Page 1
Vipersat CDM-570/L, CDD-56X
Parameter Editor
User Guide
Part Number MN-0000038 Revision 1
Page 2

Page 3

Vipersat CDM-570/L, CDD-56X
Parameter Editor
User Guide
Part Number MN-0000038
Document Revision 1
Software version 1.5.4.55
February 6, 2009
Page 4

COMTECH EF DATA
VIPERSAT Network Products Group
3215 Skyway Court
Fremont, CA 94539
USA
Phone: (510) 252-1462
Fax: (510) 252-1695
www.comtechefdata.com
Part Number: MN-0000038
Revision: 1
Software Version 1.5.4.55
©2009 by Comtech EF Data, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be copied or
reproduced by any means without prior written permission of Comtech EF Data.
Comtech reserves the right to revise this publication at any time without obligation to provide
notification of such revision. Comtech periodically revises and improves its products and
therefore the information in this document is subject to change without prior notice. Comtech
makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including but limited to the implied
warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. No responsibility for any errors
or omissions that may pertain to the material herein is assumed. Comtech makes no
commitment to update nor to keep current the information contained in this document.
All products, names and services are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
Printed in the United States of America
Page 5
Document Revision History
Revision Date Description
0
11/26/08
Initial release.
1
2/06/09
New functionality in this release: Tree View user interface.
Page 6

{ This Page is Intentionally Blank }
Page 7

Table of Contents
Chapter 1
General
How to Use This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Manual Organization . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Chapter 1 — General . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Chapter 2 — Using Parameter Editor . . 1-1
Appendix A — Glossary . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Conventions and References . . . . . . . . 1-2
Product Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Parameter Editor Features . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Customer Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Contact Information . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Reader Comments / Corrections . . . . 1-4
Chapter 2
Using Parameter Editor
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
DLL Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Updating DLL Files . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Configuration Changes . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Parameter Editor Tree Menu . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Configuration Alert . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
HDLC Addressing Mode . . . . . . . . 2-6
Enable All Downlink Multicast . . . . . . 2-7
DHCP Server IP Address . . . . . . . . 2-7
Dynamic Buffer Latency . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Adding a Route . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Modifying a Route . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
QoS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Enable Quality of Service . . . . . . . 2-11
Enable SAR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Rules Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Developing QoS Rules in a VMS Network 2-12
Defining QoS Rules . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Rule Max/Priority & Rule Min/Max Modes .
2-14
Diff Serv QoS Mode . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
Modem as IGMP Server. . . . . . . . 2-22
Modem as IGMP Client . . . . . . . . 2-23
Managed Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Vipersat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
Role Designation . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
Enable VFS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-28
Enable Heart Beat . . . . . . . . . . 2-28
Enable SOTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-28
Carrier Inhibit Timer . . . . . . . . . 2-29
Network ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-29
Database Version . . . . . . . . . . . 2-29
Node Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
Multicast Management Address . . . 2-30
STDMA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
Enable STDMA . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
Enable Power Hunt . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
Enable Low Data Rate Fast Acquisition . .
2-31
Allocation Method . . . . . . . . . . . 2-32
Group ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-34
Slot Data Length . . . . . . . . . . . 2-35
Stats Collection . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-35
Burst Map Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-36
Preamble . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-36
Guard Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-36
Remote List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-37
Automatic Remote Removal . . . . . 2-38
Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-39
Application Switch Detection . . . . . 2-40
Load Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-45
Hitless Switching . . . . . . . . . . . 2-48
DPC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-49
Enable Dynamic Power Control . . . 2-50
Minimum Power . . . . . . . . . . . 2-50
Maximum Power . . . . . . . . . . . 2-51
Target Eb/N0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-51
Speed Up Eb/N0 . . . . . . . . . . . 2-51
Target Range For No Power Adjust . 2-51
Target IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . 2-51
Home State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-52
Admin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-54
User Names and Passwords . . . . . 2-54
Enable Ping Reply . . . . . . . . . . 2-55
Enable Telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-55
ToC i
Page 8

Telnet Inactivity Timeout . . . . . . . 2-55
Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-55
SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-56
Enable SNMP for Modem Configuration .
2-57
Enable Authentication Trap . . . . . . 2-57
Trap Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-57
Trap Destination Addresses . . . . . . 2-58
Community Strings . . . . . . . . . . 2-58
System Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-58
System Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-58
System Location . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-59
SMTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-59
Server IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . 2-60
Domain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-60
Destination Name . . . . . . . . . . . 2-60
Compression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-60
Tx Header Compression . . . . . . . 2-60
Tx Payload Compression . . . . . . . 2-61
Triple DES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-62
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-65
Upgrade Image . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-65
Base Modem Image . . . . . . . . . 2-66
Enable Redundancy . . . . . . . . . 2-66
Codecast Address . . . . . . . . . . 2-66
Event Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-66
Automatically Save PARAM After CONFIG
Change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-66
Appendix A
Glossary
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Index
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Index-1
ii CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 9

List of Figures
Chapter 2 Figures
Figure 2-1 Tree Menus, Vipersat Modes. . . . . 2-3
Figure 2-2 Alert, Parameter Conflict . . . . . . . . 2-4
Figure 2-3 Network dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Figure 2-4 HDLC Addressing Mode Menu . . . 2-6
Figure 2-5 Routing dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Figure 2-6 Add Route dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Figure 2-7 Multicast Network Address . . . . . . 2-9
Figure 2-8 Modify Route dialog . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Figure 2-9 QoS dialog, Max/Priority Mode . . 2-11
Figure 2-10 Add Quality Of Service Rule dialog . .
2-13
Figure 2-11 Add QoS Rule, Max/Priority Mode 2-15
Figure 2-12 Protocol Drop-Down Menu. . . . . 2-16
Figure 2-13 QoS Tab, Diff Serv Mode. . . . . . 2-18
Figure 2-14 Modify DiffServ Rule . . . . . . . . . 2-19
Figure 2-15 IGMP dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
Figure 2-16 IGMP Server dialog . . . . . . . . . . 2-22
Figure 2-17 IGMP Client dialog. . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
Figure 2-18 Managed Switch dialog . . . . . . . 2-25
Figure 2-19 VLAN dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
Figure 2-20 Vipersat dialog, Hub Unit . . . . . . 2-27
Figure 2-21 STDMA dialog, Hub Unit . . . . . . 2-31
Figure 2-22 STDMA dialog, Remote Unit . . . 2-32
Figure 2-23 Bandwidth Allocation Method. . . 2-33
Figure 2-24 STDMA Remote List, ECM . . . . 2-37
Figure 2-25 Remote Entry dialog, ECM . . . . 2-38
Figure 2-26 Automatic Remote Removal . . . 2-39
Figure 2-27 Switching dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-40
Figure 2-28 Application Switch Detection, Remote
Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-41
Figure 2-29 Type of Service Switching List . . 2-43
Figure 2-30 Type of Service Entry. . . . . . . . . 2-44
Figure 2-31 Load Switching, Remote Unit. . . 2-45
Figure 2-32 Hitless Switching dialog . . . . . . . 2-48
Figure 2-33 DPC dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-50
Figure 2-34 Home State, Enable STDMA . . . 2-52
Figure 2-35 Home State dialog, Modulator . . 2-52
Figure 2-36 Admin dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-54
Figure 2-37 Authentication dialog . . . . . . . . . 2-55
Figure 2-38 Admin dialog, Enabled . . . . . . . . 2-55
Figure 2-39 Access dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-56
Figure 2-40 SNMP dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-57
Figure 2-41 SMTP Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-59
Figure 2-42 Compression dialog . . . . . . . . . . 2-61
Figure 2-43 Triple DES dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-63
Figure 2-44 Modify DES Key dialog . . . . . . . 2-64
Figure 2-45 Maintenance dialog . . . . . . . . . . 2-65
LoF iii
Page 10

{ This Page is Intentionally Blank }
iv CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 11

Chapter 2 Tables
Table 2-1 DiffServ Code Points (DSCP). . . . . 2-19
Table 2-2 Expedited and Assured Forwarding,
DSCP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
Table 2-3 Vipersat unit Network Functions and
Roles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-28
List of Tables
LoT v
Page 12

{ This Page is Intentionally Blank }
vi CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 13

GENERAL
How to Use This Manual
This manual documents the features and functions of the Vipersat Parameter
Editor software user interface, and guides the user in how to use this product for
configuring a Comtech modem/router to operate in a Vipersat satellite network.
Workstation users, as well as network administrators and operators responsible
for the configuration and maintenance of the Vipersat satellite network, are the
intended audience for this document.
C
HAPTER
Manual Organization
This User Guide is organized into the following sections:
Chapter 1 — General
Contains Parameter Editor product description, customer support information,
and manual conventions and references.
Chapter 2 — Using Parameter Editor
Covers the Parameter Editor dialogs and the associated fields that are used to
configure the CDM-570/570L and the CDD-56X series modems.
Appendix A — Glossary
A glossary of terms that pertain to Vipersat satellite network technology.
Chapter 1 - General 1-1
Page 14
How to Use This Manual
Conventions and References
The following conventions are utilized in this manual to assist the reader:
NOTE
Note: Provides important information relevant to the accompanying
text.
Tip: Provides complementary information that facilitates the
associated actions or instructions.
Caution: Provides explanatory text that notifies the reader of
possible consequences of an action.
Warning: Provides precautionary text that describes a potentially
hazardous situation. Failure to take or avoid a specified
action may result in damage to equipment.
The following documents are referenced in this manual, and provide supplementary information for the reader:
• CDM-570/570L Modem Installation and Operation Manual (Part Number
MN/CDM570L.IOM)
• Vipersat CDM-570/570L User Guide (Part Number MN/22125)
• CDD-564L Quad Demodulator Installation and Operation Manual (Part
Number MN/CDD564L.IOM)
• Vipersat CDD-56X Series User Guide (Part Number MN/22137)
• Vipersat Management System User Guide (Part Number MN/22156)
• Vipersat Load Utility User Guide (Part Number MN/22117)
1-2 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 15

Product Description
Introduction
The Parameter (Param) Editor provides a simple graphical user interface (GUI)
for making configuration changes to modem/routers used in a Vipersat satellite
network. Accessible from both the VMS and VLoad, the Parameter Editor operates on the param files that store the operating parameters for network terminals.
This user guide documents the Parameter Editor as it applies to the CDM-570/
570L modem and the CDD-56X series of demodulators.
The Parameter Editor is the same in both the VMS and VLoad. However, the
way edited parameters are applied to the Vipersat network modem/routers
differs between the two. Once a modem’s configuration has been changed using
the VMS, the change is immediately applied to the modem. In contrast, changes
made using the VLoad utility are not applied until the new param file is Put
(uploaded) to the unit by the operator.
Product Description
NOTE
Note: Many of the parameters will interact with other parameters. Carefully
read the instructions before making changes to a unit’s configuration
settings.
Parameter modifications may also be made directly to the modem/router using
either a direct console connection or a Telnet connection. Refer to the modem/
router’s documentation for
tions directly at the unit.
For more information on using the Parameter Editor with the VMS, refer to the
Vipersat Management System User Guide.
For more information on using the Parameter Editor with VLoad, refer to the
Vipersat Load Utility User Guide.
details on making equipment parameter modifica-
Parameter Editor Features
The Parameter Editor software has the following features:
• Simple yet comprehensive graphical user interface.
• Integrated with both the VMS and VLoad.
• Context sensitive for device type as well as for unit role (Hub/Remote).
• Functions with multiple .dll files.
Chapter 1 - General 1-3
Page 16

Customer Support
Customer Support
Contact Information
Contact Comtech Vipersat Networks Customer Support for information or
assistance with product support, service, or training on any Vipersat product.
Mail: 3215 Skyway Court
Phone: 1+510-252-1462
Fax: 1+510-252-1695
Email: supportcvni@comtechefdata.com
Web: www.comtechefdata.com
Reader Comments / Corrections
If the reader would like to submit any comments or corrections regarding this
manual and its contents, please forward them to a Comtech Vipersat Customer
Support representative. All input is appreciated.
Fremont, CA 94539
USA
1-4 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 17

USING PARAMETER EDITOR
General
DLL Files
C
HAPTER
The Parameter Editor is a shared run-time Dynamic Link Library (DLL) file
which is called from both VLoad and VMS software applications. It is used as
an extension to both of these programs in providing an extendable User Interface. This file resides in a locally sourced directory for access by the host application.
To access the Parameter Editor from either the VMS or VLoad, the appropriate
DLL files are required. There is a DLL file for each modem firmware version.
For example, ParamEdit-5.4.dll is utilized for modems that are running firmware v1.5.4. For networks that have multiple modem firmware versions, multiple DLL files are required.
Please note that the naming convention for these files may differ, depending on
what version of VMS or VLoad is used. Prior to VMS v3.6.2 and VLoad v3.4.1,
the convention used is
ware version. For VMS v3.6.2 and later, and VLoad v3.4.1 and later, the
convention used includes the modem designation and firmware version (e.g.,
ParamEdit-CDM5XX-x.x.dll).
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-1
ParamEdit-x.x.dll, where x.x identifies the modem firm-
Page 18
General
Updating DLL Files
To update the Parameter Editor for one or both of the installed applications,
VLoad and/or VMS, the new DLL file is simply copied into the appropriate
directory for that application.
VMS Update
On both the VMS Client machine and the VMS Server, copy the distributed
DLL file to the following directory:
C:\Program Files\Vipersat\VMS\3.0\bin
Vload Update
Copy the distributed DLL file into the same local directory that holds the VLoad
application (.exe).
These DLL file updates will not cause any disruption to the host applications.
Configuration Changes
When changes are made to a modem unit configuration with Parameter Editor,
these changes can either be saved by clicking on the OK button at the bottom of
the window, or ignored by clicking on the Cancel button or closing the Editor.
Caution: Clicking the OK button saves all of the data from all of the menu
categories simultaneously to the modem unit Param file. The OK and
Cancel buttons do not apply to any single category, but apply to all
categories in the Parameter Editor.
Because the Parameter Editor closes after a save operation, it is recommended
that all changes be input prior to clicking on the OK button.
2-2 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 19

