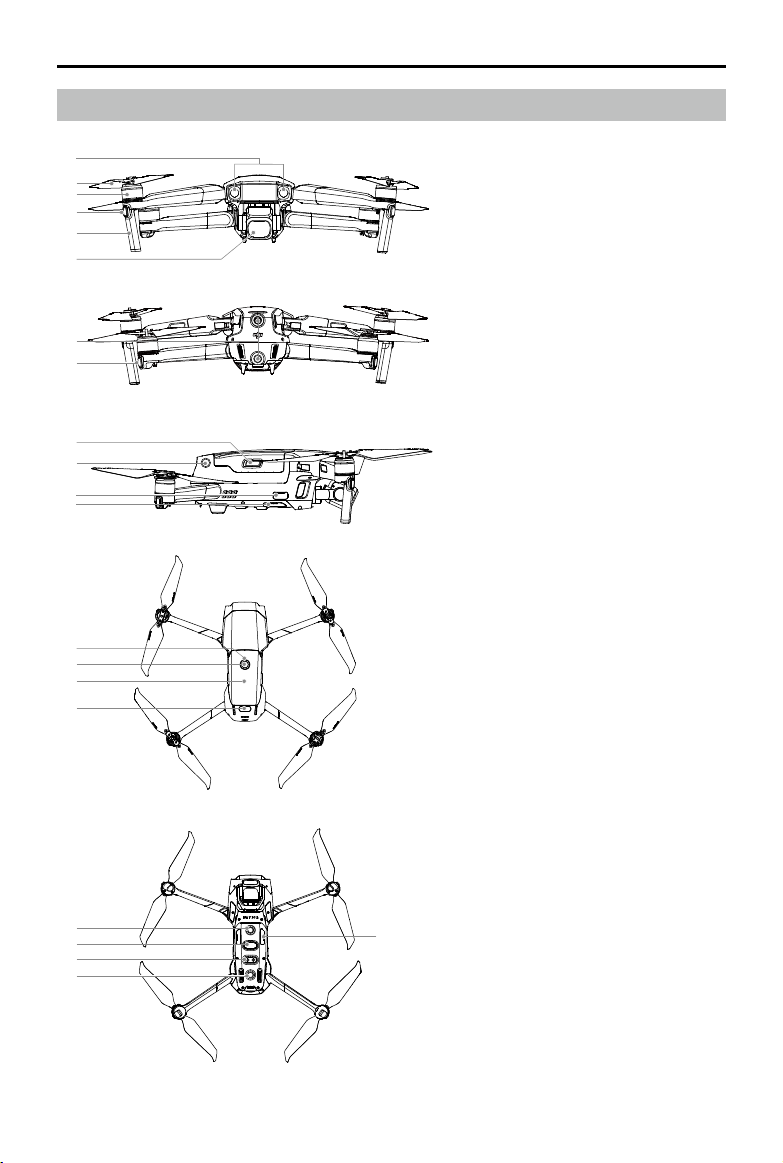
Aircraft Diagram
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
1. Forward Vision System
2. Propellers
3. Motors
4. Front LEDs
5. Antennas
6. Gimbal and Camera
7. Backward Vision System
8. Aircraft Status Indicator
9. Battery Buckles
10. Lateral Vision System
11. USB-C Port
12. Link Button/Linking Status
Indicator
13. Battery Level LEDs
14. Power Button
15. Intelligent Flight Battery
16. Upward Infrared Sensing System
17. Downward Vision System
18. microSD Card Slot
19. Downward Infrared Sensing
System
20. Auxiliary Bottom Light
17
19
20
17
18
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
9
Page 10
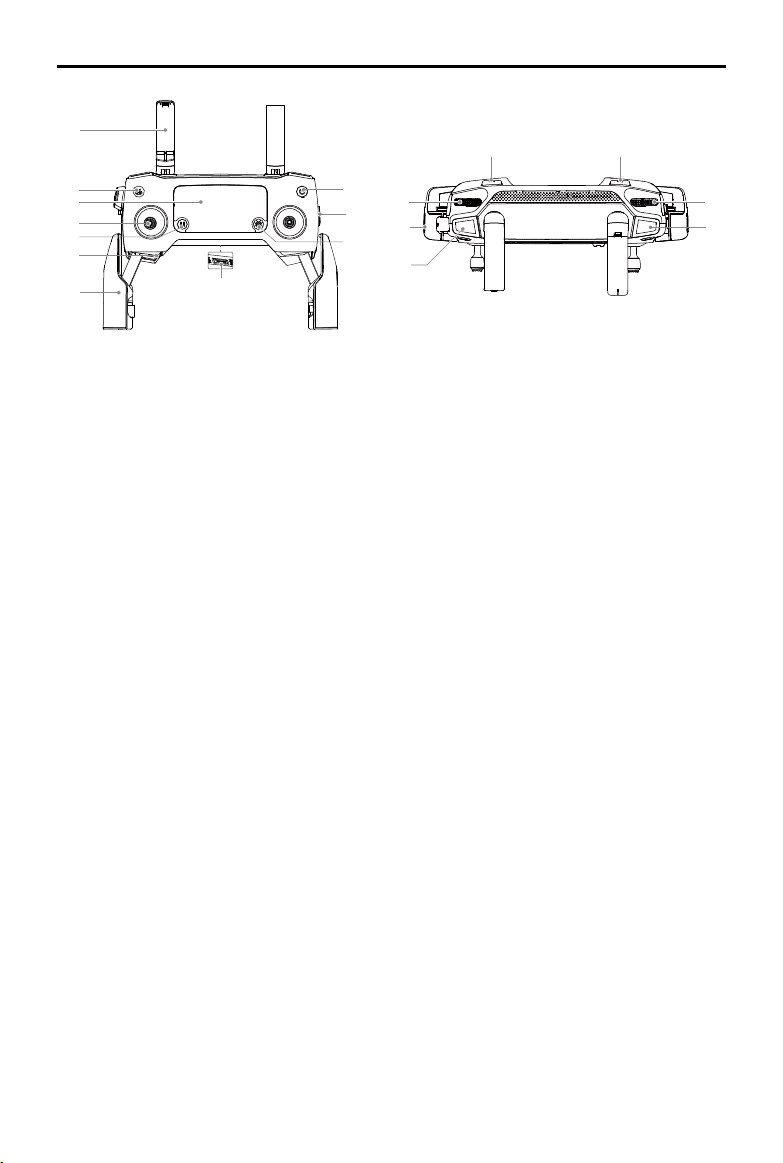
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1. Antennas
Relay aircraft control and video wireless
signals.
2. Return to Home (RTH) Button
Press and hold the button to initiate RTH.
The aircraft returns to the last recorded home
point. Press again to cancel RTH.
3. LCD Screen
Displays the aircraft and Remote Controller
system status.
4. Removable Control Sticks
The removable control sticks are easy to
store. The default ight control is set to Mode
2. Set the ight control mode in DJI GO 4.
5. Flight Pause Button
Press to make the aircraft brake and hover in
place (only when GPS or Vision System are
available). Please note that the flight pause
button has different functions in different
Intelligent Flight Modes. For details, refer to
the Intelligent Flight Mode section.
6. Control Sticks Storage Slot
For storing the control sticks.
7. Mobile Device Clamps
Securely mount your mobile device onto the
remote controller.
8. Reserve Video-Downlink Port (USB)
Connect to a mobile device for video
12
11
13
10
14
9
15
18
17
16
downlink via a standard USB cable.
9. 5D Button
The default configuration is listed below.
The conguration can be adjusted based on
your preferences in DJI GO 4.
Left: Decrease EV value.
Right: Increase EV value.
Up: Recenter gimbal/gimbal downward.
Down: Recenter gimbal/gimbal downward.
Press down: Bring up DJI GO 4 Intelligent
Flight menu.
10. Flight Mode Switch
Switch between S-mode, P-mode, and
T-mode.
11. Power Button
Press once to check the current battery
level. Press once, then again, and hold to
turn on/o the remote controller.
12. C1 Button (Customizable)
The default configuration is center focus.
Adjust the conguration in DJI GO 4 based
on your preferences.
13. Gimbal Dial
Controls the camera's tilt.
14. Video-Downlink/Power Port (micro USB)
Connect to a mobile device for video
linking via the RC cable. Connect to the
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
10
©
Page 11

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
AC Power Adapter to charge the remote controller
battery.
15. Record Button
Press to start recording video. Press again to stop
recording.
16. Focus/Shutter Button
Press halfway to autofocus. Press once to take
photos according to the mode selected in the DJI
GO 4.
17. Aperture/Shutter Adjustment Dial (Mavic 2 Pro)
Turn the dial to adjust the exposure compensation
(when in P-mode), aperture (when in Aperture
Priority and Manual mode), or shutter (when in
S-mode).
Zoom Adjustment Dial (Mavic 2 Zoom)
Turn to adjust the zoom of the Mavic 2
Zoom camera.
18. C2 Button (Customizable)
The default configuration is playback.
Adjust the configuration in DJI GO 4
based on your preferences.
Activation
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom requires activation before rst time use. Follow the onscreen guide to activate
the Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom using DJI GO 4.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
11
Page 12

Aircraft
This section introduces the ight
controller, Forward, Backward and
Downward Vision Systems, and the
Intelligent Flight Battery.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
12
©
Page 13

