Page 1
Please read and save these instructions. Read carefully before attempting to assemble, install, operate or maintain the product described.
Protect yourself and others by observing all safety information. Failure to comply with instructions could result in personal injury and/or
property damage! Retain instructions for future reference.
IN211104AV 9/99
Operating Instructions & Parts Manual Models WG3000 and WG3060
Wire Feed
Arc Welder
This line of Campbell Hausfeld wire feed
welders is designed to be used on
standard 115V household current. The
welders are equipped with infinite wire
speed control to accurately select the
proper wire feed rate needed for various
welding conditions. Internal components
are thermostatically protected.
These welders are designed for use with
Flux Core Arc Welding (Gasless) or Gas
Metal Arc Welding (Mig) process. As
delivered from the factory, this welder
can weld with .024” (.6 mm) to .035”
(.9 mm) diameter wire. A starter spool
of .035” (.9 mm) flux-cored wire and a
.040 tip are included.
Unpacking
Some welder components may be
found in the wire feed compartment.
When unpacking, inspect carefully for
any damage that may have occurred
during transit. Report any damaged or
missing items by calling (800) 746-5641.
Circuit Requirements
This equipment
requires a dedicated 115 volt circuit. Refer to the
following chart for the correct circuit
breaker or fuse rating. Do not run
other appliances, lights, or tools on
this circuit while operating this
equipment. Extension cords are not
recommended. Blown fuses and tripped
circuit breakers can result from failure
to comply with this recommendation.
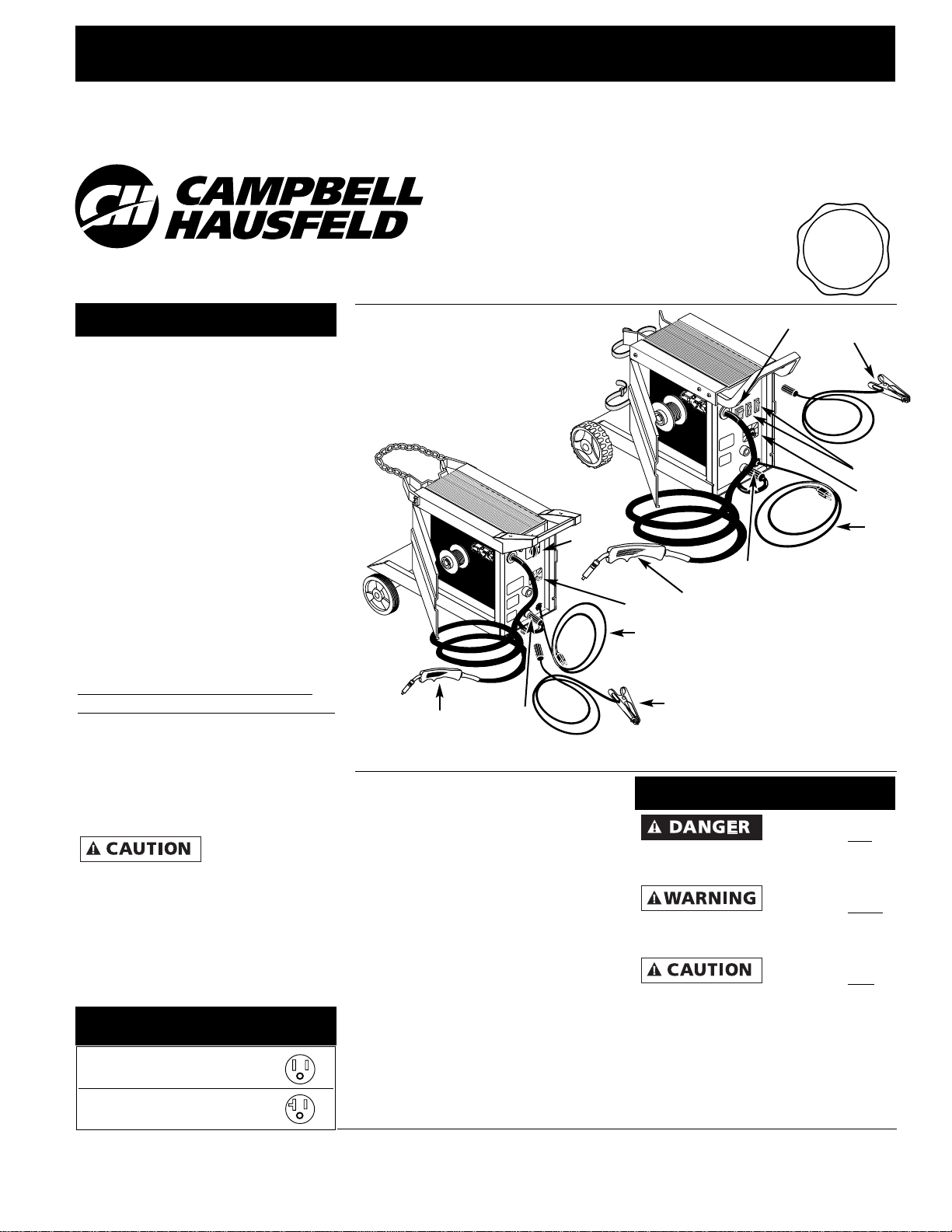
Components and Controls
1. Work Clamp - connect to work
piece.
2. Wire Feed Gun with .040 tip
3. Power Cord - plug into 115 volt
outlet.
4. On/Off Switch
5. Infinite Wire Speed Control -
turns clockwise to increase wire
speed and counterclockwise to
decrease wire speed.
6. Heat Selector - Selects welding
power. Four selections are possible
7. Polarity Hook-up - Attach torch
cable to (+) for MIG and (-) for flux
core wire.
Heat Circuit Breaker or
Selector Slow Blow Fuse
Danger means a
hazard that will
cause death or serious injury if the
warning is ignored.
Warning means a
hazard that could
cause death or serious injury if the
warning is ignored.
Caution means a
hazard that may
cause minor or moderate injury if the
warning is ignored. It also may mean a
hazard that will only cause damage to
property.
NOTE: Note means any additional
information pertaining to the product
or its proper usage.
MODEL WG3000
Low (1-2) 15 amp
High (3-4) 20 amp
Description
MODEL WG3060
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4 & 6
5
5
6
7
Figure 1
General Safety
© 1999 Campbell Hausfeld / Scott Fetzer
For parts, product & service information
visit www.campbellhausfeld.com
7
A
N
R
C
U
E
S
S
A
Y
T
I
L
Need
BUILT TO LAST
TM
A
U
Q
Assistance?
Call Us First!
1-800-746-5641
P
R
O
G
R
A
M
Page 2
2
Wire Feed Arc Welder
Torch is “live” (has
current potential)
at all times when machine is turned on
(WG3000 only).
Always keep a fire
extinguisher accessible while
performing arc welding operations.
● Before starting or servicing any
electric arc welder, read and
understand all instructions. Failure
to follow safety precautions or
instructions can cause equipment
damage and/or serious personal
injury or death.
● All installation, maintenance, repair
and operation of this equipment
should be performed by qualified
persons only in accordance with
national, state, and local codes.
Improper use of electric arc
welders can cause electric
shock, injury, and death!
Take all precautions described in this
manual to reduce the possibility of
electric shock.
● Verify that all components of the
arc welder are clean and in good
condition prior to operating the
welder. Be sure that the insulation
on all cables, wire feed gun, and
power cords is not damaged.
Always repair or replace damaged
components before operating the
welder. Always keep welder panels,
shields, etc. in place when operating
the welder.
● Always wear dry, protective clothing
and welding gloves, and insulated
footwear.
● Always operate the welder in a
clean, dry, well ventilated area. Do
not operate the welder in humid,
wet, rainy, or poorly ventilated
areas.
● Be sure that the work piece is
properly supported and grounded
prior to beginning any electric arc
welding operation.
● Coiled welding cable should be
spread out before use to avoid
overheating and damage to
insulation.
Never immerse the
wire or wire feed
gun in water. If the welder becomes
wet for any reason, be absolutely
certain that it is completely clean and
dry prior to attempting use!
● Always shut the equipment off and
unplug the power prior to moving
the unit.
● Always attach the work lead first.
● Verify that the work piece is
securely grounded.
● Always shut off electric arc welding
equipment when not in use and,
and cut off any excess wire from the
wire feed gun.
● Never allow any part of the body to
touch the flux core wire and ground
or grounded work piece at the same
time.
● Awkward welding conditions and
positions can be electrically
hazardous. When crouching,
kneeling or at elevations, be sure to
insulate all conductive parts, wear
appropriate protective clothing, and
take precautions to prevent injury
from falls.
● Never attempt to use this
equipment at current settings or
duty cycles higher than those
specified on the equipment labels.
● Never use an electric arc welder to
thaw frozen pipes.
Flying sparks and hot metal
can cause injury. As welds
cool, slag can be thrown off.
Take all precautions described in this
manual to reduce the possibility of
injury from flying sparks and hot metal.
● Wear ANSI approved face shield or
safety glasses with side shield
protection when chipping or
grinding metal parts.
● Wear ear plugs when welding
overhead to prevent spatter or slag
from falling into ears.
Electric arc welding
operations produce intense
light and heat and
ultraviolet (UV) rays. This intense light
and UV rays can cause injury to eyes
and skin. Take all precautions described
in this manual to reduce the possibility
of injury to eyes and skin.
● All persons operating this
equipment or in the area while
equipment is in use must wear
protective welding gear including:
welding helmet or shield with at
least shade 10, flame resistant
clothing, leather welding gloves,
and full foot protection.
Never look at arc
welding operations
without eye protection as described
above. Never use a shade filter lens
that is cracked, broken, or rated below
number 10. Warn others in the area not
to look at the arc.
Electric arc welding
operations cause sparks and
heat metal to temperatures
that can cause severe burns! Use
protective gloves and clothing when
performing any metal working
operation. Take all precautions
described in this manual to reduce the
possibility of skin and clothing burns.
● Make sure that all persons in the
welding area are protected from
heat, sparks, and ultraviolet rays.
Use additional face shields and
flame resistant barriers as needed.
● Never touch work pieces until
completely cooled.
Heat and sparks produced
during electric arc welding
and other metal working
operations can ignite flammable and
explosive materials! Take all
precautions described in this manual to
reduce the possibility of flames and
explosions.
● Remove all flammable materials
within 35 feet (10.7 m) of welding
arc. If removal is not possible,
tightly cover flammable materials
with fire proof covers.
● Do not operate any electric arc
welder in areas where flammable or
explosive vapors may be present.
● Take precautions to be sure that
flying sparks and heat do not cause
flames in hidden areas, cracks,
behind bulkheads, etc.
Fire hazard! Do not weld on
containers or pipes that
contain or have contained
flammable materials or gaseous or
liquid combustibles.
Arc welding closed cylinders
or containers such as tanks
or drums can cause explosion
if not properly vented! Verify that any
cylinder or container to be welded has
an adequate ventilation hole, so that
expanding gases can be released.
General Safety
(Continued)
www.campbellhausfeld.com
Page 3
Code for Safety in Welding and
Cutting
CSA Standard W117.2, from Canadian
Standards Association, Standards Sales,
178 Rexdale Boulevard, Rexdale,
Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3
Cutting And Welding Processes
NFPA Standard 51B, from National Fire
Protection Association, Batterymarch
Park, Quicy, MA 02269
Safe Practices For Occupational And
Educational Eye And Face
Protection
ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American
National Standards Institute, 1430
Broadway, New York, NY 10018
Refer to the Material Safety Data
Sheets and the manufacturers
instructions for metals, wire, coatings
and cleaners.
Selecting the proper location can
significantly increase performance,
reliability and life of the arc welder.
● For best results locate the welder in
an environment that is clean and
dry. Dust and dirt in the welder
retain moisture and increase wear
of moving parts.
● Place the welder in an area that
provides at least 12” (30,48 cm) of
ventilation space at both the front
and rear of the unit. Keep all
obstructions away from this
ventilation space.
● Store wire in a clean, dry location
with low humidity to preserve the
wire coating.
● The receptacle used for the welder
must be properly grounded and the
welder must be the only load on the
power supply circuit. Refer to the
Circuit Amps chart on page 1 for
correct circuit capacity.
● The use of an extension cord is not
recommended for electric arc
welding machines. The voltage drop
in the extension cord may significantly degrade the performance of
the welder.
Model WG3000
Welder components listed below
are in the wire feed compartment.
Open and remove.
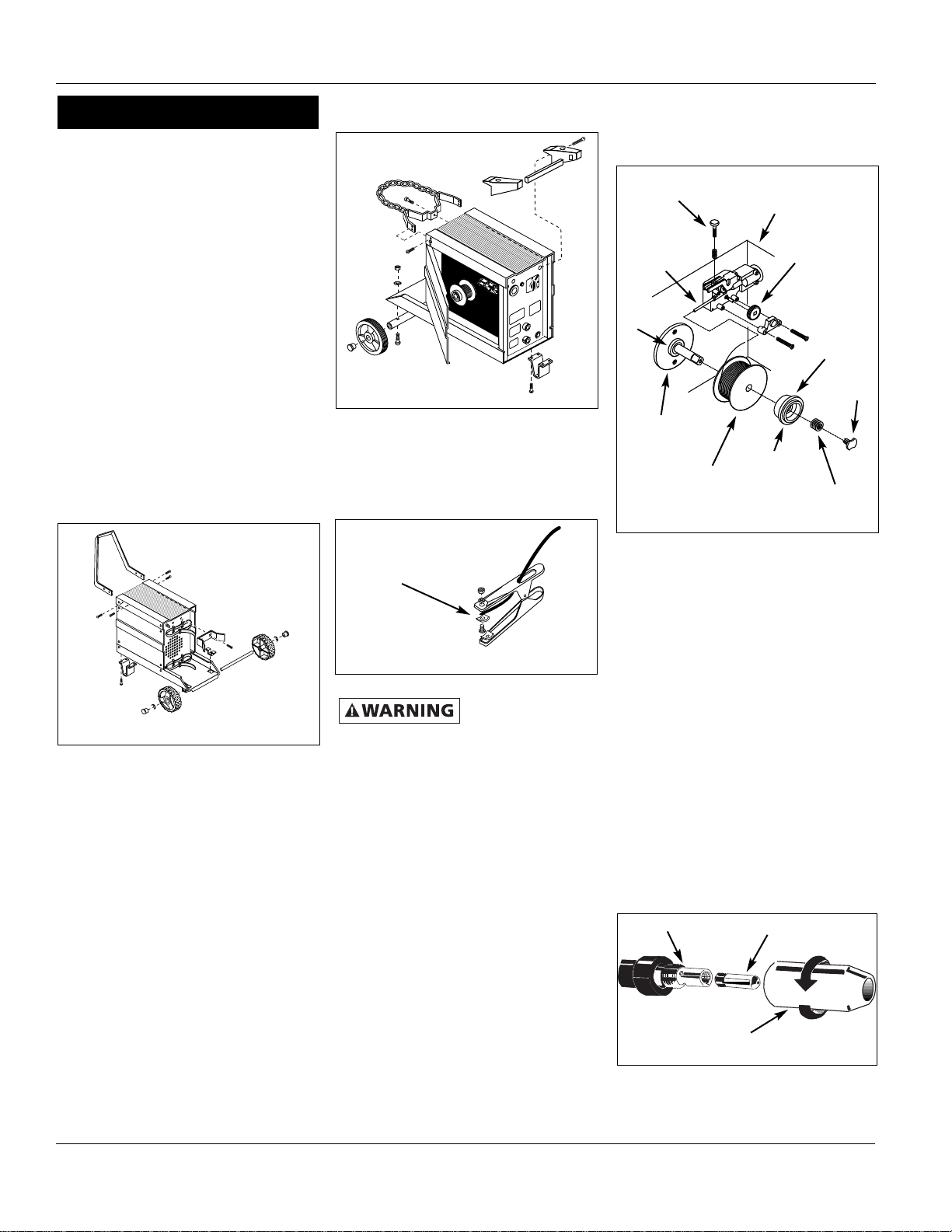
HANDLE ASSEMBLY
1. Remove screws from handle. Slide
handle between welder front panel
Do not breathe fumes that
are produced by the arc
welding operation. These
fumes are dangerous. If the welding
area cannot be adequately ventilated,
be sure to use an air supplied
respirator.
● Keep the head and face out of the
welding fumes.
● Do not perform electric arc welding
operations on metals that are
galvanized or cadmium plated, or
contain zinc, mercury, or beryllium
without completing the following
precautions:
a. Remove the coating from the
base metal.
b. Make sure that the welding area
is well ventilated.
c. Use an air-supplied respirator.
Extremely toxic fumes are created
when these metals are heated.
The electromagnetic field
that is generated during arc
welding may interfere with
the operation of various
electrical and electronic devices such as
cardiac pacemakers. Persons using such
devices should consult with their
physician prior to performing any
electric arc welding operations.
● Route the wire gun and work cables
together and secure with tape
when possible.
● Never wrap arc welder cables
around the body.
● Always position the wire gun and
work leads so that they are on the
same side of the body.
● Exposure to electromagnetic fields
during welding may have other
health effects which are not known.
Always be sure
that the welding
area is secure and free of hazards
(sparks, flames, glowing metal or slag)
prior to leaving. Be sure that
equipment is turned off and excess
wire is cut off. Be sure that cables are
loosely coiled and out of the way. Be
sure that all metal and slag has cooled.
Cylinders can explode if
damaged. Shielding gas
3
WG3000 and WG3060
cylinders contain gas under high
pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can
explode. Since gas cylinders are
normally part of the welding process,
be sure to treat them carefully.
● Protect compressed gas cylinders
from excessive heat, mechanical
shocks, and arcs.
● Install and secure cylinders in an
upright position by chaining them
to stationary support or equipment
cylinder rack to prevent falling or
tipping.
● Keep cylinders away from any
welding or other electrical circuits.
● Never allow a welding electrode to
touch any cylinder.
● Use only correct shielding gas
cylinders, regulators, hoses, and
fittings designed for the specific
application; maintain them and
associated parts in good condition.
● Turn face away from valve outlet
when opening cylinder valve.
● Keep protective cap in place over
valve except when cylinder is in use
or connected for use.
● Read and follow instructions on
compressed gas cylinders, associated
equipment, and CGA publication P-1
listed in Safety Standards.
Never use
flammable gasses
with MIG welders. Only inert or nonflammable gasses such as carbon
dioxide, argon, helium, or mixtures of
one or more of these gasses are
suitable for MIG welding.
Never lift cylinders
off the ground by
their valves, caps, or with chains or slings.
ADDITIONAL SAFETY STANDARDS
ANSI Standard Z49.1 from American
Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJune Rd.
Miami, FL 33126
Safety and Health Standards
OSHA 29 CFR 1910, from
Superintendent of Documents, U.S.
Government Printing Office,
Washington, D.C. 20402
National Electrical Code
NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire
Protection Association, Batterymarch
Park, Quincy, MA 02269
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases
in Cylinders
CGA Pamphlet P-1, from Compressed Gas
Association, 1235 Jefferson Davis
Highway, Suite 501, Arlington, VA 22202
General Safety
(Continued)
Installation
Assembly
www.campbellhausfeld.com
Page 4
and top cover aligning the holes in
handle with holes in top cover.
2. Fasten screws through top cover and
into handle.
WHEEL AND AXLE ASSEMBLY
1. Insert axle supports into slots in the
welder housing.
2. Insert axle through the axle supports
and firmly push wheels onto axle.
3. Secure wheel with e-clips and wheel
caps.
GAS CYLINDER BRACKET ASSEMBLY
1. Place bracket on welder aligning the
holes in welder housing.
2. Fasten screws through bracket and
into cabinet.
FOOT ASSEMBLY
1. Place foot on welder and align holes
in the welder housing.
2. Fasten screws through foot into
cabinet.
Model WG3060
HANDLE ASSEMBLY
1. Place handle assembly on welder
aligning the holes in welder front
panel.
2. Fasten screws through handle ends
and into cabinet.
WHEEL AND AXLE ASSEMBLY
1. Attach axle on welder housing with
attaching hardware.
2. Insert wheels onto axle and lightly
tap in wheel caps.
GAS CYLINDER BRACKET ASSEMBLY
1. Place bracket on welder aligning the
holes in welder housing.
2. Fasten screws through bracket into
cabinet.
FOOT ASSEMBLY
1. Place foot on welder and align holes
in the welder housing.
2. Fasten screws through foot into
cabinet.
Work Clamp (All Models)
1. Loosen hex nut on work clamp.
2. Insert cord through clamp handle and
slide bare wire under the clamp block.
Tighten hex nut making sure bare
wire is clamped securely (Figure 4).
Wire Installation
Welding power
may be applied to
the output terminals, feed roll, work
clamp, gun cable connection and
welding wire even when the the gun
switch is not activated. Do not touch
these parts when the welding machine
is on.
NOTE: Before installing welding wire,
be sure that the diameter of the
welding wire matches the groove in the
drive roller on the wire feed
mechanism and the wire matches the
contact tip in the end of the gun. A
mismatch on any item could cause the
wire to slip or bind.
1. Verify the unit is off and open the
panel on the welder to expose the
wire feed mechanism.
2. Remove the spool quick lock, by
pushing in and rotating 1/4 turn
counterclockwise. The knob, spring,
and spool spacer can now be removed.
NOTE: Spool spacer and spindle spacer
act as an 8” spool spindle adapter.
Purchase of an adapter is not necessary.
* See Figure 5 for assembly.
4
Wire Feed Arc Welder
3. Loosen the wire feed tensioning
screw on the drive mechanism. This
allows initial feeding of the wire into
the gun liner by hand.
4. Install the wire spool onto the
spindle so that the wire can come off
the spool on the end closest to the
wire feed guide tube. Do not cut
the wire loose yet. Install the spool
spacer, spring, and quick lock knob
by pushing in and turning the knob
1/4 rotation clockwise.
5. Hold the wire and cut the wire end
from the spool. Do not allow the wire
to unravel. Be sure that the end of the
wire is straight and free of burrs.
6. Feed the wire through the wire feed
guide tube, over the groove in the
drive roll and into the gun liner.
Tighten the wire feed tensioning screw
so that it is snug. Do not over tighten.
7. Remove the nozzle by turning
counterclockwise. Then unscrew
the contact tip from the end of the
welding torch (See Figure 6). Plug the
welder into the proper power supply
receptacle.
HINT: Keep torch cable straight when
feeding wire.
8. Turn on the welder and set the wire
speed rate to 5. Activate the gun
Assembly (Continued)
Figure 2 - WG3000 Assembly
Figure 3 - WG3060 Assembly
Clamping
Block
Figure 4 - Work Clamp Assembly
Tension
Screw
Panel
Drive Roller
Spool
Spacer
Guide
Tube
Spindle
4” or 8”
Spool
Spring
Spool
Lock
Figure 5 - Weld Wire Routing
Torch Neck
Contact Tip
Nozzle
Figure 6 - Torch Nozzle
Spindle
Spacer
www.campbellhausfeld.com
*Reverse
position and
insert into 8”
spool
Page 5