Parameter Editor Tree Menu
The Parameter Editor displays the editable parameter categories for each
network modem/router in the form of a tree menu, as shown in figure 2-1. The
tree appearance will vary depending on the selected Network Addressing Mode,
the Role Designation, and whether the unit has both a modulator and a demodulator, or a demodulator(s) only.
Vipersat Hub Vipersat Remote Expansion w/o Mod
Parameter Editor Tree Menu
Figure 2-1
Tree Menus, Vipersat Modes
From the VMS, the Parameter Editor is accessed by selecting the modem
Configure command.
From VLoad, the Parameter Editor is accessed by clicking on the Edit Param
File button.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-3
Page 20
Parameter Editor Tree Menu
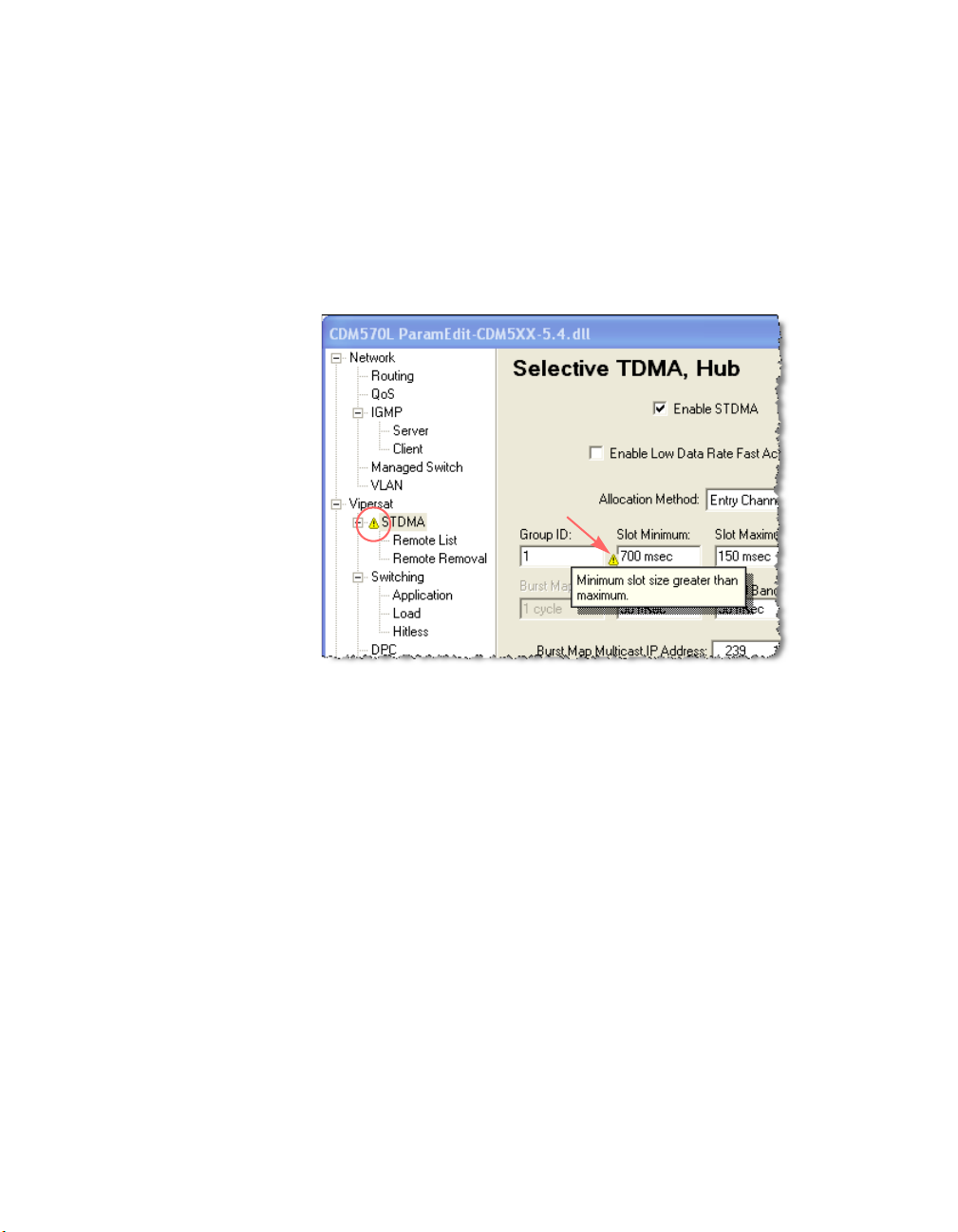
Configuration Alert
Parameter Editor performs a check of the configuration settings that are input by
the user. If any settings are found to be in conflict for the unit, an alert message
is generated to inform the user that an adjustment is necessary. When a dialog
containing a conflicting parameter setting is exited, an alert icon will appear in
front of the associated menu item (figure 2-2). Upon re-opening the dialog, an
alert icon will be displayed next to the field in question. Clicking on the icon
will display a pop-up info-tip that explains the conflict.
Figure 2-2
Alert, Parameter Conflict
The following sections describe each of the menu items and their associated
parameter settings.
2-4 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 21
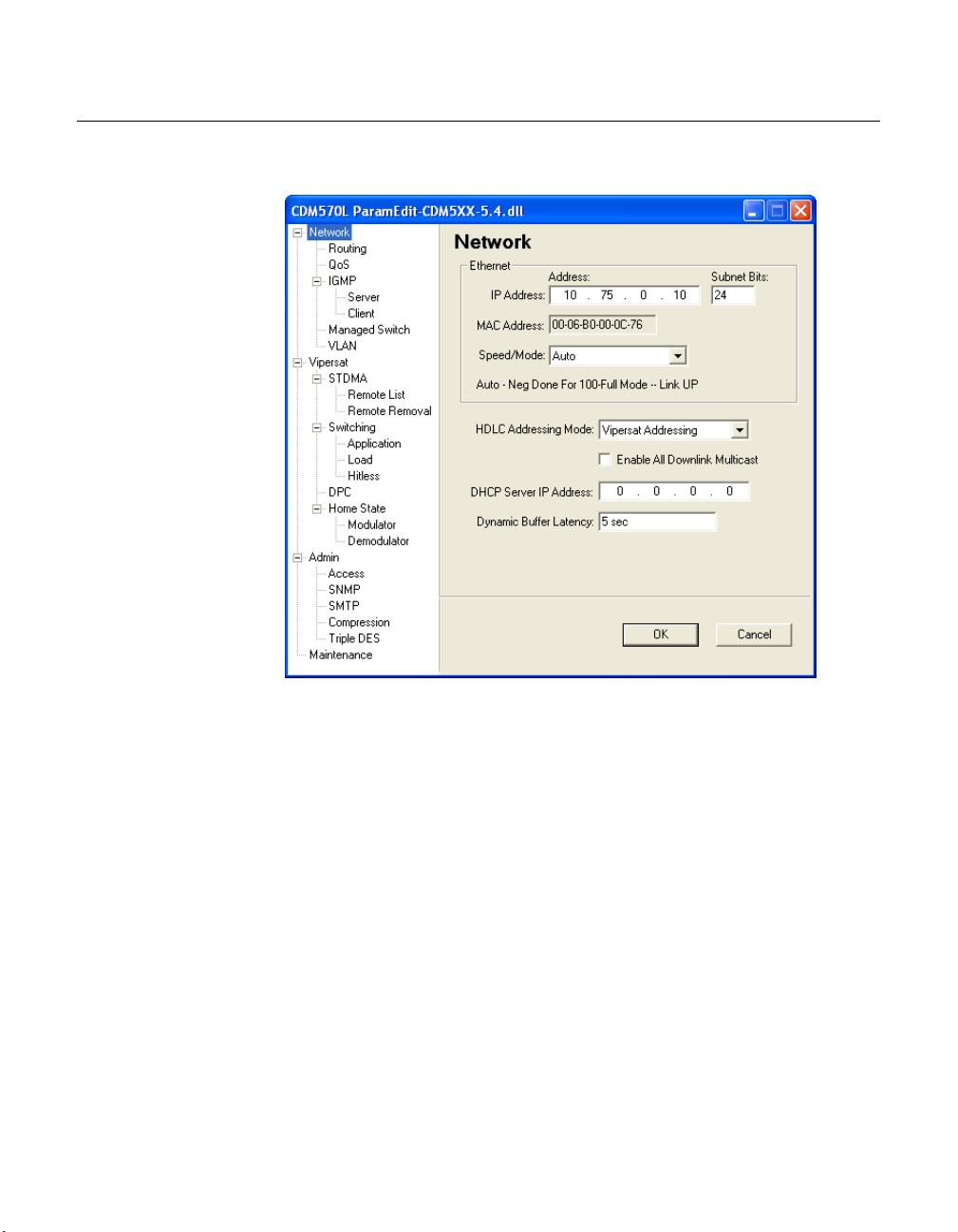
Network
Network
The network interface parameters are set in the Network dialog, figure 2-3.
Figure 2-3
Network dialog
Ethernet
The following Ethernet parameters can be configured for this modem unit.
IP Address
Enter the IP address that is assigned to this modem unit.
Subnet Bits
Enter the number of subnet bits associated with this modem unit’s IP address.
MAC Address
The modem unit’s MAC address is read-only. This parameter can not be modified by the user.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-5
Page 22
Network
Speed/Mode
Select the speed and mode for the connection from the options on the dropdown menu.
NOTE
Note: Auto mode is recommended unless the operator is absolutely certain the
device being connected does not have auto-negotiation available.
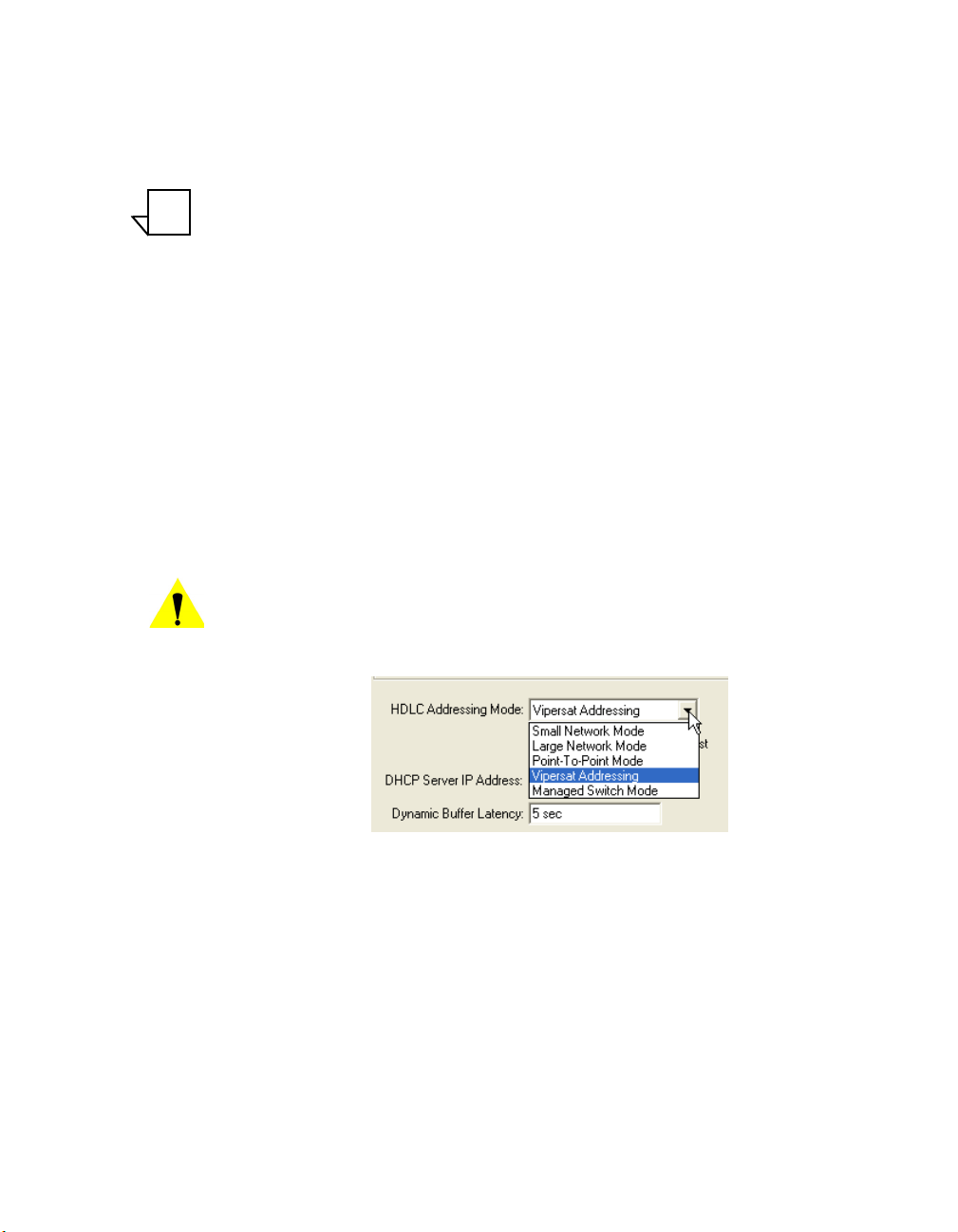
HDLC Addressing Mode
The drop-down menu for HDLC (High-level Data Link Control) Addressing
Mode shown in figure 2-4 displays five available modes (only the first four
modes are displayed for a CDD-56X):
• Small Network Mode
• Large Network Mode
• Point-to-Point Mode
• Vipersat Addressing
• Managed Switch Mode
Caution: Only the Vipersat Addressing mode configures the target modem to
communicate in a Vipersat network. Selecting any other mode will
remove the unit from the network.
Figure 2-4
HDLC Addressing Mode Menu
When using the ParamEditor to configure a modem for operation in an environment other than a Vipersat network, refer to the unit’s documentation for details
on setting and configuring the device.
Managed Switch Mode
The Managed Switch mode uses a bridging mode which is not supported in
Vipersat networks. Refer to the CDM-570/570L’s documentation for availability and detailed information on this mode.
2-6 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 23

