Datasheet TDE1898CSP, TDE1898CFP, TDE1898CDP, TDE1897CFP, TDE1897CDP Datasheet (SGS Thomson Microelectronics)
Page 1

TDE1897C
TDE1898C
0.5A HIGH-SIDE DRIVER
INDUSTRIALINTELLIGENT POWER SWITCH
PRELIMINARY DATA
0.5A OUTPUT CURRENT
18V TO 35V SUPPLY VOLTAGE RANGE
INTERNALCURRENTLIMITING
THERMALSHUTDOWN
OPENGROUND PROTECTION
INTERNAL NEGATIVE VOLTAGE CLAMPING
TO V
DIFFERENTIAL INPUTS WITH LARGE COM-
MON MODE RANGE AND THRESHOLD
HYSTERESIS
UNDERVO LTAGELOCKOUTWITHHYSTER ESIS
OPENLOAD DETECTION
TWO DIAGNOSTIC OUTPUTS
OUTPUTSTATUS LED DRIVER
DESCRIPTION
The TDE1897C/TDE1898C is a monolithic Intelligent Power Switch in Multipower BCD Technol-
BLOCKDIAGRAM
- 45V FOR FAST DEMAGNETIZATION
S
MULTIPOWERBCD TECHNOLOGY
Minidip SIP9 SO20
ORDERING NUMBERS:
TDE1897CDP TDE1898CSP TDE1897CFP
TDE1898CDP TDE1898CFP
ogy, for driving inductive or resistive loads. An internal Clamping Diode enables the fast demagnetizationof inductive loads.
Diagnostic for CPU feedback and extensive use
of electrical protections make this device inherently indistructible and suitable for general purpose industrial applications.
October 1995
1/12
Page 2

