Page 1

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe
Directions For Use
Pump MK4
Model: 8005PK201
en
s
Page 2

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Contents
Introduction ..............................................................................................2
About This Manual ........................................................................................3
TCI Overview ..............................................................................................4
Creating a Data Set ........................................................................................7
Features of the Pump ......................................................................................8
Controls and Indicators ...................................................................................9
Symbol Definitions .......................................................................................10
Main Display Features ....................................................................................11
Operating Precautions ...................................................................................13
Getting Started ..........................................................................................16
Syringe Loading ..........................................................................................18
Starting the Pump ........................................................................................21
Basic Features ............................................................................................23
Operations During Use ...................................................................................25
Alarms and Warnings .....................................................................................27
Prompts .................................................................................................28
Configured Options ......................................................................................29
Specifications ............................................................................................33
Recognised Syringes .....................................................................................36
Associated Products ......................................................................................37
Compatible Extension Sets ...............................................................................38
Maintenance .............................................................................................41
Occlusion Pressure Limits ................................................................................43
IrDA, RS232 and Nurse call Specification ..................................................................44
Trumpet Curves and Start-up Curves .....................................................................46
Profiles from TCI Mode ...................................................................................47
Products and Spare Parts .................................................................................50
Service Contacts .........................................................................................51
Page
1000DF00741 Issue 5
1/52
Page 3

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Introduction
Introduction
This Directions for use can be used with the Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump MK4.
The Pumps can be identified as MK4 version by the MK4 on
w
The Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump (hereinafter referred to as Pump) provides the user with an infusion tool for the administration of drugs
for anaesthesia. The embedded software within the Pump is loaded with three compartment pharmacokinetic predictive models and
has 4 modes of operation:
1. Continuous infusion (ml/h)
2. Total Intravenous Anaesthesia (TIVA) mode.
3. Total Intravenous Anaesthesia (TIVA) with TCI predictions mode.
4. TCI Mode
The Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump has a user friendly interface that displays the infusion rate, the total drug dose delivered, and the
estimated plasma and effect-site concentrations to enable the user to follow the drug prescription information from the relevant
country.
the label on the rear case, see image right, or by verifying the
software version as 3.3.0 or above on power up.
– In this mode the user is able to select the infusion rate and administer bolus doses as required.
– In this mode the user is able to select the infusion rate and administer bolus doses as required. The pharmacokinetic model is
used to estimate the plasma and effect site concentration.
• Plasma target-controlled infusion (TCI).
– In this mode the user selects the desired (target) plasma drug concentration, and the pharmacokinetic model is used to
calculate the infusion rates required to achieve that concentration. A graphic display shows the trajectory of the estimated
plasma and effect site drug concentration over time.
• Effect Site target-controlled infusion (TCI).
– In this mode the user sets the desired effect site target concentration and the pharmacodynamic model is used to calculate
the infusion rates required to achieve that concentration. A graphic display shows the trajectory of the estimated effect site
and plasma concentration over time.
Intended Purpose
The Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump is intended for use by medical staff for purposes of controlling infusion rate and volume.
Conditions of Use
The Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump should only be operated by a clinician competent in use of automated syringe pumps and postplacement management of intravenous catheters.
Use of the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump does not limit the responsibility of the anaesthetist for drugs administration. It is important that
users operating the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump are fully aware of the available literature for any model used in association with a drug
and that they refer to the prescribed information for rate and dosing limits. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Interactions among
anaesthetic drugs are known, but are not taken into account in the calculation of the plasma and effect site concentrations.
The user should be appropriately trained in the use of the Pump and should follow the recommendations of this Direction For Use
(DFU).
In particular, the user must be aware that starting the Pump in a TCI mode will result in the automatic infusion of a pre-calculated bolus
dose followed by an infusion to achieve the selected target concentration. The initial parameter calculations are displayed on screen
prior to starting the infusion. It is thus essential that the user verifies that the patient characteristics and the selected infusion rate or
target concentration conform with the drug prescribing information of the relevant country.
CareFusion has verified the accuracy of the mathematical model implementation as well as pump delivery accuracy - (specification and
accuracy of pump - delivery are available in 'Profiles from TCI Mode' section).
Different drugs are associated with dedicated models – each model consists of a set of standard pharmacokinetic parameters which can
be selected and used by the embedded 3 compartment model used in the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump (where use of that drug in TCI
mode is authorised);
Diprivan from ASTRA-ZENECA is the only recommended Propofol formulation to be used in TCI mode as per prescribing information.
This Pump includes the Marsh model for the calculation of the Diprivan infusion rates, and plasma and effect-site concentrations.
When Remifentanil and Sufentanil are used in TCI mode, – the Minto and Gepts models respectively – are used to calculate the required
infusion rates.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
2/52
Page 4

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
About This Manual
CareFusion cannot guarantee the continued system accuracy with other manufacturer’s syringes as identified in the
w
Indications
The Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump is indicated for the administration of drugs for anaesthesia
Contraindications
The Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pumps are contraindicated for:
‘Recognised Syringes’ table. Manufacturers may change syringe specification significant to system accuracy without
prior notification.
• enteral therapies
• epidural infusion therapies
About This Manual
The user must be thoroughly familiar with the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump described in this manual prior to use.
All illustrations used in this manual show typical settings and values which may be used in setting up the functions of the Pump. These
settings and values are for illustrative use only. Where stated, a minimum infusion rate refers to a nominal rate of 1.0ml/h, and an
intermediate infusion rate refers to a nominal rate of 5.0ml/h. The complete range of infusion rates, settings and values are shown in the
'Specifications' section.
It is important to ensure that you only refer to the most recent version of the Directions for Use and Technical Service
w
Conventions used in this manual
BOLD Used for Display names, software commands, controls and indicators referenced in this manual, for
'Single quotes' Used to indicate cross-references made to another section of this manual.
Italics Used to refer to other documents or manuals and also used for emphasis.
w
Manual for your CareFusion products. These documents are referenced on www.carefusion.com. Copies can be
obtained by contacting your local CareFusion representative.
example, Battery Indicator, PURGE, ON/OFF button.
Important Information: Wherever this symbol is shown an Important note is found. These notes highlight
an aspect of use that is important for the user to be aware of when operating the Pump.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
3/52
Page 5
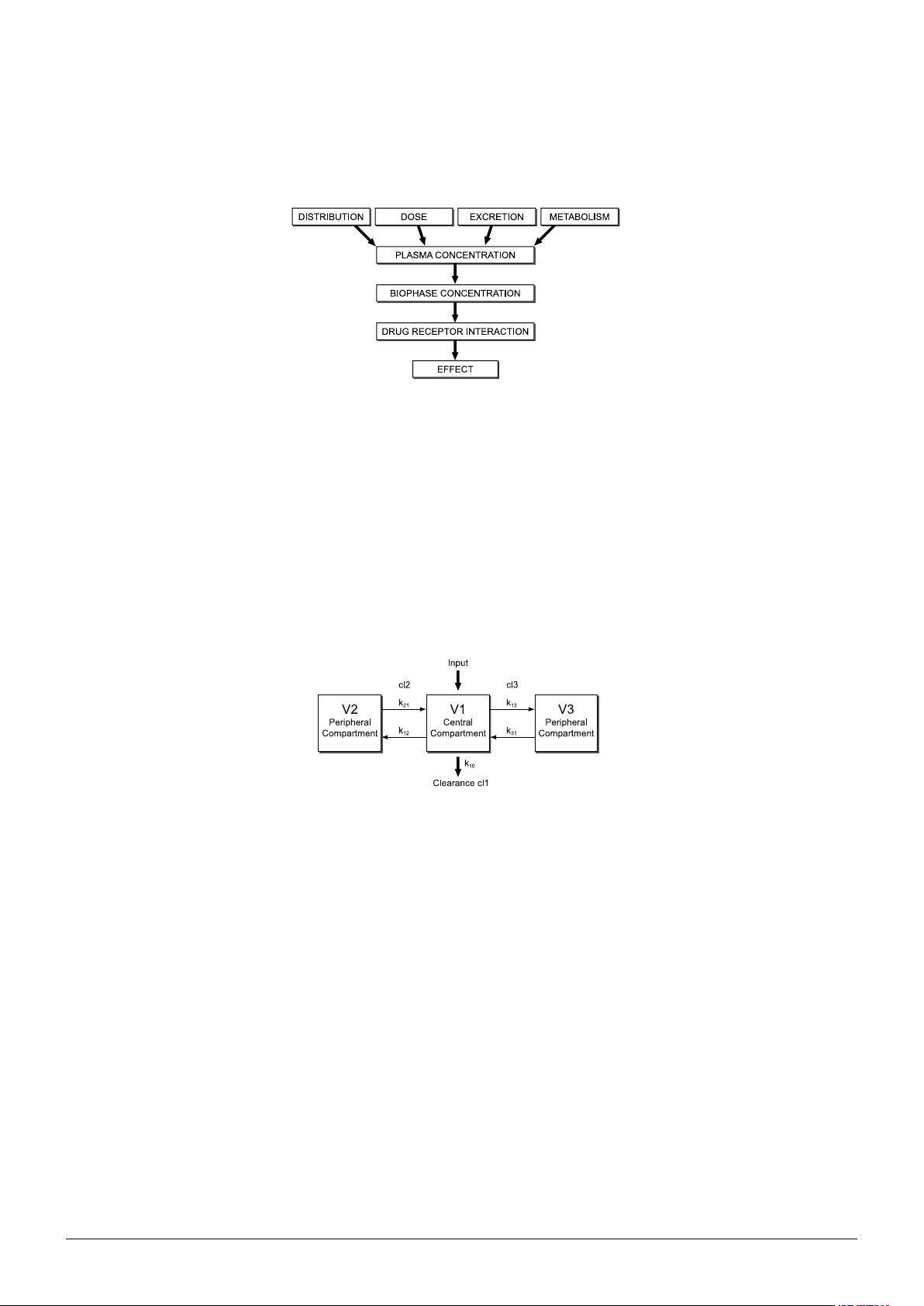
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
TCI Overview
TCI Overview
The dose-response relationship can be divided into three parts: the relationship between administered dose and plasma concentration
(the pharmacokinetic phase), the relationship between effect organ concentration and clinical effect (the pharmacodynamic phase) and
the coupling between pharmacokinetics and dynamics. The ultimate goal when administering a particular dose of a drug is to obtain
the desired clinical effect, for which a specific therapeutic concentration of the drug at the site of action (the receptor) is necessary.
Fig. 1: Schematic representation of the pharmacokinetic and dynamic processes determining the relationship between administered dose
and resulting effect intensity of a drug. Pharmacokinetic factors such as distribution, metabolism, and/or excretion determine the relationship
between drug dose and drug-concentration in the plasma and bio-phase (effect-site). In the bio-phase the drug interacts with the receptor
resulting in the pharmacological effect.
Until recently, when intravenous anaesthetic agents were used for induction or maintenance of anaesthesia, they were administered
either manually (by hand) or by simple infusion pumps (the anaesthetist calculated the infusion according to the body weight
of the patient). Inline measurement of concentrations is not possible, and the polyexponential equations required to predict the
concentrations requires vast computer processing power. Based on the pioneering work of Kruger-Thiemer2 and Schwilden et al.3, the
TCI concept was developed during the 1980’s and early 1990’s, as advances in computer technology made inline predictions of drug
concentrations feasible.
The pharmacokinetic behaviour of most anaesthetic drugs can be described mathematically with a 3-compartment model: usually a
central compartment (V1), a vessel-rich compartment (V2) and a vessel-poor compartment (V3) are described. Transfer of drug between
different compartments (distribution) is described by rate constants (k
by the rate constant k10 (Fig. 2). The aim of TCI techniques is to use pharmacokinetic modelling to calculate the infusion rates required to
achieve a desired plasma concentration. Thus, instead of specifying an infusion rate, the user specifies a "target" concentration, based on
clinical judgement. When a concentration in the plasma compartment is targeted, this is called "open-loop plasma targeted TCI". When a
certain concentration at the effect compartment is targeted, then this is called "open-loop effect-site targeted TCI".
1
, k21, k31 and k13) or clearances. Drug metabolism is described
12
Fig. 2: Schematic representation of the three compartment model used for target-controlled infusions.
For anaesthetic agents the effect-site (or bio-phase) is not the plasma4 but the brain, where concentrations cannot be directly measured.
Until the early 1990’s it was considered that blood-brain equilibration was virtually instantaneous. Early TCI systems were thus all
plasma-targeted. For many drugs the relationship between plasma concentration and clinical effect was described, usually in terms of
the Cp50 or Cp95 (the concentrations required to elicit a specified clinical effect in 50 or 95% of patients respectively). For an example
see Ausems et al.
5
During the 1990’s it was increasingly appreciated that after a change in plasma concentration there is a temporal delay in equilibration
between the plasma and effect-site concentrations. The clinical effect changes in parallel with the effect-site concentration, and so
for most drugs the rate of drug transfer into and from the site of action can be characterized by the time-course of drug effect
6,7
. This
means that the effect can be transferred to concentrations, thereby resulting in a quantitative approach. The concentration at the site of
action is called "the effect-site concentration" and the corresponding compartment8 (see Fig. 3) is called "the effect-site compartment".
Because the actual amount of drug entering the brain is very small, the effect-site compartment can be regarded as having no volume,
the rate constant k1e can be ignored and the rate constant keo can be used to describe the rate of equilibration between the plasma and
effect-site compartments.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
4/52
Page 6
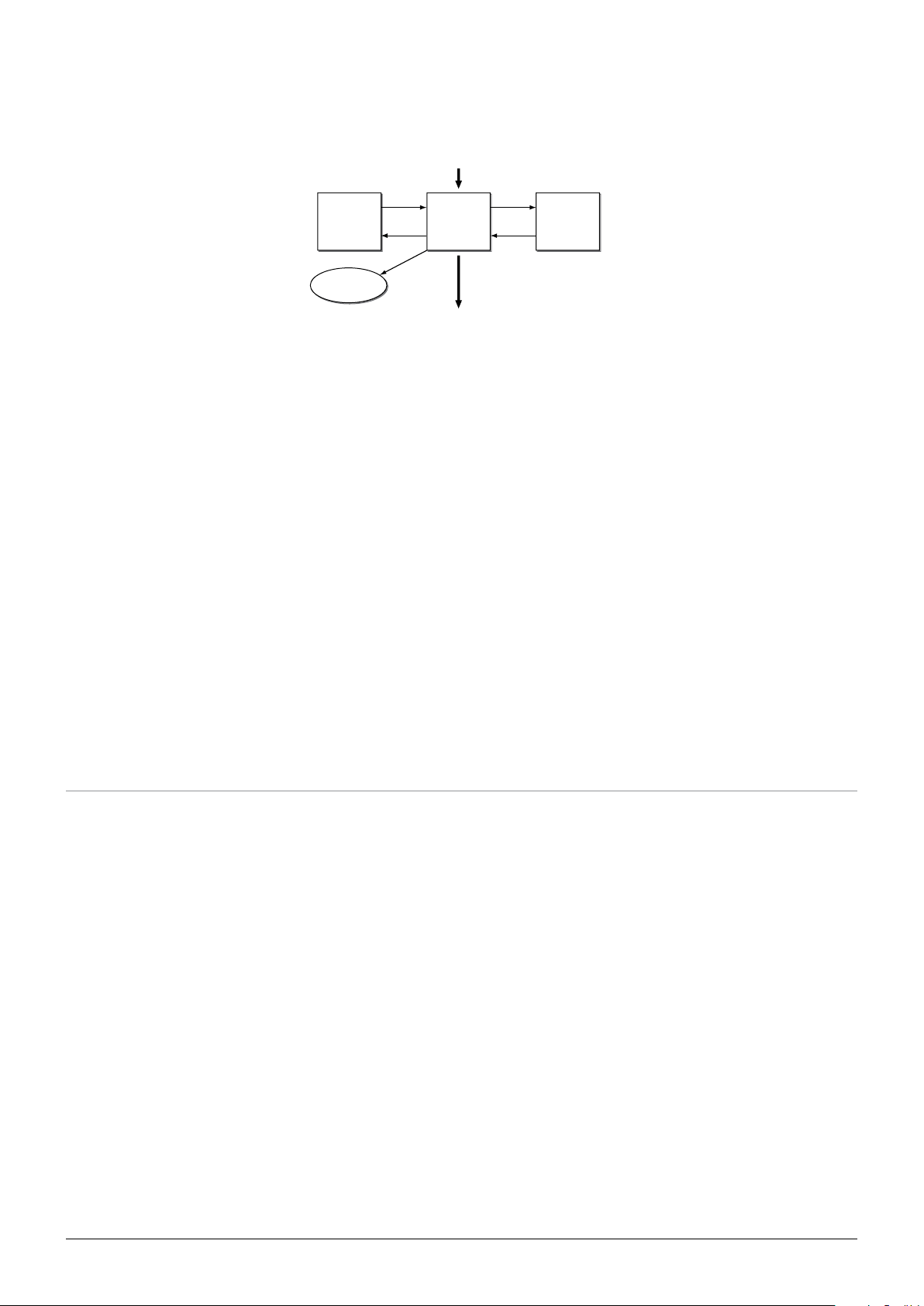
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Input
TCI Overview
Knowledge of the keo for various agents has made targeting of the effect-site possible. With effect-site targeting the TCI system first
calculates the necessary plasma concentration profile required to achieve the effect-site target as rapidly as possible, and then calculates
the infusion rates required to achieve that plasma concentration profile (Fig 3). Effect Site vs Plasma Concentration will generate a larger
induction dose followed by a pause in the infusion to allow plasma to equilibrate with effect site concentration.
cl2
k
V2
Peripheral
Compartment
Effect
Compartment
Fig. 3: Schematic representation of the concentration-effect relationship.
21
k
12
k
eo
V1 V3
Central
Compartment
Clearance cl1
cl3
k
13
Peripheral
k
31
Compartment
k
10
TCI infusion pumps can provide optimal control of anaesthesia when the three elements mentioned above have been accurately
modelled and described. Firstly, the model that controls the Pump has to work accurately (The models used in the Alaris PK Plus Syringe
Pump are well-validated and accepted). Secondly, the pharmacokinetic parameter set of a particular drug used by the computer model
should match the pharmacokinetics of the patient (it should be remembered that the models described in the literature are based on
"population" data, and apply to an "average" patient. They do not take account of the inter-patient pharmacokinetic variability). Thirdly,
the pharmacodynamics of the administered drug should be well understood to enable the user to select the plasma or effect-site
concentration needed for the required effect (with most anaesthetic agents there is broad inter-patient pharmacodynamic variability,
and so the user needs to match knowledge of the general population pharmacodynamic data with careful observation of the individual
patient to ascertain that individual’s sensitivity to the drug, to enable titration to effect if necessary).
Note: Specific model parameters are available in the "TCI Overview" section or directly on the Pump via the information key when
selecting drugs. Users should refer to the drug- prescribing information to verify that TCI mode is authorised in their respective
countries.
References :
1. Danhof M: Does variability explain (all) variability in drug effects ?, Topics in pharmaceutical science. Edited by Breimer DD, Crommelin DJA, Midha KK. Noordwijk, Amsterdam
Med. Press BV, 1989, pp 573-586
2. Kruger-Theimer E: Continuous intravenous infusion and multicompartment accumulation. Eur J Pharmacol 1968; 4: 317-324
3. Schwilden H: A general method for calculating the dosage scheme in linear pharmacokinetics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1981; 20: 379-86
4. Shafer SL: Towards optimal intravenous dosing strategies. Seminars in Anesthesia 1993; 12: 222-234
5. Ausems ME, Hug CC, Jr., Stanski DR, Burm AG: Plasma concentrations of alfentanil required to supplement nitrous oxide anesthesia for general surgery. Anesthesiology 1986;
65: 362-73
6. Schnider TW, Minto CF, Stanski DR: The effect compartment concept in pharmacodynamic modelling. Anaesthetic Pharmacology Review 1994; 2: 204-213
7. Shafer SL: Principles of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics., Principles and practice of anesthesiology. 2nd Edition. Edited by Longnecker DE, Tinker JH, Morgan GE.
New York, Mosby-Year Book, 1998, pp 1159- 1210
8. Shafer SL, Gregg KM: Algorithms to rapidly achieve and maintain stable drug concentrations at the site of drug effect with a computer-controlled infusion pump. J
Pharmacokinet Biopharm 1992; 20: 147-69
TCI Precautions
When first starting the infusion the pharmacokinetic / pharmacodynamic models within the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump are
reset to zero. Therefore, for any reason, if the Pump is switched off during the surgical procedure all current pharmacokinetic /
pharmacodynamic model information will be lost. Under such circumstances switching the Pump off and on and restarting the infusion
whilst the patient contains a significant residual drug dose could result in an over-infusion and, therefore, the Pump should not be
restarted in TCI mode.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
5/52
Page 7