5
WG3000 and WG3060
switch until the wire feeds out past
the torch end. Turn welder off.
9. Carefully slip the contact tip over the
wire and screw it into the torch neck.
Install the nozzle by turning clock-
wise (See Figure 6). Cut the wire off
approximately 1/4” from the end of
the nozzle.
POLARITY
For gas shielded welding, connect the
cable coming out of the torch to the (+)
socket and the work clamp cable to the
(-) socket on the front panel. For fluxcore (no-gas) welding, connect torch to
(-) and work clamp to (+).
DUTY CYCLE / THERMOSTATIC
PROTECTION
Welder duty cycle is the percentage of
actual weld time that can occur in a ten
minute interval. For example, at a 10%
duty cycle, actual welding can occur for
one minute, then the welder must cool
for nine minutes.
Internal components of this welder are
protected from overheating with an
automatic thermal switch. A yellow
lamp is illuminated on the front panel
if the duty cycle is exceeded. Welding
operations may continue when the
yellow lamp is no longer illuminated.
MODEL WT1000
1. Remove the lens retainer from the
face shield with a regular screwdriver
by prying against the shield and post
of the lens retainer.
2. Remove the protective film covering
from both sides of each lens cover.
Put one clear lens cover on each side
of the shaded lens. Place these three
lenses together into the face shield
and secure with the lens retainer. The
lens retainer should snap into the
second notch in the face shield.
3. Position one of the holes in the
adjustment arm over the pins which
are located in the ear area of the face
shield. These adjustment arms control
the closeness of fit and can be easily
repositioned if necessary.
4. Position the headgear inside the face
shield. Assemble the helmet by
inserting the stud screw through the
headgear and shield into the tension
nut as shown. Do not tighten tension
nut completely.
5. Trial fit the welding helmet. Adjust
headgear ratchet band to a
comfortable position and lower the
face shield. If the shield is too far or
too close to the face, use a different
hole in the adjustment arm. Adjust
the tension nuts so that helmet can be
easily lowered over the face by
nodding the head.
Improper handling
and maintenance
of compressed gas cylinders and
regulators can result in serious injury
or death! Always secure gas cylinders
to the tank bracket kit, a wall or other
fixed support to prevent the cylinder
from falling over. Read, understand,
and follow all the compressed gases
and equipment hazards in the safety
instructions.
NOTE: Shielding gas is not required if
flux-cored welding wire is used.
GAS TYPES
There are 3 types of gas generally used
for gas metal arc welding; 100% argon,
a mixture of 75% argon and 25%
carbon dioxide (C25) or 100% carbon
dioxide. However, 100% carbon
dioxide is not recommended due to
unsatisfactory weld beads. This welder
does not perform well with 100%
carbon dioxide. The 75/25 mixture is
recommended for general steel
welding. For aluminum welding, use
100% argon. Cylinders of either type
gas may be obtained at your local
welding supply outlet. Secure cylinder
in place on your welding machine or
other support to prevent the cylinder
from falling over.
NOTE: Use of incorrect gas may lead to
little or no penetration of welding
electrode (wire).
REGULATOR
The regulator provides a constant
shielding gas pressure and flow rate
during the welding process. Each
regulator is designed to be used with a
specific gas or mixture of gases. The
argon and argon mixture use the same
thread type. The 100% carbon dioxide
uses a different thread type. An adapter
is available at your local welding gas
supplier to change between the two.
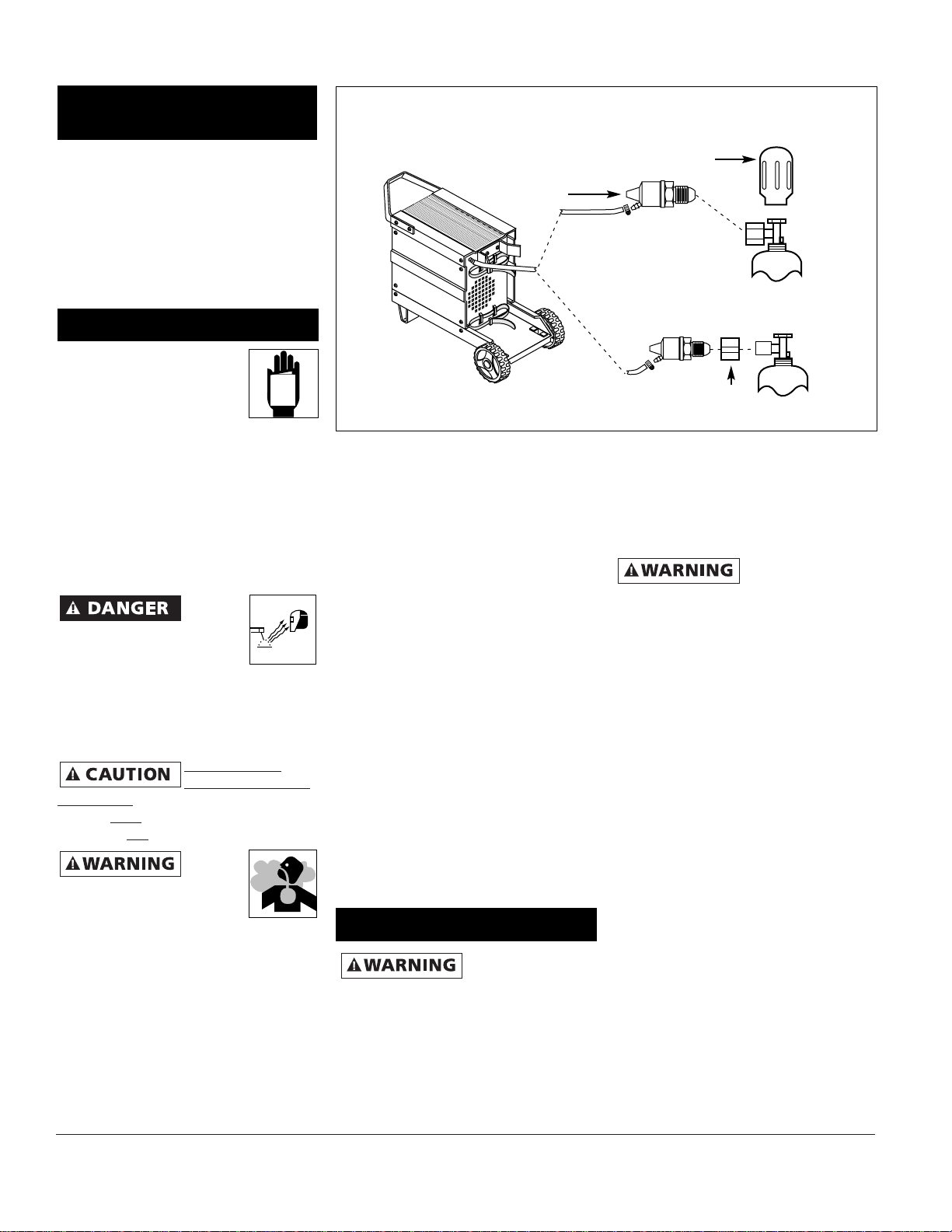
HOOKUP PROCEDURE
Cylinder gas is
under high
pressure. Point cylinder outlet away
from yourself and any bystanders
before opening.
1. These units fit a 20 cubic ft bottle.
2. With the cylinder securely installed,
remove the cylinder cap, stand to the
side of the cylinder opposite the
outlet, and open the valve slightly,
turning counterclockwise. When gas
is emitted from the cylinder, close the
valve by turning clockwise. This will
blow out dust or dirt that may have
accumulated around the valve seat.
3. Install the regulator onto the
cylinder valve, keeping the face of
the gauges in the vertical position
and tighten the stem nut securely to
the gas valve.
4. Install one end of the gas hose to
the fitting on the rear of the welder
and the other end to the fitting on
the regulator using hose clamps on
each connection. Make sure the gas
hose is not kinked or twisted.
5. Once again, stand opposite the
cylinder outlet and slowly open the
cylinder valve. Inspect for leaks in
the connections.
6. Pull the trigger on the gun to allow
the gas to flow. While the trigger is
pulled and gas is flowing, adjust the
gas regulator to 30-35 cfh (cubic
feet per hour)*. Release the trigger.
Contact Tip Markings
Wire Size mm
.024” or .6
.030” or .8
.035” or .9
.040” or 1.0
Assembly (Continued)
Figure 7
Headgear
Face Shield
Shaded Lens
Clear Lens Cover (2)
Post
Lens Retainer
Adjustment
Arm (2)
Tension Nut (2)
Stud Screw (2)
Welding Helmet
Assembly
Shielding Gas
Installation
www.campbellhausfeld.com
Page 6
6
Wire Feed Arc Welder
*NOTE: Campbell Hausfeld regulator
WT600100AV is factory preset at 30 cfh.
No adjustment is necessary. Also, a popout indicator in the end of the regulator
shows the amount of gas left in the
cylinder. When not extended, there is
approximately 10 minutes of welding
left before the cylinder is empty.
7. Remember to close the gas valve
when finished welding.
1. Be sure to read,
understand, and comply
with all precautions in
the General Safety
Information section. Be
sure to read the entire section
entitled Welding Guidelines prior to
using this equipment.
2. Verify welder is off.
3. Verify that the surfaces of metals to
be joined are free from dirt, rust,
paint, oil, scale or other contaminants. These contaminants make
welding difficult and cause poor
welds.
All persons operating this
equipment or in the area
while equipment is in use
must wear protective welding gear
including: eye protection with proper
shade, flame resistant clothing, leather
welding gloves, and full foot
protection.
WHETHER OR
NOT THE TRIGGER
IS PULLED, the WG3000 welding
wire is LIVE
whenever the welder
is turned ON
.
If heating, welding, or
cutting materials that are
galvanized, zinc plated, lead,
or cadmium plated refer to the General
Safety Information Section for
instructions. Extremely toxic fumes are
created when these metals are heated.
4. Connect the work clamp to the
work piece or workbench (if metal).
Make sure the contact is secure.
Avoid surfaces with paint, varnish,
corrosion, or non-metallic materials.
5. Position the Heat Selector on the
front panel to the desired setting.
See application decal inside door of
wire feed compartment for proper
heat settings.
NOTE: These settings are general
guidelines only. Heat setting may vary
according to welding conditions and
materials.
6. Rotate the Wire Speed Control to
setting number 5 to start with, then
adjust as needed after test weld.
7. Plug the input cord into a proper
voltage receptacle with proper
circuit capacity (See Chart under
circuit requirements on page 1).
8. Switch the welder ON.
9. Verify that the wire is extended
1/4” from the contact tip. If not,
squeeze the trigger to feed
additional wire, release the trigger,
and cut wire to proper length.
10. Position the wire feed gun near the
work piece, lower the welding
helmet by nodding the head, or
position the hand shield, and
squeeze the gun trigger. Adjust heat
setting and wire speed as needed.
11. When finished welding, turn welder
off and store properly.
Disconnect power
supply and turn
machine off before inspecting or
servicing any components. Keep the
wire compartment cover closed at all
times unless the wire needs
replacement.
Before every use:
1. Check condition of weld cables and
immediately repair or replace any
cables with damaged insulation.
2. Check condition of power cord and
immediately repair or replace any
cord if damaged.
3. Inspect the condition of the gun tip
and nozzle. Remove any weld slag.
Replace gun tip or nozzle if
damaged.
Do not operate this
welding machine
with cracked or missing insulation on
welding cables, wire feed gun, or
power cord.
Every 3 months:
1. Replace any unreadable safety
labels on the welder.
2. Use compressed air to blow all dust
and lint from the ventilation
openings.
3. Clean the wire groove on the drive
roll. Remove wire from the feed
mechanism, remove screws from the
drive roll housing. Use a small wire
brush to clean the drive roll. Replace
if worn or damaged.
Consumer and Wear Parts
The following parts require routine
maintenance:
• Wire feed drive roller
• Gun liner - replace if worn
• Nozzle/contact tips
• Wire - this welder will accept either
4” or 8” diameter spools. Welding wire
is susceptible to moisture and oxidizes
over time, so it is important to select a
spool size that will be used within
approximately 6 months. For mild steel
welding, AWS ER70S6 solid wire or
AWS E71T-GS flux-core wire is
recommended.
• Contact tips - use Campbell Hausfeld,
Tweco
®
, and other compatible tips.
Pop-out
Indicator
Cap
CO
2
Adapter
ARGON OR
ARGON MIX
INSTALLATION
CO
2
INSTALLATION
Figure 8 - Hookup
Operation
Maintenance
OR
Shielding Gas
Installation (Continued)
www.campbellhausfeld.com
MANUAL
Page 7
7
WG3000 and WG3060
• Nozzle - use Tweco®style or compatible
nozzle. Use Campbell Hausfeld nozzle
model WT5021 found at place of
purchase of welder, or use Tweco
®
style
nozzle (or compatible nozzle) found at
local welding supply store.
Changing Wire Sizes
DRIVE ROLLER
There are two grooves in the Drive
Roller. The small groove is for .024 (.6
mm) wire and the other is for .030 .035 (.8 - .9 mm) wire. Remove the
roller cover and flip the drive roll to
choose the correct groove (see Parts
Breakdown).
FLUX CORE WIRE
Due to small inconsistencies in wire
diameter, using one size larger tip is
recommended. For example:
• If wire diameter is .030, use .035 tip.
• If wire diameter is .035, use .040 tip.
This welder is setup for .035 (.9 mm)
wire and has a .040 tip. Since this
welder uses .030 and .035 Flux Core
Wire, the drive roller should be in its
factory pre-set condition.
Welding Guidelines
General
This line of welding machines can
utilize the Flux Cored Arc Welding
(Gasless) process or the Gas Metal Arc
Welding (MIG) process. The weld must
be protected (shielded) from
contaminates in the air while it is
molten. The gasless process uses a
tubular wire with a flux material inside.
The flux creates a shielding gas when
melted. The MIG process uses inert gas
to shield the weld while molten.
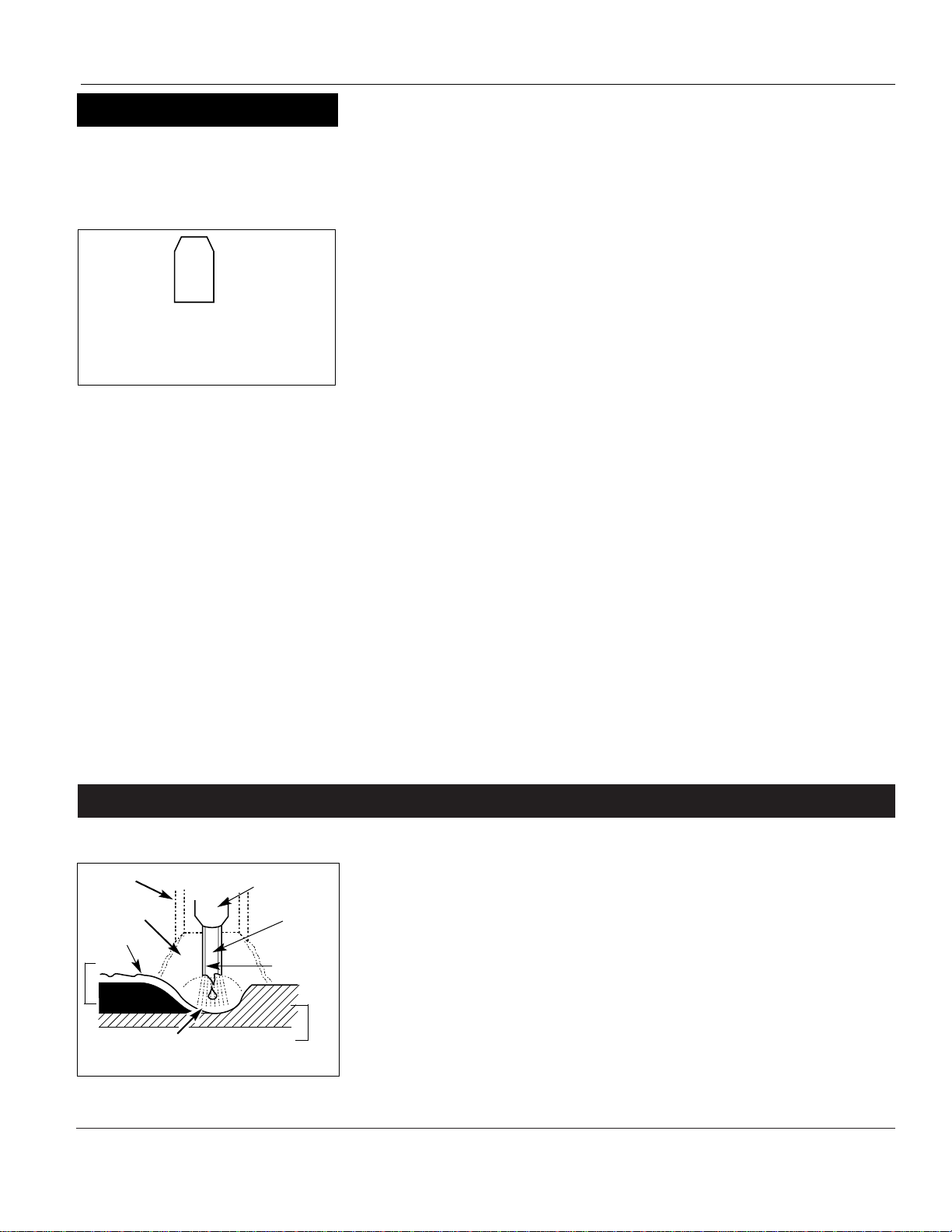
When current is produced by a
transformer (welding machine) and
flows through the circuit to the weld
wire, an arc is formed between the end
of the weld wire and the work piece.
This arc melts the wire and the work
piece. The melted metal of the weld
wire flows into the molten crater and
forms a bond with the work piece as
shown (Figure 10).
Arc Welding Basics
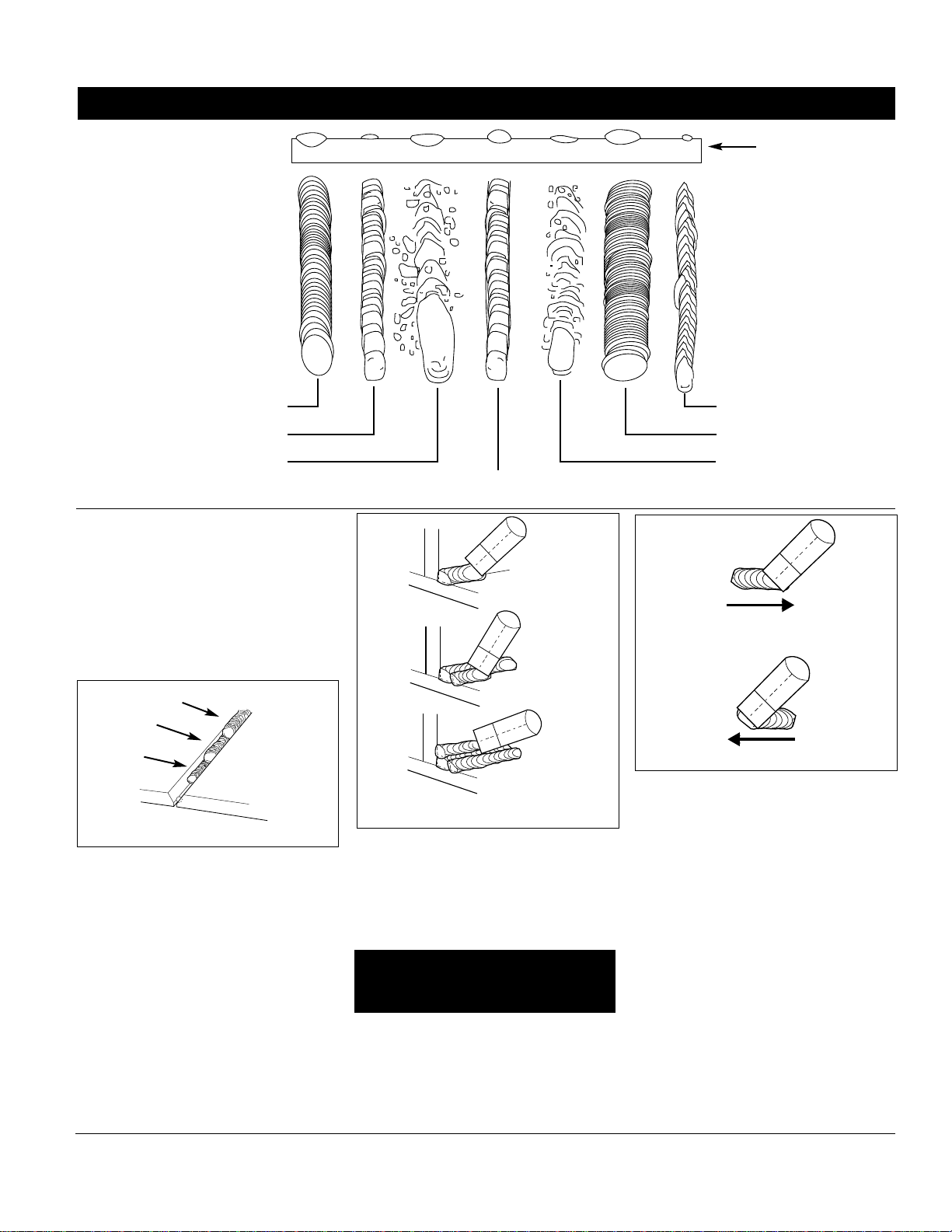
Five basic techniques affect weld
quality. These are: wire selection, heat
setting, weld angle, wire speed, and
travel speed. An understanding of
these techniques is necessary for
effective welds.
HEAT SETTING
The correct heat involves the adjustment of the welding machine to the
required setting. Heat or voltage is
regulated by a switch on the welder.
Maintenance
(Continued)
Slag
Weld
Wire
Flux
(Gasless
only)
Work Piece
Shielding
Gas
Contact
Tip
Crater
Nozzle
Figure 10 - Weld Components
MIG
WT5021
Figure 9 - Nozzle
MIG WIRE
Since MIG wire maintains fair wire
diameter consistency, the contact tip
used should match the wire size used.
When using .024 (.6 mm) wire, use the
small groove on the drive roller. When
using .030 - .035 (.8 - .9 mm) MIG or
Aluminum wire, use the factory set
large groove.
ALUMINUM WIRE
When using Aluminum wire, it is best
to use a larger size tip than the wire
size being used. For example:
• If wire diameter is .030, use .035 tip.
When using .030 - .035 (.8 - .9 mm) MIG
or Aluminum wire, use the factory set
large groove. Aluminum wire is very
weak and should not have the same
tension on the drive roller as Flux Core
or MIG wire should. When tensioning
Aluminum wire down to the Drive
Roller, turn the tension screw three full
turns or until the Drive Roller begins to
grip the wire and feed it through the
torch cable.
Call (800) 746-5641
for replacement parts.
www.campbellhausfeld.com
Page 8
The heat setting used depends on the
size (diameter) and type of wire,
position of the weld, and the thickness
of the work piece. Consult specifications listed on the welder. It is
suggested that the welder practice with
scrap metal to adjust settings and
compare welds with Figure 12.
WIRE TYPE AND SIZE
The correct choice of wire type involves
a variety of factors, such as welding
position, work piece material type,
thickness and condition of surface to be
welded. The American Welding Society,
AWS, has set up certain requirements
for each type of wire.
FLUX-CORE WIRE
E - 7
0 T - GS
Weld strength, times
10,000 psi
Welding positions (0
for flat or horizontal,
1 for any position)
Tubular flux core wire
Flux type
AWS E71T-GS or E71T-11 is
recommended for this welder.
SOLID WIRE
ER - 70
S - 6
Weld strength, times
1,000 psi
Solid wire
Wire composition
ER-70S6 is recommended for this
welder.
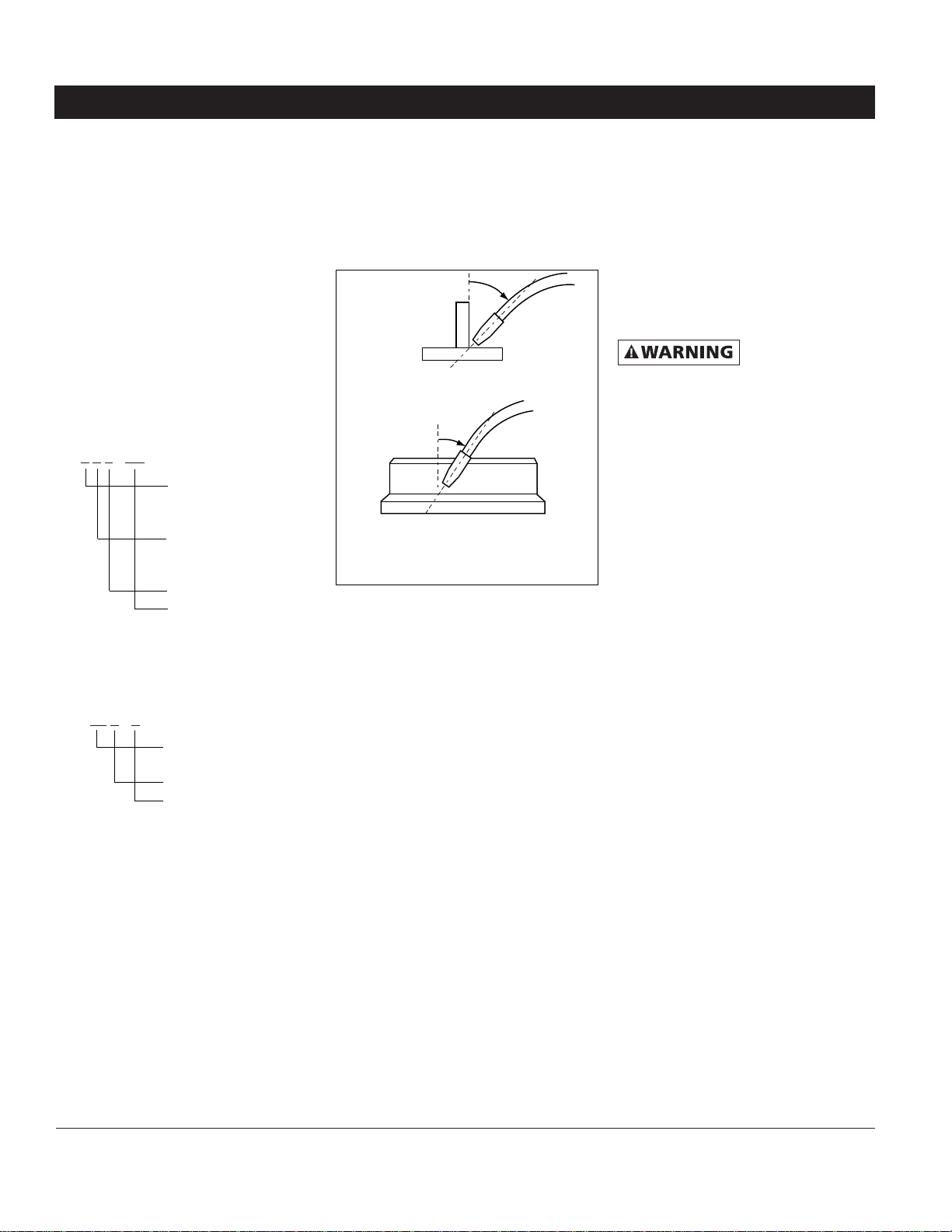
WELD ANGLE
Weld angle is the angle at which the
nozzle is held during the welding
process. Using the correct angle
ensures proper penetration and bead
formation. As different welding
positions and weld joints become
necessary, nozzle angle becomes an
increasingly important factor in
obtaining a satisfactory weld. Weld
angle involves two positions - travel
angle and work angle.
Travel angle is the angle in the line of
welding and may vary from 5º to 45º
8
Wire Feed Arc Welder
Welding Guidelines (Continued)
from the vertical, depending on
welding conditions.
Work angle is the angle from horizontal, measured at right angles to the
line of welding. For most applications, a
45º travel angle and 45º work angle is
sufficient. For specific applications,
consult an arc welding handbook.
WIRE SPEED
The wire speed is controlled by the
knob on the front panel. The speed
needs to be “tuned” to the rate at
which the wire is being melted in the
arc. Tuning is one of the most critical
functions in wire feed welding. Tuning
should be performed on a scrap piece
of metal the same type and thickness as
that to be welded. Begin welding with
one hand “dragging” the gun nozzle
across the scrap piece while adjusting
the wire speed with the other hand.
Too slow of speed will cause sputtering
and the wire will burn up into the
contact tip. Too fast a speed will also
cause a sputtering sound and the wire
will push into the plate before melting.
A smooth buzzing sound indicates the
wire speed is properly tuned. For
aluminum, wire speed is typically set
higher (7 - 9 speed range).
NOTE: Repeat the tuning procedure
each time there is a change in heat
setting, wire diameter or type, or work
piece material type or thickness.
TRAVEL SPEED
The travel speed is the rate at which
the torch is moved across the weld
area. Factors such as diameter and type
of weld wire, amperage, position, and
work piece material thickness all affect
the speed of travel necessary for
completing a good weld (See Fig. 12).
When the speed is too fast, the bead is
narrow and bead ripples are pointed as
shown. When the speed is too slow, the
weld metal piles up and the bead is
high and wide. For aluminum, travel
speed is typically faster.
SLAG REMOVAL (FLUX-CORE WIRE
ONLY)
Wear ANSI
approved safety
glasses (ANSI Standard Z87.1) and
protective clothing when removing
slag. Hot, flying debris can cause
personal injury to anyone in the area.
After completing the weld, wait for the
welded sections to cool. A protective
coating called slag now covers the weld
bead which prevents contaminants in
the air from reacting with the molten
metal. Once the weld cools to the point
that it is no longer glowing red, the
slag can be removed. Removal is done
with a chipping hammer. Lightly tap
the slag with the hammer and break it
loose from the weld bead. The final
clean-up is done with a wire brush.
NOTE: When making multiple weld
passes, remove the slag before each
pass.
WELDING POSITIONS
Four basic welding positions can be
used; flat, horizontal, vertical, and
overhead. Welding in the flat position
is easier than any of the others because
welding speed can be increased, the
molten metal has less tendency to run,
better penetration can be achieved,
and the work is less fatiguing. Welding
is performed with the wire at a 45º
travel angle and 45º work angle.
Other positions require different
techniques such as a weaving pass,
circular pass, and jogging. A higher skill
level is required to complete these
welds.
Overhead welding is the least desirable
position as it is the most difficult and
dangerous. Heat setting and wire
selection will vary depending upon the
position.
All work should be performed in the
flat position if possible. For specific
applications, consult an arc welding
technical manual.
TRAVEL ANGLE
WORK ANGLE
5º - 45º
5º - 45º
Figure 11 - Weld Angle
www.campbellhausfeld.com
Page 9
stainless steel brush to eliminate any
oxides on the weld and grounding
surface. 100% Argon must be used
when welding aluminum. If Argon is not
used, metal penetration is unlikely.
1. Verify that welder is OFF and power
cord disconnected.
2. Remove welder cover to expose the
ON/OFF switch.
9
WG3000 and WG3060
Normal Heat, Wire Speed, Travel
Speed
Heat Too Low
Heat Too High
Wire Speed Too Fast
Wire Speed Too Slow
Travel Speed Too Slow
Travel Speed Too Fast
Base Metal
Figure 12 - Weld Appearance
Figure 14 - Multiple Weld Passes
Welding Guidelines (Continued)
WELD PASSES
Sometimes more then one pass is
necessary to fill the joint. The root pass
is first, followed by filler passes and
the cover pass. If the pieces are thick, it
may be necessary to bevel the edges
that are joined at a 60º angle.
NOTE: Remember to remove the slag
before each pass for gasless process.
PUSH VS PULL TECHNIQUE
The type and thickness of the work
piece dictates which way to point the
gun nozzle. For thin materials (18 gauge
and up) and all aluminum, the nozzle
should point out in front of the weld
puddle and push the puddle across the
workpiece. For thicker steel, the nozzle
should point into the puddle to increase
weld penetration. This is called
backhand or pull technique
(See Figure 15).
ALUMINUM WELDING
Any aluminum surface to be welded,
must be cleaned thoroughly with a
Figure 13 - Weld Passes
Cover
Filler
Root
3. Disconnect the black and white
power cord wires connected to the
ON/OFF switch.
4. Disconnect the green power cord
wire connected to welder frame.
5. Loosen the cord strain screw(s) and
pull cord out of strain relief.
6. Install new cord in reverse order.
PUSH
PULL
Figure 15
Supply Cable
Replacement
www.campbellhausfeld.com
Page 10

