Page 1

Serial Cable Connection Guide
Document ID: 12219
Contents
Introduction
Prerequisites
Requirements
Components Used
Conventions
Overview
DTE or DCE?
Male or Female
Signaling
Ordering
Cisco 7000 Series Cables
Cisco AGS+ Cables
Cisco 4000 Series Cables
NP−2T Cables
NP−4T Cables
Cisco 3000 Series Cables
Cisco 2500 Series Cables
Cisco 500−CS Series Cables
Related Information
Introduction
This document guides you through the process of selecting the right serial cables for your network.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
The information presented in this document was created from devices in a specific lab environment. All of the
devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If you are working in a live
network, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command before using it.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, see the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Page 2
Overview
One of the critical parts of setting up any router is the selection of the serial cables to connect the router to the
serial devices in your network. There are so many different serial cables, with seemingly similar features,
finding the correct cable can be tricky. This document guides you through the process of selecting the right
serial cables for your network.
The selection of the proper serial cable involves answering three questions:
Is the router being connected to a data terminal equipment (DTE) or data communications equipment
•
(DCE) device?
Is a male or female connector required on the cable?•
What signaling standard does the device require?•
With the answers to these questions, along with the model of your router, you can find the part number of the
cable required from the tables that follow.
DTE or DCE?
Devices that communicate over a serial interface are divided into two classes: DTE and DCE. The most
important difference between these types of devices is that the DCE device supplies the clock signal that
paces the communications on the bus. The documentation provided with the device should indicate whether it
is DTE or DCE (some devices have a jumper to select either mode). If you cannot find the information in the