Pharmacokinetic models in Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump and their parameters
Drug: Diprivan Model: Marsh (weight adjusted)
Age Limit: 16 years upwards
Unit of Plasma Concentration: µg/ml
Max. Plasma Concentration: 15 µg/ml
Vc = 0.228 x mass (litres x kg-1)
k10 = 0.119 minutes
k12 = 0.112 minutes
k13 = 0.0419 minutes
k21 = 0.055 minutes
k31 = 0.0033 minutes
keo = 0.26 minutes
Reference from the literature: Marsh et al.: Brit J Anaesth 1991, 67, 41-48
Drug : Remifentanil Model: Minto
Age Limit: 12 years upwards
Unit of Plasma Concentration: ng/ml
Max. Plasma concentration: 20 ng/ml
Vc = 5.1 - 0.0201 x (age-40) + 0.072 x (lbm-55)
V2 = 9.82 - 0.0811 x (age-40) + 0.108 x (lbm-55)
V3 = 5.42
cl1 = 2.6 - 0.0162 x (age - 40) + 0.0191 x (lbm - 55)
cl2 = 2.05 - 0.0301 x (age - 40)
cl3 = 0.076 - 0.00113 x (age - 40)
k
= cl1 / Vc
10
k12 = cl2 / Vc
k
= cl3 / Vc
13
= cl2 / V2
k
21
k31 = cl3 / V3
keo = 0.595 - 0.007 x (age - 40)
Reference from the literature : Minto et al.: Anesthesiology 1997, 86, 10 - 33
-1
-1
-1
-1
-1
-1
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
TCI Overview
Drug : Sufentanil Model: Gepts (not weight adjusted)
Age Limit: 12 years upwards
Unit of Plasma Concentration: ng/ml
Max. Plasma concentration: 2 ng/ml
Vc = 14.3 l
k
= 0.0645 minutes
10
k12 = 0.1086 minutes
k13 = 0.0229 minutes
k21 = 0.0245 minutes
k31 = 0.0013 minutes
-1
-1
-1
-1
-1
Reference from the literature : Gepts et al.: Anesthesiology 1995, 83, 1194-1204
Additional :
k
calculated with time to peak effect 5.6 minutes (keo = 0.17559 minutes-1) (reference: Shafer et al Anesthesiology. 1991 Jan;74(1):53-
eo
63)
1000DF00741 Issue 5
6/52
Page 8
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Creating a Data Set
Creating a Data Set
To fully utilise the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump a Data Set will need to be developed, reviewed, approved, released, uploaded and
verified according to the following process. Refer to the Alaris PK Editor Software Directions for Use (1000CH00016) for further details
and operating precautions.
1. Create Master Lists (Using Alaris PK Editor Software)
• Master Drugs* A list of drug names and standard concentrations. These may be for TIVA use or
may have an associated PK/PD model for TCI use.
• Alaris PK Plus Syringe Library Configure syringes enabled for use
2. Create Profile (Using Alaris PK Editor Software)
• Profile Drugs* Drugs and concentrations for this profile with defaults, minimum and
maximum limits and targets and occlusion level.
• Pump Configuration** Pump configuration settings and general options.
3. Review, Approve and Release (Using Alaris PK Editor Software)
• Review and Approve Entire Data Set Report to be printed, reviewed and signed as proof of approval
by an authorised person according to Hospital protocol. Signed printout to be
kept safe for use during verification procedure.
• Release Data Set status to be promoted to Released (password is required).
4. Upload Data Set to Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump (Using Alaris PK Editor Transfer Tool)
5. Verify Data Set Upload
• First or Individual Pump Verification On completion of upload record CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) number
shown on the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump.
Download the Data Set from the Pump using the Alaris PK Verification Tool.
Compare Data Set downloaded with the approved signed Data Set printout.
Reviewer should sign the printout and also record the CRC number on the
printout as record.
• Subsequent Pump Verification On subsequent uploads of the Data Set compare CRC number on the Pump
with CRC number recorded on First Pump Verification.
6. Switch the Pump on and verify that the start-up splash screen displays the correct data set name and version. The Pump is now
ready to use.
w
*Drug parameters have to be in accordance to local protocols and prescribed information.
Data set transfers should only be performed by qualified technical personnel.
** See important note in Configured Options section.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
7/52
Page 9

Features of the Pump
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Features of the Pump
ON/OFF
RUN
Display
Release lever
for MDI
High visibility
Alarm Indicator
PURGE/BOLUS
MUTE
PRESSURE
OPTION
Finger
Grips
Extension set
hook
Rating Plate (see Symbol Definitions for an
explanation of the symbols used)
Release
lever for
Rotating
Cam
HOLD
M
e
Shelf for chevron
keys and softkeys
d
i
c
a
l
D
e
v
i
c
e
I
n
t
e
r
f
a
c
e
(
M
D
I
Syringe Clamp
)
Positive Plunger
Grippers
Rotating Cam to
lock on to horizontal
rectangular bars
Carrying
Handle
IR Communications
port
Potential
Equalisation (PE)
connector
1000DF00741 Issue 5
Folded Pole
Clamp
8/52
RS232
Connector
Extension set
hook
Page 10
Controls and Indicators
Controls:
Symbol Description
ON/OFF button - Press once to switch the Pump on. Press and hold down for 3 seconds to switch the
Pump off.
a
Note: Pump can only be switched off at specific stages of operation, see 'Power Down Sequence'
section in Configured Options for further details.
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Controls and Indicators
b
h
R
i
d
RUN button - Press to start the infusion. The green LED will flash during infusion.
HOLD button - Press to put the infusion on hold. The amber LED will be lit while on hold.
MUTE button - Press to silence alarm for two minutes.
Note: Callback alarm only:
– The two minutes silence can be configured using the Alaris PK Editor Software.
– when not in alarm press and hold until three audible beeps are sounded for 60 minutes
silence
PURGE/BOLUS button - Press to access PURGE or BOLUS softkeys. Press and hold down softkey to
operate.
PURGE the extension set during set up.
• Pump is on hold
• Extension set must not be connected to the patient
• Volume Infused (VI) is not added
BOLUS - fluid or drug delivered at an accelerated rate.
• Pump is infusing
• Extension set is connected to the patient
• VI is added
OPTION button - Press to access optional features, see 'Basic Features' section.
e
PRESSURE button - Use this button to display the pumping pressure and alarm level.
f
CHEVRON keys - Double or single for faster/slower increase or decrease of values shown on display.
BLANK SOFTKEYS - Use in conjunction with the prompts shown on the display.
g
Indicators:
Symbol Description
BATTERY indicator - When illuminated the Pump is running on the internal battery. When flashing the
j
S
battery power is low with less than 30 minutes of use remaining.
AC POWER indicator - When illuminated the Pump is connected to an AC Power Supply and the battery
is being charged.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
9/52
Page 11