10
Troubleshooting Chart - Welder
Symptom Possible Cause(s) Corrective Action
1. Duty cycle exceeded
2. Poor work clamp connection
3. Defective power switch
4. Blown breaker or fuse
1. Wrong size gun tip
2. Gun liner clogged or
damaged
3. Gun tip clogged or damaged
4. Feed roller worn
5. Not enough tension
Slag inside gun nozzle
1. Poor contact
2. Using an extension cord with
excessive length
1. Wire jammed
2. Out of wire
3. Not enough tension
4. Wire liner worn
5. Fuse blown
6. Wire disconnected internally
7. Contact tip clogged
1. Wire speed too slow
2. Travel speed too slow or heat
is too high
For Information About This Product, Call 1-800-746-5641
Bead is intermittently too
thin
Bead is intermittently too
thick
Ragged depressions at
edge of weld
Weld bead does not
penetrate base metal
Wire sputters and sticks
1. Inconsistent travel speed
2. Output heat setting too low
1. Slow and/or inconsistent travel
speed
2. Output heat setting too high
1. Travel speed too fast
2. Wire speed too fast
3. Output heat setting too high
1. Inconsistent travel speed
2. Output heat setting too low
3. No or low shielding gas
4. Wrong shielding gas (aluminum)
5. Extension cord is too long
6. (Aluminum) Possible oxide buidup on surface
1. Damp wire
2. Wire speed too fast
3. Wrong type of wire
4. No or low shielding gas
1. Allow welder to cool until ON/OFF Switch lamp goes out
2. Be sure all connections are secure, and attaching surface is
clean
3. Replace switch
4. Reduce circuit load, reset breaker or replace fuse
1. Use proper size gun tip
2. Clean or replace gun liner
3. Clean or replace gun tip
4. Replace
5. Tighten tensioning screw
Clean slag from gun nozzle
1. Be sure all connections are secure, and attaching surface is
clean
2. Never use an extension cord longer than 20 ft
1. Reload wire
2. Replace wire spool
3. Tighten tensioning screws if wire is slipping
4. Replace liner
5. Replace fuse on wire feed control board inside welder,
(1.6 amp time delay)
6. Call 1-800-746-5641 for assistance
7. Replace contact tip
1. Run speed in 7 - 10 range
2. Increase the travel speed or reduce heat settings
No output
Wire tangles at drive roller
Gun nozzle arcs to work
surface
Work clamp and/or cable
gets hot
Wire does not feed
(Aluminum) Wire burns back
into tip or (Aluminum) Metal
bubbles or burns through
Troubleshooting Chart - Welds
Symptom Possible Cause(s) Corrective Action
1. Decrease and maintain constant travel speed
2. Increase output heat setting
1. Increase and maintain travel speed
2. Reduce output heat setting
1. Decrease travel speed
2. Decrease wire speed
3. Reduce output heat setting
1. Decrease and maintain constant travel speed
2. Increase output heat setting
3. Use gas for MIG process or refill bottle
4. Use only 100% Argon gas
5. Never use an extension cord longer than 20 ft
6. Clean surface thoroughly with a stainless steel brush only
1. Use dry wire and store in dry location
2. Reduce wire speed
3. Use flux core wire when not using gas
4. Use gas for MIG process or refill bottle
www.campbellhausfeld.com
Page 11

11
Limited 5-3-1 Warranty
1. Duration: The manufacturer warrants that it will repair, at no charge for parts or labor, the Welder, Welding Gun, or Cables, proven defective in material or
workmanship, during the following time period(s) after date of original retail purchase:
For 5 Years: The Welder Transformer and Rectifier
For 3 Years: The Entire Welder (excluding clamps, welding gun, electrode holder, cables, or accessories packed with welder)
For 1 Year: The Welding Clamps, MIG Gun, Electrode Holder, Accessories, and Welding Cables (as applicable)
2. Who Gives This Warranty (Warrantor):
The Campbell Group / A Scott Fetzer Company
100 Production Drive
Harrison, OH 45030
Telephone: (513)-367-4811
3. Who Receives This Warranty (Purchaser): The original purchaser of the Campbell Hausfeld product.
4. What is covered under this warranty: Defects in material and workmanship which occur within the duration of the warranty period. This warranty
extends to the Welder, the Welders Transformer and Rectifier, Welding Gun or Electrode Holder, and cables only.
5. What is not covered under this warranty:
A. Implied warranties, including those of merchantability and FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE LIMITED IN DURATION TO THIS EXPRESS
WARRANTY. After this period, all risks of loss, from whatever reason, shall be on the purchaser. Some states do not allow limitations on how long an
implied warranty lasts, so above limitations may not apply to you.
B. ANY INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL LOSS, DAMAGE, OR EXPENSE THAT MAY RESULT FROM ANY DEFECT FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION OF
THE CAMPBELL HAUSFELD PRODUCT. Some states do not allow limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts, so above limitations may not apply
to you.
C. This warranty does not apply to any accessory items included with the product which are subject to wear from usage; the repair or replacement of
these items shall be at the expense of the owner. These MIG items include but are not limited to; Contact Tips, Nozzles, Gun Liners, Drive Rollers, Felt
Wire Cleaner. In addition, this warranty does not extend to any damage caused by the untimely replacement or maintenance of any of the previously
listed CONSUMABLE parts.
D. Any failure that results from accident, purchaser’s abuse, neglect or failure to operate products in accordance with instructions provided in the owner’s
manual(s) supplied with the product.
E. Pre-delivery service, i.e. assembly and adjustment.
7. Responsibilities of Warrantor under this warranty: Repair or replace, at Warrantor’s option, products or components which have failed within duration
of the warranty period.
8. Responsibilities of purchaser under this warranty:
A. Deliver or ship the Campbell Hausfeld product or component to Campbell Hausfeld. Freight costs, if any, must be borne by the purchaser.
B. Use reasonable care in the operation and maintenance of the products as described in the owner’s manual(s).
9. When Warrantor will perform repair or replacement under this warranty: Repair or replacement will be scheduled and serviced according to the
normal work flow at the servicing location, and depending on the availability of replacement parts.
This Limited Warranty gives you specific legal rights and you may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
WG3000 and WG3060
www.campbellhausfeld.com
Page 12
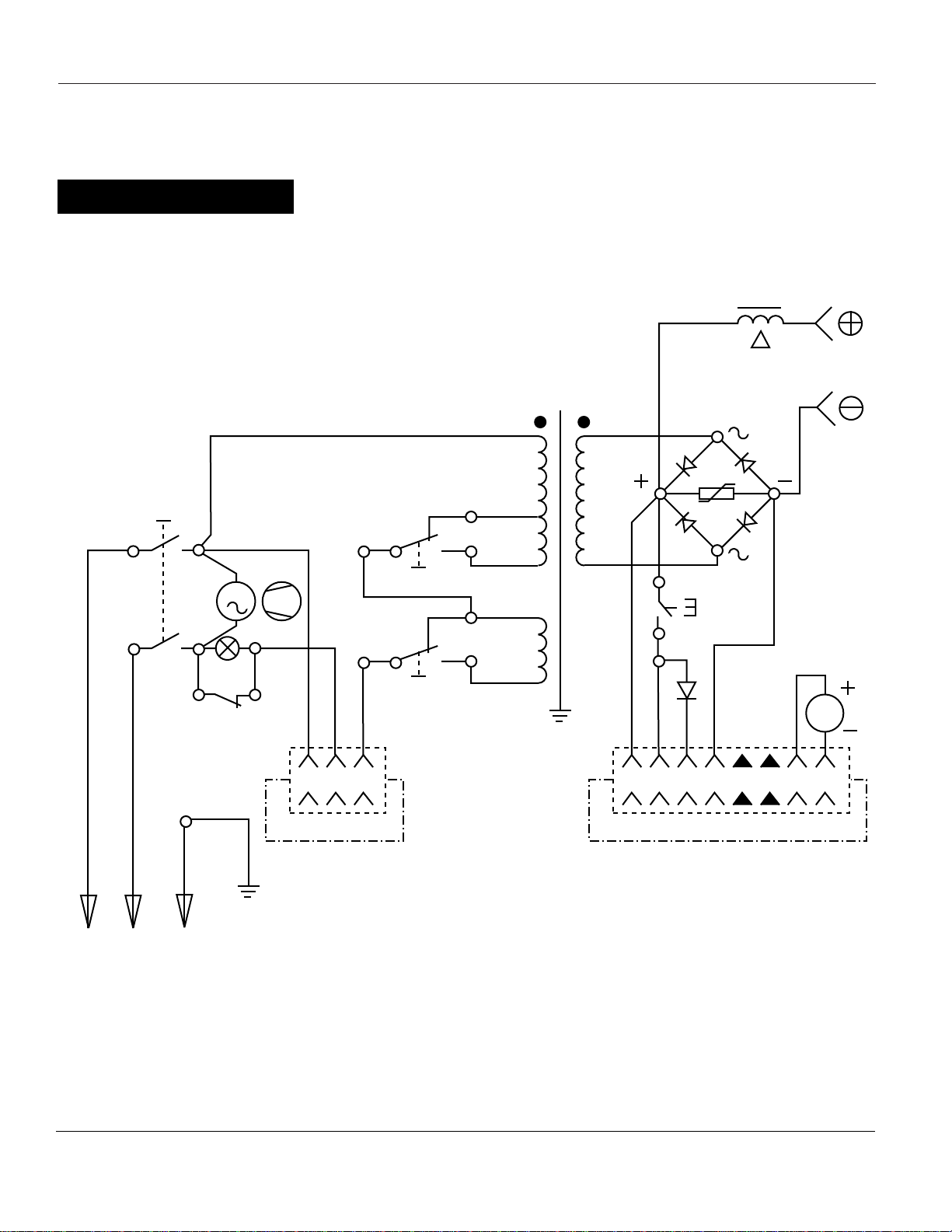
12
WG3000 Wiring Diagram
ON / OFF
MAX
MIN
Gun
Wire Feed Arc Welder WG3000
www.campbellhausfeld.com
T2
S5
T1
White
L2 (N)
Black
L1
S1
Green
M1
S5
Ground
S2
S3
2
1
S4
M
=
5 6 7 84321678
Page 13
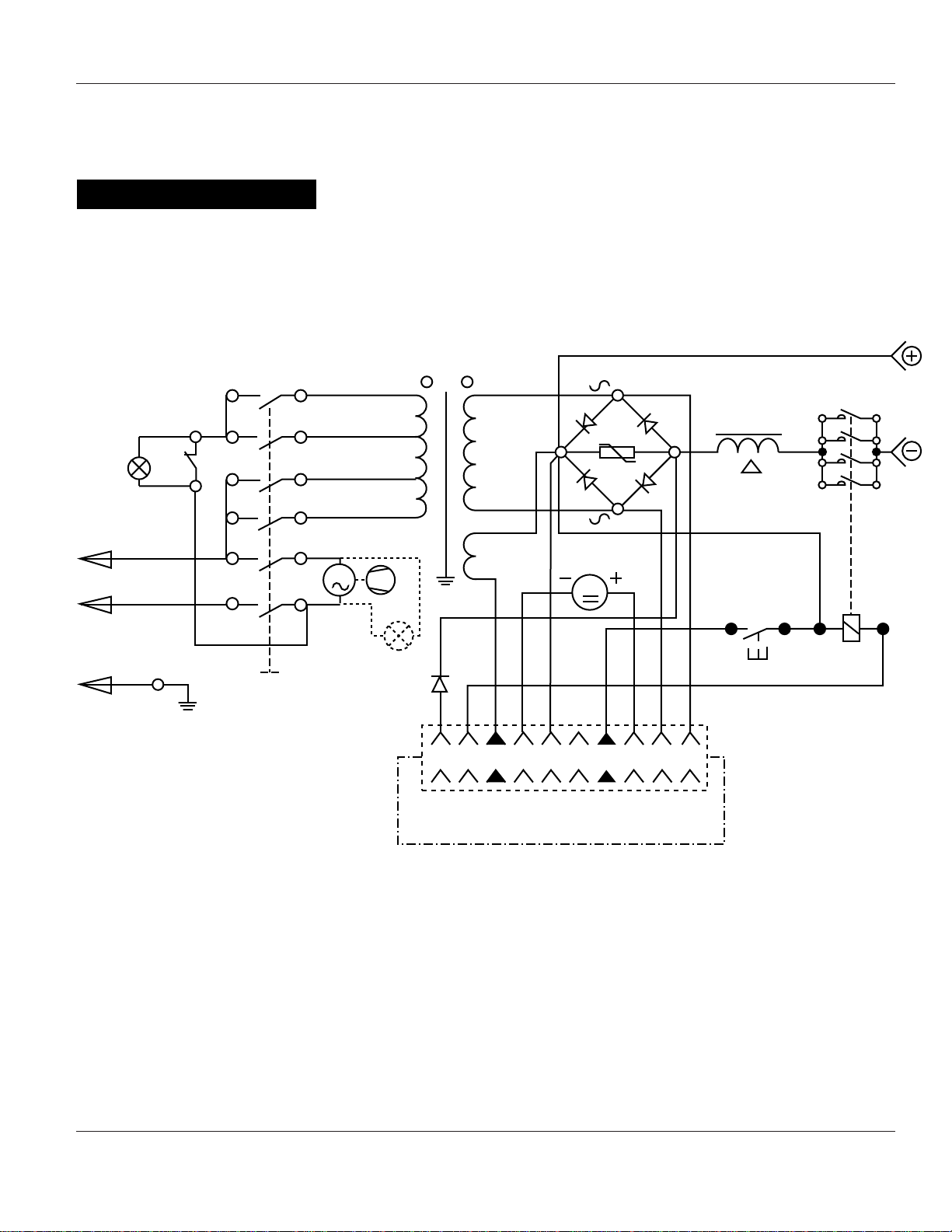
13
WG3060 Wiring Diagram
Wire Feed Arc Welder WG3060
www.campbellhausfeld.com
LG
L2 (N) White
L1 (R) Black
Green
C1
S20127°
Ground
S1
1
2
3
4
A2
M1
A1
LV
T1
RD
M
5 6 7 8 9 104321
T2
S2
S3
K-A2
K
K-A1
Page 14
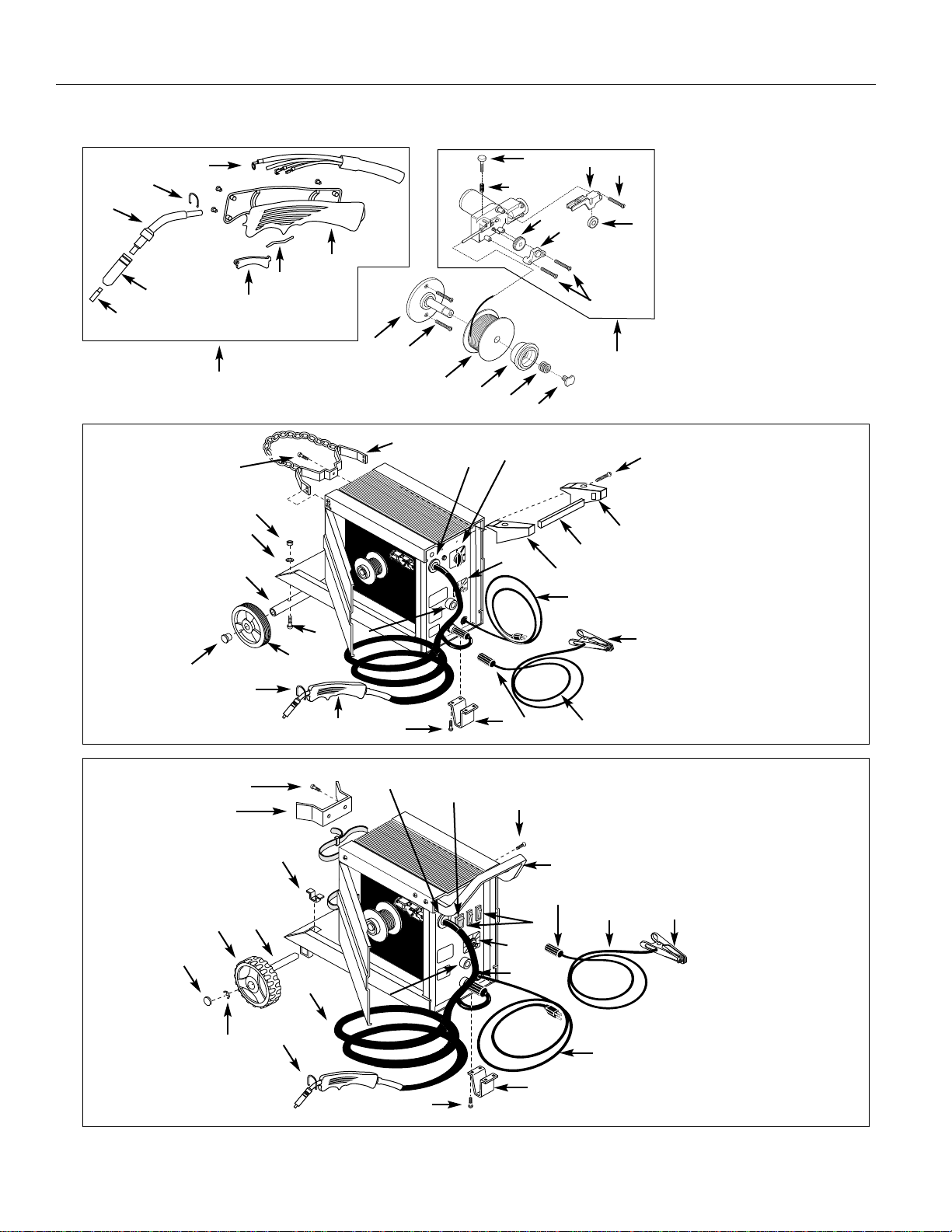
14
For Replacement Parts, call 1-800-746-5641
Address parts correspondence to:
The Campbell Group
Attn: Parts Department
100 Production Drive
Harrison, Ohio 45030 U.S.A.
Please provide following information:
- Model number
- Serial number (if any)
- Part description and number as
shown in parts list
Wire Feed Arc Welder
MODEL WG3060
MODEL WG3000
2
4
6
8
8
1
1
3
3
5
7
7
9 & 10
11
11 & 30
12
14
14
15
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
27
28
29
31
32
32
33
33
34
35
35
36
37
38
38
39
39
40
40
42
42
43
44
45
46
43
47
47
48
3
49
1
47
43
9 & 10
50
www.campbellhausfeld.com
** Contact Tip (See chart on Page 15)
40
40
Page 15

15
1 Torch assembly and hose (Includes Nos. 2-6, 34 and 50) WC600700AV WC600700AV 1
2 Torch body, front and back WC600201AV WC600201AV 1
3 Hanger clip WC600003AV WC600003AV 1
4 Nozzle, Tweco®Style WT502100AJ WT502100AJ 1
5 Trigger knob WC600202AV WC600202AV 1
6 Torch contact spring WC600203AV WC600203AV 1
7 Work clamp (Cord not included) WC100100AV WC100100AV 1
8 Welding cable 8 AWG (6 ft) ❋ ❋ 1
9 Wire speed knob WC400201AV WC400201AV 1
10 Wire speed control board WC400200AV WC400600AV 1
11 Heat selector switch WC400300AV — 2
Heath selector switch — WC400500AV 1
12 On/off switch WC400000AV — 1
13 Safety decal DK670100AV DK670100AV 1
14 Handle WC300600AV WC300700AV 1
15 Power cord 14-3 AWG (6 ft) Type SJT WC000100AV WC000100AV 1
16 Spool spindle WC500300AV WC500300AV 1
17 #10-32 x .5” Pan head sheet metal screw ❋ ❋ 2
18 Wire-flux core .035” (.9mm) diameter WE200500AJ WE200500AJ 1
19 Spool adapter WC500200AV WC500200AV 1
20 Spool spring WC500101AV WC500101AV 1
21 Spool locking hub WC500100AV WC500100AV 1
22 Drive deck assembly (Includes Nos. 23-29) WC500000AV WC500400AV 1
23 Tension spring WC500003AV WC500003AV 1
24 Tension screw WC500002AV WC500002AV 1
25 Roller .6-.9mm (.024-.035 in.) WC500001AV WC500001AV 1
26 Roller cover WC500004AV WC500004AV 1
27 #8-36 x 1.5” Pan head screw ❋ ❋ 3
28 Swing arm WC500005AV WC500005AV 1
29 Swing arm roller WC500007AV WC500007AV 1
30 Heat selector knob — WC400401AV 1
31 Strain relief WC102000AV WC102000AV 2
32 Wheel WC701200AV WC701300AV 2
33 Front foot WC702100AV WC702300AV 1
34 Liner, metal WC600007AV WC600007AV 1
35 Gas cylinder bracket WC702200AV WC702400AV 1
36 Handle support (Right) — WC300800AV 1
37 Handle support (Left) — WC300900AV 1
38 Axle WC703100AV WC703200AV 1
39 Wheel hub WC703500AV WC703400AV 1
40 Dinse connector WC000200AV WC000200AV 2
41 Dinse socket WC000300AV WC000300AV 2
42 Torch ring WC600009AV WC600009AV 1
43 #10-24 x 1/2” Screw ❋ ❋ 9
44 Axle support WC703600AV — 2
45 5mm I.D. e-ring ❋ — 2
46 #10-24 x 2” Screw — ❋ 2
47 #8-36 x 1” Screw — ❋ 2
48 #8 Flatwasher — ❋ 2
49 #8-36 Nut — ❋ 2
50 Swan neck with Diffuser WC600701AV WC600701AV 1
❋ Standard hardware item, available at local hardware or welder supply store
Replacement Parts List - Models WG3000 and WG3060
Ref Part Number for Models:
No. Description WG3000 WG3060 Qty
OPTIONAL WIRE
Type Description Part Number
Mig ER70S6 .024” WE300000AJ
Mig ER70S6 .030” WE300500AJ
Mig ER70S6 .035” WE301000AJ
Flux E71T-GS .030” WE200000AJ
Flux E71T-GS .035” WE200500AJ
WG3000 and WG3060
www.campbellhausfeld.com
**OPTIONAL CONTACT TIPS
Size
mm in. Part Number
0.6 0.024 WT501200AV
0.8 0.030 WT501300AV
0.9 0.035 WT501400AV
Page 16

Wire Feed Arc Welder Models WG3000 and WG3060
Glossary of Welding Terms
AC or Alternating Current - electric
current that reverses direction
periodically. Sixty cycle current travels
in both directions sixty times per
second.
Arc Length - the distance from the
end of the electrode to the point
where the arc makes contact with the
work surface.
Base Metal - the material to be
welded.
Butt Joint - a joint between two
members aligned approximately in the
same plane.
Crater - a pool, or pocket, that is
formed as the arc comes in contact with
the base metal.
DC or Direct Current - electric current
which flows only in one direction. The
polarity (+ or -) determines which
direction the current is flowing.
DC Reverse Polarity - occurs when
the electrode holder is connected to
the positive pole of the welding
machine. Reverse Polarity directs more
heat into melting the electrode rather
then the work piece. It is used on
thinner material.
DC Straight Polarity - occurs when
the electrode holder is connected to
the negative pole of the welding
machine. With straight polarity more
heat is directed to the work piece for
better penetration on thicker material.
Electrode - a coated metal wire having
approximately the same composition as
the material being welded.
Fillet Weld - approximately a triangle
in cross-section, joining two surfaces at
right angles to each other in a lap, T or
corner joint.
Flux - a coating, when heated, that
produces a shielding gas around the
welding area. This gas protects the
parent and filler metals from impurities
in the air.
Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) also called Gasless, is a welding process
used with a wire-feed welding
machine. The weld wire is tubular with
flux material contained inside for
shielding.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) also called MIG, is a welding process
used with a wire feed welding
machine. The wire is solid and an inert
gas is used for shielding.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) also called TIG, is a welding process
used with welding equipment with a
high frequency generator. The arc is
created between a non-consumable
tungsten electrode and the work piece.
Filler metal may or may not be used.
Lap Joint - a joint between two
overlapping members in parallel
planes.
Open Circuit Voltage (OCV) - the
voltage between the electrode and the
work clamp of the welding machine
when no current is flowing (not
welding). The OCV determines how
quickly the arc is struck.
Overlap - occurs when the amperage is
set too low. In this instance, the molten
metal falls from the electrode without
actually fusing into the base metal.
Porosity - gas pockets, or cavities,
formed during weld solidification. They
weaken the weld.
Penetration - the depth into the work
piece that has been heat effected by
the arc during the welding process. A
good weld achieves 100% penetration
meaning that the entire thickness of
the work piece has been heated and
resolidified. The heat effected area
should be easily seen on the opposite
side of the weld.
Shielded Metal Arc Welding
(SMAW) - also called Stick, is a welding
process with uses a consumable
electrode to support the arc. Shielding
is achieved by the melting of the flux
coating on the electrode.
Slag - a layer of flux soot that protects
the weld from oxides and other
contaminants while the weld is
solidifying (cooling). Slag should be
removed after weld has cooled.
Spatter - metal particles thrown from
the weld which cool and harden on the
work surface. Spatter can be minimized
by using a spatter resistant spray on the
work piece before welding.
Tack Weld - weld made to hold parts
in proper alignment until final welds
are made.
Travel Angle - the angle of the
electrode in the line of welding. It
varies from 5º to 45º depending on
welding conditions.
T Joint - made by placing the edge of
one piece of metal on the surface of
the other piece at approximately a 90º
angle.
Undercut - a condition that results
when welding amperage is too high.
The excessive amperage leaves a
groove in the base metal along both
sides of the bead which reduces the
strength of the weld.
Weld Pool or Puddle - a volume of
molten metal in a weld prior to its
solidification as weld metal.
Weld Bead - a narrow layer or layers of
metal deposited on the base metal as
the electrode melts. Weld bead width is
typically twice the diameter of the
electrode.
Work Angle - the angle of the
electrode from horizontal, measured at
right angles to the line of welding.
16
www.campbellhausfeld.com
Page 17

