Page 1

MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE
Technical Information
Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump
Size 070/089
powersolutions.danfoss.com
Page 2
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Revision History Table of Revisions
Date Changed Rev
Mar 2014 Converted to Danfoss layout – DITA CMS CE
Dec 2012 Formulae change, Paragraph move CD
Nov 2012 Table data CC
Aug 2012 Illustration, pages swopped CB
Jul 2012 Major update - The MDC control added CA
Oct 2011 Images and table data change BC
Sep 2011 MMC change - option “G” added, 3 “Special Hardware“ deleted BB
Jul 2011 Major update BA
Sep 2010 Table data for “Control current” AC
Aug 2010 New Backpage AB
Jun 2010 First edition AA
2 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 3

Technical Information
Contents
Description
General information
Technical specifications
Operation
Installation drawings
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Features................................................................................................................................................................................................5
System schematics...........................................................................................................................................................................5
General specification.......................................................................................................................................................................7
Technical data....................................................................................................................................................................................7
Operating parameters.................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Input speed................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
System pressure...........................................................................................................................................................................8
Charge pressure...........................................................................................................................................................................9
Charge pump inlet pressure....................................................................................................................................................9
Case pressure................................................................................................................................................................................9
External shaft seal pressure.....................................................................................................................................................9
Hydraulic fluid specifications....................................................................................................................................................... 9
Temperature................................................................................................................................................................................. 9
Viscosity..........................................................................................................................................................................................9
Filtration.......................................................................................................................................................................................10
Case Drain....................................................................................................................................................................................11
Reservoir...................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Determination of nominal pump sizes.................................................................................................................................. 11
Master model code........................................................................................................................................................................12
High Pressure Relief Valve (HPRV)............................................................................................................................................13
Charge Pressure Relief Valve (CPRV) ...................................................................................................................................... 14
Charge Pump...................................................................................................................................................................................14
Charge pump flow and power curves...............................................................................................................................14
Electrical Displacement Control (EDC), options 12 V/24 V..............................................................................................15
EDC principle..............................................................................................................................................................................15
Control signal requirements.................................................................................................................................................16
Control response.......................................................................................................................................................................16
Manual Displacement Control (MDC).....................................................................................................................................17
MDC principle............................................................................................................................................................................ 17
MDC with Control Cut-Off (CCO) – principle.................................................................................................................. 18
Manual Over Ride (MOR)............................................................................................................................................................. 19
Speed sensor description............................................................................................................................................................20
Bearing life........................................................................................................................................................................................21
Bearing life with no external shaft side load...................................................................................................................21
External radial shaft loads......................................................................................................................................................21
Mounting flange loads.................................................................................................................................................................22
Estimating overhung load moments.................................................................................................................................22
Input shafts.......................................................................................................................................................................................23
Auxiliary mounting pads.............................................................................................................................................................24
ISO 3019-1, flange 82-2 (SAE A, 9-teeth).......................................................................................................................... 24
ISO 3019-1, flange 101-2 (SAE B, 13-teeth)......................................................................................................................25
ISO 3019-1, flange 101-2 (SAE B-B, 15-teeth)..................................................................................................................25
TMP EDC dimensions....................................................................................................................................................................26
EDC dimensions..............................................................................................................................................................................28
TMP MDC dimensions.................................................................................................................................................................. 29
MDC dimensions............................................................................................................................................................................ 31
TMP MDC with Control Cut-Off (CCO) dimensions............................................................................................................32
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 3
Page 4

