Page 1

ControlSpace® ESP-88
Engineered Sound Processor,
CC-16 and CC-64 Controllers
(US and non-US units)
©2009 Bose Corporation
Service Manual
Reference Number 286448-SM Rev. 03
Electronic Copy Only
Page 2

CONTENTS
Safety Information ...........................................................................................................................................3
Warranty...........................................................................................................................................................3
Product Descriptions ...................................................................................................................................4-7
Specifications .............................................................................................................................................8-10
Electrostatic Discharge Sensitive (ESDS) Device Handling....................................................................... 11
Part List Notes ............................................................................................................................................... 11
Packaging Part List, ControlSpace® ESP-88 Chassis ................................................................................. 12
Figure 1. ESP-88 Chassis Packing View.......................................................................................................12
Packaging Part List, ControlSpace CC-16 Controller .................................................................................13
Figure 2. CC-16 Controller Packing View......................................................................................................13
Packaging Part List, ControlSpace CC-64 Controller .................................................................................14
Figure 3. CC-64 Controller Packing View......................................................................................................14
Main Part List, Control Space ESP-88 Chassis (see Figure 4) ..............................................................15-16
Figure 4. ControlSp ace ESP-88 Chassis Exploded View .............................................................................. 16
Main Part List, ControlSpace CC-16 Controller...........................................................................................17
Figure 5. ControlSpace CC-16 Controller Exploded V iew..............................................................................17
Main Part List, ControlSpaceTM CC-64 Controller .....................................................................................18
Figure 6. ControlSpace CC-64 Controller Exploded V iew..............................................................................18
Electrical Part Lists ..................................................................................................................................19-64
ESP-88 Chassis Motherboard PCB Assembly........................................................................................19-25
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly........................................................................................................26-42
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly.........................................................................43-56
ESP-88 Output PCB Assembly .....................................................................................................................57
ESP-88 LED PCB Assembly..........................................................................................................................57
CC-64 Control Center ...............................................................................................................................58-62
CC-16 Zone Controller .............................................................................................................................63-64
Disassembly Procedures .........................................................................................................................65-67
ControlSpace ESP-88 Chassis ..................................................................................................................... 65
ControlSpace CC-16 Control Center ............................................................................................................66
ControlSpace CC-64 Control Center ............................................................................................................67
Front Panel Indicators and Features............................................................................................................68
Rear Panel Controls and Connections ........................................................................................................ 69
T est Procedures, Audio Processor ESP-88 St d Version........................................................................ 71-96
Figure 7. ATS-2, ESP-88 and AuBit Switchbox Test Setup Diagram .............................................................73
Figure 8. Motherboard Top Etch Layout Diagram ..........................................................................................97
Figure 9. Motherboard VCC Etch Layout Diagram ........................................................................................97
Figure 10. Motherboard GND Etch Layout Diagram......................................................................................98
Figure 1 1. Motherboard Bottom Etch Layout Diagram ................................................................................... 98
Figure 12. MIC/Line Input PCB Topside Etch Layout Diagram ......................................................................99
Figure 13. MIC/Line Input PCB VCC Etch Layout Diagram...........................................................................99
Figure 14. MIC/Line Input PCB GND Etch Layout Diagram ........................................................................ 100
Figure 15. MIC/Line Input PCB Bottom Etch Layout Diagram ..................................................................... 100
Figure 16. DSP PCB Topside Etch Layout Diagram ....................................................................................101
Figure 17. DSP PCB VCC Etch Layout Diagram......................................................................................... 101
Figure 18. DSP PCB GND Etch Layout Diagram ........................................................................................102
Figure 19. DSP PCB Bottom Etch Layout Diagram.....................................................................................102
Figure 20. GPIO PCB Topside Etch Layout Diagram .................................................................................. 103
Figure 21. GPIO PCB VCC Etch Layout Diagram .......................................................................................103
Figure 22. GPIO PCB GND Etch Layout Diagram.......................................................................................103
Figure 23. GPIO PCB Bottom Etch Layout Diagram ................................................................................... 103
Figure 24. Output PCB Topside Etch Layout Diagram.................................................................................104
Figure 25. Output PCB Bottom Etch Layout Diagram ................................................................................. 104
Figure 26. LED PCB Topside Etch Layout Diagram .................................................................................... 104
Figure 27. LED PCB Bottom Etch Layout Diagram .....................................................................................104
Power Supply +5VDC V oltage Adjustment Procedures..................................................................... 105-106
Troubleshooting .......................................................................................................................................... 107
Service Manual Revision History ...............................................................................................................108
2
Page 3

SAFETY INFORMATION
1. Parts that have special safety characteristics are identified by the symbol on schematics
or by special notes on the parts list. Use only replacement parts that have critical characteristics
recommended by the manufacturer.
2. Make leakage current or resistance measurements to determine that exposed parts are
acceptably insulated from the supply circuit before returning the unit to the customer.
Use the following checks to perform these measurements:
A. Leakage Current Hot Check-With the unit completely reassembled, plug the AC line cord
directly into a 120V AC outlet. (Do not use an isolation transformer during this test.) Use a
leakage current tester or a metering system that complies with American National Standards
Institute (ANSI) C101.1 "Leakage Current for Appliances" and Underwriters Laboratories (UL)
UL6500 / UL60065 / IEC 60065 paragraph 9.1.1. With the unit AC switch first in the ON position
and then in OFF position, measure from a known earth ground (metal waterpipe, conduit, etc.)
to all exposed metal parts of the unit (antennas, handle bracket, metal cabinet, screwheads,
metallic overlays, control shafts, etc.), especially any exposed metal parts that offer an electrical
return path to the chassis. Any current measured must not exceed 0.5 milliamp. Reverse the
unit power cord plug in the outlet and repeat test. ANY MEASUREMENTS NOT WITHIN THE
LIMITS SPECIFIED HEREIN INDICATE A POTENTIAL SHOCK HAZARD THAT MUST BE
ELIMINATED BEFORE RETURNING THE UNIT TO THE CUSTOMER.
B. Insulation Resistance Test Cold Check-(1) Unplug the power supply and connect a jumper
wire between the two prongs of the plug. (2) Turn on the power switch of the unit. (3) Measure
the resistance with an ohmmeter between the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic
cabinet part on the unit. When testing 3 wire products, the resistance measured to the product
enclosure should be between 2 and infinite MOhms. Also, the resistance measured to exposed
input/output connectors should be between 4 and infinite MOhms. When testing 2 wire products, the resistance measured to exposed input/output connectors should be between 4 and
infinite MOhms. If it is not within the limits specified, there is the possibility of a shock hazard,
and the unit must be repaired and rechecked before it is returned to the customer.
CAUTION: The Bose® ControlSpace® ESP-88 System, CC-16 and CC-64 Controllers
contains no user-serviceable parts. To prevent warranty infractions, refer servicing
to warranty service stations or factory service.
PROPRIETARY INFORMATION
THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OF
BOSE CORPORATION WHICH IS BEING FURNISHED ONLY FOR
THE PURPOSE OF SERVICING THE IDENTIFIED BOSE PRODUCT
BY AN AUTHORIZED BOSE SERVICE CENTER OR OWNER OF
THE BOSE PRODUCT, AND SHALL NOT BE REPRODUCED OR
USED FOR ANY OTHER PURPOSE.
WARRANTY
The Bose ControlSpace ESP-88 System and CC-16 and CC-64 Controllers are covered by a
limited 5-year transferable warranty.
3
Page 4

PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
ESP-88 Chassis Overview:
The Bose
high quality audio signal processor for engineered sound applications such as churches, theaters, auditoriums, and sports venues.
The base model (ESP-88) includes eight inputs (microphone or line-level selectable) and eight
line level outputs. Four available audio slots allow the addition of up to 16 more analog audio
channels – inputs, outputs or a combination – or up to 32 more digital audio channels (AES3) as
inputs, outputs or a combination.
For large applications, multiple ESP-88s can be used per system. Multiple choices of user
controllers are available to provide end-users with simple, easy-to-use control of their
ControlSpace system.
The Bose ControlSpace Designer software is used to design systems and configure the
ESP-88 and user controllers. The software runs on a PC and communicates to the ESP-88 over
Ethernet.
Features and functions:
• Expandable and flexible cardframe architecture
• Eight mic/line analog audio input channels
• Eight line level analog audio output channels
• Four open audio expansion slots allow up to 32 analog audio channels total in a 2U chassis
• DSP expansion slot allows DSP processing power and delay times to increase fourfold
• Eight general purpose control inputs and eight general purpose control outputs (GPIO)
• GPIO expansion slot allows up to 16 control inputs and 16 control outputs
• All audio input and input channels feature tricolor level LEDs
• Design, control and configuration via PCbased software and Ethernet connection.
• Large set of signal processing modules including: Bose speaker EQs, Bose crossovers,
graphic and parametric EQs, routers, delays, matrix mixers, signal generators,
meters, compressors/Limiters, duckers, automatic gain controls, gate and source selectors.
®
ControlSpace® ESP-88 engineered sound processor is a flexible, expandable and
Modularity and Expansion
Flexible Architecture
The ESP-88 employs a flexible, modular architecture. The flexible architecture provides two
levels of DSP performance – up to 32 general-purpose I/O and up to 64 digital audio channels –
or up to 32 analog audio channels.
The base model ESP-88, includes a DSP card, two 4x4 Mic/Line cards and one GPIO card. In
this configuration, four audio and one GPIO slot are available for expansion.
Three types of optional cards are available: DSP expansion; GPIO; and Audio.
DSP Expansion Card - Daughter card for main DSP card. Increases performance by 300%.
One card can be added to an ESP-88.
GPIO Card
Fits in one of the two GPIO slots. Eight control inputs and eight control outputs. One GPIO card
can be added to an ESP-88.
4
Page 5
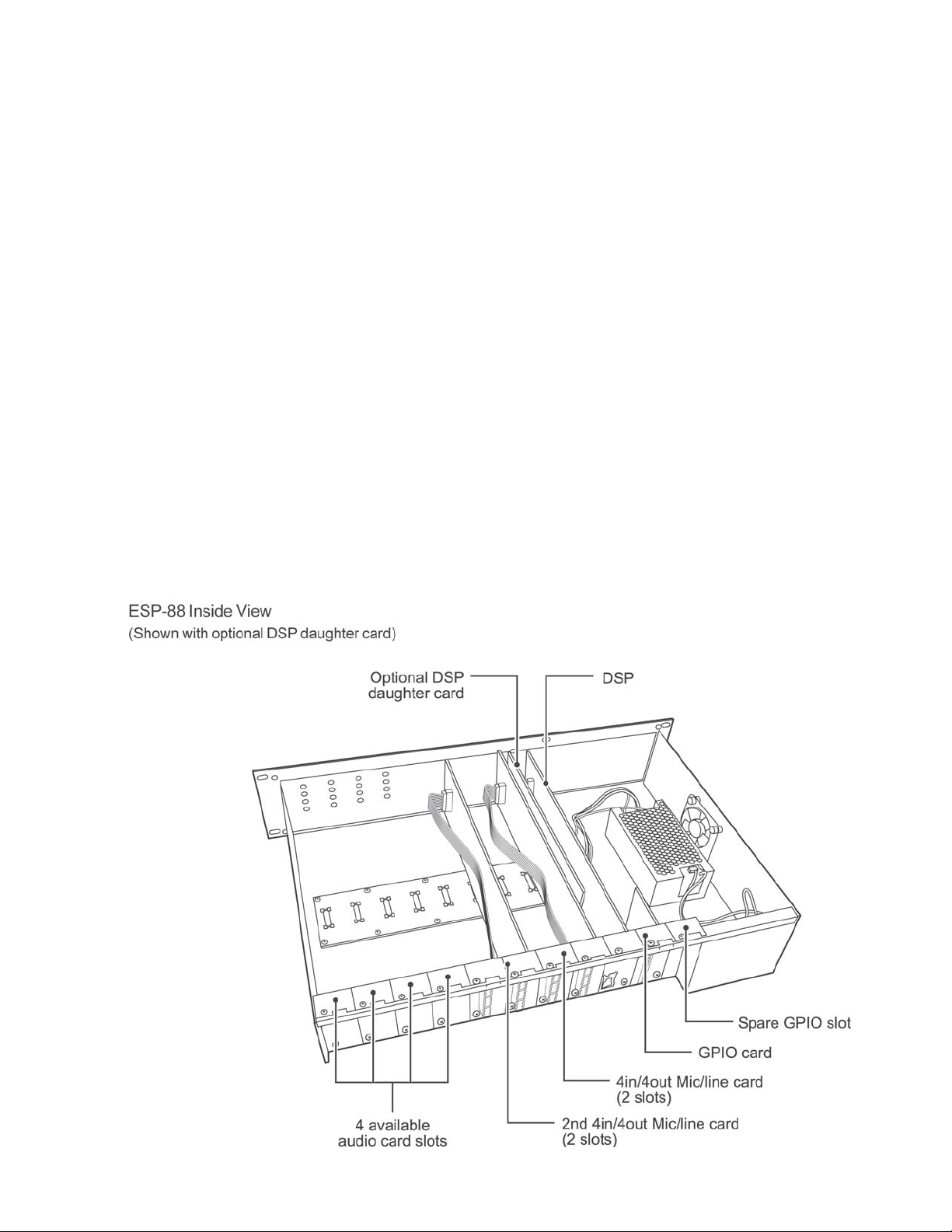
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
ESP-88 Chassis Overview (continued):
Optional Cards
Audio Cards:
4x4 Mic/Line Card (Series I)
4x4 Mic/Line Card (Series II)
Occupies two audio slots. Four microphone or line level inputs (software selectable), and four
line level outputs. The ESP-88 includes two 4x4 Mic/line cards. Two 4x4 cards can be added.
EDR Line Level Output Card
Occupies one audio slot. Four highest-quality, line level outputs.
EDR Line Level Input Card
Occupies one audio slot. Four highest-quality, line level inputs.
AES3 Output Card
Occupies one audio slot. Eight AES3 outputs (two per output connector).
AES3 Input Card
Occupies one audio slot. Eight AES3 inputs (two per input connector).
Surround Sound Card
Occupies one audio slot. One optical and one coaxial digital audio inputs.
5
Page 6

