Page 1
Evaluation Procedure
f
y
(DEP-008 A)
The Delphi DNS Series of SIP type
POL converters
The DNS, 2.4~5.5V or 10~14V input,
programmable output, non-isolated point of load
DC/DC converters, are the latest offering from
one of the world’s largest power supply
manufacturers ― Delta Electronics, Inc. The
DNS converters have flexible and programmable
tracking and sequencing features to enable a
variety of startup voltages as well as sequencing
and tracking between power modules. With
creative design technology and optimization o
component placement, these converters possess
outstanding electrical and thermal performance,
as well as extremely high reliability under highl
stressful operating conditions. All models
possess a myriad of standard protection
features.
This document guides the user through the
evaluation procedures to qualify a POL module.
The data shown in this Evaluation Procedure is
for the SIP Package Type POL evaluation board.
Please refer to the appropriate technical data
sheet for detailed performance and technical
information for the specific POL units.
DNS SIP Series
1.0 Purpose
This document guides the user in performing
electronic measurements on a DNS POL (point
of load) DC/DC converter using the Delta
Evaluation Board.
2.0 Relevant Documentation
The documentation and background information
listed below is relevant to this evaluation
procedure:
2.1 Appropriate date sheet for the DNS Series
unit under evaluation.
2.2 Power Module Evaluation Board Schematic.
2.3 Power Module Evaluation Board Layout.
2.4 General Test and Safety Procedures.
Evaluation Procedure
EP_DNS_SIP_08052004
1
Delta Electronics, Inc.
Page 2
3.0 Equipment Required
3.1 A DC Power Supply 0 - 20 V @ 0 - 20A (Agilent 6574A 0 -60V/0 - 35A or equivalent).
3.2 An oscilloscope (Tektronix TDS 3034 or equivalent) 4 Channel 300 MHz, equipped with a x1
scope probe, a x10 scope probe, and two BNC cables (length less than 20 inches/500mm)
3.3 Digital multi-meters, one with 20A range and ideally all with 4 1/2 digit resolution (DVM1, DVM2
and DVM3) (Zentech 2041 or equivalent).
3.4 An electronic load (Chroma 63030 or equivalent), 300W approximate rating, or a suitable
resistive load.