1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4 & 6
5
5
6
7
pour augmenter la vitesse de fil et
tourner au sens inverse des aiguilles
d’une montre pour réduire la vitesse
du fil.
6. Sélecteur de chaleur - Pour choisir
la puissance du soudeur. Choix de
quatre sélections.
7. Branchement de polarité - Fixer
le câble du chalumeau à (+) pour
MIG et (-) fil fourré de flux.
Danger
indique:
Manque de suivre cet avertissement
causera la perte de vie ou blessures
graves.
Avertis-
sement
indique: Manque de suivre cet avertis-
Commandes et Pièces Détachées
1. Pince de Soudeur - fixer à l’objet
de travail.
2. Pistolet d’alimentation en fil
avec buse de 0,040.
3. Cordon d’alimentation - brancher
dans une prise de courant 115 V.
4. Interrupteur Marche/Arrêt
(On/Off).
5. Commande de réglage de
vitesse de fil infini - tourner au
sens des aiguilles d’une montre
Cette série de soudeurs à l’arc alimentés
en fil Campbell Hausfeld sont conçus
pour l’utilisation sur le courant
domestique de 115V. Ces soudeurs sont
équipés d’un réglage de vitesse de fil
infini pour la sélection précise de taux
d’alimentation en fil convenable à une
variété de conditions de soudage. Les
pièces internes sont protégées d’un
thermostat.
Ces soudeurs sont conçus pour
l’utilisation avec les méthodes de
Soudage À L’Arc Fourré De Flux (sans
gaz) ou le Soudage Au Chalumeau
(Mig). Ce soudeur, livré de l’usine peut
souder avec un fil de 0,6 mm à 0,9 mm
de diamètre. Une bobine de fil fourré
de flux et une buse de 0,040 sont
compris.
Déballage
Quelques pièces détachées du
soudeur peuvent être situées dans
le compartiment d’alimentation en
fil. Lors du déballage, l’examiner
soigneusement pour rechercher toute
trace de dommage susceptible de s’être
produit en cours de transport. S’il y a
des pièces endommagées ou manquantes, composer le (800) 746-5641.
Exigences De Circuit
Cet
équipement requiert un circuit unique de 115
V. Se référer au tableau suivant pour le
disjoncteur ou la classification de
fusible correcte. Ne pas faire fonctionner les appareils électroménagers, les
lampes ou les outils sur ce circuit pendant l’utilisation de cet équipement.
Les cordons prolongateurs ne sont pas
recommandés. Manque de suivre ces
directives peut causer des fusibles
sautés et des disjoncteurs déclenchés.
S’il vous plaît lire et conserver ces instructions. Lire attentivement avant de monter, installer, utiliser ou de procéder à l’entretien du produit
décrit. Se protéger ainsi que les autres en observant toutes les instructions de sécurité, sinon, il y a risque de blessure et/ou dégâts matériels!
Conserver ces instructions comme référence.
IN211104AV 9/99
Instructions D’Utilisation & Manuel De Pièces De Rechange Modèles WG3000 et WG3060
Soudeur À L’Arc
Alimenté En Fil
MODÈLE WG3000
Sélecteur Disjoncteur ou
de Chaleur Fusée à Retardement
Bas (1-2) 15 A
Haut (3-4) 20 A
Description
MODÈLE WG3060
17 Fr
Généralités Sur La Sécurité
Figure 1
© 1999 Campbell Hausfeld / Scott Fetzer
7
A
N
R
C
U
E
S
S
P
A
R
O
Y
T
I
L
Need
A
U
Q
Assistance?
Call Us First!
1-800-746-5641
BUILT TO LAST
TM
G
R
A
M
!
ATTENTION
!
DANGER
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 18

18 Fr
Soudeur À L’Arc Alimenté En Fil
sement peut causer la perte de vie ou
blessures graves.
Attention
indique:
Manque de suivre cet avertissement
peut causer des blessures (petites ou
moyennes) ou dommage matériel.
REMARQUE: Remarque indique:
Information additionnel concernant le
produit ou son utilisation.
Le
chalumeau
est toujours “électrisé” (potentiel de
courant électrique) quand le modèle est en
marche (le modèle WG3000 seulement).
Toujours avoir un extincteur
d’incendie disponible pendant
le soudage à l’arc.
● Lire et comprendre toutes instructions
avant de démarrer un soudeur à l’arc
ou de procéder à son entretien.
Manque de suivre les précautions et
instructions de sécurité peut avoir
comme résultat, dommage à
l’équipement et/ou blessures graves,
perte de vie.
● Tous installation, entretien,
réparation et utilisation de cet
équipement doit être effectué par des
personnes qualifiées conformément
aux codes nationaux, provinciaux et
locales.
L’utilisation incorrecte des
soudeurs à l’arc électriques
peuvent causer des secousses
électriques, blessures et perte de vie.
Suivre toutes les précautions indiquées
dans ce manuel afin de réduire le
risque de secousse électrique.
● S’assurer que toutes les pièces
détachées du soudeur à l’arc soient
propres et en bon état avant d’utiliser le soudeur. S’assurer que l’isolation sur tous câbles, pistolets d’alimentation en fil et cordons d’alimentation ne soit pas endommagé.
Toujours réparer ou remplacer les
pièces détachées endommagées
avant d’utiliser le soudeur. Toujours
garder les panneaux, écrans de
soudage, etc. en place pendant
l’utilisation du soudeur.
● Toujours porter des vêtements
protecteurs et gants de soudage
secs ainsi que des chaussures
isolantes.
● Toujours faire fonctionner le
soudeur dans un endroit propre, sec
et bien ventilé. Ne jamais utiliser un
soudeur dans un endroit humide,
trempe, pluvieux ou mal-ventilé.
● S’assurer que l’objet sur lequel vous
travaillez soit bien fixé et mis à la
terre correctement avant de
commencer le soudage électrique à
l’arc.
● Le câble de soudage roulé devrait
être étendu avant l’utilisation afin
d’éviter le surchauffage et le
dommage à l’isolation.
Ne jamais
immerger
le fil ni le pistolet dans l’eau. Si le
soudeur devient trempe, il est
nécessaire qu’il soit complètement sec
et propre avant l’utilisation!
● Toujours mettre l’équipement hors
circuit et le débrancher avant de le
déplacer.
● Toujours brancher le conducteur de
travail en premier lieu.
● Vérifier que l’objet de travail soit
mis à la terre correctement.
● Toujours mettre l’équipement de
soudage électrique à l’arc hors
circuit s’il nest pas en usage et
couper l’excès de fil du pistolet.
● Ne jamais permettre que votre corps
touche le fil fourré de flux et la
terre ni l’objet de travail mis à la
terre simultanément.
● Les conditions et positions de
soudage difficiles peuvent poser des
hasards électriques. Si vous êtes
accroupis, à genoux ou aux élévations,
s’assurer que toutes les pièces
conductrices soient isolées. Porter des
vêtements protecteurs convenables et
prenez précaution contre les chutes
afin d’éviter des blessures.
● Ne jamais esayer d’utiliser cet
équipement au délà des réglages de
courant ou des facteurs d’utilisation
indiqués sur les étiquettes.
● Ne jamais utiliser un soudeur
électrique à l’arc pour dégeler les
tuyaux congelés.
Les étincelles volantes et le
métal chaud peuvent causer
des blessures. La scorie peut
s’échapper pendant le refroidissement
des soudures. Suivre toutes les
directives et précautions indiquées
dans ce manuel pour réduire la
possibilité de blessures causées par les
étincelles volantes et le métal chaud.
● Porter un masque de soudeur
approuvé par ANSI ou des lunettes
protectrices avec écrans protecteurs
de bords pendant le burinage ou
l’ébarbage des pièces en métal.
● Utiliser des protège-tympans pour le
soudage aérien afin d’éviter que la
scorie ou la bavure tombe dans les
oreilles.
Le soudage électrique à l’arc
produit la lumière et la chaleur
intense et les rayons
ultaviolets (UV) rays. Cette lumière
intense et ces rayons UV peuvent
causer des blessures aux yeux et à la
peau. Prenez toutes précautions
indiquées dans ce manuel afin de
réduire la possibilité de blessures aux
yeux et à la peau.
● Toutes personnes qui utilisent cet
équipement ou qui sont présentes là
où l’équipement est utilisé doivent
porter des vêtements de soudage
protecteurs y compris: masque ou
casque de soudeur ou écran avec une
lentille filtrante de classification d’au
moins 10, vêtements incombustibles,
gants de soudeur en cuir et la
protection complète pour les pieds.
Ne jamais
observer
le soudage sans la protection pour les
yeux indiquée ci-dessus. Ne jamais
utiliser une lentille filtrante qui est
fendue, cassée, ou classifiée moins que
le numéro 10. Avertir les autres
personnes dans l’endroit de ne pas
observer l’arc.
Le soudage électrique à l’arc
produit des étincelles et
chauffe le métal aux
températures qui peuvent causer des
brûlures sévères! Utiliser des gants et
vêtements protecteurs pendant
n’importe quel travail de métal. Prenez
toutes les précautions indiquées dans
ce manuel afin de réduire la possibilité
de brûlures de peau ou de vêtements.
● S’assurer que toutes personnes dans
l’endroit de soudage soient
protégées contre la chaleur, les
étincelles et les rayons ultraviolets.
Utiliser des écrans de visage
additionnels et écrans coupe-feu là
où nécessaire.
● Ne jamais toucher les objets de
travail avant qu’ils se refroidissent
complètement.
La chaleur et les étincelles
qui sont produits pendant le
soudage électrique à l’arc et
autres travaux de métal peuvent
allumer les matériaux inflammables et
explosifs! Prenez toutes précautions
Généralités Sur La
Sécurité
(Suite)
!
ATTENTION
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
DANGER
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 19

● Lire et suivre les instructions pour
les bouteilles de gaz et autre
équipement et la publication P-1 de
CGA indiquée dans les Normes de
Sécurité.
Ne jamais
utiliser
les gas inflammables avec les soudeurs
MIG. Seuls les gaz inertes ou
ininflammables tels que le gaz
carbonique, l’argon, le hélium ou un
mélange d’un ou plus de ceux-ci
conviennent au soudage MIG.
Ne jamais
soulever
les bouteilles par leurs soupapes,
chapeaux ni avec les chaînes ou élingues.
NORMES DE SÉCURITÉ
ADDITIONNELLES
Norme ANSI Z49.1 de l’ American
Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJune Rd.
Miami, FL 33126
Safety and Health Standards
(Normes de Sécurité et de Santé)
OSHA 29 CFR 1910, du Superintendent
of Documents, U.S. Government
Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402
National Electrical Code (Code
Électrique National)
Norme NFPA 70, du National Fire
Protection Association, Batterymarch
Park, Quincy, MA 02269
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases
in Cylinders (Manipulation Sûr des
Gaz Comprimés en Cylindres)
CGA Pamphlet P-1, du Compressed Gas
Association, 1235 Jefferson Davis
Highway, Suite 501, Arlington, VA
22202
Code for Safety in Welding and
Cutting (Code de Sécurité pour le
Soudage et le Coupage)
Norme CSA W117.2, du Canadian
Standards Association, Standards Sales,
178 Rexdale Boulevard, Rexdale,
Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3
Cutting And Welding Processes
(Procédés de Coupage et de
Soudage)
Norme NFPA 51B, du National Fire
Protection Association, Batterymarch
Park, Quicy, MA 02269
Safe Practices For Occupational And
Educational Eye And Face
Protection (Règlements
Professionnels et D’Éducation de
Sécurité pour la Protection des
Yeux et du Visage)
Norme ANSI Z87.1, de l’American
National Standards Institute, 1430
Broadway, New York, NY 10018
Se référer aux Material Safety Data
Sheets (Données De Sécurité) et les
instructions du fabriquant pour
métaux, électrodes, enduits et produits
pour le nettoyage.
indiquées dans ce manuel afin de
réduire la possibilité de flammes et
d’explosions.
● Enlever tous matériaux
inflammables à moins de 10,7
mètres (35 pieds) de l’arc de
soudage. Si ceci n’est pas possible,
couvrir les matériaux inflammables
avec des couvertures
incombustibles.
● Ne pas utiliser un soudeur électrique
à l’arc dans les endroits qui
contiennent des vapeurs
inflammables ou explosives.
● Prenez toutes précautions pour
s’assurer que les étincelles volantes
et la chaleur ne produisent pas de
flammes dans des endroits cachés,
fentes, a l’arrière des cloisons, etc.
Risque d’incendie! Ne pas
souder les récipients ni les
tuyaux qui contiennent ou ont
contenu des matériaux inflammables
ou combustibles gaseux ou liquides.
Le soudage à l’arc des
cylindres ou récipients fermés tels que les réservoirs ou
bidons peuvent causer une explosion
s’ils ne sont pas bien ventilés! Vérifier
qu’il y ait un trou de ventilation
suffisant dans n’importe quel cylindre
ou recipient pour permettre la
ventilation des gaz en expansion.
Ne pas inspirer les vapeurs
qui sont produits par le
soudage à l’arc. Ces vapeurs
sont dangereuses. Utiliser un
respirateur si l’endroit de soudage
n’est pas bien ventilé.
● Garder la tête et le visage hors des
vapeurs de soudage.
● Ne pas exécuter le soudage
électrique à l’arc sur les métaux qui
sont galvanisés ou plaqués en
cadmium, ou qui contiennent le
zinc, le mercure, ou le beryllium
sans suivre les précautions suivantes:
a. Enlever l’enduit du métal
commun.
b. S’assurer que l’endroit de
soudage soit bien ventilé.
c. Utiliser un respirateur à air fourni.
Des vapeurs extrèmement toxiques
sont produites pendant le chauffage
de ces métaux.
Le champ électromagnétique qui est
produit pendant le soudage à l’arc peut
19 Fr
WG3000 et WG3060
causer de l’interférence avec
le fonctionnement de
plusieurs appareils électriques
tels que les pacemakers
cardiaques. Toutes personnes
qui utilisent ces appareils doivent
consulter leur médecin avant
d’exécuter le soudage électrique à l’arc.
● Router l’électrode et les câbles
ensemble et les fixer avec du ruban
adhésif là où possible.
● Ne jamais envelopper les câbles de
soudage à l’arc autour de votre
corps.
● Toujours situer l’électrode et les
conducteurs de terre afin qu’ils
soient sur le même bord du corps.
● L’exposition aux champs
électromagnétiques peut avoir
autres réactions inconnues
concernant la santé.
Toujours
s’assurer
que l’endroit de soudage soit en état
sûr et sans risques (étincelles, flammes,
métal chauffé au rouge ou scorie)
avant de partir. S’assurer que
l’équipement soit hors circuit et que
l’excès de fil soient coupé. S’assurer
que les câbles soient roulés (sans
serrer) et hors du chemin. S’assurer que
tout métal et scorie soient refroidis.
Les bouteilles peuvent
exploser si endommagés. Ils
contiennent du gaz sous haute
pression. Si endommagés, les bouteilles
peuvent exploser. Puisque les
bouteilles de gaz font partie du
processus de soudage, s’assurer de bien
les respecter.
● Protéger les bouteilles de gas
comprimé contre la chaleur
excessive, les chocs mécaniques, et
les arcs.
● Installer et fixer les bouteilles dans
une position verticale en utilisant
une chaîne sur un support
stationnaire ou un support de
bouteille pour éviter le
renversement ou le basculage.
● Garder les bouteilles à l’écart du
soudage ou autres circuits
électriques.
● Ne jamais permettre que l’électrode
de soudage touche une bouteille.
● Utiliser seulement les bouteilles de
gaz corrects; régulateurs, tuyaux et
raccords conçus pour votre
application et les tenir en bon état
de marche.
● Tourner le visage à l’écart de la
soupape d’échappement en ouvrant
la soupape de la bouteille.
● Garder le chapeau protecteur en
place sur la soupape sauf si la
bouteille est en service ou branchée
pour le service.
Généralités Sur La
Sécurité
(Suite)
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
DANGER
!
DANGER
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 20

MONTAGE DU PIED
1. Placer le pied sur le soudeur et
aligner les trous dans le carter du
soudeur.
2. Fixer les vis à travers du pied et dans
la boîte.
Collier De Mise A La Terre
(Tous Les Modèles)
1. Desserrer le boulon hexagonal ou
l’écrou sur le collier de mise à la
terre.
2. Introduire le cordon à travers le
manche du collier et glisser le fil nu
sous le bloc du collier. Serrer le
boulon hexagonal en s’assurant que le
fil nu soit bien fixé (Figure 4).
Installation de Fils
La puis-
sance de
soudage peut être appliquée aux
bornes de sortie, rouleau entraîneur,
collier de mise à la terre, raccord du
câble de pistolet et le fil de soudage
même si l’interrupteur du pistolet n’est
pas activé. Ne pas toucher ces pièces
quand le soudeur soit en marche.
REMARQUE: Avant d’installer le fil à
soudage, s’assurer que le diamètre du
fil à soudage correspond à l’encoche
dans le rouleau d’entraînement du
dispositif d’alimentation et que le fil
correspond au bout de contact du
pistolet. Une mauvaise correspondance
sur n’importe quelle pièce peut causer
le glissage et le grippage du fil.
1. Vérifier que le modèle soit hors
circuit (OFF). Ouvrir le panneau sur
le soudeur afin d’exposer le dispositif
d’alimentation du fil.
2. Enlever la serrure rapide de la bobine en
appuyant et tournant 1/4 de tour au sens
inverse des aiguilles d’une montre. Le
bouton, ressort et bague d’espacement
de la bobine peuvent être enlevés.
REMARQUE: Les entretoises de bobine
et de broche fonctionnent comme
adaptateurs de 8 po (20,32 cm). L’achat
d’un adaptateur n’est pas nécessaire.
*Voir Figure 5 pour le montage.
3. Desserrer la vis de tension sur le
dispositif d’alimentation afin de
permettre l’avancement initial à la
main du fil dans la chemise du pistolet.
Collier de
serrage
Figure 4 - Montage du Collier de Mise
à la Terre
MONTAGE DE SUPPORT POUR LA
BOUTEILLE DE GAZ
1. Placer le support sur le soudeur en
alignant les trous dans le carter du
soudeur.
2. Fixer les vis à travers du support et
dans la boîte.
MONTAGE DU PIED
1. Placer le pied sur le soudeur et
aligner les trous dans le carter du
soudeur.
2. Fixer les vis à travers du pied et dans
la boîte.
Modèle WG3060
MONTAGE DU MANCHE
1. Placer le montage du manche sur le
soudeur en alignant les trous dans le
panneau d’avant du soudeur.
2. Fixer les vis à travers des bouts du
manche et dans la boîte.
MONTAGE DE ROUES ET D’ARBRE
1. Fixer l’arbre sur le carter du soudeur
avec la quincaillerie de fixation.
2. Introduire les roues sur l’arbre et les
tapper légèrement dans les
chapeaux des roues.
MONTAGE DU SUPPORT DE LA
BOUTEILLE DE GAZ
1. Placer le support sur le soudeur en
alignant les trous dans le carter du
soudeur.
2. Fixer les vis à travers du support et
dans la boîte.
20 Fr
Soudeur À L’Arc Alimenté En Fil
La selection d’un bon endroit peut
augmenter le rendement, sûreté de
fonctionnement et la vie du soudeur à
l’arc.
● Pour un meilleur résultat, situer le
soudeur dans un endroit propre et
sec. La poussière et la saleté
absorbent l’humidité dans le
soudeur et augmentent l’usure des
pièces mouvantes.
● Situer le soudeur dans un endroit
qui fournit au moins 12 po (305
mm) d’espace de ventilation devant
et derrière du modèle. Garder
l’espace de ventilation libre
d’obstructions.
● Entreposer les fils dans un endroit
propre et sec avec humidité basse
afin de conserver le fini du fil.
● Le récipient utilisé pour le soudeur
doit être mis à la terre correctement
et le soudeur doit être le seul
appareil de charge sur le circuit. Se
référer au tableau d’Ampérages de
Circuit à la page 1 pour la capacité
correcte du circuit.
● L’usage d’un cordon prolongateur
n’est pas recommandé pour les
soudeurs électriques à l’arc. La perte
de tension dans le cordon
prolongateur peut réduire le
rendement du soudeur
.
Modèle WG3000
Les pièces détachées du soudeur
indiquées ci-dessous se trouvent
dans le compartiment d’entraînement de fils. Ouvrir et enlever.
MONTAGE DU MANCHE
1. Enlever les vis du manche. Glisser le
manche entre le panneau d’avant du
soudeur et le couvercle supérieur
tout en alignant les trous dans
manche et les trous dans le couvercle
supérieur.
2. Fixer les vis à travers le couvercle
supérieur et dans le manche.
MONTAGE DE ROUE ET D’ARBRE
1. Introduire les supports d’arbre dans
les encoches du carter de soudeur.
2. Introduire l’arbre à travers des
supports et pousser les roues sur
l’arbre.
3. Fixer les roues avec les attaches en E
et les chapeaux de roues.
Installation
Montage
Figure 2 - Montage WG3000
Figure 3 - Montage WG3060
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 21

21 Fr
WG3000 et WG3060
4. Installer la bobine sur la broche afin
que le fil puisse sortir de la bobine
au bout le plus près du tube de
guidage d’avance. Ne pas couper
le fil tout de suite. Installer la
bague d’espacement, le ressort et le
bouton de serrage rapide en
appuyant et tournant le bouton 1/4
de tour au sens des aiguilles d’une
montre.
5. Tenir et couper le fil du bout de la
bobine. Ne pas permettre que le fil
se démêle. S’assurer que le bout du
fil soit droit et sans ébarbures.
6. Avancer le fil à travers du tube de
guidage du dispositif d’alimentation,
par dessus de l’encoche dans le
rouleau d’entraînement et dans la
chemise du pistolet. Serrer la vis de
tension du dispositif d’alimentation
de fil. Ne pas trop serrer.
7. Enlever la buse en tournant au sens
contraire des aiguilles d’une
montre. Ensuite dévisser la pointe
de contact du bout du chalumeau
(Voir Figure 6). Brancher le soudeur
dans la prise de courant correcte.
SUGGESTION: Garder le câble du
chalumeau droit pendant l’enfilage du fil.
8. Mettre le soudeur en marche et
régler la vitesse du fil à 5. Régler
l’interrupteur du pistolet jusqu’à ce
que le fil s’avance et dépasse le bout
du chalumeau. Mettre le soudeur
hors circuit.
9. Glisser la pointe de contact
soigneusement par dessus le fil et la visser
dans le cou du chalumeau. Installer la
buse en tournant au sens des aiguilles
d’une montre (Voir Figure 6). Tailler le
fil environ 1/4 po du bout de la buse.
POLARITÉ
Pour le soudage au chalumeau, brancher
le câble sortant du chalumeau à la
douille (+) et le câble du collier de mise à
la terre à la douille (-) sur la face du
panneau. Pour la soudure au fil fourré de
flux (sans gas), brancher le chalumeau à
(-) et le collier de mise à la terre à (+).
FACTEUR D’UTILISATION/
PROTECTION THERMOSTATIQUE
Le facteur d’utilisation de soudage est
le pourcentage du temps de soudage
actuel qui peut se faire dans un interval
de dix minutes. Par exemple, le
soudage actuel peut se produire pour
une minute à un facteur d’utilisation
de 10%, et ensuite, le soudeur doit se
refroidir pour neuf minutes.
Les pièces détachées internes de ce
soudeur sont protégées contre le
surchauffage avec un interrupteur
automatique thermique. Une lampe
jaune sur le panneau d’avant
(interrupteur on/off) est allumée si
vous dépassez le facteur d’utilisation.
Continuer avec le soudage quand la
lampe n’est pas allumée.
MODÉLE WT1000
1. Enlever le dispositif de retenue de la
lentille de la visière avec un tournevis
ordinaire en appuyant contre l’écran
et le poteau du dispositif de retenue
de la lentille.
2. Enlever la couche protectrice des deux
bords de chacun des couvercles de
lentille. Mettre un couvercle clair sur
chaque bord de la lentille teinte.
Placer les trois lentilles ensemble dans
la visière et fixer avec le dispositif de
retenue de lentille. Le dispositif de
lentille devrait s’insérer dans la
deuxième encoche de la visière.
3. Situer un des trous dans le bras de
réglage par dessus des goupilles qui
sont situées dans l’endroit de l’oreille
de la visière. Ces bras de réglage
déterminent l’ajustement et peuvent
être repositionnés facilement si
nécessaire.
4. Situer le serre-tête dans la visière.
Introduire la vis de goujon à travers du
serre-tête, de la visière et dans l’écrou
de traction comme indiqué. Ne pas
serrer l’écrou de traction
complètement.
5. Faire l’essai du casque de soudeur.
Ajuster le ressort du récepteur serretête à une position confortable et
baisser la visière. Si la visière est trop
proche ou trop loin, utiliser un
nouveau trou dans le bras de retenue.
Ajuster les écrous de traction pour
assurer que le casque peut se baisser
en inclinant la tête.
La mani-
pulation
et l’entretien incorrect des bouteilles et
régulateurs de gaz comprimé peut
résulter en blessures graves et la mort!
Toujours fixer les bouteilles de gaz
comprimé avec sûreté au nécessaire de
support du réservoir, au mur ou à un
autre système de support afin
d’empêcher le renversement des
Marques Sur La Pointe De Contacte
Taille de fil mm
,024 po ou 0,6
,030 po ou 0,8
,035 po ou 0,9
,040 po ou 1,0
Montage (Suite)
Vis de
tension
Panneau
Rouleau
d’entraînement
Entretois
e de
bobine
Tube de
guidage
Broche
Bobine 4 po
ou 8 po
Ressort
Serrure
de bobine
Figure 5 - L’Enfilement du Fil
à Soudage
Cou du
chalumeau
Pointe de
contacte
Buse
Figure 6 - Buse du Chalumeau
Entretoise
de broche
Montage du Casque
de Soudeur
Figure 7
Serre-tête
Visière
Lentille Teinte
Couvercle de Lentille Claire (2)
Poteau
Dispositif de Retenue
Bras de
Réglage (2)
Écrou de Traction (2)
Vis de Goujon (2)
Installation de Gaz
Protecteur
*Inverser et
introduire
dans la bobine
de 8 po
!
DANGER
Page 22

