Page 1

StreamNet®
In f r a s t r u c t u r e a n d
ne t w o r k de s I g n gu I d e
Page 2
ClearOne
5225 Wiley Post Way
Suite 500
Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Telephone 1.800.283.5936
1.801.974.3760
Tech Sales 1.800.705.2103
FAX 1.801.974.3669
E-mail tech.support@clearone.com
support@netstreams.com
On the Web www.clearone.com
www.netstreams.com
www.streamnetpartners.com
St r e a m Ne t
IN f r a S t r u c t u r e a N d Ne t w o r k de S I g N gu I d e
cl e a r oN e do c u m e N t
800-000-045 - June 14, 2011 (Rev. 1.1)
© 2011 ClearOne and NetStreams - All rights reserved. No
part of this document may be reproduced in any form or by
any means without written permission from ClearOne and NetStreams. Printed in the United States of America. ClearOne and
NetStreams reserves specific privileges.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
U.S. PATENTS:
US 7,643,894
US 7,711,126
International Patents:
Australia 2003-241405
Korean 10-2004-7017970
OTHER PATENTS PENDING
US 11/467,340
US 11/960,401
US 12/015,385
US 12/418,267
US 12/472,976
US 12/727,925
US 12/761,506
US 12/900,666
US 12/917,765
US 12/917,773
European 03731139.6
European 06251345.2
Canadian 2,485,104
Canadian 2,539,458
Australia 2008-207498
Page 3

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1: STREAMNET NETWORKING
STREAMNET NETWORKING GUIDE
StreamNet vs. Other AV Networks ........................................................................................................................................1
STREAMNET NETWORKING CONCEPTS
Routers ..................................................................................................................................................................................4
Default Gateway....................................................................................................................................................................4
IP Addressing........................................................................................................................................................................4
WAP ......................................................................................................................................................................................6
IGMP .....................................................................................................................................................................................8
PoE Power over Ethernet (DC to DC injection) .....................................................................................................................8
For VLAN Use Cases ............................................................................................................................................................9
AVB .....................................................................................................................................................................................10
CHAPTER 2: SWITCH CONFIGURATION SETTINGS
NETSTREAMS, CLEARONE AND DELL BRANDED SWITCHES
5424 - 5448 Implementation ...............................................................................................................................................12
6224 - 6248 Implementation ...............................................................................................................................................14
Access Ports ....................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Switch Uplinks ....................................................................................................................................................................14
Best Practices .....................................................................................................................................................................14
Non-NetStreams or ClearOne branded Implementation ....................................................................................................16
GLOSSARY
Glossary ..............................................................................................................................................................................19
Page 4

