Page 1
Video Modulator for
TDA 5666-5
FM-Audio
Preliminary Data Bipolar IC
Features
● FM-audio modulator
● Sync level clamping of video input signal
● Controlling of peak white value
● Continuous adjustment of modulation depth for
positive or negative values
● Symmetrical mixer output with separate ground area
● Symmetrical oscillator with separate RF-ground
● Low spurious radiation
● High stability of the RF-oscillator frequency
● High stability of the audio oscillator
● Internal reference voltage
● 12 V supply voltage
P-DIP-18 -5
Type Ordering Code Package
TDA 5666-5 Q67000-A5168 P-DIP-18-5
Functional Description and Application
The monolitic integrated circuit TDA 5666-5 is especially suitable as a modulator for the
48- to 860-MHz frequency range.
Video recorders, cable converters, TV-converter networks, demodulators, video
generators, video security systems, amateur TV-applications and personal computers.
Semiconductor Group 1 02.95
Page 2

TDA 5666-5
Circuit Description
Oscillator
The RF-oscillator is available at pins 3-7. The oscillator operates as a symmetrical
Colpitts circuit. The oscillator chip ground, pin 5, should be connected to ground at the
resonance circuit shielding point. An external oscillator can be injected inductively or
capacitively via pins 3 and 7. The layout of the PCB should be such as to provide a
minimum shielding attenuation between the oscillator pins 3-7 and modulator output pins
13-15 of approximately 80 dB.
For optimal residual carrier suppression, the symmetrical mixer outputs at pins 13, 15
should be connected to a matched balanced-to-unbalanced broadband transformer, e.g.
a Guanella transformer with good phase precision at 0
should be less than 3 dB. In addition, an LC-low pass filter combination is required at the
output. The cut-off frequency of the low pass filter combination must exceed the
maximum operating frequency.
o
and 180o. The transmission loss
Video
The video signal with the negative synchronous level is capacitively connected to pin 10.
The internal clamping circuit is referenced to the synchronizing level. Should the video
signal change by 6 dB, this change will be compensated by the resonance circuit which
is set by the peak white value. At pin 11, the current pulses of the peak white detector are
