Page 1

640-607
Cisco Certified Network Associate 2.0
640 - 607
CCNA 2.0
Version 3.0
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 1 -
Page 2

640 - 607
Important Note
Please Read Carefully
This product will provide you questions and answers along with detailed explanations carefully compiled and
written by our experts. Try to understand the concepts behind the questions instead of just cramming the
questions. Go through the entire document at least twice so that you make sure that you are not missing
anything.
We are constantly adding and updating our products with new questions and making the previous versions
better so email us once before your exam and we will send you the latest version of the product.
Each pdf file contains a unique serial number associated with your particular name and contact information for
security purposes. So if we find out that particular pdf file being distributed by you. Testking will reserve the
right to take legal action against you according to the International Copyright Law. So don’t distribute this PDF
file.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 2 -
Page 3

640 - 607
Q. 1
Your Ethernet network, 172.30.1.0, shuts down. Which update message is seen in your router's debug ip
rip output regarding that network?
A. subnet 172.30.1.0, metric 0
B. subnet 172.30.1.0, metric 1
C. subnet 172.30.1.0, metric 15
D. subnet 172.30.1.0, metric 16
Answer: D
Explanation: In RIP when a network in not reachable then its metric is change to 16.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid metric.
B is incorrect; this metric indicates that the network is up.
C is incorrect; this metric indicates that the network is up.
Q. 2
Which command displays the configuration register setting?
A. show register
B. show flash
C. show boot this IOS command displays the settings of the boot environment variables
D. show version
Answer: D
Explanation:
The show version command displays version information for the hardware and firmware. This includes the
register settings.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
B is incorrect; the show flash command displays information in relation to router memory and image file.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 3 -
Page 4

640 - 607
C is incorrect; the show boot IOS command displays the settings of the boot environment variables.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 128-137.
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/lan/c3550/1214ea1/3550cr/ccimtoc.htm
Q. 3
When setting up Frame Relay for point-to-point subinterfaces, which of the following must not be
configured?
A. The Frame Relay encapsulation on the physical interface
B. The local DLCI on each subinterface
C. An IP address on the physical interface
D. The subinterface type as point-to-point
Answer: C
Explanation:
When setting up Frame Relay for point-to-point subinterfaces it is recommend the network layer address, IP
address be removed from the physical interface and assign this network layer address to the subinterface.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; when establishing a Frame Relay for point-to-point subinterfaces the Frame Relay encapsulation
on the physical interface must be configured.
B is incorrect; when establishing a Frame Relay for point-to-point subinterfaces the local DLCI on each
subinterface must be configured.
D is incorrect; when establishing a Frame Relay for point-to-point subinterfaces the subinterface must be
configured as point-to-point.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 427-429.
Q. 4
Which IOS command is used to associate an ISDN phone number with the next hop router address?
A. isdn destination number
B. dialer map
C. isdn spid1
D. isdn line number
Answer: B
Explanation:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 4 -
Page 5
640 - 607
The dialer map command is used to define one or more dial-on-demand numbers to reach one or more
destinations for a particular interface. This is the exact command to associate an ISDN phone number with the
next hop router address.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
C is incorrect; the isdn spid1 command specifies the SPID required for b channel to access the ISDN network
when your router makes its call to the local ISDN exchange.
D is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 397-406.
Q. 5
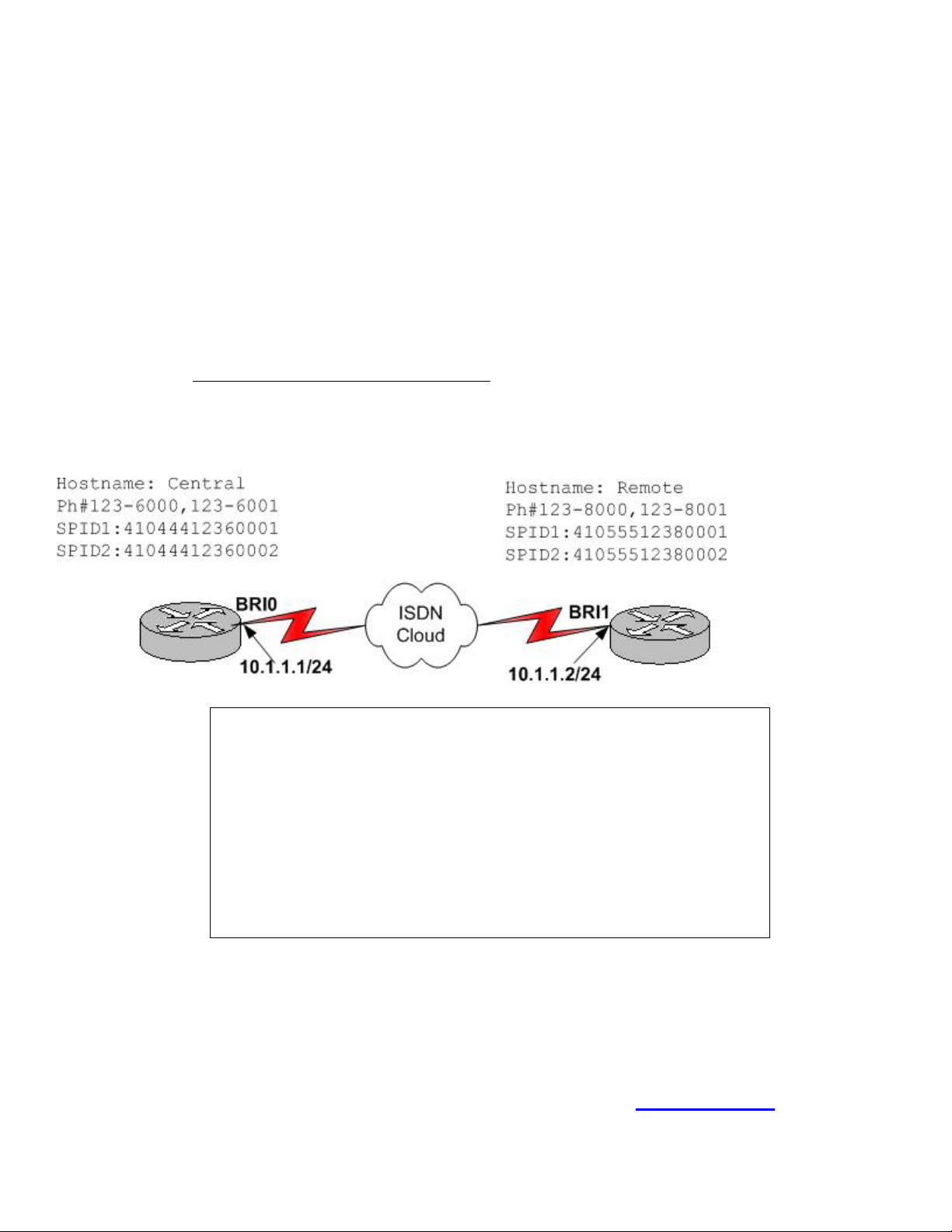
Exhibit:
Central Partial Configuration
isdn switch-type basic-ni
username Remote password cisco
interface bri0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap
isnd spid1 51055512360001
isnd spid1 51055512360002
dialer map ip 10.1.1.2 name Remote 1238001
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
Use the partial BRI configuration and graphic shown. Which additional command must be issued on the
Central router before interesting traffic will be sent to the Remote router?
A. (config-if)# dialer-group 1
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 5 -
Page 6
640 - 607
B. (config-if)# dialer-list 1
C. (config-if)# dialer map 1
D. (config-if)# dialer-route 1
Answer: A
Explanation:
Once the above commands have been entered to enabled DDR, then the last step required is to bind the traffic
destination to an interface by linking the interesting traffic definition already created. This is done with the
dialer-group command. In this case the proper command would be (config-if)# dialer-group 1.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the interesting traffic was already identified the first time the dialer-list 1 command was used.
C is incorrect; the dialer map command is used to identify the router to be dialed. In this case this has already
been done.
D is incorrect; there is no such thing as a dialer route command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 398-405.
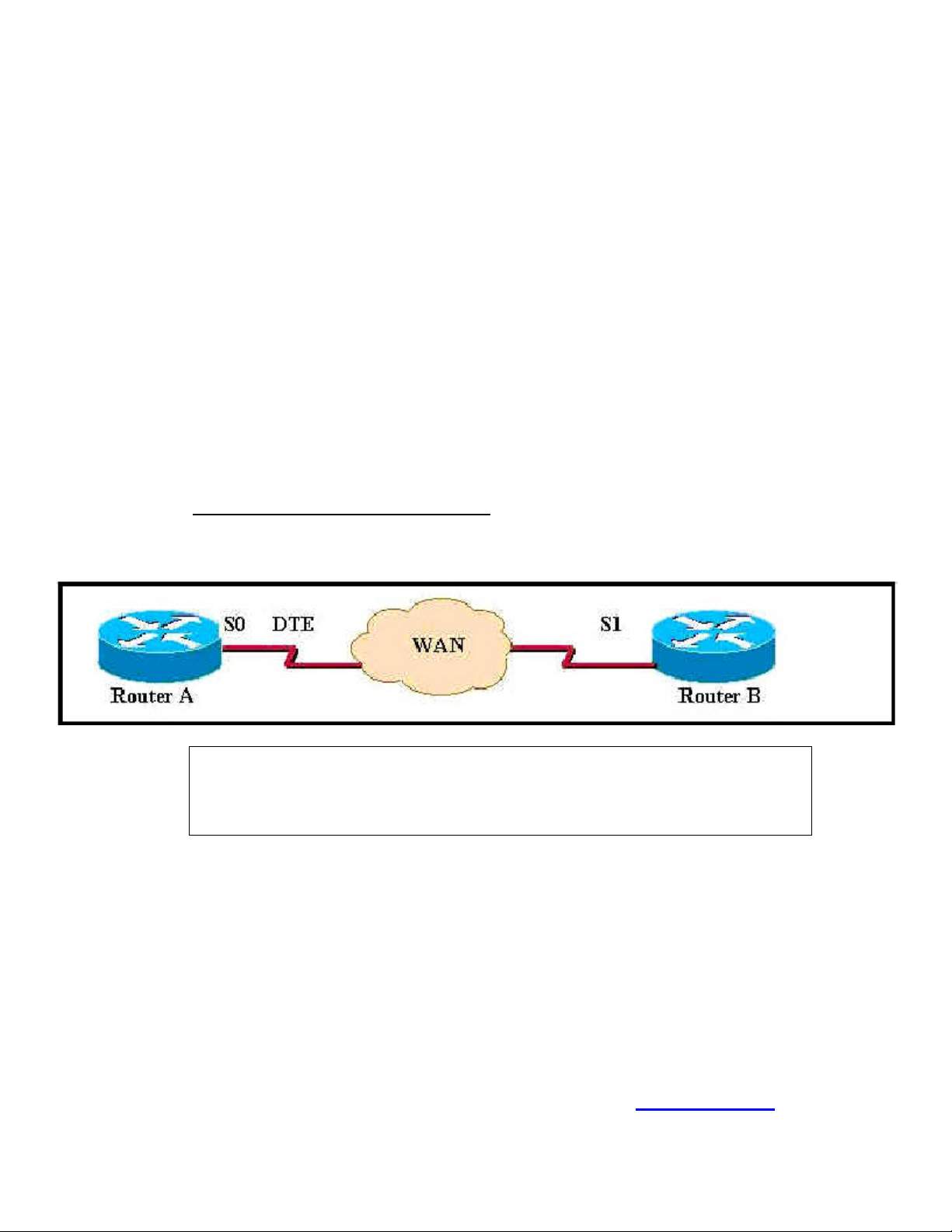
Q. 6
Exhibit:
RouterA# show interface s0
Serial 0 is up, line protocol is down
Hardware is HD64570
Internet address 10.1.1.1
Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set, keepalive set (10sec)
Router A is connected to Router B, a non-Cisco router, through the network cloud. Using the command
output shown what must be configured on Router A's interface s0 to change the line protocol from down
to up?
A. no shutdown
B. encapsulation ppp
C. interface serial point-to-point
D. clock rate 56000
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 6 -
Page 7
640 - 607
Answer: B
Explanation: To ensure that the line comes up the encapsulation type must be enabled. This is done with the
encapsulation ppp command.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the interface is already enable therefore this command in not required.
C is incorrect; the serial interface has already been created, this command would not solve the problem.
D is incorrect; this will only set the clock rate and not bring solve the problem.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 381, 105, 432, and 407.
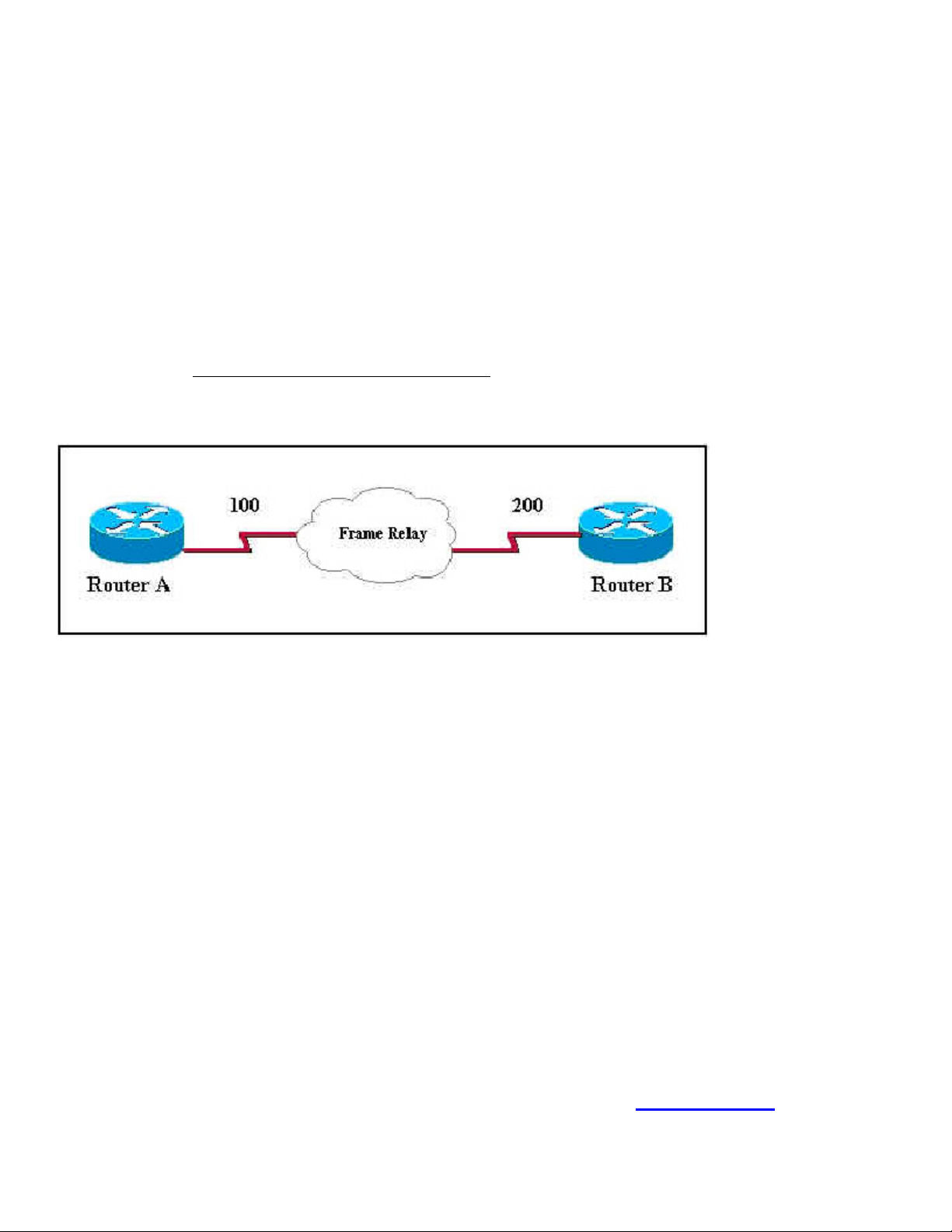
Q. 7
Exhibit:
Which Frame Relay feature allows the point-to-point Frame Relay PVC between Router A and Router B
to be identified at Router A as 100 and at Router B as 200?
A. Locally significant DLCI
B. Globally significant DLCI
C. Locally significant LMI
D. Globally significant LMI
Answer: A
Explanation:
The DLCI (Data-Link Connection Identifier) is a number that identifies the logical circuit between the router
and the Frame Relay switch. The Frame Relay switch maps the DLCIs between each pair of routers to create a
PVC. DLCIs have local significance in that the identifier references the point between the local router and the
Frame Relay switch, which it is connected.
Incorrect Answers:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 7 -
Page 8
640 - 607
B is incorrect; as the DLCI are significant to just the two routers involved in the exchange of information it is
not proper to refer to globally significant DLCI.
C is incorrect; locally significant LMI is not the answer. LMIs are responsible for managing the connection
between the routers and not the assignment of numbers.
D is incorrect; globally significant LMI is not the answer. LMIs are responsible for managing the connection
between the routers and not the assignment of numbers.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 414-416.
Q. 8
During encapsulation in which order is information packaged?
A. Data, Packet, Segment, Frame
B. Segment, Data, Packet, Frame
C. Data, Segment, Packet, Frame
D. Packet, Data, Segment, frame
Answer: C.
Explanation: Data encapsulation is a process in which information is wrapped in the data section of another
protocol. In the OSI model each layer encapsulates the layer immediately above as the data flows down the
protocol stack. The order of encapsulation is
1. Application/Presentation/Session DATA
2. Transport SEGMENT
3. Network PACKET
4. Data Link FRAMES
5. Physical BITS
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; with Data, Packet, Segment, Frame; packet and segment are inverted.
B is incorrect; with Segment, Data, Packet, Frame; data and segment are inverted.
D is incorrect; with Packet, Data, Segment, frame; the only information package in the proper order is frame.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 13.
Q. 9
Exhibit:
Router# show ipx interface e0
Ethernet0 is up, line protocol is up
IPX address is 6F2C.0000.0c5d.b36e, NOVELL_ETHER [up] line-up, RIPPQ:0, SAPPQ: 0
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 8 -
Page 9