Aircraft
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom contains a ight controller, vision systems, video downlink system, propulsion
system, and an Intelligent Flight Battery. Refer to the aircraft diagram in the Product Prole section.
Flight Modes
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom has three ight modes, plus a fourth ight mode that the aircraft switches to in
certain circumstances:
P-mode (Positioning): P-mode works best when the GPS signal is strong. The aircraft utilizes GPS and
the Vision Systems to locate itself, stabilize, and navigate between obstacles. Intelligent Flight Modes
are enabled in this mode.
When the Forward and Backward Vision Systems are enabled and lighting conditions are sucient, the
maximum ight altitude angle is 25°, the maximum forward ight speed is 31 mph (50 kph), and the
maximum backward ight speed is 27 mph (43 kph).
Note: P-mode requires larger stick movements to achieve high speeds.
The aircraft automatically changes to Attitude (ATTI) mode when the Vision Systems are unavailable or
disabled and when the GPS signal is weak or the compass experiences interference. When the Vision
Systems are unavailable, the aircraft cannot position itself or brake automatically, which increases
the risk of potential flight hazards. In ATTI mode, the aircraft may be more easily affected by its
surroundings. Environmental factors such as wind can result in horizontal shifting, which may present
hazards, especially when ying in conned spaces.
S-mode (Sport): In S-mode, the Vision Systems are disabled and the aircraft only uses GPS for
positioning. The maximum ight speed is 44.7 mph (72kph). Intelligent Flight Modes are not available
and the aircraft cannot sense or avoid obstacles.
Note: In S-mode, aircraft responses are optimized for agility and speed making it more responsive to
stick movements.
T-mode (Tripod): T-mode is based on P-mode and the ight speed is limited, which makes the aircraft
more stable during shooting. The maximum flight speed, maximum ascend speed and maximum
descend speed are 1 m/s. Intelligent Flight Modes are not available in T-mode.
The Forward, Backward, Lateral Vision Systems and the Upward Infrared Sensing System are
disabled in S-mode, which means the aircraft cannot sense obstacles on its route automatically.
The aircraft’s maximum speed and braking distance significantly increase in S-mode. A minimum
braking distance of 98.4 ft (30 m) is required in windless conditions.
Descent speed significantly increases in S-mode.
The aircraft’s responsiveness significantly increases in S-mode, which means a small stick
movement on the remote controller translates into the aircraft moving a large distance. Be
vigilant and maintain adequate maneuvering space during flight.
Use the Flight Mode switch on the remote controller to switch between Flight Modes. Enable
Multiple Flight Modes in DJI GO 4 to switch between Flight Modes.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
13
Page 14
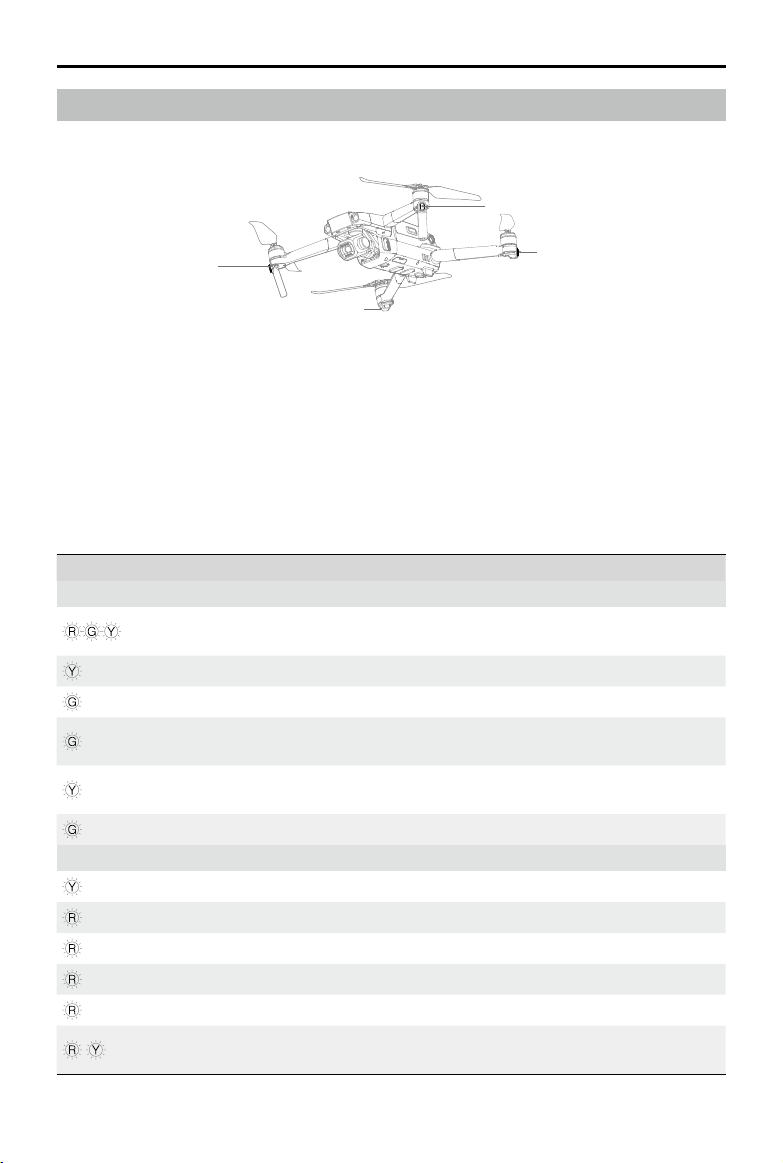
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Aircraft LEDs and Status Indicator
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom has Front LEDs and Aircraft Status Indicators as shown in the gure below.
Front LEDs
Front LEDs
Aircraft Status Indicator
The Front LEDs show the orientation of the aircraft and glow solid red when the aircraft is turned on to
indicate the front of the aircraft (they can be turned o in the DJI GO 4 app).
The Aircraft Status Indicators communicate the statuses of the aircraft’s ight control system. Refer to
the table below for more information about the aircraft states indicated by the Aircraft Status Indicators.
The Aircraft Status Indicators also ash when the Home Point is being recorded, as described in the
Return to Home section.
Aircraft Status Indicator
Aircraft Status Indicator States
Color Blinking/Solid Description of Aircraft State
Normal States
Alternating red,
green, and yellow
Yellow Blinks four times Warming up
Green Blinking slowly P-mode with GPS
Green
Yellow Blinking slowly
Green Blinking quickly Braking
Warning States
Yellow Blinking quickly Remote controller signal lost
Red Blinking slowly Low battery
Red Blinking quickly Critically low battery
Red Blinking IMU error
Red Solid Critical error
Alternating red
and yellow
Blinking
Periodically blinks
twice
Blinking quickly Compass calibration required
Turning on and performing self-diagnostic
tests
P-mode with Forward and Downward Vision
Systems
No GPS, Forward Vision System or
Downward Vision System
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
14
©
Page 15
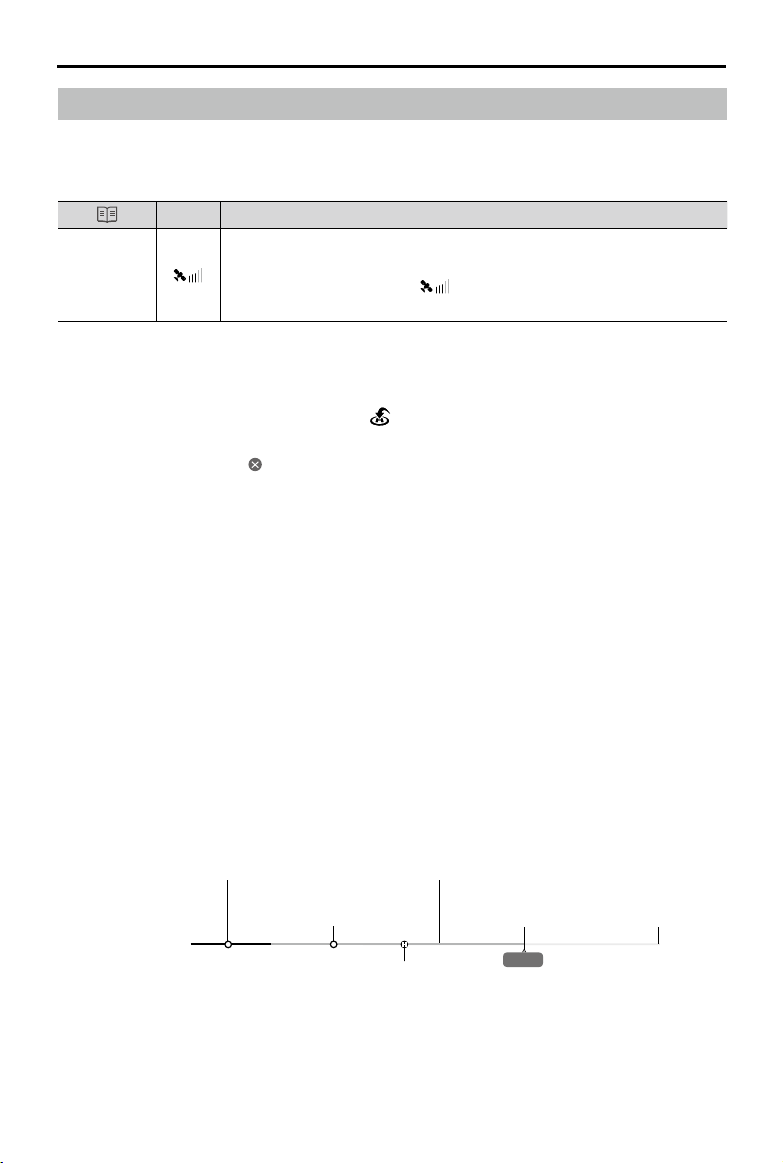
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Return to Home
The Return to Home (RTH) function brings the aircraft back to the last recorded Home Point. There are
three types of RTH: Smart RTH, Low Battery RTH, and Failsafe RTH. This section describes these three
scenarios in detail.
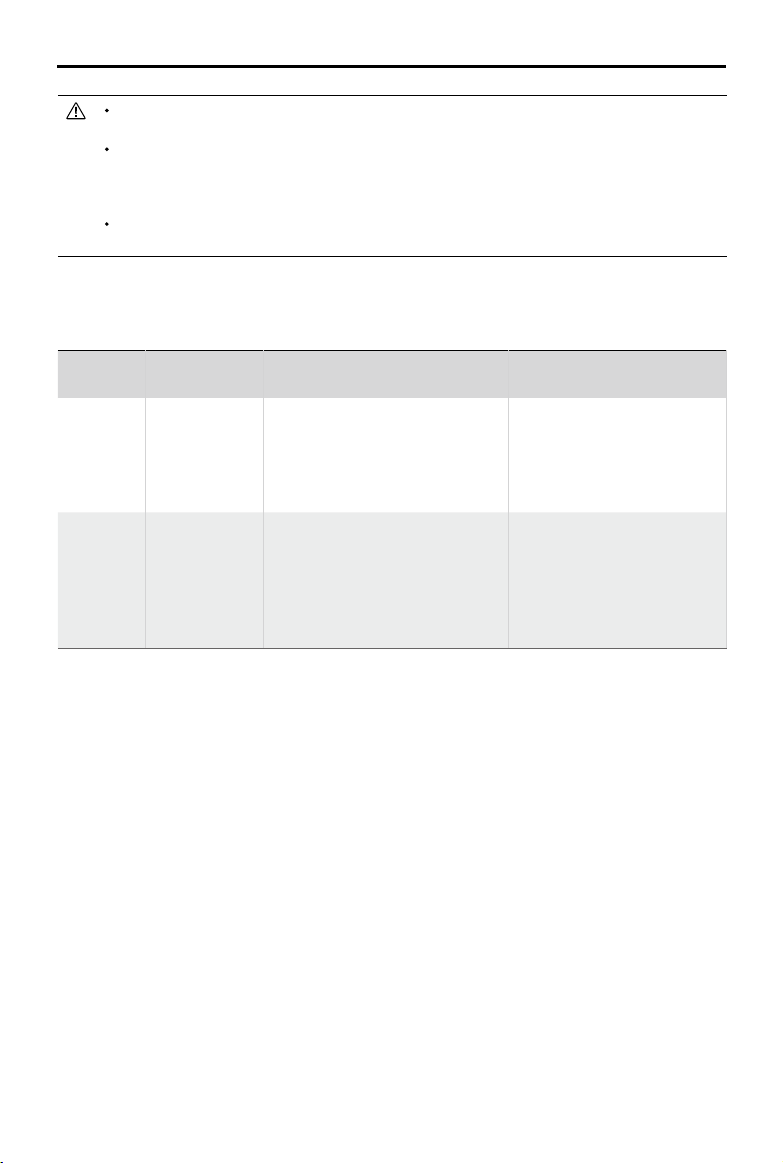
GPS
If a strong GPS signal was acquired before takeoff, the Home Point is
Home Point
the location from which the aircraft launched. The GPS signal strength is
indicated by the GPS icon ( ). The Aircraft Status Indicator will blink
green quickly when the Home Point is recorded.
Smart RTH
If the GPS signal is suciently strong, Smart RTH can be used to bring the aircraft back to the Home
Point. Smart RTH is initiated either by tapping in the DJI GO 4 app (and following the on-screen
instructions) or by pressing and holding the RTH button on the remote controller.
Exit Smart RTH by tapping in the DJI GO 4 app or by pressing the RTH button on the remote
controller.
Low Battery RTH
Low Battery RTH is triggered when the Intelligent Flight Battery is depleted to the point that the safe
return of the aircraft may be aected. Return home or land the aircraft immediately when prompted. DJI
GO 4 will display a warning when a low battery level warning is triggered. The aircraft will automatically
return to the Home Point if no action is taken after a ten-second countdown. The user can cancel the
RTH procedure by pressing the RTH button or Flight Pause button on the remote controller.
If the RTH procedure is cancelled following a low battery level warning, the Intelligent Flight Battery may
not have enough charge for the aircraft to land safely, which may lead to the aircraft crashing or being
lost. The thresholds for the battery level warnings are automatically determined based on the aircraft’s
current altitude and distance from the Home Point.
The aircraft will land automatically if the current battery level can only support the aircraft long enough
to descend from its current altitude. The user cannot cancel the auto landing but can use the remote
controller to alter the aircraft’s orientation during the landing process.
Description
Critically low battery level warning
(Red)
Low battery level warning
DJI GO 4 Battery level Indicator Bar
(Yellow)
Charge required to
return to Home Point
Battery level is
sufficient (Green)
Remaining flight time
12:29
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
15
Page 16
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
The colored zones and markers on the DJI GO 4 battery level indicator bar reect the estimated
remaining ight time. They automatically adjust according to the aircraft’s current location and status.
If the current battery level can only support the aircraft long enough to descend from its current
altitude, a critically low battery level warning triggers and the aircraft descends and lands
automatically. This procedure cannot be canceled. If there is a danger of a collision, push the
throttle up and try to navigate away.
If the battery level is sufficient, the battery level indicator bar in DJI GO 4 displays the estimated
remaining flight time based on the current battery level.
If a battery level warning appears, take action as described in the table below.
RTH and Battery Level Warnings (when using rmware v00.06.00.00 by default)
Warning
Low
Battery
Critically
Low
Battery
Level
Aircraft Status
Indicator
Blinks red slowly
Blinks red
quickly
DJI GO 4 App Remarks/Instructions
Provides the option to return to
the Home Point automatically or to
resume normal ight. If no action is
taken, the aircraft will automatically
Battery level is low. Fly the
aircraft back and land promptly,
then stop the motors and
replace the battery.
y home after 10 seconds.
The aircraft descends and lands
Display ashes red.
automatically.
This procedure cannot be
canceled. If there is a danger of
a collision, push the throttle up
and try to navigate away.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
16
©
Page 17
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
RTH and Battery Level Warnings (when using updated rmware v01.00.00.00)
Warning Instructions
Remaining battery
level supports RTH.
Remaining
battery level
supports
Emergency RTH
(when in RTH,
Low
Battery
Level
Critically
Low
Battery
Level
with a normal RC
signal, and at an
altitude higher
than 50 m).
Remaining
battery level
supports
Emergency
Landing (when
in RTH with
a normal RC
signal).
Aircraft lands
after 10 seconds
(when flying
normally with
a critical low
battery level).
Aircraft lands
automatically
(when flying
normally with an
extremely critical
low battery
level).
Aircraft Status
Indicator
Blinks red
slowly
Blinks red
quickly
DJI GO 4 App Actions
Choose RTH or
resume normal flight.
Choose Emergency
RTH or resume RTH.
Aircraft lands. Action
cannot be canceled.
Aircraft lands after
10 seconds. Action
cannot be canceled.
Aircraft lands
immediately. Action
cannot be canceled.
Select an option. If no action
is taken, the aircraft will enter
RTH.
Select an option.
Emergency RTH (aircraft
descends to 50 m and
returns to the Home Point)
or resume RTH (aircraft
flies to Home Point without
descending). If no action is
taken, the aircraft will enter
Emergency RTH.
Aircraft lands immediately.
Aircraft lands after 10
seconds.
Aircraft lands immediately.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
17
Page 18
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Failsafe RTH
The Forward Vision System allows the aircraft to create a real-time map of its flight route as it flies.
If the Home Point was successfully recorded and the compass is functioning normally, Failsafe RTH
automatically activates after the remote control signal is lost for more than two seconds.
When Failsafe RTH is activated, the aircraft starts to retrace its original ight route home. If the wireless
control signal is re-established within 60 seconds of Failsafe RTH being activated, the aircraft hovers at
its present location for 10 seconds and waits for pilot commands. The user may tap in the DJI GO 4
app or press the RTH button on the remote controller to cancel Failsafe RTH and retake control. If no
pilot command is given, the aircraft ies to the Home Point in a straight line. If the wireless control signal
is still lost 60 seconds after activating Failsafe RTH, the aircraft stops retracing its original ight route and
ies to Home Point in a straight line.
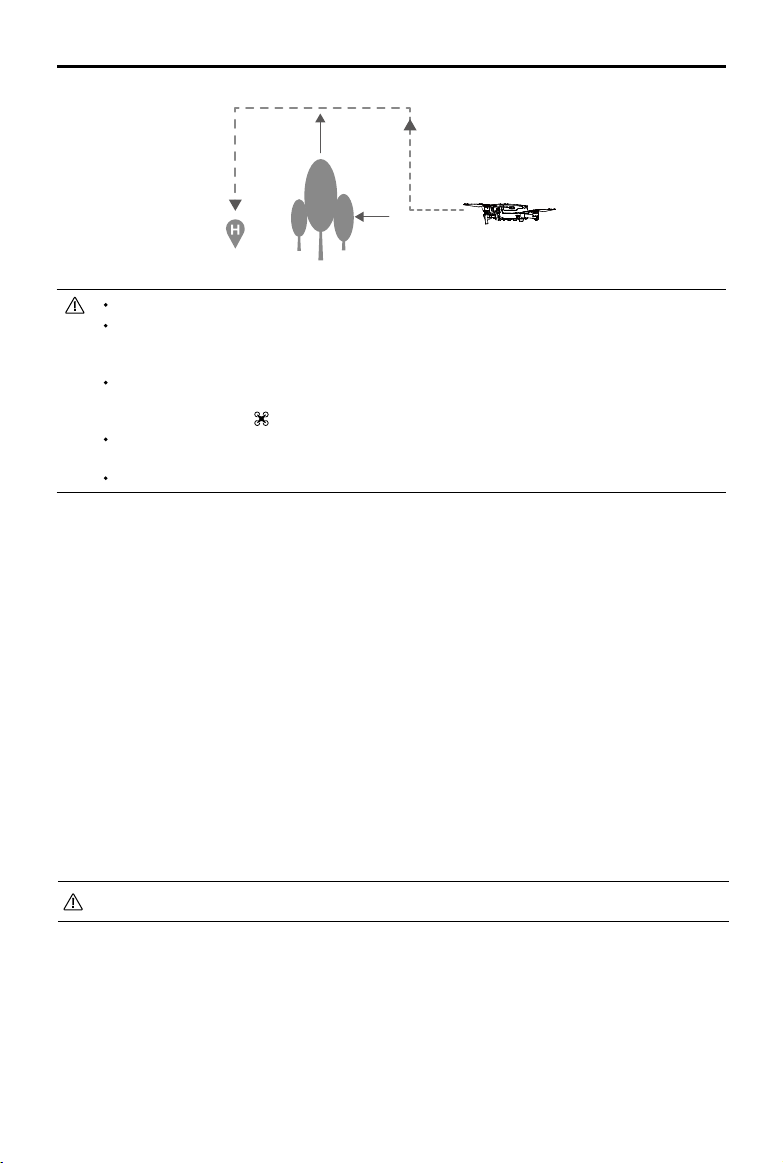
RTH Procedure
Smart RTH, Low Battery RTH, and Failsafe RTH all follow the RTH procedure:
1. The aircraft adjusts its orientation.
2. a. If the aircraft is further than 20 m from the Home Point, it ascends to the pre-set RTH altitude and
then ies to the Home Point at a speed of 12 m/s. If the current altitude is higher than the RTH
altitude, the aircraft ies to the Home Point at the current altitude. Forward and Backward vision
systems are enabled.
b. If the aircraft is between 5 m and 20 m from the Home Point, it ies to the Home Point at the
current altitude. If the current altitude is less than 2 m, the aircraft ascends to 2 m and then ies to
the Home Point at a speed of 3 m/s.
c. If the aircraft is less than 5 m from the Home Point when the RTH procedure begins, it lands
immediately.
3. After reaching the Home Point, the aircraft lands and the motors stop.
1 Record Home Point 2 Conrming Home Point
4 Signal Lost for Extended Time
×
5
RTH (adjustable altitude)
Height over HP > Failsafe Altitude
×
Elevate to Failsafe Altitude
Failsafe Altitude
Height over HP ≤ Failsafe Altitude
3 Remote Controller Signal Lost
×
6 Landing
×
Obstacle Avoidance during RTH
Provided that lighting conditions are sucient for the Forward and Backward Vision Systems to operate,
the Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom senses and actively attempts to avoid obstacles during RTH. The obstacle
avoidance procedure is as follows:
1. The aircraft decelerates when an obstacle is sensed.
2. The aircraft stops and hovers then and ascends until no obstacle is sensed.
3. The RTH procedure resumes. The aircraft ies to the Home Point at the new altitude.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
18
©
Page 19
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
The aircraft cannot return to the Home Point if the GPS signal is weak or if GPS is unavailable.
In Smart RTH and Low Battery RTH, the aircraft automatically ascends to an altitude of 65 ft
(20 m). Once the altitude is 65 ft (20 m) or higher, move the throttle stick and the aircraft stops
ascending and flies to the Home Point at its current altitude.
The aircraft cannot avoid obstacles during Failsafe RTH if the Forward and Backward Vision
Systems are unavailable. It is important to set a suitable RTH Altitude before each flight. Launch
the DJI GO 4 app, tap and then set the RTH Altitude.
During RTH, the aircraft’s speed and altitude can be controlled using the remote controller or the
DJI GO 4 app, but the flight controller controls its orientation and direction of flight.
During RTH, obstacles on either side of the aircraft cannot be detected or avoided.
Landing Protection
Landing Protection activates during Smart RTH and the aircraft performs as follows:
1. When Landing Protection determines that the ground is suitable for landing, the aircraft lands gently.
2. If Landing Protection determines that the ground is not suitable for landing, the aircraft hovers and
waits for the pilot to conrm it is suitable to land.
3. If Landing Protection is not operational, the DJI GO 4 app displays a landing prompt when the
aircraft descends below 0.5 m. Pull down on the throttle for one second or use the auto landing
slider in the app to land.
Landing Protection activates during Low Battery RTH and Failsafe RTH. The aircraft performs as
follows:
During Low Battery RTH and Failsafe RTH, the aircraft hovers at 2 m above the ground and waits for
the pilot to conrm it is suitable to land. Pull down on the throttle for one second or use the auto landing
slider in the app to land. Landing Protection activates and the aircraft performs the steps listed above.
Vision Systems are disabled during landing. Be sure to land the aircraft with caution.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
19
Page 20
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
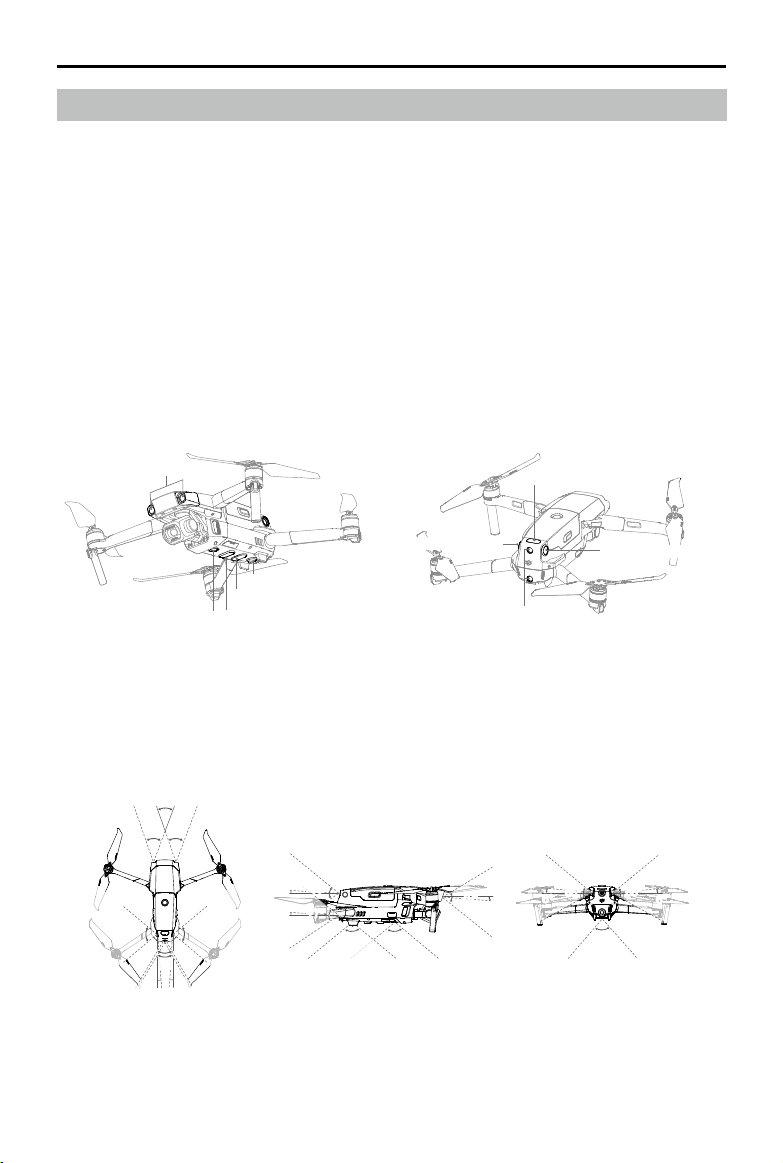
Vision Systems and Infrared Sensing Systems
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom is equipped with Forward, Backward, Downward, and Lateral Vision Systems,
and Upward and Downward Infrared Sensing Systems, providing omnidirectional obstacle sensing (if
lighting conditions are adequate).
The main components of the Forward, Backward, and Downward Vision Systems are six cameras
located on the nose, rear side, and the underside of the aircraft. Lateral Vision Systems are two cameras
located on either side of the aircraft.
The main components of the Upward and Downward Infrared Sensing Systems are two 3D infrared
modules located on the upper and underside of the aircraft.
The Downward Vision System and Infrared Sensing System helps the aircraft maintain its current
position and hover in place more precisely and to y indoors or in other environments where a GPS
signal is unavailable. In addition, the Auxiliary Bottom Light located on the underside of the aircraft
improves visibility for the Downward Vision System in weak light conditions.
Forward Vision System
Downward Vision System
Lateral Vision System
Downward Vision System
Auxiliary Bottom Light
Downward Infrared Sensing System
Upward Infrared Sensing System
Lateral Vision System
Backward Vision System
Detection Range
The detection range of the Vision Systems is depicted as followed. Please note that the aircraft cannot
sense or avoid the obstacles that are not within detection range.
40°
40° 40°
3°
80°
77°
77°
80°
60°
4°
4°
3°
100°100°
70°
5°
65°
6°
83°
65°
6°
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
20
©
Page 21
Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
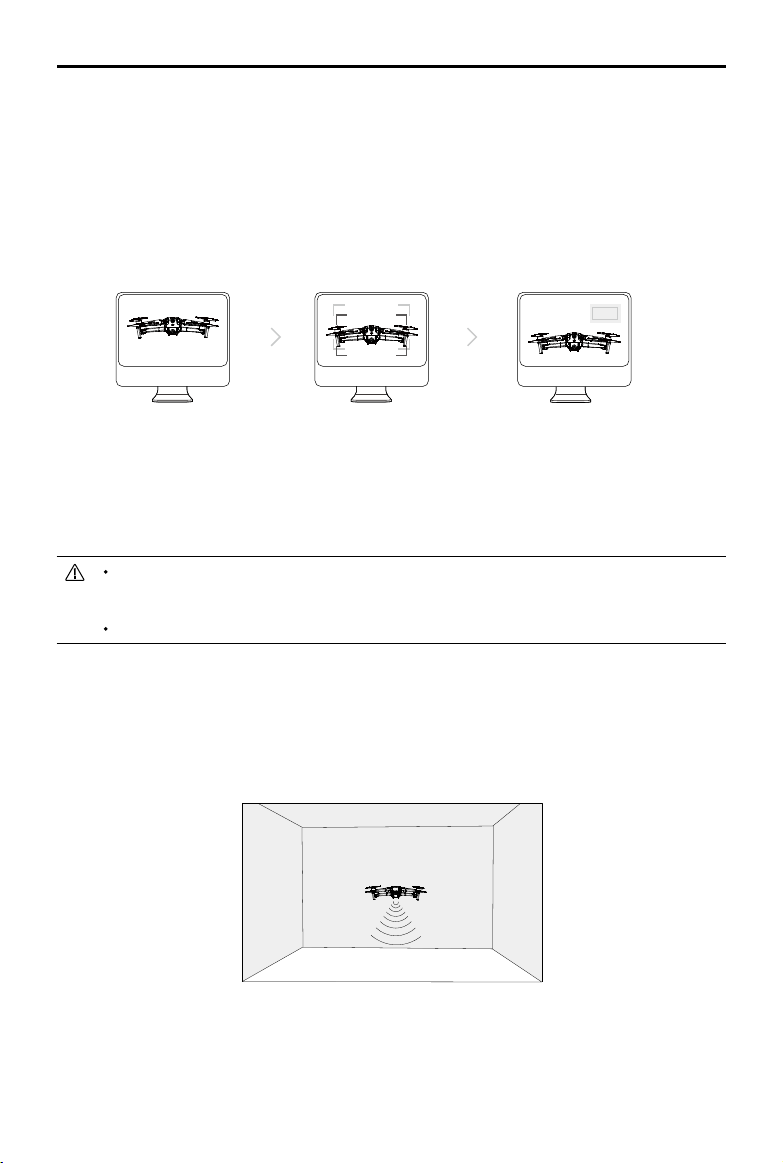
Calibrating Vision System Cameras
The Vision System cameras installed on the aircraft are factory calibrated. If the aircraft experiences
a collision, however, it may require calibration via DJI Assistant 2 or DJI GO
The most accurate way to calibrate the Vision System cameras is by using DJI Assistant 2.
Follow the steps below to calibrate the Forward Vision System cameras, then repeat the steps
to calibrate other Vision System cameras.
4.
Point the aircraft toward the screen
01
02
Align the boxes
03
Pan and tilt the aircraft
When a vision system calibration is required, DJI GO 4 sends a notication. If a computer is not nearby,
however, a quick calibration can be performed in the app. Tap the Aircraft Status bar and Vision Sensors
to start quick calibration.
Quick calibration is only a quick fix for vision system issues. When possible, connect the aircraft
to a computer to carry out a full calibration using DJI Assistant 2. Only calibrate on textured
surfaces such as grass or when lighting conditions are adequate.
Do not calibrate the aircraft on highly reflective surfaces such as marble or ceramic tiles.
Using the Vision Systems
The Downward Vision System and Infrared Sensing System activate automatically when the aircraft
is turned on. No further action is required. When using the Downward Vision System, the aircraft can
hover precisely even without GPS.
The Downward Vision System is typically used in indoor environments where GPS is unavailable. The
Downward Vision System works best when the aircraft is at altitudes of 1.6 to 33 ft (0.5 to 11 m). Please
note that the Vision Positioning function may be aected if the aircraft’s altitude is above 33ft (11 m).
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
21
Page 22