CC-16 Zone Controller
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The Bose
mounted device designed to provide end-user control of ControlSpace
systems. Custom programming allows the CC-16 to control a variety of
the system elements, from switching audio sources to selecting
“scenes” or system configurations. The CC-16 features a bitmap LCD
and four buttons for displaying and controlling the system settings.
The CC-16 connects to the ControlSpace Engineered Sound Processor (ESP-88) at the RS-485 port. Up to fifteen CC-16 units can be
used per each ESP-88 to provide localized control of the system. The
maximum distance from ESP-88 to CC-16 is 2000 feet. As a networked device, remote reprogramming is possible at any time.
Features and Functions
• 122 x 32 pixel backlit blue LCD
• LCD displays volume level and source/scene/preset setting
• Select up/down buttons for selecting sources or scenes
• Volume up/down buttons for controlling one or more gain controls
• IR receiver (for IR remote controls)
• RS-485 network supports up to fifteen CC-16 units per ESP-88
• DIP-switch for specifying network address and termination
• Universal mounting bracket
• UL and CE listed
®
ControlSpace® CC-16 zone controller is an elegant wall-
CC-64 Control Center
The Bose ControlSpace CC-64 control center is an
elegant, programmable, networked controller that
provides users with a simple and logical interface to
their ControlSpace system. Because the controller is
completely programmable, you can customize the
ControlSpace system, making only certain controls
available, and simplifying user interaction with the
system.
The CC-64 provides four rotary encoders with
circular LED arrays for a userfriendly method of
managing gain settings or scene selections. A fifth encoder provides control over programmed
“scenes” or presets. Four bank switch buttons redefine the four Gain/Selector control knobs,
providing quick access for up to 16 system gain controls or selectors. A large, 2-line by 40character backlit LCD provides the user with the names of the system elements they are controlling (gains, presets, etc.).
Using custom programming, the CC-64 can manage a variety of system elements, including
audio sources, scene selection settings, and specific system configurations. Each gain control
can be ganged so that a single control can be mapped to as many as sixteen system gains. The
CC-64 also supports a “custom mode” – intended for installers, not end users – in which any
parameter in the system can be viewed and changed using the LCD display and control knobs.
6
Page 7

PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
CC-64 Control Center (continued)
The CC-64 is a 10Base-T Ethernet device. Up to sixteen CC-64s can be used per
ControlSpace
Features
• 2-line by 40-character backlit LCD
• Sixteen Gain/Selector controls (four banks of four)
- Four rotary encoders for changing the gain level or selecting scenes/sources
- Each encoder includes a 15-segment LED array for indicating the control’s current level or
state
- The encoders feature push buttons for muting gain controls or making selections
- Ten character descriptions of the gain controls appear on the LCD above the encoder
• Four bank switch buttons with label area
• Lock function in software prevents local changes
• 10Base-T Ethernet network based
• Sixteen CC-64s per ControlSpace system
• Power over Ethernet cable or separate cable
• LEDs for status, link and network transmit/receive
• Fits standard 5-gang electrical box
• UL6500 listed and CE approved
Functions
1. LCD
2. Preset/Scene selector
- Rotate to view presets. Push to select.
- Push and hold for 5 seconds to enter Custom mode.
3. Network link indicator
4. Network receive indicator
5. Network transmit indicator
6. Bank select buttons (4). Press to select one of four bank controls
7. Bank select indicators (4). Indicates the currently selected bank
8. Bank select label area. 1.25" (31.75 mm) x .35" (9 mm) area for custom labels.
- Accepts standard 3/8" (9 mm) label stock.
9. Gain/Selector control knob. Rotary encoder (no stops). Push to mute.
10. Gain/Selector level indicators (15 levels/selections)
®
system.
7
Page 8

SPECIFICATIONS
Inputs
T ype: 8 analog, electronically balanced, microphone/line level
(software selectable)
Connectors: Phoenix/Euroblock 2-piece, 3-pin
Nominal Input Level: +4dBu/-10dBu/-20dBu/-38dBu/-44dBu/-50dBu/-60dBu
Frequency Response: 20 to 20kHz (+0.5dB / -2.0dB) at +4dBu nominal input level
Input Impedance: 2.4k ohm @ 1kHz (with or without phantom power active)
Maximum Input Level: +24dBu @ +4dBu nominal input power
Equivalent Input Noise: -115dB at -60dBu nominal input level (A-weighted/20-20kHz)
Phantom Power: +15V nominal, selectable per input
THD+N: 0.01% at +4dBu nominal input and output level
(A-weighted/20-20kHz)
Digital Resolution: 24-bit
Outputs
T ype: 8 analog, electronically balanced
Connectors: Phoenix/Euroblock 2-piece, 3-pin
Nominal Output Level: +4dBu
Output Impedance: 200 Ohms (600 Ohm load expected)
Frequency Response: 20 to 20kHz (+0.5dB/-2.0dB) at +4dBu nominal output level
Maximum Output Level: +24dBu at +4dBu nominal output level
Digital Resolution: 24-bit
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR): 80dB at +4dBu nominal output level (A-weighted/20-20kHz)
Residual Output Noise: -110dBu at output muted (A-weighted/20-20kHz)
THD+N: 0.01% at +4dBu nominal input and output level
(A-weighted/20-20kHz)
Crosstalk: < -90dB at +4dBu nominal input and output level at 1kHz
8
Page 9