640 - 607
Delay of this IPX network, in ticks is 1 throughput 0 link delay 0
IPXWAN processing not enabled on this interface.
IPX SAP update interval is 1 minute(s)
IPX type 20 propagation packet forwarding is disabled
Incoming access list is not set
Outgoing access list is not set
IPX helper access list is not set
SAP GNS processing enabled, delay 0 ms, output filter list is not set
SAP Input filter list is not set
SAP Output filter list is not set
SAP Router filter list is not set
Input filter list is not set
Output filter list is not set
Router filter list is not set
Netbios Input host access list is not set
Netbios Input bytes access list is not set
Netbios Output host access list is not set
Netbios Outpus bytes access list is not set
Updates each 60 seconds, aging multiple RIP: 3 SAP: 3
SAP interpacket delay is 55 ms, maximum size is 480 bytes
RIP interpacket delay is 55 ms, maximum size is 432 bytes
IPX accounting is disabled
IPX fast switching is configured (enabled)
RIP packets received 0, RIP packets sent 1
SAP packets received 0, SAP packets sent 1
What is the Layer 2 address as shown in the output of the show ipx interface e0 command?
A. 6F2C
B. 0000.0c
C. 5d.b35e
D. 0c5d.b363
E. 0000.0c5d.b363
F. 6F2C.0000.0c5d.b363
Answer: E
Explanation:
An IPX address is composed of two parts: the network number and the node number. For IPX the node number
is usually obtain from MAC address of the network interface. In this case the network number is 6F2C and the
node number/MAC address is 0000.0c5d.b363
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; 6F2C is the network number which is a layer 3 address.
B is incorrect; this only part of the MAC address thus incorrect.
C is incorrect; this only part of the MAC address thus incorrect.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 9 -
Page 10

640 - 607
D is incorrect; this only part of the MAC address thus incorrect.
F is incorrect; this is the IPX address. As stated previously this address is part layer 3 and part layer 2.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 332 and 345-6.
Q. 10
Which devices operate at all seven layers of the OSI model? (Choose three.)
A. Network host
B. Network management station
C. Transceiver
D. Bridge
E. Web server
F. Switch
Answer: A, B, E
Explanation: The three devices that operate at all seven layers of the OSI model are network hosts, network
management station and web server. This is how these devices are able to perform their functions.
Incorrect Answers:
C is incorrect; a transceiver is not used in a network environment.
D is incorrect; a bridge is a Layer 2 device.
F is incorrect; a switch is a Layer 2 device.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
Q. 11
With the hierarchical numbering of IP addresses what determines the portion of the address that will
identify the network number?
A. Subnet Mask
B. Dots between octets
C. Class of first octet
D. Assignments of DHCP
E. Address Resolution Protocol
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 21-22.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 10 -
Page 11
640 - 607
Answer: C.
Explanation:
In general, IP addresses contain two fields: one for the network and another for host. Class A address have a
range of 1 to 126 and the network portion of the IP address is restricted to the first eight bits (octet). Class B
address have a range of 128 –191.255.0.0 and the network portion of the IP address is contain in the first 2
octets. Class C IP addresses has a range of 192.223.255.255.0 and the network portion of the IP addresses is the
first three octets of the IP address. Class D addresses include the range of 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 and are
used for multicast address. Class E addresses have a range of 224.0.0.0 to 247.255.255.255 and are reserved for
experimental purposes.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; although the subnet mask is used by network devices to determine what part of the IP address is
used for the network, the subnet and the host address but it is not part of the IP address hierarchy.
B is incorrect; the dots are used for making the IP address readable by humans, but have no determination of the
network number.
D is incorrect; DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) provides a mechanism for allocating IP addresses
dynamically so that addresses can be reused when hosts no longer need them.
E is incorrect; Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) determines the data link layer address of the destination
devices for known destination IP addresses network number.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 215-227.
Q. 12
At which OSI layer does data translation and code formatting occur?
A. Physical
B. Data link
C. Network
D. Transport
E. Session
F. Presentation
Answer: F
Explanation:
The presentation layer provides a variety of coding and conversion functions that are applied to application
level data. These functions ensure that the data sent from the application layer of one system can be read the
application layer of another system.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the physical layer is what puts the actual data onto the wire.
B is incorrect; the data link layer is involved in converting bits into bytes, converting bytes into frames and with
error detection.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 11 -
Page 12

640 - 607
C is incorrect; the network layer provides logical addressing so that routers can perform route determination.
C is incorrect; the transport layer provides delivery of the data and error correction prior to retransmit.
E is incorrect; the session layer is responsible for establishing, managing, and terminating communications
sessions between presentation layer entities.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 11-12.
Q. 13
A packet is the protocol data unit for which layer of the OSI model?
A. Data link
B. Session
C. Presentation
D. Network
E. Transport
Answer: D
Explanation:
The packet is the encapsulation type of the Network layer.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect, the data unit of the data link layer is the frame.
B is incorrect; the session layer in not involved in the data encapsulation process.
C is incorrect; the presentation layer ensures that the receiving system can read the data and is not involved in
encasulation.
E is incorrect; the transport layer data unit is the segment.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
Q. 14
What is the result of segmenting a network with a bridge?
A. It increases the number of collision domains.
B. It decreases the number of collision domains.
C. It increases the number of broadcast domains.
D. It decreases the number of broadcast domains.
Answer: A.
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 11-13.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 12 -
Page 13
640 - 607
Explanation:
Bridge networks have the following characteristics: each segment has its own collision domain, all connected
devices are part of the same broadcast domain, and all segments must have the same data link layer
implementation.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; when a network is segmented by a bridge the collisions domains increase and not decrease.
C and D are incorrect; the addition of a bridge to a network has no effect on the number of domains.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 23-4.
Q. 15
Exhibit:
Router#show interface serial 0
Serial0 is down, line protocol is down
Hardware is HD64570
Internet address is 172.22.5.1/30
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1544 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set, keepalive set (10 sec)
Last input never, output 00:03:11, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Input queue: 0/75/0 (size/max(drops): Total output drops: 0
Queuing strategy: weighted fair
Output queue: 0/1000/64/0 (size/max active/threshold/drops)
Conversations 0/2/256 (active/max active/max total)
Reserved Conversations 0/0 (allocated/max allocated)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
11 packets output, 476 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 27 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
11 carrier transitions
DCD=down DSR=down DTR=down RTS=down CTS=down
Based on the output of the show interface serial 0 command issued on a DTE router, which OSI layer is
most likely source of the problem?
A. Physical layer
B. Data layer
C. Network layer
D. Transport layer
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 13 -
Page 14
640 - 607
Answer: A
Explanation:
The key to answering this question is “
Serial0 is down”. This indicates that the actual serial inerface is
down. Thus there is a problem with the physical layer.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the exhibit does not indicate a problem with the data link layer.
C is incorrect; the exhibit does not indicate a problem with the network layer.
D is incorrect; if the output just indicated that “
problem with the line protocol. If this was the only problem then there would’ve been a
problem with the transport layer.
line protocol is down” then a their would be a
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 107-110.
Q. 16
Exhibit:
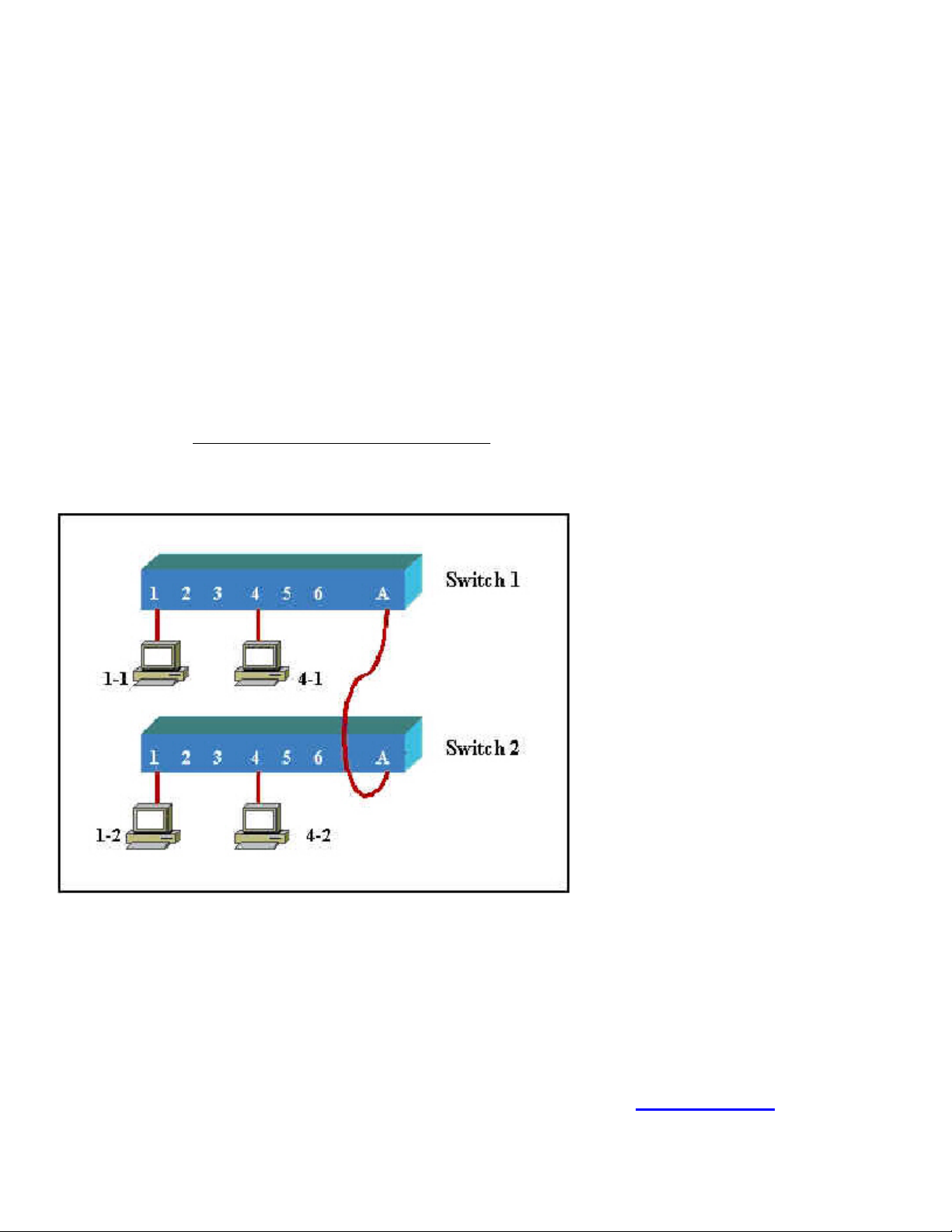
Given the network diagram, assume that ports 1 through 3 are assigned to VLAN1 and ports 4 through 6
are assigned to VLAN2 on each switch. The switches are interconnected over a trunked link.
Which of the following conditions would verify proper VLAN and trunk operation? (Choose three.)
A. Host 1-1 can ping Host 1-2
B. Host 1-1 can ping Host 4-2
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 14 -
Page 15

640 - 607
C. Host 1-1 can not ping Host 1-2
D. Host 4-1 can not ping Host 1-2
E. Host 4-1 can ping Host 4-2
Answer: A, B and E.
Explanation: If hosts from the different VLANs can ping each other then you can confirm the proper VLAN
configuration and truck operation.
Incorrect Answers:
C is incorrect; if this occurred this would indicate a problem.
D is incorrect; if this occurred this would indicate a problem.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 191-193.
Q. 17
Which of the following statements are true regarding bridges and switches? (Choose three.)
A. Switches are primarily software based while bridges are hardware based.
B. Both bridges and switches forward Layer 2 broadcasts.
C. Bridges are frequently faster than switches.
D. Switches have a higher number of ports than most bridges.
E. Bridges define broadcast domains while switches define collision domains.
F. Both bridges and switches make forwarding decisions based on Layer 2 addresses.
Answer: B, D, F
Explanation: Switches and bridges are both Data Link layer devices and make their forwarding decision based
on Layer 2 addresses. As a result they have a number of similar attributes. Switched have a higher port density.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; switches are hardware based.
C is incorrect; switches are most often faster than bridges.
E is incorrect; both define broadcast domains.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 21-22.
Q. 18
You need to add a new VLAN, named ACCOUNTS, to your switched network. Which of the following
are true regarding configuration of this VLAN? (Choose three.)
A. The VLAN must be created.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 15 -
Page 16
640 - 607
B. The VLAN must be named.
C. An IP address must be configured for the ACCOUNTS VLAN.
D. The desired ports must be added to the new VLAN:
E. The VLAN must be added to the STP domain.
Answer: A, B, D
Explanation: To add a VLAN there are a number of things that must be done. First it must be created, then
named and assigned ports.
Incorrect Answers:
C is incorrect; IP addresses do not need to be configured for VLANs.
D is incorrect; the VLAN does not need to be added to the STP domain.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 195-199.
Q. 19
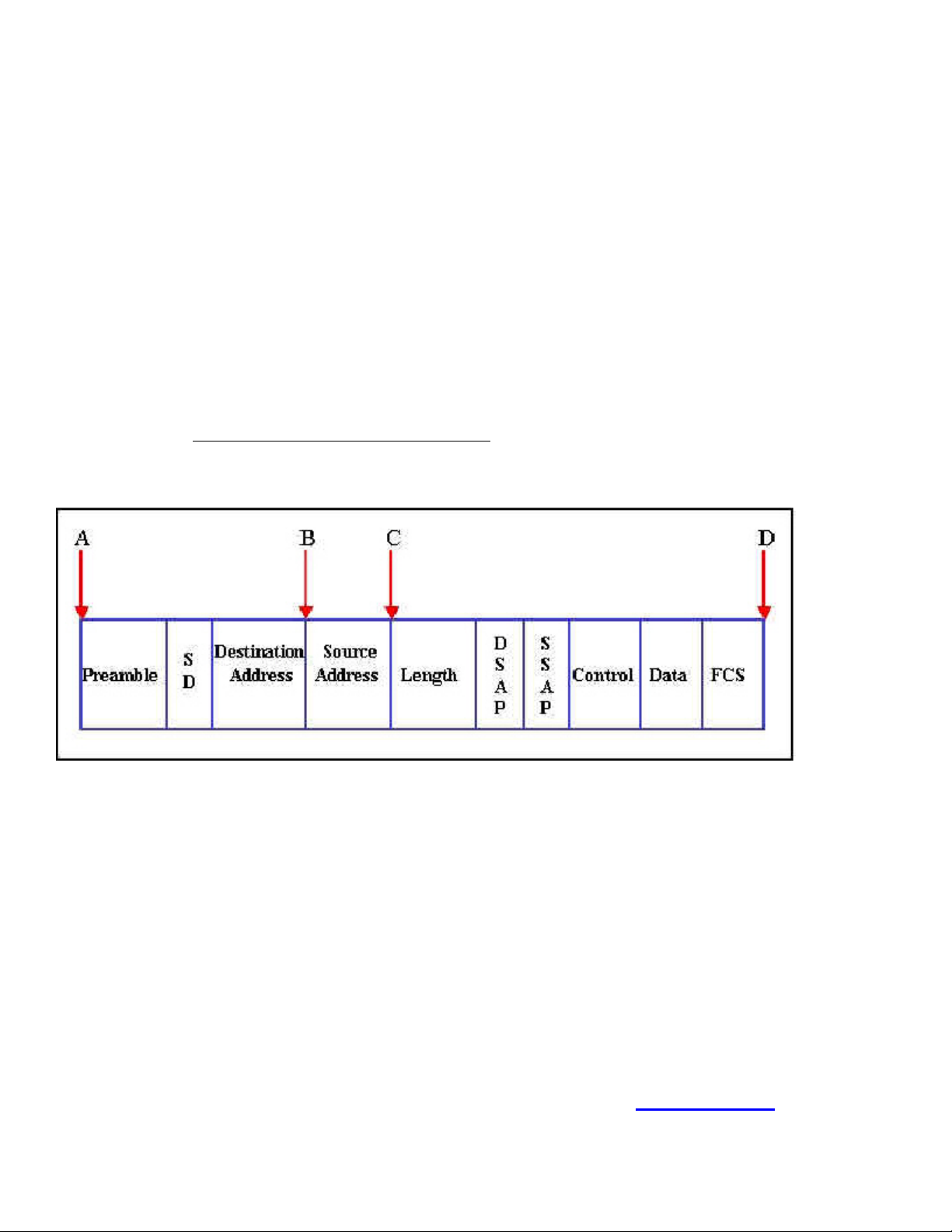
Exhibit:
At what point in the frame shown in the diagram is the store-and-forward switching decision made?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
Answer: D
Explanation: When store-and-forward is employed the complete frame must be first received.
Incorrect Answers:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 16 -
Page 17

640 - 607
A is incorrect; in a switched environment the frame will not be immediately sent.
B is incorrect; this is the point at which the cut-through mode will start sending a frame.
C is incorrect; this is the point at which the fragment-free mode start sending a frame.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 162-163.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 17 -
Page 18

640 - 607
Q. 20
Which commands could be used at the command line interface to troubleshoot LAN connectivity
problems on a router? (Choose three.)
A. ping
B. tracert
C. ipconfig
D. show ip route
E. winipcfg
F. show interfaces
Answer: A, D, F
Explanation: There are a number of commands that can be used to troubleshoot connectivity problems on a
router. The ping command verifies connectivity, the show ip route command shows a great deal of information
that is useful for troubleshooting connectivity, and the show interfaces command displays statistics for the
network interfaces on the router.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; tracert is not a valid command. The Cisco command is trace.
C and E are incorrect; these are great Microsoft troubleshooting commands but they are not valid Cisco
commands.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 124, 107-110, and 406-
407.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 18 -
Page 19