3.5 A DC power supply (GW GPC-3060D).
4.0 Equipment Set-Up and Description
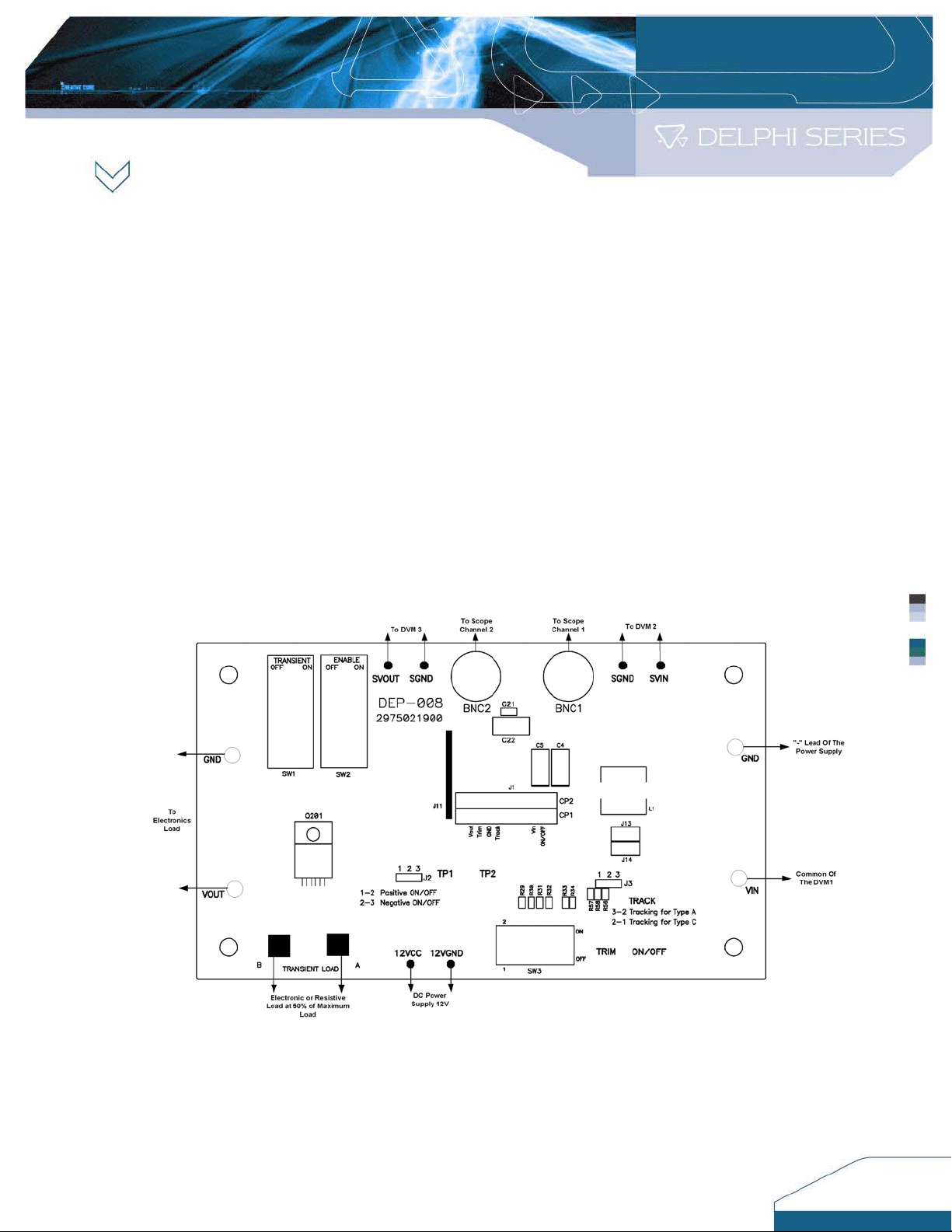
Refer to the Power Module Evaluation Board Layout (See page 20) for reference designators cited
in this document and Figure 1. Set-up Diagram.
Figure 1. Set-up Diagram
2
Page 3
4.1 Connect one lead from the “+” lead of the DC source (See Item 3.1) to the “20A” terminal of the
first multi-meter DVM1 (See Item 3.3). Then connect one lead from the “Common” of the DVM1
to the “Vin” pin of the Evaluation Board. DVM1 is used to measure the input current.
4.2 Connect one wire from the “-” lead of the DC source (See Item 3.1) to the “GND“ pin of the
Evaluation Board. Note: Use stranded leads at least equivalent to 14 AWG for all connections
in sections 4.1 and 4.2. The leads should be twisted to reduce noise coupling.
4.3 Connect the plus “+” and minus “-“ connection leads from a second multi-meter (See Item 3.3)
to the “SVin” and “SGND” pins on the Evaluation Board. This multi-meter is designated DVM2.
DVM2 is used to measure the input voltage.
4.4 Connect the plus “+” and minus “-“ connection leads from the third multi-meter (See Item 3.3) to
the “SVOUT” and “SGND” Pin on the Evaluation Board. The multi-meter is designated DVM3.
DVM3 is used to measure the output voltage.
4.5 Connect a BNC cable (length less than 20 inches/500mm) from BNC1 of the Evaluation Board
to Channel 1 of the oscilloscope (See Item 3.2). This cable is used to measure the input
voltage (between SVIN and SGND).
4.6 Connect a BNC cable (length less than 20 inches/500mm) from BNC2 of the Evaluation Board
to Channel 2 of the oscilloscope (See Item 3.2). This cable is used to measure the output
voltage (between SVOUT and SGND).
4.7 Connect the positive and negative power leads of the electronic load (ensuring correct polarity),
or an appropriate resistive load to the Evaluation Board output terminal pin (“Vout” for positive
power lead and “SGND” for the negative power lead).
4.8 Connect one lead from the “+” lead of the DC source (See Item 3.5) to the “12Vcc” on the
Evaluation Board. Then connect one lead from the “-” of the DC source (See Item 3.5) to the
“12VGND” on the Evaluation Board.