documentation, use the following general guidelines to help you select the proper class:
Selectable
DTE DCE
Terminals, Data Service
Device
Gender
* Selectable devices usually have a jumper, switch, or software
command used to select DTE or DCE.
Unit/Channel Service
Unit (DSU/CSU),
Multiplexors
Male Female Either
Modems Hubs, Routers
DTE or
DCE*
Male or Female
The gender of the connector is determined by examining the connector. If pins protrude from the base of the
connector, the connector is male. If the connector has holes to accept the pins, the connector is female. Refer
to the drawings to identify the connector that you need.
Signaling
A number of different standards defines the signaling over a serial cable (including EIA/TIA−232, X.21,
V.35, EIA/TIA−449, EIA−530, and HSSI). Each standard defines the signals on the cable, and specifies the
connector at the end of the cable. The documentation for the device being connected should indicate the
signaling standard used for that device. If you cannot find the information in the documentation, use the
illustrations below to select the signaling standard required. Select the connector that will mate with the
connector on your device, rather than the illustration that looks like the connector on the device.
Page 3
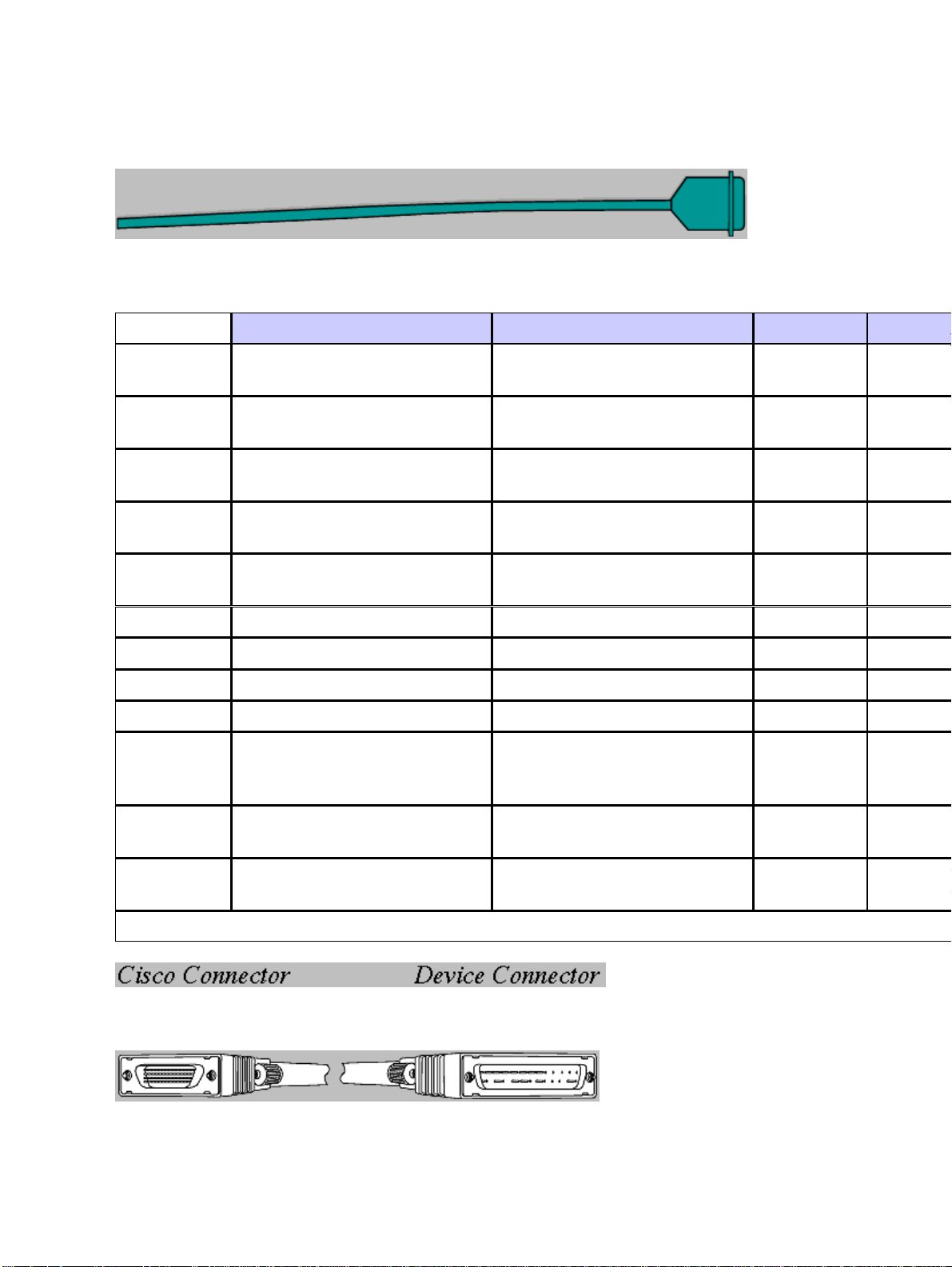
Ordering
To order serial cables and other Cisco products, contact your local account manager or Cisco customer service
at 800−553−6387.
Cisco 7000 Series Cables
CX−FSIP4 CX−FSIP8 CX−HIP CX−MIP−1CT1 CX−MIP−2CT1
Number
required
EIA/TIA−232
DTE
EIA/TIA−232
DCE
EIA/TIA−449
DTE
EIA/TIA−449
DCE
V.35 DTE
V.35 DCE
X.21 DTE
X.21 DCE
HSSI
1−4 1−8 1 1 1
CAB−232MT(=) CAB−232MT(=) −− −− −−
CAB−232FC(=) CAB−232FC(=) −− −− −−
CAB−449MT(=) CAB−449MT(=) −− −− −−
CAB−449FC(=) CAB−449FC(=) −− −− −−
CAB−V35MT(=)CAB−V35FT(=) CAB−V35MT(=)CAB−V35FT(=) −− −− −−
CAB−V35FC(=)CAB−V35MC(=) CAB−V35FC(=)CAB−V35MC(=) −− −− −−
CAB−X21MT(=) CAB−X21MT(=) −− −− −−
CAB−X21FC(=) CAB−X21FC(=) −− −− −−
CAB−HSI1=,
−− −−
CAB−,
HNUL=(M)*
−− −−
EIA/TIA−530
DTE
/Channelized
DTE is male and DCE is female, unless otherwise noted (M = male) (=) indicates spare product. * Allows connection of routers back−to−back.
