Page 1

Dell™ PowerVault™ MD3000 Storage
®
Arrays With Microsoft
®
Server
Failover Clusters
Windows
Hardware Installation and
Troubleshooting Guide
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Page 2

Notes, Notices, and Cautions
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of
your computer.
NOTICE: A NOTICE indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data
and tells you how to avoid the problem.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury,
or death.
____________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
©2008 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo, PowerEdge, PowerVault, and OpenManage are
trademarks of Dell Inc.; Microsoft, SQL Server ,Windows, and Windows NT are either trademarks or
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming
the marks and names or their products. Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and
trade names other than its own.
April 2008 Rev. A00
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Additional Information
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Cluster Solution With Dell PowerVault
MD3000 Storage Array
Cluster Hardware Requirements
Cluster Storage
Cluster Storage Management Software
Supported Dell Cluster Configurations
Other Documents You May Need
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
. . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2 Cabling Your Cluster Hardware . . . . . . . . 17
Cabling the Mouse, Keyboard, and Monitor . . . . . . 17
Cabling the Power Supplies
Cabling Your Public and Private Networks
Cabling Your Public Network
Cabling Your Private Network
Using Dual-Port Network Adapters for
Your Private Network
NIC Teaming
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
. . . . . . . 20
. . . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Contents 3
Page 4

Cabling the Storage Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Cabling the Cluster in a Non-Redundant
Configuration
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Cabling the Cluster in Redundant
Configuration With Single SAS 5/E HBAs
Cabling the Cluster in Redundant
Configuration With Dual SAS 5/E HBAs
3 Preparing Your Systems for
Clustering
Cluster Configuration Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
. . . . . . 25
. . . . . . 27
Installing the Operating System
Additional Information
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Installing the SAS 5/E HBAs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Installing the SAS 5/E HBA Drivers
. . . . . . . . . 34
Installing and Configuring the Storage
Management Software
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Adding Storage Arrays to the
Failover Cluster
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Installing and Configuring the Shared
Storage System
Setting Up Your Storage Array
Configuring Host Access
Creating a Host Group
Creating Disk Groups and Virtual Disks
Creating Host-to-Virtual Disk Mappings
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
. . . . . . . . . . . 36
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
. . . . . . . 38
. . . . . . 39
Loading RAID Controller Module NVSRAM
for Non-Redundant Configuration
. . . . . . . . . 40
4 Contents
Page 5

Troubleshooting Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Windows Operating System and
Dynamic Volumes
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Configuring the RAID Level for the
Shared Storage Subsystem
Assigning Drive Letters and Mount Points
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
. . . . . 42
Naming and Formatting Drives on
the Shared Storage System
. . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Using Advanced (Premium) PowerVault
Modular Disk Storage Manager Features
. . . . . 45
Installing and Configuring a Failover Cluster
. . . . . . 48
A Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
B Cluster Data Form
Index
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Contents 5
Page 6

6 Contents
Page 7
Introduction
This guide addresses the configuration of your Dell™ PowerVault™ MD3000
storage array for use with Microsoft
It provides information and specific configuration tasks that enable you to
deploy the shared storage for your cluster.
The guide is intended for experienced IT professionals who configure the
cluster solution and for trained service technicians who perform upgrade and
maintenance procedures. This document also addresses readers who are new
to clustering.
®
Windows Server® failover cluster nodes.
Overview
A Dell failover cluster combines specific hardware and software components
to provide enhanced availability for applications and services that run on the
cluster. A failover cluster is designed to reduce the possibility of any single
point of failure within the system that can cause the clustered applications or
services to become unavailable.
NOTE: It is recommended that you use redundant components like server and
storage power supplies, connections between the nodes and the storage array(s),
and connections to client systems or other servers in a multi-tier enterprise
application architecture in your cluster.
Additional Information
• For more information on deploying your cluster with Windows Server
2003 operating systems, see the
Windows Server 2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide
Support website at
• For more information on deploying your cluster with Windows Server
2008 operating systems, see the
Windows Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide
Support website at
support.dell.com
support.dell.com
Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft
on the Dell
.
Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft
on the Dell
.
Introduction 7
Page 8

• For a list of recommended operating systems, hardware components, and
driver or firmware versions for your failover cluster, see the
Configuration Support Matrices
website at
www.dell.com/ha
on the Dell High Availability Clustering
.
Dell Cluster
Cluster Solution With Dell PowerVault MD3000 Storage Array
The cluster solution implements a two-node clustering technology based on
the Microsoft Cluster Server software (MSCS) incorporated within the
Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2008 operating systems. This
cluster solution provides the following features:
• 3 Gbps Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) technology
• High availability of system services and resources to network clients
• Redundant paths to the shared storage
• Failure recovery for applications and services
• Flexible maintenance capabilities—allowing you to repair, maintain, or
upgrade a cluster node without taking the entire cluster offline
Cluster Hardware Requirements
Your cluster requires the following hardware components:
• Servers (nodes)
• Storage and storage management software
Table 1-1 describes the hardware requirements for your cluster nodes.
Table 1-1. Cluster Node Requirements
Component Minimum Requirement
Processor At least one processor for each cluster node.
RAM At least 256 MB RAM installed on each cluster node for
Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition.
At least 512 MB RAM installed on each cluster node for
Windows Server 2003 Enterprise x64 Edition and Windows
Server 2008 x64 Edition.
8 Introduction
Page 9

Table 1-1. Cluster Node Requirements (continued)
Component Minimum Requirement
Cluster Nodes A minimum of two identical Dell™PowerEdge™ servers are
required.
The maximum number of nodes supported in both the
Windows Server 2003 and the Windows Server 2008
operating system is two.
Host Bus Adapter
(HBA)
Network Interface
Cards (NICs)
One or two SAS 5/E HBAs for each cluster node.
At least two NICs: one NIC for the public network and
another NIC for the private network.
NOTE: It is recommended that the NICs on each public
network are identical and that the NICs on each private
network are identical.
Internal Disk
Controller
One controller connected to internal disks for each node. Use
any supported Redundant Array of Independent Disk
(RAID) controller or disk controller.
Two physical disks are required for mirroring (RAID 1) and at
least three are required for disk striping with parity (RAID 5).
NOTE: It is strongly recommended that you use
hardware-based RAID or software-based disk-fault tolerance
for the internal drives.
Cluster Storage
Table 1-2 provides the configuration requirements for the shared storage
system.
Table 1-2. Cluster Storage Requirements
Hardware
Components
Supported storage
systems
Power and cooling
requirements
Minimum Requirement
One PowerVault MD3000 RAID enclosure.
Up to two PowerVault MD1000 expansion enclosures.
Two integrated hot-pluggable power supply/cooling fan
modules.
Introduction 9
Page 10

Table 1-2. Cluster Storage Requirements (continued)
Hardware
Components
Physical disks At least two physical disks in the PowerVault MD3000 RAID
Cables Two 1-m, 2-m, or 4-m SAS cables for the non-redundant
NOTE: You can configure RAID 0 or independent disks, however such a
configuration is not recommended for a high-availability system as it does not offer
data redundancy if a disk failure occurs.
NOTE: The PowerVault MD3000 Storage Array with the Dell Failover Cluster does
not support sharing a PowerVault MD3000 RAID enclosure with other clustered or
stand-alone servers.
Minimum Requirement
enclosure.
configuration.
Four 1-m, 2-m, or 4-m SAS cables for the redundant
configuration.
Two 1-m, 2-m, or 4-m SAS cables for each additional
PowerVault MD1000 expansion enclosure.
Cluster Storage Management Software
The following sections describe various cluster storage management software
that you can install and configure on your cluster.
Dell PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager Client
The Modular Disk Storage Manager Client runs on the management station
to centrally manage the PowerVault MD3000 RAID enclosure. You can use
PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager to perform tasks such as creating
or managing RAID arrays, binding virtual disks, and downloading firmware.
Dell PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager Agent
The Modular Disk Storage Manager Agent resides on each cluster node and
collects server-based topology data that can be managed by the Modular Disk
Storage Manager Client.
10 Introduction
Page 11

