Page 1

FAN8727
Spindle + 4-CH Motor Drive IC
www.fairchildsemi.com
Features
• Built-in Power Save Circuit
• Built-in Current Limit Circuit
• Built-in Thermal Shutdown Circuit (TSD)
• Built-in Hall Bias
• Built-in FG Signal Output Circuit
• Built-in Rotational Direction Detecting Circuit
• Built-in Protection Circuit For Reverse Rotation
• Built-in Short Brake Circuit
• Built-in Normal OP-AMP
• Built-in 4-CH Balanced Transformerless (BTL) Driver
• Built-in BTL MUTE Circuit (CH1-2, CH3 and CH4)
• Corresponds to 3.3V DSP
Description
The FAN8727 is a monolithic integrated circuit suitable for a
4-CH motor driver which drives the tracking actuator, focus
actuator, sled motor, loading motor and 3-phase BLDC
spindle motor of the MDP/CAR-MD/CAR-NAVIGATION
system.
48-QFPH-1414
Typical Applications
•Mini Disk Player
• Digital Video Disk Player
• Car Mini Disk Player
• Car Navigation System
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
Ordering Information
Device Package Operating Temperature
FAN8727 48-QFPH-1414 -35°C ~ +85°C
Rev. 1.0.2
Page 2

FAN8727
Pin Assignments
H3 +
48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37
H3 −
H2 +
H2 −
H1 +
H1 −
BTLSNGD
BIAS
AVM4
MUTE12
MUTE3
MUTE4
VH
FG
ECR
EC
VCC2
PC1
SIGGND
VM
CS1
SS
DIR
SB
1
2
3
4
5
6
36
35
34
33
32
31
DO4 +
DO4 −
AVM3
DO3 +
DO3 −
BTLPGND2
FAN8727
7
8
9
10
11
12
30
29
28
27
26
25
BTLPGND1
DO2 +
DO2 −
DO1 +
DO1 −
DI1
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
A3
A2
PWRGND
A1
OPIN+
OPIN−
OPOUT
VCC1
DI4
DI3
DI2
AVM12
2
Page 3

