Page 1

E2B0036-27-Y2
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
¡ Semiconductor
This version: Nov. 1997
Previous version: Mar. 1996
MSM6665-xx
DOT MATRIX LCD CONTROLLER WITH 17-DOT COMMON DRIVER AND 80-DOT SEGMENT
DRIVER
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MSM6665-xx is a dot-matrix LCD control driver which has functions of displaying characters, cursor and arbitrators.
The MSM6665-xx is provided with a 17-dot common driver, 80-dot segment driver, display RAM
and character ROM, and is controlled with the commands from the serial interface.
The character ROM can change the font data by mask option.
The MSM6665-01 has standard ROM with 256 different character fonts.
The MSM6665-xx can drive a variety of LCD panels because of the bias voltage, which determines
the LCD driving voltage, can be optionally supplied from the external source.
FEATURES
• Logic supply voltage : 2.5 to 5.5 V
• LCD driving voltage : 3.0 to 6.0 V
• Serial interface
• Contains a 17-dot common driver and an 80-dot segment driver
• Contains ROM with character fonts of (5 x 7 dot) x 256
• Built-in RC oscillator circuit
• Provided with 80-dot arbitrators
• Switchable between 1/9 duty (1 line; characters + cursor + arbitrator) and 1/17 duty (2 lines;
characters + cursor, 1 line; arbitrator)
• Character blink operation can be switched between all-characters lighting-on mode and allcharacters lighting-off mode
• Arbitrator blink operation can be switched between 5-dot unit mode and 1-dot unit mode
• Package options:
128-pin plastic QFP (QFP128-P-1420-0.50-K) (Product name: MSM6665-01GS-K)
Al pad chip (Product name: MSM6665-xx)
xx indicates code number.
1/30
Page 2
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
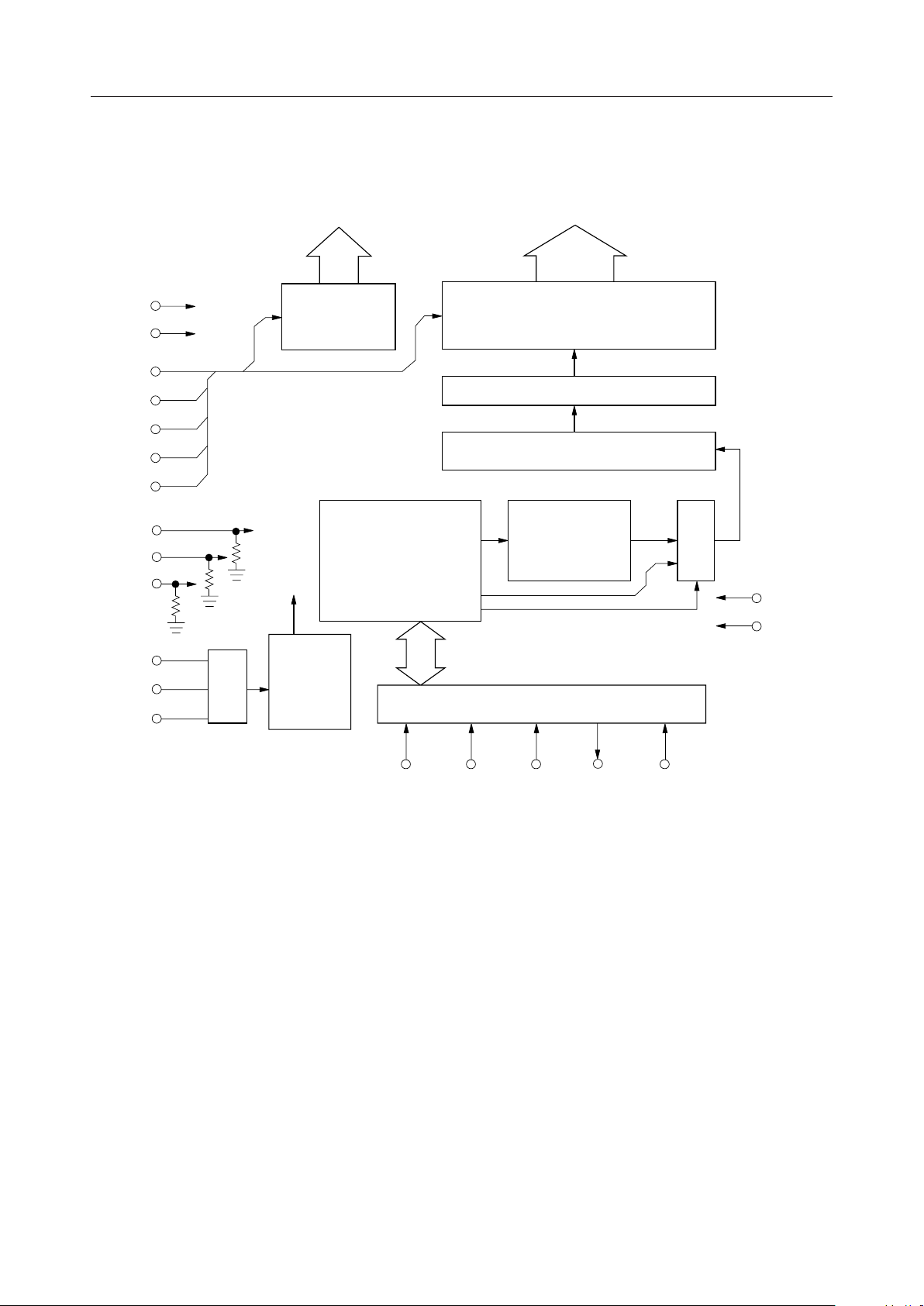
BLOCK DIAGRAM
V
DD
V
V
SS1
V
SS2
V
SS3
V
SS4
V
SS5
TEST1
TEST2
TEST3
OSC1
OSC2
OSC3
C1 - C17
17
COMMON
SS
DRIVER
S1 - S80
80
SEGMENT
DRIVER
LATCH
SHIFT REGISTER
RAM
CHARACTER
GENERATOR
ROM
F/F
GATE
(256x5x7dot)
(512-bit)
9D/
17D
RST
OSC
FREQUENCY
DIVIDER
&
TIMING
GENERATION
8
SERIAL/PARALLEL INTERFACE
CS C/ SHT SO SID
2/30
Page 3
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
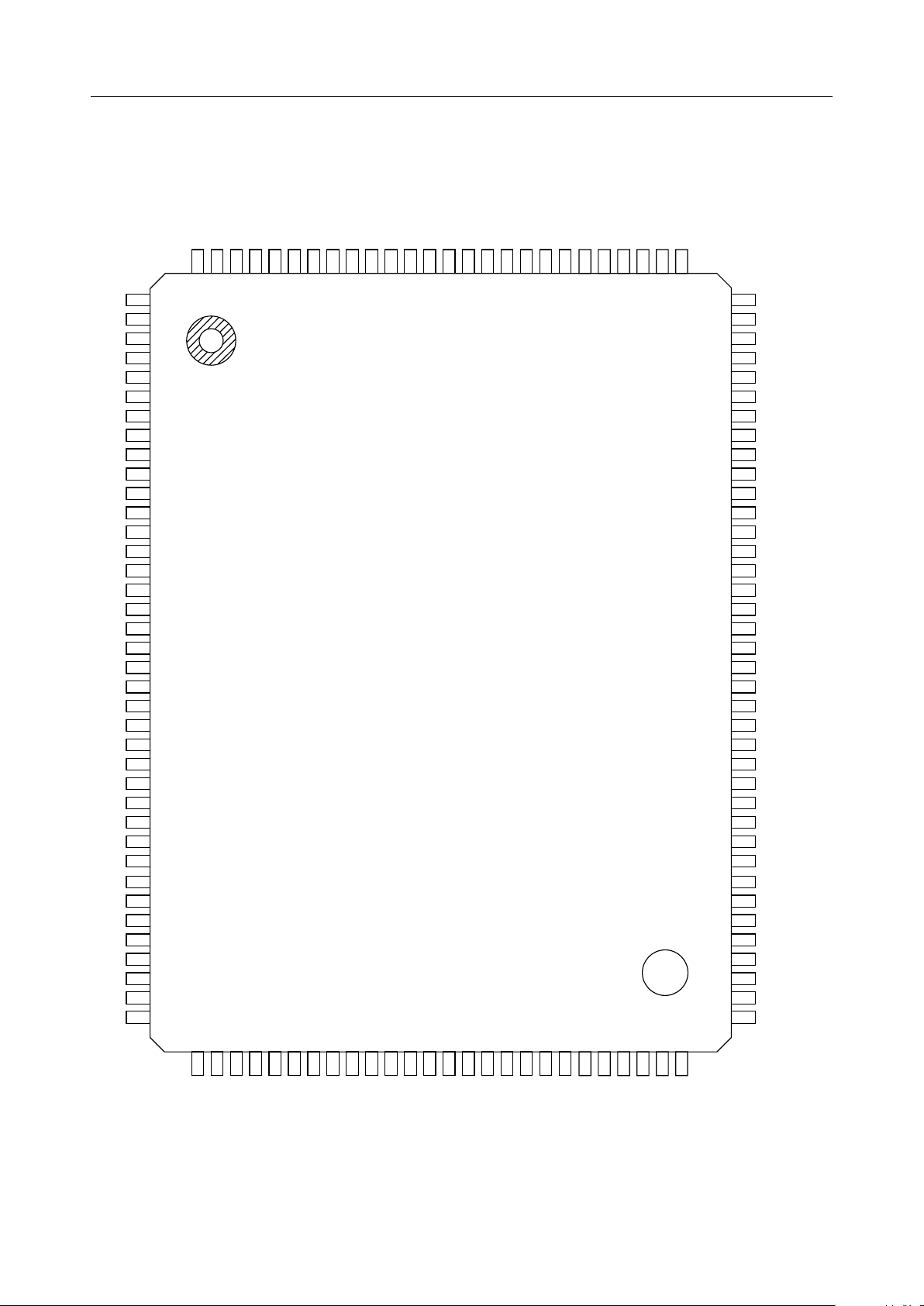
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
S77
S76
S75
S74
S73
S72
S71
S70
S69
S68
S67
S66
S65
S64
S63
S62
S61
S60
S59
S57
S56
S55
S54
S53
S52
S51
S50
S49
S48
S47
S46
NC
S45
S44
NC
S43
S42
S41
S40
S39
S38
NC
S37
S36
NC
S35
S34
S33
S32
S31
S30
S29
S28
S27
S26
S25
S24
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
S58
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
S78
108
S79
107
S80
106
NC
105
TEST2
TEST3
103
104
102
TEST1
101
OSC3
100
OSC2
NC
99
OSC1
98
V
97
96
SO
95
RST
94
9D/17D
93
SHT
92
SI
91
C/D
90
NC
89
CS
88
V
87
NC
86
V
85
V
84
V
83
V
82
VSS (GND)
81
C1
80
NC
79
C2
78
C3
77
NC
76
C4
75
C5
74
C6
73
C7
72
C8
C9
71
C10
70
C11
69
C12
68
C13
67
C14
66
C15
65
DD
SS1
SS2
SS3
SS4
SS5
39
S23
40
S22
41
S21
42
S20
43
S19
44
S18
45
S17
51
50
49
48
47
46
S11
S12
S13
S14
S15
S16
NC : No connection
128-Pin Plastic QFP
52
S10
53
S9
54
S8
55
S7
56
S6
57
S5
58
S4
49
S3
60
S2
61
S1
62
C17
63
C16
64
NC
3/30
Page 4
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Parameter UnitCondition
Supply Voltage
Bias Voltage Ta=25°C, V
Input Voltage
Power Dissipation
Storage Temperature
Symbol
V
DD
V
BI
V
I
P
D
T
STG
Ta=25°C, VDD–V
DD–VSS5
—
Ta=85°C
QFP128-1420
—
SS
*1
Rating Applicable pin
–0.3 to +7
–0.3 to +7 V VDD, V
–0.3 to V
DD
+0.3
630
–55 to +150
*1: The power dissipation depends on the heat sink characteristic of the package.
Set a junction temperature at 150°C or lower.
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter UnitCondition
Supply Voltage
Bias Voltage V
Operating Frequency
Operating Temperature
*2: RC oscillation, external input clock frequency
Symbol
V
DD
V
BI
f
op
T
op
Rating Applicable pin
VDD–V
SS
DD–VSS5
*2
——
2.5 to 5.5
3 to 6 V VDD, V
65 to 115
–40 to +85
V
V
mW
°C
V
kHz
°C
V
, V
DD
SS
SS5
All inputs
—
—
, V
V
DD
SS
SS5
OSC1
