Page 1

Active Fabric Manager (AFM)
Plug-in for OpenStack Guide 2.0
Page 2

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the
problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
© 2013 Dell Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Trademarks used in this text:
PowerConnect
of Dell Inc.
®
AMD
Devices, Inc.
either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Red Hat
™
OpenManage
,
®
Intel
Pentium
is a registered trademark and
,
Microsoft
®
Enterprise Linux
®
are registered trademarks of Novell Inc. in the United States and other countries.
Corporation and/or its affiliates.
™
Dell
, the Dell logo,
™
EqualLogic
,
®
®
Xeon
Core
,
,
AMD Opteron
®
Windows
,
®
are registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries.
Windows Server
,
®
,
Citrix
Xen
®
and
®
Dell Boomi
™
Compellent
,
Celeron
™
,
XenServer
Systems, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries.
trademarks or trademarks of VMware, Inc. in the United States or other countries.
™
Dell Precision
,
™
KACE
,
®
are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
AMD Phenom
,
®
Internet Explorer
,
®
and
VMware
™
XenMotion
®
,
™
™
and
vMotion
,
FlexAddress
,
AMD Sempron
®
MS-DOS
,
®
are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Citrix
®
,
vCenter
™
OptiPlex
™
Force10
,
™
®
Windows Vista
,
®
is a registered trademark of Oracle
Oracle
®
,
vCenter SRM
®
is a registered trademark of International
IBM
™
Latitude
,
are trademarks of Advanced Micro
™
Venue
,
PowerEdge
,
™
and
®
Active Directory
and
™
and
vSphere
Business Machines Corporation.
2013 - 12
Rev. A0X
™
Vostro
Red Hat
Novell
PowerVault
,
™
are trademarks
®
are
®
and
®
and
SUSE
®
are registered
™
,
®
Page 3

Contents
1 AFM Plug-in Overview ...............................................................................................................5
OpenStack Networking Deployment Use Cases...................................................................................................... 6
Supported Deployment Topologies.......................................................................................................................... 7
Pre-requisites for Using the Plug-In......................................................................................................................... 7
Key Considerations...................................................................................................................................................8
Using the AFM Plug-in for OpenStack......................................................................................................................8
2 Step 1: Installing the AFM Plug-in............................................................................................ 9
3 Step 2: Configuring the AFM Plug-in......................................................................................11
4 Step 3: (Optional) Configuring Static Switch Server Connectivity....................................13
5 Step 4: Installing the LLDP and Port Bonding ......................................................................15
Step 4.1: Installing the LLDP Package ................................................................................................................... 15
Step 4.2: Install and Configure Port Bonding ......................................................................................................... 15
6 Step 5: Installing the Dell OVS Agent.....................................................................................19
7 Step 6: Configuring the Dell OVS Agent.................................................................................21
Step 1: Creating the Physical and Integration bridge.............................................................................................21
Step 2: Configuring the Dell OVS Plug-in................................................................................................................ 21
Step 3: Configuring the Rootwrap ..........................................................................................................................22
Step 4: Restart the Dell OVS Agent on Nova Compute Node or Network Node.....................................................23
Step 5: Configure the Nova Compute Node or Network Node .............................................................................. 23
8 Step 7: Connecting to the AFM Server.................................................................................. 25
Step 1: Configure the AFM server IP address and Port..........................................................................................25
Step 2: Configure the AFM User Credentials for the AFM Plug-in..........................................................................25
9 Uninstalling the AFM Plug-in for OpenStack........................................................................27
10 Uninstalling the Dell OVS Agent........................................................................................... 29
Page 4

