
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
fx-82SX/
fx-250HC
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
• ••••••••••••••••••
NQPOR

CASIO ELECTRONICS CO., LTD.
Unit 6, 1000 North Circular Road,
London NW2 7JD, U.K.

ENGLISH
ESPAÑOL
FRANÇAIS
Contents
Handling Precautions … 2
Modes … 3
Basic Calculations … 5
Constant Calculations … 6
Memory Calculations … 7
Fraction Calculations … 8
Percentage Calculations … 10
Scientific Function Calculations … 11
Statistical Calculations (SD Mode) … 16
Technical Information … 18
1
33
66
— 1 —
DEUTSCH
ITALIANO
99
134

Handling Precautions
•Your calculator is made up of precision components. Never
try to take it apart.
•Avoid dropping your calculator and otherwise subjecting
it to strong impact.
• Do not store the calculator or leave it in areas exposed to
high temperature or humidity, or large amounts of dust.
When exposed to low temperature, the calculator may
require more time to display results and may even fail to
operate. Correct operation will resume once the calculator
is brought back to normal temperature.
• The display will go blank and keys will not operate during
calculations. When you are operating the keyboard, be
sure to watch the display to make sure that all your key
operations are being performed correctly.
• Never leave dead batteries in the battery compartment.
They can leak and damage the unit.
•Avoid using volatile liquids such as thinner or benzine to
clean the unit. Wipe it with a soft cloth, or with a cloth that
has been dipped in a solution of water and a neutral detergent and wring out.
• In no event will the manufacturer and its suppliers be liable
to you or any other person for any damages, expenses,
lost profits, lost savings, or any other damages arising out
of malfunction, repairs, or battery replacement. The user
should prepare physical records of data to protect against
such data loss.
• Never dispose of batteries, the liquid crystal panel, or other
components by burning them.
— 2 —
• Before assuming malfunction of the unit, be sure to carefully reread this manual and ensure that the problem is not
due to low battery power or operational error.
• The contents of this manual are subject to change without
notice.
• No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form
without the express written consent of the manufacturer.
• Keep this manual on hand for future reference.
Modes
Application
Standard deviation calculations
Normal calculations
Calculations using degrees
Calculations using radians
Calculations using grads
Number of decimal place
specification
Number of significant digit
specification
Cancels FIX and SCI settings
* Display indicators show current mode setting. Absence of
display indicator indicates COMP Mode.
— 3 —
Key
Operation
Fl
F0
F4
F5
F6
F7
F8
F9
Mode
Name*
SD
COMP
DEG
RAD
GRA
FIX
SCI
NORM

Note!
•A mode guide is located above the display screen.
• DEG, RAD, and GRA modes can be used in combination
with the COMP and SD modes.
•
does not exit SD mode.
F9
•
exits SD mode.
F0
•
does not clear SCI or FIX specifications.
F0
• Always press t before entering DEG, RAD, and GRA
modes.
• Remember to always set the operating mode and angular
unit (DEG, RAD, GRA) before starting your calculation.
— 4 —

Basic Calculations
• Use the COMP mode for basic calculations.
• Example 1: 23ѿ4.5Ҁ53
23 + 4.5 , 53 =
• Example 2: 56҂(Ҁ12)쐦(Ҁ2.5)
56 -12 E \ 2.5 E =
• Example 3: 2쐦3҂(1҂1020)
2 \ 3 -1 e 20 =
• Example 4: 7҂8Ҁ4҂5=36
7 - 8 , 4 - 5 =
• Example 5: =0.3
• Example 6: 2҂[7ѿ6҂(5ѿ4)]҃122
6
4҂5
4 - 5 \ 6 A N =
2 - O 7 + 6 -
O 5 + 4 P P =
•You can skip all P operations before the = ke y.
— 5 —
6.666666667
–25.5
268.8
19
36.
0.3
122.

