Page 1

53-1002751-01
®
®
14 December 2012
Fabric OS
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
Supporting Fabric OS v7.1.0
Page 2

Copyright © 2008-2012 Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Brocade, the B-wing symbol, BigIron, DCX, Fabric OS, FastIron, IronPoint, IronShield, IronView, IronWare, JetCore, NetIron,
SecureIron, ServerIron, StorageX, and TurboIron are registered trademarks, and Brocade Network Advisor (formerly Data Center
Fabric Manager or DCFM), Extraordinary Networks, and SAN Health are trademarks of Brocade Communications Systems, Inc., in
the United States and/or in other countries. All other brands, products, or service names are or may be trademarks or service
marks of, and are used to identify, products or services of their respective owners.
Notice: This document is for informational purposes only and does not set forth any warranty, expressed or implied, concerning
any equipment, equipment feature, or service offered or to be offered by Brocade. Brocade reserves the right to make changes to
this document at any time, without notice, and assumes no responsibility for its use. This informational document describes
features that may not be currently available. Contact a Brocade sales office for information on feature and product availability.
Export of technical data contained in this document may require an export license from the United States government.
The authors and Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. shall have no liability or responsibility to any person or entity with
respect to any loss, cost, liability, or damages arising from the information contained in this book or the computer programs that
accompany it.
The product described by this document may contain “open source” software covered by the GNU General Public License or other
open source license agreements. To find out which open source software is included in Brocade products, view the licensing
terms applicable to the open source software, and obtain a copy of the programming source code, please visit
http://www.brocade.com/support/oscd.
Brocade Communications Systems, Incorporated
Corporate and Latin American Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc.
130 Holger Way
San Jose, CA 95134
Tel: 1-408-333-8000
Fax: 1-408-333-8101
E-mail: info@brocade.com
Asia-Pacific Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems China HK, Ltd.
No. 1 Guanghua Road
Chao Yang District
Units 2718 and 2818
Beijing 100020, China
Tel: +8610 6588 8888
Fax: +8610 6588 9999
E-mail: china-info@brocade.com
European Headquarters
Brocade Communications Switzerland Sàrl
Centre Swissair
Tour B - 4ème étage
29, Route de l'Aéroport
Case Postale 105
CH-1215 Genève 15
Switzerland
Tel: +41 22 799 5640
Fax: +41 22 799 5641
E-mail: emea-info@brocade.com
Asia-Pacific Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen WFOE)
Citic Plaza
No. 233 Tian He Road North
Unit 1308 – 13th Floor
Guangzhou, China
Tel: +8620 3891 2000
Fax: +8620 3891 2111
E-mail: china-info@brocade.com
Page 3
Document History
Title Publication number Summary of changes Date
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and
Diagnostics Guide
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and
Diagnostics Guide
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and
Diagnostics Guide
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and
Diagnostics Guide
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and
Diagnostics Guide
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and
Diagnostics Guide
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and
Diagnostics Guide
53-0000853-01 First released edition. March 2008
53-1001187-01 Added support for Vir tual Fabrics, fcPing,
pathInfo, and additional troubleshooting
tips.
53-1001340-01 Added support for checking physical
connections, updated commands,
removed obsolete information, and moved
the FCIP and FICON chapters into their
respective books.
53-1001769-01 Added support for the Rolling Reboot
Detection feature and the Superping tool;
added enhancements for supportSave and
spinFab; updated commands; transferred
the iSCSI chapter into its respective book.
53-1002150-01 Added Frame Viewer and Diagnostics port
features.
53-1002150-02 Updated the Diagnostics port feature. June 2011
53-1002751-01 Updated for Fabric OS v7.1.0. December 2012
November 2008
July 2009
March 2010
April 2011
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide iii
53-1002751-01
Page 4

iv Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 5

Contents
About This Document
How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Supported hardware and software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
What’s new in this document. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
Document conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
Text formatting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
Command syntax conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
Command examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
Notes, cautions, and warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
Key terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
Brocade resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
Other industry resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Getting technical help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Document feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Chapter 1 Introduction
Troubleshooting overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Network time protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Most common problem areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Questions for common symptoms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Gathering information for your switch support provider. . . . . . . . . . . 5
Setting up your switch for FTP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Capturing a supportSave. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Capturing output from a console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Capturing command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Building a case for your switch support provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Basic information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Detailed problem information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Gathering additional information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Chapter 2 General
Licenses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Frame Viewer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Switch message logs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide v
53-1002751-01
Page 6

Switch boot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Rolling Reboot Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
FC-FC routing connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Generating and routing an ECHO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Superping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Route and statistical information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Performance issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Chapter 3 Connectivity
Port initialization and FCP auto-discovery process. . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Link issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Connection problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Checking the physical connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Checking the logical connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Checking the Name Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Link failures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Determining a successful speed negotiation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Checking for a loop initialization failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Checking for a point-to-point initialization failure . . . . . . . . . . .29
Correcting a port that has come up in the wrong mode . . . . . .30
Marginal links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Troubleshooting a marginal link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Device login issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Pinpointing problems with device logins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Media-related issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Testing a port’s external transmit and receive path . . . . . . . . .36
Testing a switch’s internal components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Testing components to and from the HBA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Segmented fabrics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Reconciling fabric parameters individually . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Downloading a correct configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Reconciling a domain ID conflict . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Reconciling incompatible software features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Port mirroring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
In-Order Delivery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Port mirroring considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Supported platforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Maximum mirror connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Configuring a port to be a mirror port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Adding a port mirror connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Deleting a port mirror connection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Displaying port mirror connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Chapter 4 Configuration
Configuration upload and download issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Gathering additional information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
vi Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 7

Brocade configuration form . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Chapter 5 Firmware Download Errors
Blade troubleshooting tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Firmware download issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Troubleshooting with the firmwareDownload command . . . . . . . . . 54
Gathering additional information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
USB error handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Considerations for downgrading firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Preinstallation messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Blade types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Firmware versions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Platform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Chapter 6 Security
Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Password recovery options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Device authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Protocol and certificate management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Gathering additional information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Gathering additional information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
FIPS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Chapter 7 Virtual Fabrics
General Virtual Fabrics troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Fabric identification issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Logical Fabric issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Base switch issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Logical switch issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Switch configuration blade compatibility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Gathering additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Chapter 8 ISL Trunking
Link issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Buffer credit issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Getting out of buffer-limited mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide vii
53-1002751-01
Page 8

Chapter 9 Zoning
Overview of corrective action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Verifying a fabric merge problem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Verifying a TI zone problem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Segmented fabrics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Zone conflicts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Correcting a fabric merge problem quickly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Changing the default zone access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Editing zone configuration members . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Reordering the zone member list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Checking for Fibre Channel connectivity problems . . . . . . . . . .78
Checking for zoning problems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Gathering additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Chapter 10 Diagnostic Features
About Fabric OS diagnostics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Diagnostic information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Power-on self test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Disabling POST. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Enabling POST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Switch status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Viewing the overall status of the switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Displaying switch information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Displaying the uptime for a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Using the SpinFab and portTest commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Debugging spinFab errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Clearing the error counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Enabling a port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
Disabling a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
Diagnostic Port (D_Port) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Understanding D_Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Supported topologies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
Using D_Port without HBAs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
Using D_Port with HBAs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Controlling testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
Example test scenarios and output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
Port information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Viewing the status of a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Displaying the port statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .106
Displaying a summary of port errors for a switch . . . . . . . . . .107
Equipment status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Checking the temperature, fan, and power supply . . . . . . . . .108
Checking the status of the fans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Checking the status of a power supply. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .109
Checking temperature status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .109
viii Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 9

System message log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110
Displaying the system message log, with no page breaks . . . 110
Displaying the system message log
one message at a time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
Clearing the system message log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
Port log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
Viewing the port log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
Syslogd configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .113
Configuring the host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .113
Configuring the switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
Automatic trace dump transfers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
Specifying a remote server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
Enabling the automatic transfer of trace dumps. . . . . . . . . . .115
Setting up periodic checking of the remote server . . . . . . . . .115
Saving comprehensive diagnostic files to the server . . . . . . .116
Appendix A Switch Type and Blade ID
Appendix B Hexadecimal Conversion
Example conversion of the hexadecimal triplet Ox616000 . .121
Decimal-to-hexadecimal conversion table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .122
Index
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide ix
53-1002751-01
Page 10

x Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 11

About This Document
In this chapter
•How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
•Supported hardware and software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
•What’s new in this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
•Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
•Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
•Getting technical help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
•Document feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
How this document is organized
The document contains the following chapters:
• Chapter 1, “Introduction,” gives a brief overview of troubleshooting the Fabric OS, and provides
procedures for gathering basic information from your switch and fabric to aid in
troubleshooting.
• Chapter 2, “General,” provides information on licensing, hardware, and syslog issues.
• Chapter 3, “Connectivity,” provides information and procedures on troubleshooting various link
issues.
• Chapter 4, “Configuration,” provides troubleshooting information and procedures for
configuration file issues.
• Chapter 5, “Firmware Download Errors,” provides procedures for troubleshooting firmware
download issues.
• Chapter 6, “Security,” provides procedures for user account and security issues.
• Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics,” provides procedures for troubleshooting Virtual Fabrics.
• Chapter 8, “ISL Trunking,” provides procedures for resolving trunking issues.
• Chapter 9, “Zoning,” provides preparations and procedures for performing firmware
downloads, as well troubleshooting information.
• Chapter 10, “Diagnostic Features,” provides procedures for the use of the diagnostics
commands for the chassis, ports, and other chassis equipment. Provides information on the
system messages.
• Appendix A, “Switch Type and Blade ID,” provides reference information to guide you in
understanding switch output.
• Appendix B, “Hexadecimal Conversion,” provide reference information for translating
hexadecimal output.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide xi
53-1002751-01
Page 12

Supported hardware and software
In those instances in which procedures or parts of procedures documented here apply to some
switches but not to others, this guide identifies which switches are supported and which are not.
Although many different software and hardware configurations are tested and supported by
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. for Fabric OS v7.1.0, documenting all possible
configurations and scenarios is beyond the scope of this document.
The following hardware platforms are supported by this release of Fabric OS:
• Brocade 300 switch
• Brocade 5100 switch
• Brocade 5300 switch
• Brocade 5410 embedded switch
• Brocade 5424 embedded switch
• Brocade 5450 embedded switch
• Brocade 5460 embedded switch
• Brocade 5470 embedded switch
• Brocade 5480 embedded switch
• Brocade 6505 switch
• Brocade 6510 switch
• Brocade 6520 switch
• Brocade 7800 extension switch
• Brocade 8000 FCoE switch
• Brocade VA-40FC
• Brocade Encryption Switch
• Brocade DCX
• Brocade DCX-4S
• Brocade DCX 8510-4
• Brocade DCX 8510-8
What’s new in this document
Updated for Brocade Fabric OS v7.1.0, including the following:
• Updated system messages related to firmware downloads. (Refer to Chapter 5, “Firmware
Download Errors,” on page 51.)
• Introduced new features available with the D_Port diagnostic tool. (Refer to Chapter 10,
“Diagnostic Features,” on page 81.)
For further information about documentation updates for this release, refer to the release notes.
xii Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 13

Document conventions
This section describes text formatting conventions and important notice formats used in this
document.
TEXT FORMATTING
The narrative-text formatting conventions that are used are as follows:
bold text Identifies command names
italic text Provides emphasis
code text Identifies CLI output
COMMAND SYNTAX CONVENTIONS
For readability, command names in the narrative portions of this guide are presented in mixed
lettercase: for example, switchShow. In actual examples, command lettercase is often all
lowercase. Otherwise, this manual specifically notes those cases in which a command is case
sensitive. Command syntax in this manual follows these conventions:
Identifies the names of user-manipulated GUI elements
Identifies keywords and operands
Identifies text to enter at the GUI or CLI
Identifies variables
Identifies paths and Internet addresses
Identifies document titles
Identifies command syntax examples
command Commands are printed in bold.
--option, option Command options are printed in bold.
-argument, arg Arguments.
[ ] Optional element.
variable Variables are printed in italics. In the help pages, values are underlined
enclosed in angled brackets < >.
... Repeat the previous element, for example “member[;member...]”
value Fixed values following arguments are printed in plain font. For example,
--show WWN
| Boolean. Elements are exclusive. Example:
--show -mode egress | ingress
or
COMMAND EXAMPLES
This book describes how to perform configuration tasks using the Fabric OS command line
interface, but does not describe the commands in detail. For complete descriptions of all Fabric OS
commands, including syntax, operand description, and sample output, refer to the Fabric OS
Command Reference.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide xiii
53-1002751-01
Page 14
NOTES, CAUTIONS, AND WARNINGS
NOTE
ATTENTION
CAUTION
DANGER
The following notices and statements are used in this manual. They are listed below in order of
increasing severity of potential hazards.
A note provides a tip, guidance, or advice, emphasizes important information, or provides a
reference to related information.
An Attention statement indicates potential damage to hardware or data.
A Caution statement alerts you to situations that can be potentially hazardous to you or cause
damage to hardware, firmware, software, or data.
A Danger statement indicates conditions or situations that can be potentially lethal or extremely
hazardous to you. Safety labels are also attached directly to products to warn of these conditions
or situations.
KEY TERMS
For definitions specific to Brocade and Fibre Channel, refer to the Brocade Glossary.
For definitions of SAN-specific terms, visit the Storage Networking Industry Association online
dictionary at:
http://www.snia.org/education/dictionary
Additional information
This section lists additional Brocade and industry-specific documentation that you might find
helpful.
BROCADE RESOURCES
To get up-to-the-minute information, go to http://my.brocade.com and register at no cost for a user
ID and password.
For practical discussions about SAN design, implementation, and maintenance, you can obtain
Building SANs with Brocade Fabric Switches through:
http://www.amazon.com
xiv Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 15

White papers, online demonstrations, and data sheets are available through the Brocade website
at:
http://www.brocade.com/products-solutions/products/index.page
For additional Brocade documentation, visit the Brocade website:
http://www.brocade.com
Release notes are available on the MyBrocade website and are also bundled with the Fabric OS
firmware.
OTHER INDUSTRY RESOURCES
For additional resource information, visit the Technical Committee T11 website. This website
provides interface standards for high-performance and mass storage applications for Fibre
Channel, storage management, and other applications:
http://www.t11.org
For information about the Fibre Channel industry, visit the Fibre Channel Industry Association
website:
http://www.fibrechannel.org
Getting technical help
Contact your switch support supplier for hardware, firmware, and software support, including
product repairs and part ordering. To expedite your call, have the following information available:
1. General Information
• Switch model
• Switch operating system version
• Error numbers and messages received
• supportSave command output
• Detailed description of the problem, including the switch or fabric behavior immediately
following the problem, and specific questions
• Description of any troubleshooting steps already performed and the results
• Serial console and Telnet session logs
• syslog message logs
2. Switch Serial Number
The switch serial number and corresponding bar code are provided on the serial number label,
as illustrated below.:
*FT00X0054E9*
FT00X0054E9
The serial number label is located as follows:
• Brocade 5424 — On the bottom of the switch module.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide xv
53-1002751-01
Page 16

• Brocade 300, 5100, and 5300 — On the switch ID pull-out tab located on the bottom of the
port side of the switch.
• Brocade 6505, 6510, and 6520— On the switch ID pull-out tab located inside the chassis
on the port side on the left.
• Brocade 7800 and 8000 — On the bottom of the chassis.
• Brocade DCX Backbone — On the bottom right on the port side of the chassis.
• Brocade DCX-4S Backbone — On the bottom right on the port side of the chassis.
• Brocade DCX 8510-4 — On the nonport side of the chassis, on the left just below the left
power supply.
• Brocade DCX 8510-8 — On the bottom right on the port side of the chassis and directly
above the cable management comb.
3. World Wide Name (WWN)
Use the licenseIdShow command to display the chassis’ WWN.
If you cannot use the licenseIdShow command because the switch is inoperable, you can get
the WWN from the same place as the serial number, except for the Brocade DCX. For the
Brocade DCX, access the numbers on the WWN cards by removing the Brocade logo plate at
the top of the nonport side of the chassis.
Document feedback
Quality is our first concern at Brocade and we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and
completeness of this document. However, if you find an error or an omission, or you think that a
topic needs further development, we want to hear from you. Forward your feedback to:
documentation@brocade.com
Provide the title and version number of the document and as much detail as possible about your
comment, including the topic heading and page number and your suggestions for improvement.
xvi Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 17

Chapter
Introduction
In this chapter
•Troubleshooting overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
•Most common problem areas. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
•Questions for common symptoms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
•Gathering information for your switch support provider. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
•Building a case for your switch support provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Troubleshooting overview
This book is a companion guide to be used in conjunction with the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
Although it provides a lot of common troubleshooting tips and techniques, it does not teach
troubleshooting methodology.
Troubleshooting should begin at the center of the SAN — the fabric. Because switches are located
between the hosts and storage devices and have visibility into both sides of the storage network,
starting with them can help narrow the search path. After eliminating the possibility of a fault within
the fabric, see if the problem is on the storage side or the host side, and continue a more detailed
diagnosis from there. Using this approach can quickly pinpoint and isolate problems.
1
For example, if a host cannot detect a storage device, run the switchShow command to determine if
the storage device is logically connected to the switch. If not, focus first on the switch directly
connecting to storage. Use your vendor-supplied storage diagnostic tools to better understand why
it is not visible to the switch. If the storage can be detected by the switch, and the host still cannot
detect the storage device, then there is still a problem between the host and switch.
Network time protocol
One of the most frustrating parts of troubleshooting is trying to synchronize switch’s message logs
and portlogs with other switches in the fabric. If you do not have NTP set up on your switches, then
trying to synchronize log files to track a problem is more difficult.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 1
53-1002751-01
Page 18

1
Most common problem areas
Most common problem areas
Tab le 1 identifies the most common problem areas that arise within SANs and identifies tools to
use to resolve them.
TABLE 1 Common troubleshooting problems and tools
Problem area Investigate Tools
Fabric • Missing devices
• Marginal links (unstable connections)
• Incorrect zoning configurations
• Incorrect switch configurations
Storage Devices
• Physical issues between switch and
devices
• Incorrect storage software
configurations
Hosts
• Physical issues between switch and
devices
• Downgrade HBA firmware
• Incorrect device driver installation
• Incorrect device driver configuration
Storage Management
Applications
• Incorrect installation and
configuration of the storage devices
that the software references.
For example, if using a
volume-management application,
check for:
- Incorrect volume installation
- Incorrect volume
configuration
• Switch LEDs
• Switch commands (for example,
switchShow or nsAllShow) for
diagnostics
• Web or GUI-based monitoring and
management software tools
• Device LEDs
• Storage diagnostic tools
• Switch commands (for example,
switchShow or nsAllShow) for
diagnostics
• Device LEDs
• Host operating system diagnostic
tools
• Device driver diagnostic tools
• Switch commands (for example,
switchShow or nsAllShow) for
diagnostics
Also, make sure you use the latest HBA
firmware recommended by the switch
supplier or on the HBA supplier's website
• Application-specific tools and
resources
Questions for common symptoms
You first must determine what the problem is. Some symptoms are obvious, such as the switch
rebooted without any user intervention, or more obscure, such as your storage is having
intermittent connectivity to a particular host. Whatever the symptom is, you must gather
information from the devices that are directly involved in the symptom.
Tab le 2 lists common symptoms and possible areas to check. You may notice that an intermittent
connectivity problem has lots of variables to look into, such as the type of connection between the
two devices, how the connection is behaving, and the port type involved.
2 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 19