TDE1897C- TDE1898C
PIN CONNECTIONS (Top view)
SIP9
Minidip
SO20
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (Minidippin reference)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
V
S–VO
V
V
I
E
P
T
T
S
I
i
O
tot
op
stg
Supply Voltage (Pins 3 - 1) (TW< 10ms) 50 V
Supply to OutputDifferential Voltage. SeealsoVCl3-2(Pins3 - 2) internally limited V
Input Voltage (Pins 7/8) -10 to VS +10 V
i
Differential Input Voltage (Pins 7 - 8) 43 V
i
Input Current (Pins 7/8) 20 mA
Output Current (Pins 2 - 1). See also ISC internally limited A
Energy from Inductive Load(TJ=85°C) 200 mJ
l
Power Dissipation. See alsoTHERMAL CHARACTERISTICS. internally limited W
Operating Temperature Range (T
) -25 to +85 °C
amb
Storage Temperature -55 to 150 °C
THERMALDATA
Symbol Description Minidip Sip SO20 Unit
Thermal Resistance Junction-case Max. 10 °C/W
Thermal Resistance Junction-ambient Max. 100 70 90 °C/W
2/12
R
th j-case
R
th j-amb
Page 3
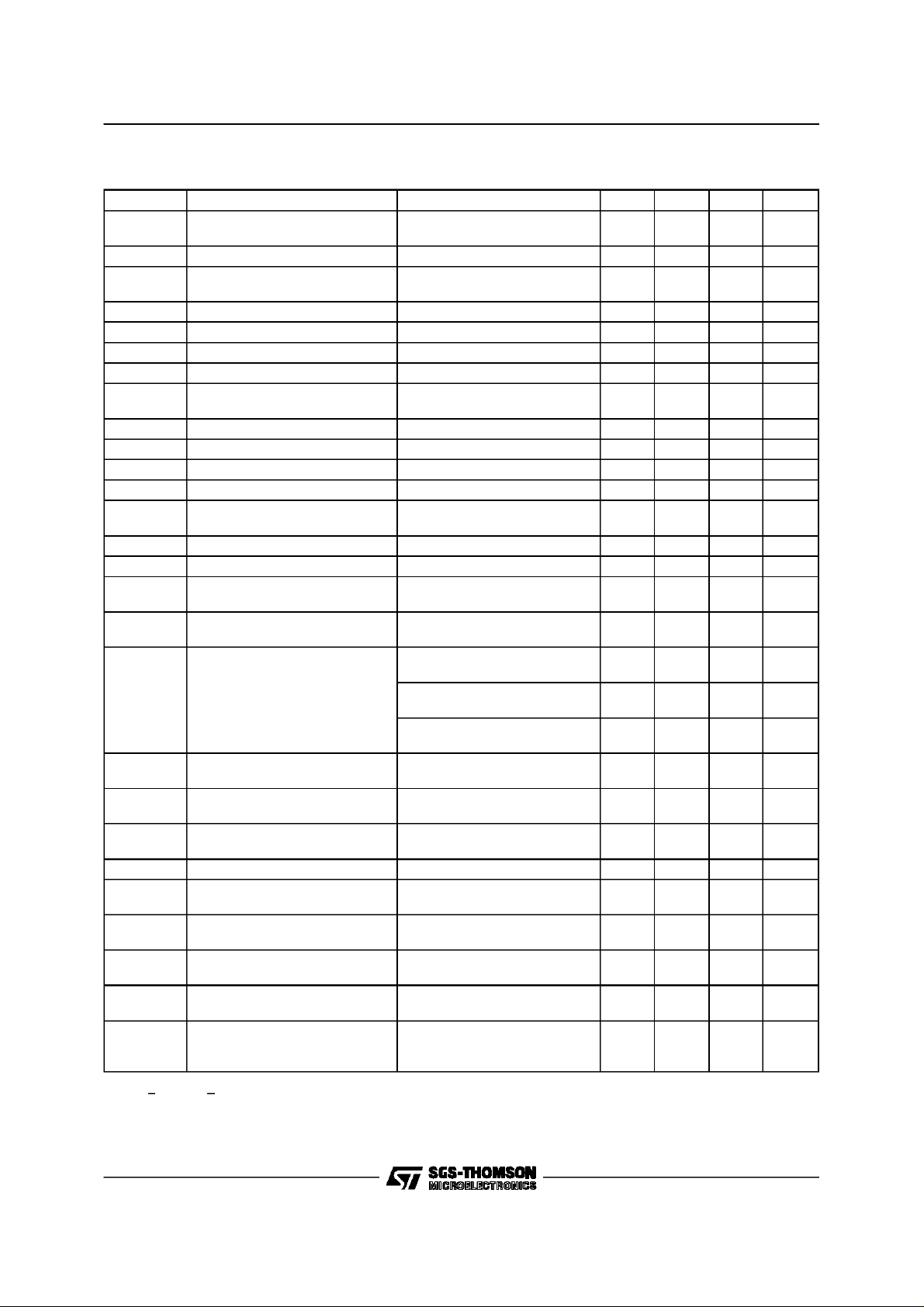
TDE1897C - TDE1898C
ELECTRICALCHARACTERISTICS (VS=24V; T
= –25 to +85°C,unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
3 Supply Voltage for Valid
V
smin
I
> 0.5mA @ V
diag
= 1.5V 9 35 V
dg1
Diagnostics
V
3 Supply Voltage (operative) 18 24 35 V
s
3 Quiescent Current
I
q
V
sth1
V
sth2
V
shys
I
sc
V
don
I
oslk
V
ol
3-2 Internal Voltage Clamp (VS-VO)@IO= -500mA 45 55 V
V
cl
I
old
7-8 Common Mode Input Voltage
V
id
I
out=Ios
=0
Undervoltage Threshold 1 (See fig. 1); T
3 Undervoltage Threshold 2 (See fig. 1); Tamb = 0 to +85°C 15.5 V
Supply Voltage Hysteresis (See fig. 1); T
Short Circuit Current VS= 18 to 35V; RL=1Ω 0.75 1.5 A
3-2 Output Voltage Drop @ I
2 OutputLeakage Current @ Vi=Vil,Vo= 0V 300 µA
2 Low State Out Voltage @ Vi=Vil;RL=∞ 0.8 1.5 V
2 Open Load Detection Current Vi=Vih;T
Range (Operative)
7-8 Input Bias Current Vi= –7 to 15V; –In = 0V –700 700 µA
I
ib
7-8 InputThreshold Voltage V+In > V–In 0.8 1.4 2 V
V
ith
7-8 Input Threshold Hysteresis
V
iths
V
il
V
ih
= 0 to +85°C11 V
amb
= 0 to +85°C 0.4 1 3 V
amb
= 625mA; Tj=25°C
out
@I
= 625mA; Tj= 125°C
out
= 0 to +85°C1 6mA
amb
VS= 18 to 35V,
V
S=Vid
7-8 < 37V
–7 15 V
V+In > V–In 50 400 mV
2.5
4.5
250
400
4
7.5
425
600
Voltage
R
7-8 Diff. InputResistance @ 0 < +In < +16V; –In = 0V
id
@ –7 < +In < 0V; –In= 0V
I
7-8 Input Offset Current V+In = V–In +Ii
ilk
0V < V
<5.5V –Ii
i
–In = GND +Ii
0V < V+In <5.5V –Ii –250
+In = GND +Ii
0V < V–In <5.5V –Ii
V
2 Output Status Threshold 1
oth1
(See fig. 1) 12 V
–20
–75 –25
–100
–50
400
150
+10
–125
–30
–15
+20 µA
+50 µA
Voltage
V
2 Output Status Threshold 2
oth2
(See fig. 1) 9 V
Voltage
V
2 Output Status Threshold
ohys
(See fig. 1) 0.3 0.7 2 V
Hysteresis
I
4 Output Status Source Current V
osd
3-4 Active Output Status Driver
V
osd
Drop Voltage
4 Output Status Driver Leakage
I
oslk
Current
5/6 Diagnostic Drop Voltage D1 / D2 = L @ I
V
dgl
out>Voth1,Vos
Vs–Vos@Ios= 2mA;
T
= -25 to 85°C
amb
V
out<Voth2,Vos
V
= 18 to 35V
S
D1 / D2 = L @ I
5/6 Diagnostic Leakage Current D1 / D2 =H @ 0 < Vdg<V
I
dglk
= 2.5V 2 4 mA
5V
=0V
diag
diag
= 0.5mA
= 3mA
s
25 µA
250
1.5
25 µA
VS= 15.6 to 35V
5/6-3 Clamping Diodes at the
V
fdg
@I
= 5mA; D1 / D2 = H 2 V
diag
Diagnostic Outputs.
Voltage Drop to V
Note Vil < 0.8V, Vih > 2V @ (V+In> V–In); Minidip pin reference.
All test not dissipative.
S
mA
mA
mV
mV
KΩ
KΩ
µA
µA
µA
µA
mV
V
3/12
Page 4