filtered through the capacitor which also determines the control time constant. The RFcarrier switches from negative to positive video modulation, when pin 12 is connected
to ground. By varying the value of resistanceR at pin 12 between
∞ ... 0Ω the modulation
depth can be increased from 70% to 100% when the modulation is negative and
decreased from 100% to 70% when the modulation is positive.
Audio
Via pin 1, the audio signal is capacitively coupled to the AF-input for the FM-modulation
of the oscillator. A parallel resonance circuit is connected to the audio carrier oscillator at
pins 17, 18. The unloaded Q of the resonant circuit must be Q = 25 and the parallel
resistor R
= 8.2 kΩ to ensure a video to audio carrier ratio of 12.5 dB. At the same time,
T
the capacitative and/or inductive reactance for the resonance frequency should have a
value of X
≈ XL≈ 800 Ω.
C
The video to audio carrier ratio can be changed by connecting an external voltage to pin
16, which deviates from the internal reference voltage.
At the output of the above described mixer the FM modulated audio signal is added to
the video signal and mixed with the oscillator signal in the RF-mixer.
Source
The internal reference voltage is available at pin 2 and has to be capacitively blocked
there.
Semiconductor Group 2
Page 3
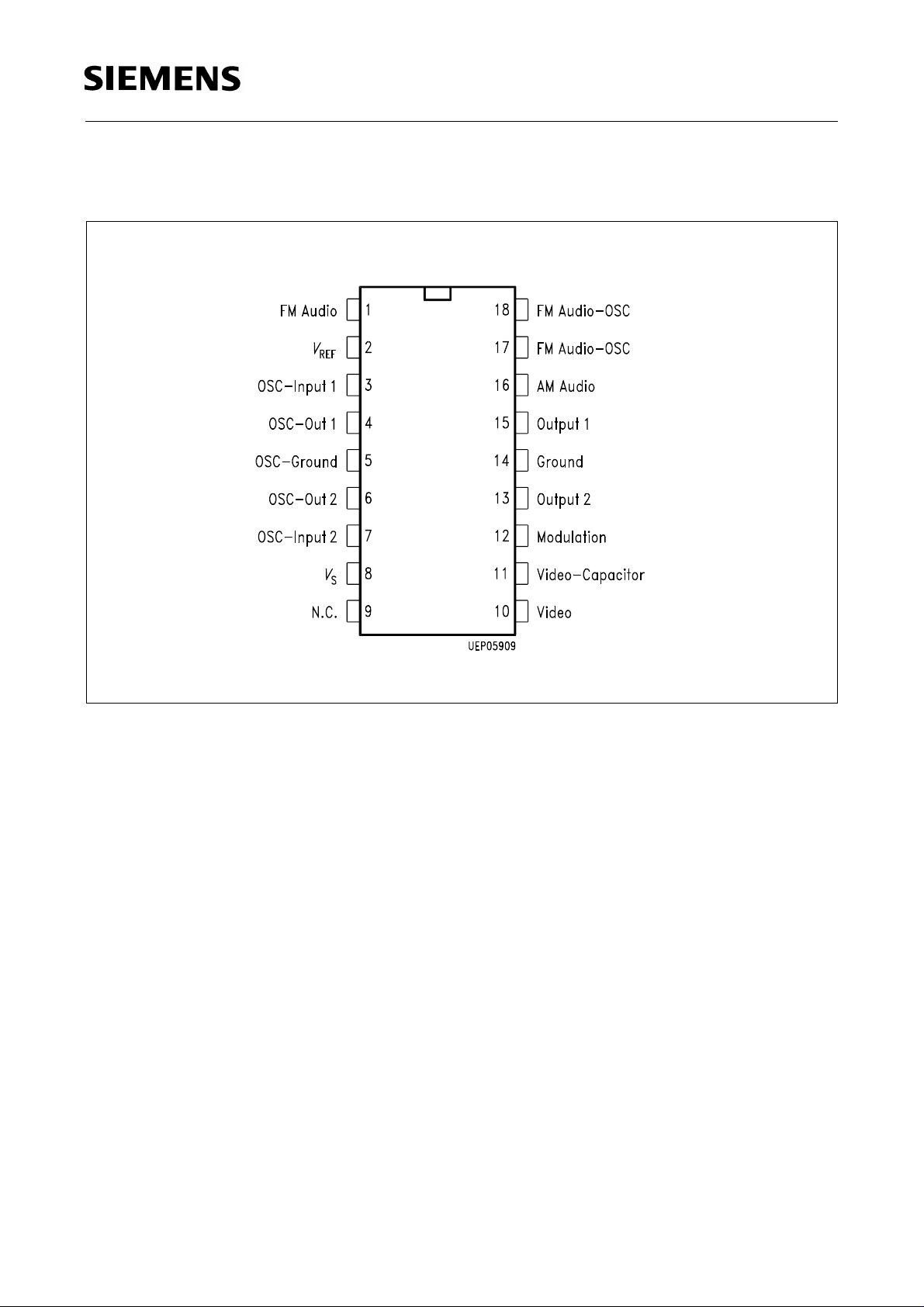
Pin Configuration
(top view)
TDA 5666-5
Semiconductor Group 3
Page 4
Pin Definitions and Functions
Pin No. Symbol Function
1 FM-Audio AF-input for FM-modulation
TDA 5666-5
2 V
REF
Internal reference voltage (7.5 V)
3 OSC-Input 1 Symmetrical oscillator input
4 OSC-Out 1 Symmetrical oscillator output
5 OSC-Ground Oscillator ground
6 OSC-Out 2 Symmetrical oscillator output
7 OSC-Input 2 Symmetrical oscillator input
8 V
S
Supply voltage (12 V)
9 N.C. Not connected
10 Video Video input with clamping
11 Video-Capacitor Connection for smoothing capacitor for video control
loop
12 Modulation Switch-over for positive and negative modulation
13 Output 2 Symmetrical RF-output
14 Ground Ground
15 Output 1 Symmetrical RF-output
16 Audio carrier ratio Video to audio carrier ratio adjustment
17 FM-Audio OSC FM-audio oscillator; symmetrical inputs for tank circuit
18 FM-Audio OSC FM-audio oscillator; symmetrical inputs for tank circuit
Semiconductor Group 4
Page 5
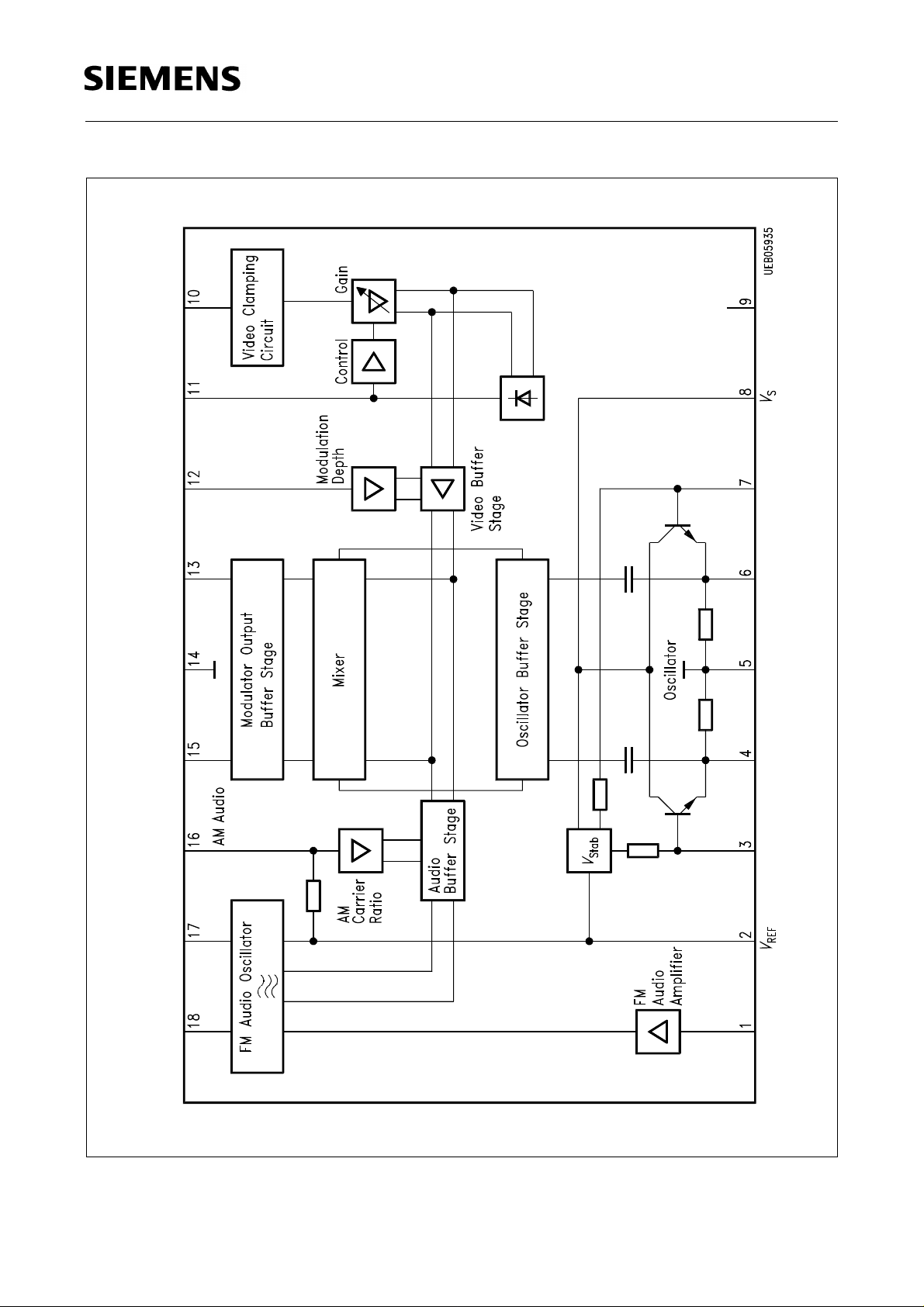
TDA 5666-5
Block Diagram
Semiconductor Group 5
Page 6
TDA 5666-5
