Page 1

BTL-5000
Magnetotherapy
USER’S GUIDE
V100RK13/07/2006
Page 2

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
CONTENTS
1 MAGNETOTHERAPY............................................................................................. 4
2 MAGNETOTHERAPY – PHYSICAL BACKGROUND.................................................... 5
2.1 Magnetic Field ................................................................................................. 5
2.1.1 Stationary Magnetic Field .............................................................................. 5
2.1.2 Alternating Magnetic Field ............................................................................. 5
2.1.3 Pulse Magnetic Field..................................................................................... 6
2.1.3.1 Device Options......................................................................................... 6
2.2 FMF Technology............................................................................................... 6
2.3 Magnetic Field Units ......................................................................................... 8
3 THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS OF MAGNETOTHERAPY ................................................... 9
3.1 Analgesic Effect ............................................................................................... 9
3.2 Antiphlogistic Effect.......................................................................................... 9
3.3 Trophic Effect .................................................................................................10
3.4 myorelaxation and spasmolytic effect, ................................................................10
3.5 Vasodilatation Effect........................................................................................10
3.6 Antiedematous Effect .......................................................................................10
4 RECOMMENDED DOSAGE OF MAGNETOTHERAPY ................................................11
5 BIBLIOGRAPHY ..................................................................................................12
6 SETTING AND CONTROL OF MAGNETOTHERAPY – TECHNICAL PARAMETERS .......15
6.1 Magnetic Field Intensity ...................................................................................15
6.2 Therapy Time..................................................................................................15
6.3 Physiological Effects........................................................................................15
6.4 Selection of Th e rapy ........................................................................................15
6.4.1 Magnetic Pulses ..........................................................................................15
6.4.1.1 Pulse, Pause, Frequency – Setting ............................................................16
6.4.2 Series of Magnetic Pulses ............................................................................16
6.4.2.1 Pulse, Pause, Frequency, Repeating – Setting of Series...............................16
6.4.3 Continuous Magnetic Field............................................................................17
6.5 Pulse Shape ...................................................................................................17
6.5.1 Rectangular Pulses......................................................................................17
6.5.2 Rectangular Protracted Pulses ......................................................................18
6.5.3 Exponential Pulses ......................................................................................19
6.5.4 Sinusoidal Pulses ........................................................................................19
6.5.5 Triangular Pulses ........................................................................................19
6.6 Modulation......................................................................................................20
6.6.1 Random Frequency ......................................................................................20
6.6.2 Burst..........................................................................................................20
6.6.3 Sine Surges ................................................................................................20
6.6.4 Trapezoid Surges ........................................................................................20
6.6.5 Symmetric Surges........................................................................................22
6.7 Test of Connected Applicator ............................................................................22
7 APPLICATORS....................................................................................................23
7.1 “DISC" Applicator ............................................................................................23
7.1.1 Technical Parameters...................................................................................23
7.1.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator .................................................24
7.2 “DOUBLE DISC" Applicator ...............................................................................25
7.2.1 Technical Parameters...................................................................................25
7.2.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator .................................................26
7.3 “Multi DISC" Applicator ....................................................................................27
7.3.1 Technical Parameters...................................................................................27
7.3.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator .................................................28
7.4 “Solenoid 30” Applicator ...................................................................................29
7.4.1 Technical Parameters...................................................................................29
7.4.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator .................................................29
7.5 “Solenoid 60” Applicator ...................................................................................30
7.5.1 Technical Parameters...................................................................................30
7.5.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator .................................................30
7.6 “Linear" Applicator...........................................................................................31
page 2 of 31
Page 3

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
7.6.1 Technical Parameters...................................................................................31
7.6.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator .................................................31
page 3 of 31
Page 4

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
1 MAGNETOTHERAPY
Magnetotherapy is one of the basic physiotherapy procedures. Its basic form - application of
static magnetic field. i.e. the permanent magnet - has been used since time immemorial as
one of natural healing sources. However, only the coming of electronics and powerful
switching elements enabled rapid development of low-frequency pulse magnet therapy, the
effects of which are several times higher than those of the static magnetic field. The recently
performed studies imply that therapy performed by means of pulse electromagnetic field is up
to 100 times more effective than the application of stationary magnetic field. That is why the
pulse magnetotherapy is nowadays becoming one of widespread physiotherapy methods. At
some conditions (e.g. chronic pains in degenerative articular diseases) this method has
proven successful as therapy with long-lasting therapeutic effect even when other therapy
methods failed.
Pulse magnetotherapy can be very effective in case of correct indication and application. It
can also be recommended for use in combination with other therapy methods, such as
pharmacotherapy, the effects of which are usually supported by magnetotherapy. That is why
magnetotherapy should neither be left out in case of comprehensive approach to treatment,
nor given preference as monotherapy.
The latest findings about physiological response of the organism to the electromagnetic field
imply the following effects of magnetotherapy:
• analgesic effect,
• antiedematous effect,
• antiphlogistic effect,
• trophic effect (acceleration of healing and growth),
• myorelaxation and spasmolytic effect,
• vasodilatation effect.
The following chapters contain brief explanation of physical background of magnetotherapy
and physiological mechanisms of its effect with emphasis on application in individual fields of
medicine.
The Encyclopaedia, which is a separate attachment of this User’s Guide, contains the list of
recommended parameters of magnetotherapy at selected diagnoses.
The designing of this device utilizes the experience acquired during the development,
manufacturing and long-standing clinical operation of the BTL-09 device and state-of-the-art
devices of the BTL-4000 and BTL-5000 series.
During the designing of new magnetic applicators for this device there was developed a brand
new technology - so called “FMF“ (“Focused Magnetic Field”) technology. Thus we managed
to increase the electromagnetic field intensity on the patient side and significantly reduce the
electromagnetic field intensity on the applicator side, turned away from the patient.
Colloquially said, the magnetic field was moved from the improper side to the side where it is
desired.
Thanks to these construction elements and thanks to state-of-the-art sources based on the
principle of electronic switching elements we have managed to reduce the power consumption
significantly while preserving the same electromagnetic field intensities.
Note
The authors of this User’s Guide are aware that such a small space is not sufficient for
detailed description of the entire magnetotherapy issue. They therefore had to make some
generalizations and simplifications resulting from the limited scope of this text. More details
you can find in the available literature (see Chapter 5 Bibliography)
page 4 of 31
Page 5

