Page 1

Dell™ XPS™ 720
Owner’s Manual
Model DCDO
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Page 2
Notes, Notices, and Cautions
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
NOTICE: A NOTICE indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the
problem.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
If you purchased a Dell™ n Series computer, any references in this document to Microsoft® Windows®
operating systems are not applicable.
____________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2007 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo, XPS, H2C, Inspiron, Dell Precision, Dimension, OptiPlex, Latitude, P owerEdge, P owerV ault,
PowerApp, TravelLite, Strike Zone, and Dell OpenManage are trademarks of Dell Inc.; Intel, Pentium, Celeron, and Intel Core 2 Extreme are
either trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation; Microsoft, Windows, Windows Vista, and the Windows Vista Start button are
either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. Bluetooth is a registered
trademark owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc. and is used by Dell under license.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products.
Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
Model DCDO
April 2007 P/N KP688 Rev. A00
Page 3

Contents
Finding Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1 Setting Up and Using Your Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Front and Back View of the Computer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Front View
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Front I/O Connectors
Back View
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Back I/O Connectors
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Attaching the Computer Stand
Installing Your Computer in an Enclosure
Connecting Monitors
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Connecting a Monitor (Without an Adapter)
Connecting a Monitor (With an Adapter)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Connecting a Monitor in a Dual Graphics Card Configuration
Connecting Two or More Monitors
Connecting a TV
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Changing the Display Settings to Support Two or More Monitors
About Your RAID Configuration
RAID Level 0 Configuration
RAID Level 1 Configuration
RAID Level 0+1 Configuration
RAID Level 5 Configuration
Configuring Your Hard Drives for RAID
Setting Your Computer to RAID-Enabled Mode
Using the NVIDIA MediaShield ROM Utility
Using NVIDIA MediaShield
Using Multimedia
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Copying CD, DVD, and Blu-ray Disc™ (BD) Media
Helpful Tips
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
. . . . . . . 25
. . . . . 28
Using a Media Card Reader (Optional)
Network Setup Wizard
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Contents 3
Page 4

Transferring Information to a New Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Power Management Options in Windows XP
Standby Mode
Hibernate Mode
Power Options Properties
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Power Management Options in Windows Vista
Sleep Mode
Hibernate Mode
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Configuring Power Management Settings
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
2 Optimizing for Greater Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Understanding Dual-Graphics Technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Understanding CPU Overclocking
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3 Dell™ QuickSet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
4 Troubleshooting
Solving Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Battery Problems
Drive Problems
E-Mail, Modem, and Internet Problems
Error Messages
IEEE 1394 Device Problems
Keyboard Problems
Lockups and Software Problems
Memory Problems
Mouse Problems
Network Problems
Power Problems
Printer Problems
Scanner Problems
Sound and Speaker Problems
Video and Monitor Problems
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
4 Contents
Power Lights
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Page 5

Diagnostic Lights. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Beep Codes
System Messages
Dell Diagnostics
Drivers
Restoring Your Operating System
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
When to Use Dell Diagnostics
Starting Dell Diagnostics From Your Hard Drive
Starting Dell Diagnostics From the Drivers and Utilities Media
Dell Diagnostics Main Menu
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
What Is a Driver?
Identifying Drivers
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Reinstalling Drivers and Utilities
Using Windows Device Driver Rollback
Using the Drivers and Utilities Media
Using Microsoft
Windows System Restore. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Using Dell PC Restore and Dell Factory Image Restore
Using the Operating System Media
Troubleshooting Software and Hardware Problems
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
. . . . . . 73
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
. . . . . . . . . . 79
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
. . . . . . . . . . . . 83
5 Removing and Installing Parts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Before You Begin. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Recommended Tools
Preparing to Work Inside Your Computer
Removing the Computer Cover
Inside View of Your Computer
System Board Components
Memory
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
DDR2 Memory Overview
Addressing Memory Configurations
Installing Memory
Removing Memory
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Contents 5
Page 6

Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Removing PCI and PCI Express Cards
Installing PCI and PCI Express Cards
Removing a PCI Express Graphics Card from a Dual Configuration
Installing a PCI Express Graphics Card in a Dual Configuration
Network Adapter and Sound Card Settings
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Drives
About Serial ATA Drives
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
General Drive Installation Guidelines
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
. . . 100
. . . . . 102
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Hard Drive
Drive Panel
Floppy Drive
Media Card Reader
Optical Drive
Liquid Cooling Assembly
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Removing a Hard Drive
Installing a Hard Drive
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Removing the Drive Panel
Replacing the Drive Panel
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Removing a Floppy Drive
Installing a Floppy Drive
Removing a Media Card Reader
Installing a Media Card Reader
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Removing an Optical Drive
Installing an Optical Drive
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Safety Instructions for Liquid Cooling Assembly
Removing the Liquid Cooling Assembly
Installing the Liquid Cooling Assembly
Processor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Removing the Processor
Installing the Processor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
6 Contents
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Fans
Removing the Card Fan
Installing the Card Fan
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Page 7

Removing the Optional Hard Drive Fan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Installing the Optional Hard Drive Fan
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
System Board
Removing the System Board
Installing the System Board
Power Supply
Power Supply (PSU) DC Connector Pin Assignments
Removing the Power Supply
Installing the Power Supply
Front I/O Panel
Front I/O-Panel Components
Removing the Front I/O Panel
Installing the I/O Panel
Battery
Replacing the Battery
Removing the Computer Stand
Replacing the Computer Cover
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
. . . . . . . . . . 143
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
6 Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
System Setup
Overview
Entering System Setup
System Setup Options
Boot Sequence
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Clearing Forgotten Passwords
Clearing CMOS Settings
Cleaning Your Computer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Computer, Keyboard, and Monitor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Mouse
Floppy Drive
CDs and DVDs
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Contents 7
Page 8

FCC Notices (U.S. Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Class A
Class B
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
FCC Identification Information
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Contacting Dell
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
Index
8 Contents
Page 9

Finding Information
NOTE: Some features or media may be optional and may not ship with your computer. Some features or media may
not be available in certain countries.
NOTE: Additional information may ship with your computer.
What Are You Looking For? Find It Here
• A diagnostic program for my computer
• Drivers for my computer
• My device documentation
• Desktop System Software (DSS)
• Warranty information
• Terms and Conditions (U.S. only)
• Safety instructions
• Regulatory information
• Ergonomics information
• End User License Agreement
Drivers and Utilities Media
Documentation and drivers are already installed on your
computer. You can use the Drivers and Utilities media to
reinstall drivers (see "Reinstalling Drivers and Utilities" on
page 76), access your documentation or run the Dell
Diagnostics (see "Dell Diagnostics" on page 72).
Readme files may also be
included on your media to
provide last-minute
updates about technical
changes to your computer
or advanced technical
reference material for
technicians and
experienced users.
NOTE: Drivers and documentation updates can be found at
support.dell.com.
Dell™ Product Information Guide
Finding Information 9
Page 10

What Are You Looking For? Find It Here
• How to set up my computer
Setup Diagram
• Service Tag and Express Service Code
• Microsoft
®
Windows® Product Key Label
Service Tag and Microsoft Windows Product Key
These labels are located on your computer.
• Use the Service Tag to
identify your computer
when you use
support.dell.com
or
contact support.
• Enter the Express
Service Code to direct
your call when contacting support.
10 Finding Information
Page 11
What Are You Looking For? Find It Here
• Solutions — Troubleshooting hints and tips, articles
from technicians, online courses, and frequently asked
questions
Dell Support Website — support.dell.com
NOTE: Select your region or business segment to view the
appropriate support site.
• Community — Online discussion with other Dell
customers
• Upgrades — Upgrade information for components, such
as the memory, hard drive, and operating system
• Customer Care — Contact information, service call and
order status, and warranty and repair information
• Service and Support — Service call status, support
history, service contract, and online discussions with
support
• Reference — Computer documentation, details on my
computer configuration, product specifications, and
white papers
• Downloads — Certified drivers, patches, and software
updates
• Desktop System Software (DSS) — If you reinstall the
operating system on your computer, you should also
reinstall the DSS utility. DSS automatically detects your
computer and operating system and installs the updates
appropriate for your configuration, providing critical
updates for your operating system and support for Dell™
3.5-inch USB floppy drives, Intel
®
Pentium® M
processors, optical drives, and USB devices. DSS is
necessary for correct operation of your Dell computer.
• How to use your Windows™ operating system
• How to work with programs and files
• How to personalize my desktop
To download Desktop System Software:
1
Go to
support.dell.com
and then enter your Service Tag or product model.
2
Select
Drivers & Downloads
3
Select your operating system and language, and then
search for the keyword
NOTE: The support.dell.com user interface may vary
depending on your selections.
Windows Help and Support
1
To access Windows Help and Support:
• In Windows XP, click
• In Windows Vista™, click the Windows Vista Start
button
2
Type a word or phrase that describes your problem, and
then click the arrow icon.
3
Click the topic that describes your problem.
4
Follow the instructions on the screen.
and click
, select your business segment,
, and then click Go.
Desktop System Software
Start and click
Help and Support
Help and Support
.
.
.
Finding Information 11
Page 12
What Are You Looking For? Find It Here
• How to reinstall my operating system
Operating System Media
The operating system is already installed on your computer.
To reinstall your operating system, use the Operating
System media.
NOTE: The color of your Operating System media varies
according to the operating system you ordered.
After you reinstall the
operating system, use the
Drivers and Utilities media
to reinstall drivers for the
devices that came with
your computer.
The operating system
product key label is located
on your computer.
12 Finding Information
Page 13
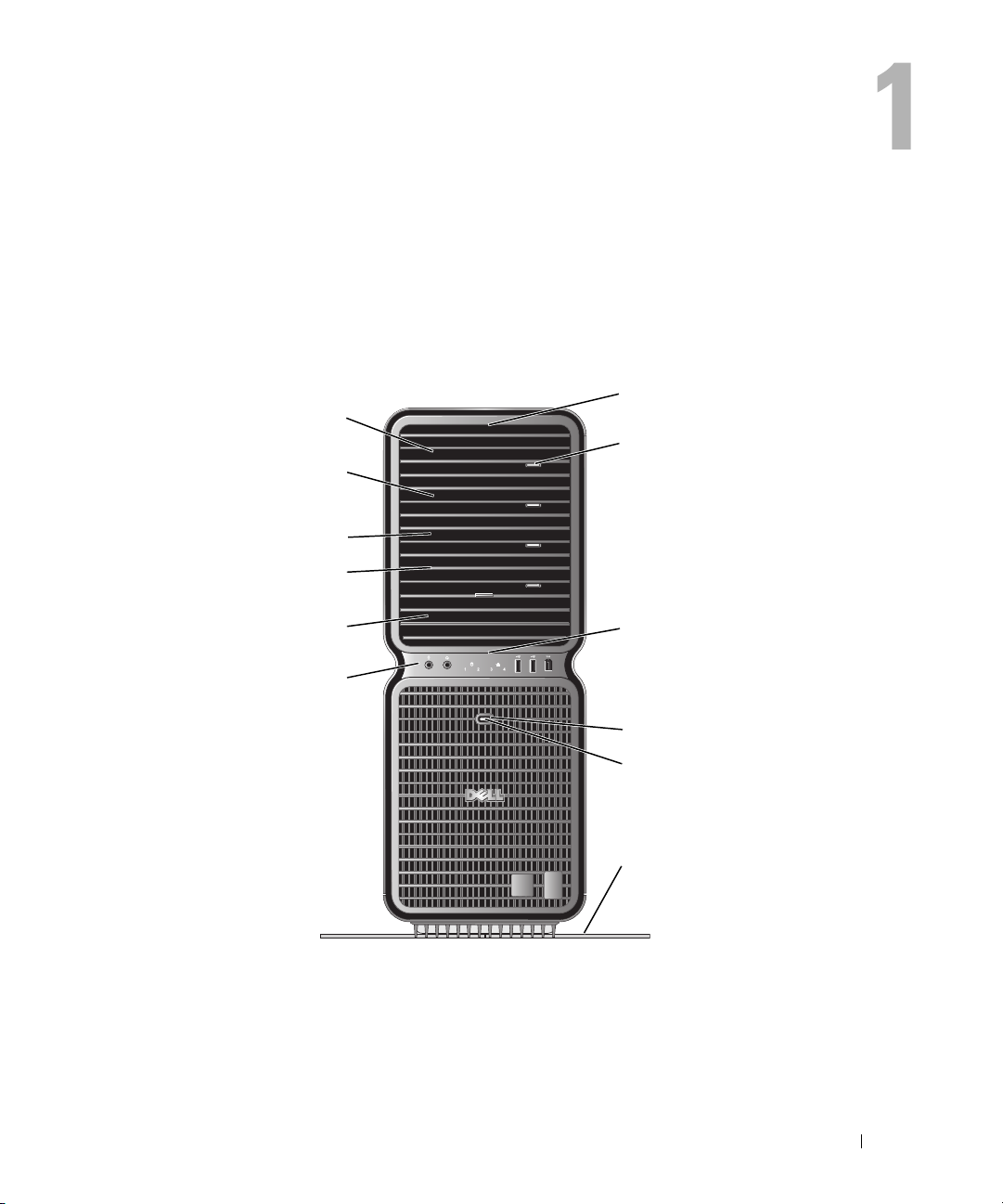
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Front and Back View of the Computer
Front View
7
6
8
5
4
3
2
1
9
10
11
12
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 13
Page 14

1 front I/O connectors Plug USB and other devices into the
Connectors" on page 15).
2 3.5-inch drive bays (2) Can hold an optional Media Card Reader or floppy drive.
3-6 5.25-inch drive bays (4) Can hold an optical or SATA hard drive in a 5.25-inch drive bay carrier.
appropriate connectors (
see "Front I/O
NOTE: The hard drive carrier is only for use in the 5.25-inch drive bays. The
floppy-drive/Media Card Reader and hard drive carriers are not interchangeable.
7 front panel LEDs (4) Use the sequence of these diagnostics lights to help troubleshoot a problem with
your computer (see "Dell Diagnostics" on page 72).
NOTE: The color of the front panel LEDs can be adjusted in system setup (see
"System Setup" on page 168).
8 optical drive tray eject
button (4)
9 front panel LEDs (4) Multi-colored lights provide illumination for the front of the computer.
Use to eject the drive tray of an optical drive.
NOTE: The optical drive tray eject button is not a handle. The self-tending doors open
automatically when the eject button is pressed and the drive tray is ejected.
NOTE: The color of the front panel LEDs can be adjusted in system setup (see
"System Setup" on page 168).
10 power button Press to turn on the computer.
NOTICE: To avoid losing data, do not use the power button to turn off the
computer. Instead, perform an operating system shutdown.
NOTE: The power button can also be used to wake the system or to place it into a
power-saving state (see "Power Management Options in Windows XP" on page 44).
11 power light The power light illuminates and blinks or remains solid to indicate different states:
• No light — The computer is turned off.
• Steady green — The computer is in a normal operating state.
• Blinking green — The computer is in a power-saving state.
• Steady amber — There may be a problem with an installed device.
• Blinking amber — An internal power problem may exist.
12 computer stand Attach the computer stand to provide stability to the system.
CAUTION: The computer stand should be installed at all times to ensure
maximum system stability. Failure to install the stand could result in the
computer tipping over, potentially resulting in bodily injury or damage to the
computer.
14 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 15

Front I/O Connectors
4567213
1 microphone connector Use the microphone connector to attach a personal computer microphone for
voice or musical input into a sound or telephony program.
2 headphone connector Use the headphone connector to attach headphones.
3 diagnostic lights (4) Use the sequence of these diagnostics lights to help troubleshoot a problem with
your computer (see "Dell Diagnostics" on page 72).
4 hard-drive activity light The hard drive light is on when the computer reads data from or writes data to the
hard drive. The light may also be on when a device such as your CD player is
operating.
5 network link light The network link light is on when a good connection exists between a network and
the computer.
6 USB 2.0 connectors (2) Use the front USB connectors for devices that you connect occasionally, such as
flash memory keys, cameras, or bootable USB devices. For more information on
bootable USB devices see "Boot Sequence" on page 175.
Dell recommends that you use the back USB connectors for devices that typically
remain connected, such as printers and keyboards.
7 IEEE 1394 connector Use the IEEE 1394 connector for high-speed data devices such as digital video
cameras and external storage devices.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 15
Page 16
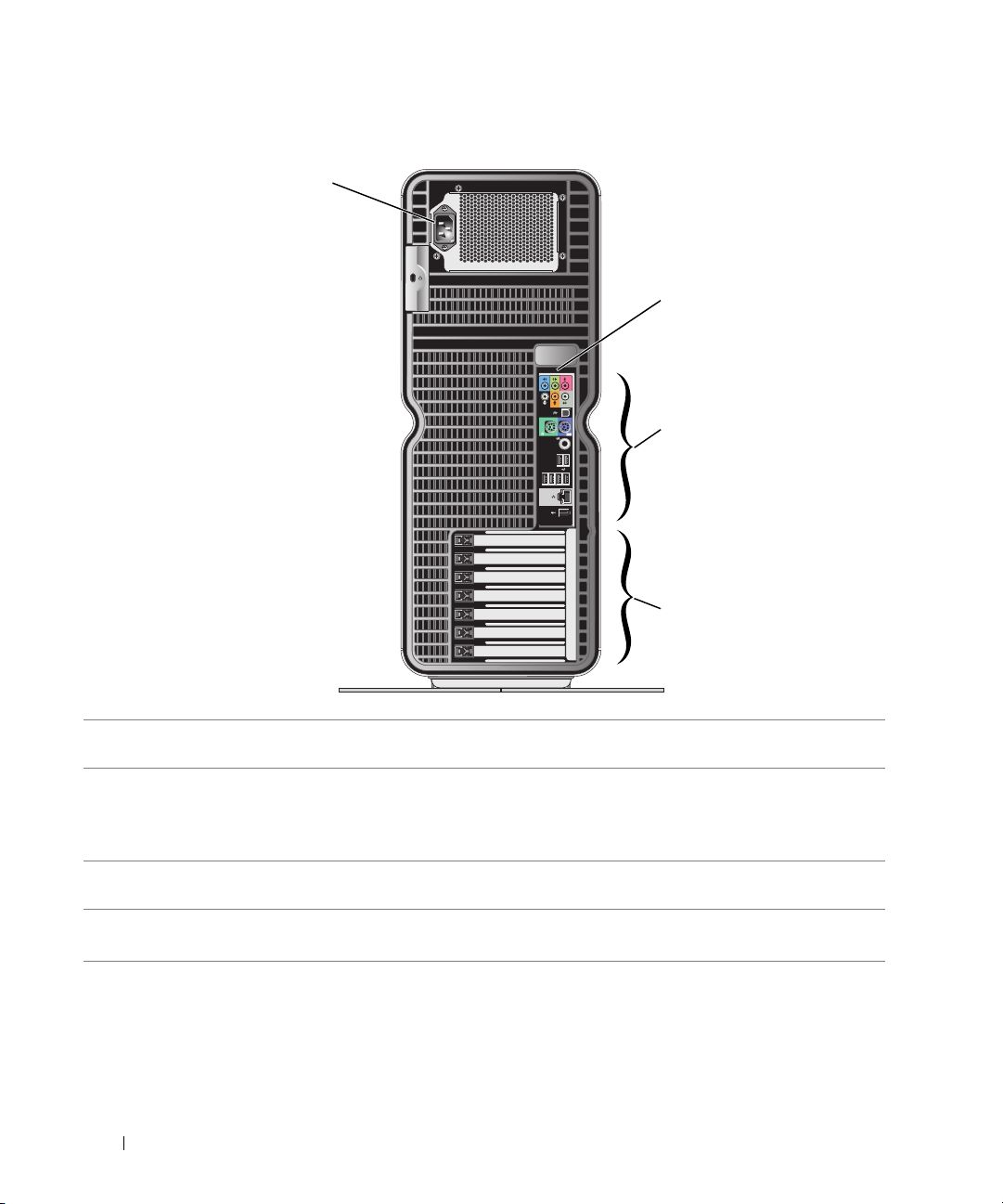
Back View
1
2
3
4
1 power connector Insert the power cable. The appearance of this connector may differ from what is
pictured.
2 back panel LEDs (2) Multi-colored lights provide illumination for the I/O panel on the back of the
computer.
NOTE: The color of the back panel LEDs can be adjusted in system setup (see
"System Setup" on page 168).
3 back I/O connectors Plug USB and other devices into the
Connectors" on page 17).
4 card slots Access connectors for any installed PCI or PCI Express cards.
appropriate connectors
(see "Back I/O
NOTE: Some connector slots support full-length cards.
16 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 17