Chapter 1: StreamNet Networking
STREAMNET NETWORKING GUIDE
StreamNet is a third-generation networked AV media and control technology that provides the
highest quality audio and video signaling and controls with unmatched scalability when compared
to other networking and legacy AV distribution technologies. StreamNet was designed to work over
Internet Protocol, and hence can be deployed over many networking topologies and infrastructures
such as fiber, UTP, power line or even wireless with the proper QoS. StreamNet system designs are
flexible and can co-exist with other networking traffic and can be used in deployments with one or
more routers, or any number of VLAN’s where necessary.
StreamNet allows your network to be shared between audio video distribution, controls and traditional PC applications. No need for multiple data infrastructures or expensive proprietary infrastructure requirements. Most commercial and enterprise buildings in the United States are already
equipped with the necessary networking hardware to deploy a StreamNet solution.
This guide was intended to provide the basic requirements needed to ensure a reliable Quality of
Service (QoS) for any StreamNet deployment. The vast majority of all StreamNet systems in place
today utilize standard commodity gigabit Ethernet or Fast Ethernet as the infrastructure and most
are provisioned on a single LAN.
StreamNet has no limit to the total number of sources, displays or control points connected to the
network. The network infrastructure needs to be designed and configured appropriately to accommodate your needs and specification.
StreamNet is synchronized to within 1 ms anywhere on the network. This time precision is assured
by a high-performance hardware-assisted StreamNet time protocol. All StreamNet audio processing is sonically transparent and the high quality 24-bit DAC and 24-bit ADC used throughout encoding and decoding are designed to ensure high quality audio and preserves dynamic range.
St r e a m Ne t v S . ot h e r av Ne t w o r k S
StreamNet technology utilizes 100% Internet Protocol that allow real time AV distribution and control. A good way to examine other network solutions is to reference the OSI model for understanding how networks are organized. You can compare these solutions based on where they are used
within the OSI network chart.
1 TechSales StreamNet Design Help: 1.800.705.2103
Page 5
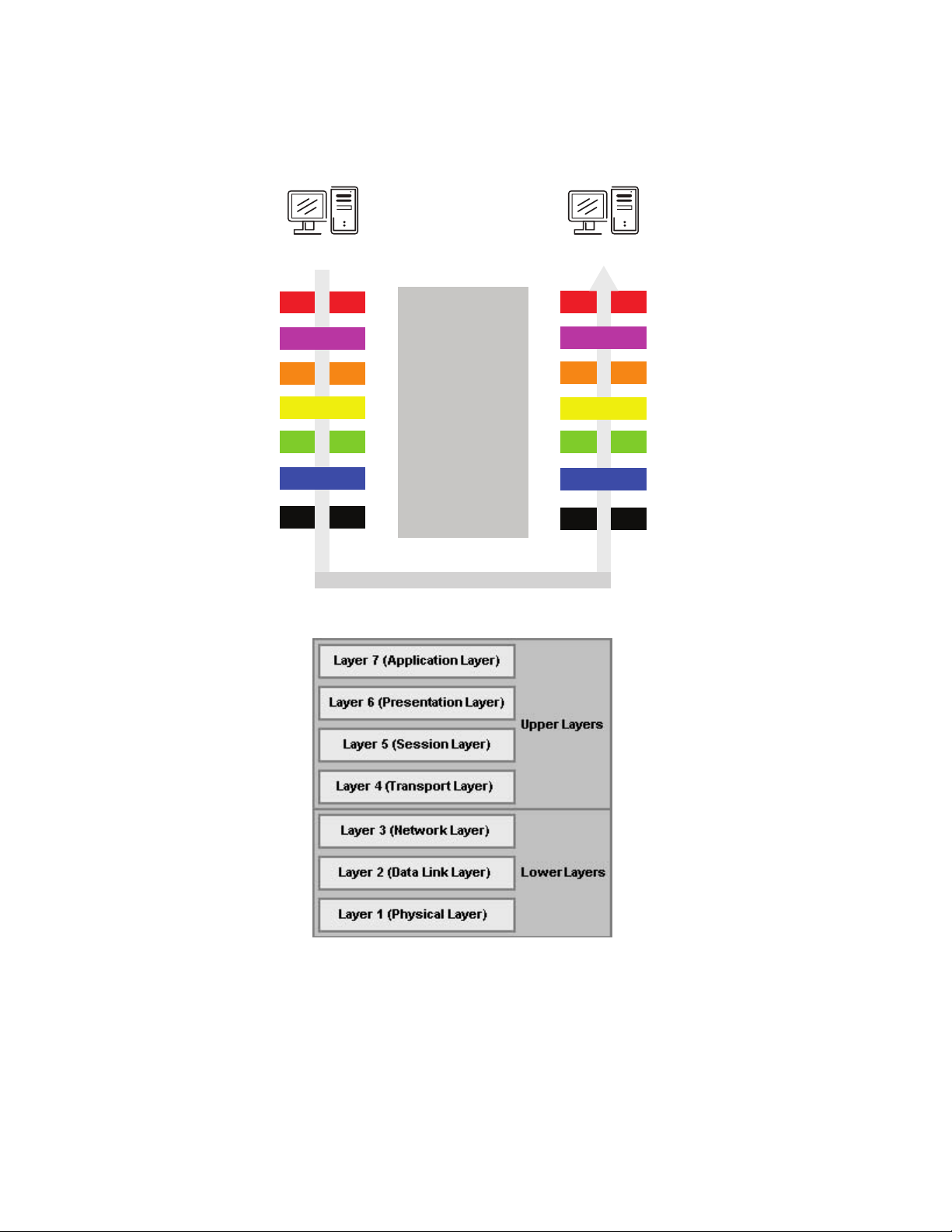
The Seven Layers of OSI
User
Application Layer
Presentation Layer
Session Layer
Tr ansport Layer
Network Layer
Data Link Layer
Physical Layer
Tr ansmit
Data
Receive
Data
PHYSICAL LINK
Chapter 1: StreamNet Networking 2
Page 6

