Page 1

Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
December 2006
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-8370-04
Page 2

CCVP, the Cisco logo, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn is a service mark of
Cisco Systems,
Inc.; and Access Registrar, Aironet, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS,
Cisco
Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, Follow Me
Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, iQuick Study, LightStream, Linksys,
MeetingPlace, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PIX, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SMARTnet, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet
Quotient, and TransPath are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0711R)
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
S
HIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The following inform ation is for FCC compliance of Class A devices:
to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required
to correct the interference at their own expense.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class B devices: The equipment described in this manual generates and may radi
installed in accordance with Cisco’s installation instructions, it may cause interference with radio and television reception. This equipment has been tested and found to
comply with the limits for a Class B digital device in accordance with the specifications in part 15 of the FCC rules. These specifications are designed to provide reasonable
protection against such interference in a residential installation. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
Modifying the equipment without Cisco’s written authorization may result in the equipment no longer complying with FCC requiremen
devices. In that event, your right to use the equipment may be limited by FCC regulations, and you may be required to correct any interference to radio or television
communications at your own expense.
You can determine whether your equipment is causing interference by turning it off. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by
peripheral devices. If the equipment causes interference to radio or television reception, try to correct the interference by using one or more of the following measures:
• Turn the television or radio antenna until the interference stops.
• Move the equipment to one side or the other of the television or radio.
• Move the equipment farther away from the television or radio.
• Plug the equipment into an outlet that is on a different circuit from the television or radio. (That is, make certain the equip
controlled by different circuit breakers or fuses.)
Modifications to this product not authorized by Cisco Systems, Inc. could void the FCC approval and negate your authority to oper
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berk
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
AL
L FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
L
IMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WI
THOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant
ate radio-frequency energy. If it is not
ts for Class A or Class B digital
the Cisco equipment or one of its
ment and the television or radio are on circuits
ate the product.
eley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display ou
document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
tput, and figures included in the
Page 3

Preface ix
Audience i-ix
Purpose i-ix
Organization i-ix
Conventions i-x
Related Publications i-xii
Locating the Product Serial Number i-xiii
CONTENTS
CHAPTER
1 Overview 1-1
Product Terminology 1-1
Autonomous Access Points 1-1
Lightweight Access Points 1-2
Guidelines for Using 1200 Series Lightweight Access Points 1-3
Hardware Features 1-3
Network Examples with Autonomous Access Points 1-7
Root Access Point on a Wired LAN 1-8
Repeater Unit that Extends Wireless Range 1-9
Central Unit in an All-Wireless Network 1-10
Bridge Network with Wireless Clients 1-10
Point-to-Point Bridge Configuration 1-11
Workgroup Bridge Network 1-11
Dual-Radio Operation 1-4
LEDs 1-5
Ethernet Port 1-5
Console Port 1-6
Power Sources 1-6
UL 2043 Certification 1-6
Anti-Theft Features 1-6
CHAPTER
OL-8370-04
Network Example with Lightweight Access Points 1-12
2 Installing the Access Point 2-1
Safety Information 2-2
FCC Safety Compliance Statement 2-2
General Safety Guidelines 2-2
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
iii
Page 4
Contents
Warnings 2-2
Unpacking the Access Point 2-3
Package Contents 2-3
Basic Installation Guidelines 2-4
Controller Discovery Process for Lightweight Access Points 2-4
Before Beginning the Installation 2-5
Deploying the Access Points on the Wireless Network 2-7
Connecting the 2.4-GHz Antennas 2-8
Connecting the 5-GHz External Antennas 2-8
Connecting the Ethernet and Power Cables 2-9
Connecting to an Ethernet Network with an Inline Power Source 2-10
Connecting to an Ethernet Network with Local Power 2-10
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
3 Mounting Instructions 3-1
Overview 3-2
Mounting on a Horizontal or Vertical Surface 3-3
Mounting Below a Suspended Ceiling 3-4
Mounting Above a Suspended Ceiling 3-5
Attaching the Access Point to the Mounting Bracket 3-8
Securing the Access Point to the Mounting Bracket 3-8
4 Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio 4-1
Upgrade Overview 4-2
Unpacking the Radio 4-2
Opening the Access Cover 4-3
Removing a Blank Spacer Card 4-4
Removing a 2.4-GHz Radio 4-5
Installing a 2.4-GHz Radio 4-7
Attaching the Compliance Labels 4-9
Placing the Labels 4-10
CHAPTER
iv
5 Upgrading the 5-GHz Radio Module 5-1
Upgrade Overview 5-2
Unpacking the Radio Module 5-2
Removing the 5-GHz Radio Access Cover 5-2
Removing a 5-GHz Radio Module 5-3
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 5

Installing a 5-GHz Radio Module 5-5
Attaching the Compliance Label 5-7
Contents
CHAPTER
6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points 6-1
Checking the Top Panel LEDs 6-2
Checking Basic Settings 6-4
Default IP Address Behavior 6-4
Default SSID and Radio Behavior 6-4
Enabling the Radio Interfaces 6-4
SSID 6-5
WEP Keys 6-5
Security Settings 6-5
Running the Carrier Busy Test 6-5
Running the Ping or Link Test 6-6
Resetting to the Default Configuration 6-7
Using the MODE Button 6-7
Using the Web Browser Interface 6-8
Reloading the Access Point Image 6-8
Using the MODE button 6-9
Web Browser Interface 6-10
Browser HTTP Interface 6-10
Browser TFTP Interface 6-10
CHAPTER
OL-8370-04
Obtaining the Access Point Image File 6-11
Obtaining the TFTP Server Software 6-12
Connecting to the Access Point Locally 6-13
7 Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points 7-1
Guidelines for Using 1200 Series Lightweight Access Points 7-2
Using DHCP Option 43 7-2
Checking the Top Panel LEDs 7-3
Manually Configuring Controller Information Using the Access Point CLI 7-5
Configuring Controller Information 7-5
Clearing Manually Entered Controller Information 7-5
Manually Resetting the Access Point to Defaults 7-6
Returning the Access Point to Autonomous Mode 7-6
Using a Controller to Return the Access Point to Autonomous Mode 7-6
Using the MODE Button to Return the Access Point to Autonomous Mode 7-7
MODE Button Setting 7-7
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
v
Page 6

Contents
Obtaining the Autonomous Access Point Image File 7-8
Obtaining the TFTP Server Software 7-9
Connecting to the Access Point Locally 7-9
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
A Translated Safety Warnings A-1
B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information B-1
Manufacturers Federal Communication Commission Declaration of Conformity Statement B-2
VCCI Statement for Japan B-4
Department of Communications—Canada B-4
Canadian Compliance Statement B-4
European Community, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein B-5
Declaration of Conformity with Regard to the 1999/5/EC (R&TTE Directive) B-5
Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure B-7
Guidelines for Operating Cisco Aironet Access Points in Japan B-8
Japanese Translation B-8
English Translation B-8
Administrative Rules for Cisco Aironet Access Points in Taiwan B-9
Access Points with IEEE 802.11a Radios B-9
Chinese Translation B-9
English Translation B-9
All Access Points B-10
Chinese Translation B-10
English Translation B-10
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
vi
Operation of Cisco Aironet Access Points in Brazil B-11
Access Point Models B-11
Regulatory Information B-11
Portuguese Translation B-11
English Translation B-11
Declaration of Conformity Statements B-12
Declaration of Conformity Statements for European Union Countries B-12
C Access Point Specifications C-1
D Channels and Maximum Power Levels D-1
E Console Cable Pinouts E-1
Overview E-2
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 7

Console Port Signals and Pinouts E-2
Contents
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
G
LOSSARY
I
NDEX
F Priming Lightweight Access Points Prior to Deployment F-1
G Configuring DHCP Option 43 for Lightweight Access Points G-1
Overview G-2
Configuring Option 43 for 1000 Series Access Points G-2
Configuring Option 43 for 1100, 1130, 1200, 1240, and 1300 Series Lightweight Access Points G-3
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
vii
Page 8

Contents
viii
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 9

Audience
Preface
This guide is for the networking professional who installs and manages the Cisco Aironet 1200 Series
Access Point. The 1200 series access point is available in autonomous and lightweight configurations.
To use this guide with autonomous access points, you should have experience working with Cisco IOS
tware and be familiar with the concepts and terminology of wireless local area networks.
sof
To use this guide with lightweight access points, you should have experience working with a Cisco
ireless LAN Controller and be familiar with the concepts and terminology of wireless local area
W
networks.
Purpose
This guide provides the information you need to install your autonomous or lightweight access point.
For detailed information about Cisco IOS commands used with autonomous access points, refer to the
Ci
information about the standard Cisco IOS Release 12.3 commands, refer to the Cisco IOS documentation
set available from the Cisco.com home page at Technical Support & Documentation. On the Technical
Support & Documentation home page, click Cisco IOS Software > Cisco IOS Software Releases 12.3
Mainline.
For information about Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers, refer to the Cisco documentation sets available
fr
Documentation home page, click Wireless and the documentation is listed under the “Wireless LAN
Controllers” section.
Organization
This guide is organized into these chapters:
Chapter 1, “Overview,” lists th
access point’s role in your network.
Chapter 2, “Installing the Access Point,” de
provides an installation summary, safety warnings, and general guidelines.
sco IOS Command Reference for Cisco Aironet Access Points and Bridges for this release. For
om the Cisco.com home page at Technical Support & Documentation. On the Technical Support &
e software and hardware features of the access point and describes the
scribes how to connect Ethernet and power cables and
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
ix
Page 10

Conventions
Preface
Chapter 3, “Mounting Instructions,” describes how to mount the access point on a desktop, wall, or
ceiling.
Chapter 4, “Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio,” pr
ovides instructions for upgrading the access point
2.4-GHz radio.
Chapter 5, “Upgrading the 5-GHz Radio Module,” provi
des instructions for upgrading the access point
5-GHz radio.
Chapter 6, “Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points,” provi
des troubleshooting procedures for
basic problems with the autonomous access point.
Chapter 7, “Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points”
provides troubleshooting procedures for basic
problems with the lightweight access point.
Appendix A, “Translated Safety Warnings,”
provides translations of the safety warnings that appear in
this publication.
Appendix B, “Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information,” in
dicates how to access the
document that provides translations of the safety warnings that appear in this publication.
Appendix C, “Access Point Specifications,”
Appendix D, “Channels and Maximum Power Levels,” li
lists technical specifications for the access point.
ndicates how to access the document that lists
the access point radio channels and the maximum power levels supported by the world’s regulatory
ains.
dom
Appendix E, “Console Cable Pinouts,” i
dentifies the pinouts for the serial console cable that connects to
the access point’s serial console port.
Appendix F, “Priming Lightweight Access Points Prior to Deployment,”
describes the procedure to
prime access points with controller information.
Appendix G, “Configuring DHCP Option 43 for Lightweight Access Points,” de
configure DHCP Option 43 for lightweight access points.
Conventions
This publication uses these conventions to convey instructions and information:
Command descriptions use these conventions:
• Commands and keywords are in boldface text.
• Arguments for which you supply values are in italic.
• Square brackets ([ ]) mean optional elements.
• Braces ({ }) group required choices, and vertical bars ( | ) separate the alternative elements.
• Braces and vertical bars within square brackets ([{ | }]) mean a required choice within an optional
Interactive examples use these conventions:
• Terminal sessions and system displays are in screen font.
• Information you enter is in boldface screen font.
• Nonprinting characters, such as passwords or tabs, are in angle brackets (< >).
Notes, cautions, and timesavers use these conventions and symbols:
scribes the procedure to
element.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
x
OL-8370-04
Page 11

Preface
Conventions
Tip Means the following will help you solve a problem. The tips information might not be troubleshooting
or even an action, but could be useful information.
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to materials not contained in
this manual.
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result equipment damage
or loss of data.
Warning
Waarschuwing
Varoitus
Attention
Warnung
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you
work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar
with standard practices for preventing accidents. (To see translations of the warnings that appear
in this publication, refer to the appendix “Translated Safety Warnings.”)
Dit waarschuwingssymbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een situatie die lichamelijk letsel kan
veroorzaken. Voordat u aan enige aperture gaat werken, dient u zich bewust te zijn van de bij
elektrische schakelingen betrokken risico’s en dient u op de hoogte te zijn van standaard
maatregelen om ongelukken te voorkomen. (Voor vertalingen van de waarschuwingen die in deze
publicatie verschijnen, kunt u het aanhangsel “Translated Safety Warnings” (Vertalingen van
veiligheidsvoorschriften) raadplegen.)
Tämä varoitusmerkki merkitsee vaaraa. Olet tilanteessa, joka voi johtaa ruumiinvammaan. Ennen
kuin työskentelet minkään laitteiston parissa, ota selvää sähkökytkentöihin liittyvistä vaaroista ja
tavanomaisista onnettomuuksien ehkäisykeinoista. (Tässä julkaisussa esiintyvien varoitusten
käännökset löydät liitteestä "Translated Safety Warnings" (käännetyt turvallisuutta koskevat
varoitukset).)
Ce symbole d’avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous trouvez dans une situation pouvant
entraîner des blessures. Avant d’accéder à cet équipement, soyez conscient des dangers posés par
les circuits électriques et familiarisez-vous avec les procédures courantes de prévention des
accidents. Pour obtenir les traductions des mises en garde figurant dans cette publication, veuillez
consulter l’annexe intitulée « Translated Safety Warnings » (Tradu
ction des avis de sécurité).
Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer Situation, die zu einer
Körperverletzung führen könnte. Bevor Sie mit der Arbeit an irgendeinem Gerät beginnen, seien Sie
sich der mit elektrischen Stromkreisen verbundenen Gefahren und der Standardpraktiken zur
Vermeidung von Unfällen bewußt. (Übersetzungen der in dieser Veröffentlichung enthaltenen
Warnhinweise finden Sie im Anhang mit dem Titel “Translated Safety Warnings” (Übersetzung der
Warnhinweise).)
Avvertenza
OL-8370-04
Questo simbolo di avvertenza indica un pericolo. Si è in una situazione che può causare infortuni.
Prima di lavorare su qualsiasi apparecchiatura, occorre conoscere i pericoli relativi ai circuiti
elettrici ed essere al corrente delle pratiche standard per la prevenzione di incidenti. La traduzione
delle avvertenze riportate in questa pubblicazione si trova nell’appendice, “Translated Safety
Warnings” (Traduzione delle avvertenze di sicurezza).
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
xi
Page 12

Related Publications
Preface
Advarsel
Aviso
¡Advertencia!
Varning!
Dette varselsymbolet betyr fare. Du befinner deg i en situasjon som kan føre til personskade. Før du
utfører arbeid på utstyr, må du være oppmerksom på de faremomentene som elektriske kretser
innebærer, samt gjøre deg kjent med vanlig praksis når det gjelder å unngå ulykker. (Hvis du vil se
oversettelser av de advarslene som finnes i denne publikasjonen, kan du se i vedlegget "Translated
Safety Warnings" [Oversatte sikkerhetsadvarsler].)
Este símbolo de aviso indica perigo. Encontra-se numa situação que lhe poderá causar danos
fisicos. Antes de começar a trabalhar com qualquer equipamento, familiarize-se com os perigos
relacionados com circuitos eléctricos, e com quaisquer práticas comuns que possam prevenir
possíveis acidentes. (Para ver as traduções dos avisos que constam desta publicação, consulte o
apêndice “Translated Safety Warnings” - “Traduções dos Avisos de Segurança”).
Este símbolo de aviso significa peligro. Existe riesgo para su integridad física. Antes de manipular
cualquier equipo, considerar los riesgos que entraña la corriente eléctrica y familiarizarse con los
procedimientos estándar de prevención de accidentes. (Para ver traducciones de las advertencias
que aparecen en esta publicación, consultar el apéndice titulado “Translated Safety Warnings.”)
Denna varningssymbol signalerar fara. Du befinner dig i en situation som kan leda till personskada.
Innan du utför arbete på någon utrustning måste du vara medveten om farorna med elkretsar och
känna till vanligt förfarande för att förebygga skador. (Se förklaringar av de varningar som
förekommer i denna publikation i appendix "Translated Safety Warnings" [Översatta
säkerhetsvarningar].)
Related Publications
These documents provide information about the 1200 series autonomous access point:
• Release Notes for Cisco Aironet Access Points
• Cisco IOS Command Reference for Cisco Aironet Access Points and Bridges
• Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points
These documents provide information about the1200 series lightweight access point and the controller:
• Release Notes for Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and Lightweight Access Points
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
Click this link to browse to the Cisco Wireless documentation home page:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/tsd_products_support_category_home.html
To browse to the 1200 series access point documentation, click Cis
“Wireless LAN Access.”
To browse to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller documentation, click C
Controllers or Cisco 2000 Series Wireless LAN Controllers listed under “Wireless LAN Controllers.”
co Aironet 1200 Series listed under
isco 4400 Series Wireless LAN
xii
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 13