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
2 MAGNETOTHERAPY – PHYSICAL BACKGROUND
2.1 MAGNETIC FIELD
Magnetic field is an integral part of electromagnetic field which consists of the electric and the
magnetic components. Both components of the electromagnetic field are mutually closely
connected and cannot exist without each other, , except in the following two special cases:
• electrostatic field in which the magnetic component of the field is zero, and
• stationary magnetic field in which the electric component is zero.
Owing to the used frequencies up to 150 Hz and owing to the design of the BTL applicators,
the magnetic component of the field predominates over the electric. For short we will call the
field by the commonly used term “magnetic field” hereinafter.
The presence of a magnetic field is sensed primarily through its force effects by which it
affects magnetically conductive things, moving charges and conductors with electric current
flowing through them. The force effects are not very important for our theory, because
biological objects are diamagnetic. However, it is necessary to take these force effects into
account in case of metal implants, especially those which are fixed in soft tissues and are not
made of antimagnetic materials.
Another interaction between the magnetic field and the matter occurs at the moment when the
matter is exposed to the magnetic field. At that moment, individual free molecules are
orientated in a way to minimize the energy inside the field. In case of biological objects, these
forces act against the bonds between atoms, molecules and ions in the tissues, which
consequently influences also the cellular processes.
The effects important for physiotherapy are based on electrodynamic induction discovered
by the physicist M. Faraday in the 19
conductor in the magnetic field, voltage appears on it. If you make a closed loop of the moving
conductor, electric current will flow through it. As Faraday discovered, this phenomenon also
works the other way around – if the magnetic field moves or changes in the course of time
(instead of the conductor), a similar effect occurs. These discoveries were only a short remove
from the application of alternating magnetic fields in therapy.
In case of living organisms, the moving charges (the conductor moving in the magnetic field)
are represented by the circulating body fluids (blood, lymph). In case of exposition to
alternating magnetic field it refers to its individual more electrically conductive parts - the
vascular bed (including circulating fluids), peripheral nerves, CNS neural paths and, last but
not least, also individual ions and charges on cellular membranes.
th
century. In practice, if you are moving the electric
2.1.1 Stationary Magnetic Field
Stationary magnetic field arises around permanent magnets but also around moving electric
charges which move at a constant speed (direct current)
Electric charge may be carried e.g. by ions (electric current flowing in liquids) and electrons
(electric current flowing in conductors). In the latter case, a magnetic field similar to that
around the permanent magnet arises around the electric conductor with constant direct
electric current flowing through it.
2.1.2 Alternating Magnetic Field
Time behaviour of this field is usually derived from the sinusoidal mains voltage. In common
practice, devices most often generate the fields of a frequency of 50 Hz and the sinusoidal
waveform. The magnetic fields of these devices change their polarity in the course of time.
These fields, even though with much lower intensity, exist in the surrounding of each electric
conductor, transformers and motors supplied from the AC mains.
page 5 of 31
Page 6
MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
2.1.3 Pulse Magnetic Field
This field is characterized by fast changes of field; individual pulses are close to rectangular
pulses, their edges are very steep. That is why in the pulse magnetic field the electric
component is higher and is permanently present beside the magnetic component. Some
studies, which deal with comparison of individual magnetic field types, point out the very high
efficiency of the pulse magnetic field in comparison with the stationary magnetic field.
Therefore the question arises whether the positive results of the pulse magnetic field are not
caused by the more intensive electric component of the field.
Out of all possible pulse types, the BTL – 5000 device has been equipped with the following
ones. These pulses cover the entire spectrum of required applications, from acute to chronic
states.
2.1.3.1 Device Options
The device can be set to generate the following
pulse types:
• rectangular pulses,
• rectangular protracted pulses,
• exponential pulses,
• sinusoidal pulses,
• triangular pulses and
• continuous magnetic field.
All the above listed magnetic field waveforms can
be further modulated and the following surges of
basic pulses can be created:
• trapezoid surges,
• sine surges,
• symmetric surges.
It is also possible to create groups of magnetic pulses - so called bursts.
The option of random sweep of the basic selected frequency is available
too.
All these parameters can be set in well-arranged manual mode. Preset
programs and recommended diagnoses are available too.
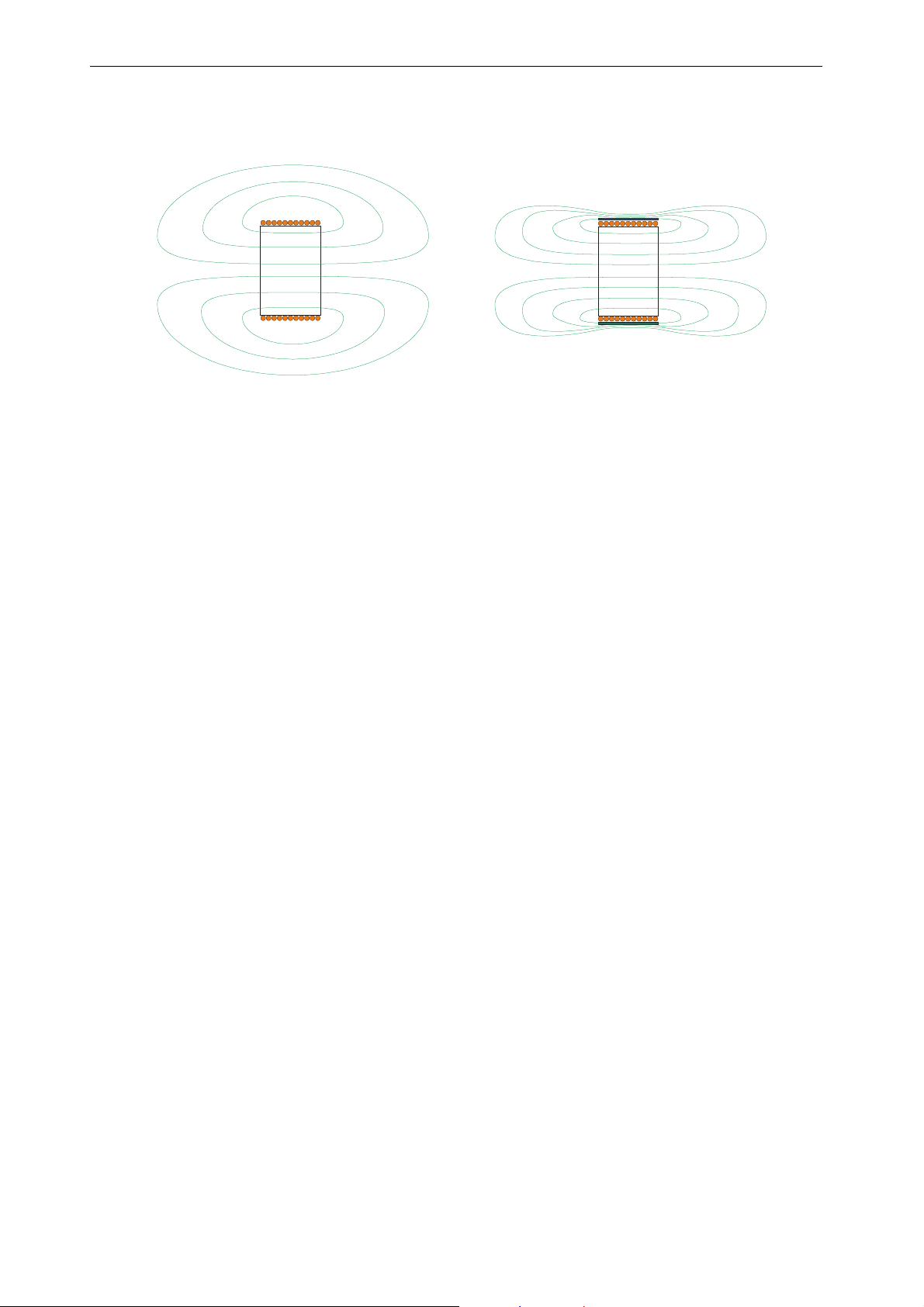
2.2 FMF TECHNOLOGY
FMF = Focused M agnetic F ield
In dependence on their spatial distribution, magnetic fields are divided into uniform and nonuniform. The uniform field has the same intensity and the same direction in all points of the
space.
The applicators were designed using state-of the-art ferromagnetic and magnetic materials
which allow to assemble highly effective magnetic concentration systems. These elements
focus the electromagnetic field into the desired space towards the treated body part.
Therefore the magnetic field of the BTL applicator is intentionally non-uniform and focused.
Standard Magnetic Applicator FMF Technology Applicator of DISC Type
page 6 of 31
Page 7
MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
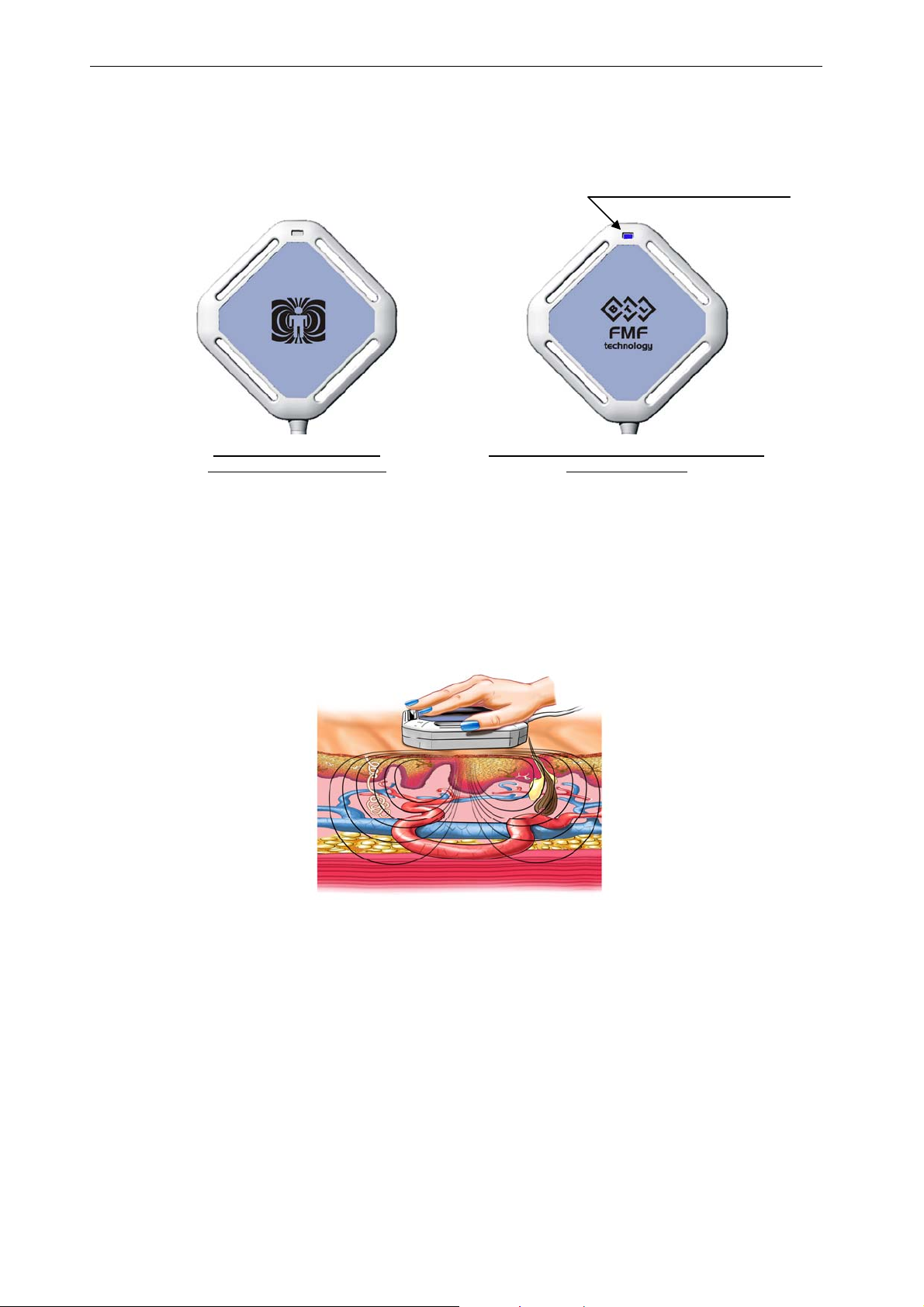
The sides of the applicator are identified as the patient side, from which the magnetic field is
emitted to a higher extent, and the operator side, at which the field intensities are several
times lower.
blue indicator light
Patient / Application
Side of the Applicator
The side is marked with the
pictograph of a “patient in the
magnetic field”. The intensities at
this side of the applicator are much
higher than those at the operator
side. During the operation of the
device the operator should not touch
Side turned away from the patient
(operator side)
Side marked with the BTL logo.
It is also equipped with blue
indicator lamp which indicates the
operation of the applicator
(continuous light, fast blinking)
and its readiness for operation (slow
blinking)
this side of the applicator.
Example of possible use of the magnetic applicator with FMF technology:
page 7 of 31
Page 8
MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
The magnetic field of the solenoid type applicators is focused inward:
Standard applicator and its FMF technology applicator magnetic
field - focused magnetic field
2.3 MAGNETIC FIELD UNITS
Devices BTL-4000 and BTL-5000 use for the magnetic field induction (B) the unit according to
the SI international unit system – Tesla (T) or its one thousandth - millitesla (mT).
Owing to the fact that the formerly used unit Gauss (G) has the following relation to millitesla:
1mT = 10 G, the display shows the converted value in mT/10.
Then, 1mT/10 = 1G.
Other magnetic field units:
Then unit of magnetic field intensity is ampere per meter (A/m).
An older unit of intensity is Oersted (Oe).
The relation between these two unit is: 1 Oe = 79.577 A/m.
The relation between the magnetic induction and the magnetic intensity is the following:
B = µ
. µo . H
r
where: B is the magnetic induction
H is the magnetic intensity
µ
µ
is the permeability of vacuum, which equals to 1.2566 . 10-6
o
is the relative permeability of the environment which expresses the magnetic
r
properties of the environment
• for vacuum it equals to 1
• for magnetically conductive materials the values are much higher than 1 (e.g.
for steel the values range from 100 to 5800)
• for air the value is similar as for vacuum, i.e. approximately 1 (1.00000038 to be
accurate)
• biological tissues from this view can be compared to water, for which the value
equals to 0.999991
It can be calculated that for biological tissues a magnetic field induction of 1mT corresponds
to a magnetic field intensity of 795.8 A/m.
page 8 of 31
Page 9