Questions for common symptoms
TABLE 2 Common symptoms
Symptom Areas to check Chapter or Document
1
Blade is faulty Firmware or application download
Hardware connections
Blade is stuck in the “LOADING” state Firmware or application download Chapter 5, “Firmware Download Errors”
Configupload or download fails FTP or SCP server or USB availability Chapter 4, “Configuration”
E_Port failed to come online Correct licensing
Fabric parameters
Zoning
EX_Port does not form Links Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Fabric merge fails Fabric segmentation Chapter 2, “General”
Fabric segments Licensing
Zoning
Virtual Fabrics
Fabric parameters
FCIP tunnel bounces FCIP tunnel, including the network between FCIP
tunnel endpoints
FCIP tunnel does not come online FCIP tunnel, including the network between FCIP
tunnel endpoints
FCIP tunnel does not form Licensing
Fabric parameters
FCIP tunnel is sluggish FCIP tunnel, including the network between FCIP
tunnel endpoints
Feature is not working Licensing Chapter 2, “General”
FCR is slowing down FCR LSAN tags Chapter 2, “General”
FICON switch does not talk to hosts FICON settings FICON Administrator’s Guide
FirmwareDownload fails FTP or SCP server or USB availability
Firmware version compatibility
Unsupported features enabled
Firmware versions on switch
Host application times out FCR LSAN tags
Marginal links
Intermittent connectivity Links
Tru nkin g
Buffer credits
FCIP tunnel
LEDs are flashing Links Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
LEDs are steady Links Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 2, “General”
Chapter 5, “Firmware Download Errors”
Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”
Chapter 2, “General”
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”
Chapter 9, “Zoning”
Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”
Chapter 9, “Zoning”
Chapter 2, “General”
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”
Chapter 9, “Zoning”
Fibre Channel over IP Administrator’s
Guide
Fibre Channel over IP Administrator’s
Guide
Chapter 2, “General”
Fibre Channel over IP Administrator’s
Guide
Fibre Channel over IP Administrator’s
Guide
Chapter 5, “Firmware Download Errors”
Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”
Chapter 2, “General”
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 8, “ISL Trunking”
Fibre Channel over IP Administrator’s
Guide
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 3
53-1002751-01
Page 20

1
Questions for common symptoms
TABLE 2 Common symptoms (Continued)
Symptom Areas to check Chapter or Document
License issues Licensing Chapter 2, “General”
LSAN is slow or times-out LSAN tagging Chapter 2, “General”
Marginal link Links Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
No connectivity between host and storage Cables
SCSI timeout errors
SCSI retry errors
Zoning
No connectivity between switches Licensing
Fabric parameters
Segmentation
Virtual Fabrics
Zoning, if applicable
No light on LEDs Links Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Performance problems Links
FCR LSAN tags
FCIP tunnels
Port cannot be moved Virtual Fabrics Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”
SCSI retry errors Buffer credits
FCIP tunnel bandwidth
SCSI timeout errors Links
HBA
Buffer credits
FCIP tunnel bandwidth
Switch constantly reboots Rolling reboot detection
FIPS Chapter 6, “Security”
Switch is unable to join fabric Security policies
Zoning
Fabric parameters
Switch reboots during configup/download Configuration file discrepancy Chapter 4, “Configuration”
Syslog messages Hardware
SNMP management station
Trunk bounces Cables are on same port group
SFPs
Tru nk ed po r ts
Trunk failed to form Licensing
Cables are on same port group
SFPs
Tru nk ed po r ts
Zoning
E_Port QoS configuration mismatch
User forgot password Password recovery Chapter 6, “Security”
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 8, “ISL Trunking”
Chapter 9, “Zoning”
Fibre Channel over IP Administrator’s
Guide
Chapter 2, “General”
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”
Chapter 9, “Zoning”
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 2, “General”
Fibre Channel over IP Administrator’s
Guide
Fibre Channel over IP Administrator’s
Guide
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 8, “ISL Trunking”
Fibre Channel over IP Administrator’s
Guide
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”
Chapter 9, “Zoning”
Chapter 2, “General”
Chapter 6, “Security”
Chapter 8, “ISL Trunking”
Chapter 2, “General”
Chapter 3, “Connectivity”
Chapter 8, “ISL Trunking”
Chapter 9, “Zoning”
4 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 21

Gathering information for your switch support provider
NOTE
TABLE 2 Common symptoms (Continued)
Symptom Areas to check Chapter or Document
1
User is unable to change switch settings RBAC settings
Account settings
Virtual Fabric does not form FIDs Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”
Zone configuration mismatch Effective configuration Chapter 9, “Zoning”
Zone content mismatch Effective configuration Chapter 9, “Zoning”
Zone type mismatch Effective configuration Chapter 9, “Zoning”
Chapter 6, “Security”
Gathering information for your switch support provider
If you are troubleshooting a production system, you must gather data quickly. As soon as a problem
is observed, perform the following tasks. For more information about these commands and their
operands, refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference.
1. Enter the supportSave command to save RASlog, TRACE, supportShow, core file, FFDC data,
and other support information from the switch, chassis, blades, and logical switches.
2. Gather console output and logs.
To execute the supportSave command on the chassis, you must log in to the switch on an account
with the admin role that has the chassis role permission.
Setting up your switch for FTP
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account with admin permissions.
2. Type the supportFtp command and respond to the prompts.
Example of supportFTP command
switch:admin> supportftp -s
Host IP Addr[1080::8:800:200C:417A]:
User Name[njoe]: userFoo
Password[********]: <hidden>
Remote Dir[support]:
supportftp: parameters changed
Capturing a supportSave
The supportSave command uses the default switch name to replace the chassis name regardless
if the chassis name has been changed to a non-factory setting. If Virtual Fabrics is enabled, the
supportSave command uses the default switch name for each logical fabric.
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account with admin permissions.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 5
53-1002751-01
Page 22

1
Gathering information for your switch support provider
2. Type the appropriate supportSave command based on your needs:
• If you are saving to an FTP or SCP server, use the following syntax:
supportSave
When invoked without operands, this command goes into interactive mode. The following
operands are optional:
-n Does not prompt for confirmation. This operand is optional; if omitted, you are prompted
for confirmation.
-c Uses the FTP parameters saved by the supportFtp command. This operand is optional; if
omitted, specify the FTP parameters through command line options or interactively. To
display the current FTP parameters, run supportFtp (on a dual-CP system, run supportFtp
on the active CP).
• On platforms that support USB devices, you can use your Brocade USB device to save the
support files. To use your USB device, use the following syntax:
supportsave [-U -d remote_dir]
-d Specifies the remote directory to which the file is to be transferred. When saving to a
USB device, the predefined
/support directory must be used.
• While running the supportSave command you may encounter a timeout. A timeout occurs
if the system is in busy state due to CPU or I/O bound from a lot of port traffic or file
access. If this occurs, an SS-1004 is generated to both the console and the RASlog to
report the error. You must rerun the supportSave command with the -t option.
Example of SS-1004 message:
SS-1004: “One or more modules timed out during supportsave. Please retry supportsave
with -t option to collect all logs.”
Changing the supportSave timeout value
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account with admin permissions.
2. Enter the supportSave command with the -t operand, and specify a value between 1 through
5.
The following example increases the supportSave modules timeout to two times of the original
timeout setting.
switch:admin> supportSave –t 2
Capturing output from a console
Some information, such as boot information is only outputted directly to the console. In order to
capture this information you have to connect directly to the switch through its management
interface, either a serial cable or an RJ-45 connection.
1. Connect directly to the switch using hyperterminal.
2. Log in to the switch using an account with admin permissions.
6 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 23

Building a case for your switch support provider
3. Set the utility to capture output from the screen.
Some utilities require this step to be performed prior to opening up a session. Check with your
utility vendor for instructions.
4. Type the command or start the process to capture the required data on the console.
Capturing command output
1. Connect to the switch through a Telnet or SSH utility.
2. Log in using an account with admin permissions.
3. Set the Telnet or SSH utility to capture output from the screen.
Some Telnet or SSH utilities require this step to be performed prior to opening up a session.
Check with your Telnet or SSH utility vendor for instructions.
4. Type the command or start the process to capture the required data on the console.
Building a case for your switch support provider
1
The questions listed “Basic information” should be printed out and answered in its entirety and be
ready to send to your switch support provider when you contact them. Having this information
immediately available expedites the information gathering process that is necessary to begin
determining the problem and finding a solution.
Basic information
1. What is the switch’s current Fabric OS level?
To determine the switch’s Fabric OS level, type the firmwareShow command and write down
the information.
2. What is the switch model?
To determine the switch model, type the switchshow command and write down the value in the
switchType field. Cross-reference this value with the chart located in Appendix A, “Switch Type
and Blade ID”.
3. Is the switch operational? Yes or no.
4. Impact assessment and urgency:
• Is the switch down? Yes or no.
• Is it a standalone switch? Yes or no.
• Are there VE, VEX, or EX ports connected to the chassis? Yes or no.
• Use the switchShow command to determine the answer.
• How large is the fabric?
• Use the nsAllShow command to determine the answer.
• Do you have encryption blades or switches installed in the fabric? Yes or no.
• Do you have Virtual Fabrics enabled in the fabric? Yes or no.
• Use the switchShow command to determine the answer.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 7
53-1002751-01
Page 24

1
Building a case for your switch support provider
• Do you have IPsec installed on the switch’s Ethernet interface? Yes or no.
• Use the ipsecConfig --show command to determine the answer.
• Do you have Inband Management installed on the switches GigE ports? Yes or no.
• User the portShow iproute geX command to determine the answer.
• Are you using NPIV? Yes or no.
• Use the switchShow command to determine the answer.
• Are there security policies turned on in the fabric? If so, what are they? Gather the output from
the following commands:
- secPolicyShow
- fddCfg --showall
- ipFilter --show
- authUtil --show
- secAuthSecret --show
- fipsCfg --showall
• Is the fabric redundant? If yes, what is the MPIO software? (List vendor and version.)
5. If you have a redundant fabric, did a failover occur?
6. Was POST enabled on the switch?
7. Which CP blade was active? (Only applicable to Brocade DCX, DCX 8510 family, and DCX-4S
enterprise-class platforms.)
Detailed problem information
Obtain as much of the following informational items as possible prior to contacting the SAN
technical support vendor.
Document the sequence of events by answering the following questions:
• When did problem occur?
• Is this a new installation?
• How long has the problem been occurring?
• Are specific devices affected?
- If so, what are their World Wide Node Names?
• What happened prior to the problem?
• Is the problem reproducible?
- If so, what are the steps to produce the problem?
• What configuration was in place when the problem occurred?
• A description of the problem with the switch or the fault with the fabric.
• The last actions or changes made to the system environment:
- settings
- supportShow output
8 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 25

Building a case for your switch support provider
1
• Host information:
- OS version and patch level
- HBA type
- HBA firmware version
- HBA driver version
- Configuration settings
• Storage information:
- Disk/tape type
- Disk/tape firmware level
- Controller type
- Controller firmware level
- Configuration settings
- Storage software (such as EMC Control Center, Veritas SPC, etc.)
• If this is a Brocade DCX, DCX 8510 family, and DCX-4S enterprise-class platforms, are the CPs
in-sync? Yes or no.
• Use the haShow command to determine the answer.
• List out when and what were the last actions or changes made to the switch, the fabric, and
the SAN or metaSAN.
• In Tab le 3, list the environmental changes added to the network.
TABLE 3 Environmental changes
Type of Change Date when change occurred
Gathering additional information
Below are features that require you to gather additional information. The additional information is
necessary in order for your switch support provider to effectively and efficiently troubleshoot your
issue. Refer to the chapter or document specified for the commands whose data you must capture:
• Configurations, see Chapter 3, “Connectivity”.
• Firmwaredownload, see Chapter 5, “Firmware Download Errors”.
• Trunking, see Chapter 8, “ISL Trunking”.
• Zoning, see Chapter 9, “Zoning”.
• FCIP tunnels, refer to the Fibre Channel over IP Administrator’s Guide.
• FICON, refer to the FICON Administrator’s Guide.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 9
53-1002751-01
Page 26

1
Building a case for your switch support provider
10 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 27

Chapter
General
In this chapter
Licenses
Some features need licenses in order to work properly. To view a list of features and their
associated licenses, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide. Licenses are created using a
switch’s License Identifier so you cannot apply one license to different switches. Before calling your
switch support provider, verify that you have the correct licenses installed by using the licenseShow
command.
2
•Licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
•Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
•Frame Viewer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
•Switch message logs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
•Switch boot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
•FC-FC routing connectivity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Time
Symptom A feature is not working.
Probable cause and recommended action
Refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide to determine if the appropriate licenses are installed
on the local switch and any connecting switches.
Determining installed licenses
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account with admin permissions.
2. Type the licenseShow command.
A list of the currently installed licenses on the switch is displayed.
Symptom Time is not in-sync.
Probable cause and recommended action
NTP is not set up on the switches in your fabric. Set up NTP on your switches in all fabrics in your
SAN and metaSAN.
For more information on setting up NTP, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 11
53-1002751-01
Page 28

2
Frame Viewer
Symptom Frames are being dropped.
Frame Viewer
When a frame is unable to reach its destination due to timeout, it is discarded. You can use Frame
Viewer to find out which flows contained the dropped frames, which can help you determine which
applications might be impacted. Using Frame Viewer, you can see exactly what time the frames
were dropped. (Timestamps are accurate to within one second.) Additionally, this assists in the
debug process.
You can view and filter up to 20 discarded frames per chip per second for 1200 seconds using a
number of fields with the framelog command.
Probable cause and recommended action
Frames are timing out.
Viewing frames.
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account with admin permissions.
2. Type the framelog --show command.
Switch message logs
Switch message logs (RAS logs) contain information on events that happen on the switch or in the
fabric. This is an effective tool in understanding what is going on in your fabric or on your switch.
Weekly review of the RAS logs is necessary to prevent minor problems from becoming larger issues,
or in catching problems at an early stage.
Below are some common problems that can occur with or in your system message log.
Symptom Inaccurate information in the system message log
Probable cause and recommended action
In rare instances, events gathered by the track change feature can report inaccurate information to
the system message log.
For example, a user enters a correct user name and password, but the login was rejected because
the maximum number of users had been reached. However, when looking at the system message
log, the login was reported as successful.
If the maximum number of switch users has been reached, the switch still performs correctly, in
that it rejects the login of additional users, even if they enter the correct user name and password
information.
However, in this limited example, the Track Change feature reports this event inaccurately to the
system message log; it appears that the login was successful. This scenario only occurs when the
maximum number of users has been reached; otherwise, the login information displayed in the
system message log reflects reality.
Refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide for information regarding enabling and disabling track
changes (TC).
12 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 29

Switch boot
Symptom MQ errors are appearing in the switch log.
Probable cause and recommended action
An MQ error is a message queue error. Identify an MQ error message by looking for the two letters
MQ followed by a number in the error message:
2004/08/24-10:04:42, [MQ-1004], 218,, ERROR, ras007, mqRead, queue =
raslog-test- string0123456-raslog, queue I
D = 1, type = 2
MQ errors can result in devices dropping from the switch’s Name Server or can prevent a switch
from joining the fabric. MQ errors are rare and difficult to troubleshoot; resolve them by working
with the switch supplier. When encountering an MQ error, issue the supportSave command to
capture debug information about the switch; then, forward the supportSave data to the switch
supplier for further investigation.
2
Symptom I
Symptom Core file or FFDC warning messages appear on the serial console or in the system log.
Switch boot
2
C bus errors are appearing in the switch log.
Probable cause and recommended action
2
I
C bus errors generally indicate defective hardware or poorly seated devices or blades; the specific
item is listed in the error message. Refer to the Fabric OS Message Reference for information
specific to the error that was received. Some Chip-Port (CPT) and Environmental Monitor (EM)
messages contain I
2
If the I
hardware, as this is the most likely cause. The next sections provide procedures for debugging the
hardware.
Probable cause and recommended action
Issue the supportSave command. The messages can be dismissed by issuing the supportSave -R
command after all data is confirmed to be collected properly.
Error example:
*** CORE FILES WARNING (10/22/08 - 05:00:01 ) ***
3416 KBytes in 1 file(s)
use "supportsave" command to upload
C message does not indicate the specific hardware that may be failing, begin debugging the
2
C-related information.
Symptom The enterprise-class platform model rebooted again after an initial bootup.
Probable cause and recommended action
This issue can occur during an enterprise-class platform boot up with two CPs. If any failure occurs
on active CP, before the standby CP is fully functional and has obtained HA sync, the Standby CP
may not be able to take on the active role to perform failover successfully.
In this case, both CPs reboot to recover from the failure.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 13
53-1002751-01
Page 30

2
ATTENTION
Switch boot
Rolling Reboot Detection
A rolling reboot occurs when a switch or enterprise-class platform has continuously experienced
unexpected reboots. This behavior is continuous until the rolling reboot is detected by the system.
Once the Rolling Reboot Detection (RRD) occurs, the switch is put into a stable state so that a
minimal supportSave can be collected and sent to your service support provider for analysis. Not
every reboot activates the Rolling Reboot Detection feature.
If a rolling reboot is caused by a panic inside Linux kernel, then the RRD feature is not activated.
Reboot classification
There are two types of reboots that occur on a switch and enterprise-class platform, expected and
unexpected. Expected reboots occur when the reboots are initialized by commands, these types of
reboots are ignored by the Rolling Reboot Detection (RRD) feature. They include the following:
• reboot
• haFailover
• fastBoot
• firmwareDownload
The RRD feature is activated and halts rebooting when an unexpected reboot reason is shown
continuously in the reboot history within a certain period of time. The period of time is switch
dependent. The following are considered unexpected reboots:
• Reset
A reset reboot may be caused by one of the following:
- Power-cycle of the switch or CP.
- Linux reboot command.
- Hardware watchdog timeout.
- Heartbeat loss-related reboot.
• Software Fault:Kernel Panic
- If the system detects an internal fatal error from which it cannot safely recover, it outputs
an error message to the console, dumps a stack trace for debugging, and then performs
an automatic reboot.
- After a kernel panic, the system may not have enough time to write the reboot reason
causing the reboot reason to be empty. This is treated as an Unknown/reset case.
• Software fault
- Software Fault:Software Watchdog
- Software Fault:ASSERT
• Software recovery failure
14 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 31

Switch boot
ATTENTION
This is an HA bootup-related issue and happens when switch is unable to recover to a stable
state. HASM log contains more detail and specific information on this type of failure, such as
one of the following:
- Failover recovery failed: This occurs when failover recovery failed and has to reboot the CP.
- Failover when standby CP unready: Occurs when the active CP has to failover, but the
standby CP is not ready to take over mastership.
- Failover when LS trans incomplete: Takes place when a logical switch transaction is
incomplete.
• Software bootup failure
This is an HA bootup-related issue and happens when a switch is unable to load the firmware
to a usable state. HASM log contains more detail and specific information on this type of
failure, such as one of the following:
- System bring up timed out: The CP failed to come up within the time allotted.
- LS configuration timed out and failed: Logical switch configuration failed and timed out.
After RRD is activated, admin level permission is required to log in. Enter the supportShow or
supportSave command to collect a limited amount of data to resolve the issue.
2
The limited supportSave used with the RRD feature does not support USB.
Restrictions
The following restrictions are applicable on the RRD feature:
• The RRD works only on CFOS-based systems and is not available on AP blades.
• If FIPS mode is enabled, then the RRD feature works in record-only mode.
• RRD relies on the bootprom and Linux kernel working properly.
• RRD only works during the 30 minutes immediately after the switch boots. If the switch does
not reboot for 30 minutes, then RRD is deactivated.
Collecting a limited supportSave on the Rolling Reboot Detection
1. Log in to the switch on the admin account.
A user account with admin privileges is not able to collect a limited supportSave.
2. After you see the message in the following example, press Enter.
3. Enter the supportSave command to go into interactive mode.
4. Respond to the prompts.
5. Once the supportSave is completed, contact you service support provider to provide them with
the data.
Below is an example of the screen on a Brocade DCX.
Fabos Version 7.1.0_main_bld23
switch login: admin
Password: <hidden text>
**************************************************************
* *
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 15
53-1002751-01
Page 32