Preface
103680
SN: AAANNNNXXXX
SN: AAANNNNXXXX
Locating the Product Serial Number
The access point serial number is located on the bottom of the cabinet (refer to Figure 1).
Figure 1 Location of Serial Number Label
The access point serial number label contains the following information:
• Model number, such as AIR-AP1232 or AIR-LAP1232
• Serial number, such as S/N: VDF0636XXXX (11 alphanumeric digits)
Locating the Product Serial Number
• MAC address, such as MAC: 00abc65094f3 (12 hexadecimal digits)
• Location of manufacture, such as Made in Singapore
You need your product serial number when requesting support from the Cisco Technical Assistance
nter.
Ce
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security
Guidelines
For information on obtaining documentation, obtaining support, providing documentation feedback,
security guidelines, and also recommended aliases and general Cisco documents, see the monthly
’s New in Cisco Product Documentation,
What
documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
xiii
Page 14

Locating the Product Serial Number
Preface
xiv
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 15

Overview
The Cisco Aironet Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point is available in autonomous and lightweight
configurations. The autonomous access points can support standalone network configurations with all
configuration settings maintained within the access points. The lightweight access points operate in
conjunction with a Cisco wireless LAN controller with all configuration information maintained within
the controller.
Product Terminology
The following terms refer to the autonomous and lightweight products:
• The term access point describes both autonomous and lightweight products.
• The term autonomous access point describes only the autonomous product.
• The term lightweight access point describs only the lightweight product.
• The term access point describes a product operating as an access point.
• The term bridge describes a product operating as a bridge.
CHA PTER
1
Autonomous Access Points
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Points (models: AIR-AP1200, AIR-AP1210, AIR-AP1220B,
AIR-AP1230B, AIR-AP1220A, AIR-AP-1230A, AIR-AP1231G, and AIR-AP1232AG) provide a
secure, affordable, and easy-to-use wireless LAN solution that combines mobility and flexibility with
the enterprise-class features required by networking professionals. With a management system based on
Cisco IOS software, the 1200 series access point is a Wi-Fi certified, wireless LAN transceiver.
The 1200 series access point can contain two radios: a 2.4-GHz radio (IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g)
n an internal mini-PCI slot and a 5-GHz radio module (IEEE 802.11a) in an external, modified cardbus
i
slot. The access point supports one radio of each type, but it does not support two 2.4-GHz or two 5-GHz
radios. You can configure the radios separately, using different settings on each radio.
The access point serves as the connection point between wireless and wired networks or as the center
nt of a stand-alone wireless network. In large installations, wireless users within radio range of an
poi
access point can roam throughout a facility while maintaining seamless, uninterrupted access to the
network.
You can configure and monitor the access point using the command-line interface (CLI), the
owser-based management system, or Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
br
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
1-1
Page 16

Lightweight Access Points
The Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Points (modes: AIR-LAP1231G and AIR-LAP1232AG) combine
mobility and flexibility with the enterprise-class features required by networking professionals. These
access points are part of the Cisco Integrated Wireless Network Solution and require no manual
configuration before they are mounted. The access point is automatically configured by a Cisco wireless
LAN controller (hereafter called a controller) using the Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP).
The access point contains two integrated radios: a 2.4-GHz radio (IEEE 802.11g) and a 5-GHz radio
EEE 802.11a). Using a controller, you can configure the radios separately with different settings on
(I
each.
Note The 1200 series lightweight does not support the 802.11b radio or the 802.11a RM20A radio module.
In the Cisco Centralized Wireless LAN architecture, access points operate in the lightweight mode (as
opp
osed to autonomous mode). The access points associate to a controller. The controller manages the
configuration, firmware, and control transactions such as 802.1x authentication. In addition, all wireless
traffic is tunneled through the controller.
LWAPP is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) draft protocol that defines the control messaging
r setup and path authentication and run-time operations. LWAPP also defines the tunneling mechanism
fo
for data traffic.
In an LWAPP environment, a lightweight access point discovers a controller by using LWAPP discovery
m
echanisms and then sends it an LWAPP join request. The controller sends the access point an LWAPP
join response allowing the access point to join the controller. When the access point is joined, the access
point attempts to download new operating system software if the software versions on the access point
and controller do not match. After an access point joins a controller, you can reassign it to any controller
on your network.
LWAPP secures the control communication between the access point and controller by means of a secure
ey distribution, utilizing X.509 certificates on both the access point and controller.
k
This chapter provides information on the following topics:
• Guidelines for Using 1200 Series Lightweight Access Points, page 1-3
Chapter 1 Overview
1-2
• Hardware Features, page 1-3
• Network Examples with Autonomous Access Points, page 1-7
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 17

Chapter 1 Overview
Guidelines for Using 1200 Series Lightweight Access Points
Guidelines for Using 1200 Series Lightweight Access Points
You should keep these guidelines in mind when you use a 1200 series lightweight access point:
• The access points can only communicate with Cisco 2006 series wireless LAN controllers or 4400
series controllers. Cisco 4100 series, Airespace 4012 series, and Airespace 4024 series controllers
are not supported because they lack the memory required to support access points running Cisco IOS
software.
• The access points do not support Wireless Domain Services (WDS) and cannot communicate with
WDS devices. However, the controller provides functionality equivalent to WDS when the access
point associates to it.
• The access points support eight BSSIDs per radio and a total of eight wireless LANs per access
point. When a lightweight access point associates to a controller, only wireless LANs with IDs 1
through 8 are pushed to the access point.
• The access points do not support Layer 2 LWAPP. They must get an IP address and discover the
controller using DHCP, DNS, or IP subnet broadcast.
• The access point console port is enabled for monitoring and debug purposes (all configuration
commands are disabled when connected to a controller).
Hardware Features
This section describes access point features. Refer to Appendix C, “Access Point Specifications,” for a
list of access point specifications.
Key hardware features of the 1200 series access point include:
• Dual-Radio Operation, page 1-4
• LEDs, page 1-5
• Ethernet Port, page 1-5
• Console Port, page 1-6
• Power Sources, page 1-6
• UL 2043 Certification, page 1-6
• Anti-Theft Features, page 1-6
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
1-3
Page 18

Hardware Features
Dual-Radio Operation
The access point can be initially configured at the factory for single- or dual-radio operation. You can
also upgrade an access point configured for single-radio operation to support dual-radio operation using
a 5-GHz radio module or a 2.4-GHz mini-PCI radio card. The access point supports one radio of each
type, but it does not support two 2.4-GHz or two 5-GHz radios.
The 1200 series access point supports these radios:
• 2.4-GHz IEEE 802.11b mini-PCI radio card: MP20B, hereafter called 802.11b radio.
• 2.4-GHz 802.11g mini-PCI radio cards: MP21G or MP31G, hereafter called the 802.11g radio.
• 5-GHz 802.11a radio modules:
Chapter 1 Overview
Note The lightweight access points do not support the MP20B 2.4-GHz IEEE 802.11b radio.
Note The autonomous access points require Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)JA or later
–
AIR-RM20A-x-K9—802.11a radio module with integrated antenna, hereafter called the
RM20A radio module.
Note The lightweight access points do not support the RM20A 5-GHz 802.11a radio module.
–
AIR-RM21A-x-K9—802.11a radio module with integrated antenna, hereafter called the
RM21A radio module.
Note The autonomous access points require Cisco IOS Release 12.3(2)JA or later.
–
AIR-RM22A-x-K9—802.11a radio module with external RP-TNC antenna connectors,
hereafter called the RM22A radio module.
Note The autonomous access points require Cisco IOS Release 12.3(2)JA or later.
Note Cisco Aironet CB20A client radios can sometimes fail to associate to the RM21A or RM22A radio
modules because the CB20A client radio does not support all the channels supported by the radio
modules. The default channel setting for the RM21A or RM22A radio module, least congested, often
results in the access point settling on one of these frequencies that the CB20A client radio does not
support: channel 149 (5745 GHz), channel 153 (5765 GHz), channel 157 (5785 GHz), and channel 161
(5805 GHz). To avoid this problem, set the channel on the RM21A or RM22A radio module to one of
the channels supported by the CB20A client radio. For additional information, refer to the Cisco IOS
Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points or the Cisco IOS Software Configuration
Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points.
1-4
The 2.4-GHz mini-PCI radio card connects to an internal mini-PCI slot. The 5-GHz radio module
connects to the access point’s modified card bus connector.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 19

Chapter 1 Overview
Radio
Status
Ethernet
86704
LEDs
Hardware Features
All 5-GHz radio modules incorporate an Unlicensed National Information Infrastructure (UNII) radio
transceiver operating in the UNII 5-GHz frequency bands. The RM21A radio modules contains dual
integrated omnidirectional antennas and directional antennas for diversity operation. For autonomous
access points, the 802.11g radio is called Radio0 and the 802.11a radio is called Radio1.
The three LEDs on the top of the access point report Ethernet activity, association status, and radio
activity.
• The Ethernet LED signals Ethernet traffic on the wired LAN, or Ethernet infrastructure. This LED
is normally green when an Ethernet cable is connected and blinks green when a packet is received
or transmitted over the Ethernet infrastructure. The LED is off when the Ethernet cable is not
connected.
• The status LED signals operational status. Green indicates that the access point is associated with
at least one wireless client. Blinking green indicates that the access point is operating normally but
is not associated with any wireless devices.
• The radio LED signals wireless traffic over the radio interface. The light is normally off, but it blinks
green whenever a packet is received or transmitted over the access point radio.
Figure 1-1 sh
ows the three status LEDs.
Ethernet Port
Figure 1-1 Access Point LEDs
OL-8370-04
The auto-sensing Ethernet port accepts an RJ-45 connector, linking the access point to your 10BASE-T
or 100BASE-T Ethernet LAN. The access point can receive power through the Ethernet cable from a
power injector, switch, or power patch panel. The Ethernet MAC address is printed on the label on the
back of the access point.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
1-5
Page 20
Hardware Features
Console Port
Power Sources
Chapter 1 Overview
The serial console port can be used to monitor the access point power-up sequences using a terminal
emulator program. Use an RJ-45 to DB-9 serial cable to connect your computer’s COM port to the access
point’s serial console port. (Refer to Appendix E, “Console Cable Pinouts,” for a description of the
console port pinouts.) Assign the following port settings to a terminal emulator to open the management
em pages: 9600 baud, 8 data bits, No parity, 1 stop bit and no flow control.
syst
The access point can receive power from an external power module or through inline power using the
Ethernet cable. Using inline power, you do not need to run a power cord to the access point.
The access point supports the following power sources:
• Power supply (input 100–240 VAC, 50–60 Hz, output 48 VDC, 0.2A minimum)
• Inline power from:
–
Cisco Aironet Power Injector (AIR-PWRINJ-FIB or AIR-PWRINJ3)
–
A switch capable of providing inline power, such as Cisco Catalyst 3500XL, 3550, 4500, or
6500 switches
UL 2043 Certification
The access point is encased in a durable metal case having adequate fire resistance and low
smoke-producing characteristics suitable for operation in a building's environmental air space, such as
above suspended ceilings, in accordance with Section 300-22(c) of the NEC, and with Sections 2-128,
12-010(3) and 12-100 of the Canadian Electrical Code, Part 1, C22.1.
Caution Only the fiber-optic power injector (AIR-PWRINJ-FIB) has been tested to UL 2043 for operation in a
building’s environmental air space; no other power injectors or power modules have been tested to UL 2043
and they should not be placed in a building’s environmental air space, such as above suspended ceilings.
Anti-Theft Features
There are two methods of securing the access point to help prevent theft:
• Security cable keyhole—You can use the security cable slot to secure the access point using a
–
An inline power patch panel, such as the Cisco Catalyst Inline Power Patch Panel
Note The Catalyst 3550-24 PWR switch supports power for access points configured with both
2.4-GHz and 5-GHz radios. Other switches and patch panels might not provide enough
power for both radios.
standard security cable, such as those used on laptop computers.
1-6
• Security hasp—When you mount the access point on a wall or ceiling using the mounting bracket
and the security hasp, you can lock the access point to the bracket with a padlock. Compatible
padlocks are Master Lock models 120T and 121T or equivalent.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 21