Multi-Path Software
Multi-path software (also referred to as the failover driver) is a software
resident on each cluster node that provides management of the redundant
data path between the server and the RAID enclosure. For the multi-path
software to correctly manage a redundant path, the configuration must
provide for redundant HBAs and cabling.
The multi-path software identifies the existence of multiple paths to a virtual
disk and establishes a preferred path to that disk. If any component in the
preferred path fails, the multi-path software automatically re-routes I/O
requests to the alternate path so that the storage array continues to operate
without interruption.
In a redundant cluster configuration, the Automatic Failback feature is
disabled by default. Therefore, when a failed component is repaired or
replaced, the virtual disk(s) do not automatically transfer to the preferred
controller. You can manually initiate a failback using the Modular Disk
Storage Manager Client or Command Line Interface (CLI).
Advanced Features
Advanced features for the PowerVault MD3000 RAID enclosure include:
• Snapshot Virtual Disk—Captures point-in-time images of a virtual disk for
backup, testing, or data processing without affecting the contents of the
source virtual disk.
• Virtual Disk Copy—Generates a full copy of data from the source virtual
disk to the target virtual disk in a storage array. You can use Virtual Disk
Copy to back up data, copy data from disk groups that use smaller-capacity
physical disks to disk groups using greater capacity physical disks, or restore
snapshot virtual disk data to the source virtual disk.
NOTE: For instructions on deploying the correct Virtual Disk options in the
cluster environment, see "Using Advanced (Premium) PowerVault Modular
Disk Storage Manager Features" on page 45.
NOTE: For more information about Modular Disk Storage Manager, Snapshot
Virtual Disk, and Virtual Disk Copy, see ""Installing and Configuring the Shared
Storage System" on page 36" and your Modular Disk Storage Manager
documentation.
Introduction 11
Page 12
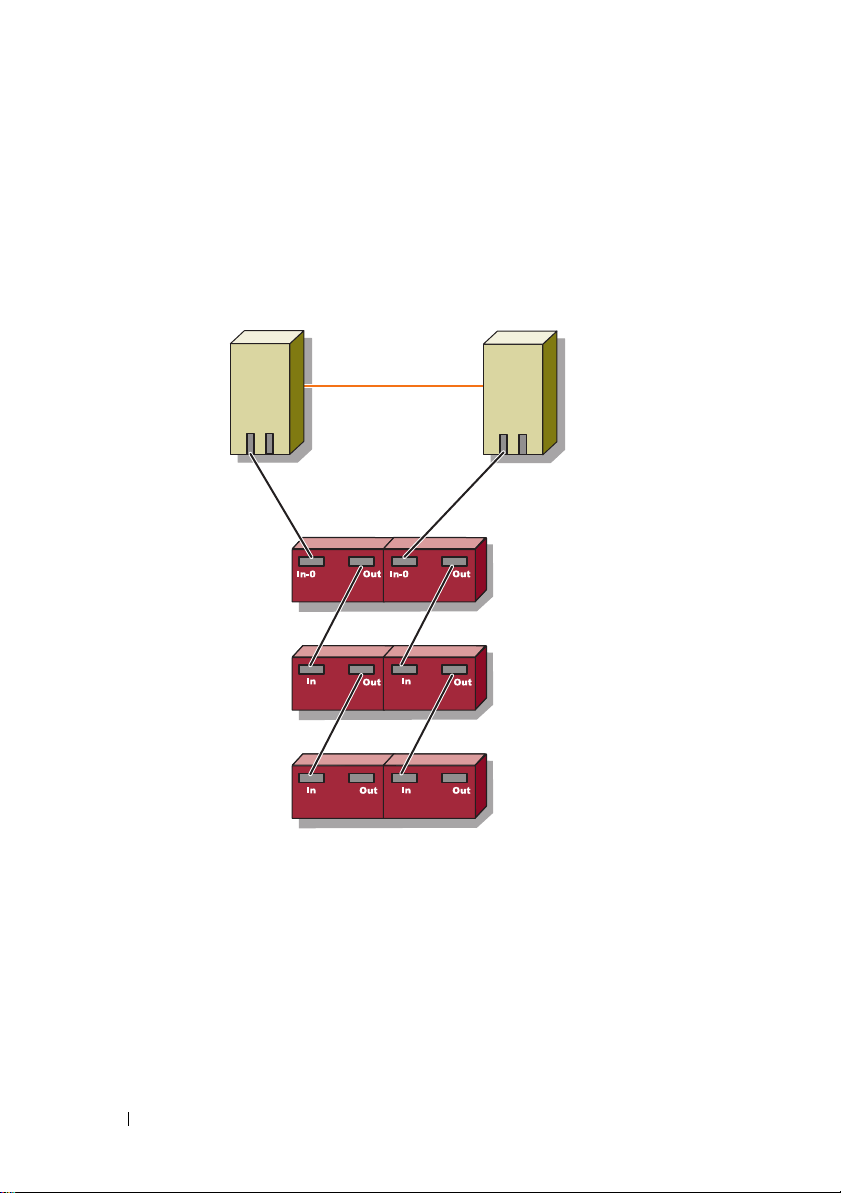
Supported Dell Cluster Configurations
Figure 1-1 to Figure 1-3 illustrate the various supported configurations for
your cluster with PowerVault MD3000 and MD1000 RAID enclosures.
Figure 1-1. Non-Redundant Cluster Configuration
Cluster Node 1
Cluster Node 2
Private Network
PowerVault MD3000 RAID
Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000 RAID
Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000 RAID
Enclosure
12 Introduction
Page 13
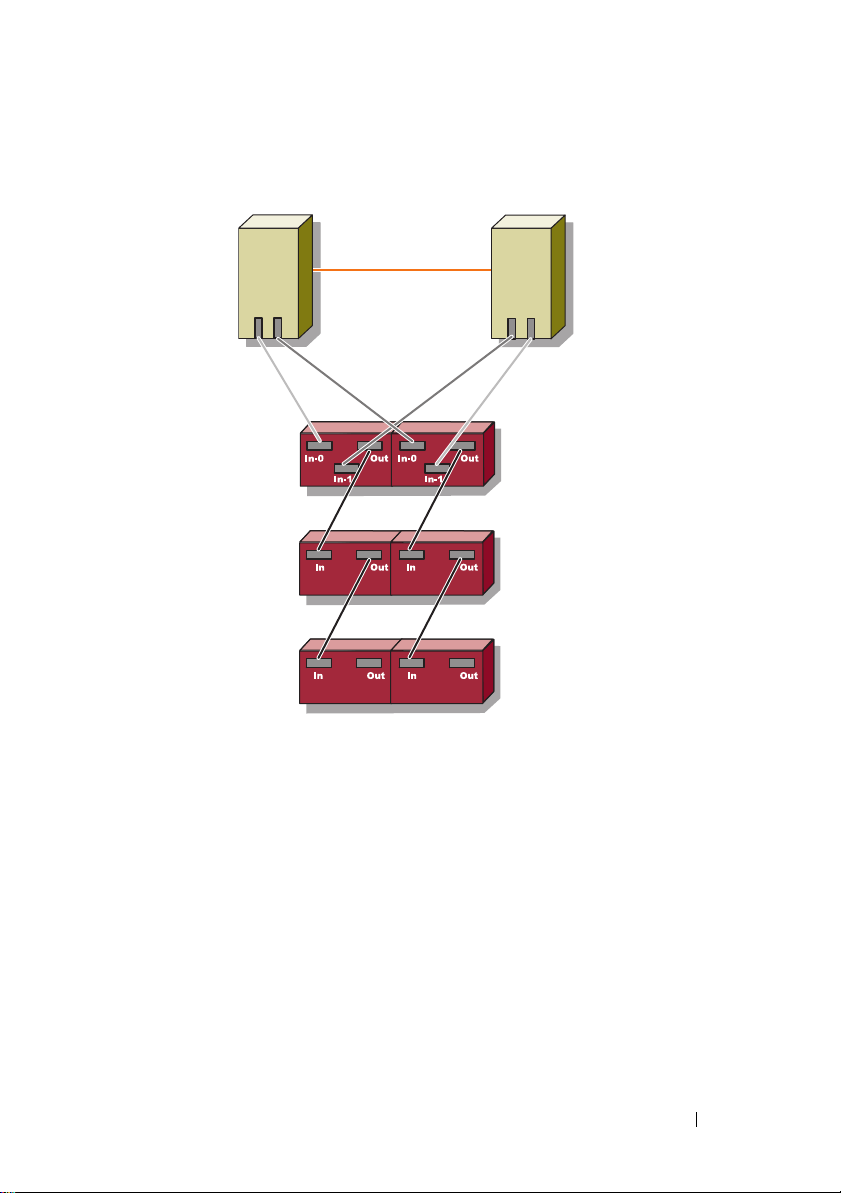
Figure 1-2. Redundant Cluster Configuration With Single SAS 5/E
Cluster Node 1 Cluster Node 2
Private Network
PowerVault MD3000
RAID Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000
RAID Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000
RAID Enclosure
Introduction 13
Page 14
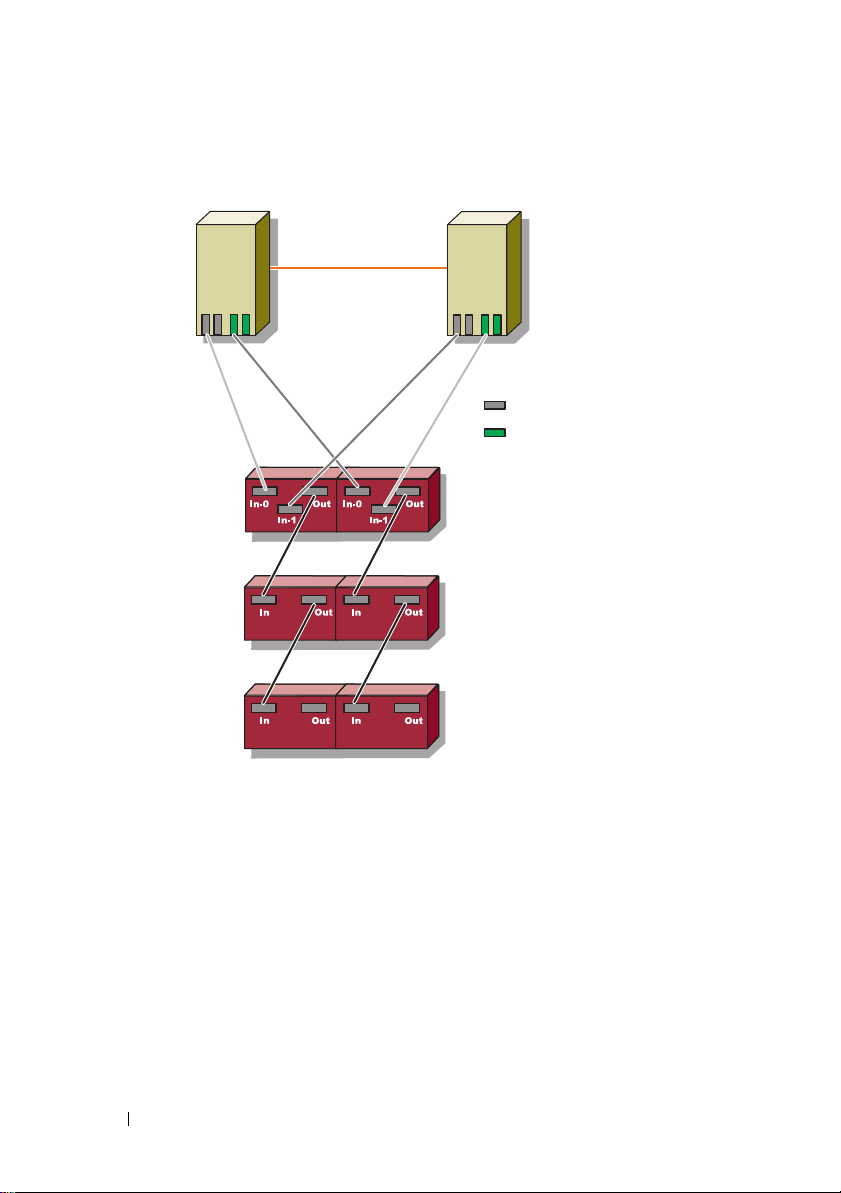
Figure 1-3. Redundant Cluster Configuration With Dual SAS 5/E
Cluster Node 1
Cluster Node 2
Private Network
Dual-port HBA 1
Dual-port HBA 2
PowerVault MD3000
RAID Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000
RAID Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000
RAID Enclosure
14 Introduction
Page 15