2
ATTENTION
* Fabric OS has detected frequent switch reboot condition. *
* Following actions can be taken to recover the switch: *
* - take off or replace the bad blades. *
* - use supportsave to collect supportsave data. *
*
* *
**************************************************************
Please change passwords for switch default accounts now.
Use Control-C to exit or press 'Enter' key to proceed.
FC-FC routing connectivity
FC-FC routing connectivity
This section describes tools you can use to troubleshoot Fibre Channel routing connectivity and
performance.
Generating and routing an ECHO
The FC-FC Routing Service enables you to route the ECHO generated when an fcPing command is
issued on a switch, providing fcPing capability between two devices in different fabrics across the
FC router.
The fcPing command sends a Fibre Channel ELS ECHO request to a pair of ports. It performs a
zone check between the source and destination. In addition, two Fibre Channel Extended Link
Service (ELS) requests are generated. The first ELS request is from the domain controller to the
source port identifier. The second ELS request is from the domain controller to the destination port
identifiers. The ELS ECHO request elicits an ELS ECHO response from a port identifier in the fabric
and validates link connectivity.
Use the fcPing command to validate link connectivity to a single device or between a pair of
devices.
There are some devices that do not support the ELS ECHO request. In these cases, the device either
does not respond to the request or send an ELS reject. When a device does not respond to the ELS
request, further debugging is required; however, do not assume that the device is not connected.
On the edge Fabric OS switch, make sure that the source and destination devices are properly
configured in the LSAN zone before entering the fcPing command. This command performs the
following functions:
• Checks the zoning configuration for the two ports specified.
• Generates an ELS ECHO request to the source port specified and validates the response.
• Generates an ELS ECHO request to the destination port specified and validates the response.
switch:admin> fcping 0x020800 22:00:00:04:cf:75:63:85
Source: 0x020800
Destination: 22:00:00:04:cf:75:63:85
Zone Check: Zoned
Pinging 0x020800 with 12 bytes of data:
received reply from 0x020800: 12 bytes time:1159 usec
received reply from 0x020800: 12 bytes time:1006 usec
received reply from 0x020800: 12 bytes time:1008 usec
received reply from 0x020800: 12 bytes time:1038 usec
16 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 33

FC-FC routing connectivity
received reply from 0x020800: 12 bytes time:1010 usec
5 frames sent, 5 frames received, 0 frames rejected,0 frames timeout
Round-trip min/avg/max = 1006/1044/1159 usec
Regardless of the device’s zoning configuration, the fcPing command sends the ELS frame to the
destination port. A destination device can take any one of the following actions:
• Send an ELS Accept to the ELS request.
• Send an ELS Reject to the ELS request.
• Ignore the ELS request.
For details about the fcPing command, refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference.
Example of one device that accepts the request and another device that rejects the request
switch:admin> fcping 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05
Source: 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4
Destination: 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05
Zone Check: Not Zoned
Pinging 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4 [0x20800] with 12 bytes of data:
received reply from 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4: 12 bytes time:1162 usec
received reply from 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4: 12 bytes time:1013 usec
received reply from 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4: 12 bytes time:1442 usec
received reply from 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4: 12 bytes time:1052 usec
received reply from 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4: 12 bytes time:1012 usec
5 frames sent, 5 frames received, 0 frames rejected, 0 frames timeout
Round-trip min/avg/max = 1012/1136/1442 usec
Pinging 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05 [0x211e8] with 12 bytes of data:
Request rejected by 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05: Command not supported: time: 1159 usec
Request rejected by 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05: Command not supported: time: 1006 usec
Request rejected by 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05: Command not supported: time: 1008 usec
Request rejected by 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05: Command not supported: time: 1038 usec
Request rejected by 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05: Command not supported: time: 1010 usec
5 frames sent, 0 frames received, 5 frames rejected, 0 frames timeout
Round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/0 usec
of fcPing with a single destination (in this example, the destination is a device node WWN)
2
switch:admin> fcping 20:00:00:00:c9:3f:7c:b8
Destination: 20:00:00:00:c9:3f:7c:b8
Pinging 20:00:00:00:c9:3f:7c:b8 [0x370501] with 12 bytes of data:
received reply from 20:00:00:00:c9:3f:7c:b8: 12 bytes time:825 usec
received reply from 20:00:00:00:c9:3f:7c:b8: 12 bytes time:713 usec
received reply from 20:00:00:00:c9:3f:7c:b8: 12 bytes time:714 usec
received reply from 20:00:00:00:c9:3f:7c:b8: 12 bytes time:741 usec
received reply from 20:00:00:00:c9:3f:7c:b8: 12 bytes time:880 usec
5 frames sent, 5 frames received, 0 frames rejected, 0 frames timeout
Round-trip min/avg/max = 713/774/880 usec
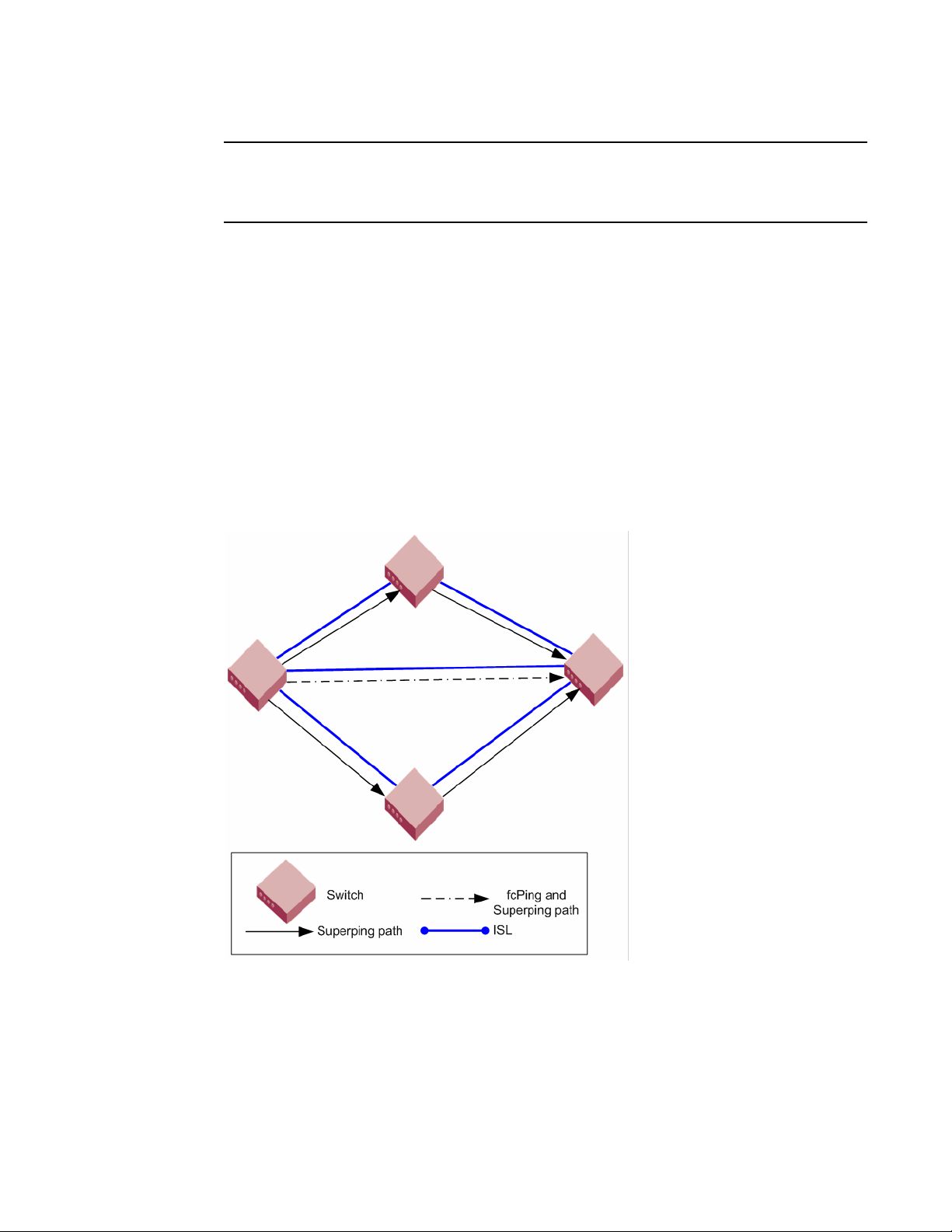
Superping
Superping refers to the fcPing --allpaths command which is a diagnostic tool used to test all least
cost ISLs between a source and destination switch. When you run the command you are provided
with a list of all available least cost paths from a source domain to a destination device. Superping
isolates links with potential failures so that you can investigate these ISLs to determine the exact
links.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 17
53-1002751-01
Page 34
2
ATTENTION
FC-FC routing connectivity
There are some devices that do not support the ELS ECHO request. In these cases, the device either
does not respond to the request or send an ELS reject. When a device does not respond to the ELS
request, further debugging is required; however, do not assume that the device is not connected.
It works by sending ECHO frames to a destination device and outputs the status of each ISL it
traverses whether or not the response from the destination device is received. Each ECHO frame
may choose any path from multiple available paths in the fabric to reach the destination device.
This utility allows you to do the following:
• Run a sanity test that exercises all the ISLs and internal links in different paths that route to the
destination device.
• Determines the least cost path to aid in designing fabric redundancy.
• Determines the specific ISLs and internal links with failures.
• Exercises all ISL links in the base fabric for a logical fabric configuration.
The number of actual paths covered when using the superping tool depends on two other
parameters that you can optionally specify. When you issue the fcPing --allpaths command
without any other options, superping covers all ISLs in the routes between source to destination, as
shown in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1 Superping and fcPing paths
18 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 35

FC-FC routing connectivity
NOTE
In the following example, superping is invoked using the fcPing --allpaths command to destination
domain 165. The following example displays each hop as (Domain1/Index1-> Domain2/Index2)
format. To reach destination domain 165 from source domain 3 there are 2 unique end-to-end
paths. In the first path, the frame traverses from egress port index 205 on source domain 3 to
ingress port index 25 on domain 207. On domain 207 the frame traverses from egress port index
42 to ingress port index 3 in domain 101. On domain 101 the frame goes from egress port index
16 to ingress port index 99 on domain 165.
ECP80:FID128:admin> fcping -allpaths 165
Pinging(size:12 bytes) destination domain 165 through all paths
PATH SWITCH1--> SWITCH2--> SWITCH3 SWITCH4 STATUS
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. (3/EMB, 3/205)[128] (207/25,207/42)[128] (101/3,101/16)[128] (165/99,165/0)[128] SUCCESS
2. (3/EMB, 3/204)[128] (207/27,207/42)[128] (101/3,101/16)[128] (165/99,165/0)[128] SUCCESS
Superping can isolate links with failures so that you can further investigate these ISLs to determine
the exact links giving the errors.
Superping provides an indication if all ISLs are covered. If all the ISLs are not covered, you can
increase the coverage count and maximum retries to transmit, so that complete coverage of all ISLs
is achieved.
2
Consider the following example in which a few errors are recorded on ISLs 3/205-->2/25,
3/204-->2/27, 2/42-->101/3, and 2/1-->101/8. But a maximum of 100 percentage
errors are recorded on internal port 0/284 on domain 2, which is the potential faulty link.
ISL COVERAGE
-------------
SNO ISL STATUS
---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 3/123[128]--> 165/96[128] SUCCESS(5/5)
2 3/205[128]--> 2/25[128] FAILURE(7/50)
3 3/204[128--> 2/27[128] FAILURE(11/50)
4 165/99[128]--> 101/16[128] SUCCESS(5/5)
6 2/42[128]--> 101/3[128] FAILURE(10/67)
7 2/1[128]--> 101/8[128] FAILURE(8/33)
INTERNAL PORT COVERAGE
-----------------------
SNO DOMAIN INTRNL_PORT STATUS
---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 2[128] 0/272 SUCCESS(40/40)
2 2[128] 0/276 SUCCESS(44/44)
3 2[128] 0/280 SUCCESS(30/30)
4 2[128] 0/284 FAILURE(20/20) <== 100% failure
When an echo frame is dropped, all the ISLs in the path are marked as failed. It is not possible to
determine the exact ISL link that dropped the frame. Due to this, all the ISLs in the path record
some failures. But the ISL with the actual error, has the maximum percentage of failures, as this
ISL when selected in any possible path causes the echo frame to be dropped and accumulates a
higher failure percentage.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 19
53-1002751-01
Page 36

2
ATTENTION
FC-FC routing connectivity
Restrictions
• Fabric reconfiguration cannot occur while using the superping tool. It is assumed that the
fabric is stable before the fcPing --allpaths command is executed.
• The control path for interswitch communication should be available, even if the data path for
device to device communication may have resource starvation.
• When executed in a fabric with trunk ports, only the trunk master index is output to the user i.e.
individual coverage statistics of each trunk-member is not available.
• All switches must have Fabric OS v6.3.0 or later.
• Superping requires that the FC Echo ELS frame is supported by end-devices.
• In TI Zones, when failover is disabled and superping is executed to destination device included
in the TI Zone then superping displays failures on all ISLs that are not part of the TI Zone. Also,
when superping is executed to a device that is not present in a TI Zone, failures are shown on
all ISLs that are part of any TI Zone.
• This feature is not supported in interopMode 2 or 3.
• In frame redirection configurations, where there is a physical host, physical target, virtual
initiator and virtual target; superping only identifies the path from the physical host to the
physical target regardless if the data path consists of the path from physical target to virtual
target through the virtual initiator.
Route and statistical information
The pathInfo command displays routing and statistical information from a source port index on the
local switch to a destination port index on another switch. This routing information describes the
full path that a data stream travels between these ports, including all intermediate switches.
Using the pathInfo command when exchange-based routing is turned on can provide different paths
with each attempt.
The routing and statistics information are provided by every switch along the path, based on the
current routing-table information and statistics calculated continuously in real time. Each switch
represents one hop.
Use the pathInfo command to display routing information from a source port on the local switch to
a destination port on another switch. The command output describes the exact data path between
these ports, including all intermediate switches.
When using this command in Fabric OS v6.3.0 across fabrics connected through an FC router, the
command represents backbone information as a single hop. The command captures details about
the FC router to which ingress and egress EX_Ports are connected, but it hides the details about
the path the frame traverses from the ingress EX_Ports to the egress EX_Ports in the backbone.
To use pathInfo across remote fabrics, you must specify both the fabric ID (FID) and the domain ID
of the remote switch. Optionally, you can specify the source PID and destination PID. You cannot
use the pathInfo command to obtain source port information across remote FCR fabrics. When
obtaining path information across remote fabrics, the destination switch must be identified by its
domain ID. Identifying the switch by name or WWN is not accepted.
Use the pathInfo command to display basic path information to a specific domain in command line
mode:
20 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 37

FC-FC routing connectivity
switch:admin> pathinfo 5
Hop In Port Domain ID (Name) Out Port BW Cost
----------------------------------------------------------------------------0 2 1 (sw0) 6 4G 500
1 23 2 (sw0) 8 4G 500
2 4 3 (sw0) 3 4G 500
3 12 4 (sw0) 18 4G 10000
4 4 7 (switch_3) 0 4G 500
5 26 5 (switch_3) E - -
To display basic and extended statistics in interactive mode:
switch:admin> pathinfo
Max hops: (1..127) [25]
Fabric Id: (1..128) [-1]
Domain|Wwn|Name: [] 8
Source port: (0..15) [-1]
Destination port: (0..255) [-1]
Source pid: (0x0..0xefff00) [ffffffff] 0x061600
Desination pid: (0x0..0xefff00) [0] 0x01f001
Basic stats (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Extended stats (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Trace reverse path (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Source route (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Timeout: (1000..30000) [10000]
Target port is Embedded
Hop In Port Domain ID (Name) Out Port BW Cost
----------------------------------------------------------------------------0 2 1 (sw0) 6 4G 500
1 23 2 (sw0) 8 4G 500
2 4 3 (sw0) 3 4G 500
3 2 4 (sw0) 24 4G 10000
4 3 7 (switch_3) 2 4G 500
5 27 5 (switch_3) 24 - -
2
Reverse path
6 24 5 (switch_3) 27 4G 500
7 2 7 (switch_3) 3 4G 500
8 24 4 (sw0) 2 4G 500
9 3 3 (sw0) 4 4G 10000
10 8 2 (sw0) 23 4G 500
11 6 1 (sw0) 2 - (output truncated)
For details about the pathInfo command, refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference.
Performance issues
Symptom General slow-down in FCR performance and scalability.
Probable cause and recommended action
As LSAN zone databases get bigger, it takes more switch resources to process them. Use the
enforce tag feature to prevent a backbone switch from accepting unwanted LSAN zone databases
into its local database.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 21
53-1002751-01
Page 38

2
Symptom Host application times out.
Probable cause and recommended action
The FCR tends to take a long time, more than 5 seconds, to present and setup paths for the proxy
devices. Certain hosts are able to do discovery much faster as a result they end up timing out. Use
the speed tag feature to always present target proxy to the host and import them faster. This helps
sensitive hosts to do a quick discovery without timing out or cause an application failure.
FC-FC routing connectivity
22 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 39

Chapter
Connectivity
In this chapter
•Port initialization and FCP auto-discovery process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
•Link issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
•Connection problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
•Link failures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
•Marginal links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
•Device login issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
•Media-related issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
•Segmented fabrics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
•Port mirroring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Port initialization and FCP auto-discovery process
3
The steps in the port initialization process represent a protocol used to discover the type of
connected device and establish the port type and port speed. The possible port types are as
follows:
• U_Port—Universal FC port. The base Fibre Channel port type and all unidentified, or uninitiated
ports are listed as U_Ports.
• L_/FL_Port—Fabric Loop port. Connects public loop devices.
• G_Port—Generic port. Acts as a transition port for non-loop fabric-capable devices.
• E_Port—Expansion port. Assigned to ISL links.
• F_Port—Fabric port. Assigned to fabric-capable devices.
• EX_Port—A type of E_Port. It connects a Fibre Channel router to an edge fabric. From the point
of view of a switch in an edge fabric, an EX_Port appears as a normal E_Port. It follows
applicable Fibre Channel standards as other E_Ports. However, the router terminates EX_Ports
rather than allowing different fabrics to merge as would happen on a switch with regular
E_Ports.
• M_Port—A mirror port. A mirror port lets you configure a switch port to connect to a port to
mirror a specific source port and destination port traffic passing though any switch port. This is
only supported between F_Ports.
• VE_Port—A virtual E_Por t. A Gigabit Ethernet switch port configured for an FCIP tunnel is called
a VE port (virtual E-port). However, with a VEX_Port at the other end it does not propagate
fabric services or routing topology information from one edge fabric to another.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 23
53-1002751-01
Page 40

3
Port initialization and FCP auto-discovery process
• VEX_Port—A virtual EX_Port. It connects a Fibre Channel router to an edge fabric. From the
point of view of a switch in an edge fabric, a VEX_Port appears as a normal VE_Port. It follows
the same Fibre Channel protocol as other VE_Ports. However, the router terminates VEX_Ports
rather than allowing different fabrics to merge as would happen on a switch with regular
VE_Ports.
Figure 2 shows the process behind port initialization. Understanding this process can help you
determine where a problem resides. For example, if your switch cannot form an E_Port, you
understand that the process never got to that point or does not recognize the switch as an E_Port.
Possible solutions would be to look at licensing and port configuration. Verify that the correct
licensing is installed or that the port is not configured as a loop port, a G_Port, or the port speed is
not set.
FIGURE 2 Simple port initialization process
The FCP auto-discovery process enables private storage devices that accept the process login
(PRLI) to communicate in a fabric.
If device probing is enabled, the embedded port logs in (PLOGI) and attempts a PRLI into the device
to retrieve information to enter into the name server. This enables private devices that do not
perform a fabric login (FLOGI), but accept PRLI, to be entered in the name server and receive full
fabric citizenship.
A fabric-capable device registers information with the Name Server during a FLOGI. These devices
typically register information with the name server before querying for a device list. The embedded
port still PLOGI and attempt PRLI with these devices.
To display the contents of a switch’s Name Server, use the nsShow or nsAllShow command. For
more information about these name server commands, refer to Fabric OS Command Reference.
24 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 41

Link issues
Symptom Port LEDs are flashing.
Symptom Port LEDs are steady.
Symptom No light from the port LEDs.
Link issues
Probable cause and recommended action
Depending on the rate of the flash and the color of the port LED this could mean several things. To
determine what is happening on either your port status LED or power status LED, refer to that
switch’s model hardware reference manual. There is a table that describes the LEDs purpose and
explains the current behavior as well as provides suggested resolutions.
Probable cause and recommended action
The color of the port LED is important in this instance. To determine what is happening on either
your port status LED or power status LED, refer to that switch’s model hardware reference manual.
There is a table that describes the LEDs purpose and explains the current behavior as well as
provides suggested resolutions.
3
Probable cause and recommended action
If there is no light coming from the port LED, then no signal is being detected. Check your cable and
SFP to determine the physical fault.
Connection problems
Determine if the problem is the target or the host, then continue to divide the suspected
problem-path in half until you can pinpoint the problem. One of the most common solutions is
zoning. Verify that the host and target are in the same zone. For more information on zoning, refer
to Chapter 9, “Zoning”.
Checking the physical connection
• Check the cables running to and from the host and storage to the switch.
This path includes the patch panel. Verify that none of the cables are damaged, including
indentations or bent cable.
• Check the SFP on the HBAs and switches.
Verify that they are known to be in good working condition. You can do this by swapping the
current SFP with a known good working SFP.
• Clean the optics.
There are many kits on the market for cleaning fiber optics. You want to find a product that
does not leave residue either from a lint-free wipe or from the solvent.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 25
53-1002751-01
Page 42

