Page 1

Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
Customer Order Number: DOC-785373=
Text Part Number: 78-5373-04
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT
NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT
ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR
THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION
PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO
LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class A devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required to correct the interference at their own expense.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class B devices: The equipment described in this manual generates and may radiate
radio-frequency energy. If it is not installed in accordance with Cisco’s installation instructions, it may cause interference with radio and television
reception. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device in accordance with the specifications in
part 15 of the FCC rules. These specifications are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference in a residential installation.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
Modifying the equipment without Cisco’s written authorization may result in the equipment no longer complying with FCC requirements for Class
A or Class B digital devices. In that event, your right to use the equipment may be limited by FCC regulations, and you may be required to correct
any interference to radio or television communications at your own expense.
You can determine whether your equipment is causing interference by turning it off. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by the Cisco
equipment or one of its peripheral devices. If the equipment causes interference to radio or television reception, try to correct the interference by
using one or more of the following measures:
• Turn the television or radio antenna until the interference stops.
• Move the equipment to one side or the other of the television or radio.
• Move the equipment farther away from the television or radio.
• Plug the equipment into an outlet that is on a different circuit from the television or radio. (That is, make certain the equipment and the television
or radio are on circuits controlled by different circuit breakers or fuses.)
Modifications to this product not authorized by Cisco Systems, Inc. could void the FCC approval and negate your authority to operate the product.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as
part of UCB’s public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE
PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED
OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL
DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR
INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
Page 3

CCSP, CCVP, the Cisco Square Bridge logo, Follow Me Browsing, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work,
Live, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Access Registrar, Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP,
CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the
Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Empowering the Internet Generation, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, FormShare,
GigaDrive, GigaStack, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, Linksys,
MeetingPlace, MGX, the Networkers logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Pack e t , PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, ProConnect, RateMUX,
ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, StrataView Plus, TeleRouter, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, and TransPath are registered
trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a
partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0502R)
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
Copyright © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 4

Page 5

About This Guide vii
Audience vii
Organization vii
Conventions vii
Obtaining Documentation ix
Cisco.com ix
Documentation DVD ix
Ordering Documentation ix
Documentation Feedback x
Cisco Product Security Overview x
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products x
Obtaining Technical Assistance xi
Cisco Technical Support Website xi
Submitting a Service Request xii
Definitions of Service Request Severity xii
CONTENTS
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information xii
1 Overview 1-1
Feature Summary 1-2
Router Ports Summary 1-3
Front Panels 1-3
Back Panels 1-4
LEDs 1-7
2 Installation 2-1
Safety 2-2
European Union Statements 2-2
Network Termination Point Statement 2-3
ISDN S/T Ports Statement 2-3
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage 2-3
Preventing Router Damage 2-4
Unpacking Your Router 2-4
78-5373-04
Preinstallation Activities 2-4
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
v
Page 6

Contents
Installing Your Router 2-5
Connecting Ethernet Devices 2-6
Connecting an ISDN Line 2-10
Connecting an IDSL Line 2-13
Connecting a Digital Telephone 2-14
Connecting an Analog Telephone, Fax, or Modem 2-15
Connecting a Terminal or PC 2-17
Connecting the Power Supply 2-18
Mounting Your Router 2-18
Mounting on a Table 2-18
Mounting on a Wall 2-19
Verifying Installation 2-20
Where to Go from Here 2-22
CHAPTER
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
G
LOSSARY
I
NDEX
3 Troubleshooting 3-1
Problems During First Startup 3-2
Problems After First Startup 3-3
Problems After Router Is Running 3-5
When Contacting Your Cisco Reseller 3-7
A ISDN and IDSL Concepts A-1
B Specifications and Cables B-1
System Specifications B-1
Port Connector Pinouts B-2
Cabling Specifications B-6
Ethernet Cable Specifications B-7
Maximum Cable Distances B-7
vi
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 7

Audience
About This Guide
This preface discusses the audience, organization, and conventions used in this guide.
This guide is intended for service technicians with all levels of experience in installing routers. The goal
of all technicians is to connect the router to the network as quickly as possible. Where relevant, this guide
explains how the router is implemented and why. Conceptual information is usually in a separate section
or appendix so that technicians who are not interested can skip this information.
Organization
This guide contains the following information:
Conventions
This section describes the conventions used in this guide.
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to additional information and
material.
• About This Guide—Describes audience, organization, conventions used in this guide, and how to
access related documentation.
• Overview—Contains router features and a description of router LEDs, ports, and other components.
• Installation—Provides information on safety, preventing damage, unpacking, and preparing for
installation as well as installing, mounting, and verifying the connections to your router.
• Troubleshooting—Describes how to identify and solve problems with your router.
• ISDN and IDSL Concepts—Describes how ISDN is implemented on the router.
• Specifications and Cables—Provides router, port, and cable specifications.
• Glossary—Defines technical terms frequently used in this guide.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
vii
Page 8

Conventions
About This Guide
Caution This symbol means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in
equipment damage or loss of data.
Warning
Waarschuwing
Varoitus
Attention
Warnung
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause
bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards
involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with the standard practices
for preventing accidents.
Dit waarschuwingssymbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een situatie die
lichamelijk letsel kan veroorzaken. Voordat u aan enige apparatuur gaat
werken, dient u zich bewust te zijn van de bij elektrische schakelingen
betrokken risico's en dient u op de hoogte te zijn van standaard maatregelen
om ongelukken te voorkomen.
Tämä varoitusmerkki merkitsee vaaraa. Olet tilanteessa, joka voi johtaa
ruumiinvammaan. Ennen kuin työskentelet minkään laitteiston parissa, ota
selvää sähkökytkentöihin liittyvistä vaaroista ja tavanomaisista
onnettomuuksien ehkäisykeinoista.
Ce symbole d'avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous trouvez dans une
situation pouvant causer des blessures ou des dommages corporels. Avant de
travailler sur un équipement, soyez conscient des dangers posés par les
circuits électriques et familiarisez-vous avec les procédures couramment
utilisées pour éviter les accidents.
Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer Situation, die
zu einer Körperverletzung führen könnte. Bevor Sie mit der Arbeit an
irgendeinem Gerät beginnen, seien Sie sich der mit elektrischen
Stromkreisen verbundenen Gefahren und der Standardpraktiken zur
Vermeidung von Unfällen bewußt.
viii
Avvertenza
Questo simbolo di avvertenza indica un pericolo. La situazione potrebbe
causare infortuni alle persone. Prima di lavorare su qualsiasi
apparecchiatura, occorre conoscere i pericoli relativi ai circuiti elettrici ed
essere al corrente delle pratiche standard per la prevenzione di incidenti.
Advarsel
Dette varselsymbolet betyr fare. Du befinner deg i en situasjon som kan føre
til personskade. Før du utfører arbeid på utstyr, må du vare oppmerksom på de
faremomentene som elektriske kretser innebærer, samt gjøre deg kjent med
vanlig praksis når det gjelder å unngå ulykker.
Aviso
Este símbolo de aviso indica perigo. Encontra-se numa situação que lhe
poderá causar danos físicos. Antes de começar a trabalhar com qualquer
equipamento, familiarize-se com os perigos relacionados com circuitos
eléctricos, e com quaisquer práticas comuns que possam prevenir possíveis
acidentes.
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 9

About This Guide
Obtaining Documentation
¡Atención!
Varning!
Este símbolo de aviso significa peligro. Existe riesgo para su integridad
física. Antes de manipular cualquier equipo, considerar los riesgos que
entraña la corriente eléctrica y familiarizarse con los procedimientos
estándar de prevención de accidentes.
Denna varningssymbol signalerar fara. Du befinner dig i en situation som kan
leda till personskada. Innan du utför arbete på någon utrustning måste du vara
medveten om farorna med elkretsar och känna till vanligt förfarande för att
förebygga skador.
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on Cisco.com. Cisco also provides several
ways to obtain technical assistance and other technical resources. These sections explain how to obtain
technical information from Cisco Systems.
Cisco.com
You can access the most current Cisco documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/home/home.htm
You can access the Cisco website at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com
You can access international Cisco websites at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Documentation DVD
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a Documentation DVD package, which
may have shipped with your product. The Documentation DVD is updated regularly and may be more
current than printed documentation. The Documentation DVD package is available as a single unit.
Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order a Cisco Documentation DVD (product
number DOC-DOCDVD=) from the Ordering tool or Cisco Marketplace.
Cisco Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/
Cisco Marketplace:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Ordering Documentation
78-5373-04
You can find instructions for ordering documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/es_inpck/pdi.htm
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
ix
Page 10

Documentation Feedback
You can order Cisco documentation in these ways:
• Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order Cisco product documentation from
the Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/
• Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by
calling Cisco Systems Corporate Headquarters (California, USA) at 408 526-7208 or, elsewhere in
North America, by calling 1 800 553-NETS (6387).
Documentation Feedback
You can send comments about technical documentation to bug-doc@cisco.com.
You can submit comments by using the response card (if present) behind the front cover of your
document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Customer Document Ordering
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
About This Guide
Cisco Product Security Overview
Cisco provides a free online Security Vulnerability Policy portal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.html
From this site, you can perform these tasks:
• Report security vulnerabilities in Cisco products.
• Obtain assistance with security incidents that involve Cisco products.
• Register to receive security information from Cisco.
A current list of security advisories and notices for Cisco products is available at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/psirt
If you prefer to see advisories and notices as they are updated in real time, you can access a Product
Security Incident Response Team Really Simple Syndication (PSIRT RSS) feed from this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_psirt_rss_feed.html
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products
Cisco is committed to delivering secure products. We test our products internally before we release them,
and we strive to correct all vulnerabilities quickly. If you think that you might have identified a
vulnerability in a Cisco product, contact PSIRT:
• Emergencies— security-alert@cisco.com
• Nonemergencies— psirt@cisco.com
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
x
78-5373-04
Page 11

About This Guide
Tip We encourage you to use Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) or a compatible product to encrypt any sensitive
information that you send to Cisco. PSIRT can work from encrypted information that is compatible with
PGP versions 2.x through 8.x.
Never use a revoked or an expired encryption key. The correct public key to use in your correspondence
with PSIRT is the one that has the most recent creation date in this public key server list:
http://pgp.mit.edu:11371/pks/lookup?search=psirt%40cisco.com&op=index&exact=on
In an emergency, you can also reach PSIRT by telephone:
• 1 877 228-7302
• 1 408 525-6532
Obtaining Technical Assistance
For all customers, partners, resellers, and distributors who hold valid Cisco service contracts, Cisco
Technical Support provides 24-hour-a-day, award-winning technical assistance. The Cisco Technical
Support Website on Cisco.com features extensive online support resources. In addition, Cisco Technical
Assistance Center (TAC) engineers provide telephone support. If you do not hold a valid Cisco service
contract, contact your reseller.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco Technical Support Website
The Cisco Technical Support Website provides online documents and tools for troubleshooting and
resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. The website is available 24 hours a day,
365 days a year, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Access to all tools on the Cisco Technical Support Website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
If you have a valid service contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can register at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Note Use the Cisco Product Identification (CPI) tool to locate your product serial number before submitting
a web or phone request for service. You can access the CPI tool from the Cisco Technical Support
Website by clicking the Too l s & R e so u r ce s link under Documentation & Tools. Choose Cisco Product
Identification Tool from the Alphabetical Index drop-down list, or click the Cisco Product
Identification Tool link under Alerts & RMAs. The CPI tool offers three search options: by product ID
or model name; by tree view; or for certain products, by copying and pasting show command output.
Search results show an illustration of your product with the serial number label location highlighted.
Locate the serial number label on your product and record the information before placing a service call.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
xi
Page 12

Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Submitting a Service Request
Using the online TAC Service Request Tool is the fastest way to open S3 and S4 service requests. (S3
and S4 service requests are those in which your network is minimally impaired or for which you require
product information.) After you describe your situation, the TAC Service Request Tool provides
recommended solutions. If your issue is not resolved using the recommended resources, your service
request is assigned to a Cisco TAC engineer. The TAC Service Request Tool is located at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/servicerequest
For S1 or S2 service requests or if you do not have Internet access, contact the Cisco TAC by telephone.
(S1 or S2 service requests are those in which your production network is down or severely degraded.)
Cisco TAC engineers are assigned immediately to S1 and S2 service requests to help keep your business
operations running smoothly.
To open a service request by telephone, use one of the following numbers:
Asia-Pacific: +61 2 8446 7411 (Australia: 1 800 805 227)
EMEA: +32 2 704 55 55
USA: 1 800 553-2447
For a complete list of Cisco TAC contacts, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/contacts
About This Guide
Definitions of Service Request Severity
To ensure that all service requests are reported in a standard format, Cisco has established severity
definitions.
Severity 1 (S1)—Your network is “down,” or there is a critical impact to your business operations. You
and Cisco will commit all necessary resources around the clock to resolve the situation.
Severity 2 (S2)—Operation of an existing network is severely degraded, or significant aspects of your
business operation are negatively affected by inadequate performance of Cisco products. You and Cisco
will commit full-time resources during normal business hours to resolve the situation.
Severity 3 (S3)—Operational performance of your network is impaired, but most business operations
remain functional. You and Cisco will commit resources during normal business hours to restore service
to satisfactory levels.
Severity 4 (S4)—You require information or assistance with Cisco product capabilities, installation, or
configuration. There is little or no effect on your business operations.
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Information about Cisco products, technologies, and network solutions is available from various online
and printed sources.
• Cisco Marketplace provides a variety of Cisco books, reference guides, and logo merchandise. Visit
Cisco Marketplace, the company store, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
xii
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 13

About This Guide
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
• Cisco Press publishes a wide range of general networking, training and certification titles. Both new
and experienced users will benefit from these publications. For current Cisco Press titles and other
information, go to Cisco Press at this URL:
http://www.ciscopress.com
• Pack et magazine is the Cisco Systems technical user magazine for maximizing Internet and
networking investments. Each quarter, Packet delivers coverage of the latest industry trends,
technology breakthroughs, and Cisco products and solutions, as well as network deployment and
troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, customer case studies, certification and training
information, and links to scores of in-depth online resources. You can access Packet magazine at
this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/packet
• iQ Magazine is the quarterly publication from Cisco Systems designed to help growing companies
learn how they can use technology to increase revenue, streamline their business, and expand
services. The publication identifies the challenges facing these companies and the technologies to
help solve them, using real-world case studies and business strategies to help readers make sound
technology investment decisions. You can access iQ Magazine at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/iqmagazine
• Internet Protocol Journal is a quarterly journal published by Cisco Systems for engineering
professionals involved in designing, developing, and operating public and private internets and
intranets. You can access the Internet Protocol Journal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/ipj
• World-class networking training is available from Cisco. You can view current offerings at
this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/learning/index.html
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
xiii
Page 14

Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
About This Guide
xiv
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 15