Constant Calculations
• Press +, ,, -,or \ twice after inputting a number to
make that number a constant.
• “K” is on the display while a constant is being used.
• Use the COMP mode for constant calculations.
• Example 1: 2.3ѿ3, then 2.3ѿ6
(2.3ѿ3) 2.3 + + 3 =
(2.3ѿ6) 6 =
• Example 2: 12҂2.3, then 12҂(앥9)
(12҂2.3) 12 - - 2.3 =
(12҂(앥9)) 9 E =
• Example 3: 17ѿ17ѿ17ѿ17҃68
(17ѿ17) 17 + + =
(17ѿ17ѿ17) =
(17ѿ17ѿ17ѿ17) =
• Example 4: 1.74҃8.3521
(1.72) 1.7 - - =
(1.73) =
(1.74) =
— 6 —
K
K
K
K
–108.
K
K
K
K
K
4.913
K
8.3521
5.3
8.3
27.6
34.
51.
68.
2.89
Memory Calculations
• Use the COMP mode for memory calculations.
• Use Y, |, A { and Z for memory calculations.
Y replaces current memory contents.
• “M” appears when there is a value in memory.
•To clear memory, press 0 Y or t Y.
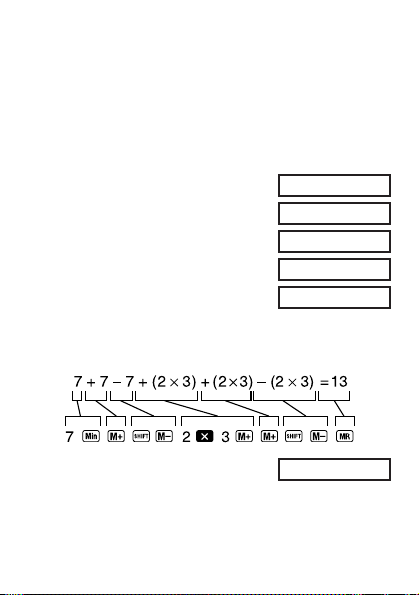
• Example 1: (53ѿ6)ѿ(23Ҁ8)ѿ(56҂2)ѿ(99쐦4)҃210.75
(53ѿ6) 53 + 6 = Y
(23앥8) 23 , 8 |
(56҂2) 56 - 2 |
(99앦4) 99 \ 4 |
(Memory recall) Z
• Example 2: To calculate the following using memory as
shown.
— 7 —
M
M
M
M
M
M
59.
15.
112.
24.75
210.75
13.
• Example 3: To calculate the following using memory and
a constant: (12҂3)앥(45҂3)ѿ(78҂3)҃135.
(12҂3) 3 - - 12 = Y
(45҂3) 45 A {
(78҂3) 78 |
(Memory recall) Z
MK
36.
MK
135.
MK
234.
MK
135.
Fraction Calculations
• Use COMP mode for fraction calculations.
•Total number of digits (including division marks) cannot
exceed 10.
• Example 1: ѿ ҃1
234
2
• Example 2: 3 ѿ1 ҃ 4
7
15
5
C 3 + 4 C 5 =
142311
12
3 C 1 C 4 +
1 C 2 C 3 =
1 7 15.
4 11 12.
• Example 3: ҃ 2 C 4
241
2
=
— 8 —
2 4.
1 2.
• Example 4: ѿ1.6҃2.1
Fraction/decimal calculation result is always decimal.
1
2
1 C 2 + 1.6 =
2.1
• Example 5: ↔ 0.5 (Fraction ↔ Decimal)
1
2
1 C 2 =
C
C
• Example 6: 1 ↔
235
3
1 C 2 C 3
A B
A B
— 9 —
1 2.
0.5
1
1 2 3.
5
1 2 3.
2.
3.

