查询CAT5251JI-00TE13供应商
CAT5251
Quad Digitally Programmable Potentiometer (DPP™) with
256 Taps and SPI Interface
FEATURES
N
E
G
F
O
R
L
A
H
L
E
A
E
E
E
E
TM
R
D
F
■ Four linear-taper digitally programmable
potentiometers
■ 256 resistor taps per potentiometer
■ End to end resistance 50kΩ or 100kΩ
■ Potentiometer control and memory access via
SPI interface
■ Low wiper resistance, typically 100
■ Nonvolatile memory storage for up to four wiper
ΩΩ
Ω
ΩΩ
settings for each potentiometer
DESCRIPTION
The CAT5251 is four Digitally Programmable
Potentiometers (DPPs™) integrated with control logic
and 16 bytes of NVRAM memory. Each DPP consists of
a series of resistive elements connected between two
externally accessible end points. The tap points between
each resistive element are connected to the wiper outputs
with CMOS switches. A separate 8-bit control register
(WCR) independently controls the wiper tap switches for
each DPP. Associated with each wiper control register
are four 8-bit non-volatile memory data registers (DR)
used for storing up to four wiper settings. Writing to the
wiper control register or any of the non-volatile data
■ Automatic recall of saved wiper settings at
power up
■ 2.5 to 6.0 volt operation
■ Standby current less than 1µA
■ 1,000,000 nonvolatile WRITE cycles
■ 100 year nonvolatile memory data retention
■ 24-lead SOIC and 24-lead TSSOP
■ Industrial temperature range
registers is via a SPI serial bus. On power-up, the
contents of the first data register (DR0) for each of the
four potentiometers is automatically loaded into its
respective wiper control register.
The CAT5251 can be used as a potentiometer or as a
two terminal, variable resistor. It is intended for circuit
level or system level adjustments in a wide variety of
applications. It is available in the -40°C to 85°C industrial
operating temperature range and offered in a 24-lead
SOIC and TSSOP package.
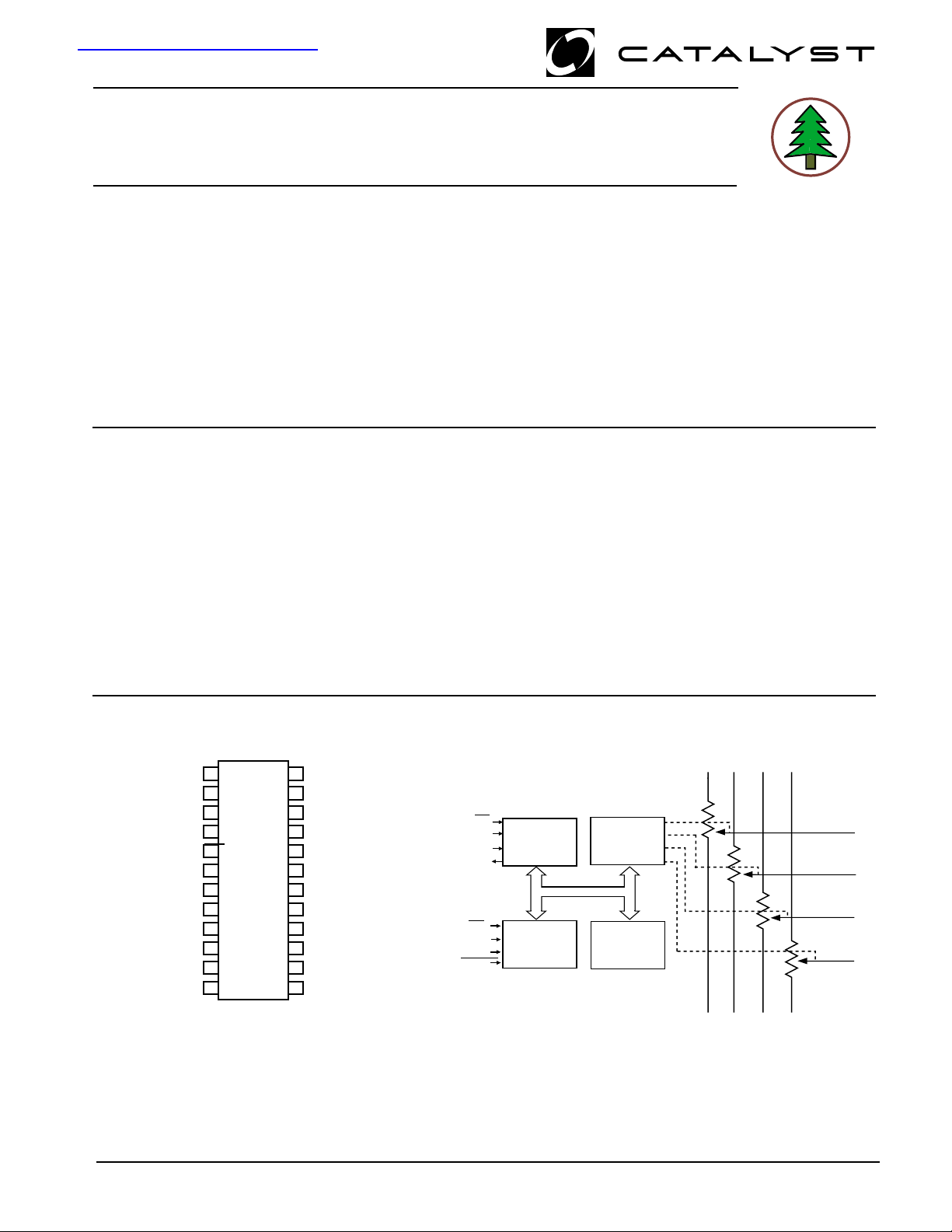
PIN CONFIGURATION
SOIC/TSSOP Package (J, W/U, Y)
CAT
5251
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
1
SO
2
A0
W3
H3
L3
NC
CC
L0
H0
W0
CS
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
R
R
R
V
R
R
R
WP
HOLD
SCK
R
L2
R
H2
R
W2
NC
GND
R
W1
R
H1
R
L1
A1
SI
FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM
CS
SCK
S
WP
A0
A1
HOLD
SI
O
SPI BUS
INTERFACE
CONTROL
LOGIC
WIPER
CONTROL
REGISTERS
NONVOLATILE
DATA
REGISTERS
R
H0
R
L0
R
H1
R
L1
R
R
H2
H3
R
W0
R
W1
R
W2
R
W3
R
R
L2
L3
© 2004 by Catalyst Semiconductor, Inc.
Characteristics subject to change without notice
1
Document No. 2017, Rev. D
CAT5251
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin
(SOIC/TSSOP) Name Function
1 SO Serial Data Output
2 A0 Device Address, LSB
3RW3Wiper Terminal for Potentiometer 3
4RH3High Reference Terminal
for Potentiometer 3
5RL3Low Reference Terminal
for Potentiometer 3
6 NC No Connect
7 VCC Supply Voltage
8R
9R
10 R
11 CS Chip Select
12 WP Write Protection
13 SI Serial Input
14 A1 Device Address
15 R
16 R
17 R
18 GND Ground
19 NC No Connect
20 R
21 R
22 R
23 SCK Bus Serial Clock
24 HOLD Hold
L0
H0
W0
L1
H1
W1
W2
H2
L2
Low Reference Terminal
for Potentiometer 0
High Reference Terminal
for Potentiometer 0
Wiper Terminal for Potentiometer 0
Low Reference Terminal
for Potentiometer 1
High Reference Terminal
for Potentiometer 1
Wiper Terminal for Potentiometer 1
Wiper Terminal for
Potentiometer 2
High Reference Terminal
for Potentiometer 2
Low Reference Terminal
for Potentiometer 2
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
SI: Serial Input
SI is the serial data input pin. This pin is used to
input all opcodes, byte addresses and data to be
written to the CAT5251. Input data is latched on the
rising edge of the serial clock.
SO: Serial Output
SO is the serial data output pin. This pin is used to
transfer data out of the CAT5251. During a read
cycle, data is shifted out on the falling edge of the
serial clock.
SCK: Serial Clock
SCK is the serial clock pin. This pin is used to
synchronize the communication between the
microcontroller and the CAT5251. Opcodes, byte
addresses or data present on the SI pin are latched
on the rising edge of the SCK. Data on the SO pin is
updated on the falling edge of the SCK.
A0, A1: Device Address Inputs
These inputs set the device address when addressing multiple devices. A total of four devices can be
addressed on a single bus. A match in the slave
address must be made with the address input in
order to initiate communication with the CAT5251.