Chapter 1 Overview
Network Examples with Autonomous Access Points
Network Examples with Autonomous Access Points
This section describes the autonomous access point’s role in three common wireless network
configurations. The autonomous access point’s default configuration is as a root unit connected to a
wired LAN or as the central unit in an all-wireless network.
The autonomous 1200 series access point supports these operating wireless modes:
• Root access point—Connected to a wired LAN and supports wireless clients.
• Repeater access point—Not connected to a wired LAN, associates to a root access point, and
supports wireless clients
• Workgroup bridge—Not connected to a wired LAN, associates to a root access point or bridge, and
supports wired network devices.
• Root bridge—Connected to a wired LAN and supports non-root bridges and wireless clients.
• Non-root bridge—Not connected to a wired LAN, associates to a root bridge, supports wireless
clients, and supports wired clients.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
1-7
Page 22
Network Examples with Autonomous Access Points
Access point
Access point
135445
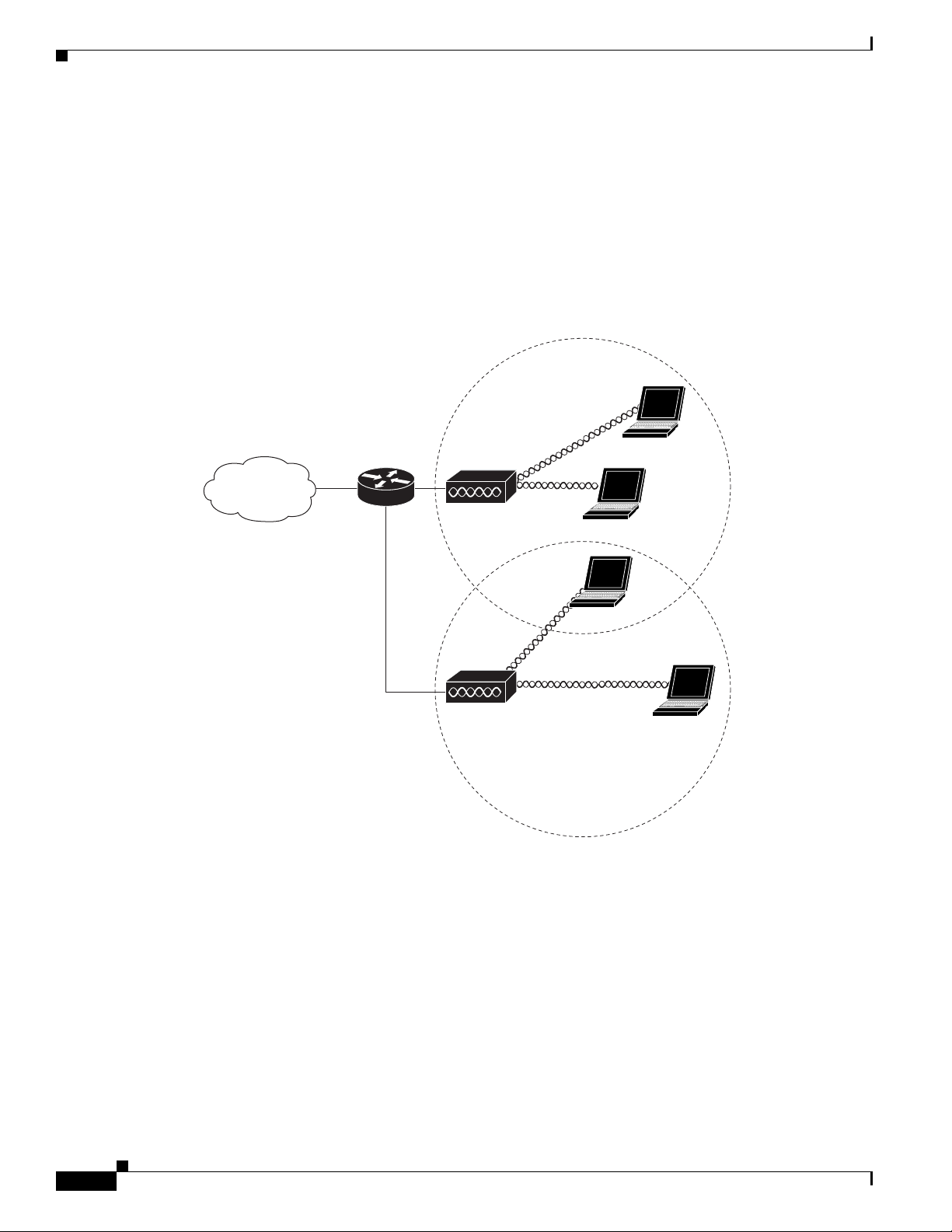
Root Access Point on a Wired LAN
An autonomous access point connected directly to a wired LAN provides a connection point for wireless
users. If more than one autonomous access point is connected to the LAN, users can roam from one area
of a facility to another without losing their connection to the network. As users move out of range of one
access point, they automatically connect to the network (associate) through another access point. The
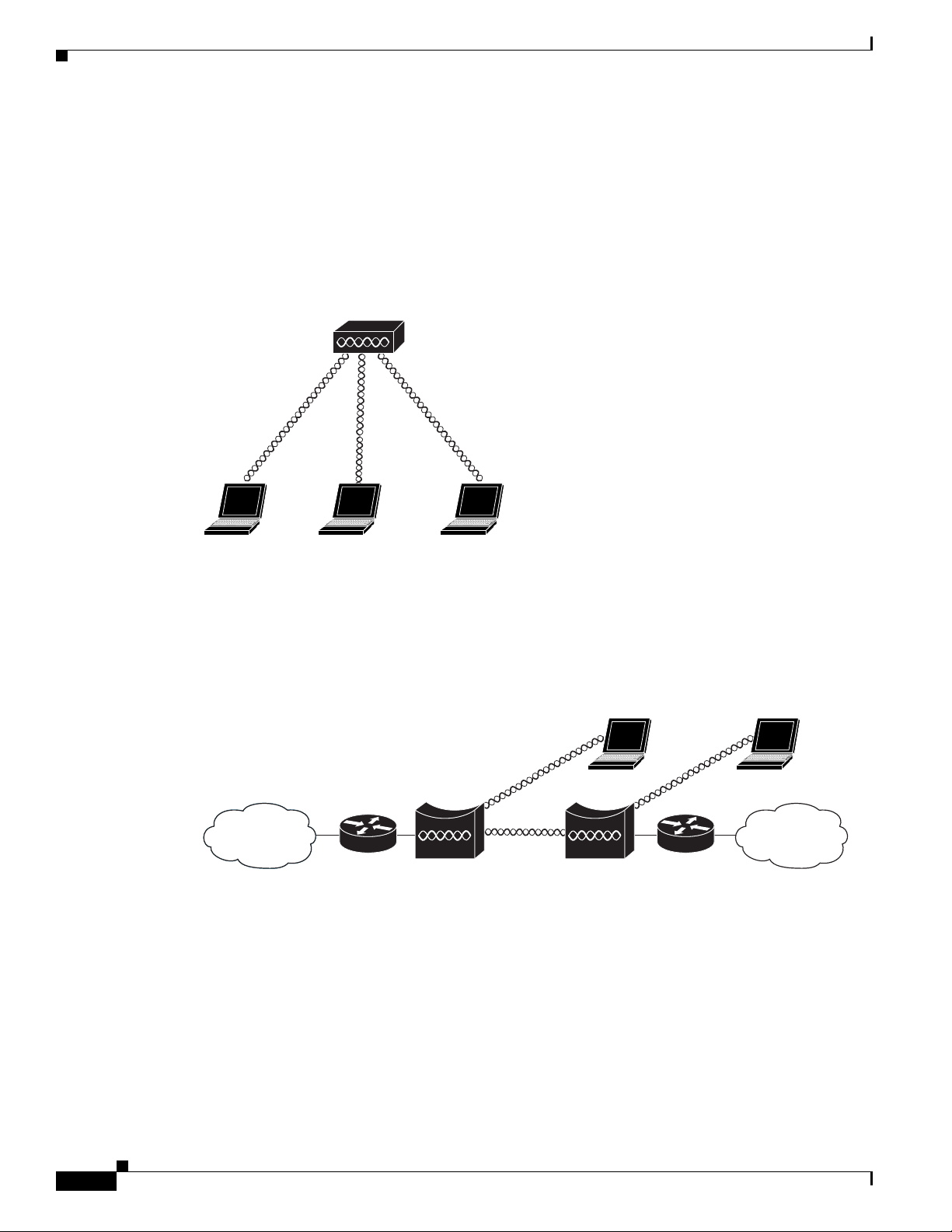
roaming process is seamless and transparent to the user. Figure 1-2 shows access points acting as root
units on a wired LAN.
Figure 1-2 Access Points as Root Units on a Wired LAN
Chapter 1 Overview
1-8
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 23
Chapter 1 Overview
Access point Repeater
135444
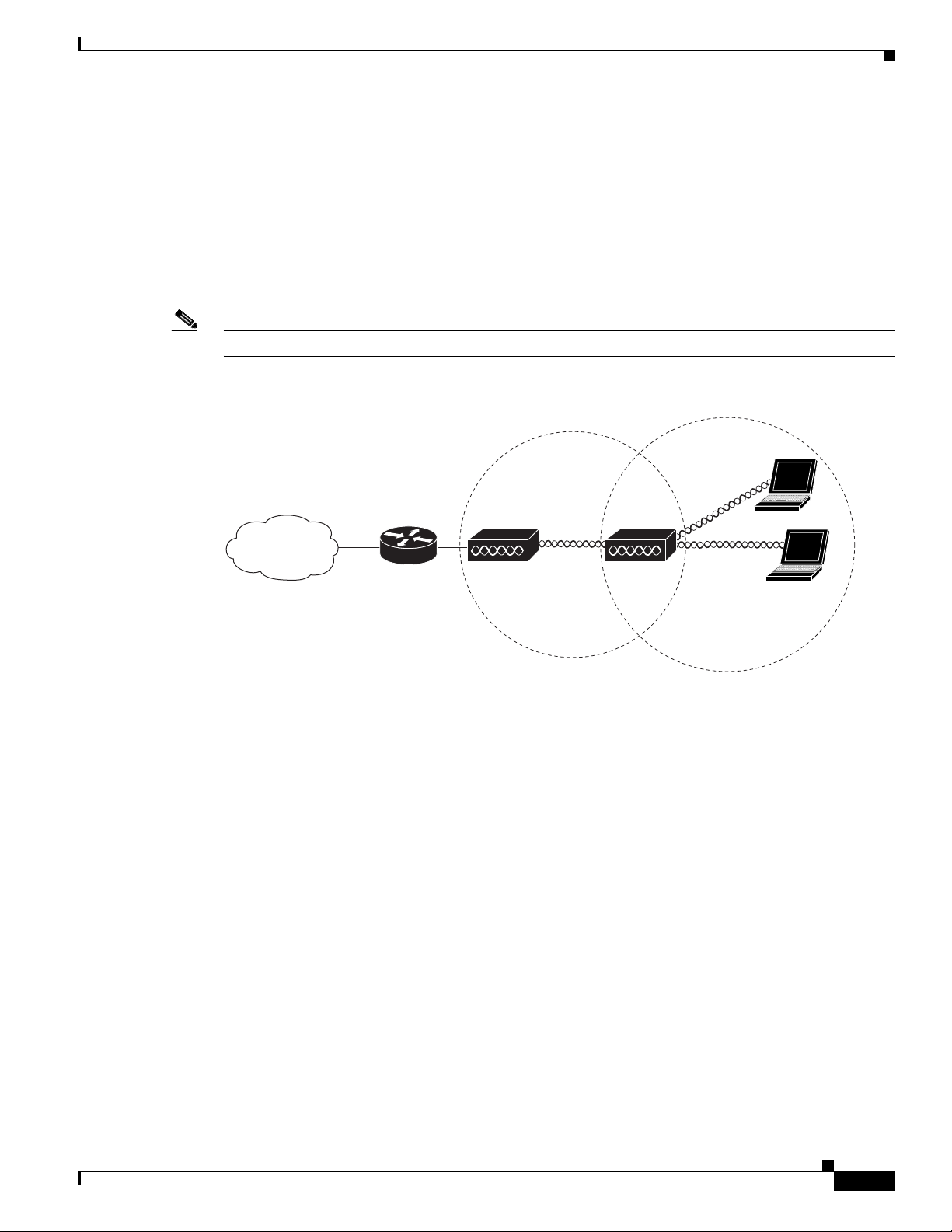
Repeater Unit that Extends Wireless Range
An autonomous access point can be configured as a stand-alone repeater to extend the range of your
infrastructure or to overcome an obstacle that blocks radio communication. The repeater forwards traffic
between wireless users and the wired LAN by sending packets to either another repeater or to an access
point connected to the wired LAN. The data is sent through the route that provides the best performance
for the client. Figure 1-3 shows an autonomous access point acting as a repeater. Consult the Ci
Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points for
point as a repeater.
Note Non-Cisco client devices might have difficulty communicating with repeater access points.
Figure 1-3 Access Point as Repeater
Network Examples with Autonomous Access Points
sco IOS
instructions on setting up an access
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
1-9
Page 24
Network Examples with Autonomous Access Points
Access point
135443
Root bridge Non-root bridge
135446
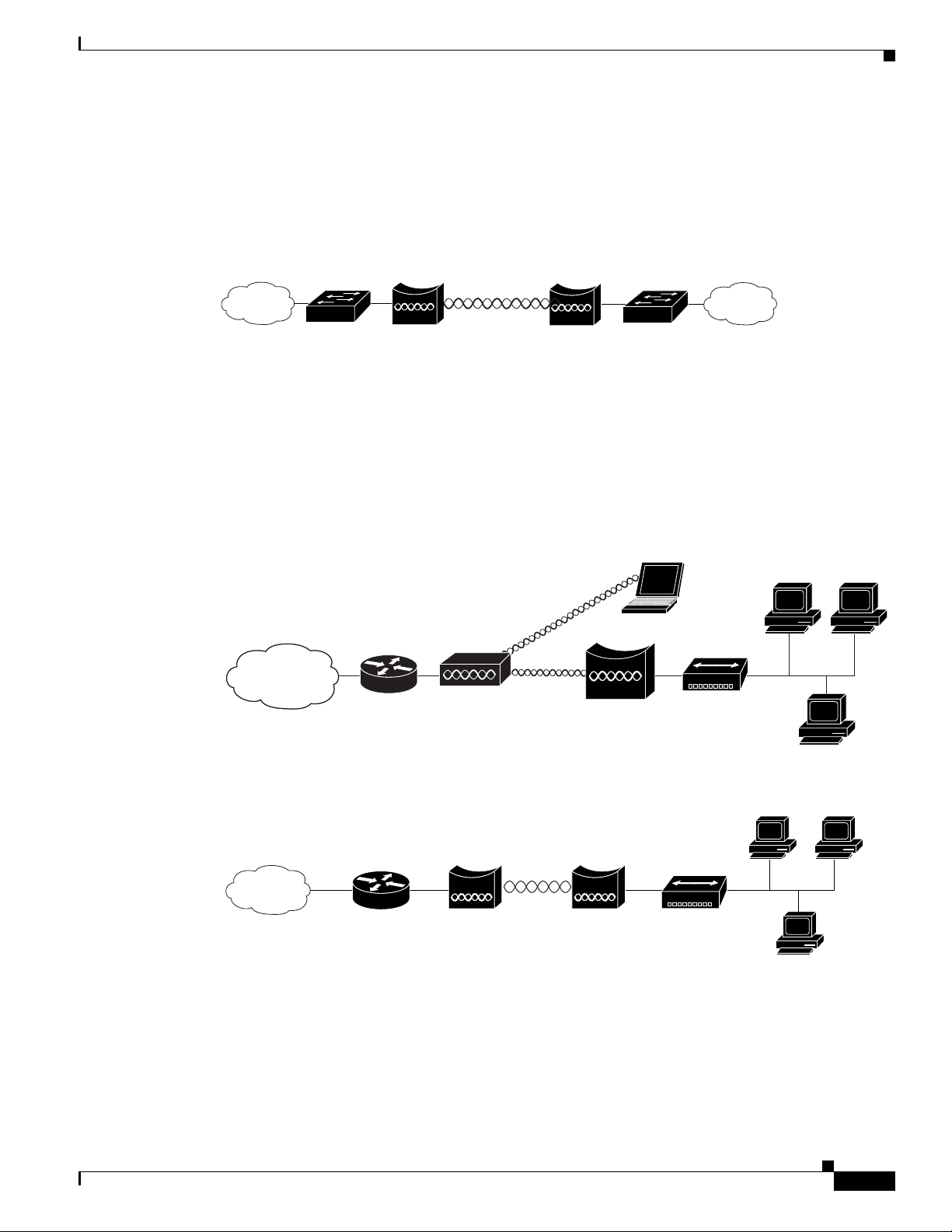
Central Unit in an All-Wireless Network
In an all-wireless network, an autonomous access point acts as a stand-alone root unit. The autonomous
access point is not attached to a wired LAN; it functions as a hub linking all stations together. The access
point serves as the focal point for communications, increasing the communication range of wireless
users. Figure 1-4 shows an autonomous access point in an all-wireless network.
Figure 1-4 Access Point as Central Unit in All-Wireless Network
Chapter 1 Overview
Bridge Network with Wireless Clients
The access point supports root bridge and non-root bridge roles used to interconnect a remote LAN to
the main LAN (see Figure 1-5). The bridge units can also support wireless clients.
Figure 1-5 Root Bridge and Non-root Bridge with Clients
1-10
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 25
Chapter 1 Overview
117029
Root bridge Non-root bridge
Access point
Workgroup bridge
135448
Bridge Workgroup
bridge
135499
Point-to-Point Bridge Configuration
In a point-to-point bridge configuration, two bridges interconnect two LAN networks using a wireless
communication link (see Figure 1-6). The bridge connected to the main LAN network is classified as a
root bridge and the other bridge is classified as a non-root bridge.
Figure 1-6 Point-to-Point Bridge Configuration
Workgroup Bridge Network
The access point supports a workgroup bridge role to interconnect remote Ethernet workstations to the
main LAN. The workgroup bridge can communicate with an access point (see Figure 1-7) or with a
bridge (see Figure 1-8).
Network Examples with Autonomous Access Points
Figure 1-7 Workgroup Bridge Communicating with an Access Point
Figure 1-8 Workgroup Bridge Communicating with a Bridge
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
1-11
Page 26
Network Example with Lightweight Access Points
158085
LWAPP
LWAPP
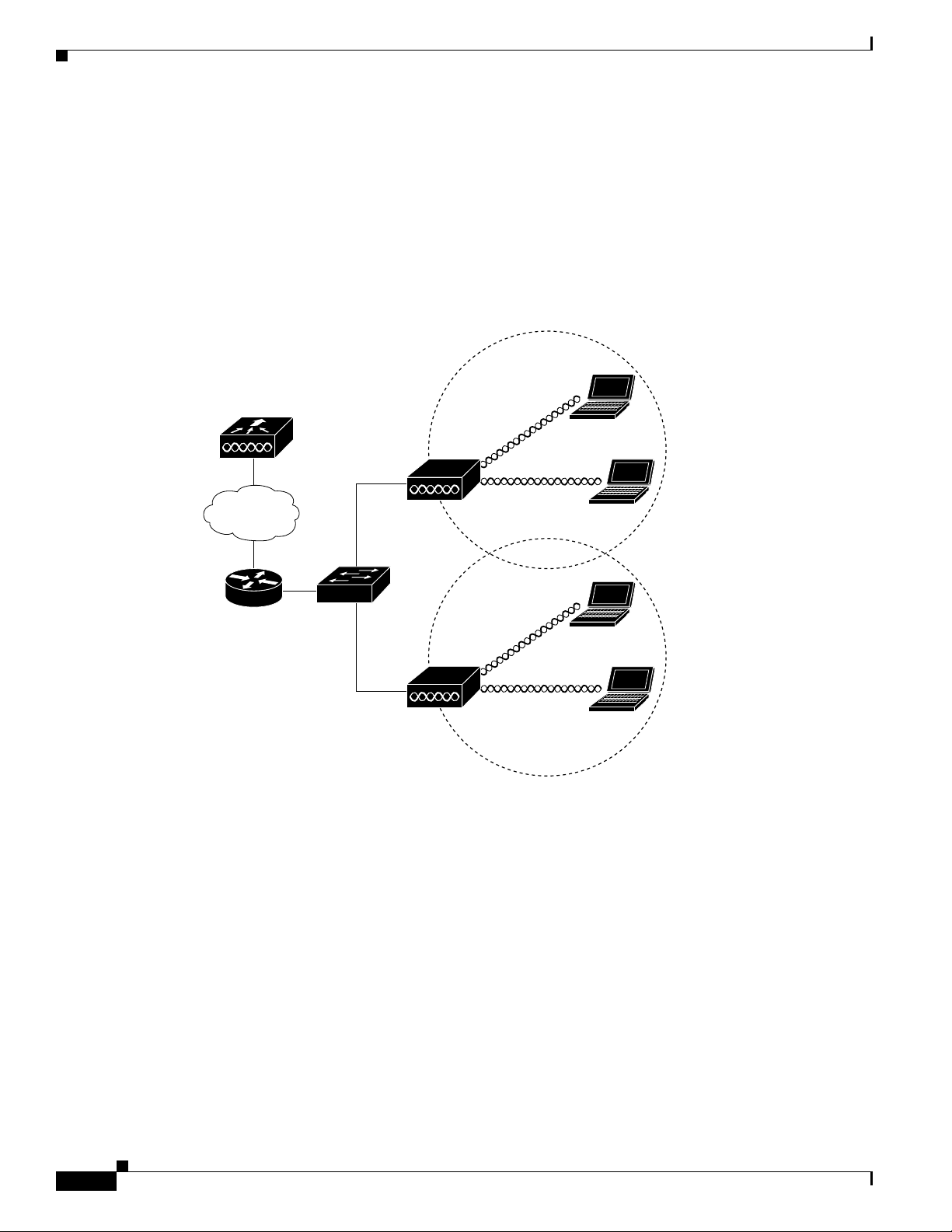
Network Example with Lightweight Access Points
The lightweight access points support Layer 3 network operation. Lightweight access points and
controllers in Layer 3 configurations use IP addresses and UDP packets, which can be routed through
large networks. Layer 3 operation is scalable and recommended by Cisco.
This section illustrates a typical wireless network configuration containing lightweight access points and
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller (see Figure 1-9).
a
Figure 1-9 Typical Lightweight Access Point Network Configuration Example
Chapter 1 Overview
1-12
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 27

Chapter 1 Overview
Network Example with Lightweight Access Points
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
1-13
Page 28