640 - 607
Q. 21
What are the effects of sustained, heavy collisions in CSMA/CD LANs? (Choose three.)
A. Increased broadcast traffic
B. Delay
C. Low throughput
D. High throughput
E. Congestion
F. Higher bandwidth
Answer: B, C, E
Explanation: Whenever there is sustained high collision environment the results are longer delays, congestion
and low throughput.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this will not increase broadcast traffic.
D is incorrect; due to the collision the throughput will decrease.
F is incorrect; the bandwidth will not be effected.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 16-17.
Q. 22
Modem networks are often described as using 100Base-TX components. What is meant by the term
'Base' in this definition?
A. It describes the signaling method for communication on the network.
B. It refers to the type of media used in the network.
C. It relates to the speed of transmission of network signals.
D. It defines the allowable length of media that can be used.
E. It defines half-duplex or full-duplex operation.
Answer: A
Explanation: There are two main signaling types: Baseband and Broadband.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; TX represents the media type. TX r= Cat 5 cable.
C is incorrect; the speed of the transmission is represented by the 100 (mbps).
D is incorrect; the maximum cable length for 100BaseTX is 100 m and is not represented in the standard name.
E is incorrect; 100BaseTX is for full-duplex operation. This cannot be interrupted from the name.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 19 -
Page 20

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 45-48.
Q. 23
Which of the following are unique characteristics of half-duplex Ethernet as compared to full-duplex
Ethernet? (Choose two.)
A. Shared collision domain.
B. Private collision domain
C. Higher effective throughput
D. Lower effective throughput
E. Private broadcast domain
Answer: A, D
Explanation: Half-duplex Ethernet have a lower effective throughput due to shared collision domain the a full-
duplex Ethernet.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the collision domain is shared not private.
C is incorrect; half-duplex as a lower effective throughput.
E is incorrect; it is a shared collision domain not a private broadcast domain.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 180-182.
Q. 24
From the DOS command prompt, you are able to ping a router but are unable to telnet it.
What is the most likely cause of the problem?
A. The PC has a bad network interface card.
B. The IP address of the router is on a different subnet.
C. No password has been set on the router vty lines.
D. The default gateway is not set on the PC.
E. The IP address of the workstation is incorrect.
Answer: C
Explanation: In order to telnet to a router a password must be set on the router’s vty line.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; you could not ping if there was a bad NIC.
B is incorrect; telnet is design to allow remote connections.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 20 -
Page 21
640 - 607
D is incorrect; there is no need to a default gateway to telnet
E is incorrect; you would not be able to ping id the IP address was wrong.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 103.
Q. 25
Exhibit:
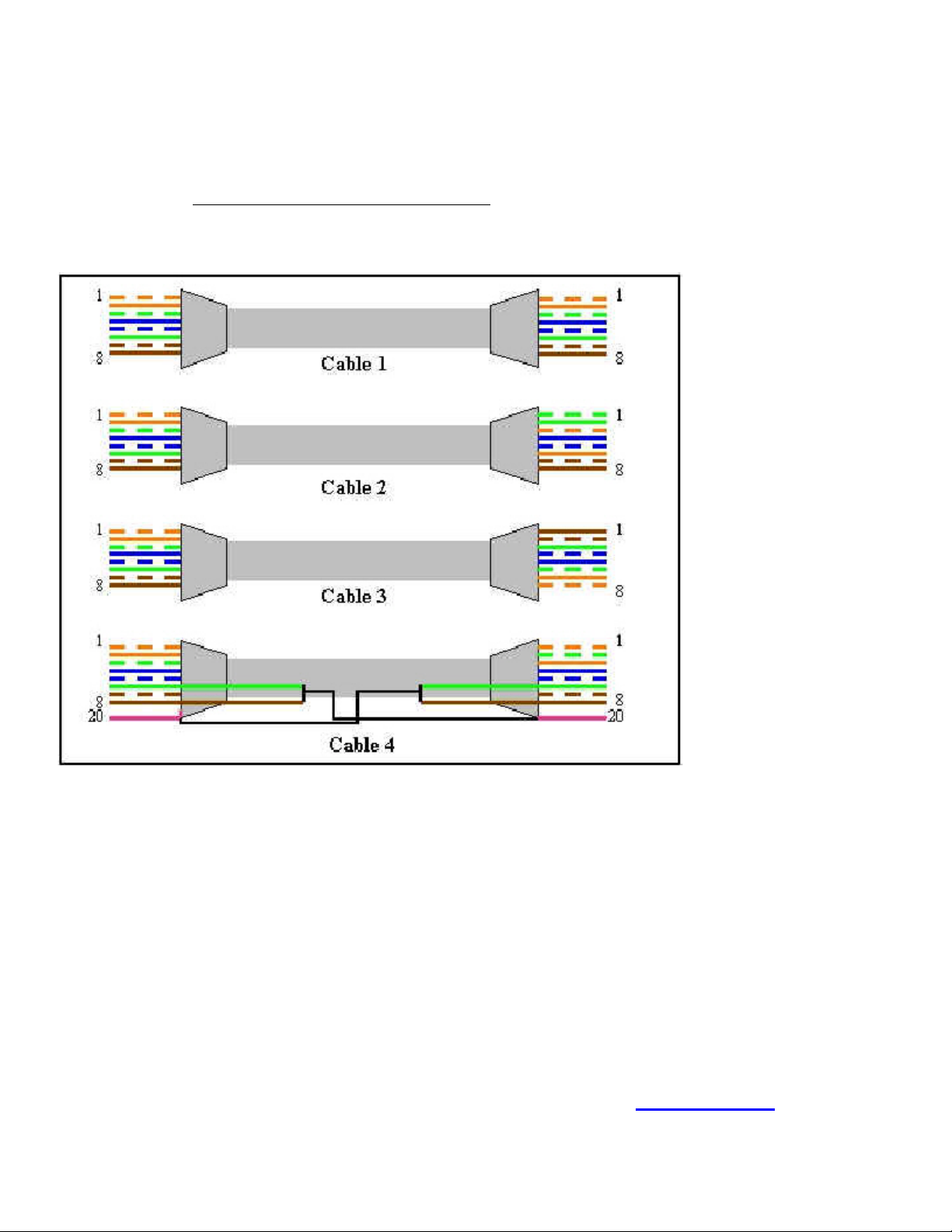
Choose the correct cable to directly connect a router to another router over the Ethernet.
A. Cable #1
B. Cable #2
C. Cable #3
D. Cable #4
Answer: C
Explanation: A crossover cable must be used to connect similar devices. A crossover cable crosses the critical
pairs in order to align, transmit, and receive signals.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 21 -
Page 22

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
B is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
D is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 51.
Q. 26
Which two commands allow you to verify address configuration in your internetwork?
A. Ping
B. Trace
C. Verify
D. Test IP
E. Echo IP
F. Config IP
Answer: A, B
Explanation: The ping command will confirm connectivity and trace will determine the routes an outgoing
packet will take.
Incorrect Answers:
C – F are incorrect; these are not valid commands.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 124.
Q. 27
Exhibit:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 22 -
Page 23
640 - 607
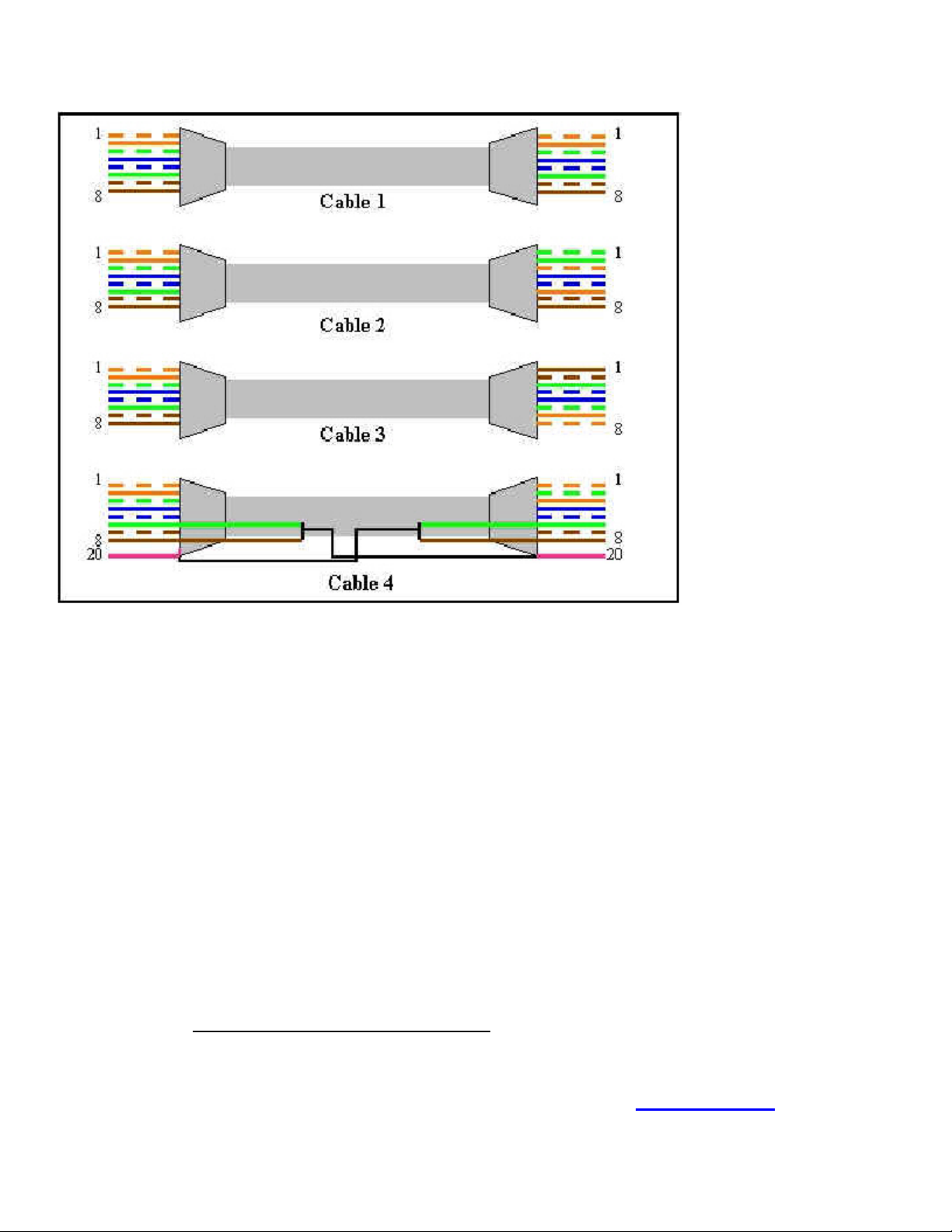
Choose the correct cable to connect an Ethernet switch to another Ethernet switch.
A. Cable #1
B. Cable #2
C. Cable #3
D. Cable #4
Answer: C
Explanation: A crossover cable must be used to connect similar devices. A crossover cable crosses the critical
pairs in order to align, transmit, and receive signals.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
B is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
D is incorrect; the critical pairs are not twisted.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 51.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 23 -
Page 24

640 - 607
Q. 28
Which command displays all routed protocols and the interfaces on which the protocol is enabled?
A. show protocols
B. show protocol brief
C. show interfaces protocol
D. show interfaces
E. show routed
F. show routed interfaces
Answer: D
Explanation: The show interfaces command displays statistics fro all interfaces configured on the switch. This
information is displayed by interface and includes the routing protocols.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
B is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
C is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
E is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
F is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 80-81.
Q. 29
If windows size is changed from 3000 to 4000 during the data transfer stage of a TCP session, what can a
sending host do?
A. Transmit 3000 bytes before waiting for an acknowledgement.
B. Transmit 4000 packets before waiting for an acknowledgement.
C. Transmit 4000 bytes before waiting for an acknowledgement.
D. Transmit 4000 segments before waiting for an acknowledgement.
E. Transmit 3000 frames before waiting for an acknowledgement.
F. Transmit 3000 packets before waiting for an acknowledgement.
Answer: C
Explanation: For TCP a window size is in bytes. When a window size increases the sending device can
increase transmission to the new size. In this case the new size 4000 bytes.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 24 -
Page 25

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; prior to the increase in bytes the old window size was 3000 bytes.
B is incorrect; window size is bytes not packets.
D is incorrect; window size is bytes not segments
E is incorrect; window size is bytes not frames.
F is incorrect; window size is bytes not packets.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 213-214.
Q. 30
Users on network 192.168.69.0/28 are complaining that they cannot access the corporate intranet server
at www.inhouse.com. In troubleshooting this problem, you find that you are able to telnet a workstation
on this network to the internal webserver via its IP address.
What is the likely cause of this problem?
A. TCP/IP failure
B. DNS failure
C. FTP failure
D. SNMP failure
Answer: B
Explanation: When you combined the fact that user cannot connect to the intranet with its domain but you can
telnet to it using the IP address, there must be a problem with the DNS. DNS translates names into addresses.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; if there was a problem with TCP/IP then you would not have been able to Telnet to web server.
C is incorrect; a problem with FTP would not cause this problem.
D is incorrect; a SNMP failure would not cause this problem.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
Q. 31
Given the network 199.141.27.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.240, identify the valid host addresses.
(Choose three.)
A. 199.141.27.33
B. 199.141.27.112
C. 199.141.27.119
D. 199.141.27.126
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 239-240.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 25 -
Page 26
640 - 607
E. 199.141.27.175
F. 199.141.27.208
Answer: A, C, D
Explanation: When you base your calculations on the network address and the provided subnet mask the valid
host addresses are 199.141.27.33, 199.141.27.119, and 199.141.27.126.
Incorrect Answers:
B, E and F are incorrect; these are not valid host addresses.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 233-236.
Q. 32
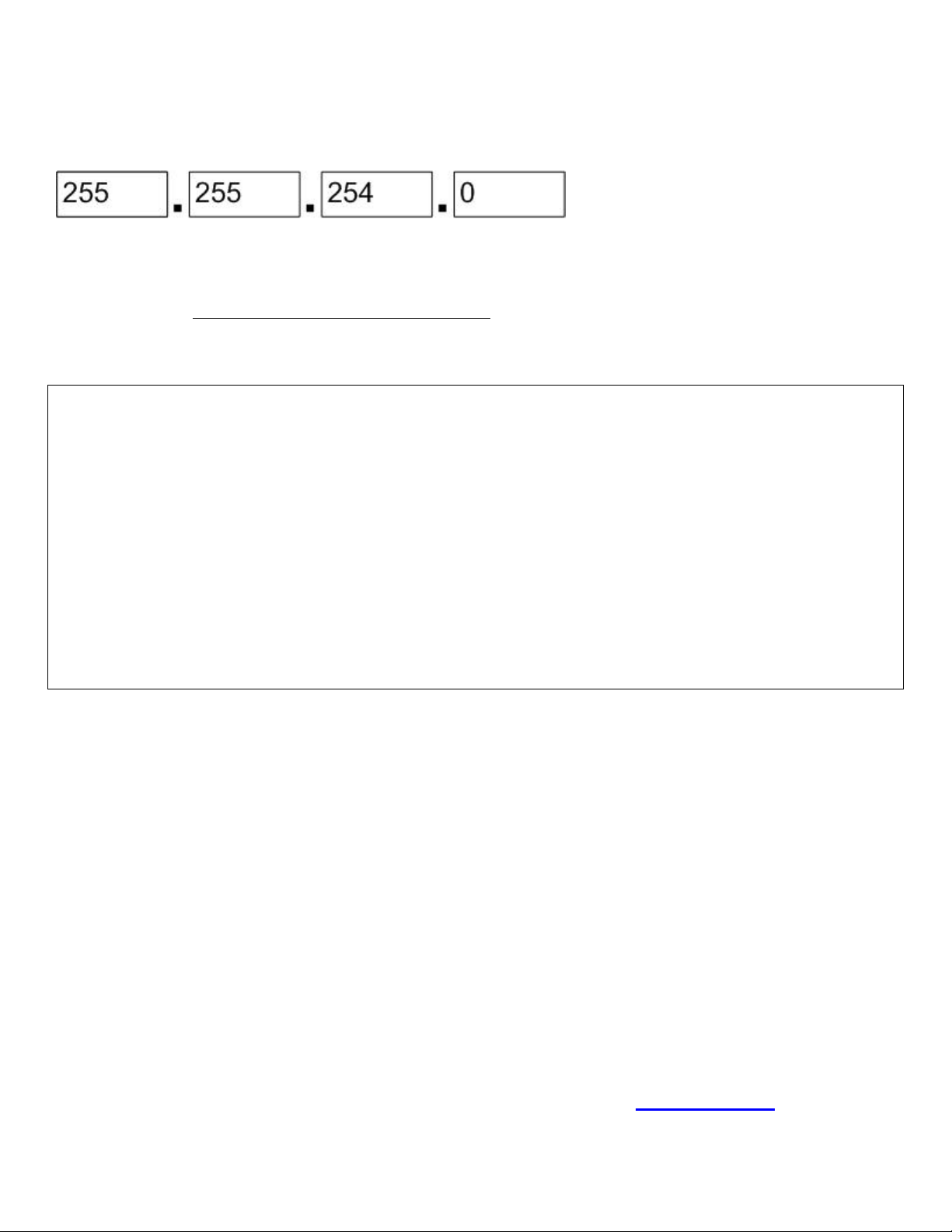
The network 172.12.0.0 needs to be divided into subnets where each subnet has the capacity of 458 IP
addresses. What would be the correct subnet mask to accomplish this division keeping the number of
subnets at the maximum.
Type the correct value in each box below.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 26 -
Page 27
640 - 607
Answer:
Explanation: In order for a Class B IP, such as 172.12.0.0, to have 458 IP available on each subnet then a
subnet mask of 255.255.254.0. This subnet mask provides for 126 subnets and 510 IPs.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 234.
Q. 33
Exhibit:
Router_B#show ip route
Codes: C-connected,s-static,I-IGRP,R-RIP,M-Mobile,B-BGP,D-EIGRP,EIGRP external,
O-OSPF,IA-OSPFinter area,EI-OSPF external type 1,E2-OSPF external type 2, E-EGP,
i-IS-IS,L1-IS-IS level-1,L2-IS-IS level-2,*-candidate default,U-per-user static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
R 192.168.8.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
C 192.168.9.0/24 is directly connected, Serial 1
R 192.168.10.0/24 [120/7] via 192.168.9.1, 00:00:02, Serial1
R 192.168.11.0/24 [120/7] via 192.168.9.1, 00:00:03, Serial1
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0
R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
R 192.168.4.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
R 192.168.5.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
R 192.168.6.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
R 192.168.7.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
Which route will not be entered into the routing table of the receiving router?
A. R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
B. R 192.168.11.0/24 [120/7] via 192.168.9.1, 00:00:03, Serial1
C. C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
D. R 192.168.5.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
Answer: D
Explanation: This route has the lowest metric of those listed and as such will not be shared with the neighbor.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this has the best metric thus it will be shared.
B is incorrect; this route has a better metric therefore it will be shared.
C is incorrect; this is a directly connected network thus it will be shared.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 27 -
Page 28

