Dell Active System Manager Version 8.0 Manual

Active System Manager
Version 8.0 User’s Guide

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your product.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you
how to avoid the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Copyright
Copyright © 2014 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and
intellectual property laws. Dell™ and the Dell logo are trademarks of Dell Inc. in the United States and/or other
jurisdictions. All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
2014 - 11
Rev. A00

Contents
1 Overview................................................................................................................. 7
About this document............................................................................................................................ 8
What is New in this Release.................................................................................................................. 8
Accessing Online Help.......................................................................................................................... 8
Other documents you may need......................................................................................................... 9
Licensing................................................................................................................................................9
2 Getting started with ASM 8.0........................................................................... 10
3 Initial setup...........................................................................................................12
Uploading license................................................................................................................................ 13
Configuring time zone and NTP settings........................................................................................... 13
Configure proxy settings.....................................................................................................................13
Configure DHCP settings....................................................................................................................14
Verifying initial setup........................................................................................................................... 14
4 Dashboard............................................................................................................15
Service states........................................................................................................................................17
5 Services.................................................................................................................18
Deploy service..................................................................................................................................... 19
Viewing service details........................................................................................................................20
Component deployment states....................................................................................................23
Editing service information.................................................................................................................23
Deleting service...................................................................................................................................24
Exporting service details..................................................................................................................... 24
Retry failed service.............................................................................................................................. 24
View Service Deployment Settings.....................................................................................................25
Migrating servers (service mobility).................................................................................................... 25
Migration prerequisites..................................................................................................................25
Migrating servers................................................................................................................................. 25
Adding components to existing service deployments...................................................................... 26
Adding applications to existing service.........................................................................................27
Adding clusters to existing service................................................................................................27
Adding Virtual Machines to existing service.................................................................................28
Adding servers to existing service.................................................................................................28
Adding storage to existing service................................................................................................29
Deleting resources from service........................................................................................................ 30

6 Templates.............................................................................................................31
Manage templates...............................................................................................................................32
Viewing template details............................................................................................................... 33
Creating template..........................................................................................................................33
Editing template information........................................................................................................34
Building template overview...........................................................................................................35
Building and publishing template................................................................................................. 35
Importing template....................................................................................................................... 36
Editing template............................................................................................................................ 36
Viewing template details............................................................................................................... 37
Deleting template..........................................................................................................................37
Cloning template...........................................................................................................................38
Deploy service...............................................................................................................................38
Decommissioning services provisioned by ASM..........................................................................39
Component types......................................................................................................................... 39
Component combinations in templates...................................................................................... 54
Sample templates................................................................................................................................54
Template – deploy Citrix XenDesktop for 500 users ................................................................. 55
Template – deploy operating system to hard drive.................................................................... 56
Template – deploy physical server and virtual machine............................................................. 57
Template – deploy virtual machines to cluster........................................................................... 58
Template – install ESXi to SD card with Fibre Channel storage..................................................59
Template – install ESXi to SD card with iSCSI storage................................................................ 60
Template – deploy Hyper-V host with iSCSI storage.................................................................. 61
Template – deploy Hyper-V cluster with iSCSI storage..............................................................63
Template – deploy Hyper-V cluster with Fibre Channel storage to SCVMM............................ 64
Template – deploy VMware cluster with NetApp storage.......................................................... 66
Template – boot from Fibre Channel SAN.................................................................................. 67
Template – boot from iSCSI SAN.................................................................................................68
Template – deploy virtual machine template clone on Hyper-V cluster...................................69
Template – deploy virtual machine template clone on VMware cluster................................... 69
Template – deploy SQL Server 2012 ...........................................................................................70
Additional template information.........................................................................................................72
Deploying ESXi cluster for SAN applications................................................................................72
7 Resources............................................................................................................. 75
Understanding All Resources tab........................................................................................................75
Resource health status..................................................................................................................76
Resource operational state........................................................................................................... 77
Resource firmware compliance status.........................................................................................78
Updating firmware.........................................................................................................................78

Viewing firmware compliance report...........................................................................................79
Discovery overview....................................................................................................................... 79
Configuring resources or chassis................................................................................................. 82
Removing resources..................................................................................................................... 90
Updating resource inventory .......................................................................................................90
Managing and unmanaging resources.........................................................................................90
Viewing resource details............................................................................................................... 91
Understanding server pools................................................................................................................94
Creating server pool......................................................................................................................94
Editing server pool........................................................................................................................ 94
Deleting server pool......................................................................................................................95
8 Settings.................................................................................................................96
Backup and restore.............................................................................................................................96
Backup details................................................................................................................................97
Editing backup settings and details.............................................................................................. 97
Editing automatically scheduled backups....................................................................................98
Backup now...................................................................................................................................98
Restore now.................................................................................................................................. 99
Credentials management................................................................................................................... 99
Creating credentials....................................................................................................................100
Editing credentials....................................................................................................................... 101
Deleting credentials.....................................................................................................................101
Getting Started...................................................................................................................................101
Application logs................................................................................................................................. 101
Exporting all log entries.............................................................................................................. 102
Purging log entries...................................................................................................................... 102
Networks........................................................................................................................................... 103
Networking..................................................................................................................................103
Repositories.......................................................................................................................................106
OS Image repositories.................................................................................................................106
Understanding Firmware tab...................................................................................................... 107
Viewing firmware bundle details................................................................................................ 108
Scheduled jobs..................................................................................................................................109
Users..................................................................................................................................................109
Creating a user.............................................................................................................................110
Deleting a user..............................................................................................................................111
Editing a user................................................................................................................................ 111
Enabling or disabling users.......................................................................................................... 111
Directory services.........................................................................................................................111
Importing users............................................................................................................................115
About roles...................................................................................................................................116