, RL: Resistor End Points
R
H
The four sets of RH and RL pins are equivalent to the
terminal connections on a mechanical potentiometer.
R
: Wiper
W
The four RW pins are equivalent to the wiper terminal
of a mechanical potentiometer.
CSCS
CS: Chip Select
CSCS
CS is the Chip select pin. CS low enables the
CAT5251 and CS high disables the CAT5251. CS
high takes the SO output pin to high impedance and
forces the devices into a Standby mode (unless an
internal write operation is underway). The CAT5251
draws ZERO current in the Standby mode. A high to
low transition on CS is required prior to any sequence
being initiated. A low to high transition on CS after a valid write sequence is what initiates an internal write cycle.
WPWP
WP: Write Protect
WPWP
WP is the Write Protect pin. The Write Protect pin will allow normal read/write operations when held high. When WP is tied low, all
non-volatile write operations to the Data registers are inhibited (change of wiper control register is allowed). WP going low while
CS is still low will interrupt a write to the registers. If the internal write cycle has already been initiated, WP going low will have no
effect on any write operation.
HOLDHOLD
HOLD: Hold
HOLDHOLD
The HOLD pin is used to pause transmission to the CAT5251 while in the middle of a serial sequence without having to retransmit entire sequence at a later time. To pause, HOLD must be brought low while SCK is low. The SO pin is in a high impedance state during the time the part is paused, and transitions on the SI pins will be ignored. To resume communication, HOLD is
brought high, while SCK is low. (HOLD should be held high any time this function is not being used.) HOLD may be tied high
directly to VCC or tied to VCC through a resistor.
Document No. 2017, Rev. D
2

SERIAL BUS PROTOCOL
CAT5251
The CAT5251 supports the SPI bus data transmission
protocol. The synchronous Serial Peripheral Interface
(SPI) helps the CAT5251 to interface directly with many
of today's popular microcontrollers. The CAT5251
contains an 8-bit instruction register .The instruction set
and the operation codes are detailed in the instruction
set table 3 on page 9.
DEVICE OPERATION
The CAT5251 is four resistor arrays integrated with an
SPI serial interface logic, four 8-bit wiper control registers
and sixteen 8-bit, non-volatile memory data registers.
Each resistor array contains 255 separate resistive
elements connected in series. The physical ends of
each array are equivalent to the fixed terminals of a
mechanical potentiometer (RH and RL). RH and RL are
symmetrical and may be interchanged. The tap positions
between and at the ends of the series resistors are
connected to the output wiper terminals (RW) by a
After the device is selected with CS going low the first
byte will be received. The part is accessed via the SI pin,
with data being clocked in on the rising edge of SCK. The
first byte contains one of the six op-codes that define the
operation to be performed.
CMOS transistor switch. Only one tap point for each
potentiometer is connected to its wiper terminal at a time
and is determined by the value of the wiper control
register. Data can be read or written to the wiper control
registers or the non-volatile memory data registers via
the SPI bus. Additional instructions allow data to be
transferred between the wiper control registers and
each respective potentiometer's non-volatile data
registers. Also, the device can be instructed to operate
in an "increment/decrement" mode.
3
Document No. 2017, Rev. D
CAT5251
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Temperature Under Bias ..................-55°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature........................-65°C to +150°C
*COMMENT
Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent
damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions outside of those listed in the operational sections
of this specification is not implied. Exposure to any absolute maximum rating for extended
periods may affect device performance and reliability.
Voltage on any Pin with
Respect to V
VCC with Respect to Ground ................ -2.0V to +7.0V
Package Power Dissipation
Capability (T
(1)(2)
................ -2.0V to +VCC +2.0V
SS
= 25°C) ................................... 1.0W
A
Recommended Operating Conditions:
V
= +2.5V to +6.0V
CC
Temperature Min Max
Industrial -40°C85°C
Lead Soldering Temperature (10 secs) ............ 300°C
Wiper Current....................................................
Note:
(1) The minimum DC input voltage is –0.5V. During transitions, inputs may undershoot to –2.0V for periods of less than 20 ns. Maximum DC voltage on output
pins is VCC +0.5V, which may overshoot to VCC +2.0V for periods of less than 20 ns.
(2) Latch-up protection is provided for stresses up to 100 mA on address and data pins from –1V to VCC +1V.
+6mA
POTENTIOMETER CHARACTERISTICS
Over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise stated.
