Page 1
TM
MP2105
1MHz, 800mA Synchronous
Step-Down Converter
The Future of Analog IC Technology
TM
DESCRIPTION
The MP2105 is a 1MHz constant frequency,
current mode, PWM step-down converter. The
device integrates a main switch and a
synchronous rectifier for high efficiency without
an external Schottky diode. It is ideal for
powering portable equipment that runs from a
single cell Lithium-Ion (Li+) battery. The
MP2105 can supply 800mA of load current from
a 2.5V to 6V input voltage. The output voltage
can be regulated as low as 0.6V. The MP2105
can also run at 100% duty cycle for low dropout
applications.
The MP2105 is available in a low profile (1mm)
5-pin, TSOT package.
EVALUATION BOARD REFERENCE
Board Number Dimensions
EV2105DJ-00A 2.0”X x 2.0”Y x 0.5”Z
FEATURES
• High Efficiency: Up to 95%
• 1MHz Constant Switching Frequency
• 800mA Available Load Current
• 2.5V to 6V Input Voltage Range
• Output Voltage as Low as 0.6V
• 100% Duty Cycle in Dropout
• Current Mode Control
• Short Circuit Protection
• Thermal Fault Protection
• <0.1µA Shutdown Current
• Space Saving 5-Pin TSOT23 Package
APPLICATIONS
• Cellular and Smart Phones
• Microprocessors and DSP Core Supplies
• PDAs
• MP3 Players
• Digital Still and Video Cameras
• Portable Instruments
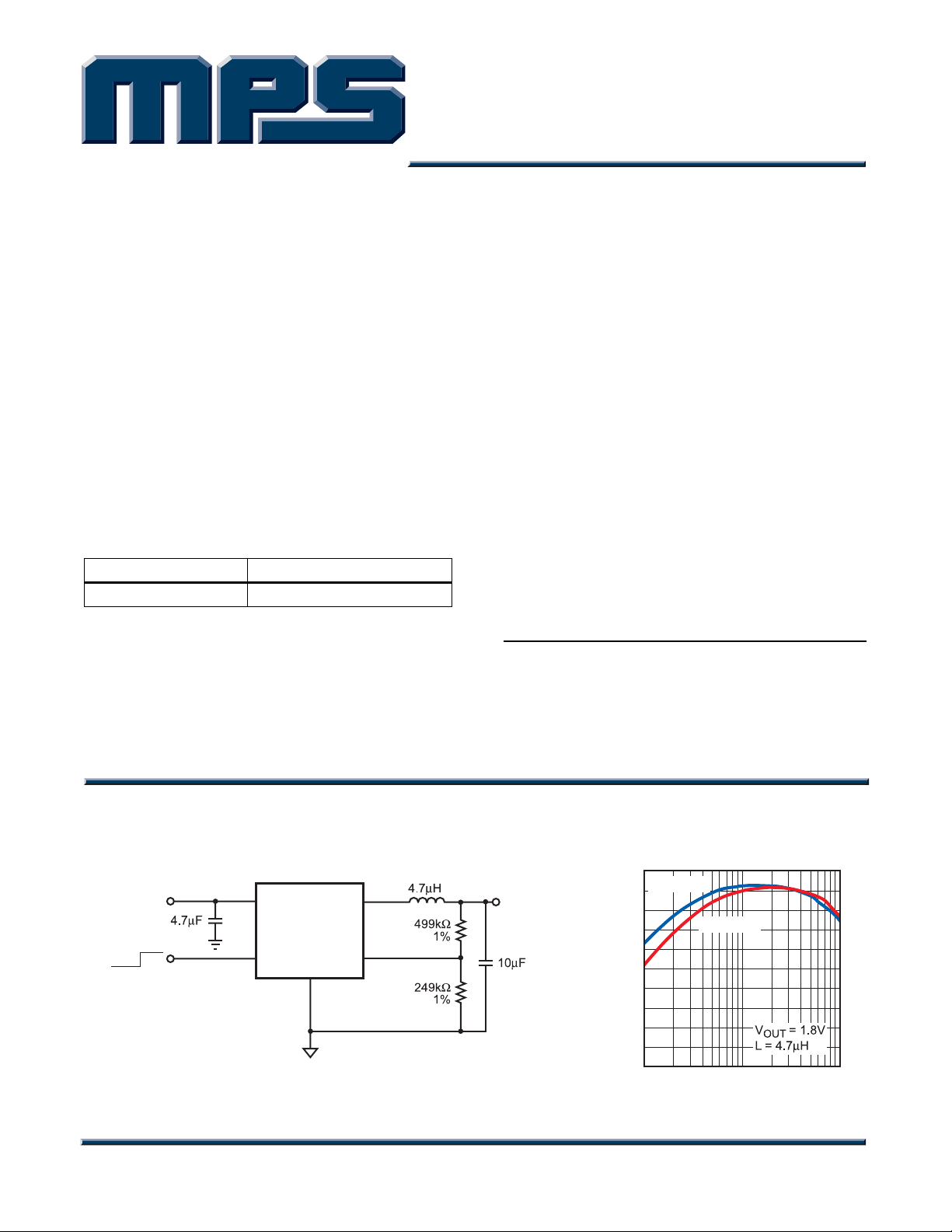
TYPICAL APPLICATION
INPUT
2.5V to 6V
OFF ON
4
1
IN
MP2105
EN
GND
2
SW
FB
“MPS” and “The Future of Analog IC Technology” are Trademarks of Monolithic
Power Systems, Inc.
Efficiency vs
Load Current
100
V
= 3.3V
3
5
OUTPUT
1.8V
800mA
MP2105_TAC_S01
IN
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
EFFICIENCY (%)
20
10
0
10 100 1000
V
= 4.2V
IN
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
MP2105-EC01
MP2105 Rev. 1.2 www.MonolithicPower.com 1
8/19/2005 MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2005 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
Page 2
TM
MP2105 – 1MHz 800mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN CONVERTER