3
Connection problems
Checking the logical connection
1. Enter the switchShow command.
2. Review the output from the command and determine if the device successfully logged in to the
switch.
• A device that is logically connected to the switch is registered as an F_, L_, E_, EX_, VE_,
VEX_, or N_Port.
• A device that is not logically connected to the switch is registered as a G_ or U_Port, if NPIV
is not on the switch.
3. Enter the slotShow -m command to verify that all blades are ENABLED and not faulty, disabled
or in some other non-available state.
4. Perform the appropriate actions based on how your missing device is connected:
• If the missing device is logically connected, proceed to the next troubleshooting procedure
(“Checking the Name Server” on page 26).
• If the missing device is not logically connected, check the device and everything on that
side of the data path. Also see “Link failures” on page 28 for additional information.
Checking the path includes verifying the following for the Host:
The Host OS is configured correctly.
The third-party vendor multi-pathing input/output (MPIO) software if it is being used, is
configured correctly.
The HBA and storage device and the driver and firmware are compatible with switch
based on the compatibility matrix.
The driver settings and binaries are up-to-date.
The device Basic Input Output System (BIOS) settings are correct.
The HBA configuration is correct according to manufacturer’s specifications.
The SFPs in the HBA are compatible with the Host’s HBA.
The SFP on the switch is compatible with the switch.
The switch settings related to the Host are configured correctly.
Checking the path includes the following for the Target:
The driver settings and binaries are up-to-date.
The device Basic Input Output System (BIOS) settings are correct.
The HBA configuration is correct according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
The SFPs in the HBA are compatible with the Target HBA.
The switch settings related to the Target are configured correctly.
See “Checking for a loop initialization failure” on page 29 as the next potential trouble
spot.
Checking the Name Server
1. Enter the nsShow command on the switch to determine if the device is attached:
switch:admin> nsshow
The Local Name Server has 9 entries {
Type Pid COS PortName NodeName TTL(sec)
26 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 43

Connection problems
*N 021a00; 2,3;20:00:00:e0:69:f0:07:c6;10:00:00:e0:69:f0:07:c6; 895
Fabric Port Name: 20:0a:00:60:69:10:8d:fd
NL 051edc; 3;21:00:00:20:37:d9:77:96;20:00:00:20:37:d9:77:96; na
FC4s: FCP [SEAGATE ST318304FC 0005]
Fabric Port Name: 20:0e:00:60:69:10:9b:5b
NL 051ee0; 3;21:00:00:20:37:d9:73:0f;20:00:00:20:37:d9:73:0f; na
FC4s: FCP [SEAGATE ST318304FC 0005]
Fabric Port Name: 20:0e:00:60:69:10:9b:5b
NL 051ee1; 3;21:00:00:20:37:d9:76:b3;20:00:00:20:37:d9:76:b3; na
FC4s: FCP [SEAGATE ST318304FC 0005]
Fabric Port Name: 20:0e:00:60:69:10:9b:5b
NL 051ee2; 3;21:00:00:20:37:d9:77:5a;20:00:00:20:37:d9:77:5a; na
FC4s: FCP [SEAGATE ST318304FC 0005]
Fabric Port Name: 20:0e:00:60:69:10:9b:5b
NL 051ee4; 3;21:00:00:20:37:d9:74:d7;20:00:00:20:37:d9:74:d7; na
FC4s: FCP [SEAGATE ST318304FC 0005]
Fabric Port Name: 20:0e:00:60:69:10:9b:5b
NL 051ee8; 3;21:00:00:20:37:d9:6f:eb;20:00:00:20:37:d9:6f:eb; na
FC4s: FCP [SEAGATE ST318304FC 0005]
Fabric Port Name: 20:0e:00:60:69:10:9b:5b
NL 051eef; 3;21:00:00:20:37:d9:77:45;20:00:00:20:37:d9:77:45; na
FC4s: FCP [SEAGATE ST318304FC 0005]
3
Fabric Port Name: 20:0e:00:60:69:10:9b:5b
N 051f00; 2,3;50:06:04:82:bc:01:9a:0c;50:06:04:82:bc:01:9a:0c; na
FC4s: FCP [EMC SYMMETRIX 5267]
Fabric Port Name: 20:0f:00:60:69:10:9b:5b
2. Look for the device in the NS list, which lists the nodes connected to that switch. This allows
you to determine if a particular node is accessible on the network.
• If the device is not present in the NS list, the problem is between the device and the
switch. There may be a time-out communication problem between edge devices and the
name server, or there may be a login issue. First check the edge device documentation to
determine if there is a time-out setting or parameter that can be reconfigured. Also, check
the port log for NS registration information and FCP probing failures (using the
fcpProbeShow command). If these queries do not help solve the problem, contact the
support organization for the product that appears to be inaccessible.
• If the device is listed in the NS, the problem is between the storage device and the host.
There may be a zoning mismatch or a host/storage issue. Proceed to Chapter 9, “Zoning”.
3. Enter the portLoginShow command to check the port login status.
4. Enter the fcpProbeShow command to display the FCP probing information for the devices
attached to the specified F_Port or L_Port. This information includes the number of successful
logins and SCSI INQUIRY commands sent over this port and a list of the attached devices.
5. Check the port log to determine whether or not the device sent the FLOGI frame to the switch,
and the switch probed the device.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 27
53-1002751-01
Page 44

3
NOTE
Link failures
Link failures
A link failure occurs when a server, storage, or switch device is connected to a switch, but the link
between the devices does not come up. This prevents the devices from communicating to or
through the switch.
If the switchShow command or LEDs indicate that the link has not come up properly, use one or
more of the following procedures.
The port negotiates the link speed with the opposite side. The negotiation usually completes in one
or two seconds; however, sometimes the speed negotiation fails.
Determining a successful speed negotiation
Skip this procedure if the port speed is set to a static speed through the portCfgSpeed command.
1. Enter the portCfgShow command to display the port speed settings of all the ports.
2. Enter the switchShow command to determine if the port has module light.
3. Enter the portCfgSpeed command to change the port speed to 1, 2, 4 or 8 Gbps, depending on
what speed can be used by both devices. This should correct the negotiation by setting to one
speed.
4. Enter the portLogShow or portLogDump command.
5. Check the events area of the output:
time task event port cmd args
----------------------------------------------------------------14:38:51.976 SPEE sn <Port#> NC 00000001,00000000,00000001
14:39:39.227 SPEE sn <Port#> NC 00000002,00000000,00000001
• In the event column, sn indicates a speed negotiation.
• In the cmd column, NC indicates the negotiation has completed.
If these fields do not appear, proceed to the step 6.
6. Correct the negotiation by entering the portCfgSpeed [slotnumber/]portnumber, speed_level
command if the fields in step 5 do not appear.
switch:admin> portcfgspeed
Usage: portCfgSpeed PortNumber Speed_Level
Speed_Level: 0 - Auto Negotiate
1 - 1Gbps
2 - 2Gbps
4 - 4Gbps
8 - 8Gbps
ax - Auto Negotiate + enhanced retries
28 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 45

Link failures
3
Checking for a loop initialization failure
1. Verify the port is an L_Port.
a. Enter the switchShow command.
b. Check the last field of the output to verify that the switch port indicates an L_Port. If a loop
device is connected to the switch, the switch port must be initialized as an L_Port.
c. Check to ensure that the state is online; otherwise, check for link failures.
Example of an online L_Port
Area Port Media Speed State Proto
=====================================
(output truncated)
66 66 -- N8 No_Module
67 67 id AN No_Sync
68 68 id N2 Online L-Port 13 public
2. Verify that loop initialization occurred if the port to which the loop device is attached does not
negotiate as an L_Port.
a. Enter the portLogShow or portLogDump command to display the port log for all ports on
the switch; or if you are looking for a specific port, enter the portLogDumpPort command.
b. Check argument number four for the loop initialization soft assigned (LISA) frame
0x11050100.
switch:admin> portlogdumpport 4
time task event port cmd args
----------------------------------------------------------------11:40:02.078 PORT Rx3 23 20 22000000,00000000,ffffffff,11050100
Received LISA frame
The LISA frame indicates that the loop initialization is complete.
3. Skip point-to-point initialization by using the portCfgLport command.
The switch changes to point-to-point initialization after the LISA phase of the loop initialization.
This behavior sometimes causes trouble with old HBAs.
Checking for a point-to-point initialization failure
1. Enter the switchShow command to confirm that the port is active and has a module that is
synchronized.
If a fabric device or another switch is connected to the switch, the switch port must be online.
2. Enter the portLogShow or portLogDump commands.
3. Verify the event area for the port state entry is pstate. The command entry AC indicates that
the port has completed point-to-point initialization.
switch:admin> portlogdumpport 4
time task event port cmd args
------------------------------------------------11:38:21.726 INTR pstate 4 AC
4. Skip over the loop initialization phase.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 29
53-1002751-01
Page 46

3
NOTE
Marginal links
After becoming an active port, the port becomes an F_Port or an E_Port depending on the
device on the opposite side. If the opposite device is a host or target device, the port becomes
an F_Port. If the opposite device is another switch, the port becomes an E_Port.
If there is a problem with the host or target device, enter portCfgGPort to force the port to try to
come up as point-to-point only.
Correcting a port that has come up in the wrong mode
1. Enter the switchShow command.
2. Check the output from the switchShow command and follow the suggested actions in Table 4 .
TABLE 4 SwitchShow output and suggested action
Output Suggested action
Disabled If the port is disabled because persistent disable or security reasons, attempt to resolve
the issue and then enter the portEnable or, if persistently disabled,
portCfgPersistentEnable command.
Bypassed The port may be testing.
Loopback The port may be testing.
E_Port If the opposite side is not another switch, the link has come up in a wrong mode. Check the
output from the portLogShow or PortLogDump commands and identify the link initialization
stage where the initialization procedure went wrong.
F_Port If the opposite side of the link is a private loop device or a switch, the link has come up in a
wrong mode. Check the output from portLogShow or PortLogDump commands.
G_Port The port has not come up as an E_Port or F_Port. Check the output from portLogShow or
PortLogDump commands and identify the link initialization stage where the initialization
procedure went wrong.
L_Port If the opposite side is not a loop device, the link has come up in a wrong mode. Check the
output from portLogShow or PortLogDump commands and identify the link initialization
stage where the initialization procedure went wrong.
If you are unable to read a portlog dump, contact your switch support provider for assistance.
Marginal links
A marginal link involves the connection between the switch and the edge device. Isolating the exact
cause of a marginal link involves analyzing and testing many of the components that make up the
link (including the switch port, switch SFP, cable, edge device, and edge device SFP).
Troubleshooting a marginal link can involve inspecting the error counters described in
“Troubleshooting a marginal link,” or running diagnostics on a link, a port, or an end-to-end path.
The portLoopbackTest command is used to verify the functional operation of a path on a switch.
This test sends frames from a given port’s transmitter and loops them back into the same port’s
receiver. The loopback is done at the parallel loopback path. The path traversed in this test does
not include the media or the fiber cable.
30 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 47

Marginal links
NOTE
Only one frame is transmitted and received at any given time. An external cable is not required to
run this test. The port LEDs flicker green rapidly while the test is running.
Tab le 5 shows the different loopback modes you can use when using portLoopbackTest to test a
marginal link.
3
TABLE 5 Loopback modes
Loopback mode Description
1 Port Loopback (loopback plugs)
2 External Serializer/Deserializer (SerDes) loopback
5 Internal (parallel) loopback (indicates no external equipment)
7 Back-end bypass and port loopback
8 Back-end bypass and SerDes loopback
9 Back-end bypass and internal loopback
Troubleshooting a marginal link
1. Enter the portErrShow command.
2. Determine whether there is a relatively high number of errors (such as CRC errors or ENC_OUT
errors), or if there are a steadily increasing number of errors to confirm a marginal link. Sample
the data every 5 minutes until you see the counters increment.
• The frames tx and rx are the number of frames being transmitted and received.
• The crc_err counter are frames with CRC errors. If this counter goes up, then the physical
path should be inspected. Check the cables to and from the switch, patch panel, and other
devices. Check the SFP by swapping it with a known good working SFP.
If you see this issue on an 8 Gbps blade, use the portCfgFillWord command to reduce EMI.
• The crc_g_eof counter are frames with CRC errors and a good EOF. The first port detecting
a CRC error marks the frame with a bad EOF and passes the frame on to its destination.
Subsequent ports in the path also detect the CRC error and the crc_err counter
increments on these ports. However, since the first port marked the frame with a bad EOF,
the good EOF counter on the subsequent ports does not increment. The marginal link
associated with the port with an increasing good EOF counter is the marginal link and the
source of the errors.
• The enc_out are errors that occur outside the frame and usually indicating a bad primitive.
To determine if you are having a cable problem, take snapshots of the port errors by using
the portErrShow command in increments of 5 to 10 minutes. If you notice the crc_err
counter go up, you have a bad or damaged cable, or a bad or damaged device in the path.
ICLs see enc_out errors when ports on one side of the link are disabled.
• The disc_c3 errors are discarded class 3 errors, which means that the switch is holding
onto the frame longer than the hold time allows. One problem this could be related to is
ISL oversubscription.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 31
53-1002751-01
Page 48

3
Marginal links
switch:admin> porterrshow
frames enc crc crc too too bad enc disc link loss loss frjt fbsy
tx rx in err g_eof shrt long eof out c3 fail sync sig
============================================================================
0: 665k 7.0k 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 0 0 1 2 0 0
1: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0
2: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
3: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
4: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
5: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
6: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
7: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
8: 78 60 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 3 6 0 0
9: 12 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 1 2 0 0
10: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
11: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
12: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
13: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
14: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
15: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
16: 665k 7.4k 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 0 0 1 2 0 0
(output truncated)
3. If you suspect a marginal link, isolate the areas by moving the suspected marginal port cable to
a different port on the switch. Reseating of SFPs may also cure marginal port problems.
If the problem stops or goes away, the switch port or the SFP is marginal (proceed to step 6).
If the problem does not stop or go away, see step 7.
4. Run portLoopbackTest on the marginal port. You need an adapter to run the loopback test for
the SFP. Otherwise, run the test on the marginal port using the loopback mode lb=5. Use the
different modes shown in Table 5 to test the port. Refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference
for additional information on this command.
5. Check the results of the loopback test and proceed as follows:
• If the loopback test failed, the port is bad. Replace the port blade or switch.
• If the loopback test did not fail, the SFP was bad.
6. Replace the SFP on the marginal port.
7. Perform the following steps to rule out cabling issues:
a. Insert a new cable in the suspected marginal port.
b. Enter the portErrShow command to determine if a problem still exists.
• If the portErrShow output displays a normal number of generated errors, the issue is
solved.
• If the portErrShow output still displays a high number of generated errors, follow the
troubleshooting procedures for the Host or Storage device in the following section,
“Device login issues”.
32 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 49

Device login issues
A correct login is when the port type matches the device type that is plugged in. In the following
example, it shows that the device connected to Port 1 is a fabric point-to-point device and it is
correctly logged in an F_Port.
switch:admin> switchshow
switchName:brcd5300
switchType:64.3
switchState:Online
switchMode:Native
switchRole:Subordinate
switchDomain:1
switchId:fffc01
switchWwn:10:00:00:05:1e:40:ff:c4
zoning:OFF
switchBeacon:OFF
FC Router:OFF
FC Router BB Fabric ID:1
Area Port Media Speed State Proto
=====================================
0 0 -- N8 No_Module
1 1 -- N4 Online FC F-Port 10:00:00:05:1e:8f:c1:31
2 2 -- N8 No_Module
3 3 -- N8 No_Module
(output truncated)
61 61 -- N8 No_Module
62 62 -- N8 No_Module
63 63 -- N8 No_Module
64 64 id N2 Online E-Port 10:00:00:05:1e:34:d0:05 "1_d1"
(Trunk master)
65 65 -- N8 No_Module
66 66 -- N8 No_Module
67 67 id AN No_Sync
68 68 id N2 Online L-Port 13 public
69 69 -- N8 No_Module
70 70 -- N8 No_Module
71 71 id N2 Online L-Port 13 public
72 72 -- N8 No_Module
73 73 -- N8 No_Module
74 74 -- N8 No_Module
75 75 -- N8 No_Module
76 76 id N2 Online E-Port 10:00:00:05:1e:34:d0:05 "1_d1"
(upstream)(Trunk master)
77 77 id N4 Online F-Port 10:00:00:06:2b:0f:6c:1f
78 78 -- N8 No_Module
79 79 id N2 Online E-Port 10:00:00:05:1e:34:d0:05 "1_d1"
(Trunk master)
Device login issues
3
Pinpointing problems with device logins
1. Log in to the switch as admin.
2. Enter the switchShow command; then, check for state logins.
3. Enter the portCfgShow command to see if the port is configured correctly.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 33
53-1002751-01
Page 50

3
Device login issues
In some cases, you may find that the port has been locked as an L_Port and the device
attached is a fabric point-to-point device such as a host or switch. This would be an incorrect
configuration for the device and therefore the device cannot log into the switch.
To correct this type of problem, remove the Lock L_Port configuration using the portCfgDefault
command.
switch:admin> portcfgshow
Ports of Slot 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
-----------------+--+--+--+--+----+--+--+--+----+--+--+--+----+--+--+-Speed AN AN AN AN AN AN AN AN AN AN AN AN AN AN AN AN
Trunk Port ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON
Long Distance .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..
VC Link Init .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..
Locked L_Port .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..
Locked G_Port .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..
Disabled E_Port .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..
ISL R_RDY Mode .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..
RSCN Suppressed .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..
Persistent Disable.. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..
NPIV capability ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON
where AN:AutoNegotiate, ..:OFF, ??:INVALID,
SN:Software controlled AutoNegotiation.
4. Enter the portErrShow command; then, check for errors that can cause login problems. A
steadily increasing number of errors can indicate a problem. Track errors by sampling the port
errors every five or ten minutes until you see the problem occur again.
5. Enter the portFlagsShow command; then, check to see how a port has logged in and where a
login failed (if a failure occurred):
switch:admin> portflagsshow
Port SNMP Physical Flags
------------------------------ 0 Offline In_Sync PRESENT U_PORT LED
1 Online In_Sync PRESENT ACTIVE F_PORT G_PORT U_PORT LOGICAL_ONLINE
LOGIN NOELP LED ACCEPT
2 Offline No_Light PRESENT U_PORT LED
3 Offline No_Module PRESENT U_PORT LED
4 Offline No_Module PRESENT U_PORT LED
5 Offline No_Light PRESENT U_PORT LED
6 Offline No_Module PRESENT U_PORT LED
7 Offline No_Module PRESENT U_PORT LED
8 Offline No_Light PRESENT U_PORT LED
9 Offline No_Light PRESENT U_PORT LED
10 Offline No_Module PRESENT U_PORT LED
11 Offline No_Module PRESENT U_PORT LED
12 Offline No_Module PRESENT U_PORT LED
13 Offline No_Module PRESENT U_PORT LED
14 Online In_Sync PRESENT ACTIVE F_PORT G_PORT U_PORT LOGICAL_ONLINE
LOGIN NOELP LED ACCEPT
15 Online In_Sync PRESENT ACTIVE E_PORT G_PORT U_PORT SEGMENTED LOGIN
LED
6. Enter the portLogDumpPort portid command where the port ID is the port number; then, view
the device-to-switch communication.
switch:admin> portlogdumpport 8 | more
time task event port cmd args
34 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 51

