Page 1

53-1002750-01
®
14 December 2012
Fabric OS
MIB Reference
Supporting Fabric OS v7.1.0
Page 2

Copyright © 2000-2012 Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Brocade, Brocade Assurance, the B-wing symbol, BigIron, DCX, Fabric OS, FastIron, MLX, NetIron, SAN Health, ServerIron,
TurboIron, VCS, and VDX are registered trademarks, and AnyIO, Brocade One, CloudPlex, Effortless Networking, ICX, NET Health,
OpenScript, and The Effortless Network are trademarks of Brocade Communications Systems, Inc., in the United States and/or in
other countries. Other brands, products, or service names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Notice: This document is for informational purposes only and does not set forth any warranty, expressed or implied, concerning
any equipment, equipment feature, or service offered or to be offered by Brocade. Brocade reserves the right to make changes to
this document at any time, without notice, and assumes no responsibility for its use. This informational document describes
features that may not be currently available. Contact a Brocade sales office for information on feature and product availability.
Export of technical data contained in this document may require an export license from the United States government.
The authors and Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. shall have no liability or responsibility to any person or entity with
respect to any loss, cost, liability, or damages arising from the information contained in this book or the computer programs that
accompany it.
The product described by this document may contain “open source” software covered by the GNU General Public License or other
open source license agreements. To find out which open source software is included in Brocade products, view the licensing
terms applicable to the open source software, and obtain a copy of the programming source code, please visit
http://www.brocade.com/support/oscd.
Brocade Communications Systems, Incorporated
Corporate and Latin American Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc.
130 Holger way
San Jose, CA 95134
Tel: 1-408-333-8000
Fax: 1-408-333-8101
E-mail: info@brocade.com
European Headquarters
Brocade Communications Switzerland Sàrl
Centre Swissair
Tour B - 4ème étage
29, Route de l'Aéroport
Case Postale 105
CH-1215 Genève 15
Switzerland
Tel: +41 22 799 5640
Fax: +41 22 799 5641
E-mail: emea-info@brocade.com
Asia-Pacific Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems China HK, Ltd.
No. 1 Guanghua Road
Chao Yang District
Units 2718 and 2818
Beijing 100020, China
Tel: +8610 6588 8888
Fax: +8610 6588 9999
E-mail: china-info@brocade.com
Asia-Pacific Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen WFOE)
Citic Plaza
No. 233 Tian He Road North
Unit 1308 – 13th Floor
Guangzhou, China
Tel: +8620 3891 2000
Fax: +8620 3891 2111
E-mail: china-info@brocade.com
Document History
Document Title Publication Number Summary of Changes Publication Date
Brocade MIB Reference Manual v2.3 53-0000069-02 December 2000
Brocade MIB Reference Manual v3.0 53-0000134-03 July 2001
Brocade MIB Reference Manual v3.0, 4.0 53-0000184-02 March 2002
Brocade MIB Reference Manual
(v4.1, v4.0.x, v3.1, v3.0.x, v2.6.x)
Brocade MIB Reference Manual
(v4.1.2, v4.1, v4.0.x, v3.1, v3.0.x, v2.6.x)
Brocade MIB Reference Manual
(v4.1.2, v4.1, v4.0.x, v3.1, v3.0.x, v2.6.x)
Brocade MIB Reference Manual
(v4.2.0, v4.1.2, v4.1, v4.0.x, v3.1, v3.0.x,
v2.6.x)
Brocade Fabric OS MIB Reference Manual 53-0000521-08 Updated to support the
53-0000521-02 Added Brocade-specific Entity
April 2003
and HA-MIBs.
53-0000521-03 Added FICON information. May 2003
53-0000521-04 Revised FICON information. October 2003
53-0000521-06 Updated to support the
December 2003
Brocade 3250, 3850, and
24000 switches.
September 2004
Brocade 4100.
Page 3

Document Title Publication Number Summary of Changes Publication Date
Brocade Fabric OS MIB Reference Manual 53-0000521-09 Updated to support the
Brocade 48000 and 200E.
Brocade Fabric OS MIB Reference Manual 53-1000045-01 Updated to support the
Brocade 4900, 7500, and
FR4-18i blade.
Brocade Fabric OS MIB Reference 53-1000241-01 Changed name, updated to
support Fabric OS v5.2.x.
Brocade Fabric OS MIB Reference 53-1000439-01 New branding, updated to
support Fabric OS v5.3.0.
Brocade Fabric OS MIB Reference 53-1000602-01 Updated to support the
Brocade DCX Data Center
Backbone Director.
Brocade Fabric OS MIB Reference 53-1000602-02 Updated to support the
Brocade 300, 5100, and
5300 switches.
Brocade Fabric OS MIB Reference 53-1001156-01 Updated to support the
Brocade DCX-4S and Brocade
Encryption Switch.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 53-1001339-01 Updated to support the
Brocade 7800 Extension
Switch, Brocade 8000 Switch,
FCOE10-24 DCX Blade, and
FX8-24 DCX Extension Blade.
Added USM MIB details,
fcipTcpConnTable, and
fcipConnStatsTable.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 53-1001768-01 Updated to support the
Brocade FC8-64 port blade
and Brocade VA-40FC. Added
BD MIB details,
swConnUnitPortStatExtention
Table, swMemUsageLimit1,
swMemUsageLimit3,
swFabricReconfigTrap,
swFabricSegmentTrap, and
swExtTrap.
April 2005
January 2006
September 2006
June 2007
October 2007
March 2008
November 2008
July 2009
March 2010
Fabric OS MIB Reference iii
53-1002750-01
Page 4

Document Title Publication Number Summary of Changes Publication Date
Fabric OS MIB Reference 53-1002151-01 Updated to support Brocade
6510, Brocade DCX 8510-8
Backbone, and Brocade DCX
8510-4 Backbone. Added
FibreAlliance extension MIB,
SNMPv2 MIB,
ipAddressTable, MIBs for
swConnUnitPortStatExtention
Table, and switch traps.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 53-1002750-01 Updated to support Brocade
6505, Brocade 6520, and
Brocade VA-40FC. Added
swDeviceStatusTrap,
swConnUnitPCSErrorCounter,
and swConnUnitPortTable.
Updated the MIB objects that
are not supported or
deprecated for this release.
Customized traps are
obsoleted.
April 2011
December 2012
iv Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 5

Contents
About This Document
How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
Supported hardware and software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
What’s new in this document. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Document conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
Text formatting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
Notes, cautions, and warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
Key terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Notice to the reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Brocade resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Other industry resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Getting technical help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xix
Document feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xx
Chapter 1 Understanding Brocade SNMP
Setting the SNMP security level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Understanding SNMP basics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Understanding MIBs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Understanding SNMP traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Object instances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Loading Brocade MIBs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Brocade MIB files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Standard MIBs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Before loading MIBs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
MIB loading order. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
SNMP CLI usage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Access Gateway and Brocade MIBs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Firmware upgrades and enabled traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Fabric OS commands for configuring SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Support for Administrative Domains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Support for Role-Based Access Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Support for IPv6 addressing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Support for Virtual Fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Customized traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Fabric OS MIB Reference v
53-1002750-01
Page 6

Chapter 2 MIB-II (RFC1213-MIB)
MIB II overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
MIB-II object hierarchy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Textual conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Objects and types imported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
System group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Interfaces group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
AT group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
IP group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
ICMP group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
TCP group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
UDP group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
EGP group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Transmission group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
SNMP group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
ifMIB group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Generic traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Chapter 3 RMON MIB Objects
RMON MIB overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
RMON MIB object hierarchy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Textual conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
RMON group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Statistics group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
History group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
History control group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Ethernet history group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Alarm group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Event group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
RMON Traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Chapter 4 FE MIB Objects
FE MIB overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB organization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Definitions for FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
fcFeConfig group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
fcFeStatus group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
fcFeError group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
fcFeAccounting group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
vi Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 7

fcFeCapabilities group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
FCFABRIC-ELEMENT-MIB (experimental branch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
FCFABRIC-ELEMENT-MIB organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Definitions for FCFABRIC-ELEMENT-MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
fcFeConfig group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
fcFeOp group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .96
fcFeError group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
fcFeAcct group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
fcFeCap group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Chapter 5 Entity MIB Objects
Entity MIB overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Entity MIB system organization of MIB objects . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Definitions for Entity MIB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Textual conventions for Entity MIB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .106
Entity MIB objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Physical entity group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Logical entity group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
Entity mapping group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
General group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
Entity MIB trap. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
Entity MIB conformance information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120
Chapter 6 SW-MIB Objects
SW-MIB overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
SW-MIB system organization of MIB objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
Textual conventions for SW-MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .132
sw traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .135
Switch system group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .141
Switch Fabric group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .149
Switch agent configuration group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Fibre Channel port group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .152
Name Server database group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .156
Event group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .158
Fabric Watch group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .159
End device group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .168
Switch group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .169
Bloom performance monitor group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .170
Trunking group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .172
Fabric OS MIB Reference vii
53-1002750-01
Page 8

Toptalker group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .173
CPU or memory usage group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Switch connectivity unit port statistics extension table . . . . . . . . .175
Chapter 7 High-Availability MIB Objects
HA-MIB overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
High-Availability group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .181
FRU table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .181
FRU history table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .183
CP table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .184
HA-MIB traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .185
Chapter 8 FICON MIB Objects
FICON MIB overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .187
SNMP traps for FICON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .187
FICON MIB system organization of MIB objects. . . . . . . . . . . .187
Textual conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .189
FICON RNID group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .191
FICON LIRR group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .193
FICON RLIR group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .194
LinkIncident MIB traps group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .195
Chapter 9 FibreAlliance MIB Objects
FibreAlliance MIB overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .197
FCMGMT-MIB system organization of MIB objects . . . . . . . . . 197
Definitions for FCMGMT-MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .203
Connectivity unit group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .204
Statistics group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .225
Service group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .230
SNMP trap registration group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .232
Revision number scalar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .233
Unsupported tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .233
FibreAlliance MIB traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .234
Chapter 10 FibreAlliance Extension MIB Objects
FibreAlliance extension MIB overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .237
Textual conventions for FA-EXT-MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .238
SFP statistics table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .239
Port configuration table for Fabric Assigned PWWN feature . . . . .239
Port configuration table for encryption or compression feature . .240
viii Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 9

Switch connectivity unit port table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .241
Chapter 11 FCIP MIB Objects
FCIP MIB overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .243
FCIP MIB system organization of MIB objects . . . . . . . . . . . . .243
FCIP entity instance table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .245
FCIP link table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .246
FCIP TCP connection table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .247
FCIP extended link table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
FCIP connection statistics table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .249
Chapter 12 iSCSI MIB Objects
iSCSI MIB overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .251
iSCSI MIB system organization of MIB objects . . . . . . . . . . . .251
iSCSI instance attributes table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .254
iSCSI node attributes table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .255
iSCSI session attributes table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .257
iSCSI session statistics table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .259
iSCSI connection attributes table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .260
Chapter 13 SNMPv2 MIB Objects
SNMPv2 MIB overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .263
SNMPv2 MIB object hierarchy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .263
SNMP target address table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .264
SNMP target parameters table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .265
SNMP community table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .266
Chapter 14 USM MIB Objects
USM MIB objects overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .269
USM statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .270
USM user group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .271
Chapter 15 IEEE 802.1x PAE MIB Objects
IEEE 802.1x PAE MIB objects overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
Dot1x PAE system group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .275
Dot1x PAE authenticator group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
Chapter 16 LLDP MIB Objects
LLDP MIB objects overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .281
Fabric OS MIB Reference ix
53-1002750-01
Page 10

LLDP MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .284
LLDP configuration group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .284
LLDP statistics group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .286
LLDP local system data group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .287
LLDP remote systems data group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .289
LLDP-EXT-DOT1-MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .291
LLDP-EXT-DOT1-MIB organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .291
lldpXdot1 configuration group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .293
lldpXdot1 local data group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .294
lldpXdot1 remote data group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .296
LLDP-EXT-DOT3-MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .297
LLDP-EXT-DOT3-MIB organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .297
lldpXdot3 configuration group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .299
lldpXdot3 local data group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .299
lldpXdot3 remote data group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .301
Chapter 17 IEEE 802.3 LAG MIB Objects
IEEE 802.3 LAG MIB overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .303
Aggregator group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .305
Aggregator port group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .307
Chapter 18 Bridge-MIB Objects
Bridge-MIB overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .313
Bridge-MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .317
Bridge-MIB traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .318
dot1d base group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .318
dot1d STP group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .319
dot1dTp group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .321
dot1d static group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .323
P-Bridge MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .324
dot1dExtBase group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .325
dot1dPriority group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .326
Q-Bridge MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .326
dot1qBase group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .326
dot1qTp group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .327
dot1qStatic group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .329
dot1qVlan group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .331
RSTP MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .333
Chapter 19 BD MIB Objects
BD MIB objects overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .335
BD Traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .336
BD configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .337
BD statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .337
x Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 11

Appendix A MIB Object Groupings
Switch variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .339
Sensor variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .339
Port variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .339
Variables for state and status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .339
Variables for statistics and measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .340
Event variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .340
ISL and end device variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .340
ISL variables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .340
End Device variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .340
SNMP configuration variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .340
iSCSI instance information variables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .341
Appendix B Mapping of CLI Counters to MIB Objects
portStatsShow command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .343
portErrShow command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .344
portStats64Show command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .345
portShow command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .346
Index
Fabric OS MIB Reference xi
53-1002750-01
Page 12

xii Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 13

About This Document
In this chapter
•How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
•Supported hardware and software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
•What’s new in this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
•Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
•Notice to the reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
•Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
•Getting technical help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xix
•Document feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xx
How this document is organized
This document is organized to help you find the information that you want as quickly and easily as
possible.
The document contains the following components:
• Chapter 1, “Understanding Brocade SNMP,” provides an introduction to Brocade SNMP and
MIBs.
• Chapter 2, “MIB-II (RFC1213-MIB),” provides information for MIB-II.
• Chapter 3, “RMON MIB Objects,” provides information for RMON MIB object types.
• Chapter 4, “FE MIB Objects,” provides information for FE MIB object types.
• Chapter 5, “Entity MIB Objects,” provides information for Entity MIB object types.
• Chapter 6, “SW-MIB Objects,” provides information for FC Switch MIB (SW-MIB) object types.
• Chapter 7, “High-Availability MIB Objects,” provides information for High-Availability MIB object
types.
• Chapter 8, “FICON MIB Objects,” provides information for FICON MIB (LINK-INCIDENT-MIB)
object types.
• Chapter 9, “FibreAlliance MIB Objects,” provides information for FibreAlliance MIB
(FCMGMT-MIB) object types.
• Chapter 10, “FibreAlliance Extension MIB Objects,” provides information for FibreAlliance
extension MIB object types.
• Chapter 11, “FCIP MIB Objects,” provides information on FCIP MIB object types.
• Chapter 12, “iSCSI MIB Objects,” provides information on iSCSI MIB object types.
• Chapter 13, “SNMPv2 MIB Objects,” provides information on SNMPv2 MIB object types.
• Chapter 14, “USM MIB Objects,” provides information on USM MIB object types.
Fabric OS MIB Reference xiii
53-1002750-01
Page 14

Supported hardware and software
• Chapter 15, “IEEE 802.1x PAE MIB Objects,” provides information on IEEE 802.1x PAE MIB
object types.
• Chapter 16, “LLDP MIB Objects,” provides information on LLDP MIB object types.
• Chapter 17, “IEEE 802.3 LAG MIB Objects,” provides information on IEEE 802.3 LAG MIB
object types.
• Chapter 18, “Bridge-MIB Objects,” provides information on Bridge-MIB object types.
• Chapter 19, “BD MIB Objects,” provides information on BD MIB object types.
• Appendix A, “MIB Object Groupings,” is a function-based listing of MIB objects.
• Appendix B, “Mapping of CLI Counters to MIB Objects,” maps the CLI counters to the
corresponding MIB objects.
Supported hardware and software
In those instances in which procedures or parts of procedures documented here apply to some
switches but not to others, this guide identifies exactly which switches are supported and which are
not.
Although many different software and hardware configurations are tested and supported by
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. for Fabric OS vx.x.x, documenting all possible
configurations and scenarios is beyond the scope of this document.
This document supports Brocade Fabric OS version 7.1.0 and earlier versions, and all switches
supporting these Fabric OS versions, including:
• Brocade 300
• Brocade 4100
• Brocade 4900
• Brocade 5000
• Brocade 5100
• Brocade 5300
• Brocade 5410
• Brocade 5424
• Brocade 5450
• Brocade 5460
• Brocade 5470
• Brocade 5480
• Brocade 6505
• Brocade 6510
• Brocade 6520
• Brocade 7500
• Brocade 7500E
• Brocade 7600
• Brocade VA-40FC
• Brocade 7800 Extension Switch
xiv Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 15

Supported hardware and software
• Brocade 8000 FCoE Switch
• Brocade Encryption Switch
• Brocade DCX Backbone and Brocade DCX-4S Backbone
- FA4-18 Fibre Channel application blade
- FCOE10-24 DCX Blade
- FS8-18 Encryption Blade
- FC8-16 port blade
- FC8-32 port blade
- FC8-48 port blade
- FC8-64 port blade
- FX8-24 DCX Extension Blade
• Brocade 48000 director
- FA4-18 Fibre Channel application blade
- FC4-16 port blade
- FC4-16IP blade
- FC4-32 port blade
- FC4-48 port blade
- FC8-16 port blade
- FC8-32 port blade
- FC8-48 port blade
- FC10-6 port blade
- FR4-18i router blade
• Brocade VA-40FC
• Brocade DCX 8510-8 Backbone and Brocade DCX 8510-4 Backbone
- FC8-64 port blade
- FC16-32 port blade
- FC16-48 port blade
- FCOE10-24 DCX Blade
- FS8-18 Encryption Blade
- FX8-24 DCX Extension Blade
The following platforms can interoperate with switches running Fabric OS v7.0.0, but cannot load
Fabric OS v7.0.0:
• Brocade 4100
• Brocade 4900
• Brocade 5000
• Brocade 7500/7500E
• Brocade 7600
• Brocade 48000
The following blades are not supported in any chassis operating with Fabric OS v7.0.0:
Fabric OS MIB Reference xv
53-1002750-01
Page 16

What’s new in this document
• FA4-18
• FC4-16IP
• FC4-16
• FC4-32
• FC4-48
What’s new in this document
The following changes have been made since this document was last released:
• Information that was added:
- Support for Brocade 6505, Brocade 6520, and Brocade VA-40FC
- The following traps included:
swDeviceStatusTrap
- The following MIB objects included:
swConnUnitPortTable
swConnUnitPortEntry
swConnUnitPortCapableSpeeds
swConnUnitPortSpeedMode
swDeviceStatus
swConnUnitPCSErrorCounter
• Information that was changed:
- Obsoleted customized traps. Refer section “Customized traps”.
- Updated the following MIB objects as not supported.
fcipExtendedLinkTcpDroppedPackets
fcipExtendedLinkTcpSmoothedRTT
fcipExtendedLinkRtxRtxTO
fcipExtendedLinkRtxDupAck
fcipExtendedLinkDupAck
xfcipExtendedLinkTcpDroppedPackets
- Updated the following MIB objects as deprecated.
swFwLastEvent
swFwLastEventVal
swFwLastEventTime
swFwBehaviorType
swFwBehaviorInt
swFwLastSeverityLevel
swFCportspeed
- Change of version number wherever applicable
For further information about new features and documentation updates for this release, refer to
the release notes.
xvi Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 17

Document conventions
NOTE
ATTENTION
CAUTION
DANGER
This section describes text formatting conventions and important notices formats.
Text formatting
The narrative-text formatting conventions that are used in this document are as follows:
bold text Identifies command names
italic text Provides emphasis
code text Identifies CLI output
For readability, command names in the narrative portions of this guide are presented in mixed
lettercase: for example, switchShow. In actual examples, command lettercase is often all
lowercase. Otherwise, this manual specifically notes those cases in which a command is case
sensitive.
Document conventions
Identifies the names of user-manipulated GUI elements
Identifies keywords and operands
Identifies text to enter at the GUI or CLI
Identifies variables
Identifies paths and Internet addresses
Identifies document titles
Identifies syntax examples
Notes, cautions, and warnings
The following notices and statements are used in this manual. They are listed below in order of
increasing severity of potential hazards.
A note provides a tip, guidance, or advice, emphasizes important information, or provides a
reference to related information.
An Attention statement indicates potential damage to hardware or data.
A Caution statement alerts you to situations that can be potentially hazardous to you or cause
damage to hardware, firmware, software, or data.
A Danger statement indicates conditions or situations that can be potentially lethal or extremely
hazardous to you. Safety labels are also attached directly to products to warn of these conditions
or situations.
Fabric OS MIB Reference xvii
53-1002750-01
Page 18