Pin Definitions
Pin Number Pin Name I/O Pin Function Description
1VHIHall Bias
2 FG O FG Signal Output
3 ECR I Torque Control Reference
4 EC I Torque Control Signal
5 VCC2 - Supply Voltage
6 PC1 - Phase Compensation Capacitor
7 SIGGND - Signal Ground
8 VM - Motor Supply Voltage
9 CS1 I Current Sensor
10 S/S I Start/stop
11 DIR O 3-Phase Rotational Direction Output
12 SB I Short Brake
13 PWRGND - Power Ground
14 A3 O 3-Phase Output 3
15 A2 O 3-Phase Output 2
16 A1 O 3-Phase Output 1
17 OPIN+ I OP-AMP Input (+)
18 OPIN- I OP-AMP Input (-)
19 OPOUT O OP-AMP Output
20 VCC1 - Supply Voltage
21 AVM12 - BTL CH1, 2 Motor Supply Voltage
22 DI4 I BTL Drive Input 4
23 DI3 I BTL Drive Input 3
24 DI2 I BTL Drive Input 2
25 DI1 I BTL Drive Input 1
26 DO1- O B TL Drive 1 Output (-)
27 DO1+ O BTL Drive 1 Output (+)
28 DO2- O B TL Drive 2 Output (-)
29 DO2+ O BTL Drive 2 Output (+)
30 BTLPGND1 - BTL Power Ground 1
31 BTLPGND2 - BTL Power Ground 2
32 DO3- O B TL Drive 3 Output (-)
33 DO3+ O BTL Drive 3 Output (+)
FAN8727
3
Page 4
FAN8727
Pin Definitions
Pin Number Pin Name I/O Pin Function Description
34 AVM3 - BTL CH3 Motor Supply Voltage
35 DO4- O B TL Drive 4 Output (-)
36 DO4+ O BTL Drive 4 Output (+)
37 MUTE4 I BTL Drive Mute CH4
38 MUTE3 I BTL Drive Mute CH3
39 MUTE12 I BTL Drive Mute CH1, 2
40 AVM4 - BTL CH4 Motor Supply Voltage
41 BIAS - BTL Bias Voltage
42 BTLSGND - BTL Drive Signal Ground
43 H1- I Hall1(-) Input
44 H1+ I Hall1(+) Input
45 H2- I Hall2(-) Input
46 H2+ I Hall2(+) Input
47 H3- I Hall3(-) Input
48 H3+ I Hall3(+) Input
(Continued)
4
Page 5
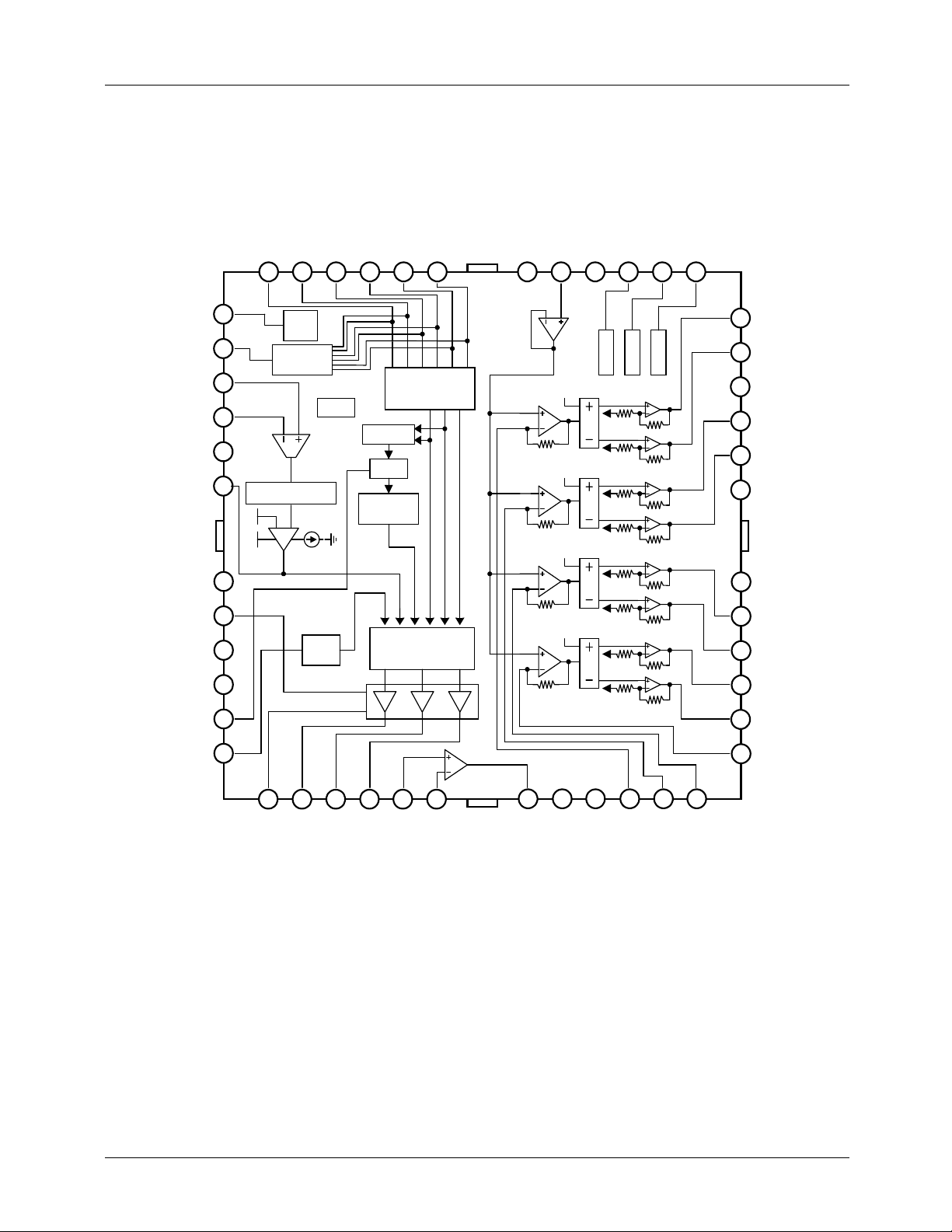
Internal Block Diagram
H3+
H3-
H2+
H2-
H1+
H1-
BIAS
BTLSGND
AVM4
MUTE12
MUTE3
FAN8727
MUTE4
37383940414248 47 46 45 44 43
VH
FG
ECR
EC
VCC2
PC1
SIGGND
VM
CS1
SS
DIR
SB
1
2
3
4
5
6
Absolute Values
CS1VM
7
8
9
10
11
12
Hall
Bias
FG
Generator
Current
Sense Amp
Output
Current Limit
Short
Brake
TSD
Hall Amp
Detection
Logic
Reverse
Rotation
Distributor
AVM4
AVM3
AVM12
AVM12
MUTE12
MUTE3
MUTE4
36
35
34
33
32
31
BTLPGND2
30
BTLPGND1
29
28
27
26
25
DO4+
DO4-
AVM3
DO3+
DO3-
DO2+
DO2-
DO1+
DO1-
DI1
13
PWRGND
A3
OPOUT
2019
VCC1
AVM12
22 2321
DI4
17
OPIN+
18
OPIN-
16
1514
A2
A1
DI3
24
DI2
5
Page 6
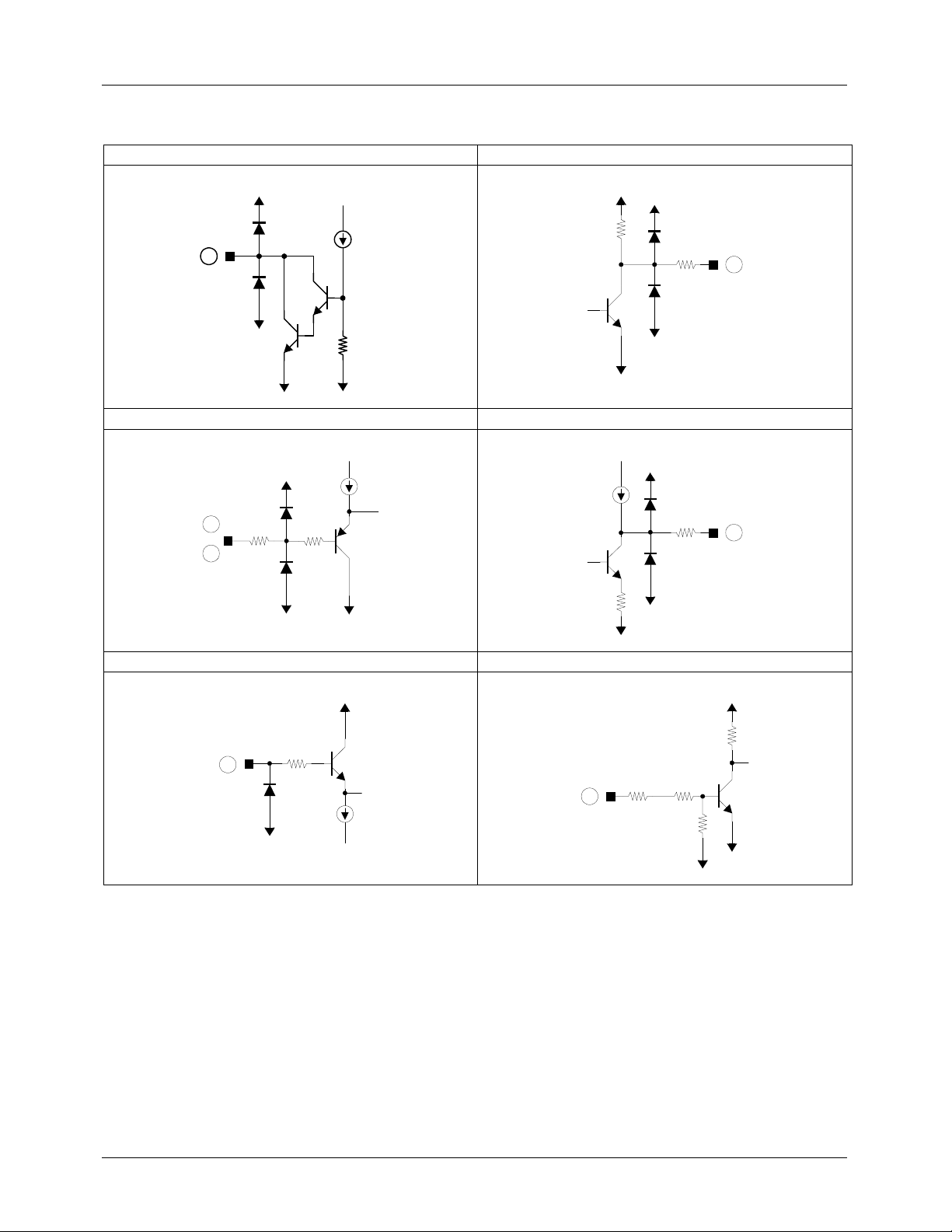
FAN8727
Equivalent Circuits
Hall Bias FG Signal Output
1
Torque Control Reference & Signal Phase Compensation Capacitor
100K
Ω
10K
2
Ω
25
Ω
3
Ω
25
4
Ω
1K
Ω
1K
Current Detector Start/Stop
9
Ω
5K
10
Ω
25
25
50K
30K
6
Ω
Ω
100K
Ω
Ω
6
Page 7