Technical Information
Description
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
The TMP axial variable displacement pump is designed primarily to be combined with other motors in
closed circuit systems to transfer hydraulic power.
It is a compact and high power density pump with integral electro-hydraulic or manual control which
regulates rate (speed) and direction of the hydraulic flow.
The pump is designed especially for transit mixer applications, where the unique user-friendly design
provides simple assembling and service for customers.
TMP EDC
TMP MDC
4 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 5
AA
B B
L2 M3
M3
M5
M4
TMMTMP
M2L2SM2
M10
L1
C2C1
M1 L1 M1
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
General information
Features
Innovative reliable design, using the latest technology
•
All interfaces accessible from one side (on the top), user friendly
•
Load independent displacement control:
•
Electric Displacement Control (EDC)
‒
Manual Displacement Control (MDC)
‒
Pump and Controls with Manual Overides
•
MDC including Emergency stop valve with function Cut off (CCO)
•
Spline and coupling shaft configurations available
•
Proven rotating group reliability
•
Integrated high pressure relief valves
•
Optional speed and temperature sensor
•
Available metric connections
•
TMP is compatible with the Danfoss family of PLUS+1® compliance technology for easy ‘Plug-and-
•
Perform’ installation.
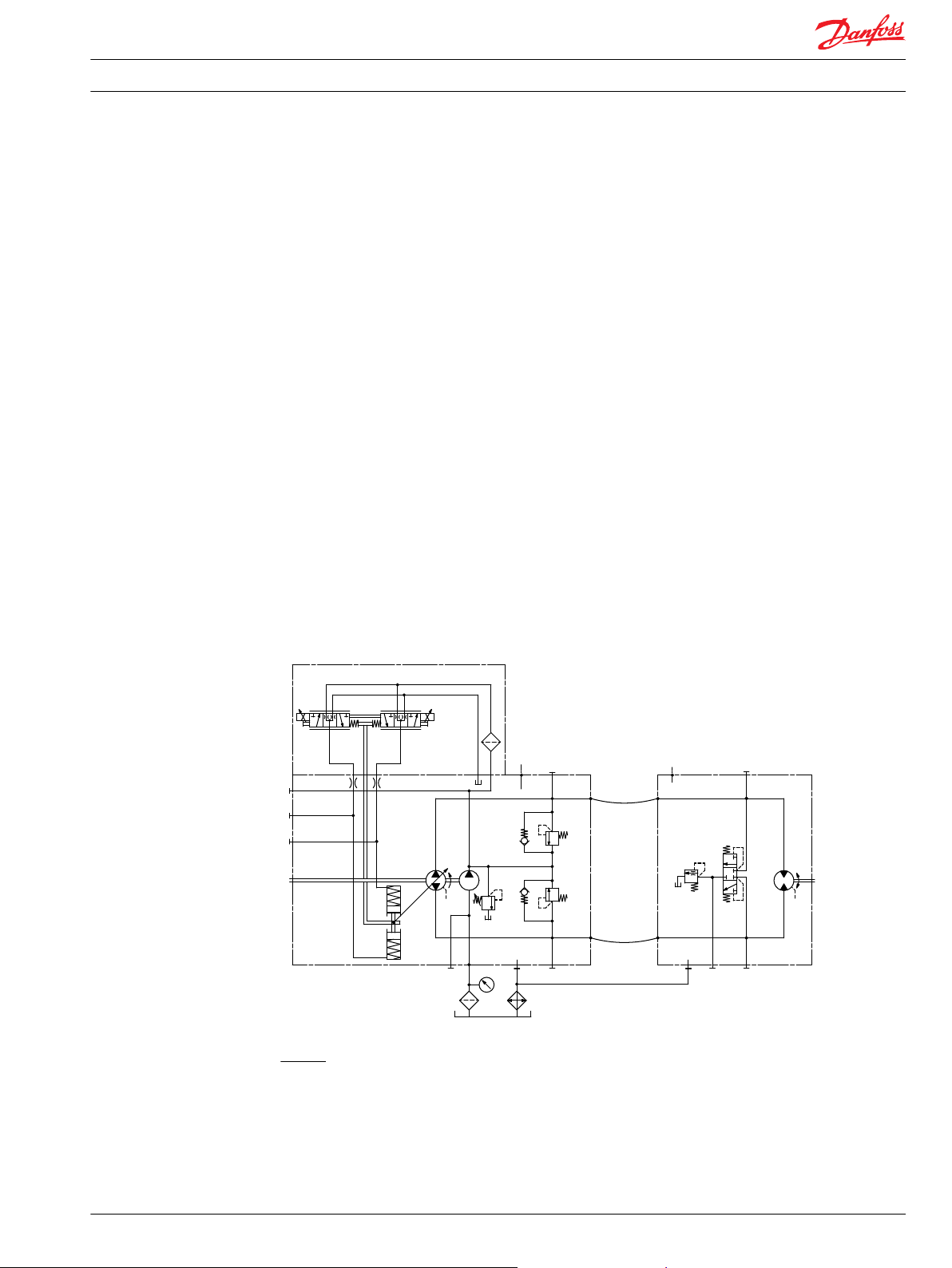
System schematics
The schematic below shows the function of a hydrostatic transmission using a TMP axial variable
displacement pump with electric proportional displacement control (EDC) and a TMM fixed displacement
motor with integrated loop flushing device. Detailed information about ports see the section Installation
drawings.
TMP EDC with TMM
Legend:
A, B – System ports
L1, L2 – Case drain ports
M1, M2 – System A/B gage ports
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 5
M3 – Charge gage port, after filtering
M4, M5 – Servo gage ports
M10 – Charge pump inlet pressure port
S – Charge inlet port
Page 6
AA
B B
L2 M3
M3
M5
M4
TMMTMP
M2
L2
M2
M10
L1 M1 L1 M1
N
‘-’ ‘+’
CW
S
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
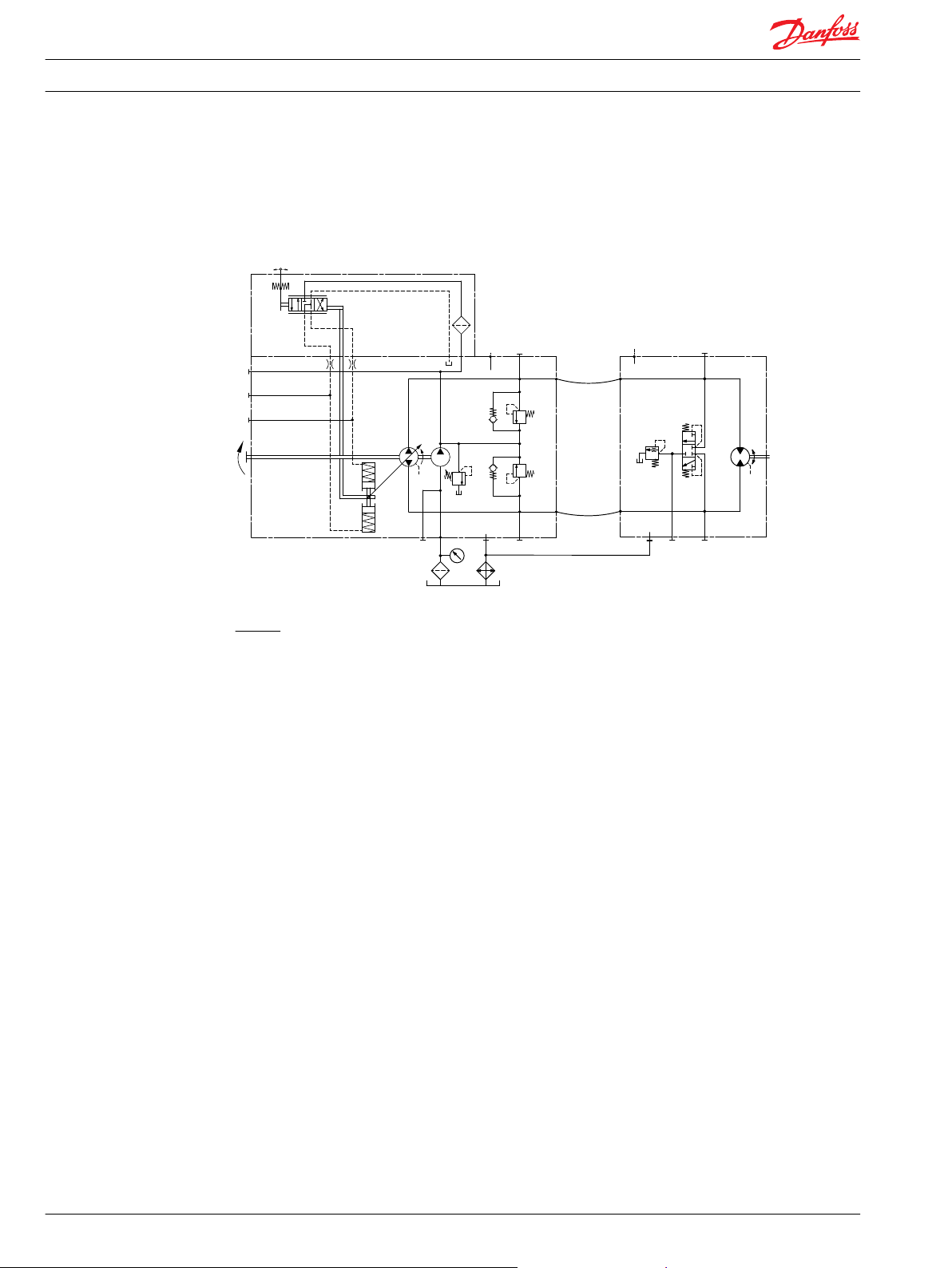
General information
The schematic below shows the function of a hydrostatic transmission using a TMP axial variable
displacement pump with manual proportional displacement control (MDC) and a TMM fixed
displacement motor with integrated loop flushing device.
TMP MDC with TMM
Legend:
A, B – System ports
L1, L2 – Case drain ports
M1, M2 – System A/B gage ports
M3 – Charge gage port, after filtering
M4, M5 – Servo gage ports
M10 – Charge pump inlet pressure port
S – Charge inlet port
6 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 7
C
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Technical specifications
General specification
General specifications
Design
Direction of rotation
Pipe connections
Recommended
installation position
Caution
The front shaft seal must not be exposed to oil pressure from outside of the unit.
Boundary position of the MDC lever must be fixed by hard stop on the customer actuation mechanism in
order to prevent any damages of MDC.
Technical data
Axial piston pump cradle swashplate design with variable displacement
Clockwise, counterclockwise
Main pressure ports: ISO split flange boss
Remaining ports: ISO straight thread O-ring boss
Pump installation position is discretionary; however the recommended control
position is on the top.
The housing must always be filled with hydraulic fluid.
Pump shaft connection is discretionary, however it is strongly recommended to use
rubber coupling if pump is driven via “cardan” shaft.
Correct installation has a significant influence on a life time of the pump.
Features Unit Size
070 089
Displacement maximum cm3 [in3] 68.3 [4.17] 89.0 [5.43]
Flow at rated (continuous) speed l/min [US gal/min] 171 [45.2] 222.5 [58.8]
Torque at maximum displacement
(theoretical)
Mass moment of inertia
of rotating components
Weight dry (standard)
Oil volume
Mounting flange
Input shaft
Auxiliary mounting flange
with metric fasteners, shaft splines
Suction port
Main port configuration
Case drain ports L1, L2
Other ports
N•m/bar
[lbf•in/1000 psi]
0.0209 kg•m
[0.0159 lbf•ft2]
61 kg [135 lb]
2 l [0.53 US gal]
SAE ISO 3019/1 flange 127-4 (SAE C)
Spline shaft SAE, 21 teeth, pitch = 16/32
Spline shaft SAE, 23 teeth, pitch = 16/32
Coupling flange Ø100 mm for Cardan, 23 teeth
(only with spline shaft SAE, 23 teeth, pitch = 16/32)
SAE A, 11 teeth, pitch = 16/32
SAE B, 13 teeth, pitch = 16/32
SAE B-B, 15 teeth, pitch = 16/32
ISO 6149-1 – M42x2 (O-ring boss)
Twin ports SAE J518b size 1, with metric screws M12
ISO 6149-1 – M22x1,5 (O-ring boss)
ISO 6149-1 straight thread O-ring boss.
See Installation drawings .
1.09
[665]
2
1.42
[867]
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 7
Page 8
C
Technical Information
Technical specifications
Operating parameters
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Operating parameters, size 070 / 089
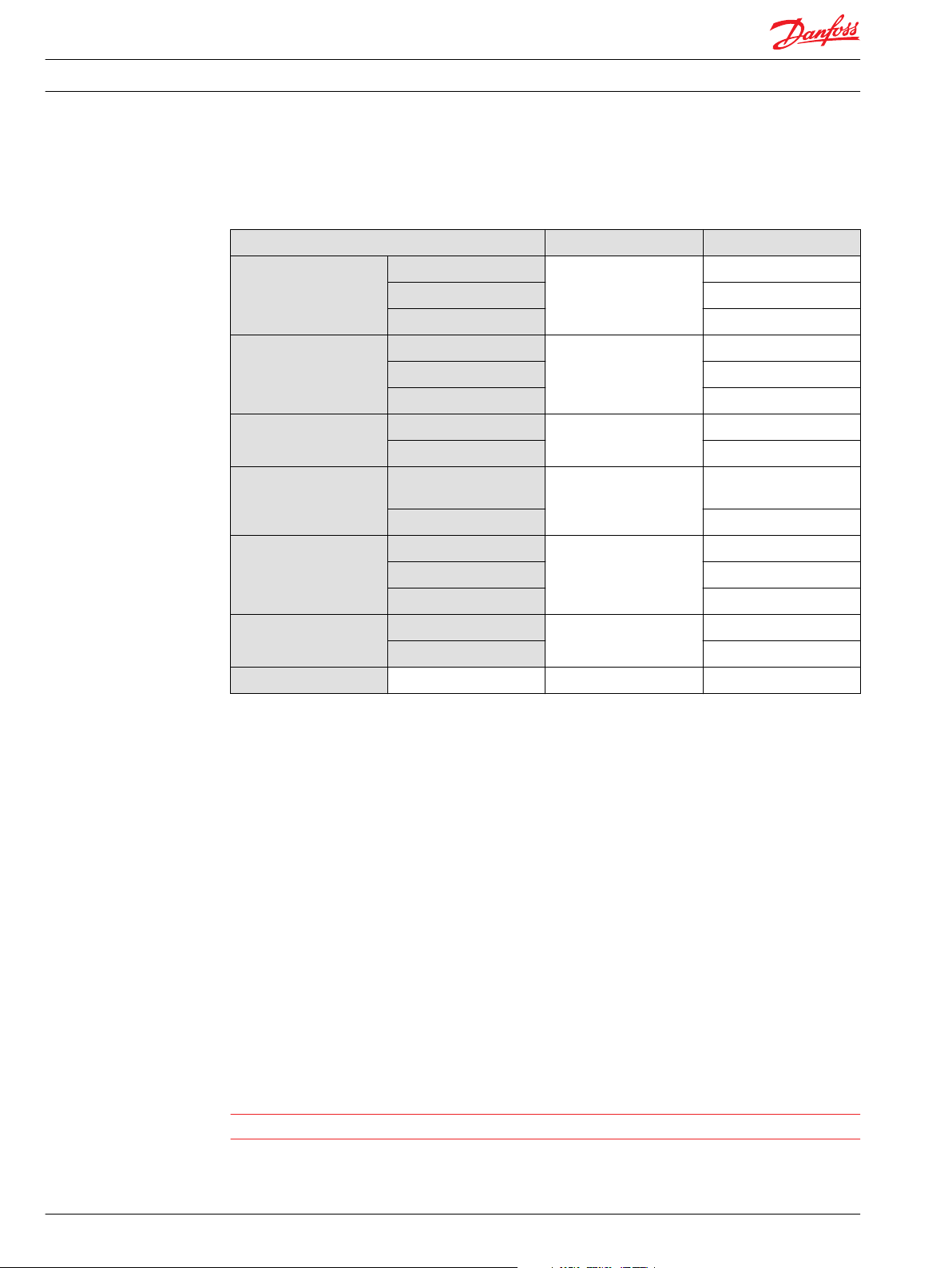
Features Unit Sizes 070 / 089
Input speed Minimum
Rated
Maximum
System pressure Max. working pressure
Maximum pressure
Minimum pressure
Charge pressure Minimum
Maximum
Control pressure Minimum (at corner
power for EDC)
Maximum
Charge pump inlet
pressure
Case pressure Rated
Lip seal external pressure
Rated
Minimum (cold start)
Maximum
Maximum
Maximum
min-1 (rpm)
bar [psi]
bar [psi]
bar [psi]
bar (absolute)
[in Hg vacuum]
bar [psi]
bar [psi]
500
2500
2900
420 [6090]
450 [6525]
10 [145]
17 [247]
30 [436]
21 [305]
30 [435]
0.7 [9]
0.2 [24]
4 [58]
3 [44]
5 [73]
0.4 [5.8]
Input speed
Minimum speed is the lowest input speed recommended during engine idle condition. Operating below
minimum speed limits the pump’s ability to maintain adequate flow for lubrication and power
transmission.
Rated speed is the highest input speed recommended at full power condition. Operating at or below this
speed should yield satisfactory product life.
Maximum speed is the highest operating speed permitted. Exceeding maximum speed reduces product
life and can cause loss of hydrostatic power and braking capacity. Never exceed the maximum speed
limit under any operating conditions.
System pressure
Maximum working pressure is the highest recommended application pressure; and it is not intended to
be a continuous pressure. Propel systems with application pressures at, or below, this pressure should
yield satisfactory unit life given proper component sizing.
Maximum pressure is the highest allowable application pressure under any circumstance. Application
pressures above maximum working pressure will only be considered with duty cycle analysis and factory
approval.
Caution
Minimum pressure must be maintained under all operating conditions to avoid cavitation.
8 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 9

