Page 1
RAM Mapping 32´4 LCD Controller for I/O mC
Features
Logic operating voltage: 2.4V~3.3V
·
LCD voltage: 3.6V~4.9V
·
Low operating current <3mAat3V
·
External 32.768kHz crystal oscillator
·
Selection of 1/2 or 1/3 bias, and selection of
·
1/2 or 1/3 or 1/4 duty LCD applications
Internal time base frequency sources
·
Two selectable buzzer frequencies
·
(2kHz/4kHz)
Built-in capacitor type bias charge pump
·
Time base or WDT overflow output
·
General Description
The HT1620 is a 128 pattern (32´4), memory
mapping, and multi-function LCD driver. The
S/W configuration feature of the HT1620
makes it suitable for multiple LCD applica
tions including LCD modules and display sub
systems. Only three or four lines are required
HT1620
8 kinds of time base/WDT clock source
·
32´4 LCD driver
·
Built-in 32´4-bit display RAM
·
3-wire serial interface
·
Internal LCD driving frequency source
·
Software configuration feature
·
R/W address auto increment
·
Data mode and command mode
·
instructions
Three data accessing modes
·
for the interface between the host controller
and the HT1620. The HT1620 consumes low
operating current owing to adopting capacitor
type bias charge pump. The HT162X series
have many kinds of products that match vari
ous applications.
-
Selection Table
HT162X
COM
SEG
Built-in Osc.
Crystal Osc.
HT1620 HT1621 HT1622 HT16220 HT1623 HT1625 HT1626 HT1627 HT16270
4 48 8 88161616
32 32 32 32 48 64 48 64 64
ÖÖ ÖÖ Ö Ö
ÖÖ ÖÖÖÖ Ö
1 July 26, 1999
Page 2
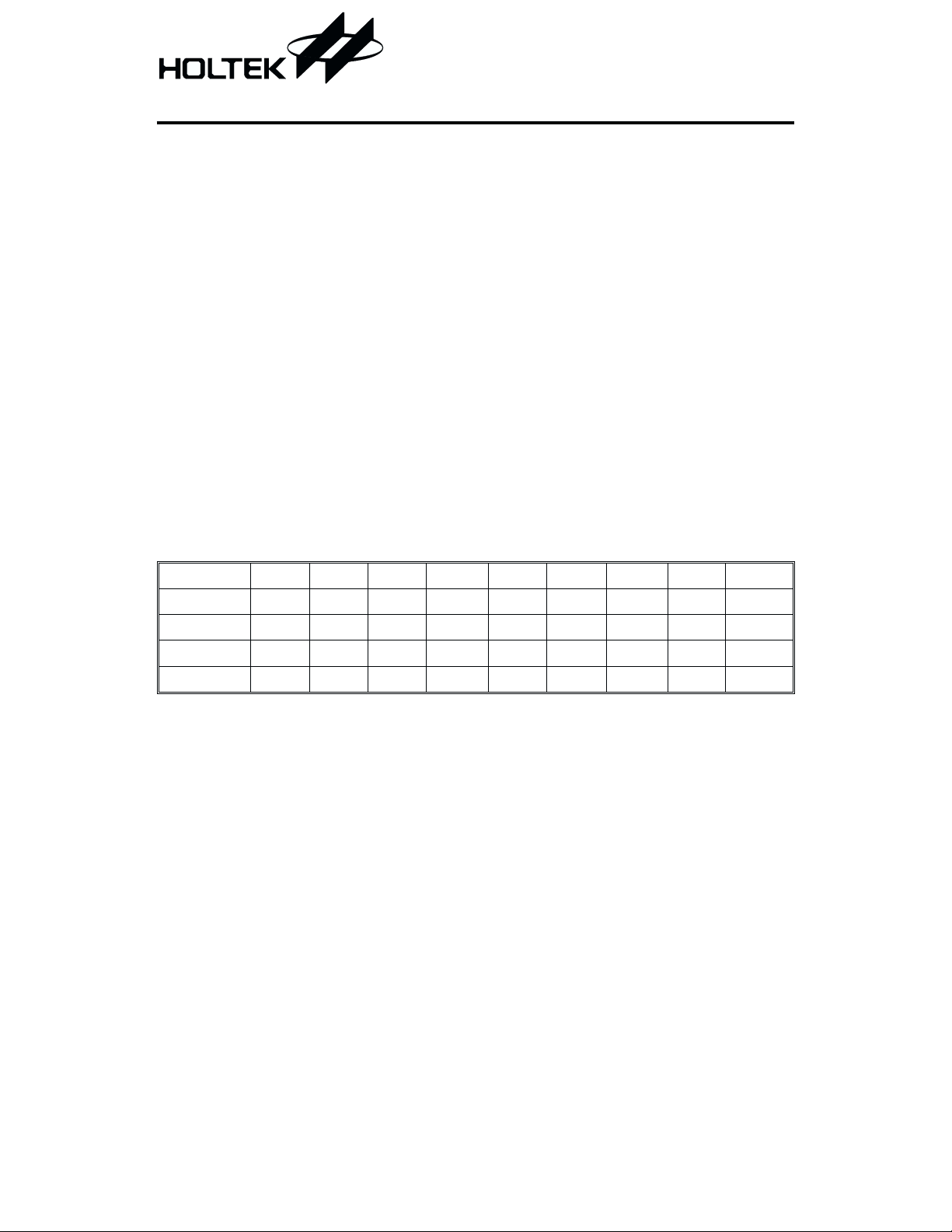
Block Diagram
HT1620
OSCO
OSCI
CS
RD
WR
DATA
VDD
VSS
BZ
BZ
C ontrol
and
Tim ing
Circuit
Tone Frequency
G enerator
D isplay R A M
LC D Driver/
Bias Circuit
W atchdog Tim er
Tim e B ase G enerator
&
Notes: CS: Chip selection
BZ, BZ
: Tone outputs
WR
,RD, DATA: Serial interface
COM0~COM3, SEG0~SEG31: LCD outputs
IRQ
: Time base or WDT overflow output
VO15N: Half voltage circuit output pin
VEE: Double voltage circuit output pin
CC1/CC2: External capacitor pin, for double voltage and half voltage circuit use
COM 0
COM 3
SEG 0
SEG 31
CC1
CC2
VO 15N
VEE
IR Q
2 July 26, 1999
Page 3
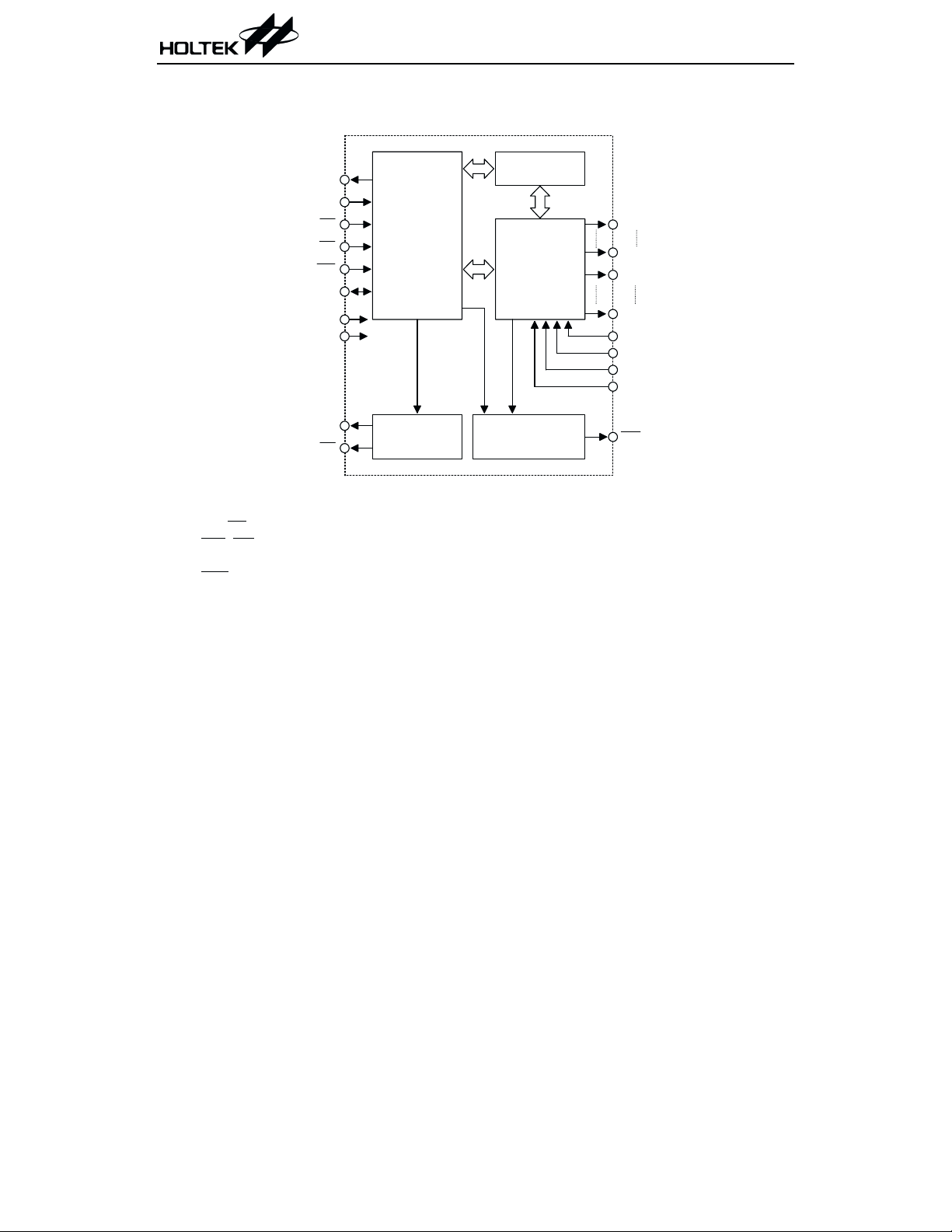
Pin Assignment
NC
CC1
BZ
BZ
HT1620
OSCO
DATA
OSCI
VDD
IR Q
VSS
WR
RD
CS
NC
NC
CC2
VO 15N
VEE
COM 0
COM 1
COM 2
COM 3