TDE1897C- TDE1898C
SOURCEDRAIN NDMOS DIODE
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
2-3 Forward On Voltage @ I
V
fsd
2-3 Forward Peak Current t = 10ms; d = 20% 2 A
I
fp
2-3 Reverse Recovery Time If= 625mA di/dt = 25A/µs 200 ns
t
rr
2-3 Forward Recovery Time 50 ns
t
fr
THERMALCHARACTERISTICS (*)
Θ Lim Junction Temp. Protect. 135 150 °C
T
H
Thermal Hysteresis 30 °C
SWITCHINGCHARACTERISTICS (VS=24V; RL=48Ω) (*)
= 625mA 1 1.5 V
fsd
t
on
t
off
t
d
Turn on Delay Time 100 µs
Turn off Delay Time 20 µs
Input Switching to Diagnostic
100 µs
Valid
Note Vil < 0.8V, Vih > 2V @ (V+In > V–In); Minidip pin reference. (*) Not tested.
Figure1
DIAGNOSTICTRUTH TABLE
Diagnostic Conditions Input Output Diag1 Diag2
Normal Operation L
H
Open Load Condition (I
)L
o<Iold
H
Short to V
S
L
H
Short Circuit to Ground (I
) (**) TDE1897C
O=ISC
TDE1898C
H <H (*) H L
HH
Output DMOS Open L
H
Overtemperature L
H
SupplyUndervoltage (V
supplyvoltage;V
S<Vsth2
S<Vsth1
in the fallingphase of the
inthe rising phaseof the supply
L
H
voltage)
(*) According to the intervention of the current limiting block.
(**) A cold lampfilament,or a capacitive load may activatethe current limiting circuit of the IPS,when theIPS is initially turned on.TDE1897
uses Diag2 to signal such condition, TDE1898 does not.
4/12
L
H
L
H
H
H
H
H
H
L
L
L
H
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
H
H
L
H
H
L
L
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
L
L
L
L
Page 5

TDE1897C - TDE1898C
APPLICATION INFORMATION
DEMAGNETIZATIONOF INDUCTIVE LOADS
An internal zener diode, limiting the voltage
across the Power MOS to between 45 and 55V
(V
), provides safe and fast demagnetization of
cl
inductiveloads without external clamping devices.
The maximum energy that can be absorbed from
an inductive load is specified as 200mJ (at
=85°C).
T
j
To define the maximumswitching frequencythree
pointshave to be considered:
1) The total power dissipation is the sum of the
On State Power and of the Demagnetization
Energy multipliedby the frequency.
2) The total energy W dissipated in the device
during a demagnetizationcycle (figg. 2, 3) is:
W = V
L
Io–
V
cl–Vs
R
L
L
cl
R
log
1 +
Vcl–V
V
s
s
Where:
V
= clamp voltage;
cl
L =inductive load;
= resistiveload;
R
L
Vs =supply voltage;
I
O=ILOAD
3) In normal conditions the operating Junction
temperatureshould remain below 125°C.
Figure 3: DemagnetizationCycle Waveforms
Figure2: InductiveLoad Equivalent Circuit
Figure 4: Normalized R
Temperature
α
1.8
RDSON (Tj)
α=
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
-25 0 25 50 75 100 125 Tj (°C)
RDSON (Tj=25°C)
DSON
vs. Junction
D93IN018
5/12
Page 6