CHA P T E R
1
Overview
The Cisco 800 series routers connect small professional offices or telecommuters over Integrated
Services Digital Network (ISDN) Basic Rate Interface (BRI) lines to the Corporate LANs and the
Internet. The routers offer bridging and multiprotocol routing capability between LAN and WAN ports.
This chapter contains the following topics:
• Feature Summary
• Router Ports Summary
• Front Panels
• Back Panels
• LEDs
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
1-1
Page 16
Feature Summary
Feature Summary
Table 1-1 summarizes the features of the Cisco 800 series routers.
Table 1-1 Cisco 800 Series Feature Summary
Feature Routers Description
10BASE-T Ethernet port(s) All Provides connection to 10BASE-T (10 Mbps)
Ethernet networks. Compatible with
10/100-Mbps devices.
ISDN BRI S/T port Cisco 801 and 803 Provides connection to ISDN S/T network.
ISDN BRI U port Cisco 802 and 804 Provides connection to ISDN U network.
IDSL port Cisco 802 IDSL
and 804 IDSL
Telephone ports Cisco 803 and 804 Provide connection to telephone, fax machine,
Internal Network Termination 1
Cisco 802 and 804 Eliminates need for an external NT1 in North
(NT1)
Flash memory All 8 MB of Flash memory.
Dynamic RAM (DRAM) All 4 MB of DRAM.
Easily distinguishable ISDN
All ISDN B-channel LEDs in a different color
B-channel LEDs
Ease of installation All Color-coded ports and cables to reduce the
Cisco IOS software All Supports Cisco IOS software.
Cisco 800 Fast Step application All Provides a Windows 95–, Windows 98–, and
Console port All Provides connection to terminal or PC for
Provides connection to IDSL network.
or modem, which are connected to telephone
services through ISDN line.
America.
1
2
2
from other LEDs.
chance of error.
Windows NT–based software tool for basic
configurations.
software configuration using command-line
interface and for troubleshooting.
Chapter 1 Overview
Note The console port is a service port.
Cable lock All Provides a way to physically secure the router.
Locking power connector All Locks power connector in place.
Wall-mount feature All Brackets on router bottom provide a way to
mount router on wall or vertical surface.
1. Although the ISDN U interfaces on the Cisco 802 and Cisco 804 routers provide internal NT1s, the routers themselves do not
function as NT1s. You cannot connect S/T devices to Cisco 802 and Cisco 804 routers.
2. An additional 8 MB of Flash memory and 4 or 8 MB of DRAM can be added at the factory or later. You can order upgrade
kits and have trained and qualified personnel add the memory. The Cisco product number for the 8-MB Flash memory upgrade
kit is MEM800-8F and the numbers for the DRAM upgrade kits are MEM800-4D and MEM800-8D.
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
1-2
78-5373-04
Page 17
Chapter 1 Overview
Router Ports Summary
Table 1-2 lists the Cisco 800 series routers and ports.
Table 1-2 Router Ports
Router Ethernet Ports ISDN Ports Telephone Ports
Cisco 801 One ISDN BRI S/T None
Cisco 802 One ISDN BRI U None
Cisco 802 IDSL One IDSL None
Cisco 803 Four ISDN BRI S/T Two
Cisco 804 Four ISDN BRI U Two
Cisco 804 IDSL Four IDSL None
Front Panels
Router Ports Summary
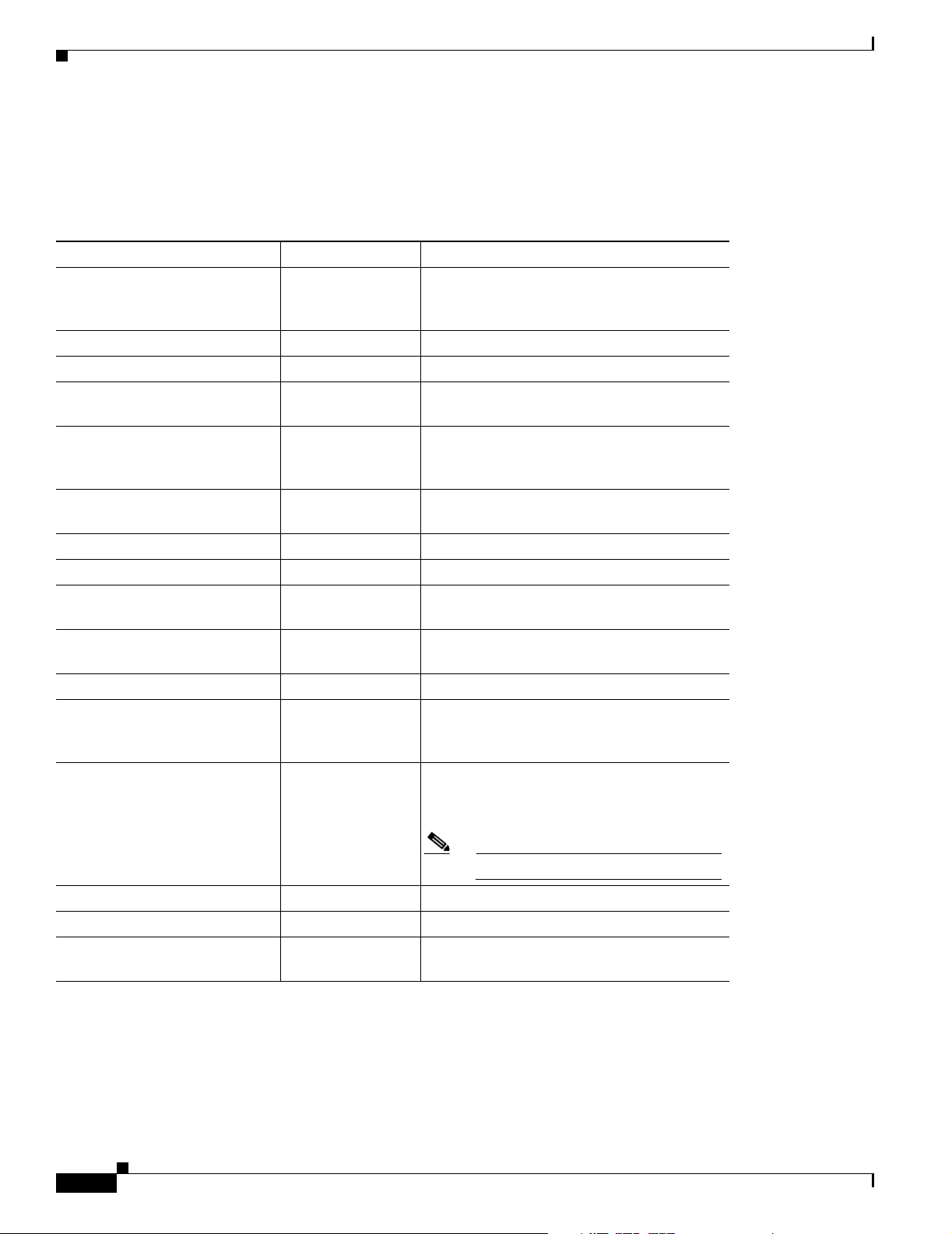
The figures in this section show the front panel of the Cisco 800 series routers.
Figure 1-1 Cisco 801, Cisco 802, and Cisco 802 IDSL Front Panel
NT1 LED on
Cisco 802 and
802 IDSL routers only
Figure 1-2 Cisco 803 and Cisco 804 Front Panel
NT1 LED on
Cisco 804 router only
11664
11665
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
1-3
Page 18
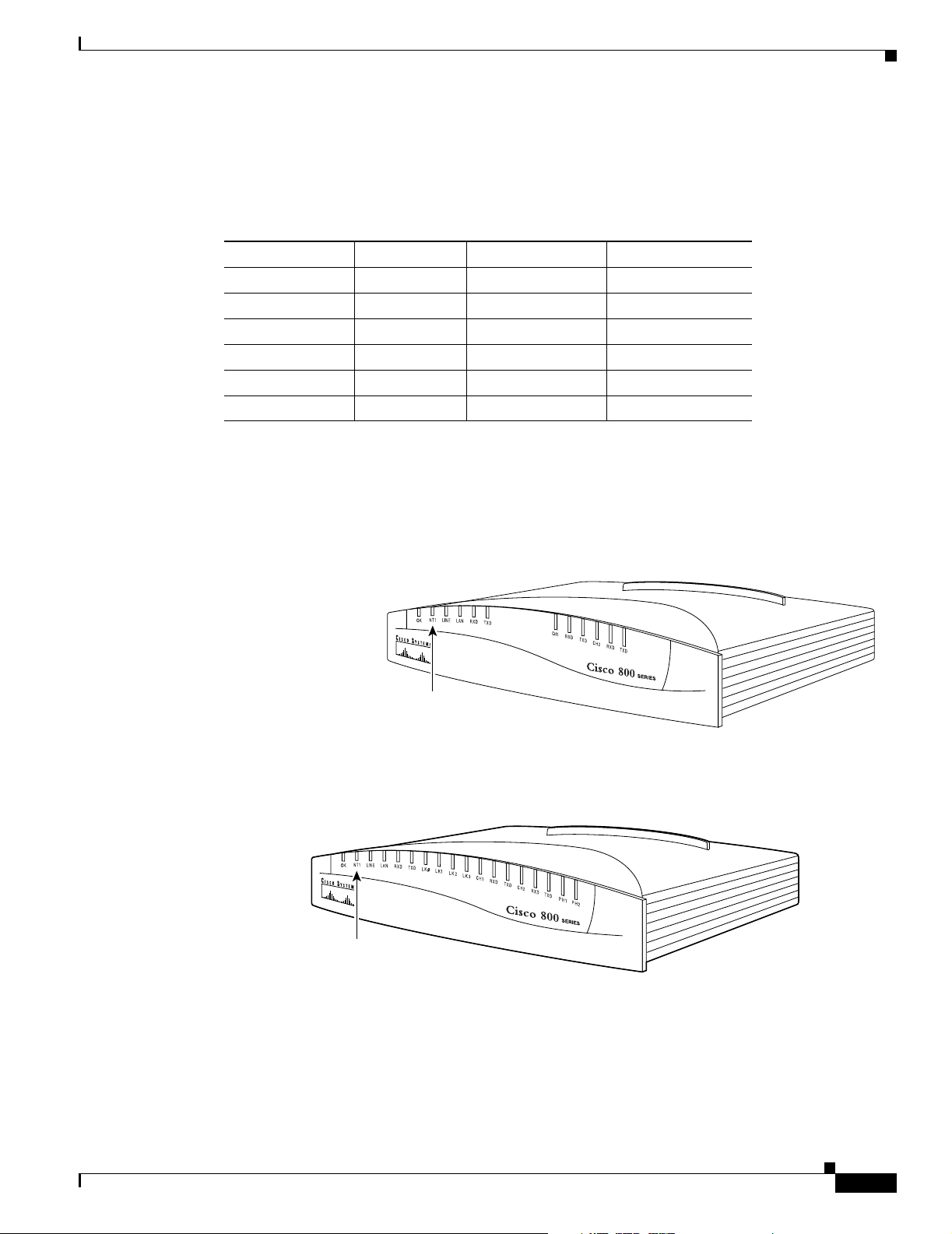
Back Panels
Chapter 1 Overview
Figure 1-3 Cisco 804 IDSL Front Panel
Back Panels
The figures in this section show the back panel of each of the Cisco 800 series routers.
If the symbol of suitability ( ) appears above a port, you can connect the port directly to a public
network that follows the European Union standards.
Warning
Figure 1-4 Cisco 801 Router Back Panel
If the symbol of suitability with an overlaid cross ( ) appears above a port, you must not connect the
port to a public network that follows the European Union standards. Connecting the port to this type
of public network can cause severe injury or damage your router.
Link LED
Indicates state
of Ethernet
port. On when
connected.
IDSL
ETHERNET
Ethernet port
Connect Ethernet
network device.
IDSL
ISDN BRI S/T port
Connect to external
NT1 or ISDN wall jack.
30770
Power switch
l = On.
= Standby or no power output.
1-4
HUB
NO HUB
ETHERNET
10 BASE T
Cable lock
Use cable
lock to
physically
secure
LINK
HUB/NO HUB button
(for Ethernet port)
Determines cable
type for Ethernet
device connection.
router.
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
Cisco 801
CONSOLE
ISDN S/T
Console port
Connect PC or
terminal.
11666
Locking power
connector
Connect power
supply.
78-5373-04
Page 19
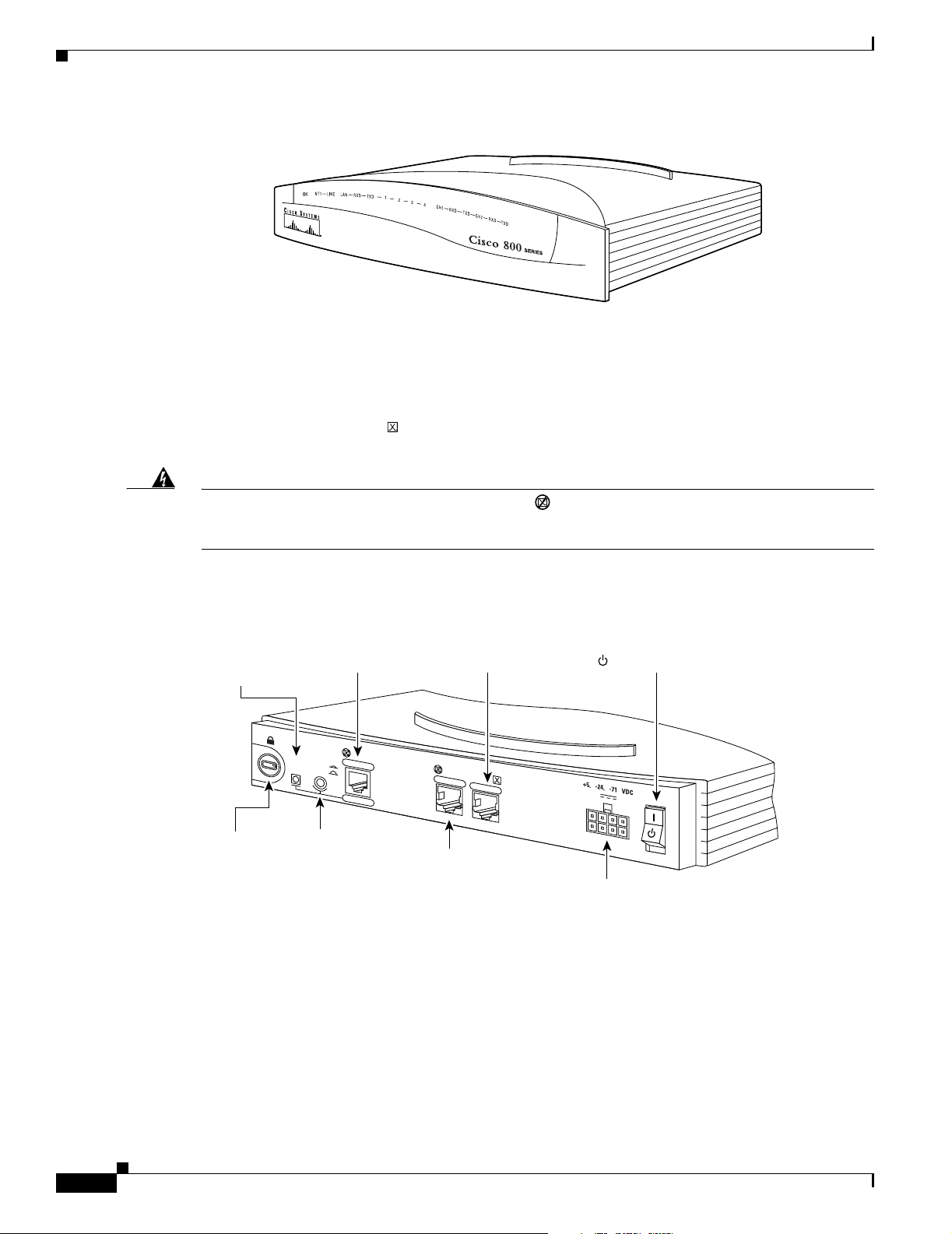
Chapter 1 Overview
Figure 1-5 Cisco 802 Router Back Panel
Back Panels
Link LED
Indicates state
of Ethernet port.
Cable lock
Use cable
lock to
physically
secure
Ethernet port
Connect Ethernet
network device.
HUB
LINK
NO HUB
HUB/NO HUB button
(for Ethernet port)
Determines cable
type for Ethernet
device connection.
router.
Figure 1-6 Cisco 803 Router Back Panel
Ethernet ports
Connect Ethernet
network devices.
ETHERNET
10 BASE T
ISDN BRI U port
Connect to
ISDN wall jack.
Cisco 802
CONSOLE
ISDN U
Console port
Connect PC
or terminal.
ISDN BRI S/T port
Connect to external
NT1 or ISDN wall jack.
Power switch
l = On.
= Standby or no power output.
Locking power
connector
Connect power
supply.
Telephone ports
Connect to telephone,
fax machine, or modem.
11667
Power switch
l = On.
= Standby or
no power output.
Cable lock
Use cable
lock to
physically
secure
router.
HUB
NO HUB
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
0
1
2
HUB/NO HUB button
(for Ethernet port 0)
Determines cable
type for Ethernet
device connection.
Cisco 803
CONSOLE
3
Console port
Connect PC or
terminal.
ISDN S/T
PHONE
1
2
Locking power
connector
Connect power
supply.
11668
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
1-5
Page 20
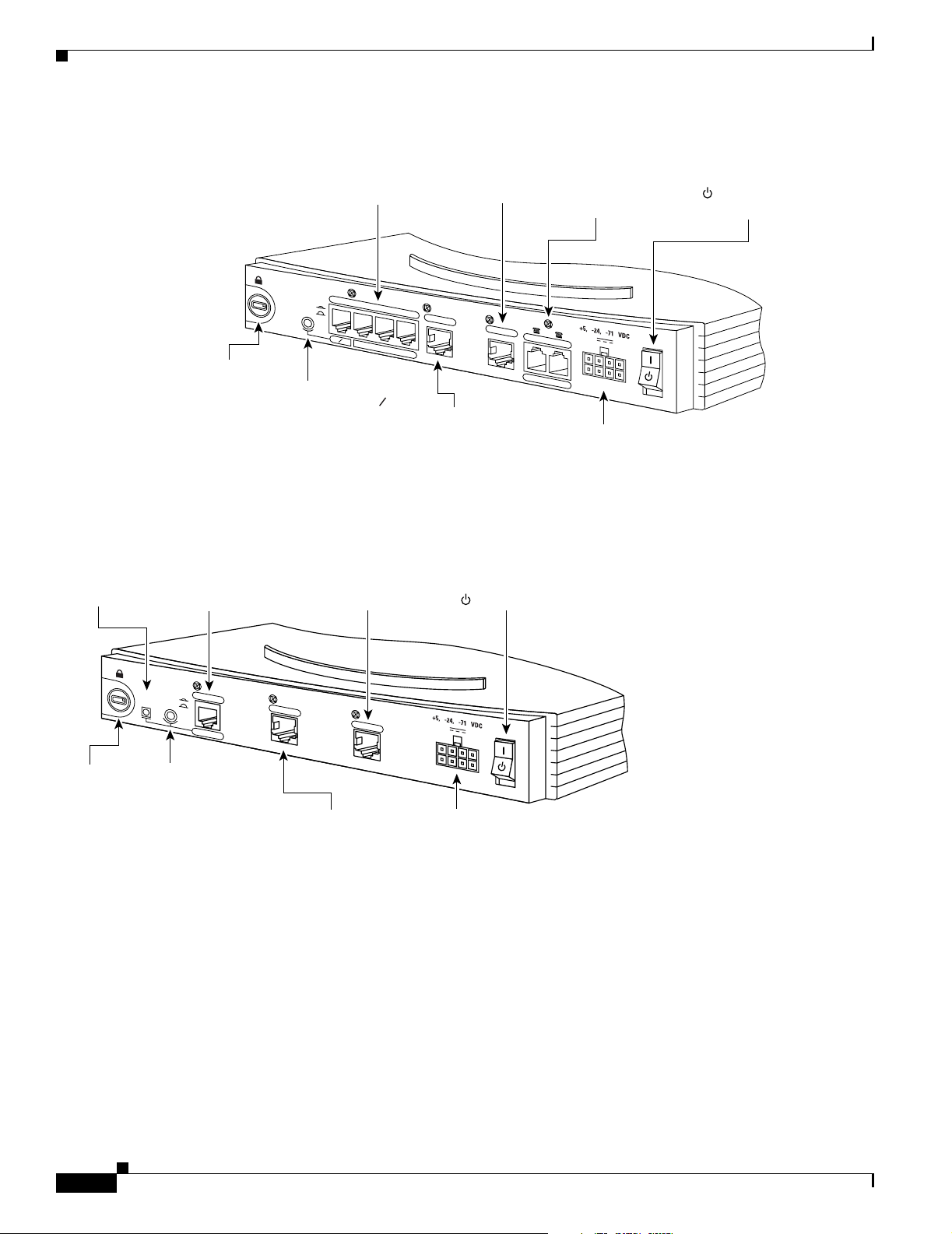
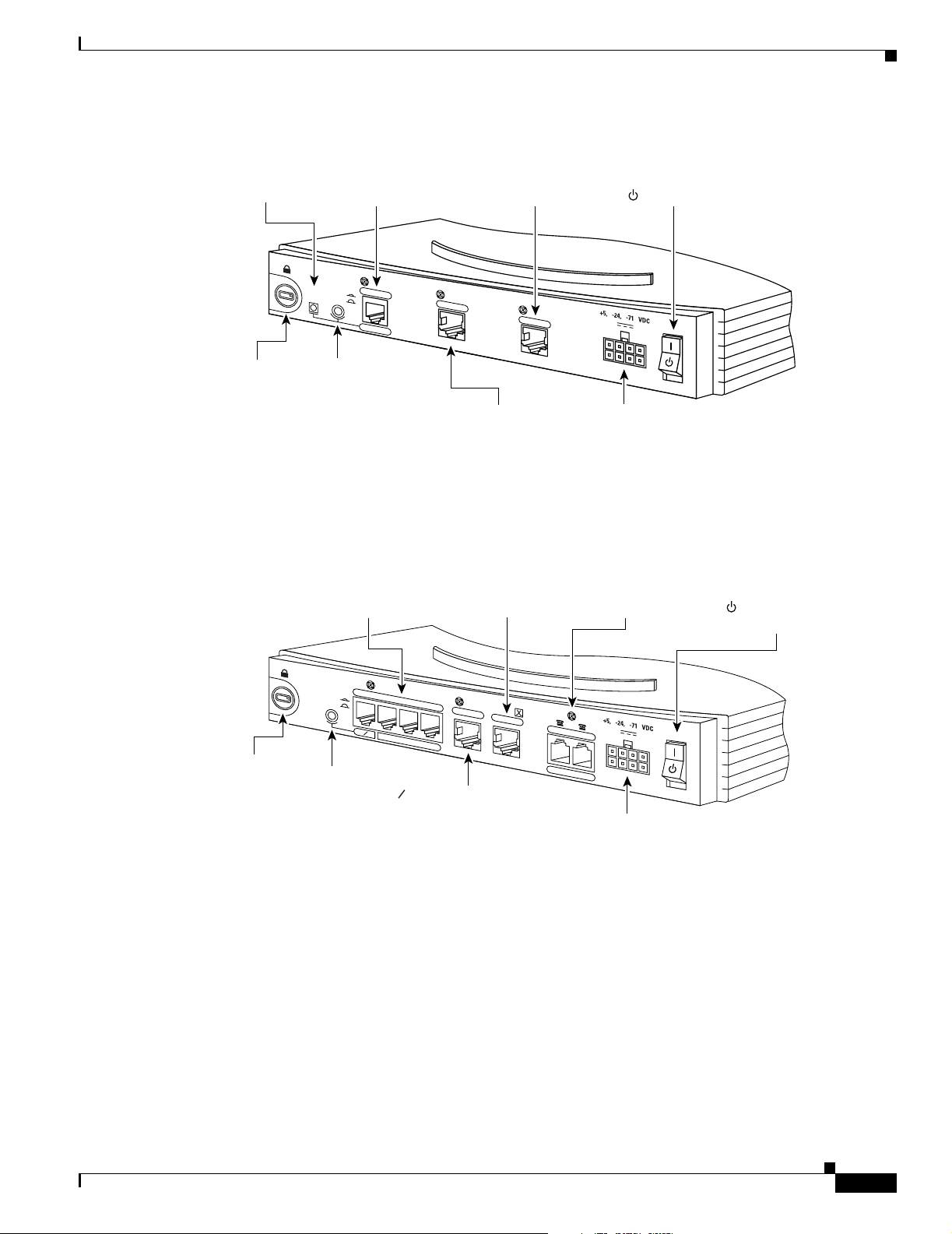
Back Panels
Figure 1-7 Cisco 804 Router Back Panel
Chapter 1 Overview
Ethernet ports
Connect Ethernet
network devices.
HUB
NO HUB
0
Cable lock
Use cable
lock to
physically
secure
router.
HUB/NO HUB button
(for Ethernet port 0)
Determines cable
type for Ethernet
device connection.
Figure 1-8 Cisco 802 IDSL Router Back Panel
Link LED
Indicates state
of Ethernet port.
Ethernet port
Connect Ethernet
network device.
IDSL port
Connect to
IDSL wall jack.
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
1
2
ISDN BRI U port
Connect to ISDN
wall jack.
Cisco 804
CONSOLE
3
Console port
Connect PC or
terminal.
Telephone ports
Connect to telephone,
fax machine, or
modem.
ISDN U
PHO
NE
1
2
Locking power
connector
Connect power
supply.
Power switch
l = On.
= Standby or no power output.
Power switch
l = On.
= Standby or no
power output.
11669
Cable lock
Use cable
lock to
physically
secure
router.
TO HUB
TO PC
ETHERNET
10 BASE T
LINK
TO HUB/TO PC
(for Ethernet port)
Determines cable
type for Ethernet
device connection.
Cisco 802 IDSL
CONSOLE
Console port
Connect PC
or terminal.
IDSL
30771
Locking power
connector
Connect power
supply.
1-6
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 21
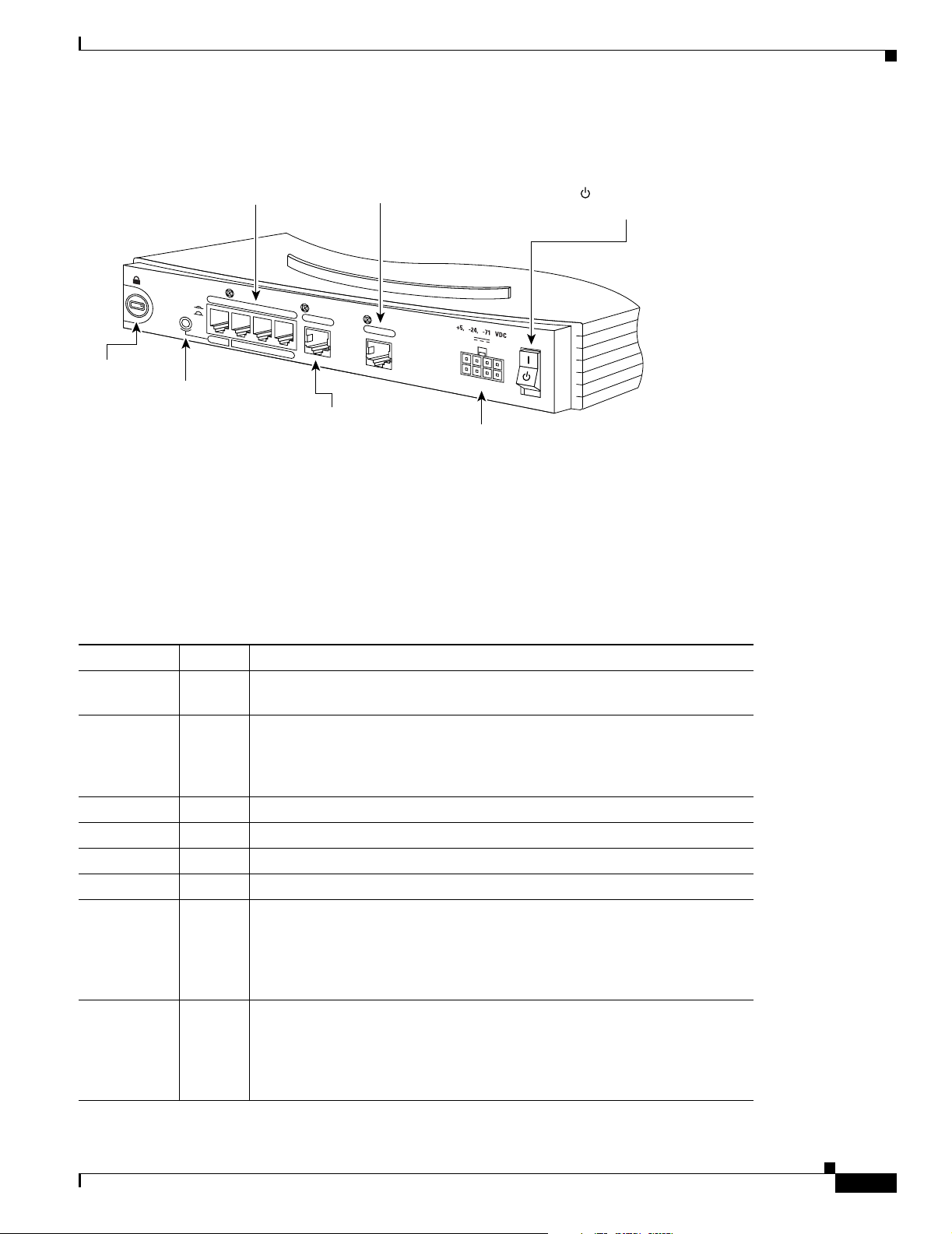
Chapter 1 Overview
Figure 1-9 Cisco 804 IDSL Router Back Panel
LEDs
Cable lock
Use cable
lock to
physically
secure
router.
LEDs
Ethernet ports
Connect Ethernet
network devices.
TO HUB
TO PC
TO HUB/TO PC
(for Ethernet port 1)
Determines cable
type for Ethernet
device connection.
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
1
2
Table 1-3 summarizes the function of each LED.
3
4
IDSL port
Connect to IDSL
wall jack.
Cisco 804 IDSL
CONSOLE
IDSL
Console port
Connect PC or
terminal.
Power switch
l = On.
= Standby or no
power output.
30772
Locking power
connector
Connect power
supply.
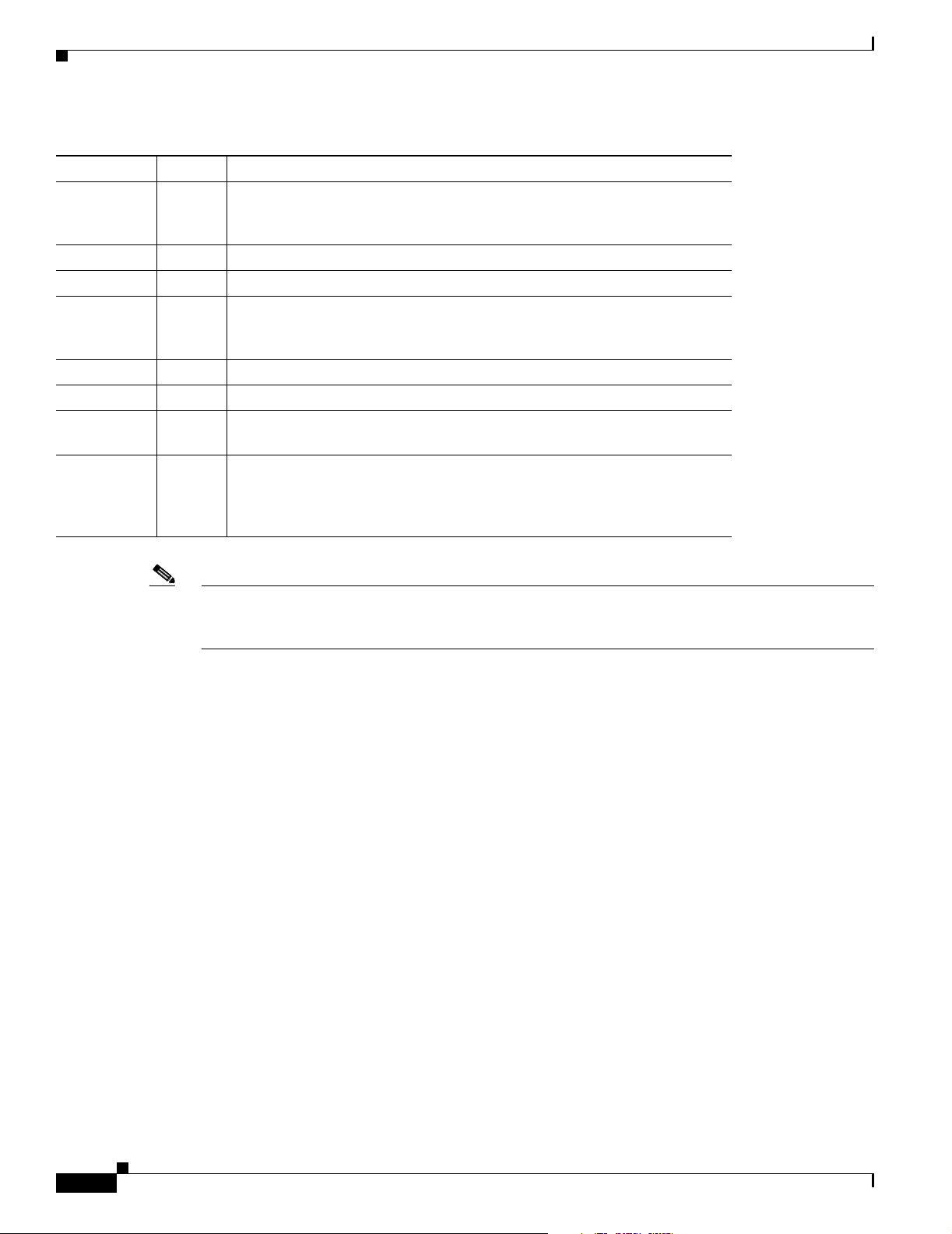
Table 1-3 LED Functions
LED Color Function
OK Green On when power is supplied to the router and when the router completes the
self-test procedure and begins operating.
NT1 Green Not applicable for Cisco 801 and 803 routers.
On when the internal NT1 and the ISDN switch are synchronized.
Blinks when the internal NT1 and the ISDN switch are attempting to
synchronize.
LINE Green On when the ISDN interface and the ISDN terminal device are synchronized.
LAN Green On when packets are sent to or received from an Ethernet port.
LAN RXD Green Blinks when an Ethernet port receives a packet.
LAN TXD Green Blinks when an Ethernet port sends a packet.
LKØ, LK1,
LK2, LK3
Green Cisco 803 and 804 routers only.
On when the Ethernet device is connected.
Off when the Ethernet device is not connected.
Blinks when the connection has a problem. See the “Troubleshooting”
chapter.
ETHERNET
1, 2, 3, 4
Green Cisco 804 IDSL routers only.
On when the Ethernet device is connected.
Off when the Ethernet device is not connected.
Blinks when the connection has a problem. See the “Troubleshooting”
chapter.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
1-7
Page 22
LEDs
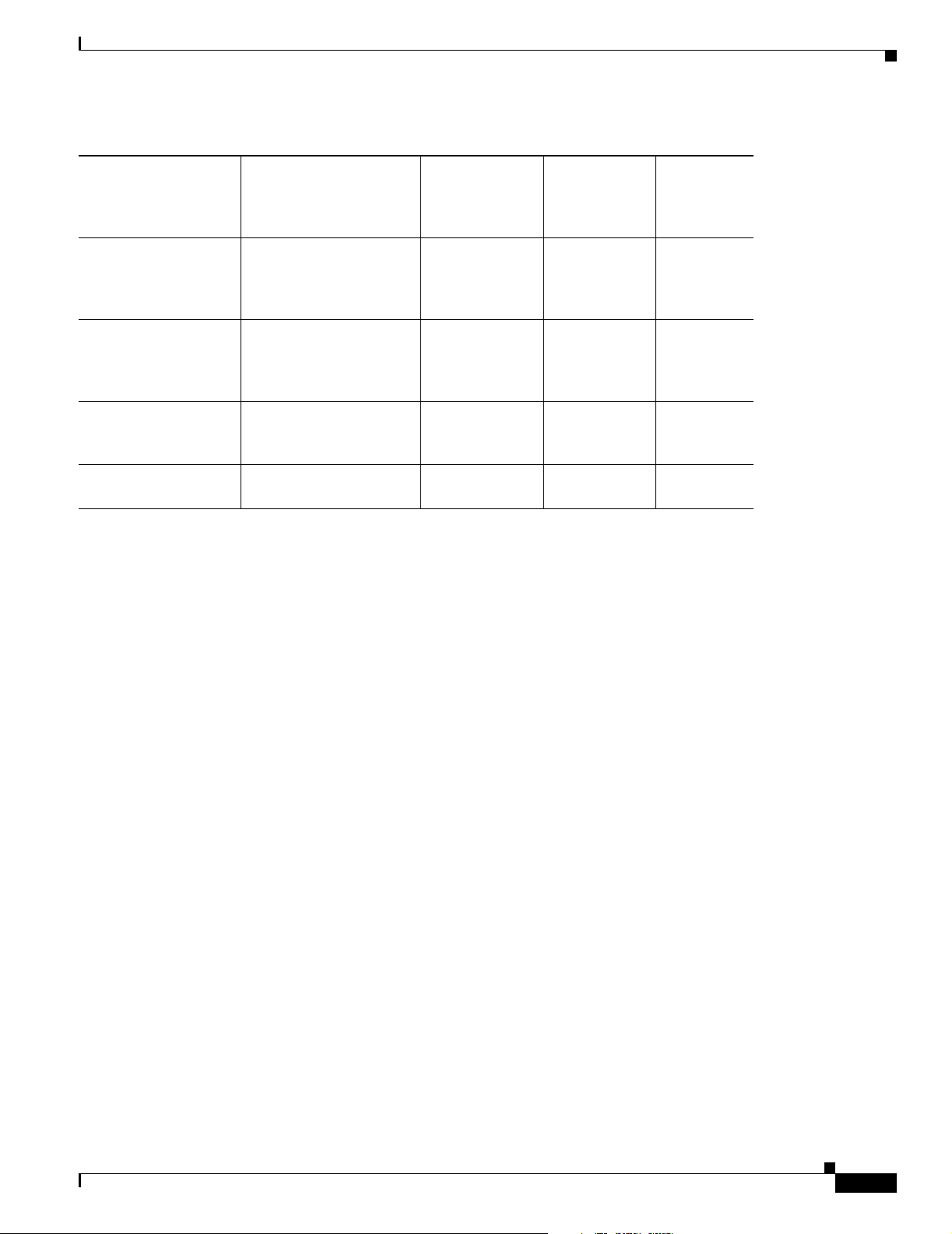
Table 1-3 LED Functions (continued)
LED Color Function
CH1 Orange Blinks when placing or receiving a call on the first ISDN B channel.
On when a call is connected on the first ISDN B channel.
For IDSL routers, see the Note following this table.
CH1 RXD Orange Blinks when packets are received from the first ISDN B channel.
CH1 TXD Orange Blinks when packets are sent from the first ISDN B channel.
CH2 Orange Blinks when placing or receiving a call on the second ISDN B channel.
On when a call is connected on the second ISDN B channel.
For IDSL routers, see the Note following this table.
CH2 RXD Orange Blinks when packets are received from the second ISDN B channel.
CH2 TXD Orange Blinks when packets are sent from the second ISDN B channel.
PH1,PH2 Green Cisco 803 and 804 routers only.
On when basic telephone service is in use.
LINK Green On back panel of Cisco 801, 802, and 802 IDSL routers only.
On when Ethernet device is connected.
Blinks when the connection has a problem. Refer to the “Troubleshooting”
chapter.
Chapter 1 Overview
Note On Cisco 802 IDSL and Cisco 804 IDSL routers, either CH1 or CH2 is on if the router has an active data
connection and the line speed is 64 kbps. CH1 and CH2 are both on if the router has an active data
connection and the line speed is 128 or 144 kbps.
1-8
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 23

