Dell W-IAP114, W-IAP115 User Manual

Dell Networking W-Series
Instant
6.4.2.0-4.1.1
Command-Line Interface
Reference Guide

Copyright
© 2014 Aruba Networks, Inc. Aruba Networks trademarks include , Aruba Networks®, Aruba
Wireless Networks®, the registered Aruba the Mobile Edge Company logo, and Aruba Mobility Management
System®. Dell™, the DELL™ logo, and PowerConnect™ are trademarks of Dell Inc.
All rights reserved. Specifications in this manual are subject to change without notice.
Originated in the USA. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Open Source Code
Certain Aruba products include Open Source software code developed by third parties, including softwarecode
subject to the GNU General Public License (GPL), GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL), or other Open
Source Licenses. Includes software from Litech Systems Design. The IF-MAP client library copyright 2011
Infoblox, Inc. All rights reserved. This product includes software developed by Lars Fenneberg, et al. The Open
Source code used can be found at this site:
http://www.arubanetworks.com/open_source
Legal Notice
The use of Aruba Networks, Inc. switching platforms and software, by all individuals or corporations, to
terminate other vendors’ VPN client devices constitutes complete acceptance of liability by that individual or
corporation for this action and indemnifies, in full, Aruba Networks, Inc. from any and all legal actions that
might be taken against it with respect to infringement of copyright on behalf of those vendors.
0511587-03 | November 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide

Chapter 1
About this Guide
This document describes the Instant command syntax and provides the following information for each
command:
l Command Syntax—The complete syntax of the command.
l Description—A brief description of the command.
l Syntax—A description of the command parameters, the applicable ranges and default values, if any.
l Usage Guidelines—Information to help you use the command, including prerequisites, prohibitions, and
related commands.
l Example—An example of how to use the command.
l Command History—The version of Instant in which the command was first introduced.
l Command Information—This table describes command modes and platforms for which this command is
applicable.
The commands are listed in alphabetical order.
Intended Audience
This guide is intended for customers who configure and use Dell Networking W-Series Instant (W-IAP).
Related Documents
In addition to this document, the Dell W-IAP product documentation includes the following:
l
Dell Networking W-Series Instant Acc e ss Point Installation Guides
l
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 Quick Start Guide
l
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 User Guide
l
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 MIB Reference Guide
l
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 Syslog Message s Reference Guide
l
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1.x Rele ase Notes
Conventions
The following conventions are used throughout this document to emphasize important concepts:
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide About this Guide | 3
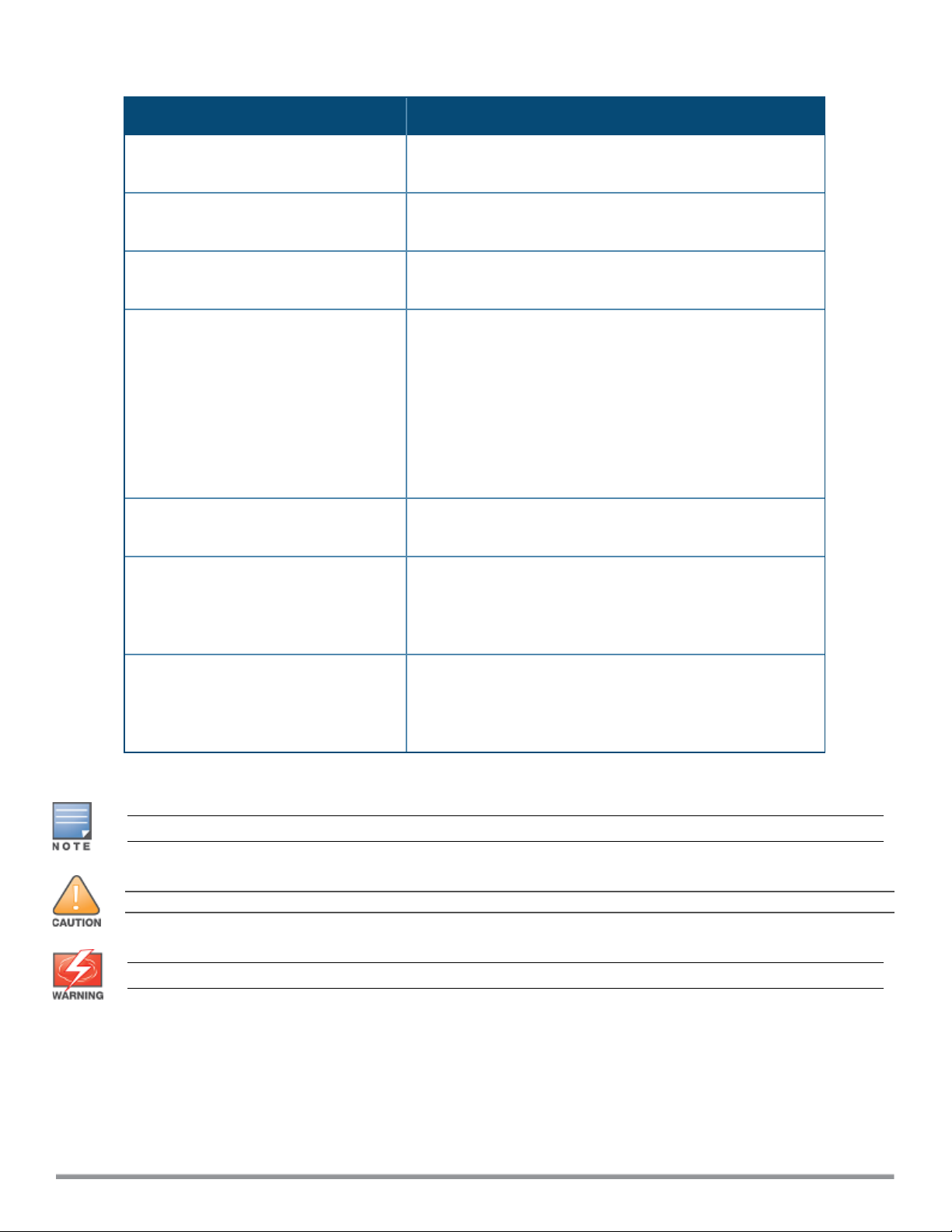
Table 1: Typographical Conventions
Type Style Description
Italics
Boldface
Commands
<angle brackets>
[square brackets]
{Item_A|Item_B}
This style is used for emphasizing important terms and to
mark the titles of books.
This style is used for command names and parameter
options when mentioned in the text.
This fixed-width font depicts command syntax and examples
of commands and command output.
In the command syntax, text within angle brackets represents
items that you should replace with information appropriate to
your specific situation.
For example, ping <ipaddr>
In this example, you would type “ping” at the system prompt
exactly as shown, followed by the IP address of the system to
which ICMP echo packets are to be sent. Do not type the
angle brackets.
In the command syntax, items enclosed in brackets are
optional. Do not type the brackets.
In the command examples, single items within curled braces
and separated by a vertical bar represent the available
choices. Enter only one choice. Do not type the braces or
bars.
{ap-name <ap-name>}|{ipaddr <ipaddr>}
Two items within curled braces indicate that both parameters
must be entered together. If two or more sets of curled
braces are separated by a vertical bar, like in the example to
the left, enter only one choice. Do not type the braces or bars.
The following informational icons are used throughout this guide:
Indicates helpful suggestions, pertinent information, and important things to remember.
Indicates a risk of damage to your hardwareor loss of data.
Indicates a risk of personal injury or death.
4 | About this Guide Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Contacting Dell
Table 2: Support Information
Support
Main Website dell.com
Contact Information dell.com/contactdell
Support Website dell.com/support
Documentation Website
dell.com/support/manuals
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide About this Guide | 5