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
3 THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS OF MAGNETOTHERAPY
Magnetotherapy is one of the commonly used physiotherapy procedures. This method has
proved successful in some diseases as therapy with long-lasting therapeutic effect (e.g. at
chronic pains of vertebrogenous aetiology or at degenerative joint diseases) even when other
therapy methods failed. However, it is necessary to consider that, like every therapeutic
procedure, magnetotherapy also has a certain failure rate.
It has been proved that for treatment of patients in acute stages it is better to use static
magnetic field at the beginning; in chronic diseases it is better to use pulse magnetotherapy.
Application of magnetotherapy must always be based on thorough medical history and detailed
examination of the patient.
It is suitable to take into account that the natural magnetic field of the Earth equals
approximately to 0.04 – 0.05 mT (0.4 – 0.5 Gauss). Devices BTL-4000 / BTL-5000 work with
magnetic fields the intensity of which may be up to 1000 times higher. Therefore the
application requires particular caution, also with respect to the fact that man has no specific
receptors for magnetic field and therefore does not perceive it directly – unlike e.g. electric
current.
The latest findings about physiological response of the organism to the electromagnetic field
imply the following effects of magnetotherapy:
• analgesic effect,
• antiphlogistic effect,
• trophic effect (acceleration of healing and growth),
• myorelaxation and spasmolytic effect,
• vasodilatation effect.
• antiedematous effect,
3.1 ANALGESIC EFFECT
The analgesic effect of magnetotherapy applies in most algesic states of muscular as well as
articular aetiology. Detailed description of this effect is quite complicated; its physiological
effects have been specified in recent years. According to these findings, the analgesic effect
of magnetotherapy is accounted for by increased secretion of endogenous opioids caused by
myorelaxation, antiphlogistic and antiedematous effect and maybe also the impact on
presinaptic inhibition of nociceptive signals at the level of medullary dorsal horns.
The treatment should be combined with aimed pharmacotherapy, manual treatment and
relaxation therapy, at least in the initial stage.
3.2 ANTIPHLOGISTIC EFFECT
This effect has not been convincingly explained so far, but recent studies agree on the
following principle:
The antiphlogistic effect is induced by increased phagocytosis of neutrophils and increased
production of hyperoxide. This is followed by induction of hyperoxide dismutase bound to
endothelium, which all probably leads to higher concentration of hydrogen peroxide in the
exposed area. Owing to the fast that hyperoxide inhibits the activity of catalase, the hydrogen
peroxide is not degraded and thus it is able to destroy leucotriens, which belong to the
strongest activators of phagocytosis.
This mechanism also explains the initial controversial acting of the magnetic field in sterile
inflammations as well as in the microbially induced inflammations. This effect also accounts
for temporary impairment of rheumatic conditions during the first two or three expositions,
when the inflammatory symptoms are intensified by increasingly produced hyperoxide.
Simultaneous medication and physical therapy is necessary; the patient must be monitored
during the therapy and in case of longer negative reaction the therapy must be stopped.
page 9 of 31
Page 10

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
3.3 TROPHIC EFFECT
The magnetic field accelerates healing of the skeleton and soft tissues. It is caused by better
blood circulation in the exposed area and by irritation of cytoplasmatic membranes. This
activates the metabolic chain, the key point of which is the change of the cAMP/cGMP ratio.
The acceleration of healing, especially of the skeleton, is described in details in the literature
(Chvojka, 1993, 2000).
3.4 MYORELAXATION AND SPASMOLYTIC EFFECT,
Increased blood circulation in the area improves washing away of acidic metabolites which
cause painful irritation. In the muscles exposed to the magnetic field there also proceeds
increased activity of LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) and efflux of the Ca
2+
ion from muscle cells.
3.5 VASODILATATION EFFECT
This effect is caused by the efflux of Ca2+ ions which causes relaxation of the tonus of the
vascular musculature and precapillary sphincters. Probably the n. vagus is also directly
influenced and the increased metabolic activity of cells in the exposed area results in creation
of EDRF and prostacyclins.
3.6 ANTIEDEMATOUS EFFECT
This effect results from the two above described effects - antiphlogistic effect of the magnet
and acceleration of healing and improved blood circulation.
page 10 of 31
Page 11