Installation
This chapter provides information on the following topics:
• Safety
• European Union Statements
• Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
• Preventing Router Damage
• Unpacking Your Router
• Preinstallation Activities
• Installing Your Router
• Mounting Your Router
• Verifying Installation
• Where to Go from Here
CHA P T E R
2
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-1
Page 24

Safety
Safety
Chapter 2 Installation
Before installing the router, read the following warnings:
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install or replace this equipment.
Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source.
Before working on a system that has a standby/off switch, turn the power to standby and unplug the
power cord.
Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings,
necklaces, and watches). Metal objects will heat up when connected to power and ground and can
cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the terminals.
The ISDN connection is regarded as a source of voltage that should be inaccessible to user contact.
Do not attempt to tamper with or open any public telephone operator (PTO)-provided equipment or
connection hardware. Any hardwired connection (other than by a nonremovable,
connect-one-time-only plug) must be made only by PTO staff or suitably trained engineers.
To avoid electric shock, do not connect safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits to telephone-network
voltage (TNV) circuits. LAN ports contain SELV circuits, and WAN ports contain TNV circuits. Some
LAN and WAN ports both use RJ-45 connectors. Use caution when connecting cables.
Warning
Warning
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations.
If the symbol of suitability with an overlaid cross ( ) appears above a port, you must not connect the
port to a public network that follows the European Union standards. Connecting the port to this type
of public network can cause severe injury or damage your router
European Union Statements
The following statements apply to Cisco 801 routers and Cisco 803 routers sold in the European Union
(EU).
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-2
78-5373-04
Page 25