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
2m以上
Follow the steps below to use the Downward Vision System:
1. Ensure the aircraft is in P-mode and place the aircraft on a at surface. Please
T P
S
note that the Downward Vision System cannot work properly on surfaces
without clear pattern variations.
2. Turn on the aircraft. The aircraft hovers in place after takeo. The Aircraft Status Indicators ash green
twice, which indicates the Downward Vision System is working.
Using the Forward and Backward Vision Systems, the aircraft can actively brake when detecting
obstacles in front. The Forward and Backward Vision Systems work best with adequate lighting and
clearly marked or textured obstacles. To allow for sucient time to break, the aircraft should not y more
than 31 mph (50 kph) when ying forward or more than 27 mph (42 kph) when ying backward.
The Lateral Vision Systems requires better lighting and more textured or clearly marked obstacles,
and cannot sense dynamic objects, such as moving people, vehicles, tree branches, or blinking lights.
Lateral Vision Systems are only available in ActiveTrack 2.0 and Tripod Mode. The angular speed is
limited to 24° /s and the lateral ight speed is limited to 18 mph (29 mph).
Lateral Vision Systems are only available in ActiveTrack 2.0 and Tripod Mode. Lateral Vision
Systems have limited ability to sense and avoid obstacles, and the performance may be affected
by the surrounding environment. Be sure to maintain line of sight with the aircraft and pay
attention to prompts in DJI GO 4. DJI takes no responsibility for any aircraft that is damaged or
lost while using Lateral Vision Systems.
The Vision System cannot work properly over surfaces that DO NOT have clear pattern
variations. The Vision System is only effective when the aircraft is at an altitude of 0.5 to 50
meters. Please note that the Vision Positioning function may be affected if the aircraft’s altitude
is above 33 ft (11 m).
The Auxiliary Bottom Light is automatically enabled when the environment light is too weak.
Please note that the Vision System cameras performance may be affected when the auxiliary
bottom light is enabled. Fly with caution if the GPS signal is weak.
The Vision System may NOT function properly when the aircraft is flying over water or snow-
covered areas.
Note that the Vision System may NOT function properly when the aircraft is flying too fast. Fly with
caution when flying at over 10 m/s (32.8 ft/s) at 2 m (6.6 ft) or over 5m/s (16.4 ft) at 1 m (3.3 ft).
Operate the aircraft cautiously when in any of the following situations:
a. Flying over monochrome surfaces (e.g., pure black, pure white, pure green).
b. Flying over highly reflective surfaces.
c. Flying over water or transparent surfaces.
d. Flying over moving surfaces or objects.
e. Flying in an area where the lighting changes frequently or drastically.
f. Flying over extremely dark (< 10 lux) or bright (> 40,000 lux) surfaces.
g. Flying over surfaces that strongly reflect or absorb infrared waves (e.g., mirrors).
h. Flying over surfaces without clear patterns or texture.
i. Flying over surfaces with repeating identical patterns or textures (e.g., tiles with the same design).
j. Flying over obstacles with small surface areas (e.g., tree branches).
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
22
©
Page 23