Network
Warning: Selecting the Managed Switch mode will invoke bridging mode in
the target CDM-570/570L. When the OK button is clicked, the
modem will be immediately disconnected from the VMS. The VMS
cannot communicate with or control a CDM-570/570L which is
operating in the bridging mode.
Enable All Downlink Multicast
When the Enable All Downlink Multicast check box is selected, the IP Module
in the modem will automatically forward all multicast packets received from the
Satellite interface to the Ethernet LAN port without regard to the Route Table.
When this feature is not selected, multicast traffic from the Satellite will not be
forwarded to the LAN unless a multicast route exists in the Route Table to
handle this type of traffic.
DHCP Server IP Address
This option allows hosts at this remote site to receive dynamically assigned IP
addresses when a DHCP server is located at the Hub site. If applicable, enter the
IP address of the DHCP server.
Dynamic Buffer Latency
A buffer period can be specified for the modem for WAN traffic. For real-time
applications, such as voice or video, this period would typically be minimized.
This field defaults to 5 seconds; the value range is from 0.200 to 5.000 seconds.
Routing
Clicking the Routing menu item displays the modem unit’s routing dialog,
shown in figure 2-5. All current Static Routes are displayed in the table listing.
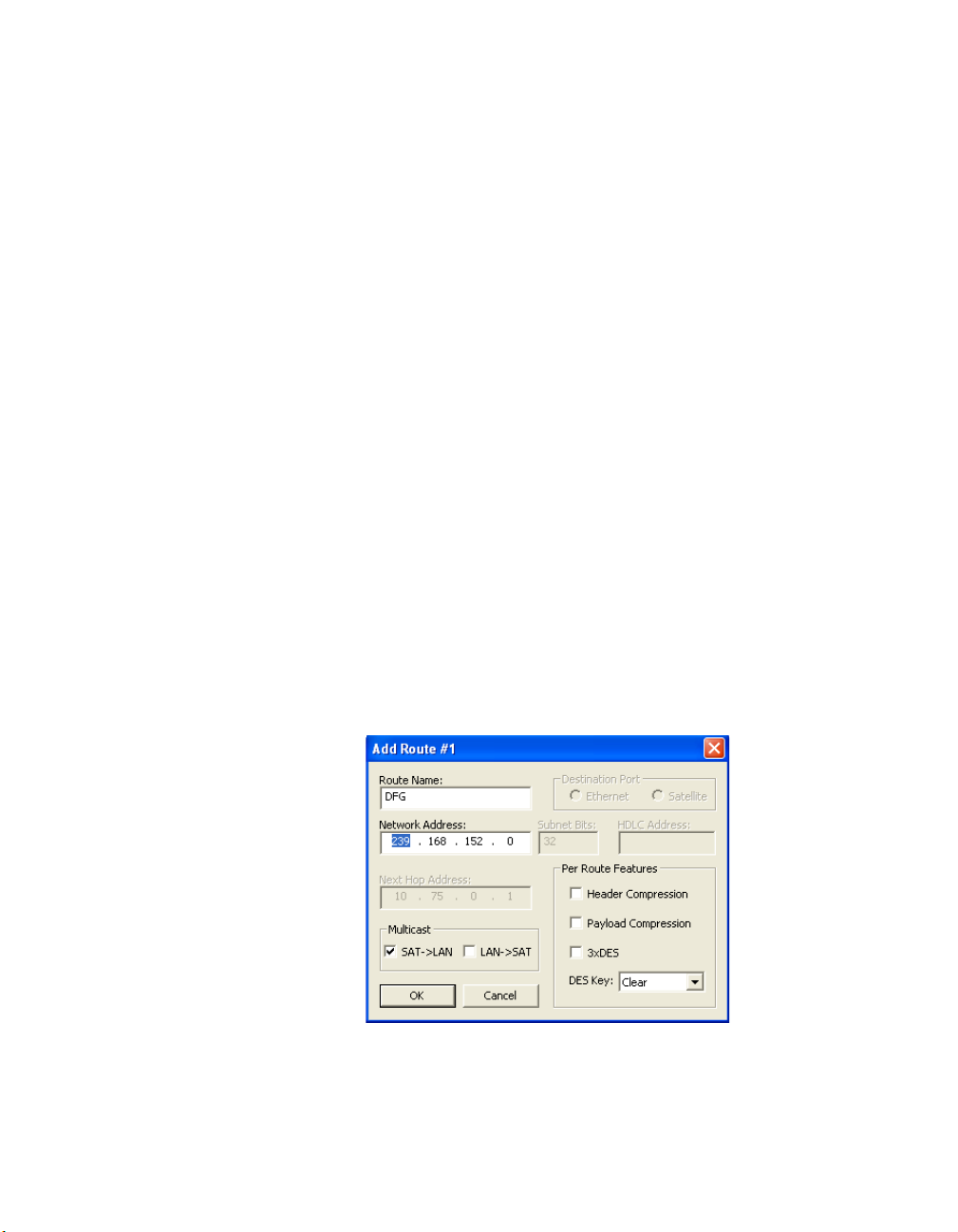
Adding a Route
To add a new static route, click the Add button at the bottom of the Routing
dialog to display the Add Route dialog shown in figure 2-6.
Route Name
Enter a designation for the route in the Route Name dialog box (maximum 13
characters).
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-7
Page 24
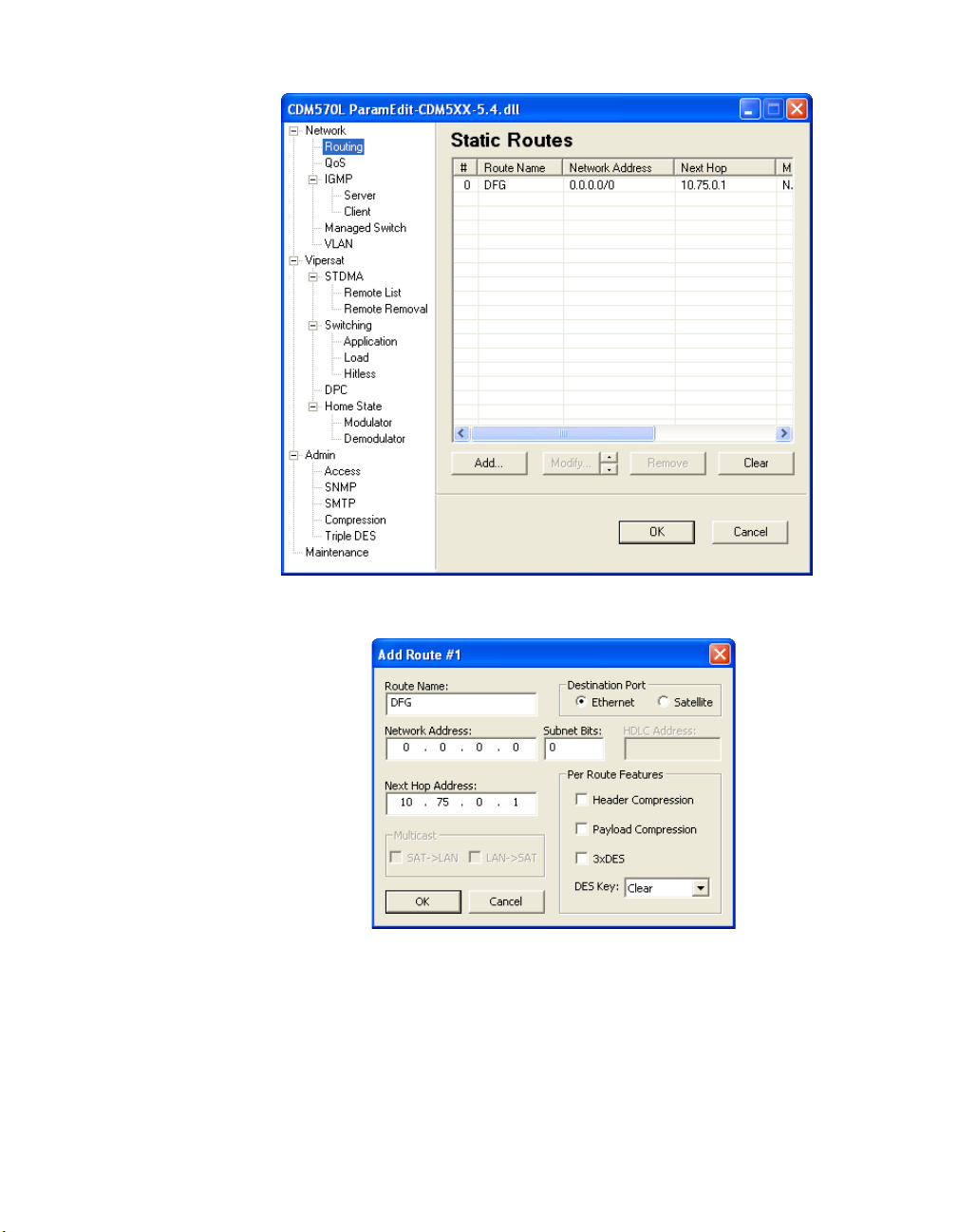
Network
Figure 2-5
Figure 2-6
Routing dialog
Add Route dialog
Destination Port
The Destination Port can be either Ethernet (LAN) or Satellite (WAN). Note
that if the Ethernet radio button is selected, the Next Hop Address box
becomes active. If the Satellite radio button is selected, the Next Hop Address
2-8 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 25
Network
box becomes inactive and the Next Hop table entry (figure 2-5) will show as
NONE.
Network Address
Enter the destination network IP address for this route to be added to the Vipersat unit’s routing table.
Subnet Bits
Enter the number of subnet bits associated with the network address.
HDLC Address
This parameter is not supported in Vipersat networks. Refer to the modem’s
user documentation for additional information.
Next Hop Address
The Next Hop Address box allows entering the IP address of the next hop for a
route which has an Ethernet destination port selected. This address must be on
the local subnet.
Multicast
If the first three digits entered in the Network Address box are in the range of
224 to 239, the address will be recognized as multicast, as shown in figure 2-7.
The Multicast box will become active, allowing the selection of Satellite to
LAN, LAN to Satellite, or both.
Figure 2-7
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-9
Multicast Network Address
Page 26
Network
Per Route Features
The Per Route Features provide optional functionality choices for the modem/
router unit. The per route features are:
• Header Compression – Refer to section “Compression” on page 2-60 for
details on setting header compression.
• Payload Compression – Refer to section “Compression” on page 2-60 for
details on setting payload compression.
•3xDES – Refer to the section “Triple DES” on page 2-62 for details on
setting the DES encryption.
•DES Key – Select the key from the drop-down list.
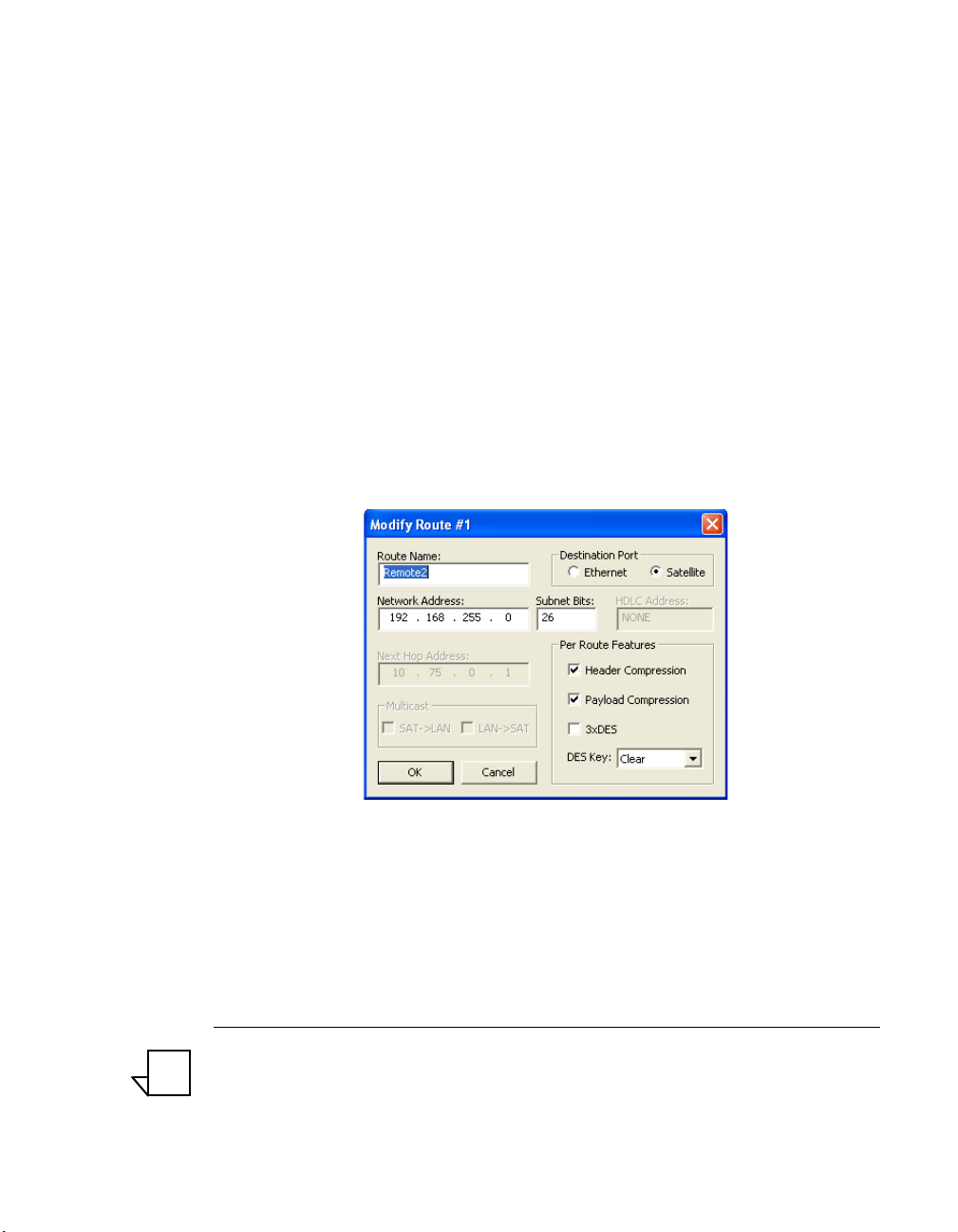
Modifying a Route
Selecting a route from the Routing table enables the Modify button. Clicking
the Modify button displays the Modify Route dialog shown in figure 2-8.
Figure 2-8
Modify Route dialog
The Modify Route dialog allows edits to be made to the fields as described
above.
QoS
NOTE
2-10 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Note: If the QoS feature (FAST code) has not been purchased for this modem,
the QoS menu item will not be displayed.
Page 27
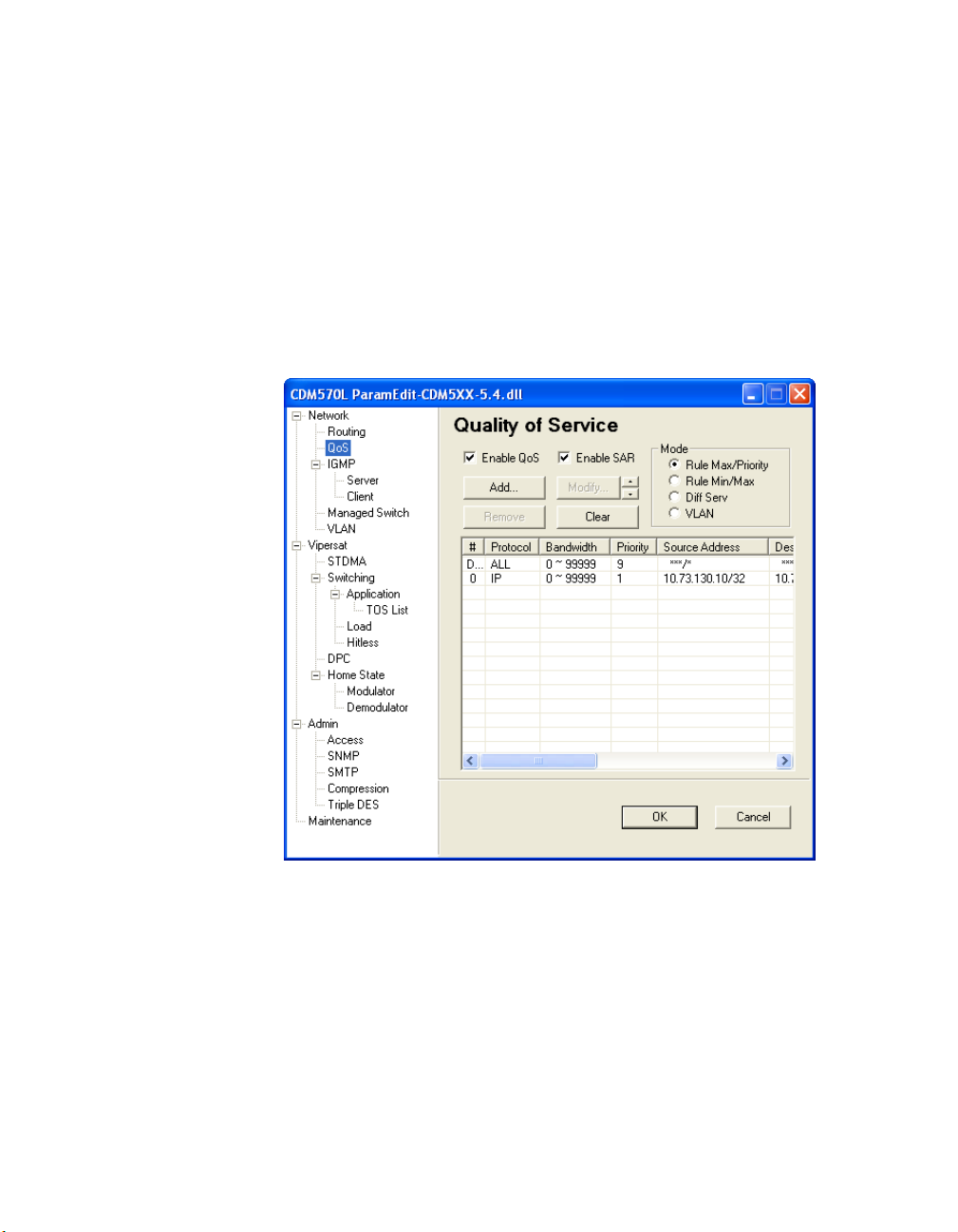
Network
The QoS menu item is not displayed for receive-only network units such
as the CDD-56X.
Selecting the QoS (Quality of Service) menu item displays the dialog shown in
figure 2-9. Quality of Service is an optional modem/router feature. If this
feature is enabled, the user may select one of four Modes of QoS operation:
• Rule Max/Priority – QoS rules based on maximum bandwidth and priority
• Rule Min/Max – QoS rules based on minimum and maximum bandwidth
• Diff Serv– QoS rules based on Differentiated Services settings
• VLAN – QoS rules based on the user priority field in the VLAN header
Figure 2-9
QoS dialog, Max/Priority Mode
Enable Quality of Service
Selecting the Enable Quality of Service box enables QoS on this modem/
router.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-11
Page 28