Other Documents You May Need
CAUTION: For important safety and regulatory information, see the safety
information that shipped with your system. Warranty information may be included
within this document or as a separate document.
NOTICE: Always read the updates included—included as release notes or readme
files—first, because they often supersede information in other documents.
NOTE: All documentation, unless indicated otherwise, is available on the Dell
Support website at support.dell.com.
• The
•The
•The
•The
• The
• The
• The
• The SAS 5/E documentation includes information on the SAS host bus
Rack Installation Guide
included with your rack solution describes
how to install your system into a rack.
Getting Started Guide
included with you Dell system provides an
overview of initially setting up your system.
Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Installation
and Troubleshooting Guide
and the
Windows Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide
Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft
provides
more information on deploying your cluster with the specific variant of the
Windows Server operating system.
Dell Cluster Configuration Support Matrices
Availability Clustering website at
www.dell.com/ha
on the Dell High
provides a list of
recommended operating systems, hardware components, and driver or
firmware versions for your failover cluster.
Setting Up Your System
document provides an overview of initially
setting up your system.
Users Guide
for your PowerEdge or PowerVault system describes
system features and technical specifications, SAS drivers, the system
setup program (if applicable), software support, and the system
configuration utility.
Installation and Troubleshooting Guide
for your PowerEdge or
PowerVault system describes how to troubleshoot the system and install or
replace system components.
adapter (HBA).
Introduction 15
Page 16

• The PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager documentation provides
instructions for using the array management software to configure
RAID systems.
• Operating system documentation describes how to install (if necessary),
configure, and use the operating system software.
• The Dell PowerVault tape library documentation provides information for
installing, troubleshooting, and upgrading the tape library.
• The PowerEdge or PowerVault User Guide describes system features,
technical specifications, the System Setup program (if applicable),
software support and the system configuration utility.
•The
PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager CLI Guide
provides
information about using the command line interface (CLI).
•The
Dell PowerVault MD3000 Resource
media provides documentation for
configuration and management tools, as well as the full documentation set
included here.
•The
Dell PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager User’s Guide
provides
instructions for using the array management software to configure RAID
systems.
•The
Dell PowerVault Modular Disk Systems Support Matrix
provides
information on supported software and hardware for PowerVault Modular
Disk systems.
•The
System Administrator’s Guide
provides system operation and
management operation.
•The
Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Installation
and Troubleshooting Guide
or the
Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft
Windows Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide
• Documentation for any components you purchased separately provides
information to configure and install these options.
• Release notes or readme files may be included to provide last-minute
updates to the system documentation or advanced technical reference
material intended for experienced users or technicians.
16 Introduction
Page 17

Cabling Your Cluster Hardware
The following sections help you connect the power, network and storage
cables to your cluster. After you have connected the hardware components,
the subsequent sections in this document provide instructions to configure
your cluster.
Cabling the Mouse, Keyboard, and Monitor
When installing a cluster configuration in a rack, you must include a switch
box to connect the mouse, keyboard, and monitor to the nodes. For
instructions on cabling each node's connections to the switch box, see the
documentation included with your rack.
Cabling the Power Supplies
To ensure that the specific power requirements are met, see the
documentation for each component in your cluster solution.
It is recommended to follow the guidelines below to protect your cluster
solution from power-related failures:
• For nodes with multiple power supplies, plug each power supply into a
separate AC circuit.
• Use uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
• For some environments, consider having backup generators and power
from separate electrical substations.
Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2 illustrate recommended methods of power cabling
for a cluster solution consisting of two Dell™ PowerEdge™ systems and one
storage system. To ensure redundancy, the primary power supplies of all the
components are grouped onto one or two circuits and the redundant power
supplies are grouped onto a different circuit.
Cabling Your Cluster Hardware 17
Page 18
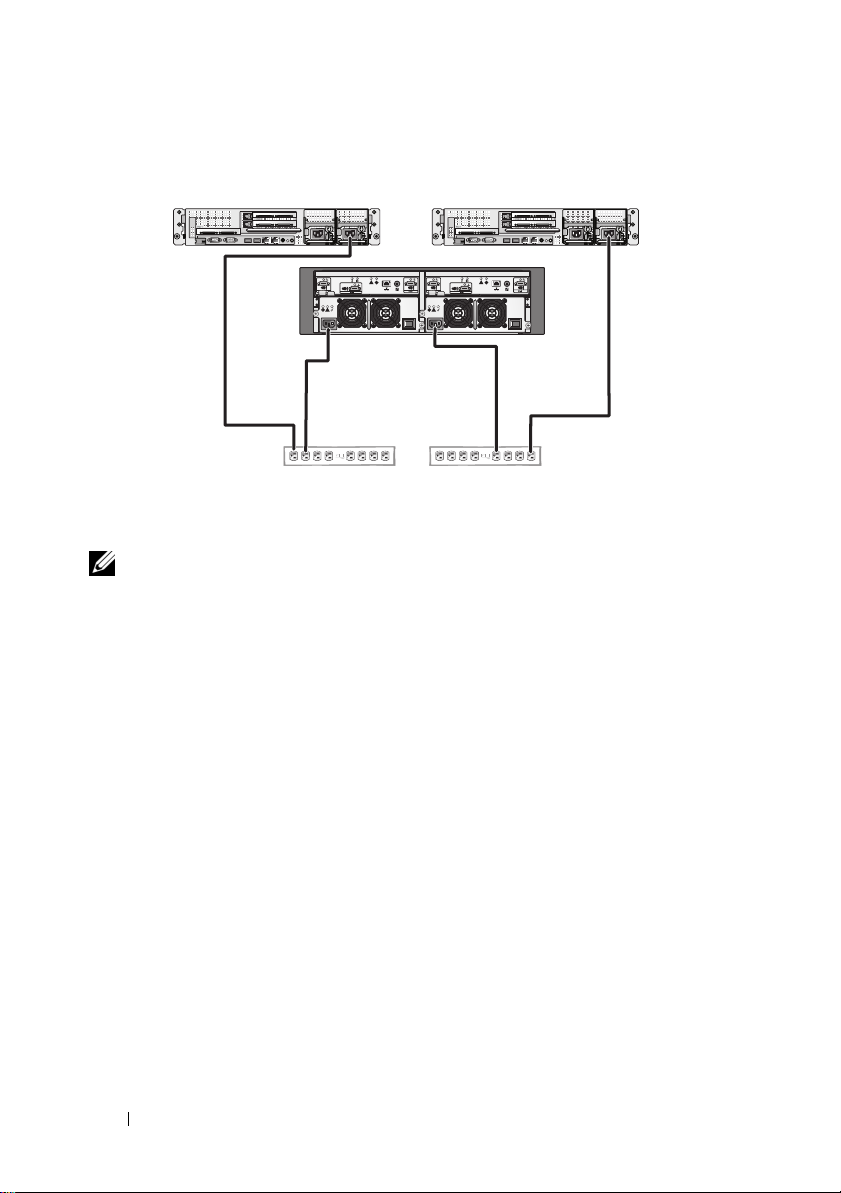
Figure 2-1. Power Cabling Example With One Power Supply in the
PowerEdge Systems
primary power supplies on one AC
power strip (or on one AC PDU [not
shown])
NOTE: This illustration is intended only to demonstrate the power distribution of the
components.
redundant power supplies on one
AC power strip (or on one AC PDU
[not shown])
18 Cabling Your Cluster Hardware
Page 19

Figure 2-2. Power Cabling Example With Two Power Supplies in the
PowerEdge Systems
primary power supplies on one
AC power strip (or on one AC
PDU [not shown])
NOTE: This illustration is intended only to demonstrate the power distribution of the
components.
redundant power supplies on
one AC power strip (or on one
AC PDU [not shown])
Cabling Your Cluster Hardware 19
Page 20