SPECIFICATIONS
Signal Processing
T ype: 32-bit floating-point digital signal processor(s)
Clock Speed: 200MHz
Maximum Calculation: 1600 MIPS/1200 MFLOPS
(6400 MIPS/4800 MFLOPS with DSP option card)
Delay Memory: 16MByte/72s (maximum)
(64MByte/288s maximum with DSP option card)
Audio Latency: 610us (analog in to analog out) (860us with DSP option card)
Sampling Rate: 48kHz
Control Inputs
T ype: 8 analog or digital inputs, 5.1k ohms internal pull-up resistor
to 5V
Connectors: Phoenix/Euroblock 2-piece, 9-pin 3.81mm pitch
Analog Input: 0V to 3.3V (max 5V; suitable for 10k ohm variable resistor)
Digital Input Voltage Range: 0V to 3.3V (threshold voltage = 1.6V; internal 5.1k ohms pulled
up to 5V)
Control Outputs
T ype: 8 digital outputs, 10k ohms internal pull-up resistors to 5V
Connectors: Phoenix/Euroblock 2-piece, 9-pin 3.81mm pitch
Output Voltage: 0V to 5V open collector
Output Current: 0.5mA (source)/10mA max (sink)
Communication Ports
LAN: 10Base-T (RJ-45)
RS-232C: D-sub 9 pin, male; DTE
RS-485: Phoenix/Euroblock 2-piece, 3-pin
Indicators
Status: Power/Status/Ethernet/Serial (RS232C + RS485)
Audio: Signal (Present/Normal/Clip) for each audio input and output
9
Page 10

SPECIFICATIONS
Expansion Slots
Audio I/O: 8 slots (4 slots occupied)
Control I/O: 2 slots (1 slot occupied) Max 16 inputs/16 outputs
DSP: 1 slot
Audio Channels
Analog: 32 max (all slots full)
Digital (AES3): 64 (all slots full)
Mechanical
Dimensions: 18.9”W x 3.5”H x 12.6”D (482 x 88 x 320mm)
Weight: 14 lb. (5.3 kg)
Electrical
Mains Voltage: 85 - 264 VAC 50/60 Hz with PFC
Power Consumption: < 35VA
Maximum Power < 70VA (at <35 degrees C ambient)
Consumption:
Environmental
Operating Temperature: < 50 degrees C at less than 35VA / < 40 degrees C at
less than 70VA
Humidity: 80% relative humidity (without condensation)
10
Page 11

ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE SENSITIVE (ESDS)
DEVICE HANDLING
This unit contains ESDS devices. We recommend the following precautions when repairing,
replacing or transporting ESDS devices:
• Perform work at an electrically grounded work station.
• Wear wrist straps that connect to the station or heel straps that connect to conductive
floor mats.
• Avoid touching the leads or contacts of ESDS devices or PC boards even if properly
grounded. Handle boards by the edges only.
• Transport or store ESDS devices in ESD protective bags, bins, or totes. Do not insert
unprotected devices into materials such as plastic, polystyrene foam, clear plastic bags,
bubble wrap or plastic trays.
PART LIST NOTES
1. This part is not normally available from Customer Service. Approval from the Field Service
Manager is required before ordering.
2. The individual parts located on the PCBs are listed in the Electrical Part List.
3. This part is critical for safety purposes. Failure to use a substitute replacement with the
same safety characteristics as the recommended replacement part might create shock, fire
and/or other hazards.
4. This part is referenced for informational purposes only. It is not stocked as a repair part. Refer
to the next higher assembly for a replacement part.
11
Page 12

PACKAGING PART LIST
Item
Description Qty. Part
Note
ControlSpace® ESP-88 Chassis
Number
1 EPE FOAM 2 312474
2 ESP-88 Chassis, US/CAN
ESP-88 Chassis, EURO
ESP-88 Chassis, UK
ESP-88 Chassis, JAPAN
ESP-88 Chassis, AUS
3 POLYBAG, L550xW600MM 1 - 4
4 CONTROLSPACE S/W CD 1 - 4
5 CD SLEEVE 1 - 4
6 POLYBAG, L300xW150MM 1 - 4
7 POWER CORD, 120V, US/ C A N
POWER CO RD, 220V, EURO
POWER CORD, 24 0V, U K
POWER CO RD, 100V, JAPA N
POWER CO RD, 240V, AUS
8 CAT-5 ETHERNET CABLE 1 - 4
9 POLYBAG, 100x60MM 3 - 4
10 TERMINAL BLOCK, 9 POS 2 305532
11 TERM BLOCK, PLUG, ORANGE 8 305535
12 TERM BLOCK, PLUG, GREEN 9 305536
13 USER MANUAL 1 275800
14 CARTON 1 275797
1 041755
1 298165
Number
041756
041758
041757
041759
298166
298168
298167
298169
3
Figure 1. ESP-88 Chassis Packing View
12
Page 13
PACKAGING PART LIST
Item
Description Qty. Part Number Note
ControlSpace® CC-16 Controller
Number
1 Foam, White EPE 1 - 4
2 CC-16 Controller 1 041761 2
3 Anti-static bag, 150 x 180 x 0.03MM 1 - 4
4 Paper Tray 1 - 4
5 Installation Manual, English Language 1 285042
6 White box 1 - 4
7 Screw, #6-32x0.7", Phillips, ZINC (US/J apan) 4 - 4
8 Bag, Poly, 40 x 60MM 2 - 4
9 Screw, M4.0x18, Phillips, ZINC (Europe) 4 - 4
- Power Supply, 15VDC, 5W, 100-240VAC Input
(not packaged w/CC-16)
1 041762 3
Figure 2. CC-16 Controller Packing View
13
Page 14