C
C
Technical Information
Technical specifications
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Charge pressure
Minimum charge pressure is the lowest pressure allowed to maintain a safe working condition in the low
side of the loop.
Maximum charge pressure is the highest charge pressure allowed by the charge relief adjustment, which
provides normal component life.
Charge pump inlet pressure
Minimum charge inlet pressure is only allowed at cold start conditions. In some applications it is
recommended to warm up the fluid (e.g. in the tank) before starting the engine and then run the engine
at limited speed. Maximum charge pump inlet pressure may be applied continuously.
Caution
At normal operating temperature, charge inlet pressure must not fall below rated charge inlet pressure
(vacuum).
Case pressure
Under normal operating conditions, the rated case pressure must not be exceeded. During cold start,
case pressure must be kept below maximum intermittent case pressure.
Hydraulic fluid specifications
External shaft seal pressure
The shaft seal is designed to withstand an external pressure up to 0.4 bar [5.8 psi] above the case
pressure. In certain applications, the input shaft seal may be exposed to external pressures.
Caution
The case pressure limits must be followed to ensure the shaft seal is not damaged.
Temperature
High temperature limits apply at the inlet port of the motor. The motor should run at or below the
maximum continuous temperature.
Cold oil generally does not affect the durability of motor components. It may affect the ability of oil to
flow and transmit power. For this reason, keep the temperature at 16°C [60 °F] above the pour point of
the hydraulic fluid.
Minimum temperature (cold start) relates to the physical properties of component materials.
Maximum continuous temperature is the allowed temperature at which normal life can be expected.
Peak temperature (intermittent) is the overheating temperature tolerable by the machine for a transient/
limited time.
Viscosity
Minimum viscosity occurs only during brief occasions of maximum ambient temperature and severe duty
cycle operation. It’s the minimum acceptable viscosity to allow normal motor life.
Maximum viscosity occurs only during cold start at very low ambient temperatures. It’s the upper limit of
viscosity that allows the motor to start.
Temperature and viscosity requirements must be concurrently satisfied. Use petroleum/mineral-based
fluids.
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 9
Page 10
Technical Information
Technical specifications
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Fluid specifications
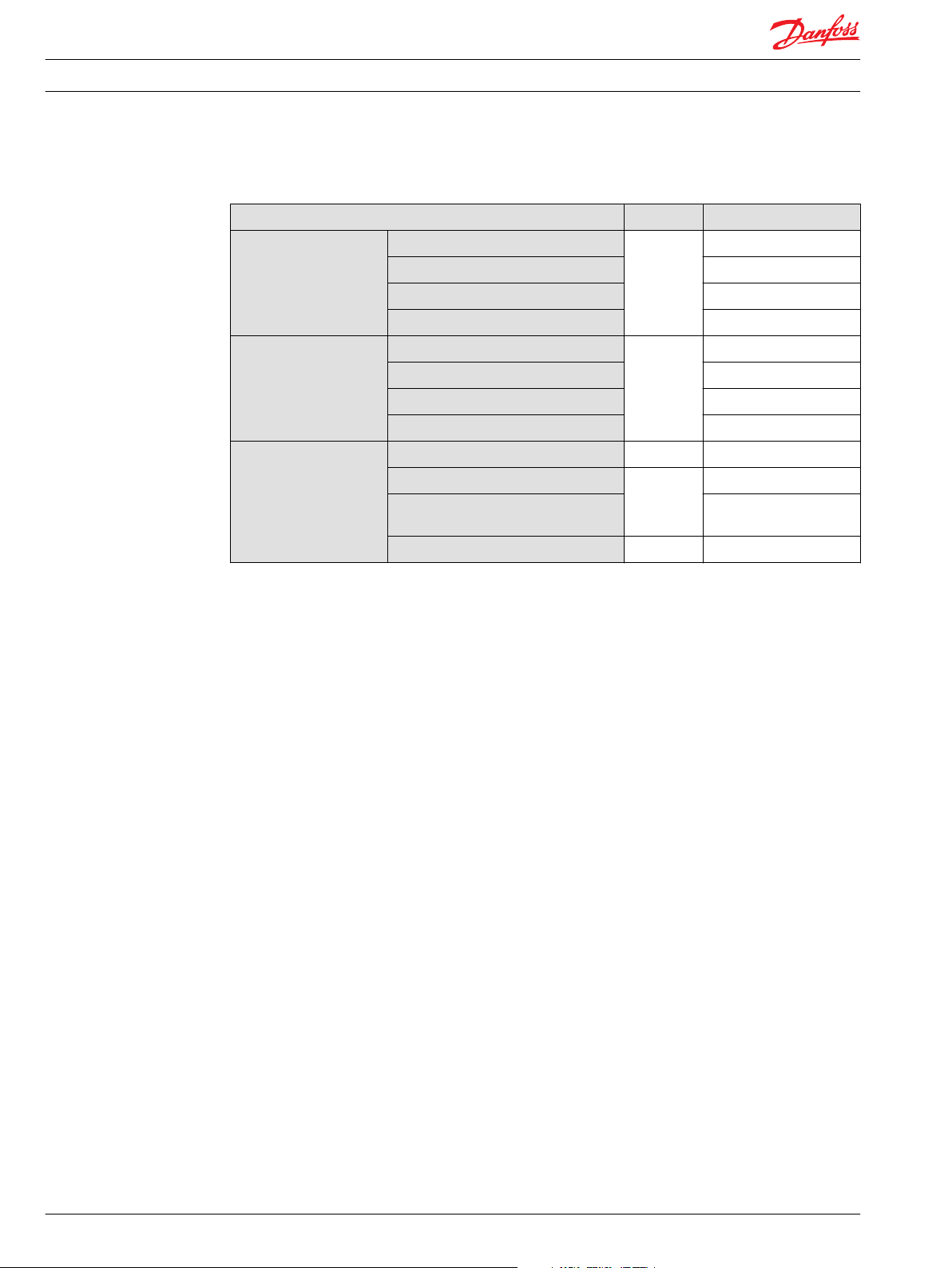
Features Unit Sizes 070 / 089
Viscosity Intermittent
Minimum
Recommended range
Maximum
Temperature range
Filtration
(recommended minimum)
2)
Minimum (cold start)
Recommended range
Rated
Maximum intermittent
Cleanliness per ISO 4406
Efficiency (charge pressure filtration)
Efficiency (suction and return line
filtration)
Recommended inlet screen mesh size
1)
3)
1)
mm2/s [SUS] 5 [42]
7 [49]
12-80 [66-370]
1600 [7500]
°C [°F] -40 [-40]
60-85 [140-185]
104 [220]
115 [240]
22/18/13
β-ratio β
µm 100 – 125
= 75 (β10 ≥ 10)
15-20
β
= 75 (β10 ≥ 2)
35-45
1)
Intermittent = Short term t < 1 min per incident and not exceeding 2 % of duty cycle based load-life.
2)
At the hottest point, normally case drain port.
3)
Cold start = Short term t < 3 min, p ≤ 50 bar [725 psi], n ≤ 1000 min-1 (rpm).
Filtration
To prevent premature wear, ensure only clean fluid enters the hydrostatic transmission circuit. A filter
capable of controlling the fluid cleanliness to ISO 4406 class 22/18/13 (SAE J1165) or better, under normal
operating conditions, is recommended.
These cleanliness levels can not be applied for hydraulic fluid residing in the component housing/case or
any other cavity after transport.
Filtration strategies for TMP include only suction filtration. The selection of a filter depends on a number
of factors including the contaminant ingression rate, the generation of contaminants in the system, the
required fluid cleanliness, and the desired maintenance interval. Filters are selected to meet the above
requirements using rating parameters of efficiency and capacity.
Filter efficiency can be measured with a Beta ratio (βX). Filter βX-ratio is a measure of filter efficiency
defined by ISO 4572. It is defined as the ratio of the number of particles greater than a given diameter (“x”
in microns) upstream of the filter to the number of these particles downstream of the filter.
For simple suction-filtered closed circuit transmissions and open circuit transmissions with return line
filtration, a filter with a β-ratio within the range of β35-45 = 75 (β10 ≥ 2) or better has been found to be
satisfactory.
For some open circuit systems, and closed circuits with cylinders being supplied from the same reservoir,
a considerably higher filter efficiency is recommended. This also applies to systems with gears or clutches
using a common reservoir.
For these systems, a charge pressure or return filtration system with a filter β-ratio in the range of β15-20
= 75 (β10 ≥ 10) or better is typically required.
Because each system is unique, only a thorough testing and evaluation program can fully validate the
filtration system. Please see Design Guidelines for Hydraulic Fluid Cleanliness Technical Information,
520L0467 for more information.
10 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 11
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Technical specifications
Case Drain
All TM pumps are equipped with two case drain ports. Port selection and case drain routing must enable
the pump housing to maintain a volume of oil not less than half full and normal operating case pressure
limits of the unit are maintained. Case drain routing and design must consider unit case pressure ratings.
A case drain line must be connected to one of the case outlets to return internal leakage to the system
reservoir.
Reservoir
The reservoir provides clean fluid, dissipates heat, removes entrained air, and allows for fluid volume
changes associated with fluid expansion during system operation. A correctly sized reservoir also
accommodates maximum volume changes during all system operating modes. It promotes de-aeration
of the fluid as it passes through, and accommodates a fluid dwell-time between 60 and 180 seconds,
allowing entrained air to escape.
Minimum reservoir capacity depends on the volume required to cool and hold the oil, allowing for
expansion due to temperature changes. A fluid volume of one to three times the motor output flow (per
minute) is satisfactory. The minimum recommended reservoir capacity is 125% of the fluid volume.
Put the return-line below the lowest expected fluid level to allow discharge into the reservoir for
maximum dwell and efficient de-aeration. A baffle (or baffles) between the return and suction lines
promotes de-aeration and reduces fluid surges.
Determination of nominal pump sizes
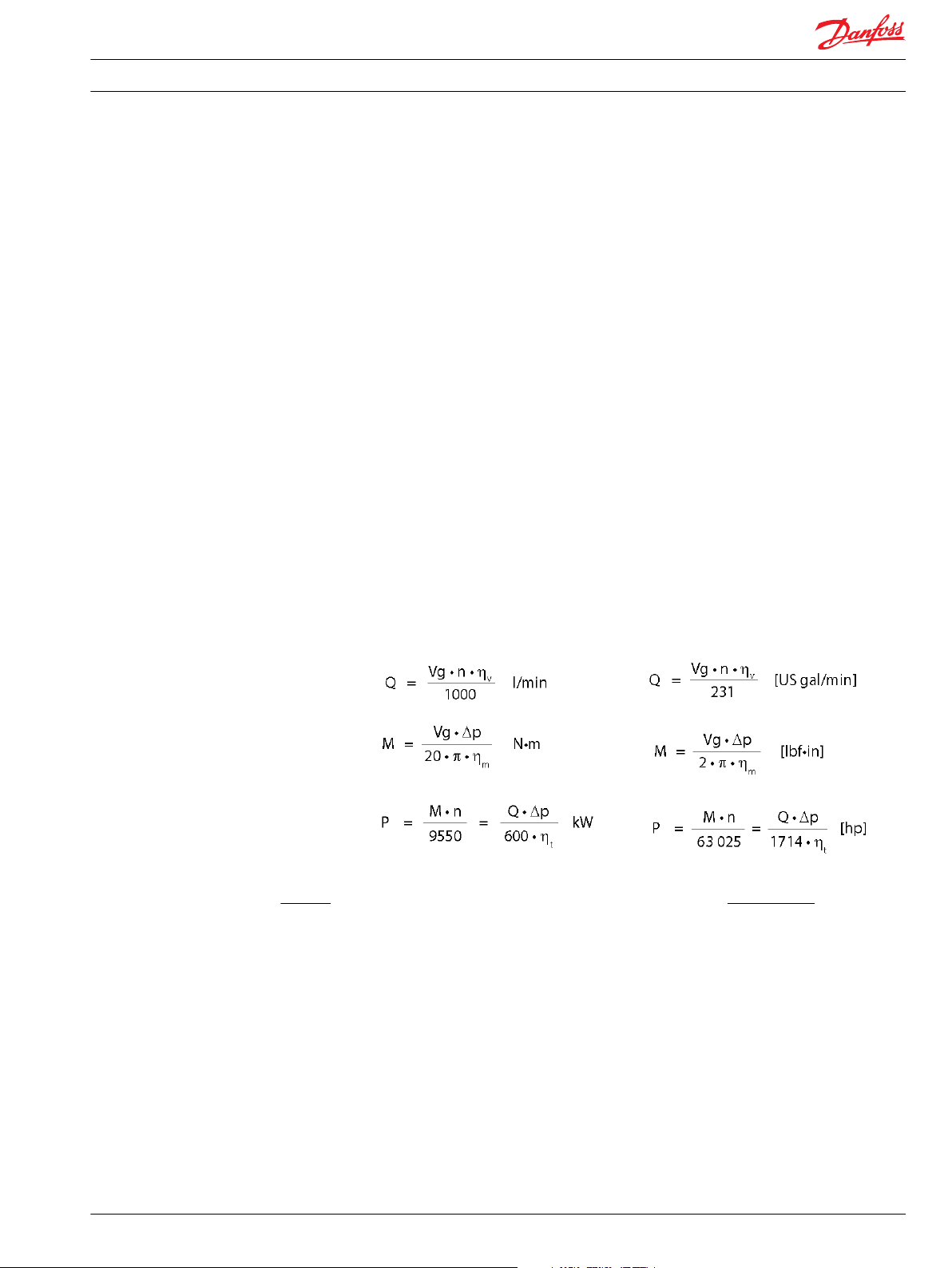
Use these formulae to determine the nominal pump size for a specific application:
Based on SI units Based on US units
Output flow:
Input torque:
Input power:
Variables: SI units [US units]
Vg
p
p
∆p
n
η
η
η
HD
ND
v
m
t
=
Displacement per rev.
=
Outlet pressure
=
Inlet pressure
=
pHD – p
ND
=
Speed
=
Volumetric efficiency
=
Mechanical (torque) efficiency
=
Overall efficiency (ηv • ηm)
cm3/rev [in3/rev]
bar [psi]
bar [psi]
bar [psi]
min-1 (rpm)
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 11
Page 12

Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Technical specifications
Master model code
A Product
TMP Transit Mixer Pump
B Frame size / Displacement
070 68.3 cm3/rev [4.17 in3/rev]
089 89.0 cm3/rev [5.43 in3/rev]
C Control
EDC024A Electrical Displacement Control (EDC - 24 V) with Manual Over Ride
EDC012A Electrical Displacement Control (EDC - 12 V) with Manual Over Ride
MDCNNNN Manual Displacement Control (MDC)
MDCA24A MDC with Control Cut-off (CCO - 24 V) and Manual Over Ride
D Sense of rotation
R Right hand (clockwise)
L Left hand (counterclockwise)
G End cap ports; High pressure setting
M42 Endcap Ports: DN 25, Type 2, 420 bar (6000 psi), ISO 6162-2;
High pressure relief valve 420 bar, (Metric connections)
M28 Endcap Ports: DN 25, Type 2, 420 bar (6000 psi), ISO 6162-2;
High pressure relief valve 280 bar, (Metric connections)
H Charge pump; Charge pump relief valve setting
20G22 Charge pump: 20 cm3/rev; Charge pump relief valve settings: 20.3-22.5 bar
J Auxiliary Mounting Pad
A ISO 3019-1, flange 82 - 2, (SAE A, 9 teeth 16/32)
B ISO 3019-1, flange 101 - 2, (SAE B, 13 teeth 16/32)
V ISO 3019-1, flange 101 - 2, (SAE B-B, 15 teeth 16/32)
N none
L Shaft
C Splined shaft, 23 teeth, pitch = 16/32
D Splined shaft, 21 teeth, pitch = 16/32
G ‘C’ Shaft option, Added Coupling 23 teeth with flange ø100 mm
12 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 13

C1 C2
Technical Information
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Technical specifications
W Special Hardware Features
NCN No sensor, Valve plate CP30
HCN Speed & Temperature sensor 53 impulsions (n, direc. T), Valve plate CP30
ACN KPP156 speed sensor (n, direc.), Valve plate CP30
F Special Features
NSN No paint, Name plate "Slovakia"
NDN No paint, Name plate "Danfoss"
BSN Black paint, Name plate "Slovakia"
BDN Black paint, Name plate "Danfoss"
GSN Gray paint, Name plate "Slovakia"
GDN Gray paint, Name plate "Danfoss"
High Pressure Relief Valve (HPRV)
The TM pumps are equipped with a combination high pressure relief and charge check valve. The highpressure relief function is a dissipative pressure control valve for the purpose of limiting excessive system
pressures.
The charge check function acts to replenish the low-pressure side of the working loop with charge oil.
Each side of the transmission loop has a dedicated HPRV valve that is non-adjustable with a factory set
pressure.
When system pressure exceeds the factory setting of the valve, oil is passed from the high pressure
system loop into the charge gallery, and into the low pressure system loop via the charge check.
The pump order code allows for different pressure settings to be used at each system port.
System schematic, single pump
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 13
Page 14
Technical Information
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Technical specifications
Charge Pressure Relief Valve (CPRV)
The charge pressure relief valve maintains charge pressure at a designated level above case pressure. The
charge pressure relief valve is a direct acting poppet valve which opens and discharges fluid to the pump
case when pressure exceeds a designated level. Standard level setting is ∆p = 21 ± 1.1 bar [304 ± 16 psi]
with the pump running at 1500 rpm and flow = 23.80 - 29.5 l/min [ 6.3 - 7.8 US gal/min].
Typical charge pressure increase is 2 bar per 10 l/min [29 psi per 2.64 US gal/min].
Charge Pump
Charge flow is required on all pumps applied in closed circuit installations. The charge pump provides
flow to make up internal leakage, maintain a positive pressure in the main circuit, provides flow for
cooling and filtration, replaces any leakage losses from external valving or auxiliary systems, and provides
flow and pressure for the control system.
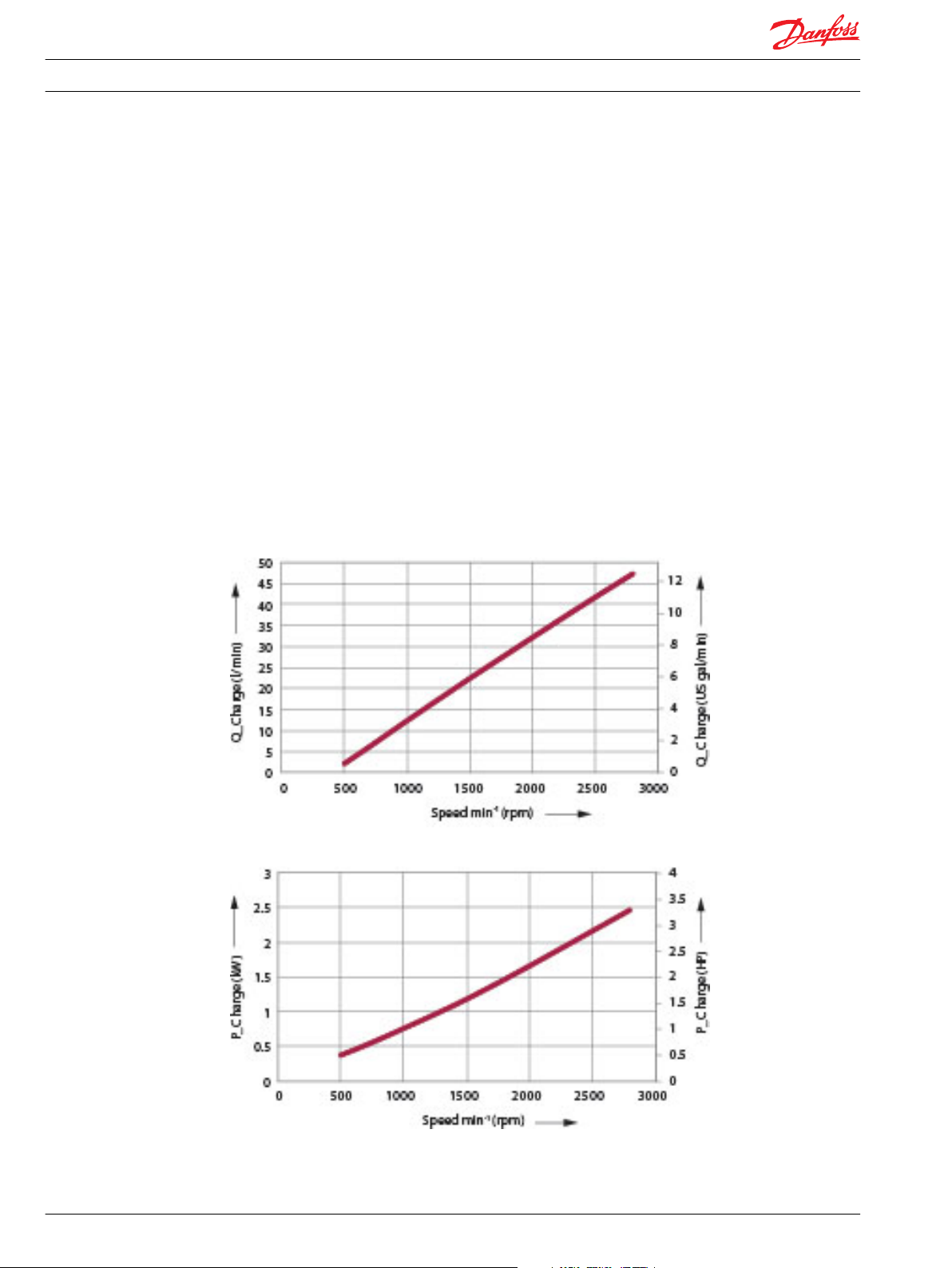
Charge pump flow and power curves
Charge pressure: 20 bar [290 psi]
Viscosity: 11 mm2/s [63 SUS]
Temperature: 80 °C [180 °F]
Charge pump flow
Charge pump power requirements
14 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 15