4
Page 5

1
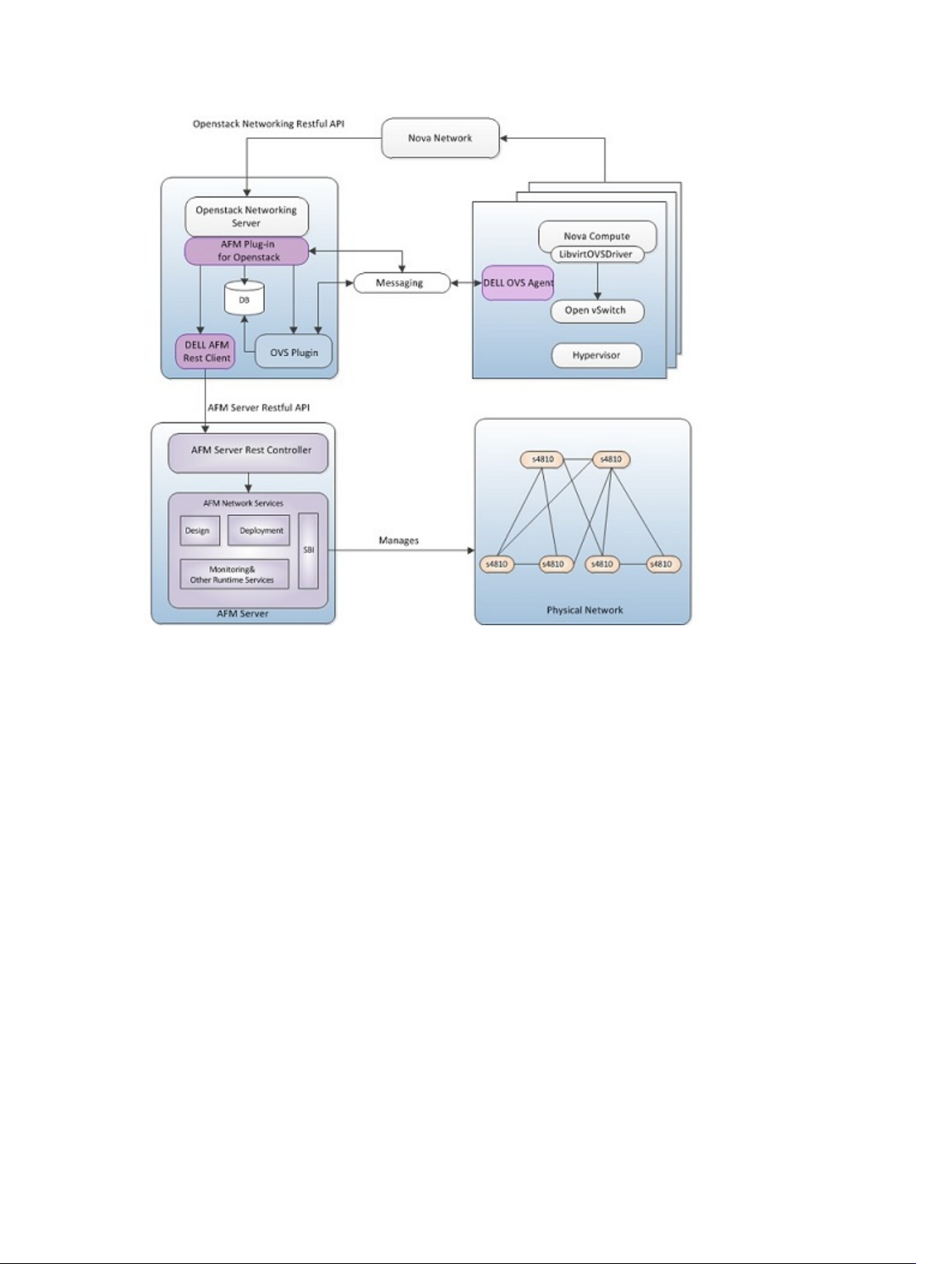
AFM Plug-in Overview
Use the Active Fabric Manager (AFM) plug-in for OpenStack to configure VLAN interfaces on the Dell Force10 Network
switches to orchestrate virtual networks through the AFM Restful APIs. The AFM plug-in enables you to configure
VLANs for a Layer 2 fabric, which is created by AFM administrators. It delegates the physical network configuration
logic to the AFM server by making requests to the AFM server through AFM Restful APIs. Upon receiving requests from
the OpenStack server restful API, the Dell Open vSwitch (OVS) agent and AFM plug-in create and maintain the logical
port infrastructure for the administrator to tag and untag VLANs.
There are 3 components to managing the physical, virtual networks, and bridges. The first component, AFM, manages
the physical network. The second and third components, the Dell OVS agent and AFM Plug-in for OpenStack, manages
the virtual networks and bridges. The AFM Plug-in runs on the controller. The Dell OVS agent runs on a Nova compute
and network node.
The AFM plug-in does the following:
• Plugs into the standard OpenStack Pluggable Networking Architecture.
• Allows the OpenStack Neutron server to communicate with AFM server.
• Integrates with the DELL AFM (Active Fabric Manager) through Restful APIs
• Provides dynamic VLAN configuration to fulfill OpenStack Cloud services Networking requirements.
• Provides dynamic discovery of Switch-Server connections through LLDP.
• Integrates with the AFM Layer 2 VLT topology to achieve switch-server connection redundancy using ‘Port Bonding’.
5
Page 6
OpenStack Networking Deployment Use Cases
The AFM plug-in supports the following OpenStack use cases:
1. Single Flat Network — All VMs can talk to each other via the shared network and to external network through the
physical route. In the simplest use case, a single OpenStack Networking network exists. This is a "shared" network,
meaning it is visible to all tenants through the OpenStack Networking API. Tenant VMs have a single NIC, and
receive a fixed IP address from the subnet(s) associated with that network.
2. Multiple Flat Network — VMs share the same shared network and can talk to each other and to VMs in other