Cabling Your Public and Private Networks
The network adapters in the cluster nodes provide at least two network
connections for each node. The network connections are described in
Ta b l e 2 - 1 .
Table 2-1. Network Connections
Network Connection Description
Public Network All connections to the client LAN.
At least one public network must be configured for mixed
mode (public mode and private mode) for private network
failover.
Private Network A dedicated connection for sharing cluster health and status
information between the cluster nodes.
Network adapters connected to the LAN can also provide
redundancy at the communications level in case the cluster
interconnect fails.
For more information on private network redundancy, see
your Microsoft
Figure 2-3 shows an example of network adapter cabling in which dedicated
network adapters in each node are connected to the public network and the
remaining network adapters are connected to each other (for the private
network).
®
Cluster Services (MSCS) documentation
20 Cabling Your Cluster Hardware
Page 21

Figure 2-3. Example of Network Cabling Connection
public network
public
network
adapter
private network
adapter
private network
cluster node 1
cluster node 2
Cabling Your Public Network
Any network adapter supported by a system running Transmission Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) may be used to connect to the public
network segments. You can install additional network adapters to support
additional public network segments or to provide redundancy in the event of
a faulty primary network adapter or switch port.
Cabling Your Private Network
The private network connection to the cluster nodes is provided by a second
or subsequent network adapter that is installed in each node. This network is
used for intra-cluster communications.
Cabling Your Cluster Hardware 21
Page 22

Table 2-2 lists the required hardware components and connection method for
two possible private network configurations.
Table 2-2. Private Network Hardware Components and Connections
Method Hardware Components Connection
Network switch Fast Ethernet or Gigabit
Ethernet network adapters
and switches
Point-to-Point
(two-node cluster
only)
Point-to-Point Copper Gigabit Ethernet
Fast Ethernet network
adapters
network adapters
Connect standard two-node
Ethernet cables from the
network adapters in both
cluster nodes to a Fast
Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet
switch.
Connect a crossover Ethernet
cable between the Gigabit
Ethernet network adapters in
both cluster nodes.
Connect a standard Ethernet
cable between the Gigabit
Ethernet network adapters in
both cluster nodes.
Using Dual-Port Network Adapters for Your Private Network
You can configure your cluster to use the public network as a failover for
private network communications. However, if dual-port network adapters are
used, do not use two ports simultaneously to support both the public and
private networks.
NIC Teaming
Network Interface Card (NIC) teaming combines two or more NICs to
provide load balancing and/or fault tolerance. Your cluster supports NIC
teaming only in a public network. NIC teaming is not supported in a private
network.
Use the same brand of NICs in a team. Do not mix brands of teaming drivers.
22 Cabling Your Cluster Hardware
Page 23

Cabling the Storage Systems
This section provides information for connecting your cluster to a storage system.
You can either use a SAS connection for in-band storage management or use an
Ethernet connection for out-of-band storage management. For out-of-band
storage management, cable the Ethernet ports on the storage array to the public
network.
NOTE: It is recommended that you configure your Dell PowerVault™ MD3000 to
use both in-band and out-of-band management paths. Establishing all management
connections to a RAID enclosure provides additional paths in the case of a
management connection failure.
NOTE: For more details on the storage hardware description, see the Dell
PowerVault MD3000 RAID Enclosure Hardware Owner’s Manual
Cabling the Cluster in a Non-Redundant Configuration
Each cluster node attaches to the storage system using one SAS cable. In this
configuration, there is only one storage path from the cluster node to the
storage system. If any component such as the HBA, cable, or storage
controller fails in the storage path, the cluster may failover. If the cluster
failover occurs, MSCS moves the cluster group to the stand-by cluster node
and accesses the data.
NOTE: Dell does not support upgrades from a non-redundant cluster configuration
to a redundant configuration.
To cable the cluster:
Install a SAS cable from the cluster node 1 HBA port 0 to the
1
RAID controller module 0 port In-0.
2
Install a SAS cable from the cluster node 2 HBA port 0 to the RAID controller module 1 port In-0.
Cabling Your Cluster Hardware 23
Page 24

Figure 2-4. Non-Redundant Cluster Configuration
cluster node 1
0
1
private network
cluster node 2
1
0
PowerVault MD3000
RAID Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000
RAID Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000
RAID Enclosure
NOTE: A multi-path driver that is used in similar configurations is required for this
configuration.
NOTE: Only RAID controller modules with one host-to-controller SAS connection
are supported in the configuration illustrated in Figure 2-4.
24 Cabling Your Cluster Hardware
Page 25

Cabling the Cluster in Redundant Configuration With Single SAS 5/E HBAs
Each cluster node attaches to the storage system using one SAS 5/E HBA and
two SAS cables. In this configuration, there are redundant storage paths from
the cluster node to the storage system. If a component fails in the storage
path such as the port, the cable, or the storage controller, the multi-path
software automatically reroutes the I/O requests to the alternate path so that
the storage array continues to operate without interruption.
To cable the cluster:
1
Connect cluster node 1 to the storage system.
a
Install a SAS cable from the cluster node 1 HBA port 0 to the
RAID controller module 0 port In-0.
b
Install a SAS cable from the cluster node 1 HBA port 1 to the
RAID controller module 1 port In-0.
2
Connect cluster node 2 to the storage system.
a
Install a SAS cable from the cluster node 2 HBA port 0 to the RAID
controller module 0 port In-0.
b
Install a SAS cable from the cluster node 2 HBA port 1 to the RAID
controller module 1 port In-0.
NOTE: If the HBA on the active node fails, MSCS moves the cluster group to the
standby node and accesses the data through the standby node.
Cabling Your Cluster Hardware 25
Page 26

Figure 2-5. Redundant Cluster Configuration With Single SAS 5/E HBA
cluster node 1
0
1
private network
cluster node 2
0
1
PowerVault MD3000
RAID Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000
RAID Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000
RAID Enclosure
26 Cabling Your Cluster Hardware
Page 27

Cabling the Cluster in Redundant Configuration With Dual SAS 5/E HBAs
Each cluster node attaches to the storage system using two SAS 5/E HBAs
and two SAS cables. In this configuration, there are redundant storage paths
from the cluster node to the storage system. If a component fails in the
storage path such as the HBA, the cable, or the storage controller, the
multi-path software automatically reroutes the I/O requests to the alternate
path so that the storage array continues to operate without interruption.
To cable the cluster:
1
Connect cluster node 1 to the storage system.
a
Install a SAS cable from the cluster node 1 HBA 1 port 0 to the
RAID controller module 0 port In-0.
b
Install a SAS cable from the cluster node 1 HBA 2 port 0 to the
RAID controller module 1 port In-0.
2
Connect cluster node 2 to the storage system.
a
Install a SAS cable from the cluster node 2 HBA 1 port 0 to the
RAID controller module 0 port In-1.
b
Install a SAS cable from the cluster node 2 HBA 2 port 0 to the
RAID controller module 1 port In-1.
Cabling Your Cluster Hardware 27
Page 28

Figure 2-6. Redundant Cluster Configuration With Dual HBAs
cluster node 1
0
0
1
1
private network
cluster node 2
0
1
0
1
Dual-port HBA 1
Dual-port HBA 2
PowerVault MD3000
RAID Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000
RAID Enclosure
PowerVault MD1000
RAID Enclosure
28 Cabling Your Cluster Hardware
Page 29

Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove and access
any of the components inside the system. For important safety and regulatory
information, see the safety information that shipped with your system.
Cluster Configuration Overview
1
Ensure that your site can handle the cluster’s power requirements.
Contact your sales representative for information about your region's
power requirements.
2
Install the servers, the shared storage array(s), and the interconnect switches (for example: in an equipment rack), and ensure that all these components are powered on.
NOTE: For more information on step 3 to step 7 and step 10 to step 12, see
"Preparing your systems for clustering" section of the Dell Failover Clusters
with Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide
or the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Installation
and Troubleshooting Guide located on the Dell Support website at
support.dell.com.
3
Deploy the operating system (including any relevant service pack and
hotfixes), network adapter drivers, and storage adapter drivers (including
Multipath I/O drivers(MPIO)) on each of the servers that will become
cluster nodes. Depending on the deployment method that is used, it may
be necessary to provide a network connection to successfully complete
this step.
NOTE: You can record the Cluster configuration and Zoning configuration
(if relevant) to the Cluster Data Form and Zoning Configuration Form,
respectively to help in planning and deployment of your cluster. For more
information, see "Cluster Data Form" on page 57.
Preparing Your Systems for Clustering 29
Page 30

4
Establish the physical network topology and the TCP/IP settings for the network adapters on each server node to provide access to the cluster public and private networks.
5
Configure each server node as a member server in the same Windows® Active Directory Domain.
NOTE: You can configure the cluster nodes as Domain Controllers. For more
information, see “Selecting a Domain Model” section of the Dell Failover
Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Installation and
Troubleshooting Guide or the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows
Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide located on the Dell
Support website at support.dell.com.
6
Establish the physical storage topology and any required storage network
settings to provide connectivity between the storage array and the servers
that will be configured as cluster nodes. Configure the storage system(s) as
described in your storage system documentation.
7
Use storage array management tools to create at least one logical unit
number (LUN). The LUN is used as a cluster quorum disk for the failover
cluster with Windows Server
®
2003 and as a witness disk for the failover
cluster with Windows Server 2008. Ensure that this LUN is presented to
the servers that will be configured as cluster nodes.
NOTE: It is highly recommended that you configure the LUN on a single node,
for security reasons, as mentioned in step 8 when you are setting up the
cluster. Later, you can configure the LUN as mentioned in step 9 so that other
cluster nodes can access it.
8
Select one of the systems and form a new failover cluster by configuring the cluster name, cluster management IP, and quorum resource.
NOTE: For Dell Failover Clusters with Windows Server 2003, run the Cluster
Validation Wizard to ensure that your system is ready to form the cluster.
9
Join the remaining node(s) to the failover cluster.
10
Configure roles for cluster networks. Take any network interfaces that are used for iSCSI storage (or for other purposes outside of the cluster) out of the control of the cluster.
11
Test the failover capabilities of your new cluster.
NOTE: For Dell Failover Clusters with Windows Server 2008, you can also use
the Cluster Validation Wizard.
30 Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
Page 31

