Page 1
SOLUTION OVERVIEW
CONFIGURING DYNAMIC MULTIPOINT VPN WITH ON-DEMAND ROUTING
OVERVIEW
This document provides a sample configuration for configuring On-Demand Routing (ODR) with Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) in hub to
spoke configuration. The DMVPN feature simplifies the hub router IPsec configuration and supports dynamic IP addresses at the spoke router.
DMVPN combines Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnels, IPsec encryption, and Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP). It provides IP
routing for remote sites, while minimizing the overhead on the network devices. This sample configuration also allows load balancing with dual
ODR hub routers, failover to a single hub when a hub router fails, and the recovery from a hub router failure when it is recovered.
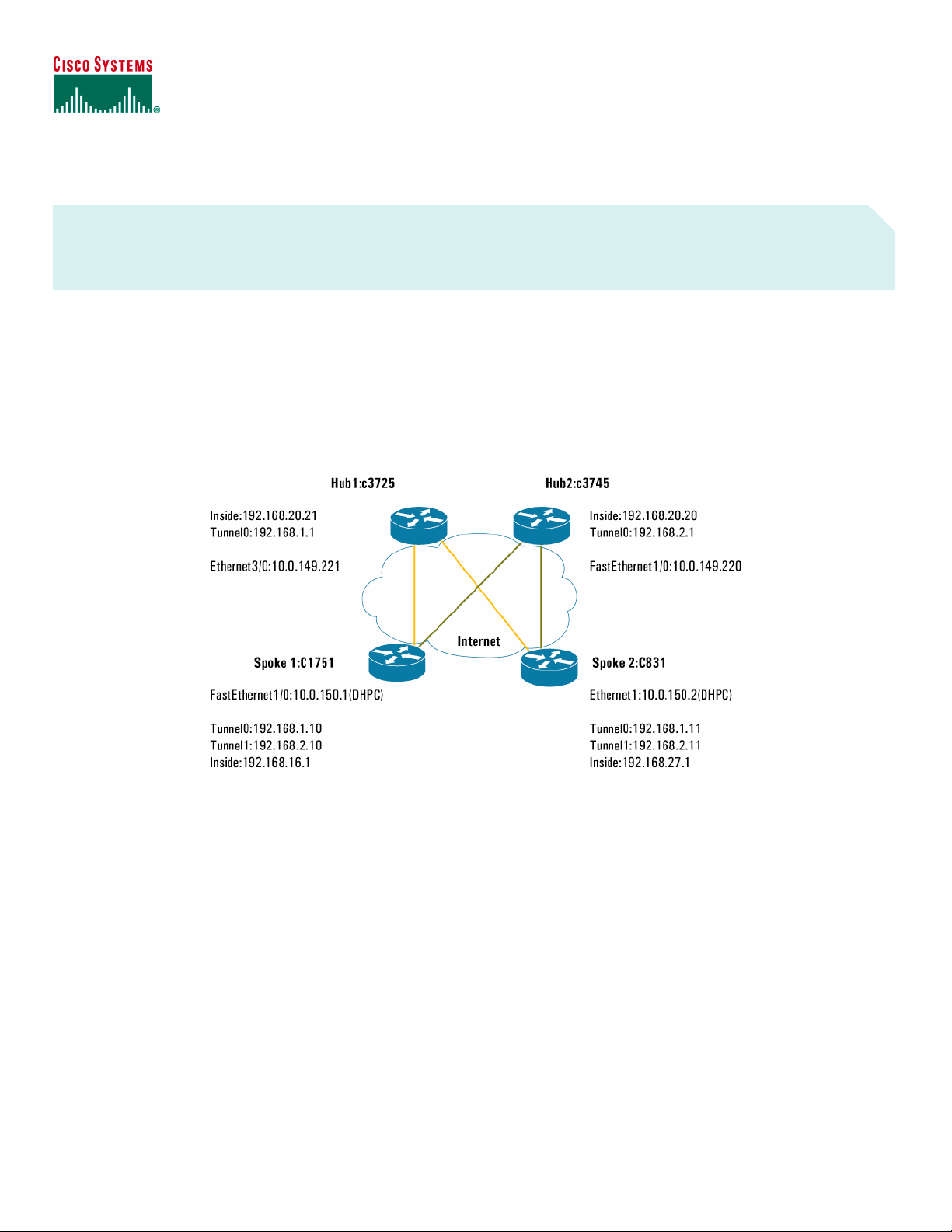
Figure 1. Network Diagram
PREREQUISITES
The sample configuration is based on the following assumptions:
• Public IP addresses for the hub routers (10.0.149.221 and 10.0.149.220)
• DMVPN network for tunnel interface on both hubs are 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24
• Spoke router can use static IP or dynamic IP addresses
• Example uses Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) as its dynamic routing protocol
• Example uses pre-shared keys for authentication
• Disabled split tunneling for the spoke router; this allows the Internet traffic to go through the hub only
LIMITATIONS
This guide provides the DMPVN configuration, but does not cover the following configuration:
• Full router security audit: run a Security Device Manager (SDM) security audit in the wizard mode to lock down and secure the router.
• Initial router configuration step: full configuration is shown in the following section.
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Important Notices and Privacy Statement.
Page 1 of 16
Page 2