What is New in Instant 6.4.0.2-4.1.1
This section lists the new and modified commands in the Instant 6.4.0.2-4.1.1 release.
New Commands
There are no new commands introduced in this release.
Modified Commands
The following commands are modified in the Instant 6.4.0.2-4.1.1 release:
Table 3: Modified Commands in 6.4.0.2-4.1.1
Command Description
wlan ssid-profile This command now enables configuring an accounting server for the specified SSID to
perform accounting functions.
show dpi-stats This command now enables the W-IAP to display the DPIstatistics for the last 15 minutes
of the SSID to which it is connected in the network.
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide

Chapter 2
Instant CLI
Instant supports the use of Command Line Interface (CLI) for scripting purposes. You can access the Instant
CLI through a Secure Shell (SSH).
To enable the SSH access to the Instant CLI:
1. From the Instant UI, navigate to System > Show advanced options.
2. Select Enabled from the Terminal access drop-down list.
3. Click OK.
Connecting to a CLI Session
On connecting to a CLI session, the system displays its host name followed by the login prompt. Use the
administrator credentials to start a CLI session. For example:
(Instant AP)
User: admin
Password: *****
If the login is successful, the privileged command mode is enabled and a command prompt is displayed. For
example:
(Instant AP)#
The privileged mode provides access to show, clear, ping, traceroute, and commit commands. The
configuration commands are available in the configuration (config) mode. To move from privileged mode to
the configuration mode, enter the following command at the command prompt:
(Instant AP)# configure terminal
The configure terminal command allows you to enter the basic configuration mode and the command prompt
is displayed as follows:
(Instant AP)(config)#
The Instant CLI allows CLI scripting in several other sub-command modes to allow the users to configure
individual interfaces, SSIDs, access rules, and security settings.
You can use the question mark (?) to view the commands available in a privileged mode, configuration mode, or
sub-mode.
Although automatic completion is supported for some commands such as configure terminal, the
complete exit and end commands must be entered at command prompt for successful execution.
Applying Configuration Changes
Each command processed by the Virtual Controller is applied on all the slave W-IAPs in a cluster. When you
make configuration changes on a master W-IAP in the CLI, all associated W-IAPs in the cluster inherit these
changes and subsequently update their configurations. The changes configured in a CLI session are saved in
the CLI context.
The CLI does not support the configuration data exceeding the 4K buffer size in a CLI session: therefore, it is
recommended that you configure fewer changes at a time and apply the changes at regular intervals.
To apply and save the configuration changes at regular intervals, use the following command in the privileged
mode:
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide Instant CLI | 7

(Instant AP)# commit apply
To apply the configuration changes to the cluster, without saving the configuration, use the following
command in the privileged mode:
(Instant AP)# commit apply no-save
To view the changes that are yet to be applied, use the following command in the privileged mode:
(Instant AP)# show uncommitted-config
To revert to the earlier configuration, use the following command in the privileged mode.
(Instant AP)# commit revert
Example:
(Instant AP)(config)# rf dot11a-radio-profile
(Instant AP)(RF dot11a Radio Profile)# beacon-interval 200
(Instant AP)(RF dot11a Radio Profile)# no legacy-mode
(Instant AP)(RF dot11a Radio Profile)# dot11h
(Instant AP)(RF dot11a Radio Profile)# interference-immunity 3
(Instant AP)(RF dot11a Radio Profile)# csa-count 2
(Instant AP)(RF dot11a Radio Profile)# spectrum-monitor
(Instant AP)(RF dot11a Radio Profile)# end
(Instant AP)# show uncommitted-config
rf dot11a-radio-profile
no legacy-mode
beacon-interval 200
no dot11h
interference-immunity 3
csa-count 1
no spectrum-monitor
Instant Access Point# commit apply
Configuration Sub-modes
Some commands in configuration mode allow you to enter into a sub-mode to configure the commands
specific to that mode. When you are in a configuration sub-mode, the command prompt changes to indicate
the current sub-mode.
You can exit a sub-command mode and return to the basic configuration mode or the privileged Exec (enable)
mode at any time by executing the exit or end command.
Deleting Configuration Settings
Use the no command to delete or negate previously-entered configurations or parameters.
l To view a list of no commands, type no at the prompt in the relevant mode or sub-mode followed by the
question mark. For example:
(Instant AP)(config) # no?
l To delete a configuration, use the no form of a configuration command. For example, the following
command removes a configured user role:
(Instant AP)(config) # no user <username>
l To negate a specific configured parameter, use the no parameter within the command. For example, the
following command deletes the PPPoE user configuration settings:
(Instant AP)(config) # pppoe-uplink-profile
(Instant AP)(pppoe_uplink_profile)# no pppoe-username
8 | Instant CLI Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide

Using Sequence Sensitive Commands
The Instant CLI does not support positioning or precedence of sequence-sensitive commands. Therefore, it is
recommended that you remove the existing configuration before adding or modifying the configuration
details for sequence-sensitive commands. You can either delete an existing profile or remove a specific
configuration by using the no… commands.
The following table lists the sequence-sensitive commands and the corresponding no command to remove the
configuration.
Table 4: Sequence-Sensitive Commands
Sequence-Sensitive Command Corresponding no command
opendns <username <password> no opendns
rule <dest> <mask> <match> <protocol> <start-port>
<end-port> {permit |deny | src-nat | dst-nat {<IPaddress> <port>| <port>}}[<option1…option9>]
mgmt-auth-server <auth-profile-name>
set-role <attribute>{{equals| not-equals| startswith| ends-with| contains} <operator> <role>| valueof}
set-vlan <attribute>{{equals| not-equals| startswith| ends-with| contains} <operator> <VLAN-ID>|
value-of}
auth-server <name> no auth-server <name>
no rule <dest> <:mask> <match>
<protocol> <start-port> <end-port>
{permit | deny | src-nat | dst-nat}
no mgmt-auth-server <auth-profilename>
no set-role <attribute>{{equals|
not-equals| starts-with| ends-with|
contains} <operator>| value-of}
no set-role
no set-vlan <attribute>{{equals|
not-equals| starts-with| ends-with|
contains} <operator>| value-of}
no set-vlan
Saving Configuration Changes
The running-config holds the current W-IAP configuration, including all pending changes which are yet to be
saved. To view the running-config of a W-IAP, use the following command:
(Instant AP) # show running-config
When you make configuration changes through the CLI, the changes affect the current running configuration
only. To save your configuration changes, use the following command in the privileged Exec mode:
(Instant AP)# write memory
Commands that Reset the W-IAP
If you use the CLI to modify a currently provisioned radio profile, the changes take place immediately. A reboot
of the W-IAP is not required to apply the configuration changes. Certain commands, however, automatically
force W-IAP to reboot. Verify the current network loads and conditions before executing the commands that
enforce a reboot of the W-IAP, as they may cause a momentary disruption in service as the unit resets.
The reload command resets a W-IAP.
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide Instant CLI | 9