P003 191
Feedback from swash-plate
PT
M14
C1 C2
P003 479E
"0"
-b -a
ba
100 %
100 %
Displacement
Current mA
Technical Information
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Technical specifications
Electrical Displacement Control (EDC), options 12 V/24 V
EDC principle
The Electrical Displacement Control (EDC) consists of a pair of proportional solenoids on each side of a
three-position, four-way porting spool. The proportional solenoid applies a force input to the spool,
which ports hydraulic pressure to either side of a double acting servo piston. Differential pressure across
the servo piston rotates the swashplate, changing the pump‘s displacement from full displacement in
one direction to full displacement in the opposite direction.
EDC
Pump displacement vs. control current
EDC schematic
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 15
Page 16
1 2
P003 480
Technical Information
Technical specifications
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Control signal requirements
Control current
Voltage a* b Pin connections
12 V 650 mA 1600 mA
24 V 310 mA 810 mA
* Factory test current, for vehicle movement or application actuation expect higher value.
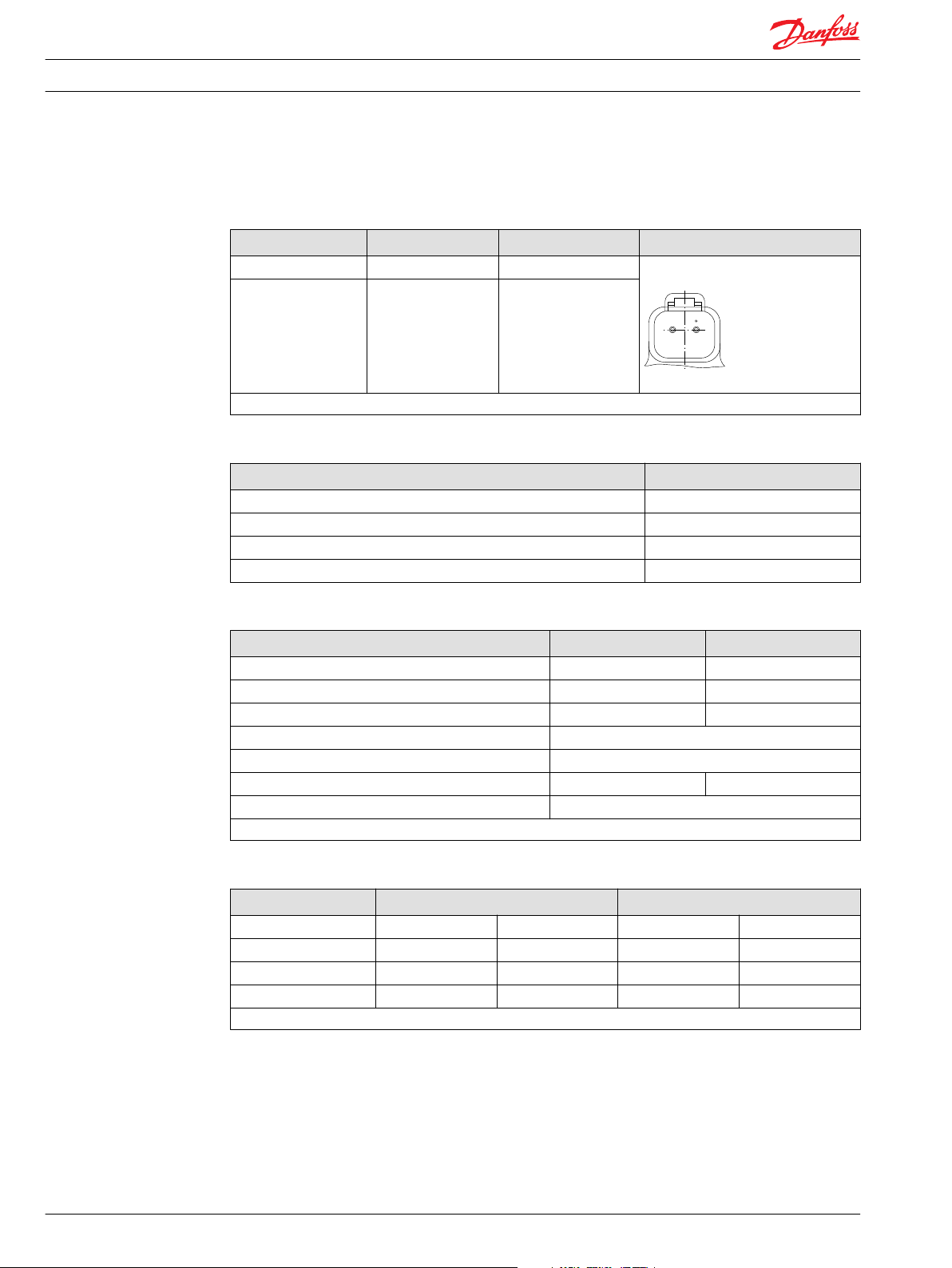
Available connector models
Description Quantity
Mating connector - Deutsch® DT06-2S 1
Wedge lock - Deutsch® W2S 1
Socket contact (16 and 18 AWG) - Deutsch® 0462-201-16141 2
Danfoss mating connector kit K29657 1
Connector
any order
Solenoid data
Voltage 12V 24V
Maximum current 1800 mA 920 mA
Coil resistance @ 20 °C [70 °F] 3.66 Ω 14.20 Ω
Coil resistance @ 80 °C [176 °F] 4.52 Ω 17.52 Ω
PWM Range 70 – 200 Hz
PWM Frequency (preferred)* 100 Hz
Inductance 33 mH 140 mH
IP Rating (IEC 60 529) + DIN 40 050, part 9 IP 67 / IP 69K (with mating connector)
* PWM signal required for optimum control performance.
Flow table
Shaft rotation CW CCW
Coil energized* C1 C2 C1 C2
Port A out in in out
Port B in out out in
Servo port pressurized M4 M5 M4 M5
* For coil location see Installation drawings.
Control response
TMP controls are available with optional control passage orifices to assist in matching the rate of
swashplate response to the application requirements (e.g. in the event of electrical failure).
Software ramp or rate limiting should be used to control vehicle response in normal operation.
16 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 17

Feedback from swasch plate
T P
N
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Technical specifications
The time required for the pump output flow to change from zero to full flow (acceleration) or full flow to
zero (deceleration) is a net function of spool porting, orifices, and charge pressure.
A swashplate response table is available for each frame indicating available swashplate response times.
Testing should be conducted to verify the proper software and orifice selection for the desired response.
TMP pumps are limited in mechanical orificing combinations. Software is envisioned as the means to
control the swashplate response in normal operating conditions. Mechanical servo orifices are to be used
only for fail-safe return to neutral in the event of an electrical failure.
Response times*
Stroking direction No orifice
Neutral to full flow 1.2 s
Full flow to neutral 0.6 s
* at the following conditions:
∆p = 200 bar [2900 psi]
•
Viscosity = 30 mm2/s [141 SUS]
•
Temperature = 50 °C [122 °F]
•
Charge pressure = 20 bar [290 psi]
•
Speed = 1800 min-1 (rpm)
•
Manual Displacement Control (MDC)
MDC principle
The Manual Displacement Control (MDC) consists of a lever with eccentric shaft centre of a threeposition, four-way porting spool. The eccentric shaft applies a force input to the spool, which ports
hydraulic pressure to either side of a double acting servo piston. Differential pressure across the servo
piston rotates the swash plate, changing the pump`s displacement from full displacement in one
direction to full displacement in the opposite direction.
MDC MDC schematic
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 17
Page 18

"0"
-b
-c
-a
b ca
100 %
100 %
Displacement
Lever angle
C
Feedback from swasch plate
T P
N
Technical Information
Technical specifications
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Pump displacement vs. lever angle
Lever angle:
a = 4° ±1°
b = 33° ± 1°
c = 40° max.
Customer “Hard Stop” of the lever = 38° +1°
Lever torque when displacement goes up:
Start at: End at: Maximum allowed torque
max. 1,5 N•m max. 3 N•m 12 N•m
Caution
Boundary position of the MDC lever must be fixed by hard stop on the customer actuation mechanism in
order to prevent any damages of MDC.
MDC with Control Cut-Off (CCO) – principle
If solenoid is loaded by voltage directly from truck battery 24 to 32 V pump work in normal mode if the
electric circuit will by switch off pump will go immediately to 0 position .
MDC with Control Cut-Off (CCO) MDC CCO schematic
For Connector model, see Control signal requirements.
18 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 19