CHA PTER
2
Installing the Access Point
This chapter describes the setup of the access point and includes the following sections:
• Safety Information, page 2-2
• Warnings, page 2-2
• Unpacking the Access Point, page 2-3
• Basic Installation Guidelines, page 2-4
• Controller Discovery Process for Lightweight Access Points, page 2-4
• Before Beginning the Installation, page 2-5
• Deploying the Access Points on the Wireless Network, page 2-7
• Connecting the 2.4-GHz Antennas, page 2-8
• Connecting the 5-GHz External Antennas, page 2-8
• Connecting the Ethernet and Power Cables, page 2-9
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
2-1
Page 29
Chapter 2 Installing the Access Point
Safety Information
Follow the guidelines in this section to ensure proper operation and safe use of the access point.
FCC Safety Compliance Statement
The FCC with its action in ET Docket 96-8 has adopted a safety standard for human exposure to radio
frequency (RF) electromagnetic energy emitted by FCC certified equipment. When used with approved
Cisco Aironet antennas, Cisco Aironet products meet the uncontrolled environmental limits found in
OET-65 and ANSI C95.1, 1991. Proper installation of this radio according to the instructions found in
this manual will result in user exposure that is substantially below the FCC recommended limits.
General Safety Guidelines
• Do not touch or move antenna(s) while the unit is transmitting or receiving.
• Do not hold any component containing a radio so that the antenna is very close to or touching any
exposed parts of the body, especially the face or eyes, while transmitting.
• The use of wireless devices in hazardous locations is limited to the constraints posed by the local
codes, the national codes, and the safety directors of such environments.
Safety Information
Warnings
Warning
Warning
Warning
Translated versions of all safety warnings are available in the safety warning document that shipped with
your access point or on Cisco.com. To browse to the document on Cisco.com, refer to Appendix A,
“Translated Safety Warnings” for instructions.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you
work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar
with standard practices for preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of
each warning to locate its translation in the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device.
Statement 1071
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Do not operate your wireless network device near unshielded blasting caps or in an explosive
environment unless the device has been modified to be especially qualified for such use.
Statement 245B
In order to comply with FCC radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, antennas should be located at a
minimum of 7.9 inches (20 cm) or more from the body of all persons.
Statement 332
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
2-2
Page 30

Unpacking the Access Point
Chapter 2 Installing the Access Point
Warning
Warning
Warning
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity.
Statement 1001
Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source.
This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that
the protective device is rated not greater than: 20A
Unpacking the Access Point
Follow these steps to unpack the access point:
Step 1 Open the shipping container and carefully remove the contents.
Step 2 Return all packing materials to the shipping container and save it.
Step 3 Ensure that all items listed in the “Package Contents” section are included in the shipment. Check each
item for damage. If any item is damaged or missing, notify your authorized Cisco sales representative.
Statement 1004
Statement 1005
Package Contents
Each access point package contains the following items:
• Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point or Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Lightweight Access Point
• Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Power Module (Universal power supply)
• Product quick start guide
• Translated safety warnings document
• Cisco product registration and Cisco documentation feedback cards
The optional 2.4-GHz radio upgrade kit is shipped with the following items:
• 2.4-GHz radio card (802.11g)
• Installation guide
• A product registration card
• A T-10 tamper-resistant Torx L-wrench
• 2.4-GHz radio product compliance label
The optional 5-GHz radio upgrade kit is shipped with the following items:
• 5-GHz radio module (RM21A or RM22A)
• Installation guide
• A product registration card and a 5-GHz radio product compliance label
2-3
• A T-10 tamper-resistant Torx L-wrench
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 31

Chapter 2 Installing the Access Point
Basic Installation Guidelines
Because the access point is a radio device, it is susceptible to interference that can reduce throughput
and range. Follow these basic guidelines to ensure the best possible performance:
• Ensure that a site survey has been performed to determine the optimum placement of access points.
• For lightweight access points, check the latest release notes to ensure that your controller software
version supports the access points to be installed. You can find the controller release notes by
selecting your controller under Wireless LAN Controllers at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/tsd_products_support_category_home.html
• Ensure that access points are not mounted closer than 20 cm (7.9 in) from
• Do not mount the access point within 3 ft (91.4 cm) of metal obstructions.
• Install the access point away from microwave ovens. Microwave ovens operate on the same
frequency as the access point and can cause signal interference.
• Do not mount the access point outside of buildings.
• Do not mount the access points on building perimeter walls unless outside coverage is desired.
Basic Installation Guidelines
the body of all persons
.
Controller Discovery Process for Lightweight Access Points
The lightweight access point supports these controller discovery processes:
• DHCP server discovery—Uses DHCP Option 43 to provide controller IP addresses to the access
points. Cisco switches support a DHCP server option. For additional information, refer to the
“Configuring DHCP Option 43 for Lightweight Access Points” section on page G-1.
• DNS server discovery—The access point uses the name CISCO-LWAPP-CONTROLLER.<local
domain> to discover the controller IP addresses from a DNS server. Where <local domain> is the
access point domain name.
• Locally stored controller IP addresses—If the access point was previously associated to a controller,
the IP addresses of the primary, secondary, and tertiary controllers are stored in the access point
non-volitile memory. The process of storing controller IP addresses in access points for later
deployment is called priming the access point. For additional information, refer to the “Priming
Lightweight Access Points Prior to Deployment” section on page F-1.
You can also manually configure controller information using CLI commands on new
out-of-the-box) access points that are not connected to a controller. For additional information refer
(
to the “Manually Configuring Controller Information Using the Access Point CLI” section on
page 7-5.
Cisco recommends that you configure a DHCP server with Option 43 to provide the controller IP
dresses to your access points. Cisco switches provide a DHCP server option that is typically used for
ad
this purpose.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
2-4
Page 32

Before Beginning the Installation
1 2 3 4 6
7 1
5
65847
74631
1 1 2 3
Before Beginning the Installation
Before you begin the installation process, please refer to Figure 2-1, Figure 2-2, and Figure 2-3 to
become familiar with the access point’s layout, connectors, and 5-GHz module location.
Figure 2-1 Access Point Layout and Connectors
1 2.4-GHz antenna connectors 5 Mode button
2 48-VDC power port 6 Status LEDs
3 Ethernet port (RJ-45) 7 Mounting bracket
4 Console port (RJ-45)
Chapter 2 Installing the Access Point
Note Do not connect Cisco 5-GHz antennas with blue labels or blue dots to the 2.4-GHz antenna connectors.
Figure 2-2 Access Point with 5-GHz Radio Module (RM21A)
1 Module mounting screws 3 Access point
2 Integrated antenna in patch position
(RM21A radio module)
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
2-5
OL-8370-04
Page 33

Chapter 2 Installing the Access Point
Figure 2-3 RM22A Radio Module with External RP-TNC Antenna Connectors
Before Beginning the Installation
]
1 Left 5-GHz antenna connector (RP-TNC) 4 Right 5-GHz antenna connector (RP-TNC)
2 Blue 5-GHz label 5 5-GHz radio
3 Module mounting screws
Note Only connect Cisco 5-GHz antennas with blue labels or blue dots to the RM22A radio module.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
2-6
Page 34

Chapter 2 Installing the Access Point
Deploying the Access Points on the Wireless Network
Deploying the Access Points on the Wireless Network
Prior to beginning the actual access point deployment, perform these tasks:
• Ensure that a site survey has been preformed.
• Ensure that your network infrastructure devices are operational and properly configured.
• For lightweight access points, perform these tasks:
–
Ensure that your controllers are connected to switch trunk ports.
–
Ensure that your switch is configured with untagged access ports for connecting your access
points.
–
Ensure that a DHCP server with Option 43 configured is reachable by your access points.
To deploy your access points, follow these steps:
Step 1 Obtain the access point location map created during your building site survey.
Step 2 Review the access point locations and identify the specific mounting methods required for each access
point location.
Step 3 For each access point perform these steps:
a. For lightweight access points, record the access point MAC address on the access point location
map. When you have completed the lightweight access point deployment, return the access point
MAC addresses and the access point locations on the access point location maps or floor plans to
your network planner or manager. The network operators can use the MAC address and location
information to create maps for precise wireless system management.
b. Mount the access point at the indicated destination using the specified mounting method. For
specific mounting instructions, see these sections:
–
Attaching the access point to the mounting plate (see the “Attaching the Access Point to the
Mounting Bracket” section on page 3-8).
–
Horizontal or vertical surface, such as a ceiling or wall (see the “Mounting on a Horizontal or
Vertical Surface” section on page 3-3).
–
Below a suspended ceiling (see the “Mounting Below a Suspended Ceiling” section on
page 3-4).
–
Above a suspended ceiling (see the “Mounting Above a Suspended Ceiling” section on
page 3-5).
c. Optionally secure the access point using a padlock or security cable (see the “Securing the Access
Point to the Mounting Bracket” section on page 3-8).
d. Connect the access point cables (Ethernet, optional power, optional antennas). For instructions see
the “Connecting the Ethernet and Power Cables” section on page 2-9.
e. On power up, verify that the access point is associated to a controller and operating normally. For
additional information, refer to the “Checking the Top Panel LEDs” section on page 6-2.
2-7
Step 4 For lightweight access points, after your access points are deployed, ensure that your controller is not
configured as a master controller. A master controller should only be used for configuring access points
and not in a working network.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 35

Chapter 2 Installing the Access Point
Connecting the 2.4-GHz Antennas
The access point supports a single antenna or dual diversity antennas. Two RP-TNC antenna connectors
are provided on the back of the unit for the 2.4-GHz radio.
Note RP-TNC antenna connectors are used for both the 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz radios. Do not connect Cisco
5-GHz antennas with blue labels or blue dots to the 2.4-GHz antenna connectors (refer to Figure 2-1 for
connector locations).
To attach your antenna or antenna cable to the access point, follow these steps:
Step 1 Attach an antenna or antenna cable to the 2.4-GHz Right/Primary (RP-TNC) antenna connector on the
back of the access point and hand tighten. If you are using two antennas for diversity coverage, attach
the second antenna or antenna cable to the 2.4-GHz Left (RP-TNC) antenna connector.
Step 2 If you are using a Cisco Aironet 2 dBi antenna, orient the antenna depending on how you intend to mount
the access point.
Connecting the 2.4-GHz Antennas
• On a table or desk, orient the antenna straight up.
• On a vertical surface, such as a wall, orient the antenna straight up.
• On a ceiling, orient the antenna straight down.
Step 3 If you are using another Cisco Aironet antenna, refer to the antenna mounting instructions that came with
your antenna.
Connecting the 5-GHz External Antennas
The access point supports an RM22A radio module for use with a single antenna or dual diversity
antennas. Two RP-TNC antenna connectors are provided on the back of the module for the 5-GHz radio.
Note RP-TNC antenna connectors are used for both the 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz radios. Only connect Cisco
5-GHz antennas with blue labels or blue dots to the 5-GHz antenna connectors (refer to Figure 2-3 for
connector locations).
If you are using the RM22A radio module, follow these steps:
Step 1 Attach the Cisco Aironet 5-GHz antenna cable to the Right/Primary 5-GHz (RP-TNC) antenna
connector on the back of the radio module and hand tighten. If you are using two antennas for diversity
coverage, attach the second antenna cable to the Left 5-GHz (RP-TNC) antenna connector.
OL-8370-04
Note The Cisco Aironet antennas have a blue marker label or blue dot near the antenna connector and
the radio module has a corresponding blue label near the 5-GHz antenna connectors.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
2-8
Page 36

Connecting the Ethernet and Power Cables
Power
cord
Universal
power supply
S
Y
S
T
R
P
S
D
U
P
L
X
M
O
D
E
S
P
E
E
D
U
T
IL
S
T
A
T
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
1
6
1
7
1
8
19
2
0
2
1
2
2
2
3
2
4
2
3
2
4
10B
a
se-T
/ 100
B
ase-T
X
10
0B
ase-F
X
Catalyst 2950
S
E
R
IE
S
S
Y
S
T
R
P
S
D
U
P
L
X
M
O
D
E
S
P
E
E
D
U
T
IL
S
T
A
T
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
14
1
5
16
1
7
1
8
1
9
2
0
2
1
2
2
2
3
2
4
2
3
2
4
10B
ase-T
/ 100B
ase-T
X
100B
ase-F
X
Catalyst 2950
S
E
R
IE
S
S
Y
S
T
R
P
S
D
U
P
L
X
M
O
D
E
S
P
E
E
D
U
T
IL
S
T
A
T
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
1
6
1
7
1
8
1
9
2
0
2
1
2
2
2
3
2
4
2
3
2
4
10B
ase-T / 100B
ase-T
X
100B
ase-F
X
Catalyst 2950
S
E
R
IE
S
S
Y
S
T
R
P
S
D
U
P
L
X
M
O
D
E
S
P
E
E
D
U
T
IL
S
T
A
T
TO
AP/ BRIDGE
TO
NETWORK
Switch with
inline power
Power injector
Access Point
Switch
(without inline power)
Switch
(without inline power)
Inline Power
Patch Panel
Option 1 Option 2 Option 3
Option 4
74164
Step 2 To mount your Cisco Aironet antenna, refer to the instructions that came with your antenna.
Connecting the Ethernet and Power Cables
The access point receives power through the Ethernet cable or an external power module. Figure 2-4
shows the power options for the access point.
Figure 2-4 Access Point Power Options
Chapter 2 Installing the Access Point
Note Currently, the Catalyst 3550-24 PWR switch supports power for both the 2.4-GHz radio and the 5-GHz
Note If you use in-line power, do not connect the power module to the access point. Using two power sources
The access point power options are listed below:
• A switch with inline power, such as a Cisco Catalyst 3500XL, 3550-24 PWR, 4000, or 6500 switch
• A Cisco Aironet Power Injector (AIR-PWRINJ-FIB or AIR-PWRINJ3)
• An inline power patch panel, such as the Cisco Catalyst Inline Power Patch Panel
• A power module (Universal power supply)
radio. Other switches and power patch panels might not provide enough power for the 5-GHz radio.
on the access point might cause the switch to shut down the port to which the access point is connected.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
2-9
OL-8370-04
Page 37

Chapter 2 Installing the Access Point
Connecting the Ethernet and Power Cables
Connecting to an Ethernet Network with an Inline Power Source
Caution The Cisco Aironet Power Injectors are designed for use with Cisco Aironet access points only. Using the
power injector with other Ethernet-ready devices can damage the equipment.
Caution Only the fiber-optic power injector (AIR-PWRINJ-FIB) has been tested to UL 2043 for operation in a
building’s environmental air space; no other power injectors or power modules have been tested to UL 2043
and they should not be placed in a building’s environmental air space, such as above suspended ceilings.
Follow these steps to connect the access point to the Ethernet LAN when you have an inline power
source:
Step 1 Connect the Ethernet cable to the RJ-45 Ethernet connector labeled Ethernet on the access point.
Step 2 Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to one of the following:
• A switch with inline power, such as a Cisco Catalyst 3500XL, 3550-24 PWR, 4000, or 6500 switch.
• An inline power switch panel, such as a Cisco Catalyst Inline Power Patch Panel.
• The end of a Cisco Aironet power injector labeled To A P /Bri d ge . Connect the other end labeled To
Network to the 10/100 Ethernet LAN.
Note If you use a power supply or power injector to power the access point, you must use the power supply
included with your access point and the Cisco Aironet Power Injector for the 1100 and 1200 series access
points.
Connecting to an Ethernet Network with Local Power
Follow these steps to connect the access point to an Ethernet LAN when you are using a local power
source:
Step 1 Connect the Ethernet cable to the RJ-45 Ethernet connector labeled Ethernet on the access point.
Step 2 Plug the other end of the Ethernet cable into an unpowered Ethernet port on your network.
Step 3 Connect the power module’s output connector to the 48-VDC power port labeled 48VDC on the access
point.
Step 4 Plug the other end of the power module into an approved 100- to 240-VAC outlet.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
2-10
Page 38

Connecting the Ethernet and Power Cables
Chapter 2 Installing the Access Point
2-11
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 39

CHA PTER
3
Mounting Instructions
This appendix provides instructions for mounting the access point to suspended ceilings, vertical
surfaces, or horizontal surfaces using the access point mounting bracket.
The following sections are included in this chapter:
• Overview, page 3-2
• Mounting on a Horizontal or Vertical Surface, page 3-3
• Mounting Below a Suspended Ceiling, page 3-4
• Mounting Above a Suspended Ceiling, page 3-5
• Attaching the Access Point to the Mounting Bracket, page 3-8
• Securing the Access Point to the Mounting Bracket, page 3-8
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
3-1
Page 40

Overview
1
546738
2 3 4
65863
2
Overview
Chapter 3 Mounting Instructions
You can mount the access point on any of the following surfaces:
• Horizontal or vertical flat surfaces, such as walls or ceilings
• Suspended ceilings
The access point ships with a detachable mounting bracket and the necessary mounting hardware.
ause it is detachable, you can use the mounting bracket as a template to mark the positions of the
Bec
mounting holes for your installation. You then install the mounting bracket and attach the access point
when you are ready. Refer to Figure 3-1 to locate the various mounting holes for the method you intend
to use.
Figure 3-1 Mounting Bracket
1 Access point mount 5 Locking detent
2 Cable tie points 6 Wall cable access
3 Ceiling mount holes 7 Suspended ceiling cable access
4 Access point mounts 8 Security hasp
Note The 1200 series access point provides adequate fire resistance and low smoke-producing characteristics
suitable for operation in a building's environmental air space (such as above suspended ceilings) in
accordance with Section 300-22(C) of the National Electrical Code (NEC).
Caution Only the fiber-optic power injector (AIR-PWRINJ-FIB) has been tested to UL 2043 for operation in a
building’s environmental air space; no other power injectors or power modules have been tested to UL 2043
and they should not be placed in a building’s environmental air space, such as above suspended ceilings.
Note If you plan to mount the access point in environmental air space and will upgrade to a 5-GHz radio, Cisco
recommends that you mount the access point horizontally with its antennas pointing down. Doing so will
result in the access point complying with regulatory requirements for environmental air space after the
5-GHz radio is installed.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
3-2
OL-8370-04
Page 41