FAN8727
Equivalent Circuits
3-Phase Rotational Direction Output Short Brake
Ω
10K
3-Phase Output OP-AMP Input
Ω
15K
(Continued)
11
Ω
25
14
15
16
12
Ω
1k
Ω
20k
Ω
2K
17
Ω
25
Ω
1K
Ω
25
Ω
2K
18
Ω
Ω
25
1K
Ω
2K
Ω
2K
OP-AMP Ouput BTL Drive Input
22
18
23
24
Ω
25
Ω
50
25
7
Page 8
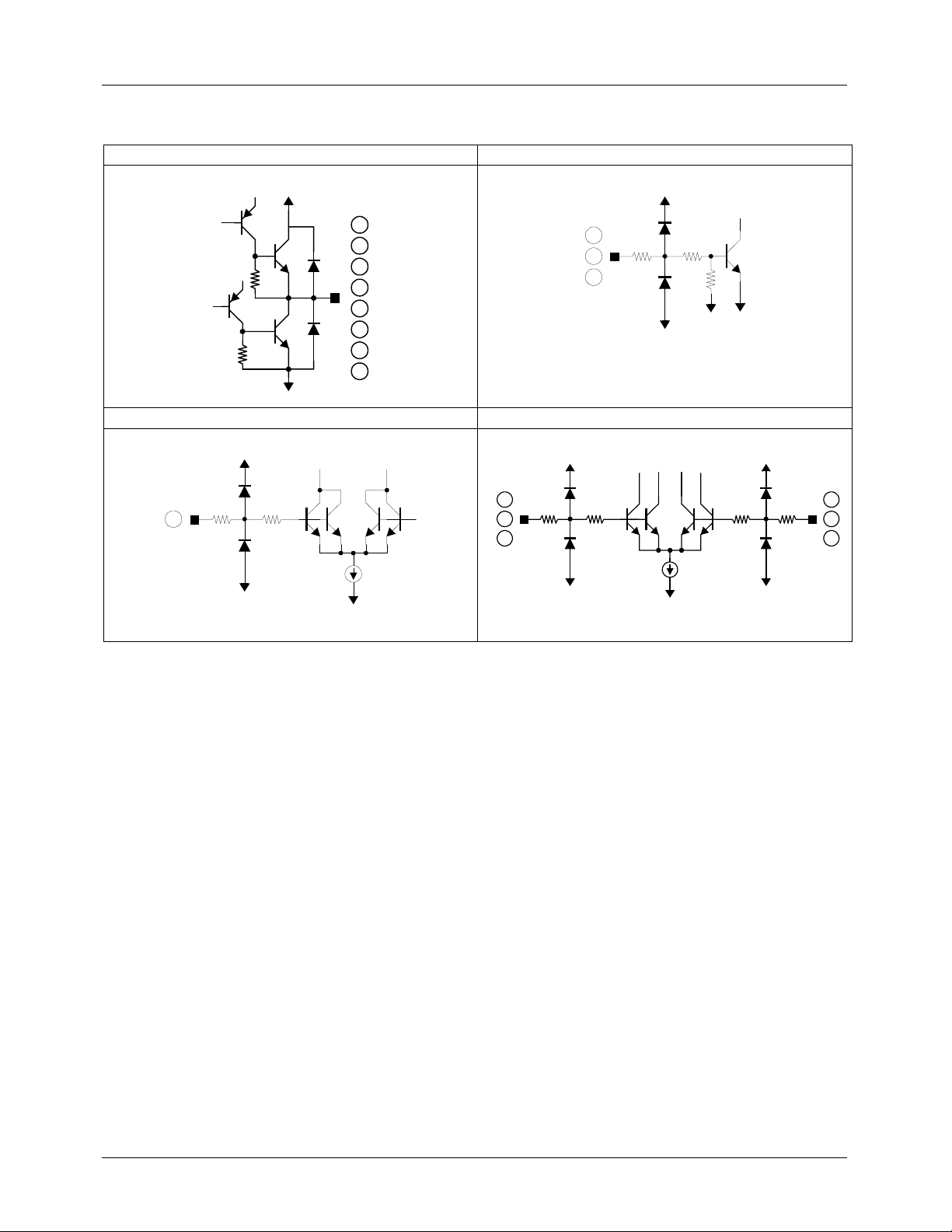
FAN8727
Equivalent Circuits
BTL Drive Output BTL Drive Mute
Ω
20K
Ω
30K
BTL Bias Voltage Hall Input
41
Ω
25
0.5K
Ω
(Continued)
26
27
28
29
32
33
35
36
37
38
39
43
45
47
Ω
25
1K
Ω
25
50K
30K
Ω
Ω
44
Ω
Ω
1K
25
46
Ω
48
8
Page 9