P003 204
W
Technical Information
Technical specifications
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Solenoid data
Voltage
Nominal current
Coil resistance @ 20 °C [70 °F]
PWM range (PWM signal required for optimum control performance)
Inductance
IP rating (IEC 60 529) + DIN 40 050, part 9
IP rating (IEC 60 529) + DIN 40 050, part 9 with mating connector
Flow table
Shaft rotation CW CCW
Lever direction*
Port A
Port B
Servo port pressurized
* For lever direction, see Installation drawings.
‘-‘ ‘+‘ ‘-‘ ‘+‘
out in in out
in out out in
M4 M5 M4 M5
24 V
700 mA
34.5 Ω
70-200 Hz
573 mH
IP 67
IP 69K
Manual Over Ride (MOR)
All controls are available with a Manual Over Ride
MOR
(MOR) either standard or as an option for
temporary actuation of the control to aid in
diagnostics.
The vehicle or device must always be in a ‘safe’
condition (i.e. vehicle lifted off the ground) when
using the MOR function.
The MOR plunger has a 4 mm diameter and must
be manually depressed to be engaged.
Depressing the plunger mechanically moves the
control spool which allows the pump to go on
stroke.
The MOR should be engaged anticipating a full
stroke response from the pump.
Warning
An O-Ring seal is used to seal the MOR plunger where initial actuation of the function will require a force
of 45 N to engage the plunger. Additional actuations typically require less force to engage the MOR
plunger. Proportional control of the pump using the MOR should not be expected.
Refer to control flow table for the relationship of solenoid to direction of flow.
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 19
Page 20

Feedback from swash-plate
PT
M14
C2
C1
Feedback from swasch plate
T P
N
4
3 2 1
P005418
5 6
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Technical specifications
Speed sensor description
MOR schematic diagram (EDC shown)
MOR schematic diagram (MDC shown)
Function of the speed sensor is to detect the shaft speed and the direction of rotation.Typically the
sensor will be mounted to the housing of a Danfoss pump or motor and senses the speed from a target
ring that is rotating inside the pump or motor. Because of the digital output signals for speed and
direction and a non speed dependent output voltage level, the sensor is ideal for high and low speed
measurements.
For diagnostics and other purposes, the sensor also has the capability to detect the case oil temperature.
The speed sensor is designed for rugged outdoor, mobile or heavy industrial speed sensing applications.
The detection of the speed is contactless. It is custom-designed for Danfoss. It is a “plug and perform”
device that does not need any calibration or adjustments.
Connector data
Connector model
Number of teeth on target ring
Order number
Connector terminal
Deutsch DTM-Series 6-Pin DTM06-6S (pins need to be gold plated)
53
149055
Sensor pinout:
1 – Speed signal 2
2 – Direction signal
3 – Speed signal 1
4 – Supply
5 – Ground
6 – Temperature
20 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 21

Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Operation
Bearing life
Bearing life with no external shaft side load
Normal bearing life with no external shaft side load in L20 hours is shown in the table below. The figures
reflect a continuous delta pressure, shaft speed, maximum displacement, and no external shaft side load.
The data is based on a standard charge pressure of 20 bar [290 psi].
Bearing life with no external shaft side load
Parameter
Shaft speed
Delta pressure – ∆p
Bearing life – L
20
Conversion of bearing life for other pressure (p) and speed (n):
Unit Size 070 Size 089
min-1 (rpm) 1800 1800
bar [psi] 240 [3480] 240 [3480]
hours 68 900 28 500
External radial shaft loads
TM pumps are designed with bearings that can accept some external radial and axial loads.
The external radial shaft load limits are a function of the load position and orientation, and the operating
conditions of the unit.
The maximum allowable radial load (Re) is based on the maximum external moment (Me) and the
distance (L) from the mounting flange to the load. In applications with external radial shaft loads,
minimize the impact by positioning the load at 0° or 180° as shown in the figure below.
The external radial and axial shaft load are limited by the bearing life L20 =10 000 [h], delta system
pressure 240 bar, speed 1800 min-1 and external radial load at 270°.
It may be determined using the following table and formula below.
Maximum external shaft load based on shaft deflection
Parameter
External radial moment – M
External axial force – F
External axial force – F
in
out
e
Unit Size 089
N•m [lbf•in] 0 70 [620]
N [lbf] -2160 [-485] -1320 [-297]
3660 [823] 2880 [648]
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 21
Page 22

L
F out (+)
270° Re
Re
Me
180° Re
90° Re
0° Re
F in (-)
M
Technical Information
Operation
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Radial load position
Where:
Re = External force to the shaft
Me = Shaft moment
L = Flange distance
Mounting flange loads
Contact your Danfoss representative for an evaluation of unit bearing life.
Estimating overhung load moments
Mounting flange load moment
Rated and maximum torque ratings
Based on SI units:
M = g • G • W • L
M = 9.81 • 30 • 61 • 0.1625
Max. load moment: M = 2917 N•m
Based on US units:
M = G • W • L
M = 30 • 134 • 6.398
Max. load moment: M = 25 818 lbf•in
Where:
M = Rated load moment N•m [lbf•in]
g = Gravity 9.81 m/s
G = Calculation factor for max. acceleration 30
22 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
2
Page 23

C
47.5 ±0.2
[1.87 ±0.008]
R2 ±0.11
[0.079 ±0.004]
20 min
[0.787]
56
[2.205]
Ø37.6 ±0.09
[Dia1.48 ±0.004]
M10-6H
Ø71.7 max [Dia2.823]
Coupling Diameter
0
-0.2
0
-0.08
Ø32
[Dia1.26 ]
0
0
-0.5
-0.02
34.35
[1.352 ]
Coupling must not protrude
beyond this point
Full spline lenght
Spline data:
Number of teeth: 23
Pitch fraction: 16/32
Pressure angle: 30°
Pitch Ø: 36.513 [1.438]
Meas. over pins: 40.973/41.024
[1.6131/1.6151]
Pin Ø: 3.048 [0.12]
Mounting flange surface
Flange SAE-C per ISO 3019-1
to be paint free
47.5 ±0.2
[1.87 ±0.008]
R2 ±0.11
[0.079 ±0.004]
20 min
[0.787]
56
[2.205]
Ø34.41 ±0.09
[Dia1.355 ±0.004]
M10-6H
Ø71.7 max [Dia2.823]
Coupling Diameter
0
-0.2
0
-0.08
Ø29
[Dia1.142 ]
0
0
-0.5
-0.02
34.35
[1.352 ]
Coupling must not protrude
beyond this point
Full spline lenght
Spline data:
Number of teeth: 21
Pitch fraction: 16/32
Pressure angle: 30°
Pitch Ø: 33.338 [1.313]
Meas. over pins: 37.783/37.833
[1.4875/1.4895]
Pin Ø: 3.048 [0.12]
Mounting flange surface
Flange SAE-C per ISO 3019-1
to be paint free
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Operation
W = Weight of pump kg [lb]
L = Distance from mounting flange to pump center of gravity m [in]
Input shafts
Rated and maximum torque ratings for each available shaft is shown in the following table:
Specifications
Spline Min active spline length Rated torque* Maximum torque**
mm [in] N•m [lbf•in] N•m [lbf•in]
21 teeth, 16/32 pitch 33 [1.3] 730 [6460] 1200 [10 620]
23 teeth, 16/32 pitch 33 [1.3] 880 [7790] 1600 [14 160]
Cardan / flange - - 2480 [21 950]
* Rated torque - measure of teeth wear
** Maximum torque - ratings are based on torsional fatigue strength
The specified torque rating of the shaft documented above is based on the cross-sectional diameter of
the shaft, through the keyway, and assumes the proper clamp and fit between shaft and coupling.
Danfoss guarantees the design and manufactured quality of the splined shaft. The customer is
responsible for the design and manufactured quality of the mating female coupling and key and applied
torque on the nut.
Danfoss has made provisions for the key in accordance to the ISO specification with the understanding
that the key is solely to assist in the installation of the mating coupling.
Caution
Torque or loading inadvertently transmitted by the customer supplied key may lead to premature shaft
failure.
ISO 3019-1 (SAE C, 23-teeth)
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 23
ISO 3019-1 (SAE C, 21-teeth)
Page 24

Paint free
58.2
[2.291]
8.5
[0.335]
9.3
[0.366]
2.3
[0.091]
Ø100 ±0.3
[Dia3.937 ±0.012]
98.8
[3.89]
92
[3.624]
12.4 ±0.25
[0.488 ±0.01]
0
-0.05
0
-0.002
Ø127
[Dia 4.999 ]
Auxiliary Mounting Pad
Flange 127 - 4
per ISO 3019 (SAE J744C)
Ø57
[Dia 2.44 ]
0
0
-0.05
-0.002
331.6
[13.056]
317.3
[12.493]
14.6 min.
[0.575]
19 min.
[0.748]
4xM10
0
+0.2
0
+0.008
10.5
[0.413 ]
Paint free
Auxiliary mounting pad
Flange 82-2 per
ISO 3019-1
(SAE J744A)
50 max [1.969]
Auxiliary pump shaft lenght
O-Ring seal required
Ref. Ø 82.27 [Dia 3.239]
I.D. x 1.78 [0.07] cross section
106.38 ±0.3
[4.188 ±0.012]
106.38 ±0.3
[4.188 ±0.012]
Ø87.12±0.13
[Dia 3.43 ±0.005]
Spline data:
Number of teeth: 9
Pitch fraction: 16/32
Pressure angle: 30°
Pitch Ø: 14.2875 [0.5625]
Typ of fit: Fillet root side per
ANSI B92.1-1970 class 6
0
+0.3
0
+0.012
1.2
[0.047 ]
0
0
+0.13
+0.005
Ø82.6
[Dia 3.252 ]
R 0.8 max
[0.031]
Technical Information
Operation
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
ISO 3019 (SAE J744C) with coupling
Auxiliary mounting pads
ISO 3019-1, flange 82-2 (SAE A, 9-teeth)
Spline: 9-teeth, 16/32 pitch, Maximum torque: 162 N•m [1430 lbf•in]
24 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 25