PACKAGING PART LIST
ControlSpace® CC-64 Controller
Item
Number
1 Install Guide, CC-64 1 285041
2 EPE Foam, 330X180X15MM 1 - 4
3 Bag, PE, Anti-Static, 330X180X0.03 MM 1 - 4
4 CC-64 Controller 1 041760 2
5 Screw, US, MSF, #6-32X0.7, MS, ZN-WH 4 - 4
6 Bag, Poly, 40X60MM 1 - 4
7 Tray, Foam, EPE, 330x180x45MM 1 - 4
8 Terminal Block, 2P, P5.08, 2ESDV-02P 1 - 4
9 Bag, Poly, 100X60MM 1 - 4
10 White Box, W9B 1 - 4
11 Computer UTP LAN Cable, 2M, CAT 5 1 - 4
- Power Supply, 15VDC, 5W, 100-240VAC Input
(not packaged w/CC-64)
Description Qty. Part Number Note
1 041762 3
Figure 3. CC-64 Controller Packing View
14
Page 15
MAIN PART LIST
Item
Description Qty. Part
Note
ControlSpace® ESP-88 Chassis (see Figure 4)
Number
1 TOP COVER 1 278505-001
2 M3x4 SCREW, MSF, MS-BK
(FOR CHASSIS/COVER)
3 M3x4 SCREW, SI, MSB, MS-BK 62 - 4
4 GIO REAR PANEL, SECC-T1, T=1.0MM 1 278516-001
5 PANEL, REAR, BLANK, SECC-T1 T=1.0MM 5 278518-001
6 DSP REAR PANEL, SECC-T1, T=1.0MM 1 278515-001
7 4CH REAR PANEL (LINE OUTPUT) SECC-T1
8 4CH REAR PANEL (MIC/LINE INPUT) SECC-T1
9 4x4 LINE OUTPUT PCB ASSY
10 4X4 MIC/LINE SERIES I I/O PCB 2 041767 2
4X4 MIC/LINE SERIES II I/O PCB 041915
11 PCB FIXED STICK, ABOVE 2 278503-001
12 MOTHERBOARD PCB ASSY 1 275796 2
13 M3x6 SCREW, MSB, M3x6mm, MS-BK 5 - 4
14 INTERNAL TOOTH WASHER,
15 LED LENS, PMMA, MF001 9 278522-001
16 FRONT ENDCAP, RIGHT, PC/ABS, C2950 (M3x3
17 DOOR, ALUMINUM 1 278520-001
18 FRONT PANEL, ALUM, FIXED 1 278519-001
19 FRONT ENDCAP, MID, PC/ABS, C2950, (M3x2
20 FRONT ENDCAP, LEFT, PC/ABS, C2950 (M3x3
21 FRONT PANEL, SECC-T1 1 278507-001
22 CHASSIS 1 278506-001
23 PCB FIXED STICK, BELOW 1 278504-001
24 SCREW, US, MSF, 4#-40x0.236, MS, BLACK 4 - 4
25 LED PCB ASSEMBLY (PART OF MIC/LINE IN/O UT
26 POWER SUPPLY , 70W, REL-70-300227 M4x12 SCREW, SI, MSB, MS-BK
28 DC FAN, +5VDC, 60MM,
29 M4x3 HEX NUT W/NYLON INSERT, SI, SS 4 - 4
30 DSP PCB ASSEMBLY 1 275794 2
31 GPIO PCB ASSEMBLY 1 041768 2
32 STAY, SECC-T1, T=1.0MM 1 278508-001
- D SP EX PAN SION CA RD - 041769
- 8-CH DIGITAL IN EXP PCB - 041765
- 8-CH DIGITAL OUT EXP PCB - 041766
- 4-CH ANALOG IN EXP PCB
T=1.0MM
T=1.0MM
(PART OF ITEM 10 BELOW)
OD 6.4xID3xT0.45MM
NUT)
NUT)
NUT)
MAIN PCB)
F-CHCO
(FOR F AN )
F6010AP-05LCW
(EDR Line Level Input Card)
4 - 4
2 278512-003
2 278512-002
2 -
7 - 4
1 278521-002
1 278521-003
1 278521-001
2 - 2
1 295622 3
4 - 4
1 295621 3
- 041764
Number
15
Page 16

MAIN PART LIST
Item
Description Qty. Part
Note
ControlSpace® ESP-88 Chassis (continued)
Number
- 4-CH ANALOG OUT EXP PCB
(EDR Line Level Output Card)
- 4-CH SDR OUTPUT PCB - 041916
- 4-CH MIC/LINE INPUT PCB - 041917
- SURROUND DECODER INPUT PCB - 302210
- AC POWER SWITCH, ROCKER, SPST, 125V/15A 1 - 3, 4
- AC SOCKET, IEC, 250V/10A 1 - 3, 4
- Power Supply Harness, Improved, ESP-88C / ESP00 (used with the Astec power supply)
- Power Supply Harness, Improved, ESP-88 / ESP88C (used with the IPD power supply)
- 041763
1 3189351 318938-
Number
001S
001S
3
3
Figure 4. ControlSpace ESP-88 Chassis Exploded View
16
Page 17
MAIN PART LIST
Item
Description Qty.
Note
ControlSpace® CC-16 Controller
Part Number
Number
1 Front plate, PC, GE, LEXAN, 241R, White 1 275432
2 Overlay, PC sheet, w/adhesive, 0.18mm 1 277488
3 Insert, plate, PC, GE, LEXAN, 241R, White 1 275434 4
4 LCD PCB Assembly 1 275817-002
5 Mounting Frame, PC, GE, LEXAN, 241R, White 1 275433 4
6 Main PCB Assembly 1 275817-001
Figure 5. ControlSpace CC-16 Controller Exploded View
17
Page 18

MAIN PART LIST
ControlSpace® CC-64 Controller
Item
Number
1 Metal EMC Shield, Case, SECC-T1, T=0.50MM 1 275816 4
2 Front Panel 1 275814 4
3 Knob 5 278523-002
4 Nylon Washer, OD=6.1MM, ID=2.95MM, T=2MM 6 - 4
5 Keyboard Overlay, Plastic, W/S, Adhesive 1 277485
6 LCM Module, STN, Blue, 12 Clock,
YMC402-11AAABUCL
7 LED PCB Assembly 1 278524-001
8 Main PCB Assembly 1 278523-001
9 Metal Panel, Aluminum 1 275815 4
10 Screw, SI, MSP, M3X11.5MM 4 - 4
11 Screw, MSB, M3X6, NI 14 - 4
12 Spacer, Support, K33-7 4 - 4
13 Sponge 1 - 4
14 PVC Washer, ID=3.1MM, T=0.3MM 4 - 4
Description Qty
Part Number
1 323977-001S
Note
Figure 6. ControlSpace CC-64 Controller Exploded View
18
Page 19