Symbol Definitions
Labelling Symbols:
Symbol Description
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Symbol Definitions
w
x
y
l
IP32
r
s
T
t
U
Consult accompanying documents.
Potential Equalisation (PE) Connector
RS232/Nurse call Connector
Defibrillation-proof type CF applied part (Degree of protection against electrical shock)
Protected against direct sprays of water up to 15° from vertical and protected against solid objects greater than
2.5mm.
Note: IP33 applies if AC power cable retainer kit, part number 1000SP01294, is fitted.
Alternating Current
Device complies with the requirements of Council Directive 93/42/EEC as amended by 2007/47/EC.
Date of Manufacture
Manufacturer
Not for Municipal Waste
W
0°C
EC REP
Fuse Rating
+40°C
Operating Temperature Range - Pump can be used between 0 and 40 degrees centigrade.
Authorised representative in the European Community
1000DF00741 Issue 5
10/52
Page 12
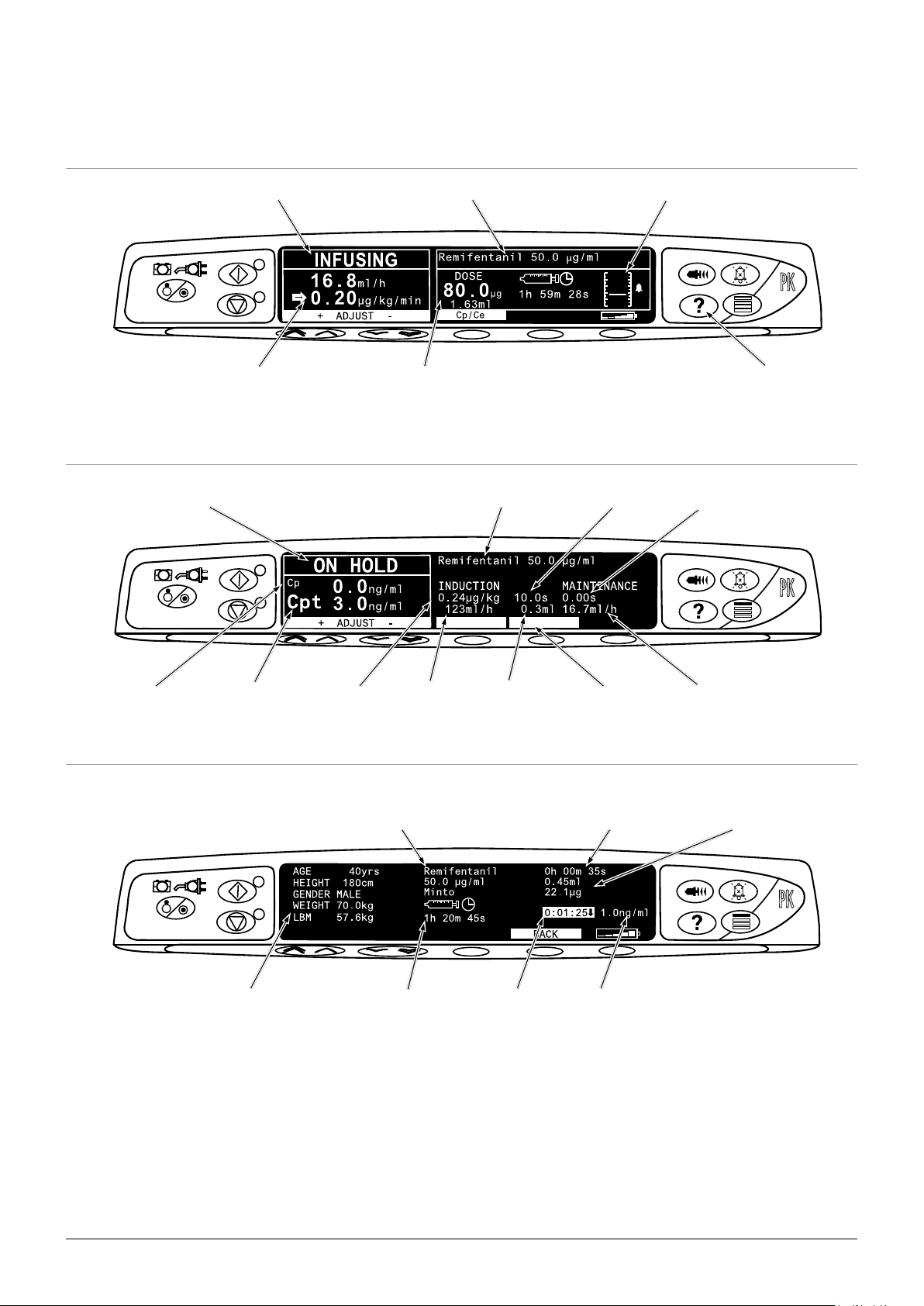
Main Display Features
CONFIRM TIME
BMI 21.6
TIVA Mode
Pump Status
Drug Name and
Concentration
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Main Display Features
Pressure Information
Flow Rate and
Dose Rate
Dose and
Volume Infused
TCI Mode
Pump Status
Plasma
Concentration
Plasma Target
Initial Induction
Dose
Initial Induction
Rate
Initial Induction
Volume
TCI Mode - MORE Information Screen
Selecting the MORE softkey will display the following additional information:
Drug Name
and Model
Drug Name and
Concentration
Induction
Duration
Time of
Induction
Operations
During Use
Pause Before
Maintenance
Initial Maintenance
Rate
Volume and
Dose InfusedElapsed Time
Patient Parameters Time to End of Infusion
at Current Rate
Press the BACK softkey to return to the TCI screen. The display will automatically revert to the TCI screen after approximately 20 seconds.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
Decrement
Time
Decrement
Concentration
11/52
Page 13
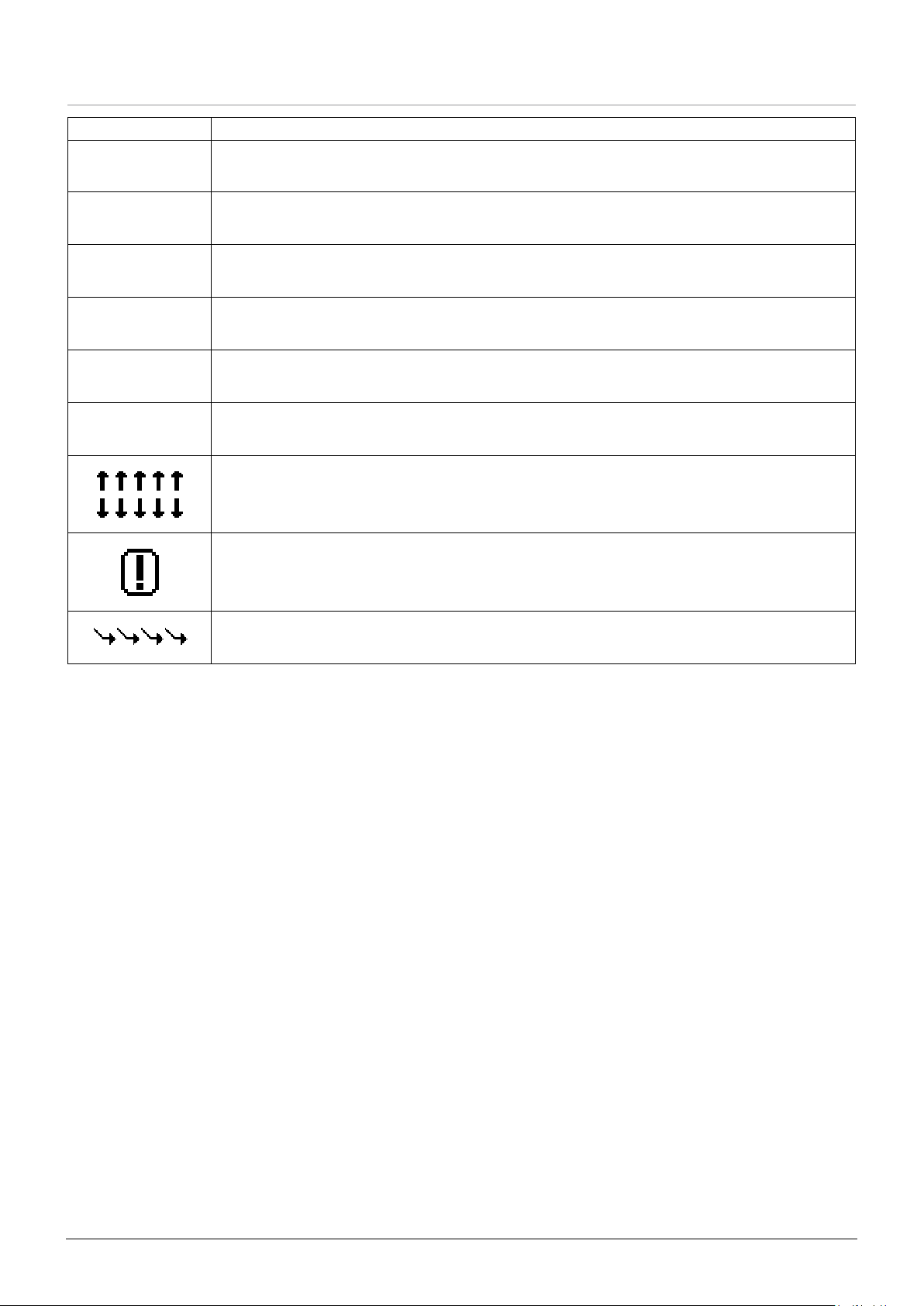
Screen Icons
Symbol Description
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Main Display Features
l
N
C
D
E
F
TIME REMAINING DISPLAY icon - Indicates time before syringe will require replacing.
BATTERY icon - Indicates battery charge level to highlight when the battery will require recharging. This can
be enabled/disabled with the Alaris PK Editor Software
Induction Phase Dose (Displayed on protocol confirmation screen)
Duration of Induction Phase (Displayed on protocol confirmation screen)
Duration of Hands Free Bolus (Displayed in bolus set-up screen)
Maintenance Phase Dose Rate (Displayed on protocol confirmation screen)
SOFT ALERT - Indicates the Pump is running at a rate above (pointing up) or below (pointing down) a Soft
Alert. (Number of arrows vary depending on drug name length)
LIMIT WARNING - Indicates the setting entered is under or exceeds a Soft Alert or setting entered is not
permitted as it exceeds a Hard Limit.
DOWN MODE - Infusion status indicating that the target concentration is below current concentration.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
12/52
Page 14
Operating Precautions
Disposable Syringes and Extension Sets
m
n
o
I
• The Pump has been calibrated for use with single-use disposable syringes. To ensure correct and accurate
operation, only use 3 piece Luer lock versions of the syringe make specified on the Pump or described in
this manual. Use of non-specified syringes or extension sets may impair the operation of the Pump and
the accuracy of the infusion.
• Uncontrolled flow or syphoning may result if the syringe is located incorrectly in the Pump, or if it is
removed from the Pump before the extension set is properly isolated from the patient. Isolation may
include closing a tap in the patient line or activating a flow stop clamp.
• Secure the extension set to the Pump using the extension set hook at the rear of the Pump. This provides
protection against accidental dislodging of the syringe from the Pump.
• When combining several apparatus and/or instruments with extension sets and other tubing, for example
via a 3-way tap, the performance of the Pump may be impacted and should be monitored closely.
• Always clamp or otherwise isolate the patient line before unclamping or removing a syringe from the
Pump. Failure to do so may result in unintended administration.
Mounting the Pump
• When more than one pump is being used on a patient, those containing high risk, critical medications
must be positioned as close to the patient's heart level as possible to avoid the risk of variations in flow or
siphoning.
• Raising a Pump whilst infusing may result in a bolus of the infusate, whereas lowering a Pump whilst
infusing may result in a delay in the infusion (an underinfusion).
• Do not mount the Pump in a vertical position with the syringe pointing upwards as this could lead to
an infusion of air which may be in the syringe. To protect against the introduction of air the user should
regularly monitor the progress of the infusion, syringe, extension line and patient connections and follow
the priming procedure specified herein.
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Operating Precautions
J
Operating Environment
• Intended environments include intensive care and operating rooms. Ensure that the Pump is
appropriately attached using the provided pole clamp. If the Pump is dropped or experiences any
severe physical disturbances, arrange a thorough inspection by Qualified Service Personnel as soon as is
practically possible. The Pump may be used as long as the temperature is within the specified range as
stated in the 'Specifications' section and on the Pump label.
• When using any infusion pump in conjunction with other pumps or devices requiring vascular access,
extra care is necessary. Adverse delivery of medication or fluids can be caused by the substantial variation
in pressures created within the infusion system by such pumps. Typical examples of those pumps are
used during dialysis, bypass or cardiac assist applications.
• The Pump is suitable for use in hospital and clinical environments other than domestic establishments
and those directly connected to the public single phase AC Power Supply network that supplies buildings
used for domestic purposes. (Consult Technical Service Manual, Qualified Service Personnel or CareFusion
for further information).
• The Pump is not intended to be used in the presence of a flammable anaesthetic mixture with air or
oxygen or nitrous oxide.
Operating Pressure
• This is a positive pressure Pump designed to achieve very accurate fluid administration by automatically
compensating for resistance encountered in the infusion system.
• The pumping pressure alarm system is not designed to provide protection against, or detection of, IV
complications which can occur.
Alarm Conditions
• Several alarm conditions detected by this Pump will stop the infusion and generate visual and audible
alarms. Users must perform regular checks to ensure that the infusion is progressing correctly and no
alarms are operating.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
13/52
Page 15

A
V
L
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Operating Precautions
Hazards
• An explosion hazard exists if the Pump is used in the presence of flammable anaesthetics. Exercise care to
locate the Pump away from any such hazardous sources.
• Dangerous Voltage: An electrical shock hazard exists if the Pump’s casing is opened or removed. Refer all
servicing to Qualified Service Personnel.
• When connected to an external power source, a three-wire (Live, Neutral, Earth) supply must be used. If
the integrity of the external protective conductor in the installation or its arrangement is in doubt, the
Pump should be operated from the battery.
• Do not open the RS232/Nurse Call protective covering when not in use. Electrostatic discharge (ESD)
precautions are required when connecting RS232/Nurse Call. Touching the pins of the connectors may
result in ESD protection failure. It is recommended that all actions must be taken by appropriately trained
personnel..
• If the Pump is dropped, subjected to excessive moisture, fluid spillage, humidity or high temperature, or
otherwise suspected to have been damaged, remove it from service for inspection by Qualified Service
Personnel. When transporting or storing the Pump, use original packaging where possible, and adhere
to temperature, humidity and pressure ranges stated in the 'Specifications' section and on the outer
packaging.
• The embedded Pump software incorporates limits and Pump configuration parameters. Qualified
personnel must ensure the appropriateness of the limits, the compatibility of the drugs, and the
performance of each Pump, as part of the overall infusion. Potential hazards include drug interactions,
and inappropriate delivery rates and pressure alarms.
• Warning: Alaris Syringe Pumps should not be modified or altered in any way, except where explicitly
directed or authorised by CareFusion. Any use of Alaris Syringe Pumps which have been altered or
modified otherwise than in strict application of directions provided by CareFusion, is at your sole risk, and
CareFusion does not provide any warranty for or endorsement on any Alaris Syringe Pump that has been
so modified or altered. CareFusion product warranty shall not apply in the event the Alaris Syringe Pump
has suffered damage or premature wear, or malfunctions or otherwise operates incorrectly, as a result of
unauthorised modification or alteration of the Alaris Syringe Pump.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
14/52
Page 16

M
MR
K
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Operating Precautions
Electromagnetic Compatibility and Interference
• The Pump is protected against the effects of external interference, including high energy radio frequency
emissions, magnetic fields and electrostatic discharge (for example, as generated by electrosurgical and
cauterising equipment, large motors, portable radios, cellular telephones etc.) and is designed to remain
safe when unreasonable levels of interference are encountered.
• Therapeutic Radiation Equipment: Do not use the Pump in the vicinity of any Therapeutic Radiation
Equipment. Levels of radiation generated by the radiation therapy equipment such as Linear Accelerator,
may severely affect functioning of the Pump. Please consult manufacturer’s recommendations for safe
distance and other precautionary requirements. For further information, please contact your local
CareFusion representative.
• Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): The Pump contains ferromagnetic materials which are susceptible
to interference with magnetic field generated by the MRI devices. Therefore, the Pump is not considered
an MRI compatible pump as such. If use of the Pump within an MRI environment is unavoidable, then
CareFusion highly recommends securing the Pump at a safe distance from the magnetic field outside
the identified ‘Controlled Access Area’ in order to evade any magnetic interference to the Pump; or
MRI image distortion. This safe distance should be established in accordance with the manufacturer's
recommendations regarding electromagnetic interference (EMI). For further information, please refer to
the product Technical Service Manual (TSM). Alternatively, contact your local CareFusion representative for
further guidance.
• Accessories: Do not use any non-recommended accessory with the Pump. The Pump is tested and
compliant with the relevant EMC claims only with the recommended accessories. Use of any accessory,
transducer or cable other than those specified by CareFusion may result in increased emissions or
decreased pump immunity.
• This Pump is a CISPR 11 Group 1 Class A device and uses RF energy only for its internal function in
the normal product offering. Therefore, its RF emissions are very low and are not likely to cause any
interference with the nearby electronic equipment. However, this Pump emits a certain level of
electromagnetic radiation which is within the levels specified by IEC/EN60601-1-2 and IEC/EN60601-2-
24. If the Pump interacts with other equipment, measures should be taken to minimise the effects, for
instance by repositioning or relocation.
• In some circumstances the Pump may be affected by an electrostatic discharge through air at levels close
to or above 15kv; or by radio frequency radiation close to or above 10v/m. If the Pump is affected by
this external interference the Pump will remain in a safe mode; the Pump will duly stop the infusion and
alert the user by generating a combination of visual and audible alarms. Should any encountered alarm
condition persist even after user intervention, it is recommended to replace that particular Pump and
quarantine the Pump for the attention of Qualified Service Personnel. (Consult Technical Service Manual
for further information).
1000DF00741 Issue 5
15/52
Page 17
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Getting Started
Getting Started
Initial Set-up
Before operating the Pump read this Directions For Use manual carefully.
w
1. Check that the Pump is complete, undamaged and that the voltage rating specified on the label is compatible with your AC Power
Supply.
2. Items supplied are:
• Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump
• User Support CD (Directions For Use)
• AC Power Cable (as requested)
• Protective Packaging
3. Connect the Pump to the AC Power Supply for at least 2½ hours to ensure that the internal battery is charged (verify that the S is
lit).
Language Selection
1. On initial start-up the Pump will display the Select Language screen.
2. Select the required language from the list displayed using the
3. Press the OK softkey to confirm your selection.
f keys.
w
• The Pump will automatically operate from its internal battery if the Pump is switched on without being connected
to the AC Power Supply.
• Should the Pump fail to perform correctly, replace in its original protective packaging, where possible and contact
Qualified Service Personnel for investigation.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
16/52
Page 18