Chapter 2 Installation
Network Termination Point Statement
This product does not contain a “Network Termination Point” (NTP) as defined by ETSI 300 386-2. This
product is classified by the manufacturer as “Terminal Equipment.” If you have any additional questions,
please contact your local network operator.
ISDN S/T Ports Statement
These ports have not been classified as “directly connected ports” to outside cables as defined by
CISPR 24, 1997 by the manufacturer. If you have any additional questions, please contact your local
network operator.
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a transfer of electrostatic charge between bodies of different
electrostatic potentials, such as a person and a piece of electrical equipment. It occurs when electronic
components are improperly handled, and it can damage equipment and impair electrical circuitry.
Electrostatic discharge is more likely to occur with the combination of synthetic fibers and dry
atmosphere.
Always use the following ESD-prevention procedures when removing and replacing components:
1. Connect the chassis to earth ground with a wire that you provide.
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
2. Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap that you provide, ensuring that it makes good skin contact.
Connect the clip to an unpainted surface of the chassis frame to safely channel unwanted ESD
voltages to ground. To properly guard against ESD damage and shocks, the wrist strap and cord must
operate effectively. If no wrist strap is available, ground yourself by touching the metal part of the
chassis. Always follow the guidelines in the preceding section, “Safety.”
3. Do not touch any exposed contact pins or connector shells of interface ports that do not have a cable
attached.
If cables are connected at one end only, do not touch the exposed pins at the unconnected end of the
cable.
Note This device is intended for use in residential and commercial environments only.
Caution Periodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap, which should be between 1 and 10
megohms (Mohms).
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-3
Page 26

Preventing Router Damage
Preventing Router Damage
Use the following guidelines when connecting devices to your router:
• Connect the color-coded cables supplied by Cisco Systems to the color-coded ports on the back
panel.
• If you must supply your own cable, see the “Cabling Specifications” section in Appendix B,
“Specifications and Cables.” If this appendix does not provide specifications for a particular cable,
we strongly recommend ordering the cable from Cisco Systems.
• If the symbol of suitability ( ) appears above a port, you can connect the port directly to a public
network that follows the European Union standards.
Chapter 2 Installation
Warning
If the symbol of suitability with an overlaid cross ( ) appears above a port, you must not connect the
port to a public network that follows the European Union standards. Connecting the port to this type
of public network can cause severe injury or damage your router.
Unpacking Your Router
Table 2-1 lists the items that come with your router. All these items are in the accessory kit that is inside
the box that your router came in. If any of the items is missing or damaged, contact your customer service
representative.
Table 2-1 Router Box Contents
Power cord (black)
•
• Desktop power supply
• Console cable (light blue)
• DB-9-to-RJ-45 adapter for use with light blue console cable
• ISDN ST cable (orange) (Cisco 801 and 803 routers)
• Ethernet cable (yellow)
• ISDN U or IDSL cable (red) (Cisco 802, 802 IDSL, 804, and
804 IDSL routers)
• RJ-45-to-RJ-11 adapter cable for use with red ISDN U cable
• Product documentation
Preinstallation Activities
Before you begin installing your Cisco 800 series router, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Order an ISDN BRI line from your telephone service provider. For more information, refer to the Cisco
800 Series Routers Software Configuration Guide.
Step 2 If you have a Cisco 801 or Cisco 803 router, do the following:
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-4
78-5373-04
Page 27

Chapter 2 Installation
Step 3 Be aware of Ethernet, ISDN, and IDSL cable distance limitations. For more information, see the
Step 4 Gather the Ethernet devices to be connected to the router: hub, server, workstation, or PC with 10- or
Step 5 If you have a Cisco 801 or Cisco 803 router and plan to connect a digital telephone, you must provide
Step 6 If you have a Cisco 803 or Cisco 804 router, gather the devices (such as an analog telephone, fax
Step 7 If you plan to configure the software using a terminal or PC connected to the router, provide the terminal
Step 8 If you plan to mount your router on a wall or vertical surface, you need to provide two number-six,
Installing Your Router
• If you are outside of North America, ask your telephone service provider if you must provide an
external Network Termination 1 (NT1) and the ISDN U cable that connects the NT1 to the ISDN
wall jack. Ask for NT1 vendors if necessary.
• If you are in North America, ask your telephone service provider for external NT1 vendors. Provide
the ISDN U cable that connects the NT1 to the ISDN wall jack.
“Maximum Cable Distances” section in Appendix B, “Specifications and Cables.”
10/100-Mbps network interface card (NIC).
an NT1 with two S/T interfaces and one U interface, a telephone cable to connect the telephone (usually
this cable is provided with the device), and an ISDN U cable that connects the NT1 to the ISDN wall
jack.
machine, or modem) that you plan on connecting to the router. You must also provide the telephone cable
to connect each device (usually this cable is provided with the device).
or PC.
3/4-in. (M3.5 x 20 mm) screws. If the wall on which you mount your router is drywall, you instead need
to provide two hollow wall-anchors (1/8-in. with 5/16-in. drill bit or M3 with 8-mm drill bit) to secure
the screws.
Step 9 If you plan to use the cable lock feature, you need to provide a Kensington or equivalent locking cable.
Installing Your Router
To install the Cisco 800 series routers, you need to perform the following tasks in the following order:
1. Connect the Ethernet devices to the router.
2. Connect the ISDN or IDSL line to the router.
3. If you have a Cisco 801 or Cisco 803 router, connect an optional digital telephone.
4. If you have a Cisco 803 or Cisco 804 router, connect an optional analog telephone, fax, or modem.
5. Connect a terminal or PC to the router (for software configuration using the command-line interface
[CLI] or for troubleshooting).
6. Connect the router to the power source.
7. Mount your router.
8. Verify the router installation.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-5
Page 28

Installing Your Router
Connecting Ethernet Devices
Table 2-2 lists the Ethernet devices you can connect to the router, connections for each device, and the
settings of the router HUB/NO HUB or TO HUB/TO PC button (the default setting is IN).
Table 2-2 Connecting Ethernet Devices
Chapter 2 Installation
Network Device
Connected to Router Router Port
Hub with equivalent to
router HUB/NO HUB
button
Cisco 801 and 802
routers: Ethernet port
Cisco 803 and 804
routers: Ethernet port Ø
Hub with equivalent to
router HUB/NO HUB
button
Cisco 801 and 802
routers: Ethernet port
Cisco 803 and 804
routers: Ethernet port Ø
Hub with equivalent to
router TO HUB/TO PC
button
Cisco 802 IDSL router:
Ethernet port
Cisco 804 IDSL router:
Ethernet port 1
Hub with equivalent to
router TO HUB/TO PC
button
Cisco 802 IDSL router:
Ethernet port
Cisco 804 IDSL router:
Ethernet port 1
Hub with equivalent to
router HUB/NO HUB
button
Hub with equivalent to
router TO HUB/TO PC
Cisco 803 and 804
routers:
Ethernet ports 1, 2, 3
Cisco 804 IDSL router:
Ethernet ports 2, 3, 4
button
Hub without equivalent
to router HUB/NO
HUB button
Cisco 801 and 802
routers: Ethernet port
Cisco 803 and 804
routers: Ethernet port Ø
Hub without equivalent
to router TO HUB/TO
PC button
Cisco 802 IDSL router:
Ethernet port
Cisco 804 IDSL router:
Ethernet port 1
Hub without equivalent
to router HUB/NO
HUB button
Hub without equivalent
to router TO HUB/TO
Cisco 803 and 804
routers:
Ethernet ports 1, 2, 3
Cisco 804 IDSL router:
Ethernet ports 2, 3, 4
PC button
Network
Device
Button
2
Setting
Ethernet Cable
1
Ty pe
Router HUB/NO
HUB, TO
HUB/TO PC
Button Setting
Straight-through IN MDI (IN)
Straight-through OUT MDI-X
(OUT)
Straight-through IN MDI (IN)
Straight-through OUT MDI (OUT)
Straight-through N/A
Straight-through N/A
3
4
MDI (IN)
MDI (IN)
Straight-through OUT MDI-X
(OUT)
Straight-through OUT MDI-X
(OUT)
Crossover N/A
3
MDI-X
(OUT)
Crossover N/A
4
MDI-X
(OUT)
2-6
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 29
Chapter 2 Installation
Table 2-2 Connecting Ethernet Devices (continued)
Installing Your Router
Network Device
Connected to Router Router Port
Server, PC, or
workstation
Cisco 801 and 802
routers: Ethernet port
Router HUB/NO
HUB, TO
Ethernet Cable
1
Ty pe
HUB/TO PC
Button Setting
Straight-through OUT N/A
Network
Device
Button
2
Setting
Cisco 803 and 804
routers: Ethernet port Ø
Server, PC, or
workstation
Cisco 802 IDSL router:
Ethernet port
Straight-through OUT N/A
Cisco 804 IDSL router:
Ethernet port 1
Server, PC, or
workstation
Cisco 803 and 804
routers:
Straight-through N/A
3
N/A
Ethernet ports 1, 2, 3
Server, PC, or
workstation
1. Cisco provides a yellow straight-through cable. You provide crossover or additional straight-through cables. For details on
cables, refer to Appendix B, “Specifications and Cables.”
2. Hub vendors choose different names for the button controlling cable selections. This table uses the Cisco 1528 Micro Hub
10/100 with an MDI/MDI-X button as an example. Determine the button name and setting for your particular hub. Refer to
your hub documentation for details.
3. On Cisco 803 and Cisco 804 routers, the HUB/NO HUB button affects only Ethernet port Ø.
4. On Cisco 804 IDSL routers, the TO HUB/TO PC button affects only Ethernet port 1.
Cisco 804 IDSL router:
Ethernet ports 2, 3, 4
Straight-through N/A
4
N/A
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-7
Page 30

Installing Your Router
Connecting Hubs
If you have a Cisco 803, 804, or 804 IDSL router, you can connect as many as four hubs.
Before connecting a hub, see Tab le 2-2, and do the following:
• Choose Ethernet cables.
• On the router, set the HUB/NO HUB or TO HUB/TO PC button.
• On the hub, set the HUB/NO HUB button or its equivalent.
Follow the steps in Figure 2-1 to connect a hub to a Cisco 800 series ISDN or IDSL router. This figure
shows a Cisco 803 router with four Ethernet ports.
Caution Always connect the yellow cable or an Ethernet cable to the yellow ports on the router. Do not connect
the cable to an ISDN S/T or U port, to an IDSL port, or to an NT1. Connecting the cable to the wrong
port or NT1 can damage your router.
Figure 2-1 Connecting a Hub
Chapter 2 Installation
2. Connect cable to:
• Yellow Ethernet
port on Cisco 801,
802 or 802 IDSL router.
• Any yellow Ethernet
port on Cisco 803,
804, or 804 IDSL router.
1. Set HUB/NO HUB
or TO HUB/TO PC button.
HUB
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
N
O
H
U
B
0
1
Cisco 803 router
Cisco 803
C
O
N
S
O
L
E
IS
D
N
S
/T
2
3
PHONE
1
2
Cisco Micro Hub 10/100
1X
2X 3X
SPEED
100BaseTX
10BaseT
LED
SOLID
BLINK
ETHERNET
6X 7X
4X
8X
MDI MDI-X
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
11674
3. Connect other
end of cable
to hub.
4. If applicable, check
setting of hub
equivalent of router
HUB/NO HUB button.
2-8
To verify your hub connection, verify that one of the following LEDs is on after you have completed the
router installation:
• LINK LED on the Cisco 801, 802, or 802 IDSL back panel.
• LKØ, LK1, LK2, or LK3 LED on the Cisco 803 or Cisco 804 front panel.
• ETHERNET 1, 2, 3, or 4 LED on the Cisco 804 IDSL front panel.
If the LED is not on, see Table 3-2 in Chapter 3, “Troubleshooting.”
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 31
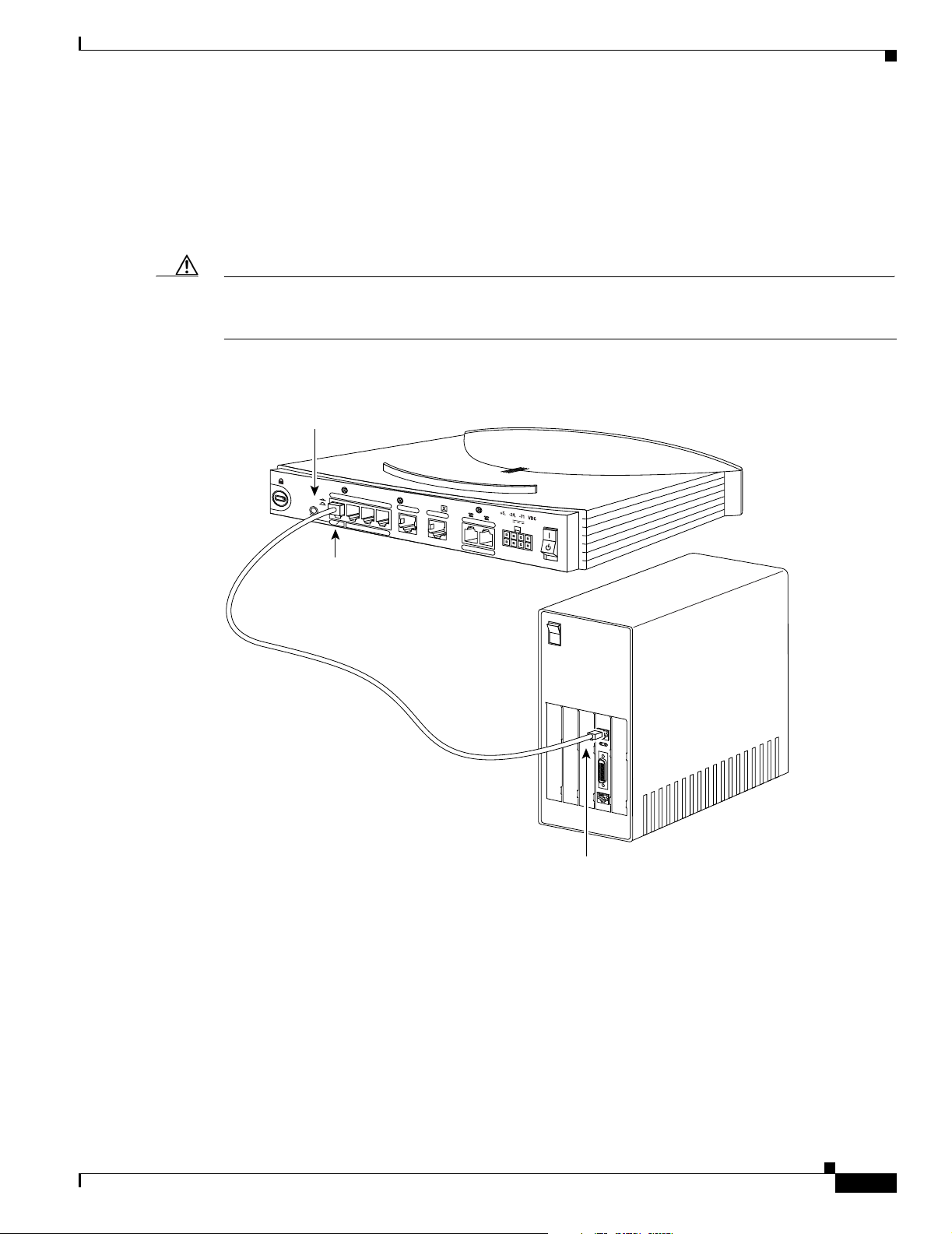
Chapter 2 Installation
Connecting a Server, PC, or Workstation
Before connecting the server, PC, or workstation, refer to Table 2-2 to determine how to set the router
HUB/NO HUB or TO HUB/TO PC button. Ensure that your device has a 10- or 10/100-Mbps NIC.
To connect one of these devices to a Cisco 800 series ISDN or IDSL router, follow the steps in
Figure 2-2.
Caution Always connect the yellow cable or an Ethernet cable to the yellow ports on the router. Do not connect
the cable to an ISDN S/T or U port, to an IDSL port, or to an NT1. Connecting the cable to the wrong
port or NT1 can damage your router.
Figure 2-2 Connecting a Server, PC, or Workstation
Installing Your Router
1. Set HUB/NO HUB
or TO HUB/TO PC button.
HUB
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
N
O
H
U
B
0
1
2. Connect cable to:
• Yellow Ethernet port on Cisco 801,
Cisco 802, or Cisco 802 IDSL router.
• Any yellow port on Cisco 803,
Cisco 804, or Cisco 804 IDSL router.
Cisco 803 router
Cisco 803
C
O
N
S
O
L
E
IS
D
N
S
/T
PHO
2
3
NE
1
2
PC
ETH
OK
LAN
SER 0
AUX
11675
78-5373-04
3. Connect other end of cable
to server, PC, or workstation.
To verify your connection, verify that one of the following LEDs is on after you have completed router
installation:
• LINK LED on the Cisco 801, 802, or 802 IDSL back panel.
• LKØ, LK1, LK2, or LK3 LED on the Cisco 803 or Cisco 804 front panel.
• ETHERNET 1, 2, 3, or 4 LED on the Cisco 804 IDSL front panel.
If the LED is not on, see Table 3-2 in Chapter 3, “Troubleshooting.”
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-9
Page 32