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 258-260.
Q. 34
Given the following routing table entry, which of the following are used by default in the calculation of
the number 1200? (Choose two.)
172.16.0.0 [100/1200] via 192.168.16.3, 00:00:55, Ethernet1
A. MTU
B. bandwidth
C. administrative distance
D. hop count
E. metric
F. delay
Answer: B, F
Explanation: By default, only bandwidth and delay are used by the IGRP metric. In this case the metric is
1200.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; MTU can be used but it is not a default.
C is incorrect; administrative distance is not used by IGRP.
D is incorrect; hop count is not used by IGRP.
E is incorrect; 1200 is the metric value.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 283-284.
Q. 35
Which method does a Cisco Catalyst switch use to identify the VLAN membership of a frame over
trunked links?
A. Frame filtering with VLAN ID
B. Frame tagging with VLAN ID
C. Frame filtering with trunk ID
D. Frame tagging with trunk ID
E. Frame filtering with VTP port ID
Answer: B
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 28 -
Page 29

640 - 607
Explanation: One form of frame tagging that VLANs use is ISL tagging. The ISL tag includes the VLAN ID.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C and E are incorrect; frame filtering will not achieve the desired result.
D is incorrect; frame tagging does not include the trunk ID.
Wendell Odom. Cisco CCNA Exam #640-507 Certification Guide. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 175.
Q. 36
A routing table contains static, RIP, and IGRP routes for the same destination network. Which route
would normally be used to forward data?
A. The IGRP route.
B. The static route.
C. The RIP route.
D. All three will load balance.
Answer: B
Explanation: If there are several routing sources providing common routing information, an administrative
distance value is used to rate the trustworthiness of each rout ing source. The lower the administrative distance
the more trustworthy it is. Static routes have a default distance of 1, IGRP has a default distance of 100, and
RIP has a default distance of 120.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; IGRP does not have the lowest administrative distance.
C is incorrect; RIP does not have the lowest administrative distance in fact it has the highest.
D is incorrect; as the administrative distance differ there can be no load balancing.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
Q. 37
Which parameter must be supplied when initializing the IGRP routing process?
A. connected network numbers
B. IP address mask
C. metric weights
D. autonomous system number
E. registered administrative id
Answer: D
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 256-258.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 29 -
Page 30
640 - 607
Explanation: IGRP requires an autonomous system number. The autonomous system number must be entered
directly after the router igrp command and before the network command.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the network command is used to identify the directly connected networks but this is done after
the autonomous system number.
B is incorrect; the IP address mask is not required.
C is incorrect; metric weights are not required.
E is incorrect; registered administrative id is not required.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 285.
Q. 38
Which of the following protocols utilizes features of both distance-vector and link-state routing?
A. RIP
B. OSPF
C. EIGRP
D. IGRP
Answer: C
Explanation: EIGRP is an example of a balanced hybrid routing protocol. It uses distance vectors with more
accurate metrics to determine the best paths to destinati on networks. However, it differs from most distance
vector protocols as it also has some features of link-state protocols.
Incorrect Answers:
A and D are incorrect; these are examples of distance vector routing protocol.
B is incorrect; OSPF is an example of a link-state routing protocol.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 275-276 and 259.
Q. 39
A host with a MAC address of 021f.2cfe.8322 is to be inserted into IPX network 4ad1.
Enter the IPX address for this host.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 30 -
Page 31

640 - 607
Answer:
Explanation:
An IPX address is composed of two parts: the network number and the node number. For IPX the node number
is usually obtain from MAC address of the network interface. In this case the network number is 4ad1 and the
node number/MAC address is 021f.2cfe.8322. Thus the ipx address is 4ad1.021f.2cfe.8322.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 332-333.
Q. 40
Exhibit
RouterA(config)#router igrp 100
RouterA(config-router)#network 192.168.3.0
RouterA(config-router)#network 192.168.4.0
RouterA(config-router)#network 192.168.5.0
RouterA(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0
RouterB(config)#router igrp 101
RouterB(config-router)#network 192.168.3.0
RouterB(config-router)#network 192.168.6.0
RouterB(config-router)#network 192.168.7.0
Given the router configuration shown, which networks will be found in RouterB's routing table,
assuming a properly configured network?
A. 192.168.3.0
192.168.4.0
192.168.5.0
192.168.6.0
192.168.7.0
172.16.0.0
B. 192.168.3.0
192.168.6.0
192.168.7.0
C. 192.168.3.0
192.168.4.0
192.168.5.0
192.168.6.0
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 31 -
Page 32

640 - 607
192.168.7.0
D. 172.16.0.0
E. 192.168.3.0
192.168.4.0
192.168.5.0
Answer: A
Explanation: IGRP routing table contains all directly connected networks and those learned by IGRP. As
Router A and Router B share a directly connected network thus they will share routing tables.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; Router B’s routing table will also contain the networks that are directly connected to Router A.
C is incorrect; the routing table will also contain 172.16.0.0.
D is incorrect; the routing table will also contain all of the associated 192.168.0.0.
E is incorrect; the routing table would also contain the other 192.168.0.0 IPs and the 172.16.0.0.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 288.
Q. 41
What are four benefits that can result from applying ISDN networking?(Choose four)
A. Full time connectivity across the ISDN supported by Cisco IOS routing using dial on demand routing
DDR.
B. Small office and home office sites can be economically supported with ISDN basic rate interface BRI
services.
C. ISDN replaces signaling system ss7 in the public switch telephone network PSTN backbone.
D. ISDN can be used as a backup service for a lease line connection between the remote and central offices.
E. Modem racking and cabling can be eliminated by integration with digital modem cards on Cisco IOS
network access servers NAS.
Answer: A, B, D, E
Explanation: When ISDN is implemented there are great deals of benefits. Among these benefits are higher
speeds, ability to use DDR, reduce need for equipment, economic to deploy in medium size companies, and the
ability to use other mediums as backup
Incorrect Answers:
C is incorrect; ISDN can be used on the existing telephone network without the need of signaling changes.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 32 -
Page 33

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 387-400.
Q. 42
You are the network administrator of the Tasti-Treats Cereal Company. You receive a cal l from a user
who is unable to reach a server at a remote site. After further review, you discover the following
information:
Local PC – 10.0.3.35/24
Default gateway – 10.0.3.1
Remote server – 10.0.5.250/240
You then conduct the following tests from the offending local PC:
ping 127.0.0.1 – successful
ping 10.0.3.35 – successful
ping 10.0.3.1 – successful
ping 10.0.5.250 – unsuccessful
Which of the following problems would create the test results listed above?
A. TCP/IP not correctly installed
B. Local physical layer problem
C. Local NIC not functioning
D. Remote physical layer problem
Answer: D
Explanation: As the ping of the remote server was unsuccessful there is a problem with the remote physical
layer problem.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; you would not be able to ping anything if TCP/IP was not correctly installed.
B is incorrect; you would not be able to ping the local IPs if there was a problem with the local physical layer.
C is incorrect; you would not be able to ping anything of the local NIC was not functioning.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 124.
Q. 43
Which command will provide you with information regarding the Layer 3 configuration of directly
connected router interfaces?
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 33 -
Page 34

640 - 607
A. show ip interface
B. show cdb neighbors
C. show cdp neighbors detail
D. show ip route
E. show ip link status
F. telnet
Answer: C
Explanation: The show cdp neighbors detail command displays information about neighboring devices. The
information displayed includes Layer 3 protocol information and Neighbor Device ID. The show cdp entry
command also results in the same information as the show cdp neighbors detail command.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the show ip interface command display IP interface information and indicates whether any
access list are set for a specific interface.
B is incorrect; the show cdp neighbors command displays such information as Neighbor Device ID and Local Interface but nothing on Layer 3 protocols.
D is incorrect; the show ip route command displays the contents of the ip routing table.
E is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
F is incorrect; the telnet command is used to establish a telnet command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 116-119, 324-324, 280,
and 120.
Q. 44
Which command is used to display the placement and direction of an IP access control list on a router?
A. show access-list
B. show ip route
C. show ip interface
D. show interface
E. show interface list
Answer: C
Explanation: The show ip interface command display IP interface information and indicates whether any
access list are set for a specific interface and it also indicates if the access list is inbound or outbound.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 34 -
Page 35

640 - 607
B is incorrect; the show ip route command displays the contents of the ip routing table.
D is incorrect; the show interface command displays the serial interface configuration.
F is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 324-325, 280, and 106
Q. 45
Which of the following commands applies to an access control list to a router interface?
A. permit access-list 101 out
B. ip access-groups 101 out
C. apply access-list 101 out
D. access-class 101 out
E. ip access-list e0 out
Answer: B
Explanation: In order for an access list to be activated the ip-access group command must be used. This
command activates the ip access list on an interface. Before you use the ip-access group command you must
take care to ensure that you have configured an access list. If you do not the result will be permit any.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C-E are not valid commands.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 305.
Q. 46
Exhibit
Router#show access-list
Extended IP access list 105
deny tcp any 172.30.24.64 0.0.0.63 eq smtp
deny tcp any any eq telnet
Router#show ip interface e0
Ethernet0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet address is 172.17.9.60/24
Broad address is 255.255.255.255
Address determined by setup command
MTU is 1500 bytes
Helper address is not set
Directed broadcast forwarding is enabled
Outgoing access list is 105
Inbound access list is not set
Proxy ARP is enabled
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 35 -
Page 36

640 - 607
Security level is default
Split horizon is enabled
Rest of configuration omitted.
What is the result of applying the access-list to Ethernet 0?
A. Only e-mail and telnet access will be permitted out of Ethernet 0.
B. All hosts on the 172.30.24.64 network will be permitted e-mail and telnet access.
C. All TCP protocols will be permitted out of Ethernet 0 except e-mail and telnet.
D. All IP traffic out of Ethernet 0 will be denied.
E. The access-list is numbered incorrectly and will fail.
Answer: D
Explanation: The exhibit is showing an extended IP access-list configuration. For this access l ist to have the
desired effect it will require a permit statement at the end as there is an implicit deny statement otherwise. The
statement should be: access-list 105 permit ip any any.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B and C are incorrect; all traffic out will be denied without a permit statement.
E is incorrect; the access-list is correctly numbered.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 310-320.
Q. 47
Which of the following are not true of standard half-duplex Ethernet circuitry?
A. It is alternate one-way communication.
B. The receive (RX) is wired directly to the transmit (TX) of the remote station.
C. The receive (TX) is wired directly to the receive (RX) of the remote station.
D. Collisions are not possible.
E. Both stations can transmit simultaneously.
Answer: A
Explanation: Half-duplex is a form of one-way communication. On half duplex circuitry if communication
does occur in both directions then collisions will result.
Incorrect Answers:
B, C, D and E are all true statements in relations to standard half-duplex Ethernet circuitry.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 36 -
Page 37

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 163-165.
Q. 48
Which of the following are true regarding passwords on a Cisco router?
A. All passwords can be encrypted.
B. All passwords can be entered using the set-up dialogue.
C. A password can be set before a user can enter the privileged mode.
D. A password can be set for individual lines.
E. TACACS or Radius password authentication can be used.
Answer: A, C, D, E
Explanation: In general enabled passwords are not encrypted but with the service password-encryption
command all passwords are encrypted. Passwords are entered in the privileged mode and they can be set for
individual lines. In addition TACAS or Radius password authentication can also be used.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the set-up dialogue box can only be used to enter some passwords.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 102-103.
Q. 49
What is the maximum number of subnets that can be assigned to networks when using the address
172.16.0.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.240.0? (Assume older version UNIX workstations are in use.)
A. 16
B. 32
C. 30
D. 14
E. It is an invalid subnet mask for the Network
Answer: D
Explanation: 172.16.0.0 is a Class B IP address. With a subnet mask of 255.255.240.0 they maximum number
of subnets are 14 and 4094 hosts.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; 16 is not a valid maximum number of subnets for a Class B IP address.
B is incorrect; 32 is not a valid maximum number of subnets for a Class B IP address.
D is incorrect; for a maximum number of subnets to be 30 the subnet mask would need to be 255.255.248.0.
E is incorrect; 255.255.240.0 is a valid subnet mask.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 37 -
Page 38

640 - 607
Q. 50
What is the maximum length of the fast Ethernet cable 100BaseTx standard?
A. 10 m
B. 50 m
C. 100 m
D. 1000 m
Answer: C
Explanation: The 100BaseTx maximum cable length is 100 m.
Incorrect Answers:
A and B are incorrect; neither 10 m nor 50 m are maximum cable lengths.
F is incorrect; this is the maximum length of fiber optic.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 45-46.
Q. 51
Which of the following are true?
A. The default is to send debug output to the console screen.
B. To view debug output from a telnet session, the "terminal monitor" command must be used.
C. If the "logging buffered" command is used, the debug output would be sent to RAM and can be viewed
with the "show log" command.
D. If the "no console logging" command were configured, output would be sent to a telnet session.
E. All of the above.
Answer: E
Explanation: Debug is one of the most powerful diagnostics tools to troubleshoot a router. By default the
output goes to the console screen. User might or might not be interested in seeing the messages as they occur.
The console port always receives syslog messages. When a user telnets to the router, however, no syslog
messages are seen unless the user issues the terminal monitor command. Another alternative for viewing syslog
messages is to have the IOS record the syslog messages in a buffer in RAM, and then use the show logging
command to display the messages. For telnet users, having the messages buffered using the global config
command logging buffered is particularly useful. The no console logging command were configured, output
would be sent to a telnet session.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B, C and D are partially correct individually.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 38 -
Page 39

640 - 607
Wendell Odom. Cisco CCNA Exam #640-507 Certification Guide. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 33.
Q. 52
What is a benefit of a virtual LAN (VLAN)?
A. It increases the number of broadcast domains.
B. It decreases the number of broadcast domains.
C. It increases the number of collision domains.
D. It decreases the number of collision domains.
E. Since it is a virtual interface, it never shuts down.
Answer: A
Explanation: A VLAN is a logical broadcast domain that can span multiple physical LAN segments. A VLAN
can be designed to provide independent broadcast domains for stations logically segmented by function, project
teams, or application without regard to the physical location of the users. Due to this the number of broadcast
domains increase.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the broadcast domains actually increase not decrease.
C is incorrect; there is no direct effect on collision domains.
D is incorrect; there is no direct effect on collision domains.
E is incorrect; virtual interfaces can be shut down.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 179-184.
Q. 53
IP RIP routing is confi gured on a router, but all i nterfaces attach to RIP network. What shoul d you use
to prevent all RIP routing updates from being sent through selected interfaces without using access lists?
A. Passive route
B. Default routes
C. Passive interface
D. Route update filtering
Answer: C
Explanation: The passive interface command will prevent the sending of RIP updates.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; passive routes as used with IGRP and not RIP.
B is incorrect; default/static routes will not prevent RIP updates.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 39 -
Page 40

640 - 607
D is incorrect; filtering is most often achieved on a router with an access list.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 254-282.
Q. 54
What are two characteristics of the RARP protocol? (Choose two.)
A. It generates parameter problem messages.
B. It maps IP addresses to Ethernet addresses.
C. It maps Ethernet addresses to IP addresses.
D. It is implemented directly on top of the data link layer.
Answer: C, D
Explanation: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) is another protocol defined at the IP layer. RARP
is used by workstations that do not know their own IP address when they come up. RARP allows workstations
to send out a request for its own IP by sending its own Layer 2 MAC address to a waiting RARP server. ARP
and RARP are implemented directly on top of the data link layer.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; RARP determine IPs based on MAC addresses.
B is incorrect; ARP maps IP addresses to MAC addresses.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 218-220.
Q. 55
What must you do to test connectivity on a dial-on-demand routing (DDR) link?
A. Increase the idle timeout parameter.
B. Send interesting traffic across the link.
C. Reboot one of the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) routers.
D. Reset the DDR Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) router statistics to zero.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Of the options provided above the best way to determine if there is connectivity on a dial-on-demand routing
link is to send interesting across the link. If there is connectivity a link will be initiated and established to send
the interesting traffic. If there is no connectivity then the link will not be established.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 40 -
Page 41

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; increasing the idle time parameter will only result in increasing the idle time.
C is incorrect; rebooting the router will only result in the router going through its post.
D is incorrect; this action will not confirm whether a DDR has connectivity or not.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 397-407.
Q.56
Which element is used to d efine the rate, i n bits per second , that a Frame Relay switch agrees to transfer
data?
A. Clock rate (CR).
B. Committed Information Rate (CIR)
C. Local management interface (LMI)
D. Data-link connection identifier (DLCI)
E. Committed Rate Measurement Interval (CRMI)
Answer: B
Explanation: CIR is the rate, in bits per second, at which the service provider states that data will be transfered.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; clock rate is the transmission medium speed, which is determined by modem clocking.
C is incorrect; LMI is a signaling standard between the router device and the Frame Rekay switch that is
responsible for managing the connection and maintaining the status between the devices.
D is incorrect; DLCI is addressing used to identify virtual circuits.
E is incorrect; this is the sampling period used in controlling CIR, but is not the rate itself.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 413-414.
Q. 57
Which term describes the process in which f rames from one network system are placed inside the frames
of another network system?
A. bridging
B. tunneling
C. data-link control
D. generic routing
E. packet switching
Answer: B
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 41 -
Page 42