Percentage Calculations
• Use COMP mode for percentage calculations.
• Example 1: To calculate 12% of 1500.
1500 - 12 A v
• Example 2: To calculate what percentage of 880 is 660.
660 \ 880 A v
• Example 3: To add 15% onto 2500.
2500 - 15 A v +
• Example 4: To discount 3500 by 25%.
3500 - 25 A v ,
• Example 5: To calculate the following, using a constant.
12% of 1200 = 144
18% of 1200 = 216
23% of 1200 = 276
180.
75.
2875.
2625.
(12%) 1200 - - 12 A v
(18%) 18 A v
(23%) 23 A v
— 10 —
K
144.
K
216.
K
276.

Scientific Function Calculations
• Use COMP mode for scientific function calculations.
• Some calculations may take a long time to complete.
•Wait for result before starting next calculation.
• =3.1415926536.
kSexagesimal ↔ Decimal Conversion
• Example: 14°25’36” ↔ 14.42667
14 I 25 I 36 I
A O
kTrigonometric/Inverse Trigonometric Functions
• Example 1: sin ( rad) (RAD mode)
6
A x \ 6 = S
• Example 2: cos 63°52’41” (DEG mode)
63 I 52 I 41 I W
• Example 3: tan (앥35gra)(GRA mode)
35 E h
• Example 4: cos–1 ( rad) (RAD mode)
2
2
2 L \ 2 = A V
— 11 —
14.42666667
14°25°36
RAD
0.5
DEG
0.440283084
–0.612800788
GRA
RAD
0.785398163
kHyperbolic/Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
• Example 1: sinh 3.6 3.6 M S
18.28545536
• Example 2: sinh앥1 30 30 M A j
4.094622224
kCommon and Natural Logarithms, Exponents
• Example 1: log 1.23 1.23 R
• Example 2: In 90 (҃loge 90) 90 T
• Example 3: 64 R \ 4 R =
• Example 4: 10
Iog 64
Iog 4
0.4
ѿ5 e
앥3
.4 A Q +
5 - 3 E A U =
• Example 5: 2
• Example 6: 2
• Example 7: e
3
앥3
2 A w 3 E =
10
2 A w 3 =
10 A U
— 12 —
0.089905111
4.49980967
3.
2.760821773
8.
0.125
22026.46579

• Example 8: log sin 40° +log cos 35° (DEG mode)
40 S R +35 W R =
To con vert to antilogarithm:
A Q
–0.278567983
0.526540784
DEG
DEG
• Example 9: 8
1/3
8 A s 3 =
k Square Roots, Cube Roots, Squares,
Reciprocals and Factorials
• Example 1: 2 ѿ 3 ҂ 5
2 L + 3 L - 5 L =
3
• Example 2: 35 ѿ
앥27
5 A D + 27 E A D =
• Example 3: 123ѿ30
2
123 + 30 A K =
1
• Example 4:
1 앥 1
3 4
3 A X , 4 A X = A X
— 13 —
5.287196909
–1.290024053
2.
1023.
12.

• Example 5: 8! 8 A f
40320.
kFIX, SCI, NORM, RND, RAN#, ENG Calculations
• Example 1: 1.234ѿ1.234, rounding result to two places
(FIX 2).
F 7 2
1.234 +1.234 =
FIX
0.00
FIX
2.47
• Example 2: 1.234ѿ1.234, rounding input to two places.
F 7 21.234 A b +
1.234 A b =
• Press F9 to clear FIX specification.
• Example 3: 1쐦 3 , displaying result with two significant
digits (SCI 2).
F 8 2
1 \ 3 =
• Press F9 to clear SCI specification.
• Example 4: To convert 56,088 meters to kilometers.
56088 J
— 14 —
FIX
2.46
SCI
0.0
SCI
3.3
56.088
–01
00
03

• Example 5: To con vert 0.08125 grams to milligrams.
.08125 J
81.25
–03
• Example 6: To generate a random number between 0.000
and 0.999.
Example (results differ each time)
A c
0.664
kCoordinate Conversion
• Example 1: To convert polar coordinates (r҃2, ҃60°) to
rectangular coordinates (x, y). (DEG mode)
x 2 A z 60 =
y A N
DEG
DEG
1.732050808
1.
ANswaps displayed value with value in memory.
• Example 2: To convert rectangular coordinates (1, 3) to
polar coordinates (r, ). (RAD mode)
r 1 A y 3 L =
θ
A N
RAD
RAD
1.047197551
2.
kPermutation
• Example: To determine how many different 4-digit values
can be produced using the numbers 1 through 7.
7 A m 4 =
— 15 —
840.