Do not mount the Pump with the AC power inlet or the syringe pointing upwards. This could affect the electrical safety
w
in the event of a fluid spill or lead to the infusion of air which may be in the syringe.
Pole Clamp Installation
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Getting Started
The pole clamp is fitted to the rear of the Pump and will provide secure
fixing to vertical I.V. poles of a diameter between 15 and 40 mm.
1. Pull the folded pole clamp towards you and unscrew the clamp to
leave enough room for the size of the pole.
2. Place Pump around pole and tighten screw until the clamp is
secured to the pole.
Ensure the pole clamp is folded away and stored
w
w
within the recessed area at the rear of the Pump before
connecting to a Docking Station/Workstation* or when
not in use.
Never mount the Pump such that the I.V. infusion stand
becomes top heavy or unstable.
Prior to each use, check the pole clamp:
• does not show any signs of excessive wear,
• does not show any signs of excessively loose movement in the extended, mountable position.
If these signs are observed, the Pumps should be taken out of service for examination by Qualified Service Personnel.
Recessed area
*
*
Docking Station/Workstation* or Equipment Rail Installation
The rotating cam can be fitted to the rectangular bar on the Docking Station/Workstation* or the equipment rail measuring 10 by 25mm.
1. Align the rotating cam on the rear of the Pump with the rectangular bar on the Docking Station/Workstation* or the equipment rail.
2. Hold the Pump horizontally, push the Pump firmly onto the rectangular bar or equipment rail.
3. The Pump should click into position when fitted to the bar.
4. Ensure that the Pump is positioned securely. Verify Pump is secure by gently pulling the Pump away from the Docking Station/
Workstation* without using the release lever. When the Pump is securely attached, it should not come off the Docking Station/
Workstation*.
5. To release, push the release lever and pull the Pump forwards.
Warning: Pump may fall off the Docking Station/Workstation* if not properly mounted which could result in user and/or
patient harm.
Rectangular bar
* Alaris Gateway Workstation and Alaris DS Docking Station
1000DF00741 Issue 5
Release lever (push to release)
Rotating cam
17/52
Page 19

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Syringe Loading
Syringe Loading
Prepare Syringe and Administration Set
To decrease potential start-up delays, delivery inaccuracies and delayed generation of occlusion alarms each time a new syringe is
loaded:
• Use smallest syringe size possible, for example, if infusing 9 ml of fluid, use a 10 ml syringe.
• Use the PURGE SYRINGE or PURGE option on the Pump to decrease the delay in the start of the infusion, see Starting the Pump
section.
Warning: Use the smallest compatible syringe size necessary to deliver the fluid or medication; this is especially
w
w
Practice Recommendations:
important when infusing high risk or life-sustaining medications at low infusion rates, especially flow rates < 0.5 ml/h.
Warning: Purge the Pump system before starting an infusion or after replacing a near-empty syringe with a
replacement syringe. When Purging ensure that the extension set is not connected to the patient.
• Tubing internal diameter: Smallbore or microbore tubing is recommended when infusing at low rates
• Filters: Internal volume, dead space, of in-line filters should be minimized
• Connection sites: Critical drugs should be connected as close to the vascular access site as possible
Positioning of Pump
Ensure that the Pump is as close to level of
patient’s heart as possible.
Patient’s heart level should be in line with
the middle of the Pump or the pressure disc
for the Alaris CC Syringe Pumps.
w
w
w
Warning: Adjusting the Pump's height relative to the patient's heart level can lead to temporary increases or
decreases in fluid delivery
Caution: If using multiple syringe pumps and it is not clinically feasible to have all Pumps level with the patient’s
heart, place the high risk or life-sustaining medications as close to the patient’s heart level as possible.
Caution: When infusing multiple high risk or life-sustaining medications, consider placing the Pumps infusing at the
lowest rates as close to the level of the patient’s heart as possible.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
18/52
Page 20

Loading and Confirming a Syringe
Warning: To securely load and confirm a syringe carefully follow the steps below. An incorrect loading of a syringe
w
may result in misidentification of the syringe type and size. If then confirmed, this may lead to significant inaccuracy
of the infusion rate and may also affect Pump performance.
Only use a syringe of the type stated on the Pump or in this manual. Using an incorrect syringe could adversely affect
the accuracy of the infusion rate and may also affect Pump performance.
When drawing fluid into the syringe, draw enough to compensate for any 'dead space' volume in the extension set and
syringe at the end of infusion as this cannot be fully infused.
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Syringe Loading
Syringe
Barrel
Barrel
Flange
Plunger
Grippers
Syringe
Clamp
Plunger
Flange
Plunger
Finger
Grips
Plunger
Holder
Syringe Flange Clamp
Place the Pump on a stable horizontal surface or secure as described previously.
Prepare, load and prime the single-use disposable syringe and extension set using standard aseptic techniques.
1. Squeeze the finger grips together on the plunger holder and slide the mechanism to the right.
2. Pull the syringe clamp forward and down.
3. Insert the syringe ensuring that the barrel flange is located in the slots on the syringe flange
clamp.
To ensure the syringe is loaded correctly, place the barrel flange in the space
w
between the syringe clamp and the syringe flange clamp. This is correct if the
syringe remains in position before the syringe clamp is closed.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
19/52
Page 21

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Syringe Loading
4. Lift the syringe clamp until it locks against the syringe barrel.
5. Squeeze the finger grips on the plunger holder and slide the mechanism to the left until it
reaches the plunger end.
6. Release the finger grips. Ensure that the plunger grippers are securing the plunger in place
and the finger grip returns to its original position.
7. Ensure that the syringe type and size match those displayed on the Pump then press CONFIRM. If required, the make of syringe
can be changed by pressing the TYPE softkey.
ON HOLD
Note: If the PURGE SYRINGE option has been enabled then the prompt to purge screen is displayed and the extension set can be
purged as required, however ensure that the extension set is not connected to the patient during this process.
CareFusion recommends limiting the number of configured syringe types and sizes available for selection on the
w
Pump.
Secure the extension set using the extension set hook at the rear of the Pump. This provides protection against
accidental dislodging of the syringe from the Pump.
Ensure that both plunger grippers are fully locked onto the plunger flange and the upper finger grip has returned to
its original position.
IVAC 50
CONFIRM
TYPE
1000DF00741 Issue 5
20/52
Page 22

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Starting the Pump
Starting the Pump
1. Connect the Pump to an AC Power Supply using the AC power cable.
2. Press the
• The Pump will run a short self-test.
w
• Check the display test pattern and ensure that no coloured rows are missing.
• Finally check that the displayed time and date are correct.
Note: A warning - REPAIRING LOGS, may be displayed if event log information was not completely stored at the previous power
3. CONFIRM PROFILE
a) NO will display select profile screen
b) YES will display the TCI MODE screen.
4. The TCI MODE selection is displayed - Answering YES selects the TCI Mode, NO will enter TIVA MODE.
The Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump allows the user to select a TCI or TIVA mode of operation. The user may, at any time, switch mode by
stopping the infusion and selecting the appropriate mode from the options menu. When in TIVA mode, if a drug with an associated
model has been selected, the current plasma and effect site concentration will be displayed. This will demonstrate to the user unfamiliar
with TCI, the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of the drug while still using TIVA mode.
a button.
Warning: two beeps are activated during this self-test and the red alarm beacon illuminates and then clears. No action
is required during this self-test.
down. This is for information only, the Pump will continue to power up as normal.
– Select profile.
– Press OK to confirm.
TIVA Mode (with or without prediction)
1. A list of available drugs and models will be displayed. Use the f keys to select the required drug and press the OK softkey.
If the drug has an associated model, an INFO softkey will be displayed. Pressing the INFO softkey will show more information on the
selection. The ml/h option allows infusions without doserate calculation.
2. CONCENTRATION -
a) Select Concentration required and OK to confirm (Only required if more than one concentration is available).
b) Press the OK softkey to confirm Concentration or press the MODIFY softkey to change Drug amount and diluent volume.
3. WEIGHT - adjust the patient weight using the
4. The remaining patient parameters for the selected drug must be entered using the
confirm. The required parameters may include the following depending on the model:
• AGE
• HEIGHT
• GENDER
• LBM and BMI (Lean Body Mass and Body Mass Index. This is for information only and is not an adjustable parameter).
5. The CONFIRM drug setup screen shows the initial infusion parameters for the drug. Press the OK softkey to accept or MODIFY to
change the drug setup.
6. INDUCTION - Using the
the OK softkey to enter. The Induction feature may be disabled reducing the dose to zero until OFF is displayed and press OK
softkey to confirm.
7. TIME - Enter the induction time in seconds over which the induction dose will be delivered. Press the OK softkey to enter.
8. MAINTENANCE - Set the maintenance dose rate in the drug protocol units. Press the OK softkey to enter.
Prime the extension set.
f keys, enter the induction dose amount per kg of patient weight (if required for dosing). Press
f keys, press the OK softkey to confirm.
f keys and press the OK softkey to
w
9. Load the syringe according to the procedure in this manual.
10. Check that the syringe type and size being used matches the display. If required, the make of syringe can be changed by pressing
the TYPE button. Press CONFIRM when the correct type and size are shown.
11. Purge (if required) - Press the
extension set is complete. Release the softkey. The volume used during purging will be displayed.
12. Connect the extension set to the patient access device.
13. Press the
green start light to indicate that the Pump is in operation. If the infusion rate exceeds the Soft Alerts then check infusion setting,
to continue with infusion at set target press the b button and then confirm OVERRIDE LIMIT by pressing the YES softkey. If
OVERRIDE LIMIT is not required press the NO softkey and adjust target concentration to be within the Soft Alerts.
w
b button to commence operation. INFUSING will be displayed. The amber stop light will be replaced by the flashing
If a model has been selected, the VOLUME softkey will be replaced by a Ce/Cp softkey. This will allow the user access
to screens showing predicted target concentrations. In this mode of operation the volume may never be cleared.
i button and then press and hold the PURGE softkey until the fluid flows and the purging of the
14. Press the
h button to halt the operation. ON HOLD will be displayed. The amber stop light will replace the green start light.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
21/52
Page 23

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Starting the Pump
TCI Mode
1. A list of available drugs and models will be displayed. Use the f keys to select the required drug and associated model and
press the OK softkey. Pressing the INFO key will show more information on the selection.
2. CONCENTRATION -
a) Select Concentration required and OK to confirm (Only required if more than one concentration is available).
b) Press the OK softkey to confirm Concentration or press the MODIFY softkey to change drug amount and diluent volume.
3. AGE - adjust the patient age using the
4. The remaining patient parameters for the selected drug must be entered using the
confirm. The required parameters may include the following depending on the model:
• HEIGHT
• GENDER
5. WEIGHT - adjust the patient weight using the
calculated using the models LBM limitations, is displayed.
• LBM and BMI (Lean Body Mass and Body Mass Index. This is for information only and is not an adjustable parameter).
6. If configuration allows, select Plasma targeting or Effect Site targeting.
Prime the extension set.
f keys, press the OK softkey to confirm.
f keys and press the OK softkey to
f keys, press the OK softkey to confirm. A permissible weight range,
w
7. Load the syringe according to the procedure in this manual.
8. Check that the syringe type and size being used matches the display. If required, the syringe brand or type can be changed by
pressing the TYPE softkey. Press the CONFIRM softkey when the correct type and size are shown.
9. The CONFIRM induction screen shows the initial infusion parameters for the drug and model selected. The screen will show blank
data until the syringe has been loaded and confirmed.
10. When a slower titration is required the induction time may be increased in Plasma Targeting (Cpt) only. Press the TIME softkey and
cap the maximum induction rate or doserate to increase the desired induction time. The cap rate will be cleared when first titration
occurs.
11. Target Concentration (Cpt or Cet) - Adjust the Target Concentration if necessary using the
Concentration and Initial Infusion predicted parameters. On confirmation, if the Target Concentration exceeds any limits, a warning
will be displayed.
Infusion cannot be started until confirmation has been made.
w
Initial infusion parameters may fluctuate from the displayed predicted values as a result of real time recalculation.
If the induction time is greater than 10s the flow rate may decrease on the last 10s period to adjust the dose to be
administered.
Maintenance flow rate will decrease over time for a fixed target.
f keys. Confirm the Target
12. Purge (if required) - Press the
IV infusion set is complete. Release the softkey. The volume used during purging will be displayed.
13. Connect the extension set to the patient access device.
14. Press the
green start light to indicate that the Pump is in operation. If the infusion rate exceeds the Soft Alerts then check infusion setting,
to continue with infusion at set target press the b button and then confirm OVERRIDE LIMIT by pressing the YES softkey. If
OVERRIDE LIMIT is not required press the NO softkey and adjust target concentration to be within the Soft Alerts.
b button to commence operation. INFUSING will be displayed. The amber stop light will be replaced by the flashing
If Target Concentration running exceeds the Soft Alerts then the display will cycle between Drug Name and Up arrows.
i button and then press and hold the PURGE softkey until the fluid flows and the purging of the
w
15. Pressing the
16. Press the
Flow Rate and
Dose Rate
Decrement Time
* The Ce value will not be displayed if there is no k
h button during infusion will maintain the current Plasma or Effect site.
h button to halt the operation. ON HOLD will be displayed. The amber stop light will replace the green start light.
Effect Site
Concentration*
Drug Name and
Concentration
Actual Time
1000DF00741 Issue 5
Plasma Concentration
Prediction
Effect Site
Prediction
(keo) defined for the selected model.
41
Trend Time
22/52
Page 24

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Basic Features
Basic Features
Bolus Infusion
BOLUS is disabled in TCI mode.
w
Bolus Administering a controlled volume of fluid or drug at an increased rate for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. The Pump
should always be infusing and always attached to the patient. (Drugs given by an IV bolus could achieve immediate and high
drug concentration levels.)
Bolus can be used at the start of an infusion or during an infusion.
The bolus feature can be configured to:
a) BOLUS Disabled
b) BOLUS Enabled
• Hands-On
• Hands-Free
BOLUS Disabled
If configured to Disabled, pressing the
A Hands-On bolus and Hands-Free bolus cannot be administered if the feature is disabled for the selected Profile or
w
specific drug. During BOLUS the pressure limit alarm is temporarily increased to the maximum level.
i button will have no effect and the Pump will continue to infuse at the set rate.
BOLUS Enabled - Hands-On
In Hands-On Bolus, press and hold the (flashing) BOLUS softkey to deliver the required bolus. The bolus rate can be adjusted. The bolus
volume is limited in the configuration.
1. During infusion press the
2. Use the
3. To deliver the bolus press and hold the BOLUS softkey. During the bolus, the volume being infused is displayed. When the desired
bolus volume has been delivered or the bolus volume limit is reached, release the softkey. The bolus volume is added to the total
volume infused.
BOLUS Enabled - Hands-Free
The Hands-Free Bolus is delivered with a single press of the (flashing) BOLUS softkey. The bolus rate and bolus volume are set by drug
profile in the data set and can be changed within limits set by the data set.
1. During infusion press the
2. Use the
the bolus delivery rate.
Note: Rate may be restricted by the syringe size and the CAP BOLUS RATE.
3. Press the flashing BOLUS softkey once to begin the delivery of the preset bolus. The display will show the bolus being delivered, the
bolus counting down and revert to main infusion display upon completion of the bolus.
4. To terminate a bolus being delivered press STOP softkey. This will stop the bolus and continue infusing at the set rate. Press the
button to stop the bolus delivery and place the Pump on hold.
5. If the bolus volume reaches the set bolus volume the bolus will stop and the Pump will revert to infuse at the set infusion rate and
continue infusing.
w
f keys to adjust the bolus rate if required.
f keys to set the bolus volume/dose required; if necessary use the RAT E softkey and the f keys to adjust
If the Hands-Free bolus option is active, then this feature will be cancelled following any interruption in delivery, e.g.
occlusion, even if the bolus delivery is incomplete.
Any Hands Free Bolus dose setting which exceeds or is under a Soft Alert must be confirmed before operation can be
continued. This is not applicable in TCI mode.
i button once to display the bolus screen.
i button to display the Hands-Free bolus selection screen.
h
1000DF00741 Issue 5
23/52
Page 25