List of bias voltages
Symbol
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2
V
SS3
V
SS4
V
SS5
1/5 bias
V
DD
VDD–1/5V
VDD–2/5V
VDD–3/5V
VDD–4/5V
V
SS5
(VBI=VDD–V
1/4 bias
V
DD
BI
BI
BI
BI
VDD–1/4V
VDD–2/4V
VDD–3/4V
V
SS5
BI
BI
BI
Remarks
Highest voltage
—
—
—
—
Lowest voltage
SS5
)
4/30
Page 5
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DC Characteristics (1)
(V
=2.5 to 3.5V, VBI=3 to 6V, Ta=–40 to +85°C)
DD
Parameter
"H" Input Voltage 1
"L" Input Voltage 1
"H" Input Voltage 2
"L" Input Voltage 2
"H" Input Current 1
"L" Input Current
"H" Input Current 2
"H" Output Voltage
"L" Output Voltage
OFF Leakage
OSC "H" Output Current
OSC "L" Output Current
COM Output Resistance
SEG Output Resistance
Supply Current 1
Supply Current 2
Symbol
V
IH1
V
IL1
V
IH2
V
IL2
I
IH1
I
IL
I
IH2
V
OH
V
OL
I
OFF
I
OH
I
OL
R
C
R
S
I
DD1
I
DD2
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit Applicable pin
External clock input
External clock input
—
—
V
I=VDD
VI=0V
Pull-down resistance, V
IO=–1.5mA
I
=500mA
O
/0V
V
I=VDD
–0.5V
V
I=VDD
=0.5V
V
I
I
=±50mA
O
=±10mA
I
O
RC oscillation, f=80kHz
C=56pF, R
=10kW
S
.
.
R=76kW, no load
External clock, f=80kHz
I=VDD
0.8V
0.8V
—VDDV OSC1
DD
0 — 0.2V
—VDDV
DD
0 — 0.2V
DD
DD
V OSC1
V
—— 1 mA
Input pins except OSC1
Input pins except OSC1
Input pins except TEST
——–1mA Input pins
0.05 — 0.4 mA TEST1-TEST3
VDD–0.5
—— VS0
— — 0.5 V S0
——±1mAS0
— — –0.25 mA OSC2, OSC3
0.25 — — mA OSC2, OSC3
—— 6kW C1-C17
——15kW S1-S80
— — 0.5 mA —
— — 100 mA—
DC Characteristics (2)
Parameter
"H" Input Voltage 1
"L" Input Voltage 1
"H" Input Voltage 2
"L" Input Voltage 2
"H" Input Current 1
"L" Input Current
"H" Input Current 2
"H" Output Voltage
"L" Output Voltage
OFF Leakage
OSC "H" Output Current
OSC "L" Output Current
COM Output Resistance
SEG Output Resistance
Supply Current 1
Supply Current 2
Symbol
V
IH1
V
IL1
V
IH2
V
IL2
I
IH1
I
IL
I
IH2
V
OH
V
OL
I
OFF
I
OH
I
OL
R
C
R
S
I
DD1
I
DD2
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit Applicable pin
External clock input
External clock input
—
—
V
I=VDD
VI=0V
Pull-down resistance, V
IO=–1.5mA
=500mA
I
O
V
/0V
I=VDD
–0.5V
V
I=VDD
=0.5V
V
I
=±50mA
I
O
I
=±10mA
O
RC oscillation, f=80kHz
C=56pF, R
=10kW
S
.
.
R=76kW, no load
External clock, f=80kHz
I=VDD
(V
=4.5 to 5.5V, VBI=3 to 6V, Ta=–40 to +85°C)
DD
0.8V
0.8V
—VDDV OSC1
DD
0 — 0.2V
—VDDV
DD
0 — 0.2V
DD
DD
V OSC1
V
—— 1 mA
Input pins except OSC1
Input pins except OSC1
Input pins except TEST
——–1mA Input pins
0.3 — 1.4 mA TEST1-TEST3
VDD–0.5
—— VS0
— — 0.5 V S0
——±1mAS0
— — –0.5 mA OSC2, OSC3
0.5 — — mA OSC2, OSC3
—— 6kW C1-C17
——15kW S1-S80
— — 1.1 mA —
— — 400 mA—
5/30
Page 6
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
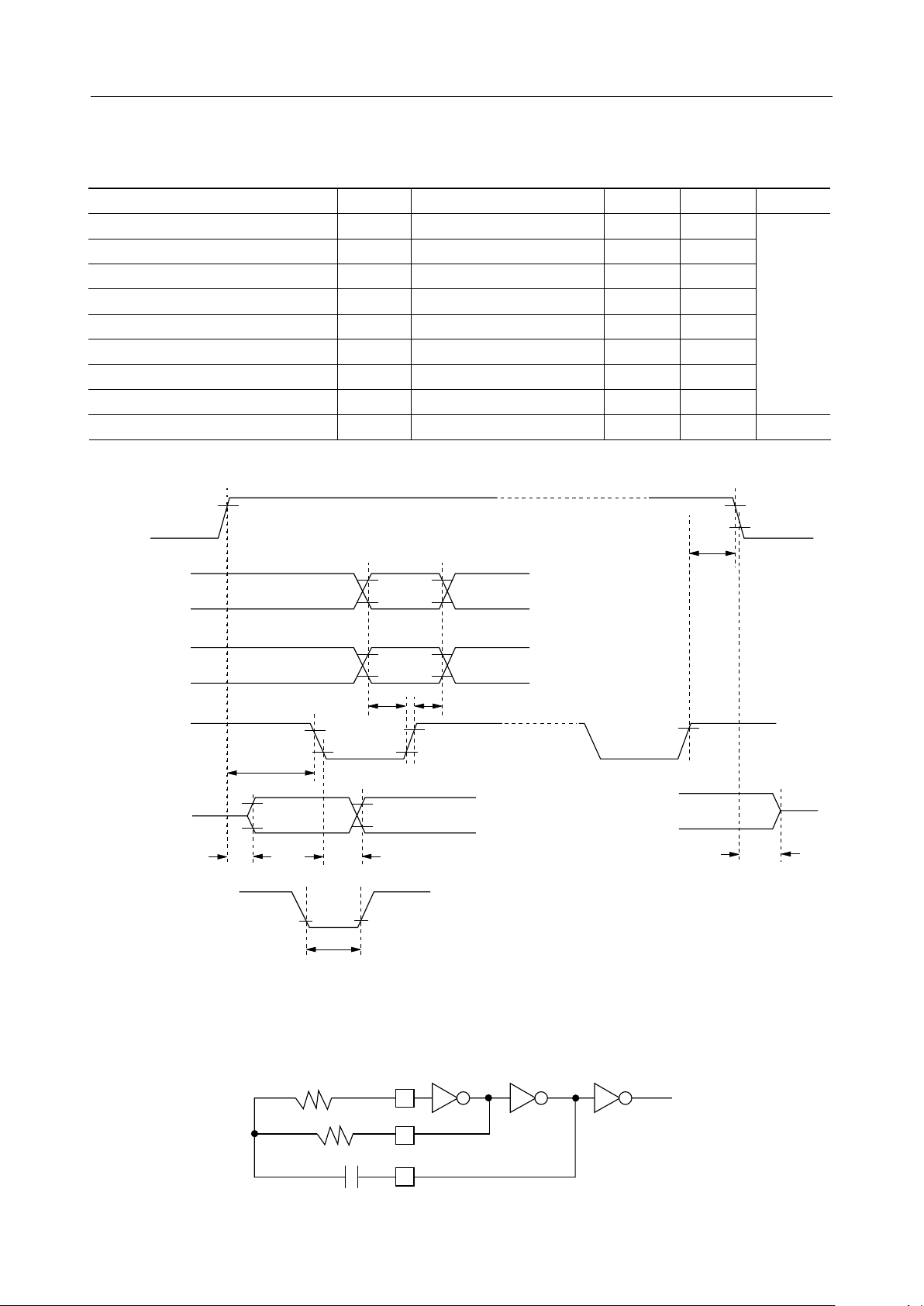
AC Characteristics
Parameter
CS Setup Time
CS Hold Time
SO ON Delay Time
SO OFF Delay Time
SO Output Delay Time
Input Setup Time
Input Hold Time
Input Waveform Rise Time, Fall Time
Reset Pulse Input Pulse Width
CS
SI
Symbol Condition
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
CS
CH
ON
OFF
DLY
t
IS
t
IH
r, tf
RT
CL=45pF
All inputs
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
V
IH2
V
IL2
(V
DD–VSS
=2.5 to 5.5V, Ta=–40 to +85°C)
Min.
300
200
—
—
0
200
200
—
5
Max.
—
—
200
200
200
—
—
50
—
t
CH
Unit
ns
µs
V
IH2
V
IL2
C/
D
SHT
SO
"Z"
t
ON
RST
Oscillation Circuit
V
IH2
V
IL2
t
IS
t
CS
V
OH
V
OL
t
DLY
V
t
RT
R
S
IL2
OSC1
t
IH
V
IH2
V
IL2
"Z"
t
OFF
*
V
=0.8V
IH2
V
IL2
=0.2V
DD
DD
VOH=VDD–0.5V
=0.5V
V
OL
R
OSC2
OSC3
C
6/30
Page 7
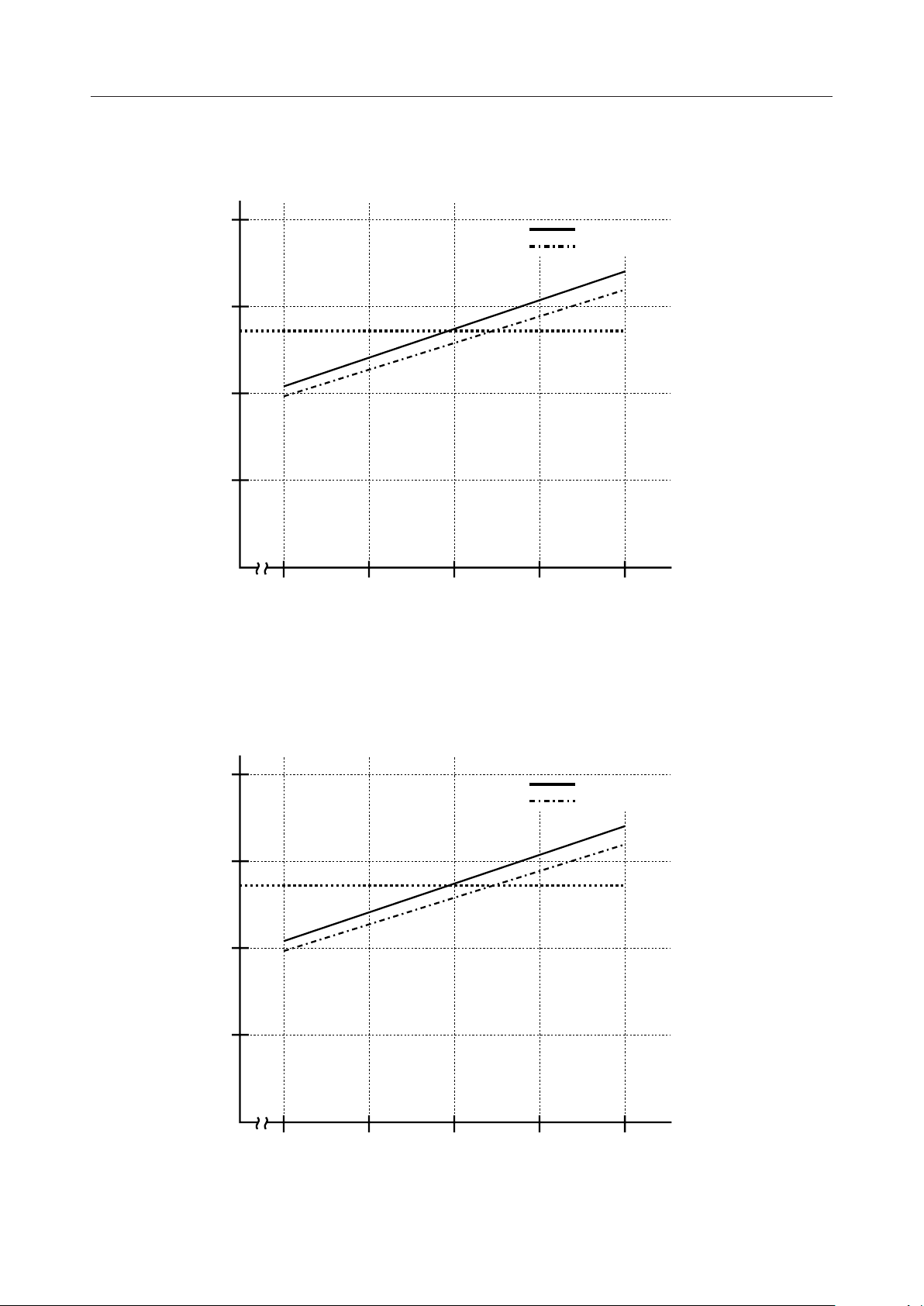
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
Oscillation Characteristics 1 (Rs=10kW, C=56pF, R variable characteristics)
1/17 duty
Frame Cycle¥2 (ms)
40
30
20
10
VDD =3.0V
V
=5.0V
DD
f=80kHz,
Frame cycle¥2=27.2ms
0
55 65 75 85 95
R Resistance (k )
W
Oscillation Characteristics 2 (Rs=10kW, R=75kW, C variable characteristics)
1/17 duty
40
30
20
Frame Cycle¥2 (ms)
10
0
VDD =3.0V
V
=5.0V
DD
f=80kHz,
Frame cycle¥2=27.2ms
35 45 55 65 75
C Capacitance (pF)
7/30
Page 8

