Page 1
Operating Instructions
Bedienungsanleitung
Instructions de Service
Type 1066
Control Head
Steuerkopf
Tête de commande
Page 2

We reserve the right to make technical changes without notice.
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten.
Sous resérve de modification techniques.
© 2002 Bürkert Werke GmbH & Co. KG
Operating Instructions 0509/04_EU-ML_00804373
Page 3

C
ONTENTS
Contents of the
Operating Instructions for the
Control Head Type 1066 for Process Valves
GENERAL INFORMATION
Symbols Used................................................................................................................. 4
Intended use ................................................................................................................... 4
Safety instructions ........................................................................................................... 4
Scope of Delivery ............................................................................................................ 5
Guarantee conditions ...................................................................................................... 5
Transport, storage ........................................................................................................... 6
english
Disposal .......................................................................................................................... 6
TECHNICAL DATA
Structure and Function of the Control Head .................................................................... 8
Characteristics ................................................................................................................ 8
Operating conditions ....................................................................................................... 9
Mechanical data .............................................................................................................. 9
Pneumatic data ............................................................................................................... 10
Electrical data .................................................................................................................10
INSTALLATION
Installation of the control head......................................................................................... 12
Flange adaptor ........................................................................................................................ 12
Installation procedure .............................................................................................................. 13
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
Pneumatic installation ..................................................................................................... 16
Wiring connections on the control head .................................................................................. 16
Electrical installation ....................................................................................................... 17
Control heads without communication .................................................................................... 17
Control heads with communiction ........................................................................................... 19
1066 - 1
Page 4

C
ONTENTS
MAINTENANCE / CLEANING
Maintenance / Cleaning .................................................................................................. 30
REPAIRS
Repairs ........................................................................................................................... 32
Removing and/or replacing the cover ..................................................................................... 32
Changing the printed circuit board .......................................................................................... 33
Replacing the valve group ...................................................................................................... 33
Changing the valve on versions for 24 / 110 / 230 V UC without communication................... 34
english
Changing the proximity switch/micro-switch........................................................................... 35
Spare parts .....................................................................................................................36
Service addresses .......................................................................................................... 36
2 - 1066
Page 5

GENERAL
GENERAL INFORMATION
INFORMATION
Symbol used................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Intended use ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Safety instructions.................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 4
Scope of Delivery.................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Guarantee conditions........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 5
Transport, storage................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Disposal ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
english
1066 - 3
Page 6

GENERAL INFORMATION
Symbols Used
The following symbols are used in these Operating Instructions:
marks a work step that must be carried out.
ATTENTION!
NOTE
Intended use
english
• The control head for process valve type 1066 is used to control pneumatically-activated process
valves and record their switching statuses. Other incidents of use are deemed non-compliant.
• The Technical Data presented in these instructions, on the datasheet and on the type plate must be
checked for consistency before commissioning and complied with during operation of the control head.
• Unauthorized rebuilding or changes to the device are not allowed for safety reasons.
• Shield the control head from interventions by unauthorized persons. To this end the control head can be
secured on the boreholes present on the cover and casing by means of a lead seal and / or cutting
screw.
• The working directions given in these instructions and safety indications must be followed and
complied with at all times. If the operating instructions, safety tips, or safety information are ignored or
not followed in the proper order, the warranty shall be void.
Indicates information which, if not followed, could result in danger to your health or to
the functionality of the machine.
Indicates important additional information, tips and recommendations.
Safety instructions
Follow the instructions of this operating manual, along with the terms of use and permitted data as
specified for process valves on the datasheets and the control head type plate, so that the device can
operate smoothly and have a long service life.
• When planning the application of the device, and during its operation, observe the general technical
rules!
• Installation and maintenance work may only be carried out by specialist staff using the correct tools!
• Use only original replacement parts for necessary repairs, and when changing these parts observe the
directions in these instructions.
• Observe the relevant accident prevention and safety regulations applicable for elekctrical equipment
while operating and maintaining the device!
• Always switch off the electrical power supply before carrying out any works on the system!
• Note that piping or valves must not be removed from a system that is under pressure!
• Take suitable measures to prevent unintentional operation or impermissible impairment.
• Following an interruption of the electrical or pneumatic supply, ensure a defined and controlled re-start
of the process!
4 - 1066
Page 7

GENERAL INFORMATION
NOTE
• Avoid larger mechanical loads on the control head, as these may lead to mechanical impairment or
destruction of the control head. These include walking on the control head, placing heavy objects on it,
heavy impacts, falling hard objects etc.
• Avoid the infiltration of moisture into the control head. When assembling in particular, make sure that all
seals are fitted according to directions and assembly screws, cable screw connections and sealing
plugs are securely tightened. Use only dried control air!
NOTE
• Avoid attaching longer and mechanically rigid attachment parts, since extensions of this type would
produce leverages through which the casing could be destroyed by hand.
NOTE
• Use only highly compatible cleaning products when cleaning the control head and rinse thoroughly with
clear water after these cleaning products have been used. The compatibility of the cleaning product
should be tested where necessary.
NOTE
The control head is designed in protection type IP67. This supposes that all seals
are positioned correctly and that casing and cover are mechanically intact.
With regard to its mechanical resistance, the plastic casing of the control
head is designed for direct attachment of flexible hoses and conduits only.
Cleaning products often contain aggressive components that may become
deposited in small grooves and cavities on the control head, and their prolonged
effect may lead to the desctruction even of high-quality plastics.
A pressure-relief valve is situated on the underside of the control head casing,
serving as rupture protection in the event of an leaky component in the control
head (leakage incident).
english
• When assembling the control head, ensure a minimum distance of 5 mm between the pressure-relief
valve and the neighbouring component so that the pressure-relief valve can disengange without
problems in the event leaking. Otherwise, the cover could literally be "exploded" in the event of leakage
in the control head.
• If these instructions are ignored, no liability will be accepted from our side, and the guarantee on the
device and its accessories will also become invalid!
Scope of Delivery
Immediately after receiving the shipment, ensure that the contents are undamaged and correspond to the
scope of the delivery listed on the enclosed packing note. In case of any discrepancies, please contact
our Call Center:
or your local Bürkert Sales Center immediately.
Guarantee conditions
Bürkert Fluid Control System, Call Center
Chr.-Bürkert-Str. 13-17, D-74653 Ingelfingen
Tel. 07940 - 10 111 / Fax 07940 - 10 91 448
E-Mail: info@de.buerkert.com
This document contains no agreement to provide a guarantee. We would refer you here to our General
Selling and Business Conditions. The precondition for the guarantee is the correct usage of the device
under compliance with the specified application conditions.
ATTENTION!
The guarantee only applies to the freedom from fault of the Head Control of the
process valves. No liability will be accepted, however, for consequential damage of any
kind that could arise from the failure or malfunctioning of the device.
1066 - 5
Page 8

GENERAL INFORMATION
Transport, storage
ATTENTION!
Disposal
english
ATTENTION!
Transport and store the appliance in its original packing only.
Storage in a dry room.
Maximum storage temperature +50 °C
When disposing of the appliance, observe the national standards for refuse disposal.
6 - 1066
Page 9

TECHNICAL DATA
TECHNICAL DATA
Structure and Function of the Control Head ................................................................................................................................................... 8
english
Characteristics............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 8
Operating conditions .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Mechanical data........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 9
Pneumatic data .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 10
Electrical data ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 10
1066 - 7
Page 10
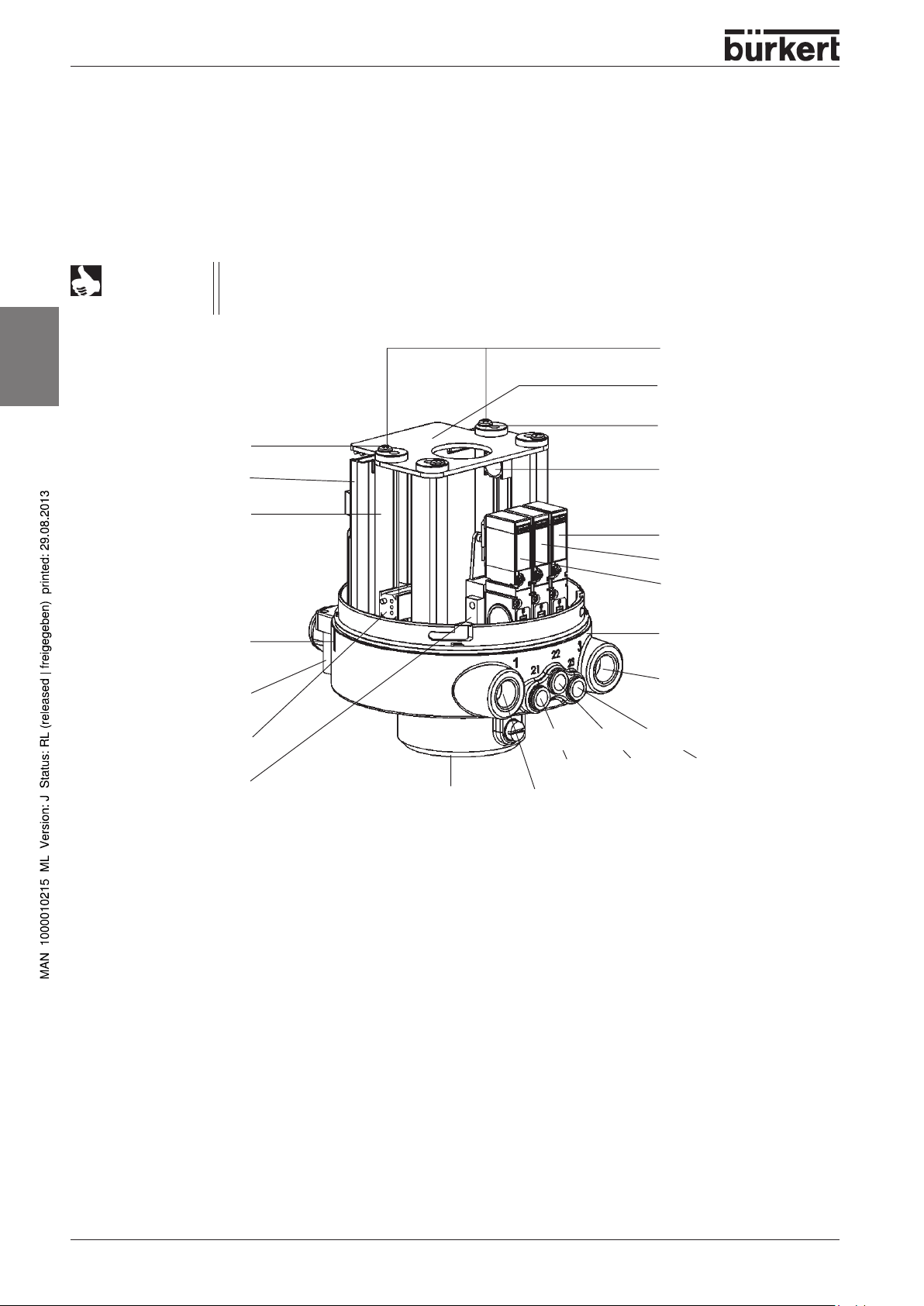
TECHNICAL DATA
Structure and Function of the Control Head
The Type 1066 control head is used to control pneumatically operated process valves from various
manufacturers. Depending on the configuration, it can be fitted with up to three solenoid valves (pilot
valves) for control of the process valve and with a maximum of three height-adjustable inductive
proximity sensors for position feedback. One of these sensors can also be an external sensor
(Attachment via 3-pole screw clamp on printed circuit board).
english
Column with spindle
mounting the cover
Electrical connection
NOTE
Adjustment of the
proximity sensor 1
Printed card
Marking for
For sealed fieldbus modules, pay attention to the numbering of the proximity switch on the
circuit board / the identification on the device, since deviations from the numbering in the
drawing below are possible.
Adjustment throug
these holes
Cover plate
Adjustment of proximity
sensor 2
Proximity sensor 2
Solenoid valve 3
Solenoid valve 2
Solenoid valve 1
Housing
Exhaust air
Proximity sensor 1
Valve flange
Characteristics
With the Type 1066 control head, there is a de-central solution for driving the process valves in addition to
the intended central solution for valve blocks. The advantages of this solution in the form of the compact
control head
Main areas of application:
unit with the pilot valves and optionally usable field bus interfaces are:
Pneumatic connections
Valve 1
Compressed airInterface to the
process valve
Lower installation outlay.
Simple commissioning.
Short response times due to the short distance between the pilot valve and the
process valve.
Foodstuff industry (e.g. dairies)
Chemical industry
Pharmaceutical industry
Valve 3Valve 2
8 - 1066
Cosmetics industry
Breweries
Page 11
TECHNICAL DATA
Options
Number of pilot valves
Operating mode / Type of application Number of pilot valves
Single-acting actuators 1
Double-acting actuators 2
Dual-seat valves with integrated air supply to both valve seats 3
Control heads without communication
8-pole screw terminal for 24 V DC
Multipol (8-pole round plug) for 24 V DC
2 x 6 screw terminals for 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
Control heads with communication
Actuator sensor interface (ASI)
DeviceNet
ATTENTION!
The connection to other (higher) bus systems is possible using commercially available
Gateways.
Operating conditions
Media Compressed air, non-oiled; neutral gases
english
Medium temperature -10 ... + 50 °C
Ambient temperature -10 ... + 50 °C
Protection class IP 67
ATTENTION!
The control head is not suitable for use outdoors!
Mechanical data
Weight 0.5 bis 0.65 kg (depending on model)
Housing material Housing PA / PPE
Cover PSU (transparent, blue-grey)
Sealing material NBR
1066 - 9
Page 12

TECHNICAL DATA
Pneumatic data
Port connections Compressed air/Exhaust air G 1/4
Service ports tube hose connection
6/4 mm or 1/4 inch, plug-in
Pressure range 2.5 to 7 bar
Air flow, control valve 110 l/min Type 6510, 40 l/min Type 6106
english
Flow: Q
Measurement at +20 °C, 6 bar pressure at the valve inlet and 1 bar
pressure difference
Response times Type 6510 / Type 6106
Opening 15 / 23 ms Closing 10 / 21 ms
Measurement at valve outlet at 6 bar and +20 °C
Opening: pressure rise 0 to 90 %
Closing: pressure fall 100 to 10 %
Control range min. stroke 2mm max. stroke 73 mm
- value air (l/min)
Nn
Electrical data
Protection class IP 67
Operating voltage
without communication 24 V DC ±10 %
24/110/230 V UC ±10 %
with communication in accordance with the ASI and DeviceNet specification
Max. electrical power loss 5 W for 3 x Type 6510 or 1 x Type 6106
Connections
Control heads
without communication: Multipol (8-pole round plug DIN 45326) for 24 V DC
(8-pole screw terminals) for 24 V DC
2 x 6-pole screw terminals for 24/110/230 V UC
Control heads
with communication:
ASI: Cut-clamp connector and cable fitting
M12 plug and cable fitting
M12 flange plug, 4-pole
DeviceNet: 5-pole M12 plug connection
Solenoid valves
Nominal power 1 W Type 6510 / 3 W Type 6106
Operating mode continuous (ED 100 %)
Proximity switches
Operating voltage 8 to 30 V DC
Output signal max. 100 mA, short-circuit proof
Micro-switch potential-free, max. 1 A switched current
10 - 1066
Page 13

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
Installation of the control head............................................................................................................................................................................................. 12
english
Flange adaptor
Installation procedure
........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 12
..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
1066 - 11
Page 14
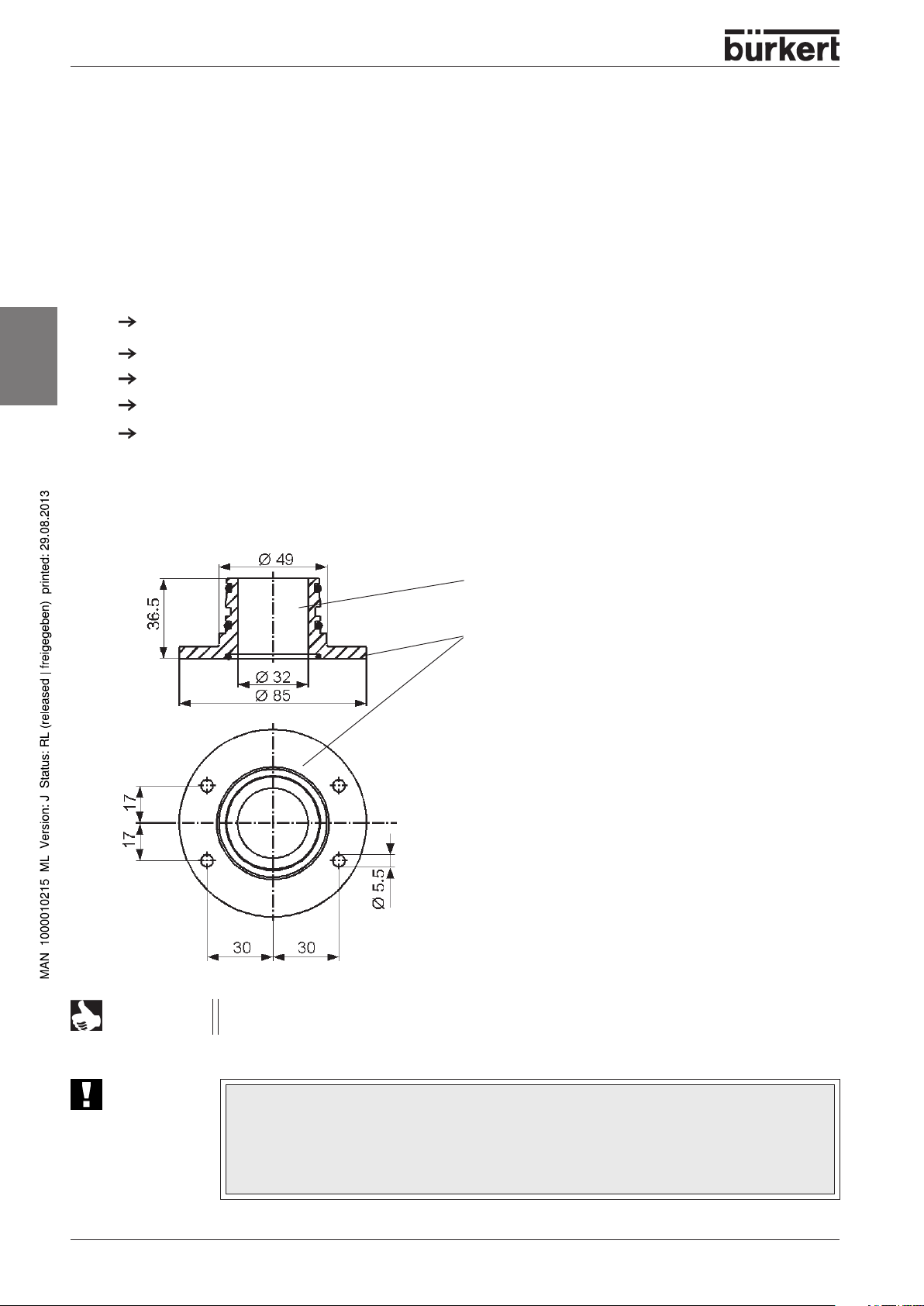
INSTALLATION
Installation of the control head
Flange adaptor
To mount the control head type 1066 on a process valve from a different manufacturer, you need an
adapter with customized flange (flange adapter) and a customized switching knob (see also Data Sheet).
The connecting part for the control head is Bürkert-specific. The flange component must be adapted to
the shape of the process valve. The drawing below shows an application for a special process valve. The
control head can be installed in any position, but preferably with the cover at the top.
When making your own flange, comply exactly with the following parameters:
Dimensions
Number of sealed positions
english
Dimension for the O-ring
Measurement tolerance
Material data
Main dimensions for the flange adapter
Cylindrical adapter part
Custom flange part
NOTE
ATTENTION!
12 - 1066
Please request detailed dimensional drawings if you are manufacturing your own flange
adapter.
A centring device is necessary for the installation of the flange adapter.
maximum permissible deviation is ± 0.1 mm. If this tolerance is exceeded, there is the
danger that the proximity sensors may not function correctly.
Use a special installation sleeve to avoid exceeding this tolerance.
The
Page 15
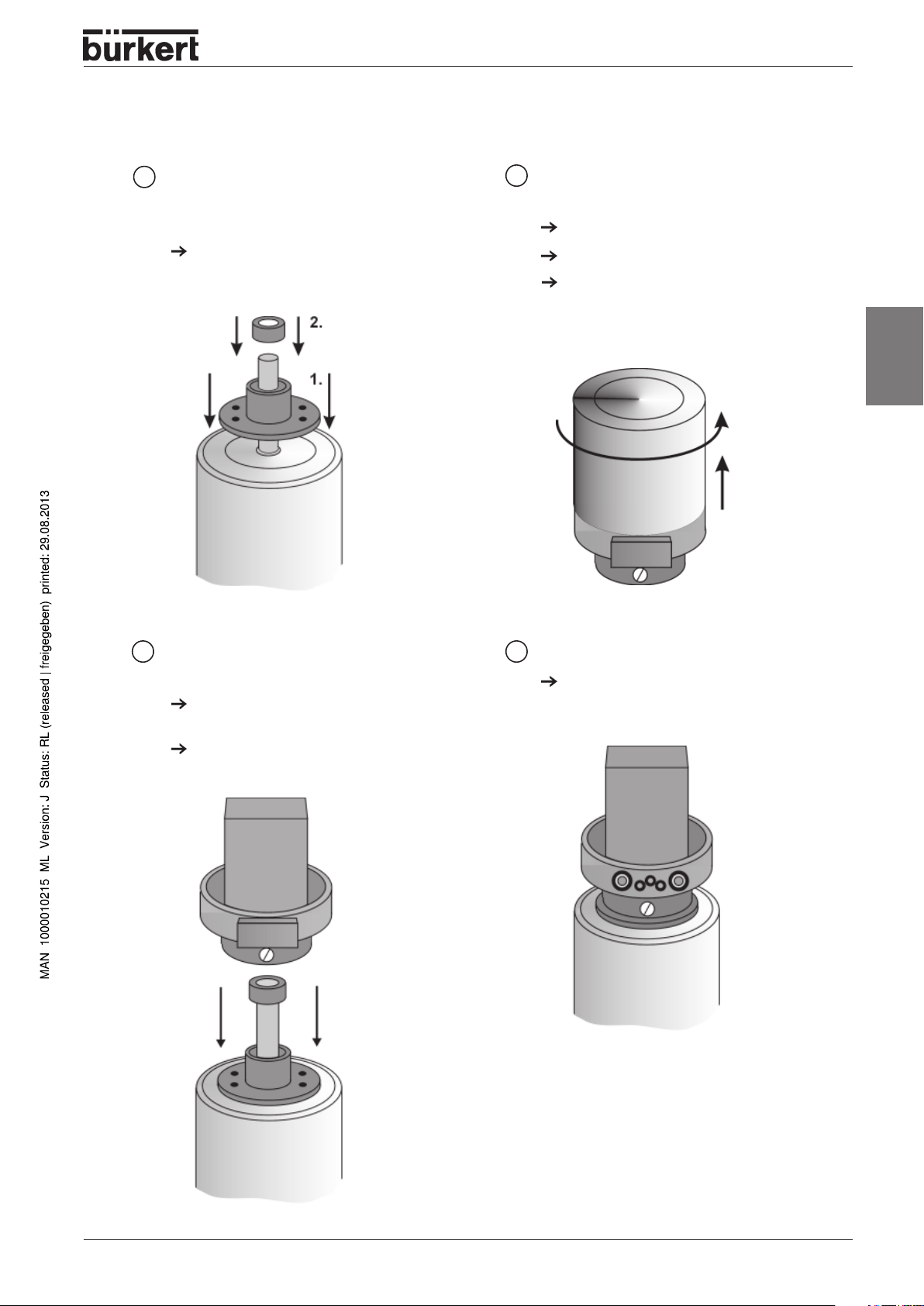
Installation procedure
Fix the flange adapter to the
1
process valve/Fix switching knob
to piston rod (customer-specific)
ensure that it is centred
INSTALLATION
Remove the cover from the control
2
head
Loosen the locking screw
Turn the cover to the left to the stop
Pull the cover off upwards
english
Insert the control head onto
3 4
the flange adapter
Position the control head
(control head can be turned through 360°)
Secure the control head using the two
screws on the side
Fit the pneumatic connections
Refer to Pneumatic Installation,
(Installation/Commissioning chapter)
1066 - 13
Page 16
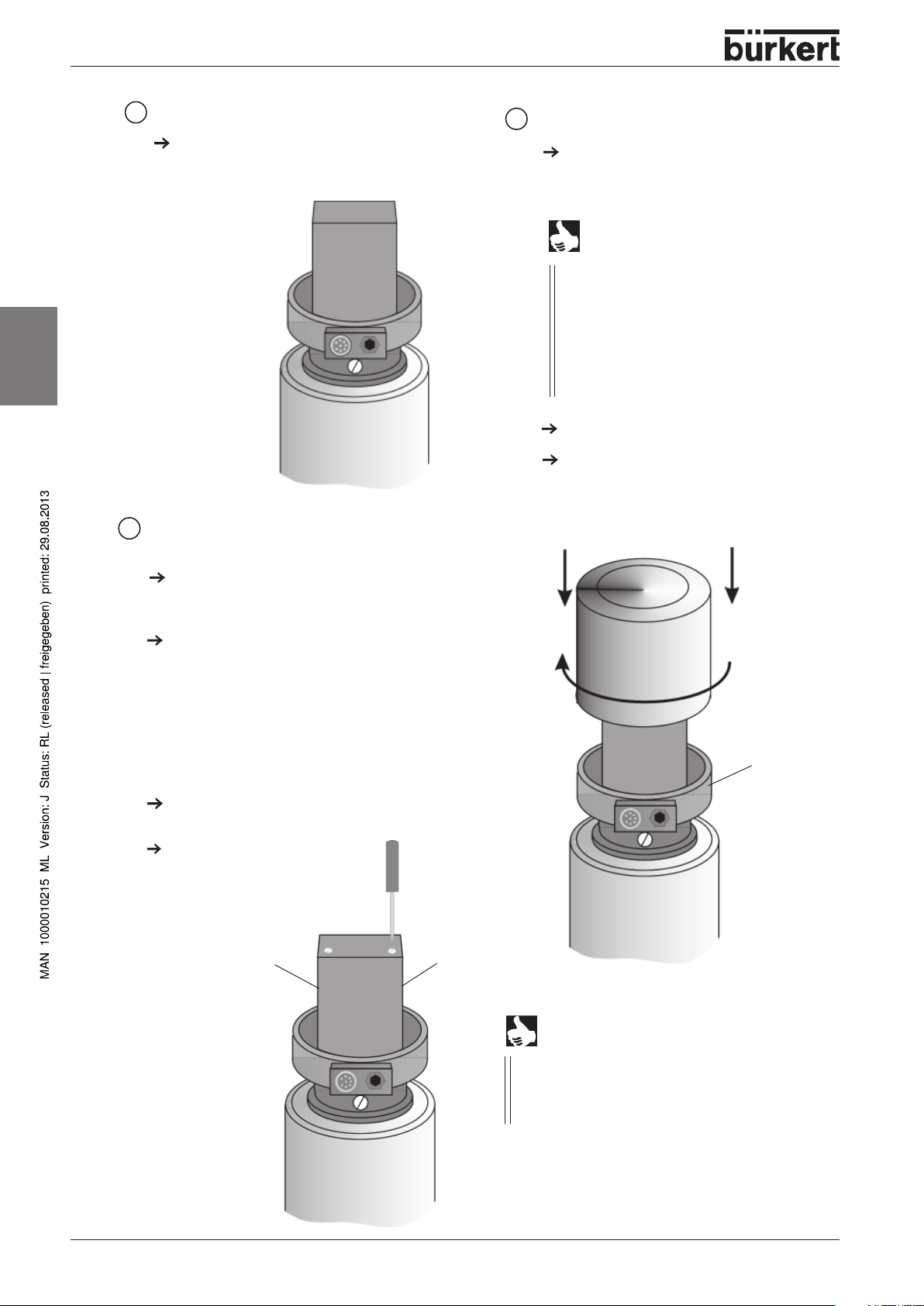
INSTALLATION
english
5
Fit the electrical connections
Control heads without and
with communication
(see chapter on electrical installation)
7
Fit the cover
Check the seat of the cover O-ring,
or pull a new O-ring onto the collar of
the cover.
Distributed across the circumference of
the casing are 4 handles that retain the
O ring when the cover is being
removed. Take care to ensure that the
newly-applied O ring is positioned
correctly under the handles and is
resting on the casing without twisting.
Fit the cover.
Turn the cover right until it reaches the
stop.
NOTE
Adjust
6
the proximity sensors
Using a screwdriver, turn the adjusting
screw (spindle) until the optimal position
of the proximity switch has been set up.
The LED mounted on the proximity switch
is an adjustment aid: it lights up when
reaching the corresponding threshold value.
the limit position micro-switches
When using micro-switches, LEDs are not
provided for reasons of cost
Set the position as for the proximity
switches
Using the switching sound
of the micro-switch
(very quiet) as a setting
aid or external electrical
continuity check.
LED
Housing
with cover
collar and
O-ring seat
LED
14 - 1066
NOTE
Secure the cover where necessary to prevent
unauthorised access by inserting a lead seal
and/or self-tapping screw in the holes in the
cover and the housing.
Page 17

INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
INSTALLATION AND
COMMISSIONING
english
Pneumatic installation...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 16
Wiring connections on the control head
................................................................................................................................................................. 16
Electrical installation .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
Control heads without communication
8-pole screw terminal for 24 V DC
Multipol (8-pole round plug to DIN 45326) for 24 V DC
2 x 6-pole screw terminals for 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
Control heads with communication
AS-Interface
...................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 19
Handling the flat cable clamp
Technical data for the ASI circuit board
Programming data
LED status display ASI
Bit allocation
........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 20
............................................................................................................................................................................................ 21
........................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 21
Number of connectable control heads and maximum length of the bus
(ASI standard case and ASI version with extended address range)
..................................................................................................................................................................... 17
....................................................................................................................................................................... 17
............................................................................................................. 18
....................................................................................................................... 18
.............................................................................................................................................................................. 19
............................................................................................................................................................................ 20
............................................................................................................................................... 20
............................................................ 22
DeviceNet
........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Explanation of terms
Technical data
...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Maximum line lengths
Safety setting for bus failure
Electrical connection
Configuration
.......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 26
LED Status Display
.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
................................................................................................................................................................................................. 24
.............................................................................................................................................................................. 25
................................................................................................................................................................................................... 25
...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 28
1066 - 15
Page 18
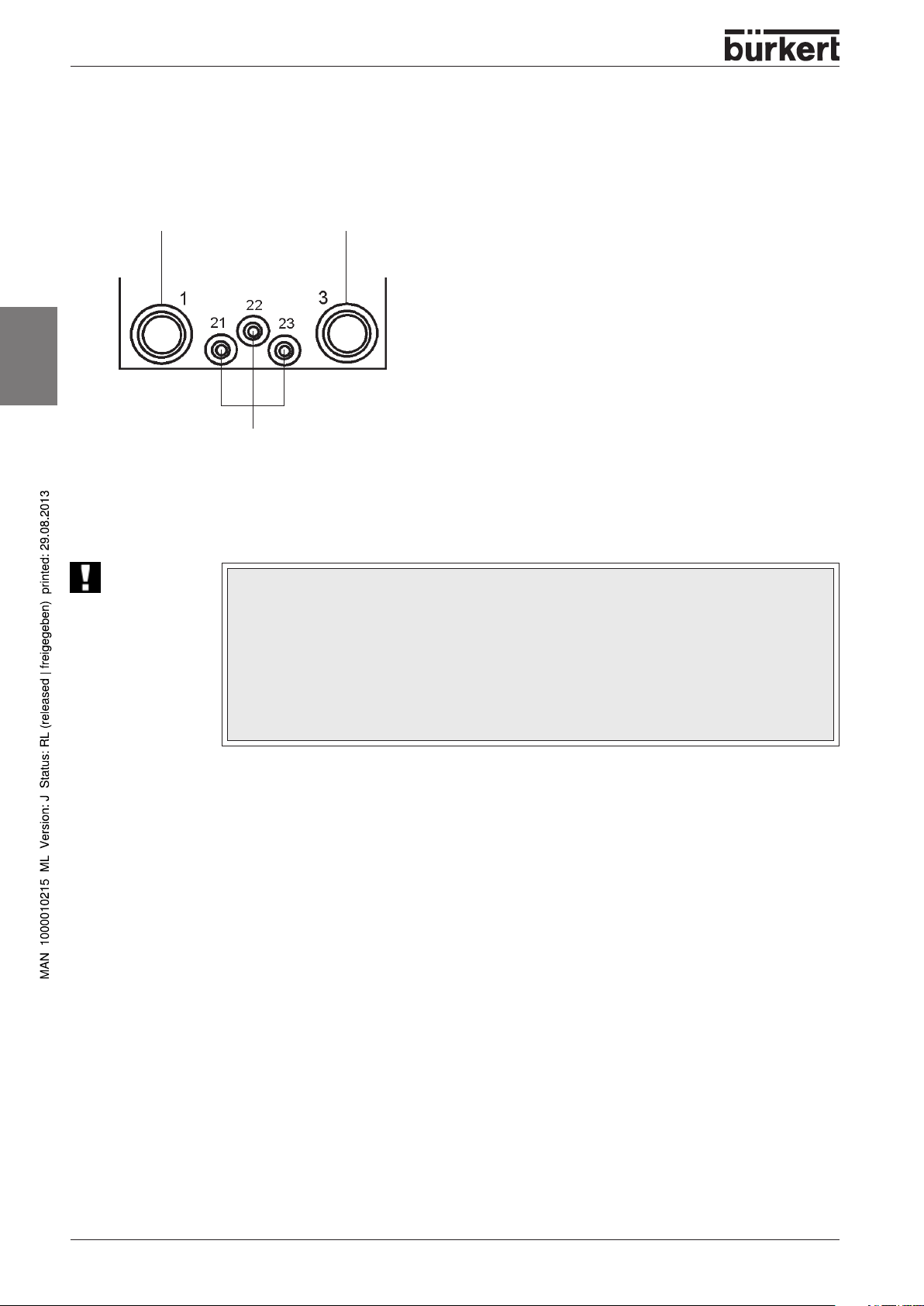
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
Pneumatic installation
Wiring connections on the control head
G 1/4 G 1/4
english
Compressed
air
ATTENTION!
Exhaust air
Plug-and-socket connections
for 6/4 mm or 1/4" hose
plug-in
for valves V1, V2 and V3
• Only use calibrated hose lines with 6 mm or ¼ " external diameter.
• Only cut these using a hose cutter (danger of damaging the hose).
• Select the length of the hose so that the control head can be removed with the
screw fitting.
• Take care to ensure a tension-free hose guide well aligned with the plug connector,
since hoses that are plugged in when tensed (contorted) may lead to leakages at
the plug connection.
16 - 1066
Page 19
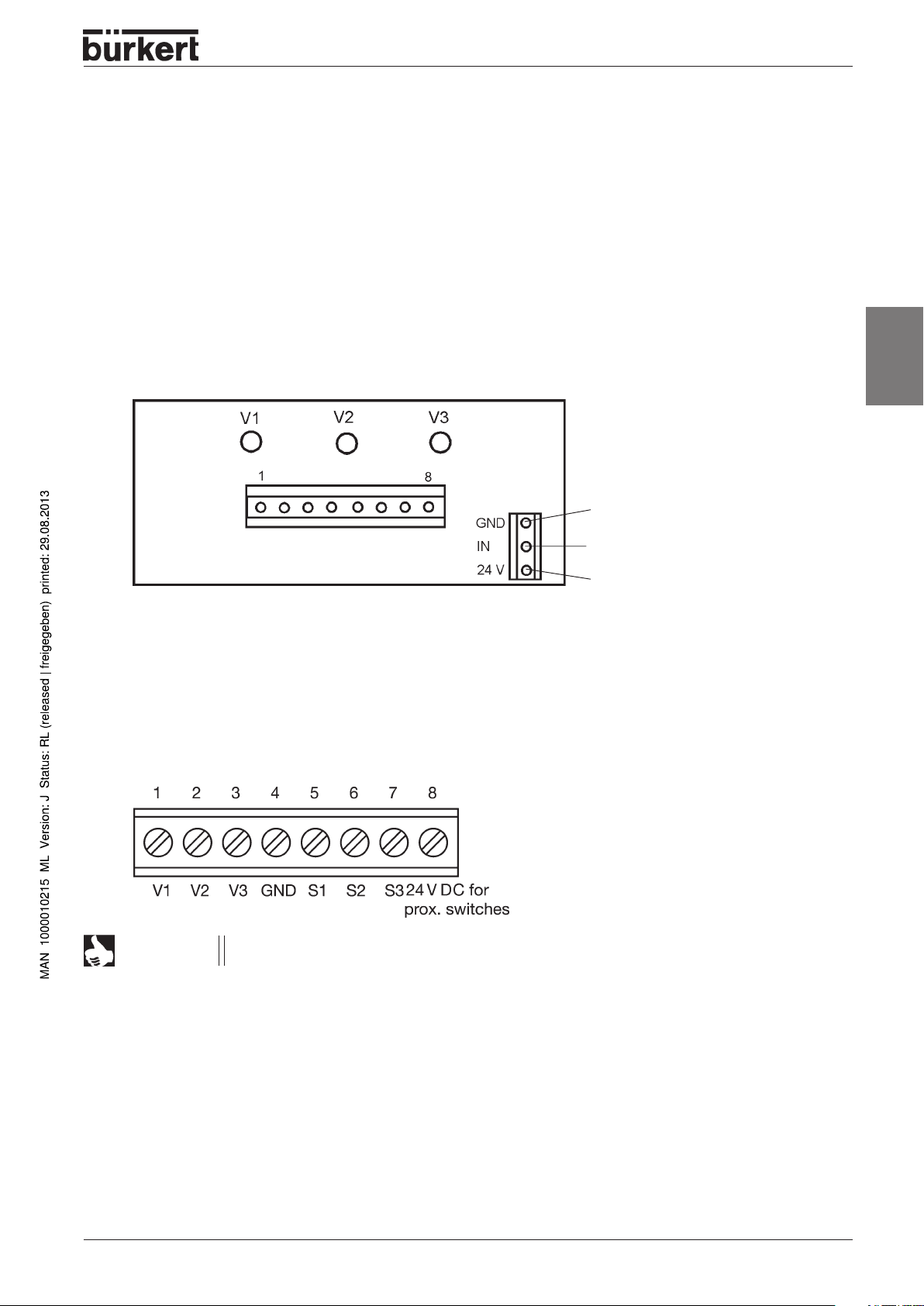
Electrical installation
Control heads without communication
There are different ways of electrically connecting control heads without communication.
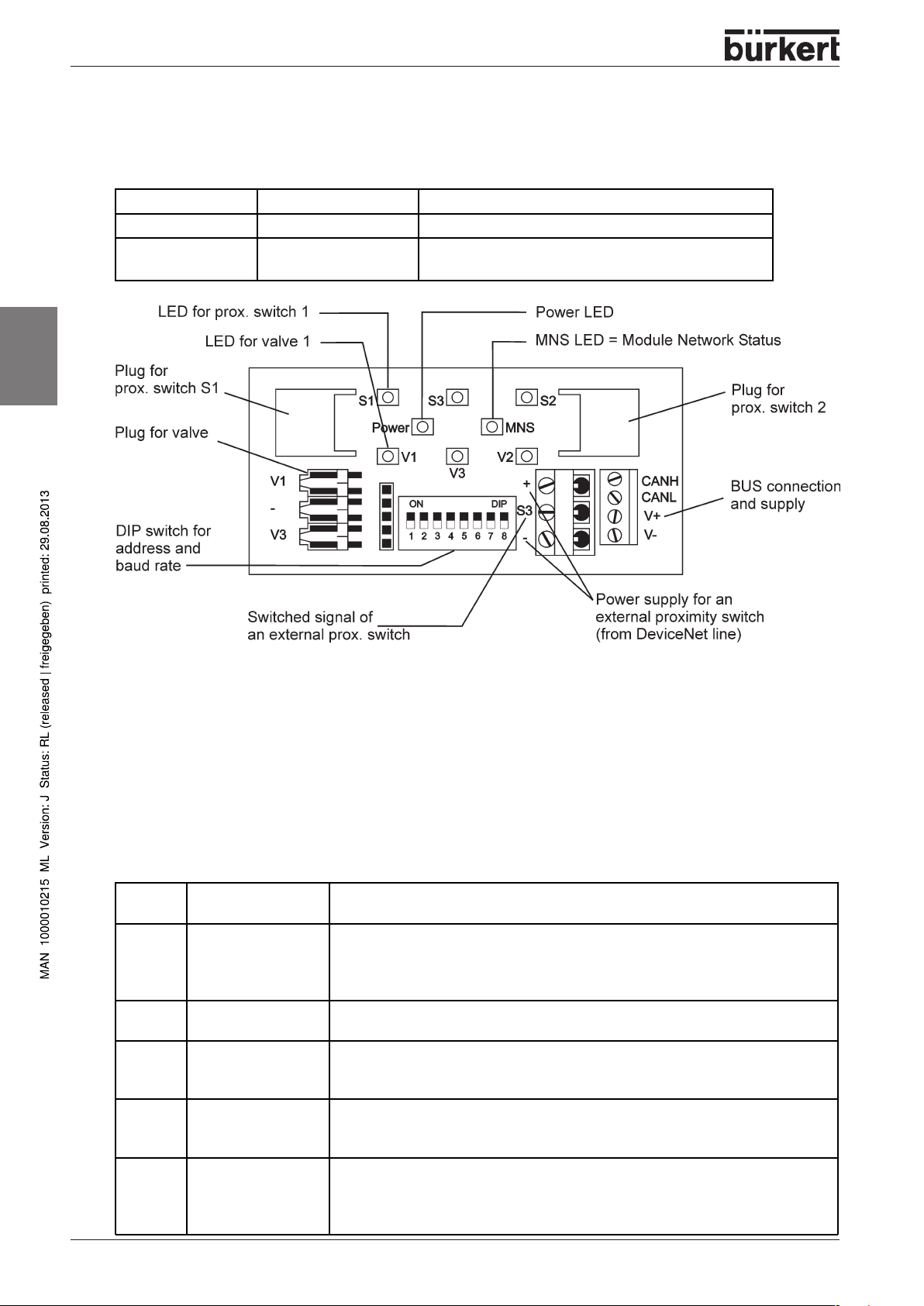
On the model for 24 V DC, status per valve is displayed uniformly with an LED in each case.
8-pole screw terminal for 24 V DC
(in interior of housing, cable duct with screw fitting for cable)
LED status display 24 V DC
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
english
Layout of the 8-pole screw terminal
NOTE
The outputs of the proximity switches are pnp-plus switching and are short-circuit proof.
Ground
Switched signal of the external
proximity switch S3
Power supply
V = valve
S = proximity switch (sensor)
1066 - 17
Page 20
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
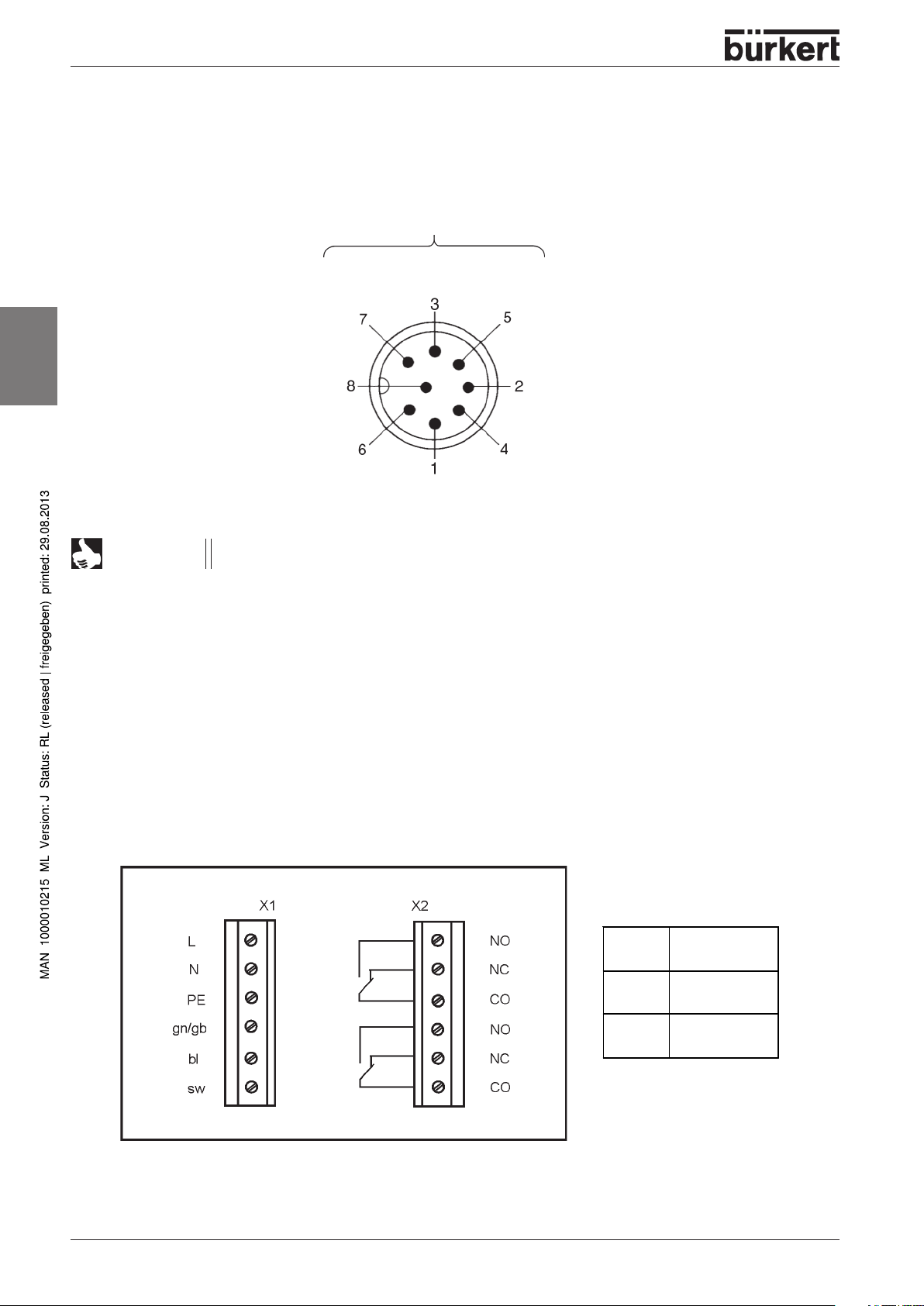
Multipol (8-pole round plug to DIN 45326) for 24 V DC
View of the sensor installed in the head, seen from the front looking at the pins, with the solder
connections below.
Outputs of the proximity switches
pnp-plus switching and are short-circuit proof
english
Proximity switch 2
Valve 3
Proximity
switch 1
24 V DC
(operating voltage for the
proximity switches)
Valve 1
Valve 2
(common earth for valves)
NOTE
The outputs of the proximity switches are pnp-plus switching and are short-circuit proof.
Proximity