Virtual appliance management.........................................................................................................122
Generating a troubleshooting bundle........................................................................................ 122
Generating and uploading the ssl certificates............................................................................122
Editing DHCP settings................................................................................................................. 124
Editing proxy settings..................................................................................................................124
License management..................................................................................................................124
Editing default time zone and NTP settings............................................................................... 125
Virtual identity pools..........................................................................................................................125
Creating virtual identity pools.....................................................................................................126
Deleting virtual identity pools..................................................................................................... 128
Exporting virtual identity pools................................................................................................... 128
9 Troubleshooting...............................................................................................129
LC operation times out while deploying server profile to a server ................................................129
Hyper-V host deployments using network storage only support certain configurations............. 129
iSCSI storage network only support static IP addressing................................................................ 129
Unable to deploy a service for compellent component with same server object and volume
names................................................................................................................................................ 129
Unable to deploy a service using the template with two Equallogic CHAP components.............130
Unable to log in to ASM using active directory using “”.................................................................. 130
Chain booting issue occurs while booting microkernel in a multi-hop DHCP environment....... 130

1
Overview
Active System Manager (ASM) is Dell’s unified management product that provides a comprehensive
infrastructure and workload automation solution for IT administrators and teams. ASM simplifies and
automates the management of heterogeneous environments enabling IT to respond more rapidly to
dynamic business needs.
IT organizations today are often burdened by complex data centers that contain a mix of technologies
from different vendors and cumbersome operational tasks for delivering services while managing the
underlying infrastructure. These tasks are typically performed through multiple management consoles for
different physical and virtual resources, which can dramatically slow down service deployment.
The new ASM features a user interface that provides an intuitive, end-to-end infrastructure and workload
automation experience through a unified console. This speeds up workload delivery and streamlines
infrastructure management, enabling IT organizations to accelerate service delivery and time to value for
customers.
What can you do with ASM?
ASM provides capabilities and benefits that allow organizations to:
• Accelerate IT service delivery by automating and centralizing key operational functions like workload
and infrastructure deployment.
• Free up IT staff to focus on higher priority projects by dramatically reducing manual steps and human
touch points.
• Use infrastructure more fully and efficiently by pooling available server, storage and network
resources that you can schedule for future use or allocate on demand.
• Standardize workload delivery processes to ensure accuracy and consistency for initial deployment,
while maintaining the flexibility to scale workloads according to business needs.
• Maximize investments in both Dell and Non-Dell IT resources with support for heterogeneous IT
environments.
How is ASM different?
ASM helps you realize these benefits through a unique set of features and capabilities designed for IT
administrators. These capabilities include:
• Template-based provisioning and orchestration — Simplify IT service delivery with a centralized
approach for capturing and applying workload-specific configuration and best practices; plus stepby-step definition and execution of tasks across the workload lifecycle.
• Infrastructure lifecycle management — Easily manage the entire infrastructure lifecycle with:
– Fast discovery, inventory, and initial configuration of assets.
7

– Full lifecycle management of physical and virtual infrastructure and workloads.
• Deep virtualization integration — Manage cluster-level and virtual machine (VM) lifecycle.
• Resource pooling and dynamic allocation — Optimize capital expenditures by creating and
managing physical and virtual IT resource pools.
• Radically simplified management — Powerful and intuitive user interface that makes it easy to set up,
deploy, and manage your IT environment and enables simplified integration with third party tools.
• Open and extensible — An architecture that integrates with the IT of today and tomorrow; this means
being able to plug a new solution into your existing architecture, as well as giving you flexibility in the
future to adopt new technical innovations.
ASM makes it easy to automate IT service delivery and to manage your IT environment end-to-end. You
can improve and accelerate service and infrastructure delivery, maximize efficiency across your IT service
lifecycle, and consistently achieve high-quality IT services.
About this document
This document version is updated for ASM, version 8.0.
What is New in this Release
• Infrastructure firmware compliance and updates
• Wizard based chassis, server and IO onboarding with advanced configuration
• 13th generation server support.
• Streamlined installation experience
• FCoE support with Brocade, Dell s5000, and Cisco Nexus
• Resource health monitoring
• Enhanced role-based access control
• Service Lifecycle Improvements including scheduling a service deployment and scaling down a
running service
Accessing Online Help
Active System Manger (ASM) online help system provides context-sensitive help available from every page
in the ASM user interface.
After you log in to ASM user interface, you can access the online help in any of the following ways:
• To open context-sensitive online help for the active page, click ?, and then click Help.
• To open context-sensitive online help for a dialog box, click ? in the dialog box.
Additionally, in the online help, use the Enter search items option in the Table of Contents to search for a
specific topic or keyword.
8

Other documents you may need
In addition to this guide, the following documents available on the Dell Support website at dell.com/
support/manuals provide additional information about the ASM.
Go to http://www.dell.com/asmdocs.
• Dell Active System Manager version 8.0 Release Notes
• Dell Active System Manager version 8.0 Quick Installation Guide
• Dell Active System Manager version 8.0 Compatibility Matrix Guide
For more information about best practices, Dell solutions, and service, see Dell Active System Manager
page on Dell Techcenter -
http://en.community.dell.com/techcenter/converged-infrastructure/w/wiki/4318.dell-active-systemmanager.aspx
Licensing
ASM licensing is based on the total number of managed resources, except for the VMware vCenter and
Windows SCVMM instances
ASM 8.0 supports following license types:
• Trial License — A Trial license can be procured through the account team and it supports up to 25
resources for 90 days.
• Standard License — A Standard license grants full access.
You will receive an e-mail from customer service with the instructions for downloading ASM. The license
file is attached to that email.
If you are using ASM for the first time, you must upload the license file through the Initial Setup wizard.
To upload and activate subsequent licenses, click Settings → Virtual Appliance Management.
After uploading an initial license, subsequent uploads replace the existing license.
9