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
4 RECOMMENDED DOSAGE OF MAGNETOTHERAPY
Suitable dosage for the particular application can be estimated from the following relations.
The resulting dose rises along with:
• higher value of magnetic induction (intensity) of the magnetic field B
• higher steepness of rising and falling edges of magnetic field pulses dB/dt [T/s],
• higher frequency of magnetic field pulses f [Hz] and
• longer time of exposition (in hours).
dose = B
* dB/dt * time of exposition * f
max
The optimum dose should range from 4 to 8.
The following procedure for selecting the optimum does of magnetotherapy is recommended:
• The applicators should be as close as possible to the patient’s body surface. Direct
contact with the body is not necessary, therapy may be applied through the clothes or
bandage.
• Magnetotherapy should be applied as soon as possible - it will better influence
functional disorders, not structural changes.
• For sterile inflammations it is suitable to use frequency up to 10 Hz.
• For microbially induced inflammations (sinusitises, osteomyelitises) it is suitable to use
pulse frequency about 25 Hz.
• In degenerative diseases of locomotive organs the recommended pulse frequency is
above 10 Hz.
• When treating tennis elbows and frozen shoulders it is suitable to expose the C-spine
at the same time.
• When treating subacute and acute vertebrogenous troubles it is also recommended to
expose the pain trigger points (TPs).
• Individual expositions must be long enough and repeated. The minimum exposition time
is at least 10 minutes, the minimum number of expositions is 10 to 15.
• The total daily time of exposition should not exceed 40 minutes.
• The best results are achieved when the first 5 to 10 expositions are performed daily or
twice a day.
• If magnetotherapy does not start to work within 20 procedures, it fails. An exception is
the treatment of pseudo-arthroses, where the first visible signs of healing can be
observed, using display methods, not sooner than after 30 procedures.
• In approximately 30% of rheumatics there can be expected subjective impairment of the
condition after first 3 expositions.
• If possible, do not end magnetotherapy at once, but by gradual prolongation of
intervals between individual expositions.
Special attention shall be paid to patients with hypotensis and hypertensis. During therapy the
significant drop of blood pressure may occur, including all side effects. This reaction usually
disappears within 30 minutes after the end of therapy and the adaptation occurs approximately
after 5 expositions.
For contraindications see the main User’s Manual of the device - document “BTL-5000 Series
– User’s Manual”, Chapter 6.4 “Contraindications”.
max
[T],
page 11 of 31
Page 12

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
5 BIBLIOGRAPHY
CALTA, J., MACHÁLEK, Z., VACEK, J. Základy fyzikální terapie pro praxi. Praha: Knihovna
REFORa, 1994.
CAPKO, J. Základy fyziatrické léčby. Praha: Grada, 1998.
HUPKA, J., KOLESÁR, J., ŽALOUDEK, K.: Fyzikální terapie. Praha: Avicenum, 1988.
CHVOJKA, J.: Magnetoterapie v klinické praxi. Městec Králové, 1993.
CHVOJKA, J.: Magnetoterapie v teorii a praxi. Praha: Professional Publishing, 2000.
IPSER, J., PŘEROVSKÝ, K. Fysiatrie, Praha: Avicenum, 1972.
JEŘÁBEK, J.: Magnetoterapie. Nový Bydžov, Hradec Králové: 2EL, 1993.
KŘ IVOHLAVÝ, J. Bolest, její diagnostika a psychoterapie. Praha: Institut pro další vzdě lávání
lékařů a farmaceutů, 1992.
MELZACK, R., WALL, P. D. Textbook of Pain. New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1984.
NIEPEL, G.: Fyzikální terapie v praxi. Receptář . Brno: IDVPZ, 1998.
PODĚBRADSKÝ, J., VAŘ EKA, I. Fyzikální terapie I.. Praha: Grada-Avicenum, 1998.
PODĚBRADSKÝ, J., VAŘ EKA, I.: Fyzikální terapie II. Praha: Grada-Avicenum, 1998.
VAŘEKA, I. Základy fyzikální terapie. Olomouc: vydavatelství UP Olomouc, 1995.
C. A. L. Bassett and M. Schink-Ascani, “Long-term Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF)
Results in Congenital Pseudarthrosis”, Calcified Tissue International, 49, 1991, pp. 216-220.
C. A. L. Bassett, R. J. Pawluk, and A. A. Pilla, “Acceleration of Fracture Repair by
Electromagnetic Fields: A Surgically Non-invasive Method”, Annals of the New York Academy
of Sciences, 238, 1974, pp. 242-262
C. A. L. Bassett, R. J. Pawluk, and A. A. Pilla, “Augmentation of Bone Repair by Inductively
Coupled Electromagnetic Fields”, Science, 184, 136, 1974, pp. 575-577
C. A. L. Bassett, A. A. Pilla, and R. J. Pawluk, “A Nonoperative Salvage of SurgicallyResistant Pseudarthroses and Non-unions by Pulsing Electromagnetic Fields”, Clinical
Orthopaedics and Related Research, 124, 1977, pp. 128-143
C. A. L. Basset, M. G. Valdest and E. Hernandez, "Modification of Fracture Repair with
Selected Pulsing Electromagnetic Fields", The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Vol. 64-A,
NO 6, 1982, pp. 888-895
Bawin, S.M. and W.R. Adey "Sensitivity of Calcium Binding in Cerebral Tissue to Weak
Environmental Electric Fields Oscillating at Low Frequency", Proceedings of the
Afafiona/Acaderny of Sciences 73(6), June, 1976, pp. 1999-2003.
A. Binder, G. Parr, B. Hazleman, and S. Fitton-Jackson, “Pulsed Electromagnetic Field
Therapy of Persistent Rotator Cuff Tendinitis: A Double-blind Controlled Assessment”, The
Lancet, 1, 8379, 1984, pp. 695-698.
Blackman, C. F., S.G. Benane, D.E. House, J.R. Rabinowitz, and W.T. Joines, "ELF
Electromagnetic Fields Cause Enhanced Efflux of Neutral Sugars from Brain Tissue In Vitro",
Technical Report, Abstract, Ninth Annual Meeting of the Bioelectromagnetics Society,
Portland, OR, June 1987, pp.21-25.
Brown, C. S., Lingm F. W., Wan, J. Z. and A. A. Pilla, "Efficacy of static magnetic field therapy
in chronic pelvic pain: A double-blind pilot study", Am J Obstet Gynecol; 187, 2002, pp. 1581-
1587.
M. A. Darendeliler, A. Darendeliler, and P. M. Sinclair, “Effects of Static Magnetic and Pulsed
Electromagnetic Fields on Bone Healing”, International Journal of Adult Orthodontic and
Orthognathic Surgery, 12, 1, 1997, pp. 43-53.
G. De Haas, M. A. Lazarovici, and D. M. Morrison, “The Effect of Low Frequency Magnetic
Fields on the Healing of the Osteotomized Rabbit Radius”, Clinical Orthopaedics and Related
Research, 145, 1979, pp. 245-251.
J. L. Fleming, M. A. Persinger, and S. A. Koren, “Magnetic Pulses Elevate Nociceptive
Thresholds: Comparisons with Opiate Receptor Compounds in Normal and Seizure-Induced
Brain-Damaged Rats”, Electro- and Magnetobiology, 13, 1, 1994, pp. 67-75.
P. A. Glazer, M. R. Heilmann, J. C. Lotz, and D. S. Bradford, “Use of Electromagnetic Fields in
a Spinal Fusion: A Rabbit Model”, Spine, 22, 1997, pp. 2351-2356.
page 12 of 31
Page 13