5.0 Thermal Management of the Converter
It is imperative that sufficient airflow needs to be provided to the converter at all times during all
portions of testing. Please refer to the applicable data sheet for the proper cooling and derating
necessary conditions to obtain accurate results when testing the converter.
3
Page 4
6.0 Tests Performed
The following tests are performed at room temperature (+25 ℃).
6.1 Input Characteristics
Input Voltage Range.
Under-Voltage Lockout.
No Load Input Current.
6.2 Output Characteristics
Line Regulation.
Load Regulation.
Output Regulation.
Output Voltage Set-point Programming
Output Voltage Margining
Output Voltage Tracking
6.3 Dynamic Characteristics
Maximum Output Voltage Deviation (due to step change in load).
Turn on Response time.
6.4 Thermal Characteristic
Efficiency
7.0 Test Set-Up
7.1 Initial Set-Up
1) Examine the part number of the power module to determine that the correct module is
being evaluated. Note: DNS04S0A0S06P A would denote the SMT package, while
DNS04S0A0R06P A would denote the SIP package. This Evaluation Board is for use with
SIP package.
2) Set the multi-meter DVM1 to the DC current 20A range. Set multi-meters DVM2 and
DVM3 to DC voltage, auto ranging.
3) Electronic Load
Turn on the Electronic Load at CR mode (or resistive load) and adjust the current level.
The maximum rated output current is 6A. Ensure the output load does not exceed the
recommended maximum current.
4) SW1 is used for on/off Transient function test. Turn SW1 to the OFF position if this function
is not being used. Turn SW1 to the ON position if the Transient function test is required.
4
Page 5
5) SW2 is used to enable or disable the converter.
For positive logic module, When SW2 is put in the ON position, the converter is ON and
when SW2 is put in the OFF position, the converter is OFF.
For negative logic module, When SW2 is put in the OFF position, the converter is ON, and
when SW2 is put in the ON position, the converter is OFF.
6) SW3 is used for the Output Voltage Set-Point Adjustment Range.
By an external voltage source:
If the converter requires a trim up, set the SW3_1 to ON position.
If the converter requires a trim down, set the SW3_2 to ON position.
By an external resistor:
If the converter requires a trim up to Vo,set, set the SW3_8 to ON position.
If the converter requires a margin trim down, set the SW3_3 to ON position.
If the converter requires a margin trim up, set the SW3_4 to ON position.
Please refer to the SW3 Function table.
SW3 Function table
Subdivide switch No. Function
Note:
1. The subdivide switch of SW3_1~4 must not be ON at the same time.
2. For the SW3_5~7 use at NPA series, must set to OFF position.
7.2 Initial Power Up
1) Turn the power supply ON, set the current limit on DC source (refer to specification of
either converter) and increase the input voltage (use DVM2 to monitor the input voltage)
until it reaches the desired value.
2) Set the switch SW2 to power module ON.
3) The converter is now operating, which can be verified by observing the DVM3 (appropriate
value for the nominal output voltage) and channel 2 of the oscilloscope (appropriate value
for the nominal output voltage).
4) Set the switch SW2 to power module OFF.
SW3_1 Voltage trim up
SW3_2 Voltage trim down
SW3_3 Resistor margin trim down
SW3_4 Resistor margin trim up
SW3_8 Resistor trim up
5
Page 6
8.0 Tests and Evaluation
8.1 Input Characteristics
8.1.1 Input Voltage Range and Under-Voltage Lockout
The DNS04xx Series of DC/DC converters will operate at full load from 2.4Vin to 5.5Vin for
5Vin (nominal) types. The DNS12xx Series DC/DC converters will operate at full load from
10Vin to 14Vin for 12Vin (nominal) types. The converters feature input under-voltage
protection, which will not allow the converter to start up unless the input voltage exceeds the
turn-on voltage threshold.
Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Set the input voltage to the desired operating point while monitoring DVM2.