TDE1897C- TDE1898C
WORST CONDITION POWER DISSIPATION IN
THEON-STATE
In IPS applications the maximum average power
dissipation occurs when the device stays for a
long time in the ON state. In such a situation the
internal temperature depends on delivered current (and related power), thermal characteristics
of the packageand ambient temperature.
At ambient temperature close to upper limit
(+85°C)and in theworst operating conditions,it is
possible that the chip temperature could increase
so much to make the thermal shutdown procedureuntimely intervene.
Our aim is to find the maximum current the IPS
can withstand in the ON state without thermal
shutdown intervention, related to ambient temperature.To this end, we should consider the followingpoints:
1) The ON resistance R
DSON
of the output
NDMOS (the real switch) of the device increases with its temperature.
Experimentalresults show that silicon resistivity increases with temperature at a constant
rate, rising of 60% from 25°Cto 125°C.
The relationship between R
DSON
and tem-
peratureis therefore:
R
DSON
= R
DSON0
( 1 + k )
( Tj± 25 )
where:
T
is the silicon temperature in °C
j
R
k is the constant rate (k = 4.711 ⋅
DSON0
isR
DSON
at Tj=25°C
10
±3
)
(see fig.4).
the third element are constant, while the first
one increases with temperature because
R
increasesas well.
DSON
3) The chip temperature must not exceed ΘLim
in order do not lose the control of the device.
The heat dissipation path is represented by
the thermal resistance of the system deviceboard-ambient (R
). In steady state condi-
th
tions, this parameter relates the power dissipated P
the ambient temperatureT
T
j
to the silicon temperature Tjand
± T
on
amb
= Pon⋅ R
th
amb
:
(2)
From this relationship, the maximum power
P
which can be dissipated without exceed-
on
ing ΘLim at a given ambient temperature
is:
T
amb
P
on
=
ΘLim ± T
amb
R
th
Replacing the expression (1) in this equation
and solvingfor I
, we can find the maximum
out
current versus ambient temperature relationship:
ΘLim ± T
I
= √
outx
amb
R
DSONx
± Pq± P
R
th
os
2) In the ON state the power dissipatedin the
device is dueto three contributes:
a) power lost in the switch:
P
out
= I
out
2
⋅ R
DSON(Iout
is theoutput cur-
rent);
b) power due to quiescent current in the ON
state Iq,sunk by thedevice in additionto
I
out:Pq=Iq⋅Vs(Vs
isthe supplyvoltage);
c) an external LED could be used to visualize
the switchstate (OUTPUT STATUS pin).
Such a LEDis driven by aninternal current
source (deliveringI
) and therefore,if Vosis
os
the voltagedrop across the LED, thedissipated power is: P
= I
⋅( V
± V
os
os
s
).
os
Thus the total ON state power consumptionis
given by:
= P
P
on
+ Pq+ P
out
os
(1)
In theright side of equation 1, the secondand
6/12
where R
course, I
maximum operative current I
xisR
DSON
values are top limited by the
outx
at Tj=ΘLim. Of
DSON
outx
(500mA
nominal).
From the expression (2) we can also find the
maximum ambient temperature T
a given power P
T
amb
=ΘLim ±
( I
out
canbe dissipated:
on
=ΘLim± Pon⋅ Rth=
2
⋅ R
+ Pq+ Pos) ⋅ R
DSONx
amb
at which
th
In particular, this relation is useful to find the
maximum ambient temperature T
which I
T
ambx
+ P
canbe delivered:
outx
=ΘLim ±(I
+ Pos) ⋅ R
q
th
outx
2
⋅ R
DSONx
+
(4)
ambx
at
Referring to application circuit in fig. 5, let us consider the worstcase:
- The supply voltage is at maximumvalue of industrial bus (30V instead of the 24V nominal
value).This means also that I
risesof 25%
outx
Page 7