2
Getting started with ASM 8.0
When you log in to ASM for the first time, the Getting Started page is displayed. This page provides a
recommended guided workflow for getting started with ASM. A check mark indicates that you have
completed the step.
NOTE: Standard users do not have the privilege to view the Getting Standard page.
The steps include:
• Step 1: Initial Setup — Click Initial Setup to configure basic settings required before you start using
ASM, such as license, virtual appliance time zone, NTP server, DHCP, and proxy server settings. To
proceed to Step 2, you must complete the initial setup configuration.
After initial setup is complete, to edit the NTP, DHCP Server, proxy server, and license information,
click Settings in the left pane, and then click Virtual Appliance Management.
• Step 2: Define Networks — Click Define Networks to define networks that are currently configured in
your environment for resources to access. To define, edit, or delete your existing networks, in the left
pane, click Settings in the left pane, and then click Networks.
• Step 3: Discover Resources — Click Discover Resources to discover one or more resources (chassis,
blade server, switch, storage, and hypervisor management software instances) that you want ASM to
manage on your network. Additionally, following information is displayed on the Disover pane.
– Discovered Resources — Indicates the number of resources that are discovered in ASM.
– Pending Resources — Indicates that the discovery is in progress for the number of resources
displayed.
– Errors — Indicates that ASM is unable to discover the number of resources displayed due to some
issues.
• Step 4: Configure Resources — Click Configure Resources to perform a firmware compliance check
on the resources that are discovered and configure the chassis as needed.
• Step 5: Publish Templates — Click Publish Templates to open the Templates page. On the
Templates page, create a new template or edit a draft default template and publish it. After the
templates are published, they are ready to deploy.
NOTE:
To view the left-hand navigation pane options, at least a template must be in the published state.
When the initial setup and discovery step are complete, you can still discover resources, create or edit
templates, and publish templates from the left pane.
If you do not want to view the Getting Started page when you log in next time, clear the Show welcome
screen on next launch check box at the bottom of the page. However, to revisit the Getting Started
page, click Settings in the left pane, and then click Getting Started.
Related Links
Discovery overview
Initial setup
10

Discovering resources
Templates
Defining or editing existing network
Configuring resources or chassis
11

3
Initial setup
The Initial Setup wizard enables you to configure the basic settings required to start using ASM.
Before you begin, gather the following information:
• The local network share that contains ASM license.
• The time zone of the virtual appliance that hosts ASM.
• The IP address or host name of at least one Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers.
• The IP address or host name, port, and credentials of the proxy server. (Optional)
• The networks in your environment for ASM to access. (Optional)
To configure the basic settings:
1. On the Welcome page, read the instructions and click Next.
2. On the Licensing page, select a valid license and click Save and Continue.
3. On the Time Zone and NTP Settings page, configure the time zone of the virtual appliance, add the
NTP server information, add then click Save and Continue.
4. (Optional) On the Proxy Settings page, select the Use a proxy server check box, enter the
configuration details, and then click Save and Continue.
5. (Optional) If you want to configure ASM appliance as a DHCP or PXE server, on the DHCP Settings
page, select the Enable DHCP/PXE server check box, enter the DHCP details, and then click Save
and Continue.
6. On the Summary page, verify the license, time zone, proxy server, and DHCP settings.
7. Click Finish to complete the initial setup.
After the initial setup is complete, if you want to edit the NTP, proxy server, DHCP settings, and license
information, click Settings in the left pane, and then click Virtual Appliance Management.
Related Links
Uploading license
Configuring time zone and NTP settings
Configure proxy settings
Configure DHCP settings
12
Uploading license
If you are using ASM for the first time, you must upload the license file through the Initial Setup wizard.
To upload a subsequent license, click Settings in the left pane, and then click Virtual Appliance
Management. In the Virtual Appliance Management page, click Edit in the License Management section.
1. On the Licensing page of the Initial Setup wizard, click Browse, and select a valid license file.
The following information is displayed based on the license selected:
• Type — Displays the license type. There are two valid license types supported in ASM:
– Standard — Full-access license type.
– Trial — Evaluation license that expires after 90 days it supports up to 25 resources.
• Total Resources — Displays the maximum number of resources allowed by the license.
• Expiration Date — Displays the expiry date of the license.
2. Click Save and Continue to activate the license.
Related Links
License management
Configuring time zone and NTP settings
On the Time Zone and NTP Settings page of the Initial Setup wizard, you can set the time zone of the
virtual appliance that host ASM and configure Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers used for time
synchronization.
NOTE: Configuring NTP will adjust your ASM system time. If the time is adjusted forward it will end
your current user session. The time will sync 5-10 minutes after this step. If this occurs, log in to
ASM again and continue with the setup process.
1. On the Time Zone and NTP Settings page of the Initial Setup wizard, from the Time Zone drop-
down list, select the time zone in which the virtual appliance operates.
2. To synchronize the time with the NTP server, enter the IP address or Fully Qualified Domain Name
(FQDN) of a
3. Click Save and Continue.
After the initial setup is complete, to change NTP server information, click Settings in the left pane, and
then click Virtual Appliance Management. On the Virtual Appliance Management page, click Edit in the
Time Zone and NTP Settings section.
Related Links
Editing default time zone and NTP settings
Preferred NTP Server and Secondary NTP Server (optional).
Configure proxy settings
If your environment uses a proxy server to communicate with external services, then you must configure
the proxy server settings in ASM.
To enable communication through a proxy server:
1. On the Proxy Settings page of the Initial Setup wizard, select the Use a proxy server check box.
2. In the Server IP Address box, enter the IP address or host name for the proxy server.
13

