Datasheet MIC5210-3.6BMM, MIC5210-3.0BMM, MIC5210-5.0BMM, MIC5210-3.3BMM, MIC5210-4.0BMM Datasheet (MICREL)
Page 1
MIC5210 Micrel
MIC5210
Dual 100mA LDO Regulator
Advance Information
General Description
The MIC5210 is a dual linear voltage regulator with very low
dropout voltage (typically 10mV at light loads and 140mV at
100mA), very low ground current (225µA at 10mA output), and
better than 3% initial accuracy. It also features individual
logic-compatible enable/shutdown control inputs.
Designed especially for hand-held battery powered devices,
the MIC5210 can be switched by a CMOS or TTL compatible
logic signal, or the enable pin can be connected to the supply
input for 3-terminal operation. When disabled, power consumption drops nearly to zero. Dropout ground current is
minimized to prolong battery life.
Key features include current limiting, overtemperature shutdown, and protection against reversed battery.
The MIC5210 is available in 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V, 4.0V and 5.0V
fixed voltage configurations. Other voltages are available;
contact Micrel for details.
Ordering Information
Features
• Micrel Mini 8™ MSOP package
• Guaranteed 100mA outputs
• Low quiescent current
• Low dropout voltage
• Wide selection of output voltages
• Tight load and line regulation
• Low temperature coefficient
• Current and thermal limiting
• Reversed input polarity protection
• Zero off-mode current
• Logic-controlled electronic enable
Applications
• Cellular telephones
• Laptop, notebook, and palmtop computers
• Battery powered equipment
• Bar code scanners
• SMPS post regulator/dc-to-dc modules
• High-efficiency linear power supplies
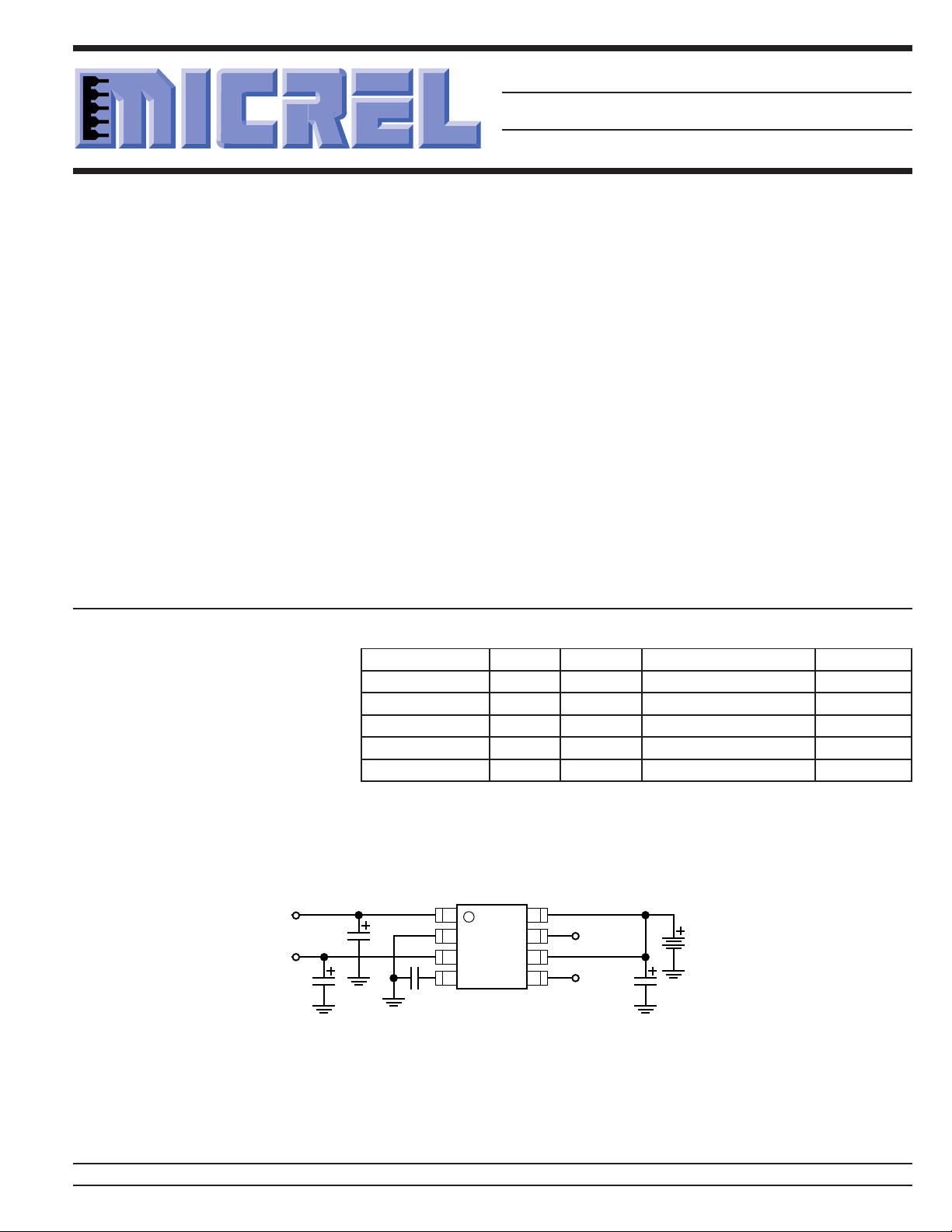
Typical Application
Output A
Output B
2.2µF
Part Number Voltage Accuracy Junction Temp. Range* Package
MIC5210-3.0BMM 3.0 1.0% –40°C to +125°C 8-lead MSOP