Notice to the reader
Key terms
For definitions specific to Brocade and Fibre Channel, see the technical glossaries on MyBrocade.
See “Brocade resources” on page xviii for instructions on accessing MyBrocade.
For definitions of SAN-specific terms, visit the Storage Networking Industry Association online
dictionary at:
http://www.snia.org/education/dictionary
Notice to the reader
This document may contain references to the trademarks of the following corporations. These
trademarks are the properties of their respective companies and corporations.
These references are made for informational purposes only.
TABLE 1
Corporation Referenced Trademarks and Products
Microsoft Corporation Windows, Windows NT, Internet Explorer
Oracle Corporation Oracle, Java
Additional information
This section lists additional Brocade and industry-specific documentation that you might find
helpful.
Brocade resources
To get up-to-the-minute information, go to http://my.brocade.com and register at no cost for a user
ID and password.
White papers, online demonstrations, and data sheets are available through the Brocade website
at:
http://www.brocade.com/products-solutions/products/index.page
For additional Brocade documentation, visit the Brocade website:
http://www.brocade.com
Release notes are available on the MyBrocade website and are also bundled with the Fabric OS
firmware.
Other industry resources
For additional resource information, visit the Technical Committee T11 website. This website
provides interface standards for high-performance and mass storage applications for Fibre
Channel, storage management, and other applications:
http://www.t11.org
xviii Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 19

For information about the Fibre Channel industry, visit the Fibre Channel Industry Association
website:
http://www.fibrechannel.org
Getting technical help
Contact your switch supplier for hardware, firmware, and software support, including product
repairs and part ordering. To expedite your call, have the following information immediately
available:
1. General Information
• Switch model
• Switch operating system version
• Software name and software version, if applicable
• Error numbers and messages received
• supportSave command output
• Detailed description of the problem, including the switch or fabric behavior immediately
following the problem, and specific questions
• Description of any troubleshooting steps already performed and the results
• Serial console and Telnet session logs
• syslog message logs
Getting technical help
2. Switch Serial Number
The switch serial number and corresponding bar code are provided on the serial number label,
as illustrated below:
*FT00X0054E9*
FT00X0054E9
The serial number label is located as follows:
• Brocade 300, 4100, 4900, 5100, 5300, 6510, 6520, 7500, 7500E, 7800, 8000,
VA-40FC, and Brocade Encryption Switch—On the switch ID pull-out tab located inside the
chassis on the port side on the left
• Brocade 5000—On the switch ID pull-out tab located on the bottom of the port side of the
switch
• Brocade 5410, 5424, 5450, 5460, 5470, 5480—Serial number label attached to the
module
• Brocade 7600—On the bottom of the chassis
• Brocade 48000—Inside the chassis next to the power supply bays
• Brocade DCX and 8510-8—On the bottom right on the port side of the chassis
• Brocade DCX-4S and 8510-4—On the bottom right on the port side of the chassis, directly
above the cable management comb
3. World Wide Name (WWN)
Fabric OS MIB Reference xix
53-1002750-01
Page 20

Document feedback
Use the licenseIdShow command to display the WWN of the chassis. If you cannot use the
licenseIdShow command because the switch is inoperable, you can get the WWN from the
same place as the serial number, except for the Brocade DCX. For the Brocade DCX, access the
numbers on the WWN cards by removing the Brocade logo plate at the top of the nonport side
of the chassis.
Document feedback
Because quality is our first concern at Brocade, we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy
and completeness of this document. However, if you find an error or an omission, or you think that
a topic needs further development, we want to hear from you. Forward your feedback to:
documentation@brocade.com
Provide the title and version number and as much detail as possible about your comment,
including the topic heading and page number and your suggestions for improvement.
xx Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 21

Chapter
Understanding Brocade SNMP
In this chapter
•Setting the SNMP security level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
•Understanding SNMP basics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
•Loading Brocade MIBs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
•Access Gateway and Brocade MIBs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
•Firmware upgrades and enabled traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
•Fabric OS commands for configuring SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
•Support for Administrative Domains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
•Support for Role-Based Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
•Support for IPv6 addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
•Support for Virtual Fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
•Customized traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1
Setting the SNMP security level
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an industry-standard method of monitoring
and managing network devices. This protocol promotes interoperability because SNMP-capable
systems must adhere to a common set of framework and language rules.
Understanding the components of SNMP makes it possible to use third-party tools to view, browse,
and manipulate Brocade switch variables (MIBs) remotely as well as to set up an enterprise-level
management process. Every Brocade switch and director supports SNMP.
Recipients for SNMP traps are restricted according to security levels. Security levels are selected
and set for a switch using the snmpconfig --set seclevel command. To select and set SNMP security
levels, issue the command snmpconfig --set seclevel after having logged in to the switch as admin.
The following example sets the SNMP security level to 1 (authentication only). This setting allows all
SNMPv1 users to perform GET and SET operations on MIBs, but creates an exception for SNMPv3
users that do not have authentication and privacy privileges (noAuthnoPriv).
switch:admin> snmpconfig --set seclevel
Select SNMP Security Level
(0 = No security, 1 = Authentication only, 2 = Authentication and Privacy, 3 =
sxNo Access): (0..3) [0]
Select SNMP SET Security Level
(0 = No security, 1 = Authentication only, 2 = Authentication and Privacy, 3 =
No Access): (0..3) [0]
Tab le 2 shows the security level options.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 1
53-1002750-01
Page 22
Understanding SNMP basics
Agent
Management Station
SNMP
MIB
Management Station
Agent
get, getnext, set
reply
TRAP
Management Station
Agent
1
TABLE 2 Security level options
Security level Protocol Query behavior Traps
No security [0]
(noAuthnoPriv)
Authentication only [1]
(authNoPriv)
Authentication and
Privacy [2]
(authPriv)
No Access [3]SNMPv1
SNMPv1
SNMPv3
SNMPv1
SNMPv3
SNMPv1
SNMPv3
SNMPv3
Understanding SNMP basics
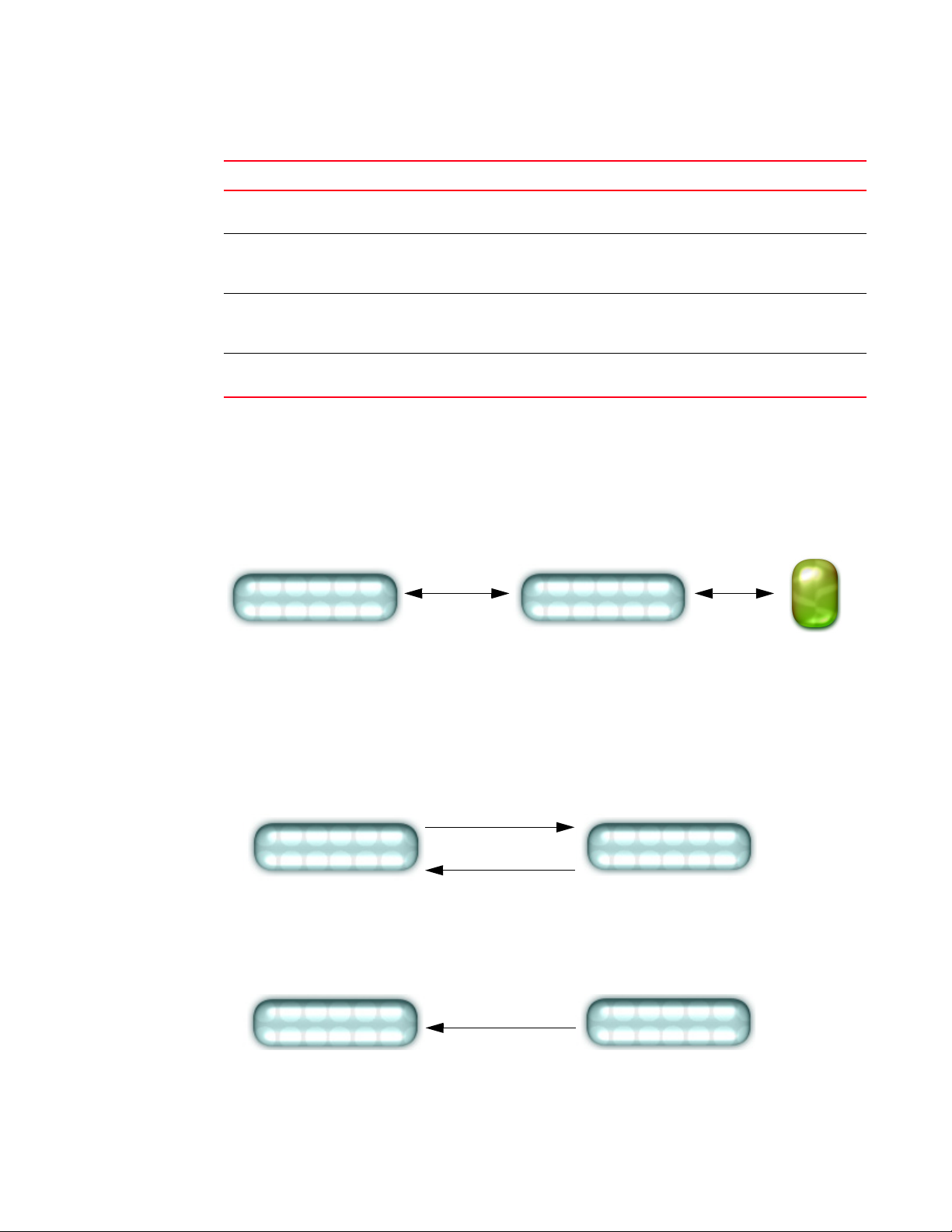
Every Brocade switch carries an agent and management information base (MIB), as shown in
Figure 1. The agent accesses information about a device and makes it available to an SNMP
network management station.
FIGURE 1 SNMP structure
Allowed.
Allowed.
Allowed.
All SNMPv3 users allowed except
noAuthNoPriv users.
Not allowed.
Only SNMPv3 users with authPriv
privilege are allowed.
Not allowed. Not Sent.
Sent.
Sent.
Sent.
Sent for all SNMPv3 users
except noAuthNoPriv users.
Not Sent.
Sent only for authPriv users.
When active, the management station can get information or set information when it queries an
agent. SNMP commands, such as get, set, getnext, and getresponse, are sent from the
management station, and the agent replies once the value is obtained or modified (Figure 2).
Agents use variables to report such data as the number of bytes and packets in and out of the
device, or the number of broadcast messages sent and received. These variables are also known
as managed objects. All managed objects are contained in the MIB.
FIGURE 2 SNMP query
The management station can also receive traps, unsolicited messages from the switch agent if an
unusual event occurs (Figure 3). For more information, refer to “Understanding SNMP traps” on
page 4.
FIGURE 3 SNMP trap
2 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 23

Understanding SNMP basics
mgmt (2)
sysObjectID (2)
iso (1)
org (3)
Brocade SW MIB
1.3.6.1.4.1.1588.2.1.1.1
dod (6)
internet (1)
experimental (3)
fcmgmt (94)
connSet (1)
enterprise (1)
private (4)
bcsi (1588)
mib-2 (1)
interface (2)
sysDescr (1)
system (1)
directory (1)
1
The agent can receive queries from one or more management stations and can send traps to up to
six management stations.
Understanding MIBs
The management information base (MIB) is a database of monitored and managed information on
a device, in this case a Brocade switch. The MIB structure can be represented by a tree hierarchy.
The root splits into three main branches: International Organization for Standardization (ISO),
Consultative Committee for International Telegraph and Telephone (CCITT), and joint ISO/CCITT.
These branches have short text strings and integers (OIDs) to identify them. Text strings describe
object names, while integers allow software to create compact, encoded representations of the
names.
Each MIB variable is assigned an object identifier (OID). The OID is the sequence of numeric labels
on the nodes along a path from the root to the object. For example, as shown in Figure 4, the
Brocade SW.MIB OID is:
1.3.6.1.4.1.1588.2.1.1.1
The corresponding name is:
iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprise.bcsi.commDev.fibreChannel.fcSwitch.sw
The other branches are part of the standard MIBs, and the portions relevant to configuring SNMP
on a Brocade switch are referenced in the remainder of this reference.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 3
53-1002750-01
FIGURE 4 Brocade MIB tree location
Use a MIB browser to access the MIB variables: all MIB browsers perform queries and load MIBs.
Page 24

Understanding SNMP basics
NOTE
1
Since different vendors vary the information in their private enterprise MIBs, it is necessary to verify
their information. The Fibre Channel MIB standards dictate that certain information be included in
all MIBs: it is the vendors’ responsibility to follow the standards. The standards are as follows:
• FibreAlliance (FA) MIB: Brocade supports v4.4. and later releases.
• Fabric Element (FE) MIB: accepted by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
Once loaded, the MAX-ACCESS provides access levels between the agent and management station.
The access levels are as follows:
• not accessible
• read create
• read only - Public
Brocade supports FE_RFC2837.mib under the MIB-II branch in Fabric OS v7.1.0, v7.0.0,
v6.4.1_fcoe, v6.4.0, v6.3.0, v6.2.0, v6.1.2_CEE, v6.1.0, and v6.0.0. The latest version of the
FE MIB references the FRAMEWORK.MIB and, based on the MIB browser, it is necessary to
load this MIB before the FE.MIB. For more information, refer to “Loading Brocade MIBs” on
page 7.
You cannot read or write to this variable.
Specifies a tabular object that can be read, modified, or created as a new row in a table.
You can only monitor information.
• read-write - Private
You can read or modify this variable.
• accessible-to-notify
You can read this information only through traps.
Understanding SNMP traps
An unsolicited message that comes to the management station from the SNMP agent on the
device is called a trap. Brocade switches send traps out on UDP port 162 and to any configured
port. In order to receive traps, the management station IP address and severity level must be
configured on the switch. Up to six trap recipients can be configured using Web Tools or the
snmpConfig command. You can define a different message severity level for each recipient so that
some recipients receive all trap messages and others receive only the most critical.
Due to design limitation, IP address validation cannot be done for trap recipients.
There are two main MIB trap choices:
• FibreAlliance MIB trap - Associated with the Fibre Alliance MIB (FA-MIB), this MIB manages SAN
switches and devices from any company that complies with Fibre Alliance specifications.
• Brocade-specific MIB trap - Associated with the Brocade-specific Brocade MIB (SW-MIB),
manages Brocade switches only.
There is some overlap in the functionality of these MIBs. If you enable both SW-MIB and FA-MIB
traps, you could receive duplicate messages for the switch events that trigger the trap.
4 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 25

Understanding SNMP basics
You can also use these additional MIBs and their associated traps: HA-MIB; FICON-MIB; and
SWEXTTRAP. In Fabric OS v6.4.0, you can use the snmpConfig command to enable or disable all
the MIBs.
An event trap (swEventTrap, connUnitEventTrap, or swFabricWatchTrap) is basically an error
message (errShow output) that is SNMP-formatted and delivered.
1
FA traps
Consider enabling the FA traps if you want to use SNMP to monitor multiple connectivity units,
including Brocade switches.
The switchStatusPolicySet command determines the FA-TRAP switch status-related outputs:
• connUnitStatusChange
This trap is generated by Fabric watch such that only the swUnitsStatusChange is controlled by
switchStatusPolicySet command.
• connUnitSensorStatusChange
This trap is generated by any sensor event.
• connUnitPortStatusChange
This trap sends the instance of connUnitPortName as part of the trap; the instance string is
NULL, if the port name is not defined for the specified port.
• connUnitEventTrap
All the external traps gets converted into swEventTrap except for AN-1006, AUTH-3001 to
AUTH-3008, FW-3001, SEC-3001 to SEC-3034, and SEC-3044 to SEC-3048 RASlog messages.
Events in the Error Log of a severity at or above the configured threshold will generate SNMP traps.
The Fibre Alliance Trap (FA-TRAP) can be configured to send traps using the snmpConfig command.
For more information on this command, refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference.
HA traps
Consider enabling these traps to monitor field-replaceable unit (FRU) status and control processor
(CP) status when you have a Brocade director in your environment:
• fruStatusChanged
This trap is generated by a FRU status change, such as a switch reboot or disabling or enabling
a FRU component such as fandisable, fanenable and so on.
• cpStatusChanged
This trap is generated by a change in the status of a CP, including a reboot or firmware
download.
• fruHistoryTrap
This trap is generated when a FRU is added or removed. It is not generated when standby CP is
removed.
The high availability trap (HA-TRAP) can be configured to send traps using the snmpConfig
command. For more information on this command, refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 5
53-1002750-01
Page 26

Understanding SNMP basics
1
SW traps
There are fourteen specific traps defined in Brocade SW-TRAP.
1. swfault (no longer supported)
2. swSensorScn (no longer supported)
3. swFCPortScn
4. swEventTrap
5. swFabricWatchTrap
6. swTrackChangesTrap
This trap is generated by a port state change.
This trap is generated by any switch event reported to the system error log.
The desired severity level is introduced to filter a swEvent trap based on the severity level.
This trap is generated when any Fabric Watch threshold is reached.
The desired severity level is introduced to filter a swFabricWatchTrap based on the severity
level.
This trap is generated by a login or a logout.
7. swIPv6ChangeTrap
This trap is generated when an IPv6 address status change event occurs. It is generated only
when IPv6 stateless state changes to the deprecation state and not for address change
notification.
8. swPmgrEventTrap
This trap is generated when any partition manager change happens.
9. swFabricReconfigTrap
The trap to be sent for tracking fabric reconfiguration.
10. swFabricSegmentTrap
The trap to be sent for tracking segmentation.
11. swExtTrap
The trap adds the SSN binding to the traps if it is enabled.
12. swStateChangeTrap
This trap is sent when the switch changes its state to online or offline.
13. swPortMoveTrap
This trap is sent when the virtual ports are moved from one switch to another.
14. swBrcdGenericTrap
This trap is sent for one of the events, such as fabric change, device change, FAPWWN change,
and FDMI events. This trap is for Brocade use.
15. swDeviceStatusTrap
This trap is sent whenever a device logs in or logs out.
6 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 27

The Brocade trap (SW-TRAP) can be configured to send traps using the snmpConfig command. For
more information on this command, refer to Table 6 or the Fabric OS Command Reference.
Object instances
MIB objects are defined by the OID, which is the type of object, and by the instance number, which
is an instance of that MIB object. A Fibre Channel port is a MIB object, and port 0 is an instance of
that object. The following is an OID number and an instance number:
1.3.6.1.4.1.1588.2.1.1.1.6.2.1.11.5
where:
1.3.6.1.4.1.1588.2.1.1.1.6.2.1.11 is the OID (of swFCPortTxWords) and 5 is the instance
ID for port 4.
You must add 1 to the port number to get its instance number in SNMP because SNMP numbering
starts at 1; switch port numbering starts at 0.
Loading Brocade MIBs
Loading Brocade MIBs
1
The Brocade MIB is a set of variables that are private extensions to the Internet standard MIB-II.
The Brocade agents support many other Internet-standard MIBs. These standard MIBs are defined
in RFC publications. To find specific MIB information, examine the Brocade proprietary MIB
structure and the standard RFC MIBs supported by Brocade.
Brocade MIB files
The Brocade MIB files are as follows:
• bd.mib
• BRCD_REG.mib
• BRCD_TC.mib
• brcdfcip.mib
• CPQ_HOST.mib
• CPQ_RACK.mib
• FA.mib
• FICON.mib
• HA.mib
• IBMBladeCenterTrapMIB.mib
• SW.mib
• faext.mib
Standard MIBs
Distribution of standard MIBs has been stopped from Fabric OS v6.4.0. Download the following
MIBs from the http://www.oidview.com/ website:
Fabric OS MIB Reference 7
53-1002750-01
Page 28

Loading Brocade MIBs
1
• SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB
• IF-MIB
• IANAifType-MIB
• INET-ADDRESS-MIB
• RFC1213-MIB
• SNMPv2-MIB
• ENTITY-MIB
• RMON-MIB
• FC-MGMT-MIB
• FCIP-MGMT-MIB
• ISCSI-MIB
• FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB
• SNMPv2-PARTY-MIB
• SNMPv2-SMI-MIB
• SNMP-VIEW-BASED-ACM-MIB
• SNMP-USER-BASED-SM-MIB
• SNMP-TARGET-MIB
• IEEE 802.1x PAE MIB
• IEEE 802.3 LAG MIB
• BRIDGE-MIB
• P-BRIDGE MIB
• Q-BRIDGE MIB
• RSTP-MIB
• LLDP MIB
• LLDP-EXT-DOT1-MIB
• LLDP-EXT-DOT3-MIB
• IP MIB
• SNMP-COMMUNITY-MIB
Before loading MIBs
Before loading Brocade MIB files, ensure that you have the correct version of SNMP for your Fabric
OS version (Table 3).
TABLE 3 Fabric OS-supported SNMP versions
Firmware SNMPv1 SNMPv2 SNMPv3
Fabric OS v5.x Yes Yes
Fabric OS v6.0.0 Yes Yes Yes
Fabric OS v6.1.0 Yes Yes Yes
Fabric OS v6.2.0 Yes Yes Yes
8 Fabric OS MIB Reference
1
Yes
2
53-1002750-01
Page 29