Back I/O Connectors
213
15
1 link integrity light
2 network adapter
connector
14
• Green — A good connection exists between a 10-Mbps network and the
computer.
• Orange — A good connection exists between a 100-Mbps network and the
computer.
• Yellow — A good connection exists between a 1000-Mbps (1-Gbps) network and
the computer.
• Off — The computer is not detecting a physical connection to the network.
NOTICE: Do not plug a telephone cable into the network adapter connector.
Use the network adapter connector to attach your computer to a network or
broadband device. Connect one end of a network cable to either a network jack or
your network or broadband device, and then connect the other end of the network
cable to the network adapter connector on your computer. A click indicates that
the network cable has been securely attached.
On computers with an additional network connector card, use the connectors on
the card and on the back of the computer when setting up multiple network
connections (such as a separate intra- and extranet).
45 6 7 8
9
10
11
1213
NOTE: Dell recommends that you use Category 5 wiring and connectors for your
network. If you must use Category 3 wiring, force the network speed to 10 Mbps to
ensure reliable operation.
3 network activity light Flashes a yellow light when the computer is transmitting or receiving network
data. A high volume of network traffic may make this light appear to be in a steady
"on" state.
4 keyboard connector Plug a standard PS/2 keyboard into the purple keyboard connector. Turn off the
computer and any attached devices before you connect a keyboard to the
computer. If you have a USB keyboard, plug it into a USB connector.
5 mouse connector Plug a standard PS/2 mouse into the green mouse connector. Turn off the
computer and any attached devices before you connect a mouse to the computer.
If you have a USB mouse, plug it into a USB connector.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 17
Page 18

6 side surround sound
connector
7 center subwoofer/LFE
connector
8 surround sound
connector
9 line-in connector Use the (blue) line-in connector to attach a record/playback device such as a
10 line-out/headphone
connector
11 microphone connector Use the (pink) microphone connector to attach a personal computer microphone
12 Optical S/PDIF
connector
13 RCA S/PDIF connector Use the RCA S/PDIF connector to transmit digital audio without going through
14 USB 2.0 connectors (6) Use the back USB connectors for devices that typically remain connected, such as
Use the (silver) side surround connector to attach additional speakers.
Use the (orange) subwoofer connector to attach a single subwoofer.
NOTE: The LFE (Low Frequency Effects) Audio channel, found in digital surround
sound audio schemes, carries only low frequency information of 80 Hz and below. The
LFE channel drives a subwoofer to provide extremely low bass extension. Systems
not using subwoofers can shunt the LFE information to the main speakers in the
surround sound setup.
Use the (black) surround sound connector to attach multichannel-capable
speakers.
cassette player, CD player, or VCR.
On computers with a sound card, use the connector on the card.
Use the (green) line-out connector to attach headphones and speakers with
integrated amplifiers.
On computers with a sound card, use the connector on the card.
for voice or musical input into a sound or telephony program.
Use the optical S/PDIF connector to transmit digital audio without going through
an analog audio conversion process.
an analog audio conversion process.
printers and keyboards.
NOTE: Dell recommends that you use the front USB connectors for devices that you
connect occasionally, such as flash memory keys, cameras, or bootable USB devices.
15 IEEE 1394 connector Use the IEEE 1394 connector for high-speed data devices such as digital video
cameras and external storage devices.
Attaching the Computer Stand
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
CAUTION: Your computer is heavy and can be difficult to maneuver. Seek assistance before attempting to lift,
move, or tilt the computer and always lift correctly to avoid injury; avoid bending over while lifting.
18 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 19

CAUTION: The computer stand should be installed at all times to ensure maximum system stability. Failure to
install the stand could result in the computer tipping over, potentially resulting in bodily injury or damage to the
computer.
1
Follow the procedures in "Before You Begin" on page 85.
2
Remove the thumb screw that is installed on the base of the computer.
NOTE: If the thumb screw is not already installed in the stand, it has been packaged separately.
3
Insert the six alignment tabs into the corresponding slots on the base of the computer, then slide the
stand forward until all six tabs catch in the slots.
4
Ensure that the screw hole on the stand is aligned with the screw hole on the base of the computer.
5
Insert the captive screw into the screw hole, then tighten the screw to secure the stand to the base of
the computer.
1
2
3
4
1 captive screw 2 stabilizing feet (closed) 3 computer stand
4 slots (6)
6
With the help of an assistant, carefully set the computer upright.
7
Carefully, lift the rear of the computer and slide the stabilizing feet outward into the open position.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 19
Page 20
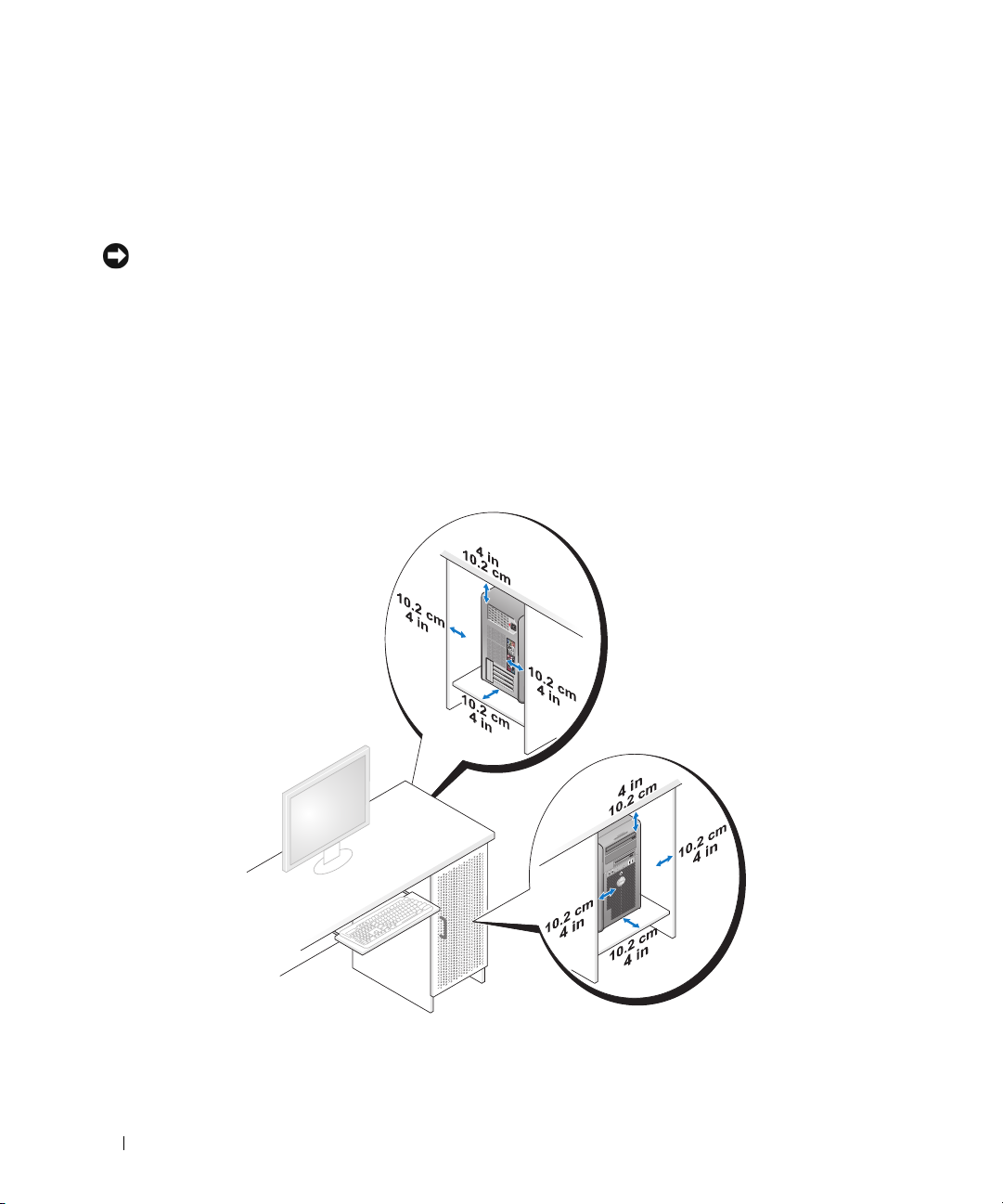
Installing Your Computer in an Enclosure
Installing your computer in an enclosure can restrict the airflow and impact your computer’s
performance, possibly causing it to overheat. Follow the guidelines below when installing your computer
in an enclosure:
NOTICE: The operating temperature specifications indicated in your Owner’s Manual reflect the maximum
ambient operating temperature. The room’s ambient temperature needs to be a consideration when installing your
computer in an enclosure. For example, if the ambient room temperature is at 25° C (77° F), depending on your
computer’s specifications, you only have 5° to 10° C (9° to 18° F) temperature margin before you reach your
computer’s maximum operating temperature. For details about your computer’s specifications, see "Specifications"
on page 163.
• Leave a 10.2 centimeter (4 inch) minimum clearance on all vented sides of the computer to permit the
airflow required for proper ventilation.
• If your enclosure has doors, they need to be of a type that allows at least 30% airflow through the
enclosure (front and back).
20 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 21
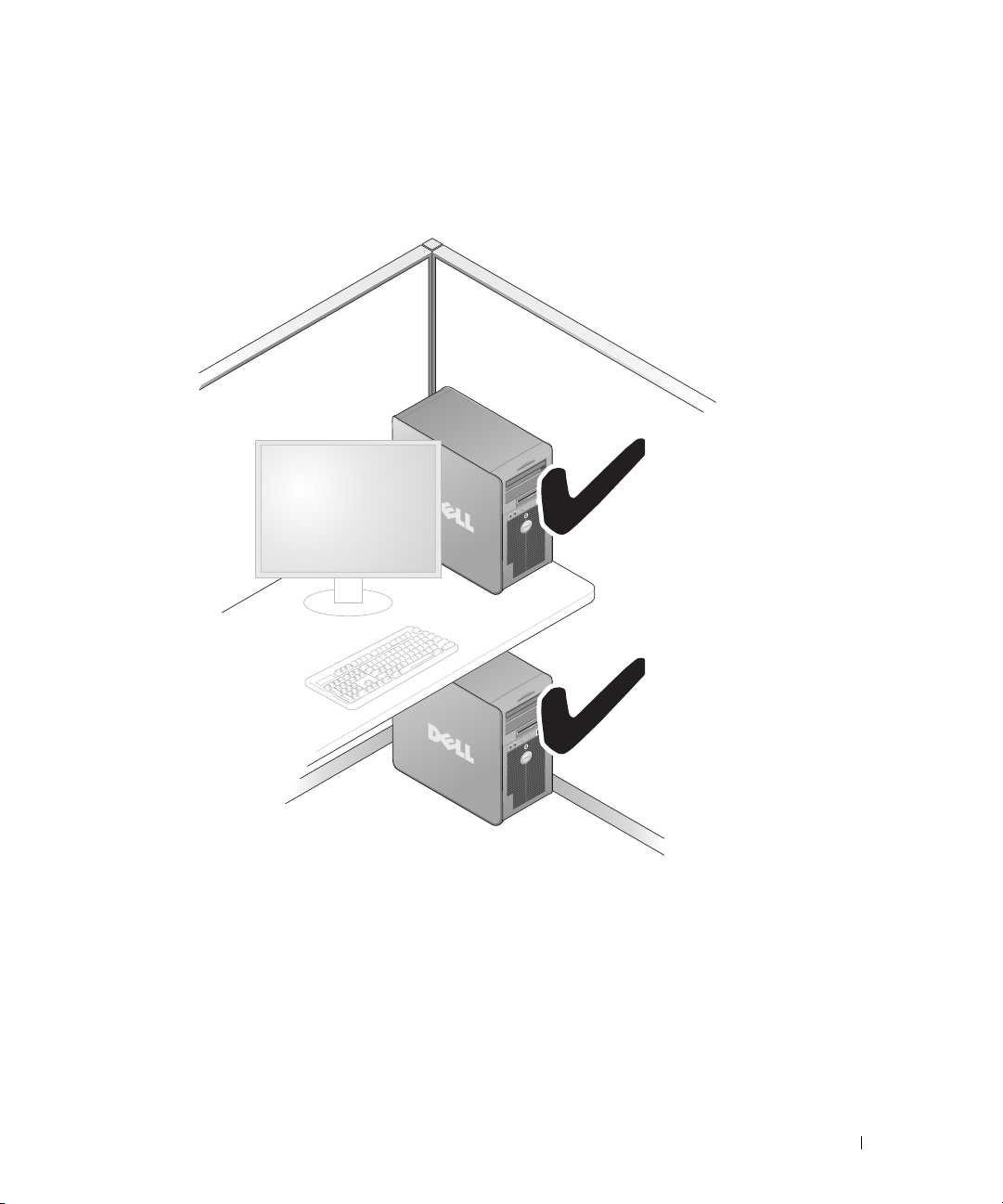
• If your computer is installed in a corner on a desk or under a desk, leave at least 5.1 centimeters
(2 inch) of clearance from the back of the computer to the wall to permit the airflow required for
proper ventilation.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 21
Page 22
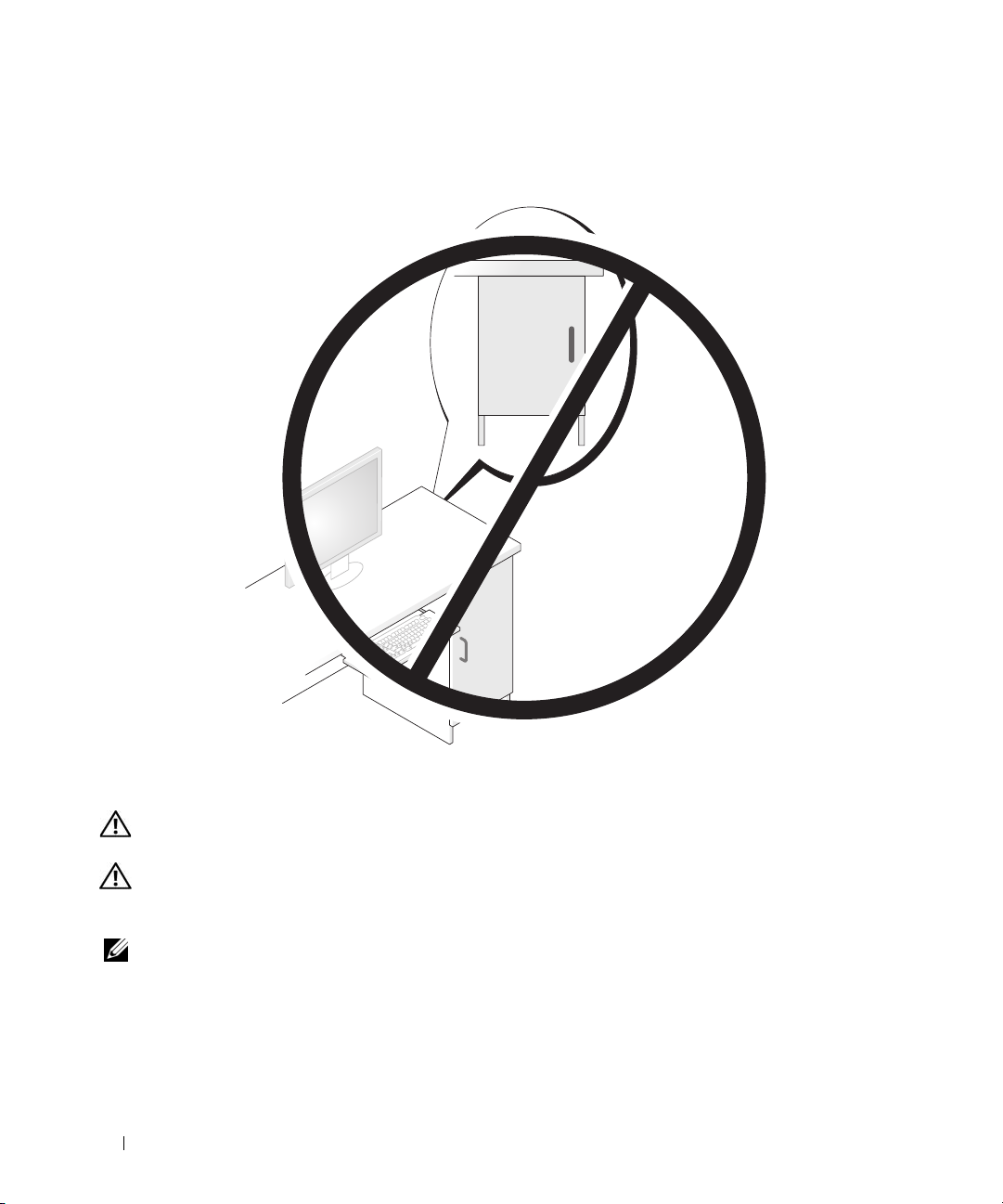
• Do not install your computer in an enclosure that does not allow airflow.
impacts your computer’s performance, possibly causing it to overheat.
Restricting the airflow
Connecting Monitors
CAUTION: Before you perform any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire, electric shock, or injury, do not overload an electrical outlet, power strip, or
convenience receptacle. The total ampere rating of all products plugged into an electrical outlet, power strip, or
other receptacle should not exceed 80 percent of the branch circuit rating.
NOTE: Depending on the options selected when you purchased your computer, your video card may have two DVI
ports, or one DVI and one VGA port.
22 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 23
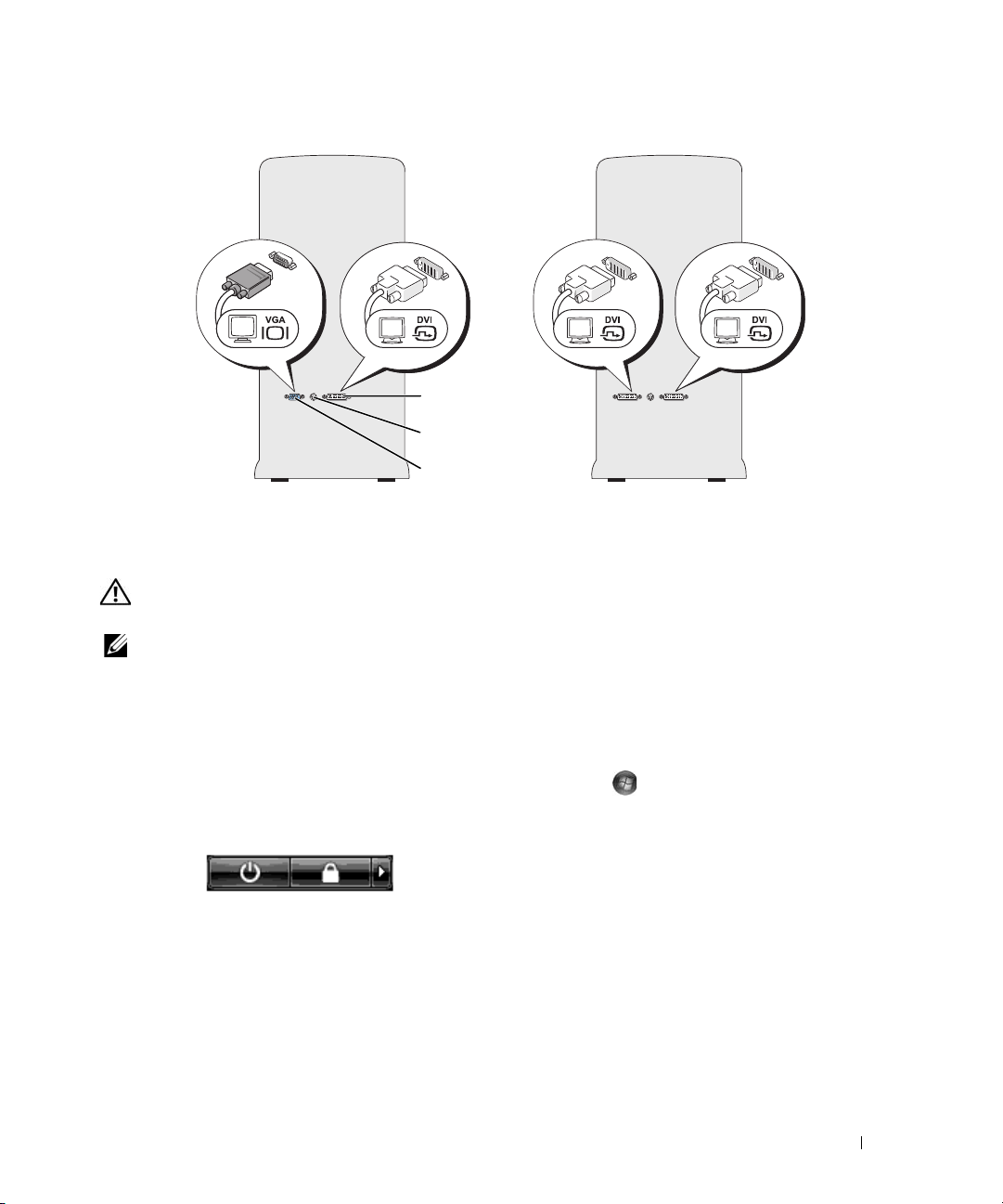
1
2
3
1 DVI (white) connector 2 TV-OUT connector 3 VGA (blue) connector
Connecting a Monitor (Without an Adapter)
CAUTION: Before you perform any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTE: If your monitor has a VGA connector and your computer does not have a VGA port, follow the instructions in
"Connecting a Monitor (With an Adapter)" on page 24.
1
Save and close all open files and exit all open programs.
2
Shut down the operating system:
• In Windows XP, click
• In Windows Vista™, click the Windows Vista Start button
corner of the Start menu as shown below, and then click
The computer turns off after the operating system shutdown process is complete.
Start→
Turn Off Computer→
Tur n o f f
,
Shut Down
.
click the arrow in the lower-right
.
3
Ensure that the computer and all attached devices are turned off. If your computer and attached
devices did not automatically turn off when you shut down your operating system, press and hold the
power button for about 4 seconds to turn them off.Disconnect the computer and all attached devices
from their electrical outlets.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 23
Page 24