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
J. D. Heckman, A. J. Ingram, R. D. Loyd, J. V. Luck Jr., and P. W. Mayer, “Nonunion
Treatment with Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields”, Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research,
161, 1981, pp. 58-66.
Hinman, M. R., Ford, J., and H. Heyl, "Effects of static magnets on chronic knee pain and
physical function: A double-blind study", Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine, Vol. 8,
No. 4, 2002, pp. 50-55.
M. Ieran, S. Zaffuto, M. Bagnacani, M. Annovi, A. Moratti, and R. Cadossi, “Effect of Low
Frequency Pulsing Electromagnetic Fields on Skin Ulcers of Venous Origin in Humans:A
Double-blind Study”, Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 8, 2, 1990, pp. 276-282.
H. Ito, Y. Shirai and Y. Gembun, "A Case of Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia Treated
with Pulsing Electromagnetic Fields, 17-Year Follow-up", J Nippon Med Sch; 67,3, 2000, pp.
198-201.
J. I. Jacobson, R. Gorman, W. S. Yamanashi, B. B. Saxena, and L. Clayton, “Low-amplitude,
Extremely Low Frequency Magnetic Fields for the Treatment of Osteoarthritic Knees: A
Double-blind Clinical Study”, Alternative Therapies, 7, 5, 2001, pp. 54-69.
Jeřábek J., "Magnetoterapie", Rehabilitace a fyzikální lékař ství; 3 (2), 1996, pp. 55-62.
W. A. Jorgensen, B. M. Frome, and C. Wallach, “Electrochemical Therapy of Pelvic Pain:
Effects of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (PEMF) on Tissue Trauma”, The European Journal of
Surgery, 574 (Supplement), 1994, pp. 83-86.
M. Kanje, A. Rusovan, B. Sisken, and G. Lundborg, “Pretreatment of Rats with Pulsed
Electromagnetic Fields Enhances Regeneration of the Sciatic Nerve”, Bioelectromagnetics, 14,
1993, pp. 353-359.
K. Konrad, K. Sevcic, K. Fõldes, E. Piroska, and E. Molnár, “Therapy with Pulsed
Electromagnetic Fields in Aseptic Loosening of Total Hip Prostheses: A Prospective Study”,
Clinical Rheumatology, 15, 4, 1996, pp. 325-328.
Kuba, J., Procházka, M., "Klinické testování přístroje k terapii magnetickým pulzním polem s
kritérii dvojitě slepě uspoř ádané studie", Rehabilitace a fyzikální lékařství, 7 (1), 2000, pp. 24-
27.
R. A. Marks, “Spine Fusion for Discogenic Low Back Pain: Outcomes in Patients Treated with
or without Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Stimulation”, Advances in Therapy, 17, 2, 2000, pp.
57-67.
H. Matsumoto, M. Ochi, Y. Abiko, Y. Hirose, T. Kaku, K. Sakaguchi, “Pulsed Electromagnetic
Fields Promote Bone Formation around Dental Implants Inserted into the Femur of Rabbits”,
Clinical Oral Implants Research, 11, 2000, pp. 354-360
V. Mooney, “A Randomized Double-blind Prospective Study of the Efficacy of Pulsed
Electromagnetic Fields for Interbody Lumbar Fusions”, Spine, 15, 7, 1990, pp. 708-712.
F. Papi, S. Ghione, C. Rosa, C. Del Seppia, and P. Luschi, “Exposure to Oscillating Magnetic
Fields Influences Sensitivity to Electrical Stimuli. II. Experiments on Humans”,
Bioelectromagnetics, 16, 1995, pp. 295-300.
Pipitone, N. and D. L. Scott. "Magnetic Pulse Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis: A
Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study", Current Medical Research and Opinion,
Vol. 17, No. 3, 2001, pp. 190-196.
T. L. Richards, M. S. Lappin, J. Acosta-Urquidi, G. H. Kraft, A. C. Heide, F. W. Lawrie, T. E.
Merrill, G. B. Melton, and C. A. Cunningham, “Double-blind Study of Pulsing Magnetic Field
Effects on Multiple Sclerosis”, The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 3, 1,
1997, pp. 21-29.
N. J. Roland, J. B. Hughes, M. B. Daley, J. A. Cook, A. S. Jones, and M. S. McCormick,
“Electromagnetic Stimulation as a Treatment of Tinnitus: A Pilot Study”, Clinical
Otolaryngology and Applied Sciences, 18, 1993, pp. 278-281.
Sadlonova, J., Korpas, J., Salat, D., Miko, L., Kudlicka, J., "The effect of the pulsatile
electromagnetic field in children suffering from bronchial asthma", Acta Physiol Hung., 90(4),
2003, pp. 327-34.
Sadlonova J, Korpas J, Vrabec M, Salat D, Buchancova J, Kudlicka J., ""The effect of the
pulsatile electromagnetic field in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease and bronchial asthma"", Bratisl Lek Listy; 103 (7-8), 2002, pp. 260-265."
E. R. Sanseverino, A. Vannini, and P. Castellacci, “Therapeutic Effects of Pulsed Magnetic
Fields on Joint Diseases", Panminerva Medica, 34, 4, 1992, pp. 187-196.
page 13 of 31
Page 14

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
F. Sartucci, L. Bonfiglio, C. Del Seppia, P. Luschi, S. Ghione, L. Murri, and F. Papi, “Changes
in Pain Perception and Painduced by Exposure to Oscillating Magnetic Fields”, Brain
Research, 769, 1997, pp. 362-366.
B. F. Sisken, M. Kanje, G. Lundborg, E. Herbst, and W. Kurtz, “Stimulation of Rat Sciatic
Nerve Regeneration with Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields”, Brain Research, 485, 1989, pp. 309-
316.
M. J. Stiller, G. H. Pak, J. L. Shupack, S. Thaler, C. Kenny, and L. Jondreau, “A Portable
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Device to Enhance Healing of Recalcitrant Venous
Ulcers: A Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial,” British Journal of Dermatology, 127,
1992, pp. 147-154.
Sweeney, K. B., Merrick, M. A., Ingersoll, Ch., D., and J. A.Swez, "Therapeutic Magnets Do
Not Affect Tissue Temperatures", J. Athl. Train., 36 (1), 2001 March, pp. 27-31.
F. Tabrah, M. Hoffmeier, F. Gilbert Jr., S. Batkin, and C. A. L. Bassett, “Bone Density
Changes in Osteoporosis prone Women Exposed to Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (PEMFs)”,
Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 5, 5, 1990, pp. 437-442.
G. C. Traina, L. Romanini, F. Benazzo, R. Cadossi, V. Canè, A. Chiabrera, M. Marcer, N.
Marchetti, and F. S. Snatori, “Use of Electric and Magnetic Stimulation in Orthopaedics and
Traumatology: Consensus Conference”, Italian Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, 24,
1, 1998, pp. 1-31.
D. H. Wilson and P. Jagadeesh, "Experimental Regeneration in Peripheral Nerves and the
Spinal Cord in Laboratory Animals Exposed to a Pulsed Electromagnetic Field”, Paraplegia,
14, 1976, pp. 12-20.
page 14 of 31
Page 15

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
6 SETTING AND CONTROL OF MAGNETOTHERAPY –
TECHNICAL PARAMETERS
6.1 MAGNETIC FIELD INTENSITY
The magnetic field intensity can be set from 1 mT/10 (i.e. 1
Gauss) and its maximum value depends on the applicator type
and the type of the selected therapy application. For the
maximum values in dependence on the applicator type see Chapter 7 Applicators.
The step of setting is 1 mT/10 (i.e. 1 Gauss).
The set intensity value represents the maximum intensity in space and time
The accuracy of the set intensity value is ± 30%.
6.2 THERAPY TIME
Can be set within the range from 1 second to 100 minutes, i.e.
from 00:01 to 99:59 [m:s].
The step of setting is 1 second
The accuracy of the set time is 2%.
6.3 PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS
The effects are defined for preset diagnoses and the user can define them for customer
diagnoses and programs, created and saved by the user.
Legend:
• A – analgesic
• E – antiedematous
• F –antiphlogistic
• S – trophic, acceleration of healing
• R – myorelaxation and spasmolytic (vasodilatation, antiedematous,...)
6.4 SELECTION OF THERAPY
Press the [therapy] button to open the dialog
box (see picture) for selection of the best
magnetic field therapy. The following therapy
options are available:
• magnetic pulses
• series of magnetic pulses
• continuous magnetic field.
The properties of individual therapies are
described in the paragraphs below.
6.4.1 Magnetic Pulses
Standard waveforms of magnetic pulses; it is possible to select between constant and
randomly swept frequency of the selected pulses. For selection of the pulse shape use the
[pulse shape] button. The following options are available:
• rectangular pulses,
• rectangular protracted pulses,
• exponential pulses,
• sinusoidal pulses and
• triangular pulses.
page 15 of 31
Page 16