Loading Brocade MIBs
TABLE 3 Fabric OS-supported SNMP versions (Continued)
Firmware SNMPv1 SNMPv2 SNMPv3
Fabric OS v6.1.2_CEE Yes No Yes
Fabric OS v6.3.0 Yes No Yes
Fabric OS v6.4.0 Yes No Yes
Fabric OS v6.4.1_fcoe Yes No Yes
Fabric OS v7.0.0 Yes No Yes
Fabric OS v7.0.1 Yes No Yes
Fabric OS v7.1.0 Yes No Yes
1. SNMPv2 is supported in Fabric OS v5.0.4 and later, but SNMPv2 traps are not supported.
2. Fabric OS v5.x supports the SNMPv3-USM MIB (snmpUsmMIB), which is available as RFC 3414.
MIB loading order
Many MIBs use definitions that are defined in other MIBs. These definitions are listed in the
IMPORTS section near the top of the MIB. When loading the Brocade MIBs, refer to Figure 5 to
ensure any MIB dependencies are loading in the correct order.
1
Fabric OS MIB Reference 9
53-1002750-01
Page 30

RFC1155-SMI
BRCD.mib
Brocade-REG-MIB
Brocade-TC
FOS 2.6.x, 3.x, 4.x, 5.x, 6.x
Brocade_RE.MIB
FOS 6.4, 7.0
FICON_v5_0.mib
FICON.MIB
FOS 6.0
Select one
Brocade_TC.mib
FOS 6.4, 7.0
BD.mib
FOS 6.4, 7.0
RFC2571
SNMP-FRAMEWORK-
MIB
ENTITY_RFC2737.mib
ENTITY-MIB
FCIP.mib
FC_RFC4044.mib
IANA IF-TYPE MIB
SNMPv2-MIB
BRCDFCIP.mib
IF.mib
Dependency
Standard MIB File
Module name
Brocade MIB
Module name
FOS supported
Legend
HA.mib
FA_v2_2.mib
FCMGMT-MIB
FOS 2.6.x
FA.mib
FCMGMT-MIB
FOS 3.x, 4.x, 5.x, 6.x
Select one
SW_v5_5.mib
FOS 2.6.x, 3.x, 4.x,
5.x
SW_v5_7.mib
FOS 6.x
SW.mib
FOS 6.4
BRIDEGE-MIB
P-BRIDEGE
MIB
RFC1213-MIB
MIB-II
RMON MIB
FE_RFC2837.mib
FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB
FOS 3.1.x, 4.x, 5.x, 6.x, 7.0
ISCSI_RFC4544.mib
IANA-ADDRESS-FAMILY
-NUMBERS-MIB
LLDP-MIB
LLDP-EXT-DOT1-
MIB
LLDP-EXT-DOT3-
MIB
INET-Address
- MIB
IEEE LAG MIB
RFC1271-MIB
RMON2-MIB
TOKEN-RING-
RMON-MIB
Q-BRIDEGE
MIB
RSTP-MIB
IEEE 802.1 PAE
MIB
faext.mib
FOS 7.0
FICON.mib
FOS 7.0
Loading Brocade MIBs
1
10 Fabric OS MIB Reference
FIGURE 5 Brocade SNMP MIB dependencies and advised installation order
53-1002750-01
Page 31

Loading Brocade MIBs
NOTE
FA.mib obsoletes the use of the connUnitPortStatFabricTable and now uses the
connUnitPortStatTable for port statistics.
All versions of Fabric OS support SNMPv1. Fabric OS v5.0.1 supports the SNMPv3-USM
(snmpUsmMIB) MIB. Fabric OS v5.3.0 supports the FCIP MIB and ifXtable.
SNMP CLI usage
The examples for configuring SNMPv3 users/traps are listed in the following section.
Configuring SNMPv3 user/traps
1. Create a user on the switch in non-VF Context using CLI userconfig, with the required role.
switch:admin> userconfig --add fa_adm -r fabricadmin -h0 -a 0-255
Setting initial password for fa_adm
Enter new password:********
Re-type new password:********
Account fa_adm has been successfully added.
switch:admin>
1
Create a user on the switch in VF Context using CLI userconfig, with the required role.
switch:admin> userconfig --add sa_user -r switchadmin -l 1-128 -h1 -c admin
Setting initial password for sa_user
Enter new password:********
Re-type new password:********
Account sa_user has been successfully added.
switch:admin>
2. Create the SNMPv3 user.
switch:root> snmpconfig --set snmpv3
SNMP Informs Enabled (true, t, false, f): [false] t
SNMPv3 user configuration(snmp user not configured in FOS user database will
have physical AD and admin role as the default):
User (rw): [snmpadmin1]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(2..2) [2]
Engine ID: [0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0] 80:00:05:23:01:0A:23:34:21
User (rw): [snmpadmin2]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3] 1
New Auth Passwd:
Verify Auth Passwd:
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(1..6) [2] 1
New Priv Passwd:
Verify Priv Passwd:
Engine ID: [0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0] 80:00:05:23:01:0A:23:34:1B
User (rw): [snmpadmin3]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(2..2) [2]
Fabric OS MIB Reference 11
53-1002750-01
Page 32

Loading Brocade MIBs
1
Engine ID: [0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0]
User (ro): [snmpuser1]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(2..2) [2]
Engine ID: [0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0]
User (ro): [snmpuser2]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(2..2) [2]
Engine ID: [0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0]
User (ro): [snmpuser3]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(2..2) [2]
Engine ID: [0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0]
SNMPv3 trap recipient configuration:
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0] 10.35.52.33
UserIndex: (1..6) [1]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0] 4
Trap recipient Port : (0..65535) [162]
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0] 10.35.52.27
UserIndex: (1..6) [2]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0] 4
Trap recipient Port : (0..65535) [162]
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0]
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0]
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0]
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0]
Committing configuration.....done.
switch:root> snmpconfig --show snmpv3
SNMP Informs = 1 (ON)
SNMPv3 USM configuration:
User 1 (rw): snmpadmin1
Auth Protocol: noAuth
Priv Protocol: noPriv
Engine ID: 80:00:05:23:01:0a:23:34:21
User 2 (rw): snmpadmin2
Auth Protocol: MD5
Priv Protocol: DES
Engine ID: 80:00:05:23:01:0a:23:34:1b
User 3 (rw): snmpadmin3
Auth Protocol: noAuth
Priv Protocol: noPriv
Engine ID: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
User 4 (ro): snmpuser1
Auth Protocol: noAuth
Priv Protocol: noPriv
Engine ID: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
User 5 (ro): snmpuser2
Auth Protocol: noAuth
Priv Protocol: noPriv
Engine ID: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
User 6 (ro): snmpuser3
Auth Protocol: noAuth
12 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 33

Loading Brocade MIBs
Priv Protocol: noPriv
Engine ID: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
SNMPv3 Trap configuration:
Trap Entry 1: 10.35.52.33
Trap Port: 162
Trap User: snmpadmin1
Trap recipient Severity level: 4
Trap Entry 2: 10.35.52.27
Trap Port: 162
Trap User: snmpadmin2
Trap recipient Severity level: 4
Trap Entry 3: No trap recipient configured yet
Trap Entry 4: No trap recipient configured yet
Trap Entry 5: No trap recipient configured yet
Trap Entry 6: No trap recipient configured yet
1
An example of the SNMPv3 user trap recipients configured with DNS names and IPv6
addressess
switch:admin> snmpconfig --set snmpv3
SNMP Informs Enabled (true, t, false, f): [false]
SNMPv3 user configuration(snmp user not configured in FOS user database will
have physical AD and admin role as the default):
User (rw): [snmpadmin1]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(2..2) [2]
User (rw): [snmpadmin2]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3] 1
New Auth Passwd:
Verify Auth Passwd:
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(1..6) [2]
User (rw): [snmpadmin3]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3] 1
New Auth Passwd:
Verify Auth Passwd:
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(1..6) [2] 1
New Priv Passwd:
Verify Priv Passwd:
User (ro): [snmpuser1]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(2..2) [2]
User (ro): [snmpuser2]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(2..2) [2]
User (ro): [snmpuser3]
Auth Protocol [MD5(1)/SHA(2)/noAuth(3)]: (1..3) [3]
Priv Protocol [DES(1)/noPriv(2)/3DES(3)/AES128(4)/AES192(5)/AES256(6)]):
(2..2) [2]
SNMPv3 trap recipient configuration:
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0] 172.26.4.102
UserIndex: (1..6) [1]
Fabric OS MIB Reference 13
53-1002750-01
Page 34

Loading Brocade MIBs
1
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0] 1
Trap recipient Port : (0..65535) [162]
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0] fe80::224:1dff:fef6:3f98
UserIndex: (1..6) [2]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0] 2
Trap recipient Port : (0..65535) [162]
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0] HCL0389U.corp.brocade.com
UserIndex: (1..6) [3]
Trap recipient Severity level : (0..5) [0] 5
Trap recipient Port : (0..65535) [162]
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0]
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0]
Trap Recipient's IP address : [0.0.0.0]
Committing configuration.....done.
DCX_128:FID128:admin>
switch:admin> snmpconfig --show snmpv3
SNMP Informs = 0 (OFF)
SNMPv3 USM configuration:
User 1 (rw): snmpadmin1
Auth Protocol: noAuth
Priv Protocol: noPriv
User 2 (rw): snmpadmin2
Auth Protocol: MD5
Priv Protocol: noPriv
User 3 (rw): snmpadmin3
Auth Protocol: MD5
Priv Protocol: DES
User 4 (ro): snmpuser1
Auth Protocol: noAuth
Priv Protocol: noPriv
User 5 (ro): snmpuser2
Auth Protocol: noAuth
Priv Protocol: noPriv
User 6 (ro): snmpuser3
Auth Protocol: noAuth
Priv Protocol: noPriv
SNMPv3 Trap configuration:
Trap Entry 1: 172.26.4.102
Trap Port: 162
Trap User: snmpadmin1
Trap recipient Severity level: 1
Trap Entry 2: fe80::224:1dff:fef6:3f98
Trap Port: 162
Trap User: snmpadmin2
Trap recipient Severity level: 2
Trap Entry 3: HCL0389U.corp.brocade.com
Trap Port: 162
Trap User: snmpadmin3
Trap recipient Severity level: 5
Trap Entry 4: No trap recipient configured yet
Trap Entry 5: No trap recipient configured yet
Trap Entry 6: No trap recipient configured yet
To display the traps and MIBs supported in Fabric OS:
14 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 35

Loading Brocade MIBs
switch:root> snmpTraps --show
# |Mib Name |Supported Traps
---|----------------|-------------------------------001|SW-MIB |sw-track-changes-trap
| |sw-fabric-watch-trap
| |sw-fc-port-scn
| |ip-v6-change-trap
| |sw-pmgr-event-trap
| |sw-event-trap
| |sw-fabric-reconfig-trap
| |sw-fabric-reconfig-trap
| |sw-state-trap
| |sw-move-port-trap
| |sw-brcd-genric-trap
002|FICON-MIB |link-rnid-device-registration
| |link-rnid-device-deregistration
| |link-lirr-listerner-added
| |link-lirr-listerner-removed
| |link-rlir-failure-incident
003|FA-MIB |conn-unit-status-change
| |conn-unit-sensor-status-change
| |conn-unit-port-status-change
| |conn-unit-event-trap
004|RFC1157 |cold-restart-trap
| |warm-restart-trap
| |if-link-up-trap
| |if-link-down-trap
| |snmp-authetication-trap
005|HA-MIB |fru-status-change-trap
| |fru-history-trap
| |cp-status-change-trap
006|BD-MIB |bd-trap
| |bd-clear-trap
1
To send all traps to the configured recipients:
switch:root> snmpTraps --send
Number of traps sent : 30
To send all traps to the recipient 10.35.52.33:
switch:root> snmpTraps --send -ip_address 10.35.52.33
Number of traps sent : 30
To send the sw-fc-port-scn trap to the confiregured recipients:
switch:root> snmpTraps --send -trap_name sw-fc-port-scn
Number of traps sent : 1
To send the sw-fc-port-scn trap to the recipient 10.35.52.33:
switch:root> snmpTraps --send -trap_name sw-fc-port-scn -ip_address
10.35.52.33
Number of traps sent : 1
To unblock port traps on all the ports or on a specific port:
switch:admin> snmptraps -unblock ALL
Fabric OS MIB Reference 15
53-1002750-01
Page 36

Loading Brocade MIBs
1
switch:admin> snmptraps -unblock -port 1/10
To block port traps on slot 1 and port 10:
Switch:admin> snmptraps -block -port 1/10
Example of accessControl configuration:
switch:admin> snmpconfig --set accessControl
SNMP access list configuration:
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 192.168.0.0
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 10.32.148.0
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true] f
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0] 10.33.0.0
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true] f
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Access host subnet area in dot notation: [0.0.0.0]
Read/Write? (true, t, false, f): [true]
Committing configuration...done.
Example of mibCapability configuration:
To enable the swFabricWatchTrap non-interactively:
switch:admin> snmpconfig --enable mibCapability -mib_name SW-MIB -trap_name
swFabricWatchTrap
Operation succeeded
To enable the swEventTrap of the SW-MIB category only (this operation disables all other SNMP
traps in this MIB category):
switch:admin> snmpconfig --set mibCapability -mib_name SW-MIB -bitmask 0x10
Operation succeeded
switch:admin> snmpconfig --show mibCapability
[...]
SW-MIB: NO
swFault: NO
swSensorScn: NO
swFCPortScn: NO
swEventTrap: YES
DesiredSeverity:None
swFabricWatchTrap: NO
DesiredSeverity:None
swTrackChangesTrap: NO
swIPv6ChangeTrap: NO
swPmgrEventTrap: NO
swFabricReconfigTrap: NO
swFabricSegmentTrap: NO
swExtTrap: NO
[...]
To enable the SW-MIB MIB only without changing the current trap configuration:
switch:admin> snmpconfig --enable mibCapability -mib_name SW-MIB
16 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 37

Loading Brocade MIBs
Operation succeeded
switch:admin> snmpconfig --show mibCapability
[...]
SW-MIB: YES
swFault: NO
swSensorScn: NO
swFCPortScn: NO
swEventTrap: YES
DesiredSeverity:None
swFabricWatchTrap: YES
DesiredSeverity:None
swTrackChangesTrap: NO
swIPv6ChangeTrap: NO
swPmgrEventTrap: NO
swFabricReconfigTrap: NO
swFabricSegmentTrap: NO
swExtTrap: NO
[...]
1
To re-enable all traps under the SW-MIB category after they were disabled:
switch:admin> snmpconfig --set mibCapability -mib_name SW-MIB -bitmask 0xFFF
Operation succeeded
switch:admin> snmpconfig --show mibCapability
[...]
SW-MIB: YES
swFault: YES
swSensorScn: YES
swFCPortScn: YES
swEventTrap: YES
DesiredSeverity:None
swFabricWatchTrap: YES
DesiredSeverity:None
swTrackChangesTrap: YES
swIPv6ChangeTrap: YES
swPmgrEventTrap: YES
swFabricReconfigTrap: Yes
swFabricSegmentTrap: Yes
swExtTrap: Yes
[...]
To display the configuration for all MIBs and associated traps:
switch:admin> snmpconfig --show mibcapability
FE-MIB: YES
SW-MIB: YES
FA-MIB: YES
FICON-MIB: YES
HA-MIB: YES
FCIP-MIB: YES
ISCSI-MIB: YES
IF-MIB: YES
BD-MIB: YES
SW-TRAP: YES
swFault: YES
swSensorScn: YES
swFCPortScn: YES
swEventTrap: YES
DesiredSeverity:None
Fabric OS MIB Reference 17
53-1002750-01
Page 38

Loading Brocade MIBs
1
swFabricWatchTrap: YES
DesiredSeverity:None
swTrackChangesTrap: YES
swIPv6ChangeTrap: YES
swPmgrEventTrap: YES
swFabricReconfigTrap: YES
swFabricSegmentTrap: YES
swExtTrap: YES
FA-TRAP: YES
connUnitStatusChange: YES
connUnitDeletedTrap: YES
connUnitEventTrap: YES
connUnitSensorStatusChange: YES
connUnitPortStatusChange: YES
FICON-TRAP: YES
linkRNIDDeviceRegistration: YES
linkRNIDDeviceDeRegistration: YES
linkLIRRListenerAdded: YES
linkLIRRListenerRemoved: YES
linkRLIRFailureIncident: YES
HA-TRAP: YES
fruStatusChanged: YES
cpStatusChanged: YES
fruHistoryTrap: YES
ISCSI-TRAP: YES
iscsiTgtLoginFailure: YES
iscsiIntrLoginFailure: YES
iscsiInstSessionFailure: YES
IF-TRAP: YES
linkDown: YES
linkUp: YES
BD-TRAP: YES
bdTrap: YES
bdClearTrap: YES
To set the system group:
DCX_128:FID128:admin> snmpconfig --set systemgroup
Example of systemGroup configuration (default)
switch:admin> snmpconfig --default systemGroup
*****
This command will reset the agent's system group configuration back to
factory default
*****
sysDescr = Fibre Channel Switch
sysLocation = End User Premise
sysContact = Field Support
authTraps = 0 (OFF)
*****
Are you sure? (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
3. Set the security level.
switch:admin> snmpconfig --set secLevel
Select SNMP GET Security Level
(0 = No security, 1 = Authentication only, 2 = Authentication and Privacy, 3 =
No Access): (0..3) [0] 2
Select SNMP SET Security Level
18 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 39

Access Gateway and Brocade MIBs
NOTE
(0 = No security, 1 = Authentication only, 2 = Authentication and Privacy, 3 =
No Access): (2..3) [2] 2
switch:admin> snmpconfig --show secLevel
GET security level = 2, SET level = 2
SNMP GET Security Level: Authentication and Privacy
SNMP SET Security Level: Authentication and Privacy
1
To set the security level to default:
DCX_128:FID128:admin> snmpconfig --default seclevel
GET security level = 0, SET level = 0
SNMP GET Security Level: No security
SNMP SET Security Level: No security
SNMP GET Security Level will be set to 'No Security'
SNMP SET Security Level will be set to 'No Security'
Do you want to continue? (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
DCX_128:FID128:admin>
DCX_128:FID128:admin> snmpconfig --show seclevel
GET security level = 0, SET level = 0
SNMP GET Security Level: No security
SNMP SET Security Level: No security
DCX_128:FID128:admin
4. In the Manager (SNMP Browser), create a user snmpadmin1 with Authentication protocol as
noAuth, Privacy protocol as noPriv, set the password and set the trap port as 162. (Same
values are set as in the switch SNMPv3 configuration.)
SNMPv3 supports AES128 and DES protocols. SNMPv3 does not support privacy protocols AES192,
AES256, and 3DES.
Access Gateway and Brocade MIBs
Tab le 4 shows the MIBs supported by Brocade Access Gateway.
.
TABLE 4 Access Gateway MIB support
MIB name Supported Description
MIB-2 Yes Updated to support Access Gateway in v5.2.1.
Entity-MIB Yes Supported in Access Gateway.
HA-MIB Yes Supported in Access Gateway.
SW-MIB No Disabled in Access Gateway because the conventions are specific to
FA-MIB Yes The connUnitSnsTable is not supported because a switch in Access
fabric switches.
In Fabric OS v6.4.0, swConnUnitPortExtensionTable is supported in
Access Gateway mode.
In Fabric OS v7.0.0, SNMP allows you to access the following tables
to support the Advanced Performance Monitoring feature on Access
Gateway, even if the SW-MIB is disabled:
• “swBlmPerfEEMntTable”
• “swBlmPerfFltMntTable”
Gateway does support name server services.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 19
53-1002750-01
Page 40

Firmware upgrades and enabled traps
1
TABLE 4 Access Gateway MIB support (Continued)
MIB name Supported Description
FE-MIB No Disabled in Access Gateway because the conventions are specific to
CPQ-Rack MIB Limited Supported on embedded switches only.
FCIP MIB No Disabled in Access Gateway because the conventions are specific to
iSCSI MIB No Disabled in Access Gateway because the conventions are specific to
IF-MIB Yes Supported in Access Gateway.
BD-MIB Yes Supported for F-ports.
IEEE 802.3 LAG MIB No Supported in Access Gateway.
IEEE 802.1x PAE MIB No Supported in Access Gateway.
LLDP MIB No Supported in Access Gateway.
BRIDGE-MIB No Supported in Access Gateway.
RMON-MIB Yes Supported in Access Gateway.
FA-Ext Yes Supported in Access Gateway.
SNMPv2 MIB Yes Supported in Access Gateway.
fabric switches.
fabric switches.
fabric switches.
Firmware upgrades and enabled traps
The pre-Fabric OS v4.4 firmware had trap group level settings (for example, traps were turned on
and off as a group). In Fabric OS v4.4 or later, you can turn on and off traps individually within a
trap group. When you upgrade to the Fabric OS v4.4 firmware or later, by default the individual
traps are turned off even if the corresponding trap group was enabled before upgrading. You must
use the snmpconfig command to turn on explicitly the individual traps within each trap group.
Fabric OS commands for configuring SNMP
Use the following commands (Table 5) to configure MIBs in the Fabric OS. For procedures for
configuring SNMP on the Brocade switches, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
TABLE 5 Commands for configuring SNMP
Command Description
snmpConfig This command has all the features of the existing agtcfg* commands; in addition, it has
SNMPv3 configuration parameters.
Enhanced in Fabric OS v6.3.0 to support SNMP Informs for SNMPv3 users.
Enhanced in Fabric OS v6.4.0 to support option-based mibcapability behavior.
snmpTraps This command supports the SNMP notification generator feature, Notification generator
framework has been implemented to send various SNMP traps.
For more information about the commands, either refer to Table 6 or the Fabric OS Command
Reference.
20 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 41