4
Connect the DVI or VGA connector of your monitor to the appropriate connector on the back of the
computer:
To connect a monitor with a DVI connector, use the (white) DVI port on your computer.
To connect a monitor with a VGA connector, use the (blue) VGA port on your computer.
Connecting a Monitor (With an Adapter)
CAUTION: Before you perform any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTE: In order to connect a monitor with a VGA connector to the DVI port on the back of your computer, a DVI-to-
VGA adapter is required.
1
Save and close all open files and exit all open programs.
2
Shut down the operating system:
• In Windows XP, click
• In Windows Vista,
shown below, and then click
The computer turns off after the operating system shutdown process is complete.
3
Ensure that the computer and all attached devices are turned off. If your computer and attached
devices did not automatically turn off when you shut down your operating system, press and hold the
power button for about 4 seconds to turn them off.
4
Connect the DVI-to-VGA adapter to the VGA connector on your monitor, and then connect the other
end of the adapter to the (white) DVI port on the back of the computer.
c
lick
Start→
Turn Off Computer→
Start
, click the arrow in the lower-right corner of the Start menu as
Shut Down
.
Tur n o f f
.
24 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 25
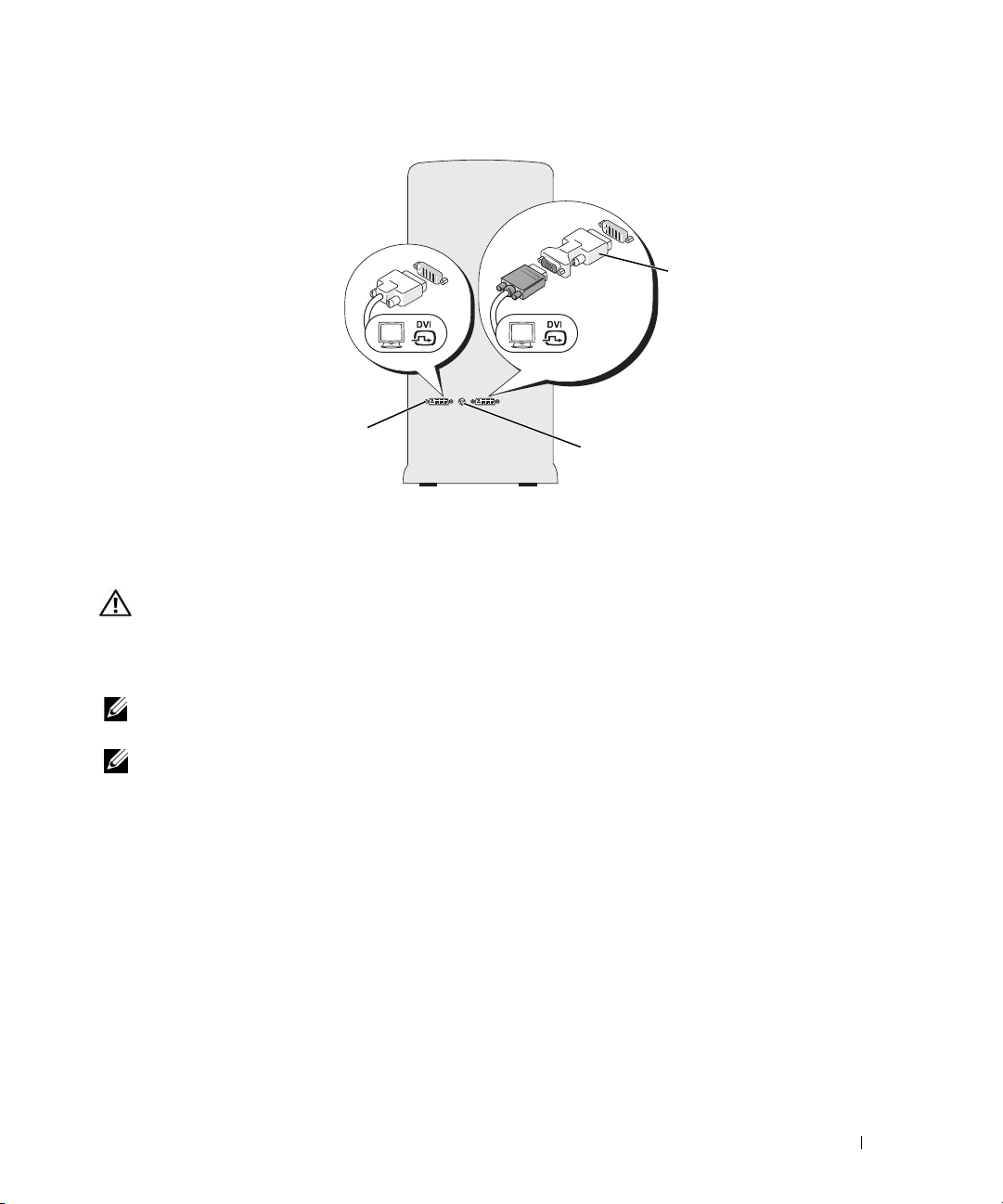
2
1
1 DVI (white) connector 2 DVI-to-VGA adapter (optional) 3 TV-OUT connector
3
Connecting a Monitor in a Dual Graphics Card Configuration
CAUTION: Before you perform any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
Dual graphics card configurations with multi-GPU technology enabled support only a single monitor.
The monitor must be connected to the primary graphics card in order to function.
NOTE: If you have modified your primary graphics card settings in the BIOS, then the left DVI connector at the rear
of your computer is the default primary connector.
NOTE: If your primary graphics card is equipped with two DVI ports and you are using a monitor with a VGA
connector, a DVI-to-VGA adapter is required to connect the monitor. See "Connecting a Monitor (With an Adapter)"
on page 24.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 25
Page 26

primary video card
1
Save and close all open files and exit all open programs.
2
Shut down the operating system:
• In Windows XP, click
Start→
• In Windows Vista, click
shown below, and then click
Turn Off Computer→
Start ,
click the arrow in the lower-right corner of the Start menu as
Shut Down
Tur n o f f
.
.
The computer turns off after the operating system shutdown process is complete.
3
Ensure that the computer and all attached devices are turned off. If your computer and attached
devices did not automatically turn off when you shut down your operating system, press and hold the
power button for about 4 seconds to turn them off.
4
Connect the DVI or VGA connector of your monitor to the appropriate connector on the computer’s
primary graphics card:
To connect a monitor with a DVI connector, use the (white) DVI port on the primary graphics card.
To connect a monitor with a VGA connector, use the (blue) VGA port on the primary graphics card.
26 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 27

Connecting Two or More Monitors
CAUTION: Before you perform any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTE: In order to connect and use two or more monitors in a dual graphics card configuration, multi-GPU
technology must be disabled. To disable multi-GPU, see "Changing the Display Settings to Support Two or More
Monitors" on page 28.
NOTE: Depending on the options selected when you purchased your computer, your video card may have two DVI
ports, or one DVI and one VGA port.
1
Save and close all open files and exit all open programs.
2
Shut down the operating system:
• In Windows XP, click
• In Windows Vista, click
shown below, and then click
The computer turns off after the operating system shutdown process is complete.
3
Ensure that the computer and all attached devices are turned off. If your computer and attached
devices did not automatically turn off when you shut down your operating system, press and hold the
power button for about 4 seconds to turn them off.
4
Connect two or more monitors to the appropriate DVI or VGA ports on the back of the computer.
Start→
Start
Turn Off Computer→
,
click the arrow in the lower-right corner of the Start menu as
Shut Down
.
Tur n o f f
.
NOTE: In order to connect a monitor with a VGA connector to the DVI port on the back of your computer, a
DVI-to-VGA adapter is required.
To connect two or more monitors directly to the DVI or VGA ports on your computer, see "Connecting
a Monitor (Without an Adapter)" on page 23.
To connect the VGA connectors of one or more monitors to the DVI port(s) on your computer, see
"Connecting a Monitor (With an Adapter)" on page 24.
5
Change the display settings to support multiple monitors (see "Changing the Display Settings to
Support Two or More Monitors" on page 28).
Connecting a TV
CAUTION: Before you perform any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTE: If you are connecting a TV to your computer, you may connect only one monitor (VGA or DVI) in addition to
the TV.
NOTE: See the documentation that came with your TV to ensure that you properly configure and connect the TV.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 27
Page 28

To connect a TV to your computer, an S-video cable is required. If you do not have an S-video cable, you
may purchase one at most consumer electronics stores. An S-video cable is not included with your
computer.
1
Save and close all open files and exit all open programs.
2
Shut down the operating system:
• In Windows XP, click
• In Windows Vista, click
shown below, and then click
Start→
Start
Turn Off Computer→
,
click the arrow in the lower-right corner of the Start menu as
Shut Down
.
Tur n o f f
.
The computer turns off after the operating system shutdown process is complete.
3
Ensure that the computer and all attached devices are turned off. If your computer and attached
devices did not automatically turn off when you shut down your operating system, press and hold the
power button for about 4 seconds to turn them off.
4
Disconnect the computer and all attached devices from their electrical outlets.
5
Connect one end of the S-video cable to the TV-OUT connector on the back of the computer.
6
Connect the other end of the S-video cable to the S-video input connector on your TV.
7
Connect one monitor, as needed, with a DVI or VGA connector as described in "Connecting Monitors"
on page 22.
Changing the Display Settings to Support Two or More Monitors
NOTE: Dual graphics card configurations with multi-GPU technology enabled support only a single monitor. In
order to connect and use two or more monitors in a dual graphics card configuration with multi-GPU technology,
multi-GPU must be disabled.
1
With your monitors connected and turned on, turn on the computer.
The Microsoft
2
Disable multi-GPU technology in the display settings (applies only to dual graphics card
configurations with multi-GPU technology enabled):
3
Enable clone mode or extended desktop mode in the display settings.
• In clone mode, all monitors display the same image.
• In extended desktop mode, you can drag objects from one screen to the other, increasing the
amount of viewable work space.
For more information on changing the display settings for your graphics card, see the device’s User’s
Guide in the Help and Support Center. (From the Help and Support Center, click User and system
guides
→ Device guides, and then select the guide for your graphics card.)
28 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
®
Windows® desktop displays on the primary monitor.
Page 29
About Your RAID Configuration
NOTICE: In order to use the migrating option to convert a RAID configuration without losing data, your hard drive
must initially be set up as a single drive RAID 0 array before the operating system is loaded onto the drive (see
"Using the NVIDIA MediaShield ROM Utility" on page 33 for instructions).
This section provides an overview of the RAID configuration you may have selected when you purchased
your computer. There are several RAID configurations available in the computer industry for different
types of uses. Your computer supports RAID level 0, RAID level 1, RAID level 5 (customer-installed), or
RAID level 0+1 (customer-installed). A RAID level 0 configuration is recommended for highperformance programs, while RAID level 1 is recommended for users that desire a high level of data
integrity.
NOTE: RAID levels do not represent a hierarchy. A RAID level 1 configuration is not inherently better or worse than
a RAID level 0 configuration.
The drives in a RAID configuration should be the same size in order to ensure that the larger drive does
not contain unallocated (and therefore unusable) space.
RAID level 0 and RAID level 1 require a minimum of two drives. RAID level 5 requires a minimum of
three drives. RAID level 0+1 requires a minimum of four drives.
RAID Level 0 Configuration
NOTICE: Because a RAID level 0 configuration provides no data redundancy, a failure of one drive results in the
loss of all data. To protect your data when using a RAID level 0 configuration, perform regular backups.
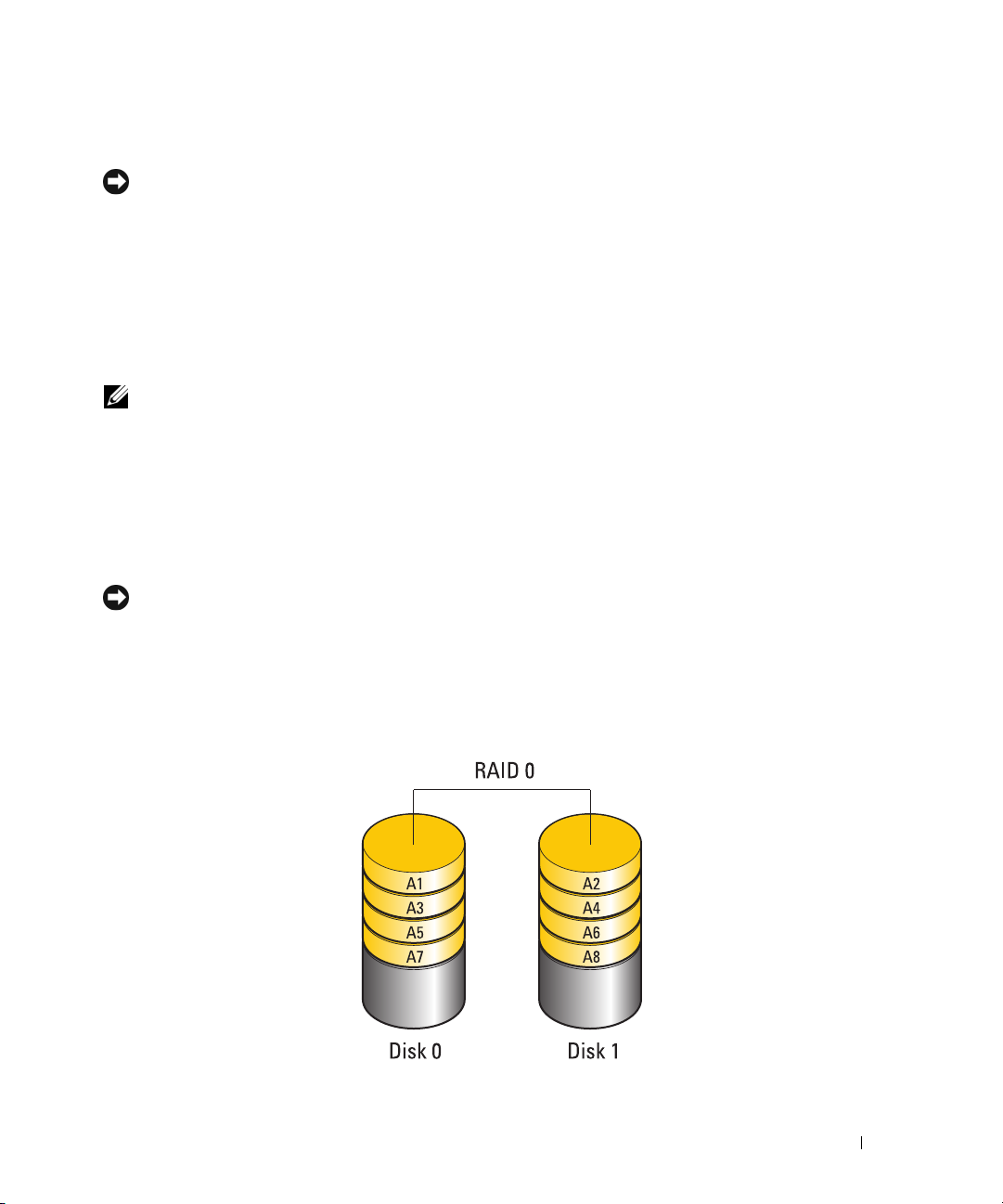
RAID level 0 uses a storage technique known as "data striping" to provide a high data access rate. Data
striping is a method of writing consecutive segments, or stripes, of data sequentially across the physical
drive(s) to create a large virtual drive. Data striping allows one of the drives to read data while the other
drive is searching for and reading the next block.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 29
Page 30

Another advantage of a RAID level 0 configuration is that it utilizes the full storage capacities of the
drives. For example, two 120-GB hard drives combine to provide 240 GB of hard drive space on which to
store data.
NOTE: In a RAID level 0 configuration, the size of the configuration is equal to the size of the smallest drive
multiplied by the number of drives in the configuration.
RAID Level 1 Configuration
RAID level 1 uses a data-redundancy storage technique known as "mirroring" to enhance data integrity.
When data is written to the primary drive, the data is also duplicated, or mirrored, on the second drive in
the configuration. A RAID level 1 configuration sacrifices high data-access rates for its data redundancy
advantages.
If a drive failure occurs, subsequent read and write operations are directed to the surviving drive. A
replacement drive can then be rebuilt using the data from the surviving drive.
NOTE: In a RAID level 1 configuration, the size of the configuration is equal to the size of the smallest drive in the
configuration.
RAID Level 0+1 Configuration
A RAID 0+1 array combines the high data access rate of a RAID level 0 array and the data protection
(redundancy) of a RAID level 1 mirror by striping data across two drives and mirroring that striped data
on a second set of two drives.
30 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 31

If a drive failure occurs, subsequent read and write operations are directed to the other surviving drives. A
replacement drive can then be rebuilt using the data from the surviving drives. Also, because data is
duplicated on the primary and additional drives, four 120-GB RAID level 1 drives collectively have a
maximum of 240-GB on which to store data.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 31
Page 32