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Units
R
POT
R
POT
I
W
R
W
R
W
V
TERM
V
N
TC
RPOT
TC
RATIO
CH/CL/C
fc Frequency Response R
Note:
(1) This parameter is tested initially and after a design or process change that affects the parameter.
(2) Absolute linearity is utilitzed to determine actual wiper voltage versus expected voltage as determined by wiper position when used as a potentiometer.
(3) Relative linearity is utilized to determine the actual change in voltage between two successive tap positions when used as a
potentiometer. It is a measure of the error in step size.
(4) LSB = R
(5) n = 0, 1, 2, ..., 255
Potentiometer Resistance (-00) 100 kΩ
Potentiometer Resistance (-50) 50 kΩ
Potentiometer Resistance +20 %
Tolerance
R
Matching 1 %
POT
Power Rating 25°C, each pot 50 mW
Wiper Current +3 mA
Wiper Resistance IW = +3mA @ VCC =3V 200 300 Ω
Wiper Resistance IW = +3mA @ VCC = 5V 100 150 Ω
Voltage on any RH or RL Pin VSS = 0V GND V
Noise (1) nV/ Hz
Resolution 0.4 %
Absolute Linearity
Relative Linearity
(2)
(3)
Temperature Coefficient of R
POT
R
w(n)(actual)-R(n)(expected)
R
-[R
w(n+1)
w(n)+LSB
(1) +300 ppm/°C
(5)
(5)
]
+0.5 LSB
Ratiometric Temp. Coefficient (1) 20 ppm/°C
W
Potentiometer Capacitances (1) 10/10/25 pF
(1)
0.4 MHz
/ 255 or (RH - RL) / 255, single pot
TOT
POT
= 50kΩ
CC
V
+1 LSB
(4)
(4)
Document No. 2017, Rev. D
4
CAT5251
D.C. OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
Over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise stated.
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Units
V
V
I
CC1
I
CC2
I
I
I
V
V
SB
LI
LO
IL
IH
OL1
OH1
Power Supply Current f
= 2.5 MHz, SO Open 1 mA
SCK
VCC = 6 V Inputs = GND
Power Supply Current fsck = 2.5 MHz, SO = Open 5 mA
Non-volatile Write VCC = 6 V Inputs = GND
Standby Current (VCC = 5.0V) VIN = GND or V
Input Leakage Current VIN = GND to V
Output Leakage Current V
= GND to V
OUT
SO Open 1 µA
CC;
CC
CC
10 µA
10 µA
Input Low Voltage -1 VCC x 0.3 V
Input High Voltage VCC x 0.7 V
+ 1.0 V
CC
Output Low Voltage (VCC = 3 V) IOL = 3 mA 0.4 V
Output High Voltage (VCC = 6 V) I
= -1.6mA VCC-0.8 V
OH
PIN CAPACITANCE
Applicable over recommended operating range from TA=25˚C, f=1.0 MHz, VCC=+5.0V (unless otherwise noted).
(1)
Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Units Conditions
C
OUT
C
IN
Output Capacitance (SO) 8 pF V
Input Capacitance (CS, SCK, SI, WP, HOLD,6pFV
OUT
=0V
IN
=0V
A0, A1)
Note:
(1) This parameter is tested initially and after a design or process change that affects the parameter.
5
Document No. 2017, Rev. D

CAT5251
A.C. CHARACTERISTICS
Over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise stated.
Test
SYMBOL PARAMETER Min Typ Max UNITS Conditions
t
SU
t
H
t
WH
t
WL
f
SCK
t
LZ
(1)
t
RI
(1)
t
FI
t
HD
t
CD
t
V
t
HO
t
DIS
t
HZ
t
CS
t
CSS
t
CSH
NOTE:
(1) This parameter is tested initially and after a design or process change that affects the parameter.
Data Setup Time 50 ns
Data Hold Time 50 ns
SCK High Time 125 ns
SCK Low Time 125 ns
Clock Frequency DC 3 MHz
HOLD to Output Low Z 50 ns
Input Rise Time 2 µs
Input Fall Time 2 µs
HOLD Setup Time 100 ns
HOLD Hold Time 100 ns
Output Valid from Clock Low 200 ns
Output Hold Time 0 ns
Output Disable Time 250 ns
HOLD to Output High Z 100 ns
CS High Time 250 ns
CS Setup Time 250 ns
CS Hold Time 250 ns
CL = 50pF
POWER UP TIMING
Over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise stated.