12
Configure highly-available applications and services on your failover
cluster. Depending on your configuration, this may also require providing
additional LUNs to the cluster or creating new cluster resource groups.
Test the failover capabilities of the new resources.
13
Configure client systems to access the highly available applications and services that are hosted on your failover cluster.
Installing the Operating System
Ensure that the Windows Server operating system installed on each cluster
node in your failover cluster has the same release, edition, service pack, and
processor architecture.
For example, all nodes in your cluster may be configured with Windows
Server 2003 R2, Enterprise x64 Edition. If the operating system varies among
nodes, it is not possible to configure a failover cluster successfully. It is
recommended to establish server roles prior to configuring a failover cluster,
depending on the operating system configured on your cluster.
For a list of Dell PowerEdge Servers, iSCSI HBAs and network switches, and
the recommended list of operating system variants, specific driver and
firmware revisions, see the Dell Cluster Configuration Support Matrices on
the Dell High Availability Clustering website at www.dell.com/ha.
NOTE: For more information on deploying your cluster with the Windows Server
2003 operating systems, see the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows
Server 2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide on the Dell Support website at
support.dell.com.
To establish communication between the cluster nodes and the shared
PowerVault MD3000 storage array and to make the shared disks in the storage
array available to the cluster:
1
Ensure that your cluster meets the requirements as described in "Before You Begin" on page 31.
2
Reserve static IP addresses for the following cluster resources and components:
• SAS connections
• Public network
Preparing Your Systems for Clustering 31
Page 32

• Private network
• Cluster virtual servers
NOTE: You must use these IP addresses when you install the Microsoft
Windows operating system and Microsoft Cluster Services (MSCS)/Failover
Cluster Service.
NOTE: For more information, see Assigning Static IP Addresses to Your
Cluster Resources and Components section of the Dell Failover Clusters with
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide or the
Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Installation and
Troubleshooting Guide located on the Dell Support website at
support.dell.com.
3
Configure the internal disks in your cluster nodes.
NOTE: For more information, see the "Configuring the Internal Drives in
Your Cluster Nodes" section of the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft
Windows Server 2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide or the Dell Failover
Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting
Guide located on the Dell Support website at support.dell.com.
4
Install and configure the Windows operating system on both the cluster nodes. Each cluster node must have its own licensed copy of the Windows operating system and Certificate of Authenticity (COA) attached.
NOTE: For more information, see the "Installing and Configuring the Windows
Operating System" section of the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft
Windows Server 2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide or the Dell
Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Installation and
Troubleshooting Guide located on the Dell Support website at
support.dell.com.
5
Install and configure the storage management software.
NOTE: For more information, see the documentation included with your Dell
PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager software or available at the Dell
Support website located at support.dell.com.
6
Configure the shared storage system(s).
NOTE: For more information, see the "Installing and Configuring the Shared
Storage System" section of the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows
Server 2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide or the Dell Failover Clusters
with Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide
located on the Dell Support website at support.dell.com.
32 Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
Page 33

7
Configure the MSCS/Failover Cluster software.
NOTE: For more information, see the "Installing and Configuring a Failover
Cluster" section of the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server
2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide or the Dell Failover Clusters with
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide
located on the Dell Support website at support.dell.com.
8
Verify cluster functionality. Ensure that:
• The cluster components are communicating with each other.
• MSCS is started.
NOTE: For more information, see the "Verifying Cluster Functionality" section
of the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Installation
and Troubleshooting Guide or the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft
Windows Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide located on the
Dell Support website at support.dell.com.
9
Verify cluster resource availability. Use Cluster Administrator/Failover Cluster Manager to check the running state of each resource group.
NOTE: For more information, see the "Verifying Cluster Resource Availability"
section of the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2003
Installation and Troubleshooting Guide or the Dell Failover Clusters with
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide
located on the Dell Support website at support.dell.com.
Additional Information
• For a list of Dell PowerEdge Servers, iSCSI HBAs, network switches,
recommended list of operating system variants, and specific driver and
firmware revisions, see the
the Dell High Availability Clustering website at
• For a general overview of cluster configuration tasks and more detailed
information about deploying your cluster see the
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide or the Dell
Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Installation and
Troubleshooting Guide located on the Dell Support website at support.dell.com
Dell Cluster Configuration Support Matrices
www.dell.com/ha
Dell Failover Clusters with
.
on
.
Preparing Your Systems for Clustering 33
Page 34

Installing the SAS 5/E HBAs
For systems with dual SAS 5/E HBAs, Dell recommends installing the cards
on separate Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) buses. Placing the
cards on separate buses improves availability and performance.
For more information about your system's PCI bus configuration, see
Cluster Configuration Support Matrices
website at
www.dell.com/ha
.
on the Dell High Availability Clustering
Installing the SAS 5/E HBA Drivers
1
Close all other programs before installing any new software.
2
Insert the
main menu.
3
Click the
The
4
Follow the instructions on each screen.
5
After you click
installation. When the installation is complete, click
the main menu.
NOTE: To install the software, you must have administrative privileges. If you do
not have administrative privileges, a message appears and you are not able to
install the software.
Dell PowerVault MD3000 Resource Media
Install the SAS 5/E Adapter Driver
Installation Wizard
Install
appears.
, the Status screen shows the progress of the
, and navigate to the
bar on the main menu.
Finish
the
Dell
to return to
Installing and Configuring the Storage Management Software
To install and configure the PowerVault MD3000 RAID enclosure in
your cluster:
1
Ensure that the PowerVault MD3000 RAID enclosure has the latest
firmware and Non-Volatile Static Random Access Memory (NVSRAM).
For more information, see your PowerVault MD3000 RAID enclosure
document and the"Loading RAID Controller Module NVSRAM for NonRedundant Configuration" on page 40.
34 Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
Page 35

2
Install the host software (multi-path software and the PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager Agent) on each cluster node, and the PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager Client software on the management station.
For more information, see your PowerVault Modular Disk Storage
Manager documentation.
3
Set the correct failback mode on each cluster node. You must merge the
PowerVault MD3000 Stand Alone to Cluster.reg
directory of the
Dell PowerVault MD3000 Resource
file located in the
\utility
media into the registry
of each node.
NOTE: If you uninstall and reinstall the multi-path I/O software or PowerVault
Modular Disk Storage Manager, you must merge the PowerVault MD3000 Stand
Alone to Cluster.reg file into the registry again.
NOTE: If you are reconfiguring a cluster node into a standalone host, you must
merge the PowerVault MD3000 Cluster to Stand Alone.reg file located in the \utility
directory of the Dell PowerVault MD3000 Resource media into the host registry.
These registry files enable correct failback operation on the host.
NOTE: The cluster node can be used as a management station.
You can manage a storage array in two ways:
• Out-of-band management
• In-band management
For out-of-band management, data is separate from commands and events.
Data travels through the host-to-controller SAS interface cables, while
commands and events travel through the Ethernet cables.
When you use out-of-band management, you must set the network
configuration for each RAID controller module including its IP address,
subnet mask, and gateway. If you are using a DHCP server, you can enable
automatic network configuration, but if you are not using a DHCP server, you
must enter the network configuration manually.
For in-band management, commands, events, and data travel through the
host-to-controller SAS interface cables. Unlike out-of-band management,
commands and events are mixed with data.
NOTE: It is recommended to use both in-band and out-of-band management.
Preparing Your Systems for Clustering 35
Page 36

Adding Storage Arrays to the Failover Cluster
To add a storage array to the PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager, click
the New link in the Array Selector area. A window is displayed that allows you
to choose the automatic or manual process to add a new storage array.
You can add the Storage Arrays using either Automatic Discovery or Manual
Discovery.
Installing and Configuring the Shared Storage System
This section provides information for installing and configuring the shared
storage systems.
Setting Up Your Storage Array
The Perform Initial Setup Tasks link located on the Summary tab provides
links to the basic steps you should follow when initially setting up a storage
array in PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager.
Initial setup tasks include:
1
Blinking the Storage Array
array on your network. The storage array can then be identified with a
label.
2
Renaming the Storage Array
help you easily identify the storage array.
3
Setting a Storage Array Password
the storage array, such as deletion of a virtual disk.
4
Setting up Alert Notifications
administrators about storage array conditions that require attention.
a
Configure Sender E-mail Settings
address, and contact information PowerVault Modular Disk Storage
Manager uses to send e-mail alerts.
b
Add or Edit E-mail Addresses
that should receive e-mail-based alerts.
c
Set Up SNMP Alerts
receive SNMP-based alerts.
— Find the physical location of the storage
— Provide a unique and memorable name to
— Prevent unapproved manipulation of
— Enable e-mail and SNMP alerts to notify
— Provide the SMTP, e-mail
— Provide information about accounts
— Provide information about hosts that should
36 Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
Page 37