shared networks and to external networks through the physical router. This use case is very similar to the above
Single Flat Network use case, except that tenants see multiple shared networks via the OpenStack Networking API
and can choose which network (or networks) to plug into.
3. Mixed Flat and Private Network —All VMs can talk to each other through the shared network and to external
networks through the physical router. VMs in a Tenant-Private Network can talk to each other but not to other
Tenant-Private Networks or external. This use case is an extension of the above flat network use cases in which
tenants also optionally have access to private per-tenant networks. In addition to seeing one or more shared
networks via the OpenStack Networking API, tenants can create additional networks that are only visible to users
of that tenant. When creating VMs, those VMs can have NICs on any of the shared networks and/or any of the
private networks belonging to the tenant. This enables the creation of "multi-tier" topologies using VMs with
multiple NICs. It also supports a model where a VM acting as a gateway can provide services such as routing,
NAT, or load balancing.
6
Page 7
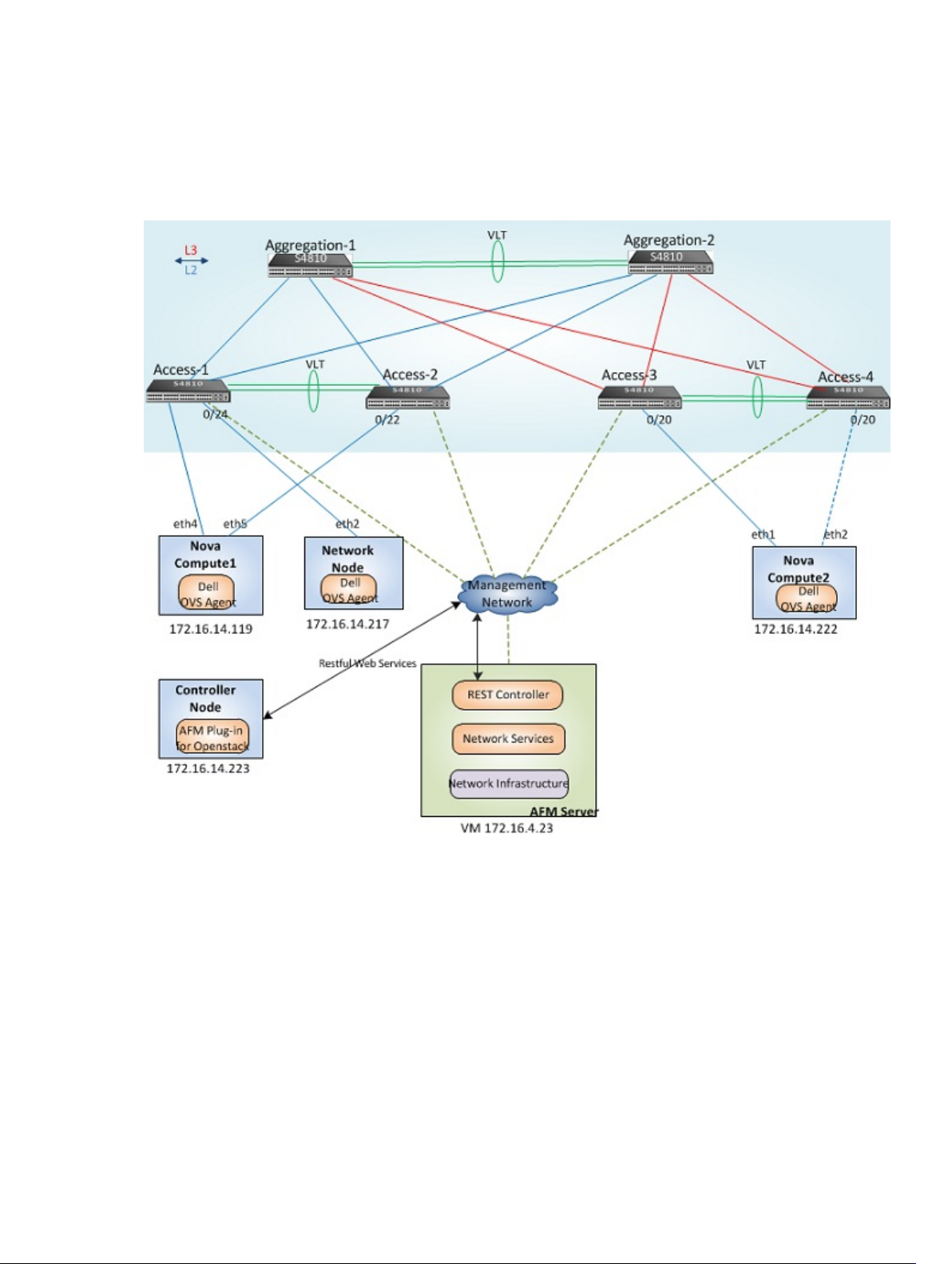
Supported Deployment Topologies
The AFM Plug-in supports the following topologies: Six S4810 switches with two aggregation nodes and four access
nodes.
The AFM Plugin is installed on the OpenStack Controller Node. The Dell OVS Agent is installed on each Nova Compute
node and Network node. At runtime, the OpenStack Neutron Server communicates with the AFM Server through a
restful API to manage the physical topology.
Pre-requisites for Using the Plug-In
Before you use the AFM plug-in for OpenStack:
• Install and configure OpenStack software, Ubuntu 12.0.4 (LTS). For information about this topic, see http://
docs.openstack.org/grizzly/basic-install/apt/content/
A typical deployment scenario is one controller node, one network node, and a series of nova compute nodes. The
OpenStack Neutron server is installed on the controller node. After the installation, make sure all the services are
started on all the nodes and the VMs can be launched before you apply the AFM plug-in for OpenStack.
7
Page 8