RAID Level 5 Configuration
RAID level 5 also uses data parity. RAID level 5 stripes both data and parity information across three or
more drives. It provides data striping at the byte level and also stripe error correction information
(rotating parity array). This results in excellent performance and good fault tolerance. RAID level 5 is one
of the most popular implementations of RAID.
RAID level 5 is faster than RAID level 1, but requires more hard drives than a RAID level 0 or RAID level
1 configuration.
If a drive failure occurs, subsequent read and write operations are directed to the other surviving drives. A
replacement drive can then be rebuilt using the data from the surviving drives. Also, because data is
duplicated on the primary and additional drives, four 120-GB RAID level 1 drives collectively have a
maximum of 360-GB on which to store data.
Configuring Your Hard Drives for RAID
Your computer can be configured for RAID, even if you did not select a RAID configuration when the
computer was purchased. For an explanation of RAID levels and their requirements, see "About Your
RAID Configuration" on page 29. For information on how to install a hard drive, see "Installing a Hard
Drive" on page 110.
You can use one of two methods to configure RAID hard drive volumes. The first method uses the
NVIDIA MediaShield ROM utility and is performed before you install the operating system onto the
hard drive. The second method uses NVIDIA MediaShield and is performed after you have installed the
operating system and NVIDIA RAID drivers.
Both methods require that you set your computer to RAID-enabled mode before you begin.
32 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 33

Setting Your Computer to RAID-Enabled Mode
1
Enter system setup (see "Entering System Setup" on page 168).
2
Press the up- and down-arrow keys to highlight
3
Press the up- and down-arrow keys to highlight the applicable SATA drive, then press <Enter>.
4
Press the left- and right-arrow keys to highlight
Drives
, then press <Enter>.
RAID On
, and then press <Enter>. Repeat the
process, as needed, for each SATA hard drive.
NOTE: For more information about RAID options, see "System Setup Options" on page 169.
5
Press <Esc>, press the left- and right-arrow keys to highlight
Save/Exit
, and then press <Enter> to
exit system setup and resume the boot process.
Using the NVIDIA MediaShield ROM Utility
NOTICE: The following procedure will result in the loss of all data on your hard drive(s). Back up any data you want
to keep before continuing.
NOTE: Do not use the following procedure to migrate an existing RAID configuration (see "Converting From One
RAID Configuration to Another RAID Configuration" on page 35.
Hard drives of any size may be used to create a RAID configuration. Ideally, however, the drives should be
of equal size to avoid unallocated or unused space. For an explanation of RAID levels and their
requirements, see "About Your RAID Configuration" on page 29. For information on how to install a hard
drive, see "Installing a Hard Drive" on page 110.
1
Enable RAID for each applicable hard drive on your computer (see "Setting Your Computer to RAIDEnabled Mode" on page 33).
2
Restart the computer.
3
Press <Ctrl><N> when prompted to enter the RAID BIOS.
NOTE: If the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Microsoft Windows desktop,
then shut down your computer and try again.
The
Define a New Array
4
Press <Tab> to navigate to the
To create a RAID 0 configuration, use the arrow keys to select
To create a RAID 1 configuration, use the arrow keys to select
To create a RAID 0+1 configuration, use the arrow keys to select
To create a RAID 5 configuration, use the arrow keys to select
5
Press <Tab> to navigate to the
window appears.
RAID Mode
Free Disks
field.
field.
Striping
Mirroring
RAID 5
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 33
.
.
Stripe Mirroring
.
.
Page 34

6
Use the up- and down-arrow keys to select a hard drive to include in the RAID array and then use the
right-arrow key to move the selected drive from the
Free Disks
field to the
Array Disks
field. Repeat for
each disk you want to include in the RAID array.
NOTE: Your computer supports a maximum of two drives per RAID 1 array and four drives per RAID 0 array.
7
After assigning the hard drives to an array, press <F9>.
The
Clear disk data
NOTICE: You will lose all data on the selected drives in the next step.
8
Press <Y> to clear all data from the selected drives.
Array List
The
9
To review the details of the array that you set up, use the arrow keys to highlight the array in the
Detail
window and press <Enter>.
The
Array Detail
NOTE: To delete an array, use the arrow keys to select the array and press <D>.
10
Press <Enter> to return to the previous screen.
11
Press <Ctrl><X> to exit the RAID BIOS.
prompt appears.
window appears.
Array
window appears.
Using NVIDIA MediaShield
NVIDIA MediaShield allows you to create, view, and manage RAID configurations.
NOTE: Use NVIDIA MediaShield to create a RAID configuration only when you are adding one or more new hard
drives to an existing (non-RAID) single-drive computer, and you want to configure the new drive(s) into a RAID
array.
Hard drives of any size may be used to create a RAID configuration using NVIDIA MediaShield. Ideally,
however, the drives should be of equal size to avoid unallocated or unused space. For an explanation of
RAID levels and their requirements, see "About Your RAID Configuration" on page 29.
Creating a RAID Array
NOTICE: The following procedure will result in the loss of all data on your hard drive(s). Back up any data you want
to keep before continuing.
NOTE: Do not use the following procedure to migrate an existing RAID configuration (see "Converting From One
RAID Configuration to Another RAID Configuration" on page 35.
1
Enable RAID on your hard drives (see "Setting Your Computer to RAID-Enabled Mode" on page 33).
2
After rebooting your computer, launch NVIDIA MediaShield.
3
Click
4
Create
NVIDIA Create Array Wizard
The
Click
Next
.
under
System Tasks
.
appears and lists the disks that are available for configuration.
34 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 35

5
Click
Custom
6
Use the drop-down box to select
0+1), or
7
Click
Next
Free Disk Selection
The
NOTE: Only RAID-enabled hard drives are listed as free disks.
8
Click to select the drives that will make up the RAID configuration, click
, then click
RAID 5
.
Next
.
Striping
(RAID 0),
Mirroring
(RAID 1),
Stripe Mirroring
.
window appears.
Next
, and then click
again.
NOTE: Your computer supports a maximum of two drives per RAID 1 array and four per RAID 0 array.
The
Clearing System Data
NOTICE: The Clear System Data option deletes all data on the selected drive.
9
Click
Next
.
10
Click
Finish
to create the RAID configuration.
window appears.
The MediaShield RAID management utility window appears and lists the array along with any other
installed hard drives.
Deleting a RAID Array
NOTE: While this procedure deletes the RAID 1 volume, it also splits the RAID 1 volume into two non-RAID hard
drives with a partition, and leaves any existing data files intact. Deleting a RAID 0 volume, however, destroys all
data on the volume.
(RAID
Next
NOTE: If your computer currently boots to RAID and you delete the RAID volume, your computer will become
unbootable.
1
Launch NVIDIA MediaShield.
2
Click to select the array you want to delete.
3
Click
4
Delete Array
The
NVIDIA Delete Array Wizard
Click
Next
.
in the
System Tasks
pane.
appears.
A confirmation screen appears with the name and size of the array that you have marked for deletion.
5
Click
Finish
to delete the RAID configuration.
The MediaShield RAID management utility window appears and lists any remaining arrays along with
any other installed hard drives.
Converting From One RAID Configuration to Another RAID Configuration
NOTICE: In order to use the migrating option to convert a RAID configuration without losing data, your hard drive
must initially be set up as a single drive RAID 0 array before the operating system is loaded onto the drive (see
"Using the NVIDIA MediaShield ROM Utility" on page 33 for instructions).
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 35
Page 36

NVIDIA MediaShield utilizes a one-step process known as migrating to change the current state of a disk
or array without losing any data. If needed, additional hard drives can be added to an existing array,
including a single-drive RAID 0 configuration for conversion to a two-drive RAID 0 configuration;
however, the capacity of the resulting array must be equal to or greater than the size of the original
configuration.
RAID 0 to RAID 1
NOTICE: Additional hard drives to be used in the (migrated) array must be no smaller than any of the drives in the
current configuration.
NOTE: Ensure that all drives to be used in the RAID configuration are RAID-enabled (see "Setting Your Computer to
RAID-Enabled Mode" on page 33.)
1
Launch NVIDIA MediaShield.
2
Click to select the array you want to convert.
3
Click
NVIDIA Convert Array Wizard
The
4
Click
5
Under
conversions cannot be performed using the migrating process.
Convert Array
in the
System Tasks
pane.
appears.
Next
.
RAID Mode Selection
, select
Mirroring, Striping, Strip Mirroring, or RAID 5
from the drop-
down menu.
6
Click
Next
.
NOTICE: You will lose all data on the selected drives in the next step.
7
Under
Free Disk Selection
, select the hard drive(s) you want to include in the (migrated) array by
clicking the checkbox beside it.
8
Click
Finish
.
The MediaShield RAID management utility window appears and displays the status of the
upgrade/migration process along with any other installed hard drives.
NOTE: The time it takes to convert an array depends on several factors, such as the speed of the CPU, the
type and size of the hard drive being used, the operating system, etc.
Rebuilding a RAID Configuration
If one of the hard drives in a RAID array fails, you can rebuild the array by restoring the data to a
replacement drive.
NOTE: Rebuilding an array can only be performed on RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 0+1 configurations.
1
Launch NVIDIA MediaShield.
2
Click to select your RAID configuration (
3
Select
Rebuild Array
The
NVIDIA Rebuild Array Wizard
in the
System Tasks
Mirroring
pane.
appears.
) in the management utility window.
36 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 37

4
Click
Next
.
5
Select the hard drive you want to rebuild by clicking the checkbox beside it.
6
Click
Next
.
7
Click
Finish
.
The MediaShield RAID management utility window appears and displays the status of the rebuild
process.
NOTE: You can use your computer while the computer is rebuilding the array.
NOTE: You can use any available (RAID-enabled) free disk to rebuild an array.
Using Multimedia
NOTICE: Do not press down on the optical drive tray when you open or close it. Keep the tray closed when you are
not using the drive.
NOTICE: Do not move the computer while playing media.
1 To open the tray, p
2
Place the disc, label side up, in the center of the tray.
3
To close the tray, press the eject button or gently push in the tray.
ress the eject button on the front of the drive.
To format CDs for storing data, to create music CDs, or to copy CDs, see the CD software that came
with your computer.
NOTE: Ensure that you follow all copyright laws when you create media.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 37
Page 38

A CD player includes the following basic buttons:
Play.
Move backward within the current track.
Pause.
Move forward within the current track.
Stop.
Go to the previous track.
Eject.
Go to the next track.
A DVD player includes the following basic buttons:
Stop.
Restart the current chapter.
Play.
Fast forward.
Pause.
Fast reverse.
Advance a single frame while in pause mode.
Go to the next title or chapter.
Continuously play the current title or chapter.
Go to the previous title or chapter.
Eject.
These controls may not exist on all players in the system. For more information on playing CDs, DVDs,
or BDs, click Help on the media player (if available).
Copying CD, DVD, and Blu-ray Disc™ (BD) Media
This section applies only to computers that have a DVD+/-RW drive or a BD-RE drive.
NOTE: Ensure that you observe all copyright laws when copying media.
NOTE: The types of optical drives offered by Dell may vary by country.
The following instructions explain how to make a copy of a CD, DVD, or BD using Roxio Creator. You
can also use Roxio Creator for other purposes, such as creating music CDs from audio files stored on
your computer or backing up important data. For help, open Roxio Creator, and then press <F1>.
38 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 39

The DVD drives and BD drives installed in Dell computers do not support HD-DVD media. For a list of
supported media formats, see "Using Blank CD, DVD, and BD Media" on page 39.
How to Copy a CD, DVD, or BD
NOTE: BD media can only be copied to other BD media. DVD media can only be copied to other DVD-
recordable/rewritable media. CD media can only be copied to other CD-recordable/rewritable media.
NOTE: Copying a BD-R to BD-RE will not produce an exact copy. Border information will be lost.
NOTE: Most commercial DVDs and BDs have copyright protection and cannot be copied using Roxio Creator.
1
Open Roxio Creator Plus.
2
Under the
3
To copy the CD, DVD, or BD:
•
Copy
tab, click
Disc Copy
If you have one optical drive
correct, and then click the
.
, insert the source disc into the drive, ensure that the settings are
Copy Disc
button to continue. The computer reads your source disc
and copies the data to a temporary folder on your computer hard drive.
When prompted, insert a blank disc into the drive and click
OK
.
If you have two optical drives
•
click the
Copy Disc
button to continue. The computer copies the data from the source disc to the
, select the drive into which you have inserted your source disc and
blank disc.
Once you have finished copying the source disc, the disc that you have created automatically ejects.
Using Blank CD, DVD, and BD Media
CD-writable drives can only write to CD recording media. DVD-writable drives can write to both CD
and DVD recording media. BD-writable drives can write to CD, DVD and BD recording media.
Use blank CD-Rs to record music or permanently store data files. After creating a CD-R, you cannot
write to that CD-R again (see the Sonic documentation for more information). Use blank CD-RWs if
you plan to erase, rewrite, or update information on that disc later.
Blank DVD+/-R or BD-R media can be used to permanently store large amounts of information. After
you create a DVD+/-R or BD-R, you cannot write to that disc again if the disc is "finalized" or "closed"
during the final stage of the disc creation process. Use blank DVD+/-RW or BD-RE media if you plan to
erase, rewrite, or update information on that disc later.
CD-Writable Drives
Media Type Read Write Rewritable
CD-R Yes Yes No
C D- RW Ye s Ye s Ye s
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 39
Page 40

DVD-Writable Drives
Media Type Read Write Rewritable
CD-R Yes Yes No
C D- RW Ye s Ye s Ye s
DVD+R Yes Yes No
DVD-R Yes Yes No
DV D +R W Yes Ye s Ye s
DV D -R W Ye s Ye s Ye s
DVD+R DL Yes Yes No
DVD-R DL Yes No No
DVD-RAM No No No
BD-Writable Drives
Media Type Read Write Rewritable
CD-R Yes Yes No
C D- RW Ye s Ye s Ye s
DVD+R Yes Yes No
DVD-R Yes Yes No
DV D +R W Yes Ye s Ye s
DV D -R W Ye s Ye s Ye s
DVD+R DL Yes Yes No
DVD-R DL Yes No No
DVD-RAM No No No
BD-R Yes Yes No
BD-RE Yes Yes Yes
Helpful Tips
• Use Microsoft Windows Explorer to drag and drop files to a CD-R or CD-RW only after you start
Roxio Creator
• Do not burn a blank CD-R or CD-RW to its maximum capacity; for example, do not copy a 650-MB
file to a blank 650-MB CD. The CD-RW drive needs 1–2 MB of the blank space to finalize the
recording.
40 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
and open a Creator project.
Page 41

• Use CD-Rs to burn music CDs that you want to play in regular stereos. CD-RWs do not play in most
home or car stereos.
• Music MP3 files can be played only on MP3 players or on computers that have MP3 software installed.
• Use a blank CD-RW to practice CD recording until you are familiar with CD recording techniques. If
you make a mistake, you can erase the data on the CD-RW and try again. You can also use blank
CD-RWs to test music file projects before you record the project permanently to a blank CD-R.
• You cannot create audio DVDs with
• Commercially available DVD players used in home theater systems may not support all available DVD
formats. For a list of formats supported by your DVD player, see the documentation provided with your
DVD player or contact the manufacturer.
• Commercially available BD players used in home theater systems may not support all available BD
formats. For a list of formats supported by your BD player, see the documentation provided with your
BD player or contact the manufacturer.
• See the Roxio website at
www.sonic.com
Roxio Creator.
for additional information.
Using a Media Card Reader (Optional)
CAUTION: Before you perform any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
Use the media card reader to transfer data directly to your computer.
The media card reader supports the following memory types:
• xD-Picture card
• SmartMedia card (SMC)
• CompactFlash card Type I and II (CF I/II)
• MicroDrive card
• SecureDigital card (SD)
• MiniSD card
• MultiMediaCard (MMC)
• Reduced-size MultiMediaCard (RS-MMC)
• Memory Stick (MS/MS Pro/MS Duo/MS Pro Duo)
For information on installing a media card reader, see "Installing a Media Card Reader" on page 121.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 41
Page 42

1
2
4
1 xD-Picture card and
SmartMedia Card (SMC)
4 CompactFlash card Type I and
II (CF I/II) and MicroDrive card
1
Inspect the media card to determine the proper orientation for insertion.
2
Slide the media card into the appropriate slot of the media card reader until it is completely seated in
2 Memory Stick (MS/MS
Pro/MS Duo/MS Pro Duo)
3 Secure Digital card
3
(SD/miniSD)/MultiMedia-Card
(MMC/RS-MMC)
the connector.
If you encounter resistance, remove the card, check for proper orientation, and then try again.
Network Setup Wizard
The Microsoft Windows operating system provides a Network Setup Wizard to guide you through the
process of sharing files, printers, or an Internet connection between computers in a home or small office.
42 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 43

Windows XP:
1
Click
Start
, point to
.
Wizard
2
On the welcome screen, click
3
Click
Checklist for creating a network
NOTE: Selecting the connection method This computer connects directly to the Internet enables the integrated
firewall provided with Windows XP SP1.
4
Complete the checklist and required preparations.
5
Return to the Network Setup Wizard and follow the instructions on the screen.
Windows Vista:
1
C
lick
Start → Connect to→ Set up a connection or network.
2
Select an option under
3
Click
Next
and follow the instructions in the wizard.
All Programs→ Accessories→ Communications
Next
.
.
Choose a connection option.
, and then click
Network Setup
Transferring Information to a New Computer
You can use your operating system "wizards" to help you transfer files and other data from one computer
to another—for example, from an old computer to a new computer. For instructions, see the following
section that corresponds to the operating system your computer is running.
Windows XP:
To prepare the new computer for the file transfer:
1
Click
Start→ All Programs→ Accessories→ System Tools → Files and Settings Transfer Wizard
The
Files and Settings Transfer Wizard
welcome screen appears.
.
2
Click
Next
.
3
On the
4
On the
CD
5
When the
the data to be transferred.
To copy data from the source computer:
1
On the source computer, insert the Windows XP
2
On the
3
Under
4
On the
5
On the
Which computer is this?
Do you have a Windows XP CD?
, and then click
Now go to your old computer
Welcome to Microsoft Windows XP
What do you want to do?
Files and Settings Transfer Wizard
Which computer is this?
Next
.
Do not
screen, click
click
, click
screen, click
New Computer
screen, click
screen appears, go to the source (old) computer that contains
Next
at this time.
Operating System
screen, click
Transfer files and settings
welcome screen, click
Old Computer
, and then click
I will use the wizard from the Windows XP
CD.
Perform additional tasks
.
Next
, and then click
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 43
Next
.
.
.
Next
.
Page 44

6
On the
7
On the
After the information has been copied, the
8
Click
To transfer data to the new computer:
1
On the
2
On the
and settings, and then click
The wizard reads the collected files and settings and applies them to your new computer.
Select a transfer method
What do you want to transfer?
Finish
.
Now go to your old computer
Where are the files and settings?
screen, click the transfer method of your preference.
Next
.
screen, select the items you want to transfer, then click
Completing the Collection Phase
screen on the new computer, click
screen, select the method you chose for transferring your files
Next
screen appears.
.
Next
.
When all of the settings and files have been applied, the
3
Click
Finished
Windows Vista:
C
lick
1
2
3
4
Start → Transfer files and settings→
In the
User Account Control
Click
Start a new transfer
Follow the instructions provided on the screen by the Windows Easy Transfer wizard.
and restart the computer.
dialog box, click
or
Continue a transfer in progress
Start Windows Easy Transfer.
Continue
Finished
.
screen appears.
.
Power Management Options in Windows XP
The Microsoft Windows XP power management features can reduce the amount of electricity your
computer uses when it is on and you are not using it. You can reduce power to just the monitor or the
hard drive, or you can use standby mode or hibernate mode to reduce power to the entire computer.
When the computer exits from a power conservation mode, it returns to the operating state it was in
prior to entering the mode.
NOTE: Windows XP Professional includes security and networking features not available in Windows XP Home
Edition. When a Windows XP Professional computer is connected to a network, different options related to security
and networking appear in certain windows.
NOTE: The procedures to activate the standby and hibernate modes may vary according to your operating system.
Standby Mode
Standby mode conserves power by turning off the display and the hard drive after a designated period of
time, known as a time-out. When the computer exits from standby mode, it returns to the operating
state it was in prior to entering standby mode.
NOTICE: If your computer loses power while in standby mode, it may lose data.
44 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 45