Physical Layer (Layer 1) - Communication technologies operate at the basic Physical Layer.
These kinds of technologies use unsophisticated protocols and basic communication techniques.
This kind of technology is most often used in point-to-point applications. Some solutions use proprietary built infrastructure and routing equipment. Examples of Layer 1 solutions would be Rocknet™, A-Net™ and EtherSound™.
Data Link Layer (Layer 2) - Technologies based on the Data Link Layer allow for more robust
communications. Ethernet is based on Layer 2 and many AV networking solutions use this infrastructure however they cannot scale beyond it. This does allow coexistence of multiple services on
the same physical connection such as audio with PC traffic.
CobraNet™ has not always been a Layer 2 solution, but has evolved to this status today. While it
pales in comparison to Internet Protocol solutions in terms of Audio and Video distribution and controls and number of channels is limited, it has had arguably the most success of any of the legacy
audio network technologies.
Network Layer (Layer 3) - Layer 3 networking is the same technology as the Internet. Dante™
and StreamNet are two examples of IP based AV technologies.
StreamNet incorporates its own discovery of network devices, and fully incorporates IGMP to manage unnecessary networking traffic. Audio video and controls are all packetized and sent over the
network using standard IEEE 802.3 packets for most supported StreamNet stream types with the
exception of MotionXT. MotionXT is a special StreamNet stream type that utilizes jumbo packets.
Other StreamNet stream types are Stereo Audio 44.1k, Stereo Audio 48k, Mono Audio 48k, Highbit-rate Audio, S/PDIF, Control, and Uncompressed HDAV.
The following information can be used to set up your switch infrastructure for reliable AV distribution.
STREAMNET NETWORKING CONCEPTS
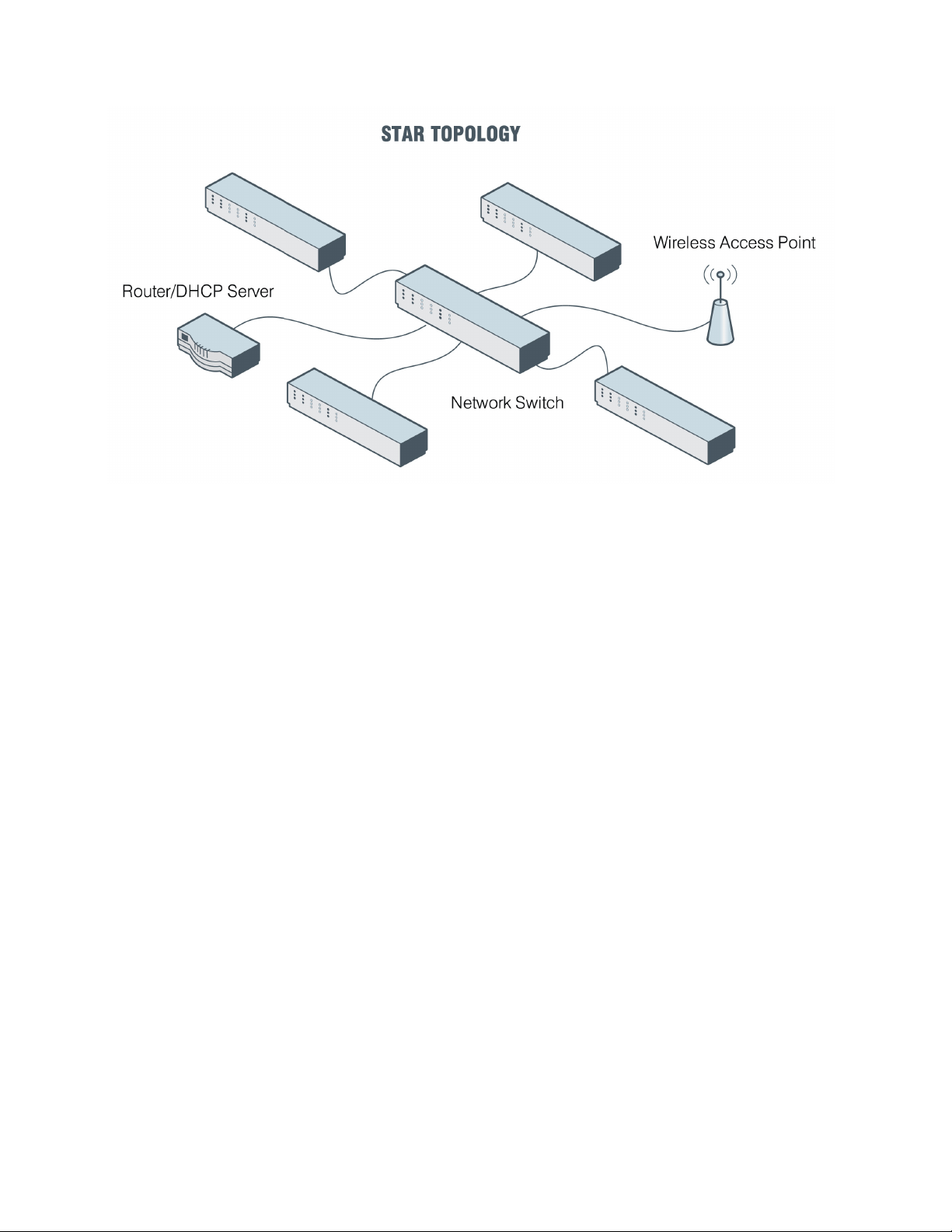
There are several different types of Network Topologies that can be used to configure a Switch Network. Ring, Mesh, Star, Line are examples of Switch Topologies available. Of these, Star Topology is
the StreamNet recommended topology. This is due to the Network and Bandwidth Load Balancing
that needs to be considered when designing a project.
Star Topology consists of several switches connected to a central, higher-capacity switch - see
example below.
3 TechSales StreamNet Design Help: 1.800.705.2103
Page 7
ro u t e r S
A Router is a Network device that connects two or more Networks together to allow data traffic to
be routed between the separate networks. Typically in a Residential scenario this is used to connect
the Local Area Network (LAN) to the Wide Area Network (WAN or Internet).
When choosing a Router to be used with the StreamNet products, it is recommended the use of
a Router that allows disabling the IGMP feature set or does not elect to subscribe to the Internet
Group management Protocol (IGMP or Multicast) as well as turning off Broadcast filters and Storm
Controls.
de f a u l t ga t e w a y
Default Gateway is a node on a network that serves as an access point to other networks. The Default Gateway and Subnet Mask are set automatically when using the DHCP option in the StreamNet Dealer Setup software. If using Static IP Addressing with the StreamNet devices the settings for
the Default Gateway can be entered in the System Settings section of the StreamNet Dealer Setup
software. (Default Gateway settings can be requested from the Network Technician or found in the
Routers LAN Configuration section of the setup software).
IP ad d r e S S I N g
Defining and Managing IP Addresses and Subnets
Managing the IP Address schemes within a network are handled by allocating, recycling and documenting IP addresses and subnets in a network. IP addressing defines Subnet sizes, Subnet assignments, Device Assignments and Dynamic Host Address Assignments within a Subnet range.
This helps reduce the possibility of the Subnet Overlapping or Duplicate IP Addresses within a
Subnet, inefficient use of IP Addresses and unnecessary complexity. Some uses of IP Address
Management are DHCP Ranges, Auto IP Ranges and Static IP Addresses.
Chapter 1: StreamNet Networking 4
Page 8

Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is an auto configuration protocol that assigns
IP Addresses to devices connected a network segment requesting the DHCP protocol. This is a
very efficient way to assign IP Addresses within a defined Subnet. DHCP will automatically assign,
recycle and maintain the IP Addresses allowed by the DHCP Server settings. This is the default
for all StreamNet devices, if the StreamNet device fails to locate a suitable DHCP server it will then
change to an Auto IP mode.
Static IP addressing is a method in which every device is given a specific controlled IP Address on
the network. This method ensures that the device IP Address will not overlap or conflict with other
IP Addresses in the network. This method requires a great deal recording, tracking and managing
assigned IP Addresses to ensure a duplicate Address is not assigned within the Subnet. Typically
used when an IP Range would consume too many available IP Addresses.
NOTE: There is no assurance that another device with a static IP address will not »
overlap.
Auto IP is a module that allows for the Automatic assignment of an IP Address to devices on the
network within a given range without the use of a DHCP server. Much like the DHCP protocol, Auto
IP allows for a device to receive an IP Address automatically on startup.
Default Auto IP settings in StreamNet Dealer Setup software:
DigiLinX Dealer Setup 2.56 and earlier versions•
Auto IP Range: 10.15.0.1 – 10.15.255.255, Subnet Mask: 255.0.0.0•
Default Gateway: 0.0.0.0, DHCP: Not in Use•
StreamNet Dealer Setup 2.60.04 and later versions•
Auto IP Range: 169.254.1.0 – 169.254.254.255, Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0•
Default Gateway: 0.0.0.0, DHCP: On by Default•
IP Address Ranges
Class A comprises networks 1.0.0.0 through 127.0.0.0. The network number is contained in the first
octet. This class provides for a 24-bit host part, allowing roughly 1.6 million hosts per network.
Class B contains networks 128.0.0.0 through 191.255.0.0; the network number is in the first two
octets. This class allows for 16,320 nets with 65,024 hosts each.
Class C networks range from 192.0.0.0 through 223.255.255.0, with the network number contained
in the first three octets. This class allows for nearly 2 million networks with up to 254 hosts.
Classes D, E, and F
Addresses falling into the range of 224.0.0.0 through 254.0.0.0 are either experimental or are reserved for special purpose use and don’t specify any network. IP Multicast, which is a service that
allows material to be transmitted to many points on an internet at one time, has been assigned
addresses from within this range.
5 TechSales StreamNet Design Help: 1.800.705.2103
Page 9

IP Address Ranges Reserved for Private Use
CLASS NETWORKS
A 10.0.0.0 through 10.255.255.255
B 172.16.0.0 through 172.31.0.0
C 192.168.0.0 through 192.168.255.0
D 224.0.0.0 thought 139.0.0.0
waP
Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a Network device that allows Wireless devices access to a connected network via WiFi, Bluetooth™ and other related standards. A WAP is typically used in conjunction with a Router on the Network to supply the DHCP Server for Automatic IP Address Assignment (A Router is not required in this scenario, Static IP Addresses can be used to allow devices
on a Network to communicate with a WAP setup). Some Wireless Routers work both as a Network
Router and Gateway as well as the Wireless Access Point. When a Wireless setup is to be used with
the StreamNet devices, the WiFi access is for 3rd party devices only (not the StreamNet devices).
Many currently shipping StreamNet devices will not work on a wireless segment or Wireless Bridge,
these StreamNet devices must be directly connected to the Master or Slave switches. When choosing a Router to be used with the StreamNet products, it is recommended using a Router capable
of disabling the IGMP feature set or does not elect to subscribe to the Internet Group Management
Protocol (IGMP or Multicast) as well as turning off Broadcast filters and Storm Controls.
Chapter 1: StreamNet Networking 6
Page 10