Installing Your Router
Connecting an ISDN Line
The procedure to connect an ISDN line depends on the router and in some cases your location. The
following sections describe the following procedures:
• Connecting an ISDN Line to Cisco 801 and Cisco 803 Routers
• Connecting an ISDN Line to Cisco 802 and Cisco 804 Routers
Connecting an ISDN Line to Cisco 801 and Cisco 803 Routers
Outside of North America, you might need to provide an external NT1 device and the ISDN U cable that
connects the NT1 to the ISDN wall jack. Contact your telephone service provider to supply the following
information:
• Whether you must supply an external NT1 and the ISDN U cable.
• If necessary, the names of NT1 vendors.
In North America, you must provide an external NT1 and the ISDN U cable that connects the NT1 to the
ISDN wall jack. Contact your telephone service provider for a list of NT1 vendors.
Chapter 2 Installation
To connect an ISDN line to a Cisco 801 or Cisco 803 router without an external NT1, follow the steps
in Figure 2-3 on page 2-11.
To connect an ISDN line to a Cisco 801 or Cisco 803 router with an external NT1, follow the steps in
Figure 2-4 on page 2-11.
Warning
Warning
Warning
Caution Always connect the orange cable to the orange ISDN S/T port on the router. Do not connect the cable to
Network hazardous voltages are present in the ISDN cable. If you detach the ISDN cable, detach the
end away from the router first to avoid possible electric shock. Network hazardous voltages also are
present on the system card in the area of the ISDN port (RJ-45 connector), regardless of when power
is turned to standby.
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity.
To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunications line cord.
a yellow Ethernet port. This will damage your router.
2-10
Caution The Cisco 800 series routers do not support the Australian IUT requirement, which specifies that the
routers must communicate for 1/2 hour after a power failure. If a power failure occurs, a Cisco 800 series
router stops communicating with other devices.
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 33
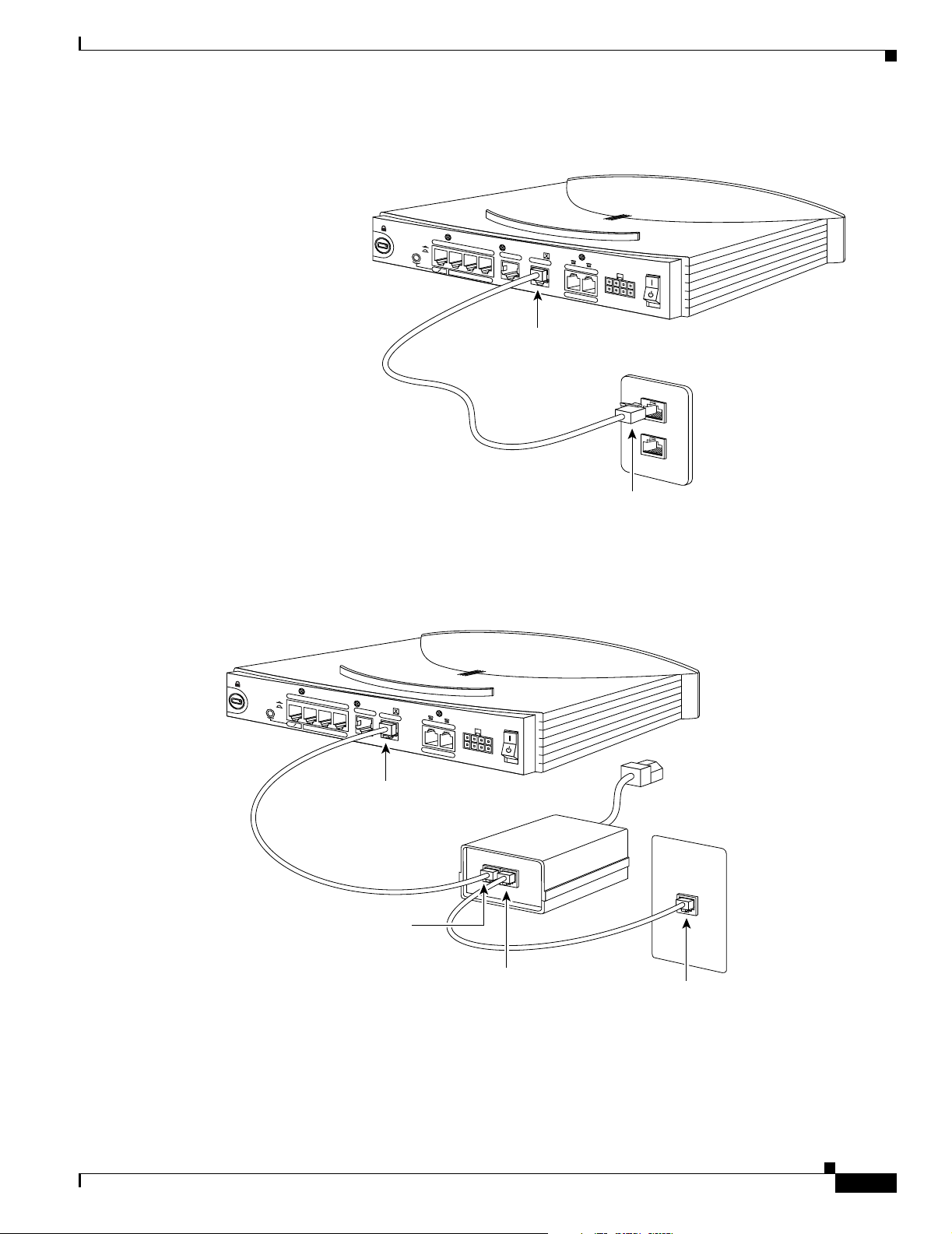
Chapter 2 Installation
Installing Your Router
Figure 2-3 Connecting an ISDN Line to Cisco 801 and Cisco 803 Routers (without External NT1)
Cisco 803 router
HUB
ETHE
RN
N
O
H
ET 10 BA
U
B
0
1
Cisco 803
SE T
C
O
N
S
O
L
E
ISD
N
S
/T
PHON
2
3
E
1
2
1. Connect orange cable
to orange ISDN S/T port.
2. Connect other end of
cable to ISDN wall jack.
Figure 2-4 Connecting ISDN to Cisco 801 and Cisco 803 Routers (with External NT1)
Cisco 803 router
11677
ISDN wall jack
HUB
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
N
O
H
U
B
0
1
2
3
1. Connect orange cable
to orange ISDN S/T port.
2. Connect other end
of cable to NT1.
C
O
N
S
Cisco 803
O
L
E
IS
D
N
S
/T
PH
ON
E
1
2
5. Connect NT1
power cord to
electrical outlet.
NT1
ISDN wall jack
3. Connect ISDN U
11676
cable to NT1.
4. Connect other end of
cable to ISDN wall jack.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-11
Page 34

Installing Your Router
Connecting an ISDN Line to Cisco 802 and Cisco 804 Routers
To connect an ISDN line to Cisco 802 and Cisco 804 routers, follow the steps in Figure 2-5.
Chapter 2 Installation
Warning
Warning
Warning
Caution Always connect the red cable to the red ISDN U port on the router. Do not connect the cable to a yellow
Network hazardous voltages are present in the ISDN cable. If you detach the ISDN cable, detach the
end away from the router first to avoid possible electric shock. Network hazardous voltages also are
present on the system card in the area of the ISDN port (RJ-45 connector), regardless of when power
is turned to standby.
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity.
To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunications line cord.
Ethernet port. This will damage your router.
Caution The Cisco 800 series routers do not support the Australian IUT requirement, which specifies that the
routers must communicate for 1/2 hour after a power failure. If a power failure occurs, a Cisco 800 series
router stops communicating with other devices.
2-12
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 35
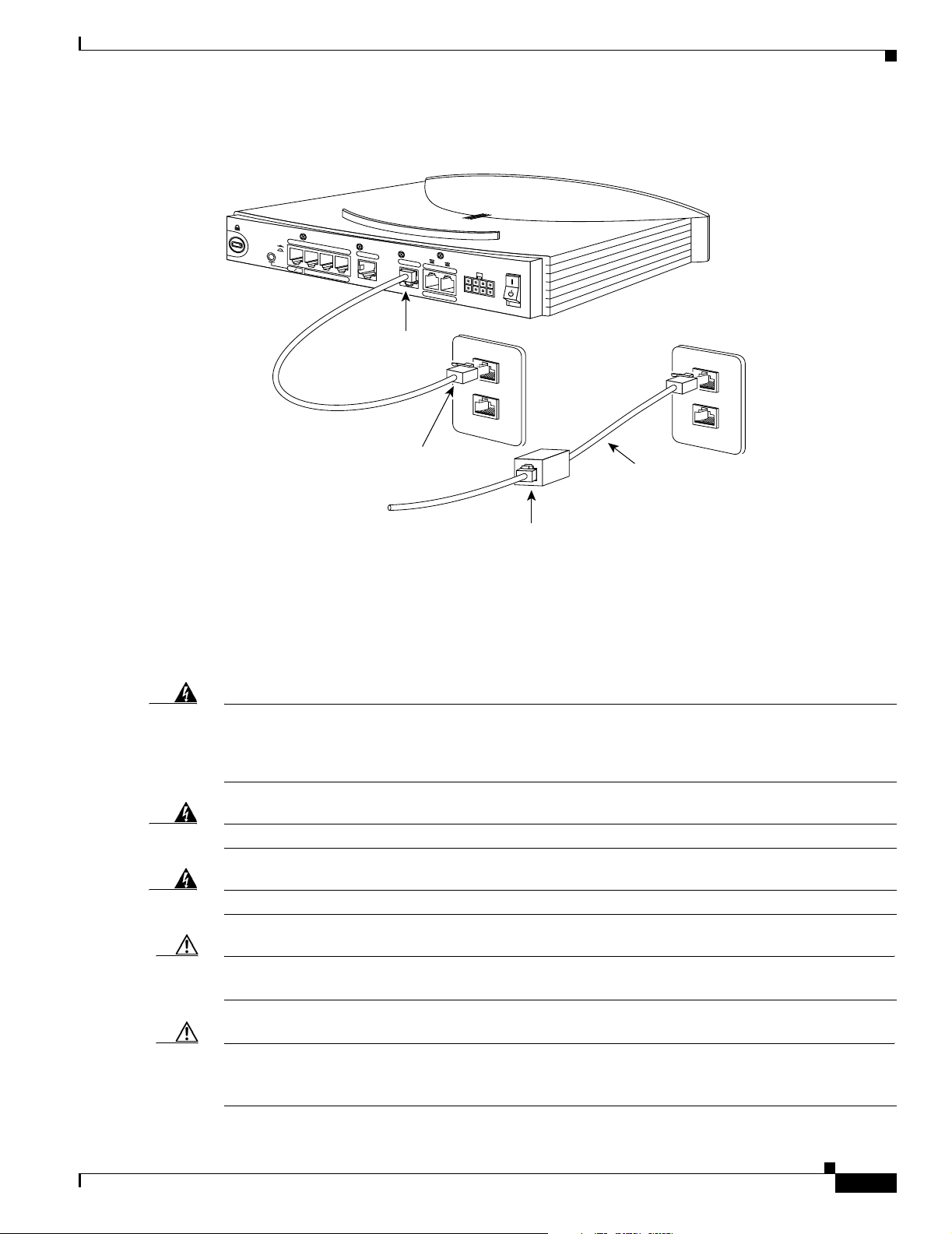
Chapter 2 Installation
Figure 2-5 Connecting ISDN to Cisco 802 or Cisco 804 Routers
Cisco 804 router
Installing Your Router
HUB
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
NO
HU
B
0
1
1. Connect red cable
2. Connect other end of
cable to ISDN wall jack.
Connecting an IDSL Line
Cisco 804
C
O
N
S
O
L
E
IS
2
3
DN U
to red ISDN U port.
PHO
NE
1
2
ISDN
wall jack
RJ-45-to-RJ-11
adapter cable
If your wall jack has an RJ-11 connector,
attach RJ-45-to-RJ-11 adapter cable
to red cable, and then connect RJ-11
connector to ISDN wall jack.
ISDN wall jack
11678
78-5373-04
Warning
Network hazardous voltages are present in the IDSL cable. If you detach the IDSL cable, detach the
end away from the router first to avoid possible electric shock. Network hazardous voltages also are
present on the system card in the area of the IDSL port (RJ-45 connector), regardless of when power
is turned to standby.
Warning
Warning
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity.
To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunications line cord.
Caution Always connect the red cable to the red IDSL port on the router. Do not connect the cable to a yellow
Ethernet port. This will damage your router.
Caution Cisco 802 IDSL and Cisco 804 IDSL routers do not support the Australian IUT requirement, which
specifies that the routers must communicate for 1/2 hour after a power failure. If a power failure occurs,
a Cisco 802 IDSL or 804 IDSL router stops communicating with other devices.
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-13
Page 36

Installing Your Router
Chapter 2 Installation
To connect an IDSL line to Cisco 802 IDSL and Cisco 804 IDSL routers, follow the steps in Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-6 Connecting the IDSL Cable to Cisco IDSL Routers
Cisco 804 IDSL router
Connecting a Digital Telephone
TO HUB
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
T
O
P
C
1
2
3
4
1. Connect red cable
to red IDSL port.
2. Connect other end of
cable to IDSL wall jack.
Cisco 804 IDSL
C
O
N
S
O
L
E
ID
S
L
IDSL
wall jack
RJ-45-to-RJ-11
adapter cable
If your wall jack has an RJ-11 connector,
attach RJ-45-to-RJ-11 adapter cable
to red cable, and then connect RJ-11
connector to IDSL wall jack.
IDSL wall jack
30773
2-14
You can connect a digital telephone, also known as an ISDN telephone, to the ISDN S/T port on Cisco
801 and Cisco 803 routers. This device connects to basic telephone services through the ISDN line.
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 37

Chapter 2 Installation
Installing Your Router
To connect a digital telephone, follow the steps in Figure 2-7. You must provide the following
equipment:
• NT1 with two S/T interfaces and one U interface.
• Telephone cable to connect digital telephone. (This cable is usually provided with the telephone.)
• ISDN U cable that connects the NT1 to the ISDN wall jack.
Figure 2-7 Connecting Digital Telephone to Cisco 801 and Cisco 803 Routers
Cisco 803 router
HUB
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
N
O
H
U
B
0
1
1. Connect orange cable
2. Connect other
Cisco 803
CO
N
S
O
L
E
IS
D
N
S
/T
PHO
2
3
NE
1
2
to orange ISDN S/T port.
end of cable
to NT1.
6. Connect NT1
power cord to
electrical outlet.
NT1
ISDN wall jack
Digital telephone
4. Connect ISDN U
cable to NT1.
3. Connect telephone
cable to digital
telephone.
Connecting an Analog Telephone, Fax, or Modem
If you have Cisco 803 or Cisco 804 routers, you can connect two devices, such as an analog touch-tone
telephone, fax machine, or modem. Each device is connected to basic telephone services through the
ISDN line.
To connect an analog telephone, fax machine, or modem, follow the steps in Figure 2-8. You must
provide the telephone cable to connect each device. The telephone cable is usually provided with the
device.
The gray PHONE 1 and PHONE 2 ports are RJ-11 connectors. If you are outside of North America, you
must buy and attach adapters that allow your telephones, faxes, or modems to be connected to these
RJ-11 connectors. In some countries, these adapters need additional electronics to convert the
14817
5. Connect other end of
cable to ISDN wall jack.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-15
Page 38