Chapter 3 Mounting Instructions
Note When mounting the access point in a building’s environmental air space, you must use Ethernet cable
suitable for operation in environmental air space in accordance with Section 300-22(C) of the National
Electrical Code (NEC).
A mounting hardware kit is provided that contains the hardware and fasteners necessary to mount the
access point. Refer to the Table 3-1 to identify the materials you need to mount your access point, then
go to the section containing the specific mounting procedure.
Ta b l e 3-1 Material Needed to Mount Access Point
Mounting Method Materials Required In Kit
Horizontal or vertical surface Four #8 x 1 in. (25.4 mm) screws
Suspended ceiling Two T-rail clips with studs
Mounting on a Horizontal or Vertical Surface
Four wall anchors
3/16 in. (4.7 mm) or 3/32 in. (2.3 mm) drill bit
Drill
Standard screwdriver
Two plastic spacers
Two 1/4–20 Keps nuts with built-in washers
Standard screwdriver
Appropriate wrench or pliers
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
Mounting on a Horizontal or Vertical Surface
Follow these steps to mount the access point on a horizontal or vertical surface.
Step 1 Use the mounting bracket as a template to mark the locations of the four mounting holes.
Step 2 Drill one of the following sized holes at the locations you marked:
• 3/16 in. (4.7 mm) if you are using wall anchors
• 1/8 in. (6.3 mm) if you are not using wall anchors
Step 3 Install the anchors into the wall if you are using them. Otherwise, go to Step 4.
Step 4 Secure the mounting bracket to the surface using the #8 fasteners.
Note On a vertical surface, mount the bracket with its security hasp facing down.
Step 5 Attach the access point to the mounting bracket.
Note You can make your installation more secure by mounting it to a stud or major structural member
and using the appropriate fasteners.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
3-3
Page 42

Mounting Below a Suspended Ceiling
1
2
2
3
5
3
4
5
74121
Mounting Below a Suspended Ceiling
Note To comply with NEC code, a #10-24 grounding lug is provided on the mounting bracket.
Chapter 3 Mounting Instructions
You should review Figu
Figure 3-2 Mounting Bracket Parts
re 3-2 before beginning the mounting process.
1 Suspended ceiling T-rail 4 Mounting bracket
2 T-rail clips 5 Keps nut (contains an attached lock washer)
3 Plastic spacer
Follow these steps to mount your access point on a suspended ceiling:
Step 1 Decide where you want to mount the access point.
Step 2 Attach two T-rail clips to the suspended ceiling T-rail.
Step 3 Use the mounting bracket to adjust the distance between the T-rail clips so that they align with the holes
in the mounting bracket.
Step 4 Use a standard screwdriver to tighten the T-rail clip studs in place on the suspended ceiling T-rail. Do
not overtighten.
Step 5 Install a plastic spacer on each T-rail clip stud. The spacer’s legs should contact the suspended ceiling
T-rail.
Step 6 Attach the mounting bracket to the T-rail clip studs and start a Keps nut on each stud.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
3-4
OL-8370-04
Page 43

Chapter 3 Mounting Instructions
Step 7 Use a wrench or pliers to tighten the Keps nuts. Do not overtighten.
Step 8 Attach the access point to the mounting bracket.
Mounting Above a Suspended Ceiling
The access point uses a metal enclosure having adequate fire resistance and low smoke-producing
characteristics suitable for operation in a building’s environmental air space (such as above suspended
ceilings) in accordance with Section 300-22(c) of the NEC.
Caution Only the fiber-optic power injector (AIR-PWRINJ-FIB) has been tested to UL 2043 for operation in a
building’s environmental air space; no other power injectors or power modules have been tested to UL 2043
and they should not be placed in a building’s environmental air space, such as above suspended ceilings.
Mounting Above a Suspended Ceiling
Note If you plan to mount the access point with a 5-GHz radio in environmental air space, Cisco recommends
that you mount the access point horizontally with its antennas pointing down. Doing so will result in the
access point complying with regulatory requirements for environmental air space with the 5-GHz radio
installed.
The access point mounting bracket is designed to be integrated into the T-bar grid above the tiles of a
suspended ceiling. Using a T-bar box hanger and bracket mounting clip (not supplied) such as the
Erico 512A and BHC, you orient the access point antenna just above the top surface of a standard ceiling
le. You may need to modify a thicker tile to allow room for the antenna.
ti
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
3-5
Page 44

Mounting Above a Suspended Ceiling
95740
4
5
6
7
3
3
1
2
2
1
95748
1
1
It may be helpful to refer to Figure 3-3 before proceeding.
Figure 3-3 Mounting Bracket Parts
Chapter 3 Mounting Instructions
1
Suspended ceiling T-rail
2
T-rail clip
3
Height adjustment screw
4
T-bar box hanger
5
Bracket mounting clip
6
Access point mounting bracket
7
Access point
The bracket mounting clip requires the use of an access point mounting bracket (700-13520-03) with
two extra holes (see Figure 3-4).
Figure 3-4 Mounting Bracket Holes
1 Extra holes
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
3-6
OL-8370-04
Page 45

Chapter 3 Mounting Instructions
Follow these steps to mount the access point above a suspended ceiling.
Step 1 Insert the bracket mounting clip’s tab into the large hole on the access point mounting bracket.
Step 2 Place the clip over the T-bar box hanger and secure it to the access point mounting bracket (see
Figure 3-5) with the 1/4-20 fastener (supplied with the T-bar hanger).
Figure 3-5 Access Point Mounting Bracket
Mounting Above a Suspended Ceiling
Note The illustration shows the access point mounting bracket mounted perpendicular to the T-bar box
hanger. You can also mount the bracket parallel to the T-bar box hanger.
Step 3 Determine the location in the ceiling where you will mount the access point and remove an adjacent
ceiling tile.
Step 4 Orient the access point 2-GHz antennas so that they are pointing down when mounted on the T-bar Box
hanger. Orient the 5-GHz antenna for patch or omnidirectional operation as desired.
Step 5 Adjust the height of the T-bar box hanger to provide antenna clearance above the ceiling tile using the
height adjusting screws (refer to Figure 3-3).
Step 6 Attach the T-rail clips on each end of the T-bar box hanger to the ceiling grid T-rails. Make sure the clips
are securely attached to the T-rails.
Step 7 Connect a drop wire to a building structural element and through the hole provided in the bracket
mounting clip. This additional support is required in order to comply with the U.S. National Electrical
Safety Code.
Step 8 Attach the access point to the access point mounting bracket (refer to the “Attaching the Access Point to
the Mounting Bracket” section.
Step 9 Connect the Ethernet cables to the access point.
Step 10 If you need additional security, you can secure the access point to a nearby immovable object using a
Kensington lock and security cable.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
3-7
Page 46

Chapter 3 Mounting Instructions
Attaching the Access Point to the Mounting Bracket
Step 11 Verify that the access point is operating before replacing the ceiling tile.
Attaching the Access Point to the Mounting Bracket
Follow these steps to attach the access point to the mounting bracket:
Step 1 Line up the three mounting pins on the access point with the large ends of the keyhole-shaped holes on
the mounting bracket.
Step 2 Insert the access point into the keyhole shaped holes and maintain a slight pressure to hold it in place.
Step 3 Slide the access point’s mounting pins into the small ends of the keyhole-shaped holes on the mounting
bracket and push the connector end of the access point. You will hear a click when the locking detent
contacts the access point and locks it into place.
Step 4 Attach and adjust the antenna(s) or antenna cables.
Step 5 Connect the Ethernet cable to the access point’s Ethernet port.
Step 6 If using local power, insert the 1200 series power module cable connector into the access point’s 48-VDC
power port.
Securing the Access Point to the Mounting Bracket
The security hasp on the mounting bracket enables you to lock the access point to the bracket to make it
more secure. When the access point is properly installed on the mounting bracket, the holes in the
security hasps line up so you can install a padlock.
Known compatible padlocks are Master Lock models 120T or 121T.
3-8
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 47

CHA PTER
4
Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio
This chapter provides instructions for upgrading the 2.4-GHz (IEEE 802.11g) radio card and includes
the following sections:
• Upgrade Overview, page 4-2
• Unpacking the Radio, page 4-2
• Opening the Access Cover, page 4-3
• Removing a Blank Spacer Card, page 4-4
• Removing a 2.4-GHz Radio, page 4-5
• Installing a 2.4-GHz Radio, page 4-7
• Attaching the Compliance Labels, page 4-9
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
4-1
Page 48

Upgrade Overview
Upgrade Overview
This section provides instructions for upgrading the access point 2.4-GHz radio. The following
operations summarize the upgrade procedure:
1. Remove all cables and power connections from the access point.
2. Follow standard electrostatic discharge (ESD) procedures.
3. Place the access point on an ESD-protected work surface.
4. Open the access point’s 2.4-GHz radio access cover.
5. For an access point without a 2.4-GHz radio feature, remove the blank spacer card.
6. For an access point with a 2.4-GHz radio feature, remove the existing 2.4-GHz radio card.
7. Install the new 2.4-GHz radio card.
8. Close the access point 2.4-GHz radio access cover.
Caution ESD can damage the Cisco Aironet radio and the internal components of the access point. It is
recommended that the 2.4-GHz radio upgrade procedures be performed by an ESD-trained service
technician at an ESD-protected workstation.
Chapter 4 Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio
Unpacking the Radio
Each 2.4-GHz radio is shipped with the following items:
• Quick start guide
• A product registration card
• A T-10 tamper-resistant Torx L-wrench
• A 1200 series access point 2.4-GHz radio compliance label
Note The IEEE 802.11g radio also contains an1100 series access point product compliance label (not needed
for a 1200 series access point) and a 1200 series access point product compliance label.
If anything is missing or damaged, contact your Cisco representative for support.
4-2
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 49

Chapter 4 Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio
1
74458
Opening the Access Cover
To open the 2.4-GHz radio access cover, follow these steps:
Step 1 Remove all cables and power connections from the access point.
Step 2 Remove all static-generating items from the work area, such as plastic material, styrofoam cups, and
other similar items.
Step 3 Place the access point and the new 2.4-GHz radio (in its antistatic bag) on an antistatic work surface.
Step 4 Discharge any static buildup on your body by touching a grounded surface (antistatic work surface)
before proceeding.
Step 5 Position the access point so that the bottom cover is facing up.
Caution The internal access point components and the 2.4-GHz radio can be damaged by ESD from improper
handling.
Step 6 Remove the bottom access cover using the T-10 tamper-resistant Torx L-wrench provided with your
Cisco radio card (see Figure 4-1).
Opening the Access Cover
Figure 4-1 Location of 2.4-GHz Radio Access Cover Screw
1 Access Cover Screw
If your access point was not configured with a 2.4-GHz radio, go to the “Removing a Blank Spacer Card”
section. If you are replacing an existing 2.4-GHz radio, go to the “Removing a 2.4-GHz Radio” section.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
4-3
Page 50

Removing a Blank Spacer Card
74248
1 3 12
Removing a Blank Spacer Card
When your access point is not factory-configured with a 2.4-GHz radio, it contains a blank spacer card
in the internal mini-PCI connector. You must remove the blank spacer card prior to installing a new
2.4-GHz radio card.
Caution Handle all components carefully and observe all ESD precautions. The internal access point components
and the 2.4-GHz radio can be damaged by ESD from improper handling.
To remove the blank spacer card from the mini-PCI connector, following these steps:
Step 1 Push the card-retaining clips (on each side of card) away from the card (see Figure 4-2). When released,
the board springs up.
Figure 4-2 Location of Retaining Clips on Blank Spacer Card
Chapter 4 Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio
1 Card-retaining clips 3 Antenna connector (black wire)
2 Antenna connector (white wire)
Step 2 Carefully bend the card near the slots in opposite directions to provide enough clearance to remove the
antenna wires.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
4-4
OL-8370-04
Page 51

Chapter 4 Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio
Step 3 Remove the antenna wires from the blank spacer card.
Caution To avoid damaging the antenna wire assemblies, handle them by their connectors.
Step 4 Remove the blank spacer card from the mini-PCI connector.
For instructions on installing the radio card, go to the “I
Removing a 2.4-GHz Radio
To remove a 2.4-GHz radio card from your access point, follow these steps:
Caution The internal access point components and the 2.4-GHz radio can be damaged by ESD from improper
handling.
Removing a 2.4-GHz Radio
nstalling a 2.4-GHz Radio” section.
Step 1 Use your fingers to carefully remove the antenna wire connectors from the 2.4-GHz radio card.
Caution The antenna connectors can be damaged by using a pair of long-nose pliers during the removal
process.
Caution To avoid damaging the antenna wire assemblies, handle them by their connectors.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
4-5
Page 52

Removing a 2.4-GHz Radio
MAIN AUX
74253
1 1
Step 2 Remove the 2.4-GHz radio card from the mini-PCI connector by performing the following operations:
Chapter 4 Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio
a. Push the card-retaining clips (on each side of card) away from the card (see Figure 4-3). When
released, the radio card springs up (see Figure 4-4).
Figure 4-3 Location of Retaining Clips on 2.4-GHz Radio Card
1 Card-retaining clips
b. Grasp the radio card only on the edges, being careful not to touch components on the board or the
gold connector pins.
c. Remove the 2.4-GHz card from the mini-PCI connector.
Step 3 Place the removed 2.4GHz radio card into an anti-static bag.
For instructions on installing a new radio card, go to the “
Installing a 2.4-GHz Radio” section.
4-6
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 53

Chapter 4 Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio
MAIN AU X
74251
3
2
1
Installing a 2.4-GHz Radio
To install a new 2.4-GHz radio card into the access point, follow these steps:
Caution The internal access point components and the 2.4-GHz radio can be damaged by ESD from improper
handling.
Step 1 Carefully remove the Cisco Aironet 2.4-GHz radio card from its anti-static bag.
Step 2 Grasp the radio card only on the edges, being careful not to touch components on the board or the gold
connector pins.
Step 3 Connect the black antenna wire connector to the radio card antenna connector marked by the black label
(see Figure 4-4).
Caution To avoid damaging the antenna wire assemblies, handle them by their connectors.
Installing a 2.4-GHz Radio
Figure 4-4 Antenna Connector Labels and Mini-PCI Connector
OL-8370-04
1 Antenna connector (black wire) 3 Mini-PCI connector
2 Antenna connector (white wire)
Step 4 Connect the white antenna wire connector to the radio card antenna connector marked by the white label
(see Figure 4-4).
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
4-7
Page 54

Installing a 2.4-GHz Radio
Step 5 Insert the radio card into the access point’s mini-PCI connector by following these steps:
Step 6 Carefully push the card down (towards the access point’s motherboard) until the card-retaining clips lock
Step 7 Carefully position the antenna wires so that the metal connectors do not touch each other.
Caution Do not allow antenna connectors to touch while power is applied, or the radio can be damaged. If they
Step 8 Reinstall the 2.4-GHz radio access cover and use the T-10 tamper-resistant Torx L-wrench to tighten the
Step 9 Look at the compliance labels on your access point. Depending on the model you originally ordered,
Chapter 4 Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio
a. Tilt the radio card at approximately 20
connector (see Figure 4-4).
b. Push the card into the mini-PCI connector until it clicks into place.
into the notches on the side of the radio card (you will hear a click).
are touching, carefully rotate them in opposite directions until they are separated.
cover’s retaining screw.
there may be up to three labels affixed to the case.
o
to 30o so that its gold pins are aligned with the mini-PCI
4-8
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 55

Chapter 4 Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio
1
2
3
103640
Attaching the Compliance Labels
There are three places on the 1200 series access point dedicated to compliance labels, one for the product
compliance label and two for the radio compliance labels. The label locations are shown in Figure 4-5.
Figure 4-5 Access Point Compliance Labels
Attaching the Compliance Labels
OL-8370-04
1 Product compliance label 3 Radio compliance label
2 Radio compliance label
The product compliance label always occupies the top space (location 1). The two spaces below
(locations 2 and 3) contain the radio compliance labels. Whether or not locations 2 or 3 contain labels
depends on how your access point is configured. For example, a dual-band access point could have two
radio compliance labels (one for each radio device installed), or it could have only a product compliance
label, depending on how it was ordered.
Make sure that your access point has the correct labels after you install or upgrade its radio configuration
hat it will be in compliance with regulations in your country.
so t
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
4-9
Page 56