(1)(2)
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units
t
PUR
t
PUW
NOTE:
(1) This parameter is tested initially and after a design or process change that affects the parameter.
(2) t
PUR
Power-up to Read Operation 1 ms
Power-up to Write Operation 1 ms
and t
are the delays required from the time VCC is stable until the specified operation can be initiated.
PUW
XDCP TIMING
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units
t
WRPO
t
WRL
Document No. 2017, Rev. D
Wiper Response Time After Power Supply Stable 5 10 µs
Wiper Response Time After Instruction Issued 5 10 µs
6

CAT5251
WRITE CYCLE LIMITS
Over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise stated.
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units
t
WR
RELIABILITY CHARACTERISTICS
Over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise stated.
Symbol Parameter Reference Test Method Min Typ Max Units
N
END
(1)
T
DR
(1)
V
ZAP
(1)
I
LTH
Note:
(1) This parameter is tested initially and after a design or process change that affects the parameter.
Figure 1. Sychronous Data Timing
Write Cycle Time 5 ms
(1)
Endurance MIL-STD-883, Test Method 1033 1,000,000 Cycles/Byte
Data Retention MIL-STD-883, Test Method 1008 100 Years
ESD Susceptibility MIL-STD-883, Test Method 3015 2000 Volts
Latch-Up JEDEC Standard 17 100 mA
V
IH
CS
V
IL
V
SCK
SO
IH
V
IL
V
IH
SI
V
IL
V
OH
HI-Z
V
OL
Note: Dashed Line= mode (1, 1)
Figure 2.
HOLDHOLD
HOLD Timing
HOLDHOLD
CS
SCK
t
CS
t
CD
t
CSH
t
DIS
HI-Z
t
CSS
t
WH
CD
t
H
t
SU
VALID IN
t
t
WL
t
RI
t
FI
t
V
t
HO
HOLD
SO
t
HD
t
HZ
t
HD
HIGH IMPEDANCE
t
LZ
7
Document No. 2017, Rev. D

CAT5251
INSTRUCTION AND REGISTER
DESCRIPTION
DEVICE TYPE / ADDRESS BYTE
The first byte sent to the CAT5251 from the master/
processor is called the Device Address Byte. The most
significant four bits of the Device Type address are a
device type identifier. These bits for the CAT5251 are
fixed at 0101[B] (refer to Table 1).
The two least significant bits in the slave address byte,
A1 - A0, are the internal slave address and must match
the physical device address which is defined by the state
of the A1 - A0 input pins for the CAT5251 to successfully
continue the command sequence. Only the device which
slave address matches the incoming device address
sent by the master executes the instruction. The A1 - A0
inputs can be actively driven by CMOS input signals or
tied to V
address byte must be set to 0.
Table 1. Identification Byte Format
or VSS. The remaining two bits in the device
CC
INSTRUCTION BYTE
The next byte sent to the CAT5251 contains the instruction
and register pointer information. The four most significant
bits used provide the instruction opcode I3-I0. The R1
and R0 bits point to one of the four data registers of each
associated potentiometer. The least two significant bits
point to one of four Wiper Control Registers. The format
is shown in Table 2.
Data Register Selection
Data Register Selected R1 R0
DR0 0 0
DR1 0 1
DR2 1 0
DR3 1 1
Device Type
Identifier
ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0 0 0 A1 A0
0101
(MSB) (LSB)
Table 2. Instruction Byte Format
Instruction
Opcode
I3 I2 I1 I0 R1 R0 P1 P0
(MSB) (LSB)
Data Register
Selection
Slave Address
WCR/Pot Selection
Document No. 2017, Rev. D
8

CAT5251
WIPER CONTROL AND DATA REGISTERS
Wiper Control Register (WCR)
The CAT5251 contains four 8-bit Wiper Control
Registers, one for each potentiometer. The Wiper
Control Register output is decoded to select one of
256 switches along its resistor array. The contents of
the WCR can be altered in four ways: it may be written
by the host via Write Wiper Control Register instruction;
it may be written by transferring the contents of one of
four associated Data Registers via the XFR Data
Register instruction; it can be modified one step at a
time by the Increment/decrement instruction (see
Instruction section for more details). Finally, it is
loaded with the content of its data register zero (DR0)
upon power-up.