Network
Enable SAR
Packet Segmentation and Reassembly (SAR) can be enabled for QoS. With this
feature, packets are made smaller to speed them through the network and
because of specified packet size restrictions for a given path.
SAR is an adaptive process; it will trigger only if the packet latency exceeds the
threshold value (default is 20 msec). Latency value is calculated based on the
satellite transmission bandwidth. The minimum segment size is limited to 480
bytes—excluding satellite HDLC header information—in order to avoid satellite overhead and consumption of CPU cycles.
Rules Table
The Rules table appears in the lower portion of the QoS dialog. Just above the
table is a button set that acts on the table, and consists of the Add, Remove,
Modify, Up/Down Arrow, and Clear buttons. When an existing rule is
selected, that rule can be repositioned in the table listing through the use of the
Up/Down Arrow buttons. Note, however, that the Default rule always occupies
the first row of the table and can not be repositioned.
Developing QoS Rules in a VMS Network
The optional QoS capabilities available in each modem/router may be utilized
whenever a modem will be handling high-priority traffic, such as video or
voice. While developing the QoS Rules to be applied to the unit, the type of traffic the modem is expected to handle must be considered.
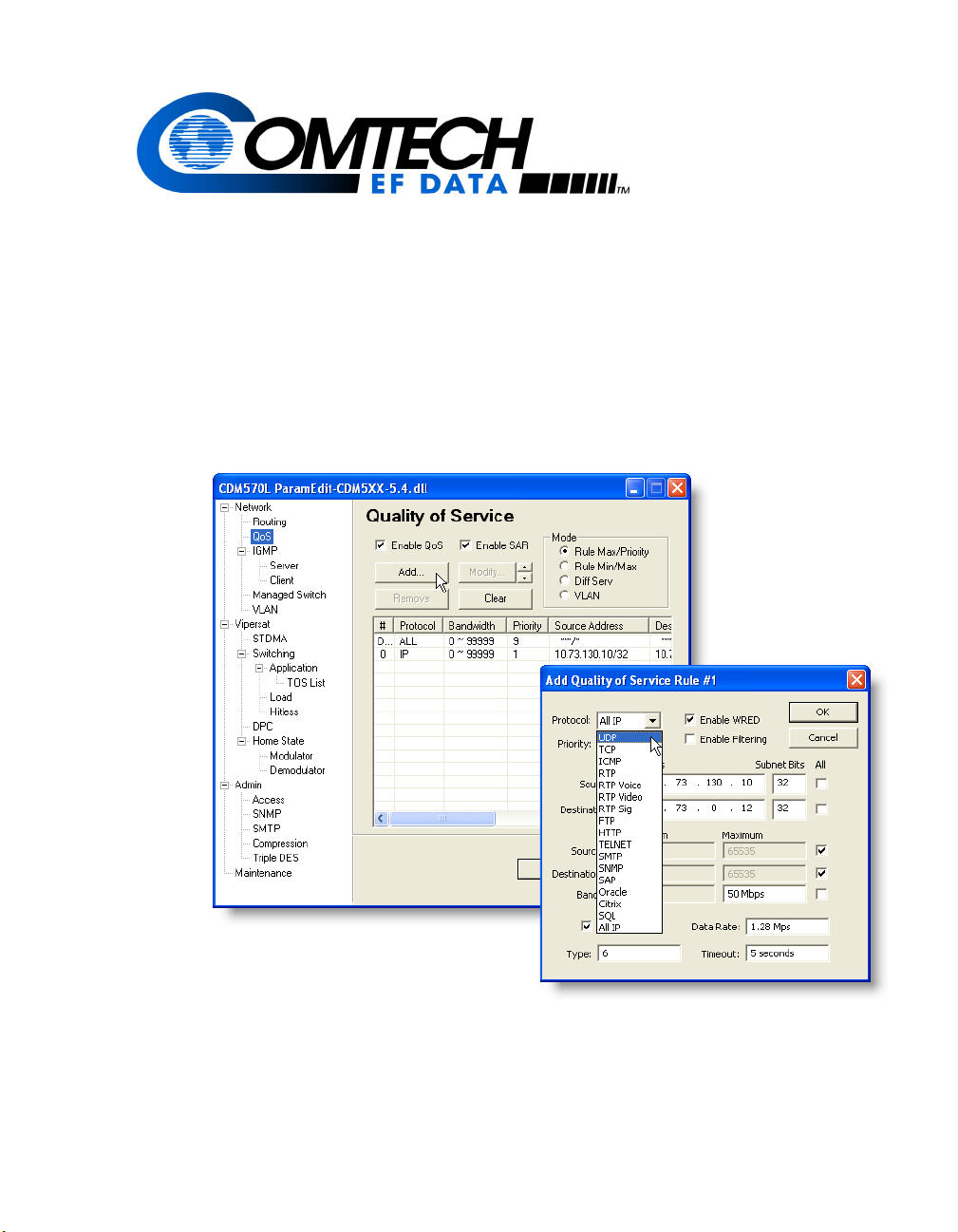
Defining QoS Rules
The QoS mode that is chosen will determine the settable parameters for defining
QoS rules. An example of a dialog for adding a rule is shown below in
figure 2-10.
QoS Rules can be assigned to up to 32 different types of flows defined by the
user. Flows can be defined by any combination of Protocol (FTP, UDP, RTP,
etc.), Source/Destination IP (specific or range), and/or Layer 3 Source/Destination Port.
2-12 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 29

Network
Figure 2-10
Add Quality Of Service Rule dialog
QoS Rule Hierarchy
It is quite possible to have traffic that meets the definitions of several QoS
Rules. All traffic will be classified into the first QoS Rule that is a match, or fall
into the Default Rule. The most specific QoS Rule will always be first. For
example, a QoS Rule that identifies a Source and Destination IP Address will be
assigned ahead of a rule that just defines RTP protocol. QoS Rules that have the
same amount of variables defined are sorted as follows:
1. By Protocol.
Protocol Priority:
a. VOCE – Voice Real Time Protocol
b. VDEO – Video Real Time Protocol
c. RTPS – Real Time Protocol Signalling
d. RTP – All Real Time Protocols
e. FTP – File Transfer Protocol
f. HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol
g. TELN – Telnet Protocol
h. SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
i. SNMP – Simple Network Management Protocol
j. SQL – Structured Query Language Protocol
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-13
Page 30

Network
k. ORCL – ORACLE Protocol
l. CTRX – CITRIX Protocol
m. SAP – Service Announcement Protocol
n. UDP – User Datagram Protocol
o. TCP – Transmission Control Protocol
p. ICMP – Internet Control Message Protocol
q. IP – All Internet Protocol
r. N-IP – All Non-Internet Protocol
2. By Source IP Address or Subnet.
3. By Destination IP Address or Subnet.
4. By Source Port (lowest port number first).
5. By Destination Port (lowest port number first).
The modem/router will sort each QoS rule as they are added, and the QoS Rules
Table will be updated to reflect the order with which rules are matched.
Rule Max/Priority & Rule Min/Max Modes
The Rule Max/Priority mode and the Rule Min/Max mode are very similar in
configuration. As the names imply, Rule Max/Priority is primarily based on the
Priority parameter and the Maximum Bandwidth parameter (the Minimum
Bandwidth parameter is not active), while Rule Min/Max is primarily based on
the Minimum and Maximum Bandwidth parameters (the Priority parameter is
not active).
Select the Rule mode radio button in the QoS dialog, then click on the Add...
button to open the Add QoS Rule dialog. Alternatively, select an existing rule
from the table and click on the Modify button to open the modify version of the
same dialog.
Note that there are All check boxes to the right of the IP addresses, Ports, and
Bandwidth fields. When an All box is checked, any range of values is accepted,
and the specific parameter fields are inactivated. Unchecking an All box, as
shown in figure 2-11, activates the fields for that parameter and allows the
values to be edited.
2-14 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 31

Network
NOTE
Figure 2-11
Add QoS Rule, Max/Priority Mode
Selecting the QoS Switching check box at the bottom of the dialog enables
entry of values into the Type, Data Rate, and Timeout fields to be used to
determine when a switch will occur.
Note: This parameter will not be active/selectable unless the modem is a
Remote and Automatic Switching is enabled. QoS Application Switching
must be enabled also for QoS switching to occur. See the section
“Switching” on page 2-39.
In each of these modes, there exists a Default rule at the top of the table that is
preconfigured and can not be removed. This rule can be modified, but the only
active parameter is Enable Filtering.
Protocol
Clicking the Protocol drop-down menu displays the available protocols. Select
the appropriate protocol from the list, as shown in figure 2-12.
When selecting a protocol for a QoS Rule, be aware that the modem/router
allows a very broad selection (such as IP) or a very specific protocol. For example, RTP traffic can consist of UDP portion (for voice or video) and a TCP
portion (for RTP signaling). These could have separate QoS Rules created or all
be included in a single Rule by selecting RTP as the protocol.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-15
Page 32

Network
Figure 2-12
Protocol Drop-Down Menu
Priority
This field is active for Rule Max/Priority mode only.
A Priority level from 1 (highest) to 9 (lowest) is assigned for each flow using
the Priority field. The modem/router classifies each packet that is to be
forwarded over the satellite using the priority assigned for the selected Protocol.
Any packet that does not meet a QoS Rule is assigned to the Default Rule and
will be assigned a Priority of 9. Priority 1 packets will be forwarded immediately, Priority 2 packets will be forwarded as soon as there are no priority 1
packets in the queue, and so on. Any latency-critical traffic, such as VoIP/RTP
should always be assigned Priority 1.
Enable WRED
Selecting the Enable WRED (Weighted Random Early Detection) check box in
the dialog shown in figure 2-11 enables this function in the modem/router.
WRED allows for more graceful dropping of packets, as QoS queues get full.
Without WRED, output buffers fill during periods of congestion. When the
buffers are full, all additional packets are dropped. Typically, packets are
dropped based upon a simple tail drop algorithm applied to packets as they were
being added to the QoS queues. This can result in large numbers of contiguous
packets being dropped all at once, which causes many protocols such as RTP
and TCP to ungracefully degrade performance in an over-consumed or bursty
scenario.
WRED applies a randomization, which means that the percentage change to
dropped packets increases as the queue becomes full, and minimizes the
2-16 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 33

Network
chances of global synchronization. Thus, WRED allows the transmission line to
be used fully at all times.
Enable Filtering
QoS allows specific flows to be designated as “filtered,” so the modem/router
will discard traffic that the user does not want to forward over a satellite link.
Selecting the Enable Filtering check box enables filtering.
IP Addressing
Specific Source and Destination IP Addresses can be specified for a rule, if
desired.
Source and Destination Ports
Selecting Source and Destination Ports should only be done if the user is aware
of the port used by the desired protocol or application. There are well known
ports for various protocols, but often only command messages use these specific
ports and data is transferred through a negotiated port.
Either specific port numbers or a range of ports can be entered using the Source
Port and Destination Port Minimum and Maximum fields.
Minimum & Maximum Bandwidth
Minimum and Maximum Bandwidth values can be assigned to a flow to restrict
the bandwidths that any particular flow will utilize. The default of no bandwidth
restriction can be set by selecting the All check box.
Note that, for Rule Max/Priority, no minimum bandwidth restriction is applied
(0 bps) and can not be edited. For Rule Min/Max, a minimum value can be
assigned to the flow that allows a committed information rate (CIR) to be
applied to a user-defined class of traffic.
Tip: Once the QoS rules are defined, each type of traffic flow should be
isolated and sent to verify that it is being sent using the intended QoS rule.
Using the QoS Queue Statistics feature in the modem unit’s CLI, the traffic
flows for all of the defined QoS rules can be monitored. Statistics
displayed include the packet rate, drop rate, transmit rate, and active
flows.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-17
Page 34

Network
Diff Serv QoS Mode
Selecting the Diff Serv Mode radio button displays the QoS dialog appearance
shown in figure 2-13. This selection makes the target unit fully compliant with
the Differentiated Services QoS standards. All rules are preconfigured.
Figure 2-13
QoS Tab, Diff Serv Mode
Rules can not be added, removed, or cleared. To modify the bandwidth settings
for a rule, select the rule and click on the Modify button. Uncheck the All box to
edit the Bandwidth settings, as shown in figure 2-14.
2-18 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 35

Network
Figure 2-14
Modify DiffServ Rule
Class Selector DiffServ Code Points (DSCP)
Some implementations of DiffServ will prioritize traffic by Class Selector
assignment. This is defined in the DiffServ Code Points (DSCP) within the IP
header. The first 3 bits of the DSCP define the Class Selector Precedence (or
Priority), as shown in table 2-1.
Table 2-1
Class Selector DSCP
DiffServ Code Points (DSCP)
Modem/Router
Priority
Precedence 1 001 000 1
Precedence 2 010 000 2
Precedence 3 011 000 3
Precedence 4 100 000 4
Precedence 5 101 000 5
Precedence 6 110 000 6
Precedence 7 111 000 7
Default 000 000 9
The modem/router will prioritize the traffic based upon the DSCP Class Selector Precedence.
NOTE
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-19
Note: All traffic that does not have the DSCP Class Selector Precedence
defined (000 000) will be placed in the Default Queue and have a Precedence of 9.
Page 36

Network
Expedited Forwarding and Assured Forwarding DSCP
Another implementation of DiffServ uses all 6 bits of the DSCP to define Expedited and Assured Forwarding, as shown in table 2-2.
Table 2-2
DiffServ Type Class Selector DSCP
Expedited Forwarding Precedence 1 101 110 1
Assured Forwarding – Class 1 Precedence 8 001 xx0 8
Assured Forwarding – Class 2 Precedence 8 010 xx0 8
Assured Forwarding – Class 3 Precedence 8 011 xx0 8
Assured Forwarding – Class 4 Precedence 8 100 xx0 8
Expedited and Assured Forwarding, DSCP
Modem/Router
Priority
Expedited Forwarding (EF) DSCP
This defines premium service and is recommended for real time traffic applications such as VoIP and video conferencing.
Assured Forwarding (AF) DSCP
This defines four service levels and also uses the last three bits of the DSCP to
define the Drop Precedence (Low, Medium, or High). The Drop Precedence
determines which packets will most likely be dropped during periods of over
congestion, similar to WRED. As a result, each of the four AF service levels
also have three Drop Precedence levels for which the modem/router provides 12
separate queues.
Minimum Bandwidth (AF only)
The minimum bandwidth specification can be assigned to a flow that allows a
committed information rate (CIR) to be applied to user-defined classes of traffic, or the default of no minimum bandwidth can be selected.
Maximum Bandwidth (AF only)
This can be assigned to a flow to restrict the maximum bandwidth that any
particular flow will utilize, or the default of no bandwidth restriction can be
selected.
NOTE
2-20 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Note: Minimum and Maximum Bandwidth is only configurable for each of the
four Assured Forwarding classes.
Page 37

Network
Typically, DiffServ is implemented using exclusively Class Selector DSCP or
exclusively Expedited and Assured Forwarding DSCP. The CDM-570/570L is
fully DiffServ compliant and will work with either DiffServ implementation or
with a combination of both.
IGMP
NOTE
Note: If the IGMP feature (FAST code) has not been purchased for this
modem, the IGMP menu item will not be displayed.
Selecting the Enable IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) box on the
IGMP dialog shown in figure 2-15 enables the receive portion of a modem unit
to use the modem as an IGMP server. The transmit portion of the terminal
utilizes the modem as an IGMP client. The IGMP dialogs configure the unit to
report an interest to join a Multicast group on an IGMP server. IGMP is used to
regulate multicast traffic on a LAN segment to prevent information of no interest from consuming bandwidth on the LAN.
Figure 2-15
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-21
IGMP dialog
Page 38

Network
Modem as IGMP Server
Figure 2-16
IGMP Server dialog
Query Period
The IGMP protocol requests that a server periodically publish to users on the
LAN the multicast IP Addresses that it can service. The IGMP Query Period
defines the time interval (in seconds) between each of these queries for
membership.
Maximum Response Time
The IGMP Maximum Response Time defines the time interval (in seconds) that
the unit should wait before it assumes that no parties are interested in the
content published via an IGMP query. This option is expressed in seconds and
the maximum response time that is accepted by the unit is Query Period minus
two seconds.
Number of Missed Responses Before Leaving IGMP Group
The number entered in this dialog box defines the number of membership
queries that go unanswered from LAN clients before the Ethernet interface will
no longer forward data for that IGMP group.
2-22 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 39

Network
For example, assume that a modem/router has the IGMP Query Period set to 60
seconds and the Number of Missed Responses set to 3. If a client joins an IGMP
group, then the service to that group will not be discontinued until no clients
respond to a query from the unit for a period of 60x3=180 seconds.
Modem as IGMP Client
NOTE
Note: If the unit is a CDD-56X, it cannot operate as an IGMP client and the
options in the Modem as IGMP Client dialog box will be grayed out and
unavailable.
Figure 2-17
IGMP Client dialog
Recognize IGMP Queries
The Recognize IGMP Queries box determines whether the modem/router will
respond to periodic queries from an IGMP server that publishes a request to join
a specified multicast group. If this box is selected, the unit will respond to an
IGMP query by requesting to join a multicast group published by the server that
is defined in the unit’s route table.
If this box is not selected, the modem/router will not respond to IGMP queries
from a server. In this type of configuration, the unit is configured to uncondi-
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-23
Page 40

Network
tionally request to join an IGMP group at an interval specified in the Unsolic-
ited Report Interval dialog box (see below).
Version
Selecting either the V1 or V2 radio button determines which version of the
IGMP protocol will be used when attempting to join a group on a multicast
server via an unsolicited report. When the modem/router is configured to recognize IGMP queries, it will respond to a query in the same version that the server
used to initiate the query.
Router Alert Option for V1 Report
Selecting the Router Alert Option for V1 Report option enables a specialcase ability to use some Cisco routers which require the definition of a router
alert option to recognize a report from a client to join a multicast group. The IP
Router Alert Option is defined in RFC2113 and was introduced by Cisco.
While this option is not part of the IGMP standard, most IGMP V2 implementations contain this option.
Check whether or not your router requires this option as most implementations
of IGMP V1 do not contain this option. This parameter is defined for those
special cases, in which a Cisco router is configured as an IGMP V1 server, to
prevent possible conflicts in networks.
If the box is selected, the modem/router will generate IGMP reports to join
multicast groups as specifically required by some Cisco router configurations. If
the box is not selected, the unit will generate IGMP reports to join multicast
groups as defined and implemented by most IGMP servers.
Unsolicited Report Interval
The Unsolicited Report Interval dialog box configures the modem/router to
generate unsolicited reports to join a multicast group at specified time intervals.
Each unsolicited report to join a multicast group will use the version of the
IGMP protocol as specified by the IGMP version being used.
The value entered for this parameter specifies the number of seconds between
unsolicited reports. Entering a zero in the dialog box means no unsolicited
reports to join a Multicast group will be generated by the unit.
2-24 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 41