Command Line Editing
The system records your most recently entered commands. You can review the history of your actions, or
reissue a recent command easily, without having to retype it.
To view items in the command history, use the up arrow key to move back through the list and the down arrow
key to move forward. To reissue a specific command, press Enter when the command appears in the
command history. You can also use the command line editing feature to make changes to the command prior
to entering it. The command line editing feature allows you to make corrections or changes to a command
without retyping. The following table lists the editing controls. To use key shortcuts, press and hold the Ctrl
button while you press a letter key.
Table 5:
Line Editing Keys
Key Effect Description
Ctrl A
Ctrl B or the
left arrow
Ctrl D
Ctrl E
Ctrl F or the
right arrow
Ctrl K
Ctrl N or the
down arrow
Ctrl P or
up arrow
Home Move the cursor to the beginning of the line.
Back Move the cursor one character left.
Delete Right Delete the character to the right of the cursor.
End Move the cursor to the end of the line.
Forward Move the cursor one character right.
Delete Right Delete all characters to the right of the cursor.
Next Display the next command in the command
history.
Previous Display the previous command in the command
history.
Ctrl T
Ctrl U
Ctrl W
Ctrl X
10 | Instant CLI Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Transpose Swap the character to the left of the cursor with
the character to the right of the cursor.
Clear Clear the line.
Delete Word Delete the characters from the cursor up to and
including the first space encountered.
Delete Left Delete all characters to the left of the cursor.