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Chassis Motherboard PCB Assembly
Resistors
Designator
JP200 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP201 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP202 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP203 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R100 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R101 1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K 4
R102 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR- 07 R00 4
R103 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR- 07 R00 4
R104 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR- 07 R00 4
R105 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR- 07 R00 4
R200 220K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07220K 4
R201 8.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078K2 4
R202 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R204 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R205 2.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K2 4
R208 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR- 07 R00 4
R209 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR- 07 R00 4
R210 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR- 07 R00 4
R211 1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K 4
R213 1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K 4
R214 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R215 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R216 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R220 2.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K2 4
R221 2.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K2 4
R236 220K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07220K 4
R238 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R239 2.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K2 4
R240 8.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078K2 4
R241 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R300 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R301 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R302 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R303 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R304 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R305 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R306 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R307 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R308 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R309 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R310 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R311 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R312 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R313 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R314 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R315 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R316 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
19
Page 20

Reference
Designator
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
R317 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R318 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R319 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R320 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R321 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R322 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R323 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R324 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R325 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R326 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R327 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R328 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R329 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R330 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R331 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R332 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R333 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R334 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R335 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R336 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R337 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R338 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R339 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R340 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R341 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R342 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R343 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R344 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R345 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R346 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R347 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R348 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R349 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R350 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R351 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R352 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R353 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R354 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R355 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R356 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R357 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R358 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R359 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R360 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R361 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R362 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R363 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Chassis Motherboard PCB Assembly
Resistors (continued)
20
Page 21
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Chassis Motherboard PCB Assembly
Resistors (continued)
Designator
R364 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R365 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R366 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R367 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R368 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R369 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R370 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R371 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R372 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R373 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R374 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R375 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R376 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R377 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R378 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R379 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R380 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R381 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R382 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R383 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R384 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R385 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R386 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R387 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R388 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R389 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R390 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R391 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R392 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R393 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R394 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R395 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
Resistor Arrays
Designator
RA100 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, ISO, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA101 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, ISO, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA102 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, ISO, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA103 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, ISO, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA104 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, ISO, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA105 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, ISO, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA106 10K, 10 PIN, 8R, 1/16W, ISO, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
21
Page 22
Reference
Designator
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
C100 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C101 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C102 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C103 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C104 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C105 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C106 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C107 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C108 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C109 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C110 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C111 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C112 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C113 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C114 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C115 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C116 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C117 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C118 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C119 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C120 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C121 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C122 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C123 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C124 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C125 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C126 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C127 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C200 47uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C201 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C202 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C203 47uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C204 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C205 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C206 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C207 47uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C208 10uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C209 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C210 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C211 10uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C212 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C220 47uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C221 47uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C222 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C223 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C300 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Chassis Motherboard PCB Assembly
Capacitors
22
Page 23
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Chassis Motherboard PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C301 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C302 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C303 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C304 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C305 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C306 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C307 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C308 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C309 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C310 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C311 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C312 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C313 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C314 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C315 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C316 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C317 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C318 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C319 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C320 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C321 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C322 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C323 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C324 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C325 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C326 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C327 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C328 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C329 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C330 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C331 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C332 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C333 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C334 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C335 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C336 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C337 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C338 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C339 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C340 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C341 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C342 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C343 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C344 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C345 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C346 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C347 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
23
Page 24

Reference
Designator
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
C348 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C349 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C350 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C351 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C352 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C353 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C354 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C355 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C356 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C357 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C358 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C359 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C360 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C361 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C362 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C363 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C364 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C365 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C366 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C367 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C368 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C369 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C370 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C371 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C372 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C373 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C374 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C375 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C376 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C377 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C378 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C379 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C380 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C381 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C382 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C383 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C384 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C385 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C386 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C387 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C388 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C389 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C390 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C391 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C392 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C393 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C394 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C395 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Chassis Motherboard PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
24
Page 25
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis Motherboard PCB Assembly
Diodes
Designator
D200 400V, 1A, 1SR154-400, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
D201 400V, 1A, 1SR154-400, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
D202 400V, 1A, 1SR154-400, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
D207 400V, 1A, 1SR154-400, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
D208 400V, 1A, 1SR154-400, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
Transistors
Designator
Q100 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRA102S 4
Q202 PNP, 60V, 1A, SOT-89 KEC KTA1668Y 4
Q203 NPN, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q205 NPN, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q211 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRA102S 4
Integrated Circuits
Designator
M100 DECODER, TSSOP-16 ONSEMI MC74VHC138DT 4
M101 OCTAL BUS BUFFER, TSSOP-20 ONSEMI MC74VHC541DT 4
M102 OCTAL BUS BUFFER, TSSOP-20 ONSEMI MC74VHC541DT 4
M103 OCTAL BUS BUFFER, TSSOP-20 ONSEMI MC74VHC541DT 4
M104 DECODER, TSSOP-16 ONSEMI MC74VHC138DT 4
M200 REGULATOR, 3.3V, 1A, TO-252 NEC UPC2933T 4
Miscellaneous
Designator
CN100 CONN, P1.0MM, 30 PIN, MALE KEL Corp. 87BMN-030S 4
CN101 CONN, P1.0MM, 30 PIN, MALE KEL Corp. 87BMN-030S 4
CN102 CONN, P1.0MM, 30 PIN, MALE KEL Corp. 87BMN-030S 4
CN103 CONN, P1.0MM, 30 PIN, MALE KEL Corp. 87BMN-030S 4
CN104 CONN, P1.0MM, 30 PIN, MALE KEL Corp. 87BMN-030S 4
CN105 CONN, P1.0MM, 30 PIN, MALE KEL Corp. 87BMN-030S 4
CN106 CONN, P1.0MM, 30 PIN, MALE KEL Corp. 87BMN-030S 4
CN107 CONN, P1.0MM, 30 PIN, MALE KEL Corp. 87BMN-030S 4
CN108 CONN, P1.0MM, 100 PIN, MALE KEL Corp. 87BMN-100S 4
CN200 W IRE TO BOARD HEADER,
CN202 W IRE TO BOARD HEADER,
CN203 W IRE TO BOARD HEADER,
CN205 W IRE TO BOARD HEADER,
CompuTime 4024406-----0N19 4
P3.96MM, 6 POLES, 2114S-06
CompuTime 4024208-----0N19 4
P2.5MM, 8 POLES, 2317SJ-08
P2.5MM, 8 POLES, 2317SJ-08
P2.5MM, 3 POLES, 2317SJ-03
CompuTime 4024208-----0N19 4
CompuTime 4024203-----0N19 4
25
Page 26