• This configuration guide uses private addresses only. When using private addresses and connecting to the Internet, an appropriate Network
Address Translation (NAT) or Port Address Translation (PAT) configuration is required to provide connectivity over the Internet.
• The ODR provides a default route only to the spoke, the configuration support hub and spoke topology; no split tunneling
PRECAUTIONS
Before configurations are made to any router, confirm the following:
• The spoke router can reach the DMVPN hub directly over the Internet.
• The DMVPN hub is configured and operational.
COMPONENTS
• Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(11)T3(fc2)
• Cisco 831, 1751, 3725 and 3745 Routers
Figure 1 illustrates the network for the sample configuration.
The information presented in this document was created from devices in a specific lab environment. All devices started with a cleared (default)
configuration. It is imperative to understand the potential impact of any command before implementing it in a live network.
This configuration uses two DMVPN hub routers. Each hub router is configured with a separate DMVPN tunnel network (192.168.1.0/24 and
192.168.2.0/24). The first tunnel on the spokes is used for direct connectivity through the first DMVPN hub and the second tunnel on the spokes
is used for the second DMVPN hub. During normal operations with dual hubs, the spoke router load-balances the traffic between both hubs.
Connectivity between the spoke routers is provided through the hub routers in hub and spoke topology. During a failure, the ODR protocol will time
out the failed path, and it will use one active path to the active hub router.
Using ODR, the hub router learns about the remote networks using the CDP protocol. By default, CDP is disabled on the tunnel interface. To allow
the hub and spoke routers to exchange routes, CDP must be enabled on the tunnel interface. ODR allows for push of the default route from the hub
router to the spoke router. The hub router configuration only accepts spoke routers network ranges defined with the “distribute-list 101 in” in order
to prevent the risk of learning the DHCP public network of spoke router from the tunnel interface with ODR. All routing protocols should be
disabled on the spoke routers to activate ODR on the spoke routers.
By default, CDP sends updates every sixty seconds. This update interval may not be frequent enough to provide faster re-convergence of IP routes on
the hub router side of the network. A quicker re-convergence rate may be necessary if the spoke connects to one of several hub routers via
asynchronous interfaces such as modem lines.
ODR expects to receive periodic CDP updates, which contain IP prefix information. When ODR fails to receive updates for routes that it has
installed in the routing table, these ODR routes are first marked invalid and eventually removed from the routing table (by default, ODR routes are
marked invalid after 180 seconds and are removed from the routing table after 240 seconds). These defaults are based on the default CDP update
interval. Configuration changes made to either the CDP or ODR timers should be reflected through changes made to both.
For additional information about configuring ODR timers, refer to:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/iosswrel/ps1835/products_configuration_guide_chapter09186a00800ca75f.html#1000989
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2 of 16
Page 3