switch 3
GND
2 x 6-pole screw terminals for 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
The 2 x 6-pole screw terminal model consists of:
Cable gland with screw fitting for cable
Max. 1 valve (Type 6106, DN1.2)
2 mechanical limit switches with potential-free contacts for position feedback
(No LED status display)
Printed circuit board with 2 x 6-pole screw terminals for 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
gn/gb green/yellow
Switch 1
Valve/Network
Switch 2
bl blue
sw black
18 - 1066
Page 21
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
Control heads with communication
AS-Interface
ASI (Actuator Sensor Interface) is a field bus system that is used for networking (mainly) binary sensors
and actuators to a master controller.
Bus line
Unscreened pairs (ASI line as ASI format cable) over which both information (data) and energy (power
supplies for the sensors and actuators) are transmitted.
Network topology
Freely selectable within wide limits, i.e., star, tree and line networks are possible. Further details can be
found in the ASWI specification.
Bus connection variants
NOTE
1. Flat cable clamp on the 1 m round cable
ASI standard connection:
2. 4-pole M12 plug on the 2 m round cable
ASI special connection 1: (on request)
Data for the round cable
The electrical values of the round cable leading directly to the control head deviate slightly
from the ASI specification. When calculating the maximum permissible line length according
to the ASI specification, the length should therefore be set longer by the factor 1.5.
ASI length = 1.5 x real length
ASI format cable
Flat cable clamp
Conductor plug with
moulded cable
Round cable (1 m long, of
which 0.2 m in the control head)
english
4-pole M12 plug for
ASI connection
M12 plug
Conductor plug with
moulded cable
Round cable (1 m long, of
which 0.2 m in the control head)
3. 4-pole M12 plug on the control head, without cable
ASI special connection 2: (on request)
ASI format cable
Flat cable clamp
Conductor plug
M12 flange plug
M12 socket
Round cable (1 m long)
ASI PIN configuration
1 = ASI+
2 = not used
3 = ASI4 = not used
1066 - 19
Page 22
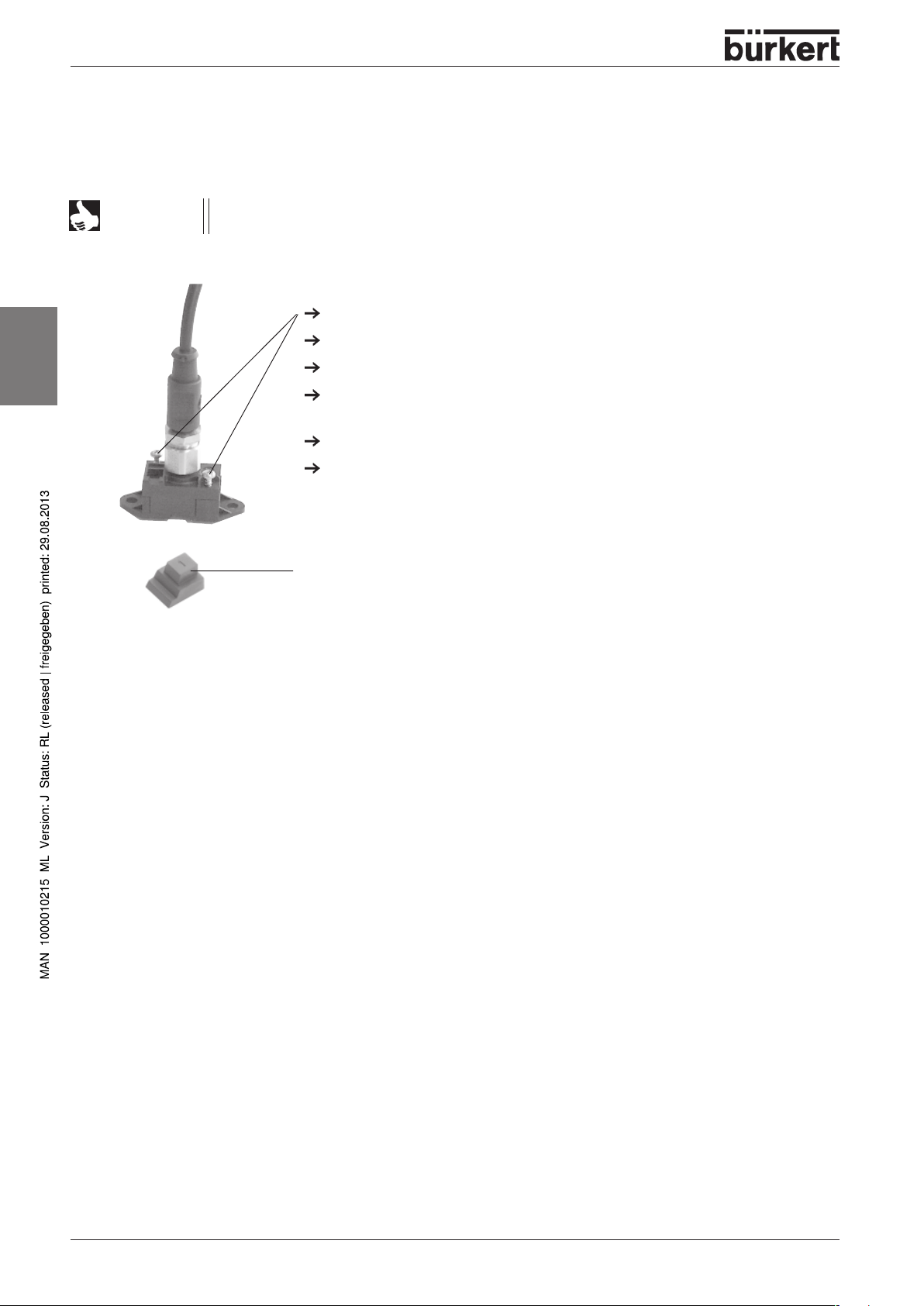
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
Handling the flat cable clamp
Contact is achieved in the form of a penetration technique using the flat cable clamp for ASI from cables.
Electrical connection is achieved in the process without cutting and skinning the cable.
english
NOTE
Close the second cable aperture using a cable seal if the flat cable terminates in the clamp
(final connection).
Connecting the flat cable clamp with conductor plug and moulded cable
with an ASI flat cable
Loosen both screws on the flat cable clamp.
Separate the upper part of the flat cable clamp from the lower part.
Lay the ASI flat cable in the correct position.
If the flat cable terminates here:
Insert the flat cable seal into the aperture in the correct position.
Place the upper part of the flat cable clamp onto the lower part.
Tighten the screws.
Done!
The electrical connection to the ASI cable has been produced.
Flat cable seal for flat cable clamp
Technical data for the ASI circuit board
Inputs 3 sensors S1 top S3, pnp plus-switching
Supply via the AS interface (24 V +20 % / -10 %), short-circuit proof, current
limited to 60 mA
Switch level High signal ≥ 10 V
Limitation of input current ≥ 6.5 mA, input current Low signal ≥ 1.5 mA
Outputs 3 valves V1 - V3
max. 3 x 1 W
Power reduction after approx. 100 ms, with integrated Watch-Dog function
Programming data
I/O-Code 7 hex (4 outputs and 4 inputs)
ID-Code F hex (see following table for bit allocation); extended ID codes 1 and 2 = F hex
Profile 7.F
20 - 1066
Page 23
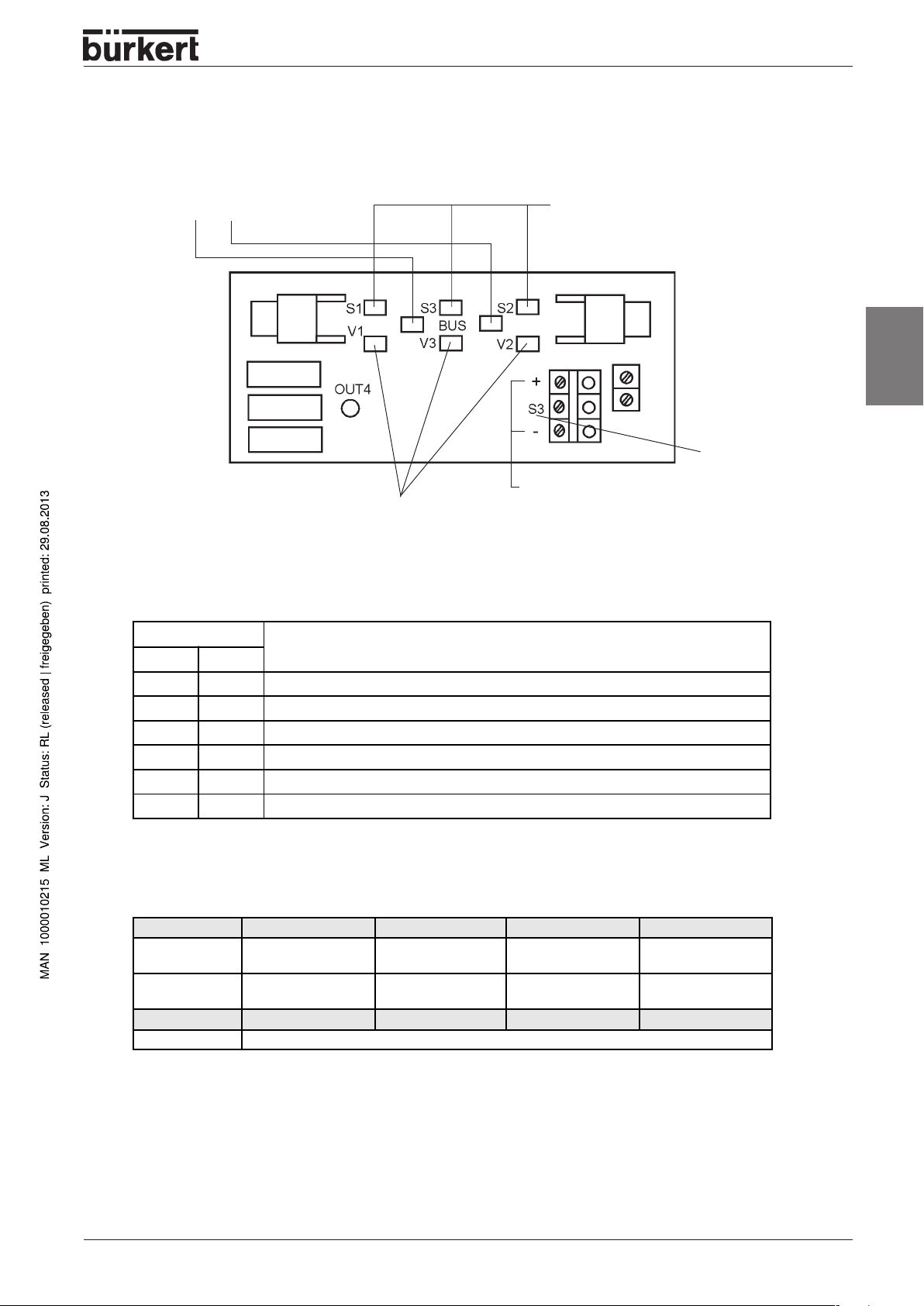
LED status display ASI
Visible part of the ASI printed circuit board
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
Status display bus
LED green red
LED's for
Valves V1 - V3
LED's for
proximity switches S1 - S3
Power supply for an
external proximity switch
(from the ASI cable)
Overview of ASI LED Status display
LED Bus status
green red
dark dark POWER OFF
dark light No data traffic (expired watch-dog with Slave address not 0)
light dark ok
blinking blinking Peripheral fault (overload in sensor supply)
blinking light Slave address equal to 0
dark blinking RESET
english
Switching signal of
an external proximity
switch
Bit allocation
Data bit D3 D2 D1 D0
Output
LED yellow
Input
Not used
Parameter bit P3 P2 P1 P0
Output
Valve 3
Input
Prox. switch 3
Prox. switch 2
Not used
Output
Valve 2
Input
Output
Valve 1
Input
Prox. switch 1
1066 - 21
Page 24
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
Number of connectable control heads and maximum length of the
bus line
I. ASI standard case
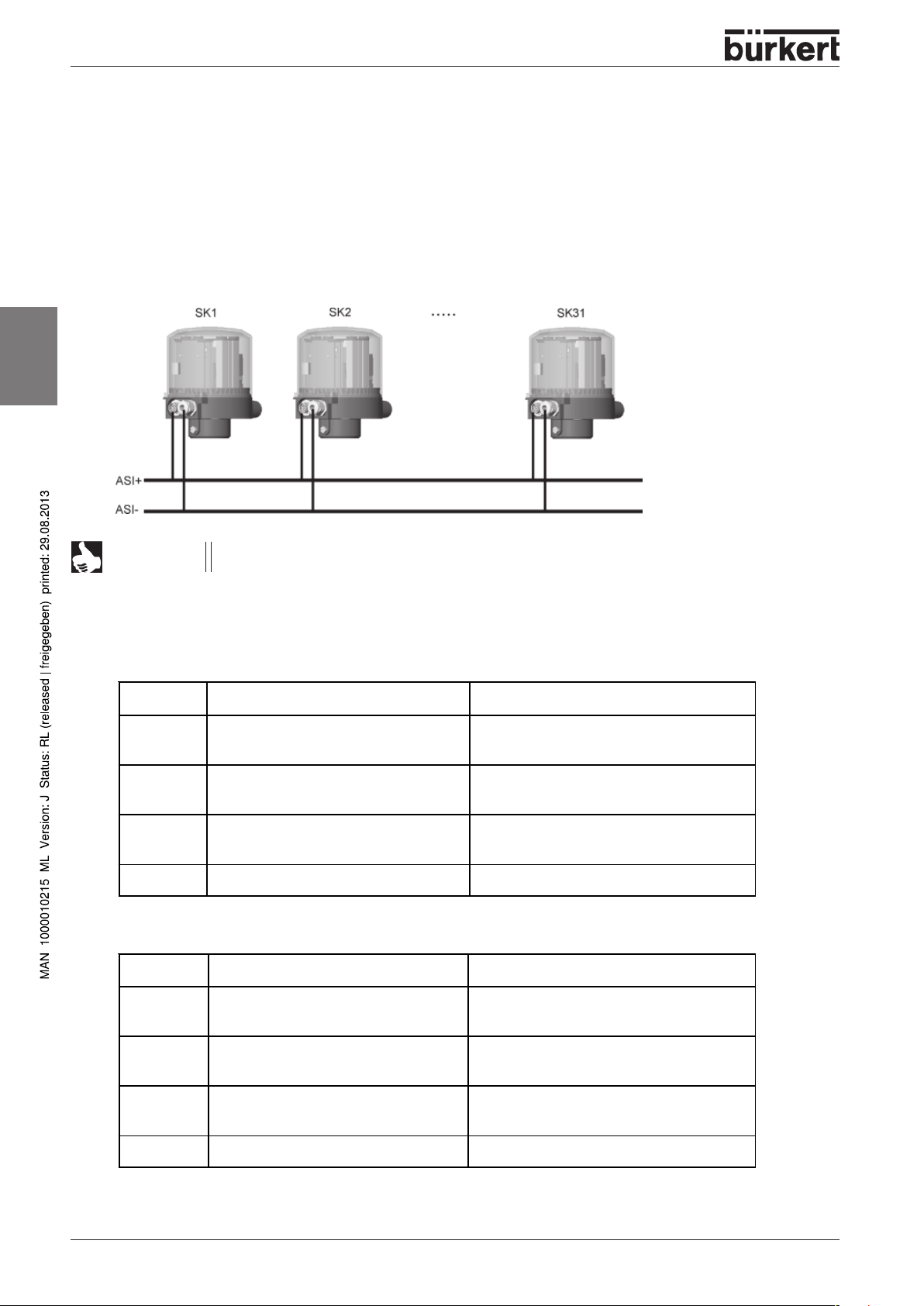
A maximum of 31 control heads can be attached to a bus line in the standard case.
According to ASI specifications the bus cable may be a maximum 100 m long.
english
NOTE
When using other cable diameters, the maximum cable length also changes (refer to ASI
specification).
Process data
Data bits for inputs (sensor and prox. switches):
Bit No. Sensor Value allocation
Bit 0 S1 (sensor 1)
Bit 1 S2 (sensor 2)
Bit 2 S3 (terminal for add. prox. switch)
Bit 3 Not used always 0
Data bits for outputs (actuators and valves):
Bit No. Valve Value allocation
0 Prox. switch 1 OFF
1 Prox. switch 1 ON
0 Prox. switch 2 OFF
1 Prox. switch 2 ON
0 Prox. switch 3 OFF
1 Prox. switch 3 ON
Bit 0 V1 (Valve 1)
Bit 1 V2 (Valve 2)
Bit 2 V3 (Valve 3)
Bit 3 Not used always 0
Parameter bits: not used
22 - 1066
0 Valve 1 OFF
1 Valve 1 ON
0 Valve 2 OFF
1 Valve 2 ON
0 Valve 3 OFF
1 Valve 3 ON
Page 25

INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
II. ASI version with extended address range (A/B Slave)
1 Master can communicate with 62 Slaves with the ASI version with extended address range (A/B Slave).
As in the standard case, the bus cable with extended address range according to ASI specifications my be
a maximum 100 m long.
NOTE
Characteristics of the A/B Slave variant compared with the standard case
• 62 Slaves per Master
• The yellow OUT 4 LED on the ASI circuit board is no longer controllable, since the fourth output bit
used up to now is now used for the addressing.
• Limitations in power supply due to the nominal current of the inductors:
Only 2 solenoid valves can be connected at the same time; the third solenoid valve can only be
hooked up after 100 ms have passed.
ATTENTION!
Differences in the addressing of ASI variants
Parameters ASI Standard device ASI device for A/B Slave addressing
Number Slaves / Master 31 62
Maximum cable lengths also vary when other cable cross sections are used (see ASI
specifications).
If an A/B Slave device is being used as a replacement for a standard device, a
configuration error arises due to the different ID codes!
english
I/O Code 7 hex 7 hex
ID Code F hex A hex
Extended ID1 F hex 7 hex
Extended ID2 F hex E hex
Profile S-7.F.F S-7.A.E
1066 - 23
Page 26

INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
DeviceNet
Explanation of terms
• DeviceNet is a field bus system that is based on the CAN protocol (Controller Area Network). It makes
possible the networking of actuators and sensors (slaves) with a master control unit (master).
• In the DeviceNet, the Type 1066 control head is a slave device according to the Predefined
Master/Slave Connection laid down in the DeviceNet specification. Polled I/O, Bit Strobed I/O and
Change of State 4 (COS) are supported as I/O connection types.
• In DeviceNet, a differentiation is made between cyclic or event-controlled transmitted process messages
of higher priority (I/O Messages) and non-cyclic management messages of lower priority (Explicit Messages).
english
Technical data
• The protocol corresponds to
NOTE
Baud rate
Adresses
Process data
Inputs
Files
A diskette with configuration files (BUE1066.EDS and BUE1066.ICO) is always delivered
with the DeviceNet models. You can also obtain these files over the Internet.
125 kBit/s, 250 kBit/s, 500 kBit/s (via DIP switch);
Factory setting: 125 kBit/s
0 ... 63 (via DIP switch);
Factory setting: 63
2 static input assemblies
(Input: from control head 1066 to DeviceNet Master/Scanner)
1 static Output Assembly
3 sensors (proximity switches) S1 - S3, pnp, plus-switching
Supply via the DeviceNet line (11 to 25 V DC)
Switching level High signal ≥ 5 V
Switching level Low signal ≤ 1.5 V
BUE1066.EDS
BUE1066.ICO
You can also obtain these files over the Internet.
DeviceNet Specification Release 2.0
Maximum line lengths
The maximum total line lengths (sum of main and drop lines) of a network depend on the baud rate.
Total line lengths
Baud rate
125 kBaud 500 m
250 kBaud 250 m
500 kBaud 100 m
1)
According to the DeviceNet specification. When using another cable type, lower maximum values
apply (refer to the DeviceNet specification).
24 - 1066
according to the DeviceNet specification
Maximum total line length when using Thick Cables according to the
DeviceNet specification
1)
Page 27
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
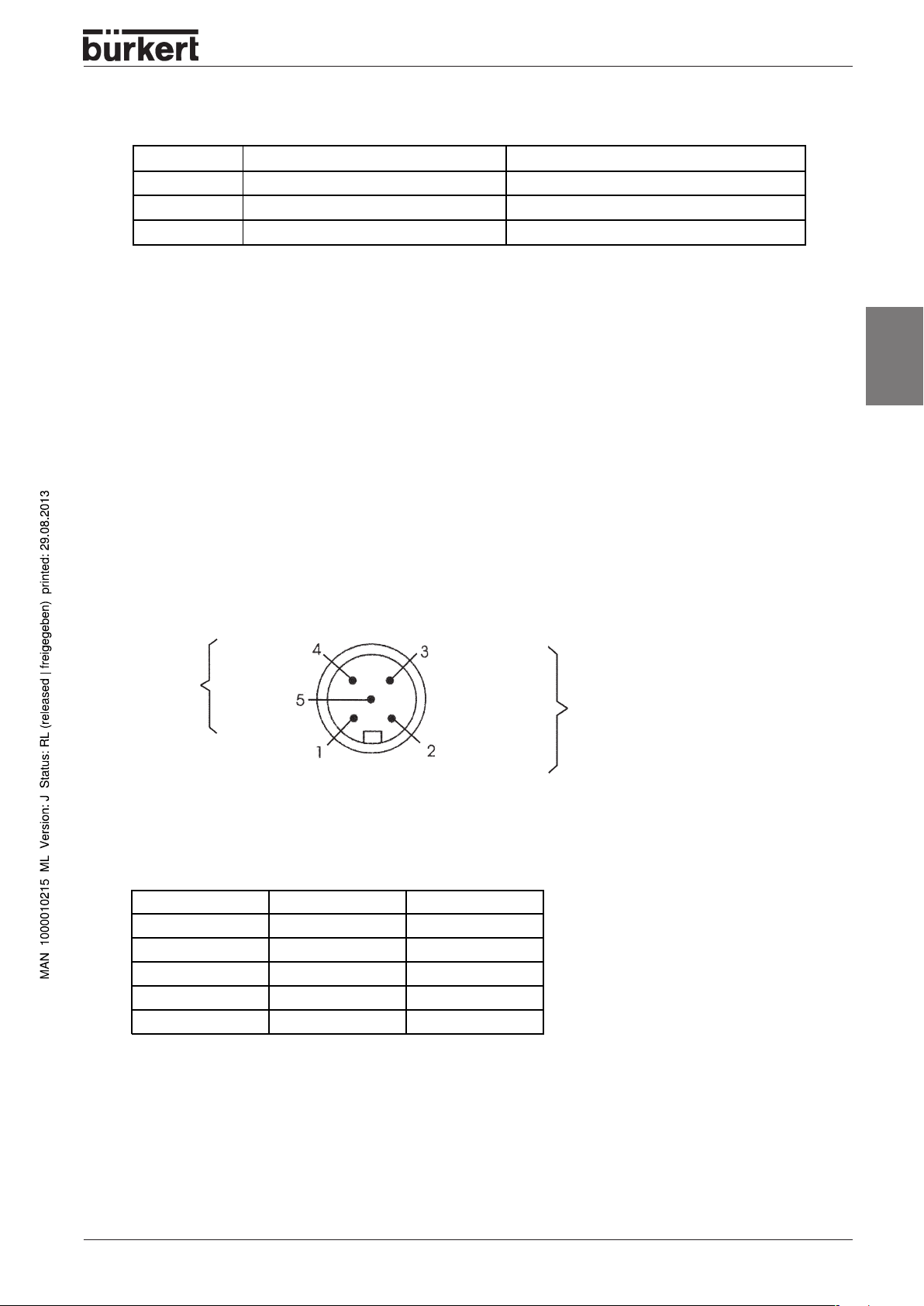
Drop line lengths
Baud rate Maximum length of a drop line Max. accumulated length in the network
125 kBaud 6 m 156 m
250 kBaud 6 m 78 m
500 kBaud 6 m 39 m
Safety setting for bus failure
In case of a bus failure, the setting of the last data byte of the bus outputs will be retained as long as
power is connected.
Electrical connection
The bus line is a 4-pole cable with an additional screen that must correspond to the DeviceNet
specifications and over which both information (data) and power (power supply for the low-power actuators
and sensors) will be transmitted.
english
Bus connection (round plug M12, 5-pole)
CAN_H
white
Data
lines
Plug viewed from the front looking at the pins (not at the solder side).
The Type 1066 control head has a 5-pole Micro-style M12 round plug. The following pin configuration
corresponds to the DeviceNet specification:
CAN_L
blue
Drain (screen)
not used
Pin Signal Colour
1 Screen not used
2V+ red
3V- black
4CAN_H white
5 CAN_L blue
Vblack
V+
red
Voltage supply
11 ... 25 V DC
max. power 5 W, if all
valves switched
(3 x Type 6510 with 1 W each)
Termination circuit for DeviceNet systems
When installing a DeviceNet system, attention must be paid to the correct termination circuit for the data
lines. This circuit prevents interference arising from signal reflection on the data lines. The main line must
therefore be terminated as both ends, as shown, with resistors of 120 Ω with 1/4 W power rating.
1066 - 25
Page 28
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
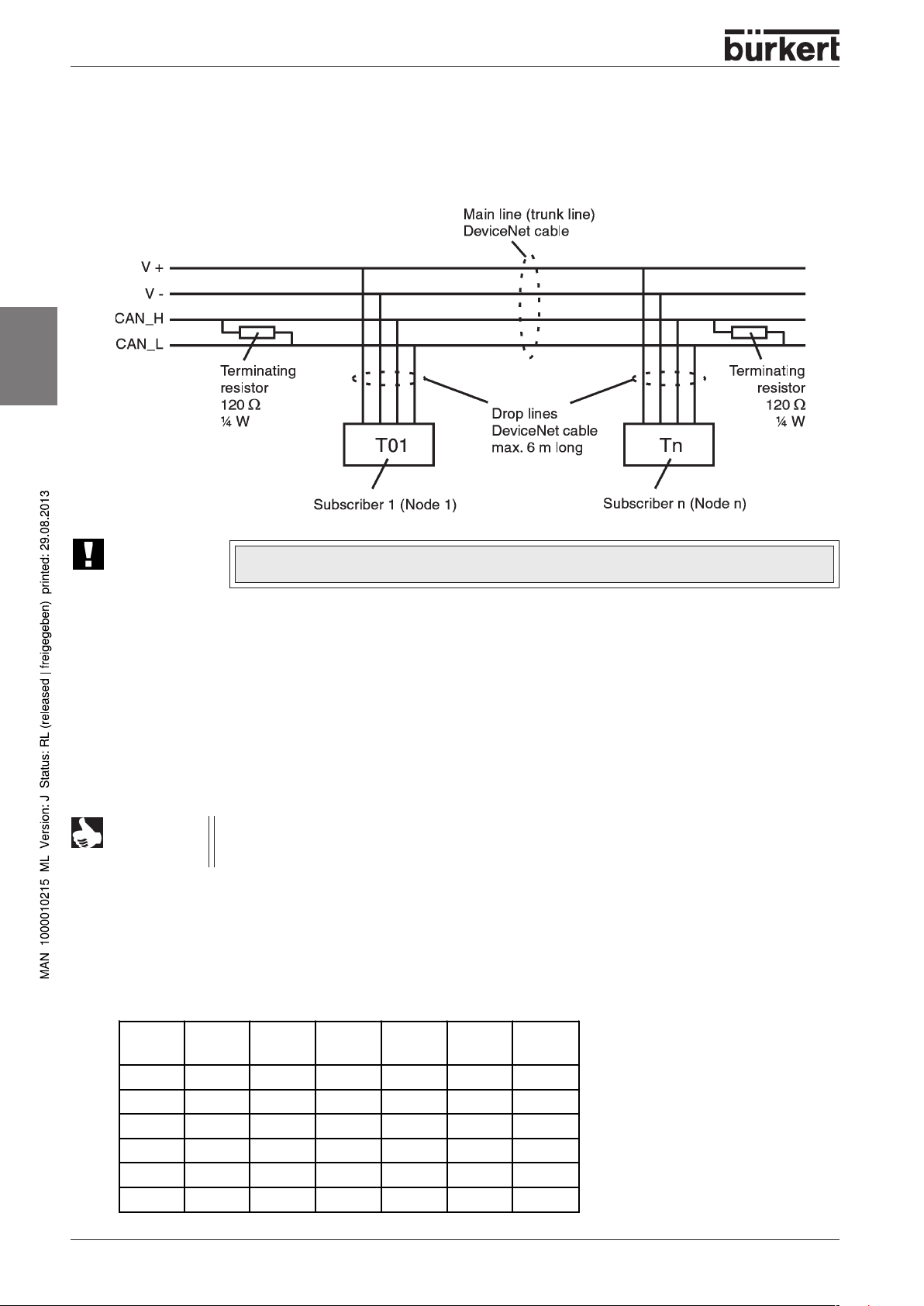
Network topology of a DeviceNet system
Line with a main line (trunk line) and several drop lines.
The main line and the drop lines are made up from identical material (see sketch).
english
ATTENTION!
To avoid reflections, fit terminating resistors at both ends of the trunk line (120
Configuration
DIP switch
8 DIP switches are fitted for the configuration:
• DIP switches 1 to 6 for the DeviceNet addresses
• DIP switches 7 and 8 for the baud rate
NOTE
Setting the DeviceNet address
MAC ID – Medium Access Control Identifier:
[Example of value allocation at switch DIP1:
DIP 1=off=0 / DIP 1=on=1 / MAC ID=DIP 1*20+DIP 2*21+...+DIP 6*25]
Before the commissioning of the controller with DeviceNet, the
into DeviceNet Configuration Tool. The required files (BUE1066.EDS and BUE1066.ICO)
are available on diskette or over the Internet.
EDS-Datei
ΩΩ
Ω
).
ΩΩ
must be read
[2
26 - 1066
=1]
DIP 2
[21=2]
DIP 1
0
off off off off off off 0
on off off off off off 1
off on off off off off 2
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
offononononon62
on on on on on on 63
DIP 3
[22=4]
DIP 4
[23=8]
DIP 5
[24=16]
DIP 6
[25=32]
MAC
ID
Page 29
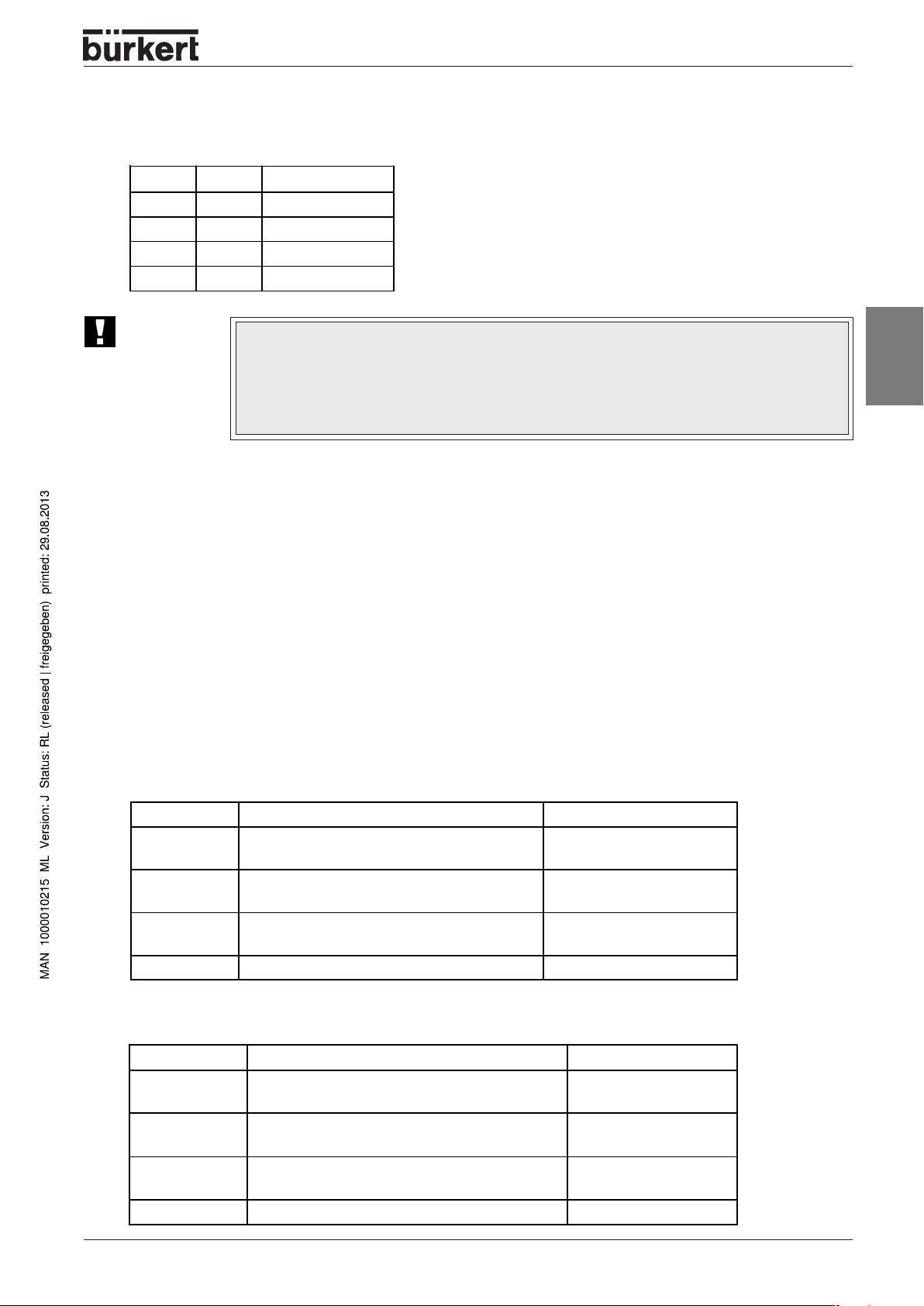
Setting the baud rate
Adapting the control head to the baud rate of the network.
DIP 7 DIP 8 Baud rate
off off 125 kBaud
on off 250 kBaud
off on 500 kBaud
on on not allowed
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
ATTENTION!
Any change to the settings using the DIP switches will only become effective
following a re-start of the device.
A re-start can be carried out by briefly unclamping and the re-clamping the control head
from/to the network or by sending a corresponding Reset Message. It is also possible be
switching the network power supply off and then on again.
Configuration of the Process Data
3 static inputs and 3 static output assemblies are available for the transmission of the process data via an
I/O connection. Selected attributes are gathered together in one object in these assemblies, in order to be
able to be transmitted together as process data via an I/O connection.
The process data can either be accessed cyclically in the connection variants "Polled I/O" and "Bit-strobed
I/O" with "Change of State" when the input values change, or non-cyclically via Explicit Messages.
The access path for non-cyclic access is: class 4
instance 1
attribute 3
With the
cyclic write access to the output data with
Get_Attribute_Single
service, non-cyclic read access can be obtained to the input data, and non-
Set_Attribute_Single.
english
1 Data Byte for inputs (sensors and/or proximity switches):
Bit Sensor Value allocation
Bit 0 S1 (Prox.switch 1)
Bit 1 S2 (Prox. switch 2)
Bit 2 S3 (Terminal for additional prox. switch)
Bit 3 ... Bit 7 Not used 0 always
1 Data Byte for inputs (sensors and/or proximity switches):
Bit Sensor Value allocation
Bit 0 S1 (Valve 1)
Bit 1 S2 (Valve 2)
Bit 2 S3 (Valve 3)
Bit 3 ... Bit 7 Not used 0 always
0 Prox. switch 1 OFF
1 Prox. switch 1 ON
0 Prox. switch 2 OFF
1 Prox. switch 2 ON
0 Prox. switch 3 OFF
1 Prox. switch 3 ON
0 Valve 1 OFF
1 Valve 1 ON
0 Valve 2 OFF
1 Valve 2 ON
0 Valve 3 OFF
1 Valve 3 ON
1066 - 27
Page 30
INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
LED Status Display
The device status will be indicated by 2 LEDs ("Power" and "MNS").
Name of the LED Type / Colour Function
POWER Single-colour, green LED lit up: device has electrical power
MNS
Tw o- c ol o u r,
red / green
english
Corresponds to MNS-LED according to DeviceNet
specification (MNS Module Network Status)
Status of the MNS LED
Once electrical power has been applied (connection of the network line), the following functional tests of
the two-coloured MNS LED are carried out:
• LED lights up green for a short time (ca. ¼ s).
• LED lights up red for a short time (ca. ¼ s).
• LED dark.
Once the functional tests have been completed, the MNS LED can indicate the device status as shown in
the table below.
LED
state
Dark
Green
Green
blinking
Red
blinking
Red Critical fault
Device status Explanation / Correction of problem
- No power supply to device.
No power /
not online
On-line, connection
to Master exists
On-line, no
connection to
Master
Connection
time-out
- Device has not yet finished the duplicate MAC ID Test (test lasts approx. 2s).
- Connect additional devices if the device is the only network participant.
- Replace the device.
- Normal operational status with connection made to Master.
- Normal operational status without connection made to Master.
- One or more connections are in the Time-Out state.
- Make new connection via the master to ensure that the I/O data will by
transmitted cyclically.
- Another device with the same MAC ID in the network > change MAC ID and
restart.
- BUS OFF as a result of communication problems.
- Check the baud rate: replace the device if necessary.
28 - 1066
Page 31

MAINTENANCE / CLEANING
MAINTENANCE / CLEANING
Maintenance / Cleaning ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 30
english
1066 - 29
Page 32

MAINTENANCE / CLEANING
Maintenance / Cleaning
When used correctly, the Type 1066 control head works without maintenance and without problems.
Repairs may only be carried out by authorised personnel using suitable tools.
Control heads operating in facilities may become contaminated by leaking medium and other influences.
In this event the facilities must be cleaned with suitable cleaning products and finally rinsed thoroughly
with water.
english
ATTENTION!
Before using cleaning materials,
the materials of the housing and the cover. ON cases of soiling, or following the use of
acidic or alkaline cleaning agents, always rinse thoroughly rinse off the control head with
clear water. In doing this, pay special attention that threaded holes and depressions are
clean and drained.
always check the compatibility of these agents with
30 - 1066
Page 33

REPAIRS
REPAIRS
english
Repairs ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 32
Removing and/or replacing the cover
Changing the printed circuit board
Replacing the valve group
Changing the valve on versions for 24 / 110 / 230 V UC without communication
Changing the proximity switch / micro-switch
....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 33
....................................................................................................................................................................... 32
................................................................................................................................................................................. 33
............................................ 34
................................................................................................................................................ 35
Spare Parts....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 36
Service Addresses ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 36
1066 - 31
Page 34

REPAIRS
Repairs
In case of the failure of certain components or modules, the control head can be repaired.
english
ATTENTION!
• Only use original spare parts for the repair work (refer to Spare Parts Table).
• Repairs may only be carried out by authorised specialists using suitable tools.
• Comply with the valid accident prevention regulations and the safety regulations.
• Ensure that the device is free of pressure and of electrical power before carrying out
any work.
• Check that the parameters of the spare parts agree with those given on the rating
plate of the control head being repaired.
Removing and/or replacing the cover
Removing the cover from the control head
Loosen the locking screw
Turn the cover to the left until it reaches the stop
Remove the cover by pulling upwards!
Fitting the cover
Check the seat of the cover O-ring, or pull
a new O-ring onto the collar of the cover.
NOTE
Distributed across the circumference
of the casing are 4 handles that
retain the O ring when the cover is
being removed.
Take care to ensure that the newlyapplied O ring is positioned correctly
under the handles and is resting on
the casing without twisting.
NOTE
Fit the cover.
Turn the cover right until it reaches the
stop.
Secure the cover where necessary to
prevent unauthorised access by
inserting a lead seal and/or a selftapping screw in the holes in the cover
and the housing.
Housing with
cover collar and
O-ring seat
32 - 1066
Page 35

Changing the printed circuit board
Proceed as follows:
Remove the cover.
Before disconnecting, mark the electrical connections so that it will
bepossible to reconnect them without error.
Disconnect all electrical connections from the printed circuit board
(plug and / or screw connections).
Loosen the four screws (Torx 10) with which the cover plate is secured.
Remove the cover plate.
Remove all circuit boards (no screw fittings).
Insert the new circuit boards.
ATTENTION!
Replace the cover plate.
ATTENTION!
Ensure the correct fit of the printed circuit boards into
the housing projections!
Ensure the correct fit of the circuit board an the screw
heads in the projections and/or the cut-outs in the
cover plate!
REPAIRS
Plate for
24 V DC
without communication
english
Replacement
ASI module, moulded
Screw down the cover plate (Torx 10; tightening torque 0.7 Nm).
Reconnect the electrical connections according to the markings made
earlier.
Refit the cover.
Replacing the valve group
The valve group consists of a connection plate with 1, 2 or 3 flanged
valves of the type 6510
housing.
NOTE
For 24 V DC without communication, ASI and
DeviceNet, only a change of the whole valve group
is permitted.
Proceed as follows:
Remove the cover.
Before disconnecting from the circuit board, mark the electrical
connections so that it will be possible to reconnect them without
error.
Disconnect all electrical connections from the printed circuit
board (screw connections).
Loosen the 2 screws (Torx 20) with which the valve group is
secured.
Remove the valve group complete with its O-rings.
Fit the new valve group complete with its O-rings.
Screw down the valve group (Torx 20; tightening torque 1.5 Nm).
Reconnect the electrical connections according to the markings made earlier.
Refit the cover, ensuring that the O-rings are correctly seated.
and the O-rings for the fluidic flange to the
Replacement
DeviceNet, moulded
Valve group, optionally
with 1, 2 or 3 valves
- 24 V DC without
communication
- ASI (24 V DC)
- DeviceNet (9 V DC)
1066 - 33
Page 36

REPAIRS
Changing the valve on versions for 24 / 110 / 230 V UC without
communication
english
For the verion for 24/110/230 V UC without communication only
paying attention to operating voltage. The valve connection plate remains in the control head.
valve model 6106
is exchanged while
Proceed as follows:
Remove the cover.
Unscrew the screws on the appliance socket.
Pull the appliance socket from the valve.
Note the mounting position of the tag connectors and the manual
override.
Loosen the 2 fixing screws on the valve body.
Remove the coil bobbin.
Loosen the 2 fixing screws on the valve body.
Remove the valve body complete with its O-rings.
Fit the new valve body together with its O-rings on the correct side
(manual override to the left)
Retighten the screws alternately and evenly
(tightening torque 0.5 Nm).
Fit the new coil bobbin on the correct side
(long tag connector to the left).
Valve
Type 6106
Alternately and evenly tighten the coil screws
(tightening torque 0.15 Nm).
Mount the appliance socket on the valve.
Secure the socket with a screw
(tightening torque 1 Nm).
Refit the cover.
34 - 1066
Page 37

Changing the proximity switch / micro-switch
Proceed as follows:
REPAIRS
Remove the cover.
Before disconnecting from the circuit board, mark the
electrical connections so that it will be possible to reconnect
them without error.
Disconnect all electrical connections to the proximity switch /
micro-switch from the printed circuit board (plug connections).
Loosen the four screws (Torx 10) with which the cover plate is
secured.
Remove the cover plate.
Note the positions of the proximity switch and the trigger of
the micro-switch.
Lift out the proximity switch / micro-switch with the adjusting
screw and the connecting cable.
Unscrew the old adjusting screws for re-use.
Screw the adjusting screws into the threaded holes on the
new proximity switch / micro-switch.
Only when there is a proximity switch:
Remove the O ring from the old proximity switch and insert it
into the clearance of the new proximity switch. (This O ring is
used to muffle vibration and prevents the proximity switch
from sliding out.)
Clearance for
O ring
Inductive proximity switch with
LED and moulded-on wire and
plug (the plug is not depicted in
the sketch)
english
Mount the new proximity switch with the adjusting screw in
the guide column.
ATTENTION!
Re-fit the cover plate.
ATTENTION!
Firmly screw down the cover plate
(Torx 10; tightening torque 0,7 Nm).
Reconnect the electrical connections to the proximity switch /
micro-switch according to the note made earlier.
Adjust the position of the proximity switch / micro-switch:
- Using a screwdriver, turn the adjusting screw (spindle)
until the optimal position of the proximity switch has been
set up.
Ensure the correct seating of the proximity switch / micro-switch in the guides
and depressions on the body.
Ensure the correct seating of the printed circuit
board and the screw heads in the projections
and cut-outs of the cover plate.
LED
LED
- The LED mounted on the proximity switch is an adjustment
aid: it lights up when reaching the corresponding threshold
value.
Refit the cover.
1066 - 35
Page 38

REPAIRS
Spare Parts
Position Spare part Order No.
english
1 ASI replacement module, sealed
2 Conductor plug straight, moulded cable, 1 m long, V 4A-M12 locking device
3 Flat cable clamp with bush, M12 outlet made of VA, gold contacts
4 Flat cable seal for clamp (if cable terminates here)
5 24 V DC board without communication
6 24 / 110 / 230 V UC board without communication
7 Inductive proximity switch (sensor)
8 Stop position microswitch complete
9 Adjusting screw for proximity switch / microswitch (1 item)
10 Shoulder screw M5 for securing the control head (10-pack)
11 Cover for control head (1 item)
12 O rings for cover (10-pack)
13 without communication, valve group with 1 valve, 24 V DC
14 without communication, valve group with 2 valves, 24 V DC
15 without communication, valve group with 3 valves, 24 V DC
16 with ASI communication, valve group with 1 valve, 24 V DC
17 with ASI communication, valve group with 2 valves, 24 V DC
18 with ASI communication, valve group with 3 valves, 24 V DC
19 with DeviceNet communication, valve group with 1 valve, 9 V DC
20 with DeviceNet communication, valve group with 2 valves, 9 V DC
21 with DeviceNet communication, valve group with 3 valves, 9 V DC
22 Single valve type 6106, 24 V UC
23 Single valve type 6106, 110 V UC
24 Single valve type 6106, 230 V UC
799 189
799 647
799 646
799 795
799 188
799 137
798 546
648 004
798 064
798 074
798 073
798 072
193 375
193 376
193 377
193 375
193 376
193 377
198 195
198 196
198 197
141 073
142 490
141 387
Positions 13 to 24 complete with O rings and fixing screws.
Service Addresses
Bürkert Werke GmbH & Co. KG Bürkert GmbH & Co. KG
Fluid Control System DC Dresden
Christian-Bürkert-Straße 13 - 17 Christian-Bürkert-Straße 2
74653 Ingelfingen 01900 Großröhrsdorf
Telephone: (0 79 40) 10 - 111 Telephone: (03 59 52) 36 - 300
Fax: (0 79 40) 10 - 448 Fax: (03 59 52) 36 - 551
36 - 1066
Page 39