PACKAGE REFERENCE
TOP VIEW
1
2
3
C 6 YW
54FB
MP1557_PD01_TSOT23-5
IN
–40°C to +85°C
EN
GND
SW
Part Number* Package Temperature
MP2105DJ TSOT23-5
For Tape & Reel, add suffix –Z (eg. MP2105DJ–Z)
*
For Lead Free, add suffix –LF (eg. MP2105DJ–LF–Z)
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(1)
VIN to GND .................................. –0.3V to +6.5V
V
to GND........................... –0.3V to VIN +0.3V
SW
V
, VEN to GND.......................... –0.3V to +6.5V
FB
Junction Temperature.............................+150°C
Lead Temperature ..................................+260°C
Storage Temperature .............–65°C to +150°C
Recommended Operating Conditions
(2)
Supply Voltage VIN............................. 2.5V to 6V
Output Voltage V
.......................... 0.6V to 6V
OUT
Operating Temperature .............–40°C to +85°C
Thermal Resistance
(3)
θ
JA
θJC
TSOT23-5.............................. 220 .... 110.. °C/W
Notes:
1) Exceeding these ratings may damage the device.
2) The device is not guaranteed to function outside of its
operating conditions.
3) Measured on approximately 1” square of 1 oz copper.
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(4)
VIN = VEN = 3.6V, TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Parameter Symbol Condition Min Typ Max Units
Supply Current VEN = VIN, VFB = 0.65V 440 600 µA
Shutdown Current VEN = 0V, VIN = 6V 0.10 1 µA
IN Undervoltage Lockout
Threshold
IN Undervoltage Lockout
Hysteresis
Regulated FB Voltage VFB
FB Input Bias Current VFB = 0.65V –50 0.5 +50 nA
PFET On Resistance ISW = 100mA 0.42 Ω
NFET On Resistance ISW = –100mA 0.26 Ω
SW Leakage Current
PFET Current Limit
Oscillator Frequency f
Thermal Shutdown Trip
Threshold
EN Trip Threshold –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C 0.3 0.96 1.5 V
EN Input Current VEN = 0V to 6V –1 +1 µA
Notes:
4) 100% production test at +25°C. Specifications over the temperature range are guaranteed by design and characterization.