Fabric OS commands for configuring SNMP
TABLE 6 Detailed description of the commands
Command Operands Arguments
1
snmpConfig --show | --set | --default |
--enable | --disable [snmpv1 | snmpv3
| accessControl | mibCapability |
systemGroup | seclevel]
--show
Displays the SNMP agent configuration data of
the specified category.
--set
Sets the SNMP agent configuration data of the
specified category. This operand displays the
current settings and then prompts you to
change the values for each parameter.
--default
Sets the SNMP agent configuration data for a
specified item to the default values. Generally,
these default values may be available in the
configuration database. The command sets to
factory defaults if the SNMP agent configuration
parameters are not available in the
configuration database.
--enable
Enables the SNMP agent configuration for the
specified category. This operand is
valid only with mibCapability and snmpv1. When
used with the snmpv1
operand, this command restores access to
SNMPv1/v2c.
--disable
Disables the SNMP agent configuration for the
specified category. This operand is valid only
with mibCapability and snmpv1. When used
with the snmpv1 operan d, this comma nd blocks
access to SNMPv1/v2c. All requests for v1/v2c
version will be dropped by the switch, and
SNMPv1 traps will be blocked from being sent,
even if trap destinations are present.
snmpv1 Selects SNMPv1-related configuration
parameters. These parameters include the
community string, trap recipient IP address,
and trap severity level associated with each
trap recipient IP address. When "0" is
configured as a trap port, traps can be received
at the default port 162.
snmpv3 Selects SNMPv3-related configuration
parameters. These parameters include the
user name, authentication protocol and
password, the privacy protocol and password,
the SNMPv3 trap recipient’s IP address, its
associated user index and trap severity level.
When "0" is configured as a trap port, traps can
be received at the default port 162. In Fabric
OS v6.3.0 and later, the --set snmpv3
command supports an interactive option to
enable or disable informs by setting the
parameter “SNMP Informs Enabled” to true or
false. If informs are enabled, all trap
destinations receive inform requests. If informs
are disabled, all trap destinations receive trap
requests. When informs are enabled, the
engine ID must be set to correspond to the
management engine IP address. Informs are by
default disabled.
accessControl Selects access-control-related
parameters. These parameters include the
access host subnet area and access
permission (read-write).
mibCapability Selects configuration
parameters related to the SNMP agent’s MIBs
and trap capability parameters. These
parameters include MIBs and traps supported
by the SNMP agent.
systemGroup Selects configuration parameters
related to the system group. These parameters
include sysDescr, sysLocation, sysContact, and
authentication failure trap.
secLevel Sets the SNMP security level.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 21
53-1002750-01
Page 42

Fabric OS commands for configuring SNMP
1
TABLE 6 Detailed description of the commands (Continued)
Command Operands Arguments
snmpConfig --set mibCapability
[-mib_name <mib_name> [ -bitmask
<bit_mask>]]
snmpConfig --enable |--disable
mibCapability -mib_name
<mib_name> [-trap_name
<trap_name>]
snmpConfig --help --help
snmptraps --send [-trap_name
<trap_name>] [-ip_address
<ip_address>]
--set mibCapability
Configures MIBs interactively. When used
without a MIB name, this command displays a
menu with supported MIBs and associated
traps, and for each MIB or trap, you are
prompted to confirm or change the default by
specifying yes or no. Specifying yes means you
can access the MIB variables with an SNMP
manager. All MIBs and associated traps are by
default enabled.
--enable mibCapability -mib_name
<mib_name>
Enables the specified MIB non-interactively.
--disable mibCapability -mib_name
<mib_name>
Disables the specified MIB non-interactively.
When used with the trap name operand, only
the specified trap is disabled.
Displays the command usage.
--send
Sends one or all SNMP traps to all configured
recipients or to a specified recipient.
-mib_name <mib_name>
Specifies the name of the MIB to be
configured. This operand is required if
you want to configure MIB traps
non-interactively. Valid MIB names include
the following:
• FE-MIB
• SW-MIB
• FA-MIB
• FICON-MIB
• HA-MIB
• FCIP-MIB
• ISCSI-MIB
• IF-MIB
• BD-MIB
-bitmask <bit_mask>
Specifies the bit mask for the MIB. In Fabric OS
v6.4.0 and later, SNMP Traps are identified by
their bit mask and can be read directly from the
switch configuration. The MIB and trap status
(enabled or disabled) status is recorded in a
64- bit counter. The last bit (bit 0) is reserved
for the MIB and the remaining bits are reserved
for the traps of that MIB. The trap's position is
allocated based on the last ID of the trap OID.
For example, the last ID of the swEventTrap is 5
so its position will be fifth from the right.
-trap_name <trap_name>
Specifies the name of the trap to be disabled.
This operand is optional. Use snmpConfig
--show mibCapability for a listing of valid traps.
-trap_name <trap_name>
Specifies the trap by name. Use snmptraps
--show for a listing of valid traps.
-ip_address <ip_address>
Specifies the recipient by its IP address. The IP
address must be specified in IPv4 format.
22 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 43

Support for Administrative Domains
TABLE 6 Detailed description of the commands (Continued)
Command Operands Arguments
snmptraps --show [port] --show
Displays all configured SNMP traps and MIBs
supported in Fabric OS. This also shows the
blocked ports trap status on all the ports.
port
Shows only those ports which have blocked
traps.
snmptraps --block | --unblock [-port
<Slot/Port> | ALL]
NOTE: This command is not supported
for linkDown and linkup traps.
snmptraps --help --help
--block
Blocks port traps on a port.
NOTE: You cannot block port traps on all the
--unblock
Unblocks port traps on a port or on all the ports.
Displays the command usage.
ports.
-port <Slot/Port>
Specifies the slot and port. You must provide a
slot for chassis systems such as DCX, DCX-4S,
and so on.
ALL
Unblocks port traps on all the ports.
1
Support for Administrative Domains
Administrative Domains are supported in Fabric OS v5.3.0 and later releases. An Administrative
Domain (AD) is a domain within a fabric. Administrative domains can be used to limit administrator
access within a fabric, and to provide service providers with a means to assign portions of a fabric
to individual consumers. An AD may contain switches, devices, and ports. An AD may also limit
access to a configured set of users.
Support for Role-Based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is supported in Fabric OS v5.3.0 and later releases. RBAC
applies a fixed set of roles that address the access control needs of a majority of customers. Each
role is a set of permissions that can be applied to a user that controls the kinds of jobs and tasks
the user can perform on a fabric or fabric element.
Support for IPv6 addressing
IPv6 addressing is supported in Fabric OS v5.3.0 and later releases.
Support for Virtual Fabric
Virtual Fabric is supported in Fabric OS v6.2.0 and later releases.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 23
53-1002750-01
Page 44

Customized traps
1
Customized traps
This is only applicable for OEM customers. FOS v7.0.0 and v7.0.1 releases supported addition of
system OID in trap OID to customized trap OID on different platforms. For example, Fabric Watch
customized trap OID is 1.3.6.1.4.1.1588.2.1.1.62.0.5 on DCX and 1.3.6.1.4.1.1588.2.1.1.71.0.5
on Brocade 5100. This feature is not supported from FOS 7.1.0 release.
24 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 45

Chapter
MIB-II (RFC1213-MIB)
In this chapter
•MIB II overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
•System group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
•Interfaces group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
•AT group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
•IP group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
•ICMP group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
•TCP group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
•UDP group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
•EGP group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
•Transmission group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
•SNMP group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
•ifMIB group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
•Generic traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
2
MIB II overview
The descriptions of each of the MIB variables in this chapter come directly from the MIB-II itself.
The notes that follow the descriptions refer to Brocade-specific information and are provided by
Brocade.
MIB-II object hierarchy
Figure 6 through Figure 16 depict the organization and structure of MIB-II.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 25
53-1002750-01
Page 46

MIB II overview
- iso
- org
- dod
- internet
- directory
- mgmt
- mib-2
- system
- interfaces
- at
- ip
- icmp
- tcp
- udp
- egp
- transmission
- snmp
- rmon
- iFMIB
- system (1.3.6.1.2.1.1)
- sysDescr 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1
- sysObjectID 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.2
- sysUpTime 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3
- sysContact 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4
- sysName 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5
- sysLocation 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6
- sysServices 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.7
2
FIGURE 6 MIB-II overall hierarchy
26 Fabric OS MIB Reference
FIGURE 7 System hierarchy
53-1002750-01
Page 47

MIB II overview
- interfaces (1.3.6.1.2.1.2)
- ifNumber 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1
- ifTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2
- ifEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1
- ifIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1
- ifDescr 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2
- ifType 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.3
- ifMtu 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.4
- ifSpeed 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5
- ifPhysAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6
- ifAdminStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.7
- ifOperStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8
- ifLastChange 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.9
- ifInOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.10
- ifInUcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.11
- ifInNUcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.12
- ifInDiscards 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.13
- ifInErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.14
- ifInUnknownProtos 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.15
- ifOutOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.16
- ifOutUcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.17
- ifOutNUcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.18
- ifOutDiscards 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.19
- ifOutErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.20
- ifOutQLen 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.21
- ifSpecific 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.22
- at (1.3.6.1.2.1.3)
- atTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.3.1
- atEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.3.1.1
- atIfIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.3.1.1.1
- atPhysAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.3.1.1.2
- atNetAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.3.1.1.3
2
Fabric OS MIB Reference 27
53-1002750-01
FIGURE 8 Interfaces hierarchy
FIGURE 9 AT hierarchy
Page 48

MIB II overview
- ip (1.3.6.1.2.1.4)
- ipForwarding 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.1
- ipDefaultTTL 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.2
- ipInReceives 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.3
- ipInHdrErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.4
- ipInAddrErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.5
- ipForwDatagrams 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.6
- ipInUnknownProtos 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.7
- ipInDiscards 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.8
- ipInDelivers 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.9
- ipOutRequests 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.10
- ipOutDiscards 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.11
- ipOutNoRoutes 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.12
- ipReasmTimeout 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.13
- ipReasmReqds 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.14
- ipReasmOKs 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.15
- ipReasmFails 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.16
- ipFragOKs 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.17
- ipFragFails 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.18
- ipFragCreates 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.19
- ipAddrTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20
- ipAddrEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1
- ipAdEntAddr 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.1
- ipAdEntIfIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.2
- ipAdEntNetMask 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.3
- ipAdEntBcastAddr 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.4
- ipAdEntReasmMaxSize 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.5
- ipRouteTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21
- ipRouteEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1
- ipRouteDest 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.1
- ipRouteIfIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.2
- ipRouteMetric1 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.3
- ipRouteMetric2 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.4
- ipRouteMetric3 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.5
- ipRouteMetric4 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.6
- ipRouteNextHop 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.7
- ipRouteType 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.8
- ipRouteProto 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.9
- ipRouteAge 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.10
- ipRouteMask 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.11
- ipRouteMetric5 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.12
- ipRouteInfo 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.13
- ipNetToMediaTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22
- ipNetToMediaEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22.1
- ipNetToMediaIfIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22.1.1
- ipNetToMediaPhysAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22.1.2
- ipNetToMediaNetAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22.1.3
- ipNetToMediaType 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22.1.4
- ipRoutingDiscards 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.23
- ipAddressTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34
- ipAddressEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1
- ipAddressAddrType 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.1
- ipAddressAddr 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.2
- ipAddressIfIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.3
2
28 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 49

FIGURE 10 IP hierarchy
- ipAddressType 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.4
- ipAddressPrefix 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.5
- ipAddressOrigin 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.6
- ipAddressStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.7
- ipAddressCreated 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.8
- ipAddressLastChanged 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.9
- ipAddressRowStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.10
- ipAddressStorageType 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.11
- icmp (1.3.6.1.2.1.5)
- icmpInMsgs 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.1
- icmpInErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.2
- icmpInDestUnreachs 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.3
- icmpInTimeExcds 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.4
- icmpInParmProbs 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.5
- icmpInSrcQuenchs 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.6
- icmpInRedirects 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.7
- icmpInEchos 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.8
- icmpInEchoReps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.9
- icmpInTimestamps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.10
- icmpInTimestampReps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.11
- icmpInAddrMasks 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.12
- icmpInAddrMaskReps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.13
- icmpOutMsgs 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.14
- icmpOutErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.15
- icmpOutDestUnreachs 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.16
- icmpOutTimeExcds 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.17
- icmpOutParmProbs 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.18
- icmpOutSrcQuenchs 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.19
- icmpOutRedirects 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.20
- icmpOutEchos 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.21
- icmpOutEchoReps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.22
- icmpOutTimestamps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.23
- icmpOutTimestampReps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.24
- icmpOutAddrMasks 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.25
- icmpOutAddrMaskReps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.26
- icmpOutSrcQuenchs 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.19
- icmpOutRedirects 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.20
- icmpOutEchos 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.21
- icmpOutEchoReps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.22
- icmpOutTimestamps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.23
- icmpOutTimestampReps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.24
- icmpOutAddrMasks 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.25
- icmpOutAddrMaskReps 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.26
MIB II overview
2
Fabric OS MIB Reference 29
53-1002750-01
FIGURE 11 ICMP hierarchy
Page 50

MIB II overview
- tcp (1.3.6.1.2.1.6)
- tcpRtoAlgorithm 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.1
- tcpRtoMin 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.2
- tcpRtoMax 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.3
- tcpMaxConn 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.4
- tcpActiveOpens 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.5
- tcpPassiveOpens 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.6
- tcpAttemptFails 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.7
- tcpEstabResets 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.8
- tcpCurrEstab 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.9
- tcpInSegs 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10
- tcpOutSegs 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11
- tcpRetransSegs 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.12
- tcpConnTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13
- tcpConnEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1
- tcpConnState 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.1
- tcpConnLocalAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.2
- tcpConnLocalPort 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.3
- tcpConnRemAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.4
- tcpConnRemPort 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.5
- tcpInErrs 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.14
- tcpOutRsts 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.15
- udp (1.3.6.1.2.1.7)
- udpInDatagrams 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1
- udpNoPorts 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.2
- udpInErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.3
- udpOutDatagrams 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4
- udpTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.5
- udpEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.5.1
- udpLocalAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.5.1.1
- EGP group
2
FIGURE 12 TCP hierarchy
FIGURE 13 UDP hierarchy
30 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 51

MIB II overview
- egp (1.3.6.1.2.1.8)
- egpInMsgs
- egpInErrors
- egpOutMsgs
- egpOutErrors
- egpNeighTable
- egpNeighEntry
- egpNeighState
- egpNeighAddr
- egpNeighAs
- egpNeighInMsgs
- egpNeighInErrs
- egpNeighOutMsgs
- egpNeighOutErrs
- egpNeighInErrMsgs
- egpNeighOutErrMsgs
- egpNeighStateUps
- egpNeighStateDowns
- egpNeighIntervalHello
- egpNeighIntervalPoll
- egpNeighMode
- egpNeighEventTrigger
- egpAs
- snmp (1.3.6.1.2.1.11)
- snmpInPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.1
- snmpOutPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.2
- snmpInBadVersions 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.3
- snmpInBadCommunityNames 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.4
- snmpInBadCommunityUses 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.5
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.7 and 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.23 is not supported.
- snmpInTooBigs 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.8
- snmpInNoSuchNames 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.9
- snmpInBadValues 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.10
- snmpInReadOnlys 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.11
- snmpInGenErrs 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.12
- snmpInTotalReqVars 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.13
- snmpInTotalSetVars 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.14
- snmpInGetRequests 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.15
- snmpInGetNexts 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.16
- snmpInSetRequests 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.17
- snmpInGetResponses 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.18
- snmpInTraps 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.19
- snmpOutTooBigs 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.20
- snmpOutNoSuchNames 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.21
- RMON group
- snmpOutGenErrs 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.24
- snmpOutGetRequests 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.25
- snmpOutGetNexts 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.26
- snmpOutSetRequests 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.27
- snmpOutGetResponses 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.28
- snmpOutTraps 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.29
- snmpEnableAuthenTraps 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.30
- snmpSilentDrops 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.31
- snmpProxyDrops 1.3.6.1.2.1.11.32
2
FIGURE 14 EGP hierarchy
Fabric OS MIB Reference 31
53-1002750-01
FIGURE 15 SNMP hierarchy
Page 52

2
- ifMIB (1.3.6.1.2.1.31)
- ifXTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1
- ifXentry 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1
- ifName 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1
- ifInMulticastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.2
- ifInBroadcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.3
- ifOutMulticastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.4
- ifOutBroadcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.5
- ifHCInOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.6
- ifHCInUcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.7
- ifHCInMulticastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.8
- ifHCInBroadcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.9
- ifHCOutOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.10
- ifHCOutUcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.11
- ifHCOutMulticastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.12
- ifHCOutBroadcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.13
- ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.14
- ifHighSpeed 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.15
- ifPromiscuousMode 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.16
- ifConnectorPresent 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.17
- ifAlias 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.18
- ifCounterDiscontinuityTime 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.17
System group
System group
32 Fabric OS MIB Reference
FIGURE 16 ifMIB hierarchy
Textual conventions
Tab le 7 lists the textual conventions used for MIB-II.
TABLE 7 MIB-II textual conventions
Type definition Value
DisplayString Octet String of size 0 to 255
PhysAddress Octet String
Objects and types imported
The following objects and types are imported from RFC1155-SMI:
• mgmt
• NetworkAddress
• IpAddress
• Counter
• Gauge
• TimeTicks
All systems must implement the System group. If an agent is not configured to have a value for any
of the System group variables, a string of length 0 is returned.
53-1002750-01
Page 53

TABLE 8
Object and OID Access Description
System group
2
sysDescr
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1
sysObjectID
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.2
sysUpTime
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3
sysContact
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4
sysName
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5
Read only A textual description of the entity. This value should include the full name
and version identification of the hardware type, software operating system,
and networking software.
This must contain only printable ASCII characters.
Set this value using the snmpconfig command. The default value is either
Fibre Channel Switch or Access Gateway.
Read only The vendor’s authoritative identification of the network management
subsystem contained in the entity. This value is allocated within the SMI
enterprises subtree (1.3.6.1.4.1) and provides an easy and unambiguous
means for determining what kind of device is being managed.
For example, if a vendor “NetYarn, Inc.” was assigned the subtree
1.3.6.1.4.1.4242, it could assign the identifier 1.3.6.1.4.1.4242.1.1 to its
“Knit Router.”
The default value is either:
• Fibre Channel Switches:
iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprises.bcsi.commDev.fibrechannel.fcS
witch.sw
• Brocade Access Gateway:
iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprises.bcsi.commDev.fibrechannel.fcS
witch.sw
Read only The time (in hundredths of a second) since the network management portion
of the system was last re-initialized.
Set this value using the switchuptime command.
Read-write The textual identification of the contact person for this managed node,
together with information on how to contact this person. The minimum length
of the string must be of four characters.
The default is Field Support.
Set this value using the snmpconfig command.
Read-write An administratively assigned name for this managed node. By convention,
this is the node’s fully qualified domain name. The default is the preassigned
name of the logical switch.
Set this value using the snmpconfig command.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 33
53-1002750-01
Page 54