• Ensure that the DNS is enabled in the OpenStack Neutron server.
• Ensure that the AFM administrator has created a fabric with the Openstack Neutron Managed option enabled at the
Fabric Name and Type screen using the AFM Design Wizard and has deployed a complete fabric that is ready for
service.
Key Considerations
When using the AFM plug-in consider the following:
• The AFM Plug-in for OpenStack resides on the OpenStack Neutron server.
• The AFM plug-in supports VLANs.
• The AFM plug-in is supported with fabrics that have 10 Gb Access switches.
Using the AFM Plug-in for OpenStack
To use the AFM plug-in for OpenStack:
1. Install the AFM software and start it.
2. Deploy the physical fabric network using the AFM.
3. Install OpenStack.
4. Install and configure the AFM plug-in for OpenStack onto the OpenStack Controller node.
5. Install the LLDP package (for dynamic discovery of server switch connectivity) and Port Bonding in the compute
and network node.
6. Install and configure the Dell OVS Agent in the compute and network node.
7. Configure the OpenStack Neutron server and the AFM plug-in.
8. Use the OpenStack GUI to create network and VM instances..
8
Page 9

Step 1: Installing the AFM Plug-in
To install the AFM plug-in for Openstack onto the Controller node where the Neutron server is located:
1. Obtain the AFM Plug-in for Openstack tar file, AFMOpenStackPlugin2.0.0.0.tar.gz from iSupport. See the Release
Notes.
2. On the Openstack server, go to the /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/ directory.
3. Untar the AFMOpenStackPlugin2.0.0.0.tar.gz. file using the following syntax:
tar –zxvf AFMOpenStackPlugin2.0.0.0.tar.gz
After you untar this file, the AFM plug-in is located at the /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/quantum/plugins/
directory.
4. Make a backup copy of the quantum-server.conf file. The file is located at the /etc/init/ directory.
5. Add the --config-file /etc/quantum/plugins/dell/dell_quantum_plugins.ini \ statement in the quantum-server.conf
file as shown below.
exec start-stop-daemon --start --chuid quantum --exec /usr/bin/quantum-server -- \
--config-file /etc/quantum/quantum.conf \
--config-file /etc/quantum/plugins/dell/quantum-server.conf \
--log-file /var/log/quantum/server.log $CONF_ARG
6. Make a backup copy of the quantum.conf file. This file is located in the /etc/quantum/ directory.
7. Navigate to the /etc/quantum/ directory and modify the quantum.conf file with the following content:
2
core_plugin = quantum.plugins.dell.network_plugin.PluginV2
8. In the /etc/quantum/plugins/dell directory, create the dell_quantum_plugins.ini file with the following content. The
default is to use dynamic port mapping (LLDP) and the parameter static_config is set false. In this file, also, add the
network_node_hostname with the network node hostname. For example, network_node_hostname=dev1openstack01
[DELL_PLUGINS]
#vswitch_plugin = quantum.plugins.openvs
afm_plugin = quantum.plugins.dell.afm.afm_plugin_v2.AFMPlugin
vswitch_plugin = quantum.plugins.openvswitch.ovs_quantum_plugin.OVSQuantumPluginV2
[DELL]
#model_class=quantum.plugins.dell.models.virt_phy_sw_v2.VirtualPhysicalSwitchModelV2
#static_config=False
network_node_hostname=dev1-openstack01
NOTE: We recommend that you use dynamic port mapping.
9. (Optional) If you want to use static mapping set the static_config= True and then add the port mapping entries
using the PORT_MAPPING syntax. .
The following example shows how to add port mapping entries.
9
Page 10

[PORT_MAPPING:<switch1 ip>]
<host1 ip> = <switch port1>
<host2 ip> = <switch port2>
<host3 ip> = <switch port5>
[PORT_MAPPING:<switch2 ip>]
<host1 ip> = <switch port1>
<host2 ip> = <switch port2>
<host3 ip> = <switch port5>
10
Page 11