3) Set the switch SW2 to the “ON or OFF” position to enable the converter. (See Item
7.1.5)
4) Test the input under voltage function while observing DVM2, DVM3 and channel 1 of the
oscilloscope. Increase the input voltage until the output of the converter reaches the
appropriate value. This will occur between 2.05 and 2.25 volts for 5Vin nominal and
between 9.0 to 10 volts for 12Vin nominal. Please refer to the appropriate converter data
sheet for the detailed specification.
8.1.2 No Load Input Current Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Set the input voltage to the desired operating point while monitoring DVM2.
3) Set the switch SW2 to the converter ON.
4) Remove/disable the output electronic load or resistive load.
5) Note the input current from DVM1.
6) The result is the No-Load Input current of the DC/DC converter.
The No-Load Input Current will be around 50 to 150 mA depending on the model under
evaluation. (Please refer to the data sheet for the detailed specification).
6
Page 7

8.2 Output Characteristics
8.2.1 Line Regulation
Line Regulation Deviation is defined as the change in output voltage caused by varying the
input voltage over a specified range while the output load and temperature remain constant.
Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Set the output power to the desired operating point.
3) Set the switch SW2 to the converter ON.
4) Adjust the input voltage across the converter’s input range (refer to specified range) while
monitoring DVM2.
5) Note the maximum +/- deviation of the output voltage over the full range of the input
operating voltage (please refer to the data sheet for the detailed specification).
8.2.2 Load Regulation
Load Regulation Deviation is defined as the change in output voltage caused by varying the
output load current over the specified range (no load to full load) while the input voltage and
temperature remain constant.
Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Set the input voltage to the desired operating level while monitoring DVM2.
3) Set the switch SW2 to the converter ON.
4) Adjust the output load across the converter’s operating load range.
5) Note the maximum +/- deviation of the output voltage over the full range of the operating
load range (please refer to the data sheet for the detailed specification).
8.2.3 Output Ripple
Output Ripple is defined as the periodic AC component on the DC/DC converter’s output
voltage. The output ripple is measured in terms of peak to peak and RMS values, both done
with a specific bandwidth.
Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Set the switch SW2 to the converter ON.
3) Adjust the input voltage while monitoring DVM2 and set the output load to the full rated
load current.
4) Adjust channel 2 on the oscilloscope to be AC coupled at 4µS/Div and at 10mV/Div using
the 20 MHz bandwidth-limit option on the scope.
5) The output ripple of the DC/DC converter is measured at full load operating power.
7
Page 8

Ω
Ω
8.2.4 Output Voltage Set-point Programming
(1) Output Voltage Set-Point Adjustment by external resistor
Output Voltage Set-point Programming can be carried out by using the external program
resistor connect between TRIM pin to ground to set output voltage set-point from 0.75Vdc to
5Vdc, the location can refer to the Evaluation Board Schematic (please refer to the data sheet
for more detailed specification). These test functions are divided into two types,
Rset of DNS04R series can be calculated by using the following equation:
21070
= 5110
R
set
−
Vo
For example, to program the output voltage of the DNS04 module to 1.8Vdc, below is the
calculation of Rtrim:
21070
=
R
set
−
The table 1 provides the Rset value required for some standard output and the location on the
Evaluation board is R33.
Table 1.
Rset of the DNS12R series can be calculated by using the following equation:
10500
= 1000
R
set
−
Vo
For example, to program the output voltage of the DNS12 module to 3.3Vdc, below is the
calculation of Rset:
10500
=
R
set
−
The table 2 provides the Rset value required for some standard output. The location on the
Evaluation board is R33.
−
7525.0
−
7525.08.1
Vo,set
0.7525 Open Open
1.2 41.973 44.2k//825k
1.5 23.077 23.7k//825k
1.8 15.004 15.4k//590k
2.5 6.947 7.15k//243k
3.3 3.160 3.16k//Open
7525.0
7525.03.3
Ω
=
150045110
Rset (k
−
−
Ω
=
31221000
Ω
) R33
Recommend Value, R//R
8
Page 9

Table 2.