Interfaces group
2
TABLE 8
Object and OID Access Description
sysLocation
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6
sysServices
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.7
Interfaces group
Implementation of the Interfaces group is mandatory for all systems. FCIP tunnel support is added
in Fabric OS 5.3.0 and later. To support FCIP tunneling, entries are created in the ifTable for each
WAN interface (GbE port), each FC port, and each FCIP tunnel (transport interface).
Read-write The physical location of this node (for example, telephone closet, 3rd floor).
The minimum length of the string must be four. The default is End User
Premise.
Set this value using the snmpconfig command.
Read only A value that indicates the set of services that this entity primarily offers. The
value is a sum. This sum initially takes the value 0. Then, for each layer, L, in
the range 1 through 7, for which this node performs transactions, 2 raised to
(L - 1) is added to the sum. For example, a node that primarily performs
routing functions has a value of 4 (2
and offers application services has a value of 72 (2
In the context of the Internet suite of protocols, values should be calculated
accordingly:
Layer functionality
3-1
). In contrast, a node that is a host
4-1
+ 2
7-1
).
• 1 = physical (for example, repeaters)
• 2 = datalink/subnetwork (for example, bridges)
• 3 = internet (for example, IP gateways)
• 4 = end-to-end (for example, IP hosts)
• 7 = applications (for example, mail relays)
For systems including OSI protocols, layers 5 and 6 also can be counted. The
return value is always 79.
Logical Inter-Switch Link (LISL) is an FC interface.
TABLE 9
Object and OID Access Description
ifNumber
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1
ifTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2
ifEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1
Read only The number of network interfaces and existing FC ports present on this
system, regardless of their current state. This number will vary across
platforms (switches).
The return value is dynamic for all Brocade switches and depends on the
number of GbE ports, FC ports and transport interfaces.
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
A list of interface entries. The number of entries is given by the value of
ifNumber.
The Interfaces table contains information on the entity’s interfaces. Each
interface is thought of as being attached to a subnetwork. Note that this term
should not be confused with subnet, which refers to an addressing
partitioning scheme used in the Internet suite of protocols.
An interface entry containing objects at the subnetwork layer and below, for a
particular interface.
34 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 55

TABLE 9
Object and OID Access Description
Interfaces group
2
ifIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1
ifDescr
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2
ifType
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.3
ifMtu
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.4
Read only A unique value for each interface.
The values range between 1 and the value of ifNumber. The value for each
interface must remain constant, at least from one re-initialization of the
entity's network management system to the next re-initialization.
For Network Interface, the number starts from 805306369 and increments
with the interface count. For FC ports, the number starts from 1073741824
and increments with the existing FC ports. Similarly the index value range for
the interfaces are as follows:
• For GbE port the number starts from 268435456
• For Ten GbE (FCoE ports) the number starts from 402653184
• For FCIP Tunnel the number starts from 536870912
• For xFCIP Tunnel the number starts from 1342177280
• For Port channel the number starts from 671088640
• For VLAN the number starts from 1207959552
Read only A textual string containing information about the interface. The ifDescr for
non-bladed switches includes: lo, eth0, and fc0. The ifDescr for Brocade
12000, 24000, and 48000 directors includes: lo, eth0, fc0, and sit0, as well
as fc1, eth0:1, and eth0:2.
Valid values:
• For WAN interface - GbE port for FCIP
• For transport interface - FCIP tunnel ID
• For FC ports - Port name (if set), otherwise, FC port <slot/port>
Read only The type of interface, designated by the physical link protocols immediately
below the network layer in the protocol stack.
• For WAN interface, FCIP Link - ethernetCsmacd (6)
• For transport interface - FCIPLink (224)
• For FC ports - Fibre Channel (56)
• For lo - softwareLoopback (24)
• For sit0 - 131
• For fc0/port0 - other
Read only The size of the largest datagram that can be sent or received on the
interface, specified in octets.
For interfaces that are used to transmit network datagrams, the value is the
size of the largest network datagram that can be sent on the interface (these
values are different for Fabric OS v4.x).
• eth0 returns 1500
• lo returns 16436
• fc0 returns 2024
• FCIP GbE returns 1500
• sit0 returns 1480
• port0 returns 2112
Fabric OS MIB Reference 35
53-1002750-01
Page 56

Interfaces group
2
TABLE 9
Object and OID Access Description
ifSpeed
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5
ifPhysAddress
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6
ifAdminStatus
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.7
ifOperStatus
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8
ifLastChange
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.9
ifInOctets
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.10
Read only An estimate (in bits per second) of the interface's current bandwidth.
For interfaces that do not vary in bandwidth or interfaces for which no
accurate estimation can be made, this object should contain the nominal
bandwidth. For Fabric OS v4.x, 2 Gbps returns.
• eth0 returns 100000000 and not null
• fc port returns 1,000,000,000 for 1 Gbps port
• fc port returns 2000000000 for 2 Gbps port
• fc port returns 4000000000 for 4 Gbps port
• For 10G, value displayed is 4294967295
• For 8G, value displayed is 4294967295
• For 16G, value displayed is 4294967295
Read only The interface's address at the protocol layer immediately below the network
layer in the protocol stack.
For interfaces that do not have such an address (for example, a serial line),
this object should contain an octet string of zero length.
• eth0 returns the MAC address for GbE ports
• lo returns null
• SNMP represents the FC port ID in ASCII hex represenation. For
example, 36:35:35:33:36 is equivalent to the decimal value of 65536.
To get the decimal value 36-30 = 6; 35-30= 5 and so on. To get the FC
port ID, convert the decimal into hex (the hex value of 65536 is 01 00
00, where the first two digits are the domain, the next two digits are the
area, and the last two digits are the port number).
ASCII hex (36:35:35:33:36) => decimal (65536) => hex (01 00 00)
Read-write The desired state of the interface.
Valid values:
• up (1)
• down (2)
• testing (3)
NOTE: The testing (3) state indicates that no operational packets can be
passed. This object is read-only in Fabric OS v4.x and later versions.
This object should return same value with ifOperStatus for WAN and FC ports
interfaces.
Read only The current operational state of the interface.
Valid values:
• up (1)
• down (2) or
• testing (3)
• unknown (4)
Active tunnels will be up; inactive tunnels will be down (configured but not
online).
NOTE: The testing (3) state indicates that no operational packets can be
passed.
Read only The value of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its current
operational state. If the current state was entered prior to the last
re-initialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object
contains a zero value.
Read only The total number of octets received on the interface, including framing
characters. This value is the number of 4-byte words received and multiplied
by four.
36 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 57

TABLE 9
Object and OID Access Description
Interfaces group
2
ifInUcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.11
ifInNUcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.12
ifInDiscards
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.13
ifInErrors
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.14
ifInUnknownProtos
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.15
ifOutOctets
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.16
ifOutUcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.17
ifOutNUcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.18
ifOutDiscards
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.19
ifOutErrors
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.20
ifOutQLen
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.21
ifSpecific
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.22
Read only The number of subnetwork-unicast packets delivered to a higher-layer
protocol.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only The number of nonunicast packets (for example, subnetwork-broadcast or
subnetwork-multicast) delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only The number of inbound packets that were chosen to be discarded (even
though no errors had been detected) to prevent their being deliverable to a
higher-layer protocol.
One possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free buffer
space.
Read only The number of inbound packets that contained errors, which thereby
prevented them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
Read only The number of packets received by way of the interface that were discarded
because of an unknown or unsupported protocol.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only The total number of octets transmitted out of the interface, including framing
characters. This value is the number of 4-byte words transmitted and
multiplied by four.
Read only The total number of packets that were requested, by higher-level protocols, to
be transmitted to a subnetwork-unicast address, including those that were
discarded or not sent.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only The total number of packets that were requested, by higher-level protocols, to
be transmitted to a nonunicast address (for example, a
subnetwork-broadcast or subnetwork-multicast), including those that were
discarded or not sent.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only The number of outbound packets that were chosen to be discarded (even
though no errors had been detected) to prevent their being transmitted. One
possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free buffer space.
Read only The number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of
errors.
Read only The length of the output packet queue (in packets).
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only A reference to MIB definitions specific to the particular media being used to
realize the interface.
If the interface is realized by an Ethernet, then the value of this object refers
to a document defining objects specific to Ethernet. If this information is not
present, its value must be set to the Object Identifier 0 0, which is a
syntactically valid object identifier, and any conferment implementation of
ASN.1 and BER must be able to generate and recognize this value.
• eth0 returns null OID
• lo returns null OID
• fc0 returns null OID
Fabric OS MIB Reference 37
53-1002750-01
Page 58

AT group
2
AT group
Implementation of the Address Translation group is mandatory for all systems. Note, however, that
this group is deprecated by MIB-II. From MIB-II onward, each network protocol group contains its
own address translation tables.
TABLE 10
Object and OID Access Description
atTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.3.1
atEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.3.1.1
atIfIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.3.1.1.1
atPhysAddress
1.3.6.1.2.1.3.1.1.2
atNetAddress
1.3.6.1.2.1.3.1.1.3
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read-write The interface on which this entry's equivalence is effective. The interface
Read-write The media-dependent physical address.
Read-write The network address (for example, the IP address) corresponding to the
The Address Translation group contains one table, which is the union across
all interfaces of the translation tables for converting a network address (for
example, an IP address) into a subnetwork-specific address. This document
refers to such a subnetwork-specific address as a physical address.
For example, for broadcast media, where ARP is in use, the translation table
is equivalent to the ARP cache; on an X.25 network, where non-algorithmic
translation to X.121 addresses is required, the translation table contains the
network address to X.121 address equivalences.
The Address Translation tables contain the network address to physical
address equivalences. Some interfaces do not use translation tables for
determining address equivalences (for example, DDN-X.25 has an
algorithmic method); if all interfaces are of this type, then the Address
Translation table is empty.
Each entry contains one network address to physical address equivalence.
identified by a particular value of this index is the same interface as
identified by the same value of ifIndex.
media-dependent physical address.
IP group
Implementation of the IP group is mandatory for all systems.
TABLE 11
Object and OID Access Description
ipForwarding
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.1
ipDefaultTTL
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.2
ipInReceives
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.3
38 Fabric OS MIB Reference
Read-write The indication of whether this entity is acting as an IP gateway in respect to
the forwarding of datagrams received by, but not addressed to, this entity.
IP gateways forward datagrams; IP hosts do not (except those
source-routed through the host).
Read-write The default value inserted into the time-to-live field of the IP header of
datagrams originated at this entity, whenever a TTL value is not supplied by
the transport layer protocol.
Read only The total number of input datagrams received from interfaces, including
those received in error.
53-1002750-01
Page 59

TABLE 11
Object and OID Access Description
IP group
2
ipInHdrErrors
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.4
ipInAddrErrors
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.5
ipForwDatagrams
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.6
ipInUnknownProtos
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.7
ipInDiscards
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.8
ipInDelivers
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.9
ipOutRequests
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.10
ipOutDiscards
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.11
ipOutNoRoutes
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.12
ipReasmTimeout
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.13
Read only The number of input datagrams discarded due to errors in their IP headers,
including bad checksums, version number mismatch, other format errors,
time-to-live exceeded, errors discovered in processing their IP options, and
so on.
Read only The number of input datagrams discarded because the IP address in their
IP header's destination field was not a valid address to be received at this
entity. This count includes invalid addresses (for example, 0.0.0.0) and
addresses of unsupported classes (for example, Class E). For entities that
are not IP gateways and therefore do not forward datagrams, this counter
includes datagrams discarded because the destination address was not a
local address.
Read only The number of input datagrams for which this entity was not final IP
destination, as a result of which an attempt was made to find a route to
forward them to that final destination. In entities that do not act as IP
gateways, this counter includes only those packets that were source-routed
through this entity, and the Source-Route option processing was
successful.
Read only The number of locally addressed datagrams received successfully but
discarded because of an unknown or unsupported protocol.
Read only The number of input IP datagrams for which no problems were encountered
to prevent their continued processing, but which were discarded (for
example, for lack of buffer space).
This counter does not include any datagrams discarded while awaiting
reassembly.
Read only The total number of input datagrams successfully delivered to IP user
protocols (including ICMP).
Read only The total number of IP datagrams that local IP user protocols (including
ICMP) supplied to IP in requests for transmission. Note that this counter
does not include any datagrams counted in ipForwDatagrams.
Read only The number of output IP datagrams for which no problem was encountered
to prevent their transmission to their destination, but which were discarded
(for example, for lack of buffer space).
NOTE: This counter would include datagrams counted in ipForwDatagrams
if any such packets met this (discretionary) discard criterion.
Read only The number of IP datagrams discarded because no route could be found to
transmit them to their destination.
NOTE: This counter includes any packets counted in ipForwDatagrams that
meet this “no-route” criterion. Note that this includes any
datagrams that a host cannot route because all of its default
gateways are down.
Read only The maximum number of seconds that received fragments are held while
they are awaiting reassembly at this entity.
ipReasmReqds
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.14
ipReasmOKs
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.15
Fabric OS MIB Reference 39
53-1002750-01
Read only The number of IP fragments received that needed to be reassembled at
this entity.
Read only The number of IP datagrams successfully reassembled.
Page 60

2
IP group
TABLE 11
Object and OID Access Description
ipReasmFails
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.16
ipFragOKs
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.17
ipFragFails
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.18
ipFragCreates
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.19
ipAddrTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20
ipAddrEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1
ipAdEntAddr
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.1
ipAdEntIfIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.2
ipAdEntNetMask
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.3
ipAdEntBcastAddr
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.4
ipAdEntReasmMaxSiz e
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.5
ipRouteTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21
ipRouteEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1
ipRouteDest
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.1
ipRouteIfIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.2
Read only The number of failures detected by the IP reassembly algorithm (for
whatever reason: timed out, errors, and so on).
NOTE: This is not necessarily a count of discarded IP fragments, because
some algorithms (notably the algorithm in RFC 815) can lose track
of the number of fragments by combining them as they are
received.
Read only The number of IP datagrams that have been successfully fragmented at
this entity.
Read only The number of IP datagrams that have been discarded because they
needed to be fragmented at this entity but could not be (for example,
because their Don't Fragment flag was set).
Read only The number of IP datagram fragments that have been generated as a
result of fragmentation at this entity.
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read only The IP address to which this entry's addressing information pertains.
Read only The index value which uniquely identifies the interface to which this entry is
Read only The subnet mask associated with the IP address of this entry. The value of
Read only The value of the least-significant bit in the IP broadcast address used for
Read only The size of the largest IP datagram that this entity can reassemble from
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read-write The destination IP address of this route.
Read-write The index value that uniquely identifies the local interface through which
The table of addressing information relevant to this entity's IP addresses.
The addressing information for one of this entity's IP addresses.
applicable. The interface identified by a particular value of this index is the
same interface as identified by the same value of ifIndex.
the mask is an IP address with all the network bits set to 1 and all the host
bits set to 0.
sending datagrams on the (logical) interface associated with the IP address
of this entry. For example, when the Internet standard all-ones broadcast
address is used, the value will be 1. This value applies to both the subnet
and network broadcasts addresses used by the entity on this (logical)
interface.
incoming IP fragmented datagrams received on this interface.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
The IP routing table contains an entry for each route currently known to this
entity.
A route to a particular destination.
An entry with a value of 0.0.0.0 is considered a default route. Multiple
routes to a single destination can appear in the table, but access to such
multiple entries is dependent on the table-access mechanisms defined by
the network management protocol in use.
the next hop of this route should be reached.
The interface identified by a particular value of this index is the same
interface identified by the same value of ifIndex.
40 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 61

TABLE 11
Object and OID Access Description
IP group
2
ipRouteMetric1
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.3
ipRouteMetric2
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.4
ipRouteMetric3
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.5
ipRouteMetric4
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.6
ipRouteNextHop
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.7
ipRouteType
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.8
ipRouteProto
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.9
ipRouteAge
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.10
Read-write The primary routing metric for this route.
The semantics of this metric are determined by the routing protocol
specified in the route's ipRouteProto value. If this metric is not used, its
value should be set to -1.
Read-write An alternate routing metric for this route.
The semantics of this metric are determined by the routing protocol
specified in the route's ipRouteProto value. If this metric is not used, its
value should be set to -1.
Read-write An alternate routing metric for this route.
The semantics of this metric are determined by the routing protocol
specified in the route's ipRouteProto value. If this metric is not used, its
value should be set to -1.
Read-write An alternate routing metric for this route.
The semantics of this metric are determined by the routing protocol
specified in the route's ipRouteProto value. If this metric is not used, its
value should be set to -1.
Read-write The IP address of the next hop of this route. (In the case of a route bound to
an interface that is realized through a broadcast media, the value of this
field is the agent’s IP address on that interface.)
Read-write The type of route. Setting this object to 2 (invalid) has the effect of
invalidating the corresponding entry in the ipRouteTable object. That is, it
effectively dissasociates the destination identified with said entry from the
route identified with said entry. It is an implementation-specific matter as to
whether the agent removes an invalidated entry from the table. Accordingly,
management stations must be prepared to receive tabular information
from agents that corresponds to entries not currently in use. Proper
interpretation of such entries requires examination of the relevant
ipRouteType object.
Valid values:
• other (1) - None of the following
• invalid (2) - An invalidated route—route to directly
• direct (3) - Connected (sub) network—route to a non-local
• indirect (4) - Host/network/subnetwork
The values direct (3) and indirect (4) refer to the notion of direct and
indirect routing in the IP architecture.
Read only The routing mechanism by which this route was learned.
Inclusion of values for gateway routing protocols is not intended to imply
that hosts should support those protocols.
Read-write The number of seconds since this route was last updated or otherwise
determined to be correct.
Older semantics cannot be implied except through knowledge of the routing
protocol by which the route was learned.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 41
53-1002750-01
Page 62

2
IP group
TABLE 11
Object and OID Access Description
ipRouteMask
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.11
ipRouteMetric5
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.12
ipRouteInfo
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.13
ipNetToMediaTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22
ipNetToMediaEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22.1
ipNetToMediaIfIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22.1.1
iipNetToMediaPhysAd dress
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22.1.2
ipNetToMediaNetAddr ess
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22.1.3
ipNetToMediaType
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.22.1.4
ipRoutingDiscards
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.23
Read-write The mask to be logical-ANDed with the destination address before being
compared to the value in the ipRouteDest field. For those systems that do
not support arbitrary subnet masks, an agent constructs the value of the
ipRouteMask by determining whether the value of the correspondent
ipRouteDest field belong to a class-A, B, or C network, and then using one
of the following:
mask network
255.0.0.0 class-A
255.255.0.0 class-B
255.255.255.0 class-C
NOTE: If the value of the ipRouteDest is 0.0.0.0 (default route), then the
mask value is also 0.0.0.0.
All IP routing subsystems implicitly use this mechanism.
Read-write An alternate routing metric for this route.
The semantics of this metric are determined by the routing protocol
specified in the route's ipRouteProto value. If this metric is not used, its
value should be set to -1.
Read only A reference to MIB definitions specific to the particular routing protocol that
is responsible for this route, as determined by the value specified in the
route's ipRouteProto value. If this information is not present, its value
should be set to the Object Identifier {0 0}, which is a syntactically valid
object identifier; any conferment implementation of ASN.1 and BER must
be able to generate and recognize this value.
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read-write The interface on which this entry's equivalence is effective.
Read-write The media-dependent physical address.
Read-write The IpAddress corresponding to the media-dependent physical address.
Read-write The type of mapping.
Read only The number of routing entries discarded even though they are valid. One
The IP Address Translation table used for mapping from IP addresses to
physical addresses.
NOTE: The IP address translation table contains the IP address to physical
address equivalences. Some interfaces do not use translation
tables for determining address equivalences. For example,
DDN-X.25 has an algorithmic method; if all interfaces are of this
type, then the Address Translation table is empty.
Each entry contains one IP address to physical address equivalence.
The interface identified by a particular value of this index is the same
interface identified by the same value of ifIndex.
possible reason for discarding such an entry could be to free buffer space
for other routing entries.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
42 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 63

TABLE 11
Object and OID Access Description
ICMP group
2
ipAddressTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34
ipAddressEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1
ipAddressAddrType
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.1
ipAddressAddr
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.2
ipAddressIfIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.3
ipAddressType
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.4
ipAddressPrefix
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.5
ipAddressOrigin
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.6
ipAddressStatus
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.7
ipAddressCreated
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.8
ipAddressLastChange d
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.9
ipAddressRowStatus
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.10
ipAddressStorageType
1.3.6.1.2.1.4.34.1.11
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read
create
Read
create
This table contains IPv4 and IPv6 addressing information relevant to the
entity's interfaces.
An address mapping for a particular interface.
The address type of ipAddressAddr.
The IP address to which this entry's addressing information pertains.
The index value that uniquely identifies the interface to which this entry is
applicable. The interface identified by a particular value of this index is the
same interface as identified by the same value of the ifIndex of IF MIB.
The type of address.
Valid values:
• unicast (1)
• anycast (2)
• broadcast (3) - This is not a valid value for IPv6 addresses.
Read only A pointer to the row in the prefix table to which this address belongs. May
be {0 0} if there is no such row.
Read only The origin of the address.
Read
create
The status of the address, describing if the address can be used for
communication.
Valid values:
• preferred (1)
• deprecated (2)
• tentative (3)
In the absence of other information, for an IPv4 address, the status is
always preferred (1).
Read only The value of sysUpTime at the time this entry was created. If this entry was
created prior to the last re-initialization of the local network management
subsystem, then this object contains a zero value.
Read only The value of sysUpTime at the time this entry was last updated. If this entry
was updated prior to the last re-initialization of the local network
management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value.
Read
create
Read
create
The status of this conceptual row.
The storage type for this conceptual row. If this object has a value of
'permanent', then no other objects are required to be able to be modified.
ICMP group
Implementation of the ICMP group is mandatory for all systems.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 43
53-1002750-01
Page 64