640 - 607
Explanation: Tunneling is the process whereby a router encapsulates one Layer 3 protocol inside another
protocol (typically IP) for transport across a network to another router. The receiving router de-encapsulates t he
packet, leaving the original packet.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; bridging occurs within the same collision domain.
C is incorrect; data link control has nothing to do within communication between networks.
D is incorrect; generic routing is not the Cisco term used for communication between networks.
E is incorrect; packet switching refers to WAN communication.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 12-14.
Q. 58
What is the protocol and what is the purpose of the following address?
238.255.255.255
A. IPX; a SAP broadcast
B. IP; a multicast address
C. IP; a reserved address
D. IP; a directed broadcast
E. IPX; a flooded broadcast
Answer: B
Explanation: Class D addresses (multicast addresses) include the following range of network numbers:
224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. 238.255.255.255 is within this range.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not an IPX address.
C is incorrect; Class E addresses (research addresses and sometimes called reserved) include the following
range of network numbers: 240.0.0.0 to 247.255.255.255.
D is incorrect; an IP directed broadcast would include the first 3 octets of the IP address and 255 would replace
the fourth octet.
F is incorrect; this is not an IPX address.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 223-224.
Q. 59
Given the configuration example:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 42 -
Page 43

640 - 607
interface ethernet0
ipx network 4a
ipx access-group 800 out
interface ethernet1
ipx network 3d
interface ethernet2
ipx network tc
access-list 800 permit 3d 4a
Which two actions result from implementing this configuration? (Choose two.)
A. IPX network 5c will not receive any traffic.
B. Traffic from network 3d for network 4a will be forwarded out e0.
C. Traffic from network 3d for network 3d will be forwarded out e0.
D. Traffic from network 3d, destined for network 4a, will be forwarded out e2.
E. The access list is applied to an outgoing interface and filters outbound traffic.
Answer: D, E
Explanation:
The key commands for this question are “ipx access-group 800 out” and “access-list 800 permit 3d 4a”. The
first command identifies the access list as an outbound access list. In the command “access-list 800 permit 3d
4a” the first network, 3d, is source network number and the second network, 4a, is the destination network.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; there is no reference to network 5c in this question.
B is incorrect; traffic from 3d to 4a will not transit e0.
C is incorrect; network 3d would not need the access list to send traffic within itself.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 353-354.
Q. 60
Which show interface serial 1 statu s statement indicates that the shutdow n command was issued on that
interface?
A. Serial 1 is up, line protocol is up.
B. Serial 1 is up, line protocol is down.
C. Serial 1 is down, line protocol is down.
D. Serial 1 is administratively down, the line protocol is down.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 43 -
Page 44

640 - 607
Answer: D
Explanation: The shutdown command administratively disables an interface. The result is the interface will be
down as will the line protocol. It will end calls in progress.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the statement shows that the interface and the protocols are both up. This would not be the case
if the shutdown command were used.
B is incorrect; this statement shows that the line is up but the line protocol is down.
C is incorrect; the line would be administratively down if the shutdown command had been used.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 107, 406-407.
Q. 61
In which three situations is a hold-down timer reset? (Choose three.)
A. When the hold-down timer expires.
B. When infinity is finally defined as some maximum number.
C. When the router exchanges update summaries at area borders.
D. When the router detect faulty LSPs propagating through the internetwork.
E. When another update is received indicating a new route with a better metric.
F. When another update is received indicating the original route to the network has been restored.
G. When the router receives a processing task proportional to the number of links in the internetwork.
Answer: A, E, F
Explanation: Holddown timers work as follows:
1. When a router receives an update from a neighbor indicating that a previously accessible network is now
in accessible, the router marks the route as inaccessible and starts the holddown timer.
2. If an update arrives from the neighboring router with a better metric than originally recorded for the
network, the router marks the network as accessible and removes the holddown timer.
3. If at any time before the holddown timer expires an update is received from a different neighboring
router with a poorer metric, the update is ignored. Ignoring an update with a poorer metric when the
holddown is in effect allows more time for the knowledge to change to propagate through the network.
4. During the holddown period, routes appear in the routing table as “possible down”.
Routers remain in holddown until one of the following events occurs: the holddown expires; another update is
received indicating a new route with a better metric; and a flush timer, which is the time a route would be held
before being removed, removes the route from the routing table.
Incorrect answers:
B, C, D and G are incorrect; none of these situations will remove a holddown timer.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 44 -
Page 45

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 269-273.
Q. 62
Which two statements about IP RIP are true? (Choose two.)
A. It limits hop counts to 31.
B. It is a link-state routing protocol.
C. It uses autonomous system numbers.
D. It is capable of load sharing over multiple paths.
E. It uses bandwidth as the metric for path selection.
F. It broadcasts updates every 30 seconds by defaults
Answer: D, F
Explanation: Key characteristics of RIP include the following: it is a distance vector protocol, hop count is
used as the metric for path selection, maximum allowable hop count is 15, broadcast routing updates every 30
seconds, RIP can be load balanced over as many as 6 equal cost paths, RIP 1 requires a major classful network
number to advertise and RIP 2 use VLSMs.
Incorrect answers:
A is incorrect; RIP’s maximum allowable hop count is 15.
B is incorrect; RIP is a distance vector protocol.
C is incorrect; it uses network numbers/VLSMs.
E is incorrect; hop count is used as the metric for path selection.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 278.
Q. 63
How does inter-VLAN communication take place?
A. It takes place through any Cisco router.
B. It takes place through a Cisco router than can run ISL.
C. It takes place through a router, but this disables all the router's Security and filtering functionality for the
VLANs.
D. For nonroutable protocols, (e.g., NetBEUI) the router provides communications between VLAN
domains.
E. Inter-VLAN communications is not possible because each VLAN is a separate broadcast domain.
Answer: B
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 45 -
Page 46

640 - 607
Explanation: In a switched environment, packets are switched only between ports designated to be within the
same “broadcast domain”. VLANs perform network portioning and traffic separation at Layer 2. So, interVLAN communication cannot occur without a Layer 3 device such as a router, because network layer (Layer 3)
devices are responsible for communicating between multiple broadcast domains. Note that, at Layer 2, an
interface uses ISL to communicate with a switch.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the router requires ISL.
C is incorrect; the router does not change the security settings.
D is incorrect; the router will not route a nonroutable protocol into the VLAN.
E is incorrect; without a router inter-VLAN communication is impossible.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 241-244.
Q. 64
What are four ways that Fast Ethernet compares to 10BaseT Ethernet? (Choose four.)
A. Fast Ethernet uses the Same Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU).
B. Fast Ethernet is based on an extension to the IEEE 802.3 specification.
C. Fast Ethernet uses the same Media Access control (MAC mechanisms).
D. Fast Ethernet preserves the frame format that is used by 10BaseT Ethernet.
E. Fast Ethernet offers a speed increase one hundred times that of the 10BaseT Ethernet.
Answer: A, B, C, and D.
Explanation: Fast Ethernet shares a great deal of similarities with 10BaseT Ethernet. These similarities are the
same MTU, same MAC mechanism and frame format. Fast Ethernet is based on IEE 820.3u, which is an
extension to IEE 820.3.
Incorrect Answers:
E is incorrect; its speed 10 times faster, not 100 times.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 44-45.
Q. 65
Which configuration mode and command combination sets the bandwidth metric of a Frame Relay
connection?
A. router(Config)# clock rate 56
B. router(Config-if)# bandwidth 56
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 46 -
Page 47

640 - 607
C. router(Config)# bandwidth 56000
D. router(Config-if)# clock rate 56000
Answer: B
Explanation: The bandwidth command overrides the default bandwidth. The bandwidth has no effect on the
actual speed of the line. Instead, it is used to compute routing metrics ad the load of the link. Bandwidth is
expressed in Kilobits. It is specified during interface configuration.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the clock rate command is used to set the bandwidth on DCE cable not a Frame Relay connection
that must not be abbreviated plus it must be used in the interface configuration mode.
C is incorrect; to change bandwi dth of an int erface you must be in the interface configuration mode and th e rate
must be expressed kilobits per second.
D is incorrect; the clock rate command is used to set the bandwidth on DCE cable not a Frame Relay
connection.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 104-106.
Q. 66
What are the two primary operating modes for frame switching? (Choose two)
A. Full duplex
B. Half duplex
C. CSMA/CD
D. Cut through
E. Fragmentation
F. Store and forward
Answer: D, F
Explanation: There are 3 primary operating modes that are used for frame switching. These modes are sore-
and-forward, cut-through and fragment free. W hen store-and-forward i s used the swi tch mu st receive t he whole
frame before it can be forwarded. During a cut-through operation, the switch forwards the frame once it
receives the Destination Address. Finally, the fragment-free mode reads the first 64 bytes before forwarding the
frame.
Incorrect Answers:
A and B are incorrect; these are transmission modes of whether the transmission is done one way at at time (half
Duplex) or simultaneous two-way (Full Duplex).
C is incorrect; this is a physical transmission medium, typically used in Ethernet LANs.
E is incorrect; there is a fragment-free mode not a fragment mode.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 47 -
Page 48

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 162-163.
Q. 67
In order to enable RIP which two tasks need to be performed? (Choose two)
A. Specify the routing protocol.
B. Configure static Rip routes.
C. Specify directly connected subnets.
D. Specify directly connected networks.
Answer: A, D
Explanation: In enable a router with RIP it takes two basic steps: select the routing protocol and identify the
networks that the router is directly connected to. These steps are achieved with the commands router rip and
network.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; there is no such thing as a static RIP route.
C is incorrect; with RIP you specify the directly connected networks, not the directly subnets.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 278-279.
Q. 68
A router on one side of a PPP li nk uses the h ost name RTR1 and the password CORP1-PWD. Which
configuration line on RTR1 enables the connection between RTR1 and other router named RTR2?
A. Username RTR2 password CORP1-PWD
B. Username RTR1 password CORP1-PWD
C. Username RTR2 password CORP2-PWD
D. Username RTR1 password CORP2-PWD
Answer: A
Explanation: We specify the username of the peer router with the password of the host router.
Incorrect Answers:
B, C and D are incorrect; the username needs to be the peer router, and the password needs to be the password
of the hosting router.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 48 -
Page 49

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 380-382.
Q. 69
Which two statements about a bridge are true. (Choose two)
A. A bridge floods multicasts.
B. A bridge floods broadcasts.
C. A bridge does not flood multicasts.
D. A bridge does not flood broadcasts.
Answer: A, B
Explanation: A bridge must send all multicasts and broadcast to all ports, since there is only one broadcast
domain.
Incorrect Answers:
C and D are incorrect, because a bridge DOES flood broadcasts and multicats.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 22.
Q. 70
What is the protocol and what is the second part of the following network addresses 172.16.0.254 ,
mask=255.255.0.0?
A. IPX:MAC addresses.
B. IP:classC directed broadcast.
C. Private IP address:node number
D. Public IP addresses:directed broadcast.
E. Private IP addresses directed broadcast.
Answer: C
Explanation: The Class B network of 172.16 is a Class B Private Address Range, and the second part (0.254)
is the host address, or node number/address.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the address is an IP address format.
B is incorrect; the question is a Class B address, if it were Class C, the mask would be 255.255.255.0
D is incorrect; 172.16 is not a public IP address.
E is incorrect; 0.254 is not a broadcast address.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 234-236.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 49 -
Page 50

640 - 607
Q. 71
Which statement about an IP network is true?
A. A broadcast source MAC contains all zeros.
B. A MAC address is part of the physical layer of the OSI model.
C. MAC addresses are used by bridges to make forwarding decisions: IP addresses are used by
routers.
D. IP addresses are now a flat addressing scheme: MAC addresses use a hierarchical addressing
scheme.
Answer: C
Explanation: A bridge uses MAC addresses to make routing decisions whereas a routers uses IP addresses to
makes its routing decisions.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; for broadcasts MAC uses the address is all ones, or X’FF’ for each octet.
B is incorrect; the MAC address is part of the Data Link Layer.
D is incorrect; it is reversed. MAC is Flat Addressing, and IP is hierarchical.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 170-173.
Q. 72
Which statement about the Committed Information Rate (CIR) is true?
A. It is the rate, in bits per second, at which the Frame Relay switch agrees to transfer data
B. It is the clock speed (port speed) of the connection (local loop) to the Frame Relay cloud
C. It is the maximum number of bits that the switch can transfer during any Committed Rate
Measurement Interval
D. It is a signaling standard between the CPE device and the FR switch. It is responsible for managing
the connection and maintaining status between the devices.
Answer: A
Explanation: CIR is the rate in bits per second at which the service provided guarantees that data will be
transferred.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; clock rate defines the clock speed.
C is incorrect; CIR can be exceeded.
D is incorrect; CIR is not a signaling standard.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 50 -
Page 51

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 414.
Q. 73
Which statement about the specialized IP addresses shown in the EXHIBIT is true?
EXHIBIT:
10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
A. They are private IP addresses.
B. They can not be leased with DHCP.
C. They are allocated for VOL PVOLP.
D. They represent IP classless addresses.
E. They are used by the inter NIC for administration.
Answer: A
Explanation: RFC 1918 defines networks and addresses 10.0.0.0 through 10.255.255.255, 172.16.0.0 through
172.31.255.255, and 192.168.0.0 through 192.168.25.255 as reserved addresses to be used as internal private
addresses and not to connect directly to the public Internet.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; they can be leased by DHCP.
C is incorrect; they are not allocated for VOL PVOLP.
D is incorrect; these range of addresses still retain their implied class.
E is incorrect; inter NIC does not use these IPs for administration.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 224.
Q. 74
What are four function/characteristics of the network layer of the OSI model? (Choose four)
A. It uses a two-part address.
B. It maintains routing tables.
C. It uses broadcast addresses.
D. It establishes network addresses.
E. It provides access to the LAN media.
F. It provides media independence for upper layers.
G. It provides path selection for Internet work communication.
Answer: A, B, C, G
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 51 -
Page 52

640 - 607
Explanation:
The network layer defined how to transport traffic between devices that are not locally attached in the same
broadcast domain. For the communication the device will require two pieces of information: a logical address
associated with the source and destination stations and a path through the network to reach the desired
destination. Both of the required information is stored in the devices routing table. The addresses within the
routing table are considered to be a logical network address that contains two parts: one part that identifies the
network and another part that uniquely identifies the host on each of those networks. If the address of the
destination device is unknown to the device it will broadcast the packet to the remaining interfaces.
Incorrect Answers:
D is incorrect; the network layer does not establish addresses rather it uses the addresses to route information.
E is incorrect; the physical layer provides access to media.
F is incorrect; the data link layer provides media independence for upper layers.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 24-6.
Q. 75
What is the result of segmenting a network with a router into segments 1 and 2?
A. It increases the number of collisions.
B. It decreases the number of broadcast domains.
C. It connects segment one’s broadcast to segment two.
D. It prevents segment one’s broadcast from getting to segment two.
Answer: D
Explanation: The broadcast domains are broken up and separated.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the number of collisions is decreased.
B is incorrect; the number of broadcast domains is increased.
C is incorrect; the broadcast domains are broken up and separated.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 26-27.
Q. 76
Which three basic switch functions increase available bandwidth on the network? (Choose three)
A. Loop avoidance.
B. Address learning
C. Hop count limiting
D. Broadcast filtering
E. Packet forward/filtering.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 52 -
Page 53

640 - 607
Answer: A, B, E
Explanation: A switch has three basic functions, which increase the available bandwidth on a network. These
functions are address learning, forward/filter decision, and loop avoidance,
Incorrect Answers:
C is incorrect; although a switch functions a lot like a multi-port bridge, a switch does not affect – nor is
affected by – the hop count.
D is incorrect; by their very design Broadcast are meant to be seen by everyone.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 146-152.
Q. 77
Which statement is true?
A. While bridges are used to segment networks they will not isolate broadcast or multicast packets.
B. A bridge looks at every packet with in its network segment and works like a hub, re-
broadcasting the packet if the destination is with in its network segment.
C. A bridge maintains a table of the IP addresses of the hosts with in its network segment and
forwards the packet directly to the destination based upon the IP address.
D. Bridge resets the hop count by keeping all packets within the network segment only packets
addressed to its specific destination host outside the network segment are allowed to pass
through the bridge.
Answer: A
Explanation: Bridges (and switches) maintain only one broadcast domain.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; if the data does not need to be transferred by the bridge, then it does not need to be
rebroadcasted.
C is incorrect; a bridge operates on layer 2 using MAC addresses, and IP addresses are Layer 3.
D is incorrect; the hop count is not reset.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
Q. 78
What is not a characteristic of a network segment on a switch?
A. The segment has its own collision domain.
B. The segment can translate from one media to a different media.
C. All devices in the segment are part of the same broadcast domain.
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 21-24.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 53 -
Page 54

640 - 607
D. One device per segment can currently send frames to the switch.
Answer: B
Explanation: A switch is usually only handle one media type at a time.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C and D are incorrect; the statements are characteristics of a network segment on a switch.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 78-80.
Q. 79
Which three are typical operational phases in a basic connection oriented network service? (Choose
three)
A. Call setup
B. Data transfer
C. Load Balancing
D. Call termination
E. Call prioritization
F. Data segmentation
G. Data link identification
Answer: A, B, D
Explanation:
In connection oriented services, the three steps are: Call Setup, Data Transfer, Call Termination.
Incorrect Options
C, E, F and G are incorrect; these options may occur but are not required.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 29-30.
Q. 80
What is a function of a reliable transport layer connections.
A. Route selection
B. Acknowledgement
C. Session checkpoints
D. System authentication
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 54 -
Page 55