CONFIGURATION OF THE CISCO 3725 ROUTER
Following are the configurations on the Hub router:
Current configuration:
!
version 12.3
!
hostname c3725-21
!
no aaa new-model
!
ip subnet-zero
ip cef
!
!
crypto isakmp policy 1
encr 3des
authentication pre-share
group 2
crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
crypto isakmp keepalive 10
!
crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto ipsec profile SDM_Profile1
set transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA
!
!
!
!
interface Tunnel0
bandwidth 1000
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
ip mtu 1400
ip nhrp authentication DMVPN_NW
ip nhrp map multicast dynamic
ip nhrp network-id 100000
ip nhrp holdtime 360
ip tcp adjust-mss 1360
no ip split-horizon eigrp 1
delay 1000
cdp enable
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3 of 16
Page 4

tunnel source FastEthernet0/0
tunnel mode gre multipoint
tunnel key 100000
tunnel protection ipsec profile SDM_Profile1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.0.149.221 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.20.21 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed 100
!
router odr
distribute-list 101 in
!
router eigrp 1
redistribute odr metric 2000 100 255 255 1400
network 192.168.1.0
network 192.168.2.0
network 192.168.20.0
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.149.207
!
!
access-list 101 permit ip any 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
!
end
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 4 of 16
Page 5

VERIFYING THE CISCO 3725 ROUTER RESULTS
Normal Operation
This section provides information that can be used to confirm that the configuration is working properly.
c3725-21#show ip route
Codes: C-connected, S-static, R-RIP, M-mobile, B-BGP
D-EIGRP, EX-EIGRP external, O-OSPF, IA-OSPF inter area
N1-OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2-OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1-OSPF external type 1, E2-OSPF external type 2
i-IS-IS, su-IS-IS summary, L1-IS-IS level-1, L2-IS-IS level-2
ia-IS-IS inter area, *-candidate default, U-per-user static route
o-ODR, P-periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 10.0.149.207 to network 0.0.0.0
o 192.168.27.0/24 [160/1] via 192.168.1.11, 00:00:52, Tunnel0
C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.0.149.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
o 192.168.16.0/24 [160/1] via 192.168.1.10, 00:00:21, Tunnel0
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Tunnel0
D 192.168.2.0/24 [90/2818560] via 192.168.20.20, 06:03:24, FastEthernet0/1
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.0.149.207
c3725-21#show crypto session detail
Crypto session current status
Code: C-IKE Configuration mode, D-Dead Peer Detection
K-Keepalives, N-NAT-traversal, X-IKE Extended Authentication
Interface: Tunnel0
Session status: UP-ACTIVE
Peer: 10.0.150.1 port 500 fvrf: (none) ivrf: (none)
Phase1_id: 10.0.150.1
Desc: (none)
IKE SA: local 10.0.149.221/500 remote 10.0.150.1/500 Active
Capabilities:D connid:10 lifetime:20:55:47
IPSEC FLOW: permit 47 host 10.0.149.221 host 10.0.150.1
Active SAs: 2, origin: crypto map
Inbound: #pkts dec’ed 6829 drop 0 life (KB/Sec) 4503324/3143
Outbound: #pkts enc’ed 65167 drop 1 life (KB/Sec) 4503313/3143
Interface: Tunnel0
Session status: UP-ACTIVE
Peer: 10.0.150.2 port 500 fvrf: (none) ivrf: (none)
Phase1_id: 10.0.150.2
Desc: (none)
IKE SA: local 10.0.149.221/500 remote 10.0.150.2/500 Active
Capabilities:D connid:11 lifetime:20:56:02
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 5 of 16
Page 6

IPSEC FLOW: permit 47 host 10.0.149.221 host 10.0.150.2
Active SAs: 2, origin: crypto map
Inbound: #pkts dec’ed 6757 drop 0 life (KB/Sec) 4427309/2860
Outbound: #pkts enc’ed 65162 drop 1 life (KB/Sec) 4427290/2860
c3725-21#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is “nhrp”
Maximum path: 0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: (default is 0)
Routing Protocol is “eigrp 1”
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
EIGRP maximum hopcount 100
EIGRP maximum metric variance 1
Redistributing: eigrp 1, odr
EIGRP NSF-aware route hold timer is 240s
Automatic network summarization is not in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.1.0
192.168.20.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.20.20 90 3d03h
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Routing Protocol is “odr”
Sending updates every 60 seconds, next due in 37 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 0, flushed after 240
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is 101
Maximum path: 4
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.1.11 160 00:00:27
192.168.1.10 160 00:00:41
Distance: (default is 160)
c3725-21#show interface tunnel 0
Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 6 of 16
Page 7