5
Configuring Host Access and Create a Host Group
— Set up one or more
hosts to access the storage array. For more information, see "Configuring
Host Access" on page 37 and "Creating a Host Group" on page 38
6
Configuring and Manage Virtual Disks
— For more information, see
"Creating Disk Groups and Virtual Disks" on page 38.
7
View and Enable Premium Features (Optional)
— If you have purchased
premium features, including Snapshot Virtual Disks and virtual disk copies,
check the premium features that are currently available and enable them if
they are turned off. For more information, see "Using Advanced (Premium)
PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager Features" on page 45.
8
Changing Network Configuration (Optional)
— Change your network
configuration by changing RAID controller network settings or obtain the
network configuration from a DHCP server.
When you are working with a non-redundant configuration, you need to load
the appropriate NVSRAM. For more information, see "Loading RAID
Controller Module NVSRAM for Non-Redundant Configuration" on page 40.
Configuring Host Access
Configuring host access allows you to either permit or deny access to a storage
array for specific hosts.
Host access configuration is the first step in setting up your storage array.
You must complete this task during initial setup and anytime you connect a new
host. When you permit host access, that host can then be mapped to a virtual
disk on the storage array.
1
On the
hosts are configured to access the array.
2
Click the
hosts.
Summary
tab, the
Configured Hosts
Hosts & Mappings
area indicates how many
link in this area to see the names of these
NOTE: Ensure that the PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager Agent service
is started on your cluster nodes.
To begin configuring host access, click the Configure tab and then click the
Configure Host Access link. PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager scans
the array and displays a list of the hosts it finds that have not yet been configured
for access to the array. To see hosts that have already been configured, click the
Vie w Hosts that currently have access to the storage array link.
Preparing Your Systems for Clustering 37
Page 38

To automatically configure a host for access to the storage array:
1
Click the
2
Select both the cluster nodes individually, or by clicking the
Configure
tab and then click the
Configure Host Access
Select All
link.
check box beneath the list.
3
Set the Host Type for all the HBA ports on each cluster node by clicking
the
View Details
–For a
– Single Path
– For a
button (next to the list).
Non-Redundant Configuration
.
Redundant Configuration
with Dual SAS 5/E HBAs, select
, select
Windows MSCS Cluster
Windows 2000/Server 2003/Server 2008 Clustered.
4
Click OK to configure access to the array for the hosts you selected.
Creating a Host Group
After you have created the hosts, follow this procedure to create a host group:
1
Click the
2
Click the
The
3
Type a name for the new host group in the text box.
4
In the
then click the
to the
5
Repeat step 4 to add the second cluster node to the host group.
6
To create the host group, click OK.
Modify
tab and then click the
Create Host Group
Create Host Group
Select Hosts to Add
Add
button located to the right of the list. The host moves
Hosts in Group List
link on the
Modify Host Topology
Modify Host Topology
link.
window.
window appears.
list, click the names of the first cluster node,
.
Creating Disk Groups and Virtual Disks
A minimum of one virtual disk is required for an active/passive configuration;
at least two virtual disks are required for an active/active configuration. In
some cases, the virtual disks may have been bound when the system was
shipped. It is still important, however, to install the management software
and to verify that the desired virtual disk configuration exists.
NOTE: Before you can create virtual disks, you must first organize the physical
disks into disk groups and configure host access. You can then create virtual disks
within a disk group.
38 Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
Page 39

To create a virtual disk, use one of the following methods:
• Automatic Configuration
• Manual Configuration
It is recommended that you create at least one virtual disk for each
application. If multiple NTFS volumes are created on a single virtual disk
using Windows Disk Management, the volumes failover together, rather
individually from node-to-node.
You can manage your virtual disks remotely using PowerVault Modular Disk
Storage Manager.
NOTE: It is recommended that you use a RAID level other than RAID 0 (which is
commonly called striping). RAID 0 configurations provide very high performance,
but do not provide the level of availability required for the quorum resource. See the
documentation for your storage system for more information about setting up RAID
levels for the system.
Disk groups are created in the non-configured capacity of a storage array, and
virtual disks are created in the free capacity of a disk group. The hosts
attached to the storage array read and write data to the virtual disks.
For more information on how to create Disk Groups and Virtual Disks, see
your PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager documentation.
Creating Host-to-Virtual Disk Mappings
To create host-to-virtual disk mappings to assign virtual disks to the host
groups containing cluster node, follow the steps:
1
Click the
2
Click the
3
The
4
Select the
mapped.
5
Verify the mapping by clicking the
the
Configure
tab.
Create Host-to-Virtual Disk Mappings
PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager
Host Group
containing the cluster nodes and virtual disks to be
Host-to-Virtual Disk Mappings
Summary
tab to ensure that the configuration was created correctly.
link.
displays a series of pages.
link on
Preparing Your Systems for Clustering 39
Page 40

Loading RAID Controller Module NVSRAM for Non-Redundant Configuration
To ensure that the non-redundant configuration is functioning properly, load
the appropriate NVSRAM file to the PowerVault MD3000 storage enclosure.
The NVSRAM file is located at the \utility\NVSRAM\ directory on the
PowerVault MD3000 Resource Media, with a prefix of Non-redundant-MSCS.
To load the NVSRAM file to the PowerVault MD3000 RAID enclosure, from
the storage management station, open the PowerVault Modular Disk Storage
Manager Client:
1
Click the
2
In the
Module NVSRAM
versions in use are displayed.
3
Click
only firmware images compatible with the current storage array
configuration are listed.
4
Select the appropriate file in the
the file you selected is not valid or is incompatible with the current storage
array configuration, an error message is displayed. Click
message and select another file.
5
Click
the RAID controller and NVSRAM firmware you selected.
6
To complete the download, click
Support
Download Firmware
Select File
Transfer...
tab, then click
. The current controller firmware and NVSRAM
to browse to the file you want to download. By default,
. A
Confirm Download
Download Firmware
window, click
File Selection
dialog box is displayed showing
Yes
.
.
Download RAID Controller
window and click OK. If
OK
to close the
40 Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
Page 41

Troubleshooting Tools
The Dell PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager establishes
communication with each managed array and determines the current array
status. When a problem occurs on a storage array, the Modular Disk Storage
Manager provides several ways to troubleshoot the problem:
• Recovery Guru—The SAS Device Miswire Recovery Guru diagnoses
critical events on the storage array and recommends step-by-step recovery
procedures for problem resolution. To access the Recovery Guru using the
PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager, click
Failure
. You can access the Recovery Guru from the
Summary
• Storage Array Profile — The Storage Array Profile provides an overview of
your storage array configuration, including firmware versions and the
current status of all devices on the storage array. To access the Storage
Array Profile, click
profile by clicking the Storage array profile link in the
Components
• Status Icons — Status icons identify the six possible health status
conditions of the storage array. For every non-optimal status icon, use the
Recovery Guru to detect and troubleshoot the problem. The six possible
health status conditions are described below:
– Optimal—Every component in the managed array is in the desired
– Needs Attention—A problem exists with the managed array that
– Fixing—A Needs Attention condition has been corrected and the
– Unresponsive—The storage management station cannot
page.
NOTE: You can generate the SAS Device Miswire Recovery Guru condition
by connecting the host port of one controller to the unused expansion port on
the second controller in a PowerVault MD3000 RAID enclosure.
Support→ View storage array profile
area of the
working condition.
requires intervention to correct it.
managed array is currently changing to an
communicate with the array, one controller, or both controllers in the
storage array. Wait at least five minutes for the storage array to return
to an
Optimal
Summary
status following a recovery procedure.
tab.
Support→ Recover from
Status
area of the
. You can view the
Hardware
Optimal
status.
Preparing Your Systems for Clustering 41
Page 42

– Contacting Device—The PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager
is establishing contact with the array.
– Needs Upgrade—The storage array is running a level of firmware that
is no longer supported by the PowerVault Modular Disk Storage
Manager.
– Support Information Bundle—The
on the
Support
tab saves all storage array data, such as profile and
Gather Support Information
link
event log information, to a file that you can send if you seek technical
assistance for problem resolution.
Windows Operating System and Dynamic Volumes
For more information on various Windows Server storage options that can be
used with your failover cluster, see the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft
Windows Server 2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide or the Dell Failover
Clusters with Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting
Guide located on the Dell Support website at support.dell.com.
Configuring the RAID Level for the Shared Storage Subsystem
You must configure the virtual disks in your shared storage subsystem into disk
groups or virtual disks using the Dell PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager
software. All virtual disks, especially if they are used for the quorum resource,
should be bound and incorporate the appropriate RAID level to ensure high
availability. For more information on the quorum resource, see "Quorum
Resource".
NOTE: It is recommended that you use a RAID level other than RAID 0 (which is
commonly called striping). RAID 0 configurations provide very high performance,
but do not provide the level of availability required for the quorum resource. For
more information about setting up RAID levels for the system, see the
documentation for your storage system.
Assigning Drive Letters and Mount Points
A mount point is a drive attached to an empty folder on an NTFS volume.
A mount point functions the same as a normal drive but is assigned a label or
name instead of a drive letter. Using mount points, a cluster can support more
shared disks than the number of available drive letters.
42 Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
Page 43