640 - 607
Answer: B
Explanation: Acknowledgement is required to insure packets were not loss and this is how a reliable transport
layer connection is maintained.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; route selection is performed by the network layer.
C and D are incorrect; these are not transport layer functions.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 28-30.
Q. 81
Using the TCP/IP suite a message is sent from host A to a destination IP address on the same LAN. How
does host A determine the destination’s MAC address?
A. It uses a Proxy ARP.
B. It uses ARP requests.
C. It uses RARP requests.
D. It uses router look up table.
Answer: B
Explanation: Address Resolution Protocol is used to resolve or map a known destination IP address to a MAC
sublayer address to allow communication.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; Proxy ARP is most often used with hosts on separate subnets.
C is incorrect; Reverse ARP is used to resolve an IP address on a given MAC address.
D is incorrect; a router’s table is not used for this.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 218-220.
Q. 82
Which three statements about common elements of the TCP/IP protocol stack are true? (Choose three)
A. IP provides connection less service and routing capabilities.
B. ARP enables devices to locate the IP address of local devices.
C. UDP provides simple connection less service without windowing or acknowledgements.
D. ICMP provides connection oriented management data to routers and layer three switches.
E. TCP enables devices to send large quantities of data using switching in a connection-oriented
manner.
Answer: A, C, E
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 55 -
Page 56

640 - 607
Explanation: The TCP/IP protocol stack is very similar to the OSI model protocol stack. With TCP/IP
connection orientated and connection less communication is possible. Both IP and UDP are both
connectionless. TCP is a connection-orientated protocol.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; RARP and not ARP provide this functionality.
D is incorrect; ICMP is connection less.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 215-218.
Q. 83
What is the tw o most common request/reply pair with ICMP messages when using the p ing command?
(Choose two)
A. Echo reply
B. Echo request
C. Source quench
D. Fragment offset
E. Information redirect
F. Destination reachable
G. Echo control message
Answer: A and B.
Explanation: The most common form of these messages are pings, ICMP echo request, and ICMP echo replies.
Incorrect Answers:
C, D, E, F, and G are incorrect; these are not types of ICMP messages.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 217-219.
Q. 84
Which two protocol tools use ICMP? (Choose two)
A. Ping
B. Telnet
C. Configure
D. Trace route
E. Show commands
F. Standard access list
Answer: A, D
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 56 -
Page 57

640 - 607
Explanation: The two protocol tools that use ICMP messaged to perform their function are ping and trace
route.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; telnet uses TCP.
C is incorrect; configure is not a protocol tool.
E and F are incorrect; they are not part of ICMP, nor do they use ICMP.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 217-218.
Q. 85
Which command successfully ping an individual IP address?
A. Router>ping 192.5.5.0
B. Router# ping 192.5.5.30
C. Router> ping 192.5.5.256
D. Router# ping 192.5.5.255
Answer: B
Explanation: In order to ping an individual IP address you must be in the privileged EXEC mode.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; to ping you must be in the privileged EXEC mode not the user EXEC mode.
C is incorrect; to ping you must be in the privileged EXEC mode not the user EXEC mode.
D is incorrect; this is not a valid individual IP address.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 69 and 123-124.
Q. 86
Your network uses a class C address of 210.10.10.0 you must now split up the network into separate
subnets to handle multiple buildings separated by router. Which two steps must you take to determine
the proper subnet mask for your network? (Choose two)
A. Determine the number of separate networks required.
B. Determine how many devices will require DHCP addressing.
C. Determine the maximum number of host that will be on each subnet.
D. Determine the minimum number of host that will be on each subnet.
E. Determine which router will be the IP default gateway for each subnet.
Answer: A, C
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 57 -
Page 58

640 - 607
Explanation: Whenever a network is going to be divided by a router a number of factors needs to be
considered when selecting a subnet mask. Two factors that need to be considered is the number of networks
that you require and the maximum number of host each subnet will require.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; DHCP addressing is not relevant in the subnet mask design.
D is incorrect; since the number of hosts has to satisfy ALL of the subnets, we must accommodate the subnet
with the highest number of hosts, so we need the maximums of each, and then take the largest of all the
maximums.
E is incorrect; this task may need to be done but this task has nothing to do with designing the new subnet mask.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 235-237.
Q. 87
How many collisions are caused by transmitting and receiving frames simultaneously in a full-duplex
Ethernet Technology?
A. One
B. Two
C. None
D. Several
Answer: C
Explanation: Full Duplex requires one and only one device to be hooked up to a switch port, and each switch
port is a separate collision domain. Since there is no contention (the node has ex clusive control of the segment)
there are no collisions.
A, B and D are incorrect; it is impossible for collision to occur within a full duplex network.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 163-165.
Q. 88
Which Cisco IOS command should you use to display the Novel IPX address assignments on a router?
A. Show IPX addresses.
B. Show IPX interface.
C. IPX network <number>
D. Display IPX addresses
E. Show IPX routing details
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 58 -
Page 59

640 - 607
Answer: B
Explanation:
The show ipx int erface command shows the status of the IPS interface and IPS parameters configured on each
interface. This includes the IPX address.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; there is no such command as show ipx addresses.
C is incorrect; the ipx network com mand is used to enabl e IPX routing on a particular interface. The <number>
parameter is used to identify the network that IPX is enabled on.
D is incorrect; whenever you want to display something on a Cisco interface you use a show command. There
is no such command as display ipx addresses.
E is incorrect; there is no such command as show ipx routing details. To show the contents of a routing table
you would use the show ipx route command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 345-347.
Q. 89
Which commands should you use to enable IGRP routing?
A. router igrp 100
network 192.168.1.0
network 10.0.0.0
B. router igrp 100
network 192.168.1.0
network 10.2.0.0
C. router igrp 100
network 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.1
network 10.2.0.0 10.2.1.1
D. router igrp 100
network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
network 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0
Answer: A
Explanation: To enable IGRP you use the router igrp and network commands. Please note an autonomous
system number must follow the router igrp command and a valid network number must follow the network
command. For RIP and IGRP network numbers must be a major class network number and does not include
neither subnet numbers nor individual addresses.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 59 -
Page 60

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the number 10.2.0.0 is the problem for this option
C is incorrect; each network identified must have its own network command.
D is incorrect; this is not correct as there is no need to use the subnet mask for the networks.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 277, 285-286.
Q. 90
Which show command should you use to view Frame Relay local management interface (LMI) traffic
statistics?
A. show lmi
B. show ip route
C. show interface
D. show statistics
E. show frame-relay lmi
Answer: E
Explanation: The show frame-relay lmi command displays lmi statistics. An example of one of these statistics
is the number of status messages sent between the local router and the Frame Relay switch.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; show lmi is not a valid command.
B is incorrect; show ip route command displays the contents of the IP routing table.
C is incorrect; show interface command displays a serial interface configuration
D is incorrect; show statistics is not a valid command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 422-423, 280, and 106.
Q. 91
Which command specifies a second subinterface on serial interface zero?
A. interface s 0.2 point - to point
B. interface 2 s 0 point to point
C. sub interface 2 s 0 point to point
D. interface 0 sub 2 point to point
E. interface s 0.1 point to point sub 2
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 60 -
Page 61

640 - 607
Answer: A
Explanation: The proper syntax for configuring a second subinterface is interface 0.2 point-to-point. Option A
is the closest to this command. The syntax after the command interface is serial interface number (0 in this
case).subinterface number (2 in this case) and this followed by the either multipoint or point-to-point.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; remember that the syntax is suppose to be number.subinterface number and that there is suppose
to be two hyphens in point -to-point.
C is incorrect; the command is interface not subinterface.
D is incorrect; the two numbers are broken by a period and not the word sub.
E is incorrect; this is not the proper syntax. Remember the interface and subinterface are identified by
number.subintreface number.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 428-429.
Q. 92
Which three tasks are required to conf igure a dial on d emand routing (DDR) Basic Rate Interface (BRI)
connection? (Choose three)
A. Define static routes.
B. Configure the dialer information.
C. Specify interesting traffic that can enable the link.
D. Define DDR password to exchange when the link comes up.
Answer: A, B, C
Explanation:
To configure standard DDR, the following steps are required:
1. Define static routes – What route do I take to get to the destination?
2. Specify interesting traffic – What traffic type should enable the link?
3. Configure the dialer information – What number do I call to get to the next hop router, and what service
parameters do I use to call?
Incorrect Answers:
D is incorrect; defining a DDR password is not required.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 400-403.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 61 -
Page 62

640 - 607
Q. 93
Which two statements accurately define IP addressing rules? (Choose Two)
A. IP multicast addresses start with 240
B. A host portion of all 1’s indicates a network broadcast
C. The value of zero (0) in the host portion means “all hosts” on the network
D. IP addresses are four octets long and contain a network portion and a host portion
Answer: B, D
Explanation: IP addresses contain 4 octets. IP addresses contain two parts: one to identify the network and the
other to determine the host. Which octet identifies what is dependant on the class of the IP address. When a
message is to be flooded the IP address contain all 1s.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; multicast broadcasts of range of IPs is 224-239t. 240 begins the range of reserved (Class E)
addresses.
C is incorrect; to flood a message to all host of a network, the IP address would contain the network
identification and then all 1s (represented by 255) in the host portion of an IP.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 222-232.
Q. 94
Which three statements about Frame Relay configuration using sub interfaces are true? (Choose three)
A. Each subinterface is configured either multi point or point to point.
B. Any network address must be removed from the physical interface.
C. The configuration of subinterfaces is done in router Config-(if)# mode.
D. Frame relay encapsulation must be configured on each sub interface.
Answer: A, B, C
Explanation: When configuring Frame Rel ay at the sub interface there are a number of points that you be kept
in mind. To configure subinterfaces on a physical interface, do the following:
1. Select the interface you want to create subinterfaces on, enter interface configuration mode, (config-if)#.
2. It is recommended that you remove any network layer address assigned to the physical interface and
assign the network layer address to the subinterface.
3. Configure Frame Relay encapsulation on the physical interface.
4. Identify the subinterface as either multipoint or point-to-point.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 62 -
Page 63

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
D is incorrect; the encapsulation type must be done on the physical interface.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 428-429.
Q. 95
What is the bandwidth capacity of an ISDN B channel?
A. 16 Kbps
B. 64 Kbps
C. 128 Kbps
D. 512 Kbps
E. 1.54 Mbps
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Bearer (B) channel transfer rate is 64 kbps.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; is the Delta (D) channel that has a transfer rate of 16 kbps.
C, D and E are incorrect; the ISDN B channel only operates at a maximum of 64 kbps.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 387-388.
Q. 96
Which command should you use to create an IP standard access list?
A. Access-list standard 172.16.4.13
B. Access-list 1 deny 172.16.4.13 0.0.0.0
C. Access-list 100 deny 172.16.4.13 0.0.0.0
D. Access-list 198 deny 172.16.4.13 255.255.255.255
Answer: B
Explanation: A standard access list is in the range of 1-99 and the proper command syntax is access-list
{access-list number} {permit or deny} {test conditions}. In this case the test condition is an ip address.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the access command must contain a number and whether the action is to be permitted or denied.
C is incorrect; 100 is an extended access-list number and not a standard number.
D is incorrect; 198 is also an extended access-list number and not a standard number.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 63 -
Page 64

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 304-305.
Q. 97
Which router command allows you to determine if an IP access list is enabled on a particular interface?
A. Router# show ip interface
B. Router> show access-list
C. Router# show ip access-list
D. Router> show interface ip access-list
Answer: A
Explanation: The show ip interface command displays IP interface information and indicates whether any
access lists are set for a specific interface.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the show access-lists command must be given in the privileged EXUC mode.
C is incorrect; even if the proper command was used the end result would the displaying of all IP access lists
running in the router, not for a particular interface.
D is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 324-325.
Q. 98
Which router command allows you to view the entire contents of all access lists?
A. Router# show interface
B. Router> show IP interface
C. Router# show access-list
D. Router> show all access list
Answer: C
Explanation: The show access-lists command will display the contents of all access lists. C is the closest to this
command.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; only access lists bound to that interface would be displayed
B is incorrect; show ip interface command must be given in the privilege EXEC mode.
D is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 64 -
Page 65

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 324-325.
Q. 99
Which statement about Ethernet networks is true?
A. The advantage of a full duplex is the ability to transmit data over Mbase2 cable.
B. Full duplex Ethernet requires a point-to-point connection when only two nodes are present.
C. Ethernet switches can use full duplex mode to connect multiple nodes to a single port of a switch.
D. Half duplex is a cut through packet processing method that is very fast with little error correction,
full duplex is store and forward method that is slower but has better error correction.
Answer: B
Explanation: Full duplex always requires there to be a point to point connection.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; full duplex is done over CAT 5 cable.
C is incorrect; full duplex can only be done if one node is attached to a particular port.
D is incorrect; Half/Full duplex is independent of cut-through and/or store and forward.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 165.
Q. 100
On a network design project you determine that a new testing application requires multiple hosts. These
hosts must be capable of sh arin g data b etw een each h ost and an en terp rise server at 10 Mb ps b an dw i dth .
Other divisions in the company use applications that require less than 2 Mbps bandwidth of the
enterprise serve.
What is your economical recommendation?
A. That the existing 10BaseT hub be replaced with 100BaseT hub to improve overall performance.
B. That a router can separate the testing application from the rest of the network thus allowing the
testing application more bandwidth.
C. That the switch be installed so that enterprise server can be provided a 100 Mbps port and each
of the testing application hosts can be given dedicated 10 Mbps ports.
D. That a bridge be placed between the enterprise server and all other users with the exception of
the testing application.
Answer: C
Explanation: With buffering in the switch, the enterprise server can serve multiple hosts at almost full capacity,
since the 100Mbps port will be faster than the rest of the users totaled as a whole.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 65 -
Page 66

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this would require all NICs to be upgraded, and result in a large collision domain with possible
poor performance.
B is incorrect; a router would become a bottleneck, and not allow efficient performance.
D is incorrect; a bridge would be a bottleneck, and not be able to provide the necessary performance and
throughput.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 31-38.
Q. 101
A network is very congested. Currently all the devices are connected through a hub. Which solution
would best decrease congestion on the network?
A. Add a second hub
B. Replace the hub with a router.
C. Replace the hub with a switch.
D. Replace the hub with a repeater.
Answer: B
Explanation: A router would break each segment into their own collision domains and broadcast domains.
This would reduce network congestion the most.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; there will still be one collision domain which would mean that the network would still be
congested.
C is incorrect; if money were a factor in your solution to network congestion then this would be the best option.
D is incorrect; a repeater does not affect congestion.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
Q. 102
What is the distance limitation for 100BaseT?
A. 607 ft
B. 25 meters
C. 1000 ft
D. 100 meters
E. 185 meters
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 20-27.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 66 -
Page 67

640 - 607
Answer: D
Explanation: A 100BaseT cable cannot be any longer than 100 meters.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B, C, & E are wrong.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 45.
Q. 103
Which command sets the clock rate to 56 Kbps on serial0?
A. clockrate 56
B. clock rate 56
C. clockrate 56000
D. clock rate 56000
E. set clockrate 56
F. serial 10 clockrate 56
G. clock rate 56000 serial 10
Answer: D
Explanation: The proper syntax to set the clock rate is clock rate {speed}. Please remember the speed cannot
be abbreviated.
Incorrect Answers:
A and C are incorrect; clock rate must be separated.
B is incorrect; the speed cannot be abbreviated and must be 56000.
E, F and G are incorrect; this are not valid commands.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 105-106.
Q. 104
If you are in IOS user mode which command do you use to enter the privileged mode?
A. Set
B. Enable
C. Configure
D. Privileges
Answer: B
Explanation: To change from the user EXEC mode to the privileged EXEC mode the command is enable.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 67 -
Page 68

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the command set must be followed by another parameter such as user and the set command
cannot be used to get into the privileged mode
C is incorrect; configure is used in privileged mode, but does not ENTER that mode.
D is incorrect; this in not valid command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 69-70.
Q. 105
In the setup dialogue what do the square bracket indicate?
A. Current or default settings.
B. Hard coded values that cannot be modified.
C. Values entered by the administrator but not saved.
D. Values that must be returned to NVRAM before becoming enabled.
Answer: A
Explanation: When in the setup dialog box the default/current settings are in the square brackets.
Incorrect Answers:
B, C, and D; the square brackets represent current or default settings.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 85.
Q. 106
Routers that have flash memory typically have preloaded copy of Cisco IOS software.
Which command should you use to make backup copy of the software image onto a network server?
A. Copy Flash TFTP
B. Save Copy TFTP
C. Write Backup TFTP
D. Write Backup (server-name)
E. Copy backup 2 (server-name)
Answer: A
Explanation: The proper command to save the IOS image is copy flash tftp. This will copy the IOS onto a tftp
server.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; there is no save command. With Cisco to save something you most often copy it.
C and D are incorrect; there is no Write command.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 68 -
Page 69

640 - 607
E is incorrect; this is not a valid command combination.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 138-139.
Q. 107
Which command retrieves the configuration file from NVRAM?
A. Config NVRAM
B. Copy NVRAM running-config
C. Copy startup-config running-config
D. Copy running-config startup-config
Answer: C
Explanation: To copy the IOS image in the NVRAM to the RAM the copy startup-config running-config
command is used.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid command combination.
B is incorrect; this is not a valid command combination.
D is incorrect; this actually copies the IOS image from the RAM to the NVRAM which is the exact opposite of
what the question asked.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 133.
Q. 108
Which command allows the user to see a system message when logging into a router?
A. Banner MOTD
B. Message MOTD
C. Banner Message
D. Message Banner
Answer: A
Explanation: In order for a user to see a message when the log into a router a message of the day will need to
be employed. The command to do this is banner motd.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the command is banner not message.
C is incorrect; the proper parameter is motd not message.
D is incorrect; this is an invalid command.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 69 -
Page 70