3. In the Port box, enter the port number for the proxy server.
4. If the proxy server requires credentials to log in, select the Use proxy credentials check box, enter
the User Name and Password, and then reenter the password to confirm.
5. Click Test Proxy Connection to test the connection to the proxy server.
6. Click Save and Continue.
After the initial setup is complete, to change the proxy settings, in the left pane, click Settings in the left
pane, and then click Virtual Appliance Management. On the Virtual Appliance Management page, click
Edit in the Proxy Settings section.
Related Links
Editing proxy settings
Configure DHCP settings
Configure the following settings if you want to set ASM appliance as a DHCP or PXE server.
NOTE: If you want to configure the DHCP server on a particular VLAN that has one or more DHCP
server already configured, then make sure to turn off the other DHCP servers on the VLAN.
1. On the DHCP Settings page, select the Enable DHCP/PXE Server check box.
NOTE: The Enable DHCP/PXE Server check box is not selected by default.
2. In the Subnet box, enter the IP address of the subnet on which DHCP server can be operated.
3. In the Netmask box, enter the subnet mask that will be used by DHCP clients.
4. In the DHCP Scope Starting IP Address box, enter the starting IP address in the range assigned to the
clients.
5. In the DHCP Scope Ending IP Address box, enter the ending IP address in the range assigned to the
clients.
6. In the Default Lease Time (DD:hh:mm:ss) box, enter the default time that an IP address is granted to
a client.
NOTE: It is recommended to set the default lease time for short duration. That is for one to
three hours.
7. In the Max Leave Time (DD:hh:mm:ss) box, enter the amount of time that an IP address is granted to
a client.
8. In the Default Gateway box, enter the gateway address. This address will be used by the DHCP
clients as the default gateway.
9. In the DNS Server box, enter the domain name system (DNS) domain name of this DHCP scope to
use with one or more DNS servers.
10. Click Save and Continue.
It may take 15 to 20 seconds to enable DHCP server.
Verifying initial setup
1. On the Summary page, verify the settings you have configured in the previous pages.
2. If the information is correct, click Finish to complete the initial setup.
3. If you want to edit any of the information, click Back or click the corresponding page name in the left
navigation bar.
14

Dashboard
The Dashboard displays the following information:
NOTE: Standard users are allowed only to view the details of the services that they have created or
for the services they have permission.
• Under Service Overview section, displays a graphical representation of the services based on their
state, total number of services deployed, and state icons that represent the service state. The number
next to each state icon indicates how many services are in a particular state. The services are
categorized based on the following states:
– Error Services (Red band on the graphic): Indicates the services for which the deployment process
is incomplete due to errors.
– Deployed Services (Green band on the graphic): Indicates the services that are deployed
successfully.
– In Progress Services (Blue band on the graphic): Indicates the services for which deployment is in
progress.
– Warning (Yellow band on the graphic): Indicates the resources in a service are in a state that
requires corrective action, but does not affect overall system health. For example, the firmware
version installed on a resource in the service is not compliant.
To display a list of services in a particular state, click the corresponding color bands on the
graphic: red, blue, green, or yellow. The following information about the services are listed at the
bottom of the graphical display:
4
* State icons. The number next to the icons indicate the number of services that are in a
particular state.
* Service name. Click to view the detailed information about the service.
* Name of the user who deployed the service.
* Date and time when the service was deployed.
* The number of resources used by the particular service based on the component type.
* Errors, if any.
From the Service History drop-down list, you can select one of the following options to filter and
view the service deployments.
* All Deployments
* Last 10 Deployments
15

* Last Week
* Last Month
* Last 6 Months
* Last Year
• Under Server Overview → Server Health, a pie chart displays the total number of servers available
across all the server pools and their state.
The state of the servers are categorized based on the following state:
– Healthy (green band on the graphic): Indicates that there is no issue with the servers and working
as expected.
– Critical (red band on the graphic): Indicates critical problems exist with one or more components
in the server. These issues should be fixed immediately.
– Warning (yellow band on the graphic): Indicates that the servers are in a state that requires
corrective action, but does not affect overall system health. For example, the firmware running on
a server is not at the required level or not compliant.
– Unknown (gray band on the graphic): Indicates that the state of the server is unknown.
• Under Server Utilization is Services, a pie chart displays the total number of servers utilized in services
and the available servers that can be used in percentage.
– Servers In Use (blue band on the pie chart) — Indicates the percentage of servers that are in use.
To view the number of servers used, move the mouse pointer over the band.
– Servers Available (gray band on the graphic) — Indicates the percentage of servers that are
available for deployment. To view the number of servers that are available, move the mouse
pointer over the band.
• Under Utilization by Server Pool, each bar represents a server pool and displays the number of
servers used and available in that server pool.
• Under Total Storage Capacity, a pie chart displays the total storage capacity utilized and available in
percentage.
– Storage Used (blue band on the graphic) — Indicates total used storage disk space in percentage.
To view the percentage of used storage disk space, move the mouse pointer over the band.
– Storage Available (gray band on the graphic) — Indicates total available storage space in
percentage. To view the percentage of available storage space, move the mouse pointer over the
band.
• Under Capacity by Storage Group, each bar represents one of the following storage groups and
displays the storage capacity used or available on the particular storage group.
– Dell EqualLogic Group
– Dell Compellent Arrays
– NetApp Arrays
The Dashboard also displays the following information in the right pane:
• Licensing Information — Displayed when any one of the of the following events occur:
– The number of resources managed by ASM exceeds the valid license count.
16
– The trial license expires.
• Deploy Service from Recent Templates — Enables you to view the most recent published templates
and use it for deployment. Click View All to view all the templates.
NOTE: Standard users are allowed only to view the recent templates that they have created.
• Recent Activity — Lists the most recent user and system initiated activities. Click View All to view all
the activities in the Logs page.
Additionally, following information is displayed on the Disover pane.
– Discovered Resources — Indicates the number of resources that are discovered in ASM.
– Pending Resources — Indicates that the discovery is in progress for the number of resources
displayed.
– Errors — Indicates that ASM is unable discover the number of resources displayed due to some
errors.
• Links to learn more about service deployments and templates.
On this page, you can:
• Click the service name to view the details information about the service. For more information, see
Viewing Service Details.
• View the most recent published templates and use it for service deployment.
Related Links
Viewing service details
Deploy service
Service states
Service states
State Icon Description
Error Indicates service deployed is failed due to some issues.
Warning Indicates that the one of more resources that are part of a
service is in a state that requires corrective action, but does
not affect overall system health. For example, the firmware
running on the resource is not at the required level or not
compliant.
In Progress Indicates service deployment is in progress.
Deployed Indicates service deployed is completed successfully.
Related Links
Dashboard
17