Media-related issues
NOTE
------------------------------------------------Thu Nov 6 16:52:39 2008
16:52:39.066 PORT scn 8 1 00010004,4302000f,02000000
16:52:39.066 PORT scn 8 2 ce3dfab0,d9672800,00000002
16:52:39.066 PORT scn 8 2 ce3dfab0,d9672800,00000080
16:52:39.066 PORT scn 8 5 00000000,00000000,00000002
16:52:39.066 PORT scn 8 1 00010004,4302000f,00000002
16:52:39.066 PORT scn 8 1 00010004,4302000f,02000000
16:52:39.071 PORT ioctl 88010004 1,0 * 4
16:52:42.311 SPEE sn 8 WS 00000000,00000000,00000000
16:52:42.558 SPEE sn 8 NM 00000000,00000000,00000000
16:52:42.558 SPEE sn 8 NF 00000000,00000000,00000000
16:52:42.558 SPEE sn 8 NC 00000001,00000000,00000000
16:52:42.559 LOOP loopscn 8 LIP 8002
16:52:42.559 LOOP loopscn 8 LIP f7f7
16:52:42.572 LOOP loopscn 8 LIM 0
16:52:42.572 PORT Tx3 8 12 22000000,00000000,ffffffff,11010000
16:52:42.572 PORT Rx3 8 12 22000000,00000000,ffffffff,11010000
16:52:42.572 PORT Tx3 8 20 22000000,00000000,ffffffff,11020000
16:52:42.572 PORT Rx3 8 20 22000000,00000000,ffffffff,11020000
16:52:42.572 PORT Tx3 8 20 22000000,00000000,ffffffff,11030000
16:52:42.572 PORT Rx3 8 20 22000000,00000000,ffffffff,11030000
3
See “Port log” on page 111 for overview information about portLogDump.
Media-related issues
This section provides procedures that help pinpoint any media-related issues, such as bad cables
and SFPs, in the fabric. The tests listed in Table 6 are a combination of structural and functional
tests that can be used to provide an overview of the hardware components and help identify
media-related issues.
• Structural tests perform basic testing of the switch circuit. If a structural test fails, replace the
main board or port blade.
• Functional tests verify the intended operational behavior of the switch by running frames
through ports or bypass circuitry.
TABLE 6 Component test descriptions
Test name Operands Checks
portTest [-ports itemlist] [-iteration count]
spinFab [-nmegs count] [-ports itemlist] [-setfail mode] Tests switch-to-switch ISL cabling and
[-userdelay time] [-timeout time]
[-pattern pattern] [-patsize size]
[-seed seed] [-listtype porttype]
Used to isolate problems to a single
replaceable element and isolate
problems to near-end terminal
equipment, far-end terminal
equipment, or transmission line.
Diagnostics can be executed every day
or on demand.
trunk group operations.
The following procedures are for checking switch-specific components.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 35
53-1002751-01
Page 52

3
Segmented fabrics
Testing a port’s external transmit and receive path
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Connect the port you want to test to any other switch port with the cable you want to test.
3. Enter the portLoopbackTest -lb_mode 2 command.
Testing a switch’s internal components
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Connect the port you want to test to any other switch port with the cable you want to test.
3. Enter the portLoopbackTest -lb_mode 5 command where 5 is the operand that causes the test
to run on the internal switch components (this is a partial list—refer to the Fabric OS Command
Reference for additional command information):
[-nframes count]—Specify the number of frames to send.
[-lb_mode mode]—Select the loopback point for the test.
[-spd_mode mode]—Select the speed mode for the test.
[-ports itemlist]—Specify a list of user ports to test.
Testing components to and from the HBA
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Enter the portTest command (refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference for information on
the command options).
See Tab le 7 on page 36 for a list of additional tests that can be used to determine the switch
components that are not functioning properly. Refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference for
additional command information.
The HBA's bcu fcDiag
For more information on using this command, refer to the Brocade Adapters Administrator’s Guide.
TABLE 7 Switch component tests
Test Function
portBeacon Sets port beaconing mode.
portLoopbackTest Performs a functional test of port N to N path. Verifies the functional components of the
turboRamTest Verifies that the on chip SRAM located in the 4 and 8 Gbps ASIC is using the Turbo-Ram BIST
--linkbeacon command can be used to beacon a target port on the switch.
switch.
circuitry. This allows the BIST controller to perform the SRAM write and read operations at a
much faster rate.
Segmented fabrics
Fabric segmentation is generally caused by one of the following conditions:
• Incompatible fabric parameters (see “Reconciling fabric parameters individually” on page 37).
36 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 53

Segmented fabrics
3
• Incompatible zoning configuration (see Chapter 9, “Zoning”).
• Domain ID conflict (see “Reconciling fabric parameters individually” on page 37).
• Fabric ID conflict (see Chapter 7, “Virtual Fabrics”).
• Incompatible security policies.
• Incorrect fabric mode.
• Incorrect policy distribution.
• Incompatible software features.
There are a number of settings that control the overall behavior and operation of the fabric. Some
of these values, such as the domain ID, are assigned automatically by the fabric and can differ
from one switch to another in the fabric. Other parameters, such as the BB credit, can be changed
for specific applications or operating environments, but must be the same among all switches to
allow the formation of a fabric.
The following fabric parameters must be identical on each switch for a fabric to merge:
• R_A_TOV
• E_D_TOV
• Data field size
• Sequence level switching
• Disable device probing
• Suppress class F traffic
• Per-frame route priority
• Long-distance fabric (not necessary on Brocade DCX, DCX-4S, 6505, 6510, 6520, and the
Brocade DCX 8510 Backbone families; for more information regarding these product types,
refer to Appendix A, “Switch Type and Blade ID”.)
Reconciling fabric parameters individually
1. Log in to one of the segmented switches as admin.
2. Enter the configShow -pattern “fabric.ops” command.
3. Log in to another switch in the same fabric as admin.
4. Enter the configShow -pattern “fabric.ops” command.
5. Compare the two switch configurations line by line and look for differences. Do this by
comparing the two Telnet windows or by printing the configShow -pattern “fabric.ops” output.
Also, verify that the fabric parameter settings (refer to the above list) are the same for both
switches.
6. Connect to the segmented switch after the discrepancy is identified.
7. Disable the switch by entering the switchDisable command.
8. Enter the configure command to edit the appropriate fabric parameters for the segmented
switch.
9. Enable the switch by entering the switchEnable command.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 37
53-1002751-01
Page 54

3
Segmented fabrics
Alternatively, you can reconcile fabric parameters by entering the configUpload command for each
switch and upload a known-good configuration file. If you do this option, the two switches must be
the same model.
Downloading a correct configuration
You can restore a segmented fabric by downloading a previously saved correct backup
configuration to the switch. Downloading in this manner reconciles any discrepancy in the fabric
parameters and allows the segmented switch to rejoin the main fabric. For details on uploading
and downloading configurations, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
Reconciling a domain ID conflict
If a domain ID conflict appears, the conflict is only reported at the point where the two fabrics are
physically connected. However, there may be several conflicting domain IDs, which appear as soon
as the initial conflict is resolved.
Typically, the fabric automatically resolves domain conflicts during fabric merges or builds unless
Insistent Domain ID (IDID) is configured. If IDID is enabled, switches that cannot be programmed
with a unique domain ID are segmented out. Check each switch that has IDID configured and make
sure their domain IDs are unique within the configuration.
Repeat the following procedure until all domain ID conflicts are resolved.
1. Enter the fabricShow command on a switch from one of the fabrics.
2. In a separate Telnet window, enter the fabricShow command on a switch from the second
fabric.
3. Compare the fabricShow output from the two fabrics. Note the number of domain ID conflicts;
there may be several duplicate domain IDs that must be changed. Determine which switches
have domain overlap and change the domain IDs for each of those switches.
4. Choose the fabric on which to change the duplicate domain ID; connect to the conflicting
switch in that fabric.
5. Enter the switchDisable command.
6. Enter the configure command.
7. When the Fabric Parameters prompt displays, type y.
8. When the Domain prompt displays, type in the new number.
9. Press enter on all prompts to accept their default settings.
10. Enter the switchEnable command.
This enables the joining switch to obtain a new domain ID as part of the process of coming
online. The fabric principal switch allocates the next available domain ID to the new switch
during this process.
11. Repeat step 4 through step 10 if additional switches have conflicting domain IDs.
Example of setting the domain ID
switch_89:FID89:admin> switchdisable
switch_89:FID89:admin> configure
Configure...
38 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 55

Segmented fabrics
Fabric parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Domain: (1..239) [1] 89
WWN Based persistent PID (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Allow XISL Use (yes, y, no, n): [yes]
R_A_TOV: (4000..120000) [10000]
E_D_TOV: (1000..5000) [2000]
WAN_TOV: (0..30000) [0]
MAX_HOPS: (7..19) [7]
Data field size: (256..2112) [2112]
Sequence Level Switching: (0..1) [0]
Disable Device Probing: (0..1) [0]
Suppress Class F Traffic: (0..1) [0]
Per-frame Route Priority: (0..1) [0]
Long Distance Fabric: (0..1) [0]
BB credit: (1..27) [16]
Disable FID Check (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Insistent Domain ID Mode (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Virtual Channel parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
F-Port login parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Zoning Operation parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
RSCN Transmission Mode (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Arbitrated Loop parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
System services (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Portlog events enable (yes, y, no, n): [no]
ssl attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
rpcd attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
webtools attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
3
WARNING: The domain ID will be changed. The port level zoning may be affected
Reconciling incompatible software features
Earlier releases of software may not be supported in new versions of Fabric OS code. This may be
due to a software feature changing or new services being supported. If you suspect that you are
trying to introduce a switch into a fabric that has an older version of code, check the release notes
to verify that any features on that switch are supported in the fabric with the newer code.
When the Management Server (MS) Platform services are enabled on a switch running Fabric OS
v7.0.0 and later and you try to merge this switch into a fabric that does not have this feature
enabled, the switch does not merge and a segmentation occurs. To resolve this, either turn the MS
Platform services off or enable them on every switch in the fabric.
In Fabric OS v7.0.0 and later, an ESC frame is used to exchange fabric parameters to detect
Enhance TI Zones, interoperability mode, and Virtual Fabric FID conflicts. If at any point during the
ESC frame exchange, a link with incompatible parameters is detected, the switch running Fabric OS
v7.0.0 and later does not join into the existing fabric. To fix this issue, refer to the Fabric OS
Administrator’s Guide for more information on that specific software feature.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 39
53-1002751-01
Page 56

3
Port mirroring
With port mirroring, you can configure a switch port to mirror the traffic between a specific source
and destination port. This is only supported between F_Ports. This is a useful way to troubleshoot a
problem port without bringing down the host and destination links to insert an inline analyzer.
Port mirroring captures traffic between two devices. It mirrors only the frames containing the
SID/DID to the mirror port. Because of the way it handles mirroring, a single mirror port can mirror
multiple mirror connections. This also means that the port cannot exceed the maximum bandwidth
of the mirror port. Attempts to mirror more traffic than what available bandwidth allows results in
the port mirror throttling the SID/DID traffic so that traffic does not exceed the maximum available
bandwidth.
The bandwidth of the mirror port is unidirectional. In general, a host (SID) talks to multiple storage
devices (DIDs). Thus, a host does not send full line rate to a single target. A mirror port configured
at 4 Gbps can only support up to 4 Gbps of traffic. A normal 4 Gbps F_Port is bi-directional and can
support up to 8 Gbps (4 Gbps transmit and 4 Gbps receive) of traffic. If the mirror port bandwidth is
exceeded, no credits are returned to the receiver port and thus those devices involved in mirror
connection see a degraded level of performance.
Use port mirroring to detect missing frames, which may occur with zoning issues or hold timeouts,
capture protocol errors, and capture ULP traffic (SCSI/FICON). This feature cannot be used on
embedded switch traffic.
Port mirroring
In-Order Delivery
If In-Order Delivery (IOD) is enabled, adding or deleting a port mirror connection causes a frame
drop. Port mirroring basically reroutes a given connection to the mirror port. The mirror traffic takes
an extra route to the mirror port. When the extra route is removed, the frames between the two
ports go directly to the destination port. The frames at the mirror port could be queued at the
destination port behind those frames that went directly to the destination port. To prevent this IOD
issue, port mirroring drops those frames from the mirror port when a connection is disabled. If IOD
has been disabled, port mirroring does not drop any frames, but does have an IOD error.
Port mirroring considerations
Before creating port mirror connections, consider the following limitations:
• A mirror port can be any port on the same switch as the source identifier port.
• If FCR is enabled, do not enable port mirroring.
• Only one domain can be mirrored. After a domain is defined, only mirror ports on the defined
domain can be used. The first connection defines the restriction on the domain, which can be
either the local domain or a remote domain.
• A switch that is capable of port mirroring can support a minimum of one and a maximum of
three mirror connections.Refer to Table 9 on page 42 to determine the number of mirror
connections your switch or blade can support.
• Mirror port bandwidth limits mirror connections.
• Deleting a port mirroring connection with IOD enabled causes frame drop between two
endpoints.
40 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 57

Port mirroring
3
• Using the firmware download procedure to downgrade to previous Fabric OS releases that do
not support port mirroring requires that you remove all the port mirroring connections. If you
downgrade to a previous versions of Fabric OS, you cannot proceed until the mirroring
connections are removed.
• Port mirroring is supported with Virtual Fabrics with the limitation that you cannot have FCR
enabled within the same 8-port group.
• If you have NPIV or 10-bit address mode enabled on a Brocade 300, 5300, 5410, 5450, 5460,
5470, 5480, 7800, and the M5424 platforms, all devices from the same NPIV port or 10-bit
addressing mode hit the same mirror connection, regardless of different AL_PAs, since the
validation is done only for the first 16-bits of the SID/DID.
• Port mirroring is not supported for the shared area ports of 48-port blades in the default
switch. However, when the ports are assigned to a 10-bit address logical switch, port mirroring
is supported.
Supported platforms
Port mirroring is supported only in FC ports. In general, a platform or blade supporting port
mirroring supports both the mirror ports and the mirror connections. Exceptions are listed in
Tab le 8.
TABLE 8 Port mirroring platform supportability
Brocade Model Fabric OS v6.1.1_enc Fabric OS v6.34.0 Fabric OS v6.4.0 Fabric OS v7.1.0
Brocade
Encryption Switch
FS8-18
DCX-4S
Brocade 8000 Port mirroring is not
FCOE10-24 Port mirroring is
FX8-24 Port mirroring is
Brocade 7800 Port mirroring is
Not supported Not supported Not supported Not supported
supported on either FC
or FCoE ports.
Port mirroring is
supported on the
Brocade FCOE
10-24.
Port mirroring is
supported over
GbE ports/FCIP VE
tunnels
Port mirroring is
supported over
GbE ports/FCIP VE
tunnels
not supported on
Europa.
supported only on
the FC ports. It is
not supported over
GbE ports/FCIP VE
tunnels
supported only on
the FC ports. It is
not supported over
GbE ports/FCIP VE
tunnels
Port mirroring is
supported on the
Brocade FCOE
10-24.
Port mirroring is
supported over
GbE ports/FCIP VE
tunnels
Port mirroring is
supported over
GbE ports/FCIP VE
tunnels
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 41
53-1002751-01
Page 58

3
NOTE
Port mirroring
Maximum mirror connections
Tab le 9 shows the maximum number of mirror connections you can add to a mirror port.
TABLE 9 Maximum number of mirror connections
Model Maximum Number of Mirror Connections
(chassis-wide)
Brocade 300 1
Brocade 5100 3
Brocade 5300 1
Brocade 5410 1
Brocade 5450 1
Brocade 5460 1
Brocade 5470 1
Brocade 5480 1
Brocade 7800 1
Brocade 6505 3
Brocade 6510 3
Brocade 6520 3
Brocade DCX 3
Brocade DCX-4S 3
Brocade 8510-4 3
Brocade 8510-8 3
Brocade Encryption Switch 3
Brocade M5424 1
FC8-16/32 3
FS8-18 3
FX8-24 3
Configuring a port to be a mirror port
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account with admin permissions.
2. Enter the portCfg mirrorport [slot number/]<port number>
--enable command.
The enable command enables the port as a mirror port. The disable command disables the mirror
port configuration.
Adding a port mirror connection
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account with admin permissions.
2. Enter the portMirror
42 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
--add slotnumber/portnumber SourceID DestID command.
53-1002751-01
Page 59

Port mirroring
The configuration database keeps information about the number of port mirror connections
configured on a switch, the number of chunks of port mirroring data that are stored, and the chunk
number. When removing a mirror connection, always use this method to ensure that the data is
cleared. Deleting a connection removes the information from the database.
3
Deleting a port mirror connection
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account with admin permissions.
2. Enter the portMirror
For example, to delete the port mirror connection on mirror port 2, you might type:
switch:admin> portMirror --del 0x011400 0x240400
--del SourceID DestID command.
Displaying port mirror connections
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account with admin permissions.
2. Enter the portMirror
You should see output similar to the following:
switch:admin> portmirror --show
Number of mirror connection(s) configured: 4
Mirror_Port SID DID State
---------------------------------------18 0x070400 0x0718e2 Enabled
18 0x070400 0x0718e3 Enabled
18 0x070400 0x0718ef Enabled
18 0x070400 0x0718e0 Enabled
--show command.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 43
53-1002751-01
Page 60

3
Port mirroring
44 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 61

Chapter
NOTE
Configuration
In this chapter
•Configuration upload and download issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
•Brocade configuration form . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Configuration upload and download issues
It is important to maintain consistent configuration settings on all switches in the same fabric
because inconsistent parameters (such as inconsistent PID formats) can cause fabric
segmentation. As part of standard configuration maintenance procedures, it is recommended that
you back up all important configuration data for every switch on a host computer server for
emergency reference.
For information about AD-enabled switches using Fabric OS v5.2.0 or later, refer to the Fabric OS
Administrator’s Guide.
4
For information about Virtual Fabrics using Fabric OS v6.3.0 or later, refer to the Fabric OS
Administrator’s Guide.
Symptom The configuration upload fails.
Probable cause and recommended action
If the configuration upload fails, It may be because of one or more of the following reasons:
• The FTP or SCP server’s host name is not known to the switch.
Verify with your network administrator that the switch has access to the FTP server.
• The USB path is not correct.
If your platform supports a USB memory device, verify that it is connected and running. Verify
that the path name is correct by using the usbStorage -l command.
Example of usbStorage -l command
switch:admin> usbstorage -l
firmwarekey\ 0B 2007 Aug 15 15:13
support\ 106MB 2007 Aug 24 05:36
support1034\ 105MB 2007 Aug 23 06:11
config\ 0B 2007 Aug 15 15:13
firmware\ 380MB 2007 Aug 15 15:13
FW_v6.0.0\ 380MB 2007 Aug 15 15:13
Available space on usbstorage 74%
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 45
53-1002751-01
Page 62

4
Configuration upload and download issues
• The FTP or SCP server’s IP address cannot be contacted.
Verify that you can connect to the FTP server. Use your local PC to connect to the FTP server or
ping the FTP server.
Example of a successful ping
C:\> ping 192.168.163.50
Pinging 192.168.163.50 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.163.50: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=61
Ping statistics for 192.168.163.50:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0%loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 4ms, Maximum = 5ms, Average = 4ms
If your ping is successful from your computer, but you cannot reach it from inside your data
center, there could be a block on the firewall to not allow FTP connections from inside the data
center. Contact your network administrator to determine if this is the cause and to resolve it by
opening the port up on both inbound and outbound UDP and TCP traffic.
Example of a failed ping
C:\> ping 192.168.163.50
Pinging 192.168.163.50 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 192.168.163.50:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
If your ping has failed then you should verify the following:
- The ports are open on the firewall.
- The FTP server is up and running.
• You do not have configuration upload permission on the switch.
There may be some restrictions if you are using Admin Domains or Role-Based Access Control.
For more information on these types of restrictions, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s
Guide.
• You do not have permission to write to directory on the FTP or SCP server.
Example of a failed login to the FTP server
The output should be similar to the following on an unsuccessful login:
C:\> ftp 192.168.163.50
Connected to 192.168.163.50
220 Welcome to Services FTP service.
User (10.10.252.50:(none)): userFoo
331 Please specify the password.
Password: <hidden>
530 Login incorrect.
Login failed.
If your login to the FTP or SCP server has failed, verify the username and password are correct.
46 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 63