MIC5210-3.3BMM 3.3 1.0% –40°C to +125°C 8-lead MSOP
MIC5210-3.6BMM 3.6 1.0% –40°C to +125°C 8-lead MSOP
MIC5210-4.0BMM 4.0 1.0% –40°C to +125°C 8-lead MSOP
MIC5210-5.0BMM 5.0 1.0% –40°C to +125°C 8-lead MSOP
Other voltages available. Contact Micrel for details.
1µF
1
2
3
4
C
BYP
470µF
MIC5210
Enable may be connected to V
8
Enable A
7
6
Enable B
5
IN
1µF
Low-Noise + Ultralow-Noise (Dual) Regulator
MM8 and Micrel Mini 8 are trademarks of Micrel, Inc.
Micrel, Inc. • 1849 Fortune Drive • San Jose, CA 95131 • USA • tel + 1 (408) 944-0800 • fax + 1 (408) 944-0970 • http://www.micrel.com
April 1997• 1 MIC5210
Page 2
MIC5210 Micrel
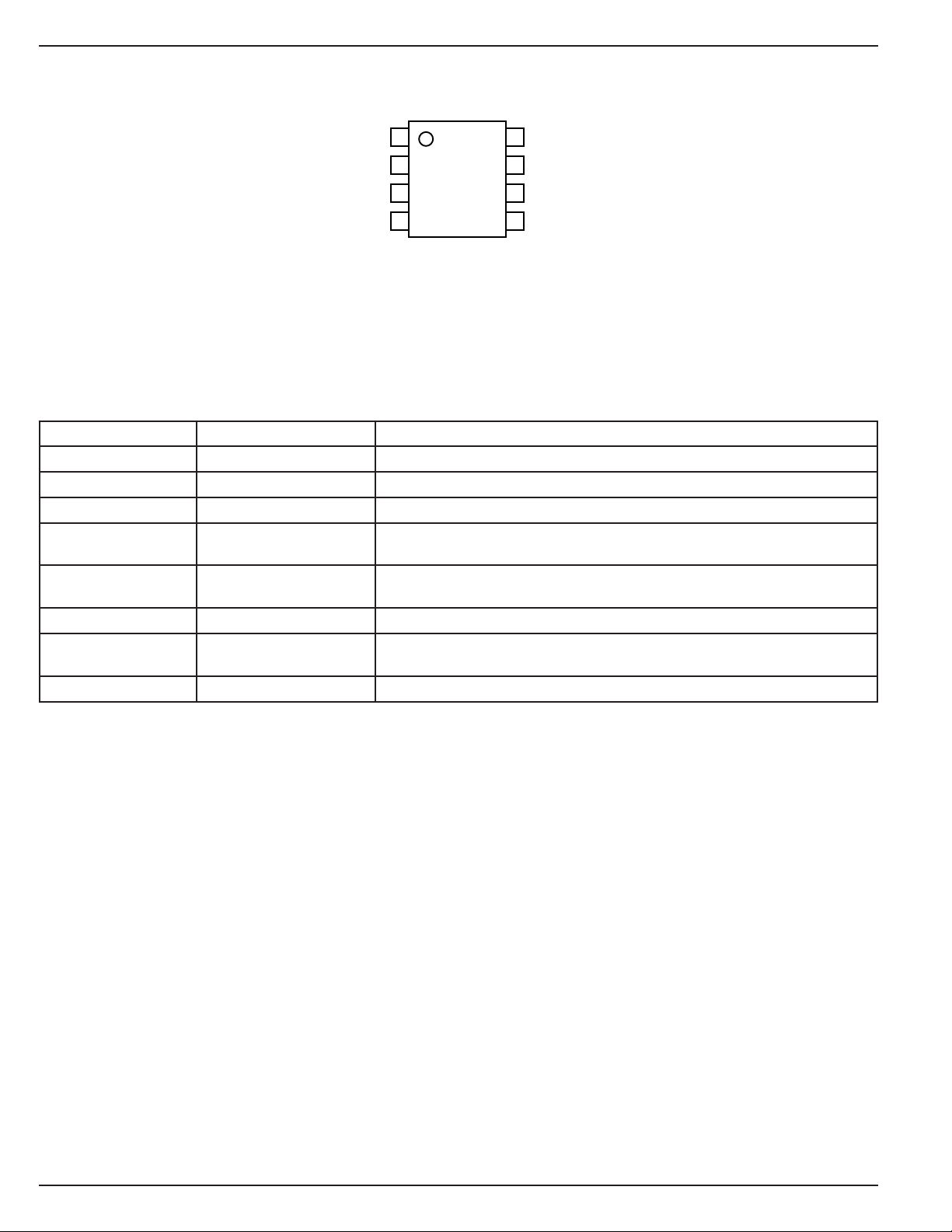
Pin Configuration
OUTA
GND
OUTB
BYPB
Pin Description
Pin Number Pin Name Pin Function
1 OUTA Regulator Output A
2 GND Ground: Both pins must be connected together.
3 OUTB Regulator Output B
4 BYPB Reference Bypass B: Connect external 470pF capacitor to GND to reduce
5 ENB Enable/Shutdown B (Input): CMOS compatible input. Logic high = enable,
6 INB Supply Input B
7 ENA Enable/Shutdown A (Input): CMOS compatible input. Logic high = enable,
8 INA Supply Input A
1
2
3
4
8
INA
7
ENA
6
INB
ENB
5
MIC5210BMM
output noise in regulator “B”. May be left open.
logic low or open = shutdown. Do not leave floating.
logic low or open = shutdown. Do not leave floating.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Supply Input Voltage (VIN) ............................ –20V to +20V
Enable Input Voltage (VEN) ........................... –20V to +20V
Power Dissipation (PD) ............................ Internally Limited
Storage Temperature Range ................... –60°C to +150°C
Recommended Operating Conditions
Supply Input Voltage (VIN) ............................... 2.5V to 16V
Enable Input Voltage (VEN) ................................. 0V to 16V
Junction Temperature (TJ) ....................... –40°C to +125°C