3
Step 2: Configuring the AFM Plug-in
To configure the OpenVSwitch to support the AFM Plug-in:
1. On the Controller where the Neutron server is located, set the parameter in the ovs_quantum_plugin.ini file in
the /etc/quantum/plugins/openvswitch/ directory as shown in the following example:
sql_connection = mysql://<
2. Set the OpenVSwitch plugin to the VLAN mode and the range of VLAN for each network as shown in the following
example:
tenant_network_type = vlan
enable_tunneling = False
network_vlan_ranges = default: <vlan_min>:<vlan_max>
3. Restart the Neutron server:
root@dev1-openstack06:~# service quantum-server restart
username
>:<
password
>@<
mysql_host
>/ovs_quantum?charset=utf8
For more information about configuring OpenVSwitch plugin, see the
docs.openstack.org/trunk/openstack-network/admin/content/index.html
Openstack Network Admin Guide
at http://
11
Page 12

12
Page 13

4
Step 3: (Optional) Configuring Static Switch Server Connectivity
The AFM Plug-in supports dynamic discovery of server switch connectivity using LLDP and static configuration of server
switch connectivity. The Dell OVS agent supports dynamic discovery of server switch connectivity on the Nova Compute
Node or Network Node. Dell recommends that you use dynamic discovery. For information about dynamic discovery,
see Installing the LLDP Package.
To configure static server switch connectivity, include the switch-server binding information in the
dell_quantum_plugins.ini file in the /etc/quantum/plugins/dell directory.
Static Switch Server Connectivity Example:
The following static switch server connectivity example shows you how to add the PORT_MAPPING parameter to the
dell_quantum_plugins.ini file with the following topology:
• Compute node, dev-openstack05, connects to the switch with an IP address of 172.16.12.232 through port 0/22
• Compute node, dev-openstack03, connects to the switch with an IP address of 172.16.12.238 through port 0/22
• Network node, dev-openstack01, connects to the switch with an IP address of 172.16.12.232 through port 0/24
[DELL_PLUGINS]
afm_plugin = quantum.plugins.dell.afm.afm_plugin_v2.AFMPlugin
vswitch_plugin = quantum.plugins.openvswitch.ovs_quantum_plugin.OVSQuantumPluginV2
[DELL]
model_class=quantum.plugins.dell.models.virt_phy_sw_v2.VirtualPhysicalSwitchModelV2
static_config=True
network_node_hostname=dev1-openstack01
[PORT_MAPPING:172.16.12.232]
dev-openstack05 = 0/22
dev-openstack01 = 0/24
[PORT_MAPPING:172.16.12.238]
dev-openstack03 = 0/22
13
Page 14

14
Page 15

Step 4: Installing the LLDP and Port Bonding
Before you install and configure the Dell OVS agent install the following on the Nova compute node and network node:
• LLDP package.
NOTE: Use the LLDP package for dynamic discovery of server switch connectivity. If you are using static
switch server connectivity, see Configuring Static Switch Server Connectivity.
• Port Bonding
Step 4.1: Installing the LLDP Package
To install LLDP on the Nova compute node. :
1. On the Nova compute node and network node, login as root.
2. Install the lldpd package using the apt-get install lldpd command.
3. Start the lldpd package using the service lldpd start command.
4. Install lldpad ( lldptool) using the apt-get install lldpad command.
5. Verify the successful installation of LLDP package on the Nova compute node and network node using the lldpctl
command to detect connected lldp neighbors.
Step 4.2: Install and Configure Port Bonding
5
When you connect to a Nova compute node and network node to the fabric that the Active Fabric Manager (AFM)
manages, you can connect to the Ethernet ports to the two leaf (or access) switches in the AFM supported topologies.
These two connections provide redundancy.
When you have two connections from a Nova compute node and network node to the switches, create a Ubuntu
Bonding port so that the compute node can use the redundancy from these two ports. For information about port
bonding, see https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UbuntuBonding?action=show&redirect=LinkAggregation.
To install and configure port bonding:
1. On the Nova compute node, install port bonding using the following command:
sudo apt-get install ifenslave-2.6
2. Verify that bonding module is in the kernel system is in the /etc/modules configuration file using the following
command.
sudo vi /etc/modules
The bonding module file should look like the following:
# /etc/modules: kernel modules to load at boot time.
#
# This file contains the names of kernel modules that should be loaded
# at boot time, one per line. Lines beginning with "#" are ignored.
loop
15
Page 16