Inhaltsverzeichnis
der Betriebsanleitung
Steuerkopf für Prozessventile Typ 1066
ALLGEMEINE HINWEISE
Darstellungsmittel ........................................................................................................... 40
Bestimmungsgemäße Verwendung ................................................................................ 40
Sicherheitshinweise........................................................................................................ 40
Lieferumfang ................................................................................................................... 41
Garantiebestimmungen ................................................................................................... 41
INHALT
Transport und Lagerung .................................................................................................. 42
Entsorgung......................................................................................................................42
TECHNISCHE DATEN
Aufbau und Funktion des Steuerkopfes .......................................................................... 44
Merkmale ........................................................................................................................44
Betriebsbedingungen...................................................................................................... 45
Mechanische Daten ........................................................................................................ 45
Pneumatische Daten....................................................................................................... 46
Elektrische Daten ............................................................................................................ 46
MONTAGE
Montage des Steuerkopfes ............................................................................................. 48
Flanschadapter ....................................................................................................................... 48
Montageablauf......................................................................................................................... 49
deutsch
INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
Pneumatische Installation ............................................................................................... 52
Anschlussbelegung am Steuerkopf ........................................................................................ 52
Elektrische Installation .................................................................................................... 53
Steuerköpfe ohne Kommunikation .......................................................................................... 53
Steuerköpfe mit Kommunikation ............................................................................................. 55
1066 - 37
Page 40

INHALT
WARTUNG / REINIGUNG
Wartung / Reinigung ....................................................................................................... 66
REPARATUR
Reparaturen .................................................................................................................... 68
Deckel abnehmen bzw. aufstecken ........................................................................................ 68
Wechsel der Leiterkarte.......................................................................................................... 69
Wechsel der Ventilgruppe ....................................................................................................... 69
Wechsel des Ventils bei Versionen für 24/110/230 V UC ohne Kommunikation ...................... 70
Wechsel Näherungsschalter / Mikroschalter .......................................................................... 70
Ersatzteile ....................................................................................................................... 72
Serviceanschriften .......................................................................................................... 72
deutsch
38 - 1066
Page 41

ALLGEMEINE HINWEISE
ALLGEMEINE
HINWEISE
Darstellungsmittel............................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 40
deutsch
Bestimmungsgemäße Verwendung .................................................................................. 40
Sicherheitshinweise ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 40
Lieferumfang............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 41
Garantiebestimmungen ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 41
Transport und Lagerung............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 42
Entsorgung.................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 42
1066 - 39
Page 42

ALLGEMEINE HINWEISE
Darstellungsmittel
In dieser Betriebsanleitung werden folgende Darstellungsmittel verwendet:
markiert einen Arbeitsschritt, den Sie ausführen müssen.
ACHTUNG!
HINWEIS
kennzeichnet Hinweise, bei deren Nichtbeachtung Ihre Gesundheit oder die Funktionsfähigkeit des Gerätes gefährdet ist.
kennzeichnet wichtige Zusatzinformationen, Tipps und Empfehlungen.
Bestimmungsgemäße Verwendung
• Der Steuerkopf für Prozessventile Typ 1066 dient zur Ansteuerung pneumatisch betätigter Prozessventile und zur Erfassung von deren Schaltzuständen. Andere Einsatzfälle gelten als nicht
bestimmungsgemäß.
deutsch
• Die in dieser Anleitung, im Datenblatt sowie auf dem Typschild aufgeführten Technischen Daten sind
vor der Inbetriebnahme auf Übereinstimmung zu prüfen und während des Betriebes des Steuerkopfes
einzuhalten.
• Eigenmächtige Umbauten und Veränderungen am Steuerkopf sind aus Sicherheitsgründen verboten.
• Schützen Sie den Steuerkopf vor Eingriffen Unbefugter. Dazu kann der Steuerkopf mit einer Plombe
und / oder einer Schneidschraube an den an Deckel und Gehäuse vorhandenen Bohrungen gesichert
werden.
• Die in dieser Anleitung gegebenen Arbeitsanweisungen und Sicherheitshinweise sind unter allen Umständen zu beachten und einzuhalten. Bei Nichtbeachtung dieser Arbeitsanweisungen und deren Reihenfolge sowie der Sicherheitshinweise oder der Sicherheitskennzeichnung erlischt der Haftungsanspruch.
Sicherheitshinweise
Beachten Sie die Hinweise dieser Betriebsanleitung sowie die Einsatzbedingungen und zulässigen Daten,
die in den Datenblättern und auf dem Typschild des Steuerkopfes für Prozessventile spezifiziert sind,
damit das Gerät einwandfrei funktioniert und lange einsatzfähig bleibt.
• Halten Sie sich bei der Einsatzplanung und dem Betrieb des Gerätes an die allgemeinen Regeln der
Technik!
• Installation und Wartungsarbeiten dürfen nur durch Fachpersonal und mit geeignetem Werkzeug erfolgen!
• Verwenden Sie für erforderliche Reparaturen nur Originalersatzteile und beachten Sie beim Wechseln
dieser Teile die Hinweise dieser Anleitung.
• Beachten Sie die geltenden Unfallverhütungs- und Sicherheitsbestimmungen während des Betriebes
und der Wartung des Gerätes!
• Schalten Sie vor Eingriffen in das System in jedem Fall die Spannung ab!
• Beachten Sie, dass in Systemen, die unter Druck stehen, Leitungen und Ventile nicht gelöst werden
dürfen!
• Treffen Sie geeignete Maßnahmen, um unbeabsichtigtes Betätigen oder unzulässige Beeinträchtigung auszuschließen!
• Gewährleisten Sie nach einer Unterbrechung der elektrischen oder pneumatischen Versorgung einen
definierten und kontrollierten Wiederanlauf des Prozesses!
40 - 1066
Page 43

ALLGEMEINE HINWEISE
HINWEIS
• Vermeiden Sie höhere mechanische Belastungen des Steuerkopfes, die zur mechanischen Beeinträchtigung oder Zerstörung des Steuerkopfes führen können. Dazu gehören Begehen, Ablegen schwerer
Gegenstände, harte Schläge, herabfallende harte Gegenstände u.a.
• Vermeiden Sie das Eindringen von Feuchte in den Steuerkopf. Achten Sie insbesondere bei der Montage auf den ordnungsgemäßen Einbau aller Dichtungen, auf fest angezogene Montageschrauben, Kabelverschraubungen und Dichtstopfen. Verwenden Sie nur getrocknete Steuerluft!
HINWEIS
• Vermeiden Sie den Anschluss längerer und mechanisch starrer Anschlussteile, da mit solch einer Verlängerung Hebelkräfte erzeugbar wären, mit denen das Gehäuse von Hand zerstört werden könnte.
HINWEIS
• Verwenden Sie zur Reinigung des Steuerkopfes nur gut verträgliche Reinigungsmittel und spülen Sie
nach Einsatz dieser Reinigungsmittel gründlich mit klarem Wasser nach. Die Verträglichkeit des
Reinigungsmittels sollte gegebenenfalls getestet werden.
Der Steuerkopf ist in der Schutzart IP67 ausgelegt. Das setzt einen guten Sitz aller
Dichtungen und die mechanische Unversehrtheit von Gehäuse und Deckel voraus.
Das Kunststoffgehäuse des Steuerkopfes ist bezüglich seiner mechanischen
Festigkeit nur für den unmittelbaren Anschluss von flexiblen Schläuchen und
Leitungen ausgelegt.
Reinigungsmittel enthalten oftmals aggressive Bestandteile, die sich in kleinen
Rillen und Vertiefungen am Steuerkopf absetzen können und deren Dauereinwirkung zur Zerstörung auch hochwertiger Kunststoffe führen kann.
deutsch
HINWEIS
• Sichern Sie bei der Montage des Steuerkopfes einen Mindestabstand von 5 mm zwischen dem Überdruckventil und dem nächsten Bauteil, damit das Überdruckventil im Leckagefall problemlos auslösen
kann. Anderenfalls könnte bei Leckage im Steuerkopf der Deckel regelrecht „abgesprengt“ werden.
• Bei Nichtbeachtung dieser Hinweise und unzulässigen Eingriffen in das Gerät entfällt jegliche Haftung
unsererseits, ebenso erlischt die Garantie auf Geräte und Zubehörteile!
Lieferumfang
Überzeugen Sie sich unmittelbar nach Erhalt der Sendung, dass der Inhalt nicht beschädigt ist und mit
dem auf dem beigelegten Packzettel angegebenen Lieferumfang übereinstimmt.
Bei Unstimmigkeiten wenden Sie sich bitte umgehend an unser Call-Center:
oder an Ihr Bürkert Vertriebs-Center.
Auf der Gehäuseunterseite des Steuerkopfes befindet sich ein Überdruckventil als
Berstschutz für den Fall eines undichten Bauelements im Steuerkopf (Leckagefall).
Bürkert Fluid Control System, Call-Center
Chr.-Bürkert-Str. 13-17, D-74653 Ingelfingen
Tel. 07940 - 10 111 / Fax 07940 - 10 91 448
E-Mail: info@de.buerkert.com
Garantiebestimmungen
Diese Druckschrift enthält keine Garantiezusagen. Wir verweisen hierzu auf unsere allgemeinen Verkaufsund Geschäftsbedingungen. Voraussetzung für die Garantie ist der bestimmungsgemäße Gebrauch des
Gerätes unter Beachtung der spezifizierten Einsatzbedingungen.
ACHTUNG!
Die Gewährleistung erstreckt sich nur auf die Fehlerfreiheit des Steuerkopfes für
Prozessventile. Es wird jedoch keine Haftung übernommen für Folgeschäden jeglicher
Art, die durch Ausfall oder Fehlfunktion des Gerätes entstehen könnten.
1066 - 41
Page 44

ALLGEMEINE HINWEISE
Transport und Lagerung
ACHTUNG!
Lagerung in einem trockenen Raum.
Maximale Lagertemperatur +50 °C
Entsorgung
ACHTUNG!
deutsch
Transportieren und lagern Sie das Gerät nur in der Originalverpackung.
Beachten Sie bei der Entsorgung des Gerätes die nationalen Abfallbeseitigungsvorschriften.
42 - 1066
Page 45

TECHNISCHE DATEN
TECHNISCHE DATEN
Aufbau und Funktion des Steuerkopfes ............................................................................................................................................................... 44
Merkmale ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 44
deutsch
Betriebsbedingungen ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 45
Mechanische Daten ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 45
Pneumatische Daten ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 46
Elektrische Daten.................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 46
1066 - 43
Page 46

TECHNISCHE DATEN
Aufbau und Funktion
Der Steuerkopf Typ 1066 dient zur Ansteuerung von pneumatisch betätigten Prozessventilen unterschiedlicher Hersteller. Er ist je nach Konfiguration mit bis zu drei Magnetventilen (Pilotventilen) zur Prozessventilansteuerung bestückbar und mit maximal drei höhenverstellbaren induktiven Näherungsschaltern
(Sensoren) zur Stellungsrückmeldung ausrüstbar. Einer dieser Sensoren kann auch ein externer Sensor
sein (Anschluss über 3-polige Schraubklemme auf Leiterplatte).
HINWEIS
Näherungsschalter 1
deutsch
Beachten Sie bei den vergossenen Feldbusmodulen die Nummerierung der Näherungsschalter auf der Platine bzw. die Kennzeichnung am Gerät, da Abweichungen zur Nummerierung in der untenstehenden Zeichnung möglich sind.
Justierung
Leiterkarte
Säule mit Spindel
Markierung für
Deckelmontage
Elektr. Anschlüsse
Justierung durch diese Bohrungen
Abdeckplatte
Justierung Näherungsschalter 2
Näherungsschalter 2
Magnetventil 3
Magnetventil 2
Magnetventil 1
Gehäuse
Abluft
Näherungsschalter 1
Ventilflansch
Merkmale
Mit dem Steuerkopf Typ 1066 existiert neben den für den eher zentralen Einsatz vorgesehenen Ventilinseln eine dezentrale Lösung zur Ansteuerung von Prozessventilen. Die Vorteile dieser Lösung in Form
der kompakten Einheit
Feldbusschnittstellen sind:
Haupteinsatzgebiete:
Pneumatische Anschlüsse
Ventil 3Ventil 2Ventil 1
Schnittstelle zum
Prozessventil
Steuerkopf
Geringer Installationsaufwand.
Einfache Inbetriebnahme.
Kurze Schaltzeiten auf Grund kurzer Wege zwischen Pilotventil und Prozessventil.
Lebensmittelindustrie (z. B. Molkereien)
Chemische Industrie
Pharmaindustrie
Kosmetikindustrie
mit den Pilotventilen, der Stellungsrückmeldung und optional nutzbaren
Druckluft
44 - 1066
Brauereien
Page 47

Optionen
Anzahl der Pilotventile
Wirkungsweise / Einsatzart Anzahl d. Pilotventile
Einfach wirkende Stellantriebe 1
Doppelt wirkende Stellantriebe 2
Doppelsitzventile mit integrierter Anlüftung beider Ventilsitze 3
Steuerköpfe ohne Kommunikation
8-polige Schraubklemme für 24 V DC
Multipol (8-poliger Rundstecker) für 24 V DC
2 x 6 Schraubklemmen für 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
TECHNISCHE DATEN
Steuerköpfe mit Kommunikation
Aktor-Sensor-Interface (ASI)
DeviceNet
ACHTUNG!
Der Anschluss an andere (höhere) Bussysteme ist über handelsübliche Gateways
möglich.
Betriebsbedingungen
Medien Druckluft, ungeölt; neutrale Gase
Mediumstemperatur -10 ... + 50 °C
Umgebungstemperatur -10 ... + 50 °C
Schutzart IP 67
deutsch
ACHTUNG!
Der Steuerkopf ist nicht für den Einsatz im Außenbereich geeignet!
Mechanische Daten
Masse 0,5 bis 0,65 kg (je nach Ausführung)
Gehäusematerial Gehäuse PA / PPE
Deckel PSU (transparent, blaugrau)
Dichtungsmaterial NBR
1066 - 45
Page 48

TECHNISCHE DATEN
Pneumatische Daten
Leitungsanschlüsse Druckluft/Abluft G 1/4
Arbeitsanschlüsse Schlauchanschluss
6/4 mm oder 1/4 Zoll steckbar
Druckbereich 2,5 bis 7 bar
Luftleistung Steuerventil 110 l/min Typ 6510, 40 l/min Typ 6106
Schaltzeiten Typ 6510 / Typ 6106
Stellbereich min. Hub 2 mm max. Hub 73 mm
deutsch
Elektrische Daten
Schutzart IP 67
Betriebsspannungen
Max. elektrische Verlustleistung 5 W bei 3 x Typ 6510 oder bei 1 x Typ 6106
Anschlüsse
Durchfluss: Q
Messung bei +20 °C, 6 bar Druck am Ventileingang und 1 bar
Druckdifferenz
Öffnen 15 / 23 ms Schließen 10 / 21 ms
Messung am Ventilausgang bei 6 bar und +20 °C
Öffnen: Druckaufbau 0 bis 90 %
Schließen: Druckabbau 100 bis 10 %
ohne Kommunikation 24 V DC ±10 %
24/110/230 V UC ±10 %
mit Kommunikation entsprechend der ASI- und DeviceNet-Spezifikation
Steuerköpfe
ohne Kommunikation: Multipol (8-poliger Rundstecker DIN 45326) für 24 V DC
8-polige Schraubklemme für 24 V DC
2 x 6-polige Schraubklemmen für 24/110/230 V UC
- Wert-Luft (l/min)
Nn
Steuerköpfe
mit Kommunikation:
ASI: Schneid-Klemm-Verbinder und Kabel-Verschraubung
M12-Stecker und Kabelverschraubung
M12-Flanschstecker, 4-polig
DeviceNet: 5-poliger Steckverbinder M12
Magnetventile
Nennleistung 1 W Typ 6510 / 3 W Typ 6106
Betriebsart Dauerbetrieb (ED 100 %)
Näherungsschalter
Betriebsspannung 8 bis 30 V DC
Ausgangssignal max. 100 mA, kurzschlussfest
Mikroschalter potentialfrei, max. 1 A Schaltstrom
46 - 1066
Page 49

MONTAGE
MONTAGE
Montage des Steuerkopfes....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 48
Flanschadapter
Montageablauf
...................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 48
......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 49
deutsch
1066 - 47
Page 50

MONTAGE
Montage des Steuerkopfes
Flanschadapter
Zur Montage des Steuerkopfes Typ 1066 an einem Prozessventil verschiedener Hersteller benötigen Sie
einen Adapter mit kundenspezifischem Flansch (Flanschadapter) und einen kundenspezifischen Schaltknopf (siehe auch Datenblatt). Das Anschlussteil für den Steuerkopf ist bürkertspezifisch. Das Flanschteil
muss der Bauform des Prozessventiles angepasst werden. Die untenstehende Zeichnung stellt ein
Applikationsbeispiel für ein spezielles Prozessventil dar. Die Einbaulage des Steuerkopfes ist beliebig,
vorzugsweise mit Deckel nach oben.
Halten Sie bei Eigenfertigung des Flanschadapters folgende Parameter exakt ein
Abmessungen
Anzahl der Dichtstellen
Abmessungen für die O-Ringe
Maßtoleranzen
Materialangaben
deutsch
Hauptabmessungen für Flanschadapter
Zylinderförmiges Adapterteil
Kundenspezifisches Flanschteil
HINWEIS
ACHTUNG!
48 - 1066
Bitte fordern Sie zur Eigenfertigung des Flanschadapters detaillierte Maßzeichnungen an!
Zur Montage des Flanschadapters ist eine Zentrierung notwendig.
zulässige Achsabweichung beträgt ±0,1 mm. Bei Überschreiten dieser Toleranz besteht
die Gefahr, dass die Näherungsschalter nicht ordnungsgemäß funktionieren.
Verwenden Sie eine spezielle Montagehülse zur Vermeidung dieser Toleranzüberschreitung.
Die maximal
Page 51

Montageablauf
Flanschadapter auf das
1
Prozessventil montieren/
Schaltknopf auf Kolbenstange
befestigen (kundenspezifisch)
Zentrierung beachten
MONTAGE
Deckel vom Steuerkopf abnehmen
2
Lösen Sie die Sicherheitsschrauben
Drehen Sie den Deckel bis zum Anschlag
nach links
Ziehen Sie den Deckel nach oben ab
deutsch
Steuerkopf auf den
3 4
Flanschadapter aufstecken
Positionieren Sie den Steuerkopf
(Steuerkopf ist um 360° frei drehbar)
Sichern Sie den Steuerkopf mittels der
zwei seitlich angeordneten Schrauben
Installation der pneumatischen
Anschlüsse
Siehe Pneumatische Installation,
(Kapitel Installation Inbetriebnahme)
1066 - 49
Page 52

MONTAGE
5
deutsch
Installation der elektrischen
Anschlüsse
Steuerköpfe ohne und
mit Kommunikation
(siehe Kapitel elektrische Installation)
7
Deckel aufsetzen
Prüfen Sie den Sitz des
Deckel-O-Rings bzw. ziehen sie einen
neuen O-Ring auf den Deckelbund
HINWEIS
Am Gehäuse existieren über den
Umfang verteilt 4 Nasen, die den
O-Ring beim Abziehen des Deckels
zurückhalten.
Achten Sie darauf, dass sich der neu
eingesetzte O-Ring korrekt unter den
Nasen befindet und durchgängig
unverdrillt am Gehäuse anliegt.
Stecken Sie den Deckel auf
Drehen Sie den Deckel bis zum
Anschlag nach rechts
Justieren
6
der Näherungsschalter
Drehen Sie mit einem Schraubendreher an der
Justierschraube (Spindel) bis die optimale Lage
der Näherungsschalter eingestellt ist.
Als Justierhilfe dient die am Näherungsschalter
angebrachte LED, sie leuchtet beim Erreichen
des betreffenden Schwellwertes auf.
der Endlagen-Mikroschalter
Bei dem Einsatz von Mikroschaltern wird aus
Kostengründen auf LEDs verzichtet.
Lageeinstellung wie bei den Näherungsschaltern
Nutzen Sie als Justierhilfe das
Schaltgeräusch des
Mikroschalters (sehr leise)
oder eine externe elektrische
Durchgangsprüfung
LED
Gehäuse mit
Deckelbund
und O-Ring-Sitz
LED
HINWEIS
50 - 1066
Sichern Sie den Deckel gegebenenfalls
gegen Fremdeingriffe durch Einführen
einer Plombe und / oder einer Schneidschraube in die an Deckel und Gehäuse
vorhandenen Bohrungen.
Page 53

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
INSTALLATION
INBETRIEBNAHME
Pneumatische Installation.......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 52
deutsch
Anschlussbelegung am Steuerkopf............................................................................................................................................................................. 52
Elektrische Installation .................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 53
Steuerköpfe ohne Kommunikation
8-polige Schraubklemme für 24 V DC
Multipol (8-poliger Rundstecker nach DIN 45326) für 24 V DC
2 x 6-polige Schraubklemme für 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
Steuerköpfe mit Kommunikation
AS-Interface
...................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 55
Handhabung der Flachkabelklemme
Technische Daten für ASI-Leiterplatten
Programmierdaten
............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 56
LED-Zustandanzeige ASI
Bitbelegung
................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 57
Anzahl anschließbarer Steuerköpfe und maximale Länge der Busleitung
(ASI-Standardfall und ASI-Version mit erweitertem Adressbereich)
DeviceNet
Begriffserklärung
Technische Daten
........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 60
................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 60
............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 60
Maximale Leitungslängen
Sicherheitseinstellung bei Ausfall des Busses
Elektrischer Anschluss
Konfigurieren
............................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 62
LED-Zustandsanzeige
................................................................................................................................................................................. 53
............................................................................................................................................................. 53
..................................................................................... 54
................................................................................................................. 54
....................................................................................................................................................................................... 55
........................................................................................................................................................ 56
................................................................................................................................................ 56
....................................................................................................................................................................................... 57
.............................................................. 57
........................................................................................................................................................................................ 60
............................................................................................................................ 61
.............................................................................................................................................................................................. 61
................................................................................................................................................................................................ 64
1066 - 51
Page 54

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
Pneumatische Installation
Anschlussbelegung am Steuerkopf
G 1/4 G 1/4
Druckluft Abluft
Steckanschlüsse
deutsch
für Schlauch 6/4 mm oder 1/4"
ACHTUNG!
steckbar
für Ventile V1, V2 und V3
• Verwenden Sie nur kalibrierte Schlauchleitungen mit 6 mm oder ¼ " Außendurchmesser.
• Schneiden Sie diese nur mit einem Schlauchschneider ab (Beschädigungsgefahr)
• Dimensionieren Sie die Schlauchlänge so, dass der Steuerkopf mit der Verschraubung
abgenommen werden kann.
• Achten Sie auf eine spannungsfreie, zum Steckverbinder gut fluchtende Schlauchführung, da verspannt (schräg) eingesteckte Schläuche zu Undichtigkeiten am Steckanschluss führen können.
52 - 1066
Page 55