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
NC
H T1620
64 Q F P
SEG 13
SEG 14
SEG 15
565758596061626364 52535455
SEG 16
51
NC
50
NC
49
NC
48
NC
47
NC
46
NC
45
SEG31
44
SEG30
43
SEG29
42
SEG28
41
SEG27
40
SEG26
39
SEG25
38
SEG24
37
SEG23
36
SEG22
35
SEG21
34
SEG20
33
NC
SEG 17
SEG 18
SEG 19
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2320 21 22 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
SEG 11
NC
SEG 9
SEG 10
SEG 12
3 July 26, 1999
Page 4
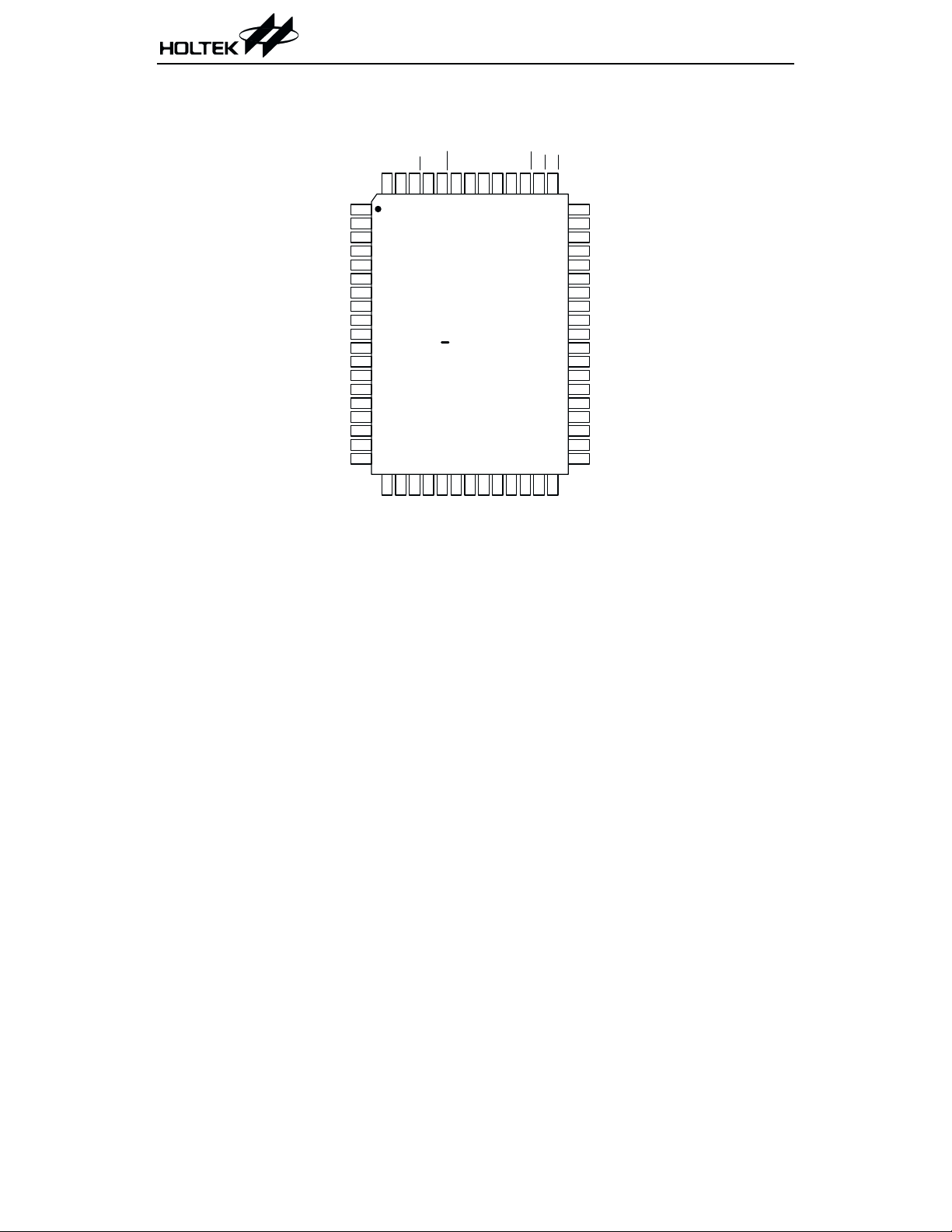
Pad Assignment
CC1
BZ
BZ
HT1620
OSCO
OSCI
VDD
IR Q
DATA
VSS
WR
RD
CS
CC2
VO 15N
VEE
COM 0
COM 1
COM 2
COM 3
SEG 0
SEG 1
SEG 2
SEG 3
SEG 4
SEG 5
441945
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
17
SEG 6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
20462147224823492450255126
18
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
(0 ,0 )
SEG13
SEG14
SEG 15
SEG 16
SEG 17
SEG 18
Chip size: 142 ´ 141 (mil)
43
27
SEG 19
2
411642
40
SEG 31
39
SEG 30
38
SEG 29
37
SEG 28
36
35
SEG 27
34
SEG 26
33
SEG 25
32
SEG 24
31
SEG 23
SEG 22
30
SEG 21
29
SEG 20
28
* The IC substrate should be connected to VDD in the PCB layout artwork.