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Pin Functional Description
• SI (Serial Input)
Input pin for inputting serially commands and display data in an 8-bit unit.
"H"="1" and "L"="0".
When CS pin is at "H" level, read-in is executed by the leading edge of SHT.
Whether input data is a command or data is determined by selecting a C/D level at the
8th leading edge of SHT.
The input data is a command if C/D="H", and display data if C/D="L".
•C/D (Command/Data)
Input pin for determining whether input data for SI pin is a command or display data.
Read-in is executed by the 8th leading edge of SHT. The input data is a command if C/
D="H", and display data if C/D="L".
• SHT (Shift Clock)
Clock input pin for reading-in SI input and C/D input.
Read-in is executed by the clock leading edge. Read-in operation is complete with 8
clocks. Inputting data during BUSY may cause malfunction.
Valid if CS pin is at "H" level.
• SO (Serial Out)
Serial output pin for reading-out BUSY/NON-BUSY and display data. "H"="1" and
"L"="0". If CS pin is at "H" level and Serial Out Enable is set with the command, output
is executed. Otherwise, this pin becomes high impedance.
BUSY/NON-BUSY is output when CS pin is at "H" level. BUSY if "L" and NON-BUSY
if "H". It goes BUSY after the 8th leading edge of SHT, then goes NON-BUSY
automatically after a specified time.
Display data is output synchronously with the leading edge of SHT.
Input the "SOE/D" instruction to set this output to serial out enable or a high impedance
state because the pin status is undefined after the power is applied.
• CS (Chip Select)
Chip Select input pin.
"Chip Select ON" if CS pin is at "H" level, and "Chip Select OFF" at "L" level. When "L"
level is input, SO pin becomes open and SHT pin becomes equivalent to "H" level inside
of the IC. Moreover, it prevents the input stages of SI, C/D and SHT pins from current
flowing.
* For SI, C/D, SHT, SO, and CS, refer to "I/O Procedure".
• RST
Direct input reset input pin.
By inputting "L" level pulse into RST pin, DISP, ABBC1/5, ABB, and BPC commands are
set as D0="0". Before turning on the power, be sure to set RST pin at "L" level once. Setting
this pin at "L" level during command execution may cause malfunction.
• 9D/17D (1/9Duty/1/17Duty)
Duty setting input pin.
1/9 duty is set if this pin is at "H" level, and 1/17 duty at "L" level. Choice depends on
the type of panel to be used.
8/30
Page 9
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
If 1/9 duty is selected, common outputs C10 to C17 should be set open.
• TEST1, TEST2, TEST3
Test signal input pins.
The manufacturer uses these pins for testing.
The user should connect this pin to GND or leave open.
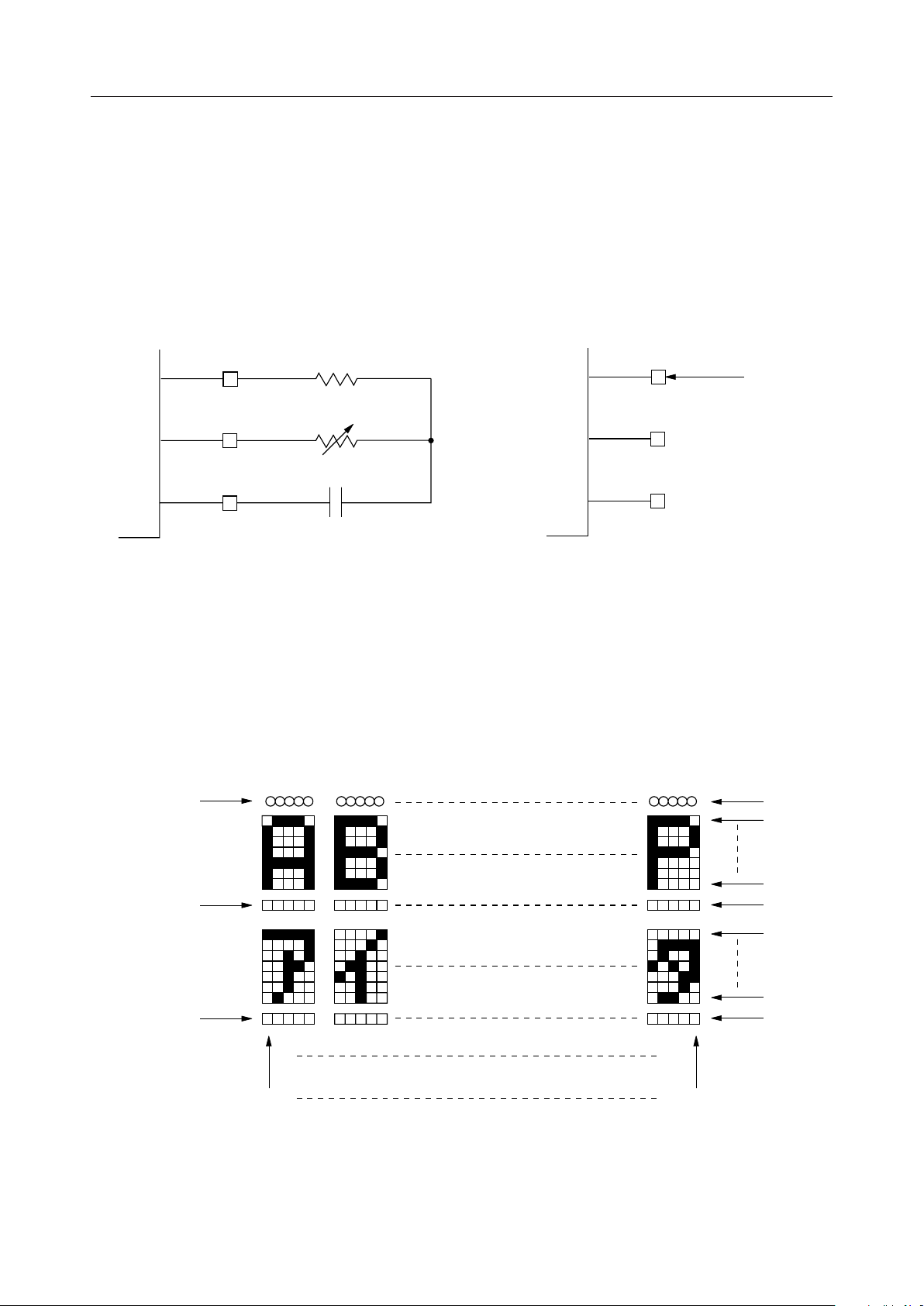
• OSC1, OSC2, OSC3
Pins used for 80kHz RC oscillation circuit formation and as external master clock input
pin. Leave OSC2 and OSC3 open during input of external master clock.
10k
76±5k
56pF
W
W
OSC1
OSC2
OSC3
< Oscillation circuit wiring diagram >
• C1 - C17, S1 - S80 (Common 1 - 17, Segment 1 - 80)
LCD output pins to be connected with the LCD panel. Turning into AC is made by frame
inversion.
Use the C1 to C9 pins during use at 1/9 duty, and leave the C10 to C17 pins open.
ÆRefer to "Relationship between panel and LCD output".
Arbitrator
OSC1
80kHz
OSC2
OPEN
OSC3
OPEN
[External master clock input][RC oscillation circuit formation]
C1
C2
Cursor
Cursor
•VDD, V
Supply voltage pins. VDD should be set at "H" level.
C8
C9
C10
C16
C17
S1 S80
<Relationship between panel and LCD output>
SS
9/30
Page 10