Elektrische Installation
Steuerköpfe ohne Kommunikation
Der elektrische Anschluss von Steuerköpfen ohne Kommunikation erfolgt in verschiedenen Varianten.
Bei der Ausführung für 24 V DC wird der Zustand je Ventil einheitlich mit je einer LED angezeigt.
8-polige Schraubklemme für 24 V DC
(im Gehäuseinneren, Kabeldurchführung mit Kabelverschraubung )
LED Zustandsanzeige 24 V DC
INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
Belegungsplan für die 8-polige Schraubklemme
V = Ventil
S = Näherungsschalter (Sensor)
für Näherungsschalter
HINWEIS
Die Ausgänge der Näherungsschalter sind pnp-plusschaltend und kurzschlussfest.
Ground
Schaltsignal des externen Näherungs-
schalters S3
Stromversorgung
deutsch
1066 - 53
Page 56

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
Multipol (8-poliger Rundstecker nach DIN 45326) für 24 V DC
Blick auf den im Kopf eingebauten Stecker, von vorn auf die Stifte gesehen, die Lötanschlüsse liegen
dahinter.
Näherungsschalter 3
Ausgänge der Näherungsschalter
pnp-plusschaltend, kurzschlussfest
Näherungsschalter 2
Näherungsschalter 1
(gemeinsame Masse für Ventile)
deutsch
HINWEIS
2 x 6-polige Schraubklemme für 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
Die Ausführung 2 x 6-polige Schraubklemme umfasst:
Leiterkarte mit 2 x 6-poligen Schraubklemmen für 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
GND
Ventil 3
Ventil 2
Die Ausgänge der Näherungsschalter sind pnp-plusschaltend und kurzschlussfest.
Kabeldurchführung mit Kabelverschraubung
Max. 1 Ventil (Typ 6106, DN1,2)
2 mechan. Mikro-Endschalter mit potentialfreien Kontakten zur Stellungsrückmeldung
(Keine LED-Zustandsanzeige)
Ventil 1
24 V DC
(Betriebsspannung für Näherungsschalter)
54 - 1066
Page 57

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
Steuerköpfe mit Kommunikation
AS-Interface
ASI (Aktor-Sensor-Interface) ist ein Feldbussystem, das zur Vernetzung von hauptsächlich binären Sensoren und Aktoren (Slaves) mit einer übergeordneten Steuerung (Master) dient.
Busleitung
Ungeschirmte Zweidrahtleitung (ASI-Leitung als ASI-Formkabel), auf der sowohl Informationen (Daten) als
auch Energie (Spannungsversorgung der Aktoren und Sensoren) übertragen werden.
Netztopologie
In breiten Grenzen frei wählbar, d. h. es sind Stern,- Baum- und Liniennetze möglich. Weitere Details finden
sie in der ASI Spezifikation.
Busanschlussvarianten
HINWEIS
1. Flachkabelklemme am 1 m Rundkabel
ASI-Standardanschluss:
2. 4-poliger M12-Stecker am 2 m Rundkabel
ASI-Sonderanschluss 1: (auf Anfrage)
Daten für das Rundkabel
Das unmittelbar zum Steuerkopf führende Rundkabel weicht in seinen elektrischen Werten
geringfügig vom ASI-Standard ab. Bei der Berechnung der max. zulässigen Leitungslänge
nach ASI-Spezifikation sollte es deshalb um den Faktor 1,5 länger als tatsächlich angesetzt werden.
ASI-Länge = 1,5 x reale Länge
deutsch
4-poliger M12-Stecker
für ASI-Anschluss
3. 4-poliger M12-Stecker am Steuerkopf, ohne Kabel
ASI-Sonderanschluss 2: (auf Anfrage)
PIN-Belegung ASI
1 = ASI+
2 = nicht belegt
3 = ASI4 = nicht belegt
1066 - 55
Page 58

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
Handhabung der Flachkabelklemme
Mit der Flachkabelklemme für ASI-Formkabel wird die Kontaktierung in Form einer Durchdringungtechnik
realisiert. Der elektrische Anschluss erfolgt dabei ohne Schneiden und ohne Abisolieren des Kabels.
HINWEIS
deutsch
Verschließen Sie die zweite Kabelöffnung mit einer Kabeldichtung, wenn das Flachkabel in
der Klemme endet (letzter Anschluss).
Verbindung der Flachkabelklemme mit Leitungsstecker und angespritztem Kabel mit einem ASI-Flachkabel
Lösen Sie die beiden Schrauben der Flachkabelklemme.
Trennen Sie das Oberteil der Flachkabelklemme vom Unterteil.
Legen Sie das ASI-Flachkabel lagegerecht ein.
Falls das Flachkabel hier endet:
Setzen Sie die Flachkabeldichtung lagegerecht in die Öffnung ein.
Plazieren Sie das Oberteil der Flachkabelklemme auf das Unterteil.
Ziehen Sie die Schrauben fest an.
Fertig!
Der elektrische Anschluss zum ASI-Kabel ist hergestellt.
Flachkabeldichtung für Flachkabelklemme
Technische Daten für ASI-Leiterplatten
Eingänge 3 Sensoren S1 - S3, pnp plusschaltend
Versorgung über AS-Interface (24 V +20 % / -10 %), kurzschlussfest,
strombegrenzt auf 60 mA
Schaltpegel High-Signal ≥ 10 V
Begrenzung Eingangsstrom ≤ 6,5 mA, Eingangsstrom Low-Signal ≤ 1,5 mA
Ausgänge 3 Ventile V1 - V3
max. 3 x 1 W
Leistungsreduzierung nach ca. 100 ms, mit integrierter Watch-Dog-Funktion
Programmierdaten
I/O-Code 7 hex (4 Ausgänge und 4 Eingänge)
ID-Code F hex (Bitbelegung siehe nachstehende Tabelle); erweiterte ID-Codes 1 und 2 = F hex
Profil 7.F
56 - 1066
Page 59

LED-Zustandsanzeige ASI
SichtbarerTeil der ASI-Leiterkarte
INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
Statusanzeige Bus
LED grün rot
LEDs für Ventile
V1 - V3
Übersicht LED-Zustandsanzeige ASI
LED Bus Status
grün rot
dunkel dunkel POWER OFF
dunkel hell kein Datenverkehr (abgelaufener Watchdog bei Slaveadresse ungleich 0)
hell dunkel ok
blinkt blinkt Peripheriefehler (Überlast in Sensorversorgung)
blinkt hell Slaveadresse gleich 0
dunkel blinkt RESET
LEDs für Näherungsschalter S1 - S3
Schaltsignal eines
externen Näherungs-
Spannungsversorgung
eines externen Näherungsschalters (aus dem ASIStrang)
schalters
deutsch
Bitbelegung
Datenbit D3 D2 D1 D0
Ausgang
LED gelb
Eingang
nicht belegt
Parameterbit P3 P2 P1 P0
Ausgang
Ventil 3
Eingang
Näherungsschalter 3
nicht belegt
Ausgang
Ventil 2
Eingang
Näherungsschalter 2
Ausgang
Ventil 1
Eingang
Näherungsschalter 1
1066 - 57
Page 60

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
Anzahl anschließbarer Steuerköpfe und maximale Länge der
Busleitung
I. ASI-Standardfall
Im Standardfall können maximal 31 Steuerköpfe an eine Busleitung angeschlossen werden.
Das Buskabel darf nach ASI-Spezifikation maximal 100 m lang sein.
deutsch
HINWEIS
Bei Einsatz anderer Kabelquerschnitte verändern sich auch die maximalen Kabellängen
(siehe ASI-Spezifikation).
Prozessdaten
Datenbits für Eingänge (Sensoren bzw. Näherungsschalter):
Bit-Nr. Sensor Wertezuordnung
Bit 0 S1 (Sensor 1)
Bit 1 S2 (Sensor 2)
Bit 2 S3 (Anschlussklemme für zusätzlichen Näherungsschalter)
Bit 3 nicht benutzt immer 0
Datenbits für Ausgänge (Aktoren bzw. Ventile):
Bit-Nr. Ventil Wertezuordnung
Bit 0 V1 (Ventil 1)
Bit 1 V2 (Ventil 2)
Bit 2 V3 (Ventil 3)
Bit 3 nicht benutzt immer 0
0 Näherungsschalter 1 OFF
1 Näherungsschalter 1 ON
0 Näherungsschalter 2 OFF
1 Näherungsschalter 2 ON
0 Näherungsschalter 3 OFF
1 Näherungsschalter 3 ON
0 Ventil 1 OFF
1 Ventil 1 ON
0 Ventil 2 OFF
1 Ventil 2 ON
0 Ventil 3 OFF
1 Ventil 3 ON
Parameterbits: nicht belegt
58 - 1066
Page 61

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
II. ASI-Version mit erweitertem Adressbereich (A/B-Slave)
Bei der ASI-Version mit erweitertem Adressbereich (A/B-Slave) kann 1 Master mit 62 Slaves kommunizieren.
Das Buskabel darf mit erweitertem Adressbereich nach ASI-Spezifikation wie im Standardfall max. 100 m
lang sein.
HINWEIS
Besonderheiten der Variante A/B-Slave gegenüber dem Standardfall
• 62 Slaves je Master
• Die gelbe LED OUT 4 auf der ASI-Leiterkarte ist nicht mehr ansteuerbar, da das bislang benutzte vierte Ausgangsbit jetzt für die Adressierung benutzt wird.
• Einschränkungen bei der Stromversorgung wegen des Nennstroms der Induktivitäten:
Gleichzeitig können nur 2 Magnetventile geschaltet werden; das dritte Magnetventil kann erst nach
Ablauf von 100 ms zugeschaltet werden.
ACHTUNG!
Unterschiede in der Adressierung der ASI-Varianten
Parameter ASI-Standard-Gerät ASI-Gerät für A/B-Slave-Adressierung
Anzahl Slaves je Master 31 62
Bei Einsatz anderer Kabelquerschnitte verändern sich auch die maximalen Kabellängen
(siehe ASI-Spezifikation).
Wird ein A/B-Slave-Gerät als Ersatz für ein Standardgerät verwendet, kommt es wegen
der unterschiedlichen ID-Codes zu einem Konfigurationsfehler!
deutsch
I/O-Code 7 hex 7 hex
ID-Code F hex A hex
Erweitert ID1 F hex 7 hex
Erweitert ID2 F hex E hex
Profil S-7.F.F S-7.A.E
1066 - 59
Page 62

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
DeviceNet
Begriffserklärung
• DeviceNet ist ein Feldbussystem, das auf dem CAN-Protokoll (Controller Area Network) basiert. Es
ermöglicht die Vernetzung von Aktoren und Sensoren (Slaves) mit übergeordneten Steuereinrichtungen
(Master).
• Im DeviceNet ist der Steuerkopf Typ 1066 ein Slave-Gerät nach dem in der DeviceNet-Spezifikation
festgelegten Predefined Master/Slave Connection Set. Als I/O-Verbindungsvarianten werden
Polled I/O, Bit Strobed I/O und Change of State (COS) unterstützt.
• Beim DeviceNet unterscheidet man zwischen zyklisch oder ereignisgesteuert übertragenen Prozessnachrichten hoher Priorität (I/O Messages) und azyklischen Managementnachrichten niederer Priorität
(Explicit Messages).
• Der Protokollablauf entspricht der
HINWEIS
deutsch
Technische Daten
Baudrate
Adresse
Prozessdaten
Eingänge
Dateien
DeviceNet-Spezifikation Release 2.0
Bei der DeviceNet-Ausführung wird eine Diskette mit Konfigurationsdateien mitgeliefert (BUE1066.EDS und BUE1066.ICO). Diese Dateien können Sie auch über
das Internet beziehen.
125 kBit/s, 250 kBit/s, 500 kBit/s (über DIP-Schalter);
Werkseinstellung: 125 kBit/s
0 ... 63 (über DIP-Schalter);
Werkseinstellung: 63
1 statisches Input-Assembly
(Input: vom Steuerkopf 1066 zum DeviceNet-Master/Scanner)
1 statisches Output-Assembly
3 Sensoren (Näherungsschalter ) S1 - S3, pnp-plusschaltend,
Versorgung über DeviceNet-Strang (11 bis 25 V DC)
Schaltpegel High-Signal ≥ 5 V
Schaltpegel Low-Signal ≤ 1,5 V
BUE1066.EDS
BUE1066.ICO
Diese Dateien können Sie auch aus dem Internet beziehen.
Maximale Leitungslängen
Maximale Gesamtleitungslänge (Summe von Haupt- und Stichleitungen) eines Netzwerks in Abhängigkeit
von der Baudrate:
Gesamtleitungslänge
Baudrate
125 kBaud 500 m
250 kBaud 250 m
500 kBaud 100 m
1)
Nach DeviceNet-Spezifikation. Bei Verwendung eines anderen Kabeltyps gelten geringere
Maximalwerte (s. DeviceNet-Spezifikation)
60 - 1066
nach DeviceNet-Spezifikation
Maximale Gesamtleitungslänge bei Verwendung des Thick Cables
nach DeviceNet-Spezifikation 1)
Page 63

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
Stichleitungslänge (Drop Lines)
Baudrate Maximallänge einer Stichleitung Max. kumulierte Länge im Netzwerk
125 kBaud 6 m 156 m
250 kBaud 6 m 78 m
500 kBaud 6 m 39 m
Sicherheitseinstellung bei Ausfall des Busses
Bei Busausfall wird die Stellung vom letzten Datenbyte der Busausgänge beibehalten, solange Spannung
anliegt.
Elektrischer Anschluss
Die Busleitung ist ein 4-adriges Kabel mit zusätzlichem Schirm, das der DeviceNet-Spezifikation entsprechen muss und über das sowohl Informationen (Daten) als auch Energie (Spannungsversorgung für
leistungsarme Aktoren und Sensoren) übertragen werden.
Bus-Anschluss (Rundstecker M12, 5polig)
Stecker von vorn auf die Stifte gesehen (nicht auf die Lötanschlüsse)!
Der Steuerkopf Typ 1066 besitzt einen 5-poligen Micro-style-Rundstecker M12.
Die nachstehende Belegung entspricht der DeviceNet-Spezifikation.
Pin Signal Farbe
1 Schirm nicht belegt
2V+ rot
3V- schwarz
4CAN_H weiß
5 CAN_L blau
deutsch
Abschlussbeschaltung für DeviceNet – Systeme
Bei der Installation eines DeviceNet–Systems ist auf die korrekte Abschlussbeschaltung der Datenleitungen zu achten. Diese Beschaltung vermeidet die Entstehung von Störungen durch Signalreflexionen
auf den Datenleitungen. Die Hauptleitung ist dazu an beiden Enden, wie gezeigt, mit Widerständen von je
120 Ω und ¼ W Verlustleistung abzuschließen.
1066 - 61
Page 64

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
Netztopologie eines DeviceNet-Systems
Linie mit einer Hauptleitung (Trunk Line) und mehreren Stichleitungen (Drop Lines).
Haupt- und Stichleitungen bestehen aus identischem Material (siehe Skizze).
deutsch
ACHTUNG!
Versehen Sie zur Vermeidung von Reflexionen die Hauptleitung an beiden Enden mit
Abschlusswiderständen (120
ΩΩ
Ω
).
ΩΩ
Konfigurieren
DIP-Schalter
Zur Konfigurierung sind 8 DIP-Schalter vorhanden:
• DIP-Schalter 1 bis 6 für die DeviceNet-Adresse.
• DIP-Schalter 7 und 8 für die Baudrate.
HINWEIS
Einstellungen der DeviceNet-Adresse
MAC ID – Medium Access Control Identifier:
[Beispiel für Wertezuordnung am Schalter DIP1:
DIP 1=off=0 / DIP 1=on=1 / MAC ID=DIP 1*20+DIP 2*21+...+DIP 6*25]
Vor der Inbetriebnahme der Steuerung mit DeviceNet muss die
DeviceNet-Konfigurationstool eingelesen werden. Die erforderlichen Dateien
(BUE1066.EDS und BUE1066.ICO) werden per Diskette oder über Internet bereitgestellt.
EDS-Datei
in das
DIP 1
[2
62 - 1066
=1]
DIP 2
[21=2]
0
off off off off off off 0
on off off off off off 1
off on off off off off 2
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
offononononon62
on on on on on on 63
DIP 3
[22=4]
DIP 4
[23=8]
DIP 5
[24=16]
DIP 6
[25=32]
MAC
ID
Page 65

Einstellen der Baudrate
Anpassen des Steuerkopfes an die Baudrate des Netzwerkes.
DIP 7 DIP 8 Baudrate
off off 125 kBaud
on off 250 kBaud
off on 500 kBaud
on on nicht erlaubt
INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
ACHTUNG!
Eine Änderung von Einstellungen durch Betätigen der DIP-Schalter wird erst nach
einem Neustart des Gerätes wirksam.
Ein Neustart kann durch kurzzeitiges Ab- und anschließendes Anklemmen des Steuerkopfes vom bzw. an das Netz oder durch das Senden einer entsprechenden Reset
Message erfolgen. Möglich ist auch das Aus-/Anschalten der Netzwerkversorgung.
Konfiguration der Prozessdaten
Zur Übertragung von Prozessdaten über eine I/O-Verbindung stehen 1 statisches Input- und 1 statisches
Output-Assembly zur Auswahl. In diesen Assemblies sind jeweils die Bitwerte der Ein- bzw. Ausgänge in einem Objekt zusammengefasst, um als Prozessdaten gemeinsam über eine I/O-Verbindung übertragen werden zu können.
Auf die Prozessdaten kann entweder zyklisch in den Verbindungsvarianten „Polled I/O“ und „Bitstrobed I/O“,
mit „Change of state“, wenn sich Eingangswerte ändern, oder azyklisch über Explicit Messages zugegriffen
werden.
Der Zugriffspfad für den azyklischen Zugriff ist: class 4
instance 1
attribute 3
Mit dem Dienst
Set_Attribute_Single
1 Datenbyte für Eingänge (Sensoren bzw. Näherungsschalter):
Get_Attribute_Single
azyklisch schreibend auf die Ausgangsdaten zugegriffen werden.
kann azyklisch lesend auf die Eingangsdaten und mit dem Dienst
deutsch
Bit Sensor Wertezuordnung
Bit 0 S1 Näherungsschalter 1)
Bit 1 S2 (Näherungsschalter 2)
Bit 2 S3 (Anschlussklemme für zusätzlichen Näherungsschalter)
Bit 3 ... Bit 7 nicht benutzt 0 immer
1 Datenbyte für Ausgänge (Aktoren bzw. Ventile):
Bit Ventil Wertezuordnung
Bit 0 V1 (Ventil 1)
Bit 1 V2 (Ventil 2)
Bit 2 V3 ( Ventil 3)
Bit 3 ... Bit 7 nicht benutzt 0 immer
0 Näherungsschalter 1 OFF
1 Näherungsschalter 1 ON
0 Näherungsschalter 2 OFF
1 Näherungsschalter 2 ON
0 Näherungsschalter 3 OFF
1 Näherungsschalter 3 ON
0 Ventil 1 OFF
1 Ventil 1 ON
0 Ventil 2 OFF
1 Ventil 2 ON
0 Ventil 3 OFF
1 Ventil 3 ON
1066 - 63
Page 66

INSTALLATION INBETRIEBNAHME
LED-Zustandsanzeige
Der Gerätezustand wird von 2 LEDs ("Power" und "MNS") angezeigt.
Name der LED Art / Farbe Funktion
POWER einfarbig grün LED leuchtet: Gerät ist mit Spannung versorgt
MNS
zweifarbig
rot / grün
deutsch
Entspricht MNS-LED laut DeviceNet Spezifikation
(MNS-Module Network Status)
Zustände der MNS-LED
Nach dem Anlegen von Spannung (Anschluss der Netzwerkleitung) wird folgender Funktionstest der
zweifarbigen MNS-LED ausgeführt:
• LED leuchtet kurzzeitig grün (ca. ¼ s).
• LED leuchtet kurzzeitig rot (ca. ¼ s).
• LED dunkel.
Nach Abschluss des Funktionstestes können durch die MNS-LED die in der folgenden Tabelle beschriebe-
nen Gerätezustände angezeigt werden.
LEDZustand
Dunkel
Grün
Grün
blinkend
Rot
blinkend
Rot Kritischer Fehler
Gerätezustand Erläuterung / Problembeseitigung
- Gerät ist nicht mit Spannung versorgt.
Keine Spannung /
nicht online
Online, Verbindung
zum Master existiert
Online, keine Verbindung zum Master
VerbindungsTime-Out
- Gerät hat Duplicate MAC-ID Test noch nicht beendet (Test dauert ca. 2 s).
- Weitere Geräte anschließen, falls Gerät einziger Netzwerkteilnehmer ist.
- Austausch des Gerätes.
- Normaler Betriebszustand mit aufgebauter Verbindung zum Master.
- Normaler Betriebszustand ohne aufgebaute Verbindung zum Master.
- Eine oder mehrere I/O-Verbindungen befinden sich im Time-Out-Zustand.
- Neuer Verbindungsaufbau durch Master, um sicherzustellen, dass I/O-
Daten zyklisch übertragen werden.
- Anderes Gerät mit derselben MAC-ID im Netzwerk > MAC-ID ändern und
neu starten.
- BUS OFF infolge von Kommunikationsproblemen.
- Baudrate überprüfen; Austausch des Gerätes, falls nicht erfolgreich.
64 - 1066
Page 67

WARTUNG REINIGUNG
WARTUNG / REINIGUNG
Wartung / Reinigung........................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 66
deutsch
1066 - 65
Page 68

WARTUNG / REINIGUNG
Wartung /Reinigung
Der Steuerkopf Typ 1066 arbeitet bei sachgemäßem Einsatz wartungs- und störungsfrei. Eine Reparatur
darf nur von autorisiertem Personal mit geeignetem Werkzeug vorgenommen werden.
Die in Anlagen betriebenen Steuerköpfe können durch austretendes Medium und andere Einflüsse verschmutzt werden. In diesem Fall müssen die Anlagen mit geeigneten Reinigungsmitteln gesäubert und
anschließend gründlich mit Wasser gespült werden.
ACHTUNG!
deutsch
Vor der Verwendung von Reinigungsmitteln
von Gehäuse- und Deckelwerkstoff mit diesen Mitteln prüfen. Spülen Sie bei Verschmutzung oder nach Anwendung von säure- oder laugenhaltigen Reinigungsmitteln den
Steuerkopf bitte gründlich mit klarem Wasser ab. Achten Sie dabei besonders auf saubere, entleerte Bohrungen und Vertiefungen.
sollten Sie unbedingt die Verträglichkeit
66 - 1066
Page 69

REPARATUR
REPARATUR
Reparaturen .................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 68
deutsch
Deckel abnehmen bzw. aufstecken
Wechsel der Leiterkarte
Wechsel der Ventilgruppe
Wechsel des Ventils bei Versionen für 24/110/230 V UC ohne Kommunikation
Wechsel Näherungsschalter / Mikroschalter
............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 69
......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 69
............................................................................................................................................................................. 68
................................................. 70
.................................................................................................................................................. 71
Ersatzteile........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 72
Serviceanschriften................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 72
1066 - 67
Page 70