Absolute Maximum Ratings ( Ta=25°°°°C)
Parameter Symbol Value Unit
Supply Voltage (BTL Signal)
Supply Voltage (Spindle Signal)
Supply Voltage (Motor)
Supply Voltage (BTL Motor)
Power Dissipation
Operating Temperature Range
Storge Temperature Range
Maximum Output Current (Spindle Part)
Maximum Output Current (BTL Part)
Note:
When mounted on 70mm × 70 mm × 1.6mm PCB (Phenolic resin material)
1.
Power dissipation is reduced 24 mW/°C for using above Ta=25°C
2.
Do not exceed Pd and SOA.
3.
V
CC1max
V
CC2max
V
Mmax
V
MBTLmax
Pd
Topr
Tstg
I
OMAXS
I
OMAXB
Pd [mW]
3,000
15
7
15
15
note
3.0
-35 ~ +85
-55 ~ +150
1.3
1
FAN8727
V
V
V
V
W
°°°°C
°°°°C
A
A
2,000
1,000
0
0
175150125100755025
Ambient Temperature, Ta [°C]
Recommended Operating Conditions ( Ta=25°°°°C)
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Operating Supply Voltage (BTL Signal) V
Operating Supply Voltage (Spindle Signal) V
Operating Supply Voltage ( Spindle Motor) V
Operating Supply Voltage (BTL Motor) V
Note: The VM should be turn on before the VCC2.
CC1
CC2
note
M
MBTL
4.5 - 13.2 V
4.5 - 5.5 V
4.5 - 13.2 V
4.5 - V
CC1
V
9
Page 10