Specifying Addresses and Identifiers in Commands
This section describes addresses and other identifiers that you can reference in CLI commands.
Table 6: Addresses and Identifiers
Address/Identifier Description
IP address For any command that requires entry of an IP address to specify a network
entity, use IPv4 network address format in the conventional dotted decimal
notation (for example, 192.0.2.1).
Netmask address For subnet addresses, specify a subnet mask in dotted decimal notation (for
example, 255.255.255.0).
Media Access Control
(MAC) address
Service Set Identifier
(SSID)
Basic Service Set
Identifier (BSSID)
Extended Service Set
Identifier (ESSID)
For any command that requires entry of a device’s hardware address, use the
hexadecimal format (for example, 00:05:4e:50:14:aa).
A unique character string (sometimes referred to as a network name),
consisting of no more than 32 characters. The SSID is case-sensitive (for
example, WLAN-01).
This entry is the unique hard-wireless MAC address of the AP. A unique BSSID
applies to each frequency— 802.11a and 802.11g—used from the AP. Use the
same format as for a MAC address.
Typically the unique logical name of a wireless network. If the ESSID includes
spaces, enclose the name in quotation marks.
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
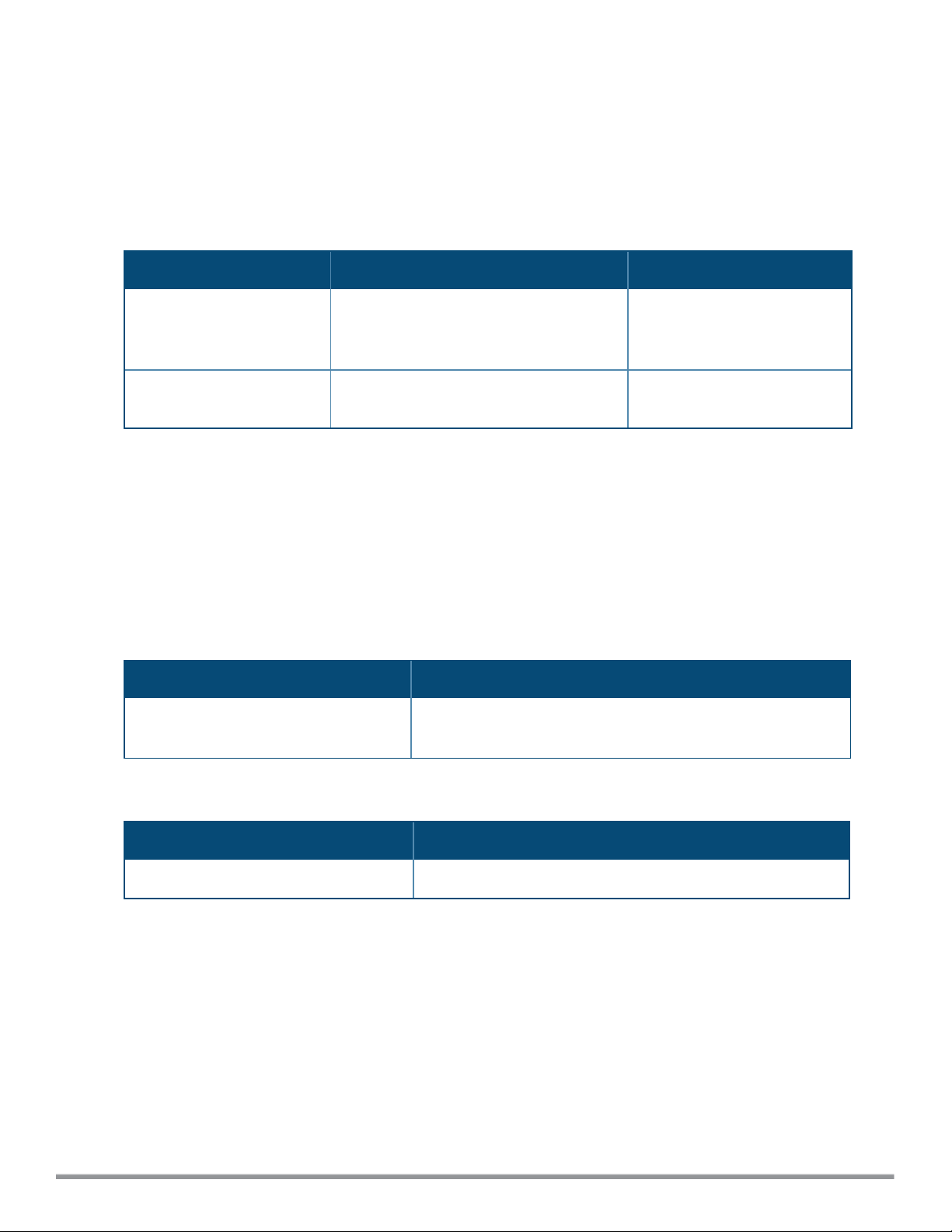
a-channel
a-channel <channel> <tx-power>
Description
This command configures 5 GHz radio channels for a specific W-IAP.
Syntax
Parameter Description Range
<channel>
<tx-power>
Configures the specified 5 GHz channel.
Configures the specified transmission
power values.
The valid channels for a band
are determined by the AP
regulatory domain.
0-127 dBm
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to configure radio channels for the 5 GHz band for a specific W-IAP.
Example
The following example configures the 5 GHz radio channel:
(Instant AP)# a-channel 44 18
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-
3.3
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Privileged EXEC mode
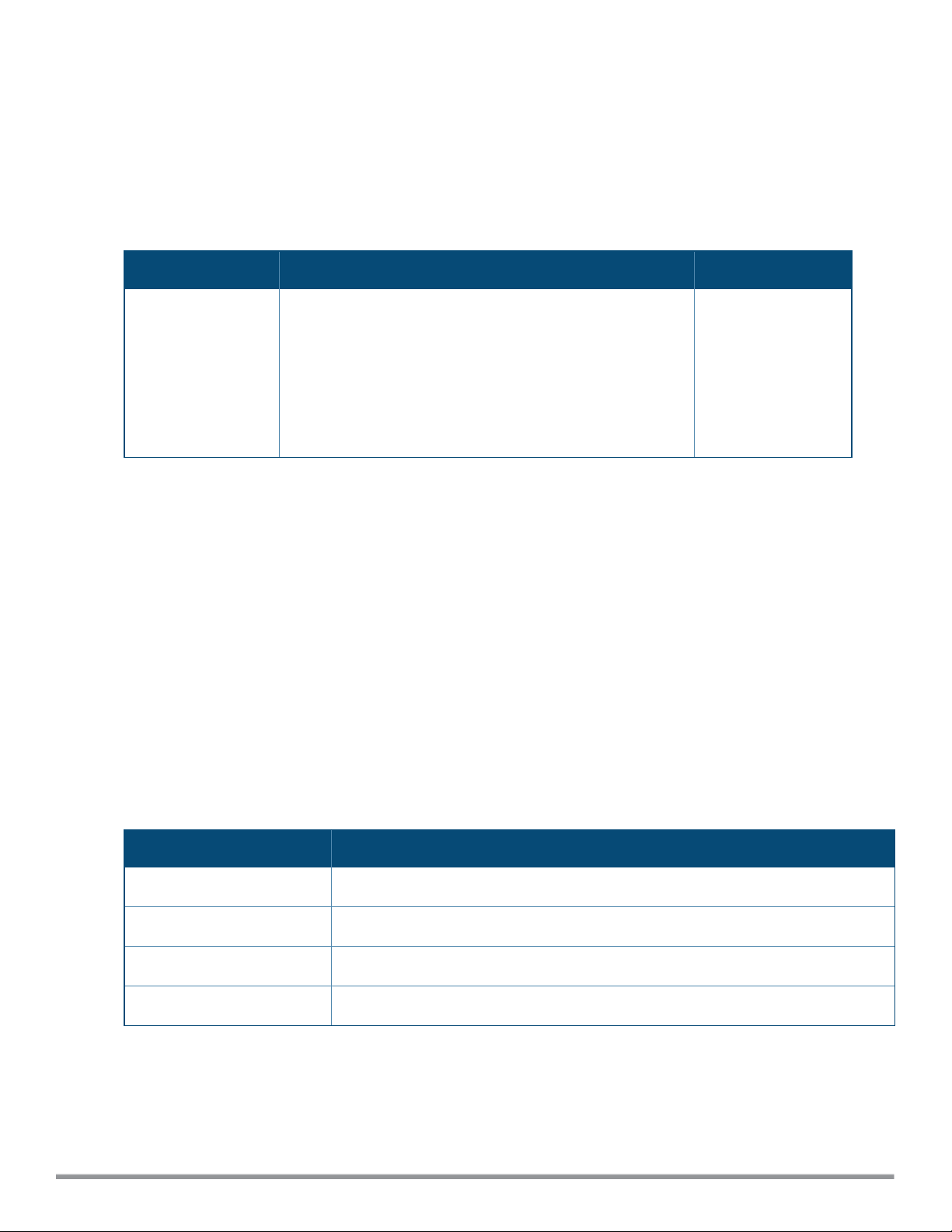
a-external-antenna
a-external-antenna <gain>
Description
This command configures external antenna connectors for a W-IAP.
Syntax
Parameter Description Range
<gain>
Configures the antenna gain. You can configure a gain value
in dBi for the following types of antenna:
l Dipole/Omni
l Panel
l Sector
Diploe/Omni - 6
Panel -14
Sector - 14
Usage Guidelines
If your W-IAP has external antenna connectors, you need to configure the transmit power of the system. The
configuration must ensure that the system’s Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power (EIRP) is in compliance
with the limit specified by the regulatory authority of the country in which the W-IAP is deployed. You can also
measure or calculate additional attenuation between the device and antenna before configuring the antenna
gain. To know if your AP device supports external antenna connectors, see the Install Guide that is shipped
along with the AP device.
EIRP and Antenna Gain
The following formula can be used to calculate the EIRP limit related RF power based on selected antennas
(antenna gain) and feeder (Coaxial Cable loss):
EIRP = Tx RF Power (dBm)+GA (dB) - FL (dB)
The following table describes this formula:
Table 7: Formula Variable Definitions
Formula Element Description
EIRP Limit specific for each country of deployment
Tx RF Power RF power measured at RF connector of the unit
GA Antenna gain
FL Feeder loss
For information on antenna gain recommended by the manufacturer, see dell.com/support.
Example
The following example configures external antenna connectors for the W-IAP with the 5 GHz radio band.
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide

(Instant AP)# a-external-antenna 14
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-
3.3
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
Privileged EXEC mode
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide

aaa test-server
aaa test-server <servername> <username>
Description
This command tests a configured authentication server.
Syntax
Parameter Description
<servername>
<username>
Allows you to specify the authentication server for which the authentication
test is run.
Allows you to specify the user name for which the authentication test is run.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to view the CPU load for application and system processes. This command allows you to
verify a configured RADIUS authentication server or the internal database. You can use this command to check
for an “out of service” RADIUS server.
Example
The following example shows the output of the aaa test-server command:
Authentication is successful
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series
Instant 6.2.1.0-3.3
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Privileged EXEC mode
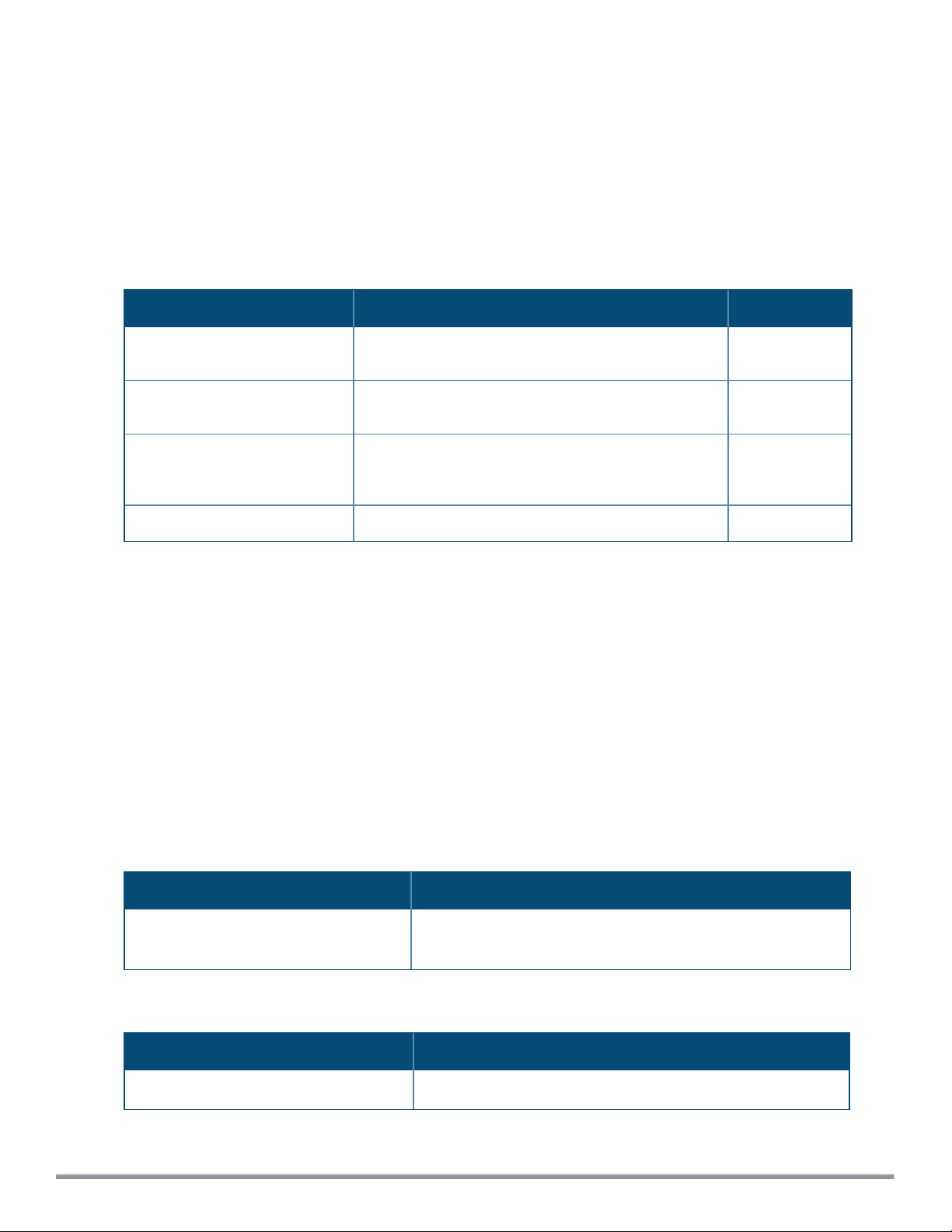
aeroscout-rtls
aeroscout-rtls <IP-address> <Port> [include-unassoc-sta]
no...
Description
This command configures the Aeroscout Real-Time Asset Location Server (RTLS) settings for Instant and sends
the Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tag information to an Aeroscout RTLS server.
Syntax
Command/Parameter Description Default
<IP-address>
<Port>
include-unassoc-stas
no
IP address of the Aeroscout RTLS server to which the
location reports are sent.
Port number of the Aeroscout RTLS server to which the
location reports are sent..
Includes the client stations not associated to any W-IAP
when mobile unit reports are sent to the Aeroscout
RTLS server.
Removes the Aeroscout RTLS configuration. —
—
—
Disabled
Usage Guidelines
This command allows you to integrate Aeroscout RTLS server with Instant by specifying the IP address and port
number of the Aeroscout RTLS server. When enabled, the RFID tag information for the stations associated with
a W-IAP are sent to the AeroScout RTLS. You can also send the RFID tag information for the stations that are
not associated with any W-IAP.
Example
The following example configures the Aeroscout RTLS server:
(Instant AP)(config)# aeroscout-rtls 192.0.2.2 3030 include-unassoc-sta
(Instant AP)(config)# end
(Instant AP)# commit apply
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-
3.3
Command was introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode
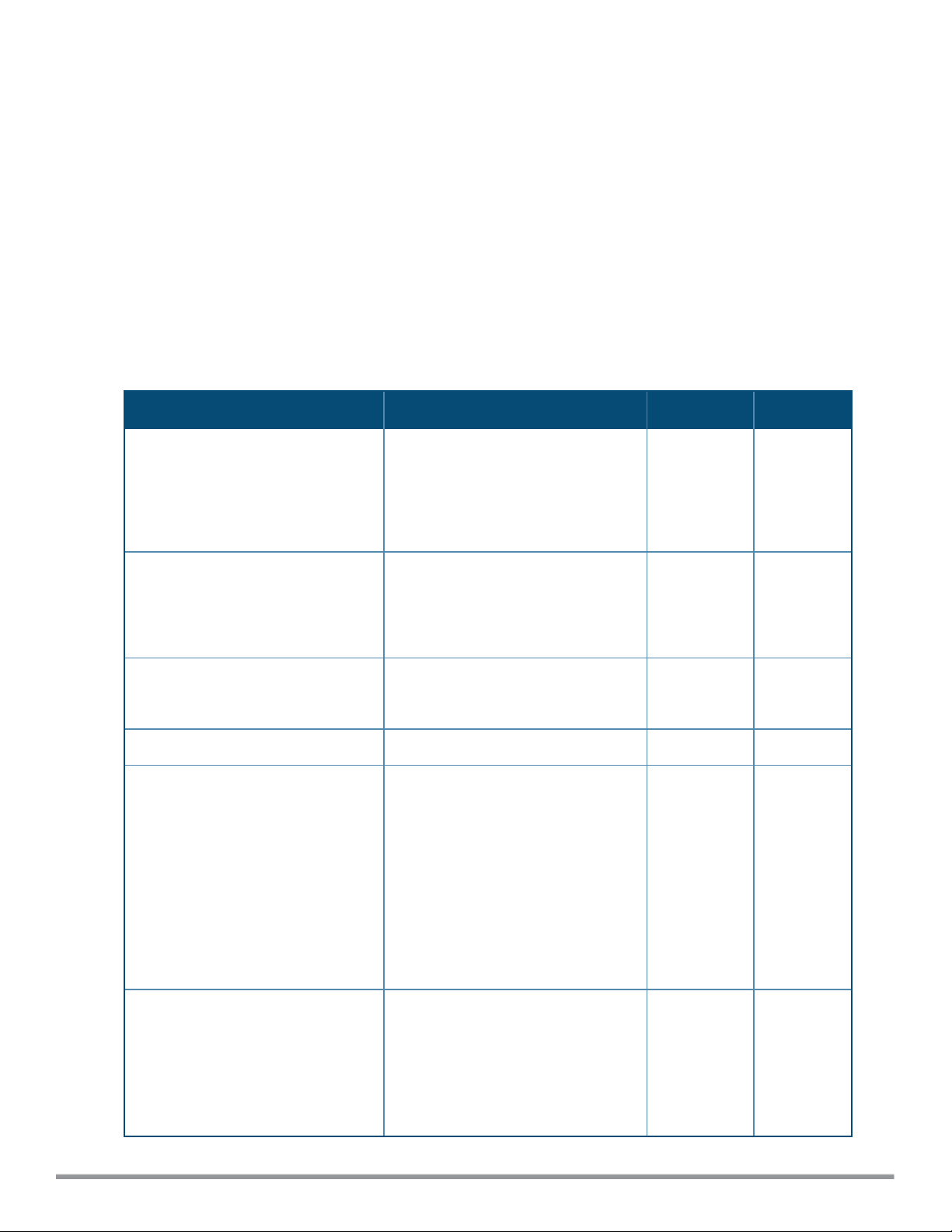
airgroup
airgroup
cppm enforce-registration
cppm-query-interval <interval>
cppm-server <server-name>
disable
enable [dlna-only| mdns-only]
enable-guest-multicast
multi-swarm
no…
Description
This command configures the AirGroup settings on a W-IAP.
Syntax
Parameter Description Range Default