4 July 26, 1999
Page 5
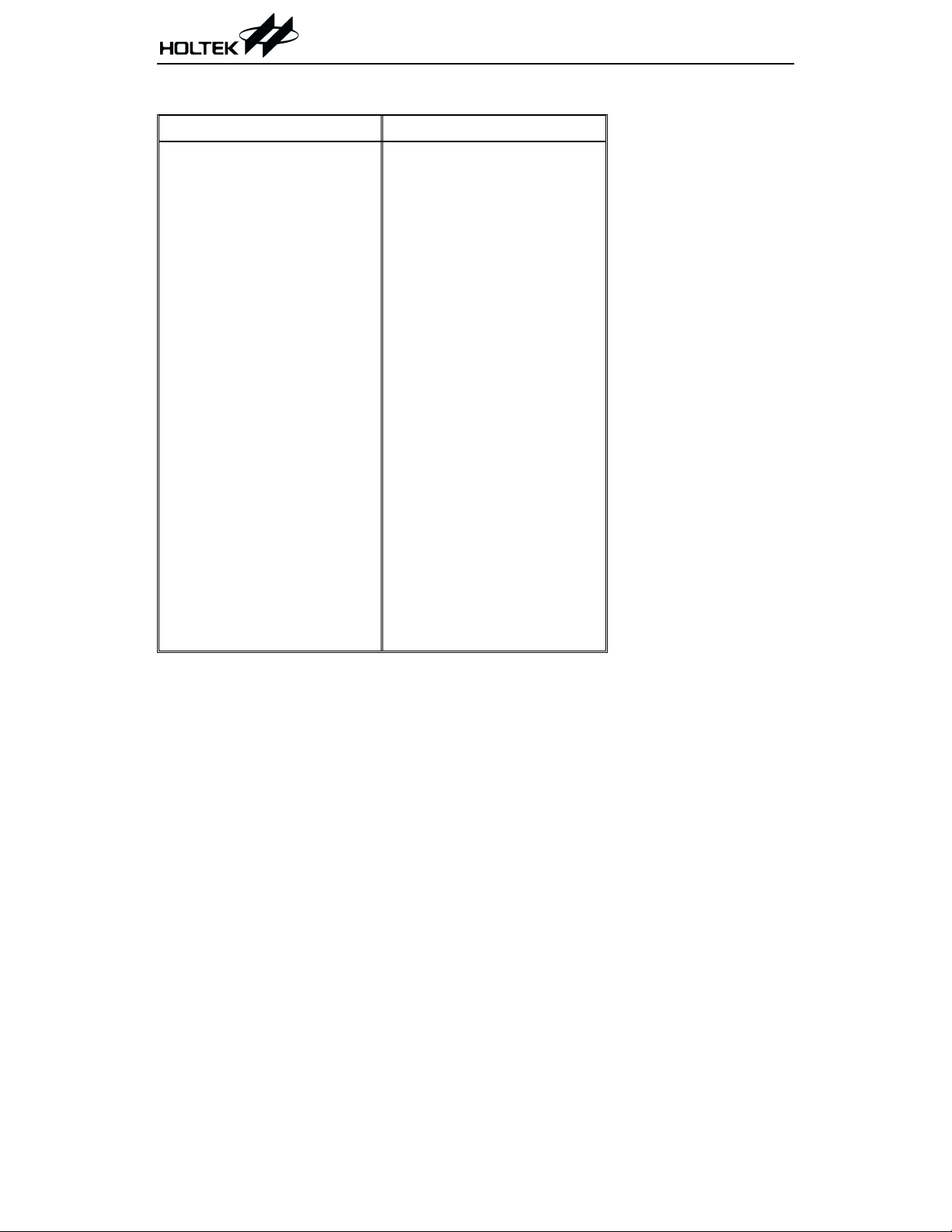
Pad Coordinates Unit: mil
Pad No. X Y Pad No. X Y
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 5.40
25 12.03
26 18.66
-61.58
-61.83
-61.83
-61.83
-61.83
-61.83
-61.83
-61.83
-61.83
-61.83 -2.68
-61.83 -9.31
-61.83 -15.94
-61.83 -22.57
-60.90 -64.26
-54.27 -64.26
-47.64 -64.26
-41.01 -64.26
-34.38 -64.26
-27.75 -64.26
-21.12 -64.26
-14.49 -64.26
-7.86 -64.26
-1.23 -64.26
63.62 27 25.29
50.83 28 66.98
43.73 29 66.98
37.10 30 66.98
30.47 31 66.98
23.84 32 66.98
17.21 33 66.98
10.58 34 66.98
3.95 35 66.98
36 66.98
37 66.98
38 66.98 3.65
39 66.98 10.28
40 65.71 64.39
41 59.08 64.39
42 52.45 64.39
43 40.59 64.39
44 29.75 64.39
45 22.95 64.39
46 16.32 64.39
47 9.56 64.39
-64.26
-64.26
-64.26
48
49
50
51
-2.21
-21.80
-39.52
-49.60
-64.26
-62.65
-56.01
-49.38
-42.76
-36.13
-29.50
-22.86
-16.24
-9.60
-2.97
64.30
64.39
64.39
63.62
HT1620
5 July 26, 1999
Page 6
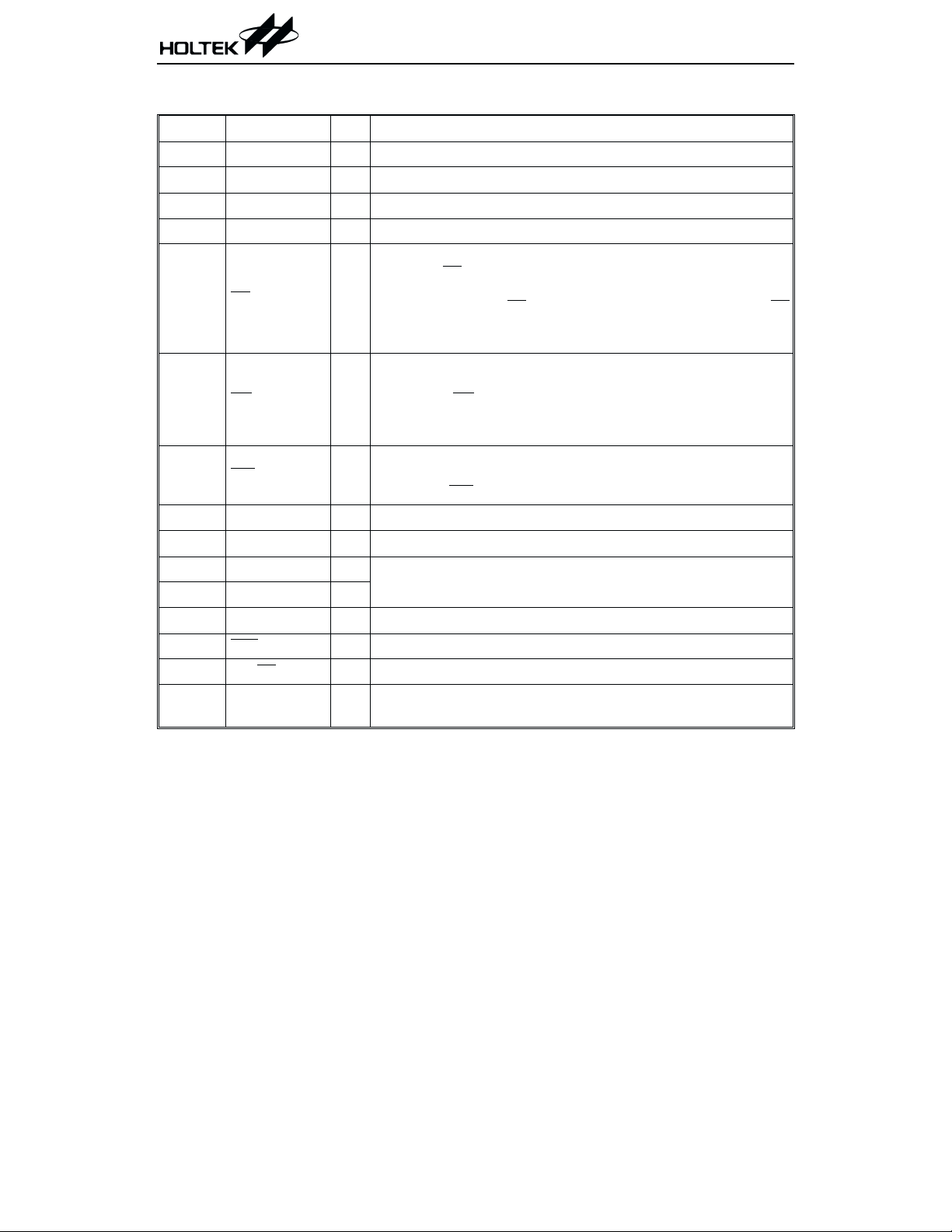
Pad Description
Pad No. Pad Name I/O Description
2 VO15N O Half voltage circuit output pin
3 VEE
4~7 COM0~COM3 O LCD common outputs
8~39 SEG0~SEG31 O LCD segment outputs
40 CS
41 RD
42 WR
43 DATA I/O Serial data input/output with pull-high resistor
44 VSS
45 OSCO O
46 OSCI I
47 VDD
48 IRQ
49, 50 BZ, BZ
51, 1 CC1, CC2 I
Double voltage circuit output pin
¾
Chip selection input with pull-high resistor
When the CS
written to the HT1620 are disabled. The serial interface circuit is
I
also reset. But if the CS