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 101-102.
Q. 109
Which line from a show spantree 1 command output ind icates that virtu al LAN1 (VLAN1) is fun ctioning
properly?
A. Root port is fast Ethernet 0/26
B. Port Ethernet 0/1 of VLAN is forwarding
C. Designated port is Ethernet 0/1, path cost 10
D. Designated root has priority 0 address 00D0.588F.B600
E. VLAN is executing the IEEE compatible spanning tree protocol.
Answer: E
Explanation: To determine if the VLAN is functioning properly on will need to examine the first line of the
output. That is, VLAN is executing the IEEE compatible spanning tree protocol.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this line indicates what the switch thinks is the root port.
B is incorrect; this line indicates which port is forwarding.
C is incorrect; this line indicates the designated port and its associated cost.
D is incorrect; this line indicated the MAC address of the designated root.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 199-200.
Q. 110
What is the most common Layer 2 device?
A. Hub
B. Router
C. Switch
D. Repeater
Answer: C
Explanation: Switches and Bridges run on Layer 2.
Incorrect Answers:
A and D are incorrect; they are Layer 1 – Physical Layer devices
B is incorrect; routers are layer 3 device.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 14-24.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 70 -
Page 71

640 - 607
Q. 111
Which encapsulation type should be used for the S0 port of Router R2?
A. SAP
B. HDLC
C. ARP
D. NOVELLETHER
Answer: B
Explanation: Actually we can answer this question using the exhibit in the following example. Router R2 S0
connects to Router R1 S0. Router R1 S0 uses HDLC, and BOTH sides must run the same protocol in order to
communicate (it is like talking the same language; you can’t have one side English and the other Side French).
So the correct answer is B – HDLC.
Incorrect answers:
A, B and C are incorrect; the two routers must have the same encapsulation type to communicate properly thus
these encapsulation types could not be used.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 368-373.
Q. 111
Exhibit
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 71 -
Page 72

640 - 607
Which command specifies a second sub interface on serial interface 0?
A. Interface s0.2 point-to-point
B. Interface 2s0 point-to-point
C. Subinterface 2s 0 point-to-point
D. Interface s0 sub2 point-to-point
E. Interface s0.1 point-to-point sub2
Answer: A
Explanation: The proper syntax for configuring a second subinterface is interface 0.2 point-to-point. Option A
is the closest to this command. The syntax after the command interface is serial interface number (0 in this
case).subinterface number (2 in this case) and this followed by the either multipoint or point-to-point.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; remember that the syntax is suppose to be number.subinterface number and that there is suppose
to be two hyphens in point -to-point.
C is incorrect; the command is interface not subinterface.
D is incorrect; the two numbers are broken by a period and not the word sub.
E is incorrect; this is not the proper syntax. Remember the interface and subinterface are identified by
number.subintreface number.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 428-429.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 72 -
Page 73

640 - 607
Q. 113
Which statement should you use to deny FTP access only from Network 210.93.105.0 to Network
223.8.151.0?
A. Access-list one deny 210.93.105.0.0.0.0.0.0 any eq ftp access-list one permit any.
B. Access-list 100 deny tcp 210.93.105.0 0.0.0.255 223.8.151.0 0.0.0.255 eq ftp
C. Access-list 100 deny ip 223.8.151.0 0.0.0.255 any eq ftp
Access-list 100 permit ip any any
D. Access-list 100 deny tcp 210.93.105.0 0.0.0.255 223.8.151.0 0.0.0.255 eq ftp
Access-list 100 permit ip any any
Answer: D
Explanation: Great care must be taken whenever an access list is configure as there is an assumption of deny
all when they do not match the access list. The proper command for configuring an extended access to deny ftp
traffic is: access-list 100 deny tcp source address destination address eq FTP. When configured this way the
access list will deny ftp traffic and permit all other.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the entire statement has syntax problems. You use a number, not a word (one) for the access list,
and the access list for this problem needs to be an extended address list in the range of 100-199.
B is incorrect; this access list will deny access, but then any non-match falls through and will be denied.
C is incorrect; this access list denies access from 223.8.151.0 to anywhere else – this is not what the problem
asked. 223.8.151.0 is supposed to be the destination, not the source.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 318-320.
Q. 114
Which network mask should you place on a class C address to accommodate a user requirement of two
sub networks with a maximum of 35 hosts on each network?
A. 255.255.255.192
B. 255.255.255.224
C. 255.255.255.240
D. 255.255.255.248
Answer: A
Explanation: For the networks, we need 2 bits. We must really accommodate for networks, because when we
subnet the formula is 2**n –2. For 35 hosts, we need a minimum of 37 hosts for the same reason, 2**n –2. We
round 37 up to the next power of 2, which is 64, and we need 6 bits for the host. We use 2+6=8 bits.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 73 -
Page 74

640 - 607
When we look at the bit locations, the first two bits of the fourth octet will be 128+64=192. Thus the subnet
mask will be 255.255.255.192. Since there is no room to adjust the allocation, everything fits fully into 8 bits,
none of the other subnet masks will provide this combination.
Incorrect Answers:
B, C and D are incorrect; these subnet mask provide too many networks and not enough host addresses.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 225-228 and 236.
Q. 115
What are two purposes of segmenting a network with a bridge? (Choose two)
A. To reduce collisions.
B. To increase collisions.
C. To add collision domains.
D. To reduce collision domains.
E. To have more broadcast domains.
Answer: A, C
Explanation: When you segment a network with a bridge you are reducing the number of collisions by creating
another collision domain.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; a bridge decreases collisions, not increases collisions.
D is incorrect; Collision domains are increased, not decreased.
E is incorrect; there is still one and only one broadcast domain.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 21-24.
Q. 116
What is an advantage of using a connectionless protocol such as UDP?
A. Packet acknowledgement may reduce overhead traffic.
B. Loss or duplication of data packets is less likely to occur.
C. Packets are not acknowledged which reduces overhead traffic.
D. The application relies on the transport layer for sequencing of the data packets.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 74 -
Page 75

640 - 607
Answer: C
Explanation: Connectionless protocols have many advantages. One of the main advantages is that there is a
reduction in overhead traffic, as acknowledgments are not sent. This does, though, increase the likeyhood of a
lost packet.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; there is no packet acknowledgement in UDP.
B is incorrect; this is the opposite, UDP does not guarantee against packet loss.
D is incorrect; UDP does not expect packet ordering.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 29-30.
Q. 117
Which statement is true when a broadcast is sent in an Ethernet/802.3 LAN?
A. The IP subnet used is 255.255.255.0
B. The IP address used is 255.255.255.255
C. The MAC address used is 00-00-00-00-00-00
D. The MAC address used is FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF.
Answer: D
Explanation: The MAC address for a broadcast is FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF.
Incorrect Answers:
A and B are incorrect; these are IP addresses and 802.3 uses MAC addresses.
C is incorrect; this is the address used for a multicast.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 149-152.
Q. 118
What are two components of an IPX address?
A. Network number; IP address.
B. MAC address; node number.
C. Network number; MAC address.
D. Network number; subnet number.
Answer: C
Explanation:
An IPX address is composed of two parts: the network number and the node number. For IPX the node number
is usually obtain from MAC address of the network interface.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 75 -
Page 76

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; an ipx address does contain the network number but it does not contain an IP address.
B is incorrect; the MAC address and node number are most often the same thing.
D is incorrect; the ipx address does not contain the subnet number.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 332-333.
Q. 119
Which two statements about integrated services digital network (ISDN) are true?
(Choose two)
A. ISDN provides only data only capability.
B. ISDN provides an integrated voice/data capability.
C. The ISDN standards define the hardware and call setup schemes for end-to-end digital connectivity.
D. Users receive more bandwidth on WANs with a leased line of 56kbps than with multiple b channels.
Answer: B, C
Explanation:
ISDN stands for Integrated Services Digital Network. ISDN refers to a collection of standards that define a
digital architecture that provides an intergraded voice/data capability to customers’ premises facility. The ISDN
standards define the hardware and call setup schemes for end-to-end digital connectivity.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; ISDN provides for voice and data capability.
D is incorrect; ISDN BRI offers a total of 144 kbps and ISDN PRI offers even more.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 390.
Q. 120
Which prompt and command combination sets RIP as the routing protocol?
A. Router# rip.
B. Router rip.
C. Router (Config)# rip.
D. Router (Config)# router rip.
Answer: D
Explanation: In order to configure RIP as the routing protocol you need to ensure that you are in the route
configuration mode and that you use the command router rip.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 76 -
Page 77

640 - 607
A is incorrect; this is both the wrong mode and command.
B is incorrect; this is both the wrong mode and command.
C is incorrect; this is the proper mode but the wrong command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 277-279.
Q. 121
What are 4 ways network management can be simplified by using the virtual LANs (VLANs)? (Choose
four)
A. VLANs allow you to implement multiple layers switching easily.
B. VLAN can group several broadcasts domains into multiple logical subnets.
C. It is no longer necessary to install cables to move a user from a new network to another.
D. Network adds, moves and changes are achieved by configuring a port into a VLAN.
E. A group of users needing high security can be put into a VLAN so that no users outside the VLANs
can communicate with them.
F. As a logical grouping of users, VLANs can be considered independent from their physical or
geographic locations.
Answer: C, D, E, F
Explanation: The introduction of VLANs into a network has a number of benefits. The benefits include:
security, segmentation and flexibility. VLANs allow you to group users into a common broadcast domain
regardless or their physical location in the internetwork. VLANs greater flexibility allows user to moved easily,
changes to the network can be as simple as configuring a port and security can be increased.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; VLANs add complexity to the switch configurations.
B is incorrect; the VLAN still maintains one broadcast domain in each VLAN
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 179-184.
Q. 122
With one method of transmitting fames through a switch the switch receives the complete frame and
checks the frame CRC before forwarding the frame. What is this transmitting method called?
A. CSMA/CD
B. Full duplex.
C. Cut through.
D. Half duplex.
E. Fragmentation.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 77 -
Page 78

640 - 607
F. Stored and forwarded.
Answer: F
Explanation: In store and forward mode, the switch must receive the complete frame before forwarding takes
place. The destination and source addresses are read, the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is performed, relevant
filters are applied, and the frame is forwarded. If the CRC is bad, the frame is discarded. The latency (or delay)
through the switch varies with frame length.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; CSMA/CD is the physical method used on a 802.3 LAN
B is incorrect; Full duplex is when you can transmit and receive at the same time.
C is incorrect; in cut-through mode the frame is forwarded after the Destination Address has been read.
D is incorrect; Half Duplex means EITHER transmit or receive, but not both at the same time,
E is incorrect; this is not a switch mode. Fragment-free mode is a switch mode.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 162-163.
Q. 123
Switching methods include cut-through, store and forwarded and a modified version of the first two
methods. Which statement about switching methods is true?
A. The stored and forward method has low latency.
B. The cut through method and switching has high latency.
C. The modified version holds the packet in memory until 50% of the packet reaches the switch.
D. The modified version holds the packet in memory until the data portion of the packet reaches the
switch.
Answer: D
Explanation: The modified cut-through (also known as fragment-free) the switch reads into the first 64 bytes
before forwarding the frame.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; Store and Forward has HIGH latency.
B is incorrect; Cut-Through has LOW latency.
C is incorrect; it is not 50%. In the modified version, the frame transmission does not start until the first 64
bytes are read.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 162-163.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 78 -
Page 79

640 - 607
Q. 124
Which technology do catalyst switches use to resolve topology loops and ensure data use flows properly
through a single network path?
A. Virtual LANs.
B. Frame filtering.
C. Cut through switching.
D. Spanning tree protocol.
Answer: D
Explanation: Spanning Tree protocol builds ONE path through all the nodes, and eliminates any loops.
Anything sent along the tree will not encounter any loops because the protocol will eliminate any loops.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; VLANs is not a loop resolution technology.
B is incorrect; Frame Filtering is not a loop resolution technology.
C is incorrect; Cut Through switching is not a loop resolution technology. Rather it is a form of forwarding.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 155-160.
Q. 125
Which two statements are true? (Choose two)
A. Ethernet 802.3 utilizes a half duplex method for data transfer.
B. In a 100mbps point to point connect, a full duplex connection can provide 400mbs of data transfer.
C. Ethernet switches can use the full duplex mode to connect multiple nodes on a single port office
switch.
D. Full duplex Ethernet takes advantage of UTP using one pair of transmission and other pair for
reception.
Answer: A and d.
Explanation: Half duplex Ethernet is most often found in a 802.3 network and full duplex achieves data
transmission by using one pair to receive data and another to send data.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; in full duplex you can maximize up to double – by transmitting and receiving at the same time,
for a nominal maximum throughput of 200mbps.
C is incorrect; when running full duplex, only one device can be attached to the port.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 79 -
Page 80

640 - 607
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 163-165.
Q. 126
What is a backoff on an 802.3 network?
A. It is latency in store and forward switching.
B. It is the time used for token passing for machine to machine.
C. It is the retransmission delay that is reinforced when a collision occurs.
D. It is the result of two nodes transmitting at a same time the frames from each transmitting device
collide and are damaged.
Answer: C
Explanation: Backoff is done when a collision occurs. Those trying to transmit at the same time “back-off” and
attempt to retransmit at a later time. A 802.3 network uses collision detection, so that the transmitters are
notified of the collision. Then using a random calculated wait time, re-transmission occurs. By using a random
wait time, hopefully both transmitter wait a different amount of time and do not attempt simultaneous
transmission again.
Incorrect Answers: A is incorrect; back off occurs after a collision has occurred and is not latency stored and forward switching.
B is incorrect; has nothing to do with the passing of the token.
D is incorrect; back off is used to prevent another collision.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 16-17.
Q. 127
You have just issued an erase startup-config command and reloaded your router. In which mode will
your router be when you reboot?
A. Setup.
B. Startup.
C. User EXEC.
D. User privileged.
E. Global configuration.
Answer: A
Explanation: When a router is booted, it will copy the startup-config from NVRAM to the RAM and begin
execution. Since the erase wiped out the startup configuration, the router can’t start. This forces the router into
setup mode, where a configuration has to be built from by scratch.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 80 -
Page 81

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
B: Incorrect because there is no configuration to startup.
C, D, E: Incorrect because there is no longer a configuration to run, these modes do not exist.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 84-90 and 134.
Q. 128
What is a key use of a device hardware address?
A. To obtain a vendor code/serial number from the user.
B. To transmit a frame from one interface to another interface.
C. To transmit a packet from one local device to another local device.
D. To transmit data from one local device to remote device across Internet.
E. To contain logical information about a device to use an end-to-end transmission.
Answer: B
Explanation: A hardware address is used to transmit frames on the hardware level.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; a vendor code/serial number is a form of hardware address, and the user does not provide it.
C is incorrect; packets and devices are at a higher level in the layers.
D is incorrect; devices are handled at a higher layer, and use different addressing.
E is incorrect; a logical device with end-to-end may span more than two hardware interfaces; device addresses
are used from interface to interface, or hop-to-hop.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 172-175.
Q. 129
Which command verifies encapsulation as well as layer 1 and layer 2 statistics on a router configured f or
Frame Relay?
A. show IP
B. show interface
C. show statistics
D. show frame-relay
Answer: B
Explanation: The show interface command will show information regarding the encapsulation and Layer 1 and
Layer 2 status. It also displays information about the DLCIs used on the Frame Relay configured serial
interface.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 81 -
Page 82

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the show ip command displays the switches current IP configuration.
C is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
D is incorrect; Frame-relay will require another parameter after the show frame-relay IOS command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 421-424 and 82.
Q. 130
Which element is used to define the rate, in bits per second, which a Frame Relay switch agrees to
transfer data?
A. Clock rate
B. Committed information rate
C. Local management interface
D. Data-link connection identifier
E. Committed rate measurement interval
Answer: B
Explanation: CIR is the rate, in bits per second, at which the service provider states that data will be transfered.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; clock rate is the transmission medium speed, which is determined by modem clocking.
Odom. Cisco CCNA Exam #640-507 Certification Guide. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 28-30
C is incorrect; LMI is a signaling standard between the router device and the Frame Rekay switch that is
responsible for managing the connection and maintaining the status between the devices.
D is incorrect; DLCI is addressing used to identify virtual circuits.
E is incorrect; this is the sampling period used in controlling CIR, but is not the rate itself.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
Q. 131
How many valid host IP addresses are available on the following network/subnetwork?
176.12.44.16/30
A. 2
B. 30
C. 254
D. 16,382
E. 65,534
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 413-414.
- 82 -
Page 83

640 - 607
Answer: A
Explanation: This is a CIDR problem, also called supernetting. When you see the /xx notation, the xx is the
consecutive number of one bits in the subnet mask. In this case, /30 = 30, and is also a subnet mask of
255.255.255.252. This leaves 2 bits (4 hosts) for host addressing, however since we reserve 2 addresses, that
leaves a net of 2 Host Addresses, max.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 227-234.
Q. 132
Which command displays the IP addresses assigned to specific host names?
A. show hosts
B. show interface
C. ping host name
D. config host name
E. show host mapping
F. show host name IP address
G. trace IP addresses host name
Answer: A
Explanation: The show hosts command displays a cached list of host names and addresses.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the show interface command is used to display the configuration of an interface.
C – G are incorrect; these are not valid commands.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 106, 240-241.
Q. 133
At which layer of the OSI model does the ping command operate?
A. Session
B. Network
C. Transport
D. Maintenance
Answer: B
Explanation:
As the ping command is used to test network connectivity it resides on the network layer of the OSI model. 124
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 83 -
Page 84