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
VSS is a GND pin. If the battery is used, VDD is connected to the positive pin, and VSS to
the negative pin.
•V
SS1
, V
SS2
, V
SS3
, V
SS4
, V
SS5
LCD bias voltages input pins.
(EXAMPLE)
Case of 1/5 bias (VBI=VDD–V
Highest voltage : V
Lowest voltage : V
V
V
V
V
DD
SS1
SS2
SS3
SS4
SS5
)
SS5
(VDD–1/5 VBI)
(VDD–2/5 VBI)
(VDD–3/5 VBI)
(VDD–4/5 VBI)
Case of 1/4 bias (VBI=VDD–V
Highest voltage : V
Lowest voltage : V
V
V
V
DD
SS1
SS2
SS4
SS5
, V
SS3
(VDD–1/4 VBI)
(VDD–2/4 VBI)
(VDD–3/4 VBI)
SS5
)
10/30
Page 11
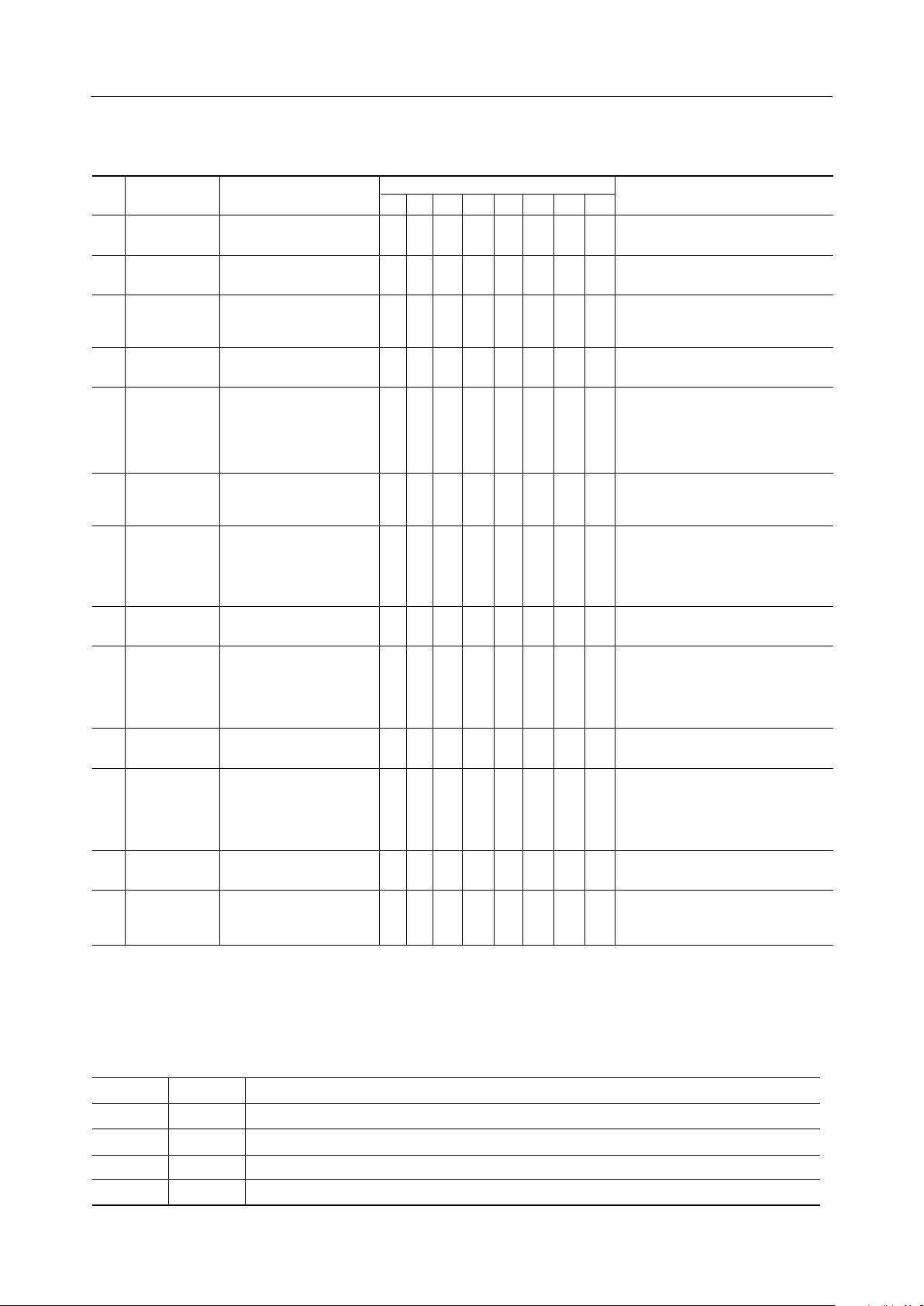
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
List of Commands
Mnemonic
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
LPA
LOT
BKCG 1/0
SOE/D
DISP
ABBC 1/5
ABB
AINC
Load Pointer Address
Load Option
Bank Change 1/0
Serial Out Enable/Disable
Display on/off
Arbitrator Blink Control
1/5 dot
Arbitrator Blink
Address Increment
Operation
D
7
6
1
15A54A43A32A21A10A0
X
X
1
1
0
1
0
0
X
0
0
1
1
0
X
0
0
1
0
1
X
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
X
1
X
0
0
1
I1
X : Don't care
Comments
Serial addresses 0 to 47
Meanings for I1 and I0 are set as in
I0
the table below.
Valid only when 1/9duty is selected.
Switching between display addresses
1/0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0 to 15 and 16 to 31.
Switching between output and high
1/0
impedance of SO
Display ON if D0="1"
Display OFF if D0="0"
1/0
When at Display OFF, V
voltage is output to all the COM and
SEG pins.
Sets arbitrator blink in a 1dot unit or
1/0
a 5dot unit. 1dot if D0="1", 5 dot if
D0="0"
Data that is input via SI after setting
D0="1", is set as data for arbitrator
1/0
blink (1-dot unit). This is cancelled by
D0=“0”
Pointer address is incremented by 1.
X
DD
level
Controls blinking of characters and
arbitrators (in 5 dots). Though arbitrator
X
blink that is set as all-blank displayed is
acceptable, blinking does not occur.
Turns cursor on or off.
X
Controls blinking of cursor.
But, though blinking setting with
X
no cursor-on setting is acceptable,
blinking does not occur.
X
CHB + CSB
Sets blink patterns of characters.
1/0
( :chara.) if D0="1", ( :chara.)
❑■
if D0="0"
10
11
12
13
9
CHB
CSC
CSB
CCB
BPC
Character Blink on/off
Cursor Control on/off
Cursor Blink on/off
Character & Cursor
Blink on/off
Blink Pattern Control
0
0
0
0
1
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
00
1/0
0
0
X
1/0
1
0
X
1/0
0
1
X
1/0
1
1
X
1
0
0
X
Notes: 1. Entering commands number 1 to 7 and number 13 does not affect pointer address.
2. By entering commands number 8 to 12 or display code data, pointer address is
automatically incremented by 1.
3. When Reset is entered, commands number 5 to 7 and number 13 are set to D0="0".
I1
0
0
1
1
I0
0
1
0
1
Operation is cancelled. (No operation)
Hereafter, equivalent to writing blank code at each AINC execution.
Hereafter, cursor-off and blink-cancellation are executed at each AINC execution.
Both of above two operations are indicated.
Operation
11/30
Page 12