St r e a m Ne t St r e a m fo r m a t S
SIGNAL TYPE STREAM TYPE NAME COMPRESSION MODE DATA RATE
Mono Audio ProStream A Uncompressed 1 Mb/s
Stereo Audio StreamNet ST Uncompressed 2 Mb/s
S/PDIF StreamNet DA Uncompressed 2 - 10 Mb/s
SD / HD Video StreamNet DV Uncompressed 50 - 880 Mb/s
SD / HD Video MotionXT Live / Cinema 5 5 Mb/s
SD / HD Video MotionXT Live / Cinema 15 15 Mb/s
SD / HD Video MotionXT Live / Cinema 30 30 Mb/s
SD / HD Video MotionXT Live / Cinema 45 45 Mb/s
SD / HD Video MotionXT Live / Cinema 60 60 Mb/s
SD / HD Video MotionXT Live / Cinema 90 90 Mb/s
SD / HD Video StreamNet 264SVC Live / Cinema 264 1 - 5 Mb/s
It is recommended for most deployments that all StreamNet AV Encoders are »
connected to the master Switch if possible to reduce uplink design complexity and lower bandwidth utilization.
Switch Stacking is a means of combining multiple Switches to act as a Single Switch with a
summed total of all Network Ports. See stacking capability per manufacturer. For any multi-switch
StreamNet deployment your master switch must always be the lowest IP address in order for IGMP
to work correctly.
Fiber Connections allow Uplinks between multiple switches to pass higher bandwidths and can
be extended greater distances than the Cat5 copper Twisted Pair limitation of 100m.
7 TechSales StreamNet Design Help: 1.800.705.2103
Page 11

IgmP
IGMP is a multicast group discovery protocol that is used between the clients and the local multicast router.
Multicast enables efficient use of network bandwidth, as each multicast datagram needs to be
transmitted only once on each network link, regardless of the number of destination hosts.
Hosts must have a way to identify their interest in joining any particular multicast group, and routers
must have a way to collect and maintain group memberships: these functions are handled by the
IGMP protocol in IPv4. In IPv6, multicast routers use the Multicast Listener Discover (MLD) protocol
to maintain group membership information.
Multicast routers must also be able to create a multicast distribution tree that enables forwarding of
Multicast Datagrams only on the links that are required to reach a destination group member.
PIM-SM, PIM-DM, and DVMRP are multicast routing protocols that are used across different
subnets, usually between the local multicast router and remote multicast router.
PIM Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) is a standard multicast routing protocol that provides
scalable inter-domain multicast routing across the Internet, independent of the mechanisms provided by any particular Unicast routing protocol.
PIM has two types: PIM-Dense Mode (PIM-DM) and PIM-Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
Poe Po w e r o v e r et h e r N e t (dc t o dc I N j e c tI o N )
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology that passes electrical power with the data on standard
Ethernet cabling. Many StreamNet devices can utilize simple PoE injectors that will allow users to
install devices with only a standard cat5 UTP cable. This is useful if the device has been installed
in a location without any additional wire or without any access to local AC electrical service.
The way this works is you connect one power injector at the head-end close to the switch location.
You connect one cat5 from the switch to the injector and then a second cat5 that would be used to
connect the injector located by the switch with the injector at the far end of the cable located by the
StreamNet device. Next you connect a power supply to the injector installed at the switch location.
Finally you would connect another injector to the cat5 at the far end of the cable by the StreamNet
device, and connect the power output to the StreamNet power input connection.
The following is a list of Current StreamNet devices that are PoE injector compatible:
Chapter 1: StreamNet Networking 8
Page 12

St r e a m Ne t Poe IN j e c t o r co m Pa t I b Il It y
BRAND PRODUCT MODEL #
NetStreams TouchLinX TL430
NetStreams TouchLinX TL700
NetStreams TouchLinX TL380
NetStreams ViewLinX VL9300
NetStreams MediaLinX MLA101
NetStreams MediaLinX MLA9101
NetStreams ControLinX CL100
NetStreams ControLinX CL9100
NetStreams DoorLinX DX100
NetStreams TheaterLinX TH100
ClearOne View TL430
ClearOne View TL700
ClearOne View VL9300
ClearOne View MLA101
ClearOne View MLA9101
ClearOne View CL100
ClearOne View CL9100
fo r vlaN uS e ca S e S
The Master Switch must be configured for IGMP Snooping and IGMP Querying (Master Switch
must be the IGMP Querier for the Network). IP Routing, IP Multicasting and IGMP must be configured globally on the Switch. IGMP will then need to be configured on each VLAN for proper IGMP/
VLAN Routing.
VLAN or Frame Tagging - All VLAN interfaces configured for VLAN Routing will need to have the
allowed VLANs added for proper VLAN communication.
TTL Settings - Each StreamNet device and control software must have a Time to Live (TTL) setting
equal to each router hop, or each VLAN depth transversal. For the example below you would set
the StreamNet devices to have a TLL of 2.
9 TechSales StreamNet Design Help: 1.800.705.2103
Page 13