Network
Managed Switch
The parameters in this dialog are not supported in Vipersat networks. Refer to
the modem’s user documentation for additional information.
Figure 2-18
Managed Switch dialog
VLAN
The Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) dialog supplements the VLAN
Priority/Max QoS mode selection, and allows configuration of tagged identifiers. VLAN tags are compatible with the VMS and Vipersat networks, but automatic switching on tags is not available.
NOTE
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-25
Note: IP Header Compression FAST feature code must be purchased and
enabled in order for a modem to pass VLAN tags.
The VLAN table listing allows Add, Modify, and Remove operations for setting
the Identifier, Priority, Tag, and Name attributes.
Page 42

Network
Figure 2-19
VLAN dialog
2-26 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 43

Vipersat
Vipersat
NOTE
Note: If the Vipersat feature (FAST code) has not been purchased for this
modem, the Vipersat menu item will not be displayed.
Clicking the Vipersat menu item displays the dialog shown in figure 2-20. This
parameter set is used to configure the modem unit with the function (role) it is to
perform in the Vipersat network and to assign associated attributes.
Figure 2-20
Vipersat dialog, Hub Unit
Role Designation
A Comtech modem/router is a flexible network component able to perform
different functions, depending on how it is used in a network. Table 2-3 lists
some typical network functions and the corresponding network role a modem
unit must have to perform its functions.
Using the radio buttons in the Role Designation box shown in figure 2-20, the
modem/router can be configured to function as a Hub or as a Remote.
In addition, the unit can be designated as an Expansion Unit for either a Hub
(switched) or a Remote (mesh) by selecting the check box. This configures the
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-27
Page 44

Vipersat
unit demod to operate in SCPC mode and to be available as a resource for dedicated communications with the other end of the satellite link.
Table 2-3
Modem/Router Network Function Hub Remote Expansion
Hub Burst Controller providing STDMA Timing
Maps
Hub Switched Demodulator
Remote STDMA Modem
Remote Mesh Demodulator
Vipersat unit Network Functions and Roles
X
XX
X
XX
Enable VFS
To allow the use of the Vipersat File Streamer with this unit, select the Enable
VFS check box.
Enable Heart Beat
Active for Hub units only.
The Heart Beat feature is a redundancy heart beat message for primary Hub
units that provides the option for a periodic communications check message to
be sent from the Hub modem to the VMS for backup recovery in N:M redundancy (protected) configurations.
Enable SOTM
Active for Hub units only.
The SOTM (Satellite On The Move) feature enables RIPv2 (Routing Information Protocol) in forward routes, providing dynamic updates to the routing table.
This allows routing configurations for Remotes to be written by the VMS via
the Hub TDM. When the VMS writes the routes, the TDM unit will generate a
RIPv2 routing update to its default gateway, specifying the new hop router for
the Remote. This will ensure that the edge router has a current table of routes to
all of the remote sites.
In applications utilizing SOTM where multiple TDMs share one router, this
option should be enabled because of the potential that the Hub TDM may
change, and thus the path to the default gateway to the Remote will change as
well. It is not necessary to enable this option when each TDM has its own
router.
2-28 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 45

Vipersat
Refer to the Vipersat VMS User Guide for implementation details.
Carrier Inhibit Timer
The Carrier Inhibit Timer parameter provides a time period to be specified
that controls when a Remote modem should mute its transmitter in the event
that there is a loss of link with the Hub. This feature is useful, for example, in an
SNG application for a mobile Remote whose antenna is no longer aligned with
the satellite and should not continue to transmit the carrier signal.
Hub Timer Setting
In a Hub unit, this parameter provides a fixed setting that can be specified for
the keep alive message sent to the Remote(s). This provides an alternate to the
Burst Map, which is variable and may become excessively long in certain applications.
When implemented, this setting is made at either the TDM outbound unit or a
switched demod.
Note that this timer setting should be at least three times faster (shorter in duration) than the timer setting at the Remote(s) to ensure that network links are
maintained.
Remote Timer Setting
In a Remote unit, this parameter provides a setting for how long the Remote has
not received the Burst Map from the Hub STDMA Controller before that
Remote mutes its transmitter.
Note that this timer setting should be at least three times greater (longer in duration) than the timer setting at the Hub to ensure that the nework link is maintained.
Network ID
The Network ID designation defines to which network the modem/router
belongs. All devices in a common network will have the same network ID.
The network ID is used by the VMS to identify Vipersat units within a network
and allows the VMS to manage multiple networks, each with its own unique
network ID number.
Database Version
The version number is read-only and displays the version of the firmware
running in this modem unit.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-29
Page 46

Vipersat
Node Name
Enter a name (sixteen characters or less) for the node which helps identify the
Vipersat unit on the network.
Multicast Management Address
The Multicast Management Address is the multicast IP address assigned to all
modem units in the Vipersat network that are managed by the VMS. This
address must match the VMS Transmit Multicast Address.
When the modem unit receives a multicast from the VMS server, it receives
maintenance and control packets, including the server’s IP address. The unit
responds to the VMS server with a unicast containing its current configuration
data, including the unit’s IP address.. When the VMS receives the unicast
response, it registers the unit on the network.
STDMA
Clicking the STDMA menu item will display the Selective TDMA dialog
shown in figure 2-21.
The fields available for edit on this dialog will vary, depending on the function/
role that this modem unit is performing in the network.
For example, the CDM-570/570L shown in figure 2-21 is operating as a Hub.
All of the fields except for Enable Power Hunt appear. In contrast, the screen
shown in figure 2-22 shows a CDM-570/570L configured as a Remote, with
only a subset of fields available for edit.
If the unit is configured as an Expansion Unit — for either a Hub or a Remote
— the only STDMA option available is the Power Hunt setting.
Enable STDMA
Selecting the Enable STDMA check box enables Selective TDMA on this unit.
This option must be selected for a Remote that is to be included in the STDMA
Burst Map, for example.
Enable Power Hunt
The STDMA Power Hunt feature is active for Remote modems only, as shown
in figure 2-22. Should link reception from a Remote be incorrect or impaired
(e.g., poor environmental conditions), the STDMA Power Hunt feature is an
option on the Remote modem that automatically adjusts the Remote transmit
2-30 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 47

Vipersat
power to ensure that burst map acknowledgements from that unit are received
by the Hub burst controller.
Figure 2-21
STDMA dialog, Hub Unit
When enabled, the burst controller sets a flag in the burst map that indicates it is
not receiving acknowledgements from an enabled Remote. When the Remote
receives the burst map, it will see the flag and automatically increase power by
3 dB above the default or Home State setting. If this closes the link, the burst
controller will clear the flag. Note that if the 3 dB increase is more than is necessary, DPC will make a down adjustment to the appropriate level and this adjustment will be added to the DPC Offset.
This feature is enabled by selecting the check box.
Enable Low Data Rate Fast Acquisition
Configurable on a Hub Burst Controller only.
Selecting this check box enables the Vipersat Burst Fast Acquisition Timing
(BFAT) feature that functions at low data rates (64 kbps to 256 kbps). This
feature allows for significantly faster acquisition times at these data rates, even
with higher noise, resulting in improved efficiency of the shared STDMA chan-
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-31
Page 48

Vipersat
nel. Since signal lock is faster at higher data rates, BFAT is not active above 256
kbps.
NOTE
Note: Note that this parameter is only active for units that have the BFAT FAST
feature code installed.
Modems must be operating at either 3/4 QPSK or .95 QPSK in order to
utilize BFAT.
Figure 2-22
STDMA dialog, Remote Unit
Allocation Method
Active for Hub modems only.
When the CDM-570/570L is being used as a Hub, it has five STDMA modes of
operation which define the method VMS uses to allocate bandwidth. Select one
of these modes from the drop-down Bandwidth Allocation Method menu
shown in figure 2-23.
•Fixed – All remotes get the same size slot, regardless of each remote’s
activity
• Dynamic Slot – size is adjusted each cycle depending on activity during
the previous cycle
2-32 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 49

Vipersat
• Dynamic Cycle – A dynamic cycle allows changing the cycle time, and
corresponding latency, as loads change always providing minimum
latency for the current traffic load.
•GIR – Guaranteed Information Rate allows assigning a guaranteed data
rate to a channel.
•Entry Channel – Entry channel mode provides an on-demand channel for
applications such as a mobile remotes.
NOTE
Figure 2-23
Note: If the Hub STDMA mode is either GIR or Entry Channel, normal load
switching is automatically disabled. In GIR mode, the Remote is
switched to SCPC as soon as the GIR threshold is reached, if there is a
switch rate defined. In Entry Channel mode, the Remote is switched to
SCPC as soon as the Hub receives the first transmission from the
Remote.
Bandwidth Allocation Method
Dynamic Cycle
In the Dynamic Cycle bandwidth allocation method, available bandwidth is
allocated to remotes proportionally based on their current bandwidth needs. The
bandwidth requirements are determined by the number of bytes in queue for
each remote divided by the total number of bytes in queue for all remotes to
determine the percentage of bandwidth to allocate for each remote.
Dynamic Slot
In the Dynamic Slot mode, the slot size for each remote is computed based on
the time (at the current data rate) needed to transmit all the Bytes in Queue. If
the result is less than the minimum slot size or more than the maximum slot
size, the slot is adjusted accordingly.
Entry Channel
The Entry Channel Mode (ECM) is the same as Dynamic Cycle mode, except
that as soon as the Hub receives an STDMA ACK, it initiates a switch to SCPC
mode based on the policy set for that remote.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-33
Page 50

Vipersat
The Entry Channel mode is designed to accommodate the needs of remotes that
will not be continuously connected to the network, but which have the need to
be able to make an on-demand connection when required, such as in a mobile
remote.
NOTE
Note: In ECM mode, the switch occurs as soon as the Hub receives an STDMA
ACK even though there may not be traffic at that time.
Fixed
In the Fixed mode, all remotes have the same slot size regardless of the type of
traffic or load.
No calculations are made to actively change slot size when operating in this
mode.
GIR (Guaranteed Information Rate)
In the GIR mode, the initial computed slot size value is the same as the
Dynamic Cycle mode except there is no maximum limit. After all remotes have
been assigned slots, the burst map is checked to see if the total cycle length
exceeds one second. If not, then all requirements are satisfied and the burst map
is complete. However, if the cycle is greater than one second, then the slots are
adjusted proportionally so that all remotes receive at least their guaranteed rate,
plus whatever excess is still available.
When the one second restriction is exceeded, remotes without a specified GIR
are reduced to the global minimum slot size and the remaining bandwidth is
distributed to remotes that have been assigned a GIR value. Remotes assigned a
GIR bandwidth allocation are given available excess bandwidth when needed.
NOTE
Note: GIR allocations are restricted so that assigned GIR totals cannot exceed
the available bandwidth to insure proper bandwidth allocation when the
network is overloaded. Attempts to enter a GIR which would result in a
spin time of more than one second will error out.
The bandwidth allocation method selected will determine which of the associated parameters are available and applicable for that allocation method.
Depending on the capability of the CDM-570/570L and its function in the
network, some of the following parameters may be grayed out and unavailable.
Group ID
Active for both Hub and Remote modems.
The STDMA group ID number defines a group of equipment which will
respond to the output of a single STDMA burst controller. This group is
2-34 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 51

Vipersat
addressable within a network which, in turn, is defined by the network ID
number assigned to the modem/router.
In an STDMA group, the allocation of bandwidth is shared among the associated remotes. Depending on the number of remotes in a network, a Hub may
have multiple burst controllers, each with its own set of remotes. This is accomplished by assigning a unique Group ID number to each controller and its
remotes.
NOTE
Note: The STDMA group number and the network ID are independent. There
can be multiple STDMA groups within a single network.
Slot Data Length
This parameter is active for the Hub modem only.
The Slot Data Length fields specify the data length, in milliseconds, for each of
the remotes in the STDMA group, and represents the amount of data that can be
transmitted or received in one spin of the STDMA cycle. This is the amount of
time that the remote is provided in the cycle to send data.
Depending on the Allocation Method that is chosen for the Hub STDMA
controller, the appearance of this parameter will vary:
• Fixed – Slot Length
• Dynamic Slot – Slot Minimum, Slot Nominal
• Dynamic Cycle – Slot Minimum, Slot Maximum
• GIR – Slot Minimum
• Entry Channel – Slot Minimum, Slot Maximum
Stats Collection
Active for Hub modems only.
The burst controller monitors statistics in the received ACK from each remote.
The statistics report the fill status of the STDMA buffers. The burst controller
builds a table of the group and calculates the relative buffer fill for each remote.
It then calculates the length of the data slot for each remote based on the Minimum Slot size plus a percentage of the available bandwidth. Idle remotes would
receive a data slot equal to the Minimum Slot size.
In the Dynamic Slot mode, the dynamic range of STDMA is a function of the
difference between the Nominal Slot size and the Minimum Slot size parameters. The speed with which STDMA reacts to changes in dynamic load is a function of the Stats Collection parameter and the Burst Map Rate parameter.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-35
Page 52

Vipersat
The value entered in the Stats Collection field defines the period of time, in
seconds, over which the CDM-570/570L will collect statistics. A longer time
will average out peak conditions, a shorter time will shorten VMS reaction time
to changing network conditions.
Burst Map Rate
Active for Hub in Fixed or Dynamic Slot only.
The Burst Map Rate field specifies the number of spin cycles that will occur
prior to each broadcast of the burst map by the burst controller to the remotes.
One cycle is the amount of time it takes for all remotes in a group to burst on the
common channel. The burst map provides each remote with its allocated bandwidth and position in the cycle.
For Dynamic Cycle, GIR, and Entry Channel modes, the number of cycles is
automatically set to one in order to ensure optimum performance for these Hub
types.
Preamble
Active for Hub modems only.
The Preamble field specifies the preamble duration, in milliseconds, for the
remotes in the group. This is the period between when the remote begins to
transmit (sends an ACK) to the Hub and when the first data packet is sent. This
allows time for signal lock to occur before data is sent, thus preventing data
loss.
Higher data rates allow for a shorter preamble, since it is easier to achieve signal
lock.
Tip: Refer to the Viper Calculator for determining preamble length values to
enter at the command prompt. For a copy of the latest Viper Calculator,
contact your Comtech Vipersat Networks representative.
NOTE
Note: When the Low Data Rate Fast Acquisition feature is enabled, the Pream-
ble length is set automatically for the unit.
Guard Band
Active for Hub modems only.
The Guard Band field defines the length of the guardband, in milliseconds, for
the remotes in the group. The Slot Guardband is the amount of time between the
point when one remote completes transmitting data and the point when the next
2-36 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 53

Vipersat
remote in the cycle begins transmitting. This delay prevents the remote from
overrunning the next terminal in the cycle.
The setting for this parameter should be obtained using the Vipersat STDMA
Calculator.
Remote List
Appears for Hub modems only.
Clicking the Remote List menu item below STDMA brings up the STDMA
Remote List dialog shown in figure 2-24.
Figure 2-24
STDMA Remote List, ECM
Use the buttons at the bottom of the dialog to perform the following actions:
• Add/Insert - Clicking the Add (Insert when a remote is selected) button
displays the Remote Entry dialog (figure 2-25). Use this dialog to enter
the Name of a remote, the remote’s IP Address, and to either disable or
enable the remote with the Disable check-box.
For STDMA set to GIR mode, enter the Switch Rate and the GIR value to
be used by this remote.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-37
Page 54

Vipersat
For STDMA set to ECM, enter the SCPC Data Rate and the Switch Type
to be used by this remote.
Figure 2-25
Remote Entry dialog, ECM
•Remove - Selecting a remote from the list, then clicking the Remove
button will remove the remote from the VMS.
•Disable - Selecting a remote from the list, then clicking the Disable button
will disable the selected remote.
•Modify - Selecting a remote from the list then clicking the Modify button
will display the Remote Entry dialog shown in figure 2-25, allowing the
information for the remote to be edited.
•Sort - Clicking the Sort button will sort the remotes in the list
•Clear - Clicking the Clear button will clear all remotes from the list.
Automatic Remote Removal
Appears for Hub modems only.
Selecting the Remote Removal menu item below STDMA displays the Automatic STDMA Remote Removal dialog shown in figure 2-26. Clicking the
Enable Remote Removal check box activates the editable fields in this dialog
that provide settings to define when an associated remote will be removed from
the group.
2-38 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 55