5
Services
A service is a deployment of a published template.
NOTE: Standard users are allowed to view only the services that they have created or for which they
have permissions.
The Services page displays the services that are in following states in both Graphical and Tabular view.
• Error Services — Indicates the services for which the deployment process is incomplete due to errors.
• Deployed Services — Indicates the services that are deployed successfully.
• In Progress Services — Indicates the services for which deployment is in progress.
• Warning Services — Indicates that the one or more resources in a service are in a state that requires
corrective action.
To switch between Graphical and Tabular view, click the Graphic icon or Table icon next to the
View As option on the top of the Services page.
To view the services based on a particular service state, select one of the following options from the
Filter By drop-down list. Alternately, in the Graphical view, click the graphic in a particular state.
• All
• Error
• Deployed
• In progress
• Warning
In the Graphical view, each graphics represents a service and has the name of the service at the bottom
of the graphic. The state icon on the graphic indicates the state of the service. The components in blue
indicate the component types that are included in the service for deployment. The components that are
in gray indicate the component types that are not included in the service.
In the Tabular view, the following information about the service is displayed.
• Status — Indicates the status of the service.
• Name — Indicates the name of the service.
• Deployed By — Indicates the name of the user who deployed the service.
• Deployed On —Indicates the date and time when the service is deployed.
Click the service in the Tabular or Graphical view to view the following information about the service in
the right pane:
• Service name and description to identify the service.
18

• Name of the user who deployed the service.
• Date and time when the service is deployed.
• Displays the name of the reference template used in the service.
• Lists the number of resources included in the service for deployment, based on the following
component types:
– Application
– Virtual Machine
– Cluster
– Server
– Storage
From the Service page, you can:
• Click Deploy New Service to deploy new service.
NOTE: Standard users are allowed to deploy services that they have created or for which they
have permissions.
• Click View Details in the right pane to view more details about the service.
• Click Update Firmware to update the firmware of one or more servers in the service that are not
compliant.
• Click Export to File to export the service details to .csv file.
NOTE: Standard users are allowed only to export the details of the services that they have
created or for which they have granted permission.
Related Links
Viewing service details
Deploy service
Deploy service
NOTE: You cannot deploy a service using a template that is in draft state. Publish the template
before you use the template to deploy a service.
To deploy a service:
1. In the left pane, click Services.
The Services page is displayed.
2. On the Services page, click Deploy New Service.
The Deploy Service wizard is displayed.
3. In the Service Information page, perform the following steps, and click Next.
a. From the Select Template drop-down list, select the template to deploy a service.
b. Enter the Service Name (required) and Service Description (optional) that identifies the service.
19

c. If you want to update the firmware running on the servers that are in the service, select Manage
Server Firmware check box, and from the Use Firmware Repository drop-down, select a
firmware repository.
NOTE: Changing the firmware repository could update the firmware level on servers for
this service. Firmware on shared devices will still be maintained by the global default
firmware repository.
d. If you want to grant permission for Standard users to use this service, under Manage Service
Permissions, select the In addition to all Admins, grant Standard Users access to this service
check box, and perform one of the following actions:
• To grant access to all Standard users, select All Standard Users option
• To grant access only to specific Standard users, select Specific Standard Users option, and
perform the following tasks:
a. Click Add User (s) to add one or more Standard users to the list.
To remove a Standard user from the list, select the Standard user and click Remove
User(s).
b. After adding the Standard users, select or clear the check box next to the Standard
users to grant or block access to the service.
4. In the Deployment Settings page, configure the require settings, and click Next. Additionally, in the
Deploy Setting page, click View All Details to view the details of the components that are part of the
service
5. In the Schedule Deployment page, perform one of the following actions:
• Deploy Now — Select this option to deploy the service immediately.
• Schedule Later — Select this option and enter the date and time to deploy the service.
Viewing service details
The <Service Name> Details page displays the state of the service at component level in Topology and
Tabular view.
To switch between Topology and Tabular view, click the topology icon or graphic icon next to
View As option on top of the <Service Name> Details page.
• In the Topology view, under Service Resources, you can view the topology of the components and
connections as structured in a selected service template.
In the Topology view, the color of the component icons indicate the following:
– The red component icon indicates the service is not deployed on a particular component due to
some issues.
– The blue component icon indicates the service is successfully deployed on the components.
– The light blue component icon indicates the service deployment is in progress.
– The yellow icon indicates particular component requires firmware update.
To view the following information about the resources, click the corresponding component icons.
20