22 Fr
Soudeur À L’Arc Alimenté En Fil
bouteilles. Il est nécessaire de lire,
comprendre, et de suivre toutes les
risques indiqués dans les instructions
de sécurité concernant les gaz
comprimés et l’équipement
REMARQUE: Le gaz n’est pas nécessaire
si le fil fourré de flux est utilisé.
TYPES DE GAZ
Il y a trois types de gaz populaires pour le
soudage à l’arc avec gaz; 100% argon, un
mélange de 75% argon et 25% gaz
carbonnique (C25) ou 100% gaz
carbonnique. Le gaz carbonnique 100%
n’est pas recommandé à cause de cordons
de soudage de qualité insuffisante. Ce
modèle de soudeur ne fonctionne pas bien
avec le gaz carbonnique 100%. Le mélange
75/25 est recommandé pour le soudage
général de l’acier. Pour le soudage
d’aluminium, utiliser 100% argon. Chaque
type de bouteille et disponible chez votre
fournisseur de matériaux de soudage.
Fixer la bouteille en place sur votre soudeur
ou sur un autre support pour éviter le
basculage de la bouteille.
REMARQUE: L’usage du type de gaz
incorrect pourrait causer le manque ou
peu de pénétration de l’électrode (fil) de
soudage.
RÉGULATEUR
Le régulateur fournit une pression et
débit constante de gaz pendant le
soudage. Chaque régulateur est conçu
pour l’utilisation avec un type ou
mélange de gaz particulier. L’argon et
les mélanges d’argon utilisent le même
type de filets. 100% gaz carbonnique
utilise un différent type de filets. Un
adaptateur est disponible chez votre
fournisseur de gaz de soudeur pour
pouvoir utiliser les deux types.
MÉTHODE DE BRANCHEMENT
Les
cylindres
de gaz sont sous haute pression. Diriger
l’orifice d’échappement à l’écart de soi-même
ou d’autres personnes avant de l’ouvrir.
1. Ces modèles conviennent aux
bouteilles de 20 pi
3
.
2. Avec la boutille bien installée, enlever le
chapeau de la bouteille, se tenir au bord
opposé de l’orifice d’échappement et
ouvrir la soupape un peu en tournant
au sens contraire des aiguilles d’une
montre. Quand le gaz sort de la
bouteille, fermer la soupape en
tournant au sens des aiguilles d’une
montre. Ceci sert à purger la poussière
qui peut s’accumuler autour du siège de
la soupape.
3. Installer le régulateur sur la soupape de
la bouteille de gaz en gardant la face
des jauges dans la position verticale et
serrer l’écrou à la soupape de gaz.
4. Installer un bout du tuyau de gaz au
raccord situé en arrière du soudeur
et l’autre bout du tuyau au raccord
du régulateur en utilisant des
colliers de serrage sur chaque
raccordement. S’assurer que le
tuyau ne soit pas tortillé.
5. Se positionner encore au bord
opposé de l’orifice d’échappement
de la bouteille et ouvrir la soupape
lentement. Inspecter pour des
fuites dans l’endroit des
raccordements.
6. Tirer la gâchette sur le pistolet afin
de permettre que le gaz s’écoule et
ajuster le régulateur du gaz à 0,85
cmh (pieds cubiques par heure)*.
Relâcher la gâchette.
*REMARQUE: Le régulateur Campbell
Hausfeld WT600100AV est réglé
d’avance à l’usine à 0,85 cmh. Aucun
ajustement est nécessaire. Un
indicateur sortant au bout du
régulateur indique la quantité de gaz
restant dans le cylindre. Si l’indicateur
n’est plus étendu, il reste environ 10
minutes dans le cylindre.
7. Fermer la soupape de gaz lorsque
vous avez fini de souder.
1. Lire, comprendre et suivre
toutes les précautions
dans la section Généralités
Sur La Sécurité. Lire la
section entière de
Directives De Soudage avant
d’utiliser l’équipement.
2. Vérifier que le soudeur soit hors
circuit (OFF).
3. Vérifier que les surfaces du métal
soient libres de saleté, rouille,
peinture, huile, écailles ou autres
polluants avant de les souder
ensemble. Ces polluants rendent la
soudure difficile et peuvent causer
de mauvaises soudures.
Toutes personnes utilisant cet
équipement ou qui sont dans
l’endroit pendant l’utilisation de
l’équipement doivent porter des
vêtements de soudage protecteurs y
compris: protection oculaire avec
lentille correcte, vêtements
incombustibles, gants de soudeur en
cuir, et protection complète pour les
pieds.
Lorsque
le
souder est EN MARCHE, la baguette
a souder (fil) WG3000 est CHARGEE
MEME SI LA GACHETTE N’EST PAS
ACTIONNEE.
Pour le chauffage, soudage
ou coupage des matériaux
galvanisés, plaqué en zinc, plomb, ou
en cadmium, se référer à la section
Généralités Sur La Sécurité pour plus
d’informations. Des vapeurs extrèmement toxiques sont produites pendant
le chauffage de ces métaux.
4. Raccorder le collier de mise à la
terre à l’objet de travail ou à l’établi
(si en métal). S’assurer que le
contact soit sûr et non-pollué par la
peinture, le vernis, la corrosion, ou
autres matériaux non-métalliques.
5. Régler le Régulateur de Chaleur
situé sur le panneau d’avant. Se
référer à la décalcomanie située à
Indicateur
sortant
Chapeau
Adaptateur CO
2
INSTALLATION D’ARGON OU MÉLANGE D’ARGON
INSTALLATION
CO
2
Figure 8 - Branchement
OU
Installation de Gaz
Protecteur (Suite)
Fonctionnement
!
AVERTISSEMENT
MANUAL
!
DANGER
!
ATTENTION
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 23

23 Fr
WG3000 et WG3060
l’intérieur de la porte du
compartiment d’entraînement de fil
pour le réglage de chaleur correct.
REMARQUE: Ces réglages sont établis
comme guides généraux. Les réglages
de chaleur sont variables selon les
conditions de soudage et le matériel
utilisé.
6. Commencer avec un réglage de
commande de vitesse numéro 5, et
l’ajuster si nécessaire après la
première soudure d’essaie.
7. Brancher le cordon d’admission dans
une prise de courant convenable
avec capacité en circuits correcte
(Voir le tableau dans la section
spécifications à la page 1).
8. Mettre le soudeur en marche (ON).
9. Vérifier que le fil dépasse la pointe
de contact par 1/4 po, sinon,
appuyer sur la gâchette pour
avancer le fil, relâcher la gâchette et
tailler le fil.
10. Mettre le pistolet près de l’objet de
travail, baisser le casque de soudeur
en inclinant la tête ou mettre l’écran
à main en position, et appuyer sur la
gâchette. Ajuster le réglage de
chaleur et la vitesse du fil si
nécessaire.
11. Une fois fini, mettre le soudeur hors
circuit (off) et l’entreposer
correctement.
Débran-
cher et
mettre la machine hors circuit (Off)
avant de vérifier ou de procéder à
l’entretien de n’importe quelle pièce
détachée. Toujours garder le couvercle
du compartiment de fil fermé sauf
pendant le changement du fil.
Avant chaque usage:
1. Vérifier la condition des câbles de
soudage et réparer ou remplacer
immédiatement, les câbles dont
l’isolation est endommagé.
2. Vérifier la condition du cordon
d’alimentation et le réparer ou le
remplacer immédiatement si
endommagé.
3. Inspecter la condition du bout du
pistolet et de la buse. Enlever la
scorie, si présente. Remplacer le
bout du pistolet ou la buse si
endommagés.
Ne pas
utiliser
ce soudeur si l’isolation sur les câbles
de soudage, le pistolet, ou le cordon
d’alimentation est fendu ou
manquant.
Chaque 3 mois:
1. Remplacer toutes étiquettes de
sécurité sur le soudeur qui ne sont
pas lisables.
2. Utiliser de l’air comprimé pour
souffler toute la poussière des
ouvertures de ventilation.
3. Nettoyer l’encoche de fil sur le
rouleau d’entraînement. Enlever le
fil du dispositif d’alimentation,
enlever les vis du carter du rouleau
d’entrainement. Utiliser une petite
brosse métallique pour nettoyer le
rouleau d’entraînement. Remplacer si usé ou endommagé.
Pièces Consommables Et Qui
Peuvent S’user
Les pièces suivantes exigent de
l’entretien ordinaire:
• Rouleau d’entraînement d’alimentation de fil
• Chemise du pistolet - remplacer si
usé
• Buse/buses de contact
• Fil - Ce soudeur acceptera les
bobines de diamètre 10,16 cm ou
20,32 cm. Le fil de soudure est
sensible à l’humidité et s’oxyde
après quelques temps. Il est
important de choisir une taille de
bobine qui sera utilisée dans une
période de 6 mois. Pour l’acier
doux, il est recommandé d’utiliser le
fil solide AWS ER70S6 ou le fil fourré
de flux AWS E71T-GS.
• Pointes de contact - utiliser
Campbell Hausfeld, Tweco
®
, et
autres pointes convenables.
• Buse - utiliser le style Tweco
®
ou un
style compatible. Utiliser la buse
Campbell Hausfeld WT5021
disponible chez votre marchand, ou
utiliser le stlye de buse Tweco
®
(ou
compatible) chez votre succursale
locale d’équipement de soudage.
Changement de Tailles de
Fils
ROULEAU D’ENTRAÎNEMENT
Il y a deux rainures dans le Rouleau
d’Entraînement. La petite rainure est
pour le fil de .024 (0,6 mm) et le
deuxième est pour le fil de .030 - .035
Entretien
(0,8 - 0,9 mm). Enlever le couvercle du
rouleau et inverser le rouleau
d’entraînement pour choisir la rainure
convenable (Voir l’Illustration de
Pièces).
FIL FOURRÉ DE FLUX
Il est recommandé d’utiliser une taille
de pointe plus large à cause de petites
différences dans le diamètre du fil. Par
example:
• Diamètre de fil .030, utiliser une
pointe de .035.
• Diamètre de fil .035, utiliser une
pointe de .040.
Ce soudeur est monté pour le fil de
.035 (0,9 mm) et a une pointe de .040.
Puisque ce soudeur accept le Fil Fourré
de Flux de .030 et .035, le rouleau
d’entraînement devrait être dans la
condition réglée d’avance à l’usine.
FIL MIG
Puisque le fil MIG maintient un
diamètre constant, utiliser une pointe
qui correspond au fil utilisé. Utiliser la
petite rainure sur le rouleau
d’entraînement avec le fil de .024 (0,6
mm). Utiliser la large rainure réglée
d’avance à l’usine pour le fil MIG ou
Aluminium .030 - .035 (0,8 - 0,9 mm).
FIL ALUMINIUM
L’utilisation d’une pointe plus large est
recommandé avec le fil Aluminium. Par
example:
• Diamètre de fil .030, utiliser une
pointe de .035.
Utiliser la rainure large réglée d’avance
à l’usine avec le fil MIG ou Aluminium
de .030 - .035 (0,8 - 0,9 mm). Le fil
Aluminium est très faible et ne devrait
avoir la même tension sur le rouleau
d’entraînement que les fils Fourré de
Flux ou MIG. En serrant le fil
Aluminium au rouleau d’entraînement,
tourner la vis de tension trois tours
complèt ou jusqu’à ce que le rouleau
d’entraînement commence à gripper le
fil et à l’enfiler à travers le câble du
chalumeau.
Composez le (800) 746-564
pour pièces de rechange.
MIG
WT5021
Figure 9 - Buse
Fonctionnement (Suite)
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 24

afin d’ajuster les réglages, et comparer
les soudures avec la Figure 12.
TYPE ET TAILLE DE FILS
Le choix correct du fil comprend une
variété de facteurs telles que la position
de soudage, le matériel de l’objet de
travail, l’épaisseur et la condition de la
surface. L’American Welding Society,
AWS, a organisé certaines exigences
pour chaque type de fil.
FIL FOURRÉ DE FLUX
E - 7 0 T - GS
Rigidité de la soudure x
68950 kPa
Positions de soudure (0
pour plate ou horizontal, 1 pour les autres
positions)
Fil fourré en flux tubulaire
Type de flux
AWS E71T-GS ou E71T-11 sont
recommandés pour ce soudeur.
FIL SOLIDE
ER - 70 S - 6
Rigidité de la soudure x
6895 kPa
Fil Solide
Composition du fil
ER-70S6 est recommandé pour ce
soudeur.
ANGLE DE SOUDURE
L’angle de soudure est l’angle de la buse
pendant le soudage. L’utilisation de
l’angle correct assure la pénétration et la
formation du cordon de soudure exigé.
L’angle de soudure est très important
pour les positions de soudure différentes
afin de produire une bonne soudure.
L’angle de soudure comprend deux
positions - l’angle de déplacement et
l’angle de travail. L’angle de
déplacement est l’angle situé dans la
ligne de la soudure et peut varier entre
5º et 45º du vertical selon les conditions
de soudage.
L’angle de travail est l’angle horizontal,
mesuré aux angles droits à la ligne de
soudage. Pour la plupart des
applications, un angle de déplacement
de 45º et un angle de travail de 45º sont
suffisants. Pour les usages spécifiques,
consulter un manuel de soudage à l’arc.
24 Fr
Soudeur À L’Arc Alimenté En Fil
VITESSE DE FIL
La vitesse de fil est réglée par le bouton
sur le paneau d’avant. La vitesse doit
être “réglée” selon le taux auquel le fil
est fondu dans l’arc. Le réglage est une
des fonctions critiques du soudage
alimenté en fil. Le réglage devrait être
effectué sur un morceau de métal
d’essai qui est de même type et
d’épaisseur que celui qui doit être
soudé. Procéder avec la soudure avec
une main en “trainant” la buse du
pistolet à travers de la pièce d’essai en
réglant la vitesse avec l’autre main.
Une vitesse trop lente causera un
crachement et le fil se brûlera dans la
pointe de contacte. Une vitesse trop
rapide peut aussi causer un bruit de
crachement et le fil s’enfoncera dans la
plaque avant de se fondre. Un bruit
constant de bourdonnement indique
que la vitesse de fil est réglée
correctement. Pour l’aluminium, la
vitesse du fil est typiquement réglée à
un réglage plus élevé (vitesse 7 - 9).
NOTE: Répéter le procédé de réglage
chaque fois qu’il y ait un changement
de réglage de chaleur, diamètre ou
type de fil, type de matériel ou
épaisseur de l’objet de travail.
VITESSE DE DEPLACEMENT
La vitesse de déplacement est la vitesse
auquelle le fil est dirigé le long de la
surface de soudage. Le diamètre et le
type de fil à soudage, l’ampérage, la
position et l’épaisseur de l’objet de
travail ont tous un effet sur la vitesse
de déplacement et peuvent avoir un
ANGLE DE DÉPLACEMENT
ANGLE DE TRAVAIL
5º - 45º
5º - 45º
Figure 11 - Angle de Soudure
Directives De Soudage
Généralités
Cette série de soudeurs peut utiliser les
procédés de soudage à L’Arc Fourré en
Flux (Sans Gaz) ou de Soudage à l‘Arc
au Métal à Gaz (MIG) . Le cordon de
soudage doit être protégé contre la
contamination dans l’air pendant qu’il
est fondu. Le procédé Sans Gaz utilise
un fil tubulaire avec un matériel flux à
l’intérieur. Le flux fondu produit un
gaz protecteur. Le procédé MIG utilise
un gaz inerte pour protéger la soudure
fondue.
Quand le courant est produit par un
transformateur (machine à souder) et
passe à travers du circuit à un fil de
soudage, un arc est produit entre le
bout du fil à soudage et l’objet de
travail. Cet arc fond le fil et l’objet. Le
métal fondu du fil à soudage s’écoule
dans le cratère fondu et produit un
adhérance avec l’objet de travail tel
qu’indiqué (Figure 10).
Principes Du Soudage a l’Arc
Les cinq techniques qui ont un effet sur
la qualité de la soudure sont: la
sélection du fil, le réglage de chaleur,
l’angle de soudure, la vitesse du fil et la
vitesse de déplacement. La compréhension de ces méthodes est nécessaire
afin d’atteindre une soudure efficace.
REGLAGE DE CHALEUR
La chaleur correcte nécessite un
ajustement du soudeur au réglage
exigé. La chaleur ou la tension est
réglée par un interrupteur sur le
soudeur. Le réglage de la chaleur
utilisé dépend sur la taille (diamètre) et
du type de fil, la position de la soudure
et l’épaisseur de l’objet. Se référer aux
spécifications indiquées sur le soudeur.
Il est recommandé que le soudeur se
pratique sur des morceaux de métal
Soudure
Fil
Flux
(sans gaz
seulement)
Objet de travail
Gaz
protecteur
Pointe de
contacte
Cratère
Buse
Figure 10 - Pièces détachées de soudage
Page 25

POSITIONS DE SOUDAGE
Il y a quatre positions générales de
soudage; plate, horizontale, verticale et
aérienne. Le soudage dans une
position plate est la plus facile. La
vitesse peut être augmentée, le métal
fondu coule moins, une meilleure
pénétration est possible et le travail est
moins fatiguant. Le soudage est
effectué avec le fil à un angle de
déplacement de 45º et un angle de
travail de 45º.
Autres positions exigent autres
techniques telles que le tissage, passe
circulaire et le jogging. Un niveau de
plus grande compétance est exigé pour
ces soudures.
La soudure aérienne est la position plus
difficile et dangereuse. Le réglage de
la chaleur et la sélection du fil varient
selon la position.
Tout le travail devrait être effectué
dans la position plate si possible. Pour
les applications spécifiques, consulter
un manuel technique de soudage.
PASSES DE SOUDAGE
Quelques fois il est nécessaire d’utiliser
plus d’une passe pour remplir le joint.
La première passe est la passe de base,
suivie par la passe de remplissage et la
passe de finition. Si les pièces sont
épaisses, il peut être nécessaire de
bisauter les bords qui sont unis à un
25 Fr
WG3000 et WG3060
Chaleur, Vitesse de fil et vitesse
de déplacement normaux
Chaleur trop basse
Chaleur trop élevée
Vitesse de fil trop rapide
Vitesse de fil trop lente
Vitesse de déplacement
trop rapide
Métal commun
Figure 12 - Apparence de la Soudure
Directives De Soudage
effet sur la qualité de la soudure (Voir
Figure 12). Lorsque la vitesse est trop
rapide, le cordon est étroit et les
ondulations du cordon sont pointus
comme indiqué. Lorsque la vitesse est
trop lente, la soudure se tasse et le
cordon est haut et large. Pour
l’aluminium, la vitesse de déplacement
et typiquement plus rapide.
ENLEVAGE DE SCORIE (FIL FOURRÉ
DE FLUX SUELEMENT
Porter
des
lunettes protectrices approvées ANSI
(ANSI Standard Z87.1) et des vêtements
protecteurs pendant l’enlevage de la
scorie chaude. Le débris chaud et
volant peut causer des blessures aux
personnes dans l’endroit.
Après avoir complété la soudure,
attendre que les sections de soudage se
refroidissent. Une couche protectrice
appelée scorie couvre le cordon de
soudure et empêche la réaction du
métal fondu avec les polluants dans
l’air. La scorie peut être enlevée une
fois que la soudure s’est refroidie et
n’est plus rouge. Enlever la scorie avec
un marteau à buriner. Frapper la scorie
légèrement avec le marteau et la
dégager du cordon de soudure. Finir
avec une brosse métallique.
REMARQUE
Enlever la scorie avant chacune des
passes multiples.
angle de 60º. Enlever la scorie avant
chaque passe pour le procédé Sans Gaz.
TECHNIQUE POUSSER VS TIRER
Le type et l’épaisseur de la pièce de
travail agissent sur la direction de la buse
du pistolet. Pour des matériaux minces,
(calibre 18 et plus) et tout l’aluminium, la
buse devrait être dirigée en avant de la
flaque de soudure et devrait pousser la
flaque à travers de l’objet de travail.
Pour de l’acier épais, la buse devrait être
dirigée dans la flaque de soudure pour
augmenter la pénétration de la soudure.
Ceci est la technique main-arrière ou
tirer (Voir Figure 15).
SOUDAGE ALUMINIUM
Toute surface aluminium doit être bien
nettoyée avec une brosse en acier
inoxydable pour éliminer les oxydes sur
la surface de soudure et meulage. Le
gaz Argon 100% doit être utilisé pour le
soudage d’aluminium. Sinon, il n’y aura
pas de pénétration.
Vitesse de déplacement trop lente
Figure 13 - Passes de Soudure
Finition
Remplissage
Base
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 26

26 Fr
Guide de dépannage - Soudeur
Symptôme Cause(s) Possible(s) Mesure Corrective
1. Facteur d’utilisation dépassé
2. Raccord au collier de mise à la
terre insuffisant
3. Interrupteur défectueux
4. Disjoncteur ou fusible sauté
1. Bout du pistolet de taille
incorrecte
2. Chemise du pistolet obstruée ou
endommagée
3. Bout du pistolet obstrué ou
endommagé
4. Rouleau d’entraînement usé
5. Tension insuffisante
Scorie dans la buse du pistolet
1. Raccordement insuffisant
2. Utilisation d’un cordon
prolongateur trop long
1. Fil étranglé
2. Plus de fil
3. Tension insuffisante
4. Chemise de fil usée
5. Fusible sautée
6. Fil débranché à l’intérieur
7. Pointe de contact obstruée
1. Vitesse de fil trop lente
2. Vitesse de déplacement trop lente
ou chaleur trop élevée
Pour des informations concernant ce produit, composer le 1-800-746-5641
1. Permettre que le soudeur se reffoidisse jusqu’à ce que la lampe
de l’indicateur ON/OFF s’éteint
2. S’assurer que tous les raccordements soient sûrs et que la surface
d’attache soit propre
3. Remplacer l’interrupteur
4. Réduire la charge sur le circuit, rajuster le disjoncteur ou
remplacer le fusible
1. Utiliser un bout de taille correcte
2. Nettoyer ou remplacer la chemise du pistolet
3. Nettoyer ou remplacer le bout du pistolet
4. Remplacer
5. Serrer la vis de tension
Nettoyer la scorie de la buse du pistolet
1. S’assurer que tous les raccordements soient sûrs et que la
surface d’attache soit propre
2. N’utilisez pas un cordon prolongateur plus que 20 pi de longueur
1. Recharger le fil
2. Remplacer la bobine de fil
3. Serrer la vis de tension si le fil patine
4. Remplacer la chemise
5. Remplacer la fusible sur la plaque de contrôle d’entraînement de
fil dans le soudeur (1,6 A à retardement)
6. Appeler 1-800-746-5641 pour l’assistance
7. Remplacer la pointe de contact
1. Vitesse de fonctionnement entre 7 - 10
2. Augmenter la vitesse de déplacement ou diminuer le réglage de
chaleur
Manque de puissance
Le fil s’emmêle au rouleau
d’entraînement
La buse du pistolet arc à la
surface de travail
Collier de mise à la terre et/ou
le câble deviennent chauds
Le fil ne s’avance pas
Le fil (Aluminium) brûle dans
la pointe ou le métal
(Aluminium) produit des
bulles ou brûle à travers
1. Vérifier que le soudeur soit HORS
CIRCUIT (OFF) et que le cordon
d’alimentation soit débranché.
2. Enlever le couvercle du soudeur afin
d’exposer l’interrupteur ON/OFF.
3. Déconnecter les fils noir et blanc du
cordon d’alimentation qui sont
branchés à l’interrupteur ON/OFF.
4. Déconnecter le fil vert du cordon
d’alimentation qui est branché au
bâti du soudeur.
5. Desserrer la(les) vis de tension du
cordon et tirer le cordon de
l’appareil de soulagement de
tension.
POUSSER
TIRER
Figure 15
Figure 14 - Passes Multiples
Remplacement du
Cordon
d’Alimentation
Soudeur À L’Arc Alimenté En Fil
Directives De Soudage (Suite)
6. Installer le nouveau cordon en
suivent les étapes à l’envers.
Page 27