Vipersat
Figure 2-26
Automatic Remote Removal
Timeout
The value entered in the Timeout field determines the number of cycles with no
connection (received ACKs) before a remote is removed from the network (the
burst map). This would be used, for example, where a mobile remote has
finished its assignment and has shut down.
After the number of cycles entered in the dialog above, the remote is removed
from the network and the bandwidth resources it had been using are available
for other uses.
Retry
The Retry field value determines the number of cycles which are allowed to
pass, following the removal of a remote, before that remote is returned to the
burst map and an attempt is made to re-establish a link.
This allows, again using a mobile remote as an example, shutting down the
remote at one location, moving it to a new location, and then automatically reestablishing a connection to the satellite network.
Switching
For a detailed description of Automatic Switching in the VMS, refer to the
Vipersat Management System User Guide.
Clicking the Switching menu item displays the dialog shown in figure 2-27.
The fields available for edit on the sub-menu dialogs will vary, depending on
the function/role that this modem unit is performing in the network.
The Vipersat Automatic Switching feature allows the modem unit to automatically adjust to varying bandwidth demands in the Vipersat network by switching between STDMA and SCPC. Automatic Switching must be enabled on a
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-39
Page 56

Vipersat
modem that will be required to send switching requests to the VMS in response
to either traffic type (Application switching) or network traffic loads (Load
switching).
Use the Enable Automatic Switching check box to enable/disable the Automatic Switching feature for this modem.
Figure 2-27
Switching dialog
Application Switch Detection
Application switching can be enabled for Video, Voice, Quality of Service
(QoS), and/or Type of Service (ToS) by selecting the appropriate check box in
the Application Switch Detection dialog (figure 2-28). Application switching
controls are only available on units configured as remotes.
NOTE
2-40 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Note: Load switching by VMS is not affected by this setting.
Application switching is capable of changing the bandwidth used, but the
change is determined entirely by the type of application being requested while
ignoring load requirements.
Page 57

Vipersat
Figure 2-28
Application Switch Detection, Remote Unit
In a system configured for application switching, the remote site CDM-570/
570L looks for a packet in the data stream coming from the LAN that is configured using the H.323 stack protocol and contains an H.225 signaling protocol.
VMS also recognizes and supports SIP signaling.
The packet is first examined to determine the port number, then, from the allocated port ranges, determines the type of application being sent.
The CDM-570/570L sends a switch request to the VMS requesting a carrier for
the application type.
Each application type will have been assigned a bandwidth allocation when the
policy for the remote site is established. A voice application, for example might
have had the bandwidth set in the policy to handle three simultaneous voice
connections. When a VoIP protocol is detected in the H.225 signaling protocol,
the CDM-570/570L requests the VMS to switch the bandwidth to accommodate
three voice circuits.
The same process applies if the protocol detected is Video.
When both VoIP and Video are requested, the bandwidth required for the Video
is used and the VoIP, which has priority, shares the SCPC with the Video.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-41
Page 58

Vipersat
Once the VMS receives the request to switch, it determines if there is a free
demodulator and whether there is bandwidth space available to handle the
requested application. If the resources are available, the VMS then performs the
switch.
Applications are streaming data. The remote CDM-570/570L looks at the
streaming data flow until it sees a break in the data exceeding 10 seconds. Once
a break is detected, the CDM-570/570L presumes that the application is terminated (or has malfunctioned), drops the carrier, and makes the bandwidth
resources available for another service.
Video Switching
Select the Video switch detection option to configure the CDM-570/570L to
recognize the presence of a video signal and request a switch by the VMS.
Voice Switching
Select the Voice switch detection option to configure the CDM-570/570L to
recognize the presence of a voice signal and request a switch by the VMS.
Quality of Service Switching
Select the Quality of Service switch detection option to configure the
CDM-570/570L to request a switch from VMS as determined by the parameters
entered for QoS, as described in the section “QoS” on page 2-10.
QoS Rule based switching is a flexible and powerful mechanism for initiating a
Vipersat switch from STDMA to SCPC mode. This feature allows traffic to be
prioritized in situations where bandwidth availability exceeds demand. QoS
based switching, in addition to prioritizing traffic, will anticipate increased
demand and preemptively allocate more bandwidth as required.
NOTE
2-42 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Note: The DiffServ Mode is not supported for QoS switching.
Caution: If the QoS switching rule is not carefully defined, it is possible to
generate many more switches resulting in using more bandwidth than
intended. This is because the QoS rules can be defined very
generally but switches are done based on the concept of a flow which
is defined as a unique combination of the following parameters:
source IP and port, destination IP and port, and protocol.
For example, if a rule is defined for UDP traffic with no restrictions on
IP or Port, then each time the system detects a new stream of traffic
with a new IP address or port number, another switch will be made.
Page 59

Vipersat
Channel Table Signaling Detection
This feature is no longer supported.
ToS Switching
Select the Type of Service switch detection check box to enable the ToS detection function for this unit.
Applying a ToS value to an application (VoIP, IPVC, or priority data) through
either preservation or classification packet stamping, allows the Vipersat
switching system to function in an encrypted network.
NOTE
Note: In addition to setting the CDM-570/570L to recognize ToS enabled traf-
fic, the ToS switch type must be included in the subnet or global policy
statement in order for the VMS to act on the switch request.
To configure the ToS switching parameters, click the ToS List menu item
below Application.
Figure 2-29
Type of Service Switching List
Clicking the Add button displays the Type of Service Entry dialog shown in
figure 2-30.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-43
Page 60

Vipersat
NOTE
Figure 2-30
Type of Service Entry
Using the drop-down menu in the ToS Code box, select the number identifying
the type of service to be made. Numbers from 1 to 63 are recognized by the
VMS as ToS codes.
In the Switch Type box, enter the number to assign for this switch type.
Numbers from 64-254 are recognized as switch types, with switch type 254 preassigned for limited priority switching. Switch type 1 is pre-assigned for Voice
and switch type 2 is pre-assigned for Video.
Note: Setting the switch type value to 254 will not allow any other switches to
occur until it is taken down. The 254 switch type affects all types of
switching including ToS, VESP, and QoS. While a 254 type switch is in
effect, the VMS continues to track switching requests then will resize to
meet these bandwidth requests when the 254 type switch is completed.
In the Name box, enter the identifying name for the ToS switch type that is
being created.
The Switch Rate (kbps) can be any value between 0 and 5000. Realistically in
an operating circuit, depending on the settings for modulation and FEC, this
value should not exceed 9.98 MHz.
The Timeout (seconds) can be any value between 0 and 60 and is the value
used to determine how long that no data is detected before closing the circuit.
Normally in a non-encrypted Vipersat network, packets are classified by the
remote CDM-570/570L using protocol classification detection and the results
are forwarded to the VMS via Automatic Switch Request (ASR) messages. The
VMS switch detector service then applies the requested bandwidth using policies which have been pre-configured in the VMS.
For example, in a non-encrypted network, if a voice application service connection is started, the CDM-570/570L’s classifier analyzes signaling and data
protocols (H.323, SIP, & Data RTP) being routed through the modem. After
2-44 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 61

Vipersat
connection detection, the process waits for data (RTP). Data is normally sent
after the receiving party answers, which then triggers the system to process an
ASR.
NOTE
NOTE
Note: ToS switching differs from other application switching in that a ToS
switch passes a data rate to the VMS.
Using the ToS classification, the detection function allows application-based
switching in encrypted networks where the signaling protocols are encrypted or
effectively hidden.
Note: Load switching by the VMS is not affected by enabling ToS detection.
Load Switching
Load switching allows SCPC switching to occur to meet bandwidth requirements in response to changing network traffic loads. Use the Enable Load
Switching check box to enable/disable this feature.
Figure 2-31
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-45
Load Switching, Remote Unit
Page 62

Vipersat
Note: Load switching must be enabled on all CDM-570/570Ls in a network in
NOTE
order for the VMS to utilize load switching when dynamically optimizing
network performance as load conditions change.
If the application rate is less than the load, the VMS will not switch. It will,
however, set up SHOD (Single Hop on Demand) if the application
requires it.
Application switching by the VMS (such as Voice and/or Video) is not
affected by this setting. However, using Load switching for real-time
applications is not recommended.
The appearance of parameters for Load Switching will differ, depending on
whether the unit is configured as a Hub or as a Remote.
SCPC Step Up Threshold
Appears for Remote modems only.
The SCPC Step Up Threshold field establishes the percentage of bandwidth
use that will trigger a switch up from the present SCPC rate to a higher rate to
ensure that there is sufficent bandwidth available for current conditions. Valid
range is from 65 to 100 %.
Typically, the default value will be acceptable, but this value can be changed to
accommodate a unique network configuration or application. Note that this
value must be greater than the value specified for the SCPC Step Down Thresh-
old (see below).
SCPC Step Down Threshold
Appears for Remote modems only.
The SCPC Step Down Threshold field establishes the percentage of band-
width use that will trigger a switch down from the present SCPC rate to a lower
rate to ensure efficient bandwidth usage. Valid range is from 1 to 95 %.
Typically, the default value will be acceptable, but this value can be changed to
accommodate a unique network configuration or application. Note that this
value must be less than the value specified for the SCPC Step Up Threshold (see
above).
SCPC Step Delay
Appears for Remote modems only.
The SCPC Step Delay field allows a switching delay period to be specified to
ensure that a premature switch up or down in the SCPC rate does not occur due
to a temporary rise or fall in traffic.
2-46 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 63

Vipersat
Typically, the default value will be acceptable, but this value can be changed to
accommodate a unique network configuration or application.
SCPC Step Up Excess
Appears for Remote modems only.
The SCPC Step Up Excess field allows adding a fixed percentage to the channel bandwidth request to accommodate additional bandwidth requirements
which may occur after a switch is made. This excess is added each time an
SCPC Step Up switch occurs, and makes additional bandwidth available for
when the demand arises while minimizing Step Up switching events.
A default value is provided and need not be changed unless it is known that
there will be a larger bandwidth requirement after the switch.
STDMA Slot Capacity
Appears for Hub modems only.
The STDMA Slot Capacity field allows setting the threshold or level of slot
capacity at which the Burst Controller sends a switch request to the VMS to
switch the Remote from STDMA mode to SCPC mode.
Typically, the default value will be acceptable, but this value can be changed to
accommodate a unique network configuration or application.
STDMA Switch Delay
Appears for Hub modems only.
In order to minimize unnecessary switching due to transient conditions, such as
a temporary spike in network traffic for example, the STDMA Switch Delay
parameter is provided. This setting is used to specify a delay before the Burst
Controller sends a switch request to the VMS to switch the Remote from
STDMA mode to SCPC mode.
Typically, the default value will be acceptable, but this value can be changed to
accommodate a unique network configuration or application.
Percent Allocation
Appears for Hub modems only.
The Percent Allocation field allows adding a fixed percentage to the channel
bandwidth request to accommodate additional bandwidth requirements which
may occur after the switch is made from STDMA to SCPC mode.
Typically, the default value (10 %) will be sufficient, but if there may be a
larger bandwidth requirement after the switch, this value can be increased. In
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-47
Page 64

Vipersat
choosing a value for this allocation, future bandwidth requirements for the channel must be balanced against efficient bandwidth utilization.
Hitless Switching
Unless inherent delays in configuring both ends of a satellite bandwidth link
during dynamic switching are accounted for, transmitted data may be lost
during the transition. The time for a switch command to be sent across the satellite link (~ 250 ms), the command processing time, as well as receiver acquisition time must be considered. The Vipersat Hitless Switching feature provides a
means to coordinate timing and utilize buffering to eliminate these data outages.
Click on the Hitless Switching menu item below Application to display the
dialog shown in figure 2-32.
Figure 2-32
Hitless Switching dialog
Modulator Delay
This field allows the operator to insert additional delay to buffer more data after
modulator transmission is ceased.
2-48 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 65

Vipersat
Demodulator Delay
This field allows the operator to insert additional delay to account for the tuning
of the demodulator.
Lock Times
Lock Time settings for the four data rates displayed can be adjusted either up or
down, but default settings based on satellite testing should be used as a starting
point. These defaults are stored in each modem unit and are restored by clicking
on the Defaults button.
The initial setting is with Hitless Switching disabled—all check boxes are
unchecked, and the lock times are displayed as -1 msec. Selecting the check box
for a data rate will activate the field for that rate, display the current lock time,
and allow that value to be edited.
DPC
The DPC dialog for a Hub or Remote operating in STDMA mode is displayed
in figure 2-33. Note that, for an Expansion unit, only the Speed Up Eb/N0 and
the Target IP Addresses fields are active.
Dynamic Power Control (DPC) is a Vipersat feature that acts to regulate the
transmit power of the Vipersat satellite modem, such that the specified receive
signal level (E
) is met for the receiving Vipersat units in the group. DPC is
b/N0
driven by the receiver demod, which notifies the transmitting modem of the
current E
b/N0
value.
Before enabling DPC, the operator should verify that a demodulator at another
terminal is receiving from this modulator, and that there is a working communications channel from that receiving station back to the modulator terminal
(InBand communications). Additionally, since DPC potentially controls the full
power range of the modulator’s output power, it is recommended that the terminal be commissioned and calibrated before usage.
Warning: Make certain that all CDM-570/570L’s in the network have their
Automatic Uplink Power Control (AUPC) turned off. Although this
Comtech modem function is available for a connection between two
point-to-point units, it will conflict when used in a network using the
network-wide DPC. Using both in a circuit will produce erratic and
unstable operation with potential data loss, low QoS, and potential
loss of the circuit connection.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-49
Page 66

Vipersat
Figure 2-33
DPC dialog
Enable Dynamic Power Control
Selecting the Enable Dynamic Power Control function on the DPC tab
enables the DPC function on the modem/router.
Minimum Power
The set value for the Minimum Power is the minimum level allowed by all
SCPC modulators. Using the values entered in the Home State dialog (see
“Home State” on page 2-52) together with the value entered for the Maximum
Power, the modem scales the Maximum Power to optimize the E
ever data rate the unit is transmitting. For this reason, it is recommended that the
Minimum Power be set to the lowest possible setting (-40.0 dBm), giving the
power adjustment the largest possible working range.
In the majority of applications, the minimum power level parameter can be set
to the default power value of -40.0 dBm. Typically, there is no problem in
allowing the modulator(s) to back off decreasing power levels to better the quality of link conditions.
b/No
for what-
2-50 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 67

Vipersat
Maximum Power
Commissioning a terminal is following the calculated link budget before terminal installation. Using these calculations, the maximum limit for modulator(s)
output power can be determined. This is the value entered in the Maximum
Power field shown in figure 2-33.
If more than one modulator is used at this location, that must also be taken into
consideration and applied to this value set point. The value set point assures that
the maximum power level is within the acceptable range for this modem and the
circuit.
The value entered sets the maximum power level allowed by all SCPC modulators.
Target Eb/N0
Enter the desired operating receive level for closed loop servo control. This is
the value used by the receiving modem’s modulator to control its output power
level.
Speed Up Eb/N0
Normally, the DPC message is sent every 60 seconds from each terminal in the
network. If the target E
Eb/N0 box, the corresponding terminal increases its DPC message send rate to
every five seconds until the target value is greater than the Speed Up E
value. This provides a loop speedup to rapidly regain link quality.
value drops below the value set in the Speed Up
b/N0
b/No
Target Range For No Power Adjust
The Target Range For No Power Adjust sets the differential between the
current E
lator to stop adjusting its power output. The default value for this parameter is
0.2 dB.
and the Target Eb/N0 value that, when reached, causes the modu-
b/N0
Target IP Address
In a VMS network, the VMS automatically assigns the Target IP Addresses.
The user will only need to fill in these addresses if the network configuration is
not a normal VMS configuration and requires a fixed IP address for DPC
communications.
Enter the IP address for the target transmitting site from which this unit will be
receiving. Up to four sites—such as for a CDD-564 quad demodulator—can be
entered.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-51
Page 68