lp
rtc
bonding
If the bonding module is not there, add the bonding keyword word into /etc/modules file.
3. Configure the network interfaces as an active and slave to the bonding interface using the following command:
sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces
The following example shows you to associate eth4 and eth5 as slaves to the bonding interface bond0. In this
example, eth4 is the active interface; eth5 is the slave interface:
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5).
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 172.16.14.119
netmask 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.14.0
broadcast 172.16.14.255
gateway 172.16.14.1
# dns-* options are implemented by the resolvconf package, if installed
dns-nameservers 10.162.168.102
dns-search santanet.dell.com
#eth4 is manually configured, and slave to the "bond0" bonded NIC
#associated interface as a slave to the bonding0 interface.
auto eth4
iface eth4 inet manual
bond-master bond0
#eth5 ditto, thus creating a 2-link bond
# associated interface as a slave to the bonding interface
auto eth5
iface eth5 inet manual
bond-master bond0
#bond0 is the bonding NIC and vcan be used like any other normal NIC.
#bond0 is configured using static network information
auto bond0
iface bond0 inet static
address 192.168.1.10
gateway 192.168.1.1
16
Page 17

netmask 255.255.255.0
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-miimon 100
bond-lacp-rate 1
bond-slaves none
4. Restart the network service by rebooting the compute node at /etc/init.d/networking restart
5. After the reboot is complete, verify the bonding interface by checking the /proc/net/bonding/ directory
The following example shows how to check the bond0 interface. In this example, the bonding mode and the slave
interface
root@dev1-openstack03:/etc/network# cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0
Ethernet Channel Bonding Driver: v3.7.1 (April 27, 2011)
Bonding Mode: IEEE 802.3ad Dynamic link aggregation
Transmit Hash Policy: layer2 (0)
MII Status: up
MII Polling Interval (ms): 100
Up Delay (ms): 0
Down Delay (ms): 0
802.3ad info
LACP rate: fast
Min links: 0
Aggregator selection policy (ad_select): stable
Active Aggregator Info:
Aggregator ID: 1
Number of ports: 1
Actor Key: 33
Partner Key: 1
Partner Mac Address: 00:00:00:00:00:00
eth4 and eth5 have a MII Status of Up.
Slave Interface: eth4
MII Status: up
Speed: 10000 Mbps
Duplex: full
Link Failure Count: 28
Permanent HW addr: 00:10:18:d0:3d:60
Aggregator ID: 1
Slave queue ID: 0
Slave Interface: eth5
MII Status: up
Speed: 10000 Mbps
Duplex: full
Link Failure Count: 28
17
Page 18

Permanent HW addr: 00:10:18:d0:3d:62
Aggregator ID: 2
Slave queue ID: 0
18
Page 19

Step 5: Installing the Dell OVS Agent
The Dell OVS Agent supports dynamic discovery of Server Switch connections using LLDP. To use the Dell OVS agent,
install it on the nova compute nodes and network node.
To install the Dell OVS Agent on the nova compute nodes and network nodes:
1. Obtain the AFM Plug-in for Openstack tar file, AFMOpenStackPlugin2.0.0.0.tar.gz, from iSupport.
2. On each Nova compute node and network node, go to /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/.
3. At the /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages directory, untar the file using the following command:
tar –zxvf AFMOpenStackPlugin2.0.0.0.tar.gz command.
The files are put in the /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/quantum/plugins/ directory.
4. After you have untar the file, make a backup file of /usr/bin/quantum-openvswitch-agent. Then copy the /usr/lib/
python2.7/dist-packages/quantum/plugins/dell/bin/quantum-openvswitch-agent
to the /usr/bin directory.
6
19
Page 20

20
Page 21

Step 6: Configuring the Dell OVS Agent
To configure the Dell OVS Agent:
1. Create the physical and integration bridge
2. Configure the Dell OVS Plug-in
3. Configure the Rootwrap
4. Restart the Dell OVS Agent on Nova Compute Node or Network Node
5. Configure the Nova Compute Node or Network Node
Step 1: Creating the Physical and Integration bridge
This section describes how to add the physical port and bonding to the Dell OVS agent. For each Ethernet port that
connects to the switches, you create a physical bridge and integration bridge. On each Nova Compute node and
network node, the physical bridge and integration bridge can be connected by one of the following ways:
• A single Ethernet port; for example, eth4.
• Port bonding two Ethernet ports. For port bonding, configure port bonding bond0 with two Ethernet ports; for
example, eth4 and eth5.
Example: Adding a Physical Port to the Dell OVS Agent
The following example shows how to create an integration bridge and add a physical port to the bridge for eth4.
ovs-vsctl add-br br-eth4 #Create a integration bridge to the bridge
ovs-vsctl add-port br-eth4 eth4 #Add a physical port
Example: Adding a Port Bonding to the Dell OVS Agent
The following examples shows how to add port bonding, bond0 , to the Dell OVS agent.
ovs-vsctl add-br br-bond0 # Create a integration bridge
ovs-vsctl add-port br-bond0 bond0 # Add the port bonding port to the bridge
7
For information about how to create a port bonding, see the Configuring Port Bonding section.
Step 2: Configuring the Dell OVS Plug-in
To configure the dell_ovs_quantum_plugin.ini file:
1. On each compute node and network node, add the following content into the OVS section of the
dell_ovs_quantum_plugin.ini file:
[OVS]
bridge_mappings = default:br-bond0
network_vlan_ranges = default:1000:1100
tenant_network_type = vlan
21
Page 22