Configuration upload and download issues
NOTE
• On a Virtual Fabrics-enabled switch, you do not have the chassis role permission set on your
user account.
Implement one change at a time, then issue the command again. By implementing one change at a
time, you are able to determine what works and what does not work. Knowing which change
corrected the problems help you to avoid this problem in future endeavors.
Symptom The configuration download fails.
Probable cause and recommended action
If the configuration download fails, It may be because of one or more of the following reasons:
• The FTP or SCP server’s host name is not known to the switch.
Verify with your network administrator that the switch has access to the FTP server.
• The USB path is incorrect.
If your platform supports a USB memory device, verify that it is connected and running. Verify
that the path name is correct. It should be the relative path from
/usb/usbstorage/brocade/configdownload or use absolute path.
Root access is required to see the above path.
4
• The FTP or SCP server’s IP address cannot be contacted.
Verify that you can connect to the FTP server. Use your local PC to connect to the FTP server or
ping the FTP server.
• There was a reason to disable the switch.
Note, however, that you must disable the switch for some configuration downloads. For more
information on how to perform a configuration download without disabling a switch, refer to the
Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
• You do not have permission on the host to perform configuration download.
There may be some restrictions if you are using Admin Domains or Role-Based Access Control.
For more information on these types of restrictions, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s
Guide.
• The configuration file you are trying to download does not exist on the host.
• The configuration file you are trying to download is not a switch configuration file.
• If you selected the (default) FTP protocol, the FTP server is not running on the host.
• The configuration file that you are trying to download uses incorrect syntax.
• The username and password are incorrect.
Symptom The switch reboots during the configuration download.
Probable cause and recommended action
If you are issuing the command with the -vf option, the rebooting is normal. You can continue with
the instructions. Otherwise issue the command again as follows:
1. Enter the configDownload -vf command to download Virtual Fabrics-related data. This causes
both CPs to reboot.
2. Enter the configDownload command, without the -vf operand, to download the regular
configuration data. This step does not cause a reboot.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 47
53-1002751-01
Page 64

4
Symptom Configuration did not seem to change after the configuration download process finished.
Probable cause and recommended action
Verify that the switch was rebooted by checking the system log. If you are doing this on a
enterprise-class platform, verify that both CPs rebooted by checking the system log.
If any error occurs during the download, such as an error about a particular key, it is important to
issue the configDefault command and attempt to repeat the configDownload command.
Brocade configuration form
Gathering additional information
Be sure to capture the output from the commands you are issuing both from the switch and from
your computer when you are analyzing the problem.
Send this and all logs to your switch support provider.
Messages captured in the logs
Configuration download generates both RASLog and Audit log messages resulting from execution
of the configDownload command.
The following messages are written to the logs:
• configDownload completed successfully … (RASLog and Audit log)
• configUpload completed successfully … (RASLog)
• configDownload not permitted … (Audit log)
• configUpload not permitted … (RASLog)
• (Warning) Downloading configuration without disabling the switch was unsuccessful. (Audit
log)
Brocade configuration form
Use this form as a hard copy reference for your configuration information.
In the hardware reference manuals for the Brocade DCX, and DCX-4S modular switches there is a
guide for FC port setting tables. Print out Tab le 10 and use it to record configuration information for
the various blades.
TABLE 10 Brocade configuration and connection
Brocade configuration settings Value
IP address
Gateway address
Chassis configuration option
Management connections
Serial cable tag
Ethernet cable tag
Configuration information
48 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 65

Brocade configuration form
TABLE 10 Brocade configuration and connection (Continued)
Brocade configuration settings Value
Domain ID
Switch name
Ethernet IP address
Ethernet subnet mask
Total number of local devices (nsShow)
Total number of devices in fabric (nsAllShow)
Total number of switches in the fabric (fabricShow)
4
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 49
53-1002751-01
Page 66

4
Brocade configuration form
50 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 67

Chapter
Firmware Download Errors
In this chapter
•Blade troubleshooting tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
•Firmware download issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
•Troubleshooting with the firmwareDownload command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
•USB error handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
•Considerations for downgrading firmware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Blade troubleshooting tips
This chapter refers to the following specific types of blades inserted into either the Brocade DCX,
DCX 8510 family, and DCX-4S enterprise-class platforms:
• FC blades or port blades contain only Fibre Channel ports: Brocade FC8-16/32/48/64.
• AP blades contain extra processors and some have specialized ports: Brocade FCOE10-24 and
FX8-24.
• CP blades have a control processor (CP) used to control the entire switch; they can be inserted
only into slots 6 and 7 on the Brocade DCX and DCX 8510-8, and slots 4 and 5 on the Brocade
DCX-4S and 8510-4.
• CR8 and CR4S-8 core blades provide ICL functionality between two Brocade DCX Backbones.
CR8 blades can be inserted only into slots 5 and 8 on the Brocade DCX. CR4S-8 blades can be
inserted only into slots 3 and 6 on the Brocade DCX-4S.
• CR16-8 and CR16-4 core blades provide ICL functionality between two Brocade DCX 8510
Backbones. CR16-8 blades can be inserted only into slots 5 and 8 on the Brocade DCX
8510-8. CR16-4 blades can be inserted only into slots 3 and 6 on the Brocade DCX 8510-4.
5
Typically, issues detected during firmware download to AP blades do not require recovery actions
on your part.
If you experience frequent failovers between CPs that have different versions of firmware, then you
may notice multiple blade firmware downloads and a longer startup time.
Symptom Relocation of internal image times out on CR8 core blade.
Probable cause and recommended action
This can be caused by issues in the co-CPU. If this happens, the firmware download process
synchronizes the partitions in the main-CPU and co-CPU by starting a firmware commit operation.
Wait at least 15 minutes for the commit operation to complete, issue the firmwareShow command
to verify the partitions are synchronized, and reissue the firmwareDownload command. If the
problem persists, you must contact the switch service provider.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 51
53-1002751-01
Page 68

5
CAUTION
Symptom The blade is faulty (issue slotShow to confirm).
Probable cause and recommended action
If the port or application blade is faulty, enter the slotPowerOff and slotPowerOn commands for the
port or application blade. If the port or application blade still appears to be faulty, remove it and
re-insert it into the chassis.
Symptom The AP blade is stuck in the “LOADING” state (issue slotShow to confirm).
Probable cause and recommended action
If the blade remains in the loading state for a significant period of time, the firmware download
times out. Remove the blade and re-insert it. When it boots up, autoleveling is triggered and the
firmware download is attempted again.
Firmware download issues
Firmware download issues
After you start the firmware download process, do not enter any disruptive commands (such as
reboot) that interrupts the process. The entire firmware download and commit process takes
approximately 17 minutes.
If there is a problem, wait for the time-out (30 minutes for network problems) before issuing the
firmwareDownload command again. Disrupting the process can render the switch inoperable and
require you to seek help from your switch service provider.
Do not disconnect the switch from power during the process because the switch could become
inoperable when rebooted.
The following symptoms describe common firmware download issues and their recommended
actions.
Symptom Firmware download times out.
Probable cause and recommended action
This can be caused by an excessively slow network. If it takes more than 30 minutes to download
firmware on a switch, or on each CP in a director, the firmware download process times out. If a
timeout occurs on a switch, the firmware download process synchronizes the two partitions on the
switch by starting a firmware commit operation. If a timeout occurs in a director, the firmware
download process synchronizes the firmware on the two partitions on the CP blades by starting a
firmware commit operation on each CP.
Wait at least 15 minutes for the commit operation to complete then use the firmwareShow
command to verify the partitions are synchronized. In some older versions of firmware, the
firmware commit operation may not be started automatically on the switch (or on the standby CP in
director). In this case, you can enter the firmwareCommit command manually on the switch (or on
the standby CP in director) to synchronize the partitions. After the firmware commit operation
completes, reissue the firmwareDownload command to upgrade the system.
52 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 69

Firmware download issues
Symptom Cannot upgrade directly to v6.3.0.
Probable cause and recommended action
If the switch is running Fabric OS v6.1.0 or earlier, you are not allowed to upgrade directly to v6.3.0
because of the “one-version” rule. Upgrade your switch to Fabric OS version v6.2.0 before
upgrading to v6.3.0. The “one-version” rule also applies to downgrading.
Symptom Server is inaccessible or firmware path is invalid.
Probable cause and recommended action
• The FTP or SCP server’s host name is not known to the switch.
Verify with your network administrator that the switch has access to the FTP server.
Verify the path to the FTP or SCP server is accessible from the switch. For more information on
checking your FTP or SCP server, see Chapter 4, “Configuration”.
• The USB path is not correct.
If your platform supports a USB memory device, verify that it is connected and running. Verify
that the path name is correct by using the usbStorage -l command.
Example of usbStorage -l command
switch:admin> usbstorage -l
firmwarekey\ 0B 2010 Mar 15 15:13
support\ 106MB 2007 Mar 24 05:36
support1034\ 105MB 2010 Mar 23 06:11
config\ 0B 2010 Mar 15 15:13
firmware\ 380MB 2010 Mar 15 15:13
FW_v7.0.0\ 380MB 2010 Mar 15 15:13
Available space on usbstorage 74%
5
Example of error message
switch:admin> firmwaredownload
Server Name or IP Address: 192.168.168.115
User Name: userFoo
File Name: /users/home/userFoo/firmware/v7.1.0
Network Protocol(1-auto-select, 2-FTP, 3-SCP) [1]: 2
Password: <hidden>
Server IP: 192.168.168.115, Protocol IPv4
Checking system settings for firmwaredownload...
Firmware access timeout.
The server is inaccessible or firmware path is invalid. Please make sure the
server name or IP address, the user/password and the firmware path are valid.
Symptom Cannot download the requested firmware.
Probable cause and recommended action
The firmware you are trying to download on the switch is incompatible. Check the firmware version
against the switch type. If the firmware is incompatible, retrieve the correct firmware version and
try again.
Example of error message
SW3900:admin> firmwaredownload
Server Name or IP Address: 192.168.126.115
User Name: userFoo
File Name: /users/home/userFoo/firmware/v7.1.0
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 53
53-1002751-01
Page 70

5
ATTENTION
Troubleshooting with the firmwareDownload command
Network Protocol(1-auto-select, 2-FTP, 3-SCP) [1]: 2
Password: <hidden>
Server IP: 192.168.168.115, Protocol IPv4
Checking system settings for firmwaredownload...
Cannot download the requested firmware because the firmware doesn't support this
platform. Please enter another firmware path.
Symptom Cannot download on a switch with Interop mode turned on.
Probable cause and recommended action
On single CP, Interop fabric does not support Coordinated HotCode Load.
Perform a firmwareDownload -o command. The operand bypasses the checking of Coordinated
HotCode Load (HCL). On single CP systems in interop fabrics, the HCL protocol is used to ensure
data traffic is not disrupted during firmware upgrades. This option allows a firmware download to
continue even if HCL is not supported in the fabric or the protocol fails. Using this option may cause
traffic disruption for some switches in the fabric.
Symptom You receive a “firmwaredownload is already in progress” message.
Probable cause and recommended action
The firmware download process has already been started and it is in progress. Wait till it
completes. You can use the firmwareDownloadStatus and firmwareShow commands to monitor its
progress. If the problem persists, contact your switch support provider.
Example of a firmwaredownload already in progress
switch:admin> firmwaredownload
Server Name or IP Address: 192.168.168.115
User Name: userFoo
File Name: /users/home/userFoo/firmware/v7.1.0
Network Protocol(1-auto-select, 2-FTP, 3-SCP) [1]: 2
Password: <hidden>
Server IP: 192.168.168.115, Protocol IPv4
Checking system settings for firmwaredownload...
Sanity check failed because firmwaredownload is already in progress.
Troubleshooting with the firmwareDownload command
A network diagnostic script and preinstallation check is a part of the firmwareDownload procedure.
The script and preinstallation check performs troubleshooting and automatically checks for any
blocking conditions. If the firmware download fails, refer to the Fabric OS Message Reference for
details about error messages. Also see, “Considerations for downgrading firmware” on page 56.
Do not run mixed firmware versions on CPs.
If a firmware download fails in a director, the firmwareDownload command synchronizes the
firmware on the two partitions of each CP by starting a firmware commit operation. Wait at least 15
minutes for this commit operation to complete before attempting another firmware download.
54 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 71

USB error handling
NOTE
If the firmware download fails in a director or enterprise-class platform, the CPs may end up with
different versions of firmware and are unable to achieve HA synchronization. In such cases, issue
the firmwareDownload -s command on the standby CP; the single mode (-s) option allows you to
upgrade the firmware on the standby CP to match the firmware version running on the active CP.
Then reissue the firmwareDownload command to download the desired firmware version to both
CPs. For example, if CP0 is running v7.0.0 on the primary and secondary partitions, and CP1 is
running v7.1.0 on the primary and secondary partitions, then synchronize them by issuing the
firmwareDownload command.
Some of the messages include error codes (as shown in the following example). These error codes
are for internal use only and you can disregard them.
Port configuration with EX ports enabled along with trunking for port(s) 63, use
the portCfgEXPort, portCfgVEXPort, and portCfgTrunkPort commands to remedy this.
Verify blade is ENABLED. (error 3)
5
Gathering additional information
You should follow these best practices for firmware download before you start the procedure:
• Keep all session logs.
• Enter the supportSave or the supportShow command before and after entering the
firmwareDownload command.
• If a problem persists, package together all of the information (the Telnet session logs and serial
console logs, output from the supportSave command) for your switch support provider. Make
sure you identify what information was gathered before and after issuing the
firmwareDownload command.
USB error handling
Tab le 11 outlines how the USB device handles errors under specific scenarios and details what
actions you should take after the error occurs.
TABLE 11 USB error handling
Scenario under which download fails Error handling Action
An access error occurs during
firmwaredownload because the
removal of the USB device, or USB
device hardware failure, etc.
USB device is not enabled. Firmwaredownload fails with an
Firmwaredownload times out
and commit is started to repair
the partitions of the CPUs that
are affected. See previous table
for details.
error message
None.
Enable the USB device using the
usbStorage -e command and retry
firmwaredownload.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 55
53-1002751-01
Page 72
5
NOTE
Considerations for downgrading firmware
Considerations for downgrading firmware
The pre-installation check of the firmwareDownload command detects all of the blocking
conditions that can prevent a successful downgrade, and warns you about all these conditions. The
error messages displayed by the firmwareDownload command states the blocking conditions and
the corresponding commands to correct them. You must address all of these blocking conditions
before proceeding. Refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide for more information regarding
individual features and commands.
To avoid failure of a firmware downgrade, verify the firmware you are downgrading to supports all
the blades in the chassis, and that the switch, blades, or chassis supports all the features you are
currently using. If not, you must disable or remove those features that are not supported.
Preinstallation messages
The system messages in this section are displayed if an exception is encountered during firmware
download. The following examples show feature-related messages that you may see if you were
upgrading from v7.0.0 to v7.1.0:
The system messages in this section are for illustration purposes only. They do not represent the
entire range of possible error messages appropriate to a wide variety of installation scenarios.
Cannot upgrade directly to 7.1. Please upgrade to 6.4 first and then upgrade
to 7.1.
Upgrade to 7.1 is not allowed because FC Fastwrite is not supported on this
version. Please use "fastwritecfg" to deconfigure FC Fastwrite for all slots
and try again.
Upgrade to 7.1 is not allowed due to the presence of ioddelay configuration.
Please reset the feature with "ioddelayreset" before upgrading to v7.1.
Upgrade to 7.1 is not allowed since base switch has R_RDY enabled ports.
Please disable the R_RDY enabled ports in base switch using portcfgislmode
command.
Firmware upgrade to Fabric OS 7.1.0 or higher is not allowed when there are
more than 4 chassis connected through Inter-Chassis Links (ICLs) and the
Enterprise ICL (EICL) license is not installed in the system. Note that even
with an EICL license installed, only 9 chassis are allowed to connect through
ICLs. You can either install an EICL license, or you must disable the
additional ICL links before performing a firmware upgrade.
This example shows hardware-related messages for a downgrade:
ecp:admin> firmwaredownload
Type of Firmware (FOS, SAS, or any application) [FOS]:
Server Name or IP Address: 10.1.2.3
User Name: userfoo
File Name: /home/userfoo/v6.3.0
Network Protocol (1-auto-select, 2-FTP, 3-SCP) [1]:
Password: <hidden>
Checking System Settings...
Version compatibility check passed.
56 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 73

Considerations for downgrading firmware
Checking version compatibility...
Version compatibility check passed..
The following items must be addressed before downloading the specified
firmware:
FC8-32E and FC8-48E are not supported by the targeted firmware. Please use
slotshow to determine which of these are installed and remove them before
continuing.
5
The messages in this section are displayed if an exception case is encountered during firmware
downgrade. The following example shows feature-related messages that you may see if you were
downgrading from v7.1.0 to v6.4.x:
Downgrade is not allowed because one or more ports name length is greater than
32 bytes. Please use "portname" CLI to check and fix the port name/length
before downgrading.
Downgrade is not allowed because Device Based Routing is configured. Please
use "aptpolicy" to change the routing policy.
Downgrade is not allowed because Location ID is configured. Please use
"configure" command to clear Location ID.
Downgrade is not allowed because the existing zone configuration is more than
1MB. To downgrade to lower firmware version modify the existing zone
configuration to 1MB or lesser.
Downgrade is not allowed because switch is in AG mode and D-Ports are
configured.Please use "switchshow" to view the D-port list and use
"portcfgdport --disable <port_no>" to disable it before downgrading.
Downgrade is not allowed because one or more ports have credit recovery
enabled. Please use "portcfgcreditrecovery --disable" command to disabled
credit recovery.
Auto CSCTL feature is enabled. If you are downgrading the firmware, please
disable the auto csctl mode using "configurechassis" command and following
that either perform powercycle on each non-CP blades or reboot the system
before performing firmwaredownload.
Downgrade is not allowed because one or more ports have FEC enabled. Please
use "portcfgfec --disable" command to disabled FEC.
The messages in this section are displayed if an exception case is encountered during firmware
downgrade. The following example shows feature-related messages that you may see if you were
downgrading from v7.1.0 to v7.0.x:
Downgrade to selected version is not allowed because few ports are configured
with Longdistance -buffers option. Please remove the configuration using
"portcfglongdistance L0" CLI or change the configuration with -distance
option.
Downgrade is not allowed because Location ID is configured. Please use
"configure" command to clear Location ID.
Downgrade is not allowed because switch is in AG mode and D-Ports are
configured. Please use "switchshow" to view the D-port list and use
"portcfgdport --disable <port_no>" to disable it before downgrading.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 57
53-1002751-01
Page 74

5
ATTENTION
Considerations for downgrading firmware
Downgrade is not allowed because R-RDY flow control ports are configured as
D-Ports. Please use "portdporttest --show all" to view the port list and
"portcfgdport --disable" to disable before downgrading.
Downgrade is not allowed because D-Port is configured with DWDM mode. Please
use "portcfgshow" to view the port list and "portcfgdport --enable" to reset
DWDM mode before downgrading.
Downgrade is not allowed because ICL ports are configured as D-Ports. Please
use "switchshow" to view the D-port list and use "portcfgdport --disable
<port_no>" to disable it before downgrading.
Downgrade is not allowed because one or more ports have credit recovery
enabled. Please use "portcfgcreditrecovery --disable" command to disabled
credit recovery.
Downgrade is not allowed because one or more ports have FEC enabled.Please use
"portcfgfec --disable" command to disabled FEC.
Blade types
Where blades are incompatible with a firmware download, they must be removed or powered off
before a firmware download begins, as noted in the following message.
Message The FC10-6 (type 39) blade is not supported by the target firmware. Please use slotshow to find out
which slot it is in and remove it first.
Probable cause and recommended action
The firmware download operation was attempting to upgrade a system to Fabric OS v7.1.0 with one
or more of the Brocade FC10-6 blades (blade ID 39) in the system. The Brocade FC10-6 blades are
not supported on firmware v7.1.0, so the firmware download operation failed.
Use the slotShow command to display which slots the Brocade FC10-6 blades occupy. Physically
remove the blades from the chassis, or use the micro-switch to turn the blade off. Retry the
firmware download operation.
Firmware versions
The system messages in this section refer to differences between the current firmware and the
firmware you are applying to the switch.
Brocade does not support upgrades from more than one previous release. For example, upgrading
from Fabric OS v7.0.0 to v7.1.0 is supported, but upgrading from Fabric OS v6.3.0 or a previous
release directly to v7.1.0 is not. In other words, upgrading a switch from Fabric OS v6.3.0 to v7.1.0
is a two-step process: first upgrade to v6.4.0, and then upgrade to v7.1.0. If you are running a
pre-Fabric OS v6.2.0 version, first you must upgrade to v6.2.0, then to v6.3.0, then to v6.4.0, and
finally to v7.1.0.
58 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 75