8-lead MSOP (θJA) ................................................... Note 1
Lead Temperature (soldering, 5 sec.) ....................... 260°C
MIC5210 2 April 1997•
Page 3
MIC5210 Micrel
Electrical Characteristics
VIN = V
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typical Max Units
V
O
∆V
O
∆V
O/VO
∆V
O/VO
V
– V
IN
I
GND
I
GND
PSRR Ripple Rejection frequency = 100Hz, IL = 100µA 75 500 dB
I
LIMIT
∆VO/∆P
e
no
ENABLE Input
V
IL
V
IH
I
IL
I
IH
+ 1V; IL = 100µA; CL = 1.0µF; VEN ≥ 2.0V; TJ = 25°C, bold values indicate –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C; unless noted.
OUT
Output Voltage Accuracy variation from specified V
OUT
–1 1 %
–2 2 %
/∆T Output Voltage Note 2 40 ppm/°C
Temperature Coefficient
Line Regulation VIN = V
+ 1V to 16V 0.004 0.012 % / V
OUT
0.05 % / V
Load Regulation IL = 0.1mA to 150mA (Note 3) 0.02 0.2 %
0.5 %
O
Dropout Voltage, Note 4 IL = 100µA1050mV
70 mV
IL = 50mA 110 150 mV
230 mV
= 100mA 140 250 mV
I
L
300 mV
IL = 150mA 165 275 mV
350 mV
Quiescent Current VEN ≤ 0.4V (shutdown) 0.01 1 µA
VEN ≤ 0.18V (shutdown) 5 µA
Ground Pin Current, Note 5 VEN ≥ 2.0V, IL = 100µA 80 125 µA
150 µA
IL = 50mA 350 600 µA
800 µA
IL = 100mA 600 1000 µA
1500 µA
= 150mA 1300 1900 µA
I
L
Current Limit V
D
Thermal Regulation Note 6 0.05 %/W
= 0V 320 500 mA
OUT
Output Noise IL = 50mA, CL = 2.2µF, 260
2500 µA
nV Hz
470pF from BYP to GND
Enable Input Logic-Low Voltage regulator shutdown 0.4 V
0.18 V
Enable Input Logic-High Voltage regulator enabled 2.0 V
Enable Input Current VIL ≤ 0.4V 0.01 –1 µA
V
≤ 0.18V –2 µA
IL
VIH ≥ 2.0V 5 20 µA
VIH ≥ 2.0V 25 µA
Note 1: Absolute maximum ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the component may occur. Electrical specifications do not apply when
Note 2: Output voltage temperature coefficient is defined as the worst case voltage change divided by the total temperature range.