Attaching the Compliance Labels
Placing the Labels
The 802.11g radio upgrade kit ships with the following labels for the 1100 and 1200 series access points:
• 1100 series access point upgrade label (AIR-1121G-x-K9 UPGRADE)—not used on the 1200 series
access point.
• 1200 series product compliance label (AIR-AP1231G-x-K9)
• 1200 series radio compliance label (AIR-MP21G-x-K9)
Chapter 4 Upgrading the 2.4-GHz Radio
Table 4-1
shows where to place the labels on your 1200 series access point, based on the model you are
upgrading. Follow these steps to place the labels correctly:
Step 1 Check the product compliance label to identify the model number of your 1200 series access point.
Step 2 Use the matrix in Table 4-1 to decide which labels to use and where to place them on the access point.
Ta b l e 4-1
1200 Series
Model
AIR-AP1200 Place over existing AIR-MP20B-x-K9
AIR-AP1210
AIR-MP21G-x-K9
Radio Compliance Label
adio compliance label or location 2 if no
r
label exists.
AIR-AP1231G-x-K9 Product
Compliance Label
—
AIR-AP1220A
AIR-AP1230A
AIR-AP1220B — Place over existing AIR-AP12xx-x-K9
roduct compliance label.
AIR-AP1230B
Step 3 Discard any labels that you did not use.
p
The radio card installation is now complete.
4-10
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 57

CHA PTER
5
Upgrading the 5-GHz Radio Module
This chapter provides instructions for upgrading a 5-GHz radio module and includes the following
sections:
• Upgrade Overview, page 5-2
• Removing the 5-GHz Radio Access Cover, page 5-2
• Removing a 5-GHz Radio Module, page 5-3
• Installing a 5-GHz Radio Module, page 5-5
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
5-1
Page 58

Upgrade Overview
Upgrade Overview
This section provides instructions for upgrading the access point 5-GHz radio module (RM21A or
RM22A). The following operations summarize the upgrade procedure:
1. Remove all cables and power connections from the access point.
2. Place your access point on a flat surface.
3. For an access point without the 5-GHz radio feature, remove the 5-GHz radio access cover.
4. For an access point with the 5-GHz radio feature, remove the existing 5-GHz radio module.
5. Install the new 5-GHz radio module.
Unpacking the Radio Module
Each 5-GHz radio module is shipped with the following items:
• Quick start guide
• A product registration card
Chapter 5 Upgrading the 5-GHz Radio Module
• A T-10 tamper-resistant Torx L-wrench
• A 5-GHz radio compliance label
• A product compliance label (supplied with RM21A and RM22A radio modules)
If anything is missing or damaged, contact your Cisco representative for support.
Removing the 5-GHz Radio Access Cover
On access points without an installed 5-GHz radio module, you must remove the access cover that covers
the 5-GHz radio slot. To remove the 5-GHz radio access cover, follow these steps:
Step 1 Remove all cables and power connections from the access point.
Step 2 Place the access point on a flat surface so that the unit is upright with the front end facing you.
5-2
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 59

Chapter 5 Upgrading the 5-GHz Radio Module
1 12
74632
74631
1 1 2 3
Step 3 Remove the 5-GHz access cover using the supplied Torx L-wrench (see Figure 5-1).
Figure 5-1 5-GHz Radio Access Cover
1 Access Cover Screws 2 Access Cover
Removing a 5-GHz Radio Module
Removing a 5-GHz Radio Module
To remove the 5-GHz radio module, follow these steps:
Step 1 Remove all cables and power connections from the access point.
Step 2 Place the access point on a flat surface so that the unit is upright with the front end facing you.
Step 3 Unscrew the two mounting screws using the supplied Torx L-wrench (Figure 5-2).
Figure 5-2 5-GHz Radio Module
1 Mounting screws 3 Access point
2 5-GHz radio module antenna
OL-8370-04
Note Do not attempt to remove the mounting screws from the module; they are captured in the module
housing.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
5-3
Page 60

Removing a 5-GHz Radio Module
74629
Step 4 Insert your fingers into the base (latch opening) of the 5-GHz radio module (closest to the access point)
and pull straight out from the access point (see Figure 5-3).
Figure 5-3 Removing the 5-GHz Radio Module
Chapter 5 Upgrading the 5-GHz Radio Module
Step 5 For a radio module with built-in antenna, fold the antenna down (towards the attached radio card) and
insert the module into a static protected bag.
Step 6 For a radio module with connectors, insert the radio module into a static protected bag.
To install a new 5-GHz radio module, see the “
Installing a 5-GHz Radio Module” section on page 5-5.
5-4
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 61

Chapter 5 Upgrading the 5-GHz Radio Module
74604
21
3 4
Installing a 5-GHz Radio Module
To install a new 5-GHz radio module (RM21A or RM22A) into your access point, follow these steps:
Step 1 Before you can install a new 5-GHz radio module, you must remove the access cover or an existing
5-GHz radio module (refer to “Removing the 5-GHz Radio Access Cover” or “Removing a 5-GHz Radio
Module”).
Step 2 Place the access point on a flat surface so that the unit is upright with the front end facing you.
Step 3 Grasp the new 5-GHz radio module by its base (with the latch opening point down or the antenna
pointing up) and insert the card into the access point’s card-bus slot (see Figure 5-4).
Figure 5-4 Installing a 5-GHz Radio Module (RM20A or RM21A Shown)
Installing a 5-GHz Radio Module
OL-8370-04
1 Access point 3 Access point card-bus slot
2 5-GHz radio module antenna 4 5-GHz radio card
Step 4 Push the 5-GHz radio module into the slot until you hear a slight click.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
5-5
Page 62

Installing a 5-GHz Radio Module
2 2
1
74630
Step 5 Tighten the 5-GHz radio module mounting screws using the supplied Torx L-wrench (see Figure 5-5).
Figure 5-5 Location of Mounting Screws (RM21A) Shown)
Chapter 5 Upgrading the 5-GHz Radio Module
5-6
1 5-GHz radio module antenna 2 Mounting screws
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 63

Chapter 5 Upgrading the 5-GHz Radio Module
1
2
3
103640
Attaching the Compliance Label
There are three places on the 1200 series access point dedicated to compliance labels, one for the product
compliance label and two for the radio compliance labels. The label locations are shown in Figure 5-6.
Figure 5-6 Access Point Compliance Label Locations
Installing a 5-GHz Radio Module
OL-8370-04
1 Product compliance label 3 Radio compliance label
2 Radio compliance label
The product compliance label always occupies the top space (location 1). The two spaces below the
product compliance label (locations 2 and 3) contain the radio compliance labels. Whether or not
locations 2 or 3 contain labels depends on how your access point is configured. For example, the access
point could have two radio compliance labels (one for each radio device installed), or the access point
could have only a product compliance label, depending on how it was ordered.
Make sure that your access point has the correct labels after you install or upgrade its radio configuration
hat it will be in compliance with regulations in your country.
so t
The AIR-MR21A and AIR RM22A radio upgrade kits ship with the following labels for the 1200 series
ccess points:
a
• 1200 series product compliance label (AIR-AP1210-x-K9)
• 1200 series radio compliance label (AIR-RM21A-x-K9 or AIR-RM22A-x-K9)
Table 5-1
shows where to place the labels on your 1200 series access point, based on the model you are
upgrading. Follow these steps to place the labels correctly:
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
5-7
Page 64

Installing a 5-GHz Radio Module
Step 1 Check the product compliance label to identify the model number of your 1200 series access point.
Step 2 Refer to Figure 5-6 for the compliance label locations.
Step 3 Use the matrix in Table 5-1 to decide which labels to use and where to place them on the access point.
Ta b l e 5-1 Locations for Compliance Labels
Chapter 5 Upgrading the 5-GHz Radio Module
1200 Series
Model
AIR-RM21A-x-K9 or AIR-RM22A-x-K9
Radio Compliance Label
AIR-AP1220A Place over existing AIR-RM20A-x-K9
adio compliance label or location 3 if no
AIR-AP1230A
r
label exists.
All other models Discard product compliance label.
Step 4 Discard any labels that you did not use.
The 5-GHz radio module installation is now complete and radio settings are at default values. To
nfigure the 5-GHz radio with your wireless network settings refer to the Cisco IOS Software
co
Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points.
AIR-AP1210-x-K9 Product
Compliance Label
Place over existing product compliance
label.
5-8
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 65

CHA PTER
6
Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
This chapter provides troubleshooting procedures for basic problems with the 1200 series autonomous
access point (models: AIR-AP1200, AIR-AP1210, AIR-AP1220B, AIR-AP1230B, AIR-AP1220A,
AIR-AP-1230A, AIR-AP1231G, and AIR-AP1232AG) . For the most up-to-date, detailed
troubleshooting information, refer to the Cisco Technical Support and Documentation website at the
following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/tsd_products_support_category_home.html
Sections in this chapter include:
• Checking the Top Panel LEDs, page 6-2
• Checking Basic Settings, page 6-4
• Resetting to the Default Configuration, page 6-7
• Reloading the Access Point Image, page 6-8
• Obtaining the Access Point Image File, page 6-11
• Obtaining the TFTP Server Software, page 6-12
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
6-1
Page 66

Checking the Top Panel LEDs
Radio
Status
Ethernet
86704
Checking the Top Panel LEDs
If your access point is not communicating, check the three LEDs on the top panel. You can use them to
quickly assess the unit’s status. Figure 6-1 shows the LEDs.
Figure 6-1 Access Point LEDs
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
The LEDs signals have the following meanings (for additional details refer to Table 6-1):
• The Ethernet LED signals traffic on the wired LAN, or Ethernet infrastructure. This LED is
normally green when an Ethernet cable is connected, and blinks green when a packet is received or
transmitted over the Ethernet infrastructure. The LED is off when the Ethernet cable is not
connected.
• The status LED signals operational status. Steady green indicates that the access point is associated
with at least one wireless client. Blinking green indicates that the access point is operating normally
but is not associated with any wireless devices.
• The radio LED blinks green to indicate radio traffic activity. The light is normally off, but it blinks
green whenever a packet is received or transmitted over the access point’s radio.
6-2
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 67

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
Table 6-1 Top Panel LED Signals
Checking the Top Panel LEDs
Message
type
Boot loader
status
Ethernet
LED
Status
LED
Radio
LED
Meaning
Green – Green DRAM memory test.
– Amber Red Board initialization test
– Blinking
green
Blinking
green
Flash memory test.
Amber Green – Ethernet initialization test.
Green Green Green Starting Cisco IOS.
Association
status
Operating
status
– Green – At least one wireless client device is
associated with the unit.
– Blinking
green
– Green Blinking
– No client devices are associated; check the
unit’s SSID and WEP settings.
Transmitting/receiving radio packets.
green
Green – – Ethernet link is operational.
Blinking
– – Transmitting/receiving Ethernet packets.
green
Boot Loader
Errors
Red – Red DRAM memory test failure.
– Red Red File system failure.
Red Red – Ethernet failure during image recovery.
Amber Green Amber Boot environment error.
Red Green Red No Cisco IOS image file.
Amber Amber Amber Boot failure.
Operation
Errors
– Green Blinking
amber
Blinking
- – Transmit/receive Ethernet errors.
Maximum retries or buffer full occurred on
the radio.
amber
– Blinking
– General warning.
amber
Configuration
Reset
– Amber – Resetting the configuration options to
factory defaults.
Failure Red Red Red Firmware failure; try disconnecting and
reconnecting unit power.
Firmware
– Red – Loading new firmware image.
Upgrade
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
6-3
Page 68

Checking Basic Settings
Checking Basic Settings
Mismatched basic settings are the most common causes of lost connectivity with wireless clients. If the
access point does not communicate with client devices, check the following areas.
Default IP Address Behavior
When you connect a 1200 series access point running Cisco IOS Release 12.3(2)JA or later software with
a default configuration to your LAN, the access point requests an IP address from your DHCP server
and, if it does not receive an IP address, continues to send requests indefinitely.
When you connect a 1200 series access point running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)JA or earlier software
with a default configuration to your LAN, the access point requests an IP address from your DHCP
server and, if it does not receive an IP address, the access point assigns a default IP address of 10.0.0.1
Default SSID and Radio Behavior
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
In Cisco IOS Release 12.3(2)JA and earlier, the access point radio is enabled by default and the default
SSID is tsunami.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)JAand later, the access point radio is disabled by default for security
reasons, and there is no default SSID. You must create an SSID and enable the radio before the access
point will allow wireless associations from other devices. These changes to the default configuration
improve the security of newly installed access points. Refer to the Cisco IOS Software Configuration
Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points for instructions on configuring the SSID and the “Enabling the
Radio Interfaces” section on page 6-4 for instructions on enabling the radio interface.
Enabling the Radio Interfaces
In Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)JA and later, the access point radios are disabled by default, and there is no
default SSID. You must create an SSID and enable the radios before the access point will allow wireless
associations from other devices. These changes to the default configuration improve the security of
newly installed access points. Refer to the Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet
Access Points for instructions on configuring the SSID.
To enable the radio interfaces, follow these instructions:
Step 1 Use your internet browser to access your access point.
Step 2 At the prompt, enter the administrator username and password. The default username is Cisco and the
default password is Cisco. The username and password are case sensitive.
Step 3 When the Summary Status page displays, click Network Interfaces > Radio0-802.11b or Network
Interfaces > Radio0-802.11g and the radio status page displays.
6-4
Step 4 Click Settings and the radio settings page displays.
Step 5 Click Enable in the Enable Radio field and click Apply.
Step 6 Click Radio1-802.11A and the radio status page displays.
Step 7 Repeat Steps 3 and 4.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 69

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
Step 8 Close your internet browser.
SSID
Wireless clients attempting to associate with the access point must use the same SSID as the access point.
If a client device’s SSID does not match the SSID of an access point in radio range, the client device will
not associate. In Cisco IOS Release 12.3(2)JA2 and earlier, the access point default SSID is tsunami.
Note In Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)JA and later, there is no default SSID. You must configure an SSID before
client devices can associate to the access point.
WEP Keys
The WEP key you use to transmit data must be set up exactly the same on your access point and any
wireless devices with which it associates. For example, if you set WEP Key 3 on your client adapter to
0987654321 and select it as the transmit key, you must also set WEP Key 3 on the access point to exactly
the same value. The access point does not need to use Key 3 as its transmit key, however.
Running the Carrier Busy Test
Refer to the Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points for instructions
on setting the access point’s WEP keys.
Security Settings
Wireless clients attempting to authenticate with your access point must support the same security options
configured in the access point, such as EAP or LEAP, MAC address authentication, Message Integrity
Check (MIC), WEP key hashing, and 802.1X protocol versions.
If a wireless client is unable to authenticate with your access point, contact the system administrator for
proper security settings in the client adapter and for the client adapter driver and firmware versions that
are compatible with the access point settings.
Note The access point MAC address that appears on the Status page in the Aironet Client Utility (ACU) is the
MAC address for the access point radio. The MAC address for the access point Ethernet port is printed
on the label on the back of the access point.
Running the Carrier Busy Test
You can use the carrier busy test to find the least congested channel for a radio interface (802.11b/g or
802.11a). You should typically run the test several times to obtain the best results and to avoid temporary
activity spikes.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
6-5
Page 70

Running the Ping or Link Test
Note The carrier busy test is primarily used for a single access point or a bridge environment. For sites with
multiple access points, a site survey is typically performed to determine the best operating locations and
operating frequencies for the access points.
Note All associated clients on the selected radio will be disassociated during the 6 to 8 seconds needed for the
carrier busy test.
Perform these steps to activate the carrier busy test:
Step 1 Use your web browser to open the access point interface.
Note The access point web-browser interface is fully compatible with Microsoft Internet Explorer
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
version 6.0 on Windows 98 and 2000 platforms, and with Netscape version 7.0 on Windows 98,
Windows 2000, and Solaris platforms.
Step 2 At the prompt, enter the administrator username and password. The default username is Cisco and the
default password is Cisco. The username and password are case sensitive.
Step 3 Click Network Interfaces and the Network Interface Summary page appears.
Step 4 Choose the radio interface experiencing problems by clicking Radio0-802.11B or Radio0-802.11G or
Radio1-802.11A. The respective radio status page appears.
Step 5 Click the Carrier Busy Test tab and the Carrier Busy Test screen appears.
Step 6 Click Start to begin the carrier busy test.
When the test completes, the results are displayed on the bottom of the screen. For each of the channel
center frequencies, the test produces a value indicating the percentage of time that the channel is busy.
Running the Ping or Link Test
You can use the ping or link test to evaluate the communication link with an associated wireless device.
With the ping or link test you can:
a. Perform a test using a specified number of packets and then display the test results.
b. Perform a test that continuously operates until you stop it and then display the test results.
Perform these steps to activate the ping or link test:
6-6
Step 1 Use your web browser to open the access point interface.
Note The access point web-browser interface is fully compatible with Microsoft Internet Explorer
version 6.0 on Windows 98 and 2000 platforms, and with Netscape version 7.0 on Windows 98,
Windows 2000, and Solaris platforms.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 71