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
Command Description
[D7, D6, D5, D4, D3, D2, D1, D0], X=don’t care
• LPA (Load Pointer Address)
[1,1,A5,A4,A3,A2,A1,A0]
The command sets "address" data into the address pointer to specify an address on
which command execution affects and an address where display data is stored. The
"address" is a number between 0H and 2FH, given by A0 through A5 in hexadecimal.
When addresses 30H through 3FH are specified, display data and CHB, CSC, CSB, CCB
commands become invalid through an address pointer is set up. Normally, the address
pointer is a loop of 0H through 2FH.
• LOT (Load Option)
[1,0,1,1,X,X,I1,I0]
This command indicates some specific operation of display at the current address which
is performed each time of AINC command execution.
Operation is specified by bit I1 and I0 of the command.
I1
0
0
1
1
I0
0
1
0
1
Operation is cancelled. (No operation)
Hereafter, equivalent to writing blank code at each AINC execution.
Hereafter, Cursor-off and blink-cancellation are executed at each AINC execution.
Both of above two operations are indicated.
Operation
Note) When blink-cancellation is executed, all RAM data, which controls blinks for each bit of the
arbitrator, go zeros.
• BKCG 1/0 (Bank Change 1/0)
[1,0,0,X,0,0,0,1/0]
Command used to do switching between display address groups (switching between
BANKs), which is valid only when 1/9duty display is selected.
When D0 is "0", display address range becomes 0 through 15, and 32 through 47.
When D0 is "1", display address range becomes 16 through 31, and 32 through 47.
Command execution and display data setting are not affected by Bank setting.
The D0 status is not changed by Reset inputting. The D0 status is unknown when the
system is powered on. So D0 must be set to "0" or "1" with the command.
• SOE/D (Serial Out Enable/Disable)
[1,0,0,X,0,1,1,1/0]
Command used to control the impedance of SO output pin.
When D0 is "1", display data is output via SO pin. When D0 is "0", SO pin goes to high
impedance.
The D0 status is not changed by Reset inputting. The D0 status is unknown when the
system is powered on. So D0 must be set to "0" or "1" with the command.
12/30
Page 13