is logic high, the data and command, read from or
is at logic low level and is input to the CS
pad, the data and command transmission between the host con
troller and the HT1620 are all enabled.
READ clock input with pull-high resistor
Data in the RAM of the HT1620 are clocked out on the falling
I
edge of the RD signal. The clocked out data will appear on the
DATA line. The host controller can use the next raising edge to
latch the clocked out data.
WRITE clock input with pull-high resistor
I
Data on the DATA line are latched into the HT1620 on the rising
edge of the WR
Negative power supply, Ground
¾
signal.
The OSCI and OSCO pads are connected to a 32.768kHz crystal
in order to generate a system clock.
Positive power supply
¾
O Time base or WDT overflow flag, NMOS open drain output
O 2kHz or 4kHz tone frequency output pair (tri-state output buffer)
External capacitor pin, for double voltage and half voltage circuit
use
HT1620
-
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Supply Voltage..............................-0.3V to 3.6V
Input Voltage .................V
-0.3V to VDD+0.3V
SS
Storage Temperature.................-50
Operating Temperature...............-25
Note: These are stress ratings only. Stresses exceeding the range specified under ²Absolute Maxi
mum Ratings² may cause substantial damage to the device. Functional operation of this de
vice at other conditions beyond those listed in the specification is not implied and prolonged
exposure to extreme conditions may affect device reliability.