TDE1897C - TDE1898C
(625mAinstead of 500mA).
- All electrical parameters of the device, concerning the calculation, are at maximum values.
- Thermal shutdown threshold is at minimum
value.
- No heat sink nor air circulation (R
R
thj-amb
).
equal to
th
Therefore:
V
= 30V, R
s
=2.5V, ΘLim = 135°C
V
os
R
thj-amb
= 100°C/W (Minidip); 90°C/W (SO20);
= 0.6Ω,Iq= 6mA, Ios= 4mA @
DSON0
70°C/W(SIP9)
It follows:
I
= 0.625mA, R
outx
P
=110mW
os
= 1.006Ω,Pq= 180mW,
DSONx
Figure5: Application Circuit.
From equation 4, we can find:
= 66.7°C(Minidip);
T
ambx
73.5°C(SO20);
87.2°C(SIP9).
Therefore, the IPS TDE1897/1898, although
guaranteed to operate up to 85°C ambient temperature,if used in the worstconditions,can meet
some limitations.
SIP9 package, which has the lowest R
thj-amb
, can
work at maximum operative current over the entire ambient temperature range in theworst conditions too. For other packages, it is necessary to
consider some reductions.
With the aid of equation 3, we can draw a derating curve giving the maximum current allowable
versus ambienttemperature. The diagrams, computed using parameter values above given, are
depicted in figg. 6 to 8.
If an increase of the operating area is needed,
heat dissipation must be improved (R
reduced)
th
e.g. by means of air cooling.
DC BUS 24V +/-25%
µP POLLING
D93IN014
+IN
-IN
D1
D2
+Vs
+
-
CONTROL
LOGIC
OUTPUT STATUSGND
Ios
OUTPUT
LOAD
7/12
Page 8

TDE1897C- TDE1898C
Figure6: Max. OutputCurrent vs. Ambient
Temperature(Minidip Package,
th j-amb
=100°C/W)
D93IN015
R
(mA)
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 (°C)
Figure8: Max. OutputCurrent vs. Ambient
Temperature(SIP9 Package,
R
(mA)
th j-amb
=70°C/W)
D93IN017
Figure 7: Max. Output Current vs. Ambient
Temperature(SO20 Package,
R
th j-amb
(mA)
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
0 20406080100(°C)
=90°C/W)
D93IN016
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 (°C)
8/12
Page 9

MINIDIPPACKAGE MECHANICAL DATA
TDE1897C - TDE1898C
DIM
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
A 3.32 0.131
a1 0.51 0.020
B 1.15 1.65 0.045 0.065
b 0.356 0.55 0.014 0.022
b1 0.204 0.304 0.008 0.012
D 10.92 0.430
E 7.95 9.75 0.313 0.384
e 2.54 0.100
e3 7.62 0.300
e4 7.62 0.300
F 6.6 0260
i 5.08 0.200
L 3.18 3.81 0.125 0.150
Z 1.52 0.060
mm inch
9/12
Page 10

TDE1897C- TDE1898C
SIP9 PACKAGEMECHANICAL DATA
DIM.
MIN. TYP. MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
mm inch
A 7.1 0.280
a1 2.7 3 0.106 0.118
B 23 0.90
B3 24.8 0.976
b1 0.5 0.020
b3 0.85 1.6 0.033 0.063
C 3.3 0.130
c1 0.43 0.017
c2 1.32 0.052
D 21.2 0.835
d1 14.5 0.571
e 2.54 0.100
e3 20.32 0.800
L 3.1 0.122
L1 3 0.118
L2 17.6 0.693
L3 0.25 0.010
L4 17.4 17.85 0.685 0,702
M 3.2 0.126
N 1 0.039
P 0.15 0.006
D
L3
L1
P
L2
L4
19
La1
e3
B
B3
N
M
b1
b3
ec1
d1
A
SIP9
C
c2
10/12
Page 11

SO20PACKAGE MECHANICAL DATA
TDE1897C - TDE1898C
DIM.
MIN. TYP. MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
A 2.65 0.104
a1 0.1 0.2 0.004 0.008
a2 2.45 0.096
b 0.35 0.49 0.014 0.019
b1 0.23 0.32 0.009 0.013
C 0.5 0.020
c1 45° (typ.)
D 12.6 13.0 0.496 0.510
E 10 10.65 0.394 0.419
e 1.27 0.050
e3 11.43 0.450
F 7.4 7.6 0.291 0.300
L 0.5 1.27 0.020 0.050
M 0.75 0.030
S8°(max.)
mm inch
11/12
Page 12

TDE1897C- TDE1898C
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics assumes no responsibility for the
consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which mayresult from its use. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics. Specification mentioned
in this publication are subject to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. SGSTHOMSON Microelectronics products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express
written approval of SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics.
1995 SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics – Printed in Italy – All Rights Reserved
Australia - Brazil - Canada- China - France - Germany - Hong Kong - Italy - Japan - Korea - Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - The Netherlands -
Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - Taiwan -Thailand - UnitedKingdom - U.S.A.
SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics GROUP OF COMPANIES
12/12
 Loading...
Loading...