Page 1

Chapter
Dual Graph
Dual Graph lets you split the display between two different
screens, which you can then use to draw different graphs at the
same time. Dual Graph gives you valuable graph analysis
capabilities.
•You should be familiar with the contents of “8-3 Graph Function
Operations” before reading this chapter.
11-1 Before Using Dual Graph
11-2 Specifying the Left and Right View Window
Parameters
11-3 Drawing a Graph in the Active Screen
11-4 Displaying a Graph in the Inactive Screen
11
Page 2
11-1 Before Using Dual Graph
1. From the Main Menu, enter the GRAPH Mode. Next, display the set up screen
P. 7
P. 11 2
and specify “Graph” for Dual Screen.
2. Press J.
• For further details about the function key menu at the bottom of the display, see
“8-1 Before Trying to Draw a Graph”.
•8,192 bytes of memory are used whenever you set the Dual Screen setting to
“Graph”.
kk
k About Dual Graph Screen Types
kk
The screen on the left side of the display is called the
on the left side of the display is called the
is the
inactive screen
execute while using Dual Graph is always applied to the active graph. To execute
a function on the right-side inactive graph, you must first make it active by moving
it into the active screen.
Active Screen
Actual graph drawing is done here.
, which contains the
active graph
inactive graph
active screen
. Conversely, the right side
. Any function that you
, and the graph
168
Inactive Screen
Use the inactive screen to make copies of active screen graphs, and for the result of
Zoom operations.
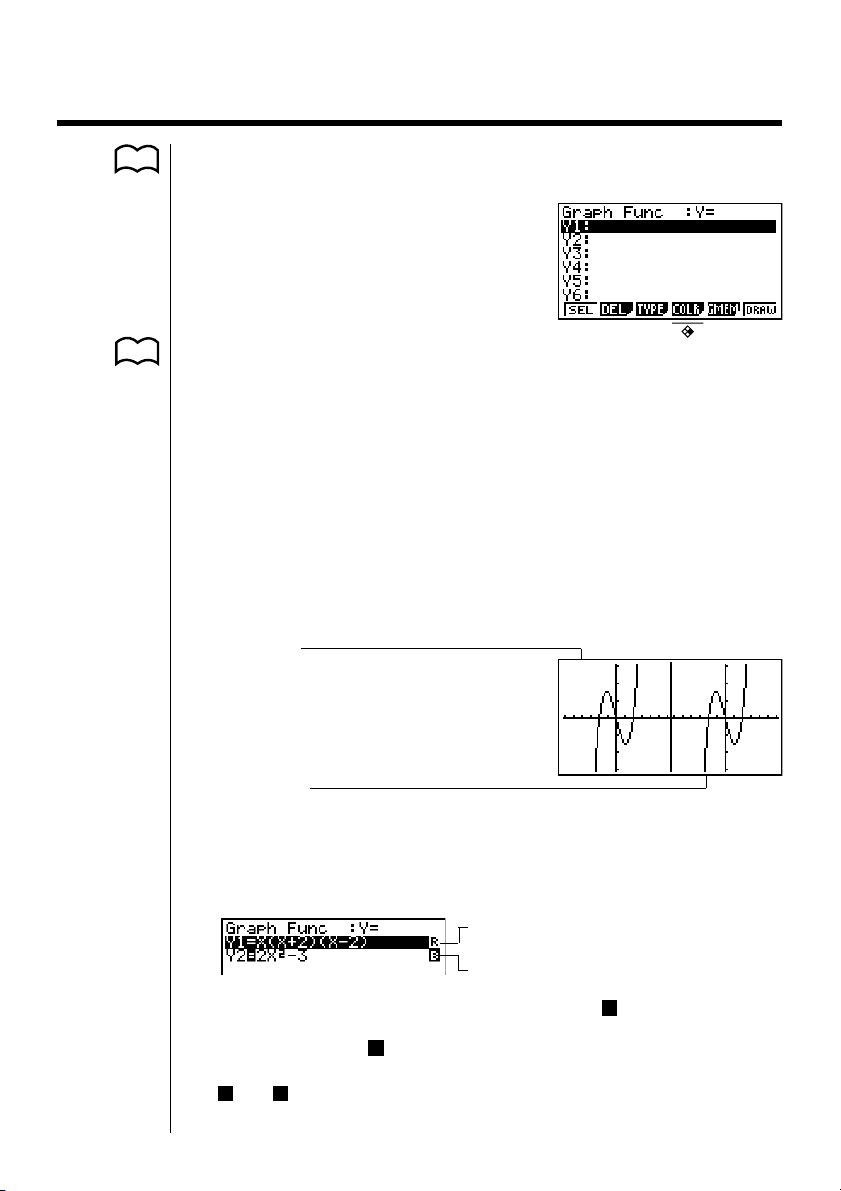
•Indicators appear to the right of the formulas in the function memory list to tell
where graphs are drawn with Dual Graph.
Indicates inactive graph (on right side of
display)
Indicates graph drawn on both sides of display
Performing a draw operation with the function marked “R” in the above example
screen causes the graph to be drawn on the right (inactive) side on the display.
The function marked “B” is drawn on both sides of the graph.
Pressing 1 (SEL) while one of the function’s is highlighted would causes its
“R” or “B” indicator to be cleared. A function without an indicator is drawn as
the active graph (on the left side of the display).
Page 3