333.2
[13.116]
317.3
[12.493]
14.6 min.
[0.575]
20.3 min.
[0.798]
R 0.8 max
[0.031]
2xM12
Paint free
Auxiliary mounting pad
Flange 101-2 per
ISO 3019-1
(SAE J744 B)
47 max [1.85]
Auxiliary pump shaft lenght
O-Ring seal required
Ref. Ø 101.32 [Dia 3.989]
I.D. x 1.78 [0.07] cross section
146 ±0.3
[5.748 ±0.012]
Ø106.8±0.13
[Dia 4.205 ±0.005]
Spline data:
Number of teeth: 13
Pitch fraction: 16/32
Pressure angle: 30°
Pitch Ø: 20.6374 [0.8125]
Typ of fit: Fillet root side per
ANSI B92.1-1970 class 6
0
+0.1
0
+0.004
1.2
[0.047 ]
0
+0.13
+0.005
Ø101.65
[Dia 4.002 ]
±0.004
±0.1
10.6
[0.417 ]
C
333.2
[13.116]
317.3
[12.493]
14.6 min.
[0.575]
20.3 min.
[0.798]
R 0.8 max
[0.031]
2xM12
Paint free
Auxiliary mounting pad
Flange 101-2 per
ISO 3019-1
(SAE J744 B)
47 max [1.85]
Auxiliary pump shaft lenght
O-Ring seal required
Ref. Ø 101.32 [Dia 3.989]
I.D. x 1.78 [0.07] cross section
146 ±0.3
[5.748 ±0.012]
Ø106.8±0.13
[Dia 4.205 ±0.005]
Spline data:
Number of teeth: 15
Pitch fraction: 16/32
Pressure angle: 30°
Pitch Ø: 23.8125 [0.9375]
Typ of fit: Fillet root side per
ANSI B92.1-1970 class 6
0
+0.1
0
+0.004
1.2
[0.047 ]
0
+0.13
+0.005
Ø101.65
[Dia 4.002 ]
±0.004
±0.1
10.6
[0.417 ]
C
Technical Information
Operation
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
ISO 3019-1, flange 101-2 (SAE B, 13-teeth)
Spline: 13-teeth, 16/32 pitch, Maximum torque: 395 N•m [3500 lbf•in]
Caution
Standard pad cover is installed only to retain coupling during shipping. Do not operate pump without an
auxiliary pump or running cover installed.
ISO 3019-1, flange 101-2 (SAE B-B, 15-teeth)
Spline: 15-teeth, 16/32 pitch, Maximum torque: 693 N•m [6130 lbf•in]
Caution
Standard pad cover is installed only to retain coupling during shipping. Do not operate pump without an
auxiliary pump or running cover installed.
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 25
Page 26

121
[4.764]
89
[3.504]
43.9
[1.728]
57.25
[2.254]
114.5
[4.508]
146
[5.748]
134.8
[5.306]
160.8
[6.329]
111.4
[4.386]
164
[6.457]
114.5
[4.508]
206
[8.11]
98.8
[3.89]
57.25
[2.254]
+0.8
+0.031
-0.3
-0.012
Ø15
[Dia 0.591 ]
Case drain port L1
use highest port as outlet
M22x1.5 - 11 min [.433] depth
Gauge port M1
System pressure Port A, M12x1.5
12.7 [0.5] full thread depth
Gauge port M4
Servo pressure M12x1.5
Gauge port M3
Charge pressure M12x1.5
12.7 [0.5] full thread depth
High pressure relief valve
Port A
Charge pressure relief valve
High pressure relief valve
Port B
Gauge port M5
Servo pressure M12x1.5
Gauge port M2
System pressure Port B,
M12x1.5; 12.7 [.5] full thread depth
Gauge port M10
Charge pump inlet pressure
M12x1.5; 12.7 [.5] full thread depth
Connector CB
Deutsch DT04-2P
Connector Deutsch DTM06-6S
Connector CB
Deutsch DT04-2P
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Installation drawings
TMP EDC dimensions
Legend: M3 – Charge gage port, after filtering: M12x1.5
26 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 27

12.4 ±0.25
[0.488 ±0.01]
Ø100 ±0.3
[Dia 3.937 ±0.012]
Ø84
[Dia 3.307 ]
292
[11.496 ]
110
[4.331]
92
[3.624]
86
[3.386]
60
[2.362]
27.8 (2x)
[1.094 ]
58.2
[2.291]
8.5
[0.335]
9.3
[0.366]
2.3
[0.091]
96
[3.781]
187
[7.366]
149
[5.87]
78.4
[3.086]
263
[10.353]
304.5
[11.99]
316.4
[12.458]
18.8
[0.738]
Ø12.5
[Dia0.492]
Ø26 (2x)
[Dia1.024]
Ø60
[Dia 2.362]
57.2 (2x)
[2.252]
Ø50 min
[Dia1.97]
0
-0.05
0
-0.002
Ø127
[Dia 4.999 ]
+0.23
+0.08
+0.009
+0.003
Ø8.1
[Dia 0.319 ]
0
-0.06
0
-0.002
57
[2.244 ]
Split flange boss
DN25 typ I 420 bar
Series per ISO 6162
M12, 21 [0.83] full thread depth
Paint free
Paint free
Charge pump inlet S
M42x2 - 6H
20 [0.79] full thread depth
Auxiliary mounting pad
Flange 127 - 4
per ISO3019 (SAE J744C)
Technical Information
Installation drawings
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
A, B – System ports: Ø 25.4 mm
L1, L2 – Case drain ports: M22x1.5
M1, M2 – System A/B gage ports: M12x1.5
M4, M5 – Servo gage ports: M12x1.5
M10 – Charge pump inlet pressure port: M12x1.5
S – Charge inlet port: M42x2
Please contact Danfoss for specific installation drawings.
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 27
Page 28
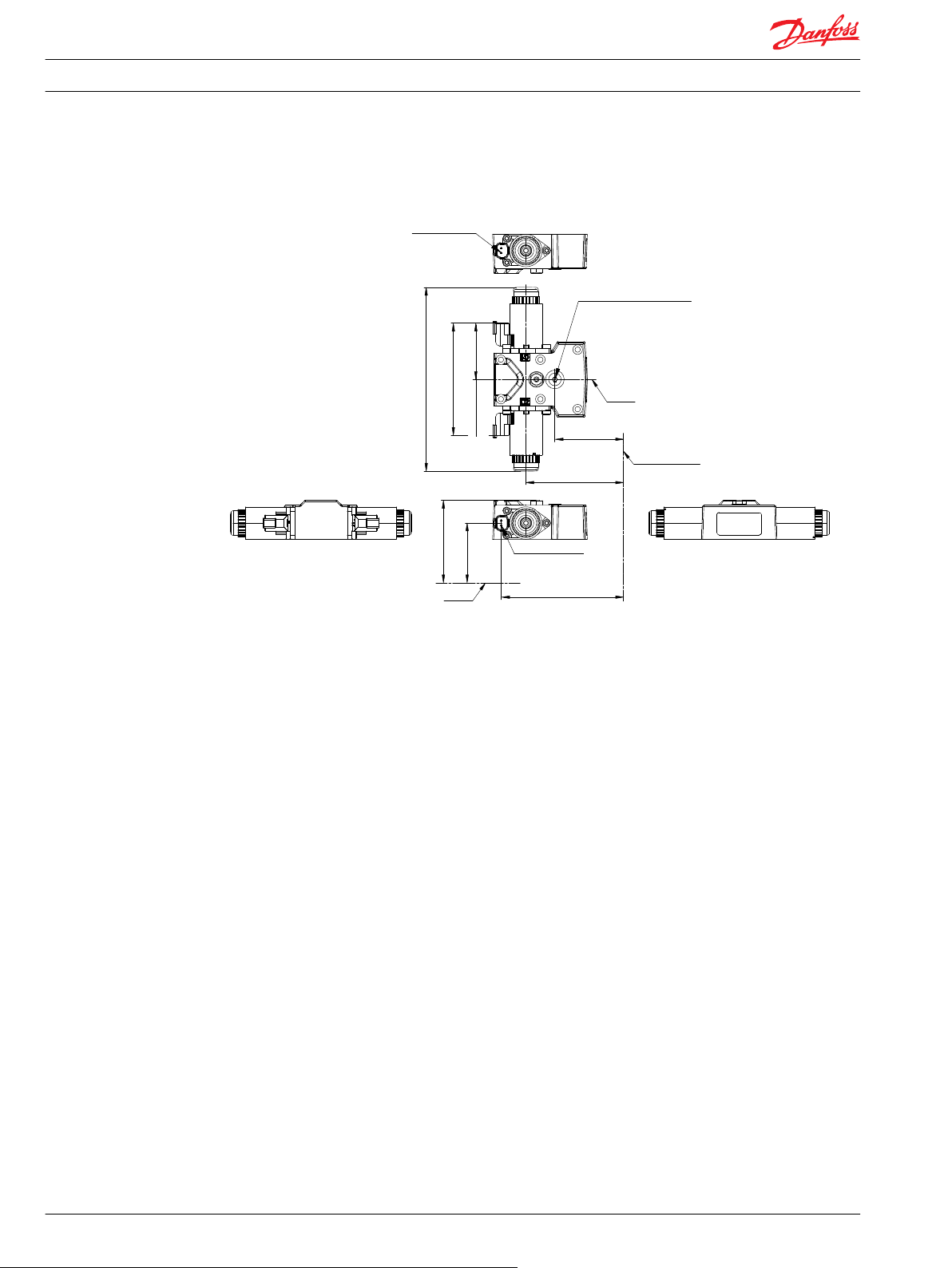
Shaft L
Mounting flange
Shaft L
Connector :
Deutsch DT04-2P
to be paint free
160.8 max
[6.33]
149 ±1.0
[5.87 ±0.04]
2x 134.8 ±1.0
[5.31 ±0.04]
2x 177 ±1.0
[6.97 ±0.04]
Connector :
Deutsch DT04-2P
to be paint free
128.4 ±2.0
[5.055 ±0.079]
64.2 ±1.0
[2.528 ±0.039]
209.0 max
[8.228]
115 ±1.0
[4.53 ±0.04]
Case gage port
Port ISO 11926-1 – 7/
16
-20
∅21 max clearance dia for fitting
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Installation drawings
EDC dimensions
Electric Displacement Control (EDC) with manual override, options 12 V and 24 V
28 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 29
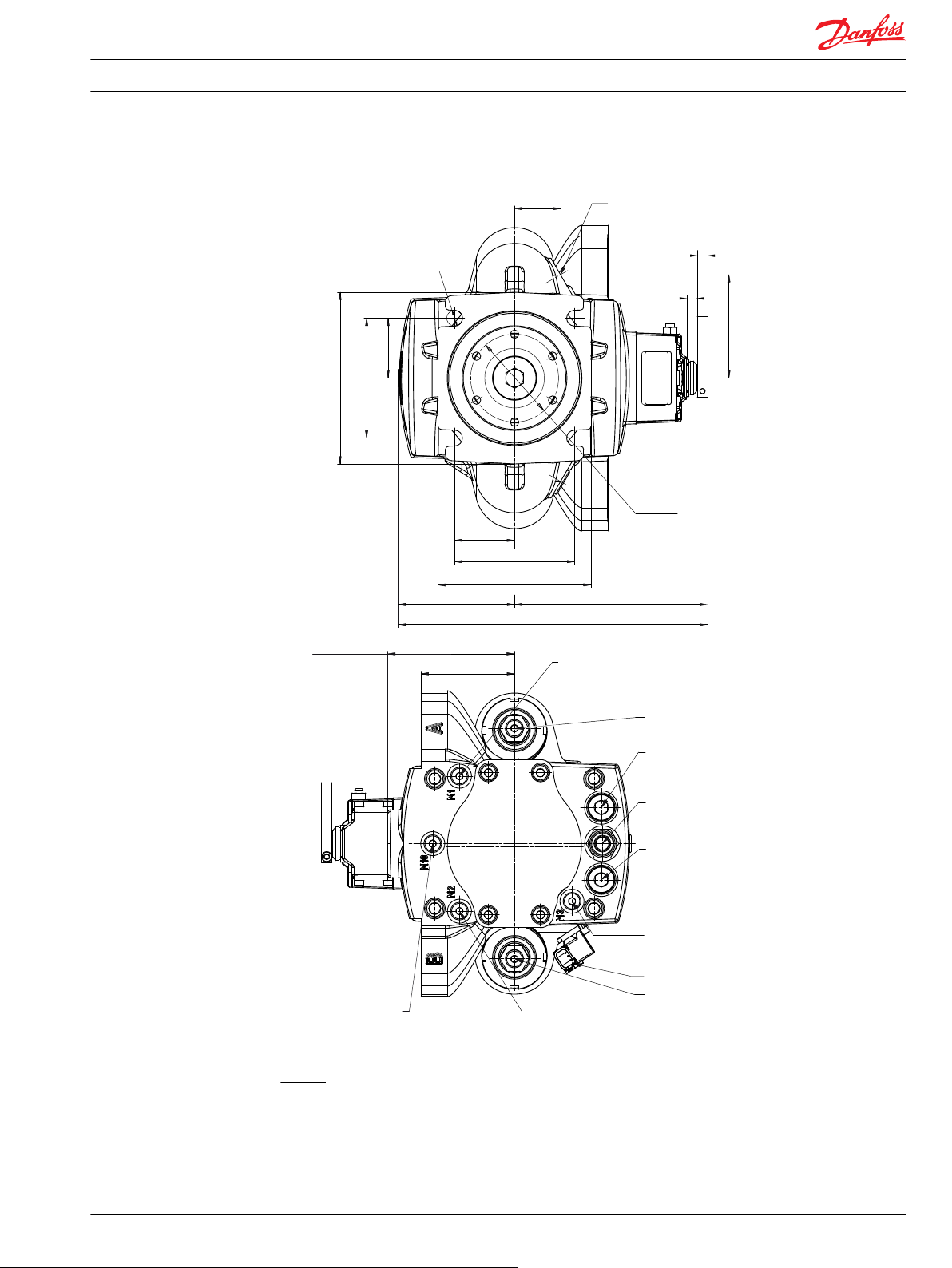
121
[4.764]
89
[3.504]
43.9
[1.728]
57.25
[2.254]
10
[0.394]
9.9
[0.389]
114.5
[4.508]
146
[5.748]
184.0
[7.254]
(295.5)
[11.635]
111.4
[4.386]
164
[6.457]
114.5
[4.508]
98.8
[3.89]
57.25
[2.254]
+0.8
+0.031
-0.3
-0.012
4 x Ø15
[Dia 0.591 ]
Ø84
[Dia 3.307]
Case drain port L1
use highest port as outlet
M22x1.5 - 11 min [.433] depth
Gauge port M1
System pressure Port A, M12x1.5
12.7 [.5] full thread depth
Gauge port M4
Servo pressure M12x1.5
Gauge port M3
Charge pressure M12x1.5
12.7 [0.5] full thread depth
High pressure relief valve
Port A
Charge pressure relief valve
High pressure relief valve
Port B
Gauge port M5
Servo pressure M12x1.5
Gauge port M2
System pressure Port B,
M12x1.5; 12.7 [.5] full thread depth
Gauge port M10
Charge pump inlet pressure
M12x1.5; 12.7 [.5] full thread depth
Connector Deutsch DTM06-6S
Charge pump inlet S
Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Installation drawings
TMP MDC dimensions
Legend:
A, B – System ports: Ø 25.4 mm
L1, L2 – Case drain ports: M22x1.5
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 29
M3 – Charge gage port, after filtering: M12x1.5
M4, M5 – Servo gage ports: M12x1.5
M10 – Charge pump inlet pressure port: M12x1.5
Page 30