The Wiper Control Register is a volatile register that
loses its contents when the CAT5251 is powered-down.
Although the register is automatically loaded with the
value in DR0 upon power-up, this may be different from
the value present at power-down.
Data Registers (DR)
Each potentiometer has four 8-bit non-volatile Data
Registers. These can be read or written directly by the
host. Data can also be transferred between any of the
Table 3. Instruction Set
four Data Registers and the associated Wiper Control
Register. Any data changes in one of the Data Registers
is a non-volatile operation and will take a maximum of
5ms.
If the application does not require storage of multiple
settings for the potentiometer; the Data Registers can be
used as standard memory locations for system
parameters or user preference data.
Write in Process
The contents of the Data Registers are saved to
nonvolatile memory when the CS input goes HIGH after
a write sequence is received. The status of the internal
write cycle can be monitored by issuing a Read Status
command to read the Write in Process (WIP) bit.
INSTRUCTIONS
Five of the ten instructions are three bytes in length.
These instructions are:
—Read Wiper Control Register - read the current
wiper position of the selected potentiometer in the WCR
—Write Wiper Control Register - change current
wiper position in the WCR of the selected potentiometer
—Read Data Register - read the contents of the
selected Data Register
Instruction Set
P1
WCR0/
P0
Operation
Register pointed to by P1-P0
Register pointed to by P1-P0
pointed to by P1-P0 and R1-R0
pointed to by P1-P0 and R1-R0
pointed to by P1-P0 and R1-R0 to its
associated Wiper Control Register
Register pointed to by P1-P0 to the Data
Register pointed to by R1-R0
pointed to by R1-R0 of all four pots to their
respective Wiper Control Register
Registers to their respective data Registers
pointed to by R1-R0 of all four pots
Latch pointed to by P1-P0
Read WIP bit to check internal
write cycle status
Instruction
Read Wiper Control
Register
Write Wiper Control Register 101000 1/0 1/0Write new value to the Wiper Control
Read Data Register 10111/01/01/0 1/0Read the contents of the Data Register
Write Data Register 11001/01/01/0 1/0Write new value to the Data Register
XFR Data Register to Wiper
Control Register
XFR Wiper Control Register
to Data Register
Global XFR Data
to Wiper Control Registers
Global XFR Wiper Control
Registers to Data Register
Increment/Decrement Wiper
Control Register
Read Status (WIP bit)
Note: 1/0 = data is one or zero
Registers
I3 I2 I1 I0 R1 R0
100100 1/0 1/0Read the contents of the Wiper Control
11011/01/01/0 1/0Transfer the contents of the Data Register
11101/01/01/0 1/0Transfer the contents of the Wiper Control
00011/01/0 0 0 Transfer the contents of the Data Registers
10001/01/0 0 0 Transfer the contents of both Wiper Control
001000 1/0 1/0Enable Increment/decrement of the Control
010100 0 1
WCR1/
9
Document No. 2017, Rev. D

CAT5251
—Write Data Register - write a new value to the
selected Data Register
—Read Status - Read the status of the WIP bit which
when set to "1" signifies a write cycle is in progress.
The basic sequence of the three byte instructions is
illustrated in Figure 8. These three-byte instructions
exchange data between the WCR and one of the Data
Registers. The WCR controls the position of the wiper.
The response of the wiper to this action will be delayed
by t
. A transfer from the WCR (current wiper position),
WRL
to a Data Register is a write to non-volatile memory and
takes a minimum of tWR to complete. The transfer can
occur between one of the four potentiometers and one
of its associated registers; or the transfer can occur
between all potentiometers and one associated register.
Four instructions require a two-byte sequence to
complete, as illustrated in Figure 7. These instructions
transfer data between the host/processor and the
CAT5251; either between the host and one of the data
registers or directly between the host and the Wiper
Control Register. These instructions are:
—XFR Data Register to Wiper Control Register
This transfers the contents of one specified Data
Register to the associated Wiper Control Register.
—XFR Wiper Control Register to Data Register
This transfers the contents of the specified Wiper
Control Register to the specified associated
Data Register.
—Global XFR Data Register to Wiper
Control Register
This transfers the contents of all specified Data
Registers to the associated Wiper Control
Registers.
—Global XFR Wiper Counter Register to
Data Register
This transfers the contents of all Wiper Control
Registers to the specified associated Data
Registers.