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Basic Features
Purge
The i button allows the delivery of a limited volume of fluid in order to purge the extension set prior to being connected to a patient
or after changing a syringe.
1. Press the
2. Press and hold the PURGE softkey until fluid flows and the purging of the extension set is complete. The volume used during
purging will be displayed, but it is not added to the volume infused.
3. When purging is complete release the PURGE softkey. Press the QUIT softkey to exit back to the main display.
i button when the Pump is not infusing. Ensure that the extension set is not connected to the patient.
During PURGE the pressure limit alarms are temporarily increased to their maximum level.
w
Pressure Level
1. To check and adjust the pressure level press the e button. A bar graph will be displayed showing the pressure alarm level and the
current pressure level.
2. Press the
3. Press OK to exit the screen.
w
f keys to increase or decrease the alarm level. The new level will be indicated on the display.
During PURGE, BOLUS and INDUCTION the pressure limit alarms are temporarily increased to their maximum level.
For TCI operation a threshold rate may be set above which the pressure limit alarms are temporarily increased to their
maximum level.
Rate Titration
Note: This is not applicable in TCI mode.
If Rate Titration is enabled the rate can be adjusted while infusing:
1. Select the new rate using the
2. The message < START TO CONFIRM > will display on screen, titration callback tone will sound and Pump continues to infuse at the
original rate.
Note: To silence the titration call back prior to the Titration Not Confirmed alarm, press and hold the
3 seconds.
3. Press the
If Rate Titration is disabled the rate can only be adjusted whilst on hold:
1. Press the
2. Select the new rate using the
3. Press the
b button to confirm the new infusion rate and start infusing at the new rate.
h button to put the Pump on hold.
b button to start infusing at the new rate.
f keys.
R button for approximately
f keys.
Clear Volume
Note: Clear Volume is not permitted in TCI mode or predictive TIVA mode.
This option enables the volume infused to be cleared.
1. Press the VOLUME softkey to display the CLEAR VOLUME option.
2. Press the YES softkey to clear the volume. Press the NO softkey to retain the volume.
Note: Selecting YES resets the volume infused in the 24H LOG option.
Concentration Target Titration
Note: This only applies to TCI mode.
Concentration Target Titration allows the rate to be adjusted while infusing:
1. Select the new target using the
• The Pump status is shown as TITRATE and the Pump continues to infuse at the original concentration target.
2. Press the
setting exceeds or is under a Soft Alert, confirmation is required before infusion can resume.
b button to confirm the new concentration target and start infusing at the new rate. If the new concentration target
f keys.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
24/52
Page 26

Operations During Use
End of Operation
This option will only appear in the options menu when the infusion has been stopped.
1. Press the
2. Select the END OF OPERATION option using the
3. Press the OK softkey indicated on the screen.
Note: Selecting this option will reset parameters for a new patient.
TCI Mode
When the Pump is on hold in predictive TIVA mode, the user is able to switch from TIVA to TCI mode.
1. Press the
2. Using the
3. Press the OK softkey indicated on the screen. A confirmation screen will be displayed.
Note: When the mode is changed to TCI mode, the initial target will be set to zero.
TIVA Mode
When the Pump is on hold in TCI mode, the user is able to switch from TCI to predictive TIVA mode.
1. Press the
2. Using the
3. Press the OK softkey indicated on the screen. A confirmation screen will be displayed.
Note: When the mode is changed to predictive TIVA mode, the initial doserate will be set to zero.
d button to access the options menu.
f keys.
d button to access the options menu.
f keys, select the TCI MODE.
d button to access the options menu.
f keys, select the TIVA MODE.
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Operations During Use
DECREMENT CONC.
In TCI mode only:
1. Press the
2. Select DECREMENT CONC.
3. Select the required DECREMENT CONC and press the OK softkey to exit.
d button to access the options menu.
Trend Size
The user is able to select the Trend Size of the Concentration Prediction graph.
1. Press the
2. Using the
3. Using the
4. Press the SELECT softkey indicated on the screen.
5. Press the RESIZE softkey to rescale the vertical axis of the graph. The initial displays calculates the scale so the peak value fills graph.
If the trend is downward the graph only fills lower part and the RESIZE option forces it to rescale.
d button to access the options menu.
f keys, select TREND SIZE.
f keys, select the required TREND SIZE option (5 Mins, 15 Mins, 30 Mins or 60 Mins).
Text/Graph Display
When in TCI mode, the user is able to select a numerical or graphical display.
1. Press the
2. Using the
option.
3. Press the OK softkey indicated on the screen.
d button to access the options menu.
f keys, select the display mode (TEXT or GRAPH DISPLAY). The options menu shows the available display mode
Dosing Summary
1. Press the d button to access the options menu.
2. Select the DOSING SUMMARY option using the
3. Press the QUIT softkey to exit the menu.
f keys and press the OK softkey.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
25/52
Page 27

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Operations During Use
24 Hour Log
This option allows the 24 hour log of volume infused to be reviewed.
1. Press the
2. Select the 24H LOG option using the
The display shows the hourly volume infused. The volume infused shown in brackets is the total volume infused since the volume was
last cleared. See example below:
07:48 - 08:00 4.34ml (4.34ml)
08:00 - 09:00 2.10ml (6.44ml)
09:00 - 10:00 2.10ml (8.54ml)
VOLUME CLEARED
3. Press the QUIT softkey to exit the log.
Event Log
This option allows the event log to be reviewed. It can be enabled/disabled.
1. Press the
2. Select the EVENT LOG option using the
3. Scroll through the log using the
Data Set Details
To review currently selected data set information:
1. Press the
2. Select DATA SET DETAILS.
3. Review the information and press the QUIT softkey to exit.
d button to access the options menu.
f keys and press the OK softkey.
d button to access the options menu.
f keys and press the OK softkey.
f keys. Press the QUIT softkey to exit the log.
d button to access the options menu.
SET BY DOSERATE/SET BY ml/h (TIVA mode only)
To set doserate to flowrate in precise increments, it may be necessary to switch between the rate adjust options SET BY DOSERATE and
SET BY ml/h. An arrow to the left of the rate display shows the rate changed when the f keys are used to increase/decrease
the infusion rate.
To precisely set a doserate, the arrow must be pointing to the doserate (mg/kg/h); the flowrate will be calculated from the doserate. To
precisely set a flowrate, the arrow must be pointing to the flowrate (ml/h); the doserate will be calculated from the flowrate.
Selecting the SET BY ml/h option:
1. Whilst the Pump is infusing, press the
2. Select the SET BY ml/h option using the
SET BY FLOWRATE option, the arrow on the display will automatically select the flowrate, the flowrate can be adjusted if required.
Selecting the SET BY DOSERATE option:
1. Whilst the Pump is infusing, press the
2. Select the SET BY DOSERATE option using the
SET BY DOSERATE option, the arrow on the display will automatically select the doserate, the doserate can be adjusted if required.
d button to access the options menu.
f keys and press the OK softkey indicated on the screen. This will select the
d button to access the options menu.
f keys and press the OK softkey indicated on the screen. This will select the
EFFECT SITE TCI
When in PLASMA TCI mode the user is able to switch to EFFECT SITE TCI mode if the configuration permits:
1. Press the
2. Select EFFECT SITE TCI using the
3. Press the OK softkey indicated on the screen. A confirmation screen will be displayed.
d button to access the options menu.
f keys.
PLASMA TCI
When in EFFECT SITE TCI mode the user is able to switch to PLASMA TCI mode if the configuration permits:
1. Press the
2. Select PLASMA TCI using the
3. Press the OK softkey indicated on the screen. A confirmation screen will be displayed.
d button to access the options menu.
f keys.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
26/52
Page 28

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
BATTERY EMPTY
High
Red
NEAR END OF INFUSION
Medium
Amber
Alarms and Warnings
Alarms and Warnings
Alarms are indicated by a combination of an audible alarm, flashing alarm indicator and a descriptive message in the display.
1. First press the
CANCEL to cancel the alarm message.
2. If the infusion has stopped, rectify the cause of the alarm then press the
w
R button to silence the alarm for a maximum of 2 minutes, then check the display for an alarm message. Press
b button to resume the infusion.
If the Pump initiates a safety processor alarm condition (an audible high pitched continuous shrill accompanied
with a red alarm indicator) and there is no error message displayed on the Pump, remove the Pump from service for
examination by Qualified Service Personnel.
Infusion will stop for all alarms that have a Red (high priority) alarm indicator.
w
Display
DRIVE DISENGAGED High Red The drive system has been disengaged during operation. Check the finger
OCCLUSION High Red Excessive pressure measured at the syringe plunger exceeding the alarm
CHECK SYRINGE High Red Incorrect size of syringe has been fitted, the syringe has not been positioned
BATTERY LOW Medium Amber Battery charge low with 30 minutes operation remaining. Battery indicator will
END OF INFUSION High Red The Pump has reached the end of the infusion and the Pump has stopped
END OF INFUSION Medium Amber The Pump has reached the end of the infusion and the Pump continues to
TITRATION NOT
CONFIRMED
AC POWER FAIL Medium Amber AC Power has been disconnected and the Pump is operating on battery power,
Error Code and Message High Red The alarm system has detected an internal malfunction. Note the malfunction
ATTENTION (with “3 Beeps”) Medium Amber Three beeps will sound if the Pump has been left on for more than 2 minutes*
Alarm
Priority
Medium Amber The infusion rate has been changed, but has not been confirmed and 2
Alarm
Indicator
Description and Troubleshooting Guide
grips and the position of the syringe.
limit. Identify and remove the cause of the blockage in the drive, syringe, or
administration system before restarting the infusion.
correctly or has been disturbed during operation. Check the syringe location
and the position.
A CHECK SYRINGE alarm may indicate the incorrect size of syringe has been
fitted; the syringe has not been positioned correctly, or has been disturbed
during operation, for example, the user opens the syringe clamp, or If the
syringe plunger loses contact with the plunger button.
If there is no identifiable cause for the CHECK SYRINGE alarm(s) then the
pump should be removed from clinical use and examined by Qualified Service
Personnel in accordance with the Alaris Syringe Pump Technical Service Manual.
flash and after 30 minutes a continuous audible alarm will indicate that the
battery is exhausted. Reconnect to the AC Power Supply to continue operation
and charge the internal battery.
The internal battery is exhausted. Connect the Pump to the AC Power Supply.
The Pump is nearing the end of the infusion. This value can be configured.
infusing. A pre-set volume will remain in the syringe to minimise the risk of the
infusion of air bubbles into the set. This value can be configured.
infuse at KVO or set rate if lower.
minutes has expired without any operation. Press the
the alarm, then press the CANCEL softkey to clear this message. Check
infusion rate and confirm by pressing the b button or press the h button
to revert to the previous rate. Press the b button to start infusion. (This
alarm only occurs if rate titration is enabled).
Note: To silence the titration call back prior to the Titration Not Confirmed
alarm, press and hold the
if this occurs when the Pump is infusing the message INFUSION CONTINUES
will be displayed. Reconnect AC Power Supply or press the
to silence the alarm and continue with battery operation. The alarm will
automatically cancel if the AC Power Supply is reconnected.
code. Remove Pump from service for examination by Qualified Service
Personnel.
(referred to as CALLBACK in the log) without starting the operation. Press the
R button for approximately 3 seconds.
Rbutton to silence
Rbutton
Rbutton to silence the alarm for a further 2 minutes*. Alternatively press
and hold down the Rbutton and wait for 3 beeps in succession, this will
put the warning alarm on standby for 60 minutes.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
27/52
Page 29

Prompts
Display Icon Description and Troubleshooting Guide
DOSE WOULD EXCEED
DOSE UNDER
DOSE NOT PERMITTED
TARGET WOULD EXCEED
BOLUS DOSE OVER
BOLUS DOSE UNDER
BOLUS DOSE NOT PERMITTED
WEIGHT OUTSIDE LIMIT
RATE NOT PERMITTED
The infusion rate has been set to a value which exceeds a Soft Alert. Check infusion
setting, to continue with infusion at set rate press the b button and then confirm
OVERRIDE LIMIT by pressing the YES softkey. If OVERRIDE LIMIT is not required press
the NO softkey and adjust rate below Soft Alert.
The infusion rate has been set to a value which is under a Soft Alert. Check infusion
setting, to continue with infusion at set rate press the b button and then confirm
OVERRIDE LIMIT by pressing the YES softkey. If OVERRIDE LIMIT is not required press
the NO softkey and adjust rate above Soft Alert.
The infusion rate has been set above a Hard Limit. Check infusion setting and adjust rate
to appropriate required rate.
The target has been set to a value which exceeds a Soft Alert. Check infusion setting,
to continue with infusion at set target press the b button and then confirm
OVERRIDE LIMIT by pressing the YES softkey. If OVERRIDE LIMIT is not required press
the NO softkey and adjust rate below Soft Alert.
The bolus dose has been set to a value which exceeds a Soft Alert. Check the
bolus setting, to continue with the bolus press the b button and then confirm
OVERRIDE LIMIT by pressing the YES softkey. If OVERRIDE LIMIT is not required press
the NO softkey and adjust dose below Soft Alert.
The bolus dose has been set to a value which is under a Soft Alert. Check the
bolus setting, to continue with the bolus press the b button and then confirm
OVERRIDE LIMIT by pressing the YES softkey. If OVERRIDE LIMIT is not required press
the NO softkey and adjust dose above Soft Alert.
The bolus dose has been set above a Hard Limit. Check bolus setting and adjust to
appropriate required dose.
The patient weight has been set to a value which exceeds or is under a Soft Alert. Check
the weight setting, to continue press the b button and then confirm OVERRIDE LIMIT
by pressing the YES softkey. If OVERRIDE LIMIT is not required press the NO softkey and
adjust the value within the limits.
The infusion rate has been set above a Hard Limit. Check infusion setting and adjust to
appropriate required rate.
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Prompts
1000DF00741 Issue 5
28/52
Page 30

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Configured Options
Configured Options
This section comprises of a list of options which are configurable. Some can be entered via the Pump configuration menu (available in
Technician Mode) and others through the Alaris PK Editor Software.
Enter the access code on Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump for Configured Options, see the Technical Service Manual for details.
Access codes should only be entered by qualified technical personnel.
w
Use Alaris PK Editor to configure general options, drug library and units enabled for each profile and to configure Syringe Brands and
Models to be enabled.
Clock Set
1. Select CLOCK SET from the Configured Options menu using the f keys and press the OK softkey.
2. Use the
3. When the correct time and date are displayed press the OK softkey to return to the Configured Options menu.
Language
This option is used to set the language of messages shown on the Pump display.
1. Select LANGUAGE from the Configured Options menu using the
2. Use the
3. When the desired language has been selected press SELECT softkey to return to the Configured Options menu.
f keys to adjust the date displayed, pressing the NEXT softkey to access the next field.
f keys and press the OK softkey.
f keys to select the language.
Contrast
This option is used to set the contrast on the Pump display.
1. Select CONTRAST from the Configured Options menu using the
2. Use the
3. When the desired value has been reached press the OK softkey to return to the Configured Options menu.
f keys to select a contrast ratio value. The contrast of the display will change when scrolling through the numbers.
f keys and press the OK softkey.
Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump General Options
1. Select GENERAL OPTIONS from the Configured Options menu using the f keys and press the OK softkey.
2. Select the option required to enable/disable or adjust and press the MODIFY softkey.
3. When all the required modifications have been carried out press the QUIT softkey.
4. Either select the next configuration option from the menu or turn the Pump off, returning it to operation as required.
NURSE CALL FITTED Enables Nurse Call (hardware option).
NURSE CALL INVERT When enabled, the nurse call output is inverted.
RS232 SELECTED Sets the Pump's communications to use RS232 (hardware option). The NURSE CALL FITTED option must
be enabled to allow RS232 to function.
Power Down Sequence
Enter the access code on Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump for alternative Power Down Sequence, see the Technical Service Manual for details.
Access codes should only be entered by qualified technical personnel.
w
ENABLED When running TCI or TIVA with predictive TCI the Pump may only be powered down by stopping the infusion,
selecting NEW OPERATION from the options menu, confirming the selection and then power down the Pump.
DISABLED In TCI or TIVA with predictive TCI the Pump may be powered down after putting the Pump on hold.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
29/52
Page 31