Vipersat
Home State
A Vipersat unit’s Home State consists of those parameters which provide a
known RF configuration that the unit will return to, either as the result of a
command by the VMS, or as it comes back on line from a reset or a power
cycle. These Home State settings are typically selected so that the unit goes to a
configuration which is optimum for its function in the network.
Figure 2-34
Figure 2-35
Home State, Enable STDMA
Home State dialog, Modulator
The Home State menu items allow enabling STDMA, Home State, and Carrier,
and setting the unit’s Transmit and Receive frequencies, data rates, coding rates,
modulation types, and power level (Transmit only) which are applied at bootup.
2-52 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 69

Vipersat
If the modem is a CDD-56X, each of the demodulators has a sub-menu item for
its own unique home state.
As with the CDM-570/570L, each of the CDD-56X’s demodulator home states
should be configured for optimum performance of its function in the network
when the unit is returned to its home state for any reason.
The home state for each demodulator can be individually enabled and each can
have its own unique parameters assigned.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-53
Page 70

Admin
Admin
The Admin dialog allows a user to define the administrative privileges for the
Vipersat unit.
Figure 2-36
Admin dialog
User Names and Passwords
NOTE
2-54 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Note: All User names and passwords are case sensitive.
Up to three levels of log in can be configured. A minimum of one and a maximum of 11 characters can be entered in the User Names and Passwords fields.
Any or all of the user names and passwords can be removed by entering
“NONE” in the field. Removing all user names and Passwords would only
allow access to the IP functions when connected via the Terminal Emulator
(serial port) connection because there is no log in required.
Modify button
To edit the User Names and Passwords fields, click on the Modify button. The
Authentication dialog shown in figure 2-37 will be displayed.
Page 71

Admin
Figure 2-37
For security purposes, the Admin password must be entered before any changes
are allowed. Clicking the OK button will enable the User Names and Passwords
fields, as shown in figure 2-38.
Figure 2-38
Authentication dialog
Admin dialog, Enabled
Enable Ping Reply
Select this check box to have this unit reply to Ping requests.
Enable Telnet
Select this check box to allow a telnet connection to this unit.
Telnet Inactivity Timeout
Enter the time, in minutes, of inactivity before a telnet session times out and is
disconnected from this unit.
Access
The Access dialog allows controlling access to the Vipersat unit by defining up
to four IP and subnet client addresses which are allowed to access the modem.
Restricting access to the unit requires that the Access Enforcement check box
be selected. If this box is checked, only those units with listed Access Client’s
IP addresses can access this modem. All other units will be denied access.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-55
Page 72

Admin
Figure 2-39
Access dialog
For detailed use and explanation of the unit’s access features, please refer to the
section “Access Lists Page” in the unit’s user documentation.
SNMP
Clicking the SNMP menu item displays the dialog shown in figure 2-40. The
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application-layer protocol
designed to facilitate the exchange of management information between
network devices. The Vipersat unit’s SNMP agent supports both SNMP v1 and
v2c.
NOTE
2-56 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Note: For proper SNMP operation, the Vipersat unit’s MIB files must be used
with the associated version of the unit’s base modem M&C and the IP
Controller’s SW. Please refer to the Vipersat unit’s documentation for
information on the required FW/SW compatibility.
Page 73

Admin
Figure 2-40
SNMP dialog
Enable SNMP for Modem Configuration
Selecting the Enable SNMP for Modem Config box, shown in figure 2-40,
enables SNMP on this modem/router.
Tip: The VMS does not use SNMP management messages. Only enable this
function if other software exists on the network which uses this
information.
Enable Authentication Trap
Selecting the Enable Authentication Trap box determines whether a MIB2
authentication trap will be sent when a protocol data unit (PDU) with an invalid
community string is encountered. A community string is invalid when it does
not match the Admin, the Read Write, or the Read Only community strings.
Trap Version
Select either SNMP version 1 or SNMP version 2 using the radio button in the
Trap Version box.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-57
Page 74

Admin
Trap Destination Addresses
Enter the trap destination IP addresses in the Trap Destination Address dialog
boxes. These are the IP addresses where all traps/notifications will be sent. If a
network management application is running in the network, it should be configured to receive traps and its IP address should be entered here.
NOTE
Note: The VMS does not use SNMP trapped messages; do not enter the VMS
server address in this field.
Community Strings
The modem/router uses community strings as a password scheme that provides
authentication before gaining access to the agent’s MIBs. In SNMP v1/v2c, the
community string is sent un-encrypted in the SNMP packets.
Caution: The network administrator must ensure that SNMP packets only
travel over a secure and private network, if security is a concern. A
packet sniffer can easily obtain the community string by viewing the
SNMP traffic on the network.
The community strings are entered into the modem/router using the fields
shown in figure 2-40, and are used to authenticate users and determine access
privileges to the SNMP agent.
The user defines three Community Strings for SNMP access:
• Read Only Community (default = public) — GET community string that
allows GET operations to all portions of the IP Module Controller and
modem MIBs.
• Read Write Community (default = private) — SET community string
that allows SET operations to all portions of the IP Module Controller and
modem MIBs.
• Trap Community (default = public) — Community string that will be set
in the Community field of all outgoing traps. This field on the trap PDU
may be checked by the network manager application to determine if the
trap came from a “trusted” agent.
System Contact
Enter user-defined SNMP contact information in this field.
System Name
Enter user-defined SNMP name information in this field.
2-58 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 75

Admin
System Location
Enter user-defined SNMP location information in this field.
SMTP
Clicking the SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) menu item displays the
dialog shown in figure 2-41, allowing the user to specify the appropriate
settings for the SMTP email server.
Figure 2-41
The SMTP settings are utilized when sending an email via the modem/router’s
Home/Support Web page by a user who is connected to the IP module through a
Web browser. Examples of these settings would be for a network administrator
or technical product support.
Refer to the modem/router user documentation for additional information on
this feature.
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-59
SMTP Tab
Page 76

Admin
Server IP Address
Enter the mail server address from where email is to be sent.
Domain
Enter the domain of the email server (usually found to the right of the @ symbol
in an email address).
Destination Name
Set the email recipient name (typically found to the left of the @ symbol in an
email address).
Compression
NOTE
NOTE
Note: If the Compression feature (FAST code) has not been purchased for this
modem/router, the Compression menu item will not be displayed.
The Compression dialog, shown in figure 2-42, sets the parameters for header
and payload compression in the modem.
This feature only applies to units that have modulators. The parameters are not
applicable to CDD-56X units or to Expansion units, since all demodulators will
automatically detect compressed packets that are received and perform decompression.
Tx Header Compression
If the Enable check box is selected, this modem will transmit packets with
compressed headers.
Note: When compression is enabled, the modem/router checks the HDLC
header to determine whether a received packet has a compressed
header. It is possible, for example, to have header compression enabled
only on some of the modems in a single STDMA group.
The first check box, for L3/L4/L5 (IP, UDP, TCP, and RTP traffic) header
compression, is always set to Enabled and appears grayed out (inactive). This
compression is configured on a per route basis, as described in the section
“Routing” on page 2-7.
2-60 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 77

Admin
Figure 2-42
Compression dialog
The second check box is for setting compression for Ethernet (L2) traffic. This
parameter is active and is configured on a per modem basis.
When L2 compression is enabled, some of the initial traffic sent between two
devices will not be received over the satellite until a full header is transmitted
(based on the Refresh rate). If a ping is sent over the satellite, it will time out
until the full header packet is sent. The header compression refresh rate can be
reduced to minimize the amount of traffic lost when traffic is first sent between
two devices.
The default refresh values (50 packets) reflect the recommended settings for a
typical modem/router used in a VMS network. However, the refresh rates can
be decreased for poor satellite link conditions, or they can be increased to
reduce overhead even further. The valid range is 1 to 600 packet(s).
Tx Payload Compression
When selecting the Per Route Features options for a route, as described in the
section “Routing” on page 2-7, header compression compresses the IP Header
and the TCP/UDP headers. Only traffic past these headers is effected by
payload compression. Payload is considered everything inside the HDLC satel-
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-61
Page 78

Admin
lite frame. Therefore, IP headers could be compressed as well. Payload
compression is an optional feature of the modem and has the following features:
• All modems used in a VMS network operate in router mode requiring that
payload compression be set on a per route basis, as described in the
section “Routing” on page 2-7.
• The compression algorithm is applied to all data (HDLC header excluded).
• Compression statistics are fed back to QoS in order to maximize WAN
utilization while optimizing priority, jitter and latency.
• The modem runs 1024 simultaneous compression sessions to maximize
compression across multiple distinct traffic flows.
• Compression algorithm is not applied to RTP streams because this traffic
is already compressed and would only increase the satellite bandwidth if
compressed again.
Receive payload compression is auto-sensed by a bit carried in packet headers
and the modem unit will perform decompression. This function is always available if the payload compression FAST code option has been purchased.
Triple DES
The Triple DES dialog, shown in figure 2-43, sets the parameters for Data
Encryption Standard in the modem.
Each modulator and demodulator in the modem has a tab for its own unique
DES keys. For example, a CDM-570/570L has one TX Encryption sub-tab and
one Rx Decryption sub-tab, while a CDD-564/564L has no Tx Encryption subtab but has four Rx Decryption sub-tabs. Thus, the DES tab can have sub-tabs
for:
• Tx Encryption Keys
• Rx Decryption Keys
The following discussion applies to the keys on both types of sub-tabs.
A 24 Byte [192-bit] 3xDES key is actually a combination of 3 single DES keys
of 8 Bytes [64-bits]. The DES tab displays each key with spaces separating the
key into 3 sections. In figure 2-43, the Transmit Keys are displayed as:
2222222222222222 4444444444444444 6666666666666666
NOTE
2-62 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Note: The sequence
scroll bar to make it visible.
6666666666666666 does not fully show in the window; use the
Page 79

Admin
Figure 2-43
Triple DES dialog
Using Key1 as an example, consider the first section as Key1A, the second as
Key1B, and the third as Key1C. Data is first encrypted with Key1A and then
decrypted with Key1B and again encrypted with Key1C. So, if a user specifies
all of the three Keys the same, (like 48 ‘1's OR all the characters in DES key the
same) the cumulative effect of 3xDES is just a single DES: when data is first
encrypted with Key1A and decrypted with Key1B, we get back the original
data, and then when encrypted with Key1C, results in a total effect of single
DES key.
Because of this, the user is required to enter unique 64-bit keys. If any 2 sections
of the Key match, the entry will not be accepted and the alert message Each
Segment Must Be Unique will appear. Also, the least significant bit of each
byte in a 3xDES key is reserved for the DES algorithm for parity. Entries of 1,
3, 5, 7, 9, B, D, or F will have all the corresponding bit positions masked. So a
Key entry of:
1111111133333333 5555555577777777 99999999BBBBBBBB
becomes
1010101032323232 5454545476767676 98989898BABABABA
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-63
Page 80

Admin
To edit a DES key, select the desired key and click the Modify button. Use the
up-down arrow buttons to move the selected key to a different position.
Tip: Double-click on the key entry to be modified and the Modify Key dialog
will be displayed.
Enter the value for each of the three portions of the DES key in the Modify Key
dialog shown in figure 2-44, then click the OK button to enter the change.
Figure 2-44
Modify DES Key dialog
2-64 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 81

Maintenance
The Maintenance dialog, shown in figure 2-45, determines what parameters
will be used during the next modem/router reboot and how errors are to be
logged by the unit.
Maintenance
Warning: The selections made in the Maintenance dialog are critical. Selecting
incorrect options can cause the unit to fail.
Figure 2-45
Maintenance dialog
Upgrade Image
Using the radio buttons in the Upgrade Image box determines the image which
will be used during the next firmware upgrade. Selecting Oldest image to be
upgraded is probably the safest selection, as it does not require the operator to
know which of the two images has the most recent firmware. The available
options are:
• Oldest - The oldest available image
• Image 1
Chapter 2 - Using Parameter Editor 2-65
Page 82

Maintenance
• Image 2
Base Modem Image
The radio button options available in the Base Modem Image determine which
image will be used to boot from following a reset of the modem unit.
Enable Redundancy
When a Remote modem is in a 1:1 redundant configuration, this parameter will
be Enabled (checked), and ParamEditor can be used to change this setting to
Disable redundancy (unchecked) for the modem.
Caution: ParamEditor can not be used to Enable Redundancy—it can only
Disable it when it has been Enabled. Once this parameter is Disabled
and the configuration is saved, this parameter will become inactive
(grayed out).
Codecast Address
Enter the multicast address to be used by the modem/router to receive Codecast
messages in this field.
Event Logging
Enable
Selecting the Enable box will enable event logging on the modem/router.
Level
The radio buttons available in the Level box allow selecting the type of data to
be logged:
• Errors only
• Errors and Warnings
• All information
Automatically Save PARAM After CONFIG Change
This parameter is not supported in Vipersat networks, and will appear grayed
out (inactive). Refer to the modem’s user documentation for additional information on this setting.
2-66 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 83

GLOSSARY
ACK A signal used in computing and other fields to indicate acknowledgement, such
as a packet message used in TCP to acknowledge the receipt of a packet.
A
A
PPENDIX
ARP Address Resolution Protocol – A protocol for a LAN device to determine the
MAC address of a locally connected device given its IP address. See also MAC.
ASR Automatic Switch Request – A switch request message generated by older
Vipersat modems (e.g., CDM-570/L) that is sent to the VMS to establish a new
satellite link or adjust bandwidth between source and destination IP addresses.
B
Base
Modem
BER Bit Error Rate (sometimes Ratio) – A measure of the number of data bits
BPS Bits Per Second – A measure of transmission speed. See also Kb/s & Mb/s.
Appendix A - Glossary A-1
The main component in a satellite communications modem that consists of a
circuit board with the modem hardware and firmware and the associated interfaces.
received incorrectly compared to the total number of bits transmitted.
Page 84

BPSK Binary Phase-Shift Keying – A digital modulation technique in which the
carrier is phase shifted +/-180 degrees (two phases). The most robust of all
PSKs, but unsuitable for high data-rate applications when bandwidth is limited
due to encoding just one bit per symbol.
BUC Block Up Converter – An upconverter so called because it converts a whole
band or “block” of frequencies to a higher band. The IF is converted to final
transmit frequency for satellite communications. The BUC is part of the satellite
ODU/transceiver.
C
C-Band A frequency band commonly used for satellite communications (and sometimes
terrestrial microwave). For terrestrial earth stations, the receive frequency band
is 3.625–4.2 GHz and the transmit band is 5.850–6.425 GHz. See also Ku-band.
CDD Comtech Data Demodulator
CDM Comtech Data Modem
CIR Committed Information Rate – The guaranteed minimum bandwidth assigned
to a remote terminal.
CLI Command Line Interface – A mechanism for interacting with a computer oper-
ating system or software by typing commands to perform specific tasks.
Codecast A network coding based ad hoc multicast protocol well-suited for multimedia
applications with low-loss, low-latency constraints. Because data is streamed
with no verification, high delivery ratios are obtained with very low overhead.
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check – A method of applying a checksum to a block of
data to determine if any errors occurred during transmission over communications links.
CXR Carrier – A radio frequency transmission linking points and over which infor-
mation may be carried.
D
DAMA Demand Assigned Multiple Access – A process whereby communications links
are only activated when there is an actual demand.
dBm Decibel referenced to 1 milliwatt.
A-2 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 85

DES Data Encryption Standard – A federal standard method for encrypting informa-
tion for secure transmission. The Vipersat system offers 3xDES (Triple DES)
for encrypting traffic.
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol – An Internet protocol for automating
the configuration of computers that use TCP/IP.
DLL Dynamic Link Library – The implementation of the shared library concept in
the Microsoft Windows system.
DPC Dynamic Power Control
DSCP Differentiated Services Code Point – The 6-bit field in an IP packet header that
is used for packet classification purposes and is the portion of ToS that is
detected by Vipersat modems.
DVB Digital Video Broadcast
DVP Digital Voice Processor – Used in packet voice applications.
E
Eb/NoEb/No is the ratio of Eb (energy per bit) and No (noise power density per Hz).
The bit error rate (BER) for digital data is a decreasing function of this ratio. E
is the energy of an information bit measured in Joules or, equivalently, in Watts
per Hertz.
b
F
FAST Code Fully Accessible System Topology Code – Designation for feature code used
by Comtech EF Data for their satellite modems. The FAST method makes it
easy to quickly upgrade the feature options of a modem while it is running live
in the network, either on site or remotely.
FEC Forward Error Correction – A process whereby data being transmitted over a
communications link can have error correction bits added which may be used at
the receiving end to determine/correct any transmission errors which may occur.
Flash Non-volatile computer memory that can be electrically erased and repro-
grammed.
FTP File Transfer Protocol – An application for transferring computer files over the
Internet. See also TFTP.
Appendix A - Glossary A-3
Page 86