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
The following modulations can be applied on the magnetic pulses:
• burst,
• sine surges,
• trapezoid surges and
• symmetric surges.
6.4.1.1 Pulse, Pause, Frequency – Setting
On pressing of the displayed window the dialog box opens, in
which it is possible to set the following pulse parameters:
pulse length, pause between pulses and pulse frequency.
Owing to the fact that these values are mutually
interconnected through mathematical definitions, any
change of a value implies automatic changes of the
other values.
At setting it is necessary to realize that the pause
length must be always longer than the pulse length
(construction limits).
The limits for setting differ for various pulse shapes for details see Chapter 6.5 Pulse Shape.
6.4.2 Series of Magnetic Pulses
These very interesting magnetic pulse waveforms were first used in the BTL-09 device, but
were limited to rectangular pulses only. Devices BTL-4000 / 5000 offer these pulses for all
pulse shapes:
• rectangular pulses,
• rectangular protracted pulses,
• exponential pulses,
• sinusoidal pulses and
• triangular pulses.
In principle is it a mix of pulses of various length and frequency in one series to be repeated.
It is advantageous to combine for example long pulses of low frequency with very short pulses
of high repeating frequency and thus cumulate the therapy effect.
It is also possible to select between constant and randomly swept frequency of the selected
pulses.
The following modulations can be applied on the magnetic pulses:
• sine surges,
• trapezoid surges and
• symmetric surges.
6.4.2.1 Pulse, Pause, Frequency, Repeating – Setting of Series
After pressing of the displayed button the dialog box opens, in
which it is possible to set the following parameters of the
series of pulses: pulse length, pause between pulses, pulse
frequency, number in the series and length of the series.
For each period – part of the series – it is possible to
set the standard pulse parameters:
• pulse length,
• length of pause between pulses,
• pulse frequency and
• number of pulses with this setting to be
generated. After the end of generation of this
part the program passes to another one.
page 16 of 31
Page 17

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
The limits for setting of the pulse length, pause and frequency differ for various pulse shapes
– for details see Chapter 6.5 Pulse Shape.
The number of repetitions of individual pulses can be set within the range from 1 to 255.
The step of setting is 1 .
The window displays the total number of parts in the series and the [add new] button, the field
for displaying the number of the part being edited (10 in this case) and the button for deleting
of the selected part of the series.
In total it is possible to set 13 parts in one series.
Owing to the fact that the values of the pulse length, pause and frequency are mutually
interconnected through mathematical definitions, any change of a value implies automatic
changes of the other values.
At setting it is necessary to realize that the pause length must be always longer than the pulse
length (construction limits).
6.4.3 Continuous Magnetic Field
The BTL 4000 / 5000 devices enable to generate stationary magnetic field,
which is similar to the fields around permanent magnets. This field is
recommended for the applications where the effects of the pulse
electromagnetic field could cause serious problems and it is therefore contraindicated - e.g. in
case of increased bleeding conditions, acute states, post-operative conditions etc. The effect
of this field is also increased by the presence of permanent magnets in our “disc” type
applicators. The application of this type of field is recommended in the first stages of
magnetotherapy; approximately after the first or second week it is recommended to change
over to the pulse field.
Continuous magnetic field can be modulated by slow magnetic field surges of a length of
several seconds or more.
• sine surges,
• trapezoid surges and
• symmetric surges.
6.5 PULSE SHAPE
This button serves for selection of the required shape of magnetic pulses. The following
options are available:
• rectangular pulses
• rectangular protracted pulses
• exponential pulses
• sinusoidal pulses
• triangular pulses.
6.5.1 Rectangular Pulses
These pulses are a sort of “gold standard” in pulse magnetotherapy. In addition to the options
that are available in the BTL-09 device, device BTL 4000 / 5000 provides also modulation of
contour of the following pulses:
• trapezoid surges,
• sine surges,
• symmetric surges and
• bursts.
Rectangular pulses can be set within the following range:
• pulse length t
from 3 ms to 255 ms
p
o step of setting: 1 ms (from 3 ms to 30 ms)
2 ms (from 30 ms to 50 ms)
5 ms (from 50 ms to 100 ms)
10 ms (from 100 ms to 255 ms)
o a specific value (e.g. 58 ms) can be set using the keyboard
• pause between pulses t
o the set pause is always longer than the set pulse length: t
from 3 ms to 65,000 ms
i
> tp
i
page 17 of 31
Page 18

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
o step of setting: 1 ms (from 3 ms to 30 ms)
2 ms (from 30 ms to 50 ms)
5 ms (from 50 ms to 100 ms)
10 ms (from 100 ms to 200 ms)
20 ms (from 200 ms to 500 ms)
50 ms (from 500 ms to 1000 ms)
100 ms (from 1,000 ms to 65,000 ms)
o a specific value (e.g. 583 ms) can be set using the keyboard
• the frequency of pulses can be set within the range from 0.015 Hz to 166 Hz
o step of setting: 0.01 Hz (from 0.01 Hz to 0.30 Hz)
0.02 Hz (from 0.30 Hz to 0.50 Hz)
0.05 Hz (from 0.50 Hz to 1.00 Hz)
0.10 Hz (from 1.00 Hz to 5.00 Hz)
0.50 Hz (from 5.00 Hz to 10.0 Hz)
1.00 Hz (from 10.0 Hz to 30.0 Hz)
2.00 Hz (from 30.0 Hz to 50.0 Hz)
5.00 Hz (from 50.0 Hz to 70.0 Hz)
10.0 Hz (from 70.0 Hz to 100 Hz)
15.0 Hz (from 100.0 Hz to 166 Hz)
o the specific value is calculated by the device from the values of pulse length
and pause length
f = 1 / (t
+ tp)
i
6.5.2 Rectangular Protracted Pulses
On the basis of our experience with pulse magnetic fields we designed this new
type of currents which utilizes the advantageous properties of rectangular pulses
– big steepness of the rising and falling edges. At the same time it significantly
reduces the power consumption of the generated magnetic field pulses and
extends the duration of the pulse. So it is possible to generate pulses of higher intensities
than at standard rectangular pulses with the same power consumption (the same heating of
the applicators).
Similarly as in standard rectangular pulses, all modulations of pulse contours are available
here, including random frequency sweep, preset programs and recommended diagnoses.
Protracted rectangular pulses can be set within the following range:
• pulse length t
from 6 ms to 510 ms
p
o step of setting: 1 ms (from 6 ms to 30 ms)
2 ms (from 30 ms to 50 ms)
5 ms (from 50 ms to 100 ms)
10 ms (from 100 ms to 510 ms)
o a specific value (e.g. 58 ms) can be set using the keyboard
• pause between pulses t
o the set pause is always longer than the set pulse length: t
from 6 ms to 65,000 ms
i
> tp
i
o step of setting: 1 ms (from 6 ms to 30 ms)
2 ms (from 30 ms to 50 ms)
5 ms (from 50 ms to 100 ms)
10 ms (from 100 ms to 200 ms)
20 ms (from 200 ms to 500 ms)
50 ms (from 500 ms to 1000 ms)
100 ms (from 1,000 ms to 65,000 ms)
o a specific value (e.g. 583 ms) can be set using the keyboard
• the frequency of pulses can be set within the range from 0.015 Hz to 83.3 Hz
o step of setting: 0.01 Hz (from 0.01 Hz to 0.30 Hz)
0.02 Hz (from 0.30 Hz to 0.50 Hz)
0.05 Hz (from 0.50 Hz to 1.00 Hz)
0.10 Hz (from 1.00 Hz to 5.00 Hz)
0.50 Hz (from 5.00 Hz to 10.0 Hz)
1.00 Hz (from 10.0 Hz to 30.0 Hz)
2.00 Hz (from 30.0 Hz to 50.0 Hz)
5.00 Hz (from 50.0 Hz to 70.0 Hz)
10.0 Hz (from 70.0 Hz to 83.3 Hz)
page 18 of 31
Page 19