– IP Address. (Click the IP address of a Dell resource to open the Element Manager.)
– Hypervisor IP Address (for servers only)
– Deployment state
• In the Tabular view, under Service Resources, the following information is displayed based on the
resource types in the service.
– Under Applications, you can view the following information about the application deployed on
the virtual machines:
* Name
* IP Address
* Asset/Service Tag
– Under Virtual Machines, you can view the following information about the virtual machines
configured on the clusters:
* Hostname
* OS Type
* CPUs
* Disk Size
* Memory
– Under Clusters, you can view the following information about the clusters created on VMware
vCenter or Microsoft virtualization environments:
* IP Address
* Asset/Service Tag
* Manufacturer
* Model
– Under Physical Servers, you can view the following information about the servers that are part of a
service
:
* IP Address
* Hypervisor IP Address
* Asset/Service Tag
* Manufacturer
* Model
– Under Storage, you can view the following information and view the volumes created on a
particular storage and the size of the volumes.
* IP Address
* Asset/Service Tag
* Manufacturer
* Model
• Under Service Information, you can view the following information:
– Name of the service
21
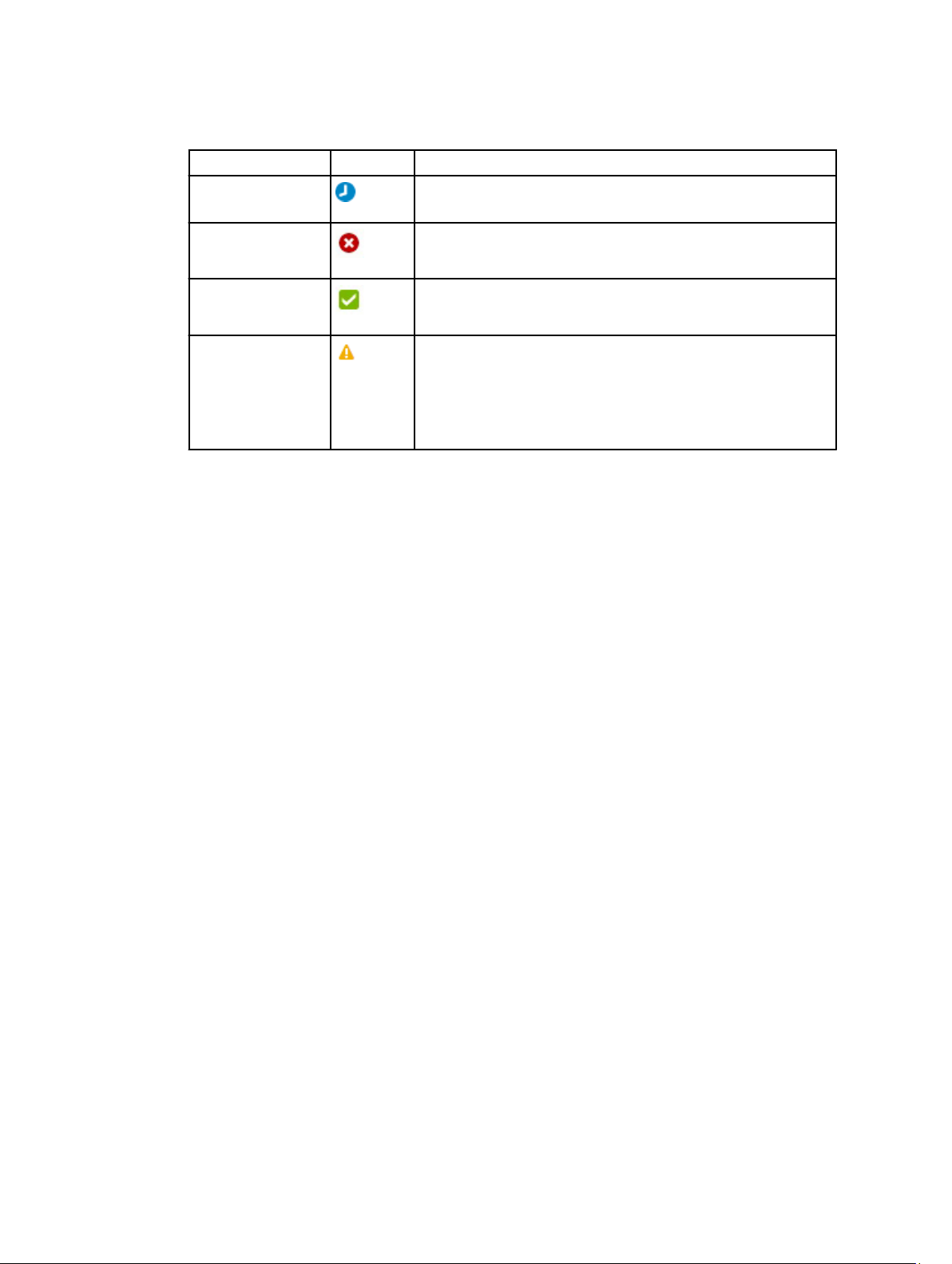
– State — Displays one of the following state based on the deployment status of a service.
Service State Icon Description
In Progress Indicates service deployment is in progress.
Error Indicates service deployment is failed due to some issues.
Successful Indicates service deployment is completed successfully.
Warning Indicates that the one of more resource that are part of a
service is in a state that requires corrective action, but does
not affect overall system health. For example, the firmware
running on the resource is not at the required level or not
compliant.
– Deployed By — Displays the name of the user who deployed the service.
– Deployed On — Displays the date and time when the service is deployed.
– Reference Template — Displays the name of the reference template used in the service.
– Reference Firmware Repository — Displays the reference firmware repository.
– User Permissions — Displays one of the following:
* Enabled — Indicates that the permission is granted for one or more Standard users to deploy
this service.
* Disabled — Indicates that the permission is not granted for Standard users to deploy this
service.
Under Service Actions, you can:
• Click Delete to delete a service or resources in the service.
• Click Retry to redeploy a failed service.
• Click View All Settings to view the settings configured on the resources in a service for deployment.
• Click Export to File to export the service details to a .csv file.
Under Resource Actions, you can:
• From the Add Resources drop-down list, select the type of the resources that you want to add to the
service.
• Click Migrate Server(s) to migrate a server’s settings to another server in a designated server pool.
Alternatively, to migrate a server’s settings, click the server component icon on the topology view, and
click Migrate Server(s).
• Click Delete Resources to delete resources from a service.
Under Firmware Actions, click View Firmware Compliance Report link to view the firmware compliance
report.
In the Recent Activity section, click View Components or View Logs to either view the deployment state
of the resources or view the log entries.
Related Links
22