kCombination
• Example: To determine how many different 4-member
groups can be organized in a group of 10 individuals.
10 A n 4 =
210.
Statisticasl Calculations (SD Mode)
• Press Flto enter the SD Mode for statistical calcula-
tions using standard deviation.
• If FIX or SCI is on the display, press F9 first.
• Data input always starts with Au.
• Example: To calculate nҀ1, n, o, n, ⌺x, and ⌺x2 for the
following data : 55, 54, 51, 55, 53, 53, 54, 52.
Enter SD Mode. F l
Input Data. A u 55 }
54 } 51 }
55 } 53 } }
54 } 52 }
Sample standard deviatio
Population standard deviation
n
A q
A p
— 16 —
52.
1.407885953
1.316956719
SD
0.
SD
SD
SD

Arithmetic mean A `
Number of data A r
Sum of values A o
Sum of squares of values A a
53.375
427.
22805.
SD
SD
8.
SD
SD
• }} inputs the same data twice (as above).
•You can also input multiple entries of the same data using
-. To input the data 110 ten times, for example, press
110 -10 }.
• The above results can be obtained in any order, and not
necessarily that shown above.
•To delete data you have just input, press A[.
— 17 —

kMaking Corrections During Data Input
• Example 1: To change data you have just input.
Correct Actual
51 } 50 }A [
130 31 }
130 31 }
• Example 2: To change data you previously input.
Correct
51 }
130 31 }
120 -
120 31
Actual Correction
49 }
120 30 }
Correction
51 }
t130 -
31 }
t130 -
31 }
49 A [
51 }
120 - 30 A [130 31 }
Technical Information
kKey and Their Functions
• General
Arithmetic calculations .......................... +, ,, -,
............. \, =
— 18 —

Clear (retains memory) ......................... k
Number input ........................................ 0 – 9, l
Power off ............................................... i
Power on; All clear ................................ t
Sign change .......................................... E
• Memory
Memory in ............................................. Y
Memory minus ...................................... A {
Memory plus ......................................... |
Memory recall ....................................... Z
• Special
Decimal-to-sexagesimal ........................ A O
Display/memory swap ........................... A N,
............. A d
Exponent ............................................... e
Internal rounding ................................... A b
Parentheses .......................................... O, P
Pi (3.1415926536) ................................ A x
Select mode .......................................... F
Sexagesimal-to-decimal ........................ I
Shifts key functions ............................... A
— 19 —

• Scientific Functions
Arc cosine ............................................. A V
Arc sine ................................................. A j
Arc tangent ............................................ A g
Common antilogarithm .......................... A Q
Common logarithm ................................ R
Cosine ...................................................W
Cube root .............................................. A D
Engineering ...........................................J, A P
Factorial ................................................ A f
Fraction ................................................. C
Fraction ................................................. A B
Hyperbolic ............................................. M
Natural antilogarithm ............................. A U
Natural logarithm ................................... T
Percent .................................................. A v
Polar-to-rectangular .............................. A z
Power ....................................................A w
Random number ................................... A c
Reciprocal ............................................. A X
Rectangular-to-polar ............................. A y
Root ...................................................... A s
Sine ....................................................... S
— 20 —

Square .................................................. A K
Square root ........................................... L
Tangent ................................................. h
Permutation ........................................... A m
Combination .......................................... A n
• Statistics (SD Mode)
Arithmetic mean .................................... A `
Data delete ............................................ A [
Data input .............................................. }
Number of data ..................................... A r
Population standard deviation ............... A p
Sample standard deviation ................... A q
Statistical register clear ......................... A u
Sum of squares of values ..................... A a
Sum of values ....................................... A o
kExponential Display Formats
This calculator can display up to 10 digits. Larger values are
automatically displayed using exponential notation. In the
case of decimal value, you can select between two formats
that determine at what point exponential notation is used.
— 21 —