Rising Edge 2.15 2.30 2.40 V
55 mV
TA = +25°C 0.588 0.600 0.612
–40°C ≤ T
V
= 0V, VIN = 6V,
EN
V
= 0V or 6V
SW
Duty Cycle = 100%,
Current Pulse Width < 1ms
0.85 1.05 1.25 MHz
OSC
≤ +85°C 0.582 0.600 0.618
A
–1 +1 µA
1.2 1.6 2.1 A
145
V
°C
MP2105 Rev. 1.2 www.MonolithicPower.com 2
8/19/2005 MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2005 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3
TM
MP2105 – 1MHz 800mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN CONVERTER
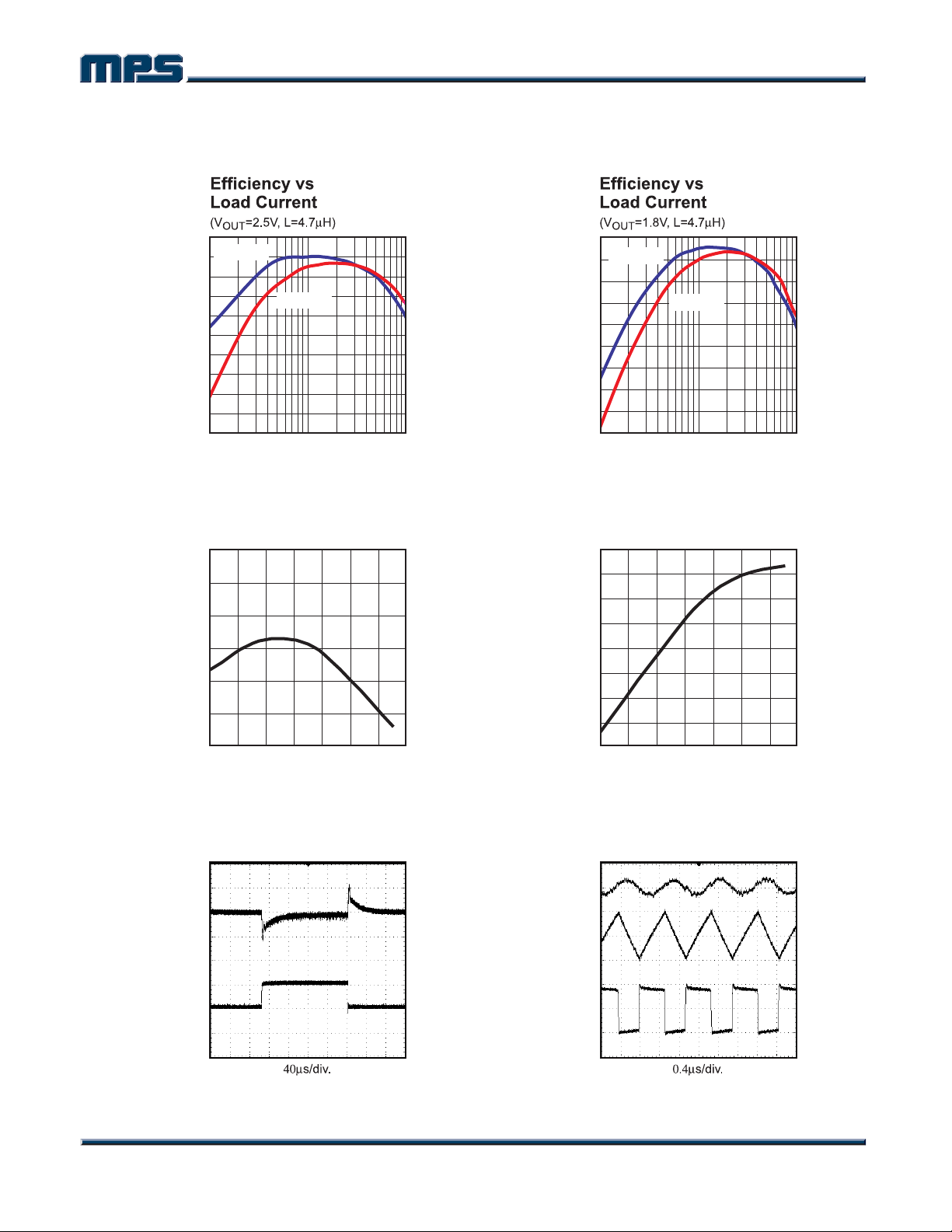
TYPCIAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
VIN = 3.3V, V
= 1.8V, L1 = 4.7µH, C1 = 4.7µF, C3 = 10µF, TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.