Ω
−
=
−
Vo,set
0.7525 Open Open
1.2 22.464 23.7k//432k
1.5 13.047 14.0k//191k
1.8 9.024 9.53k//169k
2.5 5.009 5.23k//118k
3.3 3.122 3.16k//261k
5.0 1.472 1.5k//78.7k
Rset (k
) R33
Recommend Value, R//R
Test
1. Put the resistor to program the desired output voltage set point by follow Table 1 and Table
2 for the standard output.
2. Set the input voltage to the desired operating level while monitoring DVM2.
3. Turn on the fan.
4. Set the enable switch SW2 to the “ON” position to enable the converter.
5. Adjust the output load across the converter’s operating load range.
6. Note the output voltage over the full range of the operating load range (please refer to the
data sheet for the detailed specification).
(2) Output Voltage Set-Point Adjustment by external voltage source
For DNS series, trim to Vo,set using an external voltage source, connect it between the
TRIM pin and GND pin. Please refer to the Table 3 and Table 4 as below for the
appropriate Vout. The value of Vtrim is specified as follows:
For DNS04xx series
()
×−= VoutVtrim
For example, to program the output voltage of a DNS04 module to 3.3 Vdc, Vtrim is
calculated as follows:
()
×−=
Table 3. : Vo,set adjustment range by use of external voltage source.
Product Part
7525.01698.07.0
VVtrim 267.07525.03.31698.07.0
Normal
Output Set
Voltage
(Vdc)
0.7525 Open
Vrim (V)
1.2 0.6240
DNS04S0A0R06P A/B/C
DNS04S0A0R06N A/B/C
1.5 0.5730
1.8 0.5220
2.5 0.4030
3.3 0.2670
9
Page 10

For DNS12xx series
−
=
()
×−= VoutVtrim V
For example, to program the output voltage of a DNS12 module to 3.3 Vdc, Vtrim is
calculated as follows
()
Table 4. : Vo,set adjustment range by use of external voltage source.
Product Part
DNS12S0A0S06P A/B/C
DNS12S0A0S06N A/B/C
7525.00667.07.0
−×−=Vtrim V
53.07525.03.30667.07.0
Output Set
Voltage
Normal
Vrim (V)
(Vdc)
0.7525 Open
1.2 0.670
1.5 0.650
1.8 0.630
2.5 0.583
3.3 0.530
5.0 0.4167
8.2.5 Voltage Margining
Output voltage margining can be carry out by connecting a resistor from the Trim pin to ground
pin for trim up and connecting a resistor from Trim pin to Output pin for Trim down. The Rmarginup is for trim up and Rmargin-down is for trim down. (Please refer to the data sheet and
Evaluation Board Schematic for the detailed information).
A software tool for voltage margining calculation is available to ask for. The values of Rmarginup and Rmargin-down for a specific output voltage and margin percentage can then be figured
out. Please consult your local Delta Field Application Engineer or sales persons for additional
information.
Test
1) Connect a trim resistor for a desired voltage value (Please refer to Table 1 and Table 2).
2) Turn on the fan.
3) Adjust the input voltage while monitoring DVM2 and with output load set to the desired
operating point.
4) Set the enable switch SW2 to the “ON” position to enable converter.
5) Use SW3 (refer to Item 7.1_6) for Trim setup.
6) Note the voltage by observing DVM3.
7) Test the Load Regulation (refer to Item 8.2.2).
10 11
Page 11

8.2.6 Voltage Tracking
The DNS family was designed for applications that have output voltage tracking requirements
during power-up and power-down. The devices have a TRACK pin to implement three types
of tracking method: sequential, ratio-metric and simultaneous. TRACK simplifies the task of
supply voltage tracking in a power system by enabling modules to track each other, or any
external voltage, during power-up and power-down.
By connecting multiple modules together, customers can get multiple modules to track their
output voltages to the voltage applied on the TRACK pin.