G
G.729 ITU standard for LD-CELP (Low Delay – Code Excited Linear Prediction)
voice encoding at 8 kb/s.
GIR Guaranteed Information Rate
Group ID A number assigned to equipment which defines it as a member of a group when
addressed by the VMS burst controller.
GUI Graphical User Interface – A form of graphical shell or user interface to a
computer operating system or software application.
H
H.323 A protocol standard for multimedia communications designed to support real-
time transfer of audio (such as voice over IP) and video data over packet
networks. Quality of Service is a key feature of H.323. An alternative to SIP.
HDLC High-Level Data Link Control – A standard defining how data may be transmit-
ted down a synchronous serial link.
HPA High Power Amplifier – The amplifier used in satellite communications to raise
the transmit signal to the correct power level prior to transmission to satellite.
HTTP Hyper Text Transfer Protocol – The Internet standard for World Wide Web
(WWW) operation.
Hub The central site of a network which links to a number of satellite earth sites
(remotes).
I
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol
IDU Indoor Unit – In a VSAT system, the satellite modem is referred to as the IDU.
IF Intermediate Frequency – In satellite systems, IF frequencies are usually
centered around 70 or 140 MHz (video/TV), or 1200 MHz (L-band).
A-4 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 87

IFL Intra-Facility Link – The coaxial cabling used to connect the satellite ODU to
the IDU. Carries the inbound and the outbound signals, and the 24 VDC for the
LNB.
Image A binary firmware file that provides the operational code for the processor(s) in
a network unit.
IP Internet Protocol – A format for data packets used on networks accessing the
Internet.
ISP Internet Service Provider – A company providing Internet access.
ITU International Telecommunications Union
K
Kb/s Kilo bits per second – 1000 bits/second. A measure of transmission speed. See
also bps & Mb/s.
Ku-Band A frequency band used for satellite communications. For terrestrial earth
stations the receive frequency band is in the range 10.95–12.75 GHz and the
transmit frequency band is 13.75–14.5 GHz. See also C-band.
L
L-Band A frequency band commonly used as an IF for satellite systems using block up/
down conversion. Typically 950–1450 MHz Rx, 1250–1750 MHz Tx.
LAN Local Area Network
LLA Low Latency Application
LNA Low Noise Amplifier – An amplifier with very low noise temperature used as
the first amplifier in the receive chain of a satellite system.
LNB Low Noise Block – A downconvertor so called because it converts a whole
band or “block” of frequencies to a lower band. The LNB (similar to an LNA) is
part of the satellite ODU/transceiver.
LNC Low Noise Converter – A combined low noise amplifier and block down
converter, typically with an L-band IF.
LO Local Oscillator – Component used in upconverters, downconverters, and tran-
sponders for frequency translation (heterodyne) of the carrier signal.
Appendix A - Glossary A-5
Page 88

M
M&C Monitor & Control
MAC Media Access Control – A protocol controlling access to the physical layer of
an Ethernet network.
Mb/s Mega Bits per Second – 1 Million bits/second. A measure of transmission
speed. See also bps & kb/s.
Modem Modulator and demodulator units combined.
Multicast Transmitting a single message simultaneously to multiple destinations (group)
on the IP network.
Multi-
command
A command that allows multiple input choices in a single command execution.
N
NAT Network Address Translation – An Internet standard that enables a LAN to use
one set of IP addresses for internal (private) traffic and a second set of addresses
for external (public) traffic.
NIC Network Interface Controller – The network interface for a PC/workstation that
provides Ethernet connectivity. Depending on the computer, the NIC can either
be built into the motherboard, or be an expansion card. Some computers (e.g.,
servers) have multiple NICs, each identified by a unique IP address.
NMS Network Management System
NOC Network Operation Center – Has access to any earth station installed using the
VIPERSAT Management System (VMS). A NOC can remotely interrogate,
control, and log network activities.
NP Network Processor
O
ODU Outdoor Unit – In a VSAT system, the RF components (transceiver) are usually
installed outdoors on the antenna structure itself and are thus referred to as an
ODU. The ODU typically includes the BUC and LNB, and is connected to the
IDU/modem by the IFL cabling.
A-6 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 89

P
PLDM Path Loss Data Message – A packet message that is sent by older Vipersat
modems (e.g., CDM-570/L) to the VMS every sixty seconds, providing status
update and operating parameter information.
PSK Phase-Shift Keying – A digital modulation scheme that conveys data by chang-
ing the phase of a base reference signal, the carrier wave. Different PSKs are
used, depending on the data rate required. Examples are binary phase-shift
keying (BPSK or 2-PSK) which uses two phases, and quadrature phase-shift
keying (QPSK) which uses four phases.
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network – The world’s public circuit-switched
telephone network, digital and analog, and includes mobile as well as land-line
voice and data communications.
Q
QAM Quadrature Amplitude Modulation – A digital modulation technique in which
the amplitude of two carrier waves is changed to represent the data signal. These
two waves are 90 degrees out of phase with each other.
QoS Quality of Service
QPSK Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying – A digital modulation technique in which the
carrier is phase shifted +/- 90 or +/-180 degrees. With four phases, QPSK can
encode two bits per symbol—twice the rate of BPSK. However, it also uses
twice the power. Also known as 4-PSK or 4-QAM.
R
Remote Satellite earth site that links to a central network site (Hub).
RF Radio Frequency – A generic term for signals at frequencies above those used
for baseband or IF.
RFC Request For Comment – The official publication channel for Internet standards
(such as communication protocols) issued by the Internet Engineering Task
Force (IETF).
Appendix A - Glossary A-7
Page 90

RIP Routing Information Protocol
RS-232 A common electrical/physical standard issued by the IEEE used for point to
point serial communications up to approximately 115 kb/s.
RTP Real-time Transport Protocol – A standardized packet format for delivering
real-time applications such as audio and video over the Internet. Frequently
used in streaming media systems, videoconferencing, and VoIP.
Rx Receive
S
SCPC Single Channel Per Carrier – A satellite communications technique where an
individual channel is transmitted to the designated carrier frequency. Some
applications use SCPC instead of burst transmissions because they require guaranteed, unrestricted bandwidth.
SIP Session Initiation Protocol – A general purpose protocol for multimedia
communications, commonly used for voice over IP (VoIP) signaling. An alternative to the H.323 protocol.
SNG Satellite News Gathering – A satellite uplink van/truck with television crew on
location conducting a live report for a newscast.
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol – A protocol defining how devices from
different vendors may be managed using a common network management
system.
SOTM Satellite On The Move – The ability of a mobile remote terminal to roam across
satellite beams to preserve link integrity and to automatically connect from one
satellite and/or hub to another in a global network.
Star
Topology
STDMA Selective Time Division Multiple Access – A multiple access technique where
Streamload
Protocol
SUM Status Update Message – A packet message that is sent by newer Vipersat
A-8 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
A network topology which, if drawn as a logical representation, resembles a star
with a hub at the center.
users time-share access to a common channel with variable-sized time slots
allocated on usage.
A proprietary Vipersat data streaming protocol.
modems (e.g., SLM-5650A) to the VMS every sixty seconds, providing status
update and operating parameter information.
Page 91

T
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol – A standard for networking
over unreliable transmission paths. See also UDP.
TDM Time Division Multiplexing – A method of multiplexing that provides the
transmission of two or more signals on the same communication path or channel, but at different times by utilizing recurrent timeslots.
TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol – A simple file transfer protocol used over reli-
able transmission paths. See also FTP.
ToS Type of Service
Tx Transmit
U
UDP User Datagram Protocol – A standard for networking over reliable transmission
paths.
UDP
multicast
Unicast Transmitting information/data packets to a single destination on the IP network.
A multicast transmission using the UDP protocol.
V
VESP Vipersat External Switching Protocol – A switch-request protocol that allows
external VPN equipment and Real-time proprietary applications to negotiate
bandwidth requests between any two subnets on a Vipersat network. VESP is
used by newer Vipersat modems (e.g., SLM-5650A) to send a switch request to
the VMS to establish a new satellite link or adjust bandwidth for an existing
link.
VCS Vipersat Circuit Scheduler – A proprietary satellite communication scheduling
system used to schedule Vipersat network resources in support of a variety of
high-priority applications such as video conferencing and scheduled broadcasting.
Appendix A - Glossary A-9
Page 92

VFS Vipersat File Streamer – A file transfer application utilizing UDP and a proprie-
tary Streamload protocol to transmit data across the Vipersat network.
VLoad Vipersat Load Utility – A comprehensive tool for managing and distributing
application, configuration, and identification information for the modem/routers
in Vipersat satellite networks.
VMS Vipersat Management System – A comprehensive M&C tool providing rapid
and responsive control of Vipersat satellite networks. Comprised of client and
server components.
VNO Virtual Network Operator – A provider of management services that does not
own the telecommunication infrastructure. The Comtech Vipersat Network
Products’ VNO solution allows satellite space segment operators to selectively
expose resources in their satellite network to other service providers, customers,
or partners.
VoIP Voice over IP – The routing of voice communications over the Internet or
through any IP-based network.
VOS Vipersat Object Service – The main software service of the VMS application.
W
Wizard A specialized program which performs a specific function, such as installing an
application.
WRED Weighted Random Early Detection – A queue management algorithm with
congestion avoidance capabilities and packet classification (QoS) providing
prioritization.
A-10 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 93

CHAPTER 0INDEX
A
access, 2-55
access client
access enforcement
admin
, 2-54
authentication
enable ping reply
enable telnet
telnet timeout
, 2-55
, 2-55
, 2-54
, 2-55
, 2-55
, 2-55
user names & passwords
application switch detection
automatic switching
, 2-39
B
bandwidth allocation
dynamic cycle
dynamic slot
entry channel
fixed
, 2-32, 2-34
GIR
, 2-33, 2-34
burst map rate
, 2-33
, 2-32, 2-33
, 2-33
, 2-35
C
codecast address, 2-66
compression
header
payload
, 2-60
, 2-10
, 2-10
tx header
enable
, 2-60
refresh rate
, 2-60
tx payload
enable
, 2-61
refresh rate
configuration alert
, 2-61
, 2-4
conventions and references
customer support
, 1-4
D
DES, 2-62
rx decryption keys
tx encryption keys
, 2-62
, 2-62
, 2-54
, 2-40
, 1-2
DHCP server IP address
differential services
DiffServ
, 2-18
DiffServ Code Points
disable remote
DLL files
updating
DPC
, 2-49
, 2-37
, 2-1
, 2-2
, 2-7
, 2-18
, 2-19
enable dynamic power control
maximum power
minimum power
speed up Eb/N0
target Eb/N0
target IP address
target range
DSCP
, 2-19
assured forwarding
expedited forwarding
, 2-51
, 2-50
, 2-51
, 2-51
, 2-51
, 2-51
, 2-20
, 2-20
dynamic
cycle
, 2-33
link library
power control
slot
, 2-1
, 2-49
, 2-32, 2-33
E
Eb/N0, 2-49, 2-51
ECM
, 2-33
enable
all downlink multicast
authentication trap
automatic switching
BFAT
, 2-31
dynamic power control
event logging
filtering
heart beat
IGMP
, 2-21
load switching
ping reply
power hunt
, 2-66
, 2-17
, 2-28
, 2-45
, 2-55
, 2-30
QoS switching
, 2-7
, 2-57
, 2-15, 2-40
, 2-50
, 2-15
, 2-50
Index-1
Page 94

quality of service
redundancy
, 2-11
, 2-66
segmentation/reassembly
SNMP for modem config
SOTM
, 2-28
STDMA
telnet
ToS switching
tx header compression
VFS
WRED
, 2-30
, 2-55
, 2-43
, 2-60
, 2-28
, 2-16
encryption
3xDES
entry channel
, 2-10
, 2-33
F
FAST code
BFAT
, 2-32
compression
IGMP
, 2-21
QoS
, 2-10
Vipersat
features
, 1-3
fixed mode
, 2-60
, 2-27
, 2-32, 2-34
G
general, 1-1
GIR
, 2-33, 2-34
glossary
, 1-1, A-1
guaranteed information rate
H
header compression, 2-10
hitless switching
demodulator delay
lock times
modulator delay
home
, 2-52
how to use this manual
, 2-48
, 2-49
, 2-49
, 2-48
, 1-1
I
IGMP, 2-21
enable
, 2-21
maximum response time
, 2-12
, 2-57
, 2-33, 2-34
, 2-22
missed responses
modem as client
modem as server
queries
, 2-23
query period
router alert option
unsolicited report interval
version
, 2-24
, 2-22
, 2-21
, 2-21
, 2-22
, 2-24
, 2-24
L
load switching, 2-45
enable
percent allocation
SCPC step delay
, 2-45
, 2-47
, 2-46
SCPC step down threshold
SCPC step up excess
SCPC step up threshold
STDMA slot capacity
STDMA switch delay
, 2-47
, 2-46
, 2-47
, 2-47
M
maintenance, 2-65
base modem image
codecast address
enable redundancy
event logging
upgrade image
managed switch
managed switch mode
multicast address
, 2-66
, 2-66
, 2-66
, 2-66
, 2-65
, 2-25
, 2-6
, 2-9, 2-66
multicast management address
N
network, 2-5
dynamic buffer latency
ethernet
, 2-5
HDLC addressing mode
, 2-7
, 2-6
P
parameter editor
features
general
using
payload compression
, 1-3
, 1-1
, 1-1
, 2-10
, 2-46
, 2-30
Index-2 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
Page 95

preamble
duration
product description
, 2-36
, 1-3
Q
QoS, 2-10
diff serv
DSCP
, 2-18
, 2-19
enable
filtering
quality of service
segmentation/reassembly
WRED
mode
priority
protocol
rules
switching
quality of service
, 2-17
, 2-11
, 2-12
, 2-16
, 2-11
, 2-16
, 2-15
, 2-12
, 2-15
, 2-10
R
routing, 2-7
add route
destination port
modify route
multicast
next hop
per route features
3xDES
header compression
payload compression
, 2-7
, 2-8
, 2-10
, 2-9
, 2-9
, 2-10
, 2-10
, 2-10
, 2-10
S
saving changes, 2-2
simple mail transfer protocol
simple network management protocol
SMTP
, 2-59
destination name
domain
, 2-60
server IP address
SNMP
, 2-56
community strings
, 2-60
, 2-60
, 2-58
enable
authentication trap
, 2-59
, 2-57
, 2-56
SNMP for modem config
trap
destination address
version
, 2-57
static route
adding
STDMA
allocation method
, 2-7
, 2-30
, 2-32
automatic remote removal
burst map rate
, 2-36
enable
low data rate fast acquisition
power hunt
STDMA
group ID
guard band
, 2-30
, 2-30
, 2-34
, 2-36
mode
dynamic cycle
dynamic slot
entry channel
fixed
, 2-32, 2-34
GIR
, 2-32, 2-34
preamble
remote list
slot data length
stats collection
switching
, 2-39
application
quality of service
type of service
video
, 2-42
voice
, 2-42
, 2-32, 2-33
, 2-32, 2-33
, 2-32, 2-33
, 2-36
, 2-37
, 2-35
, 2-35
, 2-40
, 2-42
, 2-43
enable
automatic switching
load switching
hitless switching
load
, 2-45
, 2-45
, 2-48
telnet
enable
timeout
ToS
code
enable detection
, 2-55
, 2-55
, 2-43
, 2-44
, 2-43
, 2-57
, 2-58
, 2-38
, 2-31
, 2-40
T
Index-3
Page 96

switch rate
switch type
timeout
type of service
, 2-44
, 2-44
, 2-44
, 2-43
U
using parameter editor, 1-1
V
Vipersat, 2-27
carrier inhibit timer
database version
enable
heart beat
, 2-28
, 2-29
, 2-29
SOTM
, 2-28
VFS
, 2-28
multicast management address
network ID
node name
role
, 2-27
expansion
hub
remote
VLoad
, 2-1
user guide
VMS
, 2-1
user guide
, 2-29
, 2-30
, 2-27
, 2-27
, 2-27
, 1-2, 1-3
, 1-2, 1-3, 2-29, 2-39
, 2-30
Index-4 CDM-570/L, CDD-56X Parameter Editor User Guide
 Loading...
Loading...