2
ICMP group
TABLE 12
Object and OID Access Description
icmpInMsgs
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.1
icmpInErrors
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.2
icmpInDestUnreachs
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.3
icmpInTimeExcds
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.4
icmpInParmProbs
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.5
icmpInSrcQuenchs
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.6
icmpInRedirects
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.7
icmpInEchos
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.8
icmpInEchoReps
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.9
icmpInTimestamps
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.10
icmpInTimestampRep s
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.11
icmpInAddrMasks
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.12
icmpInAddrMaskReps
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.13
icmpOutMsgs
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.14
icmpOutErrors
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.15
icmpOutDestUnreachs
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.16
icmpOutTimeExcds
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.17
icmpOutParmProbs
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.18
icmpOutSrcQuenchs
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.19
Read only The total number of ICMP messages that the entity received.
This counter includes all ICMP messages counted by icmpInErrors.
Read only The number of ICMP messages that the entity received but determined to
have ICMP-specific errors (bad ICMP checksums, bad length, and so on).
Read only The number of ICMP Destination Unreachable messages received.
Read only The number of ICMP Time Exceeded messages received.
Read only The number of ICMP Parameter Problem messages received.
Read only The number of ICMP Source Quench messages received.
Read only The number of ICMP Redirect messages received.
Read only The number of ICMP Echo (request) messages received.
Read only The number of ICMP Echo Reply messages received.
Read only The number of ICMP Timestamp (request) messages received.
Read only The number of ICMP Timestamp Reply messages received.
Read only The number of ICMP Address Mask Request messages received.
Read only The number of ICMP Address Mask Reply messages received.
Read only The total number of ICMP messages that this entity attempted to send.
NOTE: This counter includes all those counted by icmpOutErrors.
Read only The number of ICMP messages that this entity did not send due to
problems discovered within ICMP such as a lack of buffers. This value must
not include errors discovered outside the ICMP layer such as the inability of
IP to route the resultant datagram. In some implementations there might
be no types of error that contribute to this counter's value.
Read only The number of ICMP Destination Unreachable messages sent.
Read only The number of ICMP Time Exceeded messages sent.
Read only The number of ICMP Parameter Problem messages sent.
Read only The number of ICMP Source Quench messages sent.
44 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 65

TABLE 12
Object and OID Access Description
TCP group
2
TCP group
icmpOutRedirects
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.20
icmpOutEchos
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.21
icmpOutEchoReps
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.22
icmpOutTimestamps
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.23
icmpOutTimestampRe ps
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.24
icmpOutAddrMasks
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.25
icmpOutAddrMaskRep s
1.3.6.1.2.1.5.26
Read only The number of ICMP Redirect messages sent. For a host, this object is
always 0, since hosts do not send redirects.
Read only The number of ICMP Echo (request) messages sent.
Read only The number of ICMP Echo Reply messages sent.
Read only The number of ICMP Timestamp (request) messages sent.
Read only The number of ICMP Timestamp Reply messages sent.
Read only The number of ICMP Address Mask Request messages sent.
Read only The number of ICMP Address Mask Reply messages sent.
Implementation of the TCP group is mandatory for all systems that implement the TCP.
Instances of object types that represent information about a particular TCP connection are
transient; they persist only as long as the connection in question.
TABLE 13
Object and OID Access Description
tcpRtoAlgorithm
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.1
tcpRtoMin
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.2
tcpRtoMax
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.3
tcpMaxConn
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.4
tcpActiveOpens
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.5
Read only The algorithm used to determine the time-out value used for
retransmitting unacknowledged octets.
Read only The minimum value permitted by a TCP implementation for the
retransmission time-out, measured in milliseconds.
More refined semantics for objects of this type depend upon the
algorithm used to determine the retransmission time-out. In particular,
when the time-out algorithm is 3 (rsre), an object of this type has the
semantics of the LBOUND quantity described in RFC 793.
Read only The maximum value permitted by a TCP implementation for the
retransmission time-out, measured in milliseconds.
More refined semantics for objects of this type depend upon the
algorithm used to determine the retransmission time-out. In particular,
when the time-out algorithm is 3 (rsre), an object of this type has the
semantics of the UBOUND quantity described in RFC 793.
Read only The limit on the total number of TCP connections the entity can
support. In entities where the maximum number of connections is
dynamic, this object should contain the value -1.
Read only The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition to
the SYN-SENT state from the CLOSED state.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 45
53-1002750-01
Page 66

2
TCP group
TABLE 13
Object and OID Access Description
tcpPassiveOpens
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.6
tcpAttemptFails
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.7
tcpEstabResets
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.8
tcpCurrEstab
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.9
tcpInSegs
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10
tcpOutSegs
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11
tcpRetransSegs
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.12
tcpConnTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13
tcpConnEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1
Read only The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition to
the SYN-RCVD state from the LISTEN state.
Read only The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition to
the CLOSED state from either the SYN-SENT state or the SYN-RCVD
state, plus the number of times TCP connections have made a direct
transition to the LISTEN state from the SYN-RCVD state.
Read only The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition to
the CLOSED state from either the ESTABLISHED state or the
CLOSE-WAIT state.
Read only The number of TCP connections for which the current state is either
ESTABLISHED or CLOSE-WAIT.
Read only The total number of segments received, including those received in
error. This count includes segments received on currently established
connections.
Read only The total number of segments sent, including those on current
connections but excluding those containing only retransmitted octets.
Read only The total number of segments retransmitted; that is, the number of
TCP segments transmitted containing one or more previously
transmitted octets.
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
A table containing TCP connection-specific information.
Information about a particular current TCP connection. An object of
this type is transient, in that it ceases to exist when (or soon after) the
connection makes the transition to the CLOSED state.
46 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 67

TABLE 13
Object and OID Access Description
UDP group
2
tcpConnState
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.1
tcpConnLocalAddress
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.2
tcpConnLocalPort
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.3
tcpConnRemAddress
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.4
tcpConnRemPort
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.5
tcpInErrs
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.14
tcpOutRsts
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.15
Read-write The state of this TCP connection.
The only value that might be set by a management station is deleteTCB
(12). Accordingly, it is appropriate for an agent to return a badValue
response if a management station attempts to set this object to any
other value.
If a management station sets this object to the value delete12 (TCB),
then this has the effect of deleting the TCB (as defined in RFC 793) of
the corresponding connection on the managed node, resulting in
immediate termination of the connection.
As an implementation-specific option, a RST segment might be sent
from the managed node to the other TCP endpoint (note, however, that
RST segments are not sent reliably).
Valid values:
• closed
• listen
• synSent (3)
• synReceived (4)
• established (5)
• finWait1 (6)
• finWait2 (7)
• closeWait (8)
• lastAck (9)
• closing (10)
• timeWait (11)
• deleteTCB (12)
NOTE: Fabric OS v3.1.x and v4.x do not allow the SET operation on
this variable.
Read only The local IP address for this TCP connection. In the case of a
connection in the listen state that is willing to accept connections for
any IP interface associated with the node, the value 0.0.0.0 is used.
Read only The local port number for this TCP connection.
Read only The remote IP address for this TCP connection.
Read only The remote port number for this TCP connection.
Read only The total number of segments received in error (for example, bad TCP
checksums).
Read only The number of TCP segments sent containing the RST flag.
UDP group
Implementation of the UDP group is mandatory for all systems that implement the UDP.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 47
53-1002750-01
Page 68

2
EGP group
TABLE 14
Object and OID Access Description
EGP group
udpInDatagrams
1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1
udpNoPorts
1.3.6.1.2.1.7.2
udpInErrors
1.3.6.1.2.1.7.3
udpOutDatagrams
1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4
udpTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.7.5
udpEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.7.5.1
udpLocalAddress
1.3.6.1.2.1.7.5.1.1
udpLocalPort
1.3.6.1.2.1.7.5.1.2
Read only The total number of UDP datagrams delivered to UDP users.
Read only The total number of received UDP datagrams for which there was no
application at the destination port.
Read only The number of received UDP datagrams that could not be delivered for
reasons other than the lack of an application at the destination port.
Read only The total number of UDP datagrams sent from this entity.
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read only The local IP address for this UDP listener. In the case of a UDP listener
Read only The local port number for this UDP listener.
The UDP listener table contains information about this entity’s UDP
end-points on which a local application is currently accepting datagrams.
Information about a particular current UDP listener.
that is willing to accept datagrams for any IP interface associated with
the node, the value 0.0.0.0 is used.
Brocade does not support the EGP group. This section is not applicable. For complete information
regarding the EGP group, refer to RFC 1213.
Transmission group
Brocade does not support the Transmission group. This section is not applicable. For complete
information regarding the Transmission group, refer to RFC 1213.
SNMP group
Implementation of the SNMP group is mandatory for all systems that support an SNMP protocol
entity. Some of the objects defined next are zero-valued in those SNMP implementations that are
optimized to support only those functions specific to either a management agent or a management
station. All of the objects that follow refer to an SNMP entity, and there might be several SNMP
entities residing on a managed node (for example, if the node is acting as a management station).
48 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 69

TABLE 15
Object and OID Access Description
SNMP group
2
snmpInPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.1
snmpOutPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.2
snmpInBadVersions
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.3
snmpInBadCommunityN ames
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.4
snmpInBadCommunityU ses
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.5
snmpInASNParseErrs
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.6
snmpInTooBigs
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.8
snmpInNoSuchNames
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.9
snmpInBadValues
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.10
snmpInReadOnlys
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.11
snmpInGenErrs
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.12
snmpInTotalReqVars
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.13
snmpInTotalSetVars
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.14
snmpInGetRequests
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.15
snmpInGetNexts
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.16
snmpInSetRequests
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.17
snmpInGetResponses
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.18
snmpInTraps
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.19
Read only The total number of messages delivered to the SNMP entity from the
transport service.
Read only The total number of SNMP messages that were passed from the
SNMP protocol entity to the transport service.
Read only The total number of SNMP messages that were delivered to the SNMP
protocol entity and were for an unsupported SNMP version.
Read only The total number of SNMP messages delivered to the SNMP protocol
entity that used a SNMP community name not known to said entity.
Read only The total number of SNMP messages delivered to the SNMP protocol
entity that represented an SNMP operation that was not allowed by the
SNMP community named in the message.
Read only The total number of ASN.1 or BER errors encountered by the SNMP
protocol entity when decoding received SNMP messages.
Read only The total number of SNMP PDUs that were delivered to the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
“tooBig.”
Read only The total number of SNMP PDUs that were delivered to the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
“noSuchName.”
Read only The total number of SNMP PDUs that were delivered to the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
badValue.
Read only The total number valid SNMP PDUs that were delivered to the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
read-only.
Read only The total number of SNMP PDUs that were delivered to the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
“genErr.”
Read only The total number of MIB objects that have been retrieved successfully
by the SNMP protocol entity as the result of receiving valid SNMP
Get-Request and Get-Next PDUs.
Read only The total number of MIB objects that have been altered successfully
by the SNMP protocol entity as the result of receiving valid SNMP
Set-Request PDUs.
Read only The total number of SNMP Get-Request PDUs that have been
accepted and processed by the SNMP protocol entity.
Read only The total number of SNMP Get-Next PDUs that have been accepted
and processed by the SNMP protocol entity.
Read only The total number of SNMP Set-Request PDUs that have been accepted
and processed by the SNMP protocol entity.
Read only The total number of SNMP Get-Response PDUs that have been
accepted and processed by the SNMP protocol entity.
Read only The total number of SNMP Trap PDUs that have been accepted and
processed by the SNMP protocol entity.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 49
53-1002750-01
Page 70

2
SNMP group
TABLE 15
Object and OID Access Description
snmpOutTooBigs
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.20
snmpOutNoSuchNames
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.21
snmpOutBadValues
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.22
snmpOutGenErrs
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.24
snmpOutGetRequests
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.25
snmpOutGetNexts
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.26
snmpOutSetRequests
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.27
snmpOutGetResponses
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.28
snmpOutTraps
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.29
snmpEnableAuthenTraps
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.30
snmpSilentDrops
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.31
snmpProxyDrops
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.32
Read only The total number of SNMP PDUs that were generated by the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is too
large.
Read only The total number of SNMP PDUs that were generated by the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
“noSuchName.”
Read only The total number of SNMP PDUs that were generated by the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
“badValue.”
Read only The total number of SNMP PDUs that were generated by the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
“genErr.”
Read only The total number of SNMP Get-Request PDUs that have been
generated by the SNMP protocol entity.
Read only The total number of SNMP Get-Next PDUs that have been generated
by the SNMP protocol entity.
Read only The total number of SNMP Set-Request PDUs that have been
generated by the SNMP protocol entity.
Read only The total number of SNMP Get-Response PDUs that have been
generated by the SNMP protocol entity.
Read only The total number of SNMP Trap PDUs that have been generated by the
SNMP protocol entity.
Read only Indicates whether the SNMP agent process is permitted to generate
authentication-failure traps. The value of this object overrides any
configuration information; as such, it provides a means whereby all
authentication-failure traps might be disabled.
Possible values are:
• enabled (1)
• disabled (2)
This object is stored in nonvolatile memory so that it remains constant
between re-initialization of the switch. This value can be changed with
the snmpconfig command.
Read only The total number of Confirmed Class PDUs (such as GetRequest-PDUs,
GetNextRequest-PDUs, GetBulkRequest-PDUs, SetRequest-PDUs, and
InformRequest-PDUs) delivered to the SNMP entity and which were
silently dropped because the size of a reply containing an alternate
Response Class PDU (such as a Response-PDU) with an empty
variable-bindings field was greater than either a local constraint or the
maximum message size associated with the originator of the request.
Read only The total number of Confirmed Class PDUs (such as GetRequest-PDUs,
GetNextRequest-PDUs, GetBulkRequest-PDUs, SetRequest-PDUs, and
InformRequest-PDUs) delivered to the SNMP entity and which were
silently dropped because the transmission of the (possibly translated)
message to a proxy target failed in a manner (other than a time-out)
such that no Response Class PDU (such as a Response-PDU) could be
returned.
50 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 71

NOTE
ifMIB group
ifMIB group
2
snmpInBadTypes and snmpOutReadOnlys are not supported.
The ifMIB group is implemented in Fabric OS v5.3.0 and later versions to support FCIP tunnels.
There are entries in the ifXTable for each WAN interface (GbE port), each FC port, and each FCIP
tunnel (transport interface). The ifXtable is used to support 64-bit FC statistics counters.
TABLE 16
Object and OID Access Description
ifXTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1
ifXentry
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1
ifName
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1
ifInMulticastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.2
ifInBroadcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.3
ifOutMulticastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.4
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read only The textual name of the interface. The value of this object should be
Read only The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher
Read only The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher
Read only The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be
A list of interface entries. The number of entries is given by the value
of ifNumber. This table contains additional objects for the interface
table.
An entry in the ifXtable containing additional management
information applicable to a particular interface.
the name of the interface as assigned by the local device and should
be suitable for use in commands entered at the devices console. This
might be a text name, such as `le0 or a simple port number, such as
`1, depending on the interface naming syntax of the device. If several
entries in the iftable together represent a single interface as named
by the device, then each will have the same value of ifName. Note
that for an agent which responds to SNMP queries concerning an
interface on some other (proxied) device, then the value of ifName for
such an interface is the proxied devices local name for it. If there is no
local name, or this object is otherwise not applicable, then this object
contains a zero-length string.
(sub-)layer, which were addressed to a multicast address at this
sub-layer. For a MAC layer protocol, this includes both Group and
Functional addresses. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can
occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other
times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
(sub-)layer, which were addressed to a broadcast address at this
sub-layer. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at
re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as
indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
transmitted, and which were addressed to a multicast address at this
sub-layer, including those that were discarded or not sent. For a MAC
layer protocol, this includes both Group and Functional addresses.
Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at
re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as
indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 51
53-1002750-01
Page 72

2
ifMIB group
TABLE 16
Object and OID Access Description
ifOutBroadcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.5
ifHCInOctets
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.6
ifHCInUcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.7
ifHCInMulticastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.8
ifHCInBroadcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.9
ifHCOutOctets
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.10
ifHCOutUcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.11
Read only The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be
transmitted, and which were addressed to a Broadcast address at
this sub-layer, including those that were discarded or not sent. For a
MAC layer protocol, this includes both Group and Functional
addresses. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at
re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as
indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only The total number of octets received on the interface, including
framing characters. This object is a 64-bit version of ifInOctets.
Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at
re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as
indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.
This value is the number of 4-byte words received and multiplied by
four.
Read only The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher
(sub-)layer, which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast
address at this sub-layer. This object is a 64-bit version of
ifInUcastPkts. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at
re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as
indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.
Read only The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher
(sub-)layer, which were addressed to a multicast address at this
sub-layer. For a MAC layer protocol, this includes both Group and
Functional addresses. This object is a 64-bit version of
ifInMulticastPkts. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can
occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other
times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher
(sub-)layer, which were addressed to a broadcast address at this
sub-layer. This object is a 64-bit version of ifInBroadcastPkts.
Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at
re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as
indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only The total number of octets transmitted out of the interface, including
framing characters. This object is a 64-bit version of ifOutOctets.
Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at
re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as
indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.
This value is the number of 4-byte words transmitted and multiplied
by four.
Read only The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be
transmitted, and which were not addressed to a multicast or
broadcast address at this sub-layer, including those that were
discarded or not sent. This object is a 64-bit version of
ifOutUcastPkts. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur
at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as
indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.
52 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 73

TABLE 16
Object and OID Access Description
ifMIB group
2
ifHCOutMulticastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.12
ifHCOutBroadcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.13
ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.14
ifHighSpeed
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.15
ifPromiscuousMode
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.16
ifConnectorPresent
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.17
Read only The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be
transmitted, and which were addressed to a multicast address at this
sub-layer, including those that were discarded or not sent. For a MAC
layer protocol, this includes both Group and Functional addresses.
This object is a 64-bit version of ifOutMulticastPkts. Discontinuities in
the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the
management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of
ifCounterDiscontinuityTime
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be
transmitted, and which were addressed to a broadcast address at this
sub-layer, including those that were discarded or not sent. This object
is a 64-bit version of ifOutBroadcastPkts. Discontinuities in the value
of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management
system, and at other times as indicated by the value of
ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read-write Indicates whether linkUp or linkDown traps should be generated for
this interface. By default, this object should have the value enabled
(1) for interfaces which do not operate on any other interface (as
defined in the ifStackTable), and disabled (2) otherwise.
Read only An estimate of the current operational speed of the interface in
millions of bits per second. A unit of 1000 equals 1,000,000 bps.
For 1 Gbps, the value is 1000.
For 2 Gbps, the value is 2000.
For 4 Gbps, 8 Gbps, 10 Gbps, and 16 Gbps, the value is 16000.
Read-write This object has a value of false(2) if this interface only accepts
packets or frames that are addressed to this station. This object has a
value of true(1) when the station accepts all packets or frames
transmitted on the media. The value true(1) is only legal on certain
types of media. If legal, setting this object to a value of true(1) may
require the interface to be reset before becoming effective. The value
of ifPromiscuousMode does not affect the reception of broadcast and
multicast packets or frames by the interface.
Hard-coded to false.
Read only Set to true when media is connected, otherwise false. For virtual FC
ports, it is always false.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 53
53-1002750-01
Page 74

2
Generic traps
TABLE 16
Object and OID Access Description
ifAlias
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.18
ifCounterDiscontinuityTi me
1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.17
Read-write This object is an alias name for the interface as specified by a
network manager, and provides a non-volatile handle for the
interface. On the first instantiation of an interface, the value of ifAlias
associated with that interface is the zero-length string. As and when a
value is written into an instance of ifAlias through a network
management set operation, then the agent must retain the supplied
value in the ifAlias instance associated with the same interface for as
long as that interface remains instantiated, including across all
re-initializations or reboots of the network management system,
including those which result in a change of the interfaces ifIndex
value. An example of the value which a network manager might store
in this object for a WAN interface is the (Telcos) circuit number or
identifier of the interface. Some agents may support write-access only
for interfaces having particular values of iftype. An agent which
supports write access to this object is required to keep the value in
non-volatile storage, but it may limit the length of new values
depending on how much storage is already occupied by the current
values for other interfaces.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Read only The value of sysUpTime on the most recent occasion at which any one
or more of this interfaces counters suffered a discontinuity. The
relevant counters are the specific instances associated with this
interface of any Counter32 or Counter64 object contained in the
iftable or ifXTable. If no such discontinuities have occurred since the
last re-initialization of the local management subsystem, then this
object contains a zero value.
NOTE: This object is not supported.
Generic traps
TABLE 17
Trap name and OID Description
coldStart
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.1
A coldStart trap signifies that the sending protocol entity is re-initializing itself such
that the agent's configuration or the protocol entity implementation may be altered.
This trap is generated for the following switch events:
• reboot
• fastboot
warmStart
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.2
A warmStart trap signifies that the sending protocol entity is re-initializing itself such
that neither the agent configuration nor the protocol entity implementation is altered.
This trap is generated for the following switch events:
• firmwaredownload
• hafailover
54 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 75