To set standby mode to automatically activate after a defined period of inactivity:
1
Click
Start
and click
2
Under
Pick a category
3
Under
or pick a Control Panel icon
To immediately activate standby mode without a period of inactivity, click Start→ Turn Off
Computer
To exit from standby mode, press a key on the keyboard or move the mouse.
→
Stand by.
Control Panel
, click
Performance and Maintenance
.
, click
Power Options
.
.
Hibernate Mode
Hibernate mode conserves power by copying system data to a reserved area on the hard drive, and then
completely turning off the computer. When the computer exits from hibernate mode, the desktop is
restored to the state it was in
To activate hibernate mode:
Click
Start
1
2
Under
3
Under
4
Define your hibernate settings on the
To exit from hibernate mode, press the power button. The computer may take a short time to exit from
hibernate mode. Because the keyboard and mouse do not function in hibernate mode, pressing a key on
the keyboard or moving the mouse does not bring the computer out of hibernation.
Because hibernate mode requires a special file on your hard drive with enough disk space to store the
contents of the computer memory, Dell creates an appropriately sized hibernate mode file before
shipping the computer to you. If the computer’s hard drive becomes corrupted, Windows XP recreates
the hibernate file automatically.
and click
Pick a category
or pick a Control Panel icon
prior to entering hibernate mode.
Control Panel
, click
.
Performance and Maintenance
, click
Power Options
Power Schemes
tab,
.
.
Advanced
tab, and
Hibernate
tab.
Power Options Properties
Define your standby mode settings, hibernate mode settings, and other power settings in the Power
Options Properties window.
1
Click
Start
and click
2
Under
Pick a category
3
Under
or pick a Control Panel icon
4
Define your power settings on the
To access the Power Options Properties window:
Control Panel
, click
.
Performance and Maintenance
, click
Power Options
Power Schemes
tab,
.
Advanced
.
tab, and
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 45
Hibernate
tab.
Page 46

Power Schemes Tab
Each standard power setting is called a scheme. If you want to select one of the standard Windows
schemes installed on your computer, choose a scheme from the Power schemes drop-down menu. The
settings for each scheme appear in the fields below the scheme name. Each scheme has different settings
for starting standby mode, hibernate mode, turning off the monitor, and turning off the hard drive.
NOTICE: If you set the hard drive to time-out before the monitor does, your computer may appear to be locked up.
To recover, press any key on the keyboard or click the mouse. To avoid this problem, always set the monitor to timeout before the hard drive.
The Power schemes drop-down menu displays the following schemes:
•
Always On
•
Home/Office Desk
Portable/Laptop
•
•
Presentation
•
Minimal Power Management
Max Battery
•
(default) — If you want to use your computer with no power conservation.
— If you want your home or office computer to run with little power conservation.
— If your computer is a portable computer that you use for traveling.
— If you want your computer to run without interruption (using no power conservation).
— If you want your computer to run with minimal power conservation.
— If your computer is a portable computer and you run your computer from batteries for
extended periods of time.
If you want to change the default settings for a scheme, click the drop-down menu in the Turn off
monitor, Turn off hard disks, System stand by, or System hibernates field, and then select a time-out
from the displayed list. Changing the time-out for a scheme field permanently changes the default
settings for that scheme, unless you click Save As and enter a new name for the changed scheme.
Advanced Tab
The Advanced tab allows you to:
• Place the power options icon in the Windows taskbar for quick access.
• Set the computer to prompt you for your Windows password before the computer exits from standby
mode or hibernate mode.
• Program the power button to activate standby mode, activate hibernate mode, or turn off the
computer.
To program these functions, click an option from the corresponding drop-down menu and click OK.
Hibernate Tab
The Hibernate tab allows you to enable hibernate mode. If you want to use the hibernate settings as
defined on the Power Schemes tab, click the Enable hibernate support check box on the Hibernate tab.
For more information on power management options:
Click
Start
1
2
3
and click
In the
Help and Support
In the
Performance and maintenance
Help and Support
window, click
window, click
.
Performance and maintenance
Conserving power on your computer
.
.
46 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 47

Power Management Options in Windows Vista
The Microsoft Vista power management features can reduce the amount of electricity your computer
uses when it is on and you are not using it. You can reduce power to just the monitor or the hard drive, or
you can use sleep mode or hibernate mode to reduce power to the entire computer. When the computer
exits from a power conservation mode, it returns to the operating state it was in prior to entering the
mode.
Sleep Mode
Sleep mode conserves power by turning off the display and the hard drive after a predetermined period of
inactivity (a time-out). When the computer exits sleep mode, it returns to the same operating state it
was in before entering sleep mode.
To enter sleep mode in Windows Vista, click
menu, and then
To exit sleep mode, press a key on the keyboard or move the mouse.
click Sleep.
Hibernate Mode
Hibernate mode conserves power by copying system data to a reserved area on the hard drive and then
completely turning off the computer. When the computer exits hibernate mode, it returns to the same
operating state it was in before entering hibernate mode.
To manually enter hibernate mode in Windows Vista, click
corner of the Start menu, and then
click Hibernate.
Start
,
click the arrow in the lower-right corner of the Start
Start
,
click the arrow in the lower-right
Configuring Power Management Settings
You can use the Windows Power Options Properties to configure the power management settings on your
computer.
To access Power Options Properties, click
Power Options.
Start
→ Control Panel→ System and Maintenance
Setting Up and Using Your Computer 47
→
Page 48

48 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Page 49

Optimizing for Greater Performance
Understanding Dual-Graphics Technology
With dual-graphics technology, an optional second PCI Express graphics card will significantly
increase graphics performance on your computer. Benefits of this technology can be seen in the
improved portrayal of the 3-D graphics used in gaming and design applications.
Each graphics card includes at least one GPU (graphics processing unit). In dual graphics card
configurations, multiple GPUs dynamically share their workload to provide the best possible
performance. For a given application, the software selects the optimum rendering (processing)
mode.
For more information about your graphics card, go to support.dell.com.
Understanding CPU Overclocking
NOTICE: Dell does not recommend operating the processor or other system components beyond the factory
default settings. This may cause system instability and reduce the operating life of your system components.
NOTICE: Dell Technical Support will verify the full functionality of the CPU at the factory default setting and
support the CPU performance settings available within the system BIOS. Dell does not provide technical
support for any hardware or software issues arising from any third party applications used to enable
overclocking, such as NVIDIA nTune 5.0.
Overclocking is the process of causing a computer component to run faster than designed or
designated by the component manufacturer. Depending upon your application (such as gaming or
video editing), your performance may benefit from overclocking different subsystems within your
computer.
The Dell™ XPS™ 720 H
processor and an H
overall thermal capacity.
T
he processor has been overclocked through CPU multiplier overclocking via the BIOS to speeds
faster than the standard speed of the processor.
You can make limited adjustments to the CPU operating frequency in system setup. For more
information on accessing system setup, see "System Setup" on page 168. For information on
performance options, see "Performance" on page 171.
C™ Edition ships with an overclocked Intel® Core™2 Extreme Edition
2
Ceramic (also called H2C™ or Hot-to-Cold) cooling system designed to improve
2
Optimizing for Greater Performance 49
Page 50

50 Optimizing for Greater Performance
Page 51

Dell™ QuickSet
NOTE: This feature may not be available on your computer.
Dell™ QuickSet allows you to select and adjust LED light effects, also known as LightFX™.
You can start QuickSet by either clicking, double-clicking, or right-clicking the QuickSet icon in the
Microsoft
For more information about QuickSet, right-click the QuickSet icon and select Help.
®
Windows® taskbar. The taskbar is located in the lower-right corner of your screen.
Dell™ QuickSet 51
Page 52

52 Dell™ QuickSet
Page 53

Troubleshooting
Solving Problems
Follow these tips when you troubleshoot your computer:
• If you added or removed a part before the problem started, review the installation procedures and
ensure that the part is correctly installed.
• If a peripheral device does not work, ensure that the device is properly connected.
• If an error message appears on the screen, write down the exact message. This message may help
support personnel diagnose and fix the problem(s).
• If an error message occurs in a program, see the program’s documentation.
NOTE: The procedures in this document were written for the Windows default view, so they may not apply if
you set your Dell™ computer to the Windows Classic view.
Battery Problems
CAUTION: There is a danger of a new battery exploding if it is incorrectly installed. Replace the battery
only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Discard used batteries according
to the manufacturer's instructions.
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the
Product Information Guide.
R
EPLACE THE BATTERY — If you have to repeatedly reset time and date information after turning on the
computer, or if an incorrect time or date displays during start-up, replace the battery (see "Replacing the
Battery" on page 158). If the battery still does not work properly, contact Dell (see "Contacting Dell" on
page 181).
Drive Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the
Product Information Guide.
NSURE THAT MICROSOFT
E
Windows XP:
• Click
Windows Vista™:
• Click the Windows Vista Start button and click
Start
and click
®
WINDOWS® RECOGNIZES THE DRIVE —
My Computer
.
Computer
.
Troubleshooting 53
Page 54

If the drive is not listed, perform a full scan with your antivirus software to check for and remove viruses. Viruses can
sometimes prevent Windows from recognizing the drive.
T
EST THE DRIVE —
• Insert another disc to eliminate the possibility that the original drive is defective.
• Insert a bootable floppy disk and restart the computer.
CLEAN THE DRIVE OR DISK — See "Cleaning Your Computer" on page 178.
HECK THE CABLE CONNECTIONS
C
RUN THE HARDWARE TROUBLESHOOTER — See "Troubleshooting Software and Hardware Problems" on page 83.
UN THE DELL DIAGNOSTICS — See "Dell Diagnostics" on page 72.
R
Optical drive problems
NOTE: High-speed optical drive vibration is normal and may cause noise, which does not indicate a defect in the
drive or the media.
NOTE: Because of different regions worldwide and different disc formats, not all DVD titles work in all DVD drives.
A
DJUST THE WINDOWS VOLUME CONTROL —
• Click the speaker icon in the lower-right corner of your screen.
• Ensure that the volume is turned up by clicking the slidebar and dragging it up.
• Ensure that the sound is not muted by clicking any boxes that are checked.
CHECK THE SPEAKERS AND SUBWOOFER — See "Sound and Speaker Problems" on page 63.
Problems writing to an optical drive
CLOSE OTHER PROGRAMS — The optical drive must receive a steady stream of data during the writing process.
If the stream is interrupted, an error occurs. Try closing all programs before you write to the optical.
T
URN OFF STANDBY MODE IN WINDOWS BEFORE WRITING TO A DISC — See "Configuring Power Management
Settings" on page 47 or search for the keyword standby in Windows Help and Support for information on power
management modes.
Hard drive problems
RUN CHECK DISK —
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start
and click
2
Right-click
3
Click
4
Click
Local Disk C:
Properties→ To ol s→
Scan for and attempt recovery of bad sectors
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start
and click
2
Right-click
Local Disk C:
54 Troubleshooting
My Computer
.
Check Now
Computer
.
.
.
and click
Start
.
.
Page 55

3
Click
Properties→ To ol s→
User Account Control
The
Check Now
.
window may appear. If you are an administrator on the computer, click
Continue
;
otherwise, contact your administrator to continue the desired action.
4
Follow the instructions on the screen.
E-Mail, Modem, and Internet Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTE: Connect the modem to an analog telephone jack only. The modem does not operate while it is connected to
a digital telephone network.
NOTE: Do not plug a telephone cable into the network adapter connector (see "Back I/O Connectors" on page 17).
C
HECK THE MICROSOFT OUTLOOK
attachments:
1
In Outlook Express, click
2
Click
Do not allow attachments
CHECK THE TELEPHONE LINE CONNECTION
CHECK THE TELEPHONE JACK
CONNECT THE MODEM DIRECTLY TO THE TELEPHONE WALL JACK
USE A DIFFERENT TELEPHONE LINE —
• Verify that the telephone line is connected to the jack on the modem (the jack has either a green label or a connectorshaped icon next to it).
• Ensure that you hear a click when you insert the telephone line connector into the modem.
• Disconnect the telephone line from the modem and connect it to a telephone, then listen for a dial tone.
• If you have other telephone devices sharing the line, such as an answering machine, fax machine, surge protector, or
line splitter, bypass them and use the telephone to connect the modem directly to the telephone wall jack. If you are
using a line that is 3 meters (10 feet) or more in length, try a shorter one.
RUN THE MODEM DIAGNOSTIC TOOL —
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start→
All Programs→
2
Follow the instructions on the screen to identify and resolve modem problems. Modem Helper is not available on
certain computers.
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start
→
All Programs→ Modem Diagnostic Tool
2
Follow the instructions on the screen to identify and resolve modem problems. Modem diagnostics are not available
on all computers.
®
EXPRESS SECURITY SETTINGS — If you cannot open your e-mail
Tools→
Options→
Security
.
to remove the checkmark, as needed.
Modem Helper
.
.
Troubleshooting 55
Page 56

VERIFY THAT THE MODEM IS COMMUNICATING WITH WINDOWS —
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start→
Control Panel→
2
Click the COM port for your modem→ Properties→ Diagnostics→
Printers and Other Hardware→ Phone and Modem Options→ Modems
Query Modem
to verify that the modem is
.
communicating with Windows.
If all commands receive responses, the modem is operating properly.
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start
→
Control Panel→
2
Click the COM port for your modem→
Hardware and Sound→
Properties → Diagnostics→
Phone and Modem Options→ Modems
Query Modem
to verify that the modem is
.
communicating with Windows.
If all commands receive responses, the modem is operating properly.
E
NSURE THAT YOU ARE CONNECTED TO THE INTERNET — Ensure that you have subscribed to an Internet provider.
With the Outlook Express e-mail program open, click File. If Work Offline has a checkmark next to it, click the
checkmark to remove it and connect to the Internet. For help, contact your Internet service provider.
Error Messages
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
If the error message is not listed, see the documentation for the operating system or the program that
was running when the message appeared.
A FILENAME CANNOT CONTAIN ANY OF THE FOLLOWING CHARACTERS: \ / : * ? “ < > | — Do not use these
characters in filenames.
A
REQUIRED .DLL FILE WAS NOT FOUND — The program that you are trying to open is missing an essential file. To
remove and then reinstall the program:
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start→
Control Panel→ Add or Remove Programs→ Programs and Features
2
Select the program you want to remove.
3
Click
Uninstall
4
See the program documentation for installation instructions.
.
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start
→
Control Panel→ Programs→ Programs and Features
2
Select the program you want to remove.
3
Click
Uninstall
4
See the program documentation for installation instructions.
.
.
drive letter :\ IS NOT ACCESSIBLE. THE DEVICE IS NOT READY — The drive cannot read the disk. Insert a disk
into the drive and try again.
I
NSERT BOOTABLE MEDIA — Insert a bootable floppy disk, CD, or DVD.
ON-SYSTEM DISK ERROR — Remove the floppy disk from the floppy drive and restart your computer.
N
.
56 Troubleshooting
Page 57

NOT ENOUGH MEMORY OR RESOURCES. CLOSE SOME PROGRAMS AND TRY AGAIN — Close all windows and open
the program that you want to use. In some cases, you may have to restart your computer to restore computer
resources. If so, run the program that you want to use first.
PERATING SYSTEM NOT FOUND — Contact Dell (see "Contacting Dell" on page 181).
O
IEEE 1394 Device Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTE: Your computer supports only IEEE 1394a standard.
NSURE THAT THE CABLE FOR THE IEEE 1394 DEVICE IS PROPERLY INSERTED INTO THE DEVICE AND INTO THE
E
CONNECTOR ON THE COMPUTER
ENSURE THAT THE IEEE 1394 DEVICE IS ENABLED IN SYSTEM SETUP — See "System Setup Options" on
page 169.
E
NSURE THAT THE IEEE 1394 DEVICE IS RECOGNIZED BY WINDOWS —
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start
and click
2
Under
Pick a Category
Manager
.
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start
→
2
Click
Device Manager.
If your IEEE 1394 device is listed, Windows recognizes the device.
I
F YOU HAVE PROBLEMS WITH A DELL IEEE 1394 DEVICE — Contact Dell (see "Contacting Dell" on page 181).
F YOU HAVE PROBLEMS WITH AN IEEE 1394 DEVICE NOT PROVIDED BY DELL — Contact the IEEE 1394 device
I
manufacturer.
Control Panel
, click
.
Performance and Maintenance→
Control Panel→ Hardware and Sound
.
System→
System Properties
→
Hardware→
Device
Keyboard Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
HECK THE KEYBOARD CABLE —
C
• Ensure that the keyboard cable is firmly connected to the computer.
• Shut down the computer (see "Preparing to Work Inside Your Computer" on page 85), reconnect the keyboard cable
as shown on the setup diagram for your computer, and then restart the computer.
• Ensure that the cable is not damaged or frayed and check cable connectors for bent or broken pins. Straighten any
bent pins.
• Remove any keyboard extension cables and connect the keyboard directly to the computer.
TEST THE KEYBOARD — Connect a properly working keyboard to the computer, then try using the keyboard.
R
UN THE HARDWARE TROUBLESHOOTER — See "Troubleshooting Software and Hardware Problems" on page 83.
Troubleshooting 57
Page 58

Lockups and Software Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
The computer does not start up
CHECK THE DIAGNOSTIC LIGHTS — See "Diagnostic Lights" on page 66.
E
NSURE THAT THE POWER CABLE IS FIRMLY CONNECTED TO THE COMPUTER AND TO THE ELECTRICAL OUTLET
The computer stops responding
NOTICE: You may lose data if you are unable to perform an operating system shutdown.
T
URN THE COMPUTER OFF — If you are unable to get a response by pressing a key on your keyboard or moving your
mouse, press and hold the power button for at least 8 to 10 seconds (until the computer turns off), and then restart
your computer.
A program stops responding
END THE PROGRAM —
1
Press <Ctrl><Shift><Esc> simultaneously to access the Task Manager.
2
Click the
3
Click to select the program that is no longer responding.
4
Click
A program crashes repeatedly
Applications
End Task
tab.
.
NOTE: Most software includes installation instructions in its documentation or on a floppy disk, CD, or DVD.
C
HECK THE SOFTWARE DOCUMENTATION — If necessary, uninstall and then reinstall the program.
A program is designed for an earlier Windows operating system
RUN THE PROGRAM COMPATIBILITY WIZARD —
Windows XP:
The Program Compatibility Wizard configures a program so that it runs in an environment similar to non-XP
operating system environments.
1
Click
Start→
All Programs→ Accessories→ Program Compatibility Wizard→ Next
2
Follow the instructions on the screen.
.
Windows Vista:
The Program Compatibility Wizard configures a program so that it runs in an environment similar to non-Windows
Vista operating system environments.
1
Click
Start
→
Control Panel→ Programs→ Use an older program with this version of Windows.
2
In the welcome screen, click
3
Follow the instructions on the screen.
Next
.
58 Troubleshooting
Page 59

A solid blue screen appears
TURN THE COMPUTER OFF — If you are unable to get a response by pressing a key on your keyboard or moving your
mouse, press and hold the power button for at least 8 to 10 seconds (until the computer turns off), and then restart
your computer.
Other software problems
CHECK THE SOFTWARE DOCUMENTATION OR CONTACT THE SOFTWARE MANUFACTURER FOR TROUBLESHOOTING
INFORMATION —
• Ensure that the program is compatible with the operating system installed on your computer.
• Ensure that your computer meets the minimum hardware requirements needed to run the software. See the software
documentation for information.
• Ensure that the program is installed and configured properly.
• Verify that the device drivers do not conflict with the program.
• If necessary, uninstall and then reinstall the program.
BACK UP YOUR FILES IMMEDIATELY
USE A VIRUS- SCANNING PROGRAM TO CHECK THE HARD DRIVE, FLOPPY DISKS, CDS, OR DVDS
SAVE AND CLOSE ANY OPEN FILES OR PROGRAMS AND SHUT DOWN YOUR COMPUTER THROUGH THE START MENU
Memory Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
I
F YOU RECEIVE AN INSUFFICIENT MEMORY MESSAGE —
• Save and close any open files and exit any open programs you are not using to see if that resolves the problem.
• See the software documentation for minimum memory requirements. If necessary, install additional memory (see
"Installing Memory" on page 92).
• Reseat the memory modules (see "Memory" on page 90) to ensure that your computer is successfully communicating
with the memory.
• Run the Dell Diagnostics (see "Dell Diagnostics" on page 72).
IF YOU EXPERIENCE OTHER MEMORY PROBLEMS —
• Reseat the memory modules (see "Memory" on page 90) to ensure that your computer is successfully communicating
with the memory.
• Ensure that you are following the memory installation guidelines (see "Installing Memory" on page 92).
• Ensure that the memory you are using is supported by your computer. For more information about the type of
memory supported by your computer, see "Memory" on page 163.
• Run the Dell Diagnostics (see "Dell Diagnostics" on page 72).
Troubleshooting 59
Page 60