6 July 26, 1999
o
Cto125oC
o
Cto75oC
-
-
Page 7

HT1620
D.C. Characteristics
Symbol Parameter
V
I
I
V
V
I
I
I
I
I
I
R
DD
STB
OL1
OH1
OL2
OH2
OL3
OH3
Operating Voltage
DD
Operating Current 3V No load*
Standby Current 3V No load*
Input Low Voltage 3V DATA, WR,CS,RD
IL
Input High Voltage 3V DATA, WR,CS,RD 2.4
IH
DATA, BZ, BZ, IRQ 3V
DATA, BZ, BZ 3V
LCD Common Sink
Current
LCD Common Source
Current
LCD Segment Sink
Current
LCD Segment Source
Current
Pull-high Resister 3V DATA, WR,CS,RD 40 80 150
PH
Test Conditions
V
DD
Conditions
¾¾
V
=0.3V
OL
V
=2.7V
OH
=0.3V
V
3V
3V
3V
3V
OL
=2.7V
V
OH
=0.3V
V
OL
=2.7V
V
OH
Ta=25°C
Min. Typ. Max. Unit
2.4
¾
¾
¾¾
¾¾
¾
0.8 1.6
-0.6 -1.2 ¾
80 150
3.3 V
23
1
0.6 V
3.0 V
¾
¾mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
-70 -120 ¾mA
70 140
¾mA
-30 -60 ¾mA
kW
* No load: LCD OFF, Buzzer OFF, CS=WR=RD=High
A.C. Characteristics
Symbol Parameter
f
SYS
System Clock 3V Crystal 32kHz
LCD Frame Frequency
f
LCD
LCD Frame Frequency 1/2 Duty
LCD Frame Frequency 1/3 Duty
LCD Frame Frequency 1/4 Duty
t
COM
f
CLK
f
TONE
LCD Common Period
Serial Data Clock 3V
Tone Frequency
Test Conditions
V
DD
¾
¾¾
¾¾
¾¾
¾
¾¾ ¾
7 July 26, 1999
Conditions
Crystal 32kHz
n: Number of COM
Write mode
Read mode
Ta=25°C
Min. Typ. Max. Unit
32
¾
64
¾
64
56
64
n/f
¾
LCD
¾¾
¾¾
2or4
kHz
¾
Hz
¾
Hz
¾
Hz
¾
Hz
¾
s
¾
150 kHz
75 kHz
kHz
¾
Page 8

HT1620
Symbol Parameter
t
CS
t
CLK
t
r,tf
t
su
t
h
t
su1
t
h1
WR, RD
Clock
Serial Interface Reset Pulse
Width (Figure 3)
WR,RDInput Pulse Width
Rise/Fall Time Serial Data Clock
Width (Figure 1)
Setup Time for DATA to WR,RD
Clock Width (Figure 2)
Hold Time for DATA to WR,RD
Clock Width (Figure 2)
Setup Time for CS to WR,RD
Clock Width (Figure 3)
Hold Time for CS to WR,RDClock
Width (Figure 3)
90%
50%
10%
t
f
t
CLK
t
r
(Figure 1)
t
CLK
Test Conditions
V
DD
¾
Conditions
CS
Write mode 3.34
3V
Read mode 6.67
3V
3V
3V
3V
3V
V
DD
GND
W R , R D
Clock
¾¾
¾¾
¾¾
¾¾
¾¾
DB
Min. Typ. Max. Unit
250
¾
¾
¾¾
¾¾
VALID D ATA
50%
t
su
120
120
120
100
100
t
50%
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
h
ns
ms
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
V
DD
GND
V
DD
GND
CS
WR, RD
Clock
50%
50%
FIRST
Clock
t
su1
Figure 1
LAST
Clock
Figure 3
Figure 2
t
CS
t
h1
V
DD
GND
V
DD
GND
8 July 26, 1999
Page 9

Functional Description
HT1620
Display memory - RAM structure
The static display RAM is organized into 32´4
bits and stores the display data. The contents of
the RAM are directly mapped to the contents of
the LCD driver. Data in the RAM can be ac
cessed by the READ, WRITE and READ-MOD
IFY-WRITE commands. The following is a map
ping from the RAM to the LCD patterns.
COM 0COM 1COM 2COM 3
SEG 0
SEG 1
SEG 2
SEG 3
SEG 31
D 3 D 2 D 1 D 0
Data 4 bits
(D 3, D 2, D 1, D 0)
Data
0
1
2
3
31
Addr
Address 6 bits
(A 5, A 4, ..., A0)
RAM mapping
Time base and watchdog timer - WDT
The time base generator and WDT share the
same divided (/256) counter. TIMER DIS/EN/CLR,
WDT DIS/EN/CLR and IRQ
EN/DIS are independent from each other. Once the WDT
time-out occurs, the IRQ
low level until the CLR WDT or the IRQ
pin will stay at a logic
DIS
command is issued.
Tim e Base
C lock S ource
/256
VDD
Buzzer tone output
A simple tone generator is implemented in the
HT1620. The tone generator can output a pair
of differential driving signals on the BZ and BZ
which are used to generate a single tone.
-
LCD driver
-
The HT1620 is a 128 (32´4) pattern LCD driver.
It can be configured as 1/2 or 1/3 bias and 2 or 3
or 4 commons of LCD driver by the S/W configu
ration. This feature makes the HT1620 suitable
for multiple LCD applications. The LCD driving
clock is derived from the system clock. The value
of the driving clock is always 256Hz even when it
is at a 32.768kHz crystal oscillator frequency. The
LCD corresponding commands are summarized
in the table.
The bold form of100,namely 100, indicates
the command mode ID. If successive commands
have been issued, the command mode ID will be
omitted, except for the first command. The LCD
OFF command turns the LCD display off by dis
abling the LCD bias generator. The LCD ON
command, on the other hand, turns the LCD
display on by enabling the LCD bias generator.
The BIAS and COM are the LCD panel related
commands. With the use of the LCD related
commands, the HT1620 can be compatible with
most types of LCD panels.