cppm enforce-registration
cppm-query-interval
<interval>
cppm-server <server-name>
disable
enable [dlna-only| mdns-only]
Enforces the discovery of the CPPM
registered devices. When enabled,
only devices registered with CPPM
will be discovered by Bonjour® or
DLNAdevices, based on the CPPM
policy configured.
Configures a time interval at which
Instant sends a query to ClearPass
Policy Manager for mapping the
access privileges of each device to the
available services.
Configures the ClearPass Policy
Manager server information for
AirGroup policy.
Disables the AirGroup feature. — —
Enables the mDNS or DLNAor both.
When dlna-only command is executed
with enable, the DLNA support is
enabled for AirGroup enabled
devices.
— Enabled
1-24 10 hours
— —
— —
When mdns-only command is
executed with enable, the Bonjour
support is enabled for AirGroup
enabled devices.
enable-guest-multicast
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Allows the users to use the Bonjour or
DLNAservices enabled in a guest
VLAN. When enabled, the Bonjour or
DLNAdevices will be visible only in
the guest VLAN and AirGroup will not
discover or enforce policies in guest
— —
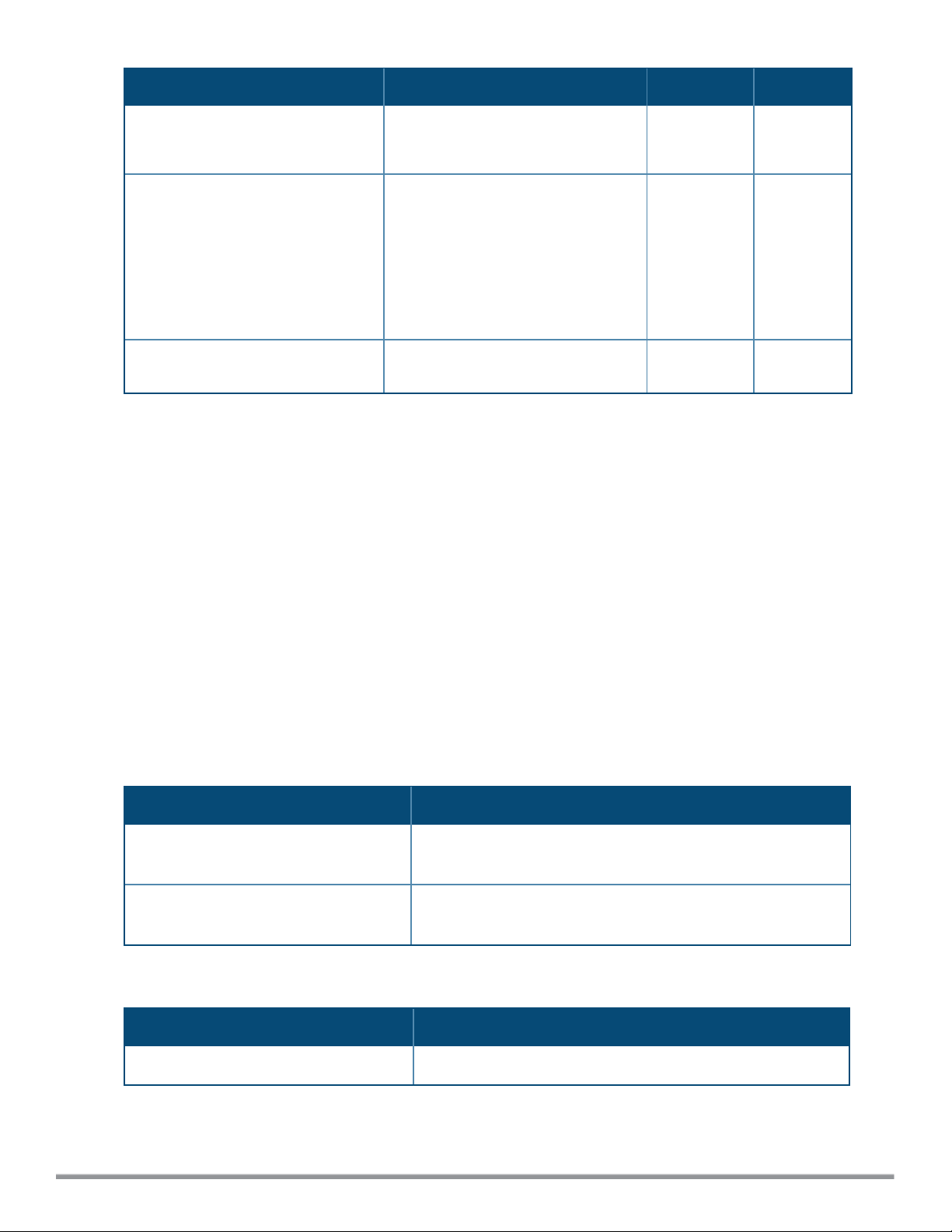
Parameter Description Range Default
VLAN.
multi-swarm
no…
Enables inter cluster mobility. When
enabled, the W-IAP shares the mDNS
database information with the other
clusters. The AirGroup records in the
Virtual Controller can be shared with
all the Virtual Controllers specified for
L3 Mobility.
Removes the specified configuration
parameter.
— Disabled
— —
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to configure the AirGroup, the availability of the AirGroup services, and ClearPass Policy
Manager (CPPM) servers.
Example
The following example configures an AirGroup profile:
(Instant AP)(config)# airgroup
(Instant AP)(airgroup)# enable
(Instant AP)(airgroup)# cppm enforce-registration
(Instant AP)(airgroup)# cppm-server Test
(Instant AP)(airgroup)# cppm-query-interval 10
(Instant AP)(airgroup)# enable-guest-multicast
(Instant AP)(airgroup)# multi-swarm
(Instant AP)(airgroup)# end
(Instant AP)# commit apply
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.0.2-
4.1
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-
3.3
This command is modified.
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode and AirGroup configuration sub-mode.
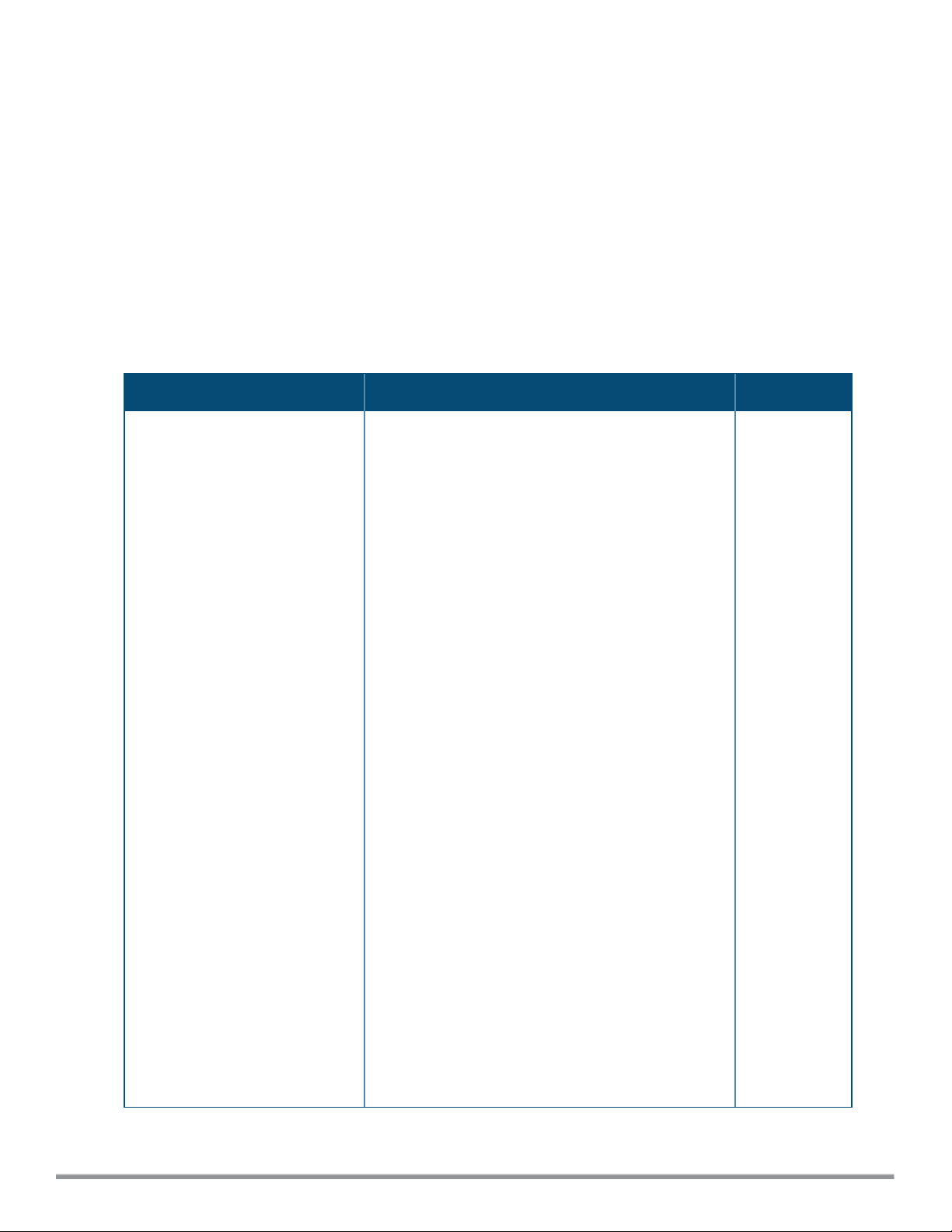
airgroupservice
airgroupservice <airgroupservice>
description <description>
disable
disallow-role <role>
disallow-vlan <VLAN-ID>
enable
id <AirGroupservice-ID>
no…
Description
This command configures the availability of AirGroup services for the W-IAP clients.
Syntax
Parameter Description Default
<airgroupservice>
Specifies the AirGroup service to configure.
The following pre-configured services are available
for W-IAP clients:
l AirPlay™— Apple® AirPlay allows wireless