INCREMENT/DECREMENT COMMAND
The final command is Increment/Decrement (Figure 9
and 10). The Increment/Decrement command is different from the other commands. Once the command is
issued the master can clock the selected wiper up and/
or down in one segment steps; thereby providing a fine
tuning capability to the host. For each SCK clock pulse
(t
) while SI is HIGH, the selected wiper will move one
HIGH
resistor segment towards the RH terminal. Similarly, for
each SCK clock pulse while SI is LOW, the selected
wiper will move one resistor segment towards the R
terminal.
See Instructions format for more detail.
L
Figure 7. Two-Byte Instruction Sequence
SI
0101
ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0
Device ID
00
A3
A1
A2 A0
Internal
Address
Figure 8. Three-Byte Instruction Sequence
010100
ID3 ID2
Device ID
ID1
ID0
A3
A2 A1 A0
Internal
Address
I3
I1
I2
Instruction
Opcode
Figure 9. Increment/Decrement Instruction Sequence
SI
010100
ID3 ID2 ID1ID0
Device ID
A3
A2 A1 A0
Internal
Address
I3 I2
Instruction
Opcode
I1
I3
I0
I0
I2 I1
Instruction
Opcode
R1 R0
Data
Register
Address
R0 P1 P0
R1
Data
Register
Address
I0
R1 R0 P1
Register
Address
P1 P0SID7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Pot/WCR
Address
Pot/WCR
Address
P0
Pot/WCR
Address
WCR[7:0]
Data Register D[7:0]
I
N
C
1
or
I
N
C
2
N
C
n
D
I
E
C
1
D
E
C
n
Document No. 2017, Rev. D
10

Figure 10. Increment/Decrement Timing Limits
INC/DEC
Command
Issued
SCK
SI
t
WRL
CAT5251
R
W
Voltage Out
INSTRUCTION FORMAT
Read Wiper Control Register (WCR)
DEVICE ADDRESSES INSTRUCTION DATA
0 1 0 1 0 0 A A 1 0 0 1 0 0 P P 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CS CS
10 10
Write Wiper Control Register (WCR)
DEVICE ADDRESSES INSTRUCTION DATA
0 1 0 1 0 0 A A 1 0 1 0 0 0 P P 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CS CS
10 10
Read Data Register (DR)
DEVICE ADDRESSES INSTRUCTION DATA
0 1 0 1 0 0 A A 1 0 1 1 R R P P 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CS CS
10 1010
High Voltage
Write Cycle
Write Data Register (DR)
DEVICE ADDRESSES INSTRUCTION DATA
0 1 0 1 0 0 A A 1 1 0 0 R R P P 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CS CS
10 1010
Read (WIP) Status
DEVICE ADDRESSES INSTRUCTION DATA
0 1 0 1 0 0 A A 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
CS CS
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
W
I
P
11
Document No. 2017, Rev. D

CAT5251
INSTRUCTION FORMAT (continued)
Global Transfer Data Register (DR) to Wiper Control Register (WCR)
DEVICE ADDRESSES INSTRUCTION
0 1 0 1 0 0 A A 0 0 0 1 R R 0 0
CS CS
Global Transfer Wiper Control Register (WCR) to Data Register (DR)
DEVICE ADDRESSES INSTRUCTION
0 1 0 1 0 0 A A 1 0 0 0 R R 0 0
CS CS
Transfer Wiper Control Register (WCR) to Data Register (DR)
10 10
10 10
High Voltage
Write Cycle
DEVICE ADDRESSES INSTRUCTION
0 1 0 1 0 0 A A 1 1 1 0 R R P P
CS CS
10 1010
High Voltage
Write Cycle
Transfer Data Register (DR) to Wiper Control Register (WCR)
DEVICE ADDRESSES INSTRUCTION
0 1 0 1 0 0 A A 1 1 0 1 R R P P
CS CS
10 1010
Increment (I)/Decrement (D) Wiper Control Register (WCR)
DEVICE ADDRESSES INSTRUCTION DATA
0 1 0 1 0 0 A A 0 0 1 0 0 0 P P I/D I/D I/D I/D
CS CS
1 0 1 0
Notes:
(1) Any write or transfer to the Non-volatile Data Registers is followed by a high voltage cycle after a STOP has been issued.