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Resistors
Designator
JP100 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP101 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP102 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP103 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP104 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP200 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP201 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP202 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP203 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP204 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP300 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP301 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP400 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP401 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP500 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP501 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP550 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
JP551 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R100 100K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710 0K 4
R101 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R102 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R103 100K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710 0K 4
R110 1.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K3 4
R112 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R115 82 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0782R 4
R117 68 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0768R 4
R120 1.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K3 4
R122 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R125 82 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0782R 4
R127 68 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0768R 4
R131 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R132 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R133 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R134 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R135 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R136 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R137 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R138 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R141 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R142 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R143 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R144 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R145 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R146 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R147 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R148 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R149 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
Name
26
Page 27
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Resistors (continued)
Designator
R150 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R151 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R152 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R153 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R156 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R157 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R158 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R159 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R160 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R161 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R162 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R163 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R164 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R165 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R166 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R167 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R168 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R169 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R170 1.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K8 4
R171 1.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K2 4
R172 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R173 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R174 1.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K8 4
R175 1.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K2 4
R176 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R200 100K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710 0K 4
R201 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R202 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R203 100K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710 0K 4
R210 1.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K3 4
R212 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R215 82 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0782R 4
R217 68 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0768R 4
R220 1.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K3 4
R222 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R225 82 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0782R 4
R227 68 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0768R 4
R231 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R232 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R233 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R234 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R235 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R236 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R237 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R238 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07680R 4
R241 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R242 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
27
Name
Page 28
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Resistors (continued)
Designator
R243 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R244 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R245 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R246 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R247 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R248 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R249 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R250 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R251 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R252 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R253 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R256 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R257 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R258 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R259 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R260 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R261 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R262 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R263 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R264 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R265 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R266 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R267 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R268 39K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0739K 4
R269 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R270 1.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K8 4
R271 1.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K2 4
R272 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R273 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R274 1.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K8 4
R275 1.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K2 4
R276 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R300 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R301 47K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0747K 4
R302 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R303 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R304 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R305 47K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0747K 4
R307 16K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0716K 4
R308 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R309 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R310 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R311 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R312 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R313 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R314 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R315 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
Name
28
Page 29
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Resistors (continued)
Designator
R316 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R317 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R318 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R319 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R320 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R321 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R322 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R323 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R324 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R325 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R326 8.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078K2 4
R327 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R328 5.6K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K6 4
R329 3.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-073K3 4
R330 8.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078K2 4
R331 1.5K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K5 4
R332 2.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K2 4
R333 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R334 2.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K7 4
R336 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R337 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R338 16K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0716K 4
R339 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R340 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R341 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R342 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R343 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R344 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R345 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R346 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R347 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R348 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R349 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R350 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R351 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R352 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R353 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R354 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R355 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R356 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R357 8.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078K2 4
R358 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R359 5.6K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K6 4
R360 3.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-073K3 4
R361 8.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078K2 4
R362 1.5K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K5 4
R363 2.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K2 4
29
Name
Page 30

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Resistors (continued)
Designator
R364 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R365 2.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K7 4
R366 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R367 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R368 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R369 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R370 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R371 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R400 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R401 47K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0747K 4
R402 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R403 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R404 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R405 47K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0747K 4
R407 16K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0716K 4
R408 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R409 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R410 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R411 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R412 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R413 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R414 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R415 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R416 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R417 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R418 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R419 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R420 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R421 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R422 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R423 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R424 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R425 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R426 8.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078K2 4
R427 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R428 5.6K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K6 4
R429 3.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-073K3 4
R430 8.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078K2 4
R431 1.5K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K5 4
R432 2.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K2 4
R433 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R434 2.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K7 4
R436 16K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0716K 4
R437 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R438 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R439 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R440 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
Name
30
Page 31

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Resistors (continued)
Designator
R441 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R442 18 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0718R 4
R443 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R444 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R445 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R446 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R447 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R448 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R449 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R450 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R451 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R452 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R453 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R454 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R455 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R456 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R457 8.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078K2 4
R458 6.8K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-076K8 4
R459 5.6K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K6 4
R460 3.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-073K3 4
R461 8.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078K2 4
R462 1.5K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K5 4
R463 2.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K2 4
R464 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R465 2.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-072K7 4
R466 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R467 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R468 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R469 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R470 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R471 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R504 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R505 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R506 470 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07470R 4
R507 470 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07470R 4
R508 470 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07470R 4
R509 470 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07470R 4
R510 3.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-073K3 4
R511 3.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-073K3 4
R512 5.1 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075R1 4
R515 5.1 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075R1 4
R516 3.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-073K3 4
R517 3.3K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-073K3 4
R518 470 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07470R 4
R519 470 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07470R 4
R520 470 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07470R 4
R521 470 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07470R 4
31
Name
Page 32

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Resistors (continued)
Designator
R522 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R523 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R524 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R525 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R526 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R527 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R552 5.1 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075R1 4
R555 5.1 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075R1 4
R556 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R557 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R558 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R559 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R560 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R561 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R562 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R563 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R700 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R702 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R703 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R706 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R707 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R708 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R709 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R710 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R711 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R712 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R713 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R714 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R716 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R719 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R720 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R721 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R722 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R723 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R724 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R725 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R726 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R727 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R728 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R730 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R731 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R732 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R733 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R734 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R735 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R736 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R737 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
Name
32
Page 33

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Resistors (continued)
Designator
R738 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R740 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R741 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R742 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
Designator
RA550 10K, 10 PIN, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA700 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA701 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA702 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA703 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA704 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA705 33 OHM, 8 PIN, 1/16W, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA706 10K, 10 PIN, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
Designator
C100 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C101 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C102 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C103 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C104 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C105 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C108 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C109 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C110 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C111 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C112 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C113 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C114 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Sams ung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C115 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C116 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C117 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C118 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C119 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C120 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C121 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C122 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C123 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C124 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C125 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C126 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C127 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C128 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
Resistor Arrays
Capacitors
33
Name
Name
Name
Page 34

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C129 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C130 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C131 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C132 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C133 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C134 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C135 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C136 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C139 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C140 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C141 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C142 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C143 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C144 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C145 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C146 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C147 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C148 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C149 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C200 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C201 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C202 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C203 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C204 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C205 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C208 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C209 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C210 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C211 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C212 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C213 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C214 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C215 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C216 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C217 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C218 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C219 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C220 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C221 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C222 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C223 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C224 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C225 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C226 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C227 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C228 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C229 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
Name
34
Page 35