streaming of music, video, and slideshows from
your iOS device to Apple TV® and other devices
that support the AirPlay feature.
l AirPrint™— Apple® AirPrint allows you to print
from an iPad®, iPhone®, or iPod® Touch directly
to any AirPrint compatible printers.
l iTunes— iTunes service is used by iTunes Wi-Fi
sync and iTunes home-sharing applications across
all Apple® devices.
l RemoteMgmt— Use this service for remote login,
remote management, and FTP utilities on Apple®
devices.
l Sharing— Applications such as disk sharing and
file sharing, use the service ID that are part of this
service on one or more Apple® devices.
l Chat— The iChat® (Instant Messenger)
application on Apple® devices uses this service.
l ChromeCast—ChromeCast service allows you to
use a ChromeCast device to play audio or video
content on a high definition television by
streaming content through Wi-Fi from the Internet
or local network.
l DLNAMedia—Applications such as Windows
Media Player use this service to browse and play
media content on a remote device.
l DLNAPrint—This service is used by printers that
support DLNA.
—
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Parameter Description Default
You can allow all services or add custom services. Up
to 10 services can be configured on a W-IAP.
description <description>
disable
disallow-role <role>
disallow-vlan <VLAN-ID>
enable
id <airgroupserviceid>
no…
Adds a description to the AirGroup service profile. —
Disables AirGroup services for the profile. —
Restricts the user roles specified for role from
accessing the AirGroup service.
Restricts the AirGroup servers connected on the
specified VLANs from being discovered.
Enables the AirGroup service for the profile. —
Allows you to specify the AirGroup service ID
corresponding to the service that you are trying to
configure.
NOTE: The service IDs cannot be added for the preconfigured services.
Removes the AirGroup service configuration. —
Disabled
Disabled
—
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to enforce AirGroup service policies and define the availability of a services for an AirGroup
profile. When configuring AirGroup service for an AirGroup profile, you can also restrict specific user roles and
VLANs from availing the AirGroup services.
Example
The following example configures AirGroup services:
(Instant AP)(config)# airgroupservice AirPlay
(Instant AP)(airgroup-service)# description AirPlay Service
(Instant AP)(airgroup-service)# disallow-role guest
(Instant AP)(airgroup-service)# disallow-vlan 200
(Instant AP)(airgroup-service)# end
(Instant AP)# commit apply
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.0.2-
4.1
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.3.1.1-
4.0
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-
3.3
This command is modified.
This command is modified.
This command is introduced.
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide

Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
Configuration mode and AirGroup services configuration submode.
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide

airwave-rtls
airwave-rtls <IP-address> <Port> <key> <frequency> [include-unassoc-sta]
no…
Description
This command integrates W-AirWave Real-Time Asset Location Server (RTLS) settings for Instant and sends the
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tag information to a W-AirWave RTLS server with the RTLS feed to
accurately locate the wireless clients.
Syntax
Command/Parameter Description Default
<IP-address>
<Port>
<key>
<frequency>
include-unassoc-sta
no…
Configures the IP address of the W-AirWave RTLS
server.
Configures the port for the W-AirWave RTLS server. —
Configures key for service authorization. —
Configures the frequency at which packets are sent to
the RTLS server in seconds.
When enabled, this option sends mobile unit reports to
the W-AirWave RTLS server for the client stations that
are not associated to any W-IAP (unassociated
stations).
Removes the specified configuration parameter. —
—
5
Disabled
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to send the RFID tag information to W-AirWave RTLS. Specify the IP address and port
number of the W-AirWave server, to which the location reports must be sent. You can also send reports of the
unassociated clients to the RTLS server for tracking purposes.
Example
The following command enables W-AirWave RTLS:
(Instant AP)(config) # airwave-rtls ams-ip 192.0.2.3 3030 pass@1234 5 include-unassoc-sta
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-3.3
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode
ale-report-interval
ale-report-interval <seconds>
no…
Description
This command configures the interval at which a W-IAP sends data to the Analytics and Location Engine (ALE)
server.
Syntax
Command/Parameter Description
ale-report-interval
<seconds>
no…
Configures an interval at which the
Virtual Controller can report the W-IAP
and client details to the ALE server.
Removes the specified configuration
parameter.
Range Default
6–60 seconds 30
— —
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to specify an interval for W-IAP and ALE server communication.
Example
The following example configures the ALE server details:
(Instant AP)(config)# ale-report-interval 60
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.3.1.1-4.0
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode
ale-server
ale-server <server>
no…
Description
This command configures Analytics and Location Engine (ALE) server details for W-IAP integration with ALE.
Syntax
Command/Parameter Description
ale-server <server>
no…
Allows you to specify the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or IP
address of the ALE server.
Removes the specified configuration parameter.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to enable a W-IAP for ALE support.
Example
The following example configures the ALE server details:
(Instant AP)(config)# ale-server AleServer1
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.3.1.1-4.0
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode.
alg
alg
sccp-disable
sip-disable
vocera-disable
no…
Description
This command allows you to modify the configuration settings for Application Layer Gateway (ALG) protocols
enabled on a W-IAP. An application-level gateway consists of a security component that augments a firewall or
NAT used in a network.
Syntax
Command/Parameter Description Default
sccp-disable
sip-disable
vocera-disable
no…
Disables the Skinny Call Control Protocol (SCCP). Enabled
Disables the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for VOIP
and other text and multimedia sessions.
Disables the VOCERA protocol. Enabled
Removes the specified configuration parameter.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to functions such as SIP, Vocera, and Cisco Skinny protocols for ALG.
Example
The following example configures the ALG protocols:
(Instant AP)(config)# alg
(Instant AP)(ALG)# sccp-disable
(Instant AP)(ALG)# no sip-disable
(Instant AP)(ALG)# no vocera-disable
(Instant AP)(ALG)# end
(Instant AP)# commit apply
Command History
Enabled
—
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-3.3
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode and ALG configuration sub-mode.

allow-new-aps
allow-new-aps
no…
Description
This command allows the new access points to join the W-IAP cluster.
Syntax
Command/Parameter Description
allow-new-aps
no
Allows new access points in the domain.
Removes the specified configuration parameter.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to allow the new access points to join the W-IAP cluster.
Example
The following command allows the new W-IAPs to join the cluster.
(Instant AP)(config)# allow-new-aps
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-3.3
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode
allowed-ap
allowed-ap <MAC-address>
no…
Description
This command allows an AP to join the W-IAP cluster.
Syntax
Command/Parameter Description
allowed-ap <MAC-address>
no…
Specifies the MACaddress of the W-IAP that is allowed to join the
cluster.
Removes the specified configuration parameter.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to allow a W-IAP to join the cluster.
Example
The following command configures an allowed W-IAP:
(Instant AP)(config)# allowed-ap 01:23:45:67:89:AB
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-3.3
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode

ams-backup-ip
ams-backup-ip <IP-address or domain name>
no…
Description
This command adds the IP address or domain name of the backup W-AirWave Management server.
Syntax
Parameter Description
<IP-address or domain
name>
no…
Configures the IP address or domain name of the secondary W-AirWave
Management Server.
Removes the specified configuration parameter.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to add the IP address or domain name of the backup W-AirWave Management Server. The
backup server provides connectivity when the W-AirWave primary server is down. If the W-IAP cannot send
data to the primary server, the Virtual Controller switches to the backup server automatically.
Example
The following command configures a W-AirWave backup server.
(Instant AP)(config)# ams-backup-ip 192.0.2.1
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-3.3
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode
ams-identity
ams-identity <Name>
Description
This command uniquely identifies the group of W-IAPs managed or monitored by the W-AirWave Management
console. The name can be a location, vendor, department, or any other identifier.
Syntax
Parameter Description
ams-identity <Name>
Configures a name that uniquely identifies the W-IAP on the WAirWave Management server. The name defined for this command
will be displayed under the Groups tab in the W-AirWave user
interface.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to assign an identity for the W-IAPs monitored or managed by the W-AirWave Management
Server.
Example
The following command configures a W-AirWave identifier:
(Instant AP)(config)# ams-identity dell
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-
3.3
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode
ams-ip
ams-ip <IP-address or domain name>
no…
Description
This command configures the IP address or domain name of the W-AirWave Management console for a W-IAP.
Syntax
Parameter Description
<IP-address or domain name>
Configures the IP address or domain name of anW-AirWave
Management server for a W-IAP.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to configure the IP address or domain name of the AMS console for a W-IAP.
Example
The following command configures the W-AirWave Server.
(Instant AP)(config)# ams-ip 192.0.1.2
Command History
Version Description
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.2.1.0-
3.3
This command is introduced.
Command Information
W-IAP Platform Command Mode
All platforms
0511587-03 | September 2014 Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.4.2.0-4.1.1 | CLI Reference Guide
Configuration mode
 Loading...
Loading...