27 Fr
Cordon de soudure trop mince
par intervalles
Cordon de soudre trop épais
par intervalles
Enfoncements en lambeaux au
bord de la soudure
Le cordon de soudure ne
pénètre pas le métal commun
Le fil crache et se colle
1. Vitesse de déplacement irrégulière
2. Réglage de chaleur de sortie trop
bas
1. Vitesse de déplacement lente et/ou
irrégulière
2. Réglage de chaleur de sortie trop
élevé
1. Vitesse de déplacement trop rapide
2. Vitesse de fil trop rapide
3. Réglage de chaleur de sortie trop
élevé
1. Vitesse de déplacement irrégulière
2. Réglage de chaleur de sortie trop
bas
3. Manque de/niveau bas de gaz
protecteur
4. Type de gaz incorrect (Aluminium)
5. Cordon prolongateur trop long
6. Accumulation possible d’oxydes sur
la surface (Aluminium)
1. Fil humide
2. Vitesse de fil trop rapide
3. Type de fil incorrect
4. Manque de/niveau bas de gaz
protecteur
Guide de dépannage - Soudures
Symptôme Cause(s) Possible(s) Mesure Corrective
1. Diminuer et maintenir une vitesse de déplacement constante
2. Augmenter le réglage de chaleur de sortie
1. Augmenter et maintenir une vitesse de déplacement constante
2. Diminuer le réglage de chaleur de sortie
1. Diminuer la vitesse de déplacement
2. Diminuer la vitesse de fil
3. Diminuer le réglage de chaleur de sortie
1. Diminuer et maintenir une vitesse de déplacement constante
2. Augmenter le réglage de chaleur de sortie
3. Utiliser le gaz pour la méthode MIG ou remplir la bouteille
4. Utiliser le gaz Argon 100% seulement
5. N’utilisez pas un cordon prolongateur plus que 20 pi de long
6. Bien nettoyer la surface avec une brosse métallique seulement
1. Utiliser un fil sec et l’entreposer dans un endroit sec
2. Diminuer la vitesse de fil
3. Utilisez le fil fourré de flux si vous n’utilisez pas de gaz
4. Utiliser le gaz pour la méthode MIG ou remplir la bouteille
Garantie Limitée 5-3-1
1. Durée: Le fabriquant garantie la réparation, sans frais pour les pièces et main-d’oeuvre, le Soudeur, le Pistolet Soudeur, Câbles, qui se sont révèlés défectueux
en matière ou fabrication, pendant les durées suivantes après la date d’achat initial:
Pour 5 Ans: Le Transformateur de Soudeur et Redresseur
Pour 3 Ans: Le Soudeur En Entier (à l’exclusion des colliers, pistolet, câbles, ou accessoires emballés avec le soudeur)
Pour 1 An: Colliers De Mise À La Terre, Pistolet MIG, Porte-électrodes, Accessoires, et Câbles de Soudage (si applicable)
2. Garantie Accordée Par (Garant):
Campbell Hausfeld/ A Scott Fetzer Company
100 Production Drive
Harrison, OH 45030
Telephone: (513)-367-4811
3. Bénéficiaire De Cette Garantie (Acheteur): L’acheteur initial du produit Campbell Hausfeld .
4. Couverture De La Présente Garantie: Défauts de matière et de fabrication qui se révèlent pendant la période de validité de la garantie. Cette garantie
comprend le Soudeur, le Transformateur du Soudeur et Redresseur, Pistolet du Soudeur ou le Porte-Électrode, et câbles seulement.
5. La Présente Garantie Ne Couvre Pas:
A. Les garanties implicites, y compris celles de commercialisabilité et D’ADAPTION À UNE FONCTION PARTICULIÈRE SONT LIMITÉES EN DURÉE À CETTE
GARANTIE. Après cette durée, tout risques de perte, quoi que ce soit, devient la responsabilité de l’acheteur. Certaines Provinces n’autorisant pas de
limitations de durée pour les garanties implicites. Les limitations précédentes peuvent donc ne pas s’appliquer.
B. TOUT DOMMAGE, PERTE OU DÉPENSE FORTUIT OU INDIRECT POUVANT RÉSULTER DE TOUT DÉFAUT, PANNE OU MAUVAIS FONCTIONNEMENT DU
PRODUIT CAMPBELL HAUSFELD. Certaines Provinces n’autorisent pas l’exclusion ni la limitation des dommages fortuits ou indirects. La limitation ou
exclusion précédente peut donc ne pas s’appliquer.
C. Les accessoires qui sont compris avec le produit et qui sont soumis à l’usure par l’usage normal; la réparation ou le remplacement de ces objets sont la
responsabilité de l’acheteur. Ces pièces MIG comprennent, mais ne sont pas limités à; Pointes De Contact, Buses, Doublures de Pistolet, Rouleaux
D’Entraînement, Nettoyant pour Fil en Feutre. Additionnellement, cette garantie ne comprend pas le dommage causé par le remplacement ou entretien
prématuré des pièces USABLES précédentes.
D. Toute panne résultant d’un accident, d’une utilisation abusive, de la négligence ou d’une utilisation ne respectant pas les instructions données dans le(s)
manuel(s) accompagnant le produit.
E. Service avant livraison, i.e. montage et ajustement.
7. Responsabilités Du Garant Aux Termes De Cette Garantie: Réparation ou remplacement, au choix du Garant, des produits ou pièces qui se sont révélés
défectueux pendant la durée de validité de la garantie.
8. Responsibilités De L’Acheteur Aux Termes De Cette Garantie:
A. Livraison ou expédition du produit ou pièce Campbell Hausfeld à Campbell Hausfeld. Taux de frais , si applicable, sont la responsabilité de l’acheteur.
B. Utilisation et entretien du produit avec un soin raisonable, ainsi que le décri(vent)t le(s) mnuel(s) d’utilisation.
9. Réparation ou Remplacement Effectué Par Le Garant Aux Termes De La Présente Garantie: La réparation ou le remplacement sera prévu et exécuté
en fonction de la charge de travail dans le centre d’entretien et dépendra de la disponibilité des pièces de rechange.
Cette garantie limitée confère des droits précis. L’acheteur peut également jouir d’autres droits qui varient d’une Province à l’autre.
WG3000 et WG3060
Page 28

Blanc
Noir
Vert
28 Fr
Soudeur À L’Arc Alimenté En Fil WG3000
Schéma d’installation de fils WG3000
MIN
MAX
Mise à la terre
Pistolet
MARCH/ARRÊT (ON/OFF)
S1
S2
M1
S3
S5
2
1
T2
S5
T1
S4
M
=
White
L2 (N)
Black
L1
Green
Ground
5 6 7 84321678
Page 29

29 Fr
Schéma d’installation de fils WG3060
Mise À La Terre
Noir
Blanc
Vert
Soudeur À L’Arc Alimenté En Fil WG3060
LG
L2 (N) White
L1 (R) Black
Green
C1
S20127°
Ground
S1
1
2
3
4
A2
M1
A1
LV
T1
RD
M
5 6 7 8 9 104321
T2
S2
S3
K-A2
K
K-A1
Page 30

2
4
6
8
8
1
1
3
3
5
7
7
9 & 10
11
11 & 30
12
14
14
15
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
27
28
29
31
32
32
33
33
34
35
35
36
37
38
38
39
39
40
40
42
42
43
44
45
46
43
47
47
48
3
49
1
47
43
9 &10
30 Fr
Pour pièces de rechange, composer 1-800-746-5641
Correspondance:
The Campbell Group
Attn: Parts Department
100 Production Drive
Harrison, Ohio 45030 U.S.A.
S’il vous plaît fournir l’information
suivante:
- Numéro de modèle
- Numéro de série (si applicable)
- Numéro et description de la pièce
Soudeur À L’Arc Alimenté En Fil
MODÈLE WG3060
MODÈLE WG3000
50
** Pointe de Contact (Tableau, Page 31)
40
40
Page 31

31 Fr
1 Assemblage de chalumeau et tuyau (Nos. 2-6, 34 et 50 compris) WC600700AV WC600700AV 1
2 Corps du chalumeau, avant et arrière WC600201AV WC600201AV 1
3 Attache du crochet WC600003AV WC600003AV 1
4 Buse, type Tweco
®
WT502100AJ WT502100AJ 1
5 Bouton de gâchette WC600202AV WC600202AV 1
6 Ressort de contact de chalumeau WC600203AV WC600203AV 1
7 Collier de mise à la terre (Cordon non-compris) WC100100AV WC100100AV 1
8 Câble de soudage 8 AWG (1,83 m) ❋ ❋ 1
9 Bouton de vitesse de fil WC400201AV WC400201AV 1
10 Panneau de contrôle pour vitesse de fil WC400200AV WC400600AV 1
11 Interrupteur de sélection de chaleur WC400300AV — 2
Interrupteur de sélection de chaleur — WC400500AV 1
12 Interrupteur on/off WC400000AV — 1
13 Décalcomanie de sécurité DK670100AV DK670100AV 1
14 Poignée WC300600AV WC300700AV 1
15 Cordon d’alimentation 14-3 AWG (1,83 m) Type SJT WC000100AV WC000100AV 1
16 Broche de bobine WC500300AV WC500300AV 1
17 Vis à métaux #10 - 32 x 0,5 po ❋ ❋ 2
18 Fil fourré de flux diamètre 0,035 po (0,9 mm) WE200500AJ WE200500AJ 1
19 Adaptateur de bobine WC500200AV WC500200AV 1
20 Ressort de bobine WC500101AV WC500101AV 1
21 Moyeu de serrage de bobine WC500100AV WC500100AV 1
22 Assemblage d’entraînement (Nos. 23-29 compris) WC500000AV WC500400AV 1
23 Ressort de tension WC500003AV WC500003AV 1
24 Vis de tension WC500002AV WC500002AV 1
25 Rouleau 0,6 -0,9 mm ( 0,024 - 0,035 po) WC500001AV WC500001AV 1
26 Couvercle de rouleau WC500004AV WC500004AV 1
27 Vis #8 - 36 x 1,5 po ❋ ❋ 3
28 Bras articulé WC500005AV WC500005AV 1
29 Galet pivoté WC500007AV WC500007AV 1
30 Bouton de sélection de chaleur — WC400401AV 1
31 Soulagement de tension WC102000AV WC102000AV 2
32 Roue WC701200AV WC701300AV 2
33 Pied, avant WC702100AV WC702300AV 1
34 Chemise, métal WC600007AV WC600007AV 1
35 Support de bouteille de gaz WC702200AV WC702400AV 1
36 Support de manche (Droit) — WC300800AV 1
37 Support de manche (Gauche) — WC300900AV 1
38 Arbre WC703100AV WC703200AV 1
39 Moyeu de roue WC703500AV WC703400AV 1
40 Raccord dinse WC000200AV WC000200AV 2
41 Prise dinse WC000300AV WC000300AV 2
42 Bague de chalumeau WC600009AV WC600009AV 1
43 Vis #10 - 24 x 1/2 po ❋ ❋ 9
44 Support d’arbre WC703600AV — 2
45 Bague en E, 5 mm D.I. ❋ — 2
46 Vis #10 - 24 x 2 po — ❋ 2
47 Vis #8 - 36 x 1 po — ❋ 2
48 Rondelle plate #8 — ❋ 2
49 Écrou #8 - 36 — ❋ 2
50 Col de Cygne avec Diffuseur WC600701AV WC600701AV 1
❋ Quincaillerie ordinaire, disponible dans votre quartier ou de votre fournisseur de matériaux de soudage
Liste De Pièces De Rechange - Modèles WG3000 et WG3060
Nº de Numéro de pièces pour modèles:
Réf. Description WG3000 WG3060 Qté.
FIL EN OPTION
Type Description Numéro de pièce
Mig ER70S6 ,024 po WE300000AJ
Mig ER70S6 ,030 po WE300500AJ
Mig ER70S6 ,035 po WE301000AJ
Flux E71T-GS ,030 po WE200000AJ
Flux E71T-GS ,035 po WE200500AJ
WG3000 et WG3060
**POINTES DE CONTACT EN OPTION
Taille
mm po Numéro de Pièce
0,6 0,024 WT501200AV
0,8 0,030 WT501300AV
0,9 0,035 WT501400AV
Page 32

Soudeur À L’Arc Alimenté En Fil WG3000 et WG3060
Lexique de Termes de Soudage
CA ou Courant Alternatif - courant
électrique qui change de direction
périodiquement. Le courant à soixante
cycles voyage dans les deux directions
soixante fois par seconde.
Longueur de L’Arc - La distance du
bout de l’électrode jusqu’au point où
l’arc contacte la surface de travail.
Métal Commun - le matériel qui doit
être soudé.
Joint en Bout - un joint entre deux
pièces qui sont alignées
approximativement dans le même plan.
Cratère - une flaque ou poche qui est
produite quand l’arc contacte le métal
commun.
CC ou Courant Continu - courant
électrique d’une direction seulement.
La polarité (+ ou -) détermine la
direction du courant.
CC Polarité Inversée - quand le porteélectrode est branché au pôle positif du
soudeur. La Polarité Inversée dirige plus
de chaleur dans l’électrode plutôt que
sur l’objet de travail pour l’utilisation
sur les matériaux plus minces.
CC Polarité Ordinaire - quand le
porte-électrode est branché au pôle
négatif du soudeur. Plus de chaleur est
dirigé vers l’objet de travail pour
meilleur pénétration des matériaux
épais.
Électrode - un fil en métal enrobé
ayant approximativement la même
composition du matériel qui doit être
soudé.
Soudure en Cordon - dimension
approx. d’un triangle, profil en travers,
qui uni les deux surfaces à angles droits
en soudure à recouvrement, en T ou en
coin.
Flux - un enduit qui produit un gaz
protecteur autour de l’endroit de
soudage lors du chauffage. Ce gaz
protège les métaux de base et d’apport
contre les impuretés de l’air.
Soudure À L’Arc Fourré de Flux
(FCAW) - ou Sans Gaz est une
méthode de soudage utilisée avec un
soudeur à alimentation en fil. Le fil de
soudage est tubulaire avec du flux à
l’intérieur pour la protection.
Soudure À L’arc Au Chalumeau
(GMAW) - la soudure MIG est une
méthode utilisée avec un soudeur à
alimentation en fil. Le fil est solide et
un gaz inerte est utilisé pour la
protection.
Soudure À L’Arc Tungstène Au
Chalumeau (GTAW) - la soudure TIG
est une méthode de soudage utilisée
avec de l’équipement de soudage qui a
une génératrice à haute fréquence.
L’arc est crée entre un électrode
tungstène non-usable et l’objet de
travail. Un bouche-pores peut être
utilisé.
Soudure à Recouvrement - un joint
entre deux pièces en chevauchement.
Tension au Repos (OCV) - la tension
entre l’électrode et le collier de mise à
la terre quand il n’y a pas de flux de
courant (pas de soudage). Ceci
détermine la vitesse auquelle l’arc est
amorçé.
Chevauchement - se produit quand le
réglage d’ampérage est trops bas. En ce
cas, le métal fondu tombe de
l’électrode sans se fondre dans le métal
commun.
Porosité - des soufflures, ou creux
formés pendant la solidification de la
soudure qui affaiblissent la soudure.
Pénétration - la profondeur que la
chaleur affecte l’objet pendant la
soudure. Une soudure de haute qualité
est celle qui atteint 100% de
pénétration. C’est à dire que l’objet de
travail en entier a été chauffé et
solidifié à nouveau. Les endroits
affectés par la chaleur devraient être
visibles sur l’inverse de la soudure.
Soudure À L’Arc Au Métal Enrobé
(SMAW) - est une méthode de soudage
qui utilise une électrode usable pour
soutenir un arc. L’enduit de flux fondu
sur l’électrode fournit la protection.
Scorie - une couche d’encrassement de
flux qui protège la soudure des oxydes
et autres polluants pendant le
refroidissement de la soudure. Enlever
la scorie après que la soudure s’est
refroidie.
Bavure - particules métalliques
volantes qui se refroidissent sur la
surface de travail. La bavure peut être
diminuée si vous utilisez un agent
vaporisateur qui résiste la bavure sur
l’objet de travail avant de souder.
Point de Soudure - une soudure
utilisée pour tenir les pièces en
alignement jusqu’à ce que les soudures
actuelles soient complétées.
L’Angle de Déplacement - l’angle de
l’électrode dans la ligne de
soudure.Ceci varie entre 5º et 45º selon
les conditions.
Joint en T - placer le bord d’un
morceau de métal sur l’autre à un
angle de 90º. Caniveau - une condition
résultant d’un ampérage trop haut qui
produit une rainure dans le métal
commun le long des deux côtés du
cordon de soudure et sert à affaiblir la
soudure.
Flaque de Soudure - un volume de
métal fondu dans une soudure avant sa
soldification.
Cordon de Soudage - une(des)
couche(s) étroite(s) de métal placé(s) sur
le métal commun pendant que
l’électrode fonde. Le cordon de
soudage est typiquement deux fois le
diamètre de l’électrode.
Angle de Travail - l’angle de
l’électrode du horizontal mesuré à
angle droit de la ligne de soudure.
32 Fr
Page 33

1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4 & 6
5
5
6
7
Sírvase leer y guardar estas instrucciones.Lea con cuidado antes de tratar de armar, instalar, manejar o darle servicio al producto descrito en
este manual. Protéjase Ud. y a los demás observando todas las reglas de seguridad. El no seguir las instrucciones podría resultar en heridas y/o
daños a su propiedad.Guarde este manual como referencia.
33 Sp
Manual de Instrucciones y Lista de Repuestos Modelos WG3000 y WG3060
Soldadora Con Arco
Con Alambre
Continuo
Esta línea de soldadoras con arcos de
Campbell Hausfeld está diseñada para
usarse con corriente estándard de 115
voltios. Estas soldadoras le ofrecen una
perilla para controlar la velocidad del
alambre que le permite seleccionar con
exactitud la velocidad necesaria para
diferentes tipos de soldaduras. Los
componentes internos tienen un sistema
de protección termostática.
Estas soldadoras están diseñadas para soldar
con arcos eléctricos (sin gas) o con gases
inertes (Mig). La unidad incluye una bobina
pequeña de alambre de fundente revestiido
de 0,9 mm y una boquilla de 0,040.
Para desempacar
Algunas piezas de la soldadora se
encuentran en el compartimiento
para almacenar el alambre.
Al desempacar este producto, revíselo
con cuidado para cerciorarse de que
esté en perfecto estado. Si la soldadora
está dañada o le faltan piezas
comuníquese con el distribuidor de
Campbell Hausfeld más cercano a su
domicilio.
Requerimientos eléctricos
Este
equipo
debe conectarse a un circuito de 115
voltios. En la tabla a continuación se le
explica el tipo de cortacircuitos o
fusibles necesarios. Nunca conecte
otros artefactos, lámparas o
herramientas al mismo circuito donde
está conectada la soldadora. No le
recomendamos el uso de cordones de
extensión. Si no sigue esta
recomendación podría activarse el
cortacircuitos o quemarse los fusibles.
Componentes y Controles
1. Pinza - conéctela a la pieza de
trabajo.
2. Pistola para alimentar el
alambre con boquilla de 0,040.
3. Cordón eléctrico - conéctelo a un
tomacorrientes de 115 voltios.
4. Interruptor
5. Perilla para controlar la
velocidad - Gírela en el mismo
sentido de las agujas del reloj para
aumentar la velocidad de
alimentación del alambre y en el
sentido contrario para disminuirla.
6. Perilla para controlar el
amperaje - Para seleccionar la
energía eléctrica para soldar. Le
permite seleccionar 4 niveles.
7. Conexión de la polaridad - Para
soldar con gases inertes (MIG),
conecte el cable del soplete al (+) y
conéctelo al (-) para soldar con
alambres con fundente revestido.
Ésto le
indica
que hay una situación que le
ocasionará la muerte o heridas de
gravedad si ignora la advertencia.
Ésto le
indica
que hay una situación que podría
ocasionarle la muerte o heridas de
gravedad si ignora la advertencia.
Ésto le
indica
que hay una situación que podría
MODELO WG3000
Descripción
MODELO WG3060
IN211104AV 9/99
Figura 1
© 1999 Campbell Hausfeld / Scott Fetzer
Medidas de Seguridad
Diám. del Cortacircuito o
Electrodo Fusible de acción
retardada
1-2 15 amp
3-4 20 amp
7
A
N
R
C
U
E
S
S
P
A
R
O
Y
G
T
I
R
L
TM
BUILT TO LAST
Need
A
U
Q
Assistance?
Call Us First!
1-800-746-5641
A
M
!
PRECAUCION
!
PELIGRO
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
PRECAUCION
Page 34

34 Sp
ocasionarle heridas leves o moderadas
si ignora la advertencia. Igualmente, le
puede indicar una situación que podría
ocasionarle daños a su propiedad.
NOTA: Ésto le indica cualquier
información adicional sobre el
producto o el uso adecuado del mismo.
El soplete
siempre
tiene “corriente eléctrica” (o podría
tenerla) cuando la unidad está encendida
(Sólo en el modelo WG3000).
Siempre mantenga un
extingidor de incendio
accesible cuando esté soldando con
arcos eléctricos.
● Antes de encender o darle servicio a
las soldadoras eléctricas de arco,
debe leer y comprender todas las
instrucciones. Si no sigue las
medidas de seguridad e
instrucciones suministradas en el
manual, podría ocasionarle daños al
equipo, y/o sufrir heridas graves o
la muerte.
● Todos los trabajos de instalación,
mantenimiento, reparación y
operación de esta soldadora deben
ser hechos por una persona
calificada siguiendo los códigos
nacionales, estatales y
locales.
¡El uso inadecuado de soldadoras de
arcos eléctricos de arco podría
ocasionarle choques eléctricos, heridas
y la muerte! Siga todas las
instrucciones suministradas en este
manual para reducir las posibilidades
de electrocutamiento.
● Cerciórese de que todos los
componentes de la soldadora de
arcos eléctricos estén limpios y en
buen estado antes de utilizarla.
Cerciórese de que los forros
aislantes de todos los cables, pinzas
porta-electrodos y cordones
eléctricos no estén dañados.
Siempre repare o reemplace las
piezas dañadas antes de utilizar la
soldadora. Siempre mantenga todas
las tapas de la soldadora en su lugar
mientras la esté utilizando.
● Siempre use vestimenta adecuada
para soldar que esté seca, al igual
que guantes y zapatos aislantes
para soldadores.
● Use la soldadora sólo en áreas
limpias, secas y bien ventiladas. No
la use en áreas húmedas, mojadas o
que no estén bien ventiladas.
● Antes de comenzar a soldar con esta
soldadora, cerciórese de que la
pieza esté bien fija y conectada a
tierra.
● Debe desenrollar los cables de la
soldadora para evitar que se
sobrecalienten y se les dañe el forro
aislante.
¡Nunca
sumerja
el alambre ni la pistola en agua! Si la
soldadora se moja por cualquier motivo,
cerciórese de que esté completamente
seca antes de tratar de usarla.
● Siempre apague la unidad y
desconéctela antes de moverla a
otro sitio.
● Siempre conecte el cable de
conexión a tierra primero.
● Cerciórese de que la pieza esté
conectada a tierra adecuadamente.
● Siempre apague la soldadora de
arcos eléctricos y córtele el resto de
alambre a la pistola cuando no la
esté usando.
● Nunca toque el alambre de
fundente y la tierra o pieza
conectada a tierra al mismo tiempo.
● Al soldar en ciertas posiciones o
condiciones puede tener peligro de
electrocutamiento. Al estar en
cuclillas, arrodillado o en alturas,
cerciórese de aislar todas las piezas
que puedan conducir electricidad,
use ropa adecuada para soldar y
tome precauciones para no caerse.
● Nunca trate de usar este equipo con
corrientes eléctricas o ciclajes
diferentes a los especificados en las
etiquetas.
● Nunca use una soldadora eléctrica
para descongelar tuberías que se
hayan congelado.
Las chispas y el metal caliente
le pueden ocasionar heridas.
Cuando la pieza que soldó se enfrie, la
escoria podría despegarse. Tome todas
las precauciones descritas en este
manual para reducir las posibilidades
de que sufra heridas por estas razones.
● Sólo use máscaras aprobadas por la
organización norteamericana ANSI
o anteojos de seguridad con
protección lateral al tratar de cortar
o esmerilar piezas de metal.
● Si va a soldar piezas que estén por
encima de usted debe protegerse
los oidos para evitar que le caigan
residuos adentro.
Al soldar con arcos eléctricos
se producen luces intensas,
calor y rayos ultravioletas. Éstos le
podrían ocasionar heridas en la vista y
la piel. Tome todas las medidas de
precaución descritas en este manual
para reducir las posibilidades de
heridas en la vista o la piel.
● Todos los operadores o personas
que se encuentren en el área de
trabajo mientras estén usando el
equipo deben usar la vestimenta
adecuada incluyendo: máscara de
soldador con los niveles de
oscuridad especificados en la tabla a
continuación, ropa resistente al
fuego, guantes de cuero para soldar
y zapatos de protección.
Nunca
mire
hacia el área donde esté soldando sin
protegerse la vista tal como se ha
descrito anteriormente. Nunca use
lentes oscuros que estén partidos,
rotos o de un número menor de 10.
Adviértale a las otras personas en el
área que no deben mirar el arco.
¡Al soldar con arcos eléctricos
puede crear chispas y calentar
el metal a temperaturas que le podrían
ocasionar quemaduras graves! Use
guantes y ropa de protección para
hacer este tipo de trabajo. Tome todas
las medidas de precaución descritas en
este manual para reducir las
posibilidades de quemarse la piel o la
ropa.
● Cerciórese de que todas la personas
que se encuentren en el área de
trabajo estén protegidas contra el
calor, las chispas, y los rayos
ultravioletas. Utilice máscaras y
barreras antillamas cuando sea
necesario.
● Nunca toque las piezas que ha
soldado hasta que éstas se hayan
enfriado por completo.
¡El calor y las chispas
producidas al soldar con arcos
eléctricos y otros trabajos con
metales podrían encender materiales
inflamables o explosivos! Tome todas
las medidas de precaución descritas en
este manual para reducir las
posibilidades de llamas o explosiones.
● Mueva todos los materiales
inflamables que se encuentren en
un perimetro de 10,7 m (35 pies) del
área. Si no lo puede hacer, deberá
Soldadora Con Arco Con Alambre Continuo
Medidas de Seguridad
(Continuación)
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
PELIGRO
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
Page 35

su país. En EUA le recomendamos
que lea la publicación P-1 de la CGA.
Nunca use
gases
inflamables con soldadoras de gases
inertes (MIG). Sólo use gasesinertes o
gases no inflamables tales como
dióxido de carbono, argón, helio o
mezclas de uno ó más de estos gases
apropiados para usarse para soldar con
gases inertes.
Nunca
alce los
cilindros por las válvulas o tapas ni
utilice cadenas o eslingas para hacerlo.
MEDIDAS DE SEGURIDAD
ADICIONALES
Aquellas personas que vivan y trabajen
en los Estados Unidos deben percatarse
de que según las leyes de este pais los
siguientes códigos aplican para el
trabajo con soldadoras :
ANSI Standard Z49.1, OSHA 29 CFR
1910, NFPA Standard 70, CGA Pamphlet
P-1, CSA Standard W117.2, NFPA
Standard 51B ANSI Standard Z87.1.
Aquellas personas que residan en paises
latinoamericanos deben consultar los
códigos y regulaciones que se apliquen
en sus respectivos paises. Igualmente,
todos los usuarios deben consultar las
medidas de seguridad suministradas
por los fabricantes de los productos que
vayan a utilizar.
Al ubicacar la soldadora en un sitio
adecuado puede aumentar el
rendimiento, la fiabilidad y la duración
de la soldadora de arcos eléctricos.
● Para obtener mejores resultados
ubique la soldadora en un área que
esté limpia y seca. El polvo y las
impurezas en la soldadora acumulan la humedad y aumenta el
desgasto de las piezas movibles.
● Coloque la soldadora en un área
donde tenga por lo menos 30,48 cm
(12”) de espacio para ventilación al
frente y detrás de la unidad.
Mantenga despejada el área de
ventilación.
● Almacene los alambres en un sitio
limpio, seco y con poca humedad
para conservar la capa de fundente.
● El tomacorrientes que use para
conectar la soldadora debe estar
conectado a tierra adecuadamente
y la soldadora debe ser el único
artefacto conectado a este circuito.
Vea la tabla de Circuitos y Amperios
en la página 1 donde se le dan
instrucciones al respecto.
cubrirlos con algún material que los
aisle del fuego.
● No use una soldadora de arcos
eléctricos en áreas donde pueda
haber vapores inflamables o
explosivos.
● Tome todas las precauciones
necesarias para evitar que las
chispas y el calor ocasionen llamas
en áreas poco accesibles, ranuras,
detrás de divisiones, etc
.
¡Peligro de incendio! No
suelde envases o tuberías que
contengan o hayan contenido
materiales inflamables o combustibles
gaseosos o líquidos.
Si suelda cilindros cerrados o
tambores con soldadoras de
arcos eléctricos podría ocasionar
explosiones si éstos no están bien
ventilados! Cerciórese de que cualquier
cilindro o envase que vaya a soldar
tenga un orificio de ventilación para
liberar los gases.
No respire los gases emitidos
al soldar con arcos eléctricos.
Éstos son peligrosos. Si no puede
ventilar adecuadamente el área de
trabajo, cerciórese de usar una máscara
para respirar.
● Mantenga la cabeza y la cara
alejada de los humos emitidos al
soldar.
● Para soldar metales galvanizados o
con baños de cadio, metales que
contengan zinc, mercurio o berilio
con arcos eléctricos debe tomar las
siguientes precauciones:
a. Quítele la capa al metal.
b. Cerciórese de que el área de
trabajo esté bien ventilada.
c. Use un máscara para respirar.
Estos metales emiten humos
sumamente tóxicos al calentarse.
El campo electro-magnetico
generado al soldar con arcos
eléctricos podría interferir
con el funcionamiento de varios
artefactos eléctricos y electrónicos
tales como marcapasos. Aquellas
personas que usen estos artefactos le
35 Sp
WG3000 y WG3060
deben consultar a su médico antes de
soldar con arcos eléctricos.
● Coloque los cables de la pistola y de
trabajo juntos y únalos con cinta
pegante si es posible.
● Nunca se enrolle los cables de la
soldadora en el cuerpo.
● Siempre coloque todos los cables de
modo que estén del mismo lado del
cuerpo.
● El contacto con los campos
electromagnéticos producidos al
soldar pueden ocasionar problemas
de salud desconocidos hasta ahora.
Cercióre-
se de que
el área de trabajo esté libre de peligros
(chispas, llamas, metales al rojo vivo o
escorias) antes de irse. Cerciórese de
que ha apagado la soldadora y le ha
quitado el electrodo. Cerciórese de que
los cables estén enrollados y almacenados. Cerciórese de que tanto el metal
como la escoria se hayan enfriado.
Los cilindros pueden explotar
si están dañados. Estos
cilindros contienen gases a
presiones muy altas. Si están dañados,
los cilindros pueden explotar. Como
generalmente se utilizan cilindros de
gases para soldar, cerciórese de
manipularlos con mucho cuidado.
● Proteja los cilindros de gases
comprimidos contra temperaturas
excesivas, golpes, caídas y arcos
eléctricos.
● Instale los cilindros en posición
vertical y asegúrelos con una cadena
a una base fija o a la basee de la
unidad para evitar que se caigan o
se viren.
● Mantenga los cilindros alejados del
área donde esté soldando o de otros
circuitos eléctricos.
● Nunca permita el contacto entre el
electrodo y los cilindros.
● Use sólo cilindros, reguladores,
mangueras y conectores adecuados
para el tipo de gases utilizados para
soldar; manténgalos en buenas
condiciones de trabajo.
● Voltée la cara, en dirección opuesta
a la salida de la válvula, cuando la
esté abriendo.
● Siempre mantenga la válvula
tapada excepto cuando esté usando
el cilindro o lo tenga conectado
para trabajar.
● Lea las instrucciones sobre cilindros
para almacenar gases disponibles en
Medidas de Seguridad
(Continuación)
Instalación
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
PELIGRO
!
PELIGRO
!
ADVERTENCIA
Page 36