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
• DISP (Display on/off)
[1,0,0,X,1,0,0,1/0]
Command used to control lighing-on and lighting-off for the LCD panel.
When D0 is "1", the display of the LCD panel goes on, and When D0 is "0", it goes off.
When the display is off, the VDD level voltage is output on all of pins of both the segment
driver and the common driver.
D0 is set to "0" after inputting Reset.
• ABBC 1/5 (Arbitrator Blink Control 1/5 dot)
[1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1/0]
Command used to do switching between arbitrator’s blinking in a 1-dot unit and or in
a 5-dot unit.
When D0 is "1", arbitrator’s blinking comes in the 1-dot unit mode.
When D0 is "0", it comes in the 5-dot unit mode.
D0="0" is set after inputting Reset.
Note) 1-dot unit blink setting Æ • See ABB.
5-dot unit blink setting Æ • See CHB.
• ABB (Arbitrator Blink)
[1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1/0]
Command used to control on/off of blinking, which is valid only when arbitrator’s
blinking is set in the 1-dot unit mode.
Data , which are entered via SI pin after setting D0="1", are taken as arbitrator blink data
(1-dot unit).
Input blink data correspond to each of arbitrator’s dots. When "1", blinking is on, and
when "0", blinking is off.
Note that the arbitrator, which arbitrator-on is not specified, is not able to blink, though
blink-setting is available. Dummy data must be entered into the arbitrator blink data D5
thru D7.
It is impossible to write data in addressed 00H through 31H.
D0="0" is set after inputting Reset.
Note) If blink is set in the 5-dot unit mode, ABB command setting (D0="1" or "0") is
available, but blink-on/off setting via input of display data is impossible.
• AINC (Address Increment)
[1,0,0,X,1,X,1,X]
Command used to increment the value of the address pointer by 1.
The pointer is increment by 1 each time this command is executed. The operation set by
LOT command is given to the address before being increased by 1 each time this
command is execution.
13/30
Page 14

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
• CHB (Character Blink on/off)
[0,X,X,X,0,0,1/0,X]
Command used to control blinking of characters and arbitrator (5-dot unit).
This command is executed to the address indicated by the address pointer. Blinking is
on by setting D1="1", and off by setting D1="0".
For blinking of characters, all lighting-on or all lighting-off, and characters-displaying
are repeated.
Choosing between all lighting-on and all lighting-off is controlled by BPC command.
For arbitrator, only lighting bits repeat lighting-off or lighting-off. The blink control or
arbitrator is valid only when ABBC1/5="0" and in the 5-dot unit mode.
Refer to "BPC".
• CSC (Cursor Control on/off)
[0,X,X,X,0,1,1/0,X]
Command used to control lighting-on and lighting-off of cursor.
This command is executed to the address indicated by the address pointer.The cursor
is lighting on by setting D1="1", and lighting off by setting D1="0".
• CSB (Cursor Blink on/off)
[0,X,X,X,0,1,1/0,X]
Command used to control blinking of cursor.
This command is executed to the address indicated by the address pointer. Blinking is
on by setting D1="1", and off by setting D1="0".
The blinking in the address, where cursor-lighting-on is not specified, does not occur,
though the command of blinking is acceptable. Blinking starts by specifying cursorlighting-on.
• CCB (Character & Cursor Blink on/off)
[0,X,X,X,1,1,1/0,X]
Command used to execute both CHB command and CSB command.
• BPC (Blink Pattern Control)
[1,0,0,X,0,0,1,1/0]
Command used to control blink patterns of characters.
When D0="1" is set, all lighting-off (35 dots) and characters-displaying are repeated.
When D0="0" is set, all lighting-on (35 dots) and characters-displaying are repeated.
When D0="1" is set, if characters are blank, their blinkings do not occur in appearance.
When D0="0" is set, if characters are in all lighting-on, their blinkings do not occur in
appearance.
D0 is set to "0" affer inputting Reset.
[D0 = "1"] [D0 = "0"]
• Increment (+1) in address pointer
When display data or arbitrator data (1-dot unit) is entered or when the following
commands are executed, the address pointer is incremented by 1.
AINC, CHB, CSC, CSB and CCB.
14/30
Page 15

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
I/O Procedure
• Input timing (command input, display data input)
8-bit input synchronization is taken by this leading edge.
If input in an 8-bit unit is kept, the following leading edges of CS is not needed.
CS
C/ D
SI
SHT
SO
"Z"
NON-BUSY/
MSB
BUSY
don't care C/D
• Output timing (display code data output)
Code data or arbitrator data indicated by the address pointer is always output, provided
that the SOE command has already been input.
CS
Synchronization in an 8-bit unit.
LSB
BUSY
17D : Max=[Master clock cycle] x 10
9D : Max=[Master clock cycle] x 20
C/ D
SHT
SO
NON-BUSY/ BUSY
"Z"
MSB
don't care
LSB
BUSY
NON-BUSY
17D : Max=[Master clock cycle] x 10
9D : Max=[Master clock cycle] x 20
Note) If CS is set at "L" level when 8-bit read-out is not complete, and CS is set at "H" level again, then
read-out operation is executed, uncomplete data will be output continually and the remaining
read-out data will be zero.
15/30
Page 16

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
Method of Calculating Various Types of Frequencies
• Original Clock Frequency and Blink Frequency
Blink cycle calculation
([Original clock cycle] x 5) x 214 = Blink cycle ............................................. Formula 1
From formula 1, the blink frequency can be calculated.
Example) When the original clock is 80kHz:
Clock cycle Ts=12.5 [µs]
From formula 1,
Blink cycle Tb=(12.5 x 10-6 x 5) x 214 = 1.024 [s]
Thus,
Blink frequency = 1 [Hz]
• Original Clock Frequency and Frame Frequency
Frame cycle calculation
1/9 DUTY: (Original clock cycle) x 1152 = Frame cycle.............................Formula 2
1/17 DUTY: (Original clock cycle) x 1088 = Frame cycle...........................Formula 3
From formulas 2 and 3, the frame frequency can be calculated.
Example) In the original clock 80kHz and 1/17 DUTY specifications:
Clock cycle Ts=12.5 [µs]
From formula 3,
Frame cycle Tf=12.5 x 10-6 x 1088 = 13.6 [ms]
Thus,
Frame frequency = 73.5 [Hz]
16/30
Page 17

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
Display and Memory Address
Arbitrator
Character 1
Display
RAM map
32
16
16
Cursor 1
Character 2
Cursor 2
33
0
0
1
1
17
17
47
15
15
31
31
Arbitrator
Character 1
Cursor 1
Character 2
Cursor 2
Note Characters are entered with codes.
Arbitrator is displayed with no CG ROM. The relationship between input data and display is shown
below.
S5n+1
D4 D0
S5n+5
Dummy input is required for serial data D7 through D5.
Either "1" or "0" is available for data to be input into D7 through D5.
n : 0-15
17/30
Page 18
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
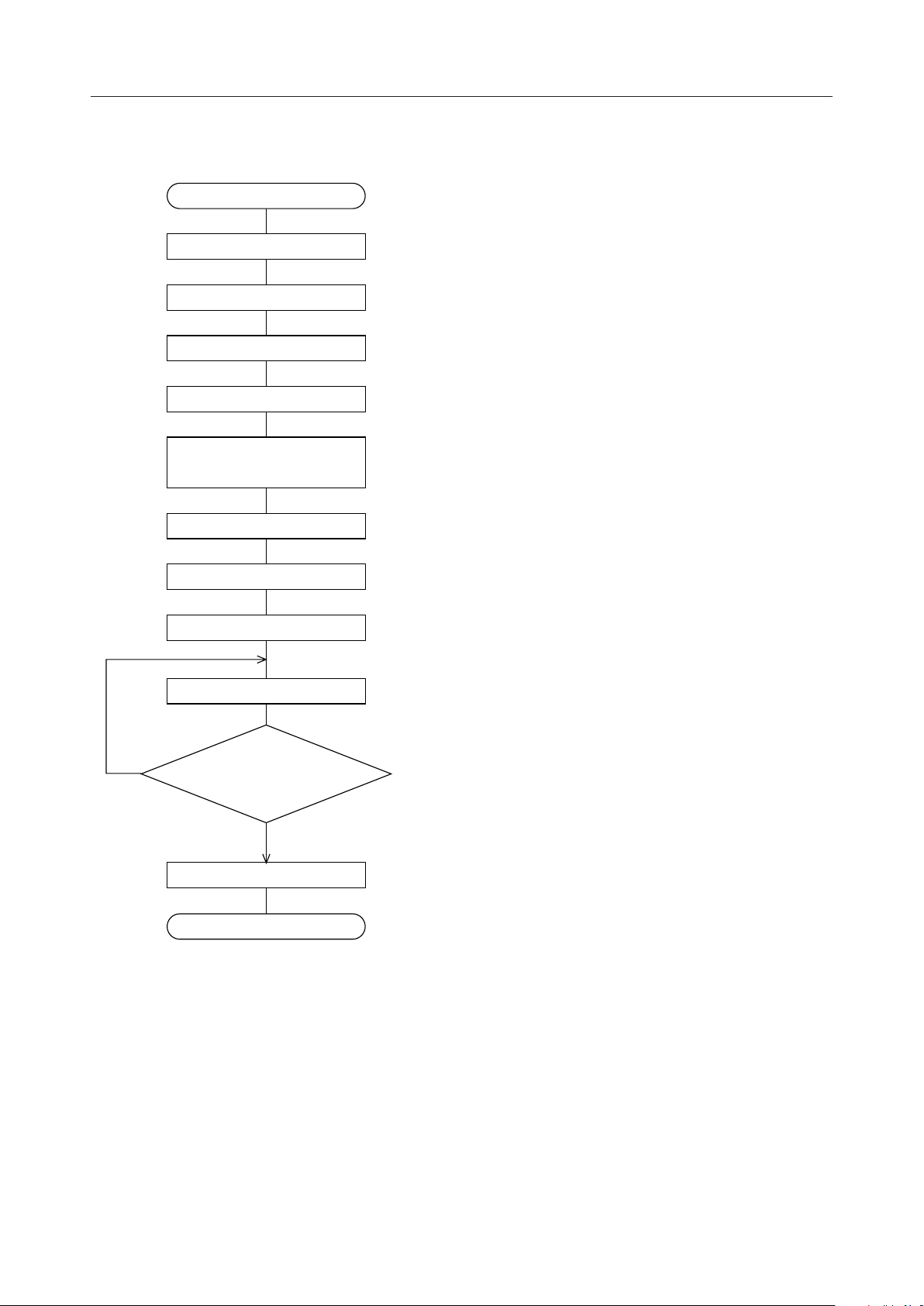
Flowchart for Power-On Timing
Turn on power
Reset input 5ms required; external reset input or power-on reset input
CS="H" The device is enabled.
SOE/D, D0="1" Make the SO output enable, to perform busy detection.
NO
Wait for 20 clocks
BPC and BKCG
command set
LOT, I1="1", I0="1"
AINC executed 48 times Input the AINC command to clear the RAM data.
LOT, I1="0", I0="0" Release the Load Option.
Input display data for initial screen
Is Input of display data for
initial screen completed?
YES
Input a wait for the SOE/D command processing. (For the processing
of each command after this, perform busy detection. *1)
Set the blink pattern and bank change mode.
Set the Load Option. (Blank-code writing and blink-cancellation
are executed each time the AINC command is executed.)
DISP, D0="1" Display is turned on and the initial screen is displayed.
Normal operation
*1 After the required commands and display data are entered, perform busy detection
based on the SO pin status. When it is confirmed that the status has been changed
from BUSY (SO="L") to NON-BUSY (SO="H"), enter the next data.
If busy detection is not performed, wait for 10 master oscillation clocks when used at
1/17 duty or for 20 master oscillation clocks when at 1/9 duty, then enter the next
data.
18/30
Page 19

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
Waveforms Applied to LCD
1/17 duty (1/5 bias)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
V
DD
V
SS1
V
C1
C2
SS2
V
SS3
V
SS4
V
SS5
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2
V
SS3
V
SS4
V
SS5
C17
Sn
= lighting on
= lighting off
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2
V
SS3
V
SS4
V
SS5
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2
V
SS3
V
SS4
V
SS5
19/30
Page 20

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
1/9 duty (1/4 bias)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
V
DD
V
SS1
C1
C2
V
SS2, 3
V
SS4
V
SS5
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2, 3
V
SS4
V
SS5
C9
Sn
= lighting on
= lighting off
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2, 3
V
SS4
V
SS5
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2, 3
V
SS4
V
SS5
20/30
Page 21

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
1/17 duty (1/4 bias)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
C1
C2
C17
Sn
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2, 3
V
SS4
V
SS5
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2, 3
V
SS4
V
SS5
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2, 3
V
SS4
V
SS5
V
DD
V
SS1
V
SS2, 3
V
SS4
V
SS5
= lighting on
= lighting off
21/30
Page 22

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
Codes and Character Fonts of Code -01
00H : 08H : 10H : 18H : 20H : SP 28H : ( 30H : 0 38H : 8
01H : 09H : 11H : 19H : 21H : ! 29H : ) 31H : 1 00H : 9
02H : 0AH : 12H : 1AH : 22H : " 2AH : 32H : 2 3AH : :
03H : 0BH : 13H : 1BH : 23H : # 2BH : + 33H : 3 3BH : ;
04H : 0CH : 14H : 1CH : 24H : $ 2CH : , 34H : 4 3CH : <
05H : 0DH : 15H : 1DH : 25H : % 2DH : – 35H : 5 3DH : =
06H : 0EH : 16H : 1EH : 26H : & 2EH : . 36H : 6 3EH : >
07H : 0FH : 17H : 1FH : 27H : ' 2FH : / 37H : 7 3FH : ?
22/30
Page 23

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
40H : @ 48H : H 50H : P
41H : A 49H : I 51H : Q
42H : B 4AH : J 52H : R
43H : C 4BH : K 53H : S
58H : X
59H : Y
5AH : Z
5BH : [
60H : ` 68H : h
61H : a 69H : i
62H : b 64H : j
63H : c 6BH : k
70H : p
71H : q
72H : r
73H : s
78H : x
79H : y
7AH : z
7BH : {
44H : D 4CH : L 54H : T
45H : E 4DH : M 55H : U
46H : F 4EH : N 56H : V
47H : G 4FH : O 57H : W
5CH :
5DH : ]
5EH : ^
5FH : _
/
64H : d 6CH : I
65H : e 6DH : m
66H : f 6EH : n
67H : g 6FH : o
74H : t
75H : u
76H : v
77H : w
7CH :
70H : }
7EH : ~
7FH : £
23/30
Page 24

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
Ä
8ØH :
81H : A 89H : a 91H : ö 99H : i A1H : 49H : B1H : B9H :
82H : Æ 8AH : à 92H : Ù 9AH : ¿ A2H : AAH : B2H : BAH :
83H : Ç 93H : ü 9BH : § A3H : ABH : B3H : BBH :
88H : ä 9ØH : n 98H : A0H : ¥ A8H : B0H : — B8H :
8BH : a
84H : É 8CH : æ 94H : a 9CH : ° A4H : aCH : B4H : BCH :
85H : N 8DH : ç 95H : b 9DH : ¨ A5H : ADH : B5H : BDH :
86H : Ö 8EH : é 96H : Ø 9EH : º A6H : AEH : B6H : BEH :
87H : Ü 8FH : è 97H : ø 9FH : ¢ 27H : 2FH : 37H : 3FH :
24/30
Page 25