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
ISO
SHUTTEREVWB
CAPACITY
P
Course Lock
Waypoint
Keep the sensors clean at all times. DO NOT tamper with the sensors. Do not obstruct the Infrared
Sensing System.
The Vision System may not be able to recognize patterns on the ground in low light conditions
(less than 100 lux).
If the aircraft speed exceeds 31 mph (50kph), the Vision System does not have enough time to
brake and stop the aircraft at a safe distance from an obstacle.
If the aircraft experiences a collision, camera calibration is required. Calibrate the front cameras
if DJI GO 4 prompts you to do so.
Do not fly on days that are rainy, smoggy, or if there is no clear sight.
Check the following every time before takeoff:
a. Ensure there are no stickers or any other obstructions over the glass of the Infrared Sensing
and Vision System.
b. If there is any dirt, dust, or water on the glass of the Infrared Sensing and Vision System,
clean it with a soft cloth. Do not use any cleanser that contains alcohol.
c. Contact DJI Support if there is any damage to the glass of the Infrared Sensing and Vision
System.
The Upward Infrared Sensing System detects straight line distances, large obstacles such as
roofs, but cannot detect tiny obstacles such as leaves or electrical wires.
Do not obstruct the Downward Vision System and Downward Infrared Sensing System before
takeoff. Otherwise, the aircraft cannot take off again after landing and will have to be restarted.
Intelligent Flight Modes
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom supports Intelligent Flight Modes including Hyperlapse, QuickShots, ActiveTrack
2.0, Point of Interest (POI 2.0), Waypoint (coming soon), TapFly, and Cinematic Mode. Select an
Intelligent Flight Mode in DJI GO 4. Ensure the battery level is sucient and the aircraft is working on
P-mode when using the Intelligent Flight Modes.
Hyperlapse
Hyperlapse shooting modes include Free, Circle, Course Lock, and Waypoint.
Position
09:29
1600 0.31/8000 4K/244K/25
Hyperlapse
In flight (GPS)
Free Circle
12
61%
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
23
Page 24

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Free
The aircraft automatically takes photos and generates a timelapse video. Free mode can be used while
the aircraft is on the ground. After takeo, control the aircraft’s altitude, ight speed, and gimbal angle
using the remote controller. Hold the control sticks and accelerate at a steady speed for two seconds
and then press the C1 button. The speed is xed and the aircraft continues to travel at that speed while
taking photos. The orientation of the aircraft can still be controlled during this time. Follow the steps
below to use Free:
1. Set the interval time and video duration. The screen displays the number of photos that will be taken
and how long the shooting time will be.
2. Tap the shutter button to begin.
Circle
The aircraft automatically takes photos while ying around the selected subject to generate a timelapse
video. Circle can be selected to travel in either a clockwise or counter-clockwise direction. Please note that
the aircraft exits from Circle if any command from the remote controller is received. Follow the steps below
to use Circle:
1. Set the interval time and video duration. The screen displays the number of photos that will be taken
and how long the shooting time will be.
2. Select a subject on the screen.
3. Tap the shutter button to begin.
CourseLock
With the Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom, Course Lock can be used in two ways. In the rst way, the orientation of
the aircraft is xed, but a subject cannot be selected. In the second way, the orientation of the aircraft is
xed and the aircraft ies around a selected object. Follow the steps below to use Course Lock:
1. Set the interval time and video duration. The screen displays the number of photos that will be taken
and how long the shooting time will be.
2. Set a ight direction.
3. Select a subject (if applicable).
4. Tap the shutter button to begin.
Waypoint
The aircraft automatically takes photos on a flight path of two to five waypoints and generates a
timelapse video. The aircraft can y in order from waypoint No. 1 to No. 5 or No. 5 to No. 1. Please note
that the aircraft exits from Waypoints if any command from the remote controller is received. Follow the
steps below to use Waypoint.
1. Set the desired waypoints and the lens direction.
2. Set the interval time and video duration. The screen displays the number of photos that will be taken
and how long the shooting time will be.
3. Tap the shutter button to begin.
The aircraft will generate a timelapse video with resolution of 1080p25 automatically, which is viewable
in the Playback menu. You can select to save the JPEG or RAW format footage and to store the footage
in built-in storage or SD card in the camera settings.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
24
©
Page 25

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
For optimal performance, it is recommended to use Hyperlapse at an altitude higher than 50 m and
to set a difference of at least two seconds between the interval time and shutter..
It is recommended to select a static subject (e.g., high-rise buildings, mountainous terrain) at a safe
distance from the aircraft (further than 15 m). Do not select a subject that is too near the aircraft.
The aircraft brakes and hovers in place if an obstacle is detected during Hyperlapse.
The aircraft only generates a video if it has taken at least 25 photos, which is the amount required
to generate a 1-second video. The video generates when a command is given from the remote
controller or if the mode is exited unexpectedly (such as when the low battery RTH is triggered).
Task Library (Coming Soon)
Use Task Library to easily record ight paths, which can be repeated later.
QuickShots
QuickShot shooting modes include Dronie, Circle, Helix, Rocket, Boomerang, Asteroid, and Dolly Zoom
(only available with Mavic 2 Zoom). The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom records a video according to the selected
shooting mode and then automatically generates a 10-second video. The video can then be viewed,
edited, or shared to social media from Playback.
Dronie: The aircraft ies backward and ascends, with the camera locked on the subject.
Circle: The aircraft circles around the subject.
Helix: The aircraft ascends and spirals around the subject.
Rocket: The aircraft ascends with the camera pointing downward.
Boomerang: The aircraft ies around the subject in an oval path, ascending as it ies away from
its starting point and descending as it ies back. The aircraft’s starting point forms one end of the
oval’s long axis, while the other end of its long axis is at the opposite side of the subject from the
starting point.
Ensure there is sucient space when using Boomerang: Allow a radius of at least 99 ft (30 m)
around the aircraft and allow at least 33 ft (10 m) above the aircraft.
Asteroid: The aircraft ies backward and upward and then takes several photos, then ies back
to its starting point. The video generated starts with a panorama of the highest position and then
shows the descent. Ensure there is sucient space when using Asteroid: Allow at least 132 ft (40 m)
behind and 164 ft (50 m) above the aircraft.
Dolly Zoom: The Mavic 2 Zoom ies backward and upward. It adjusts the zoom during ight to
keep the selected subject the same while the background changes.
When planning to use Dolly Zoom, rst select the distance between the aircraft and subject. Be
sure that there is at least three times that distance available on the rear side of the aircraft so that
there is sucient space to y.
Using QuickShots
Ensure that the aircraft is in P-mode and that the Intelligent Flight Battery is suciently charged.
Follow the steps below to use QuickShots:
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
25
Page 26

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
ISO
SHUTTEREVWB
CAPACITY
1. Take o and hover at least 6.6 ft (2 m) above the ground.
2 m
2. In DJI GO 4, tap , then select QuickShots and follow the prompts.
12
In flight (GPS)
Position
09:29
1600 0.31/8000 4K/25
Asteroid Dolly ZoomDronie HelixCircle Rocket Boomerang
61%
AFC/MF
AE
3. Select your target subject in Camera View (tap the circle on the subject or drag a box around the
subject) and choose a shooting mode. Tap “GO” to begin recording. The aircraft ies back to its
original position once shooting is nished.
4. Tap to access the video.
Exiting QuickShots
Toggle the Flight Mode switch to S-mode or T-mode to exit QuickShots anytime during shooting (when
Multiple Flight Modes is enabled in the DJI GO 4 app). Press the Flight Pause button on the remote
controller or tap in DJI GO 4 or for the emergency brake.
Please use this function at locations that are clear of buildings and other obstacles. Make sure
that there is no human, animals or other obstacles on the flight path. The aircraft will brake and
hover in place when an obstacle is detected.
Always pay attention to objects around the aircraft and use the remote control device to avoid
accidents (such as collisions) or occlusion with the aircraft.
Be extra cautious when using QuickShot in any of the following situations:
a. When the shoot subject is blocked for a long time or outside the line of sight;
b. When the shoot subject is more than 50 m away from the aircraft;
c. When the shoot subject is similar in color or patterns with the surrounding;
d. When the shoot subject is in the air;
e. When the shoot subject moves fast;
f. The lighting is extremely low (< 300 lux) or high (> 10,000 lux).
DO NOT use QuickShot in places that are close to buildings or the GPS signal is weak, to avoid
unstable flight path.
You must follow local privacy laws and regulations when using QuickShot.
Note that the lateral vision system is unavailable during QuickShot.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
26
©
Page 27

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
ISO
SHUTTEREVWB
CAPACITY
ActiveTrack 2.
0
ActiveTrack 2.0 allows you to select an object on your mobile device screen. The aircraft adjusts its ight
to track the subject. No external tracking device is required. Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom can automatically identify
up to 16 objects and uses dierent tracking strategies to track people, vehicles, and boats.
Using ActiveTrack 2.
0
Ensure that the aircraft is in P-mode and that the Intelligent Flight Battery is suciently charged. Follow
the steps below to use ActiveTrack 2.0:
1. Take o and hover at least 6.6 ft (2 m) above the ground.
2 m
2. In DJI GO 4, tap , then select ActiveTrack 2.0.
12
In flight (GPS)
ActiveTrack
09:29
1600 0.31/8000 4K/244K/25
61%
Trace
SpotlightParallel
3. For optimal performance, it is recommended to select a subject that is automatically recognized by
the aircraft. To do so, select a subject that has been recognized onscreen and tap to conrm your
selection. If the desired subject has not been recognized by the aircraft, drag a selection around it
onscreen and tap to select it manually. When the subject is selected manually, however, the ability of
the aircraft to track the subject may be aected. If the box turns red, the object cannot be identied
and it needs to be selected again.
4. The aircraft automatically avoids obstacles in its ight path. If the aircraft loses track of the subject
because it is moving too fast or is obscured, re-select the subject to resume tracking.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
27
Page 28

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
ActiveTrack 2.0 includes the following sub-modes:
Trace Parallel Spotlight
The aircraft tracks the subject at
a constant distance. Use the roll
stick and tilt stick on the remote
controller to change the distance,
and use the slider in DJI GO 4 to
y in a circle around the subject.
The framing of the subject is
adjusted using the left stick and
gimbal dial.
When detecting an obstacle in this
sub-mode, the aircraft will behave
as follows:
1. If any action is performed on
the remote controller after
The aircraft tracks the subject
at a constant angle and
distance from the front and
side. Use the roll stick on
the remote control to y in
a circle around the subject.
The framing of the subject is
adjusted using the left stick
and gimbal dial.
In this sub-mode, the aircraft
brakes and hovers in place
once an obstacle is detected.
The aircraft does not track
a subject automatically, but
keeps the camera pointed in
the direction of the subject
during ight. The remote
controller is used to maneuver
the aircraft, but control of
orientation is disabled. The
framing of the subject is
adjusted using the left stick
and gimbal dial. The aircraft
brakes immediately when an
obstacle is detected in this
sub-mode.
an obstacle is detected, the
aircraft brakes and hovers in
place.
2. If no action is taken, the aircraft
tries to avoid the obstacle.
DO NOT use ActiveTrack 2.0 in areas with people, animals, small or fine objects (e.g., tree
branches or power lines), or transparent objects (e.g., water or glass).
Operate the aircraft manually (press the Flight Pause button or toggle the Flight Mode switch to
S-mode on the remote controller) or tap in DJI GO 4 in an emergency.
Be extra vigilant when using ActiveTrack 2.0 in any of the following situations:
a. The tracked subject is not moving on a level plane.
b. The tracked subject changes shape drastically while moving.
c. The tracked subject is out of sight for an extended period.
d. The tracked subject is moving on a snowy surface.
e. The tracked subject has a similar color or pattern to its surrounding environment.
f. Available light is too low (< 300 lux) or too high (> 10,000 lux).
You must follow local privacy laws and regulations when using ActiveTrack 2.
It is recommended to only track people, vehicles, and boats. Fly with caution when tracking
other subjects.
The tracking subject may inadvertently swap to another subject if they pass nearby to each other.
There are two options when selecting the tracking speed limit. Safe mode limits the speed to no
more than 12 m/s and Max mode to no more than 20 m/s. Please note that the aircraft cannot
avoid obstacles if the speed exceeds 12 m/s.
0.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
28
©
Page 29

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
ISO
SHUTTEREVWB
CAPACITY
GO
8m/s
Speed
50m
Height
--m
Radius
P-GPS
P
Exiting ActiveTrack 2.
0
Press the Flight Pause button on the remote controller to brake immediately. Tap on the screen or
toggle the Flight Mode switch to S-mode on the remote controller to exit ActiveTrack 2.0. After exiting
ActiveTrack 2.0, the aircraft hovers in place, at which point you may choose to fly manually, track
another subject, or return to home.
Point of Interest 2.0 (POI 2.
0)
Select a static subject as the Point of Interest. Set the circle radius, ight altitude, and ight speed. The
aircraft ies around the subject according to these settings. Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom supports selecting the
POI through GPS positioning and selecting on the screen directly.
12
In flight (GPS)
Position
09:29
1600 0.31/8000 4K/244K/25
Point of Interest
61%
1. Select POI on the screen: drag a box around the desired subject and tap the “GO” icon on the
screen. The aircraft starts to measure the location of the subject and ies around the subject once
it measures the location successfully. Use the gimbal dial to adjust the subject framing. The circle
radius, ight altitude, and ight speed can also be adjusted during ight.
It is recommended to select a static subject (e.g., high-rise buildings, mountainous terrain) at a safe
distance from the aircraft (further than 10 m). Do not select a subject that is too near the aircraft.
Avoid selecting a subject without a clear pattern (e.g., a clear blue sky).
Avoid selecting subjects that are too small.
Select a subject with a clear outline. Otherwise, the subject may not be centered correctly onscreen.
The aircraft cannot be controlled while the location is being measured, but the measuring can be
stopped using the control sticks, Flight Pause button, Flight Mode switch, and the “STOP” icon.
2. Select a subject through GPS positioning: Manually y the aircraft above the subject, and then press
the C1 button or select in DJI GO 4 to conrm the subject. Fly the aircraft at least 5 m away from the
Point of Interest. The ight speed and the circle direction can be set in DJI GO 4. Tap “GO” to start
ying. Use the gimbal dial to adjust the subject framing. The circle radius, ight altitude, and ight
speed can also be adjusted during ight.
The GPS positioning has no altitude measurement.
It is recommended to adjust the gimbal tilt to -90° to make it easier to measure the GPS
location.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
29
Page 30