Mouse Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
HECK THE MOUSE CABLE —
C
• Ensure that the cable is not damaged or frayed and check cable connectors for bent or broken pins. Straighten any
bent pins.
• Remove any mouse extension cables, and connect the mouse directly to the computer.
• Verify that the mouse cable is connected as shown on the setup diagram for your computer.
RESTART THE COMPUTER —
1
Simultaneously press <Ctrl><Esc> to display the
2
Press <u>,
3
After the computer turns off, reconnect the mouse cable as shown on the setup diagram.
4
Turn on the computer.
press the up- and down-arrow keys
TEST THE MOUSE — Connect a properly working mouse to the computer, then try using the mouse.
HECK THE MOUSE SETTINGS —
C
Windows XP
1
Click
Start→ Control Panel→
2
Adjust the settings as needed.
Mouse
.
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start
→ Control Panel→ Hardware and Sound→ Mouse
2
Adjust the settings as needed.
REINSTALL THE MOUSE DRIVER — See "Drivers" on page 75.
UN THE HARDWARE TROUBLESHOOTER — See "Troubleshooting Software and Hardware Problems" on page 83.
R
Start
menu.
to highlight
Shut down
.
or
Tur n O ff
, and then press <Enter>.
Network Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
C
HECK THE NETWORK CABLE CONNECTOR — Ensure that the network cable is firmly inserted into the network
connector on the back of the computer and the network jack.
HECK THE NETWORK LIGHTS ON THE BACK OF THE COMPUTER — If the link integrity light is off (see "Controls
C
and Lights" on page 165), no network communication is occurring. Replace the network cable.
R
ESTART THE COMPUTER AND LOG ON TO THE NETWORK AGAIN
CHECK YOUR NETWORK SETTINGS — Contact your network administrator or the person who set up your network
to verify that your network settings are correct and that the network is functioning.
R
UN THE HARDWARE TROUBLESHOOTER — See "Troubleshooting Software and Hardware Problems" on page 83.
60 Troubleshooting
Page 61

Power Problems
. CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
F THE POWER LIGHT IS GREEN AND THE COMPUTER IS NOT RESPONDING — See "Diagnostic Lights" on page 66.
I
I
F THE POWER LIGHT IS BLINKING GREEN — The computer is in standby mode. Press a key on the keyboard, move
the mouse, or press the power button to resume normal operation.
F THE POWER LIGHT IS OFF — The computer is either turned off or is not receiving power.
I
• Reseat the power cable in the power connector on the back of the computer and the electrical outlet.
• Bypass power strips, power extension cables, and other power protection devices to verify that the computer turns on
properly.
• Ensure that any power strips being used are plugged into an electrical outlet and are turned on.
• Ensure that the electrical outlet is working by testing it with another device, such as a lamp.
• Ensure that the main power cable and front panel cable are securely connected to the system board (see "System
Board Components" on page 89).
IF THE POWER LIGHT IS BLINKING AMBER — The computer is receiving electrical power, but an internal power
problem may exist.
• Ensure that the voltage selection switch is set to match the AC power at your location (if applicable).
Ensure that all components and cables are properly installed and securely connected to the system board (see "System
Board Components" on page 89).
IF THE POWER LIGHT IS STEADY AMBER — A device may be malfunctioning or incorrectly installed.
• Ensure that the processor power cable is securely connected to the system board power connector (POWER2) (see
"System Board Components" on page 89).
• Remove and then reinstall all memory modules (see "Memory" on page 90).
• Remove and then reinstall any expansion cards, including graphics cards (see "Removing PCI and PCI Express Cards"
on page 95).
ELIMINATE INTERFERENCE — Some possible causes of interference are:
• Power, keyboard, and mouse extension cables
• Too many devices connected to the same power strip
• Multiple power strips connected to the same electrical outlet
Printer Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTE: If you need technical assistance for your printer, contact the printer’s manufacturer.
HECK THE PRINTER DOCUMENTATION — See the printer documentation for setup and troubleshooting
C
information.
Troubleshooting 61
Page 62

ENSURE THAT THE PRINTER IS TURNED ON
CHECK THE PRINTER CABLE CONNECTIONS —
• See the printer documentation for cable connection information.
• Ensure that the printer cables are securely connected to the printer and the computer.
TEST THE ELECTRICAL OUTLET — Ensure that the electrical outlet is working by testing it with another device, such
as a lamp.
ERIFY THAT THE PRINTER IS RECOGNIZED BY WINDOWS —
V
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start→
Control Panel→
2
If the printer is listed, right-click the printer icon.
3
Click
Properties→
(Printer Port)
Ports
. For a USB printer, ensure that the
Printers and Other Hardware→
. For a parallel printer, ensure that the
Print to the following port(s):
View installed printers or fax printers
Print to the following port(s):
setting is
setting is
USB
.
.
LPT1
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start
→ Control Panel→ Hardware and Sound→ Printer
2
If the printer is listed, right-click the printer icon.
3
Click
Properties
4
Adjust the settings, as needed.
and click
Ports
.
.
REINSTALL THE PRINTER DRIVER —SEE THE PRINTER DOCUMENTATION FOR INFORMATION ON REINSTALLING THE PRINTER DRIVER.—
Scanner Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTE: If you need technical assistance for your scanner, contact the scanner’s manufacturer.
C
HECK THE SCANNER DOCUMENTATION — See the scanner documentation for setup and troubleshooting
information.
NLOCK THE SCANNER — Ensure that your scanner is unlocked (if the scanner has a locking tab or button).
U
R
ESTART THE COMPUTER AND TRY THE SCANNER AGAIN
CHECK THE CABLE CONNECTIONS —
• See the scanner documentation for information on cable connections.
• Ensure that the scanner cables are securely connected to the scanner and the computer.
VERIFY THAT THE SCANNER IS RECOGNIZED BY MICROSOFT WINDOWS —
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start→
Control Panel→
2
If your scanner is listed, Windows recognizes the scanner.
Printers and Other Hardware→
Scanners and Cameras
.
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start
→ Control Panel→ Hardware and Sound→ Scanners and Cameras
2
If the scanner is listed, Windows recognizes the scanner.
.
REINSTALL THE SCANNER DRIVER — See the scanner documentation for instructions.
62 Troubleshooting
Page 63

Sound and Speaker Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
No sound from speakers
NOTE: The volume control in MP3 and other media players may override the Windows volume setting. Always
check to ensure that the volume on the media player(s) has not been turned down or off.
C
HECK THE SPEAKER CABLE CONNECTIONS — Ensure that the speakers are connected as shown on the setup
diagram supplied with the speakers. If you purchased a sound card, ensure that the speakers are connected to the
card.
NSURE THAT THE SUBWOOFER AND THE SPEAKERS ARE TURNED ON — See the setup diagram supplied with the
E
speakers. If your speakers have volume controls, adjust the volume, bass, or treble to eliminate distortion.
DJUST THE WINDOWS VOLUME CONTROL — Click or double-click the speaker icon in the lower-right corner of
A
your screen. Ensure that the volume is turned up and that the sound is not muted.
D
ISCONNECT HEADPHONES FROM THE HEADPHONE CONNECTOR — Sound from the speakers is automatically
disabled when headphones are connected to the computer’s front-panel headphone connector.
EST THE ELECTRICAL OUTLET — Ensure that the electrical outlet is working by testing it with another device, such
T
as a lamp.
E
LIMINATE POSSIBLE INTERFERENCE — Turn off nearby fans, fluorescent lights, or halogen lamps to check for
interference.
R
UN THE SPEAKER DIAGNOSTICS
REINSTALL THE SOUND DRIVER — See "Drivers" on page 75.
UN THE HARDWARE TROUBLESHOOTER — See "Troubleshooting Software and Hardware Problems" on page 83.
R
No sound from headphones
CHECK THE HEADPHONE CABLE CONNECTION — Ensure that the headphone cable is securely inserted into the
headphone connector (see "Front and Back View of the Computer" on page 13).
A
DJUST THE WINDOWS VOLUME CONTROL — Click or double-click the speaker icon in the lower-right corner of
your screen. Ensure that the volume is turned up and that the sound is not muted.
Video and Monitor Problems
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTICE: If your computer came with a PCI graphics card installed, removal of the card is not necessary when
installing additional graphics cards; however, the card is required for troubleshooting purposes. If you remove the
card, store it in a safe and secure location. For information about your graphics card, go to support.dell.com.
The screen is blank
NOTE: For troubleshooting procedures, see the monitor’s documentation.
Troubleshooting 63
Page 64

The screen is difficult to read
CHECK THE MONITOR CABLE CONNECTION —
• Ensure that the monitor cable is connected to the correct graphics card (for dual graphics card configurations).
• If you are using the optional
DVI-to-VGA
adapter, ensure that the adapter is correctly attached to the graphics card
and monitor.
• Ensure that the monitor cable is connected as shown on the setup diagram for your computer.
• Remove any video extension cables and connect the monitor directly to the computer.
• Swap the computer and monitor power cables to determine if the monitor’s power cable is defective.
• Check the connectors for bent or broken pins (it is normal for monitor cable connectors to have missing pins).
CHECK THE MONITOR POWER LIGHT —
• If the power light is lit or blinking, the monitor has power.
• If the power light is off, firmly press the button to ensure that the monitor is turned on.
• If the power light is blinking, press a key on the keyboard or move the mouse to resume normal operation.
TEST THE ELECTRICAL OUTLET — Ensure that the electrical outlet is working by testing it with another device, such
as a lamp.
C
HECK THE DIAGNOSTIC LIGHTS — See "Diagnostic Lights" on page 66.
HECK THE MONITOR SETTINGS — See the monitor documentation for instructions on adjusting the contrast and
C
brightness, demagnetizing (degaussing) the monitor, and running the monitor self-test.
M
OVE THE SUBWOOFER AWAY FROM THE MONITOR — If your speaker system includes a subwoofer, ensure that
the subwoofer is positioned at least 60 centimeters (2 feet) away from the monitor.
OVE THE MONITOR AWAY FROM EXTERNAL POWER SOURCES — Fans, fluorescent lights, halogen lamps, and
M
other electrical devices can cause the screen image to appear shaky. Turn off nearby devices to check for interference.
R
OTATE THE MONITOR TO ELIMINATE SUNLIGHT GLARE AND POSSIBLE INTERFERENCE
ADJUST THE WINDOWS DISPLAY SETTINGS —
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start→
Control Panel→
2
Click the area you want to change or click the
3
Try different settings for
Appearance and Themes
Color quality
and
.
Display
icon.
Screen resolution
.
Windows Vista:
1
Click
2
Adjust
Start
Resolution
→ Control Panel→ Hardware and Sound→ Personalization→ Display Settings
and
Colors
settings, as needed.
.
3D image quality is poor
CHECK THE GRAPHICS CARD POWER CABLE CONNECTION — Ensure that the power cable for the graphics card(s) is
correctly attached to the card.
HECK THE MONITOR SETTINGS — See the monitor documentation for instructions on adjusting the contrast and
C
brightness, demagnetizing (degaussing) the monitor, and running the monitor self-test.
64 Troubleshooting
Page 65

Power Lights
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
The power button light located on the front of the computer illuminates and blinks or remains solid to
indicate different states:
• If the power light is green and the computer is not responding, see "Diagnostic Lights" on page 66.
• If the power light is blinking green, the computer is in standby mode. Press a key on the keyboard,
move the mouse, or press the power button to resume normal operation.
• If the power light is off, the computer is either turned off or is not receiving power.
– Reseat the power cable into both the power connector on the back of the computer and the
electrical outlet.
– If the computer is plugged into a power strip, ensure that the power strip is plugged into an
electrical outlet and that the power strip is turned on.
– Bypass power protection devices, power strips, and power extension cables to verify that the
computer turns on properly.
– Ensure that the electrical outlet is working by testing it with another device, such as a lamp.
– Ensure that the main power cable and front panel cable are securely connected to the system
board (see "System Board Components" on page 89).
• If the power light is blinking amber, the computer is receiving electrical power, but an internal power
problem might exist.
– Ensure that the voltage selection switch is set to match the AC power at your location, if
applicable.
– Ensure that the processor power cable is securely connected to the system board (see "System
Board Components" on page 89).
• If the power light is steady amber, a device may be malfunctioning or incorrectly installed.
– Remove and then reinstall the memory modules (see "Memory" on page 90).
– Remove and then reinstall any cards (see "Cards" on page 94).
• Eliminate interference. Some possible causes of interference are:
– Power, keyboard, and mouse extension cables
– Too many devices on a power strip
– Multiple power strips connected to the same electrical outlet
Troubleshooting 65
Page 66

Diagnostic Lights
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
To help troubleshoot a problem, your computer has four lights labeled 1, 2, 3, and 4 on the front panel
(see "Front View" on page 13). When the computer starts normally, the lights flash before turning off. If
the computer malfunctions, the sequence of the lights help to identify the problem.
NOTE: After the computer completes POST, all four lights turn off before booting to the operating system.
Light Pattern Problem Description Suggested Resolution
The computer is in a normal off condition or a
possible pre-BIOS failure has occurred.
The diagnostic lights are not lit after the
system successfully boots to the operating
system.
A possible processor failure has occurred.
Memory modules are detected, but a memory
failure has occurred.
A possible graphics card failure has occurred.
• Plug the computer into a working electrical
outlet (see "Power Problems" on page 61).
• If the problem persists, contact Dell (see
"Contacting Dell
• Reseat the processor (see "Processor" on
page 132).
• If the problem persists, contact Dell (see
"Contacting Dell
• If two or more memory modules are
installed, remove the modules (see
"Removing Memory" on page 93), then
reinstall one module (see "Installing
Memory" on page 92) and restart the
computer. If the computer starts normally,
continue to install additional memory
modules (one at a time) until you have
identified a faulty module or reinstalled all
modules without error.
• If available, install working memory of the
same type into your computer (see
"Installing Memory" on page 92).
• If the problem persists, contact Dell (see
"Contacting Dell
• Reseat any installed graphics cards (see
"Cards" on page 94).
• If available, install a working graphics card
into your computer.
• If the problem persists, contact Dell (see
"Contacting Dell
" on page 181).
" on page 181).
" on page 181).
" on page 181).
66 Troubleshooting
Page 67

Light Pattern Problem Description Suggested Resolution
A possible floppy drive or hard drive failure has
occurred.
A possible USB failure has occurred. Reinstall all USB devices and check all cable
Reseat all power and data cables.
connections.
No memory modules are detected.
Memory modules are detected, but a memory
configuration or compatibility error has
occurred.
• If two or more memory modules are
installed, remove the modules (see
"Removing Memory" on page 93), then
reinstall one module (see "Installing
Memory" on page 92) and restart the
computer. If the computer starts normally,
continue to install additional memory
modules (one at a time) until you have
identified a faulty module or reinstalled all
modules without error.
• If available, install working memory of the
same type into your computer (see
"Installing Memory" on page 92).
• If the problem persists, contact Dell (see
"Contacting Dell
• Ensure that no special requirements for
memory module/connector placement exist
(see "Memory" on page 90).
• Ensure that the memory you are using is
supported by your computer (see "Memory"
on page 163).
• If the problem persists, contact Dell (see
"Contacting Dell
" on page 181).
" on page 181
).
Troubleshooting 67
Page 68

Light Pattern Problem Description Suggested Resolution
A possible expansion card failure has occurred. 1
Determine if a conflict exists by removing an
expansion card (not a graphics card) and
restarting the computer (see "Removing PCI
and PCI Express Cards" on page 95).
2
If the problem persists, reinstall the card you
removed, then remove a different card and
restart the computer.
3
Repeat this process for each expansion card
installed. If the computer starts normally,
troubleshoot the last card removed from the
computer for resource conflicts (see
"Troubleshooting Software and Hardware
Problems" on page 83).
4
If the problem persists, contact Dell (see
"Contacting Dell
Another failure has occurred.
• Ensure that all hard drive and optical drive
cables are properly connected to the system
board (see "System Board Components" on
page 89).
• If there is an error message on the screen
identifying a problem with a device (such as
the floppy drive or hard drive), check the
device to make sure it is functioning properly.
• If the operating system is attempting to boot
from a device (such as the floppy drive or
optical drive), check system setup (see
"System Setup" on page 168) to ensure the
boot sequence is correct for the devices
installed on your computer.
• If the problem persists, contact Dell (see
"Contacting Dell
" on page 181).
" on page 181).
68 Troubleshooting
Page 69

Beep Codes
Your computer might emit a series of beeps during start-up if the monitor cannot display errors or
problems. This series of beeps, called a beep code, identifies a problem. For example, beep code 1-3-1
(one possible beep code) consists of one beep, a burst of three beeps, and then one beep. This beep code
tells you that the computer encountered a memory problem.
Reseating the memory modules may correct the following beep code errors. If the problem persists,
contact Dell (see "Contacting Dell" on page 181) for instructions on obtaining technical assistance.
Code Cause
1-3-1 through 2-4-4 Memory not being properly identified or used
4-3-1 Memory failure above address 0FFFFh
If you experience any of the following beep code errors, see "Contacting Dell" on page 181 for
instructions on obtaining technical assistance.
Code Cause
1-1-2 Microprocessor register failure
1-1-3 NVRAM read/write failure
1-1-4 ROM BIOS checksum failure
1-2-1 Programmable interval timer failure
1-2-2 DMA initialization failure
1-2-3 DMA page register read/write failure
1-3 Video Memory Test failure
1-3-1 through 2-4-4 Memory not being properly identified or used
3-1-1 Slave DMA register failure
3-1-2 Master DMA register failure
3-1-3 Master interrupt mask register failure
3-1-4 Slave interrupt mask register failure
3-2-2 Interrupt vector loading failure
3-2-4 Keyboard Controller Test failure
3-3-1 NVRAM power loss
3-3-2 Invalid NVRAM configuration
3-3-4 Video Memory Test failure
3-4-1 Screen initialization failure
Troubleshooting 69
Page 70

Code Cause
3-4-2 Screen retrace failure
3-4-3 Search for video ROM failure
4-2-1 No timer tick
4-2-2 Shutdown failure
4-2-3 Gate A20 failure
4-2-4 Unexpected interrupt in protected mode
4-3-1 Memory failure above address 0FFFFh
4-3-3 Timer-chip counter 2 failure
4-3-4 Time-of-day clock stopped
4-4-1 Serial or parallel port test failure
4-4-2 Failure to decompress code to shadowed memory
4-4-3 Math-coprocessor test failure
4-4-4 Cache test failure
System Messages
NOTE: If the message you received is not listed in the table, see the documentation for either the operating system
or the program that was running when the message appeared.
Message Possible Cause Corrective Action
8042 Gate-A20
error
Address Line
Short!
C: Drive Error
C: Drive Failure
Cache Memory Bad,
Do Not Enable
Cache
70 Troubleshooting
The keyboard controller
failed its test.
An error in the address
decoding circuitry in the
memory has occurred.
The hard drive is not working
or is not configured correctly.
The cache memory is not
operating.
If you receive this message after you make
changes in the system setup program,
enter the system setup program and
restore the original value(s).
Reseat the memory modules (see
"Memory" on page 90).
Ensure that the hard drive is installed
correctly in the computer (see "Hard
Drive" on page 108) and defined correctly
in the system setup program (see "System
Setup" on page 168).
See "Contacting Dell" on page 181 for
instructions on obtaining technical
assistance.
Page 71