Hardware is Tunnel
Internet address is 192.168.1.1/24
MTU 1514 bytes, BW 1000 Kbit, DLY 10000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation TUNNEL, loopback not set
Keepalive not set
Tunnel source 10.0.149.221 (FastEthernet0/0), destination UNKNOWN
Tunnel protocol/transport multi-GRE/IP
Key 0x186A0, sequencing disabled
Checksumming of packets disabled
Fast tunneling enabled
Tunnel transmit bandwidth 8000 (kbps)
Tunnel receive bandwidth 8000 (kbps)
Tunnel protection via IPSec (profile “SDM_Profile1”)
Last input 00:00:12, output 00:00:04, output hang never
Last clearing of “show interface” counters never
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queuing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/0 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 1000 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
24158 packets input, 5290429 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
217102 packets output, 55341094 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
c3725-21#sh cdp nei
Capability Codes: R-Router, T-Trans Bridge, B-Source Route Bridge
S-Switch, H-Host, I-IGMP, r-Repeater
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
c2950-xl Fas 0/1 160 S I WS-C2950G-Fas 0/37
c1751-16.cisco.com
Tunnel0 132 R S 1751-V Tunnel0
c831-27 Tunnel0 146 R C831 Tunnel0
c2924.cisco.com Fas 0/0 123 T S WS-C2924-XFas 0/19
CONFIGURATION OF THE CISCO 1751 SPOKE ROUTER
Following are the configurations on the Cisco 1751 spoke router:
Current configuration :
!
version 12.3
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
Page 7 of 16
Page 8

!
hostname c1751-16
!
no aaa new-model
ip subnet-zero
!
ip cef
!
!
crypto isakmp policy 1
encr 3des
authentication pre-share
group 2
crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
crypto isakmp keepalive 10
!
!
crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA1 esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto ipsec profile SDM_Profile1
set transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA1
!
crypto ipsec profile SDM_Profile2
set transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA
!
!
!
!
!
interface Tunnel0
bandwidth 1000
ip address 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0
ip mtu 1400
ip nhrp authentication DMVPN_NW
ip nhrp map 192.168.1.1 10.0.149.221
ip nhrp network-id 100000
ip nhrp holdtime 360
ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.1
ip nhrp server-only
ip tcp adjust-mss 1360
delay 1000
cdp enable
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 8 of 16
Page 9

tunnel source FastEthernet0/0
tunnel destination 10.0.149.221
tunnel key 100000
tunnel protection ipsec profile SDM_Profile1
!
interface Tunnel1
bandwidth 1000
ip address 192.168.2.10 255.255.255.0
ip mtu 1400
ip nhrp authentication DMPVN_BU
ip nhrp map 192.168.2.1 10.0.149.220
ip nhrp network-id 100001
ip nhrp holdtime 360
ip nhrp nhs 192.168.2.1
ip nhrp server-only
ip tcp adjust-mss 1360
delay 1000
cdp enable
tunnel source FastEthernet0/0
tunnel destination 10.0.149.220
tunnel key 100001
tunnel protection ipsec profile SDM_Profile2
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.16.1 255.255.255.0
half-duplex
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
description $ETH-LAN$$ETH-SW-LAUNCH$
ip address dhcp
speed 100
full-duplex
!
ip classless
ip route 10.0.149.0 255.255.255.0 dhcp
!
end
Verifying the Cisco 1751 Spoke Router Results
This section provides information that can be used to confirm that the configuration is working properly.
c1751-16#show ip route
Codes: C-connected, S-static, R-RIP, M-mobile, B-BGP
D-EIGRP, EX-EIGRP external, O-OSPF, IA-OSPF inter area
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 9 of 16
Page 10