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Flight Parameter Settings
1. Flight Speed: Flight speed range is 0-10 m/s, the “+” value means the aircraft circles the point
counter-clockwise, and the “–” value means the aircraft circles the point clockwise. Adjust the speed
by sliding the onscreen slider, and use the roll stick on the remote controller to increase the value.
2. Circle Radius: Adjust the radius by sliding the onscreen slider, and use the tilt stick on the remote
controller to increase the value.
3. Circle Attitude: Adjust the attitude by sliding the onscreen slider, and use the throttle stick on the
remote controller to increase the value.
4. Gimbal Angle: Use the yaw stick to control the gimbal’s yaw, and use the gimbal dial to control the
gimbal’s tilt. Tap the icon to recenter the gimbal (If GPS Positioning is used to select the Point of
Interest, only the yaw recenters. If the Point of Interest is selected on the screen, both the yaw and
tilt recenter).
5. Circle Direction: Select the direction by sliding the onscreen button.
Exiting Point of Interest
Tap on the screen or press the Flight Pause button to pause the Point of Interest mode. Press and
hold on the Flight Pause button to exit Point of Interest mode.
The aircraft brakes and hovers in place once an obstacle is detected during POI.
If the aircraft nose is aimed towards the Point of Interest during flight, the aircraft may not be
able to avoid obstacles. Use Point of Interest in a wide open area.
Waypoints (Coming Soon)
The aircraft ies to the waypoints in order according to the settings. The ight orientation and speed
can be controlled during ight. You can select the waypoints by ying the Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom to the
waypoints and record them individually. The waypoints can also be selected and edited in the map
before takeo:
1. Add Waypoints and Point of Interest in the map. The aircraft’s camera points to the Point of Interest
when traveling through the waypoints.
2. Tap on the Waypoints and Point of Interest to set the altitude, ight speed, and other parameters.
3. Drag the Waypoints and Point of Interest to adjust the positions.
4. Flight speed, failsafe settings, and aircraft behavior can be configured after completing the
Waypoints.
5. Waypoints and Point of Interest information can be saved in the app while editing in the map and the
ight path can be recorded and repeated.
In challenging environments such as those surrounded by high-rise buildings it is recommended
to set waypoints by flying to each waypoint manually.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
30
©
Page 31

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
ISO
SHUTTEREVWB
CAPACITY
TapFly
TapFly features three sub-modes; Forward, Backward, and Free. Providing that lighting conditions are
suitable, the aircraft automatically avoids obstacles it senses.
Forward: The aircraft ies towards the target with the Forward Vision System sensing obstacles.
Backward: The aircraft ies in the opposite direction of the target with the Backward Vision System
sensing obstacles.
Free: The aircraft ies towards the target. The remote controller can be used to maneuver the orientation
of the aircraft freely. The aircraft cannot avoid obstacles in this mode. Fly with caution.
Using TapFly
Ensure that the aircraft is in P-mode and that the Intelligent Flight Battery is suciently charged. Follow
the steps below to use TapFly:
1. Take o and hover at least 3.3 ft (1 m) above the ground.
1 m
2. In DJI GO 4, tap , select TapFly, then select a sub-mode and follow the prompts.
12
In flight (GPS)
TapFly
1600 0.31/8000
12
09:29
61%
2.4G
4K/2420GB
GO
正向
Backward FreeForward
3. Tap on the target and wait for “GO” to appear. Tap “GO” to conrm the selection and the aircraft
ies to the target automatically. A prompt appears if the target cannot be reached. If this is the case,
select another target and try again. The target can be changed midight by tapping the screen.
Exiting TapFly
Press the Flight Pause button on the remote controller or pull a control stick in the direction opposite to
the direction of ight and the aircraft brakes and hovers in place. Tap the screen to resume TapFly. Tap
or toggle the Flight Mode switch to S-mode to exit TapFly.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
31
Page 32

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
DO NOT use TapFly in areas with people, animals, small or fine objects (e.g., tree branches or
power lines), or transparent objects (e.g., water or glass). TapFly may not work properly when
the aircraft is flying over water or snow-covered areas.
There may be deviations between expected and actual flight paths selected in TapFly.
The selectable range for the target direction is limited. You cannot make a selection close to the
upper or lower edges of the screen.
Cinematic Mode
Tap in DJI GO 4 to select Cinematic mode. In Cinematic mode, the aircraft’s braking distance is
extended and its rotation speed is reduced. The aircraft slows down gently until it stops, keeping
footage smooth and stable even if control inputs are choppy.
Advanced Pilot Assistance Systems
The Advanced Pilot Assistance Systems (APAS) feature is available in P-mode. When APAS is enabled,
the aircraft continues to respond to user commands and plans its path according to both control stick
inputs and the ight environment. APAS makes it easier to avoid obstacles, obtain smoother footage,
and gives a better ying experience.
When APAS is enabled, pressing the Flight Pause button on the remote controller or tapping in DJI
GO 4 brings the aircraft to a stop. The aircraft hovers for three seconds and awaits pilot commands.
To enable APAS, tap
The APAS feature is automatically disabled when using Intelligent Flight Modes and resumes
automatically after exiting Intelligent Flight Modes.
The APAS feature is only available when flying forward and backward. If the aircraft flies left or
right, APAS is disabled.
The aircraft hovers in place once there is an obstacle that cannot be avoided. The aircraft cannot
detect and avoid obstacles that are beneath it.
Make sure you use the Advanced Pilot Assistance System (APAS) when the Vision Systems
are available. Ensure there are no people, animals, small or subtle objects (e.g., tree branches,
power lines) or transparent objects (e.g., glass, water) along the desired flight path.
APAS may not function properly when the aircraft is flying over water or snow-covered area.
Be extra cautious when flying in extremely dark (< 300 lux) or bright (> 10,000 lux) environments.
APAS may not function properly when the aircraft is flying near its Flight Limits or in No-fly
Zones.
Pay attention to the Aircraft Status Bar in DJI GO 4 and ensure the aircraft is working in APAS
mode normally.
in DJI GO 4.
APAS
Flight Recorder
Flight data including ight telemetry, aircraft status information, and other parameters are automatically
saved to the aircraft’s internal data recorder. The data can be accessed using DJI Assistant 2.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
32
©
Page 33

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Attaching and Detaching the Propellers
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom use low-noise propellers. There are two varieties of the propellers, which are
designed to spin in dierent directions. White marks are used to indicate which propellers should be
attached to which motors.
Marked Unmarked
Attach on motors with white marks Attach on motors without white marks
Turn the propellers in the indicated direction to mount and tighten.
Attaching the Propellers
Attach the propellers with the white marks to the motors with white marks and the unmarked propellers
to the motors without marks. Press each propeller down onto the motor and turn until it is secure.
Marked Unmarked
Detaching the Propellers
Press the propellers down onto the motors and rotate them in the unlock direction.
Propeller blades are sharp. Handle with care.
Only use original DJI propellers. Do not mix propeller types.
Ensure that all propellers are in good condition before each flight. Do not use aged, chipped, or
broken propellers.
Ensure that the propellers and motors are installed securely before each flight.
To avoid injury, stand clear of and do not touch propellers or motors when they are spinning.
To avoid damaging the propellers, place the aircraft in the direction shown in the carrying
case during transportation or storage. Do not squeeze or bend the propellers. If propellers are
damaged, the flight performance is affected.
Ensure the motors are mounted securely and rotating smoothly. Land the aircraft immediately if
a motor is stuck and unable to rotate freely.
Keep the motors free of dust.
DO NOT attempt to modify the structure of the motors.
DO NOT touch or let your hands or body come in contact with the motors after flight as they
may be hot.
DO NOT block any of the ventilation holes on the motors or the body of the aircraft.
Ensure the ESCs sound normal when powered on.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
33
Page 34

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Intelligent Flight Battery
The Mavic 2 Intelligent Flight Battery is a 15.4 V, 3850 mAh battery with smart charging/discharging
functionality. Only use a DJI approved AC power adapter to charge the battery.
Intelligent Flight Battery AC Power Adapter
Battery Features
1. Battery Level Display: The LED indicators display the current battery level.
2. Auto-Discharging Function: To prevent swelling, the battery automatically discharges to less than
60% of the maximum battery level when it is idle for more than 10 days. It takes approximately three
to four days to discharge the battery to 65%. It is normal to feel moderate heat being emitted from
the battery during the discharging process.
3. Balanced Charging: During charging, the voltages of the battery cells are automatically balanced.
4. Overcharge Protection: The battery stops charging automatically once fully charged.
5. Temperature Detection: The battery only charges when the temperature is between 41° and 104° F (5°
and 40° C).
6. Overcurrent Protection: The battery stops charging if an excess current is detected.
7. Over-discharge Protection: Discharging stops automatically to prevent excess discharge.
8. Short Circuit Protection: The power supply is automatically cut if a short circuit is detected.
9. Battery Cell Damage Protection: DJI GO 4 displays a warning message when a damaged battery cell
is detected.
10. Hibernation Mode: The battery switches o after 20 minutes of inactivity to save power. If the
battery level is less than 10%, the battery enters Hibernation mode to prevent over-discharge. In
Hibernation mode, the battery level indicators do not illuminate. Charge the battery to wake it from
hibernation.
11. Communication: Information about the battery's voltage, capacity, and current is transmitted to the
aircraft.
Refer to the Mavic 2 Intelligent Flight Battery Safety Guidelines before use. Users take full responsibility
for all operations and usage.
Using the Battery
Battery Level LEDs
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
34
©
Power Button
Low
High
Page 35

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Checking Battery Level
The battery level LEDs display how much charge remains. If the battery is turned o, press the Power
button, and the battery level LEDs light up to display the current battery level
Powering On/O
Press the Power button once, then press again, and hold for two seconds to turn the battery on or o.
Low Temperature Notice
1. Battery capacity is signicantly reduced when ying in low-temperature environments of 14° to 41° F
(-10° to 5° C). It is recommended to hover the aircraft in place for a while to heat the battery. Ensure
to fully charge the battery before takeo.
2. Batteries cannot be used in extremely low-temperature environments of < 14° F (-10° C).
3. When in low-temperature environments, end the ight as soon as DJI GO 4 displays the low battery
level warning.
4. To ensure optimal performance of the battery, keep the battery temperature above 68° F (20° C).
5. The reduced battery capacity in low-temperature environments reduces the aircraft's wind speed
resistance performance. Please y with caution.
6. Fly with extra caution at a high sea level.
In cold environments, insert the battery into the battery compartment and turn on the aircraft for
approximately 1 to 2 minutes to warm up before taking off.
Charging the Battery
Fully charge the Intelligent Flight Battery before using for the rst time:
1. Connect the AC power adapter to a power source (100-240 V, 50/60 Hz).
2. Attach the Intelligent Flight Battery to the AC power adapter using the battery charging cable with
the battery powered o.
3. The battery level LEDs display the current battery level during charging.
4. The Intelligent Flight Battery is fully charged when the battery level LEDs are all turned o. Detach the
AC power adapter when the battery is fully charged.
Charging Time: 1 hour and 30 minutes.
DO NOT charge an Intelligent Flight Battery immediately after flight as the temperature may be too
high. Wait until it cools down to room temperature before charging again.
The AC power adapter stops charging the battery if the battery cell temperature is not within the
operating range of 41° to 104° F (5° to 40° C). The ideal charging temperature is 71.6° to 82.4° F
(22° to 28° C).
The Battery Charging Hub (not included) can charge up to four batteries. Please visit the official
DJI Online Store to learn more.
Power Outlet
AC Power Adapter
Intelligent Flight Battery
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
35
Page 36

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Battery Level LEDs During Charging
LED1 LED2 LED3 LED4
Battery Level LEDs During Charging
Battery Level
0%~25% 25%~50% 50%~75% Fully Charged
Battery Protection
Battery Protection Mechanisms
LED1 LED2 LED3 LED4 Blinking Pattern Battery Protection Item
LED2 blinks twice per second Overcurrent detected
LED2 blinks three times per
second
Short circuit detected
LED3 blinks twice per second Overcharge detected
LED3 blinks three times per
second
Over-voltage charger detected
LED4 blinks twice per second Charging temperature is too low
LED4 blinks three times per
second
Charging temperature is too high
Inserting the Intelligent Flight Battery
Insert the Intelligent Flight Battery into the aircraft’s battery compartment. Make sure it is mounted
securely and that the battery latches have clicked into place.
Click
Removing the Intelligent Flight Battery
Slide the battery latches on the sides of the Intelligent Flight Battery to open the battery compartment.
Never insert or remove the battery while it is turned on.
Ensure the battery is mounted securely.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
36
©
Page 37

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Gimbal and Camera
Gimbal
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom 3-axis gimbal provides stabilization for the camera, allowing you to capture clear
and stable images and video. The gimbal has a tilt range of -90˚ to +30˚. Gimbal settings such as Gimbal
Mode and Gimbal Auto Calibration can be selected by tapping .
Use the gimbal dial on the remote controller to control the camera’s tilt. Alternatively, enter Camera View
in DJI GO 4. Press the screen until a blue circle appears and drag the circle up and down to control
camera tilt. Dragging the circle left and right controls the aircraft’s orientation.
Gimbal Operation Modes
Two gimbal operation modes are available. Switch between the different operation modes on the
camera settings page of DJI GO 4.
Follow Mode: The angle between the gimbal’s orientation and aircraft’s nose remains constant at all
times.
FPV Mode: The gimbal synchronizes with the movement of the aircraft to provide a first-person
perspective ying experience.
When the aircraft is powered on, do not tap or knock the gimbal. To protect the gimbal during
takeoff, always take off from open and flat ground.
Precision elements in the gimbal may be damaged in a collision or impact, which may cause the
gimbal to function abnormally.
Avoid getting dust or sand on the gimbal, especially in the gimbal motors.
A gimbal motor error may occur in the following situations:
a. The aircraft is on uneven ground or the gimbal’s motion is obstructed.
b. The gimbal experiences excessive external force, such as during a collision.
DO NOT apply external force to the gimbal after the gimbal is powered on. DO NOT add any
extra payload to the gimbal as this may cause the gimbal to function abnormally or even lead to
permanent motor damage.
Make sure to remove the gimbal cover before powering on the aircraft. Also, make sure to mount
the gimbal cover when the aircraft is not in use.
Flying in heavy fog or clouds may make the gimbal wet, leading to temporary failure. The gimbal
recovers full functionality once it dries.
Camera
The Mavic 2 Pro uses a 1" CMOS sensor camera (jointly developed by DJI and Hasselblad), which
features a lens with an adjustable aperture with a range of F2.8-F11. The camera supports auto focus,
which can focus at 1 m to innity. The lters on the camera can also be replaced. The Mavic 2 Pro
camera shoots up to 4K30fps video and 20 MP photos, supports shooting modes such as Single shot,
Burst shooting, Interval, Panorama, Slow motion, and Enhanced HDR.
The Mavic 2 Zoom uses a 1/2.3" CMOS sensor camera, supports 2x optical zoom, and the lens is
24-48 mm (35 mm format equivalent). The camera supports auto focus, which can focus at 0.5 m to
innity. The camera also supports replacing lters. The Mavic 2 Zoom camera shoots up to 4K30fps
video and 12-megapixel photos, supports shooting modes such as Single shot, Burst shooting, Interval,
Panorama, Slow motion and Enhanced HDR. Mavic 2 Zoom supports 2x optical zoom and 2x digital
zoom when recording video in 1080p24/25/30.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
37
Page 38