Before Using Dual Graph 11 - 1
11-2 Specifying the Left and Right View Window
Parameters
You can specify different View Window parameter for the left and right sides of the
graph display.
uu
uTo specify View Window parameters
uu
Press !3 (V-Window) to display the View Window parameter setting screen
for the active (left side) graph.
P. 11 5
P. 11 6
P. 11 3
•{INIT}/{TRIG}/{STD} ... View Window {normal initialization}/{trigonometric
initialization}/{standardization}
•{STO}/{RCL} ... View Window setting {store}/{recall}
•{RIGHT}/{LEFT} ... {active (left)}/{inactive (right)} screen View Window setting
swap
•Use the procedures described under “View Window (V-Window) Settings” to
input parameter values.
•Use the following key operations to change to different screens while inputting
View Window parameters for the left and right side screens.
While the View Window parameter setting screen for the active graph is shown:
• 6 (RIGHT) .... displays the inactive graph View Window parameter setting
screen
While the View Window parameter setting screen for the inactive graph is
shown:
• 6 (LEFT) ...... displays the active graph View Window parameter setting
screen
169
Page 4

11-3 Drawing a Graph in the Active Screen
You can draw graphs in the active screen. You can then copy or move the graph to
the inactive screen.
uu
uDrawing a graph in the active screen
uu
Example To draw the graph of y = x (x + 1) (x – 1) in the active screen
Use the following View Window parameters:
Xmin = –2 Ymin = –2
Xmax = 2 Ymax = 2
Xscale = 0.5 Yscale = 1
Input the function.
v(v+b)(v-b)
Store the function.
w
Draw the graph.
6 (DRAW) or w
170
Page 5

11-4 Displaying a Graph in the Inactive Screen
There are two methods you can use to display a graph in the inactive screen. You
can copy a graph from the active screen to the inactive screen, or you can move
the graph from the active screen to the inactive screen. In both cases, you must
first draw the graph in the left-side active screen.
kk
k Before Displaying a Graph in the Inactive Screen
kk
After drawing a graph in the active screen, press K, and the Dual Graph
function menu appears at the bottom of the display.
• {COPY} ... {copies active graph to inactive screen}
• {SWAP} ... {switches active screen and inactive screen}
P. 139
• {PICT} ... {picture function}
kk
k Copying the Active Graph to the Inactive Screen
kk
Example To draw the graph for y = x (x + 1) (x – 1) on the active screen
and the inactive screen
Use the following View Window parameters:
Active (Left) Screen Inactive (Right) Screen
View Window parameters View Window parameters
Xmin = –2 Ymin = –2 Xmin = –4 Ymin = –3
Xmax = 2 Ymax = 2 Xmax = 4 Ymax = 3
Xscale = 0.5 Yscale = 1 Xscale = 1 Yscale = 1
Assume that the function being graphed is stored in memory area Y1.
Draw the graph in the active screen. Copy the graph to the inactive
6(DRAW) (right) screen.
K1(COPY)
• The graph is reproduced using the inactive screen View Window parameters.
171
Page 6

11 - 4 Displaying a Graph in the Inactive Screen
kk
k Switching the Contents of the Active and Inactive Screens
kk
Switch the screens.
K2(SWAP)
•Note that using 2 (SWAP) to switch the screens also switches their View
Window parameters.
kk
k Drawing Different Graphs on the Active Screen and
kk
Inactive Screen
Example To draw the graphs of the following functions on the screens
Use the View Window parameters shown below.
Assume that the functions being graphed are stored in memory areas Y1 and Y2.
Select the function for the graph that you want to end up in the inactive (right)
screen.
Draw the graph in the active screen.
noted:
Active Screen: y = x (x + 1) (x – 1)
Inactive Screen: y = 2x2 – 3
Active (Left) Screen Inactive (Right) Screen
View Window parameters View Window parameters
Xmin = –4 Ymin = –5 Xmin = –2 Ymin = –2
Xmax = 4 Ymax = 5 Xmax = 2 Ymax = 2
Xscale = 1 Yscale = 1 Xscale = 0.5 Yscale = 1
1(SEL)
6(DRAW)
172
Page 7

Displaying a Graph in the Inactive Screen 11 - 4
Swap the screens so the graph is on the inactive (right) screen.
K2(SWAP)
Select the function for the graph that you want in the now-empty active (left)
screen.
A1(SEL)
Draw the graph.
6(DRAW)
•At this point, you could perform a copy operation and superimpose the active
graph over the inactive graph.
K1(COPY)
•Pressing !6 (G ↔ T) lets you switch between display of the active and
inactive graphs, using the entire display for each.
!6(G ↔ T)
!6(G ↔ T)
!6(G ↔ T)
173
Page 8

11 - 4 Displaying a Graph in the Inactive Screen
kk
k Other Graph Functions with Dual Graph
kk
After drawing a graph using Dual Graph, you can use the trace, zoom, sketch and
P. 128
scroll functions. Note, however, that these functions are available only for the
active (left) graph. For details on using these functions, see “8-6 Other Graphing
Functions”.
•To perform any of the above operations on the inactive graph, first move the
inactive graph to the active screen.
• The graph screen will not scroll while a trace operation is being performed on
the active graph.
The following shows some example operations using the zoom function.
Example 1 To use box zoom to enlarge the graph of y = x (x + 1) (x – 1)
Use the following View Window parameters for the active graph.
Xmin = –2 Ymin = –2
Xmax = 2 Ymax = 2
Xscale = 0.5 Yscale = 1
Assume that the function is already stored in memory area Y1.
Press 6 (DRAW) or w to draw the graph.
174
!2(Zoom)1(BOX)
•Use the cursor keys to move the pointer to
one of the corners of the box and then press
w.
•Use the cursor keys to move to the opposite corner of the box and then press
w to enlarge the graph.
• The zoom operation changes the View Window parameters of the inactive
screen, so the graph in the inactive screen is cleared.
 Loading...
Loading...