2. Enrosque los tornillos en la pata y la
soldadora.
Modelo WG3060
PARA ENSAMBLAR EL MANGO
1. Coloque el ensamblaje del mango en
la tapa delantera de la soldadora
soldadora.
2. Enrosque los tornillos en los
extremos del mango y la soldadora.
PARA ENSAMBLAR LA RUEDA
Y EL EJE
1. Conecte el eje a la soldadora con los
tornillos suministrados.
2. Introduzca las ruedas en el eje y
golpée ligeramente las tapas de
las ruedas.
PARA ENSAMBLAR LA ABRAZADERA
DEL CILINDRO DE GAS
1. Coloque la abrazadera en la
soldadora y alinée los orificios.
2. Enrosque los tornillos en la
abrazadera y la soldadora.
PARA ENSAMBLAR LA PATA
1. Colóquele la pata a la soldadora y
alinée los orificios con los de la
unidad.
2. Enrosque los tornillos en la pata y la
soldadora.
Pinza (Todas Los Modelos)
1. Aflójele la tuerca hex a la pinza.
2. Introduzca el cordón a través del
mango de la pinza y deslice el
extremo pelado (sin forro) dentro de
la pinza. Apriete la tuerca hex y
cerciórese de que el alambre esté
asegurado (Figura 4).
● No es recomendable que use un
cordón de extensión con este tipo
de soldadoras. La baja de voltaje en
el cordón de extensión podría
reducir el rendimiento de la soldadora.
Modelo WG3000
Los componentes de la soldadora
enumerados a continuación vienen
en el compartimiento para
alamcenar el alambre. Ábralo y
sáquelos.
PARA ENSAMBLAR EL MANGO
1. Sáquele los tornillos al mango.
Deslice el mango entre la tapas
delantera y superior de la soldadora
y alinée los orificios del mango con
los ubicados en la tapa superior.
2. Introduzca los tornillos en los orificios
de la tapa superior y el mango.
PARA ENSAMBLAR LA RUEDA
Y EL EJE
1. Coloque las bases dentro de las
ranuras de la soldadora.
2. Introduzca el eje en las bases y
empuje con fuerza las ruedas hasta
que calcen en su sitio.
3. Asegure las ruedas con los ganchos
en e suministrados y colóqueles las
tapas.
PARA ENSAMBLAR LA ABRAZADERA
DEL CILINDRO DE GAS
1. Coloque la abrazadera en la
soldadora y alinée los orificios.
2. Enrosque los tornillos en la
abrazadera y la soldadora.
PARA ENSAMBLAR LA PATA
1. Colóquele la pata a la soldadora y
alinée los orificios con los de la
unidad.
36 Sp
Soldadora Con Arco Con Alambre Continuo
Instalacion del alambre
Los
terminales, el rollo de alambre, las pinzas, la
conexión del cable de la pistola y el
alambre para soldar podrían tener
tensión inclusive cuando el interruptor de
la pistola esté desactivado. No los toque
cuando la soldadora esté encendida.
NOTA: Antes de instalar el alambre para
soldar, cerciórese de que su diámetro sea
similar al de la ranura de la bobina en el
mecanismo de alimentación y el de la punta
de contacto de la pistola. De lo contrario el
alambre podría salirse o enrollarse.
1. Cerciórese de que la soldadora esté
apagada y levántele la tapa para
tener acceso al mecanismo de alimentación.
2. Para desactivarle el seguro al carre-
te, oprímalo y gírelo en sentido
contrario a las agujas del reloj 1/4 .
Ahora puede sacarle la perilla, el
resorte y el separador.
NOTA: Los separadores de la bobina y
el carrete actuan como un adaptador
para el carrete de 20,32 cm. No es
necesario que compre un adaptador.
*Vea las instrucciones de ensamblaje
en la Figura 5.
Ensamblaje
Figura 2 - Ensamblaje del modelo
WG3000
Figura 3 - Ensamblaje del Modelo
WG3060
Instalación (Continuación)
Bloque de la
Pinza
Figura 4 - Ensamblaje de la Pinza
Tornillo de
tensión
Panel
Rodillo del
eje de
transmisión
Separador
de la
bobina
Tubo
Guía
Bobina
Carrete de
10,16 u 20,32
cm (4” u 8”)
Resorte
Seguro
de la
bobina
Figura 5 - Para Colocar el Alambre
Separador
de la bobina
*Invierta la posición
e introduzca el
carrete de 20,32 cm
!
ADVERTENCIA
Page 37

37 Sp
WG3000 y WG3060
3. Afloje el tornillo que le suministra
tensión al alambre en el mecanismo.
Ésto le permite meter con la mano el
alambre en la pistola.
4. Coloque el carrete de alambre en el
eje de modo que salga por el extremo
más cercano al tubo de alimentación.
No corte el alambre todavía. Instale el
separador, el resorte y la manilla
girándolo 1/4 en el mismo sentido de
las agujas del reloj.
5. Sostenga el alambre y córtele el
extremo. No permita que el alambre
se desenrolle. Cerciórese de que éste
esté derecho y sin rebabas.
6. Coloque el alambre a través del tubo
de alimentación, la ranura de la bobina
y la pistola. Apriete bien el tornillo de
tensión. No la apriete en exceso.
7. Para desconectar la boquilla, gírela en
sentido contrario a las agujas del reloj.
Después, desconecte la boquilla de
contacto del extremo del soplete (Vea
la Figura 6). Conecte la soldadora a un
tomacorrientes adecuado.
IDEA: Para alimentar el alambre,
mantenga el cable del soplete derecho.
8. Encienda la soldadora y fije la
velocidad a 5. Active el interruptor
de la pistola hasta que el alambre
haya salido por el extremo del
soplete. Apague la soldadora.
9. Cuidadosamente coloque el sistema
de contacto y atorníllelo al extremo
del soplete. Para instalar la boquilla,
gírela en el mismo sentido de las
agujas del reloj(Vea la Figura 6).
Corte el alambre a aproximadamente
6,4 mm (1/4”) de la boquilla.
POLARIDAD
Para soldar con gases revestidos, conecte
el cable del soplete al (+) y el cable de la
mordaza al (-) en el panel delantero. Para
soldar con alambres con fundente
revestido (sin gas), conecte el soplete al (-)
y la pinza al (+).
CICLO DE TRABAJO / PROTECCION
TERMICA
El ciclo de trabajo de la soldadora es el
porcentaje de tiempo que está soldando
durante un período de 10 minutos. Por
ejemplo, si el ciclo de trabajo es de 10%,
sólo podrá soldar durante un minuto, y la
soldadora se debe enfriar por 9 minutos.
Las piezas internas de esta soldadora
están protegidas con un interruptor
térmico automático. Una luz amarilla,
ubicada al frente, se enciende cuando
excede el ciclo de trabajo. Podrá
continuar soldando una vez que la luz
amarilla se haya apagado.
MODELO WT1000
1. Haga fuerza en las pestañas con un
desarmador para sacar el soporte de
los lentes de la máscara.
2. Quítele la capa protectora que se
encuentra a ambos lados de la
cubierta de los lentes. Coloque una
cubierta clara a cada lado de los lentes
oscuros. Coloque los tres lentes juntos
en la máscara y sosténgalos con el
retenedor. Éste debe calzar en la
segunda apertura de la máscara.
3. Coloque uno de los orificios del brazo
de ajuste en los pasadores ubicados a
los lados de la máscara (por donde
estarían las orejassuyas al ponersela).
Este brazo le permite ajustar la
cercania y lo puede ajustar facilmente.
4. Coloque la armazón dentro de la
máscara. Luego coloque los tornillos
de cabeza redonda y apriete la tuerca
de tensión tal como se muestra. No
apriete la tuerca completamente.
5. Pruébesela, ajústela hasta que le
quede bien y cúbrase la cara. Si la
máscara le queda muy lejos o muy
cerca de la cara, use otro de los
orificios del brazo de ajuste. Ajuste la
tuerca de tensión de modo que pueda
cubrirse la cara con la máscara con sólo
mover la cabeza.
¡El mane-
jo o mantenimiento inadecuado de los cilindros de
gas y reguladores podría ocasionarle
heridas graves o la muerte! Siempre use
las abrazaderas para fijar los cilindros a
una pared u otra superficie estable, para
evitar que los cilindros se caigan. Lea,
comprenda y siga todas las instrucciones
sobre el uso adecuado y peligro al usar
este tipo de equipos que le suministramos
en las instrucciones de seguridad.
NOTA: No necesitará usar gas cuando use
alambre de fundente revestido para
soldar.
TIPO DE GASES
Hay 3 tipos de gases que generalmente se
usan para soldar con arco; 100% argón,
una mezcla de 75% argón y 25% dióxido
de carbono (C
25
) o 100% dióxido de
carbono. Sin embargo, no es
recomendable que utiliice 100% dióxido
de carbono., ya que los resultados no son
óptimos. Esta soldadora no suelda muy
bien al utlizar 100% dióxido de carbono.
Todos se pueden usar, pero la mezcla
75/25 es la recomendada para todo tipo
de soldaduras. En cualquier tienda
especializada en artículos para soldar
puede compar los cilindros de estos gases.
Cerciórese de que el cilindro esté bien
sujeto para evitar que se caiga.
NOTA: El uso de un gas inadecuado podría
ocasionar poca o ninguna penetración del
electrodo para soldar (alambre).
REGULADOR
El regulador le permite el suministro de
gas a una presión constante al igual que
un flujo al soldar. Cada regulador está
diseñado para usarse con gases o mezclas
de gases especificos. Argón y las mezclas
de argón usan roscas similares. El dióxido
carbónico puro (100%) usa una rosca
diferente. Puede comprar un adaptador
en una tienda para soldadores para
cambiar de uno a otro.
Cuello del
Soplete
Boquilla de
Contacto
Boquilla
Figura 6 - Boquilla del Soplete
Especificaciones de la boquillas de Contacto
Diám. del alambre mm
0,024” ó 0,6
0,030” ó 0,8
0,035” ó 0,9
0,040” ó 1,0
Ensamblaje
(Continuacion)
Figure 7
Armazón
Máscara
Lentes Oscuros
Cubierta Clara de los Lentes (2)
Pestaña
Soporte de los lentes
Brazo de
Ajuste (2)
Tuerca de Tensión (2)
Perno Prisionero (2)
Ensamblaje del
Casco
Instalación de la
Botella de Gas
!
PELIGRO
Page 38

38 Sp
Soldadora Con Arco Con Alambre Continuo
COMO HACER LAS CONEXIONES
El cilin-
dro de
gas está bajo una presión muy alta.
Dirija la salida del cilindro en dirección
opuesta a Ud. y otras personas antes de
abrirlo.
1. Estas unidades pueden utilizar
botellas de 0,56 m
3
.
2. Después que el cilindro esté bien
instalado, destápelo, párese en el
lado opuesto de la salida del cilindro
y comience a abrir la válvula
lentamente, girándola en sentido
contrario al de las agujas del reloj.
Cuando el cilindro comience a emitir
gas, cierre la válvula girándola en el
mismo sentido de las agujas del reloj.
Así eliminará las impurezas que se
hayan acumulado en el asiento de la
válvula.
3. Instálele el regulador a la válvula del
cilindro manteniendo las esferas del
manómetro en posición vertical y
enrosque la tuerca del vástago en la
válvula de gas.
4. Conecte uno de los extremos de la
manguera de gas al conector ubicado
en la parte posterior de la soldadora
y el otro extremo al regulador
usando las abrazaderas para hacer
estas conexiones. Cerciórese de que
la manguera de gas no esté enrollada
o doblada.
5. Una vez más, párese en el lado
opuesto a la salida del cilindro y abra
la válvula lentamente. Cerciórese de
que las conexiones no tengan fugas.
6. Oprima el gatillo de la pistola para
permitir el flujo de gas. Mantenga el
gatillo oprimido mientras ajusta el
regulador de gas a 0,85 cmh*. Suelte
el gatillo.
*NOTA: El regulador WT600100AV de
Campbell Hausfeld viene fijado de
fábrica a 0,85 cmh. No necesita
ajustarlo. Igualmente, el regulador
tiene un indicador que le permite ver la
cantidad de gas que hay en el cilindro.
Cuando el indicador no esté extendido,
el cilindro estará totalmente vacío en
aproximadamente 10 minutos.
7. Recuerde de cerrar la válvula de gas
cuando termine de soldar.
1. Cerciórese de leer,
comprender y cumplir con
todas las medidas de
precacución enumeradas en
la sección de Informaciones
Generales de Seguridad de este
manual. Igualmente, debe leer la
sección Instrucciones para soldar en
este manual antes de usar la
soldadora.
2. Cerciórese de que la soldadora esté
apagada (en OFF).
3. Cerciórese de que las superficies de
los metales que va a soldar no estén
sucias, oxidadas, pintadas, llenas de
aceite o contaminadas. Esto podría
dificultarle el trabajo y perjudicar la
calidad de la soldadura.
Todas las personas que usen
esta soldadora o que se
encuentren en el área de trabajo
cuando se esté usando la soldadora
deben usar la vestimenta adecuada de
un soldador incluyendo: lentes para
soldadores de la oscuridad adecuada
según las especificaciones dadas a
continuación, ropa resistente al fuego,
guantes de cuero para soldar y
protección para los pies.
SI EL
GATILLO
ESTA OPRIMIDO O NO, el alambre
de la soldadora WG3000 tiene
TENSIONELECTRICA cuando está
ENCENDIDA.
Si piensa calentar soldar o
cortar materiales galvanizados, cubiertos de zinc, plomo o cadium
vea las instrucciones al respecto en la
sección Informaciones Generales de
Seguridad. Al calentar estos metales se
emiten gases muy tóxicos.
4. Conecte la pinza de conexión a tierra
a la pieza que va a soldar o a la
banca (si es de metal). Cerciórese de
que el contacto sea con el metal y
que no éste no tenga pintura, barniz,
óxido o materiales no metálicos.
5. Coloque la perilla de control de
amperaje, ubicada en la parte
delantera, en el valor deseado.
Vea las instrucciones al respecto en la
tabla ubicada detrás de la puerta del
compartimiento para almacenar el
alambre.
NOTA: Estas instrucciones son sólo
sugerencias. El amperaje necesario
podría variar según las condiciones de
trabajo y los materiales.
6. Gire la perilla que controla la
velocidad del alambre hasta el
número 5 para comenzar a soldar,
haga una prueba y ajuste la
velocidad si es necesario.
7. Conecte el cordón eléctrico a un
tomacorrientes con el voltaje
necesario que esté conectado a un
circuito adecuado (Vea las
instrucciones al respecto en la tabla
de la página 1).
8. Encienda la soldadora (Coloque el
interruptor en ON).
9. Cerciórese de que haya
aproximadamente 6,4 mm (1/4”) de
alambre fuera de la boquilla de
contacto. De lo contrario, oprima el
gatillo de modo que salga más
alambre y córtelo a la longitud
adecuada.
10. Coloque la pistola soldadora cerca
de la pieza que va a soldar y mueva
la cabeza hacia abajo de modo que
la máscara del casco le cubra la cara
o cúbrase la cara con la máscara de
mano y oprima el gatillo de la
pistola. Ajuste el amperaje cuando
sea necesario.
Indicador
Tapa
Adaptador para CO
2
INSTALACION PARA
ARGON O MEZCLAS DE
ARGON
INSTALACION
PARA CO
2
Figura 8 - Conexiones
Funcionamiento
O
Instalación de la
Botella de Gas (Continuacion)
!
ADVERTENCIA
MANUAL
!
PELIGRO
!
PRECAUCION
!
ADVERTENCIA
Page 39

ALAMBRE DE ALUMINIO
Cuando utilice alambres de alumnio es
recomendable que utilice una boquilla
más grande. Por ejemplo:
• Si el diámetro es 0,8 mm use una
boquilla de 0,9mm.
Cuando utilice alambres MIG de 0,80,9mm o alambres de aluminio utilice
la ranura grande, tal como viene de
fábrica. Los alambres de aluminio son
muy débiles y no debe usarse la misma
tensón en el portabobina que cuando
utilice alambres de fundente revestido
o MIG. Para fojarle la tensión a los
alam,bres de aluminio apriete el
tornillo de tensión dándole 3 vueltas, o
hasta que el portabobinas comience a
ejercer tensión y el alambre comience a
entrar.
seleccione un carrete que lo vaya a
usar en un plazo de aprox. 6 meses.
Para soldar aceros dulce le recomendamos que use alambres sólidos AWS
ER70S6 o alambre de fundente AWS
E71T-GS.
• Boquillas de contacto - use las
boquillas Campbell Hausfeld,
Tweco
®
, u otras boquillas compatibles.
• Boquillas - use boquillas tipo Tweco
®
style u otras boquillas compatibles. Use
las boquillas Campbell Hausfeld,
modelo WT5021, disponible en la
tienda donde compró la soldadora, o
use boquillas tipo Tweco
®
(u otras
boquillas compatibles) disponibles en
tiendas locales para soldadores.
Como cambiar de alambres
PORTABOBINAS
Hay dos ranuras en el portabobinas. La
pequeña es para los carretes de 0,6mm
(0,024 ) y al otra para carretes de 0,8 0,9 mm (0,030 - 0,035). Destape el
portabobinas y voltéelo para
seleccionar la ranura correcta(vea la
lista de piezas).
ALAMBRE DE DUNDENTE
REVESTIDO
Debido a las inconsistencias del
diámtro del alambre, es recomendable
que utilice una boquilla más grande.
Por ejemplo:
• Si el diámetro es 0,8 mm use una
boquilla de 0,9mm.
• Si el diámetro es 0,9 mm, use una
boquilla de 1,0 mm.
Esta soldadora viene de fábrica lista
para utilizar alambres de 0,9 mm y con
una boquilla de 1,0 mm. Como esta
soldadora utiliza alambres de fundente
revestido de 0,8 y 0,9 mm, debe
utilizarse como viene de fábrica.
ALAMBRES DE GASES INERTES
(MIG)
Como este tipo de alambres son de un
diámetro bastante consistente, la
boquilla de contacto debe ser del
mismo diámetro del alambre utilzado.
Cuando utilice un alambre de 0,6 mm ,
use la ranura pequeña del
portabobinas. Cuando utilice alambres
MIG de 0,8-0,9mm o alambres de
aluminio utilice la ranura grande, tal
como viene de fábrica.
39 Sp
WG3000 y WG3060
11. Cuando termine de soldar, apague
la soldadora y guárdela en un sitio
adecuado.
Descon-
ecte y
apague la soldadora antes de
inspeccionar o darle servicio a
cualquier componente. Mantenga el
compartimiento para almacenar
alambres cerrado a menos que necesite
cambiar el alambre.
Antes de cada uso:
1. Chequée los cables y repare o
reemplace inmediatamente
cualquier cable cuyo forro aislante
esté dañado.
2. Chequée el cordón eléctrico y
repárelo o reemplácelo
inmediatamente si está dañado.
3. Chequée la boquilla de la pistola.
Quítele cualquier residuo de escoria.
Reemplace la boquilla si está
dañada.
Nunca
use esta
soldadora si los forros aislantes de
alguno de los cables, la pistola o el
cordón eléctrico están dañados o no
están colocados.
Cada 3 meses:
1. Reemplace cualquier etiqueta que
esté ilegible.
2. Use aire comprimido para limpiar las
aperturas de ventilación.
3. Limpie la ranura donde se coloca el
alambre en la bobina. Saque el
alambre del mecanismo de
alimentación, sáquele los tornillos a
la cubierta de la bobina. Use
un cepillo de alambres pequeño para
limpiar la bobina. Reemplácela si
está desgastada o dañada.
Piezas Consumibles o Que se
Desagstan
Las siguientes piezas requieren
mantenimiento rutinario:
• Bobina
• Forro de la pistola - reeplácelo
cuando se desgaste
• Boquilla/boquillas de contacto
• Alambre - Esta soldadora le permite
usar carretes de 10,16 cm (4”) u
20,32 cm (8”) de diámetro. El
alambre para soldar es susceptible a
la humedad y se oxida con el tiempo,
por lo tanto es muy importante que
MIG
WT5011
Figura 9 - Boquilla
Comuníquese con el
distribuidor de Campbell
Hausfeld más cercano a su
domicilio para ordenar
repuestos.
Funcionamiento
(Continuacion)
Mantenimiento
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
Page 40

Alambre sólido
ER - 70 S - 6
Resistencia,
multiplicada por
10.000 libras por
pulgadas al cuadrado
Alambre sólido
Componentes
Con esta soldadora le recomendamos
que use el alambre ER-70S6.
ANGULA PARA SOLDAR
Éste es el ángulo en el que mantiene el
electrodo para soldar. Si usa el ángulo
adecuado logrará la penetración y
acabado perfecto de la unión. Este
ángulo tiene dos aspectos - ángulo de
desplazamiento y ángulo de trabajo (Vea
la Figura 10).
El ángulo de desplazamiento es el
ángulo en la línea donde se está
soldando y puede variar entre 5º y 45º
de la línea vertical, según sean las
condiciones de trabajo.
El ángulo de trabajo es el ángulo desde
la línea horizontal, medido en ángulos
rectos en relación a la línea de soldar.
Para la mayoría de las aplicaciones se
puede usar ángulos de desplazamiento
y de trabajo de 45º. Para aplicaciones
especificas, debe consultar un libro de
referencias para soldadores.
VELOCIDAD DE ALIMENTACION DEL
ALAMBRE
Esta velocidad se controla con la perilla
ubicada en el frente de la soldadora.
debe coordinar la velocidad con la
rapidez con que se esta derritiendo el
alambre en el arco. Esta coordinación
es el factor más importante en este
tipo de soldadura. Antes de comenzar
a soldar haga una prueba en un
pedazo de metal del mismo tipo y
grosor que la pieza de trabajo.
Comience a soldar moviendo con una
mano la boquilla de la pistola por el
pedazo de metal y ajustando la
velocidad con la otra mano. Si la
velocidad es muy lenta ocasionaría
chisporroteo y el alambre se quemaría
dentro de la punta de contacto (Vea la
Figura 12). Si la velocidad es muy
rápida ocasionaría un sonido de
chisporreteo y el alambre penetraría la
placa antes de derretirse. Un sonido
parejo le indicará que la velocidad está
coordinada. Para soldar aluminio, la
velocidad del alambre es típicamente
más alta (de 7 - 9).
usada depende del tamaño (diámetro)
y tipo del alambre usado, la posición
de la soldadura y el grosor de la pieza
de trabajo.
Vea las especificaciones enumeradas en
la soldadora o en la tabla generalizada
en la sección de funcionamiento. Le
sugerimos que antes de soldar
practique en un pedazo de metal que
vaya a descartar para que ajuste los
niveles y compare la calidad de la
soldadura con las de la Fig. 11.
TIPO Y TAMANO DEL ALAMBRE
La selección del tipo correcto de
alambre depende de varios factores
tales como la posición en que va a
soldar, el tipo de material que va a
soldar, el grosor y las condiciones de la
superficie. La sociedad norteamericana
de soldadores , AWS, ha seleccionado
ciertos requerimientos para cada tipo
de alambres.
Alambre de fundente revestido
E - 7 0 T - GS
Resistencia,
multiplicada por
10.000 libras por
pulgadas al cuadrado
Posiciones (0 por
plana u horizontal, 1
por cualquier
posición)
Tipo tubular con
fundente
Tipo de fundente
Con esta soldadora le recomendamos
que use los alambres E71T-GS o E71
T-11.
General
Estas soldadoras se pueden utilizar para
soldar con alambres de fundente
revestido o para soldar metales con
arcos de gases inertes. La soldadura se
debe proteger contra contaminantes en
el aire mientras se esté derritiendo. Para soldar con un alambre con fundente
revestido se utiliza un alambre
cilindrico lleno de fundente. El
fundente crea un gas protector al
derretirse. El segundo proceso utiliza
un gas inerte para proteger la
soldadura mientras se derrite.
Cuando la corriente proviene de un
transformador (soldadora) y circula por
el circuito hasta llegar al alambre, se
forma un arco entre el extremo del
alambre y la pieza de trabajo. Este arco derrite el alambre y la pieza de trabajo. El metal derretido del alambre cae
dentro de la ranura en la pieza y se
forma la unión con la pieza de trabajo
tal como se muestra (Figura 10).
Tecnicas Basicas Para Soldar
Con Arcos
Hay cuatro aspectos que debe
considerar para lograr una soldadura
de alta calidad. Éstos son: el tipo de
alambre usado, el amperaje usado, el
ángulo para soldar, la longitud del arco
y la velocidad de desplazamiento. Es
imprescindible que siga las
recomendaciones al respecto para
lograr un acabado de alta calidad.
CORRIENTE
El nivel adecuado de corriente se logra
al ajustar la soldadora al amperaje
requerido.
La corriente representa la cantidad de
electricidad que en realidad circula y
ésta se regula con un interruptor en la
soldadora. la cantidad de corriente
40 Sp
Soldadora Con Arco Con Alambre Continuo
ANGULO DE DESPLAZAMIENTO
ANGULO PARA SOLDAR
5º - 45º
5º - 45º
Figura 11 - Ángulos para Soldar
Escoria
Soldadura
Alambre
Fundente
(Sólo
cuando no
se usa gas)
Pieza
Gas
Boquilla de
Contacto
Cráter
Boquilla
Figura 10 - Componentes de la Soldadura
Instrucciones para Soldar
Page 41