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
o the specific value is calculated by the device from the values of pulse length
and pause length
f = 1 / (t
+ tp)
i
6.5.3 Exponential Pulses
Similarly as in electrotherapy, these pulses are very interesting thanks to their
mild gradual rising and, at the same time, high pulse intensities, which they
achieve at very low power consumption. That is why they are suitable especially in
the applications where high energy of the electromagnetic field is undesirable but the high
pulse intensity is required. These pulses apply especially at stimulation of neural paths by
induced currents.
At exponential pulses it is also possible to apply surge modulations similarly as at rectangular
pulses.
Exponential pulses can be set within the following range:
• pulse length tp from 6 ms to 510 ms
o step of setting: the same as for rectangular protracted pulses
o a specific value (e.g. 58 ms) can be set using the keyboard
• pause between pulses t
o the set pause is always longer than the set pulse length: t
from 6 ms to 65,000 ms
i
> tp
i
o step of setting: the same as for rectangular protracted pulses
o a specific value (e.g. 583 ms) can be set using the keyboard
• the frequency of pulses can be set within the range from 0.015 Hz to 83.3 Hz
o step of setting: the same as for rectangular protracted pulses
o the specific value is calculated by the device from the values of pulse length
and pause length
f = 1 / (t
+ tp)
i
6.5.4 Sinusoidal Pulses
Classic sinusoidal pulses derived from the mains voltage. They are used
particularly for well-tried standard therapies. The setting options are the same as
for rectangular pulses, including modulation.
Setting options:
• pulse length t
from 6 ms to 510 ms
p
o step of setting: the same as for rectangular protracted pulses
o a specific value (e.g. 58 ms) can be set using the keyboard
• pause between pulses ti from 6 ms to 65,000 ms
o the set pause is always longer than the set pulse length: t
> tp
i
o step of setting: the same as for rectangular protracted pulses
o a specific value (e.g. 583 ms) can be set using the keyboard
• the frequency of pulses can be set within the range from 0.015 Hz to 83.3 Hz
o step of setting: the same as for rectangular protracted pulses
o the specific value is calculated by the device from the values of pulse length
and pause length
f = 1 / (t
+ tp)
i
6.5.5 Triangular Pulses
Symmetric triangular pulses with the same rising time and falling time. In some
countries their use is very widespread. The setting options are the same as for
rectangular pulses, including modulation.
Setting options:
• pulse length t
from 6 ms to 510 ms
p
o step of setting: the same as for rectangular protracted pulses
o a specific value (e.g. 58 ms) can be set using the keyboard
• pause between pulses ti from 6 ms to 65,000 ms
o the set pause is always longer than the set pulse length: t
> tp
i
o step of setting: the same as for rectangular protracted pulses
o a specific value (e.g. 583 ms) can be set using the keyboard
• the frequency of pulses can be set within the range from 0.015 Hz to 83.3 Hz
o step of setting: the same as for rectangular protracted pulses
o the specific value is calculated by the device from the values of pulse length
and pause length
f = 1 / (ti + tp)
page 19 of 31
Page 20

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
6.6 MODULATION
For detailed modulation settings press the [mag. param.] window.
6.6.1 Random Frequency
Can be selected for all pulse types. The option switches on
the sweep of the set pause length within the range from 0 to +
30%.
In the previous device BTL-09 this function was called “wave swing”. For the BTL-4000 / 5000
devices we decided to unify the name with the other types of physiotherapy, such as
electrotherapy etc.
6.6.2 Burst
This option cannot be used in the series of magnetic pulses
and the continuous field.
It is possible to set the number of pulses in one burst within the range from 3 to 10. The
length of so defined burst in [ms] is displayed in the
[burst] window.
The length of pause between individual bursts can be
set within the limit from 1 to 255 s.
The step of setting is:
• 1 s (from 1 s to 30 s)
• 2 s (from 30 s to 50 s)
• 5 s (from 50 s to 100 s)
• 10 s (from 100 s to 255 s)
• a specific value (e.g. 236 s) can be set using the keyboard.
Besides these options it is possible to use some predefined
settings – see picture, the value is displayed as the number of
pulses in burst / length of pause between bursts.
6.6.3 Sine Surges
The surge length and the pause length can be set separately,
both within the range from 1 s to 255 s.
The step of setting of both values is:
• 1 s (from 1 s to 30 s)
• 2 s (from 30 s to 50 s)
• 5 s (from 50 s to 100 s)
• 10 s (from 100 s to 255 s)
• a specific value (e.g. 236 s) can be set using
the keyboard.
It is again possible to use predefined surges for
setting.
6.6.4 Trapezoid Surges
It is possible to set:
• surge rise from 1 s to 255 s
• surge duration from 1 s to 255 s
• fall of intensity from 1 s to 255 s and
page 20 of 31
Page 21

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
• pause from 1 s to 255 s.
The step of setting of both values is:
• 1 s (from 1 s to 30 s)
• 2 s (from 30 s to 50 s)
• 5 s (from 50 s to 100 s)
• 10 s (from 100 s to 255 s)
• a specific value (e.g. 236 s) can be set using the keyboard.
It is again possible to use predefined surges for setting.
page 21 of 31
Page 22

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
6.6.5 Symmetric Surges
Another way of setting of trapezoid surges, very widespread
in some EU countries.
It is possible to set the "sweep time”, the time of
detuning and stabilization of the surge, within the
range from 1 s to 255 s.
The step of setting is:
• 1 s (from 1 s to 30 s)
• 2 s (from 30 s to 50 s)
• 5 s (from 50 s to 100 s)
• 10 s (from 100 s to 255 s)
• a specific value (e.g. 236 s) can be set using
the keyboard.
The “contour” parameter is the ratio between the change and the stable part of the surge. It
can be set within the range from 1% to 100% change. The step of setting is 1%; the influence
of setting is best seen on the animated icon on the device.
It is again possible to use predefined surges for setting.
6.7 TEST OF CONNECTED APPLICATOR
To verify the function of ther connected applicator
press the [Induction of Magnet Accessories] button.
For correct evaluation of the test it is necessary to perform
the test on a non-conducting suface - wooden or plastic.
In addition it is necessary that the double disk or
multidisk applicators are not on top of each other during
the measuring, but beside each other.
The test measures the temperature and magnetic inductivity of the connected applicator. After
the measuring the measured values are compared with the standard values and on the basic of
this comparison the device evaluates whether the applicator works properly.
If the resulting test value is “ok”, the applicator works properly.
If the test result is indicated “low value” or “high value” (see picture), the applicator probably
works improperly and it is necessary to contact the service.
Note:
Inductivity is a physical quantity which expresses the dimension of the magnetic induction flux
through the coil.
Inductivity is one of basic characteristics of the coil - it expresses the ability of the coil to
change electric power to magnetic field energy.
page 22 of 31
Page 23

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
7 APPLICATORS
The parameters of the magnetic applicators have been optimized with respect to the
recommended therapeutic applications. Using the FMF technology, the magnetic field is
focused to the treated area, which enables, while preserving the same output intensity, to
reduce the power consumption of the magnetotherapy device as well as the spurious magnetic
field on the non-patient side of the applicators, which may potentially hit the operator.
The below described types of applicators can be connected to the BTL-4000 / 5000 device.
7.1 “DISC" APPLICATOR
The Disc applicator is made of plastic. The part which comes into contact with the patient is
coated with fine durable leatherette.
The applicator is designed using the FMF technology - the patient side emits focused
magnetic field, while on the other side the magnetic field is screened so that its impact on the
surroundings is as low as possible.
Patient / application
side of the applicator
The side is marked with the
pictograph of a “patient in the
magnetic field”. The intensities at
this side of the applicator are much
higher than those at the operator
side. During the operation of the
device the operator should not touch
Side turned away from the patient
(operator side)
Side marked with the BTL logo.
It is also equipped with blue
indicator lamp which indicates the
operation of the applicator
(continuous light, fast blinking)
and its readiness for operation (slow
blinking)
this side of the applicator.
The magnetic applicator contains also a permanent magnet to increase the effect of soothing
the tissue at traumatic and bleeding conditions.
7.1.1 Technical Parameters
Identification - Type: BTL-239-1
Name: Disc
Dimensions: 130 x 130 x 30 mm
Weight: 1.05 kg
Intensity of the Permanent Magnet Field: 23 mT (230 Gauss)
Max. Intensity of Pulse Magnetic Field: 102 mT (1020 Gauss)
Max. Intensity of Magnetic Field in Total: 125 mT (1250 Gauss)
Resistance of the Applicator:
4.2 Ω
page 23 of 31
Page 24