TABLE 17
Trap name and OID Description
Generic traps
2
linkDown
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.3
linkUp
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.4
authenticationFailure
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.5
A linkDown trap signifies that the sending protocol entity recognizes a failure in one of
the communication links represented in the agent's configuration.
This trap is generated for the following ports:
• FCIP GE ports [Brocade 7800E/Brocade 7500/FR4-18i router blade/FX8-24 DCX
Extension Blade]
• ISCSI GE ports [FC4-16IP]
• FCOE 10G ports [Brocade 8000, FCOE10-24 DCX Blade]
• FCIP xGE ports [FX8-24 DCX Extension Blade]
• FCIP tunnel on GE ports
• FCIP tunnel on xGE ports
• FCIP GE ports - copper
This trap is generated for the following switch events:
• portdisable
• fcoe -disable [for FCOE ports]
Varbinds for this trap are as follows:
• ifIndex
• ifAdminStatus
• ifOperStatus
A linkUp trap signifies that the sending protocol entity recognizes that one of the
communication links represented in the agent's configuration has come up.
This trap is generated for the following ports:
• FCIP GE ports [Brocade 7800E/Brocade 7500/FR4-18i router blade/FX8-24 DCX
Extension Blade]
• ISCSI GE ports [FC4-16IP]
• FCOE 10G ports [Brocade 8000, FCOE10-24 DCX Blade]
• FCIP xGE ports [FX8-24 DCX Extension Blade]
• FCIP tunnel on GE ports
• FCIP tunnel on xGE ports
• FCIP GE ports - copper
This trap is generated for the following switch events:
• portenable
• fcoe -enable
Varbinds for this trap are as follows:
• ifIndex
• ifAdminStatus
• ifOperStatus
An authenticationFailure trap signifies that the sending protocol entity is the
addressee of a protocol message that is not properly authenticated. While
implementations of the SNMP must be capable of generating this trap, they must also
be capable of suppressing the emission of such traps through an
implementation-specific mechanism.
This trap is generated when you perform GET or SET with invalid community strings
(snmpv1).
NOTE: authTraps must be enabled in the switch with the command: snmpconfig -set
systemgroup.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 55
53-1002750-01
Page 76

2
Generic traps
56 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 77

Chapter
- iso
- org
- dod
- internet
- directory
- mgmt
- mib-2
- rmon
- statistics
- history
- alarm
- event
RMON MIB Objects
In this chapter
•RMON MIB overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
•RMON group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
•Statistics group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
•History group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
•Alarm group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
•Event group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
•RMON Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
RMON MIB overview
The descriptions of each of the MIB variables in this chapter come directly from the MIB-II itself.
The notes that follow the descriptions refer to Brocade-specific information and are provided by
Brocade.
3
RMON MIB object hierarchy
Figure 17 through Figure 22 depict the organization and structure of RMON MIB.
FIGURE 17 RMON MIB overall hierarchy
Fabric OS MIB Reference 57
53-1002750-01
Page 78

RMON MIB overview
- statistics 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1
- etherStatsTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1
- etherStatsEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1
- etherStatsIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.1
- etherStatsDataSource 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.2
- etherStatsDropEvents 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.3
- etherStatsOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.4
- etherStatsPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.5
- etherStatsBroadcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.6
- etherStatsMulticastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.7
- etherStatsCRCAlignErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.8
- etherStatsUndersizePkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.9
- etherStatsOversizePkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.10
- etherStatsFragments 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.11
- etherStatsJabbers 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.12
- etherStatsCollisions 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.13
- etherStatsPkts64Octets 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.14
- etherStatsPkts65to127Octets 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.15
- etherStatsPkts128to255Octets 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.16
- etherStatsPkts256to511Octets 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.17
- etherStatsPkts512to1023Octets 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.18
- etherStatsPkts1024to1518Octets 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.19
- etherStatsOwner 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.20
- etherStatsStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.21
- history 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2
- historyControlTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1
- historyControlEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1
- historyControlIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.1
- historyControlDataSource 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.2
- historyControlBucketsRequested 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.3
- historyControlBucketsGranted 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.4
- historyControlInterval 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.5
- historyControlOwner 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.6
- historyControlStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.7
- etherHistoryTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2
- etherHistoryEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1
- etherHistoryIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.1
- etherHistorySampleIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.2
- etherHistoryIntervalStart 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.3
- etherHistoryDropEvents 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.4
- etherHistoryOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.5
- etherHistoryPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.6
- etherHistoryBroadcastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.7
- etherHistoryMulticastPkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.8
- etherHistoryCRCAlignErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.9
- etherHistoryUndersizePkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.10
- etherHistoryOversizePkts 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.11
- etherHistoryFragments 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.12
- etherHistoryJabbers 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.13
- etherHistoryCollisions 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.14
- etherHistoryUtilization 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.15
3
FIGURE 18 Statistics hierarchy
58 Fabric OS MIB Reference
FIGURE 19 History hierarchy
53-1002750-01
Page 79

FIGURE 20 Alarm hierarchy
- alarm 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3
- alarmTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1
- alarmEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1
- alarmIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.1
- alarmInterval 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.2
- alarmVariable 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.3
- alarmSampleType 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.4
- alarmValue 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.5
- alarmStartupAlarm 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.6
- alarmRisingThreshold 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.7
- alarmFallingThreshold 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.8
- alarmRisingEventIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.9
- alarmFallingEventIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.10
- alarmOwner 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.11
- alarmStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.12
- event 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9
- eventTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1
- eventEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1
- eventIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.1
- eventDescription 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.2
- eventType 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.3
- eventCommunity 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.4
- eventLastTimeSent 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.5
- eventOwner 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.6
- eventStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.7
- logTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2
- logEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2.1
- logEventIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2.1.1
- logIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2.1.2
- logTime 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2.1.3
- logDescription 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2.1.4
- rmonEventsV2 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.0
- risingAlarm 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.0.1
- fallingAlarm 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.0.2
RMON MIB overview
3
FIGURE 21 Event hierarchy
FIGURE 22 RMON traps hierarchy
Textual conventions
Tab le 18 lists the textual conventions used for RMON MIB.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 59
53-1002750-01
Page 80

RMON group
3
RMON group
TABLE 18 MIB-II textual conventions
Type definition Value Description
OwnerString Octet String of size 0 to 127 The data type used to model an administratively assigned
name of the owner of a resource.
EntryStatus Integer The status of a table entry.
1 valid
2 createRequest
3 underCreation
4 invalid
Remote network monitoring devices, often called monitors or probes, are instruments that exist for
the purpose of managing a network. This MIB defines objects for managing remote network
monitoring devices.
The groups supported under this are statistics, history, alarm, and event.
Statistics group
TABLE 19
Object and OID Access Description
statistics
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1
etherStatsTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1
etherStatsEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1
etherStatsIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.1
etherStatsDataSource
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.2
etherStatsDropEvents
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.3
etherStatsOctets
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.4
etherStatsPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.5
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read only The value of this object uniquely identifies this etherStats entry.
Read-write This object identifies the source of the data that this etherStats entry is
Read only The total number of events in which packets were dropped by the probe
Read only The total number of octets of data (including those in bad packets)
Read only The total number of packets (including bad packets, broadcast packets,
A collection of statistics kept for a particular Ethernet interface.
Statistics are enabled on an Ethernet interface using the rmon
collection stats <stats-index> command.
A list of Ethernet statistics entries.
A collection of statistics kept for a particular Ethernet interface.
configured to analyze. This source can be any Ethernet interface on this
device. To identify a particular interface, this object will identify the
instance of the ifIndex object, defined in RFC 1213 and RFC 1573 [4,6],
for the desired interface.
due to lack of resources.
NOTE: This number is not necessarily the number of packets dropped;
it is just the number of times this condition has been detected.
received on the network (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets). This object can be used as a reasonable estimate of Ethernet
utilization.
and multicast packets) received.
60 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 81

TABLE 19
Object and OID Access Description
Statistics group
3
etherStatsBroadcastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.6
etherStatsMulticastPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.7
etherStatsCRCAlignErrors
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.8
etherStatsUndersizePkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.9
etherStatsOversizePkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.10
etherStatsFragments
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.11
etherStatsJabbers
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.12
etherStatsCollisions
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.13
etherStatsPkts64Octets
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.14
etherStatsPkts65to127O ctets
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.15
etherStatsPkts128to255 Octets
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.16
etherStatsPkts256to511 Octets
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.17
Read only The total number of good packets received that were directed to the
broadcast address.
NOTE: This number does not include multicast packets.
Read only The total number of good packets received that were directed to a
multicast address.
NOTE: This number does not include packets directed to the broadcast
address.
Read only The total number of packets received that had a length (excluding
framing bits, but including FCS octets) between 64 and 1518 octets,
inclusive, but had one of the following errors:
• FCS error: A bad Frame Check Sequence (FCS) with an integral
number of octets.
• Alignment error: A bad FCS with a non-integral number of octets.
Read only The total number of packets received that were less than 64 octets long
(excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and were otherwise
well formed.
Read only The total number of packets received that were longer than 1518 octets
(excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and were otherwise
well formed.
Read only The total number of packets received that were less than 64 octets in
length (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets) and had one of
the following errors:
• FCS error: A bad FCS with an integral number of octets.
• Alignment error: A bad FCS with a non-integral number of octets.
NOTE: It is entirely normal for etherStatsFragments to increment. This
is because it counts both runts (normal occurrences due to
collisions) and noise hits.
Read only The total number of packets received that were longer than 1518 octets
(excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets), and had one of the
following errors:
• FCS error: A bad FCS with an integral number of octets.
• Alignment error: A bad FCS with a non-integral number of octets.
Read only The best estimate of the total number of collisions on this Ethernet
segment. The value returned will depend on the location of the RMON
probe.
Read only The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
64 octets in length (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Read only The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
between 65 and 127 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits
but including FCS octets).
Read only The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
between 128 and 255 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits
but including FCS octets).
Read only The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
between 256 and 511 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits
but including FCS octets).
Fabric OS MIB Reference 61
53-1002750-01
Page 82

3
History group
TABLE 19
Object and OID Access Description
History group
etherStatsPkts512to102 3Octets
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.18
etherStatsPkts1024to15 18Octets
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.19
etherStatsOwner
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.20
etherStatsStatus
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.21
Read only The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
between 512 and 1023 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits
but including FCS octets).
Read only The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
between 1024 and 1518 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing
bits but including FCS octets).
Read-write The entity that configured this entry and is therefore using the
resources assigned to it.
Read-write The status of this etherStats entry.
History control group
TABLE 20
Object and OID Access Description
history
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2
historyControlTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1
historyControlEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1
historyControlIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.1
historyControlDataSourc e
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.2
historyControlBucketsRe quested
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.3
historyControlBucketsGr anted
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.4
historyControlInterval
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.5
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read only An index that uniquely identifies an entry in the historyControl table.
Read-write This object identifies the source of the data for which historical data
Read-write The requested number of discrete time intervals over which data is to
Read only The number of discrete sampling intervals over which data is to be
Read-write The interval in seconds over which the data is sampled for each bucket
A list of parameters that set up a periodic sampling of statistics. History
is collected using the rmon collection history command.
A list of history control entries.
A list of parameters that set up a periodic sampling of statistics.
Each entry defines a set of samples at a particular interval for an
interface on the device.
was collected and placed in a media-specific table on behalf of this
historyControlEntry. This source can be any interface on the device.
be saved in the part of the media-specific table associated with this
historyControlEntry.
saved in the part of the media-specific table associated with this
historyControlEntry.
in the part of the media-specific table associated with this
historyControlEntry. This interval can be set to any number of seconds
between 1 and 3600 (1 hour). The default value is 1800.
62 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 83

TABLE 20
Object and OID Access Description
History group
3
historyControlOwner
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.6
historyControlStatus
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.1.1.7
Read-write The entity that configured this entry and is therefore using the
resources assigned to it.
Read-write The status of this historyControl entry.
Ethernet history group
TABLE 21
Object and OID Access Description
etherHistoryTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2
etherHistoryEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1
etherHistoryIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.1
etherHistorySampleIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.2
etherHistoryIntervalStart
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.3
etherHistoryDropEvents
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.4
etherHistoryOctets
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.5
etherHistoryPkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.6
etherHistoryBroadcastPk ts
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.7
etherHistoryMulticastPkt s
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.8
etherHistoryCRCAlignErro rs
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.9
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read only The history of which this entry is a part. The history identified by a
Read only An index that uniquely identifies a particular sample this entry
Read only The value of sysUpTime at the start of the interval over which this
Read only The total number of events in which packets were dropped by the probe
Read only The total number of octets of data (including those in bad packets)
Read only The number of packets (including bad packets) received during this
Read only The number of good packets received during this sampling interval that
Read only The number of good packets received during this sampling interval that
Read only The number of packets received during this sampling interval that had a
A list of Ethernet history entries.
An historical sample of Ethernet statistics on a particular Ethernet
interface.
particular value of this index is the same history as identified by the
same value of historyControlIndex.
represents among all the samples associated with the same
historyControlEntry. This index starts at 1 and increases by one as each
new sample is taken.
sample was measured.
due to lack of resources during this sampling interval.
NOTE: This number is not necessarily the number of packets dropped,
received on the network (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
sampling interval.
were directed to the broadcast address.
were directed to a multicast address.
NOTE: This number does not include packets addressed to the
length (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets) between 64 and
1518 octets, inclusive, but either had a bad Frame Check Sequence
(FCS) with an integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS with a
non-integral number of octets (Alignment Error).
it is just the number of times this condition has been detected.
broadcast address.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 63
53-1002750-01
Page 84

3
Alarm group
TABLE 21
Object and OID Access Description
Alarm group
etherHistoryUndersizePkt s
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.10
etherHistoryOversizePkts
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.11
etherHistoryFragments
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.12
etherHistoryJabbers
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.13
etherHistoryCollisions
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.14
etherHistoryUtilization
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2.2.1.15
Read only The number of packets received during this sampling interval that were
less than 64 octets (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets) but
were otherwise well formed.
Read only The number of packets received during this sampling interval that were
longer than 1518 octets (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets) but were otherwise well formed.
Read only The total number of packets received during this sampling interval that
were less than 64 octets (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets) and either had a bad Frame Check Sequence (FCS) with an
integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS with a non-integral
number of octets (Alignment Error).
Read only The number of packets received during this sampling interval that were
longer than 1518 octets (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets), and had either a bad Frame Check Sequence (FCS) with an
integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS with a non-integral
number of octets (Alignment Error).
Read only The best estimate of the total number of collisions on this Ethernet
segment during this sampling interval.
Read only The best estimate of the mean physical layer network utilization on this
interface during this sampling interval, in hundredths of a percent.
TABLE 22
Object and OID Access Description
alarm
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3
alarmTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1
alarmEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1
alarmIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.1
alarmInterval
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.2
alarmVariable
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.3
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read only An index that uniquely identifies an entry in the alarm table. Each such
Read-write The interval in seconds over which the data is sampled and compared
Read-write The object identifier of the particular variable to be sampled.
A list of alarm entries. A list of parameters that set up a periodic
checking for alarm conditions.
An alarm is created using the rmon alarm <alarm-id> command.
A list of alarm entries.
A list of parameters that set up a periodic checking for alarm conditions.
entry defines a diagnostic sample at a particular interval for an object
on the device.
with the rising and falling thresholds.
64 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 85

TABLE 22
Object and OID Access Description
Event group
3
alarmSampleType
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.4
alarmValue
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.5
alarmStartupAlarm
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.6
alarmRisingThreshold
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.7
alarmFallingThreshold
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.8
alarmRisingEventIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.9
alarmFallingEventIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.10
alarmOwner
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.11
alarmStatus
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1.12
Read-write The method of sampling the selected variable and calculating the value
to be compared against the thresholds.
If the value of this object is absoluteValue(1), the value of the selected
variable will be compared directly with the thresholds at the end of the
sampling interval. If the value of this object is deltaValue(2), the value of
the selected variable at the last sample will be subtracted from the
current value, and the difference compared with the thresholds. This
object may not be modified if the associated alarmStatus object is
equal to valid(1).
Read only The value of the statistic during the last sampling period.
Read-write The alarm that may be sent when this entry is first set to valid.
Read-write A threshold for the sampled statistic. When the current sampled value is
greater than or equal to this threshold and the value at the last
sampling interval was less than this threshold, a single event will be
generated.
After a rising event is generated, another such event will not be
generated until the sampled value falls below this threshold and
reaches the alarmFallingThreshold.
Read-write A threshold for the sampled statistic. When the current sampled value is
less than or equal to this threshold, and the value at the last sampling
interval was greater than this threshold, a single event will be
generated. After a falling event is generated, another such event will not
be generated until the sampled value rises above this threshold and
reaches the alarmRisingThreshold.
Read-write The index of the eventEntry that is used when a rising threshold is
crossed.
Read-write The index of the eventEntry that is used when a falling threshold is
crossed.
Read-write The entity that configured this entry and is therefore using the
resources assigned to it.
Read-write The status of this alarm entry.
Event group
TABLE 23
Object and OID Access Description
event
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9
eventTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1
Fabric OS MIB Reference 65
53-1002750-01
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
A set of parameters that describe an event to be generated when
certain conditions are met.
An event is created using the rmon event <event-id> command.
A list of events to be generated.
Page 86

3
Event group
TABLE 23
Object and OID Access Description
eventEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1
eventIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.1
eventDescription
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.2
eventType
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.3
eventCommunity
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.4
eventLastTimeSent
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.5
eventOwner
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.6
eventStatus
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.1.1.7
logTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2
logEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2.1
logEventIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2.1.1
logIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2.1.2
logTime
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2.1.3
logDescription
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9.2.1.4
Not
accessible
Read only An index that uniquely identifies an entry in the event table. Each such
Read-write A comment describing this event entry.
Read-write The type of notification that the probe will make about this event.
Read-write If an SNMP trap is to be sent, it will be sent to the SNMP community
Read-write The value of sysUpTime at the time this event entry last generated an
Read-write The entity that configured this entry and is therefore using the
Read-write The status of this event entry. If this object is not equal to valid (1), all
Not
accessible
Not
accessible
Read only The event entry that generated this log entry. The log identified by a
Read only An index that uniquely identifies an entry in the log table amongst those
Read only The value of sysUpTime when this log entry was created.
Read only An implementation-dependent description of the event that activated
A set of parameters that describe an event to be generated when
certain conditions are met.
entry defines one event that is to be generated when the appropriate
conditions occur.
In the case of a log, an entry is made in the log table for each event. In
the case of snmp-trap, an SNMP trap is sent to one or more
management stations.
specified by this octet string.
event. If this entry has not generated any events, this value will be zero.
resources assigned to it. If this object contains a string starting with
'monitor' and has associated entries in the log table, all connected
management stations should retrieve those log entries, as they may
have significance to all management stations connected to this device.
associated log entries will be deleted by the agent.
A set of data describing an event that has been logged.
A set of data describing an event that has been logged.
particular value of this index is associated with the same eventEntry as
identified by the same value of eventIndex.
generated by the same eventEntries.
this log entry.
66 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 87

RMON Traps
TABLE 24
Trap name and OID Variables Description
RMON Traps
3
rmonEventsV2
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.0
risingAlarm
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.0.1
fallingAlarm
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.0.2
“alarmIndex”
“alarmVariable”
“alarmSampleType”
“alarmValue”
“alarmRisingThreshold”
“alarmIndex”
“alarmVariable”
“alarmSampleType”
“alarmValue”
“alarmFallingThreshold”
Definition point for RMON notifications.
The SNMP trap that is generated when an alarm entry crosses
its rising threshold and generates an event that is configured for
sending SNMP traps.
The SNMP trap that is generated when an alarm entry crosses
its falling threshold and generates an event that is configured
for sending SNMP traps.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 67
53-1002750-01
Page 88

3
RMON Traps
68 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 89

Chapter
FE MIB Objects
In this chapter
•FE MIB overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
•FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
•fcFeConfig group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
•fcFeStatus group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
•fcFeError group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
•fcFeAccounting group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
•fcFeCapabilities group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
•FCFABRIC-ELEMENT-MIB (experimental branch). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
•fcFeConfig group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
•fcFeOp group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
•fcFeError group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
•fcFeAcct group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
•fcFeCap group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
4
FE MIB overview
Brocade supports two versions of the FE MIB:
• FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (RFC2837) in the MIB-II branch.
• FCFABRIC-ELEMENT-MIB in the experimental branch.
The version of the FE MIB supported depends on the version of the Fabric OS. Table 25 lists which
FE MIB is supported in which Fabric OS version.
TABLE 25 FE MIBs and supported Fabric OS versions
Fabric OS version FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch) FCFABRIC-ELEMENT-MIB (experimental
v7.1.0 Yes No
v7.0.0 Yes No
v6.4.1_fcoe Yes No
v6.4.0 Yes No
v6.3.0 Yes No
v6.2.0 Yes No
v6.1.2_CEE Yes No
branch)
Fabric OS MIB Reference 69
53-1002750-01
Page 90

FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch)
NOTE
NOTE
4
TABLE 25 FE MIBs and supported Fabric OS versions (Continued)
Fabric OS version FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch) FCFABRIC-ELEMENT-MIB (experimental
v6.1.0 Yes No
v6.0.0 Yes No
v5.x Yes No
v4.x Yes No
v3.1.x Yes No
v3.0.x Yes Yes
v2.6.x No Yes
The port swap feature does not have any effect on SNMP for FE MIB.
FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch)
branch)
This section contains descriptions and other information specific to FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (in the
MIB-II branch), including:
•FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
•Definitions for FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
•fcFeConfig group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
•fcFeStatus group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
•fcFeError group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
•fcFeAccounting group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
•fcFeCapabilities group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
The descriptions of each of the MIB variables in this chapter come directly from the
FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB itself. The notes that follows the descriptions typically pertain to
Brocade-specific information and are provided by Brocade.
Brocade does not support the settable “Write” function for any of the Fibre Channel FE MIB objects
except fcFxPortPhysAdminStatus.
The object types in FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB are organized into the following groupings:
• Configuration
• Operational
• Error
• Accounting
• Capability
70 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 91

FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch)
- iso
- org
- dod
- internet
- mgmt
- mib-2
- fcFeMIB
- fcFeMIBObjects
- fcFeConfig
- fcFeStatus
- fcFeError
- fcFeAccounting
- fcFeCapabilities
- fcFeMIBConformance
- fcFeMIBCompliances
- fcFeMIBMinimumCompliance
- fcFeMIBFullCompliance
- fcFeMIBGroups
- fcFeConfig
- fcFeStatus
- fcFeError
- fcFeClass1Accounting
- fcFeClass2Accounting
- fcFeClass3Accounting
- fcFeCapabilities
FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB organization
Figure 23 through Figure 28 depict the organization and structure of FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB.
4
FIGURE 23 fcFeMIB hierarchy
Fabric OS MIB Reference 71
53-1002750-01
Page 92

FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch)
- fcFeConfig
- fcFeFabricName 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.1
- fcFeElementName 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.2
- fcFeModuleCapacity 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.3
- fcFeModuleTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4
- fcFeModuleEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1
- fcFeModuleIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.1
- fcFeModuleDescr 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.2
- fcFeModuleObjectID 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.3
- fcFeModuleOperStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.4
- fcFeModuleLastChange 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.5
- fcFeModuleFxPortCapacity 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.6
- fcFeModuleName 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.7
- fcFxPortTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5
- fcFxPortEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1
- fcFxPortIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.1
- fcFxPortName 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.2
- fcFxPortFcphVersionHigh 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.3
- fcFxPortFcphVersionLow 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.4
- fcFxPortBbCredit 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.5
- fcFxPortRxBufSize 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.6
- fcFxPortRatov 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.7
- fcFxPortEdtov 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.8
- fcFxPortCosSupported 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.9
- fcFxPortIntermixSupported 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.10
- fcFxPortStackedConnMode 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.11
- fcFxPortClass2SeqDeliv 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.12
- fcFxPortClass3SeqDeliv 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.13
- fcFxPortHoldTime 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.14
4
FIGURE 24 fcFeConfig hierarchy
72 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 93

FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch)
- fcFeStatus
- fcFxPortStatusTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.1
- fcFxPortStatusEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.1.1
- fcFxPortID 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.1.1.1
- fcFxPortBbCreditAvailable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.1.1.2
- fcFxPortOperMode 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.1.1.3
- fcFxPortAdminMode 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.1.1.4
- fcFxPortPhysTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.2
- fcFxPortPhysEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.2.1
- fcFxPortPhysAdminStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.2.1.1
- fcFxPortPhysOperStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.2.1.2
- fcFxPortPhysLastChange 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.2.1.3
- fcFxPortPhysRttov 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.2.1.4
- fcFxloginTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3
- fcFxloginEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1
- fcFxPortNxLoginIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.1
- fcFxPortFcphVersionAgreed 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.2
- fcFxPortNxPortBbCredit 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.3
- fcFxPortNxPortRxDataFieldSize 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.4
- fcFxPortCosSuppAgreed 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.5
- fcFxPortIntermixSuppAgreed 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.6
- fcFxPortStackedConnModeAgreed 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.7
- fcFxPortClass2SeqDelivAgreed 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.8
- fcFxPortClass3SeqDelivAgreed 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.9
- fcFxPortNxPortName 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.10
- fcFxPortConnectedNxPort 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.11
- fcFxPortBbCreditModel 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.2.3.1.12
- fcFeError
- fcFxPortErrorTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1
- fcFxPortErrorEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1
- fcFxPortLinkFailures 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.1
- fcFxPortSyncLosses 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.2
- fcFxPortSigLosses 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.3
- fcFxPortPrimSeqProtoErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.4
- fcFxPortInvalidTxWords 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.5
- fcFxPortInvalidCrcs 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.6
- fcFxPortDelimiterErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.7
- fcFxPortAddressIdErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.8
- fcFxPortLinkResetIns 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.9
- fcFxPortLinkResetOuts 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.10
- fcFxPortOlsIns 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.11
- fcFxPortOlsOuts 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.3.1.1.12
4
FIGURE 25 fcFeStatus hierarchy
Fabric OS MIB Reference 73
53-1002750-01
FIGURE 26 fcFeError hierarchy
Page 94

FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch)
- fcFeAccounting
- fcFxPortC1AccountingTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1
- fcFxPortC1AccountingEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1
- fcFxPortC1InFrames 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1.1
- fcFxPortC1OutFrames 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1.2
- fcFxPortC1InOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1.3
- fcFxPortC1OutOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1.4
- fcFxPortC1Discards 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1.5
- fcFxPortC1FbsyFrames 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1.6
- fcFxPortC1FrjtFrames 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1.7
- fcFxPortC1InConnections 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1.8
- fcFxPortC1OutConnections 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1.9
- fcFxPortC1ConnTime 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.1.1.10
- fcFxPortC2AccountingTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.2
- fcFxPortC2AccountingEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.2.1
- fcFxPortC2InFrames 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.2.1.1
- fcFxPortC2OutFrames 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.2.1.2
- fcFxPortC2InOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.2.1.3
- fcFxPortC2OutOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.2.1.4
- fcFxPortC2Discards 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.2.1.5
- fcFxPortC2FbsyFrames 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.2.1.6
- fcFxPortC2FrjtFrames 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.2.1.7
- fcFxPortC3AccountingTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.3
- fcFxPortC3AccountingEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.3.1
- fcFxPortC3InFrames 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.3.1.1
- fcFxPortC3OutFrames 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.3.1.2
- fcFxPortC3InOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.3.1.3
- fcFxPortC3OutOctets 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.3.1.4
- fcFxPortC3Discards 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.4.3.1.5
- fcFeCapabilities
- fcFxPortCapTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1
- fcFxPortCapEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1
- fcFxPortCapFcphVersionHigh 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.1
- fcFxPortCapFcphVersionLow 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.2
- fcFxPortCapBbCreditMax 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.3
- fcFxPortCapBbCreditMin 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.4
- fcFxPortCapRxDataFieldSizeMax 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.5
- fcFxPortCapRxDataFieldSizeMin 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.6
- fcFxPortCapCos 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.7
- fcFxPortCapIntermix 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.8
- fcFxPortCapStackedConnMode 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.9
- fcFxPortCapClass2SeqDeliv 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.10
- fcFxPortCapClass3SeqDeliv 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.11
- fcFxPortCapHoldTimeMax 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.12
- fcFxPortCapHoldTimeMin 1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.5.1.1.13
4
FIGURE 27 fcFeAccounting hierarchy
74 Fabric OS MIB Reference
FIGURE 28 fcFeCapabilities hierarchy
Definitions for FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB
Tab le 26 lists the definitions for fcFeMIB.
53-1002750-01
Page 95

FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch)
TABLE 26 FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB definitions
Type definition Value Description
Display string Octet string of size 0 to 255 Represents textual information taken from the NVT ASCII
character set, as defined in pages 4, 10-11 of RFC 854.
Milliseconds Integer from 0 to 2147383647 Represents time unit value in milliseconds.
Microseconds Integer from 0 to 2147383647 Represents time unit value in microseconds.
FcNameId Octet string of size 8 World Wide Name or Fibre Channel name associated with an
FC entity. It is a Network_Destination_ID or Network_Source_ID
composed of a value up to 60 bits wide, occupying the
remaining 8 bytes while the first nibble identifies the format of
the Name_Identifier.
Name_Identifier hex values:
0 (ignored)
1 (IEEE 48-bit address)
2 (IEEE extended)
3 (locally assigned)
4 (32-bit IP address)
FabricName Octet string of size 8 The name identifier of a fabric. Each fabric provides a unique
fabric name.
Valid formats include:
IEEE 48
Local
FcPortName Octet string of size 8 The name identifier associated with a port.
Valid formats include:
IEEE 48
IEEE extended
Local
FcAddressId Octet string of size 3 A 24-bit value unique within the address space of a fabric.
FcRxDataFieldSize Integer from 128 to 2112 Receive data field size of an Nx_Port or Fx_Port.
FcBbCredit Integer from 0 to 32767 Buffer-to-buffer credit of an Nx_Port or Fx_Port.
FcphVersion Integer from 0 to 255 Version of FC-PH supported by an Nx_Port or Fx_Port.
FcStackedConnMode Integer from 1 to 3 Indicates the Class 1 Stacked Connect Mode supported by an
Nx_Port or Fx_Port.
1 (none)
2 (transparent)
3 (lockedDown)
FcCosCap Integer from 1 to 127 Class of service capability of an Nx_Port or Fx_Port.
bit 0 (Class F)
bit 1 (Class 1)
bit 2 (Class 2)
bit 3 (Class 3)
bit 4 (Class 4)
bit 5 (Class 5)
bit 6 (Class 6)
bit 7 (reserved for future)
4
Fabric OS MIB Reference 75
53-1002750-01
Page 96

FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB (MIB-II branch)
4
TABLE 26 FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB definitions (Continued)
Type definition Value Description
Fc0BaudRate Integer according to FC-0 baud
rates
Fc0BaudRateCap Integer from 0 to 127 bit 0 (other)
Fc0MediaCap Integer from 0 to 65535 bit 0 (unknown)
Fc0Medium Integer 1 (unknown)
Fc0TxType Integer 1 (unknown)
Fc0Distance Integer The FC-0 distance range associated with a port transmitter:
FcFeModuleCapacity Integer from 1 to 256 Maximum number of modules within a fabric element; returns
1 (other) None of below
2 (one-eighth) 155 Mbaud (12.5 MB/s)
4 (quarter) 266 Mbaud (25.0 MB/s)
8 (half) 532 Mbaud (50.0 MB/s)
16 (full) 1 Gbaud (100 MB/s)
32 (double) 2 Gbaud (200 MB/s)
64 (quadruple) 4 Gbaud (400 MB/s)
bit 1 (one-eighth)
bit 2 (quarter)
bit 3 (half)
bit 4 (full)
bit 5 (double)
bit 6 (quadruple)
bit 7 (Reserved for future)
bit 1 (single mode fibre (sm))
bit 2 (multimode fibre 50 micron (m5))
bit 3 (multimode fibre 62.5 micron (m6))
bit 4 (video cable (tv))
bit 5 (miniature cable (mi))
bit 6 (shielded twisted pair (stp))
bit 7 (twisted wire (tw))
bit 8 (long video (lv))
bits 9-15 (Reserved for future use)
2 (sm)
4 (m5)
8 (m6)
16 (tv)
32 (mi)
64 (stp)
128 (tw)
256 (lv)
2 (longWaveLaser (LL))
3 (shortWaveLaser (SL))
4 (longWaveLED (LE))
5 (electrical (EL))
6 (shortWaveLaser-noOFC (SN))
1 (unknown)
2 (long)
3 (intermediate)
4 (short)
1 for all devices.
76 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 97

fcFeConfig group
TABLE 26 FIBRE-CHANNEL-FE-MIB definitions (Continued)
Type definition Value Description
FcFeFxPortCapacity Integer from 1 to 640 Maximum number of Fx_Ports within a module.
For the Brocade 300, this value is 24.
For the Brocade 4100, this value is 32.
For the Brocade 4900, this value is 64.
For the Brocade 5000, this value is 32.
For the Brocade 5100, this value is 40.
For the Brocade 5300, this value is 80.
For the Brocade 7500 or 7500E, this value is 32.
For the Brocade 7600, this value is 16.
For the Brocade 7800 Extension Switch, this value is 24.
For the Brocade 8000, this value is 32.
For the Brocade Encryption switch, this value is 32.
For the Brocade DCX, this value is 640.
For the Brocade DCX-4S, this value is 320.
For the Brocade 48000, this value is 384.
For the Brocade 6505, this value is 24.
For the Brocade 6510, this value is 48.
For the Brocade 6520, this value is 96.
For the Brocade DCX 8510-4 Backbone, this value is 320.
For the Brocade DCX 8510-8 Backbone, this value is 640.
For the Brocade VA-40FC, this value is 40.
FcFeModuleIndex Integer from 1 to 256 Module index within a conceptual table.
FcFeFxPortIndex Integer from 1 to 256 Fx_Port index within a conceptual table.
FcFeNxPortIndex Integer from 1 to 256 Nx_Port index within a conceptual table.
FcFxPortMode Integer 1 (unknown)
2 (F_Port)
3 (FL_Port)
FcBbCreditModel Integer BB_Credit model of an Fx_Port.
1 (regular)
2 (alternate)
fcfeModuleFxPortCapacity Integer from 1 to 640 Maximum number of Fx_Ports within a module.
For the Brocade 8000, this value is 32.
4
fcFeConfig group
This group consists of scalar objects and tables. It contains the configuration and service
parameters of the fabric element and the Fx_Ports.
The group represents a set of parameters associated with the fabric element or an Fx_Port to
support its Nx_Ports.
Fabric OS MIB Reference 77
53-1002750-01
Page 98

fcFeConfig group
4
TABLE 27
Object and OID Access Description
fcFeFabricName
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.1
fcFeElementName
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.2
fcFeModuleCapacity
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.3
fcFeModuleTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4
fcFeModuleEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1
fcFeModuleIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.1
fcFeModuleDescr
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.2
fcFeModuleObjectID
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.3
fcFeModuleOperStatus
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.4
fcFeModuleLastChange
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.5
Read-write The Name_Identifier of the fabric to which this fabric element
belongs.
This object returns the WWN of the primary switch in the fabric.
Read-write The Name_Identifier of the fabric element.
This object returns the WWN of the switch.
Read only The maximum number of modules in the fabric element, regardless
of their current state.
The valid value for all Brocade switches is 1.
Not accessible A table that contains information about the modules, one entry for
each module in the fabric element.
Not accessible An entry containing the configuration parameters of a module.
Not accessible Identifies the module within the fabric element for which this entry
contains information. This value is never greater than
fcFeModuleCapacity. This entry never shows any value as it is shown
as non accessible in the browser.
Read only A textual description of the module. This value should include the full
name and version identification of the module. It should contain
printable ASCII characters.
Refer to “sysDescr” on page 33.
Read only The vendor’s authoritative identification of the module. This value
might be allocated within the SMI enterprises subtree (1.3.6.1.4.1)
and provides a straightforward and unambiguous means for
determining what kind of module is being managed.
For example, this object could take the value 1.3.6.1.4.1.99649.3.9
if vendor “Neufe Inc.” was assigned the subtree 1.3.6.1.4.1.99649
and had assigned the identifier 1.3.6.1.4.1.99649.3.9 to its
“FeFiFo-16 PlugInCard.”
Refer to “sysObjectID” on page 33.
Read only Indicates the operational status of the module.
Valid values:
• 1 - online, module functioning properly
• 2 - offline, module not available
• 3 - testing, module in test mode
• 4 - faulty, module is defective
Read only Contains the value of sysUpTime when the module entered its
current operational status. A value of 0 indicates that the
operational status of the module has not changed since the agent
last restarted.
78 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
Page 99

TABLE 27
Object and OID Access Description
fcFeConfig group
4
fcFeModuleFxPortCapacity
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.6
fcFeModuleName
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.4.1.7
fcFxPortTable
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5
fcFxPortEntry
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1
Read only The number of Fx_Ports that can be contained within the module.
Within each module, the ports are uniquely numbered in the range
from 1 to fcFeModuleFxPortCapacity, inclusive. However, the
numbers are not required to be contiguous.
Valid values:
• Brocade 300 24 ports
• Brocade 4100 32 ports
• Brocade 4900 64 ports
• Brocade 5000 32 ports
• Brocade 5100 40 ports
• Brocade 5300 80 ports
• Brocade 7500 or 7500E 32 ports
• Brocade 7600 16 ports
• Brocade 7800 Extension Switch 24 ports
• Brocade 8000 32 ports
• Brocade Encryption Switch 32 ports
• Brocade DCX 640 ports
• Brocade DCX-4S 320 ports
• Brocade 48000 384 ports
• Brocade 6505 24 ports
• Brocade 6510 48 ports
• Brocade 6520 96 ports
• Brocade DCX 8510-4 Backbone 320 ports
• Brocade DCX 8510-8 Backbone 640 ports
• Brocade VA-40FC 40 ports
Read-write The Name_Identifier of the module.
This object returns the WWN of the switch.
Not accessible A table that contains configuration and service parameters of the
Fx_Ports, one entry for each Fx_Port in the fabric element.
Not accessible An entry containing the configuration and service parameters of an
Fx_Port.
fcFxPortIndex
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.1
fcFxPortName
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.2
fcFxPortFcphVersionHigh
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.3
fcFxPortFcphVersionLow
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.4
fcFxPortBbCredit
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.5
Fabric OS MIB Reference 79
53-1002750-01
Not accessible Identifies the Fx_Port within the module. This number ranges from 1
to the value of fcFeModulePortCapacity for the associated module.
The value remains constant for the identified Fx_Port until the
module is re-initialized.
Read only The World Wide Name of this Fx_Port. Each Fx_Port has a unique
port World Wide Name within the fabric.
This object returns the WWN of the port.
Read only The highest or most recent version of FC-PH that the Fx_Port is
configured to support. This value is always 32.
Read only The lowest or earliest version of FC-PH that the Fx_Port is configured
to support. This value is always six.
Read only The total number of receive buffers available for holding Class 1
connect-request, and Class 2 or 3 frames from the attached
Nx_Port. It is for buffer-to-buffer flow control in the direction from the
attached Nx_Port (if applicable) to Fx_Port.
Page 100

fcFeStatus group
4
TABLE 27
Object and OID Access Description
fcFxPortRxBufSize
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.6
fcFxPortRatov
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.7
fcFxPortEdtov
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.8
fcFxPortCosSupported
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.9
fcFxPortIntermixSupported
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.10
fcFxPortStackedConnMod e
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.11
fcFxPortClass2SeqDeliv
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.12
fcFxPortClass3SeqDeliv
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.13
fcFxPortHoldTime
1.3.6.1.2.1.75.1.1.5.1.14
Read only The largest Data_Field Size (in octets) for an FT_1 frame that can be
received by the Fx_Port.
Read only The Resource_Allocation_Timeout value configured for the Fx_Port.
This is used as the time-out value for determining when to reuse an
Nx_Port resource such as a Recovery_Qualifier. It represents
E_D_TOV (Refer to “fcFxPortEdtov” on page 80) plus twice the
maximum time that a frame might be delayed within the fabric and
still be delivered.
Read only The E_D_TOV value configured for the Fx_Port. The
Error_Detect_Timeout value is used as the time-out value for
detecting an error condition.
Read only A value indicating the set of Classes of Service supported by the
Fx_Port.
Read only A flag indicating whether the Fx_Port supports an Intermixed
Dedicated Connection.
Valid values:
• 1 - true
• 2- false
Read only A value indicating the mode of Stacked Connect supported by the
Fx_Port.
Valid values:
• 1 - none
• 2 - transparent
• 3 - locked down
Read only A flag indicating whether Class 2 Sequential Delivery is supported by
the Fx_Port.
Valid values:
• 1 - true
• 2- false
Read only A flag indicating whether Class 3 Sequential Delivery is supported by
the Fx_Port.
Valid values:
• 1 - true
• 2- false
Read only The maximum time (in microseconds) that the Fx_Port holds a frame
before discarding the frame if it is unable to deliver the frame. The
value 0 means that the Fx_Port does not support this parameter.
The formula used to calculate this object is (RATOV - EDTOV - (2 *
WAN_TOV)) / (MAX_HOPS + 1)) / 2).
fcFeStatus group
This group consists of tables that contain operational status and established service parameters
for the fabric element and the attached Nx_Ports.
80 Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1002750-01
 Loading...
Loading...