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
Step 2 At the prompt, enter the administrator username and password. The default username is Cisco and the
default password is Cisco. The username and password are case sensitive.
Step 3 Click Association and the main association page appears.
Step 4 Click the MAC address of an associated wireless device, and the Statistics page for that device appears.
Step 5 Click the Ping/Link Test tab and the Ping/Link Test page appears.
Step 6 If you want to specify the number of packets to use in the test, follow these steps:
a. Enter a number of packets in the Number of Packets field
b. Enter a packet size in the Packet Size field.
c. Click Start. The test automatically stops when all packets are utilized.
Step 7 If you want to use a continuous test, follow these steps:
a. Enter a packet size in the Packet Size field.
b. Click Start to activate the test.
c. Click Stop to stop the test.
When the test stops, the test results are displayed at the bottom of the page. You should check for lost
packets that might indicate a problem with the wireless link. For best results, you should perform this
test several times.
Resetting to the Default Configuration
Resetting to the Default Configuration
If you forget the password that allows you to configure the access point, you may need to completely
reset the configuration. You can use the MODE button on the access point or the web-browser interface.
Note The following steps reset all configuration settings to factory defaults, including passwords, WEP keys,
the IP address, and the SSID.
For additional information on access point default behavior, refer to the “Default IP Address Behavior”
section on page 6-4 and the “Default SSID and Radio Behavior” section on page 6-4.
Using the MODE Button
Follow these steps to delete the current configuration and return all access point settings to the factory
defaults using the MODE button:
Step 1 Disconnect power (the power jack for external power or the Ethernet cable for in-line power) from the
access point.
Step 2 Press and hold the MODE button while you reconnect power to the access point.
Step 3 Hold the MODE button until the Status LED turns amber (approximately 2 to 3 seconds), and release the
button.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
6-7
Page 72

Reloading the Access Point Image
Step 4 After the access point reboots, you must reconfigure the access point by using the Web browser interface,
the Telnet interface, or Cisco IOS commands.
Note The access point is configured with the factory default values including the IP address (set to
receive an IP address using DHCP).
Using the Web Browser Interface
Follow the steps below to delete the current configuration and return all access point settings to the
factory defaults using the web browser interface.
Step 1 Open your Internet browser.
Note The access point web-browser interface is fully compatible with Microsoft Internet Explorer
version 6.0 on Windows 98 and 2000 platforms, and with Netscape version 7.0 on Windows 98,
Windows 2000, and Solaris platforms.
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
Step 2 Enter the access point’s IP address in the browser address line and press Enter. An Enter Network
Password screen appears.
Step 3 At the prompt, enter the administrator username and password. The default username is Cisco and the
default password is Cisco. The username and password are case sensitive. The Summary Status page
appears.
Step 4 Click System Software and the System Software screen appears.
Step 5 Click System Configuration and the System Configuration screen appears.
Step 6 Click the Reset to Defaults button.
Note If the access point is configured with a static IP address, the IP address does not change.
Step 7 After the access point reboots, you must reconfigure the access point by using the Web browser interface,
the Telnet interface, or Cisco IOS commands.
Reloading the Access Point Image
If your access point has a firmware failure, you must reload the complete access point image file using
the Web browser interface or by pressing and holding the MODE button for around 30 seconds. You can
use the browser interface if the access point firmware is still fully operational and you want to upgrade
the firmware image. However, you can use the MODE button when the access point has a corrupt
firmware image.
6-8
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 73

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
Caution Your access point must be running specific Cisco IOS software releases before you upgrade its radios;
otherwise, your access point might not be able to complete the boot sequence until the radio is removed
(see Tab le 6- 3). For additional information, refer to the Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for
Cisco Aironet Access Points.
Table 6-2 Required Cisco IOS Software Release
Radio Upgrade Required Cisco IOS Software Release
IEEE 802.11g 12.2(13)JA or later
RM21A or RM22A 12.3(2)JA or later
Using the MODE button
You can use the MODE button on the access point to reload the access point image file from an active
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server on your network or on a PC connected to the access point
Ethernet port.
Reloading the Access Point Image
Note If your access point experiences a firmware failure or a corrupt firmware image, indicated by three red
LEDs, you must reload the image from a connected TFTP server.
Note This process resets all configuration settings to factory defaults, including passwords, WEP keys, the
access point IP address, and SSIDs.
Follow the steps below to reload the access point image file:
Step 1 The PC you intend to use must be configured with a static IP address in the same subnet as the access
point.
Step 2 Place a copy of the access point image file (such as c1200-k9w7-tar.123-8.JA.tar) into the TFTP server
folder on your PC. For additional information, refer to the “Obtaining the Access Point Image File” and
“Obtaining the TFTP Server Software” sections.
Step 3 Rename the access point image file in the TFTP server folder to c1200-k9w7-tar.default.
Step 4 Activate the TFTP server.
Step 5 Connect the PC to the access point power injector using a Category 5 (CAT5) Ethernet cable.
Step 6 Disconnect power (the power jack for external power or the Ethernet cable for in-line power) from the
access point.
Step 7 Press and hold the MODE button while you reconnect power to the access point.
OL-8370-04
Step 8 Hold the MODE button until the status LED turns red (approximately 20 to 30 seconds), and release the
MODE button.
Step 9 Wait until the access point reboots as indicated by all LEDs turning green followed by the status LED
blinking green.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
6-9
Page 74

Reloading the Access Point Image
Step 10 After the access point reboots, you must reconfigure the access point by using the Web interface, the
Telnet interface, or Cisco IOS commands.
Web Browser Interface
You can also use the Web browser interface to reload the access point image file. The Web browser
interface supports loading the image file using HTTP or TFTP interfaces.
Note Your access point configuration is not changed when using the browser to reload the image file.
Browser HTTP Interface
The HTTP interface enables you to browse to the access point image file on your PC and download the
image to the access point. Follow the instructions below to use the HTTP interface:
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
Step 1 Open your Internet browser.
Note The access point web-browser interface is fully compatible with Microsoft Internet Explorer
version 6.0 on Windows 98 and 2000 platforms, and with Netscape version 7.0 on Windows 98,
Windows 2000, and Solaris platforms.
Step 2 Enter the access point’s IP address in the browser address line and press Enter. An Enter Network
Password screen appears.
Step 3 At the prompt, enter the administrator username and password. The default username is Cisco and the
default password is Cisco. The username and password are case sensitive. The Summary Status page
appears.
Step 4 Click the System Software tab and then click Software Upgrade. The HTTP Upgrade screen appears.
Step 5 Click the Browse button to locate the access point image file (such as c1200-k9w7-tar.123-8.JA.tar) on
your PC.
Step 6 Click the Upload button.
For additional information, click the Help icon on the Software Upgrade screen.
6-10
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 75

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
Browser TFTP Interface
The TFTP interface allows you to use a TFTP server on a network device to load the access point image
file. Follow the instructions below to use a TFTP server:
Step 1 Open your Internet browser.
Note The access point web-browser interface is fully compatible with Microsoft Internet Explorer
version 6.0 on Windows 98 and 2000 platforms, and with Netscape version 7.0 on Windows 98,
Windows 2000, and Solaris platforms.
Step 2 Enter the access point’s IP address in the browser address line and press Enter. An Enter Network
Password screen appears.
Step 3 At the prompt, enter the administrator username and password. The default username is Cisco and the
default password is Cisco. The username and password are case sensitive. The Summary Status page
appears.
Step 4 Click the System Software tab and then click Software Upgrade. The HTTP Upgrade screen appears.
Obtaining the Access Point Image File
Step 5 Click the TFTP Upgrade tab.
Step 6 Enter the IP address for the TFTP server in the TFTP Server field.
Step 7 Enter the file name for the access point image file (such as c1200-k9w7-tar.123-8.JA.tar) in the Upload
New System Image Tar File field. If the file is located in a subdirectory of the TFTP server root directory,
include the relative path of the TFTP server root directory with the filename. If the file is located in the
TFTP root directory, enter only the filename.
Step 8 Click the Upload button.
Step 9 When a message appears that indicates the upgrade is complete, click OK.
For additional information click the Help icon on the Software Upgrade screen.
Obtaining the Access Point Image File
Caution Your access point must be running specific Cisco IOS software releases before you upgrade its radios;
otherwise your access point might not be able to complete the boot sequence until the radio is removed
(see Tab le 6- 3). For additional information, refer to the Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for
Cisco Aironet Access Points.
OL-8370-04
Table 6-3 Required Cisco IOS Software Release
Radio Upgrade Required Cisco IOS Software Release
IEEE 802.11g 12.2(13)JA or later
RM21A or RM22A 12.3(2)JA or later
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
6-11
Page 76

Obtaining the TFTP Server Software
The access point image file can be obtained from the Cisco.com software center using these steps:
Note To download software from the Cisco.com software center, you must be a registered user. You can
register from the main Cisco.com web page at this URL: http://cisco.com.
Step 1 Use your Internet browser to access the Cisco Software Center at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/index.shtml
Step 2 Click Wireless LAN Access > Aironet Access Points > Cisco Aironet 1200 Series > Cisco Aironet
1200 Access Point. The Enter Password window appears.
Step 3 Enter your username and password in the respective fields and click OK. The Select a Software Type
page appears.
Step 4 Click IOS and the Select a Release page appears.
Step 5 Click on the IOS release for the desired access point image file, such as 12.3(8)JA.
Step 6 Click Wireless LAN and the Enter Password window appears.
Step 7 Enter your username and password in the respective fields and click OK.
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
Step 8 If you receive a Do you want to display the nonsecure items? message, click Ye s.
Step 9 On the Encryption Software Export Distribution Authorization Form, read the information and click the
appropriate box.
Step 10 Click Submit.
Step 11 If you indicated that the software is not for you or your company, follow these steps:
a. If you receive a Do you want to display the nonsecure items? message, click Ye s. The Encryption
Software Export Distribution Authorization window appears.
b. Carefully read the information and enter the Cisco.com user profile or detailed data describing the end
user of this software image in the provided fields.
c. Click Submit.
Step 12 If you receive a Do you wish to continue? security alert message, click Ye s to continue.
Step 13 Click Download.
Step 14 Carefully read the Software Download Rules and click Agree to download the image file. An Enter
Password window appears.
Step 15 Enter your username and password in the respective fields and click OK.
Step 16 Download and save the image file to your hard drive and then exit the Internet browser.
Obtaining the TFTP Server Software
You can download TFTP server software from several web sites. Cisco recommends the shareware TFTP
utility available at this URL:
http://tftpd32.jounin.net
Follow the instructions on the website for installing and using the utility.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
6-12
OL-8370-04
Page 77

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
RJ-45 serial
connector
DB-9 to RJ-45
serial cable
74005
Connecting to the Access Point Locally
The console port is enabled during power up for diagnostic and monitoring purposes, which might be
helpful if the access point is unable to associate to a controller. You can connect a PC to the console port
using a DB-9 to RJ-45 serial cable.
Step 1 Connect a nine-pin, female DB-9 to RJ-45 serial cable to the RJ-45 serial port on the access point and
to the COM port on a computer. Figure 6-2 shows the serial port connection.
Figure 6-2 Connecting the Serial Cable
Connecting to the Access Point Locally
Note The Cisco part number for the DB-9 to RJ-45 serial cable is AIR-CONCAB1200. Browse to
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace to order a serial cable.
Step 2 Set up a terminal emulator to communicate with the access point. Use the following settings for the
terminal emulator connection: 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, and no flow control.
Note When your monitoring and diagnostic activities are completed, you must remove the serial cable
from the access point.
Step 3 At the prompts, enter the administrator username and password. The default username is Cisco and the
default password is Cisco. The username and password are case sensitive.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
6-13
Page 78

Connecting to the Access Point Locally
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Autonomous Access Points
6-14
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 79

CHA PTER
7
Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points
This chapter provides troubleshooting procedures for basic problems with the 1200 series lightweight
access point (models: AIR-LAP1231G and AIR-LAP1232AG). For the most up-to-date, detailed
troubleshooting information, refer to the Cisco Technical Support and Documentation website at the
following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/tsd_products_support_category_home.html
Sections in this chapter include:
• Guidelines for Using 1200 Series Lightweight Access Points, page 7-2
• Checking the Top Panel LEDs, page 7-3
• Returning the Access Point to Autonomous Mode, page 7-6
• Returning the Access Point to Autonomous Mode, page 7-6
• Obtaining the Autonomous Access Point Image File, page 7-8
• Obtaining the TFTP Server Software, page 7-9
• Connecting to the Access Point Locally, page 7-9
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
7-1
Page 80

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points
Guidelines for Using 1200 Series Lightweight Access Points
Guidelines for Using 1200 Series Lightweight Access Points
Keep these guidelines in mind when you use a 1200 series lightweight access point:
• The access points can only communicate with 2006 series or 4400 series controllers.
Note Cisco 4100 series, Airespace 4012 series, and Airespace 4024 series controllers are not
supported because they lack the memory required to support access points running Cisco
IOS software.
• The access points do not support Wireless Domain Services (WDS) and cannot communicate with
WDS devices. However, the controller provides functionality equivalent to WDS when the access
point associates to it.
• The access points support eight Basic Service Set Identifiers (BSSIDs) per radio and a total of eight
wireless LANs per access point. When a lightweight access point associates to a controller, only
wireless LANs with IDs 1 through 8 are pushed to the access point.
• The access points do not support Layer 2 LWAPP. They must get an IP address and discover the
controller using DHCP, DNS, or IP subnet broadcast.
• The access point console port is enabled for monitoring and debug purposes (all configuration
commands are disabled when associated with a controller).
Using DHCP Option 43
You can use DHCP Option 43 to provide a list of controller IP addresses to the access points, enabling
the access point to find and join a controller. For additional information, refer to the Appendix G,
“Configuring DHCP Option 43 for Lightweight Access Points.”
7-2
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 81

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points
Radio
Status
Ethernet
86704
Checking the Top Panel LEDs
If your access point is not communicating, check the three LEDs on the top panel. You can use them to
quickly assess the unit’s status. Figure 7-1 shows the LEDs.
Figure 7-1 Access Point LEDs
Checking the Top Panel LEDs
The LEDs signals have the following meanings (for additional details refer to Table 7-1):
• The Ethernet LED signals traffic on the wired LAN, or Ethernet infrastructure. This LED is
normally green when an Ethernet cable is connected, and blinks green when a packet is received or
transmitted over the Ethernet infrastructure. The LED is off when the Ethernet cable is not
connected.
• The status LED signals operational status. Steady green indicates that the access point is associated
with at least one wireless client. Blinking green indicates that the access point is operating normally
but is not associated with any wireless devices.
• The radio LED blinks green to indicate radio traffic activity. The light is normally off, but it blinks
green whenever a packet is received or transmitted over the access point’s radio.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
7-3
Page 82

Checking the Top Panel LEDs
Table 7-1 Top Panel LED Signals
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points
Message
type
Boot loader
status
Ethernet
LED
Status
LED
Radio
LED Meaning
Green – Green DRAM memory test.
– Amber Red Board initialization test
– Blinking green Blinking green Flash memory test.
Amber Green – Ethernet initialization test.
Green Green Green Starting Cisco IOS.
Association
status
– Green – At least one wireless client device is associated with the
unit.
– Blinking green – No client devices are associated; check the unit’s SSID
and WEP settings.
Operating
status
– Green Blinking green Transmitting/receiving radio packets.
Green – – Ethernet link is operational.
Blinking green – – Transmitting/receiving Ethernet packets.
Boot Loader
Errors
Red – Red DRAM memory test failure.
– Red Red File system failure.
Red Red – Ethernet failure during image recovery.
Amber Green Amber Boot environment error.
Red Green Red No Cisco IOS image file.
Amber Amber Amber Boot failure.
Operation
Errors
– Green Blinking amber Maximum retries or buffer full occurred on the radio.
Blinking amber - – Transmit/receive Ethernet errors.
– Blinking amber – General warning.
Configuration
– Amber – Resetting the configuration options to factory defaults.
Reset
Failure Red Red Red Firmware failure; try disconnecting and reconnecting
unit power.
Firmware
– Red – Loading new firmware image.
Upgrade
Controller
status
Alternating green, red , and amber
1
Connecting to the wireless LAN controller.
Note If the access point remains in this mode for
more than five minutes, the access point is
unable to find the controller. Ensure a DHCP
server is available or that controller information
is configured on the access point.
1. This status indication has the highest priority and overrides other status indications.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
7-4
OL-8370-04
Page 83

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points
Manually Configuring Controller Information Using the Access Point CLI
Manually Configuring Controller Information Using the Access
Point CLI
In a new installation, when your access point is unable to reach a DHCP server, you can manually
configure needed controller information using the access point CLI. For information on how to connect
to the console port, see the “Connecting to the Access Point Locally” section on page 7-9.
Note The CLI commands in this section can be used only on an access point that is not associated to a
controller.
The static information configured with the CLI commands are used by the access point to connect with
a controller. After connecting with the controller, the controller reconfigures the access point with new
controller settings, but the static IP addresses for the access point and the default gateway are not
changed.
Configuring Controller Information
To manually configure controller information on a new (out-of -the-box) access point using the access
point CLI interface, you can use these EXEC mode CLI commands:
AP# lwapp ap ip address <
AP# lwapp ip default-gateway
AP# lwapp controller ip address
AP# lwapp ap hostname
Where
name
is the access point name on the controller.
Note The default (out-of-box) Enable password is Cisco.
IP address
name
> <
IP-address
IP-address
subnet mask
Clearing Manually Entered Controller Information
When you move your access point to a different location in your network, you must clear the manually
entered controller information to allow your access point to associate with a different controller.
Note This command requires the controller configured Enable password to enter the CLI EXEC mode.
To clear or remove the manually entered controller information, you can use these EXEC mode CLI
commands:
clear lwapp ap ip address
clear lwapp ip default-gateway
clear lwapp controller ip address
clear lwapp ap hostname
>
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
7-5
Page 84