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
CØH : C8H : DØH : D8H : EØH : E8H : ≠ FØH : G F8H : e
C1H : C9H : D1H : D9H : E1H : E9H : Ø F1H : F9H :
C2H : CAH : D2H : DAH : E2H : EAH : F2H : q FAH : p
C3H : D3H : DBH : E3H : EBH : F3H : X FBH : s
C4H : CCH : D4H : DCH : E4H : ECH : F4H : S FCH : ü
CBH :
l
C5H : CDH : D5H : DDH : E5H : EDH : F5H : F FDH :
C6H : CEH : D6H : DEH : E6H : Æ EEH : FEH : Y FEH :
C7H : CFH : D7H : DFH : ° E7H : ¨ EFH : F7H : W
FFH :
25/30
Page 26
¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
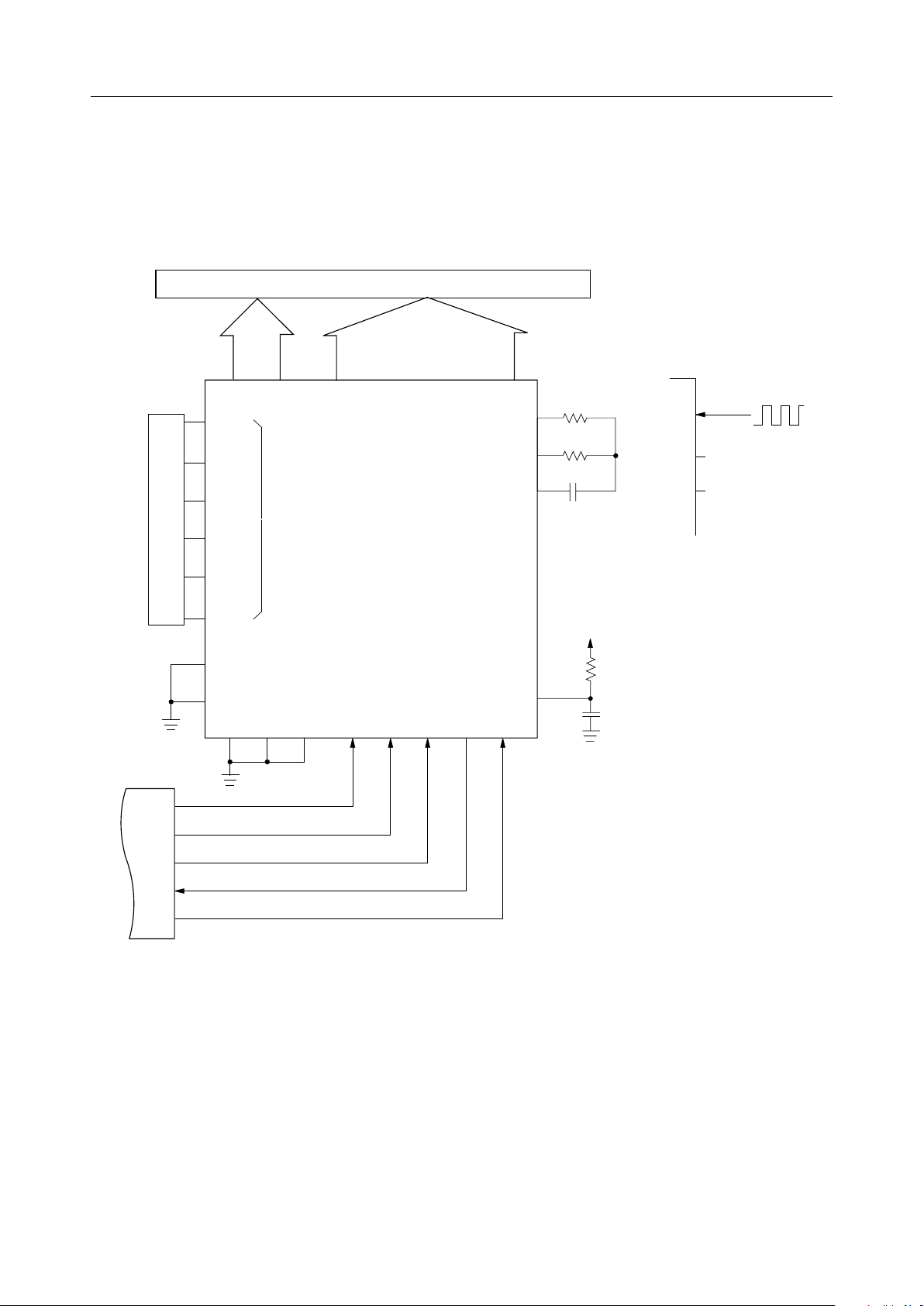
APPLICATION CIRCUIT
Example : 1/17 duty, 1/5 bias
Cursor-contained (5 x 7 dot )16-character x 2-line LCD panel
17 dot
COM SEG
C1-C17 S1 - S80
V
DD
Vss
1
Vss
2
LCD bias
Vss
3
Vss
Vss
9D/
4
5
17D
Bias Generation Circuit
Vss
1-3
TEST CS C/ SHT SO SID
80 dot
MSM6665-xx
OSC1
OSC2
OSC3
RST
10k
75k
W
W
56pF
OSC1
80kHz
OSC2
or
OSC3
OPEN
OPEN
PORT
26/30
Page 27

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
PAD CONFIGURATION
Pad layout
Chip size : 6.05 ¥ 4.98mm
Passivation film etched hole : 110 ¥ 110mm
Y
93
117
Pad Coordinates
92
59
1 33
58
X
34
Pad No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Pad Name X (mm) Y (mm) Pad No. Pad Name
C15 –2486 –2332
C14 –2336 –2332
C13 –2186 –2332
C12 –2036 –2332
C11 –1886
C10 –1736
C9 –1586
C8 –1436
C7 –1286
C6 –1136
C5
C4
C3
C2
C1
V
V
V
V
V
SS
SS5
SS4
SS3
SS2
–986
–836
–686
–536
–386
–227
–67
83
233
383
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40 S76 2870
V
SS1
CS 683
C/D 833
SI 983
SHT 1133
9D/17D 1283
RST 1433
SO 1583
V
DD
OSC1
OSC2
OSC3
TEST1
TEST2
TEST3
S80
S79
S78
S77
X (mm) Y (mm)
533 –2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
1733
1891
2308
2789
2659
2870
2870
2870
2870
2870
2870
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–2332
–1797
–1647
–1347
–1197
–1047
–897
–747
27/30
Page 28

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
Pad No. Pad Name
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
S75 2870 –567
S74 2870 –447
S73 2870 –297
S72 2870 –147
S71 2870 3
S70 2870 153
S69 2870 303
S68 2870 453
S67 603
S66
S65
S64
S63
S62
S61
S60
S59
S58
S57
S56
S55
S54
S53
S52
S51
S50
S49
S48
S47
S46
S45
S44
S43
S42
S41
S40
S39
S38
S37
S36
X (mm) Y (mm)
2870
2870
2870
2870
2870
2870
2870
2870
2870
2870
2482
2332
2182
2032
1882
1732
1582
1432
1282
1132
982
832
682
532
382
232
82
–68
–218
–368
–518
–668
753
903
1053
1203
1353
1503
1653
1803
1953
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
Pad No.
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
Pad Name X (mm) Y (mm)
S35 –818 2332
S34 –968
S33 –1118
S32 –1268
S31 –1418
S30 –1568
S29 –1718
S28 –1868
S27 –2018
S26
S25
S24
S23
S22
S21
S20
S19
S18
S17
S16
S15
S14
S13
S12
S11
S10
S9
S8
S7
S6
S5
S4
S3
S2
S1
C17
C16
–2168
–2318
–2468
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
–2870
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
2332
1803
1653
1503
1353
1203
1053
903
753
603
453
303
153
–147
–297
–447
–597
–747
–897
–1047
–1197
–1347
–1497
–1647
–1797
3
28/30
Page 29

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
Pin and Pad Correspondence
The symbol for each chip pad and package pin is equal, but the numbers for each pad and pin
are not equal.
If both chips and packaged devices are used, the number for each chip pad should be
corresponded to the number for each package pin according to each symbol listed in the table
below.
Chip
Symbol
Package
Pad Pin
C15 1 65
Symbol
OSC2 31 100
Package
Chip
Pad Pin
Package
Chip
Symbol
Pad Pin
S55 61 3
Symbol
S25 37
C14 2 66 OSC3 32 101 S54 62 4 S24
C13 3 67 TEST1 33 102 S53 63 5 S23
C12 4 68 TEST2 34 103 S52 64 6 S22
C11 5 69 TEST3 35 104 S51 65 7 S21
C10 6 70 S80 36 106 S50 66 8 S20
C9 7 71 S79 37 107 S49 67 9 S19
C8 8 72 S78 38 108 S48 68 10 S18
C7 9 73 S77 39 109 S47 69 11 S17
C6 10 74 S76 40 110 S46 70 12 S16
C5 11 75 S75 41 111 S45 71 14 S15
C4 12 76 S74 42 112 S44 72 15 S14
C3 13 78 S73 43 113 S43 73 17 S13
C2 14 79 S72 44 114 S42 74 18 S12
C1 15 81 S71 45 115 S41 75 19 S11
(GND) 16 82 S70 46 116 S40 76 20 S10
V
SS
V
SS5
V
SS4
V
SS3
V
SS2
V
SS1
17 83 S69 47 117 S39 77 21 S9
18 84 S68 48 118 S38 78 22 S8
19 85 S67 49 119 S37 79 24 S7
20 86 S66 50 120 S36 80 25 S6
21 88 S65 51 121 S35 81 27 S5
CS 22 89 S64 52 122 S34 82 28 S4
C/D 23 91 S63 53 123 S33 83 29 S3
SI 24 92 S62 54 124 S32 84 30 S2
SHT 25 93 S61 55 125 S31 85 31 S1
9D/17D 26 94 S60 56 126 S30 86 32 C17
RST 27 95 S59 57 127 S29 87 33 C16
SO 28 96 S58 58 128 S28 88 34
V
DD
29 97 S57 59 1 S27 89 35
OSC1 30 98 S56 60 2 S26 90 36
Chip
Package
Pad Pin
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
–
–
–
–
–
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
–
–
––
29/30
Page 30

¡ Semiconductor MSM6665-xx
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
(Unit : mm)
QFP128-P-1420-0.50-K
Mirror finish
Package material
Lead frame material
Pin treatment
Solder plate thickness
Package weight (g)
Epoxy resin
42 alloy
Solder plating
5 mm or more
1.19 TYP.
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The SOP, QFP, TSOP, SOJ, QFJ (PLCC), SHP and BGA are surface mount type packages, which
are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity absorbed in storage.
Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki’s responsible sales person for the
product name, package name, pin number, package code and desired mounting conditions
(reflow method, temperature and times).
30/30
 Loading...
Loading...