The cluster installation procedure does not automatically add the mount
point into the disks managed by the cluster. To add the mount point to the
cluster, create a physical disk resource in the cluster resource group for each
mount point. Ensure that the new physical disk resource is in the same cluster
resource group and is dependent on the root disk (i.e., the disk from which
the mount point is attached).
NOTE: Mount points are supported in MSCS on the Windows Server 2003 and
Windows Server 2008 operating systems only. When mounting a drive to an NTFS
volume, do not create mount points from the quorum resource or between the
clustered disks and the local disks. Mount points must be in the same cluster
resource group and must be dependent on the root disk.
Naming and Formatting Drives on the Shared Storage System
Each virtual disk being created in the PowerVault Modular Disk Storage
Manager becomes a physical disk in Windows Disk Management. For each
physical disk, perform the following:
• Write the disk signature
• Create the partition
• Assign the drive letter
• Format the partition with NTFS
NOTICE: The drive letters are manually assigned from the second node, the shared
disks are simultaneously accessible from both nodes. To ensure file system integrity
and prevent possible data loss before you install the MSCS software, prevent any
I/O activity to the shared drives by performing the following procedure on one node
at a time and ensuring that the other node is shutdown.
The number of drive letters required by individual servers in a cluster may vary.
It is recommended that the shared drives be named in reverse alphabetical
order beginning with the letter z. To assign drive letters and format drives on
the shared storage system, perform the following steps:
1
Turn off node 2 and open
2
Allow Windows to enter a signature on all new physical or logical drives.
Disk Management
on node 1.
NOTE: Do not upgrade or convert your disks to dynamic disks.
3
Locate the icon for the first unnamed, unformatted drive on the shared storage system.
Preparing Your Systems for Clustering 43
Page 44

4
Right-click the icon and select
Create
from the submenu. If the
unformatted drives are not visible, verify the following:
• The latest version of the SAS 5/E adapter driver is installed.
• The storage system is properly cabled to the servers.
5
In the dialog box, create a partition the size of the entire drive (the default)
and then click
NOTE: A virtual disk that is mapped or assigned from the storage system to a
cluster node(s) is represented as a physical disk within the Windows operating
system on each node. MSCS allows only one node to access a given physical
disk resource at a time. Therefore, if a disk is partitioned and contains multiple
NTFS volumes, concurrent access to different volumes is only possible from
the cluster node controlling the physical disk resource. If two NTFS volumes
need to be controlled by different nodes, these volumes must reside on
separate disks.
6
Click
Yes
7
With the mouse pointer on the same icon, right-click and select
Change Drive Letter and Path
8
Assign a drive letter to an NTFS volume or create a mount point.
OK
.
to confirm the partition.
from the submenu.
To assign a drive letter to an NTFS volume:
a
Click
Edit
and select the letter you want to assign to the drive
(for example, z).
b
Click OK.
c
Go to step 9.
To create a mount point:
a
Click
Add
.
b
Click
Mount
in the following empty NTFS folder.
c
Type the path to an empty folder on an NTFS volume, or click
to locate it.
d
Click OK.
e
Go to step 9.
9
Click
Yes
to confirm the changes.
10
Right-click the drive icon again and select
44 Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
Format
from the submenu.
Browse
Page 45

11
Under
Volume Label
, enter a descriptive name for the new volume; for
example, Disk_Z or Email_Data.
12
In the dialog box, change the file system to
and click the
NOTE: The NTFS file system format is required for shared-disk resources
under MSCS.
13
Click OK at the warning.
14
Click
15
Click
16
Repeat step 3 through step 15 for each remaining drive.
17
Close
18
Turn off node 1.
19
Turn on node 2.
20
On node 2, open
21
Ensure that the drive letters for node 2 are correct and re-assign the drive
Start
button.
OK
to acknowledge that the format is complete.
Close
to close the dialog box.
Disk Management
.
Disk Management
NTFS
, select
Quick Format
.
letters, if necessary. To re-assign the drive the drive letters, repeat step 7
through step 9.
22
Set the client system’s public network segment(s) to
All communications
This setting provides a redundant path for the cluster-to-cluster
communication in the event the private network fails.
,
.
Using Advanced (Premium) PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager Features
PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager includes the following
advanced features:
• Snapshot Virtual Disk
• Virtual Disk Copy
To install and enable these premium features, you must purchase a feature
key file for each feature and then specify the storage array that hosts them.
For instructions about this process, see the Premium Feature Activation card
that shipped along with your Dell PowerVault MD3000 storage array.
Preparing Your Systems for Clustering 45
Page 46

These premium features increase the high availability for your cluster
solution. It is essential that you follow the instructions below to ensure proper
cluster operations.
Snapshot Virtual Disk
Snapshot Virtual Disk captures point-in-time images of a virtual disk for
backup, testing, or data processing without affecting the contents of the
source virtual disk. You can use either Simple Path or Advanced Path to
create a snapshot for your cluster disk. The Snapshot Virtual Disk can be
mapped to the primary node (the node owning the source disk) or the
secondary node (the node not owning the source disk) for backup, testing, or
data processing.
NOTICE: Avoid mapping the Snapshot Virtual Disk to more than one node in the
cluster at any point of time. The Snapshot Virtual Disk is not managed by MSCS, so
mapping the Snapshot Virtual Disk to the host group or both nodes in the cluster
may allow both nodes to access data concurrently and thus cause data corruption.
To map the Snapshot Virtual Disk to the primary node:
1
Use Host-to-Virtual Disk Mapping in the PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager. This ensures that a different disk signature is assigned properly to the Snapshot Virtual Disk.
2
Use Windows Disk Management to re-scan for the Snapshot Virtual Disk, assign the drive letter, and start accessing the drive.
NOTE: The disks may be re-scanned several times for the Snapshot Virtual
Disk to be detected by Windows Disk Management. If the Snapshot Virtual
Disk is not detected, wait for a few minutes and re-scan the disks. Repeat the
process until the Snapshot Virtual Disk is detected; do not reboot the server.
If you need to map the Snapshot Virtual Disk to the secondary node (the
node not owning the source disk), you must map the Snapshot Virtual Disk
to the primary node first, to ensure that the snapshot is assigned a new disk
signature. Then, use the PowerVault Modular Disk Storage Manager to
unmap the Snapshot Virtual Disk from the primary node, map it to the
secondary node, and start accessing it.
NOTICE: Attempts to map the Snapshot Virtual Disk to the secondary node, prior to
obtaining the signature from the primary node, may cause the operating system to
misidentify the Snapshot Virtual Disk as an existing system volume and that may
result in data loss or inaccessible Snapshot Virtual Disk.
46 Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
Page 47

NOTE: For a cluster configuration with multiple Snapshot Virtual Disks, each virtual
disk must be mapped to the node owning the associated source disk first. The
primary node for a Snapshot Virtual Disk may not be the primary node for another
Snapshot Virtual Disk.
Virtual Disk Copy
Virtual Disk Copy generates a full copy of data from the source virtual disk to
the target virtual disk in a storage array. You can use Virtual Disk Copy to
back up data, copy data from disk groups that use smaller-capacity physical
disks to disk groups using greater-capacity physical disks, or restore Snapshot
Virtual Disk data to the source virtual disk.
To create a Virtual Disk Copy of an MSCS cluster shared disk:
Create a Snapshot Virtual Disk using the cluster shared disk as a source disk.
1
2
Do not map that Snapshot Virtual Disk to any cluster node. Then, use the newly created Snapshot Virtual Disk as the source disk for the Virtual Disk Copy.
NOTE: When you attempt to create a Virtual Disk Copy of an MSCS cluster
shared disk directly, the operation fails and displays the following error:
The operation cannot complete because the
selected virtual disk is not a source virtual
disk candidate
.
If the cluster shared disk fails and you need to restore it from the target
virtual disk, use Cluster Administrator to change the status of the cluster
group containing the failed disk to offline, and then use one of the following
methods:
1
Use Virtual Disk Copy to transfer the data from the target virtual disk to the cluster shared disk.
2
Unassign the cluster shared disk from the host group and then map the target virtual disk to the host group.
Preparing Your Systems for Clustering 47
Page 48

Installing and Configuring a Failover Cluster
You can configure the operating system services on your failover cluster, after
you have established the private and public networks and have assigned the
shared disks from the storage array to the cluster nodes.
The procedures for configuring the failover cluster are different, depending
on the Windows Server operating system you use.
For more information on deploying your cluster with Windows Server 2003
operating systems, see the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows
Server 2003 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide on the Dell Support
website at support.dell.com.
For more information on deploying your cluster with Windows Server 2008
operating systems, see the Dell Failover Clusters with Microsoft Windows
Server 2008 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide on the Dell Support
website at support.dell.com.
48 Preparing Your Systems for Clustering
Page 49

Troubleshooting
This appendix provides troubleshooting information for your cluster
configurations.
Table A-1 describes general cluster problems you may encounter and the
probable causes and solutions for each problem.
Table A-1. General Cluster Troubleshooting
Problem Probable Cause Corrective Action
The nodes cannot
access the storage
system, or the cluster
software is not
functioning with the
storage system.
The storage system is
not cabled properly to
the nodes or the
cabling between the
storage components is
incorrect.
One of the cables is
faulty.
Host Group or
Host-to-Virtual Disk
Mappings is not
created correctly.
Ensure that the cables are
connected properly from the
node to the storage system. For
more information, see "Cabling
Your Cluster Hardware" on
page 17.
Replace the faulty cable.
Verify the following:
• Host Group is created and the
cluster nodes are added to the
Host Group.
• Host-to-Virtual Disk Mapping
is created and the virtual disks
are assigned to the Host
Group containing the cluster
nodes.
Troubleshooting 49
Page 50