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; the session layer is responsible for establishing, managing, and terminating communications
sessions between presentation layer entities. This layer is not responsible for the ping command.
C is incorrect; the transport layer of the OSI model is responsible for the delivery of information in either a
reliable or unreliable manner. Ping does not reside at this layer of the OSI model.
D is incorrect; there no maintenance layer in the OSI model.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 124, 10-13.
Q. 134
Given an IP address of 172.16.2.160 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192, to which subnet does the host
belong?
A. 172.16.2.32
B. 172.16.2.64
C. 172.16.2.96
D. 172.16.2.128
E. 172.16.2.192
Answer: D
Explanation: When we look at the last octet of the subnet mask, we have 192=128+64, which is the two high
order mask bits, leaving 6 bits for host addressing. Each subnet strides 64 addresses, including broadcast,
leaving the following networks:
172.16.2.0
172.16.2.64
172.16.2.128
172.16.2.192
We now look at the host address, which is 160, and find that it fits between 128 and 192, so the network is
172.16.2.128.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 227-234.
Q. 135
Which are two ways IPX supports multiple logical networks on an individual interface? (Choose two)
A. Network number
B. Routing protocol
C. Encapsulation type
D. Autonomous system number
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 84 -
Page 85

640 - 607
Answer: A, C
Explanation:
Multiple encapsulations can be specified on an interface, but only if multiple network numbers have also been
assigned, where each network number belongs to only one encapsulation type and each encapsulation type has
only one network number. Although several encapsulation types can share the same interface, clients and
servers with different encapsulation types cannot communicate directly with each other.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; routing protocol does not enable multiple logical networks.
D is incorrect; Autonomous System Number is used with certain routing protocols, and do not provide support
of logical networks.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 335.
Q. 136
Given the following IP address from the Class B address range:
172.35.21.12
Your network plan requires no more than 126 hosts on a subnet that includes this address. When you
configure the IP address in Cisco IOS software, which value should you use as the subnet mask?
A. 255.255.0.0
B. 255.255.128.0
C. 255.255.255.128
D. 255.255.255.252
Answer: C
Explanation:
Since we have to reserve the all ones and all zeros broadcast addresses, we take 126, add 2, and round up to the
next power of 2. W e get 126+2=128, and 128 is a power of 2, and takes 7 bits of the subnet mask to represent
the host address.
In the fourth octet of the subnet mask, we have 1 bit for the network, and 7 bits for the host. This high order
NETWORK bit is the 128 bit. Based on the definition of the subnet mask, all network bits before this bit MUST
BE one, so we get:
255.255.255.128
Incorrect Answers:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 85 -
Page 86

640 - 607
A, B, and D are incorrect; they do not provide a maximum of 126 hosts.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 233-236.
Q. 137
In Cisco IOS software, which command displays the backup configuration?
A. show flash
B. show version
C. show tftp-config
D. show backup-config
E. show startup-config
Answer: E
Explanation: This shows the startup configuration in NVRAM, which is the backup for the running
configuration that runs in RAM.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; show flash command lists the contents of the flash showing the IOS images that are stored.
Remember, the backup configuration is in the NVRAM, not Flash nor RAM.
B is incorrect; this command shows information on the running configuration.
C is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
C is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 98-99, 131.
Q. 138
What are the characteristics of UDP?
A. It is reliable and acknowledged
B. It is unreliable and acknowledged
C. It is reliable and unacknowledged
D. It is unreliable and unacknowledged
Answer: D
Explanation: UDP is connectionless and unacknowledged protocol. Although UDP is responsible for
transmitting messages, no checking for segment delivery is provided at this layer. UDP depends on upper-layer
protocols for reliability.
Incorrect Answers:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 86 -
Page 87

640 - 607
A is incorrect; UDP is neither reliable nor acknowledged.
B is incorrect; UDP is not acknowledged.
C is incorrect; UDP is not reliable.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 207.
Q. 139
What are the two sublayers of the data link layer? (Choose two)
A. MAC
B. LLC
C. SAP
D. LCP
E. NetWare Core Protocol (NCP)
Answer: A, B
Explanation: The data link layer has two sublayers. These sublayers are: MAC and LLC.
Incorrect Answers:
C is incorrect; the Service Access Point is used by Netware to advertise servers, and runs at a higher layer.
D is incorrect; this protocol is used in PPP, but is not part of the data link layer itself.
E is incorrect; NCP is used by Netware, and runs at a higher layer.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages18-19.
Q. 140
Which two types of route table entries does a Layer3 router to determine the appropriate path to a
destination use? (Choose two)
A. Static route entry
B. Default route entry
C. Dynamic route entry
D. Temporary route entry
E. Permanent route entry
Answer: A, C
Explanation: When a router m ust send packets that are not directly connected it must have either a static route
or a dynamic router entry.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; A default gateway does not always determine the appropriate path.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 87 -
Page 88

640 - 607
D and E are incorrect; routes can be temporary or permanent, but this is an attribute of the route entry itself.
This does not determine path information.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 250-252.
Q. 141
Which keystroke allows IOS to complete a partial command entry?
A. <Tab>
B. <Ctrl R>
C. <Spacebar>
D. <Right Arrow>
Answer: A
Explanation: Tab completes a partially entered command if enough characters have been entered to make it
unambiguous.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; the key combination will refresh the command line and everything typed up to this point.
C is incorrect; this just produces a space.
D is incorrect; this will not produce the desired result.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 97-98.
Q. 142
Eight stations connected to separate 10Mbps ports on a layer 2 switch will give each station how many
Mbps of bandwidth?
A. 1.25
B. 4
C. 16
D. 10
E. 60
Answer: D
Explanation: Using switching technology, each port can provide full bandwidth, in this case 10mbps, so each
station can get a full 10mbps.
Incorrect Answers:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 88 -
Page 89

640 - 607
A, B, C and E are incorrect; due to the fact that each workstation is connected to it’s own 10 Mbps port, each
port can provided it full 10 mbps.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 170-175.
Q. 143
Which two WAN data link layer protocols support multiple upper layer protocols? (Choose Two)
A. PPP
B. LAPD
C. ISDN
D. HDLC
Answer: A, D
Explanation: Cisco has a proprietary HDLC. This Cisco HDLC frame uses a proprietary type field that acts as
protocol field, which makes it possible for multiple network later protocols to share the same serial link.
PPP is not a proprietary protocol. As result, it is most often used to connect devices of different vendors. In
addition, it encapsulate network layer protocol information that makes it possible to support multiple upper
layer protocols.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; LAPB is a layer 2 protocol but LAPD is not
C is incorrect; ISDN is a Layer 1 (Physical) layer protocol, not Layer 2(data link).
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 373-376.
Q. 144
Which command enables directly connected network 199.55.72.0 to be used by RIP?
A. Router(Config)# rip 199.55.0.0 B. Router(Config-router)# rip 199.55.72.0 C. Router(Config-router)# network 199.55.0.0 D. Router(Config-router)# network 199.55.72.0
Answer: D
Explanation: The network command allows the routing process to identify the interfaces will participate in the
sending and receiving of messages.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 89 -
Page 90

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A and B are incorrect; these are not valid commands. In addition, A is in the wrong mode.
C is incorrect; this is the wrong network number. The 199 is a Class C subnet, using a default mask of
255.255.255.0, the network requires 3 octets of individual (1-254) networking addressing. 199.55.0.0 will cause
a all zeros subnet broadcast.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 276-277.
Q. 145
What does the command show access-list 101 list?
A. All extended access lists.
B. All access lists within the router.
C. The contents of standard access list 101
D. The contents of extended access list 101
Answer: D
Explanation: As the command is directing that the contents of access list 101 be displayed and as 101 is a
number for an extended IP access list D is correct.
Incorrect Answers:
A and B incorrect; only access list 101 will be displayed.
C is incorrect; standard IP address lists are in the range of 1-99, IP extended address lists are in the range of
100-199.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 303, 324-325.
Q. 146
Which two commands show your access lists? (Choose two)
A. Show filters.
B. Show access-lists
C. Show IP access-list
D. Show running-Config
Answer: B, C
Explanation: There are three commands that can be used to display access lists. These commands are: show
access-lists (displays all access-lists), show access-list number (displays a specific access list) and show ip
access-lists (displays all ip access lists.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 90 -
Page 91

640 - 607
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
D is incorrect; the show running-config displays a lot of information but it does not display access list
information.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 324-325.
Q. 147
Which statement about the Point-to-Point protocol (PPP) is true?
A. PPP supports TCP/IP, but not Novell IPX
B. PPP is being phased out of existence by the Serial Line Internet protocol
C. PPP provides router-to-router and host-to-network connections over both synchronous and
asynchronous circuits.
D. PPP is an ITU-T and ANSI standard that defines the process for sending data over a packet-switched
data network
Answer: C
Explanation: PPP provide router-to-router and host-to-network connections over sychnronous and
asynchronous circuits.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; PPP supports both IP and IPX.
B is incorrect; PPP is causing SLIP to be phased out.
D is incorrect; PPP was not designed as a standard for packet-switched data networks.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) page 373.
Q. 148
Which encapsulation methods are most commonly used wi th dialup integrated services Digital Network
(ISDN)?
A. IP and IPX
B. IP and PPP
C. PPP and SDLC
D. PPP and HDLC
Answer: D
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 91 -
Page 92

640 - 607
Explanation: There are a number of WAN encapsulat ion types available. The two most commonly used are
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and Cisco High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC). The reason HDLC is
employed so much is that it is the default encapsulation type on point-to-point dedicated links and circuit
switched connections. PPP is a non-proprietary encapsulation and this is while it is used to communicate
between devices from different vendors.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; IP and IPX are not encapsulation types. They are routing protocols.
B is incorrect; only PPP is an encapsulation type.
C is incorrect; SDLC is a protocol used in IBM SNA systems.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages
372-376.
Q. 149
Which two steps are parts of the process of creating Frame Relay subinterfaces on a point-point
connection? (Choose Two)
A. Configure the router to forward all broadcast packets
B. Remove any network address assigned to the physical interface
C. Configure the local data-link connection identifier for the subinterfaces
D. Partition the total committed information rate available among the subinterfaces
Answer: B, C
Explanation: There are a number of things that must be done to configure a subinterface. Two of these steps
are: the removal of the network address from the physical interface and assign that address to the subinterface
and configure the DLCI for the subinterface.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a frame-relay task and in fact if it was done loops would most likely occur.
D is incorrect; this is not done during frame-relay subinterface creation.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 428-429.
Q. 150
Your network is having IP problems connectin g to one or more Frame Relay peer routers. Which two
commands should you use to show the routers that are reachable? (Choose two)
A. show IP map
B. show IP route
C. show frame-relay map
D. debug frame-relay map
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 92 -
Page 93

640 - 607
Answer: B, C
Explanation: The show ip route command displays the contents of the IP routing table. The routing table
includes entries for all known networks and subnetworks plus it displays how the information was learnd. The
show frame-relay map command show the Frame Relay DLCI-to-IP address mappings. When the results of
these two commands are considered together will provide the data needed to determine routing information.
Incorrect Answers:
A and D are incorrect; neither are valid commands.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 280-281, 431-432.
Q. 151
What are three benefits of integrated services digital network (ISDN)? (Choose three)
A. PVCs are faster and more reliable.
B. No specialized equipment is required.
C. Data transfer is faster than typical modems.
D. Call setup is faster than with standard telephone service.
E. It carries many types of data traffic such as voice, video, and data.
Answer: C, D, E
Explanation:
Brining digital connectivity via ISDN to a site has many benefits. These benefits include:
- The capability to carry a variety of user-traffic feeds. ISDN provides access to all-digital facilities for videos,
voice, packet-switched data, and enriched telephone network services.
- Much faster call setup than modem connections. ISDN can be set up in less than a second.
- Much faster data transfer for ISDN (64 kbps) than modems (28.8 to 56 kbps).
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; PVCs are used in Frame Relay connections and not in ISDN.
B is incorrect; ISDN does need specialized equipment such as TE1, NT2, NT1, TE2, and TAs.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
Q. 152
What are two functions of ICMP protocol? (Choose Two)
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 387-393.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 93 -
Page 94

640 - 607
A. To map IP addresses to Ethernet addresses
B. To map common names to network addresses
C. To forward SNMP alerts to management consoles
D. To generate an echo reply in response to a ping test
E. To send a host or post unreachable message from a router to the source of an undeliverable packet
Answer: D, E
Explanation: ICMP has a great many functions that it can perform. Two of these functions are: destination
unreachable messages and echo reply messages.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is done by ARP & RARP protocols.
B is incorrect; this is done by Domain Name Services (DNS).
C is incorrect; a SNMP agent does this.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 217-218.
Q. 153
Novell IPX network addresses have two configurable parts. The network administrator specifies the IPX
network number.
How is the node number determined?
A. It is the serial number of the given device.
B. It is assigned as a lease by Novell DHCP.
C. It is also set by the network administrator.
D. It is usually the MAC address of one interface.
E. It is downloaded by NetWare Core Protocol (NCP).
Answer: D
Explanation: It is determined by the MAC address, so all other options are wrong.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 335-336.
Q. 154
Which IP address range is allowable given an IP address of 172.37.2.56 and 28-bits of subnetting?
A. 172.37.2.48 to 172.37.2.63
B. 172.37.2.48 to 172.37.2.6.2
C. 172.37.2.49 to 172.37.2.62
D. 172.37.2.49 to 172.37.2.63
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 94 -
Page 95

640 - 607
E. 172.37.2.55 to 172.37.2.126
Answer: C
Explanation: When we say 28 bits of subnetting, this is similar to a CIDR question. We have a subnet mask of
28 bits of ones followed by 4 bits of zeros, or 255.255.255.240, and gives subnets with a stride of 16, or 14
hosts per subnet (16-2 because we subtract out the two broadcast ranges of all zeros and all ones)
This will yield subnets, some networks are as follows:
172.37.2.0.
172.37.2.16
172.37.2.32
172.37.2.48
172.37.2.64
etc…
So, we can fit a network of 172.37.2.48-172.37.2.63
172.37.2.48 is the network, and the all zeros broadcast range.
172.37.2.63 is the broadcast, and is the all ones broadcast range.
So, we can’t user 48 or 63, and the valid host address range would be 49-62.
C is correct; this is the only range that fits.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B, D, and E are incorrect; these are not the proper ranges with the information provided in the question.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 233-237.
Q. 155
When you use the Cisco ISO command show configuration on a router, which part of the output shows
the specific configured IP addresses and subnet masks?
A. The IP host table
B. The interfaces output
C. Each section of the output
D. Each section of the output
E. The global configuration statements
F. The section under the autonomous system number
Answer: B
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 95 -
Page 96

640 - 607
Explanation: Each interface that has the IP protocol, will show all IP addresses that were configured on that
interface, with subnet masks.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this only shows the IP to host mappings, like the mapping of a HOSTS table.
C, D, E, and F are incorrect; these options do not provide this information.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 106-110.
Q. 156
What is the connection-oriented protocol in the TCP/IP protocol stack?
A. IP
B. UDP
C. TCP
D. DNS
E. OSPF
Answer: C
Explanation: TCP is a connection-oriented, reliable protocol. In connection-orientated environment, a
connection is established between both ends before transfer of information can begin.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; IP is a connectionless protocol.
B is incorrect; UDP is a connectionless protocol.
D is incorrect; DNS is a service, not a protocol.
E is incorrect; OSPF is a routing protocol.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 206-215.
Q. 157
What does the term ‘Base’ refer to in 100BaseT?
A. Cabling type
B. Signaling type
C. 100 mode type
D. Spectrum used
E. Speed category
Answer: B
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 96 -
Page 97

640 - 607
Explanation: There are two main signaling types: Baseband and Broadband.
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; The T is the cabling type, in this case Twisted Pair.
C is incorrect; 100 is the speed, in this case 100mbps.
D is incorrect; Spectrum, such as fiber, would be part of the cabling type.
E is incorrect; 100 is the speed category, in this case 100mbps.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 44-45.
Q. 158
Click the task button & Place the encapsulation.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 97 -
Page 98

Answer:
640 - 607
Explanation:
We can also look at this as layer functions, then sort:
Step One: Physical Layer
Step Two: Transport Layer
Step Three: Application Layer
Step Four: Data Link Layer
Step Five: Network Layer
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 10-14.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 98 -
Page 99

640 - 607
Q. 159
Which command displays the interfaces using a given access list?
A. Show filters
B. Show IP interface
C. Show active list
D. Show interface parameters
E. Configure IP access list
F. Show access-list interfaces
Answer: B
Explanation: The show ip interface command displays IP interface information and indicates whether any
access lists are set for a specific interface.
Incorrect Answers:
A and C-F are incorrect; theses are not valid commands.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 324.
Q. 160
You have a Frame Relay Link on serial1. Which command displays the Local Management Interface
(LMI), data link connection identifier (DLCI), and bandwidth for that link?
A. show interface serial1
B. show frame-relay serial1
C. show protocol frame-relay serial1
D. show serial1 encapsulation frame-relay
Answer: A
Explanation: The show interfaces command displays statistics for all interfaces configured on the switch.
Incorrect Answers:
B, C and D are incorrect; these are not valid commands.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices
Q. 161
When you configu re an IP address on a Cisco Router, which command starts the IP processing on the
interface?
A. IP-Space enable
. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 81-81.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 99 -
Page 100

640 - 607
B. Network IP-Address
C. IP address IP-address subnet mask.
D. The exit command from the enable configuration
E. Copy running-configuration to startup-configuration
Answer: C
Explanation: The ip address command is used to start IP processing on a router (in fact the same command is
also used to do the same on a switch.
Incorrect Answers:
A is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
B is incorrect; the network command is most often used to identify directly connected networks.
D is incorrect; this is not a valid command.
E is incorrect; this command will copy the running config to the NVRAM.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 245, 133, 277.
Q. 162
When you issue the command show version, your router returns:
“Configuration register is 0x0101”
From where does the router boot?
A. ROM
B. NVRAM
C. FLASH
D. A TFTP server
Answer: A
Explanation: If you want your router to boot automatically from ROM you need to set the boot field to 1 (0x1).
Incorrect Answers:
B is incorrect; to boot from the NVRAM the boot field must be set from the range of 2 to F (0x2 to 0xF).
C is incorrect; to boot from FLASH the boot system flash command would need to be used.
D is incorrect; to boot from a TFTP server the boot system tftp command would need to be used.
Steve McQuerry. Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices. (Cisco Press: 2000) pages 127-130.
Q. 163
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 100 -
 Loading...
Loading...