OUT
100
VIN=3.3V
95
90
)
85
%
80
75
70
65
EFFICIENCY (
60
55
50
10 100 1000
VIN=4.2V
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Feedback Voltage vs
Temperature
0.603
0.602
0.601
0.600
0.599
0.598
FEEDBACK VOLTAGE (V)
0.597
-20
-40 +200
TEMPERATURE (°C)
+40 +60 +80 +100 -40 +200
MP2105-EC01
MP2105-TPC01
95
VIN=3.3V
90
85
)
%
80
75
70
65
EFFICIENCY (
60
55
50
10 100 1000
VIN=4.2V
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Switching Frequency vs
Temperature
1.10
1.08
1.06
1.04
1.02
1.00
0.98
0.96
SWITCHING FREQUENCY (MHz)
0.94
-20
TEMPERATURE (°C)
+40 +60 +80 +100
MP2105-EC02
MP2105-TPC02
Load Transient
(I
=0mA to 500mA step)
OUT
V
OUT
100mV/div.
I
OUT
0.5A/div.
MP2105-TPC03
MP2105 Rev. 1.2 www.MonolithicPower.com 3
8/19/2005 MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2005 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
10mV/div.
0.2A/div.
2V/div.
Light Load Operation
(I
=0mA)
OUT
V
OUT
I
L
SW
MP2105-TPC04
Page 4

TM
MP2105 – 1MHz 800mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN CONVERTER
TYPCIAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
VIN = 3.3V, V
10mV/div.
0.2A/div.
= 1.8V, L1 = 4.7µH, C1 = 4.7µF, C3 = 10µF, TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.
OUT
Heavy Load Operation
I
V
OUT
= 800mA
OUT
2V/div.
I
L
1V/div.
Startup from Shutdown
V
EN
V
OUT
SW
2V/div.
V
OUT
1V/div.
0.5A/div.
Short Circuit Protection
(No Load)
I
L
MP2105-TPC07
MP2105-TPC09
I
L
I
=0
L
0.5A/div.
MP2105-TPC08
Short Circuit Recovery
(No Load)
V
OUT
1V/div.
I
L
0.5A/div.
MP2105-TPC10
PIN FUNCTIONS
Pin # Name Description
EN 1
GND 2 Ground
SW 3 Power Switch Output. Inductor connection to drains of the internal PFET and NFET switches.
IN 4 Supply Input. Bypass to GND with a 2.2µF or greater ceramic capacitor.
FB 5
MP2105 Rev. 1.2 www.MonolithicPower.com 4
8/19/2005 MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2005 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
Regulator Enable Control Input. Drive EN above 1.5V to turn on the MP2105. Drive EN below
0.3V to turn it off (shutdown current < 0.1µA).
Feedback Input. Connect FB to the center point of the external resistor divider. The feedback
threshold voltage is 0.6V.