Message Possible Cause Corrective Action
CH-2 Timer Error An error is occurring on the
timer on the system board.
CMOS Battery
State Low
CMOS Checksum
Failure
The system configuration
information in the system
setup program is incorrect or
the battery charge may be
low.
See "Contacting Dell" on page 181 for
instructions on obtaining technical
assistance.
Enter the system setup program (see
"Entering System Setup" on page 168),
verify the system configuration, and then
restart the computer.
CMOS System
Options Not Set
CMOS Display Type
Mismatch
CMOS Memory Size
Mismatch
CMOS Time and
Date Not Set
Diskette Boot
Failure
DMA Error
DMA 1 Error
Drive A or B is present but
has failed the BIOS POST.
Error in the DMA controller
on the system board.
Ensure that the drive is installed correctly
in the computer (see "Drives" on
page 106) and defined correctly in the
system setup program (see "System Setup"
on page 168). Check the interface cable at
both ends.
The keyboard or system board may need to
be replaced.
DMA 2 Error
FDD Controller
Failure
HDD Controller
Failure
INTR1 Error
INTR2 Error
Invalid Boot
Diskette
The BIOS cannot
communicate with the floppy
drive or hard drive controller.
An interrupt channel on the
system board failed to POST.
The operating system cannot
be located on drive A or
drive C.
Ensure that the floppy drive or the hard
drive is installed correctly in the computer
(see "Drives" on page 106) and defined
correctly in the system setup program (see
"System Setup" on page 168). Check the
interface cable at both ends.
The keyboard or system board may need to
be replaced.
Enter the system setup program (see
"System Setup" on page 168) and confirm
that drive A or drive C is properly
identified.
Troubleshooting 71
Page 72

Message Possible Cause Corrective Action
Keyboard Error The BIOS has detected a
stuck key.
KB/Interface
Error
An error occurred with the
keyboard connector.
No ROM Basic The operating system cannot
be located on drive A or
drive C.
Ensure that nothing is resting on the
keyboard; if a key appears to be stuck,
carefully pry it up. If the problem persists,
you may need to replace the keyboard.
Ensure that nothing is resting on the
keyboard; if a key appears to be stuck,
carefully pry it up. If the problem persists,
you may need to replace the keyboard.
Enter the system setup program (see
"Entering System Setup" on page 168) and
confirm that drive A or drive C is properly
identified.
Dell Diagnostics
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
When to Use Dell Diagnostics
If you experience a problem with your computer, perform the checks in "Solving Problems" on page 53
and run Dell Diagnostics before you contact Dell for technical assistance.
NOTE: Dell Diagnostics only operate on Dell computers.
Run Dell Diagnostics from your hard drive or from the Drivers and Utilities media.
Starting Dell Diagnostics From Your Hard Drive
1
Turn on (or restart) your computer.
2
When the DELL logo appears, press <F12> immediately.
NOTE: Keyboard failure may result when a key is held down for extended periods of time. To avoid possible
keyboard failure, press and release <F12> in even intervals to open the Boot Device Menu.
NOTE: If at any time a message appears stating that no diagnostics utility partition has been found, run Dell
Diagnostics from your Drivers and Utilities media
Utilities Media
If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the
Microsoft
3
At the
®
Windows® desktop, then shut down your computer and try again.
Boot Device Menu
keyboard to highlight
NOTE: The Quickboot feature changes the boot sequence for the current boot only. Upon restart, the
computer boots according to the boot sequence specified in system setup.
72 Troubleshooting
" on page 73
Boot to Utility Partition
).
, use the up- and down-arrow keys or press the appropriate number on the
(see "Starting Dell Diagnostics From the Drivers and
, and then press <Enter>.
Page 73

4
At the Dell Diagnostics
Main Menu
, left-click with the mouse, or press <Tab> and then <Enter>, to
select the test you want to run (see "Dell Diagnostics Main Menu" on page 74).
NOTE: Write down any error codes and problem descriptions exactly as they appear and follow the
instructions on the screen.
5 After all tests have completed, close the test window to return to the Dell Diagnostics Main Menu.
6 Close the Main Menu window to exit Dell Diagnostics and restart the computer.
Starting Dell Diagnostics From the Drivers and Utilities Media
1
Turn on your computer.
2
Press the eject button on the front of the optical drive to open the drive tray.
3
Place the
gently push on the tray to close it.
4
Restart the computer.
5
When the DELL logo appears, press <F12> immediately.
If you wait too long and the Windows logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Windows
desktop, then shut down your computer and try again.
6
At the
keyboard to highlight
Drivers and Utilities
NOTE: Keyboard failure may result when a key on the keyboard is held down for extended periods of time. To
avoid possible keyboard failure, press and release <F12> in even intervals until the Boot Device Menu
appears.
Boot Device Menu
Onboard or USB CD-ROM
media in the center of the drive tray, then press the eject button or
, use the up- and down-arrow keys or press the appropriate number on the
, and then press <Enter>.
NOTE: The Quickboot feature changes the boot sequence for the current boot only. Upon restart, the
computer boots according to the boot sequence specified in system setup.
7
At the
CD-ROM Startup Menu
the keyboard to highlight
, use the up- and down-arrow keys or press the appropriate number on
Boot from CD-ROM
, and then press <Enter>.
If you wait too long and the Windows logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Windows
desktop, then shut down your computer and try again.
8
Press <1> to select the Dell Diagnostics.
9
At the
Dell Diagnostics Menu
10
At the Dell Diagnostics
, press <1> to select Dell Diagnostics (graphical user interface).
Main Menu
, left-click with the mouse, or press <Tab> and then <Enter>, to
select the test you want to run (see "Dell Diagnostics Main Menu" on page 74).
NOTE: Write down any error codes and problem descriptions exactly as they appear and follow the
instructions on the screen.
11 After all tests have completed, close the test window to return to the Dell Diagnostics Main Menu.
12 Remove the Drivers and Utilities media, then close the Main Menu window to exit Dell
Diagnostics and restart the computer.
Troubleshooting 73
Page 74

Dell Diagnostics Main Menu
The following tests can be run from the Dell Diagnostics Main Menu:
Option Function
Express Test Performs a quick test of system devices. The test typically takes
10 to 20 minutes and requires no interaction on your part. Run
Express Test first to increase the possibility of tracing the
problem quickly.
Extended Test Performs a thorough check of system devices. The test typically
takes an hour or more and periodically requires your input to
answer specific questions.
Custom Test Tests a specific device in the system and can be used to
customize the tests you want to run.
Symptom Tree Lists a number of common symptoms and allows you to select a
test based on the symptom of the problem you are having.
For any problem encountered during a test, a message appears with an error code and a description of the
problem. Write down the error code and problem description exactly as it appears and follow the
instructions on the screen. If you cannot resolve the problem, contact Dell (see
page 181).
NOTE: The Service Tag for your computer is located at the top of each test screen. When contacting Dell support,
have your Service Tag ready.
The following tabs provide additional information for tests run from the Custom Test or Symptom Tree
option:
"Contacting Dell" on
Tab Function
Results Displays the results of the test and any error conditions
Errors Displays error conditions encountered, error codes, and the
Help Describes the test and any requirements for running the test.
Configuration
(Custom Test only)
74 Troubleshooting
encountered.
problem description.
Displays the hardware configuration for the selected device.
The Dell Diagnostics obtains configuration information for all
devices from system setup, memory, and various internal tests,
and it displays the information in the device list in the left pane
of the screen.
NOTE: The device list may not display the names of all the
components installed on your computer or all devices attached to
your computer.
Page 75

Tab Function
Par ameters
(Custom Test only)
Allows you to customize the test, if applicable, by changing the
test settings.
Drivers
What Is a Driver?
A driver is a program that controls a device such as a printer, mouse, or keyboard. All devices require a
driver program.
A driver acts like a translator between the device and any other programs that use the device. Each device
has its own set of specialized commands that only its driver recognizes.
Dell ships your computer to you with required drivers already installed—no further installation or
configuration is needed.
NOTICE: The Drivers and Utilities media may contain drivers for operating systems that are not on your computer.
Ensure that you are installing software appropriate for your operating system.
Many drivers, such as the keyboard driver, come with your Microsoft Windows operating system. You
may need to install drivers if you:
• Upgrade your operating system.
• Reinstall your operating system.
• Connect or install a new device.
Identifying Drivers
If you experience a problem with any device, identify whether the driver is the source of your problem
and, if necessary, update the driver.
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start
and click
2
Under
Pick a Category
Manager
3
Scroll down the list of devices and check for an exclamation point (a circle with a [!]) next to the
.
device name.
If an exclamation point appears next to the device name, you may need to reinstall the driver or install
a new driver (see "Drivers" on page 75).
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start → Computer.→ System Properties→ Device Manager
NOTE: The User Account Control window may appear. If you are an administrator on the computer, click
Continue; otherwise, contact your administrator to continue.
Control Panel
, click
Performance and Maintenance→
.
System→
Hardware → Device
.
Troubleshooting 75
Page 76

2
Scroll down the list to see if any device has an exclamation point (a yellow circle with a [!]) on the
device icon.
If an exclamation point is next to the device name, you may need to reinstall the driver or install a new
driver (see "Reinstalling Drivers and Utilities" on page 76).
Reinstalling Drivers and Utilities
NOTICE: The Dell Support website at support.dell.com and your Drivers and Utilities media provide approved
drivers for Dell™ computers. If you install drivers obtained from other sources, your computer might not work
correctly.
Using Windows Device Driver Rollback
If a problem occurs on your computer after you install or update a driver, use Windows Device Driver
Rollback to replace the driver with the previously installed version.
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start
and click
2
Under
Pick a Category→
Hardware→
3
Right-click the device for which the new driver was installed, then click
4
Click
Device Manager
Driver
and click
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start → Computer→
Control Panel
.
Performance and Maintenance→
.
Roll Back Driver
.
System Properties→ Device Manager
System→ System Properties→
Properties
.
.
NOTE: The User Account Control window may appear. If you are an administrator on the computer, click
Continue; otherwise, contact your administrator to enter the Device Manager.
2
Right-click the device for which the new driver was installed and click
3
Click
Drivers
and click
Roll Back Driver
.
Properties
.
If Device Driver Rollback does not resolve the problem, then use System Restore to return your
computer to the operating state that existed before you installed the driver.
Using the Drivers and Utilities Media
If using Device Driver Rollback or System Restore does not resolve the problem, then reinstall the driver
from the Drivers and Utilities media.
1
With the Windows desktop displayed, insert the
If this is your first time to use the
2
When the
3
When the
and click
Drivers and Utilities
InstallShield Wizard Complete
Finish
76 Troubleshooting
Drivers and Utilities
installation program starts, follow the prompts on the screen.
to restart the computer.
Drivers and Utilities
media.
media, go to step 2. If not, go to step 5.
window appears, remove the
Drivers and Utilities
media
Page 77

4
When you see the Windows desktop, reinsert the
5
At the
Welcome Dell System Owner
NOTE: The Drivers and Utilities media displays drivers only for hardware that came installed in your computer. If
you installed additional hardware, the drivers for the new hardware might not be displayed by the Drivers and
Utilities media. If those drivers are not displayed, exit the Drivers and Utilities media program. For drivers
information, see the documentation that came with the device.
screen, click
Drivers and Utilities media
Next
.
.
A message appears, stating that the Drivers and Utilities media is detecting hardware in your
computer.
The drivers that are used by your computer are automatically displayed in the
Drivers and Utilities media has identified these components in your system
6
Click the driver that you want to reinstall and follow the instructions on the screen.
My Drivers—The
window.
If a particular driver is not listed, that driver is not required by your operating system.
Manually Reinstalling Drivers
After extracting driver files from the Drivers and Utilities media to your hard drive, you may be required
to update the driver manually.
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start
and click
2
Under
Pick a Category
Hardware→
3
Double-click the type of device for which you are installing the driver.
4
Right-click the device for which the driver is being reinstalled, then click
5
Click
6
Click to check
Device Manager
Driver→ Update Driver→
Control Panel
, click
.
Performance and Maintenance→
.
Install from a list or specific location (Advanced)→
Include this location in the search
, then click
System→ System Properties→
Properties
.
Next
Browse
and navigate to where the driver
.
files are located on your hard drive.
7
When the name of the appropriate driver appears, click
8
Click
Finish
and restart your computer.
Next
.
Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start → Computer→
System Properties→ Device Manager
.
NOTE: The User Account Control window may appear. If you are an administrator on the computer, click
Continue; otherwise, contact your administrator to enter the Device Manager.
2
Double-click the type of device for which you are installing the driver (for example,
3
Double-click the name of the device for which you are installing the driver.
4
Click
5
Click
Driver→
Browse
Update Driver→ Browse my computer for driver software
.
and browse to the location to which you previously copied the driver files.
Troubleshooting 77
Audio
or
Video
).
Page 78

6
When the name of the appropriate driver appears, click the name of the driver.
7
Click OK→
Next→
Finish
and restart your computer.
Restoring Your Operating System
You can restore your operating system in the following ways:
• System Restore returns your computer to an earlier operating state without affecting data files. Use
System Restore as the first solution for restoring your operating system and preserving data files.
• Dell PC Restore by Symantec (available in Windows XP) and Dell Factory Image Restore (available in
Windows Vista) restore your hard drive to the operating state it was in when you purchased the
computer. Both permanently delete all data on the hard drive and remove any programs installed after
you received the computer. Use Dell PC Restore or Dell Factory Image Restore only if System Restore
did not resolve your operating system problem.
• If you received an
system. However, using the
only
if System Restore did not resolve your operating system problem.
Using Microsoft Windows System Restore
The Windows operating systems provide a System Restore option which allows you to return your
computer to an earlier operating state (without affecting data files) if changes to the hardware, software,
or other system settings have left the computer in an undesirable operating state. Any changes that
System Restore makes to your computer are completely reversible.
Operating System
Operating System
disc with your computer, you can use it to restore your operating
disc also deletes all data on the hard drive. Use the disc
NOTICE: Make regular backups of your data files. System Restore does not monitor your data files or recover
them.
NOTE: The procedures in this document were written for the Windows default view, so they may not apply if you
set your Dell™ computer to the Windows Classic view.
Starting System Restore
Windows XP:
NOTICE: Before you restore the computer to an earlier operating state, save and close any open files and exit any
open programs. Do not alter, open, or delete any files or programs until the system restoration is complete.
1
Click
Start→
2
Click either
3
Click
Next
78 Troubleshooting
All Programs→ Accessories→ System Tools→
Restore my computer to an earlier time
and follow the remaining on-screen prompts.
or
System Restore
Create a restore point
.
.
Page 79

Windows Vista:
1
Click
Start
.
2
In the Start Search box, type
NOTE: The User Account Control window may appear. If you are an administrator on the computer, click
Continue; otherwise, contact your administrator to continue the desired action.
3
Click
Next
and follow the remaining prompts on the screen.
System Restore
and press <Enter>.
In the event that System Restore did not resolve the issue, you may undo the last system restore.
Undoing the Last System Restore
NOTICE: Before you undo the last system restore, save and close all open files and exit any open programs. Do not
alter, open, or delete any files or programs until the system restoration is complete.
Windows XP:
Click
1
2
Start→
Click
Undo my last restoration
All Programs→ Accessories→ System Tools→
and click
Next
.
System Restore
.
Windows Vista:
Click
Start
1
2
In the Start Search box, type
3
Click
Undo my last restoration
Enabling System Restore
.
System Restore
and click
Next
and press <Enter>.
.
NOTE: Windows Vista does not disable System Restore; regardless of low disk space. Therefore, the steps below
apply only to Windows XP.
If you reinstall Windows XP with less than 200 MB of free hard-disk space available, System Restore is
automatically disabled.
To see if System Restore is enabled:
1
Click
2
Click the
Start→
Control Panel→ Performance and Maintenance→ System
System Restore
tab and ensure that
Turn off System Restore
.
is unchecked.
Using Dell PC Restore and Dell Factory Image Restore
NOTICE: Using Dell PC Restore or Dell Factory Image Restore permanently deletes all data on the hard drive and
removes any programs or drivers installed after you received your computer. If possible, back up the data before
using these options. Use PC Restore or Dell Factory Image Restore only if System Restore did not resolve your
operating system problem.
NOTE: Dell PC Restore by Symantec and Dell Factory Image Restore may not be available in certain countries or
on certain computers.
Troubleshooting 79
Page 80

Use Dell PC Restore (Windows XP) or Dell Factory Image Restore (Windows Vista) only as the last
method to restore your operating system. These options restore your hard drive to the operating state it
was in when you purchased the computer. Any programs or files added since you received your
computer—including data files—are permanently deleted from the hard drive. Data files include
documents, spreadsheets, e-mail messages, digital photos, music files, and so on. If possible, back up all
data before using PC Restore or Factory Image Restore.
Windows XP: Dell PC Restore
Using PC Restore:
1
Turn on the computer.
During the boot process, a blue bar with
2
Immediately upon seeing the blue bar, press <Ctrl><F11>.
www.dell.com
appears at the top of the screen.
If you do not press <Ctrl><F11> in time, let the computer finish starting, and then restart the
computer again.
NOTICE: If you do not want to proceed with PC Restore, click Reboot.
3
Click
Restore
and click
Confirm
.
The restore process takes approximately 6 to 10 minutes to complete.
4
When prompted, click
NOTE: Do not manually shut down the computer. Click Finish and let the computer completely reboot.
5
When prompted, click
Finish
to reboot the computer.
Yes
.
The computer restarts. Because the computer is restored to its original operating state, the screens that
appear, such as the End User License Agreement, are the same ones that appeared the first time the
computer was turned on.
6
Click
Next
.
The
System Restore
7
After the computer restarts, click OK.
screen appears and the computer restarts.
Removing PC Restore:
NOTICE: Removing Dell PC Restore from the hard drive permanently deletes the PC Restore utility from your
computer. After you have removed Dell PC Restore, you will not be able to use it to restore your computer operating
system.
80 Troubleshooting
Page 81

Dell PC Restore enables you to restore your hard drive to the operating state it was in when you
purchased your computer. It is recommended that you do not remove PC Restore from your computer,
even to gain additional hard-drive space. If you remove PC Restore from the hard drive, you cannot ever
recall it, and you will never be able to use PC Restore to return your computer operating system to its
original state.
1
Log on to the computer as a local administrator.
2
In Microsoft Windows Explorer, go to
3
Double-click the filename
NOTE: If you do not log on as a local administrator, a message appears stating that you that you must log on
as administrator. Click Quit, and then log on as a local administrator.
NOTE: If the partition for PC Restore does not exist on your computer hard drive, a message appears stating
that the partition was not found. Click Quit; there is no partition to delete.
4
Click OK to remove the PC Restore partition on the hard drive.
5
Click
Yes
when a confirmation message appears.
DSRIRRemv2.exe
c:\dell\utilities\DSR
.
.
The PC Restore partition is deleted and the newly available disk space is added to the free space
allocation on the hard drive.
6
Right-click
space is available as indicated by the increased value for
7
Click
Windows Vista: Dell Factory Image Restore
Local Disk (C)
Finish
to close the
in Windows Explorer, click
PC Restore Removal
window and restart the computer.
Properties
Free Space
, and verify that the additional disk
.
Using Factory Image Restore:
1
Turn on the computer. When the Dell logo appears, press <F8> several times to access the Vista
Advanced Boot Options Window.
2
Select
Repair Your Computer
.
The System Recovery Options window appears.
3
Select a keyboard layout and click
4
To access the recovery options, log on as a local user. To access the command prompt, type
administrator
5
Click
Dell Factory Image Restore
NOTE: Depending upon your configuration, you may need to select Dell Factory Tools, then Dell Factory
Image Restore.
in the User name field, then click OK.
Next
.
.
The Dell Factory Image Restore welcome screen appears.
6
Click
Next.
The Confirm Data Deletion screen appears.
Troubleshooting 81
Page 82