REPARATUR
Reparaturen
Bei Ausfall bestimmter Bauelemente oder Baugruppen kann der Steuerkopf repariert werden.
ACHTUNG!
Deckel abnehmen bzw. aufstecken
Deckel vom Steuerkopf abnehmen
deutsch
• Verwenden Sie zur Reparatur bitte nur Originalersatzteile (siehe Ersatzteiltabelle).
• Reparaturen dürfen nur von autorisiertem Fachpersonal mit geeignetem Werkzeug vorgenommen werden.
• Beachten Sie die geltenden Unfallverhütungs- und Sicherheitsbestimmungen.
• Schalten Sie das Gerät vor Eingriffen spannungsfrei und drucklos.
• Prüfen Sie die Parameter der Ersatzteile auf ihre Übereinstimmung mit dem Typschild
des zu reparierenden Steuerkopfes.
Lösen Sie die Sicherheitsschrauben
Drehen Sie den Deckel bis zum Anschlag
nach links
Ziehen Sie den Deckel nach oben ab
Deckel aufsetzen
Prüfen Sie den Sitz des Deckel-O-Rings
bzw. ziehen Sie einen neuen O-Ring auf
den Deckelbund
HINWEIS
Am Gehäuse existieren über den
Umfang verteilt 4 Nasen, die den
O-Ring beim Abziehen des Deckels
zurückhalten.
Achten Sie darauf, dass sich der neu
eingesetzte O-Ring korrekt unter den
Nasen befindet und durchgängig
unverdrillt am Gehäuse anliegt.
HINWEIS
Stecken Sie den Deckel auf
Drehen Sie den Deckel bis zum Anschlag
nach rechts
Sichern Sie den Deckel gegebenenfalls gegen Fremdeingriffe durch Einführen einer Plombe und/oder einer
Schneidschraube in die an Deckel und
Gehäuse vorhandenen Bohrungen.
Gehäuse mit
Deckelbund und
O-Ring-Sitz
68 - 1066
Page 71

Wechsel der Leiterkarte
Gehen Sie wie folgt vor
Deckel abnehmen.
Elektrischen Anschlüsse markieren, damit nach dem Lösen
eine fehlerfreie Zuordnung möglich ist.
REPARATUR
Alle elektrischen Anschlüsse auf der Leiterkarte lösen
(Steck- und/oder Schraubverbindungen).
4 Schrauben lösen (Torx 10), mit welchen die Deckplatte befestigt ist.
Deckplatte abnehmen.
Alte Leiterkarte herausnehmen (keine Verschraubung).
Neue Leiterkarte einsetzen.
ACHTUNG!
Deckplatte aufsetzen.
ACHTUNG!
Deckplatte festschrauben (Torx 10; Drehmoment 0,7 Nm).
Elektrische Anschlüsse gemäß den vorgenommenen Markierungen
wieder herstellen.
Deckel montiern.
Beachten Sie den richtigen Sitz der Karte in den
Gehäusenasen!
Achten Sie auf den richtigen Sitz der Leiterkarte und
Schraubenköpfe in den Nasen bzw. den Aussparungen
der Deckplatte!
Wechsel der Ventilgruppe
Platine
für 24 V DC
ohne Kommunikation
Ersatzmodul
ASI, vergossen
Ersatzmodul
DeviceNet, vergossen
deutsch
Die Ventilgruppe besteht aus einer Anschlussplatte mit 1, 2 oder 3
aufgeflanschten
Fluidik-Flansch zum Gehäuse.
HINWEIS
Ventilen vom Typ 6510
Bei den Versionen 24 V DC ohne Kommunikation,
ASI und DeviceNet ist nur der Wechsel der gesamten Ventilgruppe zulässig.
und den O-Ringen für den
Gehen Sie wie folgt vor
Deckel abnehmen.
Elektrischen Anschlüsse markieren, damit nach dem Lösen
von der Leiterkarte eine fehlerfreie Zuordnung möglich ist.
Alle elektrischen Anschlüsse der Ventile lösen
(Steckverbindungen).
2 Schrauben lösen (Torx 20), mit welchen die Ventilgruppe
befestigt ist.
Ventilgruppe inkl. O-Ringen herausnehmen.
Einsetzen der neue Ventilgruppe inkl. O-Ringen .
Ventilgruppe festschrauben (Torx 20; Drehmoment 1,5 Nm).
Elektrische Anschlüsse gemäß den vorgenommenen Markierungen
wieder herstellen.
Deckel montieren, dabei auf den richtigen Sitz des O-Rings achten.
Ventilgruppe, wahlweise
mit 1, 2 oder 3 Ventilen
- 24 V DC ohne Kommunikaton
- ASI (24 V DC)
- DeviceNet (9 V DC)
1066 - 69
Page 72

REPARATUR
Wechsel des Ventils bei Versionen für 24 / 110 / 230 V UC ohne
Kommunikation
Bei der Version für 24/110/230 V UC ohne Kommunikation wird unter Beachtung der Betriebsspannung nur
das
Gehen Sie wie folgt vor:
deutsch
Ventil Typ 6106
Deckel abnehmen.
Schraube an der Gerätesteckdose lösen.
Gerätesteckdose vom Ventil abziehen.
Einbaulage der Steckerfahnen und der Handbetätigung notieren.
2 Befestigungsschrauben am Ventil lösen.
Spulenkörper abnehmen.
2 Befestigungsschrauben am Ventilgehäuse lösen.
Ventilgehäuse inkl. O-Ringen abnehmen.
Neues Ventilgehäuse inkl. O-Ringen seitenrichtig aufsetzen
(Handbetätigung nach links).
ausgetauscht. Die Ventilanschlussplatte verbleibt im Steuerkopf.
Ventil
Typ 6106
Schrauben abwechselnd, gleichmäßig anziehen
(Drehmoment 0,5 Nm).
Neuen Spulenkörper seitenrichtig aufsetzen
(lange Steckerfahne nach links).
Spulenschrauben abwechselnd, gleichmäßig anziehen
(Drehmoment 0,15 Nm).
Gerätesteckdose mit Flachdichtung auf das Ventil stecken.
Steckdose mit einer Schraube sichern
(Drehmoment 1 Nm).
Deckel montieren.
70 - 1066
Page 73

Wechsel Näherungsschalter / Mikroschalter
Gehen Sie wie folgt vor
REPARATUR
Deckel abnehmen.
Elektrischen Anschlüsse markieren, damit nach dem Lösen
von der Leiterkarte eine fehlerfreie Zuordnung möglich ist.
Elektrische Anschlüsse Näherungsschalter/Mikroschalter auf
der Leiterkarte lösen (Steckverbindungen).
4 Schrauben lösen (Torx 10), mit welchen die Deckplatte
befestigt ist.
Deckplatte abnehmen.
Position von Näherungsschalter und Auslöser des
Mikroschalters notieren.
Näherungsschalter/Mikroschalter mit Justierschraube und
Anschlusskabel nach oben herausnehmen.
Alte Justierschraube zur Wiederverwendung herausdrehen.
Justierschraube in die Gewindebohrung am neuen
Näherungsschalter/Mikroschalter einschrauben.
Nur bei Näherungsschalter:
O-Ring aus dem alten Näherungsschalter ausbauen und in die
Aussparung des neuen Näherungsschalters einsetzen.
(Dieser O-Ring dient zur Schwingungsdämpfung und
verhindert das Auswandern des Näherungsschalters.)
Aussparung
für O-Ring
Induktiver Näherungsschalter mit
LED und eingegossenen Litzen
mit Stecker
(der Stecker ist in der Skizze
nicht dargestellt)
deutsch
Neuen Näherungsschalter/Mikroschalter mit Justierschraube
in die Führungssäulen einsetzen.
ACHTUNG!
Deckplatte aufsetzen.
ACHTUNG!
Deckplatte festschrauben (Torx 10; Drehmoment 0,7 Nm).
Elektrische Anschlüsse unter Beachtung der Zuordnung
Näherungsschalter/Mikroschalter verbinden.
Position Näherungsschalter/Mikroschalter justieren:
- Drehen Sie mit einem Schraubendreher an der
Justierschraube (Spindel) bis die optimale Lage
der Näherungsschalter eingestellt ist.
Achten Sie auf den richtigen Sitz von Näherungsschalter/Mikroschalter/Justierschraube in den Führungen und Vertiefungen des Gehäuses.
Beachten Sie den richtigen Sitz der
Leiterkarte und der Schraubenköpfe in den
Nasen und Aussparungen der Deckplatte.
LED
LED
- Als Justierhilfe dient die am Näherungsschalter
angebrachte LED, sie leuchtet beim Erreichen des
betreffenden Schwellwertes auf.
Deckel montieren.
1066 - 71
Page 74

REPARATUR
Ersatzteile
Position Ersatzteil Bestell-Nr.
deutsch
1 Ersatzmodul ASI, vergossen
2 Leitungsstecker gerade, angespritztes Kabel, 1 m lang, V4A-M12-Verriegelung
3 Flachkabelklemme mit Buchse, M12-Abgang aus VA, Goldkontakte
4 Flachkabeldichtung für Klemme (falls Kabel hier endet)
5 Platine 24 V DC ohne Kommunikation
6 Platine 24/110/230 V UC ohne Kommunikation
7 Induktiver Näherungsschalter (Sensor)
8 Endlagen-Mikroschalter komplett
9 Stellschraube für Näherungsschalter / Mikroschalter (1 Stück)
10 Ansatzschraube M5 zur Befestigung des Steuerkopfes (10er Pack)
11 Deckel für Steuerkopf (1 Stück)
12 O-Ringe für Deckel (10er Pack)
13 ohne Kommunikation, Ventilgruppe mit 1 Ventil, 24 V DC
14 ohne Kommunikation, Ventilgruppe mit 2 Ventilen, 24 V DC
15 ohne Kommunikation, Ventilgruppe mit 3 Ventilen, 24 V DC
16 mit ASI-Kommunikation, Ventilgruppe mit 1 Ventil, 24 V DC
17 mit ASI-Kommunikation, Ventilgruppe mit 2 Ventilen, 24 V DC
18 mit ASI-Kommunikation, Ventilgruppe mit 3 Ventilen, 24 V DC
19 mit DeviceNet-Kommunikation, Ventilgruppe mit 1 Ventil, 9 V DC
20 mit DeviceNet-Kommunikation, Ventilgruppe mit 2 Ventilen, 9 V DC
21 mit DeviceNet-Kommunikation, Ventilgruppe mit 3 Ventilen, 9 V DC
22 Einzelventil Typ 6106, 24 V UC
23 Einzelventil Typ 6106, 110 V UC
24 Einzelventil Typ 6106, 230 V UC
799 189
799 647
799 646
799 795
799 188
799 137
798 546
648 004
798 064
798 074
798 073
798 072
193 375
193 376
193 377
193 375
193 376
193 377
198 195
198 196
198 197
141 073
142 490
141 387
Positionen 13 bis 24 komplett mit O-Ringen und Befestigungsschrauben.
Serviceanschriften
Bürkert Werke GmbH & Co. KG Bürkert GmbH & Co. KG
Steuer- und Regeltechnik DC Dresden
Christian-Bürkert-Straße 13 - 17 Christian-Bürkert-Straße 2
74653 Ingelfingen 01900 Großröhrsdorf
Telefon (0 79 40) 10 - 111 Telefon (03 59 52) 36 - 300
Telefax (0 79 40) 10 - 448 Telefax (03 59 52) 36 - 551
72 - 1066
Page 75

TABLE DES MATIÈRES
Table des matières
des instructions de service
Tête de commande pour soupapes de
processus type 1066
REMARQUES GENERALES
Représentation................................................................................................................ 76
Utilisation conforme à la destination ............................................................................... 76
Consignes générales de sécurité.................................................................................... 76
Fourniture........................................................................................................................ 77
Clauses de garantie ........................................................................................................ 77
Transport et stockage ...................................................................................................... 78
Réglementation concernant les déchets ......................................................................... 78
CARACTERISTIQUES TECHNIQUES
Structure et fonction de la tête de commande ................................................................. 80
Particularités ................................................................................................................... 80
Conditions de service ..................................................................................................... 81
Caractéristiques mécaniques.......................................................................................... 81
Caractéristiques pneumatiques ...................................................................................... 82
Caractéristiques électriques............................................................................................ 82
MONTAGE
Montage de la tête de commande ................................................................................... 84
Adaptateur de bride................................................................................................................. 84
Déroulement du montage ........................................................................................................ 85
français
INSTALLATION - MISE EN SERVICE
Installation pneumatique ................................................................................................. 88
Occupation des raccords sur la tête de commande ............................................................... 88
Installation électrique ...................................................................................................... 89
Têtes de commande sans communication ............................................................................. 89
Têtes de commande avec communication ............................................................................. 91
1066 - 73
Page 76

TABLE DES MATIÈRES
MAINTENANCE / NETTOYAGE
Maintenance / Nettoyage ................................................................................................102
REPARATION
Réparations ....................................................................................................................104
Enlever ou remettre en place le couvercle ............................................................................. 104
Changement de la carte imprimée .......................................................................................... 105
Changement du groupe de soupapes ..................................................................................... 105
Changement de la soupape pour les versions 24 / 110 / 230 V UC sans communication ..... 106
Changement du détecteur de proximité / microcontacteur ..................................................... 107
Pièces de rechange ........................................................................................................108
Adresses de service ........................................................................................................108
français
74 - 1066
Page 77

REMARQUES
GENERALES
REMARQUES GÉNÉRALES
Réprésentation ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 76
Utilisation conforme à la destination...................................................................................................................................................................... 76
Consignes générales de sécurité............................................................................................................................................................................... 76
Fourniture........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 77
Clauses de garantie........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 77
Transport et stockage.................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 78
Réglementation concernant les déchets ......................................................................................................................................................... 78
français
1066 - 75
Page 78

REMARQUES GÉNÉRALES
Symboles de représentation
Les symboles de représentation suivants sont utilisés dans cette notice de service:
marque une étape de travail devant être exécutée
ATTENTION!
REMARQUE
caractérise des instructions dont l'inobservation entraîne des risques pour votre santé
ou met en cause la fonctionnalité de l'appareil.
caractérise des informations supplémentaires importantes, des conseils et des
recommandations.
Utilisation conforme à la destination
• La tête de commande pour soupapes de processus type 1066 sert à la commande de soupapes de
processus à commande pneumatique et à la saisie de leurs états de commutation. D'autres utilisations
sont considérées comme non conformes à la destination.
• La conformité des caractérisitques techniques figurant das ces instructions, sur la fiche technique et
sur la plaquette signalétique doit être vérifiée avant la mise en service; ces caractéristiques doivent
être respectées pendant le fonctionnement de la tête de commande.
• Et transformations et modifications sur la tête de commande à l'initiative de l'utilisateur sont interdites
pour des raisons de sécurité.
français
• Assurer la tête de commande contre les interventions de personnes non autorisées. A cet effet, la tête
de commande peut être protégée en introduisant un plomb et/ou une vis auto taraudeuse das les
perçages existants sur le couvercle ou le boîtier.
• Les instructions de travail et les consignes de sécurité données das cette notice doivent être
respectées dans tous les cas. La garantie est supprimée en cas de non-respect de ces instructions de
travail et de leur ordre ainsi que des consignes de sécurité.
Consignes de sécurité
Respecter les consignes de cette notice, les conditions d'utilisation et les caractérisitques admises
spécifiées sur les fiches techniques et la plaquette signalétique de la tête de commande, afin que
l'appareil fonctionne parfaitement et demeure longtemps fonctionnel.
• S’en tenir aux règles techniques généralement reconnues lors du projet de mise en œuvre et du
service de l’appareil!
• L’installation et les interventions nécessitées par la maintenance ne doivent être effectuées que par un
personnel qualifié équipé des outils adéquats.
• Utiliser uniquement des pièces d'origine pour les réparations nécessaires et respecter les instructions
de cette notice lors du remplacement de ces pièces.
• Respecter les dispositions en vigueur de prévention des accidents pendant le service et la
maintenance de l’appareil.
• Couper le contact électrique avant toute intervention dans le système!
• Veiller dans les systèmes sous pression à ce que les conduites et soupapes ne soient pas desserrées!
• Prendre les mesures qui s’imposent pour éviter un actionnement par inadvertance de l’appareil ou une
mise en cause inadmissible de son fonctionnement.
• Assurer un redémarrage défini et contrôlé du processus après une interruption de l’alimentation
électrique ou pneumatique.
76 - 1066
Page 79

REMARQUES GÉNÉRALES
REMARQUE
• Éviter des contraintes mécaniques élevées de la tête de commande qui pourraient entraîner sa
détérioration ou sa destruction. Ces contraintes englobent la marche, le dépôt d'objets lourds, des
chocs violents, la chute d'objets durs etc.
• Éviter la pénétration d'humidité dans la tête de commande. Veiller notamment lors du montage au
positionnement correct de tous les joints, au blocage des vis de montage, des raccords de câbles et
des bouchons d'étanchéité. Utiliser exclusivement de l'air de commande séché!
REMARQUE
• Éviter de raccorder des pièces de raccordement longues et mécaniquement rigides car elles pourraient
générer des forces de levier qui permettraient de détruire le boîtier à la main.
REMARQUE
• Utiliser exclusivement pour le nettoyage de la tête de commande un détergent bien compatible et
rincer à l'eau claire après l'utilisation de ce produit. Il convient également de tester la compatibilité du
détergent.
La tête de commande est conçue en protection IP67. Celle-ci suppose une bonne
assise de tous les joints et l'absence d'usure mécanique du boîtier et du couvercle.
Au niveau de sa résistance mécanique, le boîtier en matière plastique de la tête de
commande est exclusivement conçu pour le raccordement direct de tuyaux et de
conduites flexibles.
Les détergents contiennent souvent des composants agressifs qui peuvent se
déposer dans de petits rainures ou cavités et dont d'action durable peut détériorer
même des matières plastiques de qualité.
REMARQUE
• Respecter, lors du montage de la tête de commande, une distance d'au moins 5 mm entre la soupape
de surpression et l'élément suivant, de sorte que la soupape puisse se déclencher sans problème en
cas de fuite. Le couvercle pourrait sinon être littéralement "éjecté" en cas de fuite dans la tête de
commande.
• En cas d’inobservation de ces consignes et d’interventions non autorisées dans l’appareil, nous
déclinons toute responsabilité de même qu’elles entraînent l’annulation de la garantie sur l’appareil et
les pièces accessoires!
Fourniture
Contrôler dès réception de l’envoi que le contenu n’a subi aucun dommage et qu’il correspond bien à la
fourniture figurant sur le bordereau d’envoi. En cas de désaccord, veuillez contacter au plus vite notre
centre d'appels:
ou votre revendeur Bürkert.
Sur la face inférieure du boîtier de la tête de commande se trouve une soupape de
surpression servant de protection contre l'éclatement si un élément de construction
n'est pas étanche dans la tête de commande (cas de fuite).
Bürkert Fluid Control Systems, Centre d'appel
Chr.-Bürkert-Str. 13-17, D-74653 Ingelfingen
Tel. 07940 - 10 111 / Fax 07940 - 10 91 448
E-Mail: info@de.buerkert.com
français
Clauses de garantie
Ce document ne constitue aucun assentiment de garantie. Nous vous renvoyons à cet effet à nos
conditions générales de vente et commerciales. La condition préalable au consentement de la garantie
est l’utilisation conforme de l’appareil à l’usage auquel il est destiné, compte tenu de l’observation des
conditions d’emploi spécifiées.
ATTENTION!
Les prestations de garantie ne s’étendent qu’à l’absence de défaut de la tête de
commande pour soupapes de processus. Nous déclinons, par contre, toute
responsabilité pour des dégâts consécutifs de toute nature susceptibles de survenir par
suite de défaillance ou défaut de fonctionnement de l’appareil.
1066 - 77
Page 80

REMARQUES GÉNÉRALES
Transport et stockage
ATTENTION!
Stockage dans un local sec.
Température de stockage maximale +50 °C
Le tranport et le stockage sont autorisés uniquement en emballage d'origine.
Réglementation concernant les déchets
ATTENTION!
français
Respectez les réglementations nationales en matière d'élimination des déchets.
78 - 1066
Page 81

CARACTERISTIQUES TECHNIQUES
CARACTERISTIQUES
TECHNIQUES
Structure et fonction de la tête de commande.............................................................................................................................................. 80
Particularités................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 80
Conditions de service....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 81
Caractéristiques mécaniques............................................................................................................................................................................................... 81
Caractéristiques pneumatiques ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 82
Caractéristiques électriques................................................................................................................................................................................................... 82
français
1066 - 79
Page 82

CARACTERISITQUES TECHNIQUES
Structure et fonction
La tête de commande type 1066 sert à exciter des soupapes de processus à actionnement pneumatique
de divers fabricants. Suivant la configuration, elle peut être équipée de jusqu’à trois soupapes
magnétiques (soupapes pilotes) servant à commander des soupapes de processus et de trois détecteurs
de proximité inductifs au maximum servant à rétrosignaler la position. Un de ces détecteurs peut être
aussi un capteur externe (connexion avec une borne à vis à 3 pôles sur la carte imprimée).
REMARQUE
Ajustage détecteur de
Colonne avec broche
français
Raccords électriques
Sur les modules à bus de champ scellés, tenir compte de la numérotation des détecteurs
de proximité sur la carte ou l'identification sur l'appareil, car des différences de
numérotation sont possibles avec le dessin ci-après.
proximité 1
Carte imprimée
Marquage pour
montage du
couvercle
Ajustage à travers ces
trous
Plaque de recouvrement
Ajustage détecteur de
proximité 2
Détecteur de
proximité 2
Soupape magnétique 3
Soupape magnétique 2
Soupape magnétique 1
Boîtier
Air d'échappement
Détecteur de
proximité 1
Bride de
soupape
Particularités
Avec la tête de commande de type 1066 existe une solution décentralisée pour exciter les soupapes de
processus en dehors des îles de soupapes prévues plutôt pour une mise en œuvre centralisée. Les
avantages de cette solution sous la forme d'une unité compacte avec les soupapes pilotes, la
rétrosignalistation de position et les interfaces utilisables en option, se présentent comme suit:
Domaines principaux d'application:
Raccords pneumatiques
Soupape 1
Interface avec soupape
de processus
Déploiement plus faible pour installation.
Mise en service simple.
Temps de commutation couts en raison de trajets courts entre la soupape pilote et
celle de processus.
Industrie des produits alimentaires (p.ex. laiteries)
Industrie chimique
Industrie pharmaceutique
Industrie des cosmétiques
Air comprimé
Soupape 2
Soupape 3
80 - 1066
Brasseries
Page 83

CARACTERISTIQUES TECHNIQUES
Options
Nombre de soupapes pilotes
Mode d'action / mode de fonctionnement Nombre de soupapes pilotes
Action simple vérins 1
Action double vérins 2
Soupapes à double siège avec ventilation des deux sièges 3
Têtes de commande sans communication
Bornes à vis 8 pôles pour 24 V DC
Multipôle (Connecteur rond 8 pôles) pour 24 V DC
Bornes à vis 2 x 6 pôles pour 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
Têtes de commande avec communication
Interface capteur-acteur (ASI)
DeviceNet
ATTENTION!
Le raccordement à d'autres systèmes de bus (plus élevés) est possible avec des
passerelles usuelles du commerce.
Conditions de service
Fluides Air comprimé, sans huile, gaz neutres
Température du fluide -10 ... + 50 °C
Température ambiante -10 ... + 50 °C
Protection IP 67
ATTENTION!
La tête de commande ne convient pas à un emploi à l'extérieur!
français
Caractéristiques mécaniques
Masse 0,5 à 0,65 kg (suivant la version)
Matière du boîtier Boîtier en PA / PPE
Couvercle PSU (transparent, bleu gris)
Matière des joints NBR
1066 - 81
Page 84