Page 5

TM
MP2105 – 1MHz 800mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN CONVERTER
OPERATION
The MP2105 is a constant frequency current
mode PWM step-down converter. The MP2105
is optimized for low voltage, Li-Ion battery
powered applications where high efficiency and
small size are critical. The MP2105 uses an
external resistor divider to set the output
voltage from 0.6V to 6V. The device integrates
both a main switch and a synchronous rectifier,
which provides high efficiency and eliminates
IN
an external Schottky diode. The MP2105 can
achieve 100% duty cycle. The duty cycle D of a
step-down converter is defined as:
V
where T
OUT
OSCON
is the main switch on time, and f
ON
%100fTD
V
IN
%100
×≈××=
OSC
is the oscillator frequency (1MHz).
EN
FB
BIAS
&
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
0.6V
FEEDBACK
ERROR\
AMP
+
EAMP
--
CC
17pF
ICS
SLOPE COMP
EAO
Figure 1—Functional Block Diagram
+
+
PWMCMP
--
1.0MHz
OSCILLATOR
PWM
OSC
PWM
CONTROL
LOGIC
CURRENT
SENSE
AMP
DH
DL
IAMP
10X
+
--
MAIN
SWITCH
(PCH)
SW
SYNCHRONOUS
RECTIFIER
(NCH)
GND
MP2105_BD01
MP2105 Rev. 1.2 www.MonolithicPower.com 5
8/19/2005 MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2005 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
Page 6

TM
MP2105 – 1MHz 800mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN CONVERTER
Current Mode PWM Control
Slope compensated current mode PWM control
provides stable switching and cycle-by-cycle
current limit for superior load and line response
and protection of the internal main switch and
synchronous rectifier. The MP2105 switches at a
constant frequency (1MHz) and regulates the
output voltage. During each cycle the PWM
comparator modulates the power transferred to the
load by changing the inductor peak current based
on the feedback error voltage. During normal
operation, the main switch is turned on for a certain
time to ramp the inductor current at each rising
edge of the internal oscillator, and switched off
when the peak inductor current is above the error
voltage. When the main switch is off, the
synchronous rectifier will be turned on immediately
and stay on until either the next cycle starts.
Dropout Operation
The MP2105 allows the main switch to remain on
for more than one switching cycle and increases
the duty cycle while the input voltage is dropping
close to the output voltage. When the duty cycle
reaches 100%, the main switch is held on
continuously to deliver current to the output up to
the PFET current limit. The output voltage then is
the input voltage minus the voltage drop across
the main switch and the inductor.
Short Circuit Protection
The MP2105 has short circuit protection. When
the output is shorted to ground, the oscillator
frequency is reduced to prevent the inductor
current from increasing beyond the PFET current
limit. The PFET current limit is also reduced to
lower the short circuit current. The frequency and
current limit will return to the normal values once
the short circuit condition is removed and the
feedback voltage reaches 0.6V.
Maximum Load Current
The MP2105 can operate down to 2.5V input
voltage; however the maximum load current
decreases at lower input due to large IR drop on
the main switch and synchronous rectifier. The
slope compensation signal reduces the peak
inductor current as a function of the duty cycle to
prevent sub-harmonic oscillations at duty cycles
greater than 50%. Conversely the current limit
increases as the duty cycle decreases.
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Output Voltage Setting
The external resistor divider sets the output
voltage (see Figure 3). The feedback resistor R1
also sets the feedback loop bandwidth with the
internal compensation capacitor (see Figure 1).
Choose R1 around 500kΩ for optimal transient
response. R2 is then given by:
2R
=
Table 1—Resistor Selection vs. Output
Voltage Setting
V
R1 R2
OUT
1.2V
1.5V
1.8V
2.5V
499k
499k
499k
499k
1R
V
OUT
1
−
V6.0
Ω (1%) 499kΩ (1%)
Ω (1%) 332kΩ (1%)
Ω (1%) 249kΩ (1%)
Ω (1%) 158kΩ (1%)
Inductor Selection
A 1µH to 10µH inductor with DC current rating at least
25% higher than the maximum load current is
recommended for most applications. For best
efficiency, the inductor DC resistance shall be
<200mΩ. See Table 2 for recommended inductors
and manufacturers. For most designs, the inductance
value can be derived from the following equation:
()
VVV
−×
OUTINOUT
OSCLIN
where ∆I
L
=
is Inductor Ripple Current. Choose inductor
L
fIV
×∆×
ripple current approximately 30% of the maximum
load current, 800mA.