Installing Your Router
Chapter 2 Installation
telephones, faxes, or modems to work properly with the router phone ports. For example, in the
United Kingdom, you must buy an adapter that also provides a master socket, which causes incoming
calls to ring the connected devices. For information on recommended master sockets, see Tab le 2- 3.
Warning
This equipment contains a ring signal generator (ringer), which is a source of hazardous voltage. Do
not touch the RJ-11 (phone) port wires (conductors), the conductors of a cable connected to the RJ-11
port, or the associated circuit-board when the ringer is active. The ringer is activated (indicated by a
clicking sound) by an incoming call.
Caution Do not connect the router telephone ports to the telephone wall jack. These ports are not meant for direct
connection to a public network. This connection can damage your router.
Figure 2-8 Connecting an Analog Telephone, Fax, or Modem to Cisco 803 and Cisco 804 Routers
Cisco 804 router
HUB
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
N
O
H
U
B
0
1
Cisco 804
C
O
N
S
O
L
E
IS
D
N
U
PHON
2
3
E
1
2
1. Connect telephone cable to
gray PHONE 1 or PHONE 2 port.
If you are connecting only one
device, use PHONE 1 port.
Analog
telephone
2-16
Table 2-3 Recommended Vendors for United Kingdom Master Sockets
Vendor Name Product Name For More Information
RS Components Avro Pacific Telephone Ring
Adapter (part number 303-2000)
Tandy Export Adapter
(part number 2797057)
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
11679
2. Connect other end of
cable to telephone,
fax machine, or modem.
http://www.rswww.com/
http://www.tandy.co.uk/
78-5373-04
Page 39
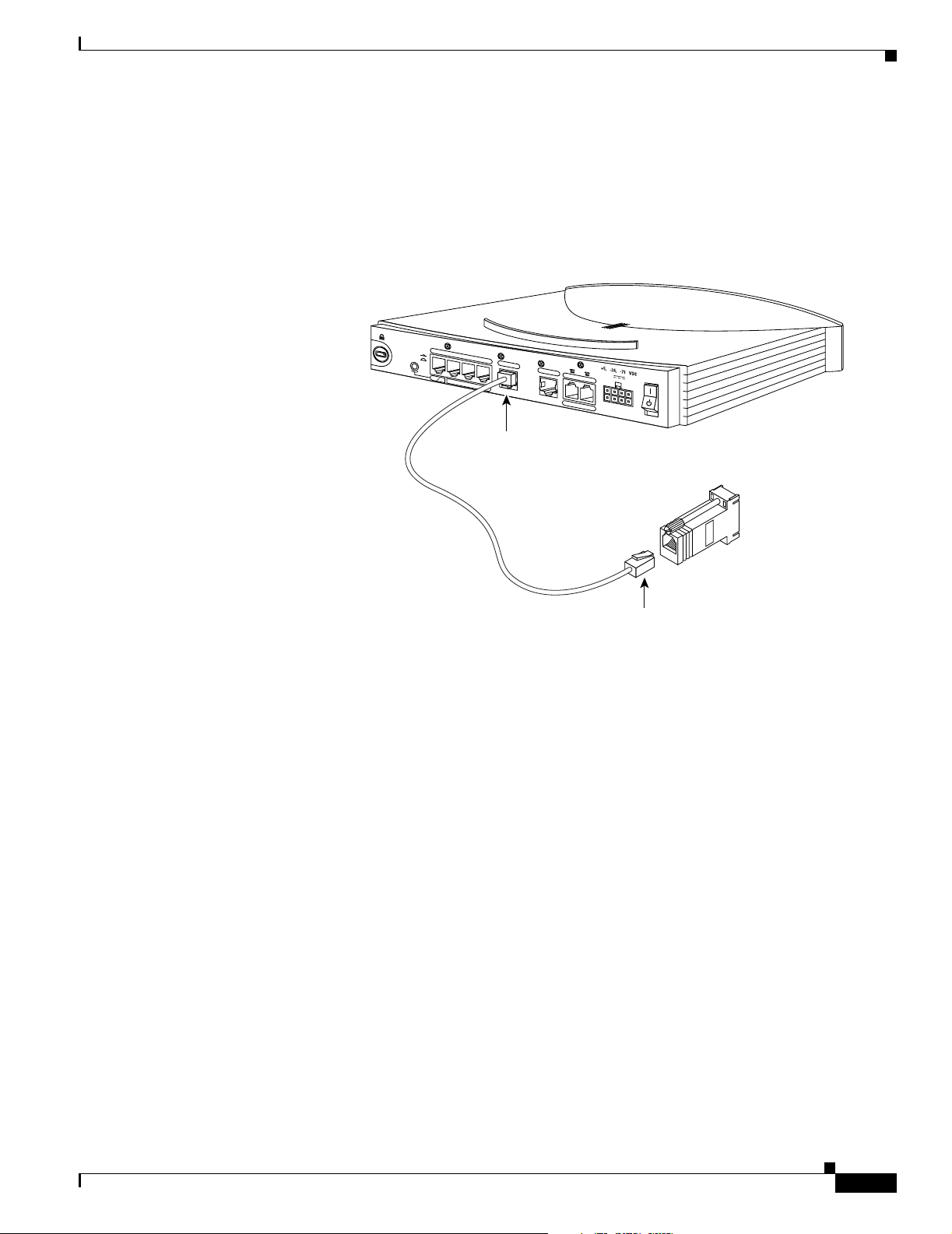
Chapter 2 Installation
Connecting a Terminal or PC
You can connect either a terminal or a PC from which you can configure the software via the CLI or
troubleshoot. To connect a terminal or PC, follow the steps in Figure 2-9.
Figure 2-9 Connecting Terminal or PC
Installing Your Router
Cisco 804 router
HUB
E
TH
ER
N
N
O
H
E
T 10 BA
U
B
SE
T
C
O
N
0
1
S
2
3
1. Connect light blue cable
to light blue CONSOLE port.
Cisco 804
O
LE
IS
D
N
U
PH
O
NE
1
2
2. If necessary, connect other end of
cable to either DB-9-to-RJ-45 adapter
or DB-25-to-RJ-45 adapter.
11680
3. Connect DB-9
connector to
terminal or PC.
DB-X-to-RJ-45
adapter
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-17
Page 40
Mounting Your Router
Connecting the Power Supply
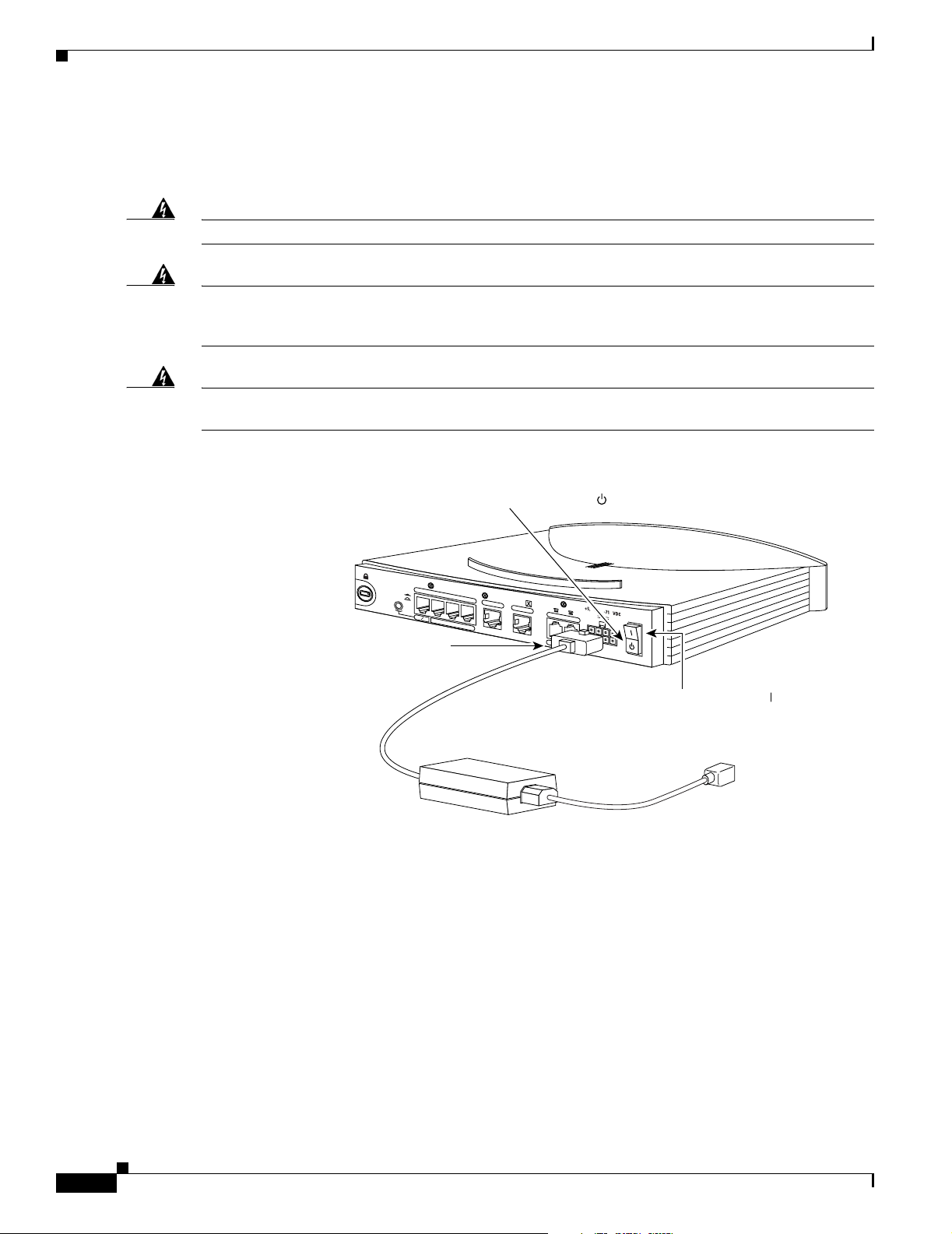
To connect the power supply, follow the steps in Figure 2-10.
Chapter 2 Installation
Warning
Warning
Warning
The device is designed to work with TN power systems.
This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that
a fuse or circuit breaker no larger than 120 VAC, 15A U.S. (240 VAC, 16A international) is used on the
phase conductors (all current-carrying conductors).
This equipment is intended to be grounded. Ensure that the host is connected to earth ground during
normal use.
Figure 2-10 Connecting the Power Supply
1. Press power switch to standby ( ).
Cisco 803 router
HUB
ETHERNET 10 BASE T
N
O
H
U
B
0
1
2. Connect power
supply cable.
Cisco 803
CONSOLE
IS
D
N
S
/T
2
3
PHONE
1
2
11673
Mounting Your Router
You can mount your router on one of the following surfaces:
• Table or other horizontal surface
• Wall or other vertical surface
Mounting on a Table
You can mount your router on a table or other horizontal surface. Use the following guidelines:
Desktop power supply
3. Connect power cord
to power supply.
5. Press power switch to on ( ).
4. Connect other end
of power cord to
electrical outlet.
2-18
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 41
Chapter 2 Installation
• Do not cover or obstruct router vents, which are located on the router sides.
• You can stack a maximum of five routers atop one another.
Mounting on a Wall
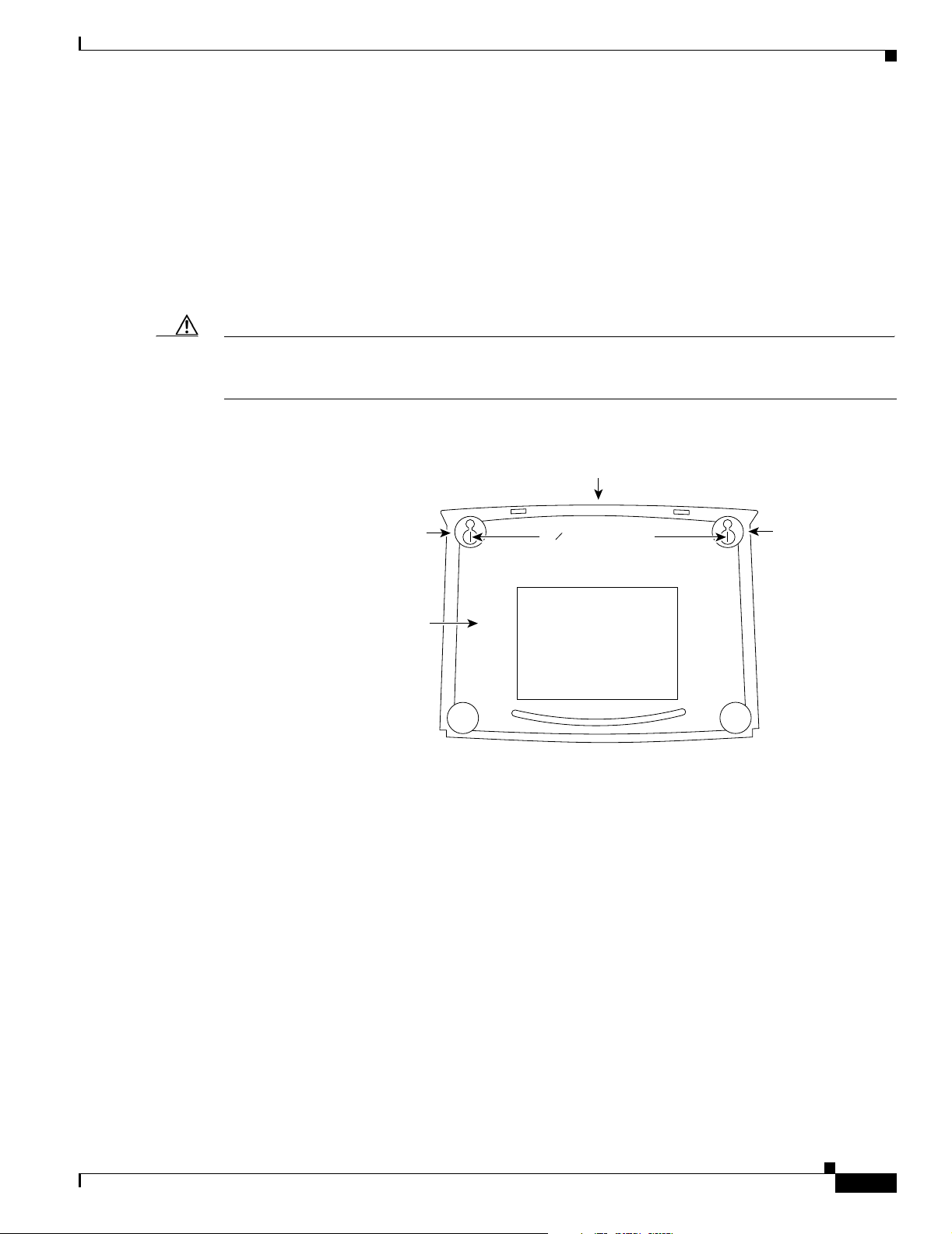
You can mount your router on a wall or other vertical surface by using the molded mounting brackets on
the bottom of the router and two number-six, 3/4-in. (M3.5 x 20 mm) screws. You must provide the
screws. Figure 2-11 shows the mounting brackets.
Caution If the wall to which you mount your router is drywall, use two hollow wall-anchors (1/8-in. with 5/16-in.
drill bit or M3 with 8-mm drill bit) to secure the screws. If the screws are not properly anchored, the
strain of the network cable connections could pull the router from the wall.
Figure 2-11 Wall-Mounting Brackets (Bottom of Router)
Mounting Your Router
Front panel of router
ounting
bracket
Bottom
of router
5
7 in. (19.35 cm)
8
Mounting
bracket
11671
When mounting the router, the following conditions must be met:
• Because you will use the LEDs as status and problem indicators, the LEDs on the front panel must
face upward and be easily visible.
• The back panel must face downward to reduce strain on the cable connections.
• The power supply must rest on a horizontal surface such as the floor or a table. If the power supply
is not supported, it might place strain on the power supply cable and cause it to disconnect from the
connector on the router back panel.
To mount the router, follow the steps in Figure 2-12. The last page of this manual provides a template
for measuring the distance between the screws.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-19
Page 42

Verifying Installation
Figure 2-12 Mounting Router on Wall
Chapter 2 Installation
1. Secure two screws 7 inches
(19.35 cm) apart in a wall
1
and in. (0.32 cm) from
8
the wall.
Wall
Wall-mount
screw
Wall
5
8
1
5
8
7 in. (19.35 cm)
in. (0.32 cm)
8
Screw
Front panel
Wall-mount
screw
Mounting
brackets
2. Hang router
on screws.
11672
Maximum distance
6 ft (18 m)
Verifying Installation
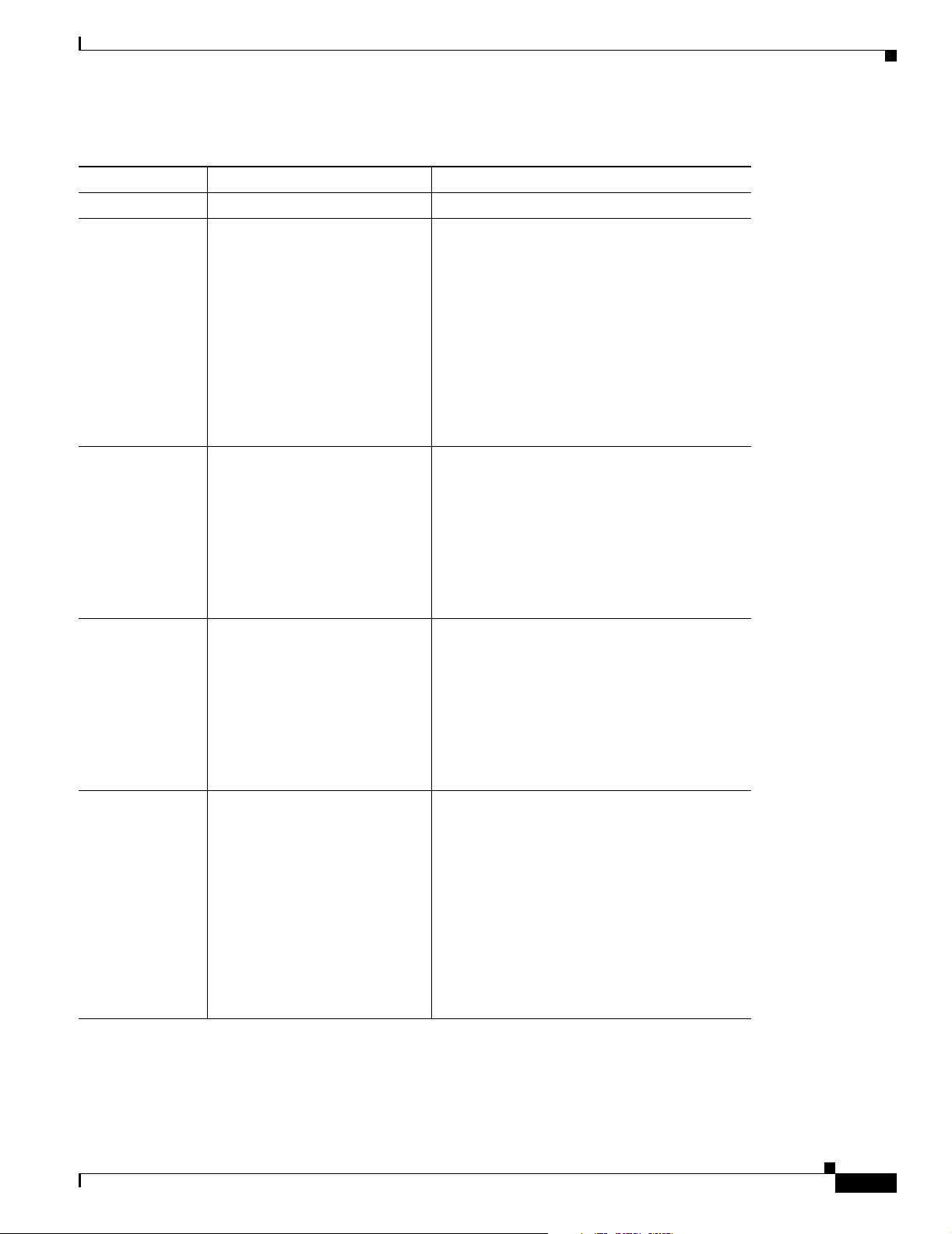
Verify the cable connections (links) by checking the LEDs listed in Tabl e 2-4 . If the LEDs are not on,
see Chapter 3, “Troubleshooting.”
The LINK LED is on the back panel of Cisco
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-20
3. Place power supply
on horizontal surface.
801 and Cisco 802 routers.
78-5373-04
Page 43
Chapter 2 Installation
Table 2-4 Verifying Installation
Power/Link LEDs To Check Normal Patterns
Power OK On
To hub, server,
PC, or
workstation
To ISDN network
using ISDN S/T
port
To ISDN network
using ISDN
Uport
• Cisco 801, 802, and 802
IDSL routers: LINK, LAN,
LAN RXD, and LAN TXD
• Cisco 803 and Cisco 804
routers:
LKØ, LK1, LK2, LK3,
LAN, LAN RXD, and LAN
TXD
• Cisco 804 IDSL router:
ETHERNET LAN, RXD,
TXD, 1, 2, 3, and 4
LINE, CH1, CH1 RXD, CH1
TXD, CH2, CH2 RXD, and CH2
TXD
NT1, LINE, CH1, CH1 RXD,
CH1 TXD, CH2, CH2 RXD, and
CH2 TXD
• LINK, LKØ, LK1, LK2, LK3, ETHERNET
1, 2, 3, 4, LAN: On. LAN is on when
indicated Ethernet port sends or receives a
packet.
• LAN RXD: blinking when an Ethernet port
receives a packet.
• LAN TXD: blinking when an Ethernet port
sends a packet.
• LINE, CH1, and CH2: On. CH1 or CH2 is
on when the router has an active voice or
data connection.
• CH1 RXD, CH2 RXD: Blinking when
indicated ISDN B channel receives a
packet.
• CH1 TXD, CH2 TXD: Blinking when
indicated ISDN B channel sends a packet.
• NT1, LINE, CH1, and CH2: On. CH1 or
CH2 is on when the router has an active
voice or data connection.
Verifying Installation
To IDSL network
using IDSL port
NT1, LINE, CH1, CH1 RXD,
CH1 TXD, CH2, CH2 RXD, and
CH2 TXD
• CH1 RXD, CH2 RXD: Blinking when
indicated ISDN B channel receives a
packet.
• CH1 TXD, CH2 TXD: Blinking when
indicated ISDN B channel sends a packet.
• NT1, LINE, CH1, and CH2: On. CH1 or
CH2 is on when the router has an active
data connection and the line speed is 64
kbps. CH1 and CH2 are both on when the
router has an active data connection and the
line speed is 128 or 144 kbps.
• CH1 RXD, CH2 RXD: Blinking when
indicated ISDN B channel receives a
packet.
• CH1 TXD, CH2 TXD: Blinking when
indicated ISDN B channel sends a packet.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
2-21
Page 44

Where to Go from Here
Table 2-4 Verifying Installation (continued)
Power/Link LEDs To Check Normal Patterns
To digital
telephone
To analog
telephone, fax, or
modem
1. You can also pick up the handset and listen for a dial tone.
LINE, CH1, CH1 RXD, CH1
TXD, CH2, CH2 RXD, and CH2
TXD
PH1 and PH2
1
• LINE, CH1, and CH2: On. CH1 or CH2 is
on when the router has an active voice
connection.
• CH1 RXD, CH2 RXD: Blinking when
indicated ISDN B channel receives a
packet.
• CH1 TXD, CH2 TXD: Blinking when
indicated ISDN B channel sends a packet.
On when telephone, fax, or modem is in use.
Chapter 2 Installation
Where to Go from Here
You have completed the hardware installation and are ready to configure the software. Cisco strongly
recommends that inexperienced network administrators use the Cisco 800 Fast Step application. Use the
Cisco 800 Fast Step CD-ROM and online help. If you are an experienced network administrator and want
to use the CLI to configure the software, refer to the Cisco 800 Series Routers Software Configuration
Guide.
2-22
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 45

CHA P T E R
3
Troubleshooting
This chapter describes problems that could occur with the Cisco 800 series router hardware, reasons for
the problems, and steps to solve the problems. The problems are grouped as follows:
• Problems during first startup
• Problems after first startup
• Problems after router is running
For information on problems that could occur with the software, refer to the Cisco 800 Series Routers
Software Configuration Guide.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
3-1
Page 46