avb
AVB is a umbrella term for a set of IEEE standards for providing time-synchronized low latency
streaming over Ethernet.
The currently proposed and adopted specifications are for synchronization, stream reservations
and traffic shaping.
Time-sensitive multi-media streaming is exactly what StreamNet was designed for and it is what
we do everyday at ClearOne. We applaud the IEEE efforts as they raise awareness of AV streaming in general and help to shift AV designers and the whole AV industry away from legacy circuit
switched project designs.
The core AVB draft standards define new functions to be added to Ethernet switches and endpoints to better support media networking. These new functions offer support for clock synchronization and Quality of Service (QoS) in Ethernet networks and introduce a new category of behavior
into Ethernet networks aimed at supporting time sensitive traffic.
The three core AVB standards being drafted for Ethernet networks are:
802.1AS - Timing and Synchronization for Time-Sensitive Applications•
802.1Qav - Forwarding and Queuing for Time-Sensitive Streams•
802.1Qat - Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP)•
AVB networks are designed to be a “defended network” constructed from AVB-capable switches
and end devices. AVB capable switches detect whether each port is connected to another AVB
capable device or switch and build islands of connectivity in which AVB services are supported.
Chapter 1: StreamNet Networking 10
Page 14

Current Ethernet switches and devices that have not implemented the AVB protocols will be prevented from becoming part of an AVB cloud. A device cannot use the AVB services to communicate
with another device if there is a non-AVB switch anywhere on the path between the two devices.
AVB is designed to provide improved QoS and simplify the switch configuration process. In time,
these efforts will also expand the interoperability of AVB switches and endpoints which in turn will
expand the penetration of digital A/V networked devices.
Since AVB protocols operate only in domains where every device is AVB capable, new Ethernet
switches and end points are required throughout the deployed system. AVB protocols cannot be
used end-to-end through a system that contains a mixture of AVB-capable and non-AVB capable
switches.
StreamNet is AVB ready - The AVB standards currently under development are a natural evolution
of the many open standards already used by StreamNet today, and as they emerge from drafts
they will be incorporated automatically. Once this takes place new StreamNet products will ship
with AVB capabilities from the factory, and for products already deployed in the field, a simple firmware update is all that is required for your StreamNet endpoints to become AVB-capable.
StreamNet systems are deployed using customers existing QoS-capable network infrastructure
and do not require any AVB capable equipment. You do not have to wait for the widespread availability of AVB switches for your networked AV requirements, a StreamNet system can deliver rich
Multi-media streaming services now, and will continue to add additional services and features in
the future as the AVB standards make progress through the respective standards bodies.
Two AVB capable Ethernet switches are reported to be unveiled available:
Lab X Technologies Titanium 411 AVB Switch (4 port+Uplink)•
BSS Audio/NETGEAR GS724T 24 Port Ethernet AVB Switch•
StreamNet also provides the follow features that are not within the scope of the AVB working groups
such as;
AV Streaming, discovery, control and synchronization over Internet Protocol enabling stream-•
ing and control through routers, wireless access points, power line, or coax for unmatched
system design flexibility
Control tunneling for legacy protocols such as serial, IR and USB in and out of AVB clouds•
Auto generated GUI and system monitoring software that allow easy to use controls and •
simple management
Easy integration with 3rd party devices•
HDCP compliance for protected content streaming•
Format conversion, and transcoding services•
Third Generation AV Streaming system architecture•
Thousands of deployed systems from stadiums to casinos to command and control centers •
to shopping malls, and many others, some of which pre-date the formation of the IEEE Audio
Video Bridging working group
11 TechSales StreamNet Design Help: 1.800.705.2103
Page 15

Chapter 2: Switch Configuration Settings
NETSTREAMS, CLEARONE AND DELL BRANDED SWITCHES
5424 - 5448 IMPLEMENTATION
Firmware and Boot Codes
SW version 2.0.0.36
Boot version 2.0.0.0
(Both Firmware and Boot Code can be requested from ClearOne Technical Support)
Dell 5424 - 5448 Switch Settings
Create VLAN and set the Switch or VLAN IP Address (StreamNet devices should reside on •
same VLAN)
Set the “Bridge Multicast Unregistered-filtering” function to forbid Forwarding-Unregistered-•
Multicast-Addresses.
Turn on IP IGMP v2 or v3 Querying, set the Query Interval, Snooping and set Interval and •
Leave Time.
Turn off STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)•
Turn on Multicast Filtering.•
Turn on Jumbo Frame Support (only needed with uncompressed streams). StreamNet stream •
packets are MTU 4096.
Configure Switchport Access for VLAN and Mode.•
Access Ports
Turn on IP IGMP Snooping.•
Turn on IP IGMP Immediate-Leave•
Turn off STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)•
Switch Uplinks•
Turn off IP IGMP Immediate-Leave•
Create an ACL (Access Control List) that blocks IP IGMP on the switch port used to connect •
the switches to a host network.
Best Practices
Review IP IGMP Query and Election processes before configuring switches.•
Create a separate VLAN for all StreamNet devices.•
Create an ACL (Access Control List) that blocks IP IGMP on the switch port used to connect •
the switches to a host network.
Chapter 2: Switch Configuration Settings 12
Page 16