• • •
Document No. 2017, Rev. D
12

ORDERING INFORMATION
Prefix Device # Suffix
CAT5251
CAT
Optional
Company ID
5251 J
Product
Number
Package
J: SOIC
I
-50
-TE13
Tape & Reel
TE13: 2000/Reel
U: TSSOP
W: SOIC (Lead free, Halogen free)
Y: TSSOP (Lead free, Halogen free)
Resistance
-50: 50kohm
-00: 100kohm
Notes:
(1) The device used in the above example is a CAT5251JI-50-TE13 (SOIC, Industrial Temperature, 50kohm, Tape & Reel)
PACKAGING INFORMATION
24-LEAD 300 MIL WIDE SOIC (J)
0.2914 (7.40)
0.2992 (7.60)
0.394 (10.00)
0.419 (10.65)
0.050 (1.27) BSC
0 —8
0.5985 (15.20)
0.6141 (15.60)
0.013 (0.33)
0.020 (0.51)
0.010 (0.25)
0.029 (0.75)
0.016 (0.40)
0.050 (1.27)
X 45
0.0926 (2.35)
0.1043 (2.65)
0.0040 (0.10)
0.0118 (0.30)
0.0091 (0.23)
0.0125 (0.32)
All Dimensions in inches (mm).
13
Document No. 2017, Rev. D

CAT5251
PACKAGING INFORMATION CON'T
24 Lead TSSOP (U)
7.8 + 0.1
-A-
7.72 TYP
6.4
PIN #1 INDENT.
3.2
1.1 MAX TYP
-C-
4.4 + 0.1
0.65 TYP
-B-
ALL LEAD TIPS
0.1 C
ALL LEAD TIPS
0.2 C B A
4.16 TYP
(1.78 TYP)
0.42 TYP
0.65 TYP
LAND PATTERN RECOMMENDATION
(0.9)
0.10 + 0.05 TYP
0.19 - 0.30 TYP
0.3 M A B S C S
All Dimensions in mm.
Document No. 2017, Rev. D
SEE DETAIL A
0.09 - 0.20 TYP
14
0o- 8
GAGE PLANE
0.25
o
0.6+0.1
SEATING PLANE
DETAIL A

REVISION HISTORY
Date Rev. Reason
11/11/2003 C Eliminated BGA package in all areas
Eliminated Commercial temperature range
5/6/2004 D Updated Functional Diagram
Updated wiper resistance from 50Ω to 100Ω
Updated notes in Absolute Max Ratings
Eliminated Commercial temp range in all areas
Updated Potentiometer Characteristics table
Updated DC Characteristics table
Updated AC Characteristics table
Added XDCP Timing Table on page 6
Corrected Sychronous Data Timing (Figure 1) drawing
Copyrights, Trademarks and Patents
Trademarks and registered trademarks of Catalyst Semiconductor include each of the following:
DPP ™ AE2 ™
Catalyst Semiconductor has been issued U.S. and foreign patents and has patent applications pending that protect its products. For a complete list of patents
issued to Catalyst Semiconductor contact the Company’s corporate office at 408.542.1000.
CATALYST SEMICONDUCTOR MAKES NO WARRANTY, REPRESENTATION OR GUARANTEE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THE SUITABILITY OF ITS
PRODUCTS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, NOR THAT THE USE OF ITS PRODUCTS WILL NOT INFRINGE ITS INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS OR THE
RIGHTS OF THIRD PARTIES WITH RESPECT TO ANY PARTICULAR USE OR APPLICATION AND SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY AND ALL LIABILITY ARISING
OUT OF ANY SUCH USE OR APPLICATION, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES.
Catalyst Semiconductor products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or
other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Catalyst Semiconductor product could create a
situation where personal injury or death may occur.
Catalyst Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes to or discontinue any product or service described herein without notice. Products with data sheets
labeled "Advance Information" or "Preliminary" and other products described herein may not be in production or offered for sale.
Catalyst Semiconductor advises customers to obtain the current version of the relevant product information before placing orders. Circuit diagrams illustrate
typical semiconductor applications and may not be complete.
Catalyst Semiconductor, Inc.
Corporate Headquarters
1250 Borregas Avenue
Sunnyvale, CA 94089
Phone: 408.542.1000
Fax: 408.542.1200
www.catalyst-semiconductor.com
Publication #: 2017
Revison: D
Issue date: 5/6/04
Type: Advance
 Loading...
Loading...