NOTA: Recuerde que debe limpiar las
escorias antes de cada paso cuando
esté soldando sin gas.
TECNICA USADA PARA SOLDAR
El tipo de material y el grosor de la pieza
que va a soldar determinan la dirección
en que debe colocar la boquilla de la
pistola. Para soldar materiales delgados
(de calibre 18 o mayores) o cualquier
tipo de aluminio debe colocar la
boquilla en frente del sedimento para
empujarlo a lo largo de la pieza. Para
soldar aceros gruesos, la boquilla se
debe dirigir directamente al sedimento
para aumentar la penetración. Esta
técnica se conoce como soldar al revés
(Vea la Figura 14).
PARA SOLDAR ALUMINIO
Cualquier pieza de aluminio que vaya a
soldar debe limpiarse bien con un cepillo
de acero inoxidable para eliminar
residuos de óxido en las superficies
donde soldará y las de conexión a
tierra. Para soldar aluminio debe
utilizar 100% Argón.Si no utiliza Argón,
será muy difícil que logre penetrar el
metal.
NOTA: Repita este proceso cada vez
que cambie el amperaje, el diámetro o
tipo de alambre o el tipo o grosor de la
pieza de trabajo.
VELOCIDAD DE DESPLAZAMIENTO
Es la velocidad con que se desplaza el
electrodo por el área a soldar. El
diámetro y tipo de electrodo, amperaje,
posición y el grosor de la pieza de
trabajo son algunos de los factores que
afectan la velocidad de desplazamiento
necesaria para lograr una soldadura de
primera (Vea la Fig. 12). Si la velocidad
es demasiado rápida, el reborde es
angosto y las ondas puntiagudas como
se muestra en la figura. Si la velocidad
es muy lenta, el metal soldado se
acumula y el reborde es alto y ancho.
Para soldar aluminio, la velocidad del
alambre es típicamente más alta.
LIMPIEZA DE ESCORIAS (SOLO
CUANDO HAYA SOLDADO CON
ALAMBRES DE FUNDENTE
Use ante-
ojos de
seguridad aprobados por la asociación
norteamericana ANSI (ANSI Standard
Z87.1) (o alguna organización similar en
sus respectivos países) y ropa de
protección para sacar la escoria. Los
residuos calientes le podrían ocasionar
heridas a las personas que se
encuentren en el área de trabajo.
Una vez que haya terminado de soldar,
espere a que las piezas soldadas se
enfríen. Una capa protectora que
llamaremos escoria cubre el reborde
para evitar que los contaminanates en
el aire reacionen con el metal
derretido. Cuando el metal se haya
enfriado un poco y no esté al rojo vivo,
podrá limpiar el escoria. Ésto lo puede
hacer con un martillo. Golpee
suavemente la escoria con el martillo
hasta que logre despegarla. Finalmente, use un cepillo de alambre para terminar de limpiar.
NOTA: Si suelda la misma área varias
veces, límpiele las escorias cada vez que
termine de soldar.
POSICIONES PARA SOLDAR
Básicamente hay 4 posiciones para
soldar: plana, horizontal, vertical y por
encima de la cabeza. Soldar en la
posición plana es lo más fácil ya que la
velocidad es mayor, el metal derretido
se chorrea menos, se puede lograr una
mayor penetración y el trabajador se
cansa menos. Para soldar en está
posición el ángulo de desplazamiento
del alambre debe ser 45º al igual que el
ángulo de trabajo.
Otras posiciones requieren técnicas
diferentes tales como paso entretejido,
circular o cruzado. Para completar este
tipo de soldadura se requiere más
experiencia en la materia.
Soldar por encima de la cabeza es la
posición más dificil y peligrosa. El
amperaje y el alambre usados varian
según la posición en que vaya a soldar.
Siempre debe tratar de soldar en una
posición plana. Para obtener
instrucciones especificas para algún tipo
de soldadura consulte un libro de
referencias para soldadores.
PASOS
Algunas veces deberá usar más de un
paso para soldar. Primero deberá hacer
un paso primordial, éste será seguido
por pasos adicionales de relleno (Vea la
Fig. 13). Si las piezas son gruesas, tal
vez sea necesario biselar los bordes
que están unidos en un ángulo de 60º.
41 Sp
WG3000 y WG3060
Amp. Normal, Long. del Arco,
Velocidad
Amperaje Muy Bajo
Amperaje Muy Alto
Velocidad del alambre es muy alta
Velocidad del Alambre
Muy Baja
Velocidad de
desplazamiento Muy Baja
Velocidad de
desplazamiento Muy
Alta
Metal Básico
Figura 12 - Apariencia de la Soldadura
Instrucciones para Soldar (Continuación)
Figura 13 - Pasos
Cubierta
Relleno
Raíz
!
ADVERTENCIA
Page 42

42 Sp
DIAGNOSTICO Diagóstico de Averías-Soldadora
Problema Posible(s) Causa(s) Acción a Tomar
1. Excedio el ciclo de trabajo
2. La pinza está mal conectada
3. El interruptor está dañado
4. El cortacircuito se activó o el
fusible está quemado
1. La boquilla de la pistola es de
un tamaño incorrecto
2. El forro de la pistola está
obstruído o dañado
3. La boquilla de la pistola está
obstruída o dañada
4. El rodillo está desgastado
5. No hay suficiente tensión
Hay escoria dentro de la boquilla
pistola
1. Hay mal contacto
2. Está usando un cordón de
extensión demasiado largo
1. El alambre está atascado
2. Se terminó el alambre
3. No hay suficiente tensión
4. El forro del alambre está dañado
5. El fusible está quemado
6. El alambre está desconectado
internamente
7. La boquilla de contacto está
obstruida
1. La velocidad de alimentación
es muy lenta
2. La velocidad de desplazamiento es
muy baja o la energía es muy alta
Para mayor Información Sobre Este Producto, Comuníquese con el Distibuidor más Cercano
1. Espere que la soldadora se enfríe, cuando el bombillo se
apague
2. Cerciórese de que las conexiones estén bien hechas y de
que la superficie esté limpia
3. Reemplace el interruptor
4. Reduzca la carga del circuito, active el cortacircuito o
reemplace el fusible
1. Use una boquilla adecuada
2. Límpielo o reemplácelo
3. Límpiela o reemplácela
4. Reemplácelo
5. Apriete el tornillo
Cerciórese de que todas las conexiones esten bien
aseguradas, y de que la superfice este limpia.
1. Cercórese de que todas las conexiones estén bien
aseguradas y que la superficie de contacto esté limpia
2. Nunca use cordones de extensión de más de 6,10 m (20
pies)
1. Recargue el alambre
2. Reemplace el carrete
3. Apriete los tornillos si el cable se desliza
4. Reemplace el forro
5. Reemplace el fusible en el tablero de control, dentro de la
soldadora (1,6 amp de accón retardada)
6. Llame al 1-800-746-5641 (en EUA) para recibir asistenciia
7. Reemplace la boquilla de contacto
1. Use velocidades entre 7 - 10
2. Aumente la velocidad de desplazamiento o disminuya la
energía
No funciona
El alambre se enrolla en la
bobina
Ocurre un arco entre la
boquilla de la pistola y la
superficie de trabajo
La pinza de trabajo y/o el
cable se calientan
El alambre no circula
(Aluminio) el alambre se
quema en el extremo de la
boquillla o (Aluminio) se
forman burbujas en el metal
o se funde completamente
Figura 14 - Pasos Múltiples
EMPUJE
HALE
Figura 15
1. Cerciórese de que la soldadora esté
APAGADA (OFF) y el cordón
Para Reemplazar el
Cable
Instrucciones para Soldar (Continuación)
Soldadora Con Arco Con Alambre Continuo
eléctrico esté desconectado del
tomacorrientes.
2. Destape la soldadora de modo que
tenga acceso a las piezas internas
del interruptor.
3. Desconecte los cables negro y
blanco que están conectados al
interruptor.
4. Desconecte el cable verde que está
conectado a la armazón de la
soldadora.
5. Afloje los tornillos del relevo de
tensión y desconecte el relevo de
tensión.
6. Para instalar el nuevo cordón siga
los pasos arriba enumerados en
orden contrario.
Page 43

1. Duración: El fabricante garantiza que reparará, sin costo alguno por repuestos o mano de obra la soldadora o la pistola o los cables que estén dañados bien
en material o mano de obre, durante los siguientes periodos después de la compra original:
Por 5 años: El transformador y rectificador de la soldadora
Por 3 años: Toda la soldadora (se excluyen: pinzas, pistola, cables, o accesorios que vienen con la soldadora)
Por 1 año: Pinzas, Pistola, Acessorios y Cable para Soldar (de haberlos)
2. QUIEN OTORGA ESTA GARANTIA (EL GARANTE):
The Campbell Group
A Scott Fetzer Company
100 Production Drive
Harrison, OH 45030
Teléfono: (513)-367-4811
3. BENEFICIARIO DE ESTA GARANTIA (EL COMPRADOR): El comprador original del producto Campbell Hausfeld.
4. Cobertura de la garantía: Defectos en material y fabricación que ocurran dentro del periodo de validez de la garantía. La garantía cubre la soldadora, el
transformador y rectificador, la pistola o el portaelectrodo y los cables sólamente.
5. Lo que no está cubierto por esta garantía:
A. Las garantías implicitas, incluyendo las garantías de comercialidad y conveniencia para un fin particular SON LIMITADAS A LA DURACION EXPRESA DE
ESTA GARANTIA. Después de este periodo, todos los riegos de pérdida, por cualquier razón, serán la responsabilidad del propietario del producto. En
algunos estados no se permiten limitaciones a la duración de las garantías implicitas, por lo tanto, en tal caso esta limitación o exclusión no es aplicable.
B. CUALQUIER PERDIDA, DAÑO INCIDENTAL, INDIRECTO O CONSECUENTE O GASTO QUE PUEDA PUEDA RESULTAR DE UN DEFECTO, FALLA O MAL
FUNCIONAMIENTO DEL PRODUCTO CAMPBELL HAUSFELD. En algunos estados no se permite la exclusión o limitación de daños incidentales o
consecuentes, por lo tanto, en tal caso esta limitación o exclusión no es aplicable.
C. Esta garantía no cubre aquellos accesorios que se desgastarán con el uso normal del producto; la reparación o reemplazo de los mismos será la
responsabilidad del propietario. Ejemplos de los productos de desgaste por el uso son (lista parcial): Bouillas de contacto, boquillas, forros internos de la
pistola, bobinas, felpa para limpiar el alambre . Además, esta garantía no cubre daños que ocurran al reemplazar o darle servicio a las piezas arriba
enumeradas.
D. Cualquier falla que resulte de un accidente, abuso, negligencia o incumplimiento de las instrucciones de funcionamiento y uso indicadas en el(los)
manual(es) que se adjuntan al producto.
E. Servicio antes de entrega, por ejemplo ensamblaje y ajustes.
7. Responsibilidades del Garante bajo esta Garantía: Reparar o reemplazar, como lo decida el garante, los productos o componentes defectuosos durante el
periodo de validez de la garantía.
8. Responsibilidades del Comprador bajo esta Garantía:
A. Entregar o enviar el producto o componente a Campbell Hausfeld. Los gastos de flete, si los hubiere, deben ser pagados por el comprador.
B. Ser cuidadoso con el funcionamiento del producto, como se indica en el(los) manual(es) del propietario.
9. Cuando efectuará el garante la reparación o reemplazo cubierto bajo esta garantía: La reparación o reemplazo dependerá del flujo normal de
trabajo del centro de servicio y de la disponibilidad de repuestos.
Esta garantía limitada le otorga derechos legales especificos y usted también puede tener derechos que varian de un estado a otro.
43 Sp
Reborde es muy delgado
en algunos sitios
Reborde es muy grueso en
algunos sitios
Los bordes de la soldadura
están disparejos
La soldadura no penetra el
metal que desea soldar
El electrodo salpica y se
pega
1. La velocidad de desplazamiento
varia
2. El nivel del amperaje es muy bajo
1. La velocidad de desplazamiento
varia o es muy lenta
2. El nivel del amperaje es muy alto
1. La velocidad de desplazamiento
es muy rápida
2. La velocidad de alimentación es
muy rápida
3. El nivel del amperaje es muy alto
1. La velocidad de desplazamiento
no es consistente
2. El nivel de energía es muy bajo
3. Se terminó el gas o el nivel de
gas es muy bajo
4. Está usando el gas incorrecto
(aluminio)
5. El cordón de extensión es muy largo
6. (Aluminio) Posiblemente se
están formando residuos de
óxido en la superficie
1. El alambre está húmedo
2. La velocidad del alambre está
muy rápida
3. Está utilizando el alambre
inadecuado
4. Se terminó el gas o el nivel de
gas es muy bajo
Diagóstico de Averías-Soldadura
Problema Posible(s) Causa(s) Acción a Tomar
1. Debe reducirla y mantenerla constante
2. Debe aumentarlo
1. Debe aumentarla y mantenerla constante
2. Debe bajarlo
1. Debe reducirla
2. Debe aumentarla
3. Debe bajarlo
1. Disminuya la velocidad y manténgala constante
2. Aumente el nivel de energía de suministro
3. Use gas, para soldar con gases inertes (MIG) o llene la
boqtella
4. Use sólo 100% Argón
5. Nunca use cordones de extensión de más de 6,10 m (20 pies)
6. Limpie bien la superficie con un cepillo de acero
inoxidable sólamente
1. Use un alambre seco y siempre debe almacenarlo e un
sitio seco
2. Reduzca la velocidad del alambre
3. Use alambre de fundente revestido cuando no esté
utilizando gases
4. Use gas, para soldar con gases inertes (MIG) o llene la
boqtella
Garantía Limitada 5-3-1
WG3000 y WG3060
Page 44

44 Sp
Alambrado Modelo WG3000
ON / OFF
MAX
MIN
Gun
Soldadora Con Arco Con Alambre Continuo WG3000
Blanco
Negro
Verde
T2
S5
T1
White
L2 (N)
Black
L1
S1
Green
M1
S5
Ground
S2
S3
2
1
S4
M
=
5 6 7 84321678
Page 45

45 Sp
Soldadora Con Arco Con Alambre Continuo WG3060
Alambrado Modelo WG3060
Negro
Blanco
Verde
LG
L2 (N) White
L1 (R) Black
Green
C1
S20127°
Ground
S1
1
2
3
4
A2
M1
A1
LV
T1
RD
M
5 6 7 8 9 104321
T2
S2
S3
K-A2
K
K-A1
Page 46

2
4
6
8
8
1
1
3
3
5
7
7
9 & 10
11
11 & 30
12
14
14
15
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
27
28
29
31
32
32
33
33
34
35
35
36
37
38
38
39
39
40
40
42
42
43
44
45
46
43
47
47
48
3
49
1
47
43
9 & 10
46 Sp
Para ordenar repuestos, comuníquese con el distribuidor
más cercano a su domicilio
Puede escribirnos a:
The Campbell Group
Attn: Parts Department
100 Production Drive
Harrison, Ohio 45030 U.S.A.
Sírvase suministrarnos la siguiente
información:
- Número del modelo
- Número de Serie (de haberlo)
- Descripción y número del repuesto
según la lista de repuestos
Soldadora Con Arco Con Alambre Continuo
MODELO WG3060
MODELO WG3000
50
** Boquilla de contacto (Vea la tabla en
la página 47)
40
40
Page 47

Gas Inerte (Mig) ER70S6 0,61 mm (,024”) WE300000AJ
Gas Inerte (Mig) ER70S6 0,76 mm (,030”) WE300500AJ
Gas Inerte (Mig) ER70S6 0,89 mm (,035”) WE301000AJ
Fundente E71T-GS 0,76 mm (,030”) WE200000AJ
Fundente E71T-GS 0,89 mm (,035”) WE200500AJ
1 Ensamblaje del soplete y manguera (Incluye Nos. 2-6, 34 y 50) WC600700AV WC600700AV 1
2 Cuerpo del soplete (Piezas posterior y delantera) WC600201AV WC600201AV 1
3 Colagadero WC600003AV WC600003AV 1
4 Boquilla, tipo Tweco
®
WT502100AJ WT502100AJ 1
5 Gatillo WC600202AV WC600202AV 1
6 Resorte de contacto del soplete WC600203AV WC600203AV 1
7 Pinza (No incluye el cordón) WC100100AV WC100100AV 1
8 Cable para soldar 8 AWG (1,83 m) ❋ ❋ 1
9 Perilla de control de velocidad WC400201AV WC400201AV 1
10 Tablero de control de velocidad WC400200AV WC400600AV 1
11 Interruptor para controlar el amperaje WC400300AV — 2
Interruptor para controlar el amperaje — WC400500AV 1
12 Interruptor WC400000AV — 1
13 Etiqueta de seguridad DK670100AV DK670100AV 1
14 Mango WC300600AV WC300700AV 1
15 Cordón eléctrico 14-3 AWG (1,83 m) Type SJT WC000100AV WC000100AV 1
16 Bobina WC500300AV WC500300AV 1
17 Tornillo metálico #10-32 x 12,7 mm (0,5”) ❋ ❋ 2
18 Alambre de fundente revestido de 0,9 mm (0,035”) diámetro WE200500AJ WE200500AJ 1
19 Adaptador de la bobina WC500200AV WC500200AV 1
20 Resorte de la bobina WC500101AV WC500101AV 1
21 Seguro de la bobina WC500100AV WC500100AV 1
22 Ensamblaje (Incluye Nos.23-29) WC500000AV WC500400AV 1
23 Resorte de tensión WC500003AV WC500003AV 1
24 Tornillo de tensión WC500002AV WC500002AV 1
25 Rodillo 0,6 - 0,9 mm (0,024 - 0,035”) WC500001AV WC500001AV 1
26 Forro del rodillo WC500004AV WC500004AV 1
27 Tornillo #8-36 x 3,81 cm (1,5”) ❋ ❋ 3
28 Brazo giratorio WC500005AV WC500005AV 1
29 Rodillo del brazo giratorio WC500007AV WC500007AV 1
30 Perilla para seleccionar el amperaje — WC400401AV 1
31 Relievo de tensión WC102000AV WC102000AV 2
32 Rueda WC701200AV WC701300AV 2
33 Pata delantera WC702100AV WC702300AV 1
34 Forro, metal WC600007AV WC600007AV 1
35 Abrazadera para el cilindro de gas WC702200AV WC702400AV 1
36 Soporte del mango (derecho) — WC300800AV 1
37 Soporte del mango (izquierdo) — WC300900AV 1
38 Eje WC703100AV WC703200AV 1
39 Cubo de la rueda WC703500AV WC703400AV 1
40 Conector WC000200AV WC000200AV 2
41 Tomacorrientes WC000300AV WC000300AV 2
42 Anillo del soplete WC600009AV WC600009AV 1
43 Tornillo #10-24 x 12,7 mm (1/2”) ❋ ❋ 9
44 Soporte del eje WC703600AV — 2
45 Anillo en E de 5 mm D.I. ❋ — 2
46 Tornillo #10-24 x 5,08 cm (2”) — ❋ 2
47 Tornillo #8-36 x 2,54 cm (1”) — ❋ 2
48 Arandela plana #8 — ❋ 2
49 Tuerca #8-36 — ❋ 2
50 Extensión con difusor WC600701AV WC600701AV 1
❋ Disponible en cualquier ferretería o tienda para soldadores
47 Sp
Lista de Repuestos - Modelos WG3000 y WG3060
No. de Para los Modelos:
Ref. Descripción WG3000 WG3060 Ctd
WG3000 y WG3060
ALAMBRE OPCIONAL
Tipo Descripción Número de la pieza
**BOQUILLAS DE CONTACTO OPCIONALES
Tamaño
mm in. Número de la pieza
0,6 0,024 WT501200AV
0,8 0,030 WT501300AV
0,9 0,035 WT501400AV
Page 48

Soldadora Con Arco Con Alambre Continuo WG3000 y WG3060
Glosario de terminología usada por soldadores
CA o Corriente Alterna - corriente
eléctrica que cambia de dirección
periódicamente. Corriente de 60 ciclos
se desplaza en ambas direcciones 60
veces por segundo.
Longitud del Arco - la distancia entre
el extremo del electrodo y el punto de
contacto con la superficie de trabajo.
Metal Básico - el material que se va a
soldar.
Unión a tope - la unión de dos
miembros alineados aproximadamente
en el mismo plano.
Cráter - el vacío que se forma cuando
el arco hace contacto con el metal
básico.
CD o Corriente Directa - corriente
eléctrica que se deplaza en un sólo
sentido. La polaridad (+ o -) determina
el sentido del desplazamiento.
CD Polaridad Reversa - ocurre
cuando el portaelectrodo está
conectado al polo positivo de la
soldadora. Esta tecnica dirije más calor
para derretir el electrodo en vez de la
pieza de trabajo. Generalmente esta
técnica se usa con piezas delgadas.
CD Polaridad Directa - oocurre
cuando el portaelectrodo está
conectado al polo negativo de la
soldadora. Con esta tecnica la mayoría
del calor se dirije a la pieza de trabajo
para lograr una mayor penetración en
piezas gruesas.
Electrodo - un alambre de metal con
una capa que tiene aproximadamente
la misma composición del material que
se va a soldar.
Soldadura de Filete - soldadura
triangular, para unir dos superficies en
ángulo recto, en T o en las esquinas.
Fundente - un material, que al
calentarse, produce una capa
protectora de gas alrededor del área de
soldadura. Esta capa protege los
metales, base y de relleno, contra las
impurezas en el aire.
Soldar con Arcos de Fundente también se conoce como soldar sin gas ,
esta técnica para soldar usa una
soldadora con alambre. El alambre es
tubular y lleno de fundente.
Soldar con Arcos de Metal Gaseoso -
es un proceso para soldar usado con
una soldadora con alambre. El alambre
es sólido y se usa un gas inerte.
Soldar con Arcos de Tungsteno -
es un proceso para soldar usado con
soldadoras con generadores de alta
frecuencia. El arco se crea entre un
electrodo no-consumible de tugnsteno
y la pieza de trabajo. No es
indispensable usar un metal de relleno.
Unión de superposición - la unión de
dos miembros superpuestos en planos
parale-los.
Voltaje de circuito abierto - el
voltaje entre el electrodo y la pinza de
conexión a tierra de la soldadora
cuando no hay flujo de corriente (no
se está soldando). Esto determina la
rápidez con que se enciende el arco.
Sobremonta - ocure si el amperaje es
demasiado bajo. En este caso, el metal
derretido se cae del electrodo sin
haberse unido al metal básico.
Porosidad - cavidad que se forma
durante la solidificación del área
soldada. Las porosidades debilitan la
unión.
Penetración - la profundidad que el
arco se penetra dentro de la pieza de
trabajo durante el proceso de soldar.
Para soldar bien se debe lograr 100%
de penetración, es decir todo el grosor
de la pieza de trabajo se debe derretir y
solidificar. El área afectada por el calor
se debe ver facilmente desde el otro
lado.
Soldar con arcos protegidos - es un
proceso de soldar que usa un electrodo
consumible para sostener el arco. La
protección se logra al derretir el
fundente del electrodo.
Escoria - una capa de residuo de
fundente que protege la unión de
óxidos y otros contaminantes mientras
los metales se solidifican (enfrian). Este
se debe limpiar una vez que el metal se
haya enfriado.
Salpiqueo - las particulas de metal que
salpican durante el proceso de soldar y
que se solidifican en la superficie de
trabajo. Esto se puede minimizar al
rociar un repelente adecuado antes de
comenzar a soldar.
Soldadura de puntos - una unión
hecha para mantener las piezas
alineadas hasta que se haya
completado el proceso de soldar.
Angulo de desplazamiento - el
angulo del electrodo con respecto a la
línea a soldar. Este varia entre los 5º y
45º según sean las condiciones.
Unión en T - es la unión del borde de
una pieza de metal con la superficie de
otra en un ángulo de 90º .
Socavación - el resultado de soldar
con un amperaje demasiado alto. Esto
ocasiona ranuras en ambos lados de la
reborde que reduce la resistencia de la
unión.
Sedimento - el volumen de metal
derretido al soldar antes de que se
solidifique como metal soldado.
Reborde - una capa delgada o capas
de metal depositado en el metal básico
cuando el electrodo se derrite.
Generalmente su grosor es el doble del
diámetro del electrodo.
Angulo de trabajo - el angulo del
electrodo con respecto a la línea
horizontal, medido en angulos rectos a
la línea de soldar.
 Loading...
Loading...