TIM ER EN /D IS
WDT EN/DIS
IR Q
-
-
CLR Tim er
Q
/4
CLR W DT
D
CK
IR Q E N /D IS
R
WDT
Timer and WDT configurations
9 July 26, 1999
Page 10

Name Command Code Function
LCD OFF
LCD ON
BIAS and COM
10000000010X
10000000011X
1000010abXcX
Turn off LCD outputs
Turn on LCD outputs
c=0: 1/2 bias option
c=1: 1/3 bias option
ab=00: 2 commons option
ab=01: 3 commons option
ab=10: 4 commons option
HT1620
Command format
The HT1620 can be configured by the S/W set
ting. There are two mode commands to configure
the HT1620 resources and to transfer the LCD
display data. The configuration mode of the
HT1620 is called command mode, and its com
mand mode ID is 100. The command mode con
sists of a system configuration command, a
system frequency selection command, an LCD
configuration command, a tone frequency selec
tion command, a timer/WDT setting command,
and an operating command. The data mode, on
the other hand, includes READ, WRITE, and
READ-MODIFY-WRITE operations. The follow
ing are the data mode IDs and the command
mode ID:
Operation Mode ID
READ Data 1 1 0
WRITE Data 1 0 1
READ-MODIFY-WRITE Data 1 0 1
COMMAND Command 1 0 0
The mode command should be issued before the
data or command is transferred. If successive
commands have been issued, the command
mode ID, 100, can be omitted. While the sys
tem is operating in the non-successive com
mand or the non-successive address data mode,
pin should be set to ²1² and the previous
the CS
operation mode will be reset also. Once the CS
pin returns to ²0², a new operation mode ID
should be issued first.
Interfacing
Only four lines are required to interface with
the HT1620. The CS
serial interface circuit and to terminate the com
munication between the host controller and the
HT1620. If the CS
command issued between the host controller and
the HT1620 are first disabled and then initial
ized. Before issuing a mode command or mode
switching, a high level pulse is required to initial
ize the serial interface of the HT1620. The DATA
line is the serial data input/output line. Data to
be read or written or commands to be written
have to be passed through the DATA line. The RD
line is the READ clock input. Data in the RAM
are clocked out on the falling edge of the RD
nal, and the clocked out data will then appear on
the DATA line. It is recommended that the host
controller read in correct data during the interval
between the rising edge and the next falling edge
of the RD
input. The data, address, and command on the
DATA line are all clocked into the HT1620 on the
rising edge of the WR
IRQ
host controller and the HT1620. The IRQ
be selected as a timer output or a WDT overflow
flag output by the S/W setting. The host control
ler can perform the time base or the WDT func
tion by connecting with the IRQ
HT1620.
signal. The WR line is the WRITE clock
line to be used as an interface between the
line is used to initialize the
pin is set to 1, the data and
signal. There is an optional
-
-
-
sig-
pin can
-
-
pin of the
10 July 26, 1999
Page 11

Timing Diagrams
READ mode (command code:110)
CS
WR
RD
HT1620
DATA
1
A5A4A3 A2
1
Memory Address 1(MA1) Data(MA2)
A1A0D0 D1
D ata(M A 1) M em ory Address 2(M A 2)
0
READ mode (successive address reading)
CS
WR
RD
A5A4A3 A2
DATA
0
1
1
Memory Address(MA) Data(MA)
A1A0D0 D1
WRITE mode (command code:101)
CS
WR
D2
D3
D2
0
1
D2
A5A4A3 A2
D3
D0 D1
1
D3
D0 D1
Data(M A+1) Data(M A+2) Data(M A+3)
A1A0D0 D1
D2
D3
D0 D1
D2
D2
D3
D3
D0
DATA
1
1
A5A4A3 A2
0
Memory Address 1(MA1) Data(MA1)
A1A0D0 D1
D2
D3
11 July 26, 1999
1
1
A5A4A3 A2
0
Memory Address 2(MA2) Data(MA2)
A1A0D0 D1
D2
D3
Page 12

WRITE mode (successive address writing)
CS
WR
HT1620
DATA
1
0
1A5A4A3 A2
A1A0D0D1
M em ory Address(M A ) D ata(M A)
D2
D3
D0D1
D2
D3
D0D1
D2
D3
D0D1
Data(M A+1) Data(M A+2) Data(MA+3)
D2
D3
D0
Note: It is recommended that the host controller should read with the data from the DATA line
between the raising edge of the RD
line and the falling edge of the next RD line.
READ-MODIFY-WRITE mode (command code:101)
CS
WR
RD
DATA
A5A4A3 A2
1
1
0
Memory Address 1(MA1) Data(MA1)
A1A0D0 D1
D2
D3
D0 D1
Data(M A1)
D2
D3
1
A5A4A3 A2
1
0
Memory Address 2(MA2) Data(MA2)
A1A0D0 D1
D2
READ-MODIFY-WRITE mode (successive address accessing)
CS
WR
D3
RD
DATA
1
1
A5A4A3 A2
0
Memory Address(MA) Data(MA)
A1A0D0 D1
D2
D3
D2
D0 D1
D3
Data(M A) Data(M A+1) Data(M A+1)
D0 D1
D2
D3
D0 D1
D2
D3
D0
D1
Data(M A+2)
D2
D3
D0
12 July 26, 1999
Page 13

Command mode (command code:100)
CS
WR
HT1620
DATA
0
1
0
C4C3C2 C1
C om m and 1
C8C7C6 C5
Mode (data and command mode)
CS
WR
DATA
RD
C om m and
or
D a ta M o d e
Address and D ata
C0
C om m and
or
D a ta M o d e
C8C7C6 C5
Address and D ata
C4C3C2 C1
C om m and iC om m and... Command
C0
C om m and
or
D a ta M o d e
or
D a ta M o d e
Address and D ata
13 July 26, 1999
Page 14

Application Circuits
0.1mF
VDD VDD
0.1mF
3M
W
0.1
HT1620
F
m
CC1 CC2
CS
*
RD
WR
m
C
DATA
*
R
IR Q
COM0 ~ COM3 SEG0~SEG31
1/2 or 1/3 Bias; 1/2, 1/3 or 1/4 D uty
H T1620
VEEVO15N
OSCI
OSCO
BZ
BZ
C rystal
32768H z
O scillator
Piezo
LC D Panel
* Notes: The connection of the IRQ and RD pin is selectable depending on the requirement of the mC.