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Configured Options
Alaris PK Editor Software - Pump Configuration
The following options are configurable via the Alaris PK Editor Software (PC based), see the Alaris PK Editor Software Directions for Use
(1000CH00016) for details on how to alter the profile configurations.
General Pump Configurations
AC Fail Warning The AC Power Failure Alarm can be set to sound or be silent if the AC power is disconnected.
Audio Volume The audio alarm volume of the Pump (high, medium or low).
Auto Night Mode Main Display (Backlight) dims between hours 21:00 and 06:00.
Battery Icon Indicator displaying the remaining estimated battery capacity.
Callback Time Adjusts the length of time before the Pump sounds the Call Back alarm.
Event Log The Event Log can be set to be displayed on the main display. Events are still recorded in the Event
Log if disabled.
Drug Override Mode Always - Any changes made to the dose rate or target concentration that are outside the editor Soft
Alerts will require confirmation before starting infusion.
Smart - Confirmation of setting will be required on the first dose rate or target concentration set
outside the editor Soft Alerts. Any subsequent changes will not require confirmation until after the
dose rate or target concentration has been confirmed inside the editor Soft Alerts. Additionally, any
changes in dose rate or target concentration from above a Soft Alert Max to below a Soft Alert Min
or from below a Soft Alert Min to above a Soft Alert Max will also need to be confirmed.
Pressure Default The default occlusion pressure alarm level.
Pressure Display Sets whether the Pressure Information is available on the main display.
Purge Rate The rate used during purge operation.
Purge Volume Max The maximum permissible purge volume.
Purge Syringe Prompt Feature which prompts the user to purge the extension set prior to the start of the infusion.
1
Bolus
Bolus Rate Default
Bolus Volume Default
1
1
KVO Allows the enabling or disabling of Keep Vein Open (KVO) at End of Infusion (EOI).
KVO Rate Sets the KVO rate at which the Pump will operate when EOI is reached.
Near End of Infusion Time Sets the Near End of Infusion warning time as time left to End of Infusion.
End of Infusion % Sets the End of Infusion point as a percentage of syringe volume.
Weight Default
Weight Minimum
Weight Maximum
Age Default
Age Minimum
Age Maximum
2
2
2
2
2
2
Bolus feature can be set to HANDS ON or HANDS FREE.
The default bolus rate.
The default bolus volume.
The patient default weight in kg.
The minimum patient weight in kg. This is a Soft Alert and can be overridden.
The maximum patient weight in kg. This is a Soft Alert and can be overridden.
The default patient age in years.
The minimum age in years. This is a Soft Alert and can be overridden.
The maximum age in years. This is a Soft Alert and can be overridden.
The approved data set contains configurable option values per profile.
w
1
The bolus configurations are used only when the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump is being used in ml/h mode. If a drug is selected then the
drug's own configuration settings are used.
2
Although a default and Soft Limits can be set for age and weight, the actual selectable range may be limited by the drug and model
chosen.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
30/52
Page 32

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Configured Options
Alaris PK Editor Software - Profile Drugs
The following drug parameters are only configurable via the Alaris PK Editor Software (PC based), and are referenced when the Alaris PK
Plus Syringe Pump is being used with a drug name selected. Refer to the Alaris PK Editor Software Directions for Use (1000CH00016) for
details on how to configure the Profile Drug Library.
TCI - these options are only displayed if the selected drug has an associated TCI model.
Clinical Trial Indicator Should be set to cause the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump to identify that a selected drug/model
is used under the responsibility of the investigator of a clinical trial protocol. Specifically for
publication studies and when drug does not make reference to the selected TCI mode of
administration in the prescribing information or, when parameter selection deviates from it.
TIVA Predictive Mode Only Only allows drugs with associated TCI model to be used in TIVA predictive mode.
Default Target Concentration The default target concentration offered when the drug is selected.
Enable Effect Site Targeting Enable effect site targeting if the model associated with the drug supports it.
Enable Target Swapping Enable switching between plasma and effect site targeting if the model associated with the
drug supports both modes.
Enable TIVA/TCI Switching Enable switching between TIVA and TCI modes.
Target Soft Alert Max Sets the target concentration soft alert maximum.
Default Decrement Concentration Sets the default decrement target concentration.
TIVA Induction Parameters
Induction ON/OFF Enables/Disables induction stage of TIVA protocol.
Dosing Units The induction dose units. This can be based on patient weight.
Default Dose The default induction dose offered.
Default Induction Time Sets the default induction time.
Soft Alert Min The induction value below which an override confirmation is required.
Soft Alert Max The induction value above which an override confirmation is required.
Hard Limit Max The maximum allowed induction dose.
Pause After Induction Enables/Disables pause after induction.
TIVA Maintenance Parameters
Dose Rate Units The maintenance rate units.
Default Dose Rate The default maintenance dose.
Soft Alert Min The maintenance dose rate below which an override confirmation is required.
Soft Alert Max The maintenance dose rate above which an override confirmation is required.
Hard Alert Max The maximum allowed maintenance dose rate.
TIVA Bolus Parameters
Bolus Type Determines bolus operation when required.
Default Rate The default bolus rate.
Dosing Units The bolus dose units. This can be based on patient weight.
Default Dose (HANDS FREE only) The default bolus offered.
Soft Alert Min (HANDS FREE only) The bolus dose value below which an override confirmation is required.
Soft Alert Max (HANDS FREE only) The bolus dose value above which an override confirmation is required.
Hard Limit Max (HANDS FREE only) The maximum allowed bolus dose.
Occlusion Alarms
Occlusion Alarm Pressure The default occlusion alarm level.
Desensitise Threshold Rate The infusion rate that, when exceeded in TCI mode, causes the occlusion detection to be
desensitised.
Concentration Limits
Minimum Concentration The minimum drug concentration.
Maximum Concentration The maximum drug concentration.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
31/52
Page 33

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Configured Options
Default Drug Profile Library
The following drug parameters are programmed in the Pump.
Diprivan 1% Diprivan 2% Remifentanil Remifentanil TIVA* Sufentanil
Model Marsh Marsh Minto n/a Gepts
Min Concentration 10mg/ml 20mg/ml 20µg/ml 20µg/ml 0.2µg/ml
Max Concentration 10mg/ml 20mg/ml 50µg/ml 250µg/ml 5.0µg/ml
Induction Default 1.0mg/kg 1.0mg/kg 1.0µg/kg 1.0µg/kg 0.15µg/kg
Induction Soft Max 2.5mg/kg 2.5mg/kg 1.5µg/kg 1.5µg/kg 0.5µg/kg
Induction Hard Max 4.0mg/kg 4.0mg/kg 2.0µg/kg 2.0µg/kg 2.0µg/kg
Induction Time 30s 30s 45s 45s 45s
Maintenance Default 8mg/kg/h 8mg/kg/h 0.2µg/kg/minutes 0.2µg/kg/minutes 0.1µg/kg/h
Maintenance Soft Max 14mg/kg/h 14mg/kg/h 1µg/kg/minutes 1µg/kg/minutes 1µg/kg/h
Maintenance Hard Max 20mg/kg/h 20mg/kg/h 2µg/kg/minutes 2µg/kg/minutes 2µg/kg/h
Default Bolus Rate 1200ml/h 600ml/h 600ml/h 600ml/h 1200ml/h
Default Bolus 1.0mg/kg 1.0mg/kg 1.0µg/kg 1.0µg/kg 0.15µg/kg
Bolus Soft Max 2.5mg/kg 2.5mg/kg 1.5µg/kg 1.5µg/kg 1.0µg/kg
Bolus Hard Max 5.0mg/kg 5.0mg/kg 2.0µg/kg 2.0µg/kg 2.0µg/kg
Default Target Conc. 4.0µg/ml 4.0µg/ml 3.0ng/ml 0.15ng/ml
Target Conc. Soft Max 10µg/ml 10µg/ml 8.0ng/ml 1.0ng/ml
Target Conc. Hard Max 15µg/ml 15µg/ml 20ng/ml 2.0ng/ml
Decrement Conc. 1µg/ml 1µg/ml 1ng/ml 0.05ng/ml
Infusion Rate Limits 1200ml/h 600ml/h 1200ml/h 1200ml/h 1200ml/h
*This drug does not have an associated model and, therefore, cannot be run in TCI mode.
Default values are derived from publications and expert assessment and are given as reference only. It is recommended
w
that, before starting the infusion or confirming a titrated value, the values are checked to ensure that they conform
to hospital protocol.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
32/52
Page 34

Specifications
Infusion Specifications
Maximum infusion rate can be set as part of the configuration.
0.1ml/h - 150ml/h 5ml syringes
0.1ml/h - 300ml/h 10ml syringes
0.1ml/h - 600ml/h 20ml syringes
0.1ml/h - 900ml/h 30ml syringes
0.1ml/h - 1200ml/h 50ml syringes
Infusion Rate Increments:
Rate Range (ml/h) Single Chevron Key Increments (ml/h) Double Chevron Key Increments (ml/h)
0.10 to 9.99 0.01 0.10
10.0 to 99.9 0.1 1.0
100 to 999 1 10
1000 to 1200 10 100
The Volume Infused range is 0.0ml - 9990ml.
Bolus Specifications
Selected maximum rates are shown below
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Specifications
150ml/h 5ml syringes
300ml/h 10ml syringes
600ml/h 20ml syringes
900ml/h 30ml syringes
1200ml/h 50ml syringes
The default bolus volume can be set as part of the configuration.
• Minimum: 0.1ml
• Maximum: 100.0ml
• Increments of 0.1ml; default 5.0ml
During BOLUS the pressure limit alarms are temporarily increased to their maximum level.
Bolus Volume Accuracy*
Selected maximum rates are shown below
Bolus Volume Typical Typical Maximum Typical Minimum Pump Specification
0.1ml 1.9% 6.2% -7.3% ± 10%
25ml 0.2% 0.5% -0.1% ± 5%
* - Using BD Plastipak 50ml syringe at 5ml/h under normal conditions (95% confidence / 95% of pumps)
Critical Volume
The bolus which can occur in the event of a single internal fault condition with a 50 ml syringe is : Maximum Overinfusion - 0.87ml.
Purge Specifications
The purge rate is limited to the maximum rate for the syringe and can be set as part of the configuration.
100ml/h - 500ml/h.
The purge volume range is 0.5ml - 5ml.
During PURGE the pressure limit alarms are temporarily increased to their maximum level.
End Of Syringe Rate
Stop, KVO (0.1ml/h to 2.5ml/h), or set rate if lower than KVO.
Near End Of Infusion Alarm
1 minute -15minutes to end of infusion, or 10% of syringe volume, whichever occurs later.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
33/52
Page 35

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
End Of Infusion (EOI) Alarm
0.1% - 5% of syringe volume.
Maximum Pumping Pressure Limit
Highest alarm level 1000mmHg (nominal at L-10)
Occlusion Accuracy without pressure set (% of full scale)*
Pressure mmHg
L-0
approx. 50mmHg
Temp. 23°C ±18% ±21% ±23% ±28%
* - Using most common 50ml syringes under normal conditions (95% confidence / 95% of pumps).
System Accuracy (continuous ml/h and TIVA)
Volumetric Mean +/- 2% (nominal).
• Derating - Temperature +/- 0.5% (5 - 40ºC), High Rates +/-2.0% (rates > syringe volume/h eg. >50ml/h in a 50ml syringe.)
System accuracy is +/-2% typical by volume as measured using the trumpet curve test method defined in
w
EN/IEC60601-2-24 at rates of 1.0ml/h (23ºC) and above when the Pump is used with the recommended syringes.
Caution: Infusion volume accuracy may be compromised at rates below 1.0ml/h. Differences in factors such as size
and plunger force in recognised syringes can cause variations in accuracy and trumpet curves. See also 'trumpet
curves' section in this manual.
L-3
approx. 300mmHg
L-5
approx. 500mmHg
L-10
approx. 1000mmHg
Specifications
Electrical Classification
Class I product. Continuous Mode Operation, Transportable.
Battery Specifications
Rechargeable sealed NiMH. Automatically charges when the Pump is connected to AC power.
Mean Time To Power Down from fully charged @ 5ml/h and 23°C ± 2°C under normal conditions is 6 hours*.
*95% lower confidence interval of 5 hours 50 minutes
Charging takes 2½ hours from discharge to 90% charge.
In TCI mode, a fully charged battery allows at least one full syringe to be infused.
Memory Retention
The electronic memory of the Pump will be retained for at least 6 months when not powered up.
Fuse Type
2 x T 1.25L250V
AC Power Supply
115 - 230VAC, 50 - 60Hz, 30VA (under maximum charging conditions) 10VA (minimum).
Dimensions
310 mm (w) x 121 mm (h) x 200 mm (d).
Weight
2.4 kg (excluding power cable).
Protection against fluid ingress
IP32 - Protected against direct sprays of water up to 15° from vertical and protected against solid objects greater than 2.5mm.
Note: IP33 applies if mains retainer kit, part number 1000SP01294, is fitted.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
34/52
Page 36

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Alarm Conditions
Drive Disengaged Occlusion Attention (Nurse Callback)
Check Syringe Near End Of Infusion End of Infusion
Battery Low Battery Empty AC Power Fail
Titration not confirmed Internal Malfunction Concentration not Permitted
Dose Would Exceed Target Would Exceed Dose Under
Dose not Permitted Bolus Dose not Permitted Rate not Permitted
Bolus Dose Under Bolus Dose Over Weight Outside Limit
Environmental Specifications
Operating Temperature 0°C - +40°C
Operating Relative Humidity 20% - 90%
Operating Atmospheric Pressure 700hPa - 1060hPa
Transport and Storage Temperature -30°C - +50°C
Transport and Storage Relative Humidity 10% - 95%
Transport and Storage Atmospheric Pressure 500hPa - 1060hPa
Electrical/Mechanical Safety
Complies with EN/IEC60601-1 and EN/IEC60601-2-24.
Specifications
Potential Equalisation Conductor
The function of the Potential Equalisation Connector (Conductor) is to provide a direct connection between the Pump and the potential
equalisation busbar of the electrical installation. To use the Potential Equalisation Connector, connect the Potential Equalisation
Connector on the Pump to the potential equalisation busbar of the electrical installation.
EMC
Complies with EN/IEC60601-1-2, EN/IEC60601-2-24
1000DF00741 Issue 5
35/52
Page 37

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Recognised Syringes
Recognised Syringes
The Pump is calibrated and labelled for use with single-use disposable Luer lock syringes. Only use the size and type of syringe specified
on the Pump display. The full list of permitted syringe models is dependent on the software version of the Pump.
5ml 10ml 20ml 30ml 50ml
IVAC™
AstraZeneca™*
B Braun Omnifix™*
B Braun Perfusor™*
BD Perfusion*
BD Plastipak™*
BD Precise™*
Codan™*
Codan Perfusion*
Fresenius Injectomat*
Monoject™
Pentaferte*
Rapiject
Terumo™*
2*
1*
ü ü ü ü ü
ü ü
ü ü ü ü ü
ü ü
ü ü ü ü
ü ü
ü ü ü ü ü
ü ü ü ü
ü ü ü ü ü
ü
ü
ü
ü
ü
1
- The Rapiject 50ml syringe is a specialised syringe with a large diameter barrel. To provide protection against accidental dislodging
always ensure the extension set is secured using the extension set hook - see 'Loading and Confirming a Syringe' section.
2
- Ξ TYCO / Healthcare KENDALL - MONOJECT.
To minimise the risk of incorrect confirmation of the syringe type it is recommended that only syringe types available
w
w
in the hospital are configured on the Pump.
CareFusion has characterized a range of syringes as identified in the ‘Recognised Syringes’ table. CareFusion cannot
guarantee the continued system accuracy of these recognised syringes* as the manufacturer may change syringe
specification significant to system accuracy without prior notification.
Subject to the above, BD branded Luer lock syringes can be confirmed as BD Plastipak syringes due to there being no
significant variance in dimensions.
In no event shall CareFusion be liable for any damages of any kind or nature, including without limitation, direct or
indirect, special, consequential, or incidental damages arising from, or in connection with the use of syringes not
listed in the ‘Recognised Syringes’ table.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
36/52
Page 38