Considerations for downgrading firmware
Message Cannot upgrade directly to v6.3.0. Upgrade your switch to v6.2.0 first before upgrading to the
requested version.
Probable cause and recommended action
If the switch is running v6.1.0 or earlier, you are not allowed to upgrade directly to v6.3.0 because
of the “two-version” rule.
Upgrade your switch to Fabric OS version v6.2.0 before upgrading to v6.3.0
Message Non-disruptive firmwaredownload is not supported when downgrading to 6.1. Please use
firmwaredownload -s to download the 6.1 firmware.
Probable cause and recommended action
If the switch is running v6.2.0, you are not allowed to downgrade directly to v6.1.x without causing
disruption to your fabric.
Downgrade using the firmwareDownload -s command. For more information on using this
command, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
Message Firmwaredownload of blade application firmware failed. Reissue firmwareDownload to recover.
Probable cause and recommended action
5
The firmware download operation was attempting to upgrade the SAS image while the blade was
operational.
Retry the firmwareDownload command again.
Platform
This system message pertains to switch features or fabric-wide settings that must be removed or
disabled before downgrading the firmware.
Message Downgrade is not allowed because VF is enabled. Please run "lscfg - -config" and "lscfg - -delete"
commands to remove the non-default LS first, then run "fosconfig - -disable vf" to disable VF before
proceeding.
Probable cause and recommended action
You cannot downgrade because Virtual Fabrics are enabled. Delete the logical switches, delete the
base switch, and disable Virtual Fabrics prior to downgrading the firmware.
Routing
This system message refers to any route settings that must be changed prior to downgrading the
switch’s firmware.
Message Downgrade is not allowed because IOD Delay value is configured for one or more domains. Please
use "ioddelayshow and ioddelayreset" to disable them before downgrading.
Probable cause and recommended action
If the switch is running v6.2.0 or later, and IOD Delay value is configured for one or more domains,
you cannot downgrade the switch to v6.1.0 or earlier.
Use the iodDelayReset command to reset the IOD delay to its default value.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 59
53-1002751-01
Page 76

5
Considerations for downgrading firmware
60 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 77

Chapter
Security
In this chapter
Passwords
The following section describes various ways to recover forgotten passwords.
Symptom User forgot password.
Probable cause and recommended action
6
•Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
•Device authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
•Protocol and certificate management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
•SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
•FIPS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
If you know the root password, you can use this procedure to recover the password for the default
accounts of user, admin, and factory. If you do not know the root password, you must contact your
service support provider to recover admin passwords.
Recovering passwords
1. Open a CLI connection (serial or Telnet) to the switch.
2. Log in as root.
3. Enter the command for the type of password that was lost:
passwd user
passwd admin
passwd factory
4. Enter the requested information at the prompts.
Symptom Unable to log in as root password.
Probable cause and recommended action
To recover your root password, contact your switch service provider.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 61
53-1002751-01
Page 78

6
Symptom Unable to log into the boot PROM.
Probable cause and recommended action
To recover a lost boot PROM password, contact your switch service provider. You must have
previously set a recovery string to recover the boot PROM password.
This does not work on lost or forgotten passwords in the account database.
Password recovery options
Tab le 12 describes the options available when one or more types of passwords are lost.
TABLE 12 Password recovery options
Topic Solution
Device authentication
If all the passwords are forgotten, what is the
password recovery mechanism? Are these
procedures non-disruptive recovery procedures?
If a user has only the root password, what is the
password recovery mechanism?
How to recover boot PROM password? Contact your switch service provider and provide the
How do I recover a user, admin, or factory password? Refer to “Passwords” on page 61 for more information on
Symptom User is unable to modify switch settings.
Probable cause and recommended action
The most common error when managing user accounts is not setting up the default Admin Domain
and access control list or role-based access control (RBAC).
Errors such as a user not being able to run a command or modify switch settings are usually related
to what role the user has been assigned.
Device authentication
Contact your switch service provider. A non-disruptive
procedure is available.
Use passwd command to set other passwords.
Use passwdDefault command to set all passwords to
default.
recovery string.
recovering these passwords.
Symptom Switch is unable to authenticate device.
Probable cause and recommended action
When the device authentication policy is set to ON, the switch expects a FLOGI with the FC-SP bit
set. If this bit is not set, the switch rejects the FLOGI with reason LS_LOGICAL_ERROR (0x03), in the
switch log with the explanation of “Authentication Required”(0x48), and disables the port. Set the
device authentication policy mode on the switch to ON.
62 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 79

Protocol and certificate management
Symptom Switch is unable to form an F_Port.
Probable cause and recommended action
Regardless of the device authentication policy mode on the switch, the F_Port is disabled if the
DH-CHAP protocol fails to authenticate. If the HBA sets the FC-SP bit during FLOGI and the switch
sends a FLOGI accept with FC-SP bit set, then the switch expects the HBA to start the
AUTH_NEGOTIATE. From this point on until the AUTH_NEGOTIATE is completed, all ELS and CT
frames, except the AUTH_NEGOTIATE ELS frame, are blocked by the switch. During this time, the
Fibre Channel driver rejects all other ELS frames. The F_Port does not form until the
AUTH_NEGOTIATE is completed. It is the HBA's responsibility to send an Authentication Negotiation
ELS frame after receiving the FLOGI accept frame with the FC-SP bit set.
Protocol and certificate management
This section provides information and procedures for troubleshooting standard Fabric OS security
features such as protocol and certificate management.
Symptom Troubleshooting certificates
Probable cause and recommended action
6
If you receive messages in the browser or in a pop-up window when logging in to the target switch
using HTTPS, refer to Table 13 for recommended actions you can take to correct the problem.
TABLE 13 SSL messages and actions
Message Action
The page cannot be displayed The SSL certificate is not installed correctly or HTTPS is not
enabled correctly. Make sure that the certificate has not expired,
that HTTPS is enabled, and that certificate file names are
configured correctly.
The security certificate was issued by a
company you have not chosen to trust.
The security certificate has expired or is not yet
valid
The name on the security certificate is invalid
or does not match the name of the site file
This page contains both secure and nonsecure
items. Do you want to display the nonsecure
items?
The certificate is not installed in the browser. Install it as
described in the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
Either the certificate file is corrupted or it needs to be updated.
Click View Certificate to verify the certificate content. If it is
corrupted or out of date, obtain and install a new certificate.
The certificate is not installed correctly in the Java Plug-in. Install
it as described in the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
Click No in this pop-up window. The session opens with a closed
lock icon on the lower-right corner of the browser, indicating an
encrypted connection.
Gathering additional information
For security-related issues, use the following guidelines to gather additional data for your switch
support provider.
• Perform a supportSave -n command.
• If not sure about the problem area, collect a supportSave -n from all switches in the fabric.
• If you think it may be related to E_Port authentication then collect a supportSave -n from both
switches of the affected E_Port.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 63
53-1002751-01
Page 80

6
SNMP
Symptom SNMP management station server is unable to receive traps from fabric.
SNMP
• If you think this is a policy-related issue, FCS switch or other security server-related issue then
use supportSave -n to collect data from the Primary FCS switch and all affected switches.
• If login-related, then also include the following information:
- Does login problem appear on a Serial, CP IP, or Switch IP address connection?
- Is it CP0 or CP1?
- Is the CP in active or standby?
- Is it the first time login after firmwareDownload and reboot?
This section describes symptoms with associated causes and recommended actions for
SNMP-related issues.
Probable cause and recommended action
There are several causes related to this generic issue. You must verify the following:
FIPS
• There are no port filters in the firewalls between the fabric and the SNMP management station.
• If your SNMP management station is a dual-homed server, check that the routing tables are
set up correctly for your network.
If you continue to have problems, collect the data in the next section and contact your switch
support provider.
Gathering additional information
In addition to supportSave, gather the MIB browser snapshot with the problem (like Adventnet
screen snapshot) for an MIB variable.
This section describes symptoms with associated causes and recommended actions for problems
related to FIPS.
Symptom When FIPS is turned on, the switch constantly reboots.
Probable cause and recommended action
When FIPS is turned on the switch runs conditional tests each time it is rebooted. These tests run
random number generators and are executed to verify the randomness of the random number
generator. The conditional tests are executed each time prior to using the random number provided
by the random number generator.
The results of all self-tests, for both power-up and conditional, are recorded in the system log or are
output to the local console. This includes logging both passing and failing results. If the tests fail on
your switch it constantly reboots. Because boot PROM access is disabled you are not able to exit
out of the reboot. You must send the switch back to your switch service provider for repair.
64 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 81

Chapter
Virtual Fabrics
In this chapter
•General Virtual Fabrics troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
•Fabric identification issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
•Logical Fabric issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
•Base switch issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
•Logical switch issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
•Switch configuration blade compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
•Gathering additional information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
General Virtual Fabrics troubleshooting
All of the following constraints apply when the Virtual Fabrics feature is enabled:
7
• The base fabric works only in Brocade native mode, not in an interoperable mode.
• The base switch does not have any devices. The base fabric can have devices in remote Layer
2 switches; traffic between those devices is supported.
• A non-base switch in a Virtual Fabric-capable chassis must not be part of a fabric that serves
as a base fabric for some other logical fabric traffic. Although software does not detect or
prevent users from deploying such a configuration, such a configuration is not supported.
• ICL ports can only be in the base or default switch. If XISL is turned off, you can connect ICLs to
other logical switches.
• A default switch can be configured as a base switch in the Brocade 5100 and 5300 switches,
but not in a Brocade DCX or DCX-4S. Fabric IDs of default switches cannot be manually
changed.
• The default switch is able to participate in a logical fabric using extended ISLs (XISLs). In the
Brocade DCX and DCX-4S, the default switch does not participate in a logical fabric and is a
purely Layer 2 logical switch.
• EX_ and VEX_Ports are supported in the base switch. EX_Ports cannot be part of any other
switch other than the base switch.
• EX_ and VEX_Ports cannot connect to a fabric that has a logical switch with the Allow XISL use
mode on. The port is disabled with the reason
• Fabric OS v6.2.0 and later support external device sharing only through EX_Ports. Internal
device sharing (sharing a device in a logical fabric with other fabrics, without having an
EX_Port) is not supported.
• A logical fabric cannot have EX_Ports using extended ISLs and cannot serve as a backbone to
any EX_Port traffic. Similarly, the default switch cannot be part of a fabric that serves as a
backbone to any EX_Port traffic.
Conflict: XISL capability domain.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 65
53-1002751-01
Page 82

7
NOTE
Fabric identification issues
• VE_Ports cannot exist in a logical switch that has XISL use turned on. Although VE_Ports are
allowed in a base switch, Fabric OS v6.2.0 and later do not support the use of VE_Ports to
carry traffic for logical fabrics using XISLs. They can be used to carry FCR traffic through
EX_Ports and VEX_Ports. You should make sure your configuration does not result in the use of
VE_Ports in a base switch for logical fabric traffic.
• Admin Domains are mutually exclusive with Virtual Fabrics. When Virtual Fabrics is enabled, all
access control is based on the Virtual Fabric context.
• Traffic Isolation zones with no-failover option are not supported in logical fabrics. TI zones
defined in the base fabric for logical fabric traffic must allow failover.
A new option “Disable FID check” has been added to configure fabric parameter options. This can
be used to disable FID check for FICON logical switches.
Fabric identification issues
Symptom E_Ports directly connecting two logical switches do not form, or are disabled.
Probable cause and recommended action
The FIDs on each of the logical switches must be the same.
Use the lsCfg
--change FID -newfid FID command to change the FID.
Symptom Invalid FID.
Probable cause and recommended action
FIDs for switches may be from 1 through 128 as long as they are not already in use, except for
EX_Ports, which are only assigned FIDs from 1 through 127.
Use the lsCfg
Symptom The FID is currently in use.
Probable cause and recommended action
You may not create two (2) or more logical switches with the same FID.
Use the lsCfg
Logical Fabric issues
Symptom Logical port <port_number> disabled.
Probable cause and recommended action
--show command to view the current FIDs on the chassis and then the lsCfg
--show command to verify whether the FID is in use. If it is, use another FID.
--show and fcrFabricShow commands to view FIDs in use.
This message indicates an LISL was disabled because of some protocol conflict or security or policy
violation. This can result in possible traffic issues. You should resolve the cause of the conflict and
reenable the LISL by using the lfCfg
66 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
--lislenable command.
53-1002751-01
Page 83

Symptom The switch with domain <domain> with firmware version <fw version> has joined the FID <fid>
fabric and may not be compatible with XISL use.
Probable cause and recommended action
This message indicates the specified switch in the logical fabric that is using XISLs is running an
incompatible firmware version and must be upgraded to Fabric OS v6.2.0 or later.
Base switch issues
All logical switches in a fabric should have the same base switch attribute. If a base switch is
connected to a non-base switch, then you must take the appropriate action to resolve the conflict.
Symptom EX_Port is disabled with reason “Export in non base switch”.
Probable cause and recommended action
An EX_Port has to be in the base switch.
Base switch issues
7
Use the lsCfg
FID -slot [slot | slot_range] -port [ port | port_range] [-force] command and move the port to the
base switch. If the port is not intended to be used as an EX_Port, use the portCfgDefault command
to reset the port to its default configuration.
Symptom An EX_ or VEX_Port is disabled with reason Conflict: XISL capability domain.
Probable cause and recommended action
Use the configure command to set the value on the Allow XISL use to OFF on all logical switches of
the connecting edge fabric.
Symptom E_Ports connecting two logical switches are disabled.
Probable cause and recommended action
If a base switch is directly connected to a non-base switch, all E_Ports to that logical switch are
disabled.
Symptom Fabric ID and base switch are conflicted.
Probable cause and recommended action
If there is a Fabric ID conflict and a base switch conflict that exists between two switches, the
Fabric ID conflict is detected first.
Use the lsCfg
--create FID -b base command to create a base switch. Then use the lsCfg --config
--change FID -newfid FID command to change the FID.
Symptom A base switch already exists on this system.
Probable cause and recommended action
Only one base switch is allowed on a platform. Use the lsCfg
--create FID -b base command to remove the current base switch, and then create a new one.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 67
53-1002751-01
--delete FID command, then the lsCfg
Page 84

7
CAUTION
Logical switch issues
When a logical switch is created, all configuration for the logical switch is set to factory defaults.
When a logical switch is deleted, all configuration for the logical switch is deleted permanently
and is not recoverable.
Symptom The indicated slot is empty.
Probable cause and recommended action
You used the lsCfg command and an empty slot was specified.
Reissue the command with the appropriate slot number.
Symptom Validation of switch configuration changes is not supported on this platform.
Probable cause and recommended action
This platform is unknown to the logical switch subsystem.
Logical switch issues
Symptom Given slot number is not valid on this platform.
Probable cause and recommended action
You are specifying a slot number that is not valid on the platform, for example, slot 0 on a Brocade
DCX or slot 12 on a Brocade DCX-4S.
Symptom Slot must be enabled to configure ports.
Probable cause and recommended action
You may only attempt to configure ports on enabled blades (blades may be faulted).
Symptom Unable to determine slot type.
Probable cause and recommended action
The slot type is not known to the logical switch. Verify the slot and try again.
Symptom There are no ports on this slot.
Probable cause and recommended action
There are no configurable ports on the slot indicated by the lsCfg command. Verify the ports and try
again.
Symptom Unable to remove ports from their current switch.
Probable cause and recommended action
When moving ports to a switch, you must first remove them from the switch in which they reside.
This error message is displayed if this step fails.
68 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 85

Switch configuration blade compatibility
Symptom A non-GE blade is within the slot range.
Probable cause and recommended action
You are attempting to configure a GE port on a slot that does not contain GE ports.
Symptom A port or ports is already in the current switch.
Probable cause and recommended action
You may not move a port to the same switch.
Symptom The maximum number of switches for this platform has been reached.
Probable cause and recommended action
Each platform that supports Virtual Fabrics has a maximum number of logical switches that may be
supported. The platform has reached this limit.
Symptom Unable to create the switch.
Probable cause and recommended action
There was an error while creating the switch.
7
Symptom A port or ports cannot be moved to the requested switch because it would exceed the 256 area
limit for this switch.
Probable cause and recommended action
The area limit would be exceeded if the lsCfg command were allowed.
Symptom A port or ports cannot be moved to the requested switch because it may only exist in a base or
default switch.
Probable cause and recommended action
You are attempting to move ports on a core blade into a nondefault or non-base switch.
Switch configuration blade compatibility
Symptom A slot in the chassis displays a FAULTY(91) in the output of the slotShow command.
Probable cause and recommended action
When an enterprise-class platform is coming up or when a blade is inserted, the switch
configuration is checked based on the blade type. If the configuration does not match with the
blade type, the blade is faulted. This is displayed as FAULTY(91) in the output of the slotShow
command.
Use the lsCfg –restore_slot_to_default command to correct the problem. Once the configuration
discrepancy has been fixed, you may use slotPowerOff followed by slotPowerOn to recover.
>lscfg –restore_slot_to_default 1
>slotpoweroff 1
>slotpoweron 1
Slot Blade Type ID Model Name Status
------------------------------------------------- 1 SW BLADE 77 FC8-64 ENABLED
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 69
53-1002751-01
Page 86

7
2 SW BLADE 97 FC16-32 ENABLED
3 SW BLADE 96 FC16-48 ENABLED
4 SW BLADE 96 FC16-48 ENABLED
5 CORE BLADE 98 CR16-8 ENABLED
6 CP BLADE 50 CP8 ENABLED
7 CP BLADE 50 CP8 ENABLED
8 CORE BLADE 98 CR16-8 ENABLED
9 SW BLADE 55 FC8-32 ENABLED
10 SW BLADE 96 FC16-48 ENABLED
11 AP BLADE 75 FX8-24 ENABLED
12 SW BLADE 97 FC16-32 ENABLED
Gathering additional information
Gathering additional information
For Virtual Fabrics-related issues, use the following guidelines to gather additional data for your
switch support provider:
• Perform the supportSave command.
• If not sure about the problem area, perform the supportSave command on all chassis and
logical switches in the fabric.
• If you think it may be related to E_Port authentication, then perform the supportSave -n
command on both switches or logical switches of the affected E_Port.
70 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 87

Chapter
ISL Trunking
In this chapter
Link issues
This section describes trunking link issues that can come up and recommended actions to take to
correct the problems.
Symptom A link that is part of an ISL trunk failed.
Probable cause and recommended action
Use the trunkDebug port1 port2 command to troubleshoot the problem, as shown in the following
procedure.
8
•Link issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
•Buffer credit issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Enter the trunkDebug port1 port2 command:
where:
port1 Specify the area number or index of port 1. Use the switchShow command to
view the area or index numbers for a port. This operand is required.
port2 Specify the area number or index of port 2. Use the switchShow command to
view the area or index numbers for a port. This operand is required.
Example of an unformed E_Port
This example shows that port 3 is not configured as an E_Port:
ecp:admin> trunkdebug 126, 127
port 126 is not E/EX port
port 127 is not E/EX port
Example of a formed E_Port
ecp:admin> trunkdebug 100, 101
port 100 and 101 connect to the switch 10:00:00:05:1e:34:02:45
The trunkDebug command displays the possible reason that two ports cannot be trunked. Possible
reasons are:
• The switch does not support trunking.
• A trunking license is required.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 71
53-1002751-01
Page 88

8
Buffer credit issues
• Trunking is not supported in switch interoperability mode.
• Port trunking is disabled.
• The port is not an E_Port.
• The port is not 2 Gbps, 4 Gbps, or 8 Gbps.
• The port connects to a switch other than the one you want it to.
To correct this issue, connect additional ISLs to the switch with which you want to
communicate.
• The ports are not the same speed or they are not set to an invalid speed.
Manually set port speeds to a speed supported on both sides of the trunk.
• The ports are not set to the same long distance mode.
Set the long distance mode to the same setting on all ports on both sides of the trunk.
• Local or remote ports are not in the same port group.
Move all ISLs to the same port group. The port groups begin at port 0 and are in groups of 4 or
8, depending on the switch model. Until this is done, the ISLs do not trunk.
• The difference in the cable length among trunked links is greater than the allowed difference.
Buffer credit issues
This section describes a trunk going online and offline or hosts not being able to talk to a storage
device.
Symptom Trunk goes offline and online (bounces).
Probable cause and recommended action
A port disabled at one end because of buffer underallocation causes all the disabled ports at the
other end to become enabled. Some of these enabled ports become disabled because of a lack of
buffers, which in turn triggers ports to be enabled once again at the other end.
While the system is stabilizing the buffer allocation, it warns that ports are disabled because of a
lack of buffers, but it does not send a message to the console when buffers are enabled. The
system requires a few passes to stabilize the buffer allocation. Ultimately, the number of ports for
which buffers are available come up and stabilize. You should wait for stabilization, and then
proceed with correcting the buffer allocation situation.
Getting out of buffer-limited mode
Occurs on LD_Ports.
1. Change the LD port speed to a lower speed (of non-buffer limited ports).
2. Change the LD port’s estimated distance to a shorter distance (of non-buffer limited ports).
3. Change LD back to L0 (of non-buffer limited ports).
4. If you are in buffer-limited mode on the LD port, then increase the estimated distance.
5. Enable any of these changes on the buffer-limited port or switch by issuing the commands
portDisable and portEnable.
72 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 89