CAB−232MT(=)
CAB−232FC(=)
CAB−530MT= CAB−530MT= −− −− −−
−− −− −−
CAB−7KCT1DB15
CAB−7KCT1NULL*
Page 4
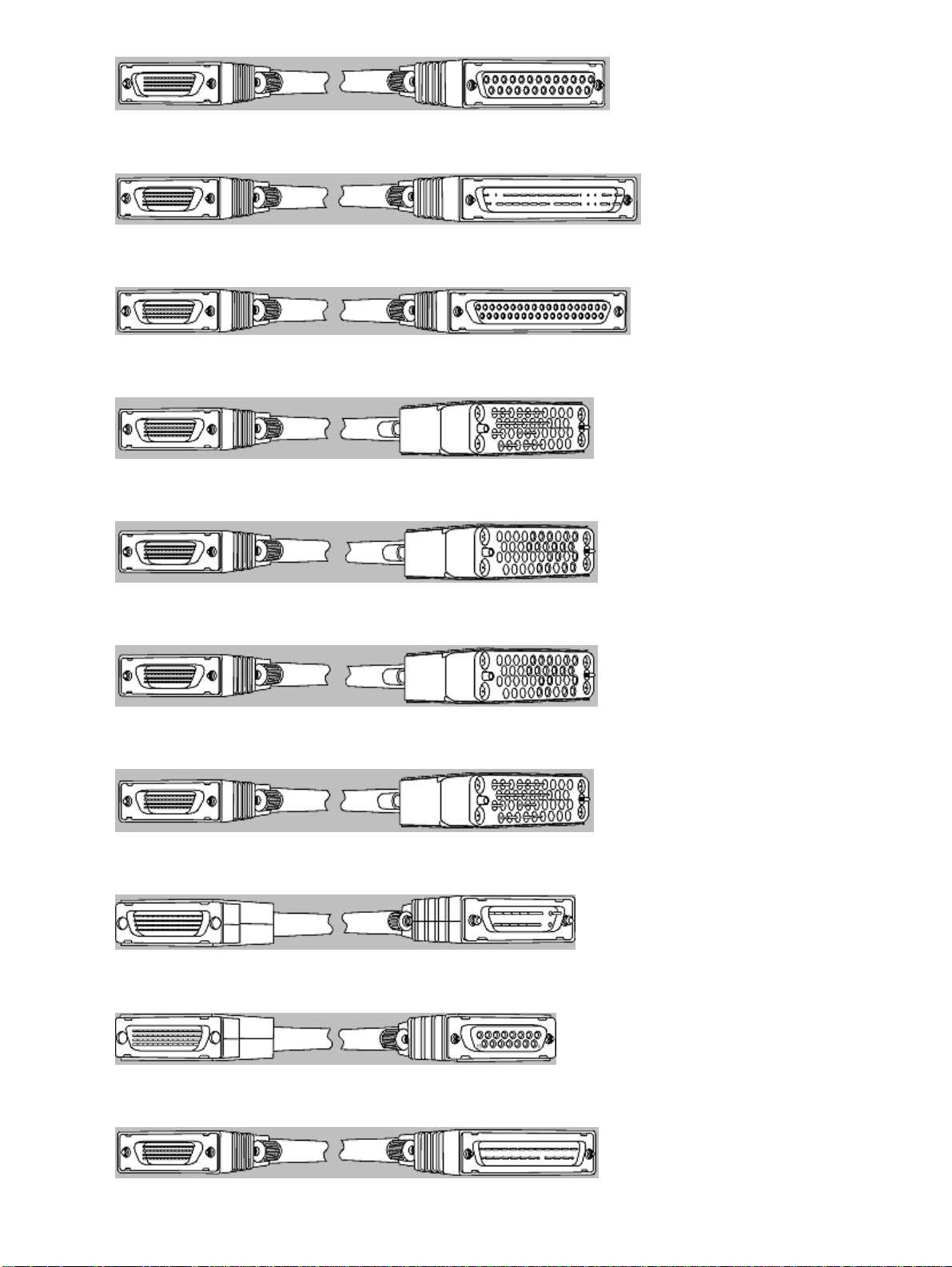
CAB−449MT(=)
CAB−449FC(=)
CAB−V35MT(=)
CAB−V35FT(=)
CAB−V35FC(=)
CAB−V35MC(=)
CAB−X21MT(=)
CAB−X21FC(=)
CAB−530MT=
Page 5
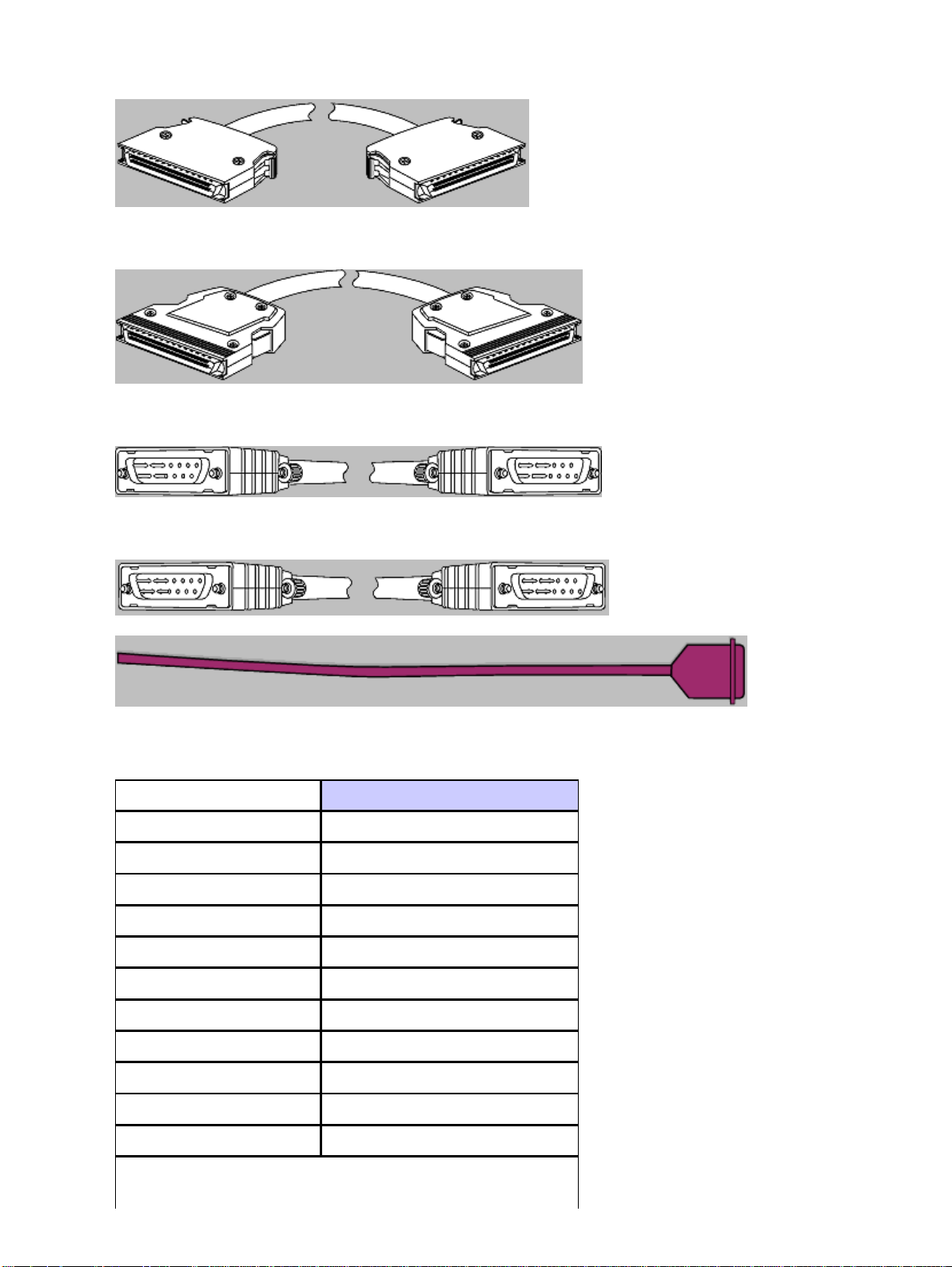
CAB−HSI1=
CAB−HNUL=(M)
CAB−7KCT1DB15
CAB−7KCT1NULL
Cisco AGS+ Cables
AGS+
Number Required
EIA/TIA−232 DTE
EIA/TIA−232 DCE
EIA/TIA−449 DTE
EIA/TIA−449 DCE
V.35 DTE
V.35 DCE
X.21 DTE
X.21 DCE
HSSI
EIA/TIA−530 DTE
DTE is male, and DCE is female, unless otherwise noted (M =
Optional
CAB−R23=
CAB−R23=
CAB−R44=
CAB−R44=
CAB−VTM(=), CAB−VTF(=)
CAB−VCM(=), CAB−VCF(=)
−−−
CAB−X21CF=