• NORM 1
With NORM 1, exponential notation is automatically used
for integer values with more than 10 digits and decimal values
with more than two decimal places.
• NORM 2
With NORM 2, exponential notation is automatically used
for integer values with more than 10 digits and decimal values
with more than nine decimal places.
To switch between NORM 1 and NORM 2
Press F9. There is no indication on the display of which
for mat is currently in effect, but you can determine the setting
by performing the following calculation.
0.005
5.
–03
NORM 1 format
NORM 2 format
1 \ 200 =
• All of the examples in this manual show calculation results
using the NORM 1 format.
kWhen you have a problem...
If calculation results are not what you expect or if an error
occurs, perform the following steps.
1. F0 (COMP mode)
2. F4 (DEG mode)
3. F9 (NORM mode)
4. Check the formula you are working with to confirm it is
correct.
5. Enter the correct modes to perform the calculation and
try again.
— 22 —

kMaking Corrections During Calculations
• If you make a mistake when inputting a value (but did not
yet press an arithmetic operator key), press k to clear
the value and then input the correct one.
• In a series of calculations, press k while an intermediate
result is displayed to clear only the last calculation performed.
•To change the operator key (+, , , -, \, Aw,
As, etc.) you just pressed, simply press the correct
operator key. In this case, the operator of the last key
you press is used, but the operation retains the order of
precedence of the operation for the first key you pressed.
kOverflow or Error Check
The following conditions make further calculation impossible.
a. When a result (whether intermediate or final) or a
total accumulated in memory is greater than
±9.999999999 ҂ 10
display.)
b. When function calculations are performed using a value
that exceeds the input range. (“–E–” indicator appears
on the display.)
c. When an illogical operation (such as an attempt to calcu-
late o and
calculations. (“–E–” indicator appears on the display.)
d. When an illegal mathematical operation (such as division
by zero) is performed. (“–E–” indicator appears on display.)
99
. (“–E–” indicator appears on the
while n ҃ 0) is performed during statistical
n
— 23 —

e. The total number of nested parentheses levels exceeds
six, or when more than 18 pairs of parentheses are used.
(“– 1–” indicator appears on the display.)
•To clear any of the above conditions, press t and per-
form the calculation from the beginning.
• In the case of condition e, you could also press k. This
clears the intermediate result just prior to the overflow, so
you can continue with the calculation from that point.
• No error occurs when the result is within the range of
ѿ(1҂10
Ҁ99
) to Ҁ(1҂10
Ҁ99
). Instead, the display shows all
zeros.
kPower Supply
This calculator is powered by two AA-size manganese dry
batteries (R6P (SUM-3) or UM-3). Replace batteries as soon
as possible when display characters become dim and difficult
to read.
• Press t to turn power on.
• Press i to turn power off.
•Power automatically turns off (but data in memory is re-
tained) if no key operation is performed for about six
minutes.
Important!
Incorrect use of batteries can cause them to burst or leak,
possible damaging the calculator.
• Be sure to replace the batteries at least once every two
years, regardless of how much the calculator is used. Old
batteries may leak, causing serious damage to the interior
of the calculator.
— 24 —