Associated Products
The Alaris Gateway Workstation
Product SKU 80203UNS0y-xx
Supply Voltage 115-230VAC, ~50-60Hz
Electrical Rating 460VA (Maximum)
Protection Against Electrical Shock Class 1
Classification Continuous Operation
Supply to Pump 115-230V, ~50-60Hz, 60VA
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Associated Products
The Alaris DS Docking Station
y = Connectivity option - 1, 2 or 3
xx = Configuration
Product SKU 80283UNS00-xx
Supply Voltage 230VAC, 50 or 60Hz
Electrical Rating 500VA (nominal)
Protection Against Electrical Shock Class 1
Classification Continuous Operation
Supply to Pump 20VA max 230V 50-60Hz
1000DF00741 Issue 5
37/52
Page 39

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Compatible Extension Sets
Compatible Extension Sets
The Pump uses standard, single-use, disposable extension sets and syringes with Luer lock connectors. The user is responsible for
verifying the suitability of a product used, if it is not recommended by CareFusion.
20038E7D
3 way extension set with 3 SmartSite™ Needle-Free Valves, low priming volume, 13cm
MFX2271
2 way set with anti-syphon valve and backcheck valve, 210cm
20062E7D
3 way extension set with 3 SmartSite Needle-Free Valves and one backcheck valve,
16cm
MFX2270
3 way set with 2 anti-syphon valves and backcheck valve, 210cm
MFX2290
3 way set with 2 anti-syphon valves and backcheck valve, low priming volume, 209cm
MFX2284
3 way tap (blue) with extension, 100cm
MFX2291
2 way set with anti-syphon valve and backcheck valve, low priming volume, 209cm
MFX2233E
3 way extension set with 2 backcheck valves, SmartSite Needle-Free Valve and clamp,
low priming volume 10cm
1000DF00741 Issue 5
38/52
Page 40

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Compatible Extension Sets
2309E-0006
Bag spike with SmartSite Needle-Free Valve and backcheck valve
MFX2293
Extension set with backcheck valve, 14cm. Priming Volume: 0.9ml
500-013V
Y Connector set 3-way with 2 anti-syphon valves and backcheck valve, 190cm
2205E-0006
Vial adaptor with SmartSite Needle-Free Valve, for 20mm vials
500-012V
Y Connector set 2-way with anti-syphon valve and backcheck valve, 210cm
500-002V
Y Connector set 2-way with anti-syphon valve and backcheck valve, 15cm
500-003V
Y Connector set 3-way with 2 anti-syphon valves and backcheck valve, 15cm
MFX2282EV
3 way tap with extension and SmartSite Needle-Free Valve, 30cm
MFX2284EV
3 way tap with extension and SmartSite Needle-Free Valve, 100cm
MFX2280EV
3 way tap with extension and SmartSite Needle-Free Valve, 10cm
MFX2283EV
3 way tap with extension and SmartSite Needle-Free Valve, 50cm
MFX2285EV
3 way tap with extension and SmartSite Needle-Free Valve, 120cm
1000DF00741 Issue 5
39/52
Page 41

PB-G40710
Low Sorbing PE lined extension set with clamp, 100cm
PB-G40715
Low Sorbing PE lined extension set with clamp, 150cm
PB-G40720
Low sorbing PE lined extension set with clamp 200cm
G40615K
Low sorbing PE extension set 150cm
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Compatible Extension Sets
G40215K
Extension set, opaque PVC, 150cm
30262E-0006
Extension set with 2 SmartSite Needle-Free Valve ports, 102cm
G40015
Standard PVC Syringe Extension Set, 150cm.
Priming Volume: 2.6ml
G40020B
Standard PVC Syringe Extension Set, 200cm.
Priming Volume:1.4ml
G40320V
Opaque White PVC Syringe Extension Set, 200cm.
Priming Volume: 1.4 ml
G40620K
Polyethylene Syringe Extension Set, 200cm.
Priming Volume: 1.8ml
• New sets are continuously being developed for our customers. Please contact your local CareFusion representative
w
for availability.
• It is recommended that extension sets are changed in accordance with the Directions for Use. Carefully read the
Directions For Use supplied with the extension set prior to use.
Please note these drawings are not to scale
1000DF00741 Issue 5
40/52
Page 42

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Maintenance
Maintenance
Routine Maintenance Procedures
To ensure that this Pump remains in good operating condition, it is important to keep it clean and carry out the routine maintenance
procedures described below.
Interval Routine Maintenance Procedure
As per Hospital Policy
Each usage
Thoroughly clean external surfaces of the Pump before and after prolonged period of
storage.
1. Inspect AC Power Supply plug and cable for damage.
2. Inspect case, keypad and plunger for damage.
3. Check Start up self test operation is correct.
Before the transfer of the Pump to a
new patient and as required
If the Pump is dropped, damaged, subjected to excessive moisture or high temperature, immediately take it out of
w
w
service for examination by Qualified Service Personnel.
All preventative and corrective maintenance and all such activities shall be performed at a compliant work place in
accordance with the information supplied. CareFusion will not be responsible should any of these actions be
performed outside the instructions or information supplied by CareFusion. For Preventative and Corrective
Maintenance instructions please refer to the Technical Service Manual (TSM).
All preventative and corrective maintenance and all such activities should be performed by Qualified Service
Personnel only, with reference to the TSM.
Please refer to Technical Service Manual for calibration procedures. The units of measurement used in the calibration
procedure are standard SI (The International System of Units) units.
Clean the Pump by wiping over with a lint-free cloth lightly dampened with warm water and
a standard disinfectant / detergent solution.
Battery Operation
The internal rechargeable battery allows continued operation when the AC power is unavailable, for example during patient transfer
or AC power failure. Mean Time To Battery Empty from fully charged @ 5ml/h and 20°C under normal conditions is 6 hours*. From the
battery low alarm it will take about 2½ hours to 90% charge when reconnected to the AC Power Supply, whether the Pump is in use or
not.
The battery is maintenance free, sealed Nickel Metal Hydride and requires no routine servicing. However, to achieve optimum operation,
ensure that the battery is fully recharged after full discharge, before storage, and at regular 3 month intervals during storage.
It is recommended that only Qualified Service Personnel replace the battery, only use a CareFusion recommended battery. For further
information regarding the replacement of batteries refer to the Technical Service Manual.
The battery pack used in this Alaris Syringe Pump is manufactured by CareFusion and includes a proprietary PCB (printed circuit board)
designed specifically for the Alaris Syringe Pump, and in conjunction with Alaris Syringe Pump software, controls battery use, charge
and temperature. Any use of battery packs that are not manufactured by CareFusion in the Alaris Syringe Pump is at your sole risk,
and CareFusion does not provide any warranty for or endorsement on any battery packs that are not manufactured by CareFusion.
CareFusion product warranty shall not apply in the event the Alaris Syringe Pump has suffered damage or premature wear, or
malfunctions or otherwise operates incorrectly, as a result of use with a battery pack that is not manufactured by CareFusion.
*95% lower confidence interval of 5 hours 50 minutes
1000DF00741 Issue 5
41/52
Page 43

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Maintenance
Cleaning and Storage
Before the transfer of the Pump to a new patient and periodically during the use, clean the Pump by wiping over with a lint-free cloth
lightly dampened with warm water and a standard disinfectant / detergent solution.
Do not use the following disinfectant types:
• Disinfectants which are known to be corrosive to metals must not be used, these include:
• NaDcc (such as Presept),
• Hypochlorites (such as Chlorasol),
• Aldehydes (such as Cidex),
• Cationic Surfactants >1% (such as Benzalkonium Chloride).
• Mixture of Alcohol & Chemicals with Cationic surfactants >1% Chlorohydrocarbons (such as Amberclens)
• Use of Iodine (such as Betadine) will cause surface discoloration.
• Concentrated Isopropyl alcohol based cleaners will degrade plastic parts.
Recommended cleaners are:
Brand Concentration
Hibiscrub 20% (v/v)
Virkon 1% (w/v)
The following products were tested and are acceptable for use on the Pump if used in accordance with the specified manufacturer’s
guidelines.
• Warm soapy water
• Mild detergent in water (e.g. Young’s Hospec)
• 40% Isopropyl Alcohol in water
• Chlor-Clean
• Hibiscrub
• Tristel Fuse sachets
• Tristel Trio wipes system
• Tuffie 5 wipe
• Virkon Disinfectant
Before cleaning always switch off and disconnect from the AC Power Supply. Never allow liquid to enter the casing
w
and avoid excess fluid build up on the Pump. Do not use aggressive cleaning agents as these may damage the exterior
surface of the Pump. Do not steam autoclave, ethylene oxide sterilise or immerse this Pump in any fluid.
If the Pump has visible cracks or damage to the case do not clean and immediately take it out of service for
examination by Qualified Service Personnel.
The syringe and extension sets are disposable single use items and should be discarded after use according to their manufacturers’
instructions.
If the Pump is to be stored for an extended period it should be first cleaned and the internal battery fully charged. Store in a clean, dry
atmosphere at room temperature and, if available, employ the original packaging for protection.
Once every 3 months during storage, carry out functional tests as described in the Technical Service Manual and ensure that the internal
battery is fully charged.
Disposal
Information on Disposal for Users of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment
U symbol on the product and/or accompanying documents means that used electrical and electronic products should not be
This
mixed with household waste.
If you wish to discard electrical and electronic equipment, please contact your CareFusion affiliate office or distributor for further
information.
Disposing of this product correctly will help to save valuable resources and prevent any potential negative effects on human health and
the environment which could otherwise arise from inappropriate waste handling.
Information on Disposal in Countries outside the European Union
U symbol is only valid in the European Union. The product should be disposed of taking environmental factors into consideration.
This
To ensure no risk or hazard, remove the internal rechargeable battery and the Nickel Metal Hydride battery from the control board and
dispose of as outlined by the local country regulations. All other components can be safely disposed of as per local regulations.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
42/52
Page 44

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Occlusion Pressure Limits
Occlusion Pressure Limits
Time to alarm following occlusion is achieved in less than 30 minutes at rates of 1 ml/h and higher by the appropriate selection of
occlusion levels.
The following graphs show the typical values for time to alarm and bolus volume that can be expected in the event of an occlusion when
the BD Plastipak 50 ml syringe is selected with a G40020B standard extension set.
Time to alarm - 1.0 ml/h Time to alarm - 5.0 ml/h
— typical
— typical
hr:min
Occlusion Level Occlusion Level
Bolus Volume
— typical
ml
Occlusion Level
Tests at low alarm levels may alarm immediately - the force at these levels is commonly less than the friction in the syringe (with no
additional fluid pressure). The result is that the pressure relating to the low forces will be less than the nominal quoted occlusion
pressure.
hr:min
1000DF00741 Issue 5
43/52
Page 45

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
IrDA, RS232 and Nurse call Specification
IrDA, RS232 and Nurse call Specification
IrDA / RS232 / Nurse call Feature
The IrDA or RS232 / Nurse call is a feature on the Pump that allows connection to a PC or another Alaris Syringe Pump. This allows data to
be transferred between the Pump and a PC or another Alaris Syringe Pump, (e.g. data sets to be uploaded to the Pump, Event Reports to
be downloaded from the Pump and the Pump to be monitored remotely via a suitable central monitoring or computer system).
The nurse call interface provides a remote backup to the internal audible alarm. It should not be relied upon to replace
w
IrDA
monitoring of the internal alarm.
Refer to the Technical Service Manual for further information regarding the RS232 interface. Since it is possible to
control the syringe Pump using the RS232 interface at some distance from the Pump and hence remote from the
patient, responsibility for the control of the Pump is vested in the software run on the computer control system.
The assessment for the suitability of any software used in the clinical environment to control or receive data from the
Pump lies with the user of the equipment. This software should include detection of the disconnection or other failure
of the RS232 cable. The protocol is detailed in the Alaris Syringe Pump Communications Protocol and is for general
information only.
Any connected analogue and digital components are required to meet IEC/EN60950 for data processing and
IEC/EN60601 for medical devices. Anyone connecting additional devices to the signal input or output is a system
configurator and responsible for meeting the requirements of the system standard IEC/EN60601-1-1.
Baud Rate 115.2 kBaud
Start Bits 1 Start Bit
Data Bits 8 Data Bits
Parity No Parity
Stop Bits 1 stop bit
1000DF00741 Issue 5
44/52
Page 46

RS232 / Nurse call Connection Data
Nurse call Specification -
Connector D Type - 9 Pin
TXD/RXD EIA RS232-C Standard
TXD Output Voltage Range Minimum: -5V (mark), +5V (space)
Typical: -7V (mark), +7V (space) with 3kΩ load to ground
RXD Input Voltage Range -30V - +30V max.
RXD Input Thresholds Low: 0.6V minimum
High: 3.0V maximum
RXD Input Resistance 3kΩ minimum
Enable Active, Low:-7V to -12V
Active, High:+7V to +12V,
Inactive: Floating/open circuit, allows isolated RS232 circuitry to power down.
Isolation Socket/Pump 1.5kV (dc, or ac peak)
Baud Rate 115.2 kBaud
Start Bits 1 Start Bit
Data Bits 8 Data Bits
Parity No Parity
Stop Bits 1 stop bit
Nurse Call Relay Contacts Pins 1, 8 + 9, 30V dc, 1A rating
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
IrDA, RS232 and Nurse call Specification
- powers up the isolated RS232 circuitry
Typical Connection Data -
1. Nurse call (Relay) Normally Closed (NC C)
2. Transmit Data (TXD) Output
3. Received Data (RXD) Input
4. Power Input (DSR)
5. Ground (GND)
6. Not used
7. Power Input (CTS)
8. Nurse call (Relay) Normally open (NC O)
9. Nurse call (Relay) Common (NC COM)
1000DF00741 Issue 5
45/52
Page 47

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Trumpet Curves and Start-up Curves
Trumpet Curves and Start-up Curves
In this Pump, as with all infusion systems, the action of the pumping mechanism and variations in individual syringes cause short-term
fluctuations in rate accuracy.
The following curves show typical performance of the system in two ways: 1) the delay in onset of fluid flow when infusion commences
(start-up curves), and 2) the accuracy of fluid delivery over various time periods is measured (trumpet curves).
The start-up curves represent continuous flow versus operating time from the start of the infusion. They exhibit the delay in onset of
delivery due to mechanical compliance and provide a visual representation of uniformity. Trumpet curves are derived from the second
hour of this data. Tests performed per EN/IEC60601-2-24:1998 standard.
Trumpet curves are named for their characteristic shape. They display discrete data averaged over particular time periods or observation
windows, not continuous data versus operating time. Over long observation windows, short term fluctuations have little effect on
accuracy as represented by the flat part of the curve. As the observation window is reduced, short term fluctuations have greater effects
as represented by the mouth of the trumpet.
Knowledge of system accuracy over various observation windows may be of interest when certain drugs are being administered. Short
term fluctuations in rate accuracy may have clinical impact depending on the half-life of the drug being infused, therefore the clinical
effect cannot be determined from the trumpet curves alone.
Start-up and trumpet curves may not be indicative of operation under negative pressure.
w
Differences in factors such as size and plunger force in recognised syringes produced by other manufacturers can cause
variations in accuracy and trumpet curves as compared to those represented. Additional curves for recognised syringes are
available upon written request.
For applications where flow uniformity is a concern, rates of 1.0ml/h or above are recommended.
Start-up Trend. BD Plastipak 5ml @ 0.1ml/h Trumpet Curve. BD Plastipak 5ml @ 0.1ml/h
Rate (ml/h)
Time (mins) Observation Window (mins)
Start-up Trend. BD Plastipak 50 ml @ 1.0 ml/h Trumpet Curve. BD Plastipak 50 ml @ 1.0 ml/h
Rate (ml/h)
Time (mins) Observation Window (mins)
Start-up Trend. BD Plastipak 50 ml @ 5.0 ml/h Trumpet Curve. BD Plastipak 50 ml @ 5.0 ml/h
Error (%)
Maximum Error Minimum Error Linear Mean = +4.5%
Error (%)
Maximum Error Minimum Error Linear Mean = -1.8%
Rate (ml/h)
Error (%)
Time (mins) Observation Window (mins)
Maximum Error Minimum Error Linear Mean = -0.1%
1000DF00741 Issue 5
46/52
Page 48