Table A-1. General Cluster Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Probable Cause Corrective Action
One of the nodes takes a
long time to join the
cluster.
OR
One of the nodes fail to
join the cluster.
The node-to-node
network has failed due
to a cabling or
hardware failure. Long
delays in node-to-node
communications may
be normal.
Check the network cabling.
Ensure that the node-to-node
interconnection and the public
network are connected to the
correct NICs. Verify that the
nodes can communicate with
each other by running the ping
command from each node to
the other node. Try both the
host name and IP address when
using the ping command.
One or more nodes
may have the Internet
Connection Firewall
enabled, blocking
Remote Procedure
Call (RPC)
communications
between the nodes.
Configure the Internet
Connection Firewall to allow
communications that are
required by the Microsoft
Cluster Service (MSCS) and the
clustered applications or
services. For more information,
see Microsoft Knowledge Base
article KB883398 at the
Microsoft Support website at
support.microsoft.com.
®
50 Troubleshooting
Page 51

Table A-1. General Cluster Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Probable Cause Corrective Action
Attempts to connect to
a cluster using Cluster
Administrator fail.
The Cluster Service
has not been started.
A cluster has not been
formed on the system.
The system has just
been booted and
services are still
starting.
Verify that MSCS is running and
that a cluster has been formed.
Use the Event Viewer and look
for the following events logged
by the Cluster Service:
Microsoft Cluster
Service successfully
formed a cluster on
this node
OR
Microsoft Cluster
Service successfully
joined the cluster
If these events do not appear in
Event Viewer and for
instructions on setting up the
cluster on your system and
starting the MSCS, see the
Microsoft Cluster Service
Administrator's Guide.
The cluster network
name is not
responding on the
network because the
Internet Connection
Firewall is enabled on
one or more nodes.
Configure the Internet
Connection Firewall to allow
communications that are
required by MSCS and the
clustered applications or
services. For more information,
see Microsoft Knowledge Base
article KB883398 at the
Microsoft Support website at
support.microsoft.com.
.
.
Troubleshooting 51
Page 52

Table A-1. General Cluster Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Probable Cause Corrective Action
You are prompted to
configure one network
instead of two during
MSCS installation.
The TCP/IP
configuration is
incorrect.
The node-to-node network and
public network must be assigned
static IP addresses on different
subnets. For information about
assigning the network IPs, see
the "Assigning Static IP
Addresses to Your Cluster
Resources and Components"
section of the Dell Failover
Clusters with Microsoft
Windows Server 2003
Installation and Troubleshooting
Guide or the Dell Failover
Clusters with Microsoft
Windows Server 2008
Installation and Troubleshooting
Guide located on the Dell
Support site at
support.dell.com.
The private (point-topoint) network is
disconnected.
Ensure that all systems are
turned on so that the NICs in
the private network are
available.
Using Microsoft
Windows NT
remotely administer a
Windows Server
®
4.0 to
®
2003
cluster generates error
messages.
Some resources in
Windows Server 2003
are not supported in
Windows NT 4.0.
It is recommended that you use
Microsoft Windows
Professional or Windows Server
2003 for remote administration
of a cluster running
Windows Server 2003.
®
XP
52 Troubleshooting
Page 53

Table A-1. General Cluster Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Probable Cause Corrective Action
Unable to add a node to
the cluster.
The disks on the shared
cluster storage appear
unreadable or
uninitialized in
Windows Disk
Administration.
The new node cannot
access the shared
disks. The shared disks
are enumerated by the
operating system
differently on the
cluster nodes.
One or more nodes
may have the Internet
Connection Firewall
enabled, blocking
RPC communications
between the nodes
This situation is
normal if you stopped
the Cluster Service. If
you are running
Windows Server 2003,
this situation is
normal if the cluster
node does not own the
cluster disk.
Ensure that the new cluster
node can enumerate the cluster
disks using Windows Disk
Administration. If the disks do
not appear in Disk
Administration, check the
following:
• Check all cable connections
• Check all zone configurations
• Check the Access Control
settings on the attached
storage systems
Minimum
the
Advanced
• Use the
Configure the Internet
Connection Firewall to allow
communications that are
required by the MSCS and the
clustered applications or
services. For more information
see the Microsoft Knowledge
Base article KB883398 at the
Microsoft Support website at
support.microsoft.com.
No action required.
option with
option.
Troubleshooting 53
Page 54

Table A-1. General Cluster Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Probable Cause Corrective Action
MSCS does not operate
correctly on a cluster
running Windows
Server 2003 and the
Internet Firewall
enabled.
The Windows
Internet Connection
Firewall is enabled,
which may conflict
with MSCS.
Perform the following steps:
1
On the Windows desktop,
right-click
click
2
In the
My Computer
Manage
Computer
Management
Services
click
3
In the
Services
double-click
4
In the
Cluster Services
window, click the
5
Click the
First Failure
down arrow and select
the Service
6
Click the
.
Second Failure
drop-down arrow and select
Restart the Service
7
Click OK.
For information on how to
configure your cluster with the
Windows Internet Connection
Firewall enabled, see Microsoft
Base (KB) articles 258469 and
883398 at the Microsoft
Support website at
support.microsoft.com and the
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
Technet website at
www.microsoft.com/technet.
and
.
window, double.
window,
Cluster Services
Recovery
tab.
drop-
Restart
.
.
54 Troubleshooting
Page 55

Table A-1. General Cluster Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Probable Cause Corrective Action
Public network clients
cannot access the
applications or services
that are provided by the
cluster.
Virtual Disks fail over
continuously between
the two storage
controllers when a
storage path fails.
Virtual Disk Copy
operation fails.
One or more nodes
may have the Internet
Connection Firewall
enabled, blocking
RPC communications
between the nodes.
The failback mode for
the cluster node(s) is
not set properly.
The Virtual Disk Copy
operation uses the
cluster disk as the
source disk.
Configure the Internet
Connection Firewall to allow
communications that are
required by the MSCS and the
clustered applications or
services.
See Microsoft Knowledge Base
article KB883398 at the
Microsoft Support website at
support.microsoft.com for more
information.
Set the correct failback mode on
each cluster node. You must
merge the PowerVault MD3000
Stand Alone to Cluster.reg file
located in the \utility directory
of the Dell PowerVault MD3000
Resource
of each node.
To perform a Virtual Disk Copy
operation on the cluster share
disk, create a snapshot of the
disk, and then perform a Virtual
Disk Copy of the snapshot
virtual disk.
media
into the registry
Troubleshooting 55
Page 56

Table A-1. General Cluster Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Probable Cause Corrective Action
Unable to assign the
drive letter to the
snapshot virtual disk.
Unable to access the
snapshot virtual disk.
System Error Log
displays a warning with
event 59 from partmgr
stating that the
snapshot virtual disk is a
redundant path of a
cluster disk.
In a non-redundant
configuration, the
Recovery Guru in the
Modular Disk Storage
Manager Client reports
virtual disks not on the
preferred controller, and
the enclosure status
Light Emitting Diode
(LED) is blinking
amber.
The snapshot virtual
disk has been
erroneously mapped
to the node that does
not own the source
disk.
The NVSRAM for the
non-redundant
configuration has not
been loaded.
Unmap the snapshot virtual disk
from the node not owning the
source disk, then assign it to the
node that owns the source disk.
For more information, see
"Using Advanced (Premium)
PowerVault Modular Disk
Storage Manager Features" on
page 45.
Load the correct NVSRAM for
the non-redundant
configuration.
56 Troubleshooting
Page 57

Cluster Data Form
You can attach the following form in a convenient location near each cluster
node or rack to record information about the cluster. Use the form when you
call for technical support.
Table B-1. Cluster Data Form
Cluster
Information
Cluster name
and IP address
Server type
Installer
Date installed
Applications
Location
Notes
Table B-2. Node Data Form
Node Name Service Tag Number Public IP Address Private IP Address
Cluster Solution
Cluster Data Form 57
Page 58

Table B-3. Additional Networks Data Form
Additional Networks
Table B-4. Dell PowerVault MD3000 Data Form
Dell™
PowerVault™
MD3000 Name
Service Tag IP Address Number of Disks,
Virtual Disk
Information
58 Cluster Data Form
Page 59

Index
B
Blinking, 36
C
Certificate of Authenticity, 32
Cluster Nodes, 9
Cluster.reg, 35
Contacting Device Status
Icon, 42
F
Fixing Status Icon, 41
H
hot-pluggable, 9
I
M
Microsoft Cluster Server
software, 8
mount point, 42
Multi-path software, 11
N
Needs Attention, 41
Needs Attention Status Icon, 41
Needs Upgrade Status Icon, 42
NTFS, 39, 45
NVSRAM, 34, 37
O
Optimal Status Icon, 41
Out-of-band management, 35
out-of-band storage
management, 23
In-band management, 35
in-band storage management, 23
Index 59
Page 60

P
PERC RAID Adapter
installing, 34
PowerVault 22xS storage system
clustering, 43
Processor, 8
R
RAM, 8
Recovery Guru, 41
S
Snapshot Virtual Disk, 11
static IP addresses, 31
Status Icons, 41
Storage Array Profile, 41
Support Information Bundle
Status Icon, 42
U
Unresponsive, 41
Unresponsive Status Icon, 41
V
Virtual Disk Copy, 11
60 Index
 Loading...
Loading...