FAN8727
Electrical Characteristics
(Ta=25°C, V
=5V, VM=12V)
CC2
Parameter Symbol Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Circuit Current 1 I
Circuit Current 2 I
CC 1
CC2
Power Save=0V - 0.3 1 mA
Power Save=5V - 4.5 6 mA
START/STOP
On Voltage Range V
Off Voltage Range V
PSON
PSOFF
L-H Circuit On 2.5 - - V
H-L Circuit Off - - 0.5 V
HALL BIAS
Hall Bias Voltage V
HB
IHB= 20mA - 1.2 1.8 V
HALL AMP
Hall Bias Current I
In-Phase in Voltage Range V
Minimum in Level
note
V
HA
HAR
INH
- -15uA
- 1.5 - 4.0 V
-60--mVpp
TORQUE CONTROL
In Voltage Range E
Offset Voltage (-)
note
Offset Voltage (+) E
E
COFF-
COFF+
In Current E
In/Output Gain G
C
CIN
EC
ECR= 2.5V -100 -50 -20 mV
ECR= 2.5V 20 50 100 mV
EC= ECR= 2.5V -5 -1 - uA
ECR= 2.5V, RCS= 0.5Ω 0.41 0.51 0.61 A / V
- 0.5 - 3.3 V
FG
FG Output Voltage (H) V
FG Output Voltage (L) V
Input Voltage Range
note
V
FGH
FHL
FGR
IFG= -10uA 3.0 - V
CC
IFG= 10uA - - 0.5 V
Hn+, Hn- input D-range 1.5 - 4.0 V
OUTPUT BLOCK
Saturation Voltage (Upper TR) V
Saturation Voltage (Lower TR) V
Torque Limit Current I
OH
OL
TL
IO= -300mA - 0.9 1.6 V
IO= 300mA - 0.2 0.6 V
RCS= 0.5Ω 560 700 840 mA
DIRECTION DETECTOR
Dir Output Voltage (H) V
Dir Output Voltage (L) V
DIRH
DIRL
IFG= -10uA 3.0 - V
CC
IFG= 10uA - - 0.5 V
SHORT BRAKE
On Voltage Range V
Off Voltage Range V
Note: Guaranteed field ( No EDS / Final test )
SBON
SBOFF
-2.5-V
CC
-0-1.0V
V
V
V
10
Page 11

FAN8727
=12V, V
(Continued)
=12V, RL=24Ω)
MBTL
Electrical Characteristics
BTL Drive Part (Ta=25°C, V
CC1
Parameter Symbol Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Quiescent Circuit Current I
Output Offset Voltage V
Maximum Output
Amplitude Voltage
V
Voltage Gain G
Ripple Rejection Ratio
Slew Rate
note
CH Mute off Voltage V
CH Mute On Voltage V
note
MOFFCH
MONCH
CC
OO
OM
VC
VIN=0.1Vrms, 1kHz 10.5 12.0 13.5 dB
RR VIN=0.1Vrms, 120kHz - 60 - dB
SR 120Hz, 2Vpp - 1.0 - V/us
Pin37, 38, 39 = Variation - - 1.0 V
Pin37, 38, 39 = Variation 2.5 - - V
- - 18 25 mA
--40-40mV
- 9.5 10.5 - V
NORMAL OP- AMP
Input Offset Voltage V
Input Bias Current I
High Level Output Voltage V
Low Level Output Voltage V
Output Sink Current I
Output Source Current I
note
note
note
G
CMRR1 f=1kHz, VIN= -20dB - 80 - dB
Open Loop Voltage Gain
Ripple Rejection Ratio
Slew Rate
note
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
OF
B1
OH1
OL1
SINK
SOU1
VO1
f=1kHz, VIN= -75dB - 75 - dB
RR1 f=120Hz, VIN= -20dB - 65 - dB
SR1 f=120Hz, 2Vp-p - 1 - V/us
- -20 - +20 mV
- - - 600 nA
-11--V
---0.1V
-1025-mA
-58-mA
Note: Guaranteed field ( No EDS / Final test )
11
Page 12