NOTICE: If you do not want to proceed with Factory Image Restore, click Cancel.
7
Click the checkbox to confirm that you want to continue reformatting the hard drive and restoring the
system software to the factory condition, then click
Next
.
The restore process begins and may take five or more minutes to complete. A message appears when
the operating system and factory-installed applications have been restored to factory condition.
8
Click
Finish
to reboot the system.
Using the Operating System Media
Before you Begin
If you are considering reinstalling the Windows operating system to correct a problem with a newly
installed driver, first try using Windows Device Driver Rollback. See "Using Windows Device Driver
Rollback" on page 76. If Device Driver Rollback does not resolve the problem, then use
return your operating system to the operating state it was in before you installed the new device driver.
See "Using Microsoft
NOTICE: Before performing the installation, back up all data files on your primary hard drive. For conventional
hard drive configurations, the primary hard drive is the first drive detected by the computer.
Windows System Restore" on page 78.
To reinstall Windows, you need the following items:
•Dell™
•Dell
Operating System
Drivers and Utilities
media
media
System Restore
to
NOTE: The
computer. Use the
which you ordered your computer, or whether you requested the media, the
and
Reinstalling Windows XP or Windows Vista
Dell
Drivers and Utilities
Dell
Operating System
media
contains drivers that were installed during the assembly of the
Drivers and Utilities
media may not ship with your computer.
media
to load any required drivers. Depending on the region from
Dell
Drivers and Utilities
media
The reinstallation process can take 1 to 2 hours to complete. After you reinstall the operating system, you
must also reinstall the device drivers, virus protection program, and other software.
NOTICE: The Operating System media provides options for reinstalling Windows XP. The options can overwrite
files and possibly affect programs that are installed on your hard drive. Therefore, do not reinstall Windows XP
unless a Dell technical support representative instructs you to do so.
1
Save and close any open files and exit any open programs.
2
Insert the
3
Click
4
Restart the computer.
Operating System
Exit
if the
Install Windows
disc.
message appears.
When the DELL logo appears, press <F12> immediately.
NOTE: If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the
Microsoft
®
Windows® desktop; then, shut down your computer and try again.
82 Troubleshooting
Page 83

NOTE: The next steps change the boot sequence for one time only. On the next start-up, the computer boots
according to the devices specified in the system setup program.
5
When the boot device list appears, highlight
6
Press any key to
7
Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the installation.
Boot from CD-ROM
CD/DVD/CD-RW Drive
.
and press <Enter>.
Troubleshooting Software and Hardware Problems
If a device is either not detected during the operating system setup or is detected but incorrectly
configured, you can use the Hardware Troubleshooter to resolve the incompatibility.
Windows XP:
1
Click
Start
and click
2
Ty p e
hardware troubleshooter
3
Click
Hardware Troubleshooter
4
In the
Hardware Troubleshooter
click
Next
.
Windows Vista:
Click
1
2
3
Start
Ty p e
hardware troubleshooter
In the search results, select the option that best describes the problem and follow the remaining
troubleshooting steps.
Help and Support
and click
Help and Support.
in the
Search Results
list, click
.
in the
Search
field and click the arrow to start the search.
list.
I need to resolve a hardware conflict on my computer
in the search field and press <Enter> to start the search.
, and
Troubleshooting 83
Page 84

84 Troubleshooting
Page 85

Removing and Installing Parts
Before You Begin
This chapter provides procedures for removing and installing the components in your computer.
Unless otherwise noted, each procedure assumes that a component can be replaced by performing
the removal procedure in reverse order.
Recommended Tools
The procedures in this document may require one or more of the following tools:
• Small flat-blade screwdriver
• Phillips screwdriver
• Flash BIOS update (see the Dell support website at
support.dell.com
Preparing to Work Inside Your Computer
Use the following safety guidelines to help protect your computer from potential damage and to
help ensure your own personal safety.
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the
Product Information Guide.
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire, electric shock, or injury, do not overload an electrical outlet, power
strip, or convenience receptacle. The total ampere rating of all products plugged into an electrical outlet,
power strip, or other receptacle should not exceed 80 percent of the branch circuit rating.
)
CAUTION: Your computer is heavy and can be difficult to maneuver. Seek assistance before attempting to
lift, move, or tilt the computer and always lift correctly to avoid injury; avoid bending over while lifting.
CAUTION: The liquid cooling assembly is not user serviceable or upgradeable. All required service should
be done by qualified service personnel only. The liquid cooling assembly in your system contains a nonrefillable coolant. In the event of a coolant leak, shut down your system immediately. Unplug your system
from the power outlet and contact Dell Technical Support. In the event of skin contact with the coolant,
wash your skin with soap and water. Seek medical attention if irritation develops. In the event of eye contact
with the coolant, rinse your eyes immediately with water, with your eyelids open, for 15 minutes. Seek
medical attention if irritation persists.
NOTICE: Only a certified service technician should perform repairs on your computer. Damage due to
servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty.
Removing and Installing Parts 85
Page 86

NOTICE: To avoid electrostatic discharge and damage to internal components, ground yourself by using a wrist
grounding strap or by periodically touching an unpainted metal surface on the computer chassis.
NOTICE: Handle components and cards with care. Do not touch the components or contacts on a card. Instead,
hold a card by its edges or by its metal mounting bracket. Hold a component such as a microprocessor by its edges,
not by its pins.
NOTICE: When disconnecting a cable, pull on the cable’s connector or its strain-relief loop, not on the cable itself.
Some cables have connectors with locking tabs; before disconnecting this type of cable, press inward on the
locking tabs to release the connector. When connecting or disconnecting a cable, ensure that the connectors are
correctly oriented and aligned to avoid damage to the connector and/or the connector’s pins.
1
Ensure that the work surface is level and protected to prevent either the surface or the computer from
being scratched.
NOTICE: To avoid losing data, save any work in progress and exit all open programs before turning off your
computer.
2
Shut down the operating system:
• In Windows XP, click
• In Windows Vista,
c
shown below, and then click
Start→
lick
Turn Off Computer→
Tur n o f f
.
Start , click the arrow in the lower-right corner of the Start menu as
Shut Down
.
The computer turns off after the operating system shutdown process is complete.
3
Ensure that the computer and all attached devices are turned off. If your computer and attached
devices did not automatically turn off when you shut down your operating system, press and hold the
power button for about 4 seconds to turn them off.
NOTICE: When disconnecting a network cable, first unplug the cable from your computer and then unplug it from
the network port or device.
4
Disconnect all external cables from the computer.
5
Carefully, lift the rear of the computer and rotate the stabilizing feet into the closed position.
6
With the help of an assistant, carefully lay the computer down on a flat surface with the computer
cover facing up.
Removing the Computer Cover
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
CAUTION: To guard against electrical shock, always unplug your computer from the electrical outlet before
removing the cover.
86 Removing and Installing Parts
Page 87

NOTICE: To avoid electrostatic discharge and damage to internal components, ground yourself by using a wrist
grounding strap or by periodically touching an unpainted metal surface on the computer chassis.
1
Follow the procedures in "Before You Begin" on page 85.
2
Pull back on the cover release latch.
NOTICE: Ensure that sufficient space exists to support the removed cover—at least 30 centimeters (1 foot) of
desktop space.
1
2
3
4
1 computer cover 2 cover release latch 3 cover hinge tabs
4 stabilizing feet (closed)
3
With the cover release latch pulled back, grip the sides of the cover, then pivot the top of the cover up
and away from the computer.
4
Slide the cover forward and up to remove it from the hinge slots, then set it aside in a secure and
protected location.
Removing and Installing Parts 87
Page 88

Inside View of Your Computer
2
1
5
1 optical drive bays (4) 2 floppy drive/media card
reader
4 card fan 5 liquid cooling assembly
3
4
3 hard drive bays (4)
88 Removing and Installing Parts
Page 89

System Board Components
1
28
27
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
25
24
192022 2123
1 white memory module
connectors (DIMM_1-2)
4 IDE drive connector (IDE) 5 front I/O panel connector
7 power button (PWR_BT) 8 FlexBay connector (INT_USB) 9 main power connector
10 SATA connectors (SATA0-5) 11 front USB connector
2 black memory module
connectors (DIMM_3-4)
(FRONTPANEL)
(FRNT_USB)
3 hard drive fan connector
(FAN_HDD)
6 back LED connector
(POWER1)
12 front panel 1394 connector
(FP1394)
Removing and Installing Parts 89
16
17
18
Page 90

13 PCI-Express x1 card slot
(SLOT1)
This slot is not available in the
dual-graphics configuration
16 PCI-Express x16 card slot
(SLOT4)
19 PCI-Express x16 card slot
(SLOT7)
22 password jumper
(PASSWORD)
25 card cage fan connector
(FAN_CAGE)
28 processor fan connector
(FAN1_CPU)
14 PCI-Express x16 card slot
(SLOT2)
17 PCI card slot (SLOT5) 18 PCI card slot (SLOT6)
20 RTC reset jumper (RTCRST) 21 battery socket (BATTERY)
23 power connector (POWER2) 24 floppy drive (DSKT)
26 liquid cooling assembly
(TEC_PUMP)
15 PCI card slot (SLOT3)
This slot is not available in the
dual-graphics or doublewidth, single graphics
configuration.
27 processor (CPU)
Memory
You can increase your computer memory by installing memory modules on the system board.
Your computer supports DDR2 memory. For additional information on the type of memory supported by
your computer, see "Memory" on page 163.
DDR2 Memory Overview
• DDR2 memory modules should be installed in
memory modules are not installed in matched pairs, the computer will continue to operate, but with a
slight reduction in performance. See the label on the upper-right or upper-left corner of the module to
determine the module’s capacity.
pairs of matched memory size and speed
. If the DDR2
NOTE: Always install DDR2 memory modules in the order indicated on the system board.
The recommended memory configurations are:
– A pair of matched memory modules installed in DIMM connectors 1 and 2
or
90 Removing and Installing Parts
Page 91

– A pair of matched memory modules installed in DIMM connectors 1 and 2 and another matched
pair installed in DIMM connectors 3 and 4
NOTICE: Do not install ECC memory modules.
• If you install mixed pairs of PC2-5300 (DDR2 667-MHz) and PC2-6400 (DDR2 800-MHz) memory,
the modules function at the speed of the slowest module installed.
• Be sure to install a single memory module in DIMM connector 1, the connector closest to the
processor, before you install modules in any other connector.
.
B
A
A matched pair of modules in DIMM connectors 1
and 2 (white securing clips)
NOTICE: If you remove your original memory modules from the computer during a memory upgrade, keep them
separate from any new modules that you may have, even if you purchased the new modules from Dell. If possible,
do not pair an original memory module with a new memory module. Otherwise, your computer may not start
properly. You should install your original memory modules in pairs either in DIMM connectors 1 and 2 or DIMM
connectors 3 and 4.
NOTE: Memory purchased from Dell is covered under your computer warranty.
B matched pair of memory modules in DIMM
connectors 3 and 4 (black securing clips)
Addressing Memory Configurations
If you are using a 32-bit operating system such as Microsoft® Windows Vista™, your computer will
support a maximum of 4 GB of memory. If you are using a 64-bit operating system, your computer will
support a maximum of 8 GB (2-GB DIMMs in each of the four slots) of memory.
Removing and Installing Parts 91
Page 92

Installing Memory
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTICE: To avoid electrostatic discharge and damage to internal components, ground yourself by using a wrist
grounding strap or by periodically touching an unpainted metal surface on the computer chassis.
1
Follow the procedures in "Before You Begin" on page 85.
2
Remove the computer cover (see "Removing the Computer Cover" on page 86).
3
Press out the securing clip at each end of the memory module connector.
1
2
3
1 memory connector closest to
processor
4
Align the notch on the bottom of the module with the crossbar in the connector.
1 cutouts (2) 2 memory module 3 notch
4crossbar
2 securing clips (2) 3 memory connector
3
2
1
4
92 Removing and Installing Parts
Page 93

NOTICE: To avoid damage to the memory module, press the module straight down into the connector while you
apply equal force to each end of the module.
5
Insert the module into the connector until the module snaps into position.
If you insert the module correctly, the securing clips snap into the cutouts at each end of the module.
6
Replace the computer cover (see "Replacing the Computer Cover" on page 160).
NOTICE: To connect a network cable, first plug the cable into the network port or device and then plug it into the
computer.
7
Connect your computer and devices to electrical outlets, and turn them on.
8
When the message appears stating that memory size has changed, press <F1> to continue.
9
Log on to your computer.
10
Right-click the
11
Click the
12
To verify that the memory is installed correctly, check the amount of memory (RAM) listed.
My Computer
General
tab.
icon on your Windows desktop and click
Properties
.
Removing Memory
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
NOTICE: To avoid electrostatic discharge and damage to internal components, ground yourself by using a wrist
grounding strap or by periodically touching an unpainted metal surface on the computer chassis.
1
Follow the procedures in "Before You Begin" on page 85.
2
Press out the securing clip at each end of the memory module connector.
3
Grasp the module and pull up.
If the module is difficult to remove, gently ease the module back and forth to remove it from the
connector.
Removing and Installing Parts 93
Page 94

Cards
CAUTION: Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the Product
Information Guide.
Your computer provides the following slots for PCI and PCI Express cards:
• Three PCI card slots
• Two PCI Express x16 card slots (can be used in a dual-graphics configuration)
• One PCI Express x16 card slot (wired as x8)
• One PCI Express x1 card slot
NOTE: If a graphics card is installed in each of the PCI Express x16 card slots in the dual-graphics configuration,
the PCI Express x1 and one PCI card slot are not accessible for use.
1
2
5
3
1 PCI card 2 PCI Express x16 card 3 PCI Express x16 card slot
4 PCI Express x1 card slot 5 PCI Express x1 card
4
94 Removing and Installing Parts
Page 95

Removing PCI and PCI Express Cards
NOTICE: To avoid electrostatic discharge and damage to internal components, ground yourself by using a wrist
grounding strap or by periodically touching an unpainted metal surface on the computer chassis.
NOTICE: If your computer came with a PCI graphics card installed, removal of the card is not necessary when
installing additional graphics cards; however, the card is required for troubleshooting purposes. If you remove the
card, store it in a safe and secure location.
NOTICE: If you have the optional dual graphics card configuration, see "Removing a PCI Express Graphics Card
from a Dual Configuration" on page 100 to remove or replace a graphics card.
1
Follow the procedures in "Before You Begin" on page 85.
2
Remove the computer cover (see "Removing the Computer Cover" on page 86).
3
Disconnect any cables connected to the card.
4
Press down the tab on the top of the card retainer at the appropriate card slot and pivot the card
retainer back through the chassis wall.
5
If present, press the tab on the card retention device that lays over the installed cards and lift it to gain
full access to the card.
1
2
4
1 release tab 2 card retainer 3 alignment guide
4 fan bracket
Removing and Installing Parts 95
3
Page 96

6
Press the release tab (if present) on the system board connector as you grasp the card by its top corners,
and then ease the card out of the connector.
NOTE: If the card is full length, press the release tab on the end of the alignment guides on the fan bracket.
1
2
3
1 PCI Express x16 card 2 securing tab 3 PCI Express x16 card slot
7
Install a filler bracket in the empty card-slot opening. If you are replacing the card, see "Installing PCI
and PCI Express Cards" on page 97.
NOTE: Installing filler brackets over empty card-slot openings is necessary to maintain FCC certification of
the computer. The brackets also keep dust and dirt out of your computer.
NOTICE: Before rotating the card retainer back into place, ensure that the tops of all cards and filler brackets are
flush with the alignment bar and the notch in the top of each card or filler bracket fits around the alignment guide.
NOTICE: Do not route card cables over or behind the cards. Cables routed over the cards can prevent the
computer cover from closing properly or cause damage to the equipment.
8
Rotate the card retainer back into its original position; push its tip so that its tab clicks into place.
NOTICE: To connect a network cable, first plug the cable into the network port or device and then plug the cable
into the computer.
9
If present, lower the card retention device that lays over the installed cards and snap it into place.
10
Replace the computer cover (see "Replacing the Computer Cover" on page 160), reconnect the
computer and devices to electrical outlets, and then turn them on.
11
Uninstall the driver for the card that you removed.
NOTE: If you removed a sound card or a network adapter, see "Network Adapter and Sound Card Settings" on
page 105.
96 Removing and Installing Parts
Page 97

Installing PCI and PCI Express Cards
NOTICE: To avoid electrostatic discharge and damage to internal components, ground yourself by using a wrist
grounding strap or by periodically touching an unpainted metal surface on the computer chassis.
NOTICE: If your computer came with a PCI graphics card installed, removal of the card is not necessary when
installing additional graphics cards; however, the card is required for troubleshooting purposes. If you remove the
card, store it in a safe and secure location.
NOTICE: If you have or are upgrading to the optional dual-graphics configuration, see "Installing a PCI Express
Graphics Card in a Dual Configuration" on page 102 to install a graphics card.
1
Follow the procedures in "Before You Begin" on page 85.
2
Remove the computer cover (see "Removing the Computer Cover" on page 86).
3
If present, press the tab on the card retention device that lays over the installed cards and rotate it
upwards to gain full access to the card.
4
Press down the tab on the top of the card retainer at the appropriate card slot and pivot the card
retainer back through the chassis wall.
1
2
4
1 release tab 2 card retainer 3 alignment guide
4 fan bracket
Removing and Installing Parts 97
3
Page 98

5
Remove the filler bracket or existing card (see "Removing PCI and PCI Express Cards" on page 95) to
create a card-slot opening.
6
Prepare the card for installation.
See the documentation that came with the card for information on configuring the card, making
internal connections, or otherwise customizing it for your computer.
7
Position the card so that it is aligned with the slot and the securing tab (if present) is aligned with the
securing slot.
NOTE: If the card is full length, insert the card guide into the alignment slot on the fan bracket.
1
3
1 PCI Express x16 card 2 securing tab 3 PCI Express x16 card slot
NOTICE: Ensure that you release the securing tab to seat the card. If the card is not installed correctly, you may
damage the system board.
8
Gently pull the securing tab (if present) and place the card in the connector. Press down firmly and
2
ensure that the card is fully seated in the slot.
98 Removing and Installing Parts
Page 99

2
3
1
6
4
5
1 card connector (seated) 2 card connector (not seated) 3 bracket properly aligned
within slot
4 bracket improperly aligned
outside of slot
NOTICE: Do not route card cables over or behind the cards. Cables routed over the cards can prevent the
computer cover from closing properly or cause damage to the equipment.
5 alignment bar 6 alignment guide
NOTICE: An incorrectly attached graphics power cable may result in degraded graphics performance.
9
Connect any cables that should be attached to the card.
See the documentation for the card for information about the card’s cable connections.
NOTICE: Before rotating the card retainer back into place, ensure that the tops of all cards and filler brackets are
flush with the alignment bar and the notch in the top of each card or filler bracket fits around the alignment guide.
10
Rotate the card retainer back into its original position; push its tip so that its tab clicks into place.
11
If present, lower the card retention device that lays over the installed cards and snap it into place.
NOTICE: To connect a network cable, first plug the cable into the network port or device and then plug the cable
into the computer.
12
Replace the computer cover (see "Replacing the Computer Cover" on page 160), reconnect the
computer and devices to electrical outlets, and then turn them on.
Removing and Installing Parts 99
Page 100

13
Install any drivers required for the card as described in the card documentation.
NOTE: If you installed a sound card or a network adapter, see "Network Adapter and Sound Card Settings" on
page 105.
Removing a PCI Express Graphics Card from a Dual Configuration
NOTE: This section regards dual configurations of PCI Express x16 graphics cards only. For removal of any other
type of PCI or PCI Express cards, see "Removing PCI and PCI Express Cards" on page 95.
1
Follow the procedures in "Before You Begin" on page 85.
2
Remove the computer cover (see "Removing the Computer Cover" on page 86).
3
If present, press the tab on the card retention device that lays over the installed cards and rotate it
upwards to gain full access to the card.
4
Gently securing both graphics cards with one hand, remove the graphics card bridge (if present) with
your other hand by pulling it up and away from the computer. Set it aside.
1
2
1 graphics card bridge 2 power connectors (2) 3 dual-PCI Express graphics
100 Removing and Installing Parts
3
cards
 Loading...
Loading...