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Ensure the temperature and humidity is suitable for the camera during usage and storage.
Use a lens cleanser to clean the lens to avoid damage.
DO NOT block any ventilation holes on the camera as the heat generated may damage the device
and hurt the user.
Storing the Photos and Videos
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom comes with 8 GB of internal storage and also supports the use of a microSD
card to store your photos and videos. A UHS-I Speed Grade 3 rating microSD card is required due to
the fast read and write speeds necessary for high-resolution video data.
Do not remove the microSD card from the aircraft while it is turned on. Otherwise, the microSD
card may be damaged.
To ensure the stability of the camera system, single video recordings are limited to 30 minutes.
Check camera settings before use to ensure they are configured as desired.
Before shooting important pictures or videos, shoot a few images to test the camera is operating
correctly.
Photos or videos cannot be transmitted or copied from the camera if the Intelligent Flight Battery
is powered off.
Be sure to power off the Intelligent Flight Battery correctly. Otherwise, your camera parameters
will NOT be saved and any recorded videos may be damaged. Note: Regardless of the reason,
DJI is not responsible for any failure of an image or video to be recorded or having been recorded
in a way that is not machine-readable.
Video Edit
The Mavic 2 Pro supports video formats MP4 and MOV, providing Normal, D-Log, and HLG color
modes. In Normal mode, H.264 and H.265 code formats are supported. In D-Log or HLG mode, only
H.265 is supported.
For the Mavic 2 Pro, Full FOV down samples from the 5.5K sensor to 4K resolution while HW crops in
the center for ner image quality but less FOV. Full FOV view is 75° and HQ view is 55°. You can select
between them according to your actual shooting demands.
Mavic 2 Zoom supports video formats MP4 and MOV, providing Normal and D-Cinelike color modes.
H.264 and H.265 code formats are supported.
The software below has been tested by DJI and is recommended for playing or editing videos.
Software Mac Version Win Version
Adobe Premier Pro CC 2018 v12.1.1 (10) v12.1.1 (10)
Davinci Resolve v15.0 free v14.3 Studio
Apple Final Cut Pro X v10.4.3 /
Apple QuickTime v10.4 (928.5.1) /
Apple iMovie v10.4.2 /
VLC Player v3.0.2 v3.0.2
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
38
©
Page 39

Remote Controller
This section describes the features
of the remote controller and includes
instructions for controlling the aircraft
and the camera.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
39
Page 40

Remote Controller
Built into the remote controller is DJI’s long-range transmission technology OcuSync 2.0, offering a
maximum transmission range of 5 mi (8 km) and displaying video from the aircraft to DJI GO 4 on your
mobile device at up to 1080p. Easily control the aircraft and camera using the onboard buttons. An
onboard LCD screen gives real-time aircraft data information and the detachable control sticks make
the remote controller easier to store.
In a wide-open area with no electromagnetic interference, OcuSync 2.0 smoothly transmits video links
at up to 1080p, no matter how the ight attitude is changed. The remote controller works at both 2.4
GHz and 5.8 GHz, automatically selecting the best transmission channel. OcuSync 2.0 reduces the
latency to 120-130 ms by improving the camera performance through the video decoding algorithm and
the wireless link.
Auto Focus is supported during shooting even in low light conditions. The Mavic 2 Pro supports
aperture and shutter adjustment and the Mavic 2 Zoom supports zoom in/out by using the Zoom
Adjustment Dial.
The built-in battery has a capacity of 3950 mAh and a maximum run time of 2 hours and 15 minutes.
The remote controller charges the mobile device with a charging ability of 500 mA@5V. The remote
controller automatically charges Android devices. For iOS devices, rst be sure that charging is enabled
in DJI GO 4. Charging for iOS devices is disabled by default and needs to be enabled each time the
remote controller is powered on.
Using the Remote Controller
Press the Power button to display the current battery level on the LCD screen. Press once, then again,
and hold to turn the remote controller on or o.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
40
©
Page 41

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Charging the Battery
Connect the provided AC power adapter to the power port on the remote controller. It takes
approximately 2 hours and 15 minutes to charge the remote controller battery fully. Remove the RC
cable from the remote controller before charging.
Power Outlet
AC Power Adapter
USB Adapter
Controlling the Camera
Use the Aperture/Shutter Adjustment Dial to adjust the aperture and shutter parameters (Mavic 2 Pro
only).
Use the Record button to start/stop recording.
Use the Focus/Shutter button to auto focus and take photos.
Use the Zoom Adjustment Dial to zoom in/out (Mavic 2 Zoom only).
3
2
1
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
41
Page 42

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Controlling the Aircraft
The control sticks control the aircraft’s orientation (yaw), forward/ backward movement (pitch), altitude
(throttle), and left/right movement (roll). The control stick mode determines the function of each control
stick movement. Three preprogrammed modes (Mode 1, Mode 2, and Mode 3) are available and
custom modes can be congured in DJI GO 4. The default mode is Mode 2.
In each of the three pre-programmed modes, the Mavic 2 hovers in place at a constant orientation when
both sticks are centered. Pushing a control stick away from the center position performs the functions
shown in the gure below.
Mode 1
Mode 2
Mode 3
Left Stick
Left Stick Right Stick
Forward
Backward
Turn RightTurn Left
Up
Down
Turn RightTurn Left
Forward
Right Stick
Right StickLeft Stick
Up
Down
RightLeft
Forward
Backward
RightLeft
Up
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
42
©
Backward
Down
RightLeft
Turn RightTurn Left
Page 43

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Remote
Controller
(Mode 2)
( Indicates Nose Direction)
Aircraft
Remarks
Moving the left stick up or down changes the
aircraft’s altitude. Push the stick up to ascend
and down to descend. The more the stick is
pushed away from the center position, the faster
the aircraft will change altitude. Always push the
stick gently to prevent sudden and unexpected
changes in altitude.
Moving the left stick to the left or right controls
the orientation of the aircraft. Push the stick left to
rotate the aircraft counter-clockwise and right to
rotate the aircraft clockwise. The more the stick is
pushed away from the center position, the faster
the aircraft will rotate.
Moving the right stick up and down changes the
aircraft’s pitch. Push the stick up to fly forward
and down to y backward. The more the stick is
pushed away from the center position, the faster
the aircraft will move.
Moving the right stick to the left or right changes
the aircraft’s roll. Push the stick left to y left and
right to fly right. The more the stick is pushed
away from the center position, the faster the
aircraft will move.
It is recommended to remove the control sticks and store in the storage slots on the remote
controller during storage or transportation to avoid damage.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
43
Page 44

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Flight Mode Switch
Toggle the switch to select the desired ight mode.
Position Flight Mode
S S-mode
S
T P
P P-mode
T T-mode
Regardless of which position the switch is in on the remote controller, the Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom begins
in P-mode by default. To switch ight modes, rst go to Camera View in DJI GO 4, tap and enable
“Multiple Flight Modes”. After enabling multiple ight modes, toggle the switch to P and then to S or T to
switch ight modes.
RTH Button
Press and hold the RTH button to start the Return to Home (RTH) procedure where the aircraft returns
to the last recorded Home Point. Press this button again to cancel RTH and regain control of the
aircraft. Refer to the Return to Home section for more information about RTH.
C1 and C2 Button
The functions of the C1 and C2 buttons are set in DJI GO 4. The default conguration for the C1 button
is Center Focus and the default conguration for the C2 button is Playback. Remote Controller Alert
Remote controller will sound an alert during RTH or when the battery level is low. RTH Alert and low
battery level (6% to 15%) alert can be canceled by pressing the power button once, and the critical
battery level (less than 5%) alert can not be canceled.
Remote Controller Alert
Remote controller will sound an alert during RTH or when the battery level is low. RTH Alert and low
battery level (6% to 15%) alert can be canceled by pressing the power button once, and the critical
battery level (less than 5%) alert can not be canceled.
Optimal Transmission Zone
The signal between the aircraft and the remote controller is most reliable when the antennas are
positioned in relation to the aircraft as depicted below.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
44
©
Page 45

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
strong
weak
Ensure that the aircraft is ying within the optimal transmission zone. To maintain optimal transmission
performance, adjust the remote controller and antennas according to the gure above.
LCD Screen
The LCD Screen displays various system statuses including real-time ight telemetry and battery levels.
Refer to the gure below for the meaning of each icon on the LCD Screen.
GPS signal strength
System status prompt
Flight speed
RC battery level
Distance to the ground
Flight mode*
Vision System
Aircraft battery level
RC signal strength
Flight distance
Exposure compensation
Ascend/Descend
Flight altitude
Camera status
Motor rotation
speed
Micro SD
placement
Sport modes
* On the remote controller’s screen, the Primary remote controller displays “MCTL” while the Secondary remote
controller will display the ight mode.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
45
Page 46

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Dual Remote Controller Mode (Coming soon)
The Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom supports Dual Remote Controller Mode, which allows two remote controllers to
connect to the same aircraft.
Both the Primary remote controller and the Secondary remote controller can control the orientation of
the aircraft and the movement of the gimbal and camera operation.
Please note the dierent operations of the Primary and Secondary remote controller listed below.
1. Gimbal Dial
Both the Primary remote controller and the Secondary remote controller can control the gimbal
dial, but the Primary remote controller has priority. For example, the Secondary remote controller is
unable to control the gimbal dial when the Primary remote controller is using the gimbal dial. After
the Primary remote controller has stopped controlling the gimbal dial for two seconds or more, the
Secondary remote controller can control the gimbal dial.
2. Control Stick
Both the Primary remote controller and the Secondary remote controller can control the orientation
of the aircraft using control sticks. The Primary remote controller has priority. The Secondary remote
controller is unable to control the aircraft’s orientation when the Primary remote controller is operating
the control sticks. After the control sticks are idle for two seconds or more, the Secondary remote
controller can control the aircraft’s orientation.
If the control sticks on the Primary remote controller are pushed down and inward, the motors of the
aircraft stop. If the same action is performed on the Secondary remote controller, however, the aircraft
does not respond.
The control sticks on the Primary remote controller need to be released so that the Secondary remote
controller can control the aircraft.
3. Flight Mode Switch
The ight mode can only be switched on the Primary remote controller. The Flight Mode Switch is
disabled on the Secondary remote controller.
4. DJI GO 4 Settings
The display and parameter settings for the Primary and Secondary remote controllers in DJI GO 4
are the same. The Secondary remote controller can only congure the ight controller, vision system,
video transmission, and Intelligent Flight Battery. Display and parameter settings for the Primary and
Secondary remote controllers are the same in DJI GO 4.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
46
©
Page 47

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Linking the Remote Controller
The remote controller is linked to your aircraft before delivery. Linking is only required when using a new
remote controller for the rst time. Follow these steps to link a new remote controller:
1. Power on the aircraft and the remote controller.
2. Launch DJI GO 4.
3. Enter “Camera” and tap on and then tap the button to conrm. The remote controller is ready
to link.
4. Locate the linking button on the side of the aircraft, as shown in the gure below. Press the link
button to start linking. The Linking Status Indicator displays solid green once the remote controller
successfully links to the aircraft, and the LCD screen on the remote controller displays the aircraft’s
information.
Linking Status Indicator
Ensure the remote controller is within 1.6 ft (0.5 m) of the aircraft during linking.
The remote controller will unlink itself from an aircraft if a new remote controller links to the same
aircraft.
In Dual Remote Controller Mode, the Secondary remote controller must also be relinked to the
aircraft when the Primary remote controller is relinked to the aircraft.
Fully charge the remote controller before each flight.
If the remote controller is powered on and is NOT in use for five minutes, an alert will sound.
After 10 minutes, it will automatically power off. Move the sticks to cancel the alert.
Adjust the mobile device clamp to ensure the mobile device is secure.
Ensure the antennas of the remote controller are unfolded and adjusted to the proper position to
achieve optimal transmission quality.
Repair or replace the remote controller if damaged. A damaged remote controller antenna
greatly decreases performance.
Fully charge the battery at least once every three months to maintain battery health.
Ensure the control sticks are mounted securely.
Link Button
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
47
Page 48

DJI GO 4 App
This section introduces the main
functions of the DJI GO 4 app.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
48
©
Page 49

DJI GO 4 App
Use this app to control the gimbal, camera, and other aircraft functions. The app features Equipment,
Editor, SkyPixel, and Me sections, which are used for conguring your aircraft, and editing and sharing
your photos and videos with others.
Equipment
Device Menu
If it is not already selected, select Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom from the device menu in the top left corner of the
screen.
Function Menu
Tap in the top right corner of the screen to open the Function menu. The menu has ve options:
Scan QR Code: Scan a QR code to connect to an aircraft.
Academy: Use the ight simulator, watch tutorials, and read the product manuals.
Flight Records: Access all your ight records.
GEO Zones: Read information about GEO Zones.
Find My Drone: Get the map coordinates of your aircraft’s last-recorded location and command the
aircraft to blink its LEDs and make a beeping sound.
Camera View
Enter Camera View on the Equipment screen with your mobile device connected to the aircraft.
10 118 97654321
25
24
23
22
21
In flight (GPS)
APAS
09:29
Position
ISO Shutter
200 1/100
12
EV CAPACITY
WB 自动
-0.3
5600K RAW 21
61%
12
AE
13
14
15
16
17
20
1. System Status Bar
Inight(GPS)
: This icon indicates aircraft ight status and displays various warning messages.
2. Obstacle Detection Status
: Red bars display when obstacles are close to the aircraft. Orange bars display when
obstacles are in the detection range.
H 10.0MD 30M
VS 2.0M/S VPS 2.0MH.S 10.0 M/S
19
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
18
49
Page 50