2. If the interfaces for the bridge are not operational, on each Nova compute node and network node , run the
following command to bring up all the Ethernet ports and physical bridges:
# ifconfig –a
For example, on a Nova Compute Node and network node with eth4 and eth5 connected to switches, execute the
following commands to ensure that
# ifconfig –a eth5 up
# ifconfig –a eth4 up
interface
up
eth5 and eth4 are operational:
Step 3: Configuring the Rootwrap
The Dell OVS agent uses the Ubuntu shell command, which requires that you configure the Neutron Rootwrap
To configure the Neutron Rootwrap:
1. On the Nova Compute and Network Nodes, navigate to the /etc/quantum/plugins/dell/agent/
dell_ovs_quantum_plugin.ini directory
2. In the dell_ovs_quantum_plugin.ini file, search for the keyword [AGENT]
3. Add the following line under the [AGENT] section
[AGENT]
root_helper = sudo /usr/bin/quantum-rootwrap /etc/quantum/rootwrap.conf
4. Navigate to the etc/quantum/ directory.
5. In the rootwrap.conf file, search for the [DEFAULT] keyword.
6. Add the following line under [DEFAULT] section:
[DEFAULT]
root_helper = sudo /usr/bin/quantum-rootwrap /etc/quantum/rootwrap.conf
7. Navigate to the /etc/quantum/rootwrap.d/openvswitch-plugin.filters directory.
8. In the openvswitch-plugin.filters file, add the hostname and lldpctl commands to the file as shown in the following
example:
# quantum-rootwrap command filters for nodes on which quantum is
# expected to control network
#
# This file should be owned by (and only-writeable by) the root user
# format seems to be
# cmd-name: filter-name, raw-command, user, args
[Filters]
# openvswitch-agent
# unclear whether both variants are necessary, but I'm transliterating
# from the old mechanism
ovs-vsctl: CommandFilter, /bin/ovs-vsctl, root
ovs-vsctl_usr: CommandFilter, /usr/bin/ovs-vsctl, root
ovs-vsctl_sbin: CommandFilter, /sbin/ovs-vsctl, root
ovs-vsctl_sbin_usr: CommandFilter, /usr/sbin/ovs-vsctl, root
ovs-ofctl: CommandFilter, /bin/ovs-ofctl, root
ovs-ofctl_usr: CommandFilter, /usr/bin/ovs-ofctl, root
22
Page 23

ovs-ofctl_sbin: CommandFilter, /sbin/ovs-ofctl, root
ovs-ofctl_sbin_usr: CommandFilter, /usr/sbin/ovs-ofctl, root
xe: CommandFilter, /sbin/xe, root
xe_usr: CommandFilter, /usr/sbin/xe, root
hostname: CommandFilter, /bin/hostname, root
lldpctl: CommandFilter, /usr/sbin/lldpctl, root
# ip_lib
ip: IpFilter, /sbin/ip, root
ip_usr: IpFilter, /usr/sbin/ip, root
ip_exec: IpNetnsExecFilter, /sbin/ip, root
ip_exec_usr: IpNetnsExecFilter, /usr/sbin/ip, root
Step 4: Restart the Dell OVS Agent on Nova Compute Node or Network Node
To restart the Dell OVS Agent on Nova Compute Node or Network Node:
1. Navigate to the /etc/init/ directory
2. Make a backup of the existing quantum-plugin-openvswitch-agent.conf file.
3. Change the quantum-plugin-openvswitch-agent.conf file as follows so that the Dell OVS Agent configuration is
selected and runs it.
exec start-stop-daemon --start --chuid quantum --exec /usr/bin/quantum-openvswitch-agent --config-file=/etc/
quantum/quantum.conf --config-file=/etc/quantum/plugins/dell/agent/dell_ovs_quantum_plugin.ini --logfile=/var/log/quantum/openvswitch-agent.log
NOTE: The following configuration picks up the Dell OVS agent and runs it.
--config-file=/etc/quantum/plugins/dell/agent/dell_ovs_quantum_plugin.ini
4. On each Nova Compute Node or Network Node, start the Dell OVS Agent by executing the service quantum-pluginopenvswitch-agent restart command.
Step 5: Configure the Nova Compute Node or Network Node
To test the connectivity of VM instances on different Compute Nodes, apply the nova security rule and modify the
administrator password settings. These security rules allow the VMs to ping each other.
Pre-requisities
To execute these commands, install the Nova CLI client needs to be installed on each compute node or network node.
For information about install the Nova client, refer to standard CLI installation guide from Openstack. http://
docs.openstack.org/cli/quick-start/content/index.html
To test the connectivity of VM instances on different compute nodes:
1. On each Nova Compute Node, add the Nova Security Rule to allow the firewall to have access to ICMP and TCP.
nova secgroup-add-rule default icmp -1 -1 0.0.0.0/0
nova secgroup-add-rule default tcp 22 22 0.0.0.0/0
2. The following configuration needs to be done after the Nova CLI is installed
export OS_USERNAME=admin
export OS_PASSWORD=password
23
Page 24