FAN8727
Calculation of Gain & Torque Limit Current
VM VM
Current / Voltage
EC
ECR
Convertor
+
Gm
−
Absolute
Values
−
Vin
R1
+
VM
Max. output current limiting
+
Vmax
−
0.255 which is made from GM times R1 is fixed value within IC.
Gain
0.255
-------------- -=
R
S
Vmax (see above block diagram) is setted to 350mV.
Itl mA[]
Vmax
--------------- -
R
S
350 mV[]
----------------------- -==
R
S
Negative
Feedback loop
−
+
Driver
+
I
O
R
Power
Transistors
Commutation
Distributor
H1
−
V
S
S
+
CS1 (Pin 9)
H2
H3
Output
Current sense
I
O
U
V
W
12
Page 13

FAN8727
Application Information
1. Mute Function
1) Mute Control Voltage Condition
When using the mute function, the applied control voltage condition is as follows.
MUTE ON Voltage 2.5[V] Above Mute Function Operation
MUTE OFF Voltage OPEN or 0.5[V] Below Normal Operation
2) Separated Channel Mute Function
These pins are used for individual channel mute operation.
- When the mute pins (pin 37, 38 and 39) are OPEN or the voltage of the mute pins are below 0.5[V], the mute circuit is
stopped and BTL output cir cui t s ope r at e norm al l y.
- When the mute pins (pin 37, 38 and 39) are above 2.5[V], the mute circuits are activ ated so that the BTL output circu its
will be muted.
- If the junction temperature rises above 175°C, then the thermal shutdown (TSD) circuit is activated and all the output
circuits (4-CH BTL Drivers and 3-phase BLDC Driver) are muted.
2. 4-CH Balanced Transformerless (Btl) Driver
VCC
Vbias
Vin
Rextern
41
22 23
24 25
DRIVE
AMP
X2
+
AMP1
−
10k
Q1
Q3
27
29
33
36
M
LEVEL
SHIFT
GND
Q2
26
28
32
Q4
35
DRIVE
AMP
X2
- The voltage, Vbias, is the reference voltage given by the external bias voltage of pin 41.
- The input signals, Vin, through t he pin s (pi n 22, 23 , 24 and 2 5) are amp lified 1 0K/Re xtern t ime s and th en f ed to the l evel
shift.
- The level shift produces the current due to the difference between the input signal (Vin) and the arbitrary reference
voltage (Vbia s). The current produced as + ∆I and - ∆I are fed into the drive buffers.
- The drive buffer operates the power TR of the output stage according to the state of the input signal(Vin).
- The output stage is the BTL driver, and the motor (or actuator) is rotating in forward direction by operating TR Q1 and
TR Q4. On the other hand, if TR Q2 and TR Q3 are operating, the motor (or actuator) is rotating in reverse direction.
- When the input signal Vin, through the pin (pin 22, 23, 24 and 25) is below the Vbias, then the motor (actuator) is in
forward direction.
13
Page 14

FAN8727
- When the input signal Vin, through the pin (pin 22, 23, 24 and 25) is above the Vbias, then the motor (actuator) is in
reverse direction.
- If you want to change the gain, then modify the external resistor's value (Rextern )
3. T o rque & Output Current Control
Torque Control & Output Current Control
V
M
+
−
Torque sense amp
V
AMP
E
C
+
−
E
CR
−
+
- By amplifying the voltage difference between E
(V
) for the current sense AMP.
AMP
and ECR from the Servo IC, the torque sense AMP produces the input
C
Current sen s e a m p
TSD
Gain
Controller
- The current sense AMP produces the input for the Gain controller to allo w the output cu rrent (I
controlled by the input voltage (V
converted into V
RNF
.
), where the output current (IO) is detected by the sense resistor (RNF) and is
AMP
V
M
R
NF
V
RNF
I
O
Driver
) of the driver to be
O
- In the end, the signals of the Servo IC control the velocity of the motor by controlling the output current (I
driver.
- When the junction temperature rises up to about 175°C, then the output drive circuit will be shut down.
- The range of the torque control input voltage is as shown below.
V
RNF
[V]
Reverse
Forward
Rotation
M
) of the
O
3 mV
The input range (E
14
Ecoff−
) of the Torque Sense AMP is 0.5V ~ 3.3V
C
Ecoff+
0
E
CR-EC
[V]
Ec < E
Ec > E
Forward rotation
CR
Stop after detecting
CR
reverse rotation
Page 15