Dell 5424 - 5448 CLI Commands for Configuring the Services
Create VLAN and set the Switch or VLAN IP address (StreamNet devices should reside on •
same VLAN)
Configure
Interface VLAN 1
IP Address 10.1.0.1 255.0.0.0 (any IP Address and Subnet can be used)
Set the “Bridge Multicast Forbidden Forward-Unregistered” function to forbid Forwarding-•
Unregister -Multicast-Addresses.
Configure
Interface Range Ethernet All
Bridge Multicast Forbidden Forward-Unregistered
Turn on IP IGMP Snooping Querier and set Leave Time•
Configure
IP IGMP Snooping
Interface VLAN 1
IP IGMP Snooping Querier Enable
IP IGMP Snooping Leave-Time-Out Immediate-Leave
Turn off STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)•
Configure
No Spanning-Tree
Turn on Multicast Filtering.•
Configure
Bridge Multicast Filtering
Turn on Jumbo Frame Support (only needed with uncompressed streams). StreamNet stream •
packets are MTU 4096.
Configure
Port Jumbo-Frame
Configure Switchport Access and Mode for VLAN.•
Configure
Interface Range Ethernet All
Switchport access VLAN 1
Switchport mode access
13 TechSales StreamNet Design Help: 1.800.705.2103
Page 17

6224 - 6248 IMPLEMENTATION
Dell 6224 - 6248 Switch Settings
Create VLAN and set the Switch or VLAN IP address (StreamNet devices should reside on •
same VLAN)
Set the “Bridge Multicast Forbidden Forward-Unregistered” function to forbid Forwarding-•
Unregistered-Multicast-Addresses.
Set the “Network Directed Broadcast” function to forward Broadcast commands.•
Turn on IP IGMP v2 or v3 Querying and set the Query Interval.•
Turn on IP IGMP v2 or v3 Snooping, set Interval and Leave Time•
Turn on IP Routing.•
Turn off STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) or set STP to Rapid Mode.•
Turn on Multicast Filtering.•
Turn on Jumbo Frame Support (only needed with uncompressed streams). StreamNet stream •
packets are MTU 4096.
Configure Switchport Access for VLAN and Mode.•
Turn off IP IGMP Snooping TCN Flooding.•
ACCESS PORTS
Turn on Switchport Host Mode.•
Turn on IP IGMP Snooping.•
Turn on IP IGMP Immediate-Leave or Fast-Leave.•
Turn off STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) or set STP to rapid mode.•
Turn off IP IGMP Snooping TCN Flooding.•
SWITCH UPLINKS
Turn off IP IGMP Immediate-Leave or Fast-Leave.•
BEST PRACTICES
Review IP IGMP Query and Election processes before configuring switches.•
Create a separate VLAN for all StreamNet devices.•
Create an ACL (Access Control List) that blocks IP IGMP on the switch port used to connect •
the StreamNet switches to a host network.
Chapter 2: Switch Configuration Settings 14
Page 18

Set the “Network Directed Broadcast” function to Forward Broadcast commands.•
Configure
Interface VLAN 2
Routing
IP netdirbcast
Turn on IP IGMP v2 or v3 Querying and set the Query Interval.•
Configure
Interface VLAN 2
IP igmp
IP IGMP Version 2
IP IGMP Query-interval 125
Turn on IP IGMP v2 or v3 Snooping, set Interval and Leave Time•
Configure
IP IGMP Snooping
IP IGMP Snooping Querier
IP IGMP Snooping Querier version 2
IP IGMP Snooping Querier Query-interval 125
Interface Range Ethernet All
IP IGMP Snooping Leave-Time-Out Immediate-Leave
Turn on IP Routing•
Configure
IP Routing
Turn off STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) or set STP to Rapid Mode.•
Configure
No Spanning-Tree
OR
Spanning-Tree Mode RSTP
Turn on Multicast Filtering•
Configure
Bridge Multicast Filtering
Turn on Jumbo Frame Support (only needed with uncompressed streams). StreamNet stream •
packets are MTU 4096.
Configure
Interface Range Ethernet All
MTU 4096
15 TechSales StreamNet Design Help: 1.800.705.2103
Page 19