CARACTERISITQUES TECHNIQUES
Caractéristiques pneumatiques
Raccords des conduites Air comprimé G 1/4
Raccords de travail, raccord de tuyau souple
6/4 mm ou 1/4 de pouce enfichable
Plage de pression 2,5 à 7 bar
Débit d'air soupape pilote 110 l/min type 6510, 40 l/min type 6106
Circulation valeur air: Q
Mesure à +20 °C, 6 bars de pression à l'entrée de la soupape et 1
bar de différence de pression
Temps de commutation Type 6510 / type 6106
Ouverture 15 / 23 ms,fermeture 10 / 21 ms
Mesure à la sortie de la soupape à 6 bars et +20 °C
Ouverture: montée de la pression de 0 à 90 %
Fermeture: descente de la pression de 100 à 10 %
Plage de réglage Course min. 2 mm Course max. 73 mm
(l/min)
Nn
Caractéristiques électriques
Protection IP 67
Tension de service
français
Puissance électrique max. dissipée 5 W avec 3 x type 6510 ou 1 x type 6106
Raccords
Soupapes magnétiques
sans communication 24 V DC ±10 %
24/110/230 V UC ±10 %
avec communication conformément à la spécification ASI et DeviceNet
têtes de commande
sans communication: Multipôle (connecteur rond 8 pôles DIN 45326) pour 24 V DC
borne à vis 8 pôles pour 24 V DC
borne à vis 2x6 pôles pour 24/110/230 V UC
têtes de commande
avec communication:
ASI: Raccord par déplacement d'isolation et passe câble à vis
Connecteur M12 et passe câble à vis
Raccord à bride M12, 4 pôles
DeviceNet: Connecteur à fiche M12, 5 pôles
Puissance nominale 1 W type 6510 / 3 W type 6106
Mode de service service permanent (ED 100 %)
Détecteurs de proximité
Tension de service 8 à 30 V DC
Signal de sortie max. 100 mA, résistant aux courts-circuits
Microcontacteur sans potentiel, max. 1 A courant de commutation.
82 - 1066
Page 85

MONTAGE
MONTAGE
Montage de la tête de commande.................................................................................................................................................................................. 84
Adaptateur de bride
Déroulement du montage
.......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 84
.......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 85
français
1066 - 83
Page 86

MONTAGE
Montage de la tête de commande
Adaptateur de bride
Pour monter la tête de soupape de type 1066 sur une soupape de processus de divers fabricants, vous
avez besoin d'un adaptateur muni d'une bride spéciale pour le client (adaptateur de bride) et d'un bouton
de commande spécial pour le client (voir aussi fiche technique). La partie raccordement à la tête de
commande est spécifique à Bürkert. La partie bride doit être adaptée à la forme de la soupape de
processus. Le dessin ci-dessous montre un exemple d’application pour une soupape de processus
spéciale. La position de montage de la tête de commande est quelconque, de préférence avec le
couvercle orienté vers le haut.
Respecter exactement en cas de propre fabrication de l’adaptateur de bride les paramètres suivants:
Cotes
Nombre de zones d'étanchéité
Cotes pour les joints toriques
Tolérances de cotes
Indications de matière
Cotes principales pour adaptateur de bride
français
Partie cylindrique de l'adaptateur
Partie de bride spécifique au client
REMARQUE
ATTENTION!
84 - 1066
Veuillez demander des dessins de cotes détaillés pour la propre fabrication de
l'adaptateur de bride!
Un centrage est nécessaire pour le montage de l'adaptateur de bride.
maximal toléré de l'axe est de ± 0,1 mm. En cas de dépassement de cette tolérance, il
y a le risque que les détecteurs de proximité ne fonctionnent pas correctement.
Utiliser une douille spéciale de montage pour éviter de dépasser cette tolérance.
L'écart
Page 87

Déroulement du montage
MONTAGE
Fixer l'adaptateur de bride sur la
1 2
soupape de processus/Fixer le
bouton de commande sur la tige
du piston (spécial pour le client)
Veiller au centrage
Enlever le couvercle de la tête
de commande
Dévisser les vis de sécurité
Tourner le couvercle à fond vers la
gauche
Tirer le couvercle vers le haut
français
Mettre la tête de commande en place
3
sur l'adaptateur de bride
Positionner la tête de commande
(la tête de commande peut tourner sur 360°)
Bloquer la tête de commande à l'aide des
deux vis placées latéralement
Installation des raccords
4
pneumatiques
Voir installation pneumatique,
(chapitre Installation/mise en service)
1066 - 85
Page 88

MONTAGE
français
Installation des raccords
5
électriques
Têtes de commande sans et avec
communication
(voir chapitre Installation électrique)
6
Ajustage des détecteurs de proximité
Tourner la vis de réglage (broche) à l'aide d'un
tournevis jusqu'à ce que la position optimale
des détecteurs de proximité soit atteinte.
Remettre le couvercle en place
7
Contrôler le siège du joint torique du
couvercle ou tirer un nouveau joint
torique sur le collet du couvercle.
REMARQUE
Le boîtier comporte 4 tenons répartis
sur la circonférence, qui retiennent le
joint torique lors de l'extraction du
couvercle.
Veiller à ce que le nouveau joint
torique se trouve correctement sous
les tenons et soit appliqué en continu,
sans torsion, contre le boîtier.
Mettre le couvercle en place
Tourner à fond le couvercle vers la
droite
La LED placée sur le détecteur de proximité
sert d'aide ajuster. Elle s'allume lorsque la
valeur de seuil concernée est atteinte.
Le microcontacteur de fin de course
Lors de l'emploi de microcontacteurs on renonce
aux LED pour des raisons de coûts.
Réglage de position comme pour les
détecteurs de proximité.
Utiliser comme aide à l'ajustage le bruit de
commutation du microcontacteur (très faible)
ou un contrôle de passage électrique externe.
LED
LED
Boîtier avec
collet de
couvercle et
siège du joint
torique
REMARQUE
Assurer le couvercle le cas échéant
contre toute intervention étrangère en
introduisant un plomb et / ou une vis
auto taraudeuse dans les perçages
existants sur le couvercle et le boîtier.
86 - 1066
Page 89

INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
INSTALLATION
MISE EN SERVICE
Installation pneumatique.............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 88
Occupation des raccords sur la tête de commande
.............................................................................................................................. 88
Installation électrique ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 89
Têtes de commande sans communication
Borne à vis 8 pôles pour 24 V DC
Multipôle (Connecteur rond 8 pôles selon DIN 45326) pour 24 V DC
Borne à bis 2 x 6 pôles pour 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
Têtes de commande avec communication
Interface AS
..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 91
Manipulation de la borne à câble plat
Caractéristiques techniques pour cartes imprimées ASI
Données de programmation
Affichage LED d'état ASI
Occupation des bits
..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 93
.............................................................................................................................................................................. 92
....................................................................................................................................................................................... 93
Nombre de têtes de commande pouvant être raccordées et longueur maximale
de la ligne de bus
(cas ASI standard et version ASI avec une zone d'adresses étendue)
........................................................................................................................................................ 89
....................................................................................................................................................................... 89
.................................................................. 90
........................................................................................................................... 90
........................................................................................................................................................ 91
..................................................................................................................................................... 92
............................................................................................ 92
.................................................. 94
français
DeviceNet
Signification du terme
Caractéristiques techniques
Longueurs maximales de ligne
........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 96
................................................................................................................................................................................................. 96
............................................................................................................................................................................. 96
....................................................................................................................................................................... 96
Réglage de sécurité en cas de défaillance du bus
Raccordement électrique
Configuration
......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 98
Affichage LED d'état
...................................................................................................................................................................................... 97
.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 100
............................................................................................................... 97
1066 - 87
Page 90

INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
Installation pneumatique
Occupation des raccords sur la tête de commande
G 1/4 G 1/4
ATTENTION!
français
Air
comprimé
Air
d'échappement
Raccords enfichables
pour conduites souples 6/4 mm ou 1/4"
enfichables
pour soupapes V1, V2 et V3
• Utiliser uniquement que des conduites souples calibrées ayant un diamètre extérieur
de 6 mm ou ¼ "
• Ne couper ces dernière qu'avec un coupe-flexible (risque de détérioration)
• Dimensionner la longueur des conduites de manière à ce que la tête de commande
puisse être enlevée avec le raccord à vis.
• Veiller à ce que la conduite souple soit sans tension et bien alignée avec le
connecteur enfichable, car les conduites souples enfichées avec une torsion (en
biais) peuvent entraîner des fuites au raccord enfichable.
88 - 1066
Page 91

Installation électrique
Têtes de commande sans communication
Le raccordement électrique de têtes de commande sans communication s'effecture selon différentes
variantes. Dans l'exécution pour 24 V DC, l'état de chaque soupape est signalé par une DEL.
Bornes à vis 8 pôles pour 24 V DC
(à l'intérieur du boîtier, passage de câble avec passe câble à vis)
Affichage d'état LED multipôle 24 V DC
INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
Terre
Signal de commutation du détecteur de
proximité externe S3
Alimentation électrique
français
Plan d'occupation pour la borne à vis 8 pôles
V = soupape
S = détecteur de proximité
(capteur)
pour détecteurs
de proximité
REMARQUE
Les sorties des détecteurs de proximité sont à commutation plus pnp et résistantes aux
cours-circuits.
1066 - 89
Page 92

INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
Multipôle (Connecteur rond 8 pôles selon DIN 45326) pour 24 V DC
Coup d'œil du connecteur incorporé dans la tête vu de devant sur les broches, les connexions soudées se
trouvent derrière.
Sorties des détecteurs de proximité
à commutation plus pnp, résistantes aux courts-circuits
Détecteur de
proximité 3
Détecteur de
proximité 2
Détecteur de
proximité 1
REMARQUE
français
Borne à vis 2 x 6 pôles pour 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
La version à borne à vis 2 x 6 pôles comprend
GND
(masse commune pour
soupapes)
Soupape 3
Soupape 2
Les sorties des détecteurs de proximité sont à commutation plus pnp et résitantes aux
courts-circuits.
Passage de câble par passe câble à vis
Max. 1 soupape (type 5106, DN1,2)
2 microcontacteurs de fin de course à contacts sans potentiel pour rétrosignaler la position
(pas d'affichage d'état LED)
24 V DC
(tension de service pour les
détecteurs de proximité)
Soupape 1
Carte imprimée avec bornes à vis 2 x 6 pôles pour 24 / 110 / 230 V UC
90 - 1066
gn/gb vert/jaune
bl bleu
sw noir
Page 93

Têtes de commande avec communication
Interface AS
ASI (Actor Sensor Interface) est un système de bus de champ qui sert essentiellement à mettre en
réseau des capteurs et acteurs binaires (slaves) avec une commande de rang supérieur (master).
Ligne de bus
Ligne non blindée à deux fils (ligne ASI comme câble profilé) sur laquelle sont transmis aussi bien des
informations (données) que de l’énergie (alimentation en tension des acteurs et capteurs).
Topologie de réseau
Choix libre dans une large mesure, c.-à-d. des réseaux en étoile, arborescents et linéaires sont possibles.
Vous trouverez d’autres détails dans les spécifications ASI.
Variantes de raccordement au bus
INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
REMARQUE
Données pour le câble rond
Les valeurs électriques du câble rond conduisant immédiatement à la tête de commande
s’écartent très peu du standard ASI. Lors du calcul de la longueur de ligne maximale
tolérée selon les spécifications ASI, il devrait être, en conséquence, plus long d’un facteur
1,5 que fixé effectivement.
Longueur ASI = 1,5 x longueur réelle
1. Borne de câble plat au câble rond de 1 m
Raccord standard ASI:
Câble ASIprofilé
Borne de câble plat
Connecteur de conduite avec câble
injecté
Câble rond (longueur 1 m, dont
0,2 m dans la tête de commande)
2. Connecteur M12 4 pôles au câble rond de 2 m,
Raccord spécial ASI 1: (sur demande)
Connecteur M12
Connecteur de conduite avec câble injecté
français
Connecteur M12 à 4
pôles pour raccord
ASI
Câble rond (longueur 2 m, dont
0,2 m dans la tête de commande)
3. Connecteur M12 4 pôles sur la tête de commande, sans câble
Raccord spécial ASI 2: (sur demande)
Câble profilé ASI
Borne de câble plat
Connecteur de conduite
Connecteur
à bride M12
Douille M12
Câble rond (longueur 1 m)
Occupation des
broches ASI
1 = ASI+
2 = pas occupé
3 = ASI4 = pas occupé
1066 - 91
Page 94

INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
Manipulation de la borne de câble plat
La borne de câble plat pour câbles ASI réalise le contact sous forme d'une technique de pénétration. Le
raccordement électrique s'établit sans couper, ni dénuder le câble.
REMARQUE
français
Fermer la deuxième ouverture de câble avec un joint à câble lorsque le câble plat s'arrête
dans la borne (dernier raccord).
Raccordement de la borne de câble plat à connecteur de conduite et câble
injecté avec un câble plat ASI
Dévisser les deux vis de la borne de câble plat.
Séparer la partie supérieure de la borne de câble plat de la partie
inférieure.
Insérer le câble plat ASI en position correcte.
Si le câble s'arrête ici:
Insérer le joint de câble plat en position correcte dans l'ouverture.
Disposer la partie supérieure de la borne de câble plat sr la partie
inférieure.
Bloquer les vis.
Terminé!
Le raccordement électrique au câble ASI est établi.
Joint de câble plat pour borne de câble plat.
Caractéristiques techniques des cartes imprimées ASI
Entrées 3 capteurs S1 - S3, pnp à commutation positive
Alimentation par interface AS (24 V +20 % / -10 %) résistant aux courts-circuits, à
courant limité à 60 mA
Niveau de commande High-Signal ≥ 10 V
Limitation du courant d’entrée ≥ 6,5 mA, courant d’entrée Low signal ≤ 1,5 mA
Sorties 3 soupapes V1 - V3
max. 3 x 1 W
Réduction de puissance après env. 100 ms par fonction der chien de garde intégrée
Données de programmation
Code I/O 7 hex (4 sorties et 4 entrées)
Code ID F hex (occupation des bits voir la table ci-après) codes ID étendus 1 et 2 = F hex
Profil 7F
92 - 1066
Page 95

Affichage d'état LED ASI
Partie visible de la carte imprimée ASI
INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
Affichage d'état bus
LED verte rouge
LEDs pour soupapes
V1 - V3
Aperçu sur l'affichage d'état ASI
LEDs pour
détecteurs de proximité S1 - S3
Signal de
commutation d'un
détecteur externe de
proximité
Alimentation en tension d'un
détecteur de proximité externe
(venant de la branche ASI)
français
LED État du bus
vert rouge
éteinte éteinte POWER OFF
éteinte allumée pas de circulation de données (chien de garde écoulé pour l'adresse slave
allumée éteinte ok
clignote clignote erreur dans périphérie (surcharge dans l'alimentation du capteur)
clignote allumée adresse slave égale à 0
éteinte clignote RESET
différente de 0)
Occupation des bits
Bit utile D3 D2 D1 D0
Sortie
LED jaune
Entrée
inoccupé
Bit paramètre P3 P2 P1 P0
détecteur de proximité 3
Sortie
soupape 3
Entrée
Sortie
soupape 2
Entrée
détecteur de proximité 2
inoccupé
Sortie
soupape 1
Entrée
détecteur de proximité 1
1066 - 93
Page 96

INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
Nombre de têtes de commandes raccordables et longueur
maximale de la ligne de bus
I. Cas ASI standard
Dans le cas standard, 31 têtes de commande au maximum peuvent être raccordées à une ligne de bus.
Le câble de bus ne doit pas dépasser 100 m conformément à la spécification ASI.
REMARQUE
français
Données de processus
Bits utiles pour les entrées (capteurs ou détecteurs de proximité):
Bits utiles pour les sorties (acteurs ou soupapes):
Lors de l’emploi d’autres sections de câble, les longueurs de câble changent également
(voir spécifications ASI).
N° bit Capteur Assignation de valeur
Bit 0 S1 (capteur 1)
Bit 1 S2 (capteur 2)
Bit 2 S3 (borne de branchement pour autres détecteurs)
Bit 3 inutilisé toujours 0
N° bit soupape Assignation de valeur
Bit 0 V1 (soupape 1)
Bit 1 V2 (soupape 2)
Bit 2 V3 (soupape 3)
Bit 3 inutilisé toujours 0
0 détecteur de proximité 1 OFF
1 détecteur de proximité 1 ON
0 détecteur de proximité 2 OFF
1 détecteur de proximité 2 ON
0 détecteur de proximité 3 OFF
1 détecteur de proximité 3 ON
0 soupape 1 OFF
1 soupape 1 ON
0 soupape 2 OFF
1 soupape 2 ON
0 soupape 3 OFF
1 soupape 3 ON
Bits de paramétre inoccupé
94 - 1066
Page 97

INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
II. Version ASI avec zone d'adresse étendue (A / D-esclave)
Dans la version ASI à zone d'adressage étendue (esclave A / B), 1 maître peut communiquer avec 62
esclaves.
Avec une zone d'adressage étendue selon la spécification ASI, le câble de bus ne doit pas dépasser une
longueur de 100 m comme dans le cas standard.
REMARQUE
Particularités de l'esclave A / B par rapport au cas standard
• 62 esclaves par maître
• La LED OUT 4 sur la carte imprimée ASI ne peut plus être excitée car le quatrième bit de sortie utilisé
auparavant est désormais utilisé pour l'adressage.
• Restrictions de l'alimentation électrique en raison du courant nominal des inductances:
seuls 2 électrovannes peuvent être commandées simultanément; la troisième électrovanne peut
uniquement être mise en circuit après 100 ms.
ATTENTION!
Différences dans l'adressage des variantes ASI
Paramètre Appareil ASI standard Appareil ASI pour adressage
Nombre d'esclaves par maître 31 62
En cas d'utilisation d'autres sections de câbles, les longueurs de câbles se modifient
également (voir la spécification ASI).
Si un appareil esclave A / B est utilisé en remplacement d'un appareil standard, il se
produit une erreur de configuration en raison du code ID différent!
esclave A / B
français
Code I/O 7 hex 7 hex
Code ID F hex A hex
ID1 étendu F hex 7 hex
ID2 étendu F hex E hex
Profil S-7.F.F S-7.A.E
1066 - 95
Page 98

INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
DeviceNet
Signification du terme
• DeviceNet est un système de bus basé sur le protocole CAN (Controller Area Network) . Il permet la
mise en réseau d’acteurs et de capteurs (slaves) avec des équipements de commande de rang
supérieur (master).
• Dans le DeviceNet, la tête de commande type 1066 est un appareil slave selon le set de connexions
Master/Slave prédéfini dans les spécifications du DeviceNet. En tant que variantes de connexion I/O,
polled I/O, bit strobed I/O et change of state I/O (COS) sont supportés.
• On distingue chez DeviceNet entre messages de processus transmis de manière cyclique ou
commandés par événement de plus haute priorité (I/O messages) et les messages de gestion
acycliques de moindre priorité (explicit messages).
• Le déroulement du protocole correspond aux
REMARQUE
Caractéristiques techniques
français
Vitesse de transmission
Adresse
Données de processus
Entrées
Fichiers
spécifications DeviceNet, version 2.0
Dans la version avec DeviceNet, une disquette est livrée comportant des fichiers de
configuration (BUE1066, EDS et BUE1066.ICO). Ces fichiers peuvent être également
obtenus sur Internet.
125 kBit/s, 250 kBit/s, 500 kBit/s (par contacteurs DIP);
Réglage usine: 125 kBit/s
0 ... 63 (par contacteurs DIP);
Réglage usine: 63
1 assemblages statiques input
(input de la tête de commande 1066 au master DeviceNet (scanner)
1 assemblage statique output
3 capteurs (détecteurs de proximité) S1 - S3 à commutation plus pnp,
Alimentation par la branche du DeviceNet (11 à 25 V DC)
Niveau de commande High Signal ≥ 5 V
Niveau de commande Low Signal ≤ 1,5 V
BUE1066.EDS
BUE1066.ICO
Ces fichiers peuvent également être obtenus sur Internet.
Longueurs maximales de ligne
Longueur totale maximale de ligne (somme des lignes principales et des tronçons de ligne) d’un réseau
en fonction de la vitesse de transmission:
Longueur totale de ligne
Vitesse de
transmission
125 kBaud 500 m
250 kBaud 250 m
500 kBaud 100 m
1)
Selon les spécifications DeviceNet , lors de l’utilisation d’un autre type de câble, des valeurs maxima
les inférieures sont applicables (v. Spécifications DeviceNet)
96 - 1066
Longueur totale maximale en utilisant des câbles Thick selon les
spécifications DeviceNet
d'après les spécifications DeviceNet
1)
Page 99

Longueur des tronçons de ligne (drop lines)
INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
Vitesse de
transmission
125 kBaud 6 m 156 m
250 kBaud 6 m 78 m
500 kBaud 6 m 39 m
Longueur maximale d'un tronçon Longueur max. cumulée dans le réseau
Réglage de sécurité en cas de défaillance du bus
En cas de défaillance du bus, la position du dernier octet de données des sorties du bus est conservée
tant que la tension est présente.
Raccordement électrique
La ligne de bus est un câble à 4 conducteurs avec un blindage supplémentaire qui doit correspondre aux
spécifications DeviceNet et par lequel aussi bien des informations (données) que de l’énergie
(alimentation en tension pour les acteurs et capteurs de faible puissance) sont transmises.
Raccordement du bus (connecteur rond M12, 5 pôles)
français
CAN_H
blanc
Lignes de
données
Connecteur vu de devant sur les broches (pas sur les connexions soudées)!
La tête de commande type 1066 possède un connecteur rond M12 micro-style 5 pôles.
L'occupation ci-après correspond aux spécifications DeviceNet.
Broche Signal Couleur
CAN_L
bleu
Drain (blindage)
(inoccupé)
1 Blindage inoccupé
2 V+ rouge
3 V- noir
4 CAN_H blanc
5 CAN_L bleu
Vnoir
V+
rouge
Alimentation en tension
11 ... 25 V DC
Puissance max. 5 W, si toutes
les soupapes commutées
(3 x type 6610 avec chacune 1 W)
Montage de fermeture pour systèmes DeviceNet
Lors de l’installation d’un système DeviceNet, il faut veiller au montage de fermeture correct des lignes de
données. Ce montage évite la génération de perturbations dues à des réflexions de signaux sur les lignes
de données. La ligne principale doit être fermée aux deux extrémités, comme montré, par des résistances
de chacune 120 Ω et ¼ W de puissance dissipée.
1066 - 97
Page 100

INSTALLATION / MISE EN SERVICE
Topologie de réseau d'un système DeviceNet
Ligne avec une ligne principale (trunk line) et plusieurs tronçons (drop lines).
Ligne principale et tronçons de ligne sont en matière identique (voir dessin).
ATTENTION!
français
Configuration
Contacteurs DIP
8 contacteurs DIP existent pour configurer:
• Contacteur DIP 1 à 6 pour l'adresse du DeviceNet.
• Contacteur DIP 7 et 8 pour la vitesse de transmission.
REMARQUE
Réglages de l'adresse DeviceNet
MAC ID – Medium Access Control Identifier:
[Exemple d'affectation de valeurs au contacteur DIP1:
DIP 1=off=0 / DIP 1=on=1 / MAC ID=DIP 1*20+DIP 2*21+...+DIP 6*25]
Munir les deux extrémités de la ligne principale de résistances de fermeture 120
éviter des réflexions
Avant la mise en service de la commande avec DeviceNet, le fichier EDS doit être
enregistré dans l’outil de configuration du DeviceNet. Les fichiers nécessaires
(BUE1066.EDS et BUE1066.ICO) seront mis à disposition par disquette ou Internet.
.
ΩΩ
Ω pour
ΩΩ
[2
98 - 1066
=1]
DIP 2
[21=2]
DIP 1
0
off off off off off off 0
on off off off off off 1
off on off off off off 2
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
offononononon62
on on on on on on 63
DIP 3
[22=4]
DIP 4
[23=8]
DIP 5
[24=16]
DIP 6
[25=32]
MAC
ID
 Loading...
Loading...