export OS_TENANT_NAME=admin
export OS_AUTH_URL=http://localhost:5000/v2.0
24
Page 25

8
Step 7: Connecting to the AFM Server
To connect to the AFM server:
1. Configure the AFM server IP address and port on the Openstack Controller node
2. Configure the AFM user credentials for the AFM Plug-in on the AFM server
Step 1: Configure the AFM server IP address and Port
The AFM plug-in requires that you configure the AFM server IP and port on the Openstack Controller node to connect to
the AFM server for Restful API calls.
To connect to the AFM server from the Controller node:
On the Openstack Controller node, modify the /etc/quantum/plugins/dell/dell_quantum_plugins.ini file so that it contains
the following information:
• AFM server IP address
• Port number
Example: Connecting to AFM Server from Openstack Controller Node
[AFM_REST_CLIENT]
afm_user_name=
afm_user_key=
host = 172.16.4.221
port = 443
Step 2: Configure the AFM User Credentials for the AFM Plug-in
The AFM server requires a user login for the AFM plug-in to make Restful API calls to the AFM server for VLAN tagging
and untagging. Although the AFM plug-in can use the superuser role to log into the AFM server and tag VLANs
associated with Restful APIs on the AFM server, we recommend that you create another user with an admin role instead
of superuser role.
To create a user with an administrative role to make Restful API calls to the AFM server for VLAN tagging and
untagging:
1. Log onto AFM server using AFM server URL. For example, if the AFM server IP address is 172.16.4.23, type
172.16.4.23/ as the URL from your browser
2. Go to Administration > User Account screen.
25
Page 26

3. Click the Add User link.
4. From the Role pull-down menu, select the Admin option.
5. In the First Name and Last Name fields, enter the name of the user.
6. In the User Name field, enter the user name. For example, quantumuser.
7. In the Password field, enter the password.
8. In the Confirm Password field, confirm the password.
9. In the Sessions Allowed pull-down menu, select 5 for the number sessions allowed for the user.
10. For the remaining options: Sessions Allowed, Session Timeout, Unsuccessful Login Limit, and Lock Duration,
accept the default values.
11. Click OK to create the new user on the AFM server.
12. On the Nuetron server, run the encryption scripts from the AFM plug-in
#cd /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/quantum/plugins/dell/bin
#./afm_generate_key.sh –u “<userid>” –p “<newpassword>”
This command updates the following:
– afm_user_name and afm_user_key in /etc/quantum/plugins/dell/dell_quantum_plugins.ini .file
– /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/quantum/plugins/dell/common/cipher_data.txt file, which is used for
encryption/decryption of the password.
The AFM plug-in uses this user created on the AFM server to log into AFM server to tag VLANs through Restful
APIs.
26
Page 27

Uninstalling the AFM Plug-in for OpenStack
The AFM Plug-in is located at the OpenStack Neutron plugins directory.
To uninstall the AFM Plug-in, restore the configuration files that you have changed and then remove the AFM plug-in
directory.
1. Run the following command to stop the Dell Neutron plugin.
root@dev1-openstack06:~# service quantum-server stop
2. Modify the following statement by removing the line "--config-file /etc/quantum/plugins/dell/
dell_quantum_plugins.ini \ from the quantum-server.conf file located in the /etc/init/ directory.
exec start-stop-daemon --start --chuid quantum --exec /usr/bin/quantum-server -- \
--config-file /etc/quantum/quantum.conf \
--log-file /var/log/quantum/server.log $CONF_ARG
3. Restore the /etc/quantum/quantum.conf file.
4. Remove the /etc/quantum/plugins/dell directory and all the files in it.
5. Restore the /etc/quantum/plugins/openvswitch/ovs_quantum_plugin.ini file.
9
27
Page 28

28
Page 29

Uninstalling the Dell OVS Agent
To uninstall the Dell OVS agent:
1. Run the service quantum-plugin-openvswitch-agent stop command.
2. Restore the /usr/bin/quantum-openvswitch-agent file from the backup.
3. Restore the /etc/init/quantum-plugin-openvswitch-agent.conf file.
4. Remove the /etc/quantum/plugins/dell directory and all the files in it.
10
29
 Loading...
Loading...