CAB−HSI1=, CAB−HNUL=(M)*
−−−
Page 6

male). (=) indicates spare product. * Allows connection of
routers back−to−back.
CAB−R23=
CAB−R44=
CAB−VTM(=)
CAB−VTF(=)
CAB−VCM(=)
CAB−VCF(=)
CAB−X21CF=
CAB−HSI1
Page 7

CAB−HNUL=(M)
Cisco 4000 Series Cables
NP−2T NP−4T
Number
Required
EIA/TIA−232
DTE
EIA/TIA−232
DCE
EIA/TIA−449
DTE
EIA/TIA−449
DCE
V.35 DTE
1−2 1−4
CAB−NP232T(=) CAB−232MT(=)
CAB−NP232C(=) CAB−232FC(=)
CAB−NP449T(=) CAB−449MT(=)
CAB−NP449C(=) CAB−449FC(=)
CAB−NPV35TV2(=)
CAB−V35MT(=),
CAB−V35FT(=)
V.35 DCE
X.21 DTE
X.21 DCE
EIA/TIA−530
DTE
DTE is male and DCE is female, unless otherwise noted (M =
male). (=) indicates spare product.
CAB−NPV35CV2(=)
CAB−NPX21T(=) CAB−X21MT(=)
CAB−NPX21C(=) CAB−X21FC(=)
CAB−3C530(=) CAB−530MT(=)
CAB−V35FC(=),
CAB−V35MC(=)
NP−2T Cables
CAB−NP232T(=)
Page 8

CAB−NP232C(=)
CAB−NP449T(=)
CAB−NP449C(=)
CAB−NPV35TV2(=)
CAB−NPV35CV2(=)
CAB−NPX21T(=)
CAB−NPX21C(=)
CAB−3C530(=)
NP−4T Cables
CAB−232MT(=)
CAB−232FC(=)
Page 9

CAB−449MT(=)
CAB−449FC(=)
CAB−V35MT(=)
CAB−V35FT(=)
CAB−V35FC(=)
CAB−V35MC(=)
CAB−X21MT(=)<
CAB−X21FC(=)
CAB−530MT(=)
Page 10

Cisco 3000 Series Cables
3102 3202 3104 3204
Number
Required
EIA/TIA−232
DTE
EIA/TIA−232
DCE
EIA/TIA−449
DTE
EIA/TIA−449
DCE
V.35 DTE
V.35 DCE
X.21 DTE
X.21 DCE
EIA/TIA−530
DTE
DTE is male and DCE is female, unless otherwise noted (M = male). (=) indicates spare product.