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Profiles from TCI Mode
Profiles from TCI Mode
When targeting in TCI Mode the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump will automatically calculate the flow rate profile from the specific
pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model for the selected drug. This section of the Directions For Use is intended to help users
understand the profiled infusion and the performance accuracy attained from the TCI Pump.
Induction Bolus and maintenance rates are displayed before starting the titration. When initially starting the infusion or after increasing
the target (plasma or effect) concentration by titration, the Pump will first deliver a bolus dose through a typically short, high rate
infusion. On completion of this bolus, the Pump will immediately switch to a lower maintenance rate (when plasma target mode is used)
or will pause for a period of time before switching to a lower maintenance rate (when effect site targeting mode is used). Once the
maintenance phase is reached, any reduction made to the target (plasma or effect) concentration will typically result in the infusion rate
reducing to zero until the predicted plasma (or effect) concentration reduces the new target value.
The Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump updates the pharmacokinetic model driving the plasma (or effect) concentration prediction and the
infusion rate every 10 seconds. The infusion rate graph, shown in the Infusion Rate vs Target concentration graphs was measured in
accordance with the protocol described in the IEC60601-2-24
The Pump solves the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic algorithms so that the target (plasma or effect) concentration is attained as
rapidly and as accurately as possible. However, the User may need to take into consideration the limitations of the physical system in
attaining the target (plasma or effect) concentration; this includes:
• The limit on the flow rate permitted by the infusion pump mechanism;
• The limit on the flow rate permitted by the syringe size;
• The patient / drug dose limitation from the prescribing information to insure the safety of the administration;
• The variation in individual patient response to reach the plasma (or effect) concentration;
• The model specific cap rate.
A true assessment of the performance of the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump can be made if the volumetric error, that is the difference
between the actual volume infused and the predicted volume infused, is calculated. For the Infusion Rate vs Target concentration
graphs, over a one hour period, the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump has a mean volumetric accuracy in TCI Mode better than ±5%
By measuring the volume from the flow rate profile delivered from the Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump and then introducing this into a
reverse pharmacokinetic model the predicted plasma (or effect) concentration can be calculated from the flow rate. These are illustrated
in the Predicted vs Ideal Concentration graphs, showing the typical performance of the system against changes in the target plasma (or
effect) concentration for a typical, idealised profile. For the same targeted profile, the deviation of the predicted plasmatic (or effect)
concentration (back calculated from the volume collected) from the expected Ideal plasma (or effect) concentration, results from the
volumetric inaccuracy of the system (Pump and syringe). The Alaris PK Plus Syringe Pump will track the predicted plasma (or effect)
concentration to within ±5%
delays may decrease the accuracy of the predicted plasma (or effect) concentration particularly where high syringe drug concentrations
are used in conjunction with large sizes of syringes and low target plasma (or effect) concentrations as the syringe plunger motion over
time (proportional to the flow rate accuracy) will be significantly reduced.
2
of that calculated by pharmacokinetic model over a one hour period. Flow rate inaccuracies and start-up
1
Standard, with the data sample period reduced from 30 to 10 seconds.
2
.
For a given drug concentration, the volumetric error is proportional to the dose rate error. Knowledge of the system
w
The graphs illustrated in this section are for a Diprivan (1% Concentration); Diprivan (2% concentration), Remifentenil (50µg/ml
concentration), and Sufentanil (5µg/ml concentration) are given for comparison. As an illustration of the effect the syringe size has on
system performance, Remifentenil (50µg/ml concentration) is shown with a 50ml and 5ml syringe respectively.
The target (plasma or effect) concentrations shown are for illustrative purposes only.
Note:
1
IEC60601-2-24: Particular Requirements for the Safety of Infusion Devices;
2
95% Confidence / 95% Population.
accuracy over different time intervals may be of interest when assessing the impact of administering short-half
life drugs. In these circumstances, short-term fluctuation in the infusion rate could have a clinical impact that
cannot be determined from the performance profiles shown in Figures below. In general, the volumetric error
will increase with small induction and maintenance rates, which may occur when with large volume syringes, high
syringe concentrations, low patient weights and low target (plasma or effect) concentrations. For applications
where system accuracy is important, maintenance rates less than 1.0 ml/h are not recommended; syringe sizes, drug
concentrations / dilutions and target (plasma or effect) concentrations should be selected accordingly to ensure the
maintenance rate exceeds this lower limit.
1000DF00741 Issue 5
47/52
Page 49

Infusion Rate vs Target Concentration
1000
1100
1200
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
8.0
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
550
600
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
8.0
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
0
5
0
5
0
5
0
5
4.0
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
0
5
0
5
0
5
0
5
4.0
100
120
140
160
180
200
220
240
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
Diprivan 1% Marsh Model BD 50ml Syringe Diprivan 2% Marsh Model BD 50ml Syringe
• Patient Age: 40 Years
• Patient Weight: 60kg
• Drug Concentration: 10mg/ml
• Volumetric Accuracy: +0.1%
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Profiles from TCI Mode
• Patient Age: 40 Years
• Patient Weight: 60kg
• Drug Concentration: 20mg/ml
• Volumetric Accuracy: -0.4%
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
Rate (ml/h)
200
100
0
Time Interval (mins) Time Interval (mins)
Remifentanil Minto Model BD 5ml Syringe Remifentanil Minto Model BD 50ml Syringe
• Patient Age: 75 Years
• Patient Weight: 65kg
• Patient Height: 175cm
• Patient Gender: Male
• Drug Concentration: 50µg/ml
• Volumetric Accuracy: -0.2%
Rate (ml/h)
5
0
7.
6.
5.
4.
3.
2.
1.
0.
Target Plasma Concentration (µg/ml)
Rate (ml/h)
50
0
7.
6.
5.
4.
3.
2.
1.
0.
Target Plasma Concentration (µg/ml)
• Patient Age: 75 Years
• Patient Weight: 65kg
• Patient Height: 175cm
• Patient Gender: Male
• Drug Concentration: 50µg/ml
• Volumetric Accuracy: -1.6%
3.
3.
2.
2.
1.
1.
0.
0.
Target Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
Rate (ml/h)
5
0
3.
3.
2.
2.
1.
1.
0.
0.
Target Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
Time Interval (mins) Time Interval (mins)
Sufentanil Gepts Model BD 50ml Syringe
(Plasma Target)
• Drug Concentration: 5.0µg/ml
• VTarget Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
80
Rate (ml/h)
60
40
20
0
Time Interval (mins)
1000DF00741 Issue 5
Target Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
48/52
Page 50

Predicted vs Ideal Concentration
0.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.0
8.0
0.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.0
8.0
0.
0.
1.
1.
2.
2.
3.
3.
4.0
4.0
0.
0.
1.
1.
2.
2.
3.
3.
4.0
4.0
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.40
Diprivan 1% Marsh Model BD 50ml Syringe Diprivan 2% Marsh Model BD 50ml Syringe
• Patient Age: 40 Years
• Patient Weight: 60kg
• Drug Concentration: 10mg/ml
• Plasma Concentration Accuracy: +0.2%
Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Profiles from TCI Mode
• Patient Age: 40 Years
• Patient Weight: 60kg
• Drug Concentration: 20mg/ml
• Plasma Concentration Accuracy: -0.3%
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
Predicted Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
Time Interval (mins) Time Interval (mins)
Remifentanil Minto Model BD 5ml Syringe Remifentanil Minto Model BD 50ml Syringe
• Patient Age: 75 Years
• Patient Weight: 65kg
• Patient Height: 175cm
• Patient Gender: Male
• Drug Concentration: 50µg/ml
• Plasma Concentration Accuracy: +0.2%
5
0
5
0
5
0
5
0
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
Predicted Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
7.0
6.0
5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.0
0.0
Ideal Plasma Concentration (µg/ml)
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Predicted Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
7.0
6.0
5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.0
0.0
Ideal Plasma Concentration (µg/ml)
• Patient Age: 75 Years
• Patient Weight: 65kg
• Patient Height: 175cm
• Patient Gender: Male
• Drug Concentration: 50µg/ml
• Plasma Concentration Accuracy: +0.5%
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
Ideal Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
5
0
5
0
5
0
5
0
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
Predicted Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
Ideal Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
0.0
Time Interval (mins) Time Interval (mins)
Sufentanil Gepts Model BD 50ml Syringe
• Drug Concentration: 5.0µg/ml
• Plasma Concentration Accuracy: +3.1%
0.35
0.30
0.25
0.20
0.15
0.10
0.05
Ideal Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
Predicted Plasma Concentration (ng/ml)
0.00
Time Interval (mins)
1000DF00741 Issue 5
49/52
Page 51

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Products and Spare Parts
Products and Spare Parts
Spare Parts
A comprehensive list of spare parts for this Pump is included within the Technical Service Manual.
The Technical Service Manual (1000SM00001) is now available in electronic format on the World Wide Web at :-
www.carefusion.co.uk/alaris-technical/
A username and password are required to access our manuals. Please contact a local customer services representative to obtain login
details.
Part Number Description
1000SP01122 Internal Battery Pack
1001FAOPT91 AC Power Lead - UK
1001FAOPT92 AC Power Lead - European
Alaris PK Editor Software
Part Number Description
1000SP00624 Alaris PK Editor
1000CD00123 Alaris PK Editor Drug Models - Adult
1000CD00124 Alaris PK Editor Drug Models - Paediatric
1000DF00741 Issue 5
50/52
Page 52

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Service Contacts
Service Contacts
For service contact your local Affiliate Office or Distributor.
AE DE HU PT
CareFusion,
PO Box 5527,
Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
Tel: (971) 4 28 22 842 Tel: (49) 6221 305 0 Tel: (36) 1 488 0232
Fax: (971) 4 28 22 914 Fax: (49) 6221 305 216 Fax: (36) 1 201 5987 Fax: +351 219 152 598
AU DK IT SE
CareFusion,
3/167 Prospect Highway,
PO Box 355
Seven Hills, NSW 2147,
Australia.
Tel: (61) 1800 833 372 Tlf. (45)70 20 30 74 Tél: (39) 055 30 33 93 00 Tel: (46) 8 544 43 200
Fax: (61) 1800 833 518 Fax. (45)70 20 30 98 Fax: (39) 055 34 00 24 Fax: (46) 8 544 43 225
BE ES NL US
CareFusion,
Erembodegem-Dorp 86
B-9320 Erembodegem
Belgium.
Tel: +32 (0) 2 267 38 99 Tel: (34) 902 555 660 Tel: +31 (0)30 2289 711 Tel: (1) 800 854 7128
Fax: +32 (0) 2 267 99 21 Fax: (34) 902 555 661 Fax: +31 (0)30 2289 713 Fax: (1) 858 458 6179
CA FR NO ZA
CareFusion,
235 Shields Court,
Markham,
Ontario L3R 8V2,
Canada.
Tel: (1) 905-752-3333 Tél: (33) 01 30 02 81 41 Tel: (47) 64 00 99 00 Tel: (27) (0) 860 597 572
Fax: (1) 905-752-3343 Fax: (33) 01 30 02 81 31 Fax: (27) 21 5107567
CH FI NZ
CareFusion,
A-One Business Centre
Zone d’activitiés Vers-la-Pièce
n° 10
1180 Rolle / Switzerland
Ph.: 0848 244 433 Tel: +358 207871 090 Tel: 09 270 2420
Fax: 0848 244 100 Fax: 09 270 6285
CN GB PL
康尔福盛(上海)商贸有限公司
地址:上海市浦东新区张杨路
500号24楼E.F.G.H单元
电话:+86-21-60369369
4008788885
传真:+86-21-60369399
CareFusion,
Tullastr. 8-12
69126 Heidelberg,
Deutschland.
CareFusion,
Firskovvej 25 B,
2800 Lyngby,
Danmark.
CareFusion,
Edificio Veganova,
Avenida de La Vega, nº1,
Bloque 1 - Planta 1,
28108 Alcobendas, Madrid,
España.
CareFusion,
Parc d’affaire le Val Saint Quentin
2, rue René Caudron
78960 Voisins le Bretonneux
France
CareFusion,
Kuortaneenkatu 2,
00510 Helsinki
CareFusion,
The Crescent, Jays Close,
Basingstoke,
Hampshire, RG22 4BS,
United Kingdom.
Tel: (44) 0800 917 8776 Tel: (48) 22 377 11 00
Fax: (44) 1256 330860 Fax: (48) 22 377 11 01 Rev. O
CareFusion,
Döbrentei tér 1,
H-1013 Budapest,
Magyarország.
Tel: (36) 1 488 0233
CareFusion,
Via Ticino 4,
50019 Sesto Fiorentino,
Firenze, Italia.
CareFusion,
De Molen 8-10,
3994 DB Houten,
Nederland.
CareFusion,
Fjordveien 3
1363 HØVIK
Norge.
CareFusion,
14B George Bourke Drive,
Mt Wellington 1060,
PO Box 14-518,
Panmure 1741, Auckland,
New Zealand
Freephone: 0508 422734
Becton Dickinson Polska Sp. z o.o.
ul. Osmańska 14
02-823 Warszawa
Polska.
CareFusion,
Avda. São Miguel, 296 Atelier 14
2775-751 Carcavelos, Lisboa
Portugal
Tel: +351 219 152 593
CareFusion,
Hammarbacken 4B,
191 46 Sollentuna,
Sverige.
CareFusion,
10020 Pacific Mesa Blvd.,
San Diego, CA 92121,
USA.
CareFusion,
Unit 2 Oude Molen Business Park,
Oude Molen Road, Ndabeni,
Cape Town 7405, South Africa.
Tel: (27) 21 510 7562
1000DF00741 Issue 5
51/52
Page 53

Alaris™ PK Plus Syringe Pump
Service Contacts
Page Intentionally Left Blank
1000DF00741 Issue 5
52/52
Page 54

CareFusion, Alaris, IVAC, SmartSite and the
CareFusion logo are trademarks or registered
trademarks of CareFusion Corporation or one of its
affiliates. All rights reserved.
All other trademarks are property of their
respective owners.
© 2018 CareFusion Corporation or one of its
affiliates. All rights reserved.
This document contains proprietary information
of CareFusion Corporation or one of its affiliates,
and its receipt or possession does not convey any
rights to reproduce its contents, or to manufacture
or sell any product described. Reproduction,
disclosure, or use other than for the intended
purpose without specific written authorization of
CareFusion Corporation or one of its affiliates is
strictly forbidden.
CareFusion Switzerland 317 Sarl,
A-One Business Centre, Z.A Vers –La-
t
Pièce n° 10, CH-1180, Rolle
CareFusion UK 305 Ltd., The Crescent,
EC REP
Jays Close, Basingstoke, Hampshire,
RG22 4BS, UK
1000DF00741 Issue 5
carefusion.com
 Loading...
Loading...