4. Power Save Function
FAN8727
Bias block
100k
Q1
Start
Stop
V
CC
10
30KΩ
12KΩ
- This function block operates the power saving function.
- The power save circuit is activated by operating TR Q1.
- When the SS (Start/Stop) pin 10 i s h igh (V
), the TR Q1 is turned on so that the bias circuit is enabled. On the other
CC
hand, when the SS (Start/Stop) pin 10 is Open or Low (GND), the TR Q1 is turned off so that the bias circuit is disabled.
- The power save operation controlled by SS (pin 10) input conditions is as follows;
Pin#10 FAN8727
HIGH START
OPEN/LOW STOP
5. Short Brake Function
V
M
MOTOR
ON
OFF
V
CC
12
1KΩ
80KΩ
Drive logic
Q1
OFF
ON
14
15
16
When the pick-up part moves from the inner to the outer spindle of the MD, the brake function of the reverse voltage is commonly employed to rate the rotational velocity of the spindle motor.However, if the spindle motor rotates rapidly, the brake
function of the reverse voltage may produce too much heat at the drive IC.
To remove these shortcomings and to enhance efficiency, the short brake function is added to FAN8 727. When the short brake
function is active, all upper Power transistors are turned off and the lower Power transistors turned on, so as to reduce the rotational velocity of the motor. The short brake operation controlled by SB (pin 12), and the inputs conditions are as follows.
Pin#12 SHORT BRAKE
HIGH ON
LOW OFF
15
Page 16

FAN8727
6. Thermal Shutdown (Tsd) Function
When the junction temperature rises up to about 175°C, then the output drive circuit is shut down, when the junction temperature falls off to about 160°C, the output drive circuit will be normally operated. It has the temperature hysteresis of about 15°C.
7. Rotational Direction Detecting Function
V
CC
H2+
H2−
H3+
H3−
+
D
R
Q
CK
D-F/F
−
+
−
DIR
11
< E
E
C
CR
EC > E
CR
Rotation DIR
Forward Low
Reverse High
- The forward and reverse rotations of the MD are detected by the cir cuit, as shown in the above Table.
- The rotational direction of the MD can be learned by the output waveforms of the hall sensor and/or the driver. Let the
three hall sensors be H1, H2 and H3 respectively. If the hall sensors turn on in the order, H1 → H2 → H3, of the reverse
rotation, the output waveforms of the hall sensors will be as shown below.
H1
H2
H3
( a)
Inversely, if the hall sensors turn on i n t he or de r, H3→ H2→ H1, of the forward r ota ti on , t h e ou t pu t w ave f or ms of the hall sensors will be as shown mext page.
16
Page 17

H1
H2
FAN8727
H3
( b)
In the cases above, the value of H2 at the falling edges of H3 is Low in figure <a>, while High in figure <b>. The rotational
direction detector takes advantage of this phenomenon.
8. Reverse Rotation Preventing Function
E
+
E
H2+
H2−
H3+
H3−
CR
C
−
+
−
+
−
DQ
CK
D-F/F
Current
Sense
Amp
Gain
Controller
Driver
M
- The forward and reverse rotation of the moto r are detected, as shown in the table below, by the circuit shown above.
Consequent ly at reverse rotation, the D- F/F output Q b e comes Low and cuts off the output current sense Amp, resulting
in the stoppage of the Gain controller function.
- When the MD is rotating in forward direction, E
controlling time of E
gets longer, MD slows down, stops, and then rotates in the reverse direction. To prevent the
C>ECR
is sometimes controlled to retard and/or stop the MD. As the
C>ECR
MD from rotating in the reverse direction, a reverse rotation resistant function is required. Its operational principles are
discussed below.
Rotation H2 H3 D-F/F
Reverse Rotation Preventer
E
C<ECR
EC>E
CR
Forward H H → L H Forward Brake and Stop
Reverse L H → LL - Stop
17
Page 18

FAN8727
9. FG Output Function
The FG output, which detects the number of rotations of the MD, is generated by combination zero-crossing the output waveforms of the hall sensors. The FG output circuit is as shown below.
+
H1
H2
H3
−
+
−
FG OUTPUT
+
−
10. Hall Sensor Connection
External Hall sensors are used in series or parallel connection as shown below.
V
CC
HALL 1 HALL 2
1
VH
HALL 3
V
CC
HALL 1
HALL 2
HALL 3
1
VH
18
Page 19

FAN8727
11. Hall Input Output Timming Chart
The 3-phase hall signal is amplified in the hall amplifiers and sent to the matrix section, where the signal is further amplified
and combined. After the signal is converted to a current in the amplitude control circuit, the current is supplied to the output
driver, which then provides a motor drive current. The phases of the hall input signal, output voltage, and output current are
shown below.
H1 +
H2 +
H3 +
A1 output current
A1 output voltage
A2 output current
A2 output voltage
A3 output current
A3 output voltage
19
Page 20