Chapter
Zoning
In this chapter
•Overview of corrective action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
•Segmented fabrics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
•Zone conflicts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
•Gathering additional information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Overview of corrective action
The following overview provides a basic starting point for you to troubleshoot your zoning problem.
1. Verify that you have a zone problem.
2. Determine the nature of the zone conflict.
3. Take the appropriate steps to correct zone conflict.
9
To correct a merge conflict without disrupting the fabric, first verify that it was a fabric merge
problem, then edit zone configuration members, and then reorder the zone member list if
necessary.
The newly changed zone configuration are not effective until you issue the cfgEnable command.
This should be done during a maintenance window because this may cause disruption in large
fabrics.
Verifying a fabric merge problem
1. Enter the switchShow command to validate that the segmentation is because of a zone issue.
2. Review “Segmented fabrics,” to view the different types of zone discrepancies and determine
what might be causing the conflict.
Verifying a TI zone problem
Use the zone --show command to display information about TI zones. This command displays the
following information for each zone:
• zone name
• E_Port members
• N_Port members
• configured status (the latest status, which may or may not have been activated by cfgEnable)
• enabled status (the status that has been activated by cfgEnable)
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 73
53-1002751-01
Page 90

9
Segmented fabrics
If you enter the cfgShow command to display information about all zones, the TI zones appear in
the defined zone configuration only and do not appear in the effective zone configuration.
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Enter the zone
zone --show [name]
--show command.
where:
name The name of the zone to be displayed. If the name is omitted, the command
displays information about all TI zones in the defined configuration.
To display information about the TI zone purplezone:
switch:admin> zone --show purplezone
Defined TI zone configuration:
TI Zone Name: redzone:
Port List: 1,2; 1,3; 3,3; 4,5
Configured Status: Activated / Failover-Enabled
Enabled Status: Activated / Failover-Enabled
To display information about all TI zones in the defined configuration:
switch:admin> zone --show
Defined TI zone configuration:
TI Zone Name: greenzone:
Port List: 2,2; 3,3; 5,3; 4,11;
Configured Status: Activated / Failover-Enabled
Enabled Status: Activated / Failover-Enabled
TI Zone Name: purplezone:
Port List: 1,2; 1,3; 3,3; 4,5;
Configured Status: Activated / Failover-Enabled
Enabled Status: Deactivated / Failover-Enabled
TI Zone Name: bluezone:
Port List: 9,2; 9,3; 8,3; 8,5;
Configured Status: Deactivated / Failover-Disabled
Enabled Status: Activated / Failover-Enabled
Segmented fabrics
This section discusses fabric segmentation. Fabric segmentation occurs when two or more
switches are joined together by ISLs and do not communicate to each other. Each switch appears
as a separate fabric when you use the fabricShow command.
74 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 91

Zone conflicts
ATTENTION
Symptom Zone conflict appears in logs and fabric is segmented.
Probable cause and recommended action
This issue is usually caused by incompatible zoning configurations. Verify the following are true:
• The effective cfg (zone set) on each end of the segmented ISL is identical.
• Any zone object with the same name has the same entries in the same sequence.
Symptom Fabric segmentation is caused by a “configuration mismatch”.
Probable cause and recommended action
Occurs when zoning is enabled in both fabrics and the zone configurations are different in each
fabric.
Symptom Fabric segmentation is caused by a “type mismatch”.
Probable cause and recommended action
Occurs when the name of a zone object in one fabric is also used for a different type of zone object
in the other fabric. A zone object is any device in a zone
Symptom Fabric segmentation is caused by a “content mismatch”.
.
9
Probable cause and recommended action
Occurs when the definition in one fabric is different from the definition of a zone object with the
same name in the other fabric.
Zone conflicts
Zone conflicts can be resolved by saving a configuration file with the configUpload command,
examining the zoning information in the file, and performing a cut and paste operation so that the
configuration information matches in the fabrics being merged.
After examining the configuration file, you can choose to resolve zone conflicts by using the
cfgDisable command followed by the cfgClear command on the incorrectly configured segmented
fabric, then enter the cfgSave command followed by the portDisable and portEnable commands on
one of the ISL ports that connects the fabrics. This causes a merge, making the fabric consistent
with the correct configuration.
Be careful using the cfgClear command because it deletes the defined configuration.
Tab le 14 summarizes commands that are useful for debugging zoning issues.
TABLE 14 Commands for debugging zoning
Command Function
aliCreate Use to create a zone alias.
aliDelete Use to delete a zone alias.
cfgCreate Use to create a zone configuration.
cfgShow Displays zoning configuration.
cfgDisable Disables the active (effective) configuration
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 75
53-1002751-01
Page 92

9
ATTENTION
ATTENTION
Zone conflicts
TABLE 14 Commands for debugging zoning (Continued)
Command Function
cfgEnable Use to enable and activate (make effective) the specified configuration.
cfgSave Use to save changes to the zone configuration database.
cfgTransAbort Use to abort the current zoning transaction without committing it.
cfgTransShow Use to display the ID of the current zoning transaction
defZone Sets the default zone access mode to No Access, initializes a zoning transaction (if one is not
already in progress), and creates the reserved zoning objects.
licenseShow Displays current license keys and associated (licensed) products.
switchShow Displays currently enabled configuration and any E_Port segmentations resulting from zone
conflicts.
zoneAdd Use to add a member to an existing zone.
zoneCreate Use to create a zone. Before a zone becomes active, the cfgSave and cfgEnable commands
must be used.
zoneHelp Displays help information for zone commands.
zoneShow Displays zone information.
.
For more information about setting up zoning on your switch, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s
Guide.
You can correct zone conflicts by using the cfgClear command to clear the zoning database.
The cfgClear command is a disruptive procedure.
Correcting a fabric merge problem quickly
1. Determine which switches have the incorrect zoning configuration; then, log in to the switches
as admin.
2. Enter the switchDisable command on all problem switches.
3. Enter the cfgDisable command on each switch.
4. Enter the cfgClear command on each switch.
5. Enter the cfgSave command on each switch to commit the change.
The cfgClear command clears the zoning database on the switch where the command is run.
6. Enter the switchEnable command on each switch once the zoning configuration has been
cleared.
This forces the zones to merge and populates the switches with the correct zoning database.
The fabrics then merge.
76 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 93

Zone conflicts
9
Changing the default zone access
A switch is not allowed to merge with another switch that has an active effective configuration if the
default zone is set to “no access”. Before the switch can join, the default zone setting has to be set
to “all access”. When the default zone no access option is enabled and the active configuration is
disabled by using the cfgDisable command, a special hidden configuration with no members is
activated. This configuration does not allow the switch to merge with switches that have an active
effective configuration.
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account with admin permissions.
2. Display the current setting with the defZone –show command.
3. If your default zone is set to “no access”, use the defZone –allaccess command to change the
default zone.
4. Enter the cfgSave command to save the current configuration.
Editing zone configuration members
1. Log in to one of the switches in a segmented fabric as admin.
2. Enter the cfgShow command and print the output.
3. Start another Telnet session and connect to the next fabric as an admin.
4. Enter the cfgShow command and print the output.
5. Compare the two fabric zone configurations line by line and look for an incompatible
configuration.
6. Connect to one of the fabrics.
7. Run zone configure edit commands to edit the fabric zone configuration for the segmented
switch (see Table 14 on page 75 for specific commands).
If the zoneset members between two switches are not listed in the same order in both
configurations, the configurations are considered a mismatch; this results in the switches
being segmented in the fabric.
For example:
[cfg1 = z1; z2] is different from [cfg1 = z2; z1], even though the members of the
configuration are the same.
One simple approach to making sure that the zoneset members are in the same order is to
keep the members in alphabetical order.
Reordering the zone member list
1. Obtain the output from the cfgShow command for both switches.
2. Compare the order in which the zone members are listed. Members must be listed in the same
order.
3. Rearrange zone members so the configuration for both switches is the same. Arrange zone
members in alphabetical order, if possible.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 77
53-1002751-01
Page 94

9
Zone conflicts
Checking for Fibre Channel connectivity problems
Enter the fcPing command (refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference for more information on
this command), which checks the zoning configuration for the two ports specified by:
• Generates an Extended Link Service (ELS) frame ECHO request to the source port specified
and validates the response.
• Generates an ELS ECHO request to the destination port specified and validates the response.
Regardless of the device’s zoning, the fcPing command sends the ELS frame to the destination
port. A device can take any of the following actions:
• Send an ELS Accept to the ELS request.
• Send an ELS Reject to the ELS request.
• Ignore the ELS request.
There are some devices that do not support the ELS ECHO request. In these cases, the device
either does not respond to the request or send an ELS reject. When a device does not respond to
the ELS request, further debugging is required; however, do not assume that the device is not
connected to the Fibre Channel.
Following is sample output from the fcPing command in which one device accepts the request and
another device rejects the request:
switch:admin> fcping 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05
Source: 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4
Destination: 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05
Zone Check: Not Zoned
Pinging 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4 [0x20800] with 12 bytes of date:
received reply from 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4: 12 bytes time:1162 usec
received reply from 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4: 12 bytes time:1013 usec
received reply from 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4: 12 bytes time:1442 usec
received reply from 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4: 12 bytes time:1052 usec
received reply from 10:00:00:00:c9:29:0e:c4: 12 bytes time:1012 usec
5 frames sent, 5 frames received, 0 frames rejected, 0 frames timeout
Round-trip min/avg/max = 1012/1136/1442 usec
Pinging 21:00:00:20:37:25:ad:05 [0x211e8] with 12 bytes of data:
Request rejected
Request rejected
Request rejected
Request rejected
Request rejected
5 frames sent, 0 frames received, 5 frames rejected, 0 frames timeout
Round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/0 usec
switch:admin>
Following is sample output from the fcPing command in which one device accepts the request and
another device does not respond to the request:
switch:admin> fcping 0x020800 22:00:00:04:cf:75:63:85
Source: 0x20800
Destination: 22:00:00:04:cf:75:63:85
Zone Check: Zoned
Pinging 0x020800 with 12 bytes of data:
received reply from 0x020800: 12 bytes time:1159 usec
78 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 95

Zone conflicts
received reply from 0x020800: 12 bytes time:1006 usec
received reply from 0x020800: 12 bytes time:1008 usec
received reply from 0x020800: 12 bytes time:1038 usec
received reply from 0x020800: 12 bytes time:1010 usec
5 frames sent, 5 frames received, 0 frames rejected, 0 frames timeout
Round-trip min/avg/max = 1006/1044/1159 usec
Pinging 22:00:00:04:cf:75:63:85 [0x217d9] with 12 bytes of data:
Request timed out
Request timed out
Request timed out
Request timed out
Request timed out
5 frames sent, 0 frames received, 0 frames rejected, 5 frames timeout
Round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/0 usec
switch:admin>
For details about the fcPing command, refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference.
Checking for zoning problems
1. Enter the cfgActvShow command to determine if zoning is enabled.
9
• If zoning is enabled, it is possible that the problem is being caused by zoning enforcement
(for example, two devices in different zones cannot detect each other).
• If zoning is disabled, check the default zone mode by entering the defZone --show
command. If it is no access, change it to all access. To modify default zone mode from no
access to all access, enter the defZone
--all command, and then the cfgSave command.
2. Confirm that the specific edge devices that must communicate with each other are in the same
zone.
• If they are not in the same zone and zoning is enabled, proceed to step 3.
• If they are in the same zone, perform the following tasks:
Enter the portCamShow command on the host port to verify that the target is present.
Enter the portCamShow command on the target.
Enter the nsZoneMember command with the port ID for the zoned devices on the host
and target to determine whether the name server is aware that these devices are
zoned together.
3. Resolve zoning conflicts by putting the devices into the same zoning configuration.
4. Verify that no configuration is active by using the cfgActvShow command. Enter the defZone
--show command to display the current state of the zone access mode and the access level.
The defZone command sets the default zone access mode to No Access
switch:admin> defzone --show
Default Zone Access Mode
committed - No Access
transaction - No Transaction
.
See “Zone conflicts” on page 75 for additional information.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 79
53-1002751-01
Page 96

9
Gathering additional information
Gathering additional information
Collect the data from a supportSave -n command. Then collect the data from the cfgTransShow
command. For the port having the problem, collect the data from the filterPortShow <port>
command.
80 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 97

Chapter
Diagnostic Features
In this chapter
•About Fabric OS diagnostics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
•Diagnostic information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
•Power-on self test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
•Switch status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
•Using the SpinFab and portTest commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
•Diagnostic Port (D_Port) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
•Port information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
•Equipment status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
•System message log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
•Port log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
•Syslogd configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
•Automatic trace dump transfers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
10
About Fabric OS diagnostics
The purpose of the diagnostic subsystem is to evaluate the integrity of the system hardware.
Diagnostics are invoked in the one of the following ways:
• Automatically during the power-on self test (POST).
• Automatically on an individual blade whenever it is installed into a director chassis.
• Manually using Fabric OS CLI commands.
The error messages generated during these test activities are sent to the serial console and system
message logs, whose output formats may differ slightly.
Use the diagHelp command to receive a list of all available diagnostic commands.
Refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference for a complete description of each command.
Diagnostic information
On the switch you can enter the supportShow command to dump important diagnostic and status
information to the session screen, where you can review it or capture its data. If you are using a
Telnet client, you may have to set up the client to capture the data prior to opening the session
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 81
53-1002751-01
Page 98

10
Most information can be captured using the supportSave command and downloaded by FTP off the
switch, but when you are collecting information from specialized commands, such as supportShow,
this information has to be captured using a Telnet client.
To save a set of files that customer support technicians can use to further diagnose the switch
condition, enter the supportSave command. The command prompts for an FTP server, packages
the following files, and sends them to the specified server:
• The output of the supportShow command.
• The contents of any trace dump files on the switch.
• System message (RAS) logs.
See also “Automatic trace dump transfers” on page 115.
Power-on self test
By default, when you power on the system, the boot loader automatically performs power-on self
tests and loads a Fabric OS kernel image.
The POST tests provide a quick indication of hardware readiness when hardware is powered up.
These tests do not require user input to function. They typically operate within several minutes, and
support minimal validation because of the restriction on test duration. Their purpose is to give a
basic health check before a new switch joins a fabric.
Power-on self test
These tests are divided into two groups: POST1 and POST2. POST1 validates the hardware
interconnect of the device, and POST2 validates the ability of the device to pass data frames
between the ports. The specific set of diagnostic and test commands run during POST depends on
the switch model.
You can use the diagDisablePost command to disable both POST1 and POST2, and you can
reenable it using the diagEnablePost command. Refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference for
additional information about these commands.
The following example shows a typical boot sequence, including POST messages:
The system is coming up, please wait...
Read board ID of 0x80 from addr 0x23
Read extended model ID of 0x16 from addr 0x22
Matched board/model ID to platform index 4
PCI Bus scan at bus 0
:::
:::
Checking system RAM - press any key to stop test
Checking memory address: 00100000
System RAM test using Default POST RAM Test succeeded.
Press escape within 4 seconds to enter boot interface.
Booting "Fabric Operating System" image.
Linux/PPC load:
BootROM command line: quiet
Uncompressing Linux...done.
Now booting the kernel
Attempting to find a root file system on hda2...
82 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
Page 99

Power-on self test
modprobe: modprobe: Can't open dependencies file /lib/modules/2.4.19/modules.dep
(No such file or directory)
INIT: version 2.78 booting
INIT: Entering runlevel: 3
eth0: Link status change: Link Up. 100 Mbps Full duplex Auto (autonegotiation
complete).
INITCP: CPLD Vers: 0x95 Image ID: 0x19
uptime: 2008; sysc_qid: 0
Fabric OS (Paulsa45)
Paulsa45 console login: 2005/03/31-20:12:42, [TRCE-5000], 0,, INFO, ?, trace:,
trace_buffer.c, line: 1170
2005/03/31-20:12:42, [LOG-5000], 0,, INFO, SW4100_P45, Previous message repeat 1
time(s), trace_ulib.c, line: 540
2005/03/31-20:12:43, [HAM-1004], 219,, INFO, SW4100_P45, Processor rebooted Unknown
SNMP Research SNMP Agent Resident Module Version 15.3.1.4
Copyright 1989, 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000,
2001 SNMP Research, Inc.
sysctrld: all services Standby
FSSK 2: chassis0(0): state not synchronized
FSSK 2: Services starting a COLD recovery
2005/03/31-20:12:48, [FSS-5002], 0,, INFO, SW4100_P45, chassis0(0): state not
synchronized, svc.c, line: 318
2005/03/31-20:12:48, [FSS-5002], 0,, INFO, SW4100_P45, Services starting a COLD
recovery, mdev.c, line: 638
2005/03/31-20:12:49, [MFIC-1002], 220,, INFO, Paulsa45, Chassis FRU header not
programmed for switch NID, using defaults (applies only to FICON environments).
sysctrld: all services Active
2005/03/31-20:12:50, [DGD-5001], 0,, INFO, SW4100_P45, Slot 0 has started POST.,
main.c, line: 1189
POST1: Started running Thu Mar 31 20:12:51 GMT 2005
POST1: Test #1 - Running turboramtest
POST1: Test #2 - Running portregtest
POST1: Script PASSED with exit status of 0 Thu Mar 31 20:12:54 GMT 2005 took
(0:0:3)
POST2: Started running Thu Mar 31 20:12:55 GMT 2005
POST2: Test #1 - Running portloopbacktest (SERDES)
POST2: Test #2 - Running minicycle (SERDES)
POST2: Running diagshow
POST2: Script PASSED with exit status of 0 Thu Mar 31 20:13:12 GMT 2005 took
(0:0:17)
2005/03/31-20:13:13, [BL-1000], 221,, INFO, Paulsa45, Initializing Ports...
Enabling switch...
2005/03/31-20:13:13, [BL-1001], 222,, INFO, Paulsa45, Port Initialization
Completed
2005/03/31-20:13:13, [EM-5012], 0,, INFO, SW4100_P45, EM: sent dumpready to ME.,
em.c, line: 2152
2005/03/31-20:13:13, [DGD-5002], 0,, INFO, SW4100_P45, Slot 0 has passed the POST
tests., main.c, line: 936
10
If you choose to bypass POST or after POST completes, various system services are started and the
boot process displays additional console status and progress messages.
Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 83
53-1002751-01
Page 100

10
Switch status
Disabling POST
A reboot is not required for this command to take effect.
1. Connect to the switch and log in with a user account that has admin privileges with the
chassis-role permission.
2. Enter the diagDisablePost command.
This disables POST1 and POST2.
Enabling POST
A reboot is not required for this command to take effect.
1. Connect to the switch and log in with a user account that has admin privileges with the
chassis-role permission.
2. Enter the diagEnablePost command to enable POST with rebooting the switch.
switch:admin> diagenablepost
Config update Succeeded
Diagnostic POST is now enabled.
Switch status
Use the switchStatusShow command to display the overall status of the switch, including its power
supplies, fans, and temperature. If the status of any one of these components is either marginal or
down, the overall status of the switch is also displayed as marginal or down. If all components have
a healthy status, the switch displays a healthy status.
To modify the rules used to classify the health of each component use the switchStatusPolicySet
command. To view the rules, use the switchStatusPolicyShow command.
Viewing the overall status of the switch
1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin.
2. Enter the switchStatusShow command:
ecp:admin> switchstatusshow
Switch Health Report Report time: 02/20/2008 06:02:51 PM
Switch Name: brcdDCXbb
IP address:192.168.234.63
SwitchState:DOWN
Duration:00:37
Power supplies monitorDOWN
Temperatures monitor HEALTHY
Fans monitor DOWN
WWN servers monitor HEALTHY
Standby CP monitor HEALTHY
Blades monitor HEALTHY
Core Blades monitorHEALTHY
Flash monitor HEALTHY
Marginal ports monitorHEALTHY
84 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide
53-1002751-01
 Loading...
Loading...