Absolute Maximum Ratings
T
= 0 to 70oC
A
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Remarks
min. typ. max.
Supply voltage pin 8 V
Current from pin 2 –I
Voltage at pin 1
Voltage at pin 2
Voltage at pin 10
V
V
V
S
2
1
2
10
– 0.3 14.5 V
02mAV
0
6
0
2
8.5
1.5
V
V
Vpp only via C
= 7-8 V
2
V
= 10-13.5 V
S
(max. 1 µF)
Capacitance at pin 2
Capacitance at pin 11
Voltage at pin 12
Voltage at pin 13
Voltage at pin 15
Voltage at pin 16
C
C
V
V
V
V
2
11
12
13
15
16
0
0
– 0.3
V
2
V
2
V2-1.5
100
15
1.4
V
S
V
S
VS+1.5
nF
µF
V
V
V
V V
= 10-13.5 V
S
According to the application circuit, only the provided circuitry can be connected
to pins 3,4,6,7,17 and 18.
Junction temperature T
Storage temperature T
j
stg
150
– 40 125
o
C
o
C
Thermal resistance R
Operating Range
Supply voltage V
Video input frequency f
Audio input frequency f
Output frequency f
Ambient temperature T
Audio oscillator f
Voltage at pin 2
Voltage at pin 13,15
th
S
Video
AF
Q
A
OSC
V
2
V
13, 15
80 K/W
10 13.5 V
0 6 MHz
0 20 kHz
30 860 MHz depending on
the oscillator
circuitry at
pins 3-7
070
o
C
4 7 MHz
6.75
V
2
7.75
V
S
V
V
Semiconductor Group 6
Page 7
AC/DC-Characteristics
T
= 25oC; VS = 12 V
A
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test
min. typ. max.
Condition
Source
TDA 5666-5
Test
Circuit
Current consumption
Current consumption
Reference voltage V
I
8
I13 + I
2
Oscillator
Oscillator frequency
f
OSC
range
Switch-on, warm up drift; (T
C
selfheating of the component.
∆ f
OSC
Frequency drift as
function of V
S
RF-output
∆ f
OSC
R
13;R15
impedance
C13 = C
15
15
2.0
20
2.6
26
3.4
mA
mA
I2 = 0 mA 1
6.75 7.25 7.75 V 0 ≤ I2≤ 1 mA 1
30 860 MHz external circuitry
adjusted to
frequency
-value of capacitor in osc. circuit is 0) drift is referenced only to
0
0
– 50
– 200
– 500
– 500
kHz
Ch 30
kHz
t = 0.5-10 s;
TA = const.
Ch 40
–150 150 kHz VS= 10-13.5 V
TA = const.;
Ch 40
10
kΩ
parallel
equivalent circuit
0.5 1 2.0
15
pF
parallel
equivalent circuit
1
1
1
1
1
RF-output voltage V
RF-output phase α
RF-output voltage
Q
13, 15
∆V
Q
2.5 4.5 5.5 mVrms Ch 40; video
140 180 220 deg
0
changes
Intermodulation ratio α
Harmonic wave ratio α
∆V
∆V
Q
Q
IMR
O
0
0
50 75 dB fVC + 1.07 MHz 2
35 dB fVC + 8.8 MHz
Semiconductor Group 7
1.5
1.5
1.5
dB
dB
dB
100% white;
without audiosignal
f = 543-623 MHz
Ch 30...40
f = 100-300 MHz
f = 48-100 MHz
without video
1
1
1
1
2
Page 8

AC/DC-Characteristics (cont’d)
TA = 25oC; VS = 12 V
TDA 5666-5
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test
min. typ. max.
Condition
Test
Circuit
Unmodulated video and audio carrier, measured with the spectrum analyzer as difference
between video carrier signal level and sideband signal level; loaded Q factor QL of the audio
oscillator resonance circuit adjusted by RP to provide the required video to audio carrier ratio of
12.5 dB; QU = 25
Video to audio
carrier ratio
Harmonic wave ratio
α
V/A
10 12.5 15 dB fVC+ f
AC
(5.5 MHz)
α
O
35
48
dB
fVC+ 2 f
AC
1
1
(11 MHz)
Harmonic wave ratio
α
O
42
48
dB
fVC+ 3 f
AC
1
(16.5 MHz)
All remaining harmonic waves; multiple of fundamental wave of video carrier, without video
signal, measured with spectrum analyzer; f
= 523.25-623.25 MHz; pin 12 open
VC
α 15 dB 1
Residual carrier
α
R
32 dB Ch 30...40 3
suppression
Signal-to-noise in
α
N/V
48 74 dB Ch 30...40 4
video; unmodulated
audio carrier
Interference product
α
ratio audio in video
FM-modulation of
audio carrier
Unweighted FM-
α
interference level
ratio video in audio
Signal-to-noise ratio
α
of audio oscillator
Video
Video input current
–I
at pin 10
Video input voltage
V
at pin 10
Modulation depth m
A/V
V/A
N/A
10
10
D/N
48 60 dB Ch 30...40 4
48 54 dB Ch 39; test
picture FuBK
48 54 dB FM-audio carrier 5
01µAC
≤ 100 nF 1
10
0.7 1.4 Vpp C10≤ 100 nF 1
60 70 80 % staircase signal at
video input;
V
Video
= 1 Vpp
5
6
Semiconductor Group 8
Page 9

AC/DC-Characteristics (cont’d)
TA = 25oC; VS = 12 V
TDA 5666-5
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test
Condition
∆V
Video
± 3 dB;
TA= 0-60oC
VS= 10-13.5 V
Stability of mod.
∆m
depth
∆m
∆m
Differential gain α
Differential phase Φ
dif
dif
min. typ. max.
D
D
D
1
1
1
± 2.5
± 2.5
± 2.5
%
%
%
10 % 7
15 deg measured with
= 1 Vpp
Test
Circuit
6
6
6
7
measurement
demodulator,
video test signals
and vector scope
Amplitude response of video signal; V
= 1 Vpp with additional modulation f = 15 kHz-5 MHz
Video
sine signal between black and white
α
V
0 1.5 dB 8
Period of time required for peak white detector to reach steady state for full modulation depth with
1-white pulse per half frame when control is already in the steady state
t 650µsCat pin
I
leakage
11 = 10µF;
≤ 2 µA
1
Setting time for video signal change from 0 Vpp to 1.4 Vpp; video blanking signal content is
uniform white level
t 120 500 µs1
Setting time for video blanking signal from 100% white level to 42% grey level with subsequent
rise in grey level to 71% of video blanking signal (due to decontrol process)
t 0.4 2 10 min 1
Audio
Audio oscillator frequency range; unloaded Q factor of resonance circuit Q
f
resonance
Switch-on, warm-up drift of oscillator frequency; T
= 5.5 MHz
f
A/OSC
4 7 MHz 1
-value of capacitor in audio oscillator circuit
C
= 25;
u
is 0, the drift is only based on self-heating of component
Audio signal
frequency deviation
∆ f
∆ f
A/OSC
A/OSC
5 15 kHz TA = const.; 1
5 10 kHz VS = 10.0-13.5 V;
Qu = 25
1
FM-mod.; total
THD
FM
0.6 1.5 % V1 = 150 mVrms 9
harmonic distortion
Semiconductor Group 9
Page 10

AC/DC-Characteristics (cont’d)
T
= 25oC; VS = 12 V
A
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test
min. typ. max.
Condition
TDA 5666-5
Test
Circuit
FM-mod.; static
mod. characteristic
FM-mod.; dynamic
mod. characteristic
Audio preamplifier
input impedance
(dynamic)
∆ f
∆ f
∆V
Z
1
A/OSC
A/OSC
AF
± 150 ± 210 ± 270 kHz ∆V
/
0.25 0.32 0.39 kHz/
AF
=
V1-
V2=± 1
mV
200 kΩ 1
V1
1
Semiconductor Group 10
Page 11

TDA 5666-5
Test Circuit 1
Test and Measurement Circuit for FM-Audio Carrier and Negative Video
Modulation
Semiconductor Group 11
Page 12

TDA 5666-5
Test Circuit 2
Description of the Measurement Configuration to Measure the 1.07-MHz Moire
CC-level lies below the activation point and has been set to provide a ratio of 17 dB with respect to
the video carrier.
fVC = 623.25 MHz
Semiconductor Group 12
Page 13

TDA 5666-5
Test Circuit 3
Description of the Measurement Configuration to Measure the Residual Carrier
Suppression
Semiconductor Group 13
Page 14

TDA 5666-5
Test Circuit 4
Description of the Measurement Configuration to Measure the Audio and/or Noise
in Video during FM-modulation of the Audio Carrier
Calibration: AF-signals are switched off, video signal is present at video input, modulation
measurement device set at AM is adjusted to video carrier; filter: 300 Hz...20 kHz;
detector: (P+P)/2; Wave analyzer at video signal level (16 kHz) adjusted and
resultant level as reference av defined.
1) Measurement of audio interference product ratio in video while the audio carrier FM modulated:
AF-signal is connected to FM-audio input; video signal is present at video input; Modulation
measurement device set at AM; filter: 300 Hz...20 kHz; detector: (P+P)/2; the automatic RF-level
position of the measurement device is switched off; wave analyzer at video signal level 1 kHz or
2 kHz or 3 kHz adjusted and resultant level is set to aA. The audio noise ratio in video results
from a
2) Measurement of signal-to-noise ratio in video without FM-modulation of audio carrier: AF-signals
are switched off; video signal is switched on; modulation measurement device set at AM; filter:
300 Hz...3 kHz; detector: RMS x ; Wave analyzer at video signal level (16 kHz) detuned; read
out in dB to reference level of calibration is a
3) The noise limit of the measurement device is approx. 85 dB.
= aA-aV (dB).
A/V
2
;
N/V
Semiconductor Group 14
Page 15

TDA 5666-5
Test Circuit 5
Description of the Measurement Configuration to Measure the Video and/or Noise
in Audio
Calibration: AF-signal of f = 1 kHz, corresponding with a nominal deviation of 30 kHz, is
connected to the audio input, and the demodulated AF-reference level at the audio
measurement device is defined as 0 dB. No video signal is present.
Measuring: 1) The AF-signal is switched off and the FuBK-video signal is connected to the video
input with V
level is measured as ratio a
2) AF- and video signal are switched off. The noise ratio in relation to the AFreference calibration level is measured as signal-to-noise ratio in the audio signal
a
.
N/A
= 1 Vpp. The audio level in relation to the AF-reference calibration
vid
.
V/A
Semiconductor Group 15
Page 16

TDA 5666-5
Test Circuit 6
Description of the Measurement Configuration to Measure the Modulation Depth
for Positive and Negative Modulation
Calibration: A zero reference signal with the TV-measuring receiver is given to the video signal.
A video signal with V
Measuring: 1) Modulation depth m
value – sync level in relation to range zero reference – sync level gives m
2) Modulation depth m
= 1 Vpp is connected to the video input.
vid
for negative modulation: pin 12 open, range peak white
D/N
for positive modulation: pin 12 to ground, range peak
D/P
D/N
.
white value – sync level in relation to range zero reference – peak white value gives
m
.
D/P
Semiconductor Group 16
Page 17

TDA 5666-5
Test Circuit 7
Description of the Measurement Configuration to Measure the Differential Gain
and Phase
Semiconductor Group 17
Page 18

TDA 5666-5
Test Circuit 8
Description of the Measurement Configuration to Measure the Video Amplitude
Response
Semiconductor Group 18
Page 19

TDA 5666-5
Test Circuit 9
Description of the Measurement Configuration to Measure the Harmonic
Distorsion Factor
Semiconductor Group 19
Page 20

TDA 5666-5
Application Circuit
Semiconductor Group 20
Page 21

Diagram
Function of Video Signal Connection
TDA 5666-5
a) Demodulated RF-output video signal V
b) V
= f (V
11
10rms
)
13/15rms
= f (V
10rms
); f
= 16 kHz
mod
Semiconductor Group 21
Page 22

Plastic Package, P-DIP-18-5
(Plastic Dual In-Line Package)
TDA 5666-5
Sorts of Packing
Package outlines for tubes, trays etc. are contained in our
Data Book “Package Information”
Semiconductor Group 22
GPS05586
Dimensions in mm
 Loading...
Loading...