• The batteries that come in the calculator when you pur-
chase it are for testing only. They may not provide full
service life.
• All data stored in memory is lost when you replace the
batteries. Be sure to write down important data before replacing the batteries.
• Always be sure to load the batteries so their positive (ѿ)
and negative (Ҁ) ends are facing correctly.
•Never mix batteries of different types.
• Never mix new batteries with old ones.
• Never try to charge batteries, take them apart, or allow
them to become shorted. Keep batteries away from direct
flame and heat.
Keep batteries out of the reach of small children. If
•
swallowed, consult with your physician immediately.
To replace the batteries
1. Press i to tur n power off.
2. Remove the screws that hold the
back cover in place, and then remove the cover.
3. Remove the old batteries.
4. Install two new batteries with the
positive (ѿ) and negative (Ҁ )
ends facing correctly.
5. Replace the back cover and
secure it in place with the screws.
tto turn power on.
6. Press
— 25 —
Screws
Batteries
Screws

kOrder of Operations and Levels
Operations are performed in the following order of precedence.
1. Functions
1/y
2. xy, x
, R →P, P →R, nPr, nCr
3. ҂, 앦
4. ѿ, Ҁ
• Operations with the same precedence are performed from
left to right, with operations enclosed in parentheses performed first. If parentheses are nested, the operaitons enclosed in the innermost set of parentheses are performed
first.
• Registers L
gisters, so calculations up to six levels can be stored.
• Each level can contain up to three open parentheses, so
parentheses can be nested up to 18 times.
• Example: The following operation uses 4 levels and 5
nested parentheses.
- O O O 3 + 4 - O O 5 + 4
2
The table below shows register contents following the
above input.
through L6 store operations. There are six re-
1
— 26 —
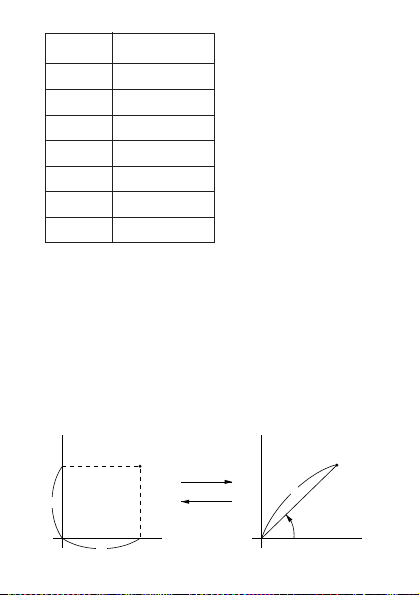
Register Contents
x
4
L
(( 5 ѿ
1
L
4 ҂
2
L
((( 3 ѿ
3
L
2 ҂
4
L
5
L
6
kFormulas, Ranges, and Conventions
The following are the formulas, ranges, and conventions that
are applied to various calculations that can be performed
using this calculator.
Coordinate Transformation
• With polar coordinates, θ can be calculated within a range
of –180°쏝θ 울180°. The calculation range is the same for
radians and grads.
Y
P (x, y)
y
X0
x
— 27 —
Pol
Rec
Y
P (r, )
θ
r
θ
X0
Permutation
• Input range: n 욷 r 욷 0 (n, r : natural numbers)
• Formula: nPr ҃
n!
(nҀr)!
Combination
• Input range: n 욷 r 욷 0 (n, r : natural numbers)
• Formula: nCr ҃
n!
n!(nҀr)!
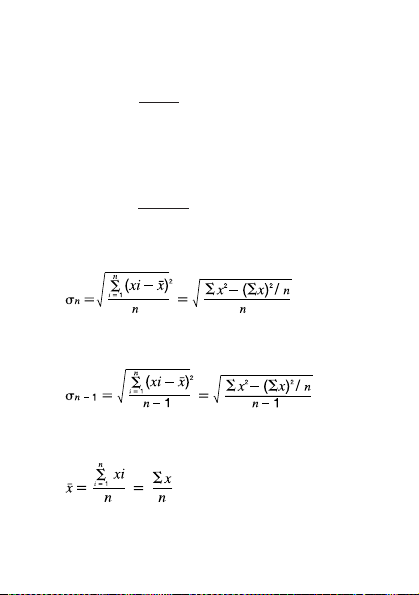
Population Standard Deviation
Sample Standard Deviation
Arithmetic Mean
— 28 —