Detailed Description
Sequential Implementation
Sequential start-up is implemented by connecting the power good signal (PWRGD pin) of PS1
to the TRACK pin of PS2 with a resistor–capacitor (RC) circuit. The waveforms of power up
and down are in Figures 4 and 5. In Figure 4, the 5V PS1 supply ramps up first. When supply
reaches its final 5V steady state value, the open collector output of the PWRGD pin releases
to the TRACK pin and the PS2 output voltage rises at the rate of the RC time constant. In
Figure 5, the PWRGD pin pull low by PS1 ENABLE off or the PS1 output voltage is below 90%
of the desired regulated voltage, and then the TRACK pin is pulled low and the PS2 power
down. Figure 3 shows the circuit diagram of sequential start-up when Vo
PWRGD of PS1.
Vin
PS1
Vin
PS2
tracks the
PS2
Vo
PS2
ENABLE
Vo
PS1
PWRGD
TRACK
R
ENABLE
C
Figure 3. PS1 and PS2 track output voltage Sequential start-up
Page 12

PS1
PS2
PS1
PS2
Figure 4: Sequential Power up Figure 5: Sequential Power down
Ratio-Metric Implementation
Ratio–metric is implemented by the selection of the resistor values of the voltage divider on
the TRACK pin. Resistors R1 and R2, in Figure 6 determine the tracking method that is
implemented.
To simplify the tracking design, set initial value of R2 equal to 20KΩ at internal circuit and set
resistor R1 for different tracking method. Figure 6 shows the circuit diagram of Ratio-Metric
start-up when Vo
Vin
tracks the Vo
PS2
PS1
PS1
.
PS2
Vin
Vo
PS2
ENABLE
Vo
PS1
R1
TRACK
ENABLE
R2
To Tracking
circuit
20K
Figure 6. PS1 and PS2 track output voltage Ratio-Metric start-up
12
Page 13

Ω
Ω
For Ratio-Metric applications that need the PS1 and PS2 outputs arrive regulation set point at
same time, use equation 1 to calculate R1, set △ V=Vo
set,PS1
–Vo
and △ V will be
set,PS2
negative. The waveforms of power up and down are showed in Figures 7 and 8.
−∆+
VrefVVo
PSset
=
R
1
2,
])[(
K
20*
------------------------------------------------------(1)
Vref
Note:
1. Vref =0.4×Vo
, please refer to Table 5 for Vref set value.
set,PS2
2. △V is the maximum difference of voltage between PS1 and PS2 supply voltage.
For example, the PS1 Vo
1 =
=
−+
=5V, the PS2 Vo
set,PS1
]32.1)7.13.3[(
KKR 75.5520*
=3.3V, R1 is calculated as follows:
set,PS2
32.1
PS1=5V
+△V=1.7V
Figure 7. Ratio–metric tracking Power up Figure 8. Ratio–metric tracking Power down
PS2=3.3V
PS1
PS2
For Ratio-Metric applications that need the PS2 supply voltage rises first at power up and falls
second at power down, use equation 2 to calculate R1, set △V≦0.4×Vo
and △V will be
set,PS2
negative. The waveforms of power up and down are showed in Figures 9 and 10.
psset
K
1
=
R
2,
−∆−
])[(
VrefVVo
20*
-----------------------------------------------------------------(2)
Vref
Note:
1. Vref =0.4×Vo
2. △V is defined as the voltage difference between Vo
its rated voltage.
, please refer to Table 5 for Vref set value.
set,PS2
and Vo
PS1
when Vo
PS2
reaches
PS2
13
Page 14

Ω
For example, the PS1 Vo
1 =
=
−−
32.1
=5V, the PS2 Vo
set,PS1
]32.1)3.13.3[(
=3.3V, R1 is calculated as follows:
set,PS2
KKR 303.1020*
PS1=5V
PS2=3.3V
PS1
PS2
-△V=1.3V
Figure 9. Ratio–metric tracking Power up Figure 10. Ratio–metric tracking Power down
Simultaneous Implementation
Similar to the ratio-metric implementation, simultaneous tracking is implemented by using a voltage
divider on the TRACK pin. The objective is to minimize the voltage difference between the power
supply outputs during power up and down. The waveforms of power up and down are showed in
Figures 13 and 14.
For type A (DNXXX0A0XXXX A), the simultaneous tracking can be accomplished by connecting
Vo
to the TRACK pin of PS2. Figure 11 shows the circuit diagram of voltage Simultaneous start-up
PS1
when Vo
tracks Vo
PS2
(only for type A).