Deploy service
Exporting service details
Exporting service details
Updating firmware
Retry failed service
Adding components to existing service deployments
Deleting service
Deleting resources from service
Migrating servers
Component deployment states
After you deploy a service, ASM assigns one or more states to the components based on the deployment
status.
The following are different types of states displayed at a component level:
• Pending — Indicates that, within a service, the deployment is not yet started for the particular
components.
• In Progress — Indicates that, within a service, service deployment is in progress for the particular
components.
• Complete — Indicates that, within a service, the service deployment is completed for the particular
components.
• Error — Indicates that, with in a service, service deployment is not successful for the particular
components.
• Cancel — Indicates that, within a failed service, deployment is not yet started for the particular
components and canceled due to other component (s) deployment failure.
Editing service information
To edit the information of a service:
1. In the left pane, click Services.
2. On the Services page, click the service, and in the right pane click View Details.
3. On the <service name> Details page, in the right pane, next to Service Information section title, click
Edit.
4. In the Edit Service Information dialog box, perform the following steps:
a. Modify the Service Name and Service Description that identifies the service.
b. If you want to update the firmware running on the servers that are part of the service, select
Manage Server Firmware check box, and from the Use Firmware Repository drop-down list,
select a firmware repository.
NOTE: Changing the firmware repository could update the firmware level on servers for
this service. Firmware on shared devices will still be maintained by the global default
firmware repository.
23

c. If you want to grant permission for Standard users to use this service, under Manage Service
Permissions, select the In addition to all Admins, grant Standard Users access to this service
check box, and perform one of the following actions:
• To grant access to all Standard users for this service, select All Standard Users option.
• To grant access only to specific Standard users for this service, select Specific Standard
Users option, and perform the following tasks:
a. Click Add User (s) to add one or more Standard users to the list.
To remove the Standard user from the list, select the Standard user and click Remove
User(s).
b. After adding the Standard users, select or clear the check box next to the Standard users
to grant or block access to the service.
Deleting service
To delete a service, perform the following steps:
NOTE: Standard users are allowed only to delete the service that they have deployed.
1. In the left pane, click Services.
2. On the Services page, click a service, and then in the right pane, click View Details.
3. On the <Service Name> Details page, under Service Actions in the right pane, click Delete.
4. In the Delete Service dialog box, perform the following steps:
NOTE: Deleting a shared resource could affect other running services.
a. Select Return Servers(s) to Resource Pool check box to return the IP/IQNs assigned to the
servers that were a part of the service and return the servers to the server pool. After the service
is deleted, the Dell servers that were part of the deleted service are rebooted, and the servers are
set to PXE boot ready for the next deployment.
b. Select Delete VM(s) check box to delete the virtual machines created on the clusters.
c. Select Delete Cluster(s) and Remove from Hyper-V and vCenter check box to remove the
clusters created on Hyper-V or vCenter and removes the Hyper-V and vCenter instances.
d. Select Delete Storage Volume(s) check box to remove the storage volumes created during the
service deployment.
Exporting service details
This feature enables you to export the service details to a .csv file.
1. In the Services page, click Export to File in the right pane.
2. Open or save the file.
Retry failed service
You can redeploy a service for which deployment is not successful due to some issues.
NOTE: Standard users can only redeploy a failed service that they have deployed.
1. In the left pane, click Services.
24

The Services page is displayed.
2. Select an error service and click View Details in the right pane.
The <Service Name> Details page is displayed.
3. In the right pane, under Service Actions, click Retry.
Click Yes when a confirmation message appears.
View Service Deployment Settings
The Service Deployment Settings page displays the settings configured on the resources in a service for
deployment.
• For more details about the Application properties, see Application Settings
• For more details about the Virtual Machine properties, see Virtual Machine Settings
• For more details about the Cluster properties, see Cluster Settings
• For more details about the Server properties, see Server Settings
• For more details about the Storage properties, see Storage Settings
Migrating servers (service mobility)
In ASM, service mobility refers to the capability to migrate server’s BIOS, NICs, storage connectivity, and
assigned identity information to another server in a designated server pool, in order to perform planned
maintenance or service activities or to respond to a hardware fault or failure issue.
Currently, migration is supported only for boot form SAN server, and it is supported only for bare metal
OS installs of Linux or Windows. It is not supported for ESXi. Therefore, the migration will not affect the
virtual machines.
It is recommended only to migrate between identically configured hardware. Different operating systems
may not boot correctly on hardware that is different.
Migration prerequisites
• ASM does not install operating systems on the boot from SAN volume. Therefore, you must install
operating system on the servers prior to migration.
• Make sure that the free servers are available in the server pool for migration, and it is compatible.
• During the migration, the operating systems will not be booted. Therefore, it is recommended to shut
down the server before migrating the boot from SAN image.
• It is recommended configure a server pool that has servers with same model, RAID, and networking
devices, including the specific slot to which network resources are connected.
Related Links
Migrating servers
Migrating servers
NOTE: Standard users can migrate the servers that are part of the server pool for with they have
permission.
25

You can migrate only one server at a time. However, after a successful migration, additional servers can
be migrated. During migration, ASM will try to identify an exact match for the hardware. If it is not
available in the server pool, a different hardware can be selected.
You may encounter some issues during configuration of the new servers. In such scenarios, you can
address the issues preventing the proper configuration of the target server, and retry the deployment.
To migrate a server’s configuration to a different server pool:
1. In the Service Details page, perform one of the following actions:
• In the topology view, click a server component, and click Migrate in the box that is displayed
• In the topology view, click a server component, and click Migrate in the right page.
2. In the Migrate Server(s) dialog box, in the State column, select the server, and then in the New
Server Pool
column, select the designated server pool to migrate.
Adding components to existing service deployments
After a successful service deployment, you can add one or more application, storage, server, cluster, and
virtual machine components to an existing service.
NOTE: Standard users are allowed only to add components to a service for which they have
permission.
NOTE: You cannot add a component of a particular type if the component type is not a part of the
service reference template.
NOTE: You cannot add components to a service for which deployment is in progress or to a failed
service deployment.
To add components to a service:
1. In the left pane, click Services.
The Services page is displayed.
2. Select a service and click View Details in the right pane.
The <Service Name> Details page is displayed.
3. In the right pane, under Resource Actions, from the Add Resources drop-down menu, click one of
the following components:
• Application — Enables you to add one or more applications to the service.
• VM — Enables you to add one or more virtual machines to the service.
• Cluster — Enables you to add one or more clusters to the service.
• Server — Enables you to add one or more servers to the service.
• Storage — to add one or more storage components to the service.
Related Links
Adding storage to existing service
Adding servers to existing service
Adding Virtual Machines to existing service
Adding clusters to existing service
Adding applications to existing service
26