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
3. Battery Level Indicator Bar
: The battery level indicator provides a dynamic display of the battery level. The colored zones on
the battery level indicator represent the power levels needed to carry out dierent functions.
4. Flight Mode
: The text next to this icon indicates the current ight mode.
Tap to congure the Flight Controller settings. These settings allow you to modify ight limits and set gain
values.
5. Camera Parameters
Displays camera parameters and the capacity of the internal storage and the microSD card.
ISO Shutter
200 1/100
EV CAPACITY
WB AUTO
-0.3
5600K RAW 21
Mavic 2 Pro:
Displays camera parameters and the capacity of the internal storage and the microSD card. Also displays
camera focus mode, AE value, and focus parameters.
Mavic 2 Zoom:
Displays camera parameters and the capacity of the internal storage and the microSD card. Also displays
focus parameters.
6. GPS Signal Strength
: Shows the current GPS signal strength. White bars indicate adequate GPS strength.
7. Vision Systems Status
: Tap this button to enable or disable features provided by the Vision Systems, and it displays the status
for all vision systems. Icon in green indicates the corresponding vision system is available. Icon in red
indicates the corresponding vision system is unavailable.
8. Remote Controller Signal
: This icon shows the strength of the remote controller signal. The icon will blink when an interference
is recognized during flight. When there are no additional warnings in DJI GO 4, it means that the
interference will not aect operation and overall ight experience.
9. HD Video Link Signal Strength
: This icon shows the strength of the HD video downlink connection between the aircraft and the
remote controller. The icon will blink when an interference is recognized during ight. When there are no
additional warnings in DJI GO 4, it means that the interference will not aect operation and overall ight
experience.
10. Battery Settings
61%
: Shows the current battery level. Tap to view the battery information menu, set the various battery
warning thresholds, and view the battery warning history.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
50
©
Page 51

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
11. Focus/Metering Button
/ : Tap to switch between focus and metering mode. Tap to select object for focusing or metering.
Auto Focus-Continuous will be triggered automatically according to the status of the aircraft and camera
after enabling Auto Focus.
12. General Settings :
: Tap to enter the General Settings menu to set units of measurement, enable/disable
livestream, and adjust ight route display settings.
13. Auto Exposure Lock
: Tap to lock the exposure value.
AE
14. Gimbal Slider
: Displays the gimbal tilt angle.
15. Photo/Video Toggle
: Tap to switch between photo and video recording modes.
16. Shoot/Record Button
/ : Tap to start shooting photos or recording video.
17. Camera Settings
: Tap to enter the Camera Settings menu.
Tap to set the camera’s ISO, shutter, and auto exposure settings.
Tap to select photo shooting modes. The Mavic 2 supports Single Shot, Burst Shot, Interval
Shot, and various Panorama modes.
Tap to enter the General Camera Settings menu.
18. Playback
: Tap to enter Playback and preview photos and videos as soon as they are captured.
19. Flight Telemetry
D 30M
H 10.0M
HS 10.0M/S
VS 2.0M/S
: Distance between the aircraft and the Home Point.
: Height from the Home Point.
:
Aircraft horizontal speed.
:
Aircraft vertical speed.
20. Map
Tap to view the map.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
51
Page 52

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
21. Advanced Pilot Assistance Systems
: Tap to enable/disable the APAS feature. The APAS feature is disabled if the Forward and
APAS
Backward Vision Systems are disabled or unavailable.
22. Intelligent Flight Modes
: Tap to select Intelligent Flight Modes.
23. Smart RTH
: Tap to initiate Smart RTH and have the aircraft return to the last recorded Home Point.
24. Auto Takeo/Landing
/ : Tap to initiate auto takeo or landing.
25. Back
: Tap to return to the main menu.
Please note the following when using Panorama mode:
Use Panorama mode in a static scene. If the subject moves while shooting, the final panorama
photo may look abnormal.
Use Panorama in a wide-open area and shoot at an altitude of 5 m or above.
Use Panorama in an area with many subjects and avoid shooting above water or snow.
Use Panorama when the aircraft can hover in place steadily. Do not use this mode in Attitude
mode or when flying in high winds.
Editor
An intelligent video editor is built into the DJI GO 4 app. After recording several video clips and
downloading them to your mobile device, go to Editor on the home screen. You can then select a
template and a specied number of clips which are automatically combined to create a short lm that
can be shared immediately.
SkyPixel
View and share the photos and videos in the SkyPixel page.
Me
If you already have a DJI account, you will be able to participate in forum discussions, and share your
creation with the community.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
52
©
Page 53

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Be sure to fully charge your mobile device fully before launching DJI GO
Mobile cellular data is required when using DJI GO 4. Please contact your wireless carrier for
data charges.
If you are using a phone as your mobile display device, DO NOT accept phone calls or use the
texting features during flight.
Read all safety tips, warning messages, and disclaimers carefully. Be familiar with the related
regulations in your area. You are solely responsible for being aware of all relevant regulations and
flying in a way that is compliant.
a. Read and understand the warning messages before using the Auto-take off and Auto-landing
features.
b. Read and understand the warning messages and disclaimer before setting the altitude beyond
the default limit.
c. Read and understand the warning messages and disclaimer before switching between flight
modes.
d. Read and understand the warning messages and disclaimer prompts near or in no-fly zones.
e. Read and understand the warning messages before using the Intelligent Flight Modes.
Land your aircraft immediately at a safe location if an alert shows on the app.
Review all warning messages on the checklist displayed in the app before each flight.
Use the in-app simulator to practice your flight skills if you have never operated the aircraft or if
you do not have sufficient experience to operate the aircraft with confidence.
Beginner Mode is enabled by default when you launch the app for the first time. The aircraft’s
altitude and flight distance are restricted when flying in Beginner Mode. We recommend you fly
in Beginner Mode to perfect your flight skills. Only disable Beginner Mode when you can operate
the aircraft with confidence.
Cache the map data of the area where you intend to fly the aircraft by connecting to the internet
before each flight.
The app is designed to assist your operation. Please use your sound discretion and DO NOT rely
on the app to control your aircraft. Your use of the app is subject to DJI GO 4 Terms of Use and
DJI Privacy Policy. Please read them carefully in the app.
4.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
53
Page 54

Flight
This section describes safe ight
practices and ight restrictions.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
54
©
Page 55

Flight
Once pre-ight preparation is complete, it is recommended to use the ight simulator in DJI GO 4 to
hone your ight skills and practice ying safely. Ensure that all ights are carried out in an open area.
Refer to the Remote Controller and DJI GO 4 sections for information about using the remote controller
and the app to control the aircraft.
Flight Environment Requirements
1. Do not use the aircraft in severe weather conditions including wind speeds exceeding 10 m/s, snow,
rain, and fog.
2. Fly in open areas. Tall structures and large metal structures may aect the accuracy of the onboard
compass and GPS system.
3. Avoid obstacles, crowds, high voltage power lines, trees, and bodies of water.
4. Minimize interference by avoiding areas with high levels of electromagnetism such as locations near
power lines, base stations, electrical substations, and broadcasting towers.
5. Aircraft and battery performance is subject to environmental factors such as air density and
temperature. Be very careful when ying 19685 ft (6000 m) or more above sea level, since battery
and aircraft performance may be reduced.
6. The Mavic 2 cannot use GPS within the polar areas. Use the Downward Vision System when ying in
such locations.
Flight Limits and GEO Zones
Abide by all laws and regulations when ying your Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom. Flight limitations are applied by
default to help users operate this product safely and legally. Flight limitations include altitude limits,
distance limits, and GEO Zones.
Altitude limits, distance limits, and GEO Zones function concurrently to manage flight safety when
operating in P-mode.
Flight Altitude and Distance Limits
The ight altitude and distance limits may be changed in DJI GO 4. The maximum ight altitude setting
cannot exceed 1640 ft (500 m). Based on these settings, the aircraft will y in a restricted cylinder, as
shown below:
Max Flight Altitude
Height of aircraft
when turned on
Max Radius
Home Point
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
55
Page 56

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
GPS Signal Strong Blinking Green
Flight Limits DJI GO 4 App Aircraft Status Indicator
Max Altitude
Max Distance
GPS Signal Weak Blinking Yellow
Max Altitude
Max Distance No limit
If the aircraft reaches one of the limits, you can still control the aircraft, but you cannot y it any farther.
If the aircraft ies out of the max radius, it will y back within range automatically when the
GPS signal is strong.
For safety reasons, please do not y close to airports, highways, railway stations, railway lines,
city centers, or other sensitive areas. Fly the aircraft only within your line of sight.
Aircraft's altitude cannot
exceed the specied value.
Flight distance must be within
the max radius.
Flight Limits DJI GO 4 App Aircraft Status Indicator
Height is restricted to 16 feet (5 meters)
when the GPS signal is weak and
Downward Vision System is activated.
Height is restricted to 98 feet (30 meters)
when the GPS signal is weak and
Downward Vision System is inactivated.
Warning: Height
limit reached.
Warning: Distance
limit reached.
Warning:
Height limit
reached.
N/A
N/A
N/A
GEO Zones
All GEO Zones are listed on the DJI official website at http://www.dji.com/flysafe. GEO Zones are
divided into different categories and include locations such as airports, flying fields where manned
aircraft operate at low altitudes, borders between countries, and sensitive locations such as power
plants.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
56
©
Page 57

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Pre-Flight Checklist
1. Ensure the remote control device, mobile device, and Intelligent Flight Battery are fully charged.
2. Ensure the Intelligent Flight Battery and the propellers are mounted securely.
3. Ensure the aircraft arms and propellers are unfolded.
4. Ensure the gimbal and camera are functioning normally.
5. Ensure that there is nothing obstructing the motors and that they are functioning normally.
6. Ensure that DJI GO 4 is successfully connected to the aircraft.
7. Ensure that the camera lens and Vision System sensors are clean.
8. Use only genuine DJI parts or parts certified by DJI. Unauthorized parts or parts from non-DJI
certied manufacturers may cause system malfunctions and compromise safety.
Auto Takeoff/Landing
Auto Takeoff
1. Launch DJI GO 4 and tap “GO FLY” to enter Camera View.
2. Complete all steps in the pre-ight checklist.
3. Tap .
4. If conditions are safe for takeo, slide the slider to conrm. The aircraft will take o and hover 3.9 ft (1.2 m)
above the ground.
The Aircraft Status Indicator indicates whether the aircraft is using GPS and/or the Downward
Vision System for flight control. Refer to the Aircraft LEDs and Status Indicator section for more
information. It is recommended to wait until the GPS signal is strong before using auto-takeoff.
Auto-Landing
Only use auto-landing if the Aircraft Status Indicator is blinking green. Follow the steps below to use the
auto landing feature:
1. Tap .
2. If conditions are safe to land, slide the slider to conrm. The aircraft will commence the auto landing
procedure. Warnings will appear in DJI GO 4 if the aircraft detects that conditions are not suitable to
land. Be sure to respond promptly.
Auto-landing can be aborted immediately by tapping in DJI GO 4.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
57
Page 58

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Starting/Stopping the Motors
Starting the Motors
A Combination Stick Command (CSC) is used to start the motors. Push both sticks to the inner or
outer bottom corners to start the motors. Once the motors have started spinning, release both sticks
simultaneously.
OR
Stopping the Motors
There are two methods to stop the motors:
Method 1: When the aircraft has landed, push and hold the left stick down. The motors stop after three
seconds.
Method 2: When the aircraft has landed, push the left stick down, then conduct the same CSC that
was used to start the motors, as described above. The motors stop immediately. Release
both sticks once the motors have stopped.
OR
Method 1 Method 2
Stopping Motors Mid-Flight
Stopping the motors mid-ight will cause the aircraft to crash. The motors should only be stopped midight in an emergency situation such as if a collision has occurred, a motor has stalled, the aircraft is
rolling in the air, or the aircraft is out of control and is ascending/descending very quickly. To stop the
motors mid-ight, use the same CSC that was used to start the motors.
Test Flight
Takeoff/Landing Procedures
1. Place the aircraft in an open, at area with the Aircraft Status Indicator facing towards you.
2. Turn on the aircraft and the remote controller.
3. Launch DJI GO 4 and enter Camera View.
4. Wait until the Aircraft Status Indicator blinks green indicating that the Home Point has been recorded
and it is now safe to y.
5. Gently push the throttle stick to take o or use auto-takeo.
6. Pull the throttle stick or use auto-landing to land the aircraft.
7. Turn o the aircraft and remote controller.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
58
©
Page 59

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Video Suggestions and Tips
1. The pre-ight checklist is designed to help you y safely and to ensure that you can shoot video
during ight. Go through the full pre-ight checklist before each ight.
2. Select the desired gimbal operation mode in DJI GO 4.
3. Only shoot video when ying in P-mode or T-mode.
4. Always y in good weather and avoid ying in rain or wind.
5. Choose the camera settings that best suit your needs. Settings include photo format and exposure
compensation.
6. Perform ight tests to establish ight routes and to preview scenes.
7. Push the control sticks gently to keep the aircraft movement smooth and stable.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
59
Page 60

Appendix
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
60
©
Page 61

Appendix
Specifications
Aircraft
Takeo Weight 907 g (Mavic 2 Pro); 905 g (Mavic 2 Zoom)
Dimensions Folded:
214×91×84 mm (length×width×height)
Unfolded:
322×242×84 mm (length×width×height)
Diagonal Distance 354 mm
Max Ascent Speed 5 m/s (S-mode), 4 m/s (P-mode)
Max Descent Speed 3 m/s (S-mode), 3 m/s (P-mode)
Max Speed 72 km/h (S-mode) (near sea level, no wind)
Max Service Ceiling Above
Sea Level
Max Flight Time 31 minutes (at a consistent 25 kph) (no wind)
Max Hovering Time 29 minutes (no wind)
Overall Flight Time 25 minutes ( In normal ight, 15% remaining battery level )
Max Flight Distance 18 km (at a consistent 50 kph) (no wind)
Max Wind Speed
Resistance
Max Tilt Angle 35° (S-mode, with remote controller), 25° (P-mode)
Max Angular Velocity 200°/s
Operating Temperature
Range
GNSS GPS+GLONASS
Hovering Accuracy Range Vertical:
Operating Frequency 2.400 - 2.4835 GHz;5.725 - 5.850 GHz
Transmission Power (EIRP) 2.4 GHz
Internal Storage 8 GB
Gimbal
Mechanical Range Tilt: -135 to 45°, Pan: -100 to 100°, Roll: -45 to 45°
Controllable Range Tilt: -90 to 30°, Pan: -75 to 75°
Stabilization 3-axis (tilt, roll, pan)
Max Control Speed (tilt) 120°/s
Angular Vibration Range ±0.01° (Mavic 2 Pro) ; ±0.005° (Mavic 2 Zoom)
6000 m
29–38 kph
-10°C - 40°C
± 0.1 m (when vision positioning is active)
± 0.5 m (with GPS positioning)
Horizontal:
± 0.3 m (when vision positioning is active)
± 1.5 m (with GPS positioning)
FCC: ≤26 dBm; CE: ≤20 dBm; SRRC: ≤20 dBm; MIC: ≤20 dBm
5.8 GHz
FCC: ≤26 dBm; CE: ≤14 dBm; SRRC: ≤26 dBm
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
61
Page 62