1 1−2 1−2 1−2
CAB−3C232(=) CAB−3C232(=) CAB−3C232(=) CAB−3C232(=)
−− −− CAB−3C232C(=) CAB−3C232C(=)
CAB−3C449(=) CAB−3C449(=) CAB−3C449(=) CAB−3C449(=)
−− −− CAB−3C449C(=) CAB−3C449C(=)
CAB−3CV35V2(=) CAB−3CV35V2(=) CAB−3CV35V2(=) CAB−3CV35V2(=)
−− −− CAB−3CV35V2C(=) CAB−3CV35V2C(=)
CAB−3CX21(=) CAB−3CX21(=) CAB−3CX21(=) CAB−3CX21(=)
−− −− CAB−3CX21C(=) CAB−3CX21C(=)
CAB−3C530(=) CAB−3C530(=) CAB−3C530(=) CAB−3C530(=)
CAB−3C232(=)
CAB−3C232C(=)
CAB−3C449(=)
CAB−3C449C(=)
Page 11

CAB−3CV35V2(=)
CAB−3CV35V2C(=)
CAB−3CX21(=)
CAB−3CX21C(=)
CAB−3C530(=)
Cisco 2500 Series Cables
2500
Number Required
EIA/TIA−232 DTE
EIA/TIA−232 DCE
EIA/TIA−449 DTE
EIA/TIA−449 DCE
V.35 DTE
V.35 DCE
X.21 DTE
X.21 DCE
1−2
CAB−232MT(=)
CAB−232FC(=)
CAB−449MT(=)
CAB−449FC(=)
CAB−V35MT(=), CAB−V35FT(=)
CAB−V35FC(=), CAB−V35MC(=)
CAB−X21MT(=)
CAB−X21FC(=)
Page 12

EIA/TIA−530 DTE
DTE is male and DCE is female, unless otherwise noted (M =
male). (=) indicates spare product.
CAB−232MT(=)
CAB−232FC(=)
CAB−449MT(=)
CAB−530MT(=)
CAB−449FC(=)
CAB−V35MT(=)
CAB−V35FT(=)
CAB−V35FC(=)
CAB−V35MC(=)
CAB−X21MT(=)
Page 13

CAB−X21FC(=)
CAB−530MT(=)
Cisco 500−CS Series Cables
8−16 Port
EIA/TIA−232
DCE CAB−500DCM=, CAB−500DCF=,
EIA/TIA−232
DTE CAB−500DTM(=), CAB−500DTF=,
Modem
DTE is male and DCE is female, unless otherwise noted (M =
male). (=) indicates spare product. * For each port, a
CAB−500RJ and corresponding connector must be ordered.
CAB−500RJ(=)*
CAB−500RJ(=)*
CAB−5MODCM(=), CAB−500RJ(=)*
Note: The 500−CS Series nomenclature differs from routing cables. DCE and DTE refer to the type of device
connected to. For example, to connect a terminal (DTE) device, order a CAB−500DTM(=) or
CAB−500DTF=.
CAB−500DCM=
CAB−500DCF=
CAB−500DTM(=)
CAB−500DTF=
Page 14

CAB−500RJ(=)
CAB−5MODCM(=)
Related Information
Technical Support − Cisco Systems•
Contacts & Feedback | Help | Site Map
© 2012 − 2013 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Terms & Conditions | Privacy Statement | Cookie Policy | Trademarks of
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Updated: Aug 01, 2006 Document ID: 12219
 Loading...
Loading...