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points
Returning the Access Point to Autonomous Mode
Manually Resetting the Access Point to Defaults
You can manually reset your access point to default settings using this EXEC mode CLI command:
Note This command requires the controller configured Enable password to enter the CLI EXEC mode.
clear lwapp private-config
Returning the Access Point to Autonomous Mode
You can return a lightweight access point to autonomous mode by loading a Cisco IOS release that
supports autonomous mode (such as Cisco IOS Release 12.3(8)JA or earlier). If the access point is
associated to a controller, you can use the controller to load the Cisco IOS release. If the access point is
not associated to a controller, you can load the Cisco IOS release using TFTP.
Using a Controller to Return the Access Point to Autonomous Mode
Follow these steps to return a lightweight access point to autonomous mode using a controller:
Step 1 Log into the CLI on the controller to which the access point is associated and enter this command:
config ap tftp-downgrade
(where:
tftp-server-ip-address
a)
filename
b)
D:/Images/
access-point-name
c)
gondolier.)
Step 2 Wait until the access point completes the reboot, as indicated by the Status LED turning green to indicate
a client is associated or blinking green to indicate a client is not associated.
Step 3 After the access point reboots, reconfigure it using the access point GUI or the CLI.
tftp-server-ip-address filename access-point-name
is the full path and filename of the access point image file, such as
c1200-k9w7-tar.123-8.JA.ta
is the IP address of the TFTP server
r
is the name that identifies the access point on the
7-6
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 85

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points
Returning the Access Point to Autonomous Mode
Using the MODE Button to Return the Access Point to Autonomous Mode
Follow these steps to return a lightweight access point to autonomous mode using the access point MODE
button and a TFTP server:
Note The access point MODE button is enabled by default, but you need to verify that the MODE button is
enabled (see the “MODE Button Setting” section on page 7-7).
Step 1 Set the static IP address of the PC on which your TFTP server software runs to an address between
10.0.0.2 and 10.0.0.30.
Step 2 Make sure that the PC contains the access point image file (such as c1200-k9w7-tar.123-8.JA.tar for a
1200 series access point) in the TFTP server folder and that the TFTP server is activated.
Step 3 Rename the access point image file in the TFTP server folder to c1200-k9w7-tar.default.
Step 4 Connect the PC to the access point using a Category 5 (CAT5) Ethernet cable.
Step 5 Disconnect power from the access point.
Step 6 Press and hold the MODE button while you reconnect power to the access point.
Step 7 Hold the MODE button until the Radio LED turns red (approximately 20 to 30 seconds) and then
release.
Step 8 Wait until the access point reboots, as indicated by all LEDs turning green followed by the Status LED
blinking green.
Step 9 After the access point reboots, reconfigure it using the access point GUI or the CLI.
MODE Button Setting
The access point MODE button is configured from your controller. Use these controller CLI commands
to view and configure the MODE button:
1) config ap rst-button enable <
2) config ap rst-button disable <
3) show ap config general <
(Where access-point-name
oontroller.)
access-point-name
access-point-name
access-point-name
is the name that identifies the access point on the
>/all
>/all
>
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
7-7
Page 86

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points
Obtaining the Autonomous Access Point Image File
Obtaining the Autonomous Access Point Image File
The autonomous access point image file can be obtained from the Cisco.com software center using these
steps:
Note To download software from the Cisco.com software center, you must be a registered user. You can
register from the main Cisco.com web page at this URL: http://cisco.com.
Step 1 Use your Internet browser to access the Cisco Software Center at the following URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/support/downloads/pub/MDFTree.x?butype=wireless
Step 2 Click Wireless LAN Access > Aironet Access Points > Cisco Aironet 1200 Series > Cisco Aironet
1200 Access Point. The Enter Password window appears.
Step 3 Enter your username and password in the respective fields and click OK. The Select a Software Type
page appears.
Step 4 Click IOS and the Select a Release page appears.
Step 5 Click on the IOS release for the desired access point image file, such as 12.3(8)JA.
Step 6 Click Wireless LAN and the Enter Password window appears.
Step 7 Enter your username and password in the respective fields and click OK.
Step 8 If you receive a Do you want to display the nonsecure items? message, click Ye s.
Step 9 On the Encryption Software Export Distribution Authorization Form, read the information and click the
appropriate box.
Step 10 Click Submit.
Step 11 If you indicated that the software is not for you or your company, follow these steps:
a. If you receive a Do you want to display the nonsecure items? message, click Ye s. The Encryption
Software Export Distribution Authorization window appears.
b. Carefully read the information and enter the Cisco.com user profile or detailed data describing the end
user of this software image in the provided fields.
c. Click Submit.
Step 12 If you receive a Do you wish to continue? security alert message, click Ye s to continue.
Step 13 Click Download.
Step 14 Carefully read the Software Download Rules and click Agree to download the image file. An Enter
Password window appears.
Step 15 Enter your username and password in the respective fields and click OK.
Step 16 Download and save the image file to your hard drive and then exit the Internet browser.
7-8
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 87

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points
RJ-45 serial
connector
DB-9 to RJ-45
serial cable
74005
Obtaining the TFTP Server Software
You can download TFTP server software from several web sites. Cisco recommends the shareware TFTP
utility available at this URL:
http://tftpd32.jounin.net
Follow the instructions on the website for installing and using the utility.
Connecting to the Access Point Locally
The console port is enabled during power up for diagnostic and monitoring purposes, which might be
helpful if the access point is unable to associate to a controller. You can connect a PC to the console port
using a DB-9 to RJ-45 serial cable.
Step 1 Connect a nine-pin, female DB-9 to RJ-45 serial cable to the RJ-45 serial port on the access point and
to the COM port on a computer. Figure 7-2 shows the serial port connection.
Obtaining the TFTP Server Software
Figure 7-2 Connecting the Serial Cable
Note The Cisco part number for the DB-9 to RJ-45 serial cable is AIR-CONCAB1200. Browse to
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace to order a serial cable.
Step 2 Set up a terminal emulator to communicate with the access point. Use the following settings for the
terminal emulator connection: 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, and no flow control.
Note When your monitoring and diagnostic activities are completed, you must remove the serial cable from
the access point.
OL-8370-04
Step 3 At the prompts, enter the administrator username and password. The default username is Cisco and the
default password is Cisco. The username and password are case sensitive.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
7-9
Page 88

Connecting to the Access Point Locally
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting Lightweight Access Points
7-10
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 89

APPENDIX
A
Translated Safety Warnings
For translated safety warnings, refer to the safety warning document that shipped with your access point or
that is available on Cisco.com.
To browse to the document on Cisco.com, follow these steps:
Step 1 Click this link to the Cisco Wireless documentation home page:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/tsd_products_support_category_home.html
Step 2 Click Cisco Aironet 1200 Series listed under Access Points.
Step 3 Click Install and Upgrade Guides.
Step 4 Click Safety Warnings for Cisco Aironet 1000, 1100, 1130AG, 1200, and 1240AG Series Access
Points.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
A-1
Page 90

Appendix A Translated Safety Warnings
A-2
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 91

APPENDIX
B
Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
This appendix provides declarations of conformity and regulatory information for the Cisco Aironet
1200 Series Access Point.
This appendix contains the following sections:
• Manufacturers Federal Communication Commission Declaration of Conformity Statement,
page B-2
• VCCI Statement for Japan, page B-4
• Industry Canada, page B-4
• European Community, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein, page B-5
• Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure, page B-7
• Guidelines for Operating Cisco Aironet Access Points in Japan, page B-8
• Operation of Cisco Aironet Access Points in Brazil, page B-11
• Declaration of Conformity Statements, page B-12
• Declaration of Conformity Statements for European Union Countries, page B-12
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
B-1
Page 92

Appendix B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
Tested To Comply
With FCC Standards
FOR HOME OR OFFICE USE
Manufacturers Federal Communication Commission Declaration of Conformity Statement
Manufacturers Federal Communication Commission
Declaration of Conformity Statement
Autonomous Access Point Models:
AIR-AP1200 with AIR-MP20B-A-K9 and/or AIR-RM20A-A-K9;
AIR-AP1210 with AIR-MP20B-A-K9 or AIR-MP21G-A-K9, and/or AIR-RM20A-A-K9 or
R-RM21A-A-K9 or AIR-RM22A-A-K9;
AI
AIR-AP1220B-A-K9, AIR-AP1230B-A-K9, AIR-AP1220A-A-K9, AIR-AP1230A-A-K9, or
AIR-AP1231G-A-K9
AIR-AP1232AG-A-K9
Lightweight Access Point Models:
AIR-LAP1231G-A-K9;
AIR-LAP1232AG-A-K9
FCC Certification number:
LDK 102042 (AIR-MP20B-A-K9) or
LDK 102049 (AIR-MP21G-A-K9) and/or
LDK 102045 (AIR-RM20A-A-K9)
LDK 102053 (AIR-RM21A-A-K9 and AIR-RM22A-A-K9)
Manufacturer:
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
This device complies with Part 15 rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits of a Class B digital device, pursuant
o Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
t
interference when the equipment is operated in a residential environment. This equipment generates,
uses, and radiates radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur. If this equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined
by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase separation between the equipment and receiver.
B-2
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 93

Appendix B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
Manufacturers Federal Communication Commission Declaration of Conformity Statement
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician.
Caution The Part 15 radio device operates on a non-interference basis with other devices operating at this
frequency when using integrated antennas or those listed in Ta bl e B-1. Any changes or modification to
the product not expressly approved by Cisco could void the user’s authority to operate this device.
Caution Within the 5.15 to 5.25 GHz band (5 GHz radio channels 34 to 48) the U-NII devices are restricted to
indoor operations to reduce any potential for harmful interference to co-channel Mobile Satellite System
(MSS) operations.
Ta b l e B-1 Access Point 2.4-GHz Antennas
Radio Antenna
1
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g Cisco Part Number Model Gain (dBi)
Yes – AIR-ANT1949
Yes – AIR-ANT4121
Yes – AIR-ANT24120
Yes Ye s AIR-ANT2410Y-R Yagi-directional 10.0
Yes Ye s AIR-ANT3549 Patch 8.5
Yes Ye s AIR-ANT2012 Spatial diversity 6.5
Yes Ye s AIR-ANT1729 Patch 6.0
Yes Ye s AIR-ANT2506 Omni-directional 5.1
Yes Ye s AIR-ANT3213 Omni-directional 5.0
Yes Ye s AIR-ANT1728 Omni-directional 5.0
Yes Ye s AIR-ANT3195 Patch 3.0
Yes Ye s AIR-ANT5959 Omni-directional 2.0
Yes Ye s AIR-ANT4941 Dipole 2.2
1. Not supported by lightweight access points (AIR-LAP1231G-A-K9 or AIR-LAP1232AG-A-K9)
1
1
1
Yag i 13.5
Omni-directional 12.0
Omni-directional 12.0
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
B-3
Page 94

VCCI Statement for Japan
VCCI Statement for Japan
Appendix B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
Warning
This is a Class B product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for Interference from
Information Technology Equipment (VCCI). If this is used near a radio or television receiver in a
domestic environment, it may cause radio interference. Install and use the equipment according to
the instruction manual.
Industry Canada
Canadian Compliance Statement
This Class B Digital apparatus meets all the requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing
Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numerique de la classe B respecte les exigences du Reglement sur le material broilleur du
nada.
Ca
This device complies with Class B Limits of Industry Canada. Operation is subject to the following two
nditions:
co
B-4
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Cisco Aironet 2.4-GHz Access Points are certified to the requirements of RSS-210 for 2.4-GHz spread
ctrum devices, and Cisco Aironet 54-Mbps, 5-GHz Access Points are certified to the requirements of
spe
RSS-210 for 5-GHz spread spectrum devices.The use of this device in a system operating either partially
or completely outdoors may require the user to obtain a license for the system according to the Canadian
regulations. For further information, contact your local Industry Canada office.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 95

Appendix B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
European Community, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein
European Community, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and
Liechtenstein
Declaration of Conformity with Regard to the 1999/5/EC (R&TTE Directive)
This declaration is only valid for configurations (combinations of software, firmware, and hardware)
provided and supported by Cisco Systems. The use of software or firmware not provided and supported
by Cisco Systems may result in the equipment no longer being compliant with the regulatory
requirements.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
B-5
Page 96

European Community, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein
Appendix B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
B-6
This device complies with the EMC requirements (EN 60601-1-2) of the Medical Directive 93/42/EEC.
For 2.4 GHz radios, the following standards were applied:
• Radio: EN 300.328-1, EN 300.328-2
• EMC: EN 301.489-1, EN 301.489-17
• Safety: EN 60950
The following CE mark is affixed to access points with a 2.4 GHz radio:
Note This equipment is intended to be used in all EU and EFTA countries. Outdoor use may be restricted to
certain frequencies and/or may require a license for operation. For more details, contact Cisco Corporate
Compliance.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 97

Appendix B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
49325
Note Combinations of power levels and antennas resulting in a radiated power level above 100 mW equivalent
isotropic radiated power (EIRP) are considered as not compliant with the above mentioned directive and
are not allowed for use within the European community and other countries that have adopted the
European R&TTE directive 1999/5/EC or the CEPT recommendation Rec 70.03 or both. For more
details on legal combinations of power levels and antennas, refer to the Appendix D, “Channels and
Maximum Power Levels.”
For 54 Mbps, 5 GHz access points, the following standards were applied:
• Radio: EN 301.893
• EMC: EN 301.489-1, EN 301.489-17
• Safety: EN 60950
The following CE mark is affixed to the 54 Mbps, 5 GHz access points:
• For AIR-RM20A (not supported on the AIR-LAP1232AG-A-K9)
Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure
• For AIR-RM21A and AIR-RM22A
Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure
The radio module has been found to be compliant to the requirements set forth in CFR 47 Sections
2.1091, and 15.247 (b) (4) addressing RF Exposure from radio frequency devices as defined in
Evaluating Compliance with FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic
Fields. For the IEEE 802.11B antennas, AIR-ANT24120, AIR-ANT4121 and AIR-ANT1949 the
equipment should be positioned more than 2 m (6.56 ft) from your body or nearby persons. For all other
approved antennas the equipment should be installed more than 20 cm (7.9 in.) from your body or nearby
persons.
The access point (with 5 GHz integrated antenna) must be installed to maintain a minimum 20 cm
(7.9 in.) co-located separation distance from other FCC approved indoor/outdoor antennas used with the
ccess point. Any antennas or transmitters not approved by the FCC cannot be co-located with the access
a
point antennas. The access point’s co-located 2.4 GHz (2.2 dBi) and 5 GHz integrated antennas support
a minimum separation distance of 10 cm (3.9 in.) and are compliant with the applicable FCC RF
exposure limit when transmitting simultaneously.
OL-8370-04
Note Dual antennas used for diversity operation are not considered co-located.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
B-7
Page 98

Appendix B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
03-6434-6500
43768
Guidelines for Operating Cisco Aironet Access Points in Japan
Guidelines for Operating Cisco Aironet Access Points in Japan
This section provides guidelines for avoiding interference when operating Cisco Aironet access points
in Japan. These guidelines are provided in both Japanese and English.
Japanese Translation
English Translation
This equipment operates in the same frequency bandwidth as industrial, scientific, and medical devices
such as microwave ovens and mobile object identification (RF-ID) systems (licensed premises radio
stations and unlicensed specified low-power radio stations) used in factory production lines.
1. Before using this equipment, make sure that no premises radio stations or specified low-power radio
stations of RF-ID are used in the vicinity.
2. If this equipment causes RF interference to a premises radio station of RF-ID, promptly change the
frequency or stop using the device; contact the number below and ask for recommendations on
avoiding radio interference, such as setting partitions.
3. If this equipment causes RF interference to a specified low-power radio station of RF-ID, contact
the number below.
Contact Number: 03-5549-6500
B-8
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
OL-8370-04
Page 99

Appendix B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
Administrative Rules for Cisco Aironet Access Points in Taiwan
Administrative Rules for Cisco Aironet Access Points in Taiwan
This section provides administrative rules for operating Cisco Aironet access points in Taiwan. The rules
are provided in both Chinese and English.
Access Points with IEEE 802.11a Radios
Chinese Translation
English Translation
This equipment is limited for indoor use.
OL-8370-04
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
B-9
Page 100

Administrative Rules for Cisco Aironet Access Points in Taiwan
All Access Points
Chinese Translation
Appendix B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
English Translation
Administrative Rules for Low-power Radio-Frequency Devices
Article 12
For those low-power radio-frequency devices that have already received a type-approval, companies,
b
features and functions.
Article 14
The operation of the low-power radio-frequency devices is subject to the conditions that no harmful
in
user must stop operating the device immediately and can't re-operate it until the harmful interference is
clear.
The authorized radio station means a radio-communication service operating in accordance with the
Co
The operation of the low-power radio-frequency devices is subject to the interference caused by the
ope
scientific and medical (ISM) equipment, or by an incidental radiator.
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
B-10
usiness units or users should not change its frequencies, increase its power or change its original
terference is caused to aviation safety and authorized radio station; and if interference is caused, the
mmunication Act.
ration of an authorized radio station, by another intentional or unintentional radiator, by industrial,
OL-8370-04
 Loading...
Loading...