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C230 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C231 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C232 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C233 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C234 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C235 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C236 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C239 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C240 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C241 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C242 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C243 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C244 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C245 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C246 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C247 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C248 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C249 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C300 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C301 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C302 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C303 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C304 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C305 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C306 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C307 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C308 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C309 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C310 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C311 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C312 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C313 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C314 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C315 22pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C316 22pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C317 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C318 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C319 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C320 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C321 2700pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B272KBNC 4
C322 6800pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B682KBNC 4
C323 470pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B471KBNC 4
C324 1500pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B152KBNC 4
C325 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C326 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C327 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C328 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
35
Name
Page 36

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C329 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C330 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C331 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C332 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C333 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C334 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C335 22pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C336 22pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C337 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C338 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C339 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C340 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C341 2700pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B272KBNC 4
C342 6800pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B682KBNC 4
C343 470pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B471KBNC 4
C344 1500pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B152KBNC 4
C345 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C350 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C351 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C400 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C401 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C402 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C403 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C404 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C405 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C406 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C407 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
C408 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C409 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C410 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C411 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C412 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C413 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C414 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C415 22pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C416 22pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C417 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C418 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C419 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C420 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C421 2700pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B272KBNC 4
C422 6800pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B682KBNC 4
C423 470pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B471KBNC 4
C424 1500pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B152KBNC 4
C425 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C426 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C427 10uF, BI-POLAR, 16V, 40C, 20% ELNA RVB16V100M-R 4
Name
36
Page 37

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C428 100pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C101JBNC 4
C429 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C430 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C431 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C432 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C433 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C434 220pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B221KBNC 4
C435 22pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C436 22pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C437 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C438 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C439 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C440 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C441 2700pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B272KBNC 4
C442 6800pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B682KBNC 4
C443 470pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B471KBNC 4
C444 1500pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B152KBNC 4
C445 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C450 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C451 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C500 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C501 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C502 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C503 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C504 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C505 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C506 560pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B561KBNC 4
C507 560pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B561KBNC 4
C508 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C509 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C510 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C511 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C512 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C513 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C514 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C515 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C516 560pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B561KBNC 4
C517 560pF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B561KBNC 4
C518 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C519 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C520 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C521 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C522 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C523 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C524 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C525 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C526 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
37
Name
Page 38

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C527 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C528 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C529 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C550 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C551 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C552 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C553 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C554 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C555 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C556 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C557 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C558 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C559 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C560 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C561 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C562 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C563 47uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C564 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C565 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C566 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C567 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C568 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C569 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C570 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C571 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C572 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C573 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C700 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C701 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C702 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C703 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C704 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C705 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C706 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C707 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C708 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C709 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C710 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C711 12pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C120JBNC 4
C712 12pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C120JBNC 4
C713 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C714 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C715 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C716 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C717 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C718 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C719 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
Name
38
Page 39

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C720 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C721 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C722 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C723 47pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
Designator
L100 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L101 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L102 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L103 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L104 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L105 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L200 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L201 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L202 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L203 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L204 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L205 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
Inductors
Diodes
Name
Name
Designator
D100 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D101 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D102 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D103 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D200 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D201 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D202 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D203 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D300 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D301 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D302 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D303 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D400 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D401 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D402 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D403 DIODE, SWITCHING, SC-59 Rohm DAN217 4
D700 RECT, 400V, 1A, SOD-106 Rohm 1SR154-400 4
D701 RECT, 400V, 1A, SOD-106 Rohm 1SR154-400 4
Name
39
Page 40

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Transistors
Designator
Q100 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q101 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q102 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRA102S 4
Q103 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRA102S 4
Q200 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q201 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q202 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRA102S 4
Q203 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRA102S 4
Q300 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q301 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q302 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q303 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q304 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q305 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q306 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q307 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q308 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q309 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q310 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q311 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q312 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRA102S 4
Q313 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q314 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRA102S 4
Q315 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q400 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q401 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q402 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q403 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q404 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q405 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q406 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q407 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q408 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q409 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q410 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q411 NPN, 20V, 300mA, SC-59 Toshiba 2SC3326-B 4
Q412 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRA102S 4
Q413 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q414 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRA102S 4
Q415 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q700 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q702 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q703 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q704 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q705 NPN 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Name
40
Page 41

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Integrated Circuits
Designator
M100 HI-VOLTAGE ANALOG SW
ARRAY, SOP28
M100 ANALOG SW ARRAY, SOP28 Toshiba T C9164AF 4
M101 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M102 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M103 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M104 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M200 HI-VOLTAGE ANALOG SW
M200 ANALOG SW ARRAY, SOP28 Toshiba T C9164AF 4
M201 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M202 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M203 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M204 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M300 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M301 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M302 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M303 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M400 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M401 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M402 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M403 OP-AMP, SSOP8 JRC NJM4580ETE2 4
M500 AUDIO ADC, TSSOP24 Cirrus CS5361-KZ 4
M500 A/D CONVERTER, TSSOP24,
M501 AUDIO ADC, TSSOP24 Cirrus CS5361-KZ 4
M501 A/D CONVERTER, TSSOP24,
M550 DAC, STEREO, TSSOP-20 Cirrus CS4392-KZ 4
M551 DAC, STEREO, TSSOP-20 Cirrus CS4392-KZ 4
M700 OCTAL BUFFER DRIVER,
M701 OCTAL BUFFER DRIVER,
M702 OCTAL D-TYPE FLIP-FLOP,
M703 VOLT DET, Vd=3.0V ONSEMI NCP303LSN30T1 4
M703 VOLT DET, Vd=3.0V SEIKO S-80930CNMC-G80-T2 4
M704 REG, 3.3V, 1A, TO-252 NEC UPC2933T 4
M705 REG, 5.0V, DPAK KEC KIA7805AF 4
M706 FLASH, MCU, 32K, LQFP64 RENASES HD64F3664FP 4
M707 OCTAL D-TYPE FLIP-FLOP,
M708 OCTAL BUFFER DRIVER,
ARRAY, SOP28
LEAD FREE
LEAD FREE
TSSOP20
TSSOP20
TSSOP20
TSSOP20
TSSOP20
Name
Toshiba TC9164CFG 4
Toshiba TC9164CFG 4
Cirrus CS5361-KZ 4
Cirrus CS5361-KZ 4
ONSemi MC74VHC541DT 4
ONSemi MC74VHC541DT 4
ONSEMI MC74AC273DT 4
ONSEMI MC74AC273DT 4
ONSemi MC74VHC541DT 4
41
Page 42
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
ESP-88 Chassis 4x4 PCB Assembly
Miscellaneous
Designator
CN100 HEADER, P5.08, 3 POLE, