Page 1
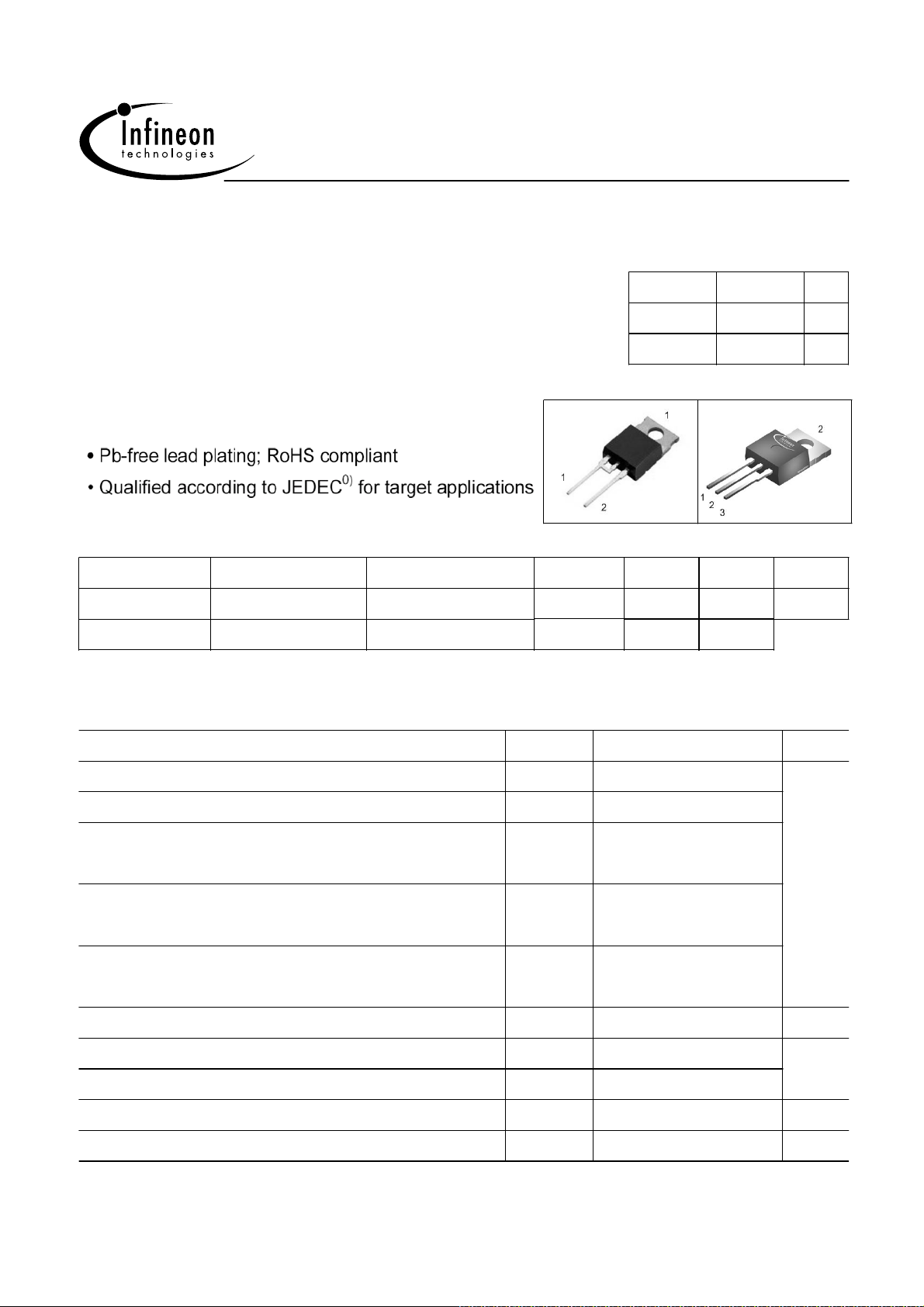
SDP10S30
SDT10S30
Silicon Carbide Schottky Diode
• Revolutionary semiconductor
material - Silicon Carbide
• Switching behavior benchmark
• No reverse recovery
• No temperature influence on
the switching behavior
• No forward recovery
Type Package Ordering Code
SDP10S30 PG-TO220-3-1. Q67040-S4372
SDT10S30 PG-TO220-2-2. Q67040-S4447
thinQ! SiC Schottky Diode
Product Summary
V
RRM
Q
c
I
F
PG-TO220-2-2. PG-TO220-3-1.
Marking
D10S30
D10S30
Pin 1 Pin 2
n.c. C
C
300
23 nC
10 A
Pin 3
A
A
V
Maximum Ratings, at Tj = 25 °C, unless otherwise specified
Parameter
Continuous forward current, T
=100°C
C
RMS forward current, f=50Hz
Surge non repetitive forward current, sine halfwave
TC=25°C, tp=10ms
Repetitive peak forward current
Tj=150°C, TC=100°C, D=0.1
Non repetitive peak forward current
tp=10µs, TC=25°C
i 2t value, T
=25°C, t
C
=10ms ∫i
p
Repetitive peak reverse voltage V
Surge peak reverse voltage V
Power dissipation, T
=25°C
C
Operating and storage temperature T
Symbol Value Unit
I
F
I
FRMS
I
FSM
I
FRM
I
FMAX
2
dt
RRM
RSM
P
tot
T
,
j
stg
10 A
14
36
45
100
6.5
300 V
300
65 W
-55... +175
A²s
°C
Rev. 1.2
Page 1
2005-02-17
Page 2
Thermal Characteristics
SDP10S30
SDT10S30
Parameter
Symbol Values Unit
min. typ. max.
Characteristics
Thermal resistance, junction - case
R
thJC
- - 2.3 K/W
Electrical Characteristics, at Tj = 25 °C, unless otherwise specified
Parameter
Symbol Values Unit
min. typ. max.
Static Characteristics
Diode forward voltage
IF=10A, Tj=25°C
=10A, Tj=150°C
I
F
Reverse current
VR=300V, Tj=25°C
=300V, Tj=150°C
V
R
V
I
F
-
-
R
-
-
1.5
1.5
15
20
1.7
1.9
200
1000
V
µA
1
Device on 40mm*40mm*1.5mm epoxy PCB FR4 with 6cm² (one layer, 70 µm thick) copper area for drain
connection. PCB is vertical without blown air.
Rev. 1.2
Page 2
2005-02-17
Page 3
Electrical Characteristics, at Tj = 25 °C, unless otherwise specified
SDP10S30
SDT10S30
Parameter
AC Characteristics
Total capacitive charge
V
=200V, IF=10A, diF/dt=-200A/µs, Tj=150°C
R
Switching time
V
=200V, IF=10A, diF/dt=-200A/µs, Tj=150°C
R
2)
1)
Total capacitance
V
=0V, TC=25°C, f=1MHz
R
V
=150V, TC=25°C, f=1MHz
R
V
=300V, TC=25°C, f=1MHz
R
Symbol Values Unit
min. typ. max.
Q
c
t
rr
C
- 23 - nC
- n.a. - ns
-
-
-
600
55
40
pF
-
-
-
Rev. 1.2
Page 3
2005-02-17
Page 4

SDP10S30
j
SDT10S30
1 Power dissipation
P
= f (TC)
tot
70
W
60
55
50
45
tot
P
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
°C
T
2 Diode forward current
= f (TC)
I
F
parameter:
11
A
F
I
180
C
Tj≤175 °C
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
°C
T
180
C
3 Typ. forward characteristic
= f (VF)
I
F
parameter:
20
A
16
14
F
I
12
10
T
, tp = 350 µs
8
6
4
2
0
0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8
-40°C
25°C
100°C
125°C
150°C
V
V
F
2.2
4 Typ. forward power dissipation vs.
average forward current
P
=
f(I
) T
F(AV)
F
32
=100°C, d = tp/T
C
W
24
F(AV)
20
P
16
12
8
4
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
d=1
d=0.5
d=0.2
d=0.1
A
I
18
F(AV)
Rev. 1.2
Page 4
2005-02-17
Page 5

SDP10S30
SDT10S30
5 Typ. reverse current vs. reverse voltage
=f(VR)
I
R
2
10
µA
1
10
0
10
R
I
-1
10
V
150°C
125°C
100°C
25°C
V
R
300
-2
10
-3
10
-4
10
50 100 150 200
6 Transient thermal impedance
Z
= f (tp)
thJC
parameter :
1
10
K/W
0
10
thJC
-1
Z
10
-2
10
-3
10
-4
10
10
SDP10S30
single pulse
-7
10
D = t
-6
10
/T
p
-5
-4
-3
10
10
10
-2
D = 0.50
0.20
0.10
0.05
0.02
0.01
s
t
p
10
0
7 Typ. capacitance vs. reverse voltage
C= f(V
parameter: T
C
450
pF
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
10
)
R
= 25 °C, f = 1 MHz
C
0
10
1
10
2
V
V
R
10
8 Typ. C stored energy
E
=f(VR)
C
2.5
µJ
C
E
1.5
1
0.5
3
0
0 50 100 150 200
300
V
V
R
Rev. 1.2
Page 5
2005-02-17
Page 6

9 Typ. capacitive charge vs. current slop
e
SDP10S30
SDT10S30
Qc=f(di
F
/dt)
parameter:
22
nC
18
16
c
14
Q
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
T
= 150 °C
j
IF*2
IF*0.5
A/µs
diF/dt
I
F
1000
Rev. 1.2
Page 6
2005-02-17
Page 7

SDP10S30
SDT10S30
PG-TO220-3-1
P-TO220-3-1
dimensions
symbol [mm] [inch]
min max min max
A 9.70 10.30 0.3819 0.4055
B 14.88 15.95 0.5858 0.6280
C 0.65 0.86 0.0256 0.0339
D 3.55 3.89 0.1398 0.1531
E 2.60 3.00 0.1024 0.1181
F 6.00 6.80 0.2362 0.2677
G 13.00 14.00 0.5118 0.5512
H 4.35 4.75 0.1713 0.1870
K 0.38 0.65 0.0150 0.0256
L 0.95 1.32 0.0374 0.0520
M
N 4.30 4.50 0.1693 0.1772
P 1.17 1.40 0.0461 0.0551
T 2.30 2.72 0.0906 0.1071
2.54 typ. 0.1 typ.
Rev. 1.2
Page 7
2005-02-17
Page 8

PG-TO-220-2-2
A
N
SDP10S30
SDT10S30
P
symbol
E
D
U
V
B
H
F
W
J
X
L
G
T
C
M
K
A 9.70 10.10 0.3819 0.3976
B 15.30 15.90 0.6024 0.6260
C 0.65 0.85 0.0256 0.0335
D 3.55 3.85 0.1398 0.1516
E 2.60 3.00 0.1024 0.1181
F 9.00 9.40 0.3543 0.3701
G 13.00 14.00 0.5118 0.5512
H 17.20 17.80 0.6772 0.7008
J 4.40 4.80 0.1732 0.1890
K 0.40 0.60 0.0157 0.0236
L
M
N
P 1.10 1.40 0.0433 0.0551
T
U
V
W
X 0.00 0.40 0.0000 0.0157
dimensions
[mm] [inch]
min ma x min ma x
0.41 typ.1.05 ty p.
2.54 ty p. 0.1 ty p.
4.4 typ. 0.173 typ.
2.4 typ. 0.095 typ.
0.26 typ.6.6 typ.
0.51 typ.13.0 typ.
7.5 typ. 0.295 typ.
Rev. 1.2
Page 8
2005-02-17
Page 9

SDP10S30
SDT10S30
Published by
Infineon Technologies AG,
Bereichs Kommunikation
St.-Martin-Strasse 53,
D-81541 München
© Infineon Technologies AG 1999
All Rights Reserved.
Attention please!
The information herein is given to describe certain components and shall not be considered as warranted
characteristics.
Terms of delivery and rights to technical change reserved.
We hereby disclaim any and all warranties, including but not limited to warranties of non-infringement,
regarding circuits, descriptions and charts stated herein.
Infineon Technologies is an approved CECC manufacturer.
Information
For further information on technology, delivery terms and conditions and prices please contact your nearest
Infineon Technologies Office in Germany or our Infineon Technologies Reprensatives worldwide (see address list).
Warnings
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous substances.
For information on the types in question please contact your nearest Infineon Technologies Office.
Infineon Technologies Components may only be used in life-support devices or systems with the express
written approval of Infineon Technologies, if a failure of such components can reasonably be expected to
cause the failure of that life-support device or system, or to affect the safety or effectiveness of that device
or system Life support devices or systems are intended to be implanted in the human body, or to support
and/or maintain and sustain and/or protect human life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health
of the user or other persons may be endangered.
Rev. 1.2
Page 9
2005-02-17
 Loading...
Loading...