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Sensing System
Sensing System Omnidirectional Obstacle Sensing
FOV Forward: Horizontal: 40°, Vertical: 70°;
Backward:Horizontal: 60°, Vertical: 77°;
Downward: Front and Back: 100°, Left and Right: 83°
Lateral: Horizontal: 80°, Vertical: 65°
Obstacle Sensing Range Forward: Precision Measurement Range: 0.5 - 20 m
Operating Environment
Velocity Range ≤31mph (50 kph) at 6.6 ft (2 m) above ground
Altitude Range 0.1 - 11 m
Operating Range 0.3 - 50 m
Camera Mavic 2 Pro Mavic 2 Zoom
Sensor 1” CMOS
Lens
ISO Range
Shutter Speed Electronic Shutter: 8–1/8000s Electronic Shutter: 8–1/8000s
Still Image Size 5472×3648 4000×3000
Still Photography Modes Single shot
Video Resolution
Detectable Range: 20 - 40 m
Eective Sensing Speed: ≤ 14m/s
Backward: Precision Measurement Range: 0.5 - 16 m
Detectable Range: 16 - 32 m
Eective Sensing Speed: ≤ 12m/s
Upward: Precision Measurement Range: 0.1 - 8 m
Downward: Precision Measurement Range: 0.5 - 11 m
Detectable Range: 11 - 22 m
Sides: Precision Measurement Range: 0.5 - 10 m
Eective Sensing Speed: ≤ 8 m/s
Surface with clear pattern and adequate lighting (lux > 1
Detects diuse reective surfaces (>20%) (walls, trees, people, etc.)
1/2.3" CMOS
Eective Pixels: 20 million
FOV: about 7
35 mm Format Equivalent: 28 mm
Aperture: f/2.8–f/
Shooting Range: 1 m to ∞
Video: 100-64
Photo: 100-3200 (auto)
100-12800 (manual)
Burst shooting: 3/5 frames
Auto Exposure Bracketing (AEB): 3/5
bracketed frames at 0.7 EV Bias
Interval (JPEG:
2/3/5/7/10/15/20/30/6
RAW: 5/7/10/15/20/30/60s)
4K: 3840×2160 24/25/30p
2.7K: 2688x1512
24/25/30/48/50/60p
FHD: 1920×1080
24/25/30/48/50/60/120p
7°
11
00
0s
Eective Pixels: 12 million
FOV: about 83° (24 mm);
about 48° (48 mm)
35 mm Format Equivalent: 24-48 mm
Aperture: f/2.8 (24 mm)–f/11 (48 mm)
Shooting Range: 0.5 m to ∞
Video: 100-320
Photo: 100-1600 (auto)
100-3200 (manual)
Single shot
Burst shooting: 3/5/7 frames
Auto Exposure Bracketing (AEB): 3/5
bracketed frames at 0.7 EV Bias
Interval (JPEG:
2/3/5/7/10/15/20/30/6
RAW: 5/7/10/15/20/30/60s)
4K: 3840×2160 24/25/30p
2.7K: 2688×1512
24/25/30/48/50/6
FHD: 1920×1080
24/25/30/48/50/60/120p
5)
0
0s
0p
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
62
©
Page 63

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Color Mode Dlog-M (10-bit), support HDR video
Max Video Bitrate 100 Mbps 100 Mbps
Supported File System FAT32: ≤ 32 GB
Photo Format JPEG / DNG (RAW) JPEG / DNG (RAW)
Video Format MP4 / MOV (MPEG-4 AVC/H.264,
Supported SD Cards Micro SD
Operating Temperature
Range
HDR Enhanced HDR, 14 EV HDR, 13 EV
Hyperlight 8dB SNR 8dB SNR
Panorama Pano (3×1):
Remote Controller
Operating Frequency 2.400 - 2.4835 GHz; 5.725 - 5.850 GHz
Max Transmission Distance FCC: 8000 m; CE: 5000 m; SRRC: 5000 m; MIC: 5000 m
Operating Temperature
Range
Battery 3950 mAh
Transmission Power (EIRP) 2.400 - 2.4835 GHz
Operating Current/Voltage 1800 mA @ 3.83 V
Supported Mobile Device
Size
Supported USB Port Types Lightning, Micro USB (Type-B), USB-C
Charger
Input 100-240 V, 50/60 Hz, 1.8 A
Output Main: 17.6 V 3.41 A or 17.0 V 3.53 A
Voltage 17.6±0.1 V or 17.0 V±0.1 V
(HLG 10-bit)
exFAT: > 32 GB
HEVC/H.265)
Supporting Micro SD with capacity
up to 128 GB and R/W speed up to
UHS-I Speed Grade 3
-10°C to 40°C -10°C to 40°C
4000×6000 (40°×80°)
W (3×3)):
8000×6000 (113°×80°)
180° (3×7)):
8192×2840 (240°×76°)
Sphere (3×8+1)):
8192×4096 (360°×126°, 360°×180°)
(unobstructed, free of interference)
0°C - 40°C
FCC:≤26 dBm; CE:≤20 dBm; SRRC:≤20 dBm; MIC: ≤20 dBm
5.725 - 5.850 GHz
FCC: ≤26 dBm; CE: ≤14 dBm; SRRC:≤26 dBm
Max length: 160 mm; max thickness: 6.5 – 8.5 mm
USB: 5 V 2 A
D-Cinelike
FAT32: ≤ 32 GB
exFAT: > 32 GB
MP4 / MOV (MPEG-4 AVC/H.264,
HEVC/H.265)
Micro SD
Supporting Micro SD with capacity
up to 128 GB and R/W speed up to
UHS-I Speed Grade 3
Pano (3×1)):
4000×6000 (41°×93°)
W (3×3)):
8000×6000 (117°×93°)
180° (3×7)):
8192×2840 (249°×87°)
Sphere): (3×8+1) 8192×4096
(360°×126°, 360°×180°)
Super Resolution): 8000×6000 (24 mm
equivalent FOV)
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
63
Page 64

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Rated Power 60 W
Intelligent Flight Battery
Capacity 3850 mAh
Voltage 15.4 V
Max Charging Voltage 17.6 V
Battery Type LiPo 4S
Energy 59.29 Wh
Net Weight 297 g
Charging Temperature
Range
Max Charging Power 80 W
APP
Video Transmission System OcuSync 2.0
Name DJI GO 4
Live View Quality
Latency (depending on
environmental conditions
and mobile device)
Required Operating
System
5℃ - 40℃
Remote Controller: 720p@30fps / 1080p@30fps
DJI Goggles: 720p@30fps / 1080p@30fps
DJI Goggles RE: 720p@30fps / 1080p@30fps
120 - 130 ms
iOS 9.0 or later
Android 4.4 or later
Calibrating the Compass
It is recommended that the compass is calibrated in any of the following situations when ying outdoors:
1. Flying at a location farther than 31 miles (50 km) away from the location the drone was last own.
2. The aircraft has not been own for more than 30 days.
3. A compass interference warning appears in DJI GO 4 and/or the Aircraft Status Indicators blink
alternating red and yellow.
DO NOT calibrate the compass in locations where magnetic interference may occur, such
as close to magnetite deposits or large metallic structures such as parking structures, steel
reinforced basements, bridges, cars, or scaffolding.
DO NOT carry objects (such as cell phones) that contain ferromagnetic materials near the aircraft
during calibration.
It is not necessary to calibrate the compass when flying indoors.
Calibration Procedure
Choose an open area to carry out the following procedure.
1. Tap the System Status Bar in DJI GO 4, select “Calibrate”, and follow the on-screen instructions.
2. Hold the aircraft horizontally and rotate it 360 degrees. The Aircraft Status Indicator will turn solid
green.
3. Hold the aircraft vertically, with its nose pointing downward, and rotate it 360 degrees around a
vertical axis.
4. If the Aircraft Status Indicator blinks red, the calibration has failed. Change your location and try the
calibration procedure again.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
64
©
Page 65

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Horizontal Calibration
The aircraft can take off immediately once calibration is complete. If you wait more than three
minutes to take off after calibration, you may need to calibrate again. It is possible that another
compass interference warning will appear while the aircraft is on the ground. This indicates
that the current location is not suitable for flying the aircraft, due to the level of magnetic
interference.
Vertical Calibration
Firmware Updates
Use DJI GO 4 or DJI Assistant 2 to update the aircraft rmware.
Using DJI GO
When you connect the aircraft or remote controller to DJI GO 4, you will be notied if a new rmware
update is available. To start updating, connect your mobile device to the internet and follow the onscreen instructions. Note that you cannot update the rmware if the remote controller is not linked to the
aircraft.
Using DJI Assistant
The USB-C port is used when connecting the aircraft to a computer to update rmware.
Follow the instructions below to update the rmware through DJI Assistant 2:
1. With the aircraft powered o, connect the aircraft to a computer via the Micro USB port using a Micro
USB cable.
2. Power on the aircraft.
3. Launch DJI Assistant 2 and log in with your DJI account.
4. Select “Mavic 2” and click on Firmware Updates on the left panel.
5. Select the rmware version that you wish to update to.
6. Wait for the rmware to download. The rmware update will start automatically.
7. Reboot the aircraft after the rmware update is complete.
4
2
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
65
Page 66

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
Ensure the aircraft is connected to the computer before powering on.
The firmware update will take around 15 minutes. It is normal that the gimbal goes limp,
aircraft status indicators blink, and the aircraft reboots. Please wait patiently until the update is
complete.
Ensure the computer has access to the Internet.
Before performing an update ensure the Intelligent Flight Battery has at least 50% power and
the remote controller has at least 30% power.
Do not disconnect the aircraft from the computer during an update.
For safety, always update the firmware to the latest version when an upgrade notification is
shown in DJI GO 4.
Firmware upgrade notifications will prompt you to proceed with an update immediately or to
update the firmware within three days. If you choose to ignore the current firmware update, you
are required to accept the prompted disclaimer. You further understand and agree that the data
includes but is not limited to user selection records and may be uploaded to and maintained on
a DJI designated server.
The remote control device may become unlinked from the aircraft after updating. Re-link the
remote control device and aircraft.
Be sure to check all connections and remove the propellers from the motors before performing
the firmware update. DO NOT disconnect the aircraft or remote controller from the computer or
internet while updating the firmware.
Remote Controller LCD Screen Menu Information
Remote Controller Status
BAT xx PCT Remote Controller battery level.
SHUTDOWN_ Remote controller is powering o.
CHARGING_ Remote controller is charging.
USB PLUGGED Mavic 2 has been connected to a computer.
FC U-DISK Flight Controller is reading data.
UPGRADING Upgrading.
BINDING Aircraft is binding with the remote controller.
Before Flight
CONNECTING_ The remote controller is connecting to the aircraft.
SYS INITING System is initiating.
READY TO GO Ready to take o.
Flight Mode
BEGINNER In Beginner Mode.
GPS MODE In P-GPS Mode.
OPTI MODE In P-OPTI Mode.
ATTI MODE In P-ATTI Mode.
SPORT MODE In Sport Mode.
Flight Status
TAKING OFF Taking o.
LANDING Landing.
GOING HOME Returning to Home.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
66
©
Page 67

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
NAV GOHOME Returning to home.
NAV LANDING Landing.
MAX ALT. Aircraft has reached maximum altitude.
MAX RADIUS Aircraft has reached maximum radius.
OBSTACLE Obstacle detected.
NO FLY ZONE Aircraft is in a No Fly zone.
Intelligent Flight Mode Status
TRIPOD In Tripod Mode.
ACTIVETRACK Using ActiveTrack.
TAP FLY Using TapFly.
COURSE LOCK In Course Lock Mode
HOME LOCK In Home Lock Mode
POI MODE In Point of Interest Mode
WAY POINT In Waypoints Mode.
FOLLOW ME In Follow Me Mode.
TERRAIN In Terrain Follow Mode.
System Waning and Error Information
SYS WARNING+CHECK APP System Warning. See DJI GO 4 app for more information.
UNACTIVATED+CHECK APP Aircraft not Activated. See DJI GO 4 app for more information.
MAG INTERF+CHECK APP Compass Error. See DJI GO 4 app for more information.
BATTERY ERR+CHECK APP Battery Error. See DJI GO 4 app for more information.
SD ERR+CHECK APP Micro SD Card Error. See DJI GO 4 app for more information.
CALIBRATING IMU Calibrating/Did not restart aircraft after calibration is
complete.
STICK ERR+RE-CTR STCK Control stick is not centered. Re-center it.
WHEEL ERR+RE-CTR WHEL Left Dial on the remote controller is not centered. Re-center it.
STICK ERR Control stick error. Calibrate the control sticks in the DJI GO 4 app.
MECH ERR Remote Controller Error. Calibrate the remote controller in the
STICK EMI3+AUTO RTH Control Sticks are experiencing severe electromagnetic
STICK EMI2+MANUAL RTH Control Sticks are experiencing electromagnetic interference
STICK EMI1 Control Sticks are experiencing slight electromagnetic
SD FULL Micro SD Card is full.
NO PROP No propellers attached.
BAT TEMP HI Intelligent Flight Battery is too hot.
BATTERY ERR Intelligent Flight Battery error.
BAT TEMP LO Intelligent Flight Battery is too cold.
LOW BATTERY Intelligent Flight Battery low battery.
RC LOW BAT Remote Controller low battery.
NO RC SIGNL Remote Controller signal lost.
RC TEMP HI Remote Controller too hot.
NO RTH Aircraft cannot Return to Home.
DJI GO 4 app. If this problem persists, contact DJI support.
interference and cannot function. The aircraft will return to home
and land immediately.
and may not function. Use Smart RTH and land the aircraft as
soon as possible.
interference, y the aircraft to another location.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
©
67
Page 68

Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom User Manual
After-Sales Information
Visit https://www.dji.com/support to learn more about after-sales service policies, repair services and
support.
2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
68
©
Page 69

DJI Support
http://www.dji.com/support
This content is subject to change.
Download the latest version from
http://www.dji.com/mavic-2
If you have any questions about this document, please contact DJI
by sending a message to DocSupport@dji.com
is a trademark of DJI.
MAVIC
Copyright © 2018 DJI All Rights Reserved.
.
 Loading...
Loading...