=2.4V~3.3V, VEE=-1/2 VDD,V
V
DD
(LCD voltage)=VDD-VEE=3/2 VDD=3.6V~4.9V.
LCD
Adjust R (external pull-high resistance) to fit user¢s time base clock.
14 July 26, 1999
Page 15

Command Summary
Name ID Command Code D/C Function Def.
READ
WRITE
READ
MODIFY
WRITE
SYS DIS
SYS EN
LCD OFF
LCD ON
TIMER DIS
WDT DIS
TIMER EN
WDT EN
TONE OFF
CLR TIMER
CLR WDT
BIAS 1/2
BIAS 1/3
TONE 4K
TONE 2K
DIS
IRQ
EN
IRQ
A5A4A3A2A1A0D0D1D2D3 D Read data from the RAM
110
A5A4A3A2A1A0D0D1D2D3 D Write data to the RAM
101
A5A4A3A2A1A0D0D D2D3 D Read and write to the RAM
101
0000-0000-X C
100
0000-0001-X C Turn on system oscillator
100
0000-0001-X C Turn off LCD bias generator Yes
100
0000-0011-X C Turn on LCD bias generator
100
0000-0100-X C Disable time base output Yes
100
0000-0101-X C
100
0000-0010-X C Enable time base output
100
0000-0111-X C
100
0000-1000-X C Turn off tone outputs Yes
100
0000-1101-X C
100
0000-111X-X C
100
0010-abX0-X C
100
0010-abX1-X C
100
010X-XXXX-X C Tone frequency, 4kHz
100
0110-XXXX-X C Tone frequency, 2kHz
100
100X-0XXX-X C Disable IRQ output Yes
100
100X-1XXX-X C Enable IRQ output
100
Turn off both system oscillator
and LCD bias generator
Disable WDT time-out flag
output
Enable WDT time-out flag
output
Clear the contents of the time base
generator
Clear the contents of the WDT
stage
LCD 1/2 bias option
ab=00: 2 commons option
ab=01: 3 commons option
ab=10: 4 commons option
LCD 1/3 bias option
ab=00: 2 commons option
ab=01: 3 commons option
ab=10: 4 commons option
HT1620
Yes
Yes
15 July 26, 1999
Page 16

HT1620
Name ID Command Code D/C Function Def.
F1
F2
F4
F8
F16
F32
F64
F128
TEST
NORMAL
101X-0000-X C
100
101X-0001-X C
100
101X-0010-X C
100
101X-0011-X C
100
101X-0100-X C
100
101X-0101-X C
100
101X-0110-X C
100
101X-0111-X C
100
1110-0000-X C
100
1110-0011-X C Normal mode Yes
100
Time base clock output: 1Hz
The WDT time-out flag after: 4s
Time base clock output: 2Hz
The WDT time-out flag after: 2s
Time base clock output: 4Hz
The WDT time-out flag after: 1s
Time base clock output: 8Hz
The WDT time-out flag after: 1/2 s
Time base clock output: 16Hz
The WDT time-out flag after: 1/4 s
Time base clock output: 32Hz
The WDT time-out flag after: 1/8 s
Time base clock output: 64Hz
The WDT time-out flag after: 1/16 s
Time base clock output: 128Hz
The WDT time-out flag after:1/32 s
Test mode, user don¢t use.
Yes
Notes: X : Don,t care
A5~A0 : RAM addresses
D3~D0 : RAM data
D/C : Data/command mode
Def. : Power on reset default
All the bold forms, namely 110, 101, and 100, are mode commands. Of these, 100indicates the
command mode ID. If successive commands have been issued, the command mode ID except for the
first command will be omitted. The source of the tone frequency and of the time base/WDT clock frequency can be derived from a 32.768kHz crystal oscillator. Calculation of the frequency is based on
the system frequency sources as stated above. It is recommended that the host controller should ini
tialize the HT1620 after power on reset, for power on reset may fail, which in turn leads to malfunc
tioning of the HT1620.
16 July 26, 1999
-
-
Page 17

HT1620
Holtek Semiconductor Inc. (Headquarters)
No.3 Creation Rd. II, Science-based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: 886-3-563-1999
Fax: 886-3-563-1189
Holtek Semiconductor Inc. (Taipei Office)
5F, No.576, Sec.7 Chung Hsiao E. Rd., Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: 886-2-2782-9635
Fax: 886-2-2782-9636
Fax: 886-2-2782-7128 (International sales hotline)
Holtek Microelectronics Enterprises Ltd.
RM.711, Tower 2, Cheung Sha Wan Plaza, 833 Cheung Sha Wan Rd., Kowloon, Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2-745-8288
Fax: 852-2-742-8657
Copyright Ó 1999 by HOLTEK SEMICONDUCTOR INC.
The information appearing in this Data Sheet is believed to be accurate at the time of publication. However, Holtek
assumes no responsibility arising from the use of the specifications described. The applications mentioned herein are
used solely for the purpose of illustration and Holtek makes no warranty or representation that such applications
will be suitable without further modification, nor recommends the use of its products for application that may pres
ent a risk to human life due to malfunction or otherwise. Holtek reserves the right to alter its products without prior
notification. For the most up-to-date information, please visit our web site at http://www.holtek.com.tw.
17 July 26, 1999
-
 Loading...
Loading...