Adding applications to existing service
To add applications to an existing service:
1. On the Add Application(s) page, add the applications to the existing service in one of the following
ways:
• If you want to clone an existing application settings to the applications that you want to add to
the service, next to New Component Settings, click Duplicate, and perform the following steps:
1. From the Resource to Duplicate drop down list, select an application that is part of the
service.
2. In the # of Instances box, enter the number of application instances that you want to add to
the service. Click Continue.
3. In the Component Name box, enter the name for the corresponding applications.
• If you want to add new application, next to New Component Settings, click New, and perform
the following steps:
1. From the Select a Component drop-down list, select one of the following cluster types:
– mssql
– citrix_xd7
– linux_postinstall
– mssql2012
– windows_postinstall
2. Under Associated Resources, to associate the newly added application component to the
existing components in the service, select the components to associate.
3. Click Continue.
Based on the component type, specific settings and properties appear automatically that are
required and can be edited. For more information specific to component type settings, see
Component Types.
2. Click Save.
Adding clusters to existing service
To add clusters to an existing service:
1. On the Add Cluster(s) page, add the clusters to the existing service in one of the following ways:
• If you want to clone an existing cluster configuration to the clusters that you want to add to the
service, next to New Component Settings, click Duplicate, and perform the following steps:
1. From the Resource to Duplicate drop-down list, select a cluster to clone.
2. In the # of Instances box, enter the number of cluster instances that you want to add to the
service. Click Continue.
3. In the Component Name box, enter the cluster name for the corresponding clusters.
• If you want to add new cluster component, next to New Component Settings, click New, and
perform the following steps:
27

1. From the Select a Component drop-down list, select one of the following cluster types:
– VMWare Cluster
– Hyper-V Cluster
2. Under Associated Resources, to associate the newly added cluster to the existing
components in the service, select the components to associate.
3. Click Continue.
Based on the component type, specific settings and properties appear automatically that are
required and can be edited. For more information specific to component type settings, see
Component Types.
2. Click Save.
Adding Virtual Machines to existing service
To add virtual machines to an existing service:
1. On the Add VM(s) page, add the virtual machines to the service in one of the following ways:
• If you want to clone an virtual machine configuration to the virtual machines that you want to
add to the service, next to New Component Settings, click Duplicate, and perform the following
steps:
1. From the Resource to Duplicate drop-down list, select a virtual machine component.
2. In the # of Instances box, enter the number of virtual machine instances that you want to
add to the service. Click Continue.
3. In the Component Name box, enter the virtual machine name for the corresponding
components.
4. In the Host Name box, enter the host name of the virtual machines.
• If you want to add new virtual machine instance, click New, and perform the following steps:
1. From the Select a Component drop-down list, select on of the following:
– vCenter Virtual Machine
– Clone vCenter Virtual Machine
– Clone Hyper-V Virtual Machine
2. Under Associated Resources, to associate the newly added virtual machine component to
the existing components in the service, select the components to associate.
3. Click Continue.
Based on the component type, specific settings and properties appear automatically that are
required and can be edited. For more information specific to component type settings, see
Component Types.
2. Click Save.
Adding servers to existing service
To add a server to an existing service:
On the Add Server(s) page, add the servers to the service in one of the following ways:
28

• If you want to clone an existing server configuration to the servers that you want to add to the
service, next to New Component Settings, click Duplicate, and perform the following steps:
1. From the Resource to Duplicate drop down list, select a server.
2. In the # of Instances box, enter the number of server instances that you want to add to the
service. Click Continue.
3. In the Component Name box, enter the name of the corresponding servers.
4. In the Server Pool box, enter the name of the server pool.
5. In the Host Name box, enter the host name for the corresponding servers.
• If you want to add new server component, next to New Component Settings, click New, and
perform the following steps:
1. From the Select a Component drop-down list, select a server component.
2. Under Associated Resources, perform one of the following actions:
– When you are adding a new component to a template, if you want to associate the
component with all the existing components, select Associate All resources option.
The new component automatically associated with the existing components.
– When you are adding a new component to a template, if you want to associate the
component only with the selected components, select Associate Selected Resources,
and then select the components to associate as needed.
Based on the component type, specific settings and properties appear automatically that are
required and can be edited. For more information specific to component type settings, see
Component Types.
When you redeploy an existing service after adding one or more servers, the following states are
displayed in the Resources page:
• The state of the existing server resources that are part of the service changes from “Deployed” to
‘Deploying”, and then changes to “Deployed” after the deployment is complete.
• The state of the new server changes from “Available” to “Reserved”. Once the deployment starts, the
state changes to “Deploying”. If the deployment is successful, the state changes to “Deployed”. If the
deployment is not successful, the state changes to “Error”.
Adding storage to existing service
To add storage components to an existing service:
1. On the Add Storage page, add the storage to the service in one of the following ways:
• If you want to clone an existing storage configuration to the storage that you want to add to the
service, next to New Component Settings, click Duplicate, and perform the following steps:
1. From the Resource to Duplicate drop down list, select a storage component.
2. In the # of Instances box, enter the number of storage instances that you want to add to the
service. Click Continue.
3. In the Component Name box, enter the storage name for the corresponding components.
29

4. In the Storage Volume box, enter the volume name in the storage.
• If you want to add new server component, next to New Component Settings. click New, and
perform the following steps:
1. From the Select a Component drop-down list, select one of the following storage
components:
– Compellent
– EqualLogic
– NetApp
2. Under Associated Resources, to associate the newly added storage component to the
existing components in the service, select the components to associate.
3. Click Continue.
Based on the component type, specific settings and properties appear automatically that are
required and can be edited. For more information specific component type settings, see
Component Types.
2. Click Save.
Deleting resources from service
1. On the Delete Resources from Service page, select the resources that you want delete from the
service.
2. Click Delete.
NOTE: Deleting a shared resource may affect other running services.
30
 Loading...
Loading...