Problems During First Startup
Problems During First Startup
Table 3-1 lists problems that could occur after you turn on the power switch for the first time.
Table 3-1 Problems During First Startup
Symptom Problem Solutions
All LEDs,
including OK
LED, are off.
No power to
router.
Perform the following steps in the following order:
• Make sure that the power switch is ON.
• Make sure that all connections to and from the power
supply are securely connected.
• Make sure that the power outlet has power.
• If the problem continues, the router might have a faulty
power supply. Contact your Cisco reseller.
Chapter 3 Troubleshooting
3-2
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 47

Chapter 3 Troubleshooting
Problems After First Startup
Table 3-2 lists problems that could occur after the router has power for the first time.
Table 3-2 Problems After First Startup
Symptom Problem Solutions
No link to an Ethernet
device. (On Cisco 801,
Cisco 802, and 802
IDSL routers, the LINK
LED on the back panel
is off. On Cisco 803 and
804 routers, the LKØ,
LK1, LK2, or LK3 LED
on the front panel is off.
On the Cisco 804 IDSL
router, the ETHERNET
1, 2, 3, or 4 LED on the
front panel is off.)
• A cable-related
problem:
–
Wrong cable.
–
Improperly
connected cable.
–
Damaged cable.
Perform the following tasks in the following
order:
• If you supply your own cable, make sure
you are using the right type of cable (either
straight-through or crossover). Check the
cable information in Table 2-2 in Chapter 2,
“Installation.”
• Check specifications in Table B-1 3 and
Table B-14 in Appendix B, “Specifications
and Cables,” to make sure the cable
complies. If it does not, replace it.
• To make sure you have cabled the devices
correctly, see Ta b le 2-2 in Chapter 2,
“Installation.”
• Make sure the connectors at both ends of
the cable are securely seated.
Problems After First Startup
No link to ISDN or
IDSL network. (NT1,
LINE, CH1, CH1 RXD,
CH1 TXD, CH2, CH2
RXD, or CH2 TXD
LED is off.)
• Improperly set router
HUB/NO HUB or
TO HUB/TO PC
button or hub
equivalent of
HUB/NO HUB button
• Improperly
functioning network
interface card (NIC)
on server, PC, or
workstation.
• If you have a
Cisco 801 or 803
router in North
America or in parts of
Europe, you might
need to connect the
router to an external
NT1 and connect the
NT1 to an ISDN wall
jack.
• Make sure the cable is not physically
damaged. If it is, replace it.
• To make sure you have set buttons correctly,
see Table 2-2 in Chapter 2, “Installation.”
• Run the NIC diagnostic supplied by the
vendor to make sure it is functioning
properly. If it is not, replace it.
• If the problem continues, call your Cisco
reseller.
• If outside of North America, contact your
telephone service provider and ask if you
must provide an NT1 and the ISDN U cable
that connects the NT1 to the ISDN wall
jack. In North America, you must provide
an NT1 and the ISDN U cable. Connect
NT1 as described in the “Connecting an
ISDN Line to Cisco 801 and Cisco 803
Routers” section in Chapter 2,
“Installation.”
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
3-3
Page 48
Problems After First Startup
Table 3-2 Problems After First Startup (continued)
Symptom Problem Solutions
• One of the following
cable-related
problems:
–
Improperly
connected cable.
–
Damaged cable.
Perform the following tasks in the following
order:
• To make sure you have cabled the ISDN or
IDSL port correctly, see the “Connecting an
ISDN Line” or “Connecting an IDSL Line”
sections in Chapter 2, “Installation.”
• Make sure the connectors at both ends of
each cable are securely connected.
• Make sure each cable is not physically
damaged. If it is, replace it with a similar
cable.
• Problem with ISDN
or IDSL line.
• Contact your telephone or Internet service
provider to determine if there is a problem
with your line.
• If the problem continues, call your Cisco
reseller.
No link to digital
telephone.
• One of the following
cable-related
problems:
–
Improperly
connected cable.
–
Damaged cable.
Perform the following tasks in the following
order:
• To make sure you have cabled the port
correctly, see the “Connecting a Digital
Telephone” section in Chapter 2,
“Installation.”
• Make sure the connectors at both ends of
each cable are securely connected.
• Make sure each cable is not physically
damaged. If it is, replace it.
• Problem with ISDN
line.
• Contact your telephone service provider to
determine if there is a problem with your
line.
• If the problem continues, call your Cisco
reseller.
No link to analog
telephone, fax machine,
or modem. (PH1 or PH2
LED on Cisco 803 and
804 routers is off.)
• One of the following
cable-related
problems:
–
Improperly
connected cable.
–
Damaged cable.
Perform the following tasks in the following
order:
• To make sure you have cabled the telephone
port correctly, see the “Connecting an
Analog Telephone, Fax, or Modem” section
in Chapter 2, “Installation.”
• Make sure the connectors at both ends of
the cable are securely connected.
Chapter 3 Troubleshooting
3-4
• Make sure the cable is not physically
damaged. If it is, replace it.
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 49

Chapter 3 Troubleshooting
Table 3-2 Problems After First Startup (continued)
Symptom Problem Solutions
• Problem with ISDN
line.
• Contact your telephone service provider to
determine if there is a problem with your
line.
• If the problem continues, call your Cisco
reseller.
Problems After Router Is Running
Table 3-3 lists problems that could occur after the router has been up and running for a while.
Table 3-3 Problems After Router Is Running
Symptom Problem Solutions
Problems with Ethernet link.
(On Cisco 801, Cisco 802,
and Cisco 802 IDSL routers,
the LINK LED on the back
panel blinks. On Cisco 803
and 804 routers, the LKØ,
LK1, LK2, or LK3 LED on the
front panel blinks. On the
Cisco 804 IDSL router, the
ETHERNET 1, 2, 3, or 4 LED
on the front panel blinks.)
Connection to an Ethernet
device is intermittent or lost.
(On Cisco 801, 802, and 802
IDSL routers, the LINK LED
on the back panel is off. On
Cisco 803 and 804 routers, the
LKØ, LK1, LK2, or LK3 LED
on the front panel is off. On the
Cisco 804 IDSL router, the
ETHERNET 1, 2, 3, or 4 LED
on the front panel is off.)
• One of the
following
cable-related
problems:
–
Disconnected
cable.
–
Damaged
cable.
• Improperly
functioning NIC on
server, PC, or
workstation.
• A cable-related
problem:
–
Disconnected
cable.
–
Damaged
cable.
• Improperly
functioning NIC on
server, PC, or
workstation.
Perform the following tasks in the following
order:
• Make sure the connectors at both ends
of the cable are securely connected.
• Make sure the cable is not physically
damaged. If it is, replace it.
• Run the NIC diagnostic supplied by the
vendor to make sure it is functioning
properly. If it is not, replace it.
• If the problem continues, call your
Cisco reseller.
• Make sure the connectors at both ends
of the cable are securely connected.
• Make sure the cable is not physically
damaged. If it is damaged, replace it.
• Run the NIC diagnostic supplied by the
vendor to determine if it is functioning
properly. If it is not, replace it.
Problems After Router Is Running
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
3-5
Page 50
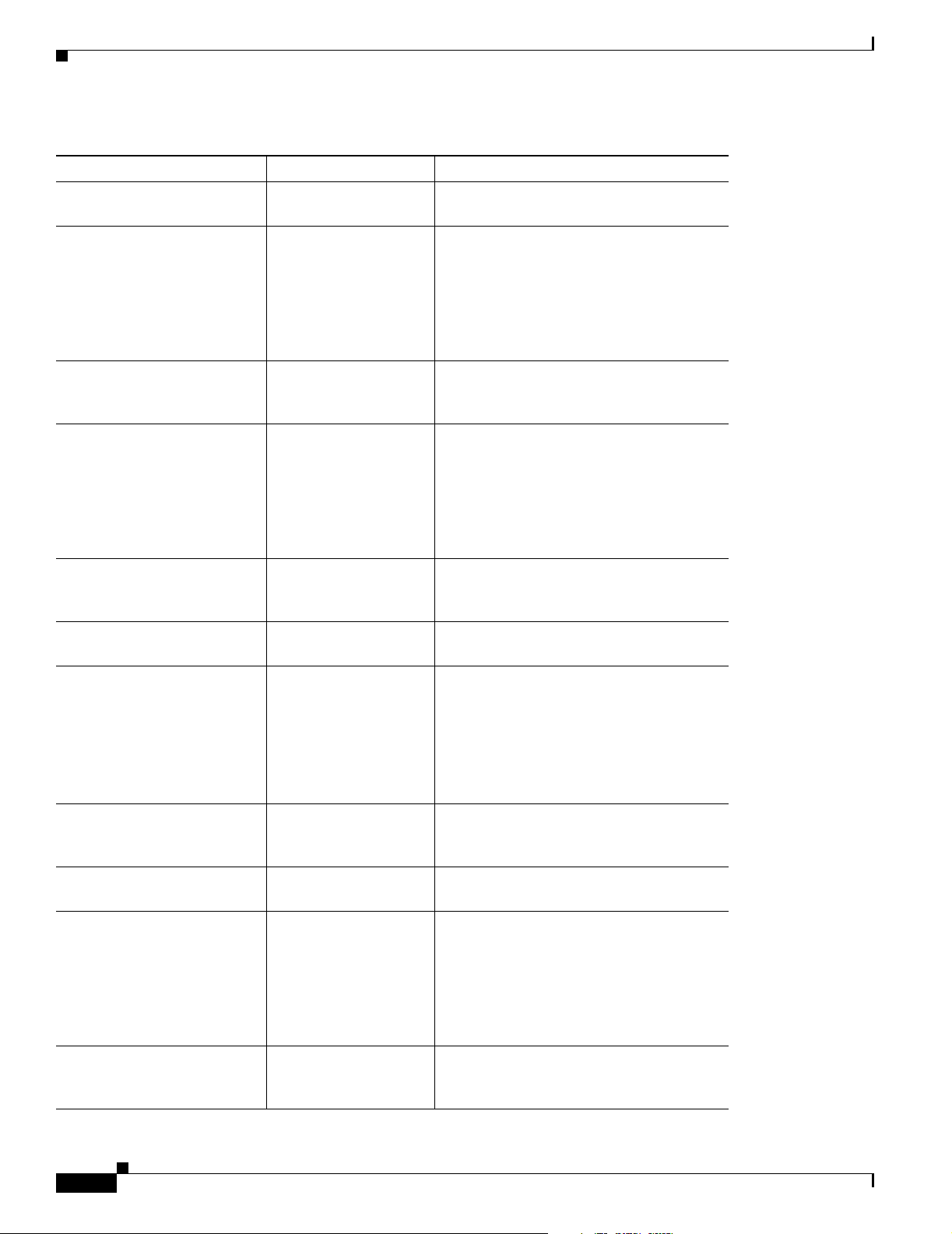
Problems After Router Is Running
Table 3-3 Problems After Router Is Running (continued)
Symptom Problem Solutions
• If the problem continues, call your
Cisco reseller.
Problems with ISDN or IDSL
link. (CH1, CH1 RXD, CH1
TXD, CH2, CH2 RXD, or
CH2 TXD are off.)
Connection to an ISDN or
IDSL network is lost. (LINE,
CH1, CH1 RXD, CH1 TXD,
CH2, CH2 RXD, or CH2 TXD
LED is off.)
Problems with link to digital
or analog telephone.
Symptoms include no dial
tone, a call that is abruptly
disconnected, and an incoming
call that does not cause the
device to ring.
Connection to digital
telephone is lost. (LINE, CH1,
CH1 RXD, CH1 TXD, CH2,
CH2 RXD, and CH2 TXD
LEDs on Cisco 801 and 803
routers are off.)
• A cable-related
problem:
–
Disconnected
cable.
–
Damaged
cable.
• Problem with ISDN
or IDSL line.
• A cable-related
problem:
–
Disconnected
cable.
–
Damaged
cable.
• Problem with ISDN
or IDSL line.
• A cable-related
problem:
–
Disconnected
cable.
–
Damaged
cable.
• Problem with ISDN
line.
• A cable-related
problem:
–
Disconnected
cable.
–
Damaged
cable.
• Problem with ISDN
line.
• Make sure the connectors at both ends
of each cable are securely connected.
• Make sure each cable is not physically
damaged. If one is damaged, replace it.
• Contact your telephone or Internet
service provider to determine if there is
a problem with your line.
• Make sure the connectors at both ends
of each cable are securely connected.
• Make sure each cable is not physically
damaged. If one is damaged, replace it.
• Contact your telephone or Internet
service provider to determine if there is
a problem with your line.
• If the problem continues, call your
Cisco reseller.
• Make sure the connectors at both ends
of each cable are securely connected.
• Make sure each cable is not physically
damaged. If one is damaged, replace it.
• Contact your telephone company to
determine if there is a problem with
your line.
• If the problem continues, call your
Cisco reseller.
• Make sure the connectors at both ends
of each cable are securely connected.
• Make sure each cable is not physically
damaged. If one is damaged, replace it.
• Contact your telephone company to
determine if there is a problem with
your line.
Chapter 3 Troubleshooting
3-6
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 51

Chapter 3 Troubleshooting
Table 3-3 Problems After Router Is Running (continued)
Symptom Problem Solutions
• If the problem continues, call your
Cisco reseller.
Connection to analog
telephone, fax machine, or
modem is lost. (PH1 or PH2
LED on Cisco 803 and 804
routers is off.)
• A cable-related
problem:
–
Disconnected
cable.
–
Damaged
cable.
• Problem with ISDN
line.
• Make sure the connectors at both ends
of the cable are securely connected.
• Make sure the cable is not physically
damaged. If it is damaged, replace it.
• Contact your telephone company to
determine if there is a problem with
your line.
• If the problem continues, call your
Cisco reseller.
When Contacting Your Cisco Reseller
When Contacting Your Cisco Reseller
Some of the solutions instruct you to contact your Cisco reseller. Before contacting your reseller, have
the following information ready:
• Router model and serial number (see the back panel of the router)
• Maintenance agreement or warranty information
• Date you received your router
• Brief description of the problem
• Brief description of the steps you have taken to solve the problem
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
3-7
Page 52

When Contacting Your Cisco Reseller
Chapter 3 Troubleshooting
3-8
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 53

CHA P T E R
A
ISDN and IDSL Concepts
This appendix provides further explanation of ISDN and IDSL concepts.
The Cisco 800 series routers provide one basic rate interface (BRI). The ISDN BRI service provided by
your telephone service provider offers two bearer channels (B channels) and one data channel (D
channel). The B channel operates at 64 kbps and carries user data. The D channel operates at 16 kbps
and carries control and signaling information although it can support user data transmission under
certain circumstances.
Cisco 801 and Cisco 803 routers have an ISDN S/T port. Cisco 802 and Cisco 804 routers have an ISDN
U port, and Cisco 802 IDSL and Cisco 804 IDSL routers have an IDSL port.
Outside North America, telephone service providers typically provide an S/T interface. The S/T
interfaces are four-wire (two pairs of wires) interfaces from the phone switch that supports full-duplex
data transfer over two pairs of wires.
In North America, telephone service providers typically provide a U interface. The U interface is a
two-wire (single pair) interface from the phone switch that supports full-duplex data transfer over a
single pair of wires.
Cisco 803 and Cisco 804 routers support data and voice applications. The data applications on these
routers are implemented through the ISDN port on these routers. The voice applications on these routers
are implemented with ISDN BRI and through the telephone ports.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
A-1
Page 54

Chapter A ISDN and IDSL Concepts
A-2
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 55