12.4 ±0.25
[0.488 ±0.01]
Ø100 ±0.3
[Dia 3.937 ±0.012]
Ø84
[Dia 3.307 ]
292
[11.496 ]
110
[4.331]
92
[3.624]
86
[3.386]
22
[0.866]
25.8
[1.016]
27.8 (2x)
[1.094 ]
58.2
[2.291]
8.5
[0.335]
9.3
[0.366]
2.3
[0.091]
96
[3.781]
87,8
[3.457]
74,5
[2.933]
187
[7.366]
139
[5.465]
78.4
[3.086]
263
[10.353]
304.5
[11.99]
M6-6H (4x)
depth 10 min
[0.3937]
316.4
[12.458]
18.8
[0.738]
Ø12.5
[Dia0.492]
Ø26 (2x)
[Dia1.024]
Ø60
[Dia 2.362]
R 50.8
[2]
57.2 (2x)
[2.252]
Ø50 min
[Dia1.97]
0
-0.05
0
-0.002
Ø127
[Dia 4.999 ]
+0.23
+0.08
+0.009
+0.003
Ø8.1
[Dia 0.319 ]
0
-0.06
0
-0.002
57
[2.244 ]
Split flange boss
DN25 typ I 420 bar
Series per ISO 6162
M12, 21 [0.83] full thread depth
Paint free
Paint free
Charge pump inlet S
M42x2 - 6H
20 [0.79]
full thread depth
Auxiliary mounting pad
Flange 127 - 4
per ISO3019 (SAE J744C)
Technical Information
Installation drawings
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
M1, M2 – System A/B gage ports: M12x1.5 S – Charge inlet port: M42x2
Please contact Danfoss for specific installation drawings.
30 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 31

M
i
n
i
m
u
m
P
o
s
i
t
i
o
n
Manual Displacement Control Handle
Maximum
Displacement
Maximum
Displacement
M
i
n
i
m
u
m
N
e
u
t
r
a
l
Torque applied to handle shaft
not to excced 12 N•m [106 lbf•in]
Technical Information
Installation drawings
MDC dimensions
TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Manual Displacement Control (MDC)
Manual Displacement Control Handle
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 31
Page 32

Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Installation drawings
TMP MDC with Control Cut-Off (CCO) dimensions
Manual Displacement Control (MDC) with CCO, 24 V and Manual Override
32 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 33

Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Installation drawings
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 33
Page 34

Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
Installation drawings
Manual displacement control with CCO, 24 V and manual override
34 L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014
Page 35

Technical Information TMP Transit Mixer Axial Piston Pump, Size 070/089
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 35
Page 36

Danfoss Power Solutions is a global manufacturer and supplier of high-quality hydraulic and
electronic components. We specialize in providing state-of-the-art technology and solutions that
excel in the harsh operating conditions of the mobile off -highway market. Building on our extensive
applications expertise, we work closely with our customers to ensure exceptional performance for a
broad range of off -highway vehicles.
We help OEMs around the world speed up system development, reduce costs and bring vehicles to
market faster.
Danfoss – Your Strongest Partner in Mobile Hydraulics.
Go to www.powersolutions.danfoss.com for further product information.
Wherever off -highway vehicles are at work, so is Danfoss.
We off er expert worldwide support for our customers, ensuring the best possible solutions for
outstanding performance. And with an extensive network of Global Service Partners, we also provide
comprehensive global service for all of our components.
Please contact the Danfoss Power Solution representative nearest you.
Danfoss
Power Solutions GmbH & Co. OHG
Krokamp 35
D-24539 Neumünster, Germany
Phone: +49 4321 871 0
Danfoss
Power Solutions ApS
Nordborgvej 81
DK-6430 Nordborg, Denmark
Phone: +45 7488 2222
Danfoss
Power Solutions US Company
2800 East 13th Street
Ames, IA 50010, USA
Phone: +1 515 239 6000
Danfoss
Power Solutions
(Shanghai) Co. Ltd.
Building #22, No. 1000 Jin Hai Rd
Jin Qiao, Pudong New District
Shanghai, China 201206
Phone: +86 21 3418 5200
Products we off er:
• Bent Axis Motors
• Closed Circuit Axial Piston
Pumps and Motors
• Displays
• Electrohydraulic Power
Steering
• Electrohydraulics
• Hydraulic Power Steering
• Integrated Systems
• Joysticks and Control
Handles
• Microcontrollers and
Software
• Open Circuit Axial Piston
Pumps
• Orbital Motors
• PLUS+1® GUIDE
• Proportional Valves
• Sensors
• Steering
• Transit Mixer Drives
Comatrol
www.comatrol.com
Schwarzmüller-Inverter
www.schwarzmuellerinverter.com
Turolla
www.turollaocg.com
Valmova
www.valmova.com
Hydro-Gear
www.hydro-gear.com
Daikin-Sauer-Danfoss
www.daikin-sauer-danfoss.com
Local address:
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to
products already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequential changes being necessary in specifications already agreed.
All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
L1006391 • Rev CE • Mar 2014 www.danfoss.com
©
Danfoss A/S, 2014
 Loading...
Loading...