PS1
PS1
Vin
Vin
PS2
Vo
PS2
ENABLE
Vo
PS1
TRACK
ENABLE
Figure 11. PS1 and PS2 track output voltage Simultaneous start-up for type A
14
Page 15

For type C (DNXXX0A0XXXX C), the simultaneous tracking can be accomplished by putting R1 equal
to 30.1K Ω through Vo
Simultaneous start-up when Vo
Vin
to the TRACK pin of PS2. Figure 12 shows the circuit diagram of
PS1
PS1
tracks the Vo
PS2
(only for type C).
PS1
PS2
Vin
Figure 12. PS1 and PS2 track output voltage Simultaneous start-up for type C
ENABLE
Vo
PS1
R1
30.1K
TRACK
ENABLE
To Tracking
circuit
20K
R2
Vo
PS2
PS1
PS1
PS2
PS2
Figure 13. Simultaneous Power up Figure 14. Simultaneous Power down
Table 5. : Vref Definition
Voset,ps2
0.7525
1.2
1.5
1.8
2.5
3.3
5.0
Vref
0.3
0.48
0.6
0.72
1.0
1.32
2.0
15
Page 16

t
t
r
r
Notes on the use of Track function:
1. For proper voltage tracking, first, The ENABLE On/Off pin of the PS2 module is lef
unconnected (or tied to GND for negative logic modules or tied to VIN for positive logic
modules), so that the modules are ON by default and second applied input voltage to the
PS1 and PS2. The TRACK pin is held at ground potential for duration of input voltage
reaches its minimum input voltage (VIN,min) and then held for at least 10mS thereafter.
This brief period gives the modules time to complete their internal soft-start initialization.
2. The PS2 output will not follow the PS1 voltage until the PS2 has completed its soft-star
time. After this time, PS2 is capable of both sinking and sourcing current when following
the voltage at the TRACK pin.
3. Notice that power down by removing the input voltage may not provide proper powe
tracking below under voltage lockout limit where the both integrated switches are off. So,
using the ENABLE On/Off signal of PS1 for power down is the preferred option for powe
tracking.
4. The TRACK pin absolute maximum voltage cannot over the Vin.
5. For type A: When Tracking is unused, put R1 equal to 1KΩ and connect TRACK pin to
+Vcc
For type C: When Tracking is unused, put R1 equal to 30.1KΩ and connect TRACK pin to
+Vcc
Test
1) Put R56 to take the place of R1 on the POL evaluation board and use the value from
above equation for different tracking purpose.
2) Use channel 1 and channel 2 measures the output voltage of PS1 and PS2.
3) For turn on, disable remote On/Off of the PS1, enable remote On/off of the PS2, and
supply input voltage to PS1 and PS2.
4) For the power on, enable switch on of PS1. In the meantime, to track power up by scope
trigger function.
5) For the power down, enable switch off of PS1 to track power down.
6) Illustration of tacking features can be found in the section of Detailed Description.
8.3 Dynamic Characteristics
8.3.1 Output Voltage Deviation
Output Voltage Deviation is defined as the response of the converter to a sudden step change
in the output load current. The output voltage deviation is characterized by two parameters:
Maximum Output Voltage Deviation and Response Time (please refer to the data sheet for the
detailed specification). The value of dynamic resistance for a defined step current is defined
as:
R
dynamic
Vout
=
*5.0
Imax
16
Page 17

f
r
Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Adjust the input voltage to the desired operating point.
3) Set the electronic or resistive load at 50% of maximum load.
4) Change channel 1 to scope probe and measure across the
5) Set the switch SW2 to the converter ON.
6) Set channel 2 on the oscilloscope to be AC coupled and to 50mV/Div and for 5mS/Div. Set
the trigger to auto and adjust the trigger point at a negative going pulse for step load
change from 50% to 100% of Io or adjust the trigger point at positive going pulse for step
load change from 100% to 50% (Please refer to data sheet for the detailed information.)
R .
dynamic
7) Measure the Peak-to-Peak deviation and capture the waveform as required.