Specifications and Cables
This appendix provides system, port, and cabling specifications for the Cisco 800 series routers.
System Specifications
Table B-1 outlines the system specifications for the routers.
Table B-1 System Specifications
Description Design Specification
Physical Dimensions
Dimensions (H x W x D) 2.0 x 9.7 x 8.3 in. (5.1 x 24.6 x 21.1 cm)
Weight (does not include desktop
power supply)
Environmental Operating Ranges
Nonoperating temperature –4 to 149°F (–20 to 65°C)
Nonoperating humidity 5 to 95%, relative humidity
Nonoperating altitude 0 to 15,000 ft (4570 m)
Operating temperature 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
Operating humidity 10 to 85%, relative humidity
Operating altitude 0 to 10,000 ft (3000 m)
Router Power
AC input voltage 100 to 250 VAC
Frequency 50 to 60 Hz
Power consumption 20W
Telephone Port Power
Vo l t a g e - 2 4 V
APPENDIX
Cisco 801 router: 1.39 lb (0.63 kg)
Cisco 802 router: 1.42 lb (0.64 kg)
Cisco 802 IDSL router: 1.42 lb (0.64 kg)
Cisco 803 router: 1.44 lb (0.65 kg)
Cisco 804 router: 1.45 lb (0.66 kg)
Cisco 804 IDSL router: 1.45 lb (0.66 kg)
B
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
B-1
Page 56
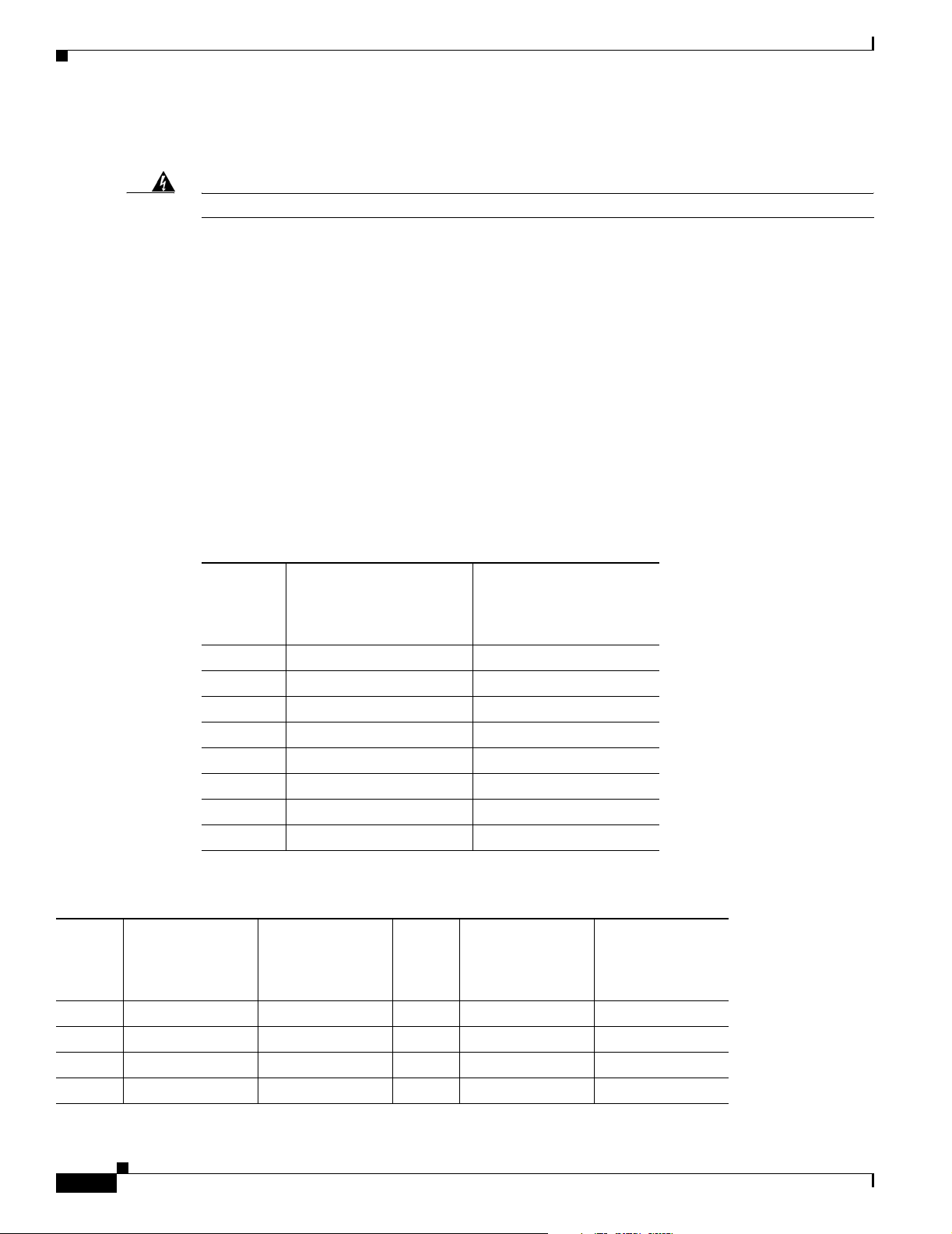
Port Connector Pinouts
Appendix B Specifications and Cables
For information on regulatory compliance, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
for Cisco 800 Series Routers document that shipped with your router.
Warning
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations.
Port Connector Pinouts
This section provides pinouts for the following connectors:
• Ethernet–Table B- 2, Tabl e B- 3 , Table B-4, Ta b le B -5, and Tab l e B-6
• Console (for connecting a terminal or PC)–Tabl e B- 7
• ISDN S/T–Table B-8
• ISDN U–Table B-9
• IDSL–Table B-10
• Telephone–Table B-11
• Power–Tab le B- 1 2
Table B-2 Cisco 801, Cisco 802, and Cisco 802 IDSL Ethernet Connector Pinouts (RJ-45)
Function
(HUB/NO HUB or
TO HUB/TO PC Button –
Pin
1TX+ RX+
2TX– RX–
3RX+ TX+
4 Unused Unused
5 Unused Unused
6RX– TX–
7 Unused Unused
8 Unused Unused
IN Position)
Function
(HUB/NO HUB or
TO HUB/TO PC Button –
OUT Position)
Table B-3 Cisco 803 and Cisco 804 Ethernet Connector Pinouts for Port Ø Only (RJ-45)
Function
(HUB/NO HUB
Button – IN
Position)
Pin
Function
(HUB/NO HUB
Button – OUT
Position)
Function
(HUB/NO HUB
Button – IN
Position) Pin
Function
(HUB/NO HUB
Button – OUT
Position)
A1 RX+ TX+ A2 RX– TX–
A3 TX+ RX+ A4 Unused Unused
A5 Unused Unused A6 TX– RX–
A7 Unused Unused A8 Unused Unused
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
B-2
78-5373-04
Page 57

Appendix B Specifications and Cables
Table B-4 Cisco 804 IDSL Ethernet Connector Pinouts for Port 1 Only (RJ-45)
Port Connector Pinouts
Pin
Function
(TO HUB/TO PC
Button –
OUT Position)
Function
(TO HUB/TO PC
Button –
IN Position) Pin
Function
(TO HUB/TO PC
Button –
OUT Position)
Function
(TO HUB/TO PC
Button –
IN Position)
A1 RX+ TX+ A2 RX– TX–
A3 TX+ RX+ A4 Unused Unused
A5 Unused Unused A6 TX– RX–
A7 Unused Unused A8 Unused Unused
Table B-5 Cisco 803 and Cisco 804 Ethernet Connector Pinouts for
Ports 1, 2, and 3 (RJ-45)
Pin Function Pin Function
B1 RX3+ B2 RX3–
B3 TX3+ B4 Unused
B5 Unused B6 TX3–
B7 Unused B8 Unused
C1 RX2+ C2 RX2–
C3 TX2+ C4 Unused
C5 Unused C6 TX2–
C7 Unused C8 Unused
D1 RX1+ D2 RX1–
D3 TX1+ D4 Unused
D5 Unused D6 TX1–
D7 Unused D8 Unused
78-5373-04
Table B-6 Cisco 804 IDSL Ethernet Connector Pinouts for
Ports 2, 3, and 4 (RJ-45)
Pin Function Pin Function
B1 RX4+ B2 RX4–
B3 TX4+ B4 Unused
B5 Unused B6 TX4–
B7 Unused B8 Unused
C1 RX3+ C2 RX3–
C3 TX3+ C4 Unused
C5 Unused C6 TX3–
C7 Unused C8 Unused
D1 RX2+ D2 RX2–
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
B-3
Page 58

Port Connector Pinouts
Appendix B Specifications and Cables
Table B-6 Cisco 804 IDSL Ethernet Connector Pinouts for
Ports 2, 3, and 4 (RJ-45) (continued)
Pin Function Pin Function
D3 TX2+ D4 Unused
D5 Unused D6 TX2–
D7 Unused D8 Unused
Table B-7 Console Connector Pinouts (RJ-45)
Pin Function
1RTS
2DTR
3TXD
4GND
5GND
6RXD
7DSR
8CTS
B-4
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 59
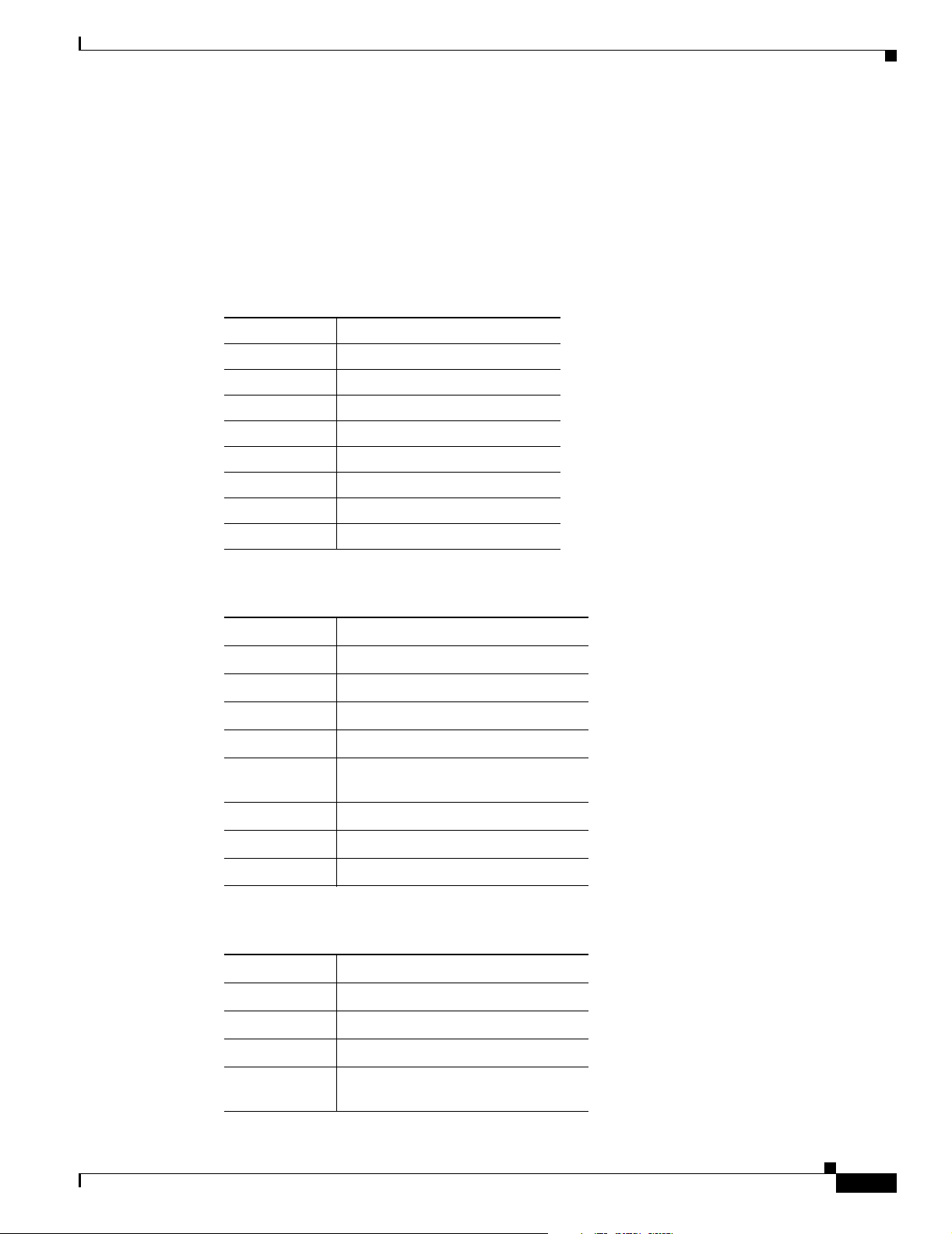
Appendix B Specifications and Cables
The console port is configured as a data communications equipment (DCE) device. The default
parameters for the console port are as follows:
• 9600 baud
• 8 data bits
• No parity
• One stop bit
Table B-8 ISDN S/T Connector Pinouts (RJ-45)
Pin Function
1Unused
2Unused
3 TXD+
4RXD+
5RXD–
6 TXD–
7Unused
8Unused
Port Connector Pinouts
Table B-9 ISDN BRI U Connector Pinouts (RJ-45)
Pin Function
1Unused
2Unused
3 Unused
4 U interface network connection (Tip)
5 U interface network connection
(Ring)
6Unused
7Unused
8Unused
Table B-10 IDSL Connector Pinouts (RJ-45)
Pin Function
1Unused
2Unused
78-5373-04
3 Unused
4 IDSL interface network connection
(Tip)
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
B-5
Page 60

Cabling Specifications
Appendix B Specifications and Cables
Table B-10 IDSL Connector Pinouts (RJ-45)
Pin Function
5 IDSL interface network connection
(Ring)
6Unused
7Unused
8Unused
Table B-11 Telephone Connector Pinouts (RJ-11)
Pin Function
1Unused
2Unused
3Ring
4Tip
5Unused
6Unused
Table B-12 Power Connector Pinouts
Pin Function
1ROF
2RTN
3Unused
4Unused
5+5
6RTN
7–71
8–24
Cabling Specifications
This section provides the following cabling specifications:
• Straight-through and crossover Ethernet cables.
• Ethernet, ISDN, IDSL and telephone cable distance limitations. (A telephone cable connects a
device to a telephone port.)
B-6
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 61

Appendix B Specifications and Cables
Ethernet Cable Specifications
Table B-13 lists the specifications for straight-through and crossover Ethernet cables. Refer to the
Glossary for definitions of straight-through Ethernet cable and crossover Ethernet cable.
Table B-13 Ethernet Cable Specifications
Type Category Shielding
10BASE-T Category 3 or 5 Shielded twisted-pair (STP)
10BASE-T N/A Unshielded twisted-pair (UTP)
Maximum Cable Distances
Table B-14 provides the maximum distances of Ethernet, ISDN, IDSL, and telephone cables that you can
use.
Table B-14 Maximum Cable Distances
Cabling Specifications
Cable Maximum Distance
Ethernet cable 328 ft (100 m)
ISDN S/T and U and IDSL
cables
Telephone cable 500 ft (152 m)
32.8 ft (10 m)
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
B-7
Page 62

Cabling Specifications
Appendix B Specifications and Cables
B-8
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 63

Numerics
GLOSSARY
10BASE-T
B
BRI
C
Cisco 800 Fast Step
Application
crossover Ethernet
cable
The 10-Mbps baseband Ethernet specification that uses two pairs of twisted-pair
cabling (Category 3 or 5): one pair for transmitting data and the other for
receiving data.
Basic Rate Interface. An ISDN interface composed of two bearer channels
(B channels) and one data channel (D channel) for circuit-switched
communication of voice, video, and data.
A Windows 95–, Windows 98–, and Windows NT–based software tool that ships
with the Cisco 800 series routers for basic configurations and verification of the
router software configuration. It also monitors the status of the ISDN interface,
error detail, and usage statistics.
A cable that wires a pin to its opposite pin; for example, RX+ is wired to TX+.
This cable connects two similar devices, for example, two data terminal
equipment (DTE) devices or two data communications equipment (DCE)
devices.
D
DRAM
E
78-5373-04
Dynamic RAM that stores information in capacitors that must be refreshed
periodically.
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
GL-1
Page 64

Glossary
EMI
ESD
F
Flash memory
H
HUB/NO HUB
button
Electromagnetic interference. The interference by electromagnetic signals that
can cause reduced data integrity and increased error rates on transmission
channels.
Electrostatic discharge. A transfer of electrostatic charge between bodies of
different electrostatic potentials, such as an operator and a piece of electrical
equipment. ESD occurs when electronic components are improperly handled
and can damage equipment and impair electrical circuitry. ESD is more likely to
occur with the combination of synthetic fibers and dry atmosphere.
The nonvolatile storage that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed so that
data can be stored, booted, and rewritten as necessary.
The Cisco 800 series routers provide a HUB/NO HUB button. This button is
associated with the Ethernet port on Cisco 801 and Cisco 802 routers and with
Ethernet port Ø on Cisco 803 and Cisco 804 routers. The setting of this button
determines the cable type (straight-through or crossover) that you use to connect
an Ethernet device. This button is the equivalent of the TO HUB/TO PC button
on the Cisco 802 IDSL and Cisco 804 IDSL routers.
I
IDSL
ISDN
N
NIC
NT1
ISDN Digital Subscriber Line. A digital communication protocol that uses an
ISDN line and supports line rates up to 144 kilobits per second (kbps).
Integrated Services Digital Network. A communication protocol that permits
telephone networks to carry data, voice, and other source traffic.
Network interface card. A board that provides network communication
capabilities to and from a computer system. Also called an adapter.
Network Termination 1. A device that provides the interface between equipment
on the customer and ISP premises.
GL-2
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 65

S
Glossary
straight-through
Ethernet cable
T
TO HUB/TO PC
button
telephone cable
A cable that wires a pin to its equivalent pin. This cable connects two dissimilar
devices, for example, a data terminal equipment (DTE) and a data
communications equipment (DCE) device. A straight-through Ethernet cable is
the most common cable used.
The Cisco 802 IDSL and Cisco 804 IDSL routers provide a TO HUB/TO PC
button that is equivalent to the HUB/NO HUB button on the other Cisco 800
series routers. This button is associated with the Ethernet port on the Cisco 802
IDSL router and with Ethernet port 1 on the Cisco 804 IDSL router. The setting
of this button determines the cable type (straight-through or crossover) that you
will use to connect an Ethernet device.
The cable used to connect a device to a telephone port.
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
GL-3
Page 66

Glossary
GL-4
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 67

INDEX
A
accessory kit 2-4
adapter, included 2-4
altitude specifications B-1
analog telephone 2-15
B
back panels, illustrated 1-4 to 1-7
B channels A-1
brackets, illustrated 2-19
BRI A-1
C
cable lock, illustrated 1-4 to 1-7
cables
and router damage
distances, maximum B-7
Ethernet, types 2-6
included with router 2-4
specifications B-6
caution statements, defined viii
Cisco reseller, contacting 3-7
connecting
analog telephone
digital telephone 2-14
Ethernet devices 2-6
fax 2-15
hubs 2-8
IDSL line 2-13
ISDN line 2-10 to 2-13
2-4
2-15
modem 2-15
PC 2-9, 2-17
power supply 2-18
server 2-9
telephones 2-14, 2-15
terminal or PC 2-17
workstation 2-9
console port
description
illustrated 1-4 to 1-7
conventions, hazard vii
1-2
D
damage
electrostatic discharge (ESD)
router, preventing 2-4
D channel A-1
digital telephone 2-14
DRAM, adding 1-2
2-3
E
electrostatic discharge (ESD), preventing 2-3
Ethernet
cable specifications
cable types 2-6
devices, connecting 2-6
port described 1-2
port illustrated 1-4 to 1-7
European Union standards 2-4
B-7
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
IN-1
Page 68

Index
F
fax, connecting 2-15
Flash memory, adding 1-2
frequency specifications B-1
front panels, illustrated 1-3
H
hazard statements, defined vii
HUB/NO HUB button
illustrated
settings 2-6 to 2-7
hubs, connecting 2-8
humidity specifications B-1
1-4 to 1-6
I
IDSL concepts A-1
IDSL LEDs, illustrated 1-4
IDSL line, connecting 2-13
IDSL port
described
illustrated 1-6, 1-7
installation
verifying
warnings 2-2
ISDN concepts A-1
ISDN line, connecting 2-10 to 2-13
ISDN S/T port
described
illustrated 1-5
ISDN U port
described
illustrated 1-5, 1-6
1-2
2-20
1-2
1-2
L
described
illustrated 1-3 to 1-6
locking power connector, illustrated 1-4 to 1-7
1-7
M
modem, connecting 2-15
mounting the router 2-18
N
network device button settings 2-6 to 2-7
NT1 feature 1-2
P
panels, illustrated 1-4 to 1-7
PC, connecting 2-9, 2-17
port connector pinouts B-2 to B-6
ports for specific routers 1-3
power
problems
specifications B-1
verifying 2-20
power supply
connecting
power switch illustrated 1-4 to 1-7
preinstallation activities 2-4
3-2
2-18
R
router
concepts
damage, preventing 2-4
features 1-2
ports 1-3
unpacking 2-4, ?? to 2-4
A-1
LEDs
IN-2
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
Page 69

S
S/T interface A-1
safety warnings 2-2
server, connecting 2-9
settings, network devices 2-6 to 2-7
specifications
cabling
system B-1
startup problems 3-2
B-6
T
table mounting 2-18
telephone
connecting
ports
described
illustrated 1-5, 1-6
temperature specifications B-1
terminal, connecting 2-17
TO HUB/TO PC button
illustrated
settings 2-6 to 2-7
troubleshooting 3-1
2-14, 2-15
1-2
1-6 to 1-7
Index
unpacking the router 2-4, ?? to 2-4
V
voltage specifications B-1
W
wall brackets, illustrated 2-19
wall mounting 2-19 to 2-20
warnings, installation 2-2
weight specifications B-1
workstation, connecting 2-9
U
U interface A-1
United Kingdom master sockets 2-16
78-5373-04
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
IN-3
Page 70

Index
IN-4
Cisco 800 Series Routers Hardware Installation Guide
78-5373-04
 Loading...
Loading...