FAN8727
Test Circuits 1
BTL Drive Part
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
VH
FG
ECR
EC
VCC2
PC1
SIGGND
VM
CS1
SS
DIR
SB
H3+
10µF
434445464748
H3−
H2+
H2−
H1+
H1−
BTLSGND
FAN8727
2.5V
BIAS
AVM4
12V
VMUTE
MUTE12
VMUTE
VMUTE
373839404142
MUTE3
BTLPGND2
BTLPGND1
DO4+
MUTE4
DO4−
AVM3
DO3+
DO3−
DO2+
DO2−
DO1+
DO1−
DI1
V
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
SW4
12V
10µF
SW3
SW2
SW1
RL4’
RL4
RL3’
RL3
V
V
RL2
RL1
20
PWRGNDA3A2
13 14 15 16 17 19 2218 20 21 2423
OPIN (+) OPIN (−)OPOUT
SW5
3
1
1MΩ
2
V
p1
V
V
IN1
A1
V
IN3
OPIN+
V
+
−
OPIN−
BTL SVCC
10µF
V
s1
12V
SW6
OPOUT
A
10µF
3
V
VCC1
1
IN3
10µF
12V
2
AVM12
D14
D13
D12
SERVO AMP
TRACKING
FOCUS
SLED
CONTROL TRAY
V
1.2kΩ
1MΩ
V
V
V
CC
SW7
1
2
3
Page 21

Test Circuits 2
Spindle Motor Drive Part
FAN8727
H3+
AAAAAA
VV
SW12
1
VH
2
2.5V
E
C
SW14
5V
A
SW13
FG
3
ECR
4
EC
5
VCC2
6
PC1
H3+
H3−
H2+
H3−
H2+
H2−
H1+
H1−
3738394042 41434445464748
H2−
H1+
H1−
BTLSGND
BIAS
AVM4
MUTE12
MUTE3
MUTE4
DO4+
DO4−
AVM3
DO3+
DO3−
BTLPGND2
36
35
34
33
32
31
FAN8727
SW15
IFR
SW16
7
SIGGND
8
VM
9
CS1
10
SS
11
DIR
12
SB
PWRGNDA3A2
13 14 15 16 17 19 20 21 22 23 24
A1
OPIN−
OPIN+
18
OPOUT
VCC1
BTLPGND1
AVM12
D14
D13
12V
V
V
SW17
SW18
DO2+
DO2−
DO1+
DO1−
DI1
D12
30
29
28
27
26
25
VSB
SW19
SW20
21
Page 22

FAN8727
Application Circuits
FOCUS TRACKING
MUTE
SLED MUTE
BTL BIAS
HALL3
HALL2
HALL1
VOLTAGE
+5V
TRAY MUTE
FG SIGNAL
SERVO
TORQUE
CONTROL
12V
ROTATE
DIRECTION
100pF
VCC
SYSTEM
CONTROL
SHORT
BREAK
10K
0.1µF
42
H3−
1
2
3
4
5
6
H3+
VH
FG
ECR
EC
VCC2
PC1
H2+
H2−
H1+
H1−
BIAS
BTLSGND
FAN8727
7
SIGGND
8
VM
CS1
9
SS
10
11
DIR
12
SB
PWRGNDA3A2
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
A1
OPIN−
OPIN+
OPOUT
VCC1
3738394041434445464748
AVM4
AVM12
MUTE12
D14
MUTE3
BTLPGND2
BTLPGND1
D13
DO4+
MUTE4
DO4−
AVM3
DO3+
DO3−
DO2+
DO2−
DO1+
DO1−
D12
DI1
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
+5V
TRAY
MOTOR
SLED
MOTOR
FOCUS
ACTUATOR
TRACKING
ACTUATOR
22
VCC
+5V
SERVO AMP
TRACKING
FOCUS
SLED
CONTROL TRAY
Page 23

FAN8727
23
Page 24

FAN8727
DISCLAIMER
FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR RESERVES THE RIGHT TO MAKE CHANGES WITHOUT FURT HER NOTICE TO ANY
PRODUCTS HEREI N TO IMPROVE RELIABILITY, FUNCTIO N OR DESIGN. FAIRCH IL D DOES NOT ASSUME ANY
LIABILITY ARISING OUT OF THE APPLICATION OR USE OF ANY PRODUCT OR CIRCUIT DESCRIBED HEREIN; NEITHER
DOES IT CONVEY ANY LICENSE UNDER IT S PATENT RIGHTS, NOR THE RIGHTS OF OTHE RS.
LIFE SUPPORT POL I CY
FAIRCHILD’S PR ODUCTS ARE NOT AUTH ORIZED FOR USE AS C RITICAL COMPONENT S IN LIFE SUPPORT DE VICES
OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT OF FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR
CORPOTATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems
which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the body,
or (b) support or sustain life, and (c) whose failure to
perform when properly used in accordance with
2. A critical component in any component of a life support
device or sy stem whose fai lure to perform can be
reasonably expec ted to cause the failur e of the life support
device or system, or to affect its safety or effec t iv ene ss .
instructions for use provided in the labeling, can be
reasonably expected to result in a significant injury of the
user.
www.fairchildsemi.com
9/6/02 0.0m 001
2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
Stock#DSxxxxxxxx
 Loading...
Loading...