Note 3: Regulation is measured at constant junction temperature using low duty cycle pulse testing. Parts are tested for load regulation in the load
Note 4: Dropout Voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 2% below its nominal value measured at 1V
Note 5: Ground pin current is the regulator quiescent current plus pass transistor base current. The total current drawn from the supply is the sum of
Note 6: Thermal regulation is defined as the change in output voltage at a time “t” after a change in power dissipation is applied, excluding load or line
operating the device outside of its operating ratings. The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of the maximum junction
temperature, T
dissipation at any ambient temperature is calculated using: P
will result in excessive die temperature, and the regulator will go into thermal shutdown. The θJA of the 8-lead MSOP (MM) is 200°C/W
mounted on a PC board (see “Thermal Considerations” section for further details).
range from 0.1mA to 150mA. Changes in output voltage due to heating effects are covered by the thermal regulation specification.
differential.
the load current plus the ground pin current.
regulation effects. Specifications are for a 150mA load pulse at VIN = 16V for t = 10ms.
, the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, θJA, and the ambient temperature, TA. The maximum allowable power
J(max)
D(max)
= (T
J(max)–TA
) θJA. Exceeding the maximum allowable power dissipation
April 1997• 3 MIC5210
Page 4

MIC5210 Micrel
√
√
Typical Characteristics
Power Supply Ripple Rejection
vs. Voltage Drop
60
50
1mA
40
30
10mA
I
OUT
= 100mA
20
C
10
RIPPLE REJECTION (dB)
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
VOLTAGE DROP (V)
OUT
= 1µF
Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
0
VIN = 6V
V
-20
-40
-60
PSRR (dB)
-80
-100
= 5V
OUT
I
= 100mA
OUT
C
= 1µF
OUT
1E+11E+21E+31E+41E+51E+61E+7
10
1k
100
10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
100k
1M
10M
Turn-On Time
vs. Bypass Capacitance
10000
1000
TIME (µs)
100
10
10 100 1000 10000
CAPACITANCE (pF)
Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
0
VIN = 6V
V
-20
-40
-60
PSRR (dB)
-80
-100
= 5V
OUT
I
= 10mA
OUT
C
= 1µF
OUT
1E+11E+21E+31E+41E+51E+61E+7
10
1k
100
10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
100k
1M
10M
Dropout Voltage
vs. Output Current
320
280
240
200
+125°C
+25°C
160
120
80
40
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (mV)
0
0 40 80 120 160
OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
–40°C
Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
0
-20
-40
-60
PSRR (dB)
-80
-100
1E+11E+21E+31E+41E+51E+61E+7
10
1k
100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10k
I
C
OUT
OUT
100k
VIN = 6V
V
= 5V
OUT
= 1mA
= 1µF
1M
10M
Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
0
-20
-40
-60
PSRR (dB)
-80
-100
1E+11E+21E+31E+41E+51E+61E+7
10
1k
100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10k
I
C
OUT
OUT
100k
VIN = 6V
V
= 5V
OUT
= 100µA
= 1µF
1M
10M
Hz)
NOISE (µV/
0.001
0.0001
Noise Performance
10
1
0.1
100mA
10mA
0.01
V
= 5V
OUT
C
= 10µF
OUT
electrolytic
1E+11E+21E+31E+41E+51E+6 1E+7
10
1k
100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1mA
10k 100k1M10M
Hz)
NOISE (µV/
0.001
0.0001
Noise Performance
10
1
100mA
0.1
0.01
V
= 5V
OUT
C
= 10µF
OUT
electrolytic
C
= 100pF
BYP
1E+11E+21E+31E+41E+51E+6 1E+7
10
100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1mA
10mA
1k
10k 100k1M10M
MIC5210 4 April 1997•
Page 5

MIC5210 Micrel
Applications Information
Enable/Shutdown
Forcing EN (enable/shutdown) high (> 2V) enables the regulator. EN is compatible with CMOS logic gates.