Configure Switchport Access and Mode for VLAN.•
Configure
Interface Range Ethernet All
Switchport access VLAN 2
Switchport mode access
NON-NETSTREAMS OR CLEARONE BRANDED IMPLEMENTATION
StreamNet Generic QoS Switch Requirements Recommendations
Requirements for Audio Only StreamNet Applications
10/100BASE-T Auto-sensing Fast Ethernet switching ports•
Recommended Gigabit uplink ports for multiple switches in network•
IGMP v2 or v3 support•
Multicast support with filtering•
Auto-negotiation for Speed, Duplex Mode and Flow Control•
Requirements for Loss-less or MotionTX Audio/Video StreamNet Applications
100/1000BASE-T auto-sensing Gigabit Ethernet switching ports•
10 Gigabit Ethernet uplink modules•
IGMP v2 or v3 support•
Multicast support with Filtering•
Auto-negotiation for Speed, Duplex Mode and Flow Control•
Additional StreamNet Requirements for Global and VLAN Applications
Set a switch or VLAN IP Address.•
Turn on IP IGMP v2 or v3 (Internet Group Management Protocol) Querying. •
Turn on IP IGMP v2 or v3 Snooping.•
Turn on IP Routing.•
Turn off STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) or set STP to Rapid Mode.•
Turn on Multicast Filtering.•
Turn off IP IGMP Snooping TCN Flooding.•
StreamNet Access Point Requirements
Turn on Switchport Host Mode.•
Turn on IP IGMP Snooping.•
Turn on IP IGMP Immediate-Leave or Fast-Leave.•
Turn off STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) or set STP to Rapid Mode.•
Turn off IP IGMP Snooping TCN Flooding.•
StreamNet Switch Uplinks Requirements
Turn off IP IGMP Immediate-Leave or Fast-Leave.•
Chapter 2: Switch Configuration Settings 16
Page 20

StreamNet Infrastructure Best Practices
Review IP IGMP Query and Election processes before configuring switches.•
Create a separate VLAN for all StreamNet devices.•
Create an ACL (Access Control List) that blocks IP IGMP on the switch port used to connect •
the StreamNet switches to a host network.
17 TechSales StreamNet Design Help: 1.800.705.2103
Page 21

Glossary
AVB - A set of standards being developed by the IEEE. These standards add new time synchro-
nization and Quality of Service (QoS) functions to Ethernet.
Ethernet - A widely available networking technology using CAT5/6 cabling or fiber links joined by
packet switches. Can operate at 100Mbps, 1Gbp and 10Gbps.
IEEE - The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers is the organization which standardizes
networking technologies like Ethernet and Firewire.
IEEE 1588 - Also known as the “Precision Time Protocol”. Provides highly accurate clock synchronization services in Ethernet and IP networks.
IEEE 802.1 - The IEEE standards working group responsible for Ethernet protocols.
IEEE 801.1AS - An Ethernet-only profile of IEEE 1588.
IEEE 802.1Qat - A protocol for reserving bandwidth in an Ethernet network.
IEEE 802.1Qav - Specifies how Ethernet packets marked with AVB QoS priority values are pro-
cessed
IEEE 802.3 - The IEEE standards working group responsible for Ethernet cabling standards
IETF - The Internet Engineering Task Force standardizes Internet Protocols.
LAN - A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network (often small) where devices can communicate
directly with all other devices.
QoS - Quality of Service. A variety of techniques used to ensure that some network traffic receives
preferential treatment from the network. For example, QoS ensures that Voice over IP telephone
calls are not interrupted by email traffic in a local network.
TCP/IP - Often refers to the full suite of Internet Protocols. The Transmission Control Protocol
(TCP) is also a specific protocol which provides reliable connections between devices. TCP is the
underlying network transport for the web.
UDP/IP - The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) provides a very efficient, message oriented encapsulation for data. It is well suited to real time applications and forms the basis for the Realtime
Transport Protocol (RTP).
Unicast -Point-to-point communication - packets travel along a path between the sender and receiver. Unicast avoids flooding packets throughout the network.
VLAN - Ethernet switches can create private LANs connecting one or more of their ports. VLANs
are isolated from each other. Some devices can be part of more than one VLAN at a time.
Glossary 18
Page 22

Service and Support
If you need assistance setting up or operating your product, please contact us. We welcome your
comments so we can continue to improve our products and better meet your needs.
te c h N I c a l Su P P o r t
Telephone: 1.800.283.5936
E-mail: tech.support@ClearOne.com
Web site: www.ClearOne.com, www.NetStreams.com
Sa l e S
Telephone: 1.800.707.6994
E-mail: sales@ClearOne.com
te c h Sa l e S
Telephone: 1.800.705.2103
E-mail: techsales@ClearOne.com
Pr o d u c t re t u r N S
All product returns require a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number. Contact ClearOne Technical Support before returning your product. Make sure you return all the items and packing materials that originally shipped with your product.
CLEARONE LOCATIONS
HEADQUARTERS:
Salt Lake City, UT USA
5225 Wiley Post Way
Suite 500
Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Tel: 801.975.7200
Toll Free: 800.945.7730
Fax: 801.977.0087
e-mail: sales@clearone.com
EMEA
Tel: 44 (0) 1189.036.053
e-mail: global@clearone.com
APAC
Tel: 801.303.3388
e-mail: global@clearone.com
19 TechSales StreamNet Design Help: 1.800.705.2103
LATAM
Tel: 801.974.3621
e-mail: global@clearone.com
Technical Sales
Tel: 800.705.2103
e-mail: techsales@clearone.com
Technical Support
Tel: 800.283.5936
e-mail: tech.support@clearone.com
 Loading...
Loading...