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
7.1.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator
The picture shows the shape of the applicator’s magnetic field on the patient side. The unit of
the intensity values is mT/10, i.e. Gauss, and the values are valid at the maximum current
flowing through the applicator. The sum of intensity of the permanent magnet field and
intensity of the pulse magnetic field is stated. The value 1250 mT/10 is in the centre, on the
surface of the applicator.
[cm]
25
20
15
10
[mT/10]
3
5
10
20
50
5
100
200
500
0
1000
1250
051015205101520 [cm]
page 24 of 31
Page 25

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
7.2 “DOUBLE DISC" APPLICATOR
The double disc applicator consists of series interconnection of two disc applicators. The
applicators are mutually orientated in the way that a linearized magnetic field arises between
them.
Similarly as disc, the “double disc” applicator is made of plastic. The part which comes into
contact with the patient is coated with fine durable leatherette.
The applicator is designed using the FMF technology - the patient side emits focused
magnetic field, while on the other side the magnetic field is screened so that its impact on the
surroundings is as low as possible.
Patient / application
side of the applicator
The side is marked with the
pictograph of a “patient in the
magnetic field”. The intensities at
this side of the applicator are much
higher than those at the operator
side. During the operation of the
device the operator should not touch
Side turned away from the patient
(operator side)
Side marked with the BTL logo.
It is also equipped with blue
indicator lamp which indicates the
operation of the applicator
(continuous light, fast blinking)
and its readiness for operation (slow
blinking)
this side of the applicator.
The magnetic applicator contains also a permanent magnet to increase the effect of soothing
the tissue at traumatic and bleeding conditions.
7.2.1 Technical Parameters
Identification - Type: BTL-239-4
Name: double disc
Dimensions: 2x 130 x 130 x 30 mm
Weight: 2.15 kg
Intensity of the Permanent Magnet Field: 23 mT (230 Gauss)
Max. Intensity of Pulse Magnetic Field: 72 mT (720 Gauss)
Max. Intensity of Magnetic Field in Total: 95 mT (950 Gauss)
Resistance of the Applicator:
8.4 Ω
page 25 of 31
Page 26

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
[cm] [cm]
7.2.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator
The picture shows the shape of the applicator’s magnetic field between the patient sides. The
unit of the intensity values is mT/10, i.e. Gauss, and the values are valid at the maximum
current flowing through the applicator. The sum of intensity of the permanent magnet field and
intensity of the pulse magnetic field is stated. The highest value 950 mT/10 is in the centre,
on the surface of the applicator.
mT/10
10
25
50
950
950
100
250
500
750
page 26 of 31
Page 27

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
7.3 “MULTI DISC" APPLICATOR
The multi disc applicator consists of series-parallel interconnection of four disc applicators.
The applicators are mutually orientated in the way that a linearized magnetic field arises
between them.
The multi disc applicator was designed as a portable substitute for the solenoid 60 applicator.
It can be well used for the applications which require the use of two double discs (application
on the extremities). See recommended diagnoses for details.
Similarly as disc, the multi disc applicator is made of plastic - harmless polypropylene. The
part which comes into contact with the patient is coated with fine durable leatherette.
The applicator is designed using the FMF technology - the patient side emits focused
magnetic field, while on the other side the magnetic field is screened so that its impact on the
surroundings is as low as possible.
Patient / application
side of the applicator
The side is marked with the
pictograph of a “patient in the
magnetic field”. The intensities at
this side of the applicator are much
higher than those at the operator
side. During the operation of the
device the operator should not touch
Side turned away from the patient
(operator side)
Side marked with the BTL logo.
It is also equipped with blue
indicator lamp which indicates the
operation of the applicator
(continuous light, fast blinking)
and its readiness for operation (slow
blinking)
this side of the applicator.
The magnetic applicator contains also a permanent magnet to increase the effect of soothing
the tissue at traumatic and bleeding conditions.
7.3.1 Technical Parameters
Identification - Type: BTL-239-5
Name: multi disc
Dimensions: 4x 130 x 130 x 30 mm
Weight: 4.30 kg
Intensity of the Permanent Magnet Field: 23 mT (230 Gauss)
Max. Intensity of Pulse Magnetic Field: 72 mT (720 Gauss)
Max. Intensity of Magnetic Field in Total: 95 mT (950 Gauss)
Resistance of the Applicator:
4.2 Ω
page 27 of 31
Page 28

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
7.3.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator
The function of the multi disc applicator is similar to that of the double disc applicator where
four disc applicators are on simultaneously during the therapy.
The intensity values are listed in Chapter 7.3.1 Technical Parameters (the unit is mT/10, i.e.
Gauss, and the values are valid at the maximum current flowing through the applicator). Then
there is stated the sum of intensity of the permanent magnet field and intensity of the pulse
magnetic field. The value 950 mT/10 is in the centre, on the surface of the applicator. The
shape of the magnetic field of one pair of discs of the multi disc is the same as for the double
disc.
page 28 of 31
Page 29

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
7.4 “SOLENOID 30” APPLICATOR
The basis of construction of this tube-shaped applicator is a carrying tube made of
polypropylene (PP), which was chosen because of its favourable mechanical parameters and
low weight. Single-layer linear coil is wound on the tube; the external magnetic field is
screened off using the FMF technology. The design of the applicator was adapted to the
requirement to create linear magnetic field in as large as possible part of the applicator.
7.4.1 Technical Parameters
Identification - Type: BTL-239-2
Name: solenoid 30
Dimensions: 340 x 340 x 300 mm
Inner Diameter: 295 mm
Weight: 5.75 kg
Max. Intensity of Pulse Magnetic Field: 9.3 mT (93 Gauss)
Resistance of the Applicator:
3.5 Ω
7.4.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator
The picture shows the shape of the applicator’s magnetic field The unit of the intensity values
is mT/10, i.e. Gauss, and the values are valid at the maximum current flowing through the
applicator.
93
90
80
10 15 20 30 40 50 60
70
80
90
93
1015203040506070
[mT/10]
0 5 10 15 20510152025 25 [cm]
page 29 of 31
Page 30

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
7.5 “SOLENOID 60” APPLICATOR
The basis of construction of this tube-shaped applicator is a carrying tube made of
polypropylene (PP), which was chosen because of its favourable mechanical parameters and
low weight. Single-layer linear coil is wound on the tube; the external magnetic field is
screened off using the FMF technology. The design of the applicator was adapted to the
requirement to create linear magnetic field in as large as possible part of the applicator.
7.5.1 Technical Parameters
Identification - Type: BTL-239-3
Name: solenoid 60
Dimensions: 620 x 540 x 300 mm
Inner Width: 580 mm
Inner Height: 480 mm
Weight: 10.0 kg
Max. Intensity of Pulse Magnetic Field: 8.5 mT (85 Gauss)
Resistance of the Applicator:
6.2 Ω
7.5.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator
The picture shows the shape of the applicator’s magnetic field The unit of the intensity values
is mT/10, i.e. Gauss, and the values are valid at the maximum current flowing through the
applicator.
85
80
70
60
50
10 20 30 40 45
50
1020304045
60
70
80
[mT/10]
0 5 10 15 20510152025 25 [cm]
page 30 of 31
Page 31

MAGNETOTERAPIE - UŽIVATELSKÁ PŘ ÍRUČ KA BTL Physiotherapy
7.6 “LINEAR" APPLICATOR
The surface of the linear applicator is made of harmless and durable leatherette. The same
type of leatherette is used on the other applicator types.
7.6.1 Technical Parameters
Identification - Type: BTL-239-6
Name: Linear
Dimensions: 600 x 290 x 20 mm
Weight: 6.10 kg
Max. Intensity of Magnetic Field in Total: 36 mT (360 Gauss)
Resistance of the Applicator:
3.0 Ω
7.6.2 Shape of the Magnetic Field of the Applicator
The picture shows the shape of the applicator’s magnetic field The unit of the intensity values
is mT/10, i.e. Gauss, and the values are valid at the maximum current flowing through the
applicator.
59 cm
page 31 of 31
 Loading...
Loading...