N1-OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2-OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1-OSPF external type 1, E2-OSPF external type 2
i-IS-IS, su-IS-IS summary, L1-IS-IS level-1, L2-IS-IS level-2
ia-IS-IS inter area, *-candidate default, U-per-user static route
o-ODR, P-periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.2.1 to network 0.0.0.0
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.150.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
S 10.0.149.0 [1/0] via 10.0.150.207
C 192.168.16.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Tunnel0
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Tunnel1
o* 0.0.0.0/0 [160/1] via 192.168.2.1, 00:00:25, Tunnel1
[160/1] via 192.168.1.1, 00:00:56, Tunnel0
c1751-16#show crypto session detail
Crypto session current status
Code: C-IKE Configuration mode, D-Dead Peer Detection
K-Keepalives, N-NAT-traversal, X-IKE Extended Authentication
Interface: Tunnel0
Session status: UP-ACTIVE
Peer: 10.0.149.221 port 500 fvrf: (none) ivrf: (none)
Phase1_id: 10.0.149.221
Desc: (none)
IKE SA: local 10.0.150.1/500 remote 10.0.149.221/500 Active
Capabilities:D connid:268435501 lifetime:20:51:40
IPSEC FLOW: permit 47 host 10.0.150.1 host 10.0.149.221
Active SAs: 2, origin: crypto map
Inbound: #pkts dec’ed 7179 drop 0 life (KB/Sec) 4607231/2896
Outbound: #pkts enc’ed 65223 drop 1 life (KB/Sec) 4607249/2896
Interface: Tunnel1
Session status: UP-ACTIVE
Peer: 10.0.149.220 port 500 fvrf: (none) ivrf: (none)
Phase1_id: 10.0.149.220
Desc: (none)
IKE SA: local 10.0.150.1/500 remote 10.0.149.220/500 Active
Capabilities:D connid:268435500 lifetime:17:04:05
IPSEC FLOW: permit 47 host 10.0.150.1 host 10.0.149.220
Active SAs: 2, origin: crypto map
Inbound: #pkts dec’ed 6767 drop 0 life (KB/Sec) 4541812/2908
Outbound: #pkts enc’ed 65226 drop 4 life (KB/Sec) 4541830/2908
c1751-16#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is “nhrp”
Maximum path: 0
Routing Information Sources:
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 10 of 16
Page 11

Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: (default is 0)
c1751-16#show cdp neighbor
Capability Codes: R-Router, T-Trans Bridge, B-Source Route Bridge
S-Switch, H-Host, I-IGMP, r-Repeater
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
c2950-xl Eth 0/0 165 S I WS-C2950G-Fas 0/6
c2950-xl Fas 0/0 165 S I WS-C2950G-Fas 0/9
c3725-21.cisco.com
Tunnel0 152 R S I 3725 Tunnel0
c3745-20.cisco.com
Tunnel1 124 R S I 3745 Tunnel0
c1751-16#
Verifying the network connectivity during a failure:
The following results shows the status on the Cisco 1751 router when the path to the first hub
fails.
c1751-16#sh ip route
Codes: C-connected, S-static, R-RIP, M-mobile, B-BGP
D-EIGRP, EX-EIGRP external, O-OSPF, IA-OSPF inter area
N1-OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2-OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1-OSPF external type 1, E2-OSPF external type 2
i-IS-IS, su-IS-IS summary, L1-IS-IS level-1, L2-IS-IS level-2
ia-IS-IS inter area, *-candidate default, U-per-user static route
o-ODR, P-periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.2.1 to network 0.0.0.0
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.150.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
S 10.0.149.0 [1/0] via 10.0.150.207
C 192.168.16.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Tunnel0
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Tunnel1
o* 0.0.0.0/0 [160/1] via 192.168.2.1, 00:00:25, Tunnel1\
CONFIGURATION OF THE OTHER ROUTERS
Cisco 3745 Router Configuration
Current configuration :
!
version 12.3
!
hostname c3745-20
!
no aaa new-model
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
Page 11 of 16
Page 12

!
resource manager
!
ip subnet-zero
ip cef
!
crypto isakmp policy 1
encr 3des
authentication pre-share
group 2
crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
crypto isakmp keepalive 10
!
!
crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto ipsec profile SDM_Profile1
set transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA
!
!
!
!
interface Tunnel0
bandwidth 1000
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
ip mtu 1400
ip nhrp authentication DMPVN_BU
ip nhrp map multicast dynamic
ip nhrp network-id 100001
ip nhrp holdtime 360
ip tcp adjust-mss 1360
no ip split-horizon eigrp 1
delay 1000
cdp enable
tunnel source FastEthernet0/0
tunnel mode gre multipoint
tunnel key 100001
tunnel protection ipsec profile SDM_Profile1 shared
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
description $FW_INSIDE$
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 12 of 16
Page 13

ip address 10.0.149.220 255.255.255.0
speed 100
full-duplex
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
description $FW_INSIDE$
ip address 192.168.20.20 255.255.255.0
speed 100
full-duplex
!
router odr
distribute-list 101 in
!
router eigrp 1
redistribute odr
network 192.168.2.0
network 192.168.20.0
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.149.207
!
access-list 101 permit ip any 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
!
end
CISCO 831 ROUTER CONFIGURATION
Current configuration :
!
version 12.3
!
hostname c831-27
!
no aaa new-model
ip subnet-zero
!
ip cef
!
crypto isakmp policy 1
encr 3des
authentication pre-share
group 2
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 13 of 16
Page 14

crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
crypto isakmp keepalive 10
!
!
crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA1 esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto ipsec profile SDM_Profile1
set transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA1
!
crypto ipsec profile SDM_Profile2
set transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA
!
!
interface Tunnel0
bandwidth 1000
ip address 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
ip mtu 1400
ip nhrp authentication DMVPN_NW
ip nhrp map 192.168.1.1 10.0.149.221
ip nhrp network-id 100000
ip nhrp holdtime 360
ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.1
ip nhrp server-only
ip tcp adjust-mss 1360
delay 1000
cdp enable
tunnel source Ethernet1
tunnel destination 10.0.149.221
tunnel key 100000
tunnel protection ipsec profile SDM_Profile1
!
interface Tunnel1
bandwidth 1000
ip address 192.168.2.11 255.255.255.0
ip mtu 1400
ip nhrp authentication DMPVN_BU
ip nhrp map 192.168.2.1 10.0.149.220
ip nhrp network-id 100001 ip nhrp holdtime 360
ip nhrp nhs 192.168.2.1
ip nhrp server-only
ip tcp adjust-mss 1360
delay 1000
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 14 of 16
Page 15

cdp enable
tunnel source Ethernet1
tunnel destination 10.0.149.220
tunnel key 100001
tunnel protection ipsec profile SDM_Profile2
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 192.168.27.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet1
ip address dhcp
duplex auto
!
ip classless
ip route 10.0.149.0 255.255.255.0 dhcp
!
end
RELATED INFORMATION
• IPsec Support Page
• An Introduction to IPsec Encryption
• Configuring On-Demand Routing, Release 12.2 Configuration Guide
• Designing Large-Scale Stub Networks with ODR, Document ID: 13710
• Configuring IPsec Network Security
• Configuring Internet Key Exchange Security ProtocolTechnical Support-Cisco Systems
• Technical Support—Cisco Systems
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 15 of 16
Page 16

Pri
nted in the USA
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
European Headquarters
Cisco Systems International BV
Haarlerbergpark
Haarlerbergweg 13-19
1101 CH Amsterdam
The Netherlands
www-europe.cisco.com
Tel: 31 0 20 357 1000
Fax: 31 0 20 357 1100
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-7660
Fax: 408 527-0883
Asia Pacific Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
168 Robinson Road
#28-01 Capital Tower
Singapore 068912
www.cisco.com
Tel: +65 6317 7777
Fax: +65 6317 7799
Cisco Systems has more than 200 offices in the following countries and regions. Addresses, phone numbers, and fax numbers are listed on
the Cisco Website at www.cisco.com/go/offices.
Argentina • Australia • Austria • Belgium • Brazil • Bulgaria • Canada • Chile • China PRC • Colombia • Costa Rica • Croatia • Cyprus
Czech Republic • Denmark • Dubai, UAE • Finland • France • Germany • Greece • Hong Kong SAR • Hungary • India • Indonesia • Ireland • Israel
Italy • Japan • Korea • Luxembourg • Malaysia • Mexico • The Netherlands • New Zealand • Norway • Peru • Philippines • Poland • Portugal
Puerto Rico • Romania • Russia • Saudi Arabia • Scotland • Singapore • Slovakia • Slovenia • South Africa • Spain • Sweden • Switzerland • Taiwan
Thailand • Turkey • Ukraine • United Kingdom • United States • Venezuela • Vietnam • Zimbabwe
Copyright 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CCSP, CCVP, the Cisco Square Bridge logo, Follow Me Browsing, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.;
Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Access Registrar, Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP,
CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity,
Empowering the Internet Generation, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, FormShare, GigaDrive, GigaStack, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ
Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, Linksys, MeetingPlace, MGX, the Networkers logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Packet, PIX, PostRouting, Pre-Routing, ProConnect, RateMUX, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, StrataView Plus, TeleRouter, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, and TransPath are
registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between
Cisco and any other company. (0502R) 205297.F_ETMG_SH_6.05
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 16 of 16
 Loading...
Loading...