If the enable/shutdown feature is not required, connect EN to
IN (supply input).
Input Capacitor
A 1µF capacitor should be placed from IN to GND if there is
more than 10 inches of wire between the input and the ac filter
capacitor or if a battery is used as the input.
Reference Bypass Capacitor
BYP (reference bypass) is connected to the internal voltage
reference. A 470pF capacitor (C
GND quiets this reference, providing a significant reduction in
output noise. C
using C
, output capacitors of 2.2µF or greater are gener-
BYP
reduces the regulator phase margin; when
BYP
ally required to maintain stability.
The start-up speed of the MIC5210 is inversely proportional to
the size of the reference bypass capacitor. Applications requiring a slow ramp-up of output voltage should consider
larger values of C
consider omitting C
. Likewise, if rapid turn-on is necessary,
BYP
.
BYP
If output noise is not a major concern, omit C
BYP open.
Output Capacitor
An output capacitor is required between OUT and GND to
prevent oscillation. The minimum size of the output capacitor
is dependent upon whether a reference bypass capacitor is
used. 1.0µF minimum is recommended when C
used (see Figure 2). 2.2µF minimum is recommended when
C
is 470µF (see Figure 1). Larger values improve the
BYP
regulator’s transient response. The output capacitor value
may be increased without limit.
The output capacitor should have an ESR (effective series
resistance) of about 5Ω or less and a resonant frequency
) connected from BYP to
BYP
and leave
BYP
BYP
is not
above 1MHz. Most tantalum or aluminum electrolytic capacitors are adequate; film types will work, but are more expensive. Since many aluminum electrolytics have electrolytes
that freeze at about –30°C, solid tantalums are recommended
for operation below –25°C.
At lower values of output current, less output capacitance is
required for output stability. The capacitor can be reduced to
0.47µF for current below 10mA or 0.33µF for currents below
1mA.
No-Load Stability
The MIC5210 will remain stable and in regulation with no load
(other than the internal voltage divider) unlike many other
voltage regulators. This is especially important in CMOS RAM
keep-alive applications.
Dual-Supply Operation
When used in dual supply systems where the regulator load
is returned to a negative supply, the output voltage must be
diode clamped to ground.
Thermal Considerations
Multilayer boards having a ground plane, wide traces near the
pads, and large supply bus lines provide better thermal
conductivity.
The MIC5210-xxBMM (8-lead MSOP) has a thermal resistance of 200°C/W when mounted on a FR4 board with
minimum trace widths and no ground plane.
PC Board θ
Dielectric
FR4 200°C
JA
MSOP Thermal Characteristics
For additional heat sink characteristics, please refer to Micrel
Application Hint 17, “Calculating P.C. Board Heat Sink Area
For Surface Mount Packages”.
April 1997• 5 MIC5210
Page 6

MIC5210 Micrel
Package Information
0.122 (3.10)
0.112 (2.84)
0.036 (0.90)
0.032 (0.81)
0.012 (0.03)
0.0256 (0.65) TYP
0.199 (5.05)
0.187 (4.74)
0.120 (3.05)
0.116 (2.95)
0.043 (1.09)
0.038 (0.97)
0.012 (0.30) R
0.008 (0.20)
0.004 (0.10)
8-Lead MSOP (MM)
MM8™ Micrel Mini 8™
5° MAX
0° MIN
DIMENSIONS:
INCH (MM)
0.007 (0.18)
0.005 (0.13)
0.012 (0.03) R
0.039 (0.99)
0.035 (0.89)
0.021 (0.53)
MIC5210 6 April 1997•
Page 7

MIC5210 Micrel
April 1997• 7 MIC5210
Page 8

MIC5210 Micrel
MICREL INC. 1849 FORTUNE DRIVE SAN JOSE, CA 95131 USA
TEL + 1 (408) 944-0800 FAX + 1 (408) 944-0970 WEB http://www.micrel.com
This information is believed to be accurate and reliable, however no responsibility is assumed by Micrel for its use nor for any infringement of patents or
other rights of third parties resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent right of Micrel Inc.
© 1997 Micrel Incorporated
MIC5210 8 April 1997•
 Loading...
Loading...