8.3.2 Turn-On Response Time.
Turn-On Response Time is defined as the time it takes for the output to rise to within 90% o
its final value from the time when the converter is enabled. The rise time is deliberately made
slower to reduce the inrush current and to eliminate any overshoot in the output voltage.
These test functions have two categories.
1.) Turn on the module by using the External switch to control input voltage.
2.) Turn on module by using the Enable on/off.
Test (Turn on the module by using the external switch)
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Turn on the input power supply and set it to the desired operating point.
3) Set channel 1 on the oscilloscope to be DC coupled and to the appropriate range for the
input voltage.
4) Connect a coaxial cable from channel 1 to BNC1 on the Evaluation Board.
5) Set channel 2 on the oscilloscope to be DC coupled and to the appropriate range for the
output voltage.
6) Connect a coaxial cable from channel 2 to BNC2 on the Evaluation Board.
7) Set the Time base to 2mS/Div
8) Set the Trigger for a one-time event and set the Trigger level at approximately 2V (rising)
or suitable trigger point (referring to data sheet) on channel 2.
9) Enable the external on/off switch to supply power and use the cursor V Bars to measure
the delay time, and then record the waveform on the oscilloscope.
Test (Turn on the module by using the Enable on/off)
1. Turn on the fan.
2. Turn on the input power supply and set it to the desired operating point.
3. Set channel 1 on the oscilloscope to be DC coupled and to 1V/division. (Please also refe
to data sheet for the detailed information).
4. Connect a scope probe from channel 1 between the on/off control pin and reference
ground (SGND) on the Evaluation Board.
17
Page 18

5. Set channel 2 on the oscilloscope to be DC coupled and to the appropriate range for the
output voltage.
6. Connect a coaxial cable from channel 2 to BNC2 on the Evaluation Board.
7. Set the Time base to 2mS/Div
8. Set the Trigger for a one-time event and set the Trigger level at approximately 2V (rising)
or suitable trigger point (referring to data sheet) on channel 2.
9. Enable the on/off switch to turn on and use the cursor V Bars to measure the delay time,
and then record the waveform on the oscilloscope.
8.4. Thermal Characteristic
8.4.1 Efficiency
Efficiency is the ratio of total output power to the input power. It is typically measured at full
load and nominal input voltage.
Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Set the enable switch SW2 to the converter ON.
3) Adjust the input voltage to the desired operating point.
4) Set the electronic or resistive Load to the desired operating point.
5) Read and note the output voltage (DVM3) and input voltage (DVM2).
6) Read and note the input and output currents from the DVM1 and the electronic load.
7) Use the following formulas to calculate the efficiency:
Efficiency= (Pout/Pin) × 100(%)
Pin = Iin × Vin
Pout = Iout × Vout
The following graph shows the efficiency curves of the DNS04S0A0R06P A module when
measuring at different operating points.
100
90
80
70
60
50
EFFICIENCY(%)
40
30
123456
LOAD (A)
3V
5V
5.5V
18
Page 19

Appendix A- Evaluation Board Schematic
19
Page 20

Appendix B - Evaluation Board Layout (Top View)
Appendix C - Evaluation Board Layout (Bottom View)
CONTACT DATA: www.deltaww.com
USA:
Telephone:
East Coast: (888) 335 8201
West Coast: (888) 335 8208
Fax: (978) 656 3964
Email: DCDC@delta-corp.com
Warranty
Delta offers a two (2) year limited warranty. Complete warranty information is listed on our web site or is available upon request
from Delta.
Information furnished by Delta is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Delta for its use,
nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties, which may result from its use. No license is granted by
implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Delta. Delta reserves the right to revise these specifications at any
time, without notice.
Europe:
Telephone:
France: +33 1 6485 1212
Germany: +49 89 370 62 897
UK: +44 777 195 6299
Fax: +33 1 6485 1212
Email: DCDC@euro.delta-corp.com
Asia:
Telephone: +886 3 4526107 x6220
Fax: +886 3 4513485
Email: DCDC@delta.com.tw
20
 Loading...
Loading...