kSpecifications
Power supply : Tw o AA-size manganese dry batteries
Battery Life: Approximately 9,000 hours continuous
Power
Consumption: 0.0004W
Input Ranges:
sinx
cosx
tanx
–1
sin
x
–1
x
cos
tan–1x
sinhx
coshx
tanhx
–1
sinh
x
–1
cosh
–1
tanh
logx/lnx
x
10
(UM-3 or R6P (SUM-3))
operation on type UM-3, 11,000 hours
continuous operation on R6P(SUM-3)
Input RangeFunctions
(DEG)앚x앚쏝9҂10
(RAD)앚x앚쏝5҂107 rad
(GRA)앚x앚쏝1҂10
9
10
grad
앚x앚울 1
100
10
앚x앚쏝 1 ҂
앚x앚울 230.2585092
앚x앚쏝 1҂
앚x앚쏝 5 ҂
1울 x 쏝 5 ҂
x
앚x앚쏝 1
x
1҂
–1҂
–99
10
10
100
10
99
10
울 x 쏝 1 ҂
100
쏝 x 쏝
For sinh and tanh,errors are
cumulative and accuracy is affected at a certain point when
x=0.
99
10
100
10
100
— 29 —
However, for tan x:
앚x앚≠ 90(2nѿ1):DEG
앚x앚≠ Ⲑ2·(2nѿ1):RAD
앚x앚≠ 100(2nѿ1):GRA

x
e
x
2
x
1/x
3
x
x!
nPr/nCr
R→P
P→R
°’ ”
y
x
Input RangeFunctions
100
–1҂
10
쏝 x 울 230.2585092
0 울 x 쏝 1 ҂
앚x앚쏝 1҂
앚x앚쏝 1҂
앚x앚쏝 1҂
0울 x 울
100
10
50
10
100
10
;
x ≠
100
10
69 (
x is an integer)
0
0 울 r 울n
10
n 쏝1҂10
(n and r are integers)
x2 ѿ y2 쏝1҂10
0 울 r 쏝 1҂10
(DEG)앚앚쏝9҂10
(RAD)앚앚쏝5҂107 rad
(GRA)앚앚쏝1҂10
Sexagesimal: 앚a앚, b, c쏝10
100
100
However, for tan
9
앚앚≠ 90(2nѿ1):DEG
앚앚≠ Ⲑ2·(2nѿ1):RAD
10
grad
앚앚≠ 100(2nѿ1):GRA
100
0 울 b, c
Decimal: 앚x앚 울2.777777777҂10
x 쏜 0: –1҂10
x ҃ 0: y 쏜 0
x 쏝 0: y ҃ n; (n is an integer)
However: –1҂10
100
쏝 y log x 쏝100
1
2nѿ1
100
쏝 y log 앚x앚쏝100
— 30 —
:
96

Input RangeFunctions
x 쏜0: y ≠ 0
100
–1҂10
쏝1/y log x 쏝100
x ҃ 0: y 쏜 0
1/y
x
x 쏝 0: y ҃ 2nѿ1; (n ≠ 0; n is an integer)
However: –1҂10
Total of integer, numerator, and denominator
a b/c
must be 10 digits or less (including division
1
n
100
쏝1/y log 앚x앚쏝100
marks).
y
, x
50
100
1/y
, x!, and
3
x , so accuracy may be
앚x앚쏝 1҂10
앚n앚쏝 1҂10
SD
n , o : n ≠ 0
n –1 : n ≠ 0, 1
• Errors are cumulative with such internal continuous
calculations as x
adversely affected.
Operating Temperature:
0°C–40°C (32°F–104°F)
Dimensions: 19(H)쎹73(W)쎹147(D) mm
Weight: 104g including batteries
— 31 —

Calculation Capacity:
• Input/ Basic Calculations
10-digit mantissa; or 10-digit mantissa plus 2-digit exponent up to 10
±99
— 32 —

CASIO COMPUTER CO., LTD.
6-2, Hon-machi 1-chome,
Shibuya-ku, Tokyo 151-8543, Japan
SA9707-B Printed in China
Imprimé en Chine
 Loading...
Loading...