The maximum inductor peak current is:
∆
I
L
+=
II
LOAD)MAX(L
2
Under light load conditions below 100mA, larger
inductance is recommended for improved efficiency.
Table 3 lists inductors recommended for this purpose.
MP2105 Rev. 1.2 www.MonolithicPower.com 6
8/19/2005 MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2005 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
Page 7

TM
MP2105 – 1MHz 800mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN CONVERTER
Table 2—Suggested Surface Mount Inductors
Saturation
Manufacturer Part Number Inductance (µH) Max DCR (Ω)
Coilcraft D01605T-472 4.7 0.150 1.20 5.4x4.2x1.8
Toko D52LC 4.7 0.087 1.14 5x5x2
Sumida CR43-4R7 4.7 0.109 1.15 4.3x4.8x3.5
Current (A)
Dimensions
LxWxH (mm3)
Table 3—Inductors for Improved Efficiency at 25mA, 50mA, under 100mA Load.
Saturation
Manufacturer Part Number Inductance (µH) Max DCR (Ω)
Coilcraft DO1605T-103MX 10 0.3 1.0 0.9
Murata LQH4C100K04 10 0.2 1.2 0.8
Sumida CR32-100 10 0.2 1.0 0.7
Sumida CR54-100 10 0.1 1.2 1.4
Input Capacitor Selection
The input capacitor reduces the surge current
drawn from the input and switching noise from
the device. The input capacitor impedance at
the switching frequency shall be less than input
source impedance to prevent high frequency
switching current passing to the input. Ceramic
capacitors with X5R or X7R dielectrics are
highly recommended because of their low ESR
and small temperature coefficients. For most
applications, a 4.7µF capacitor is sufficient.
PC Board Layout
The high current paths (GND, IN and SW)
should be placed very close to the device with
short, direct and wide traces. Input capacitor C1
needs to be as close as possible to the IN and
GND pins. The external feedback resistors shall
be placed next to the FB pin. Keep the
switching node SW short and away from the
feedback network. Figure 2 illustrates an
example of PCB layout and signal routing.
Current (A) I
RMS
(A)
Output Capacitor Selection
The output capacitor keeps output voltage
ripple small and ensures regulation loop stable.
The output capacitor impedance shall be low at
the switching frequency. Ceramic capacitors
with X5R or X7R dielectrics are recommended.
The output ripple ∆V
V
OUT
≤∆
()
is approximately:
OUT
−×
VVV
××
⎛
OUTINOUT
⎜
ESR
⎜
LfV
⎝
+×
1
OSCOSCIN
⎞
⎟
⎟
××
3Cf8
⎠
Figure 2—MP2105 Suggested Layout
MP2105 Rev. 1.2 www.MonolithicPower.com 7
8/19/2005 MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2005 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
Page 8

TM
MP2105 – 1MHz 800mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN CONVERTER
PACKAGE INFORMATION
TSOT23-5
0.950
TYP
2.90 BSC
.
0.950
TYP
3
.
10°TYP.
(2 plcs)
3
C
L
0.300(Min)
0.500(Max)
(5
PLCS)
1.00
Max.
1.60 BSC
C
L
0.87±0.03
0.00-0.10
2.80 BSC
SEATING PLANE
0.25 BSC.
Gauge Plane
10° TYP.
(2 plcs)
0.400
0.127 TYP.
0°
+
4°
-
0°
±0.10
NOTICE: The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Please contact MPS for current specifications.
Users should warrant and guarantee that third party Intellectual Property rights are not infringed upon when integrating MPS
products into any application. MPS will not assume any legal responsibility for any said applications.
MP2105 Rev. 1.2 www.MonolithicPower.com 8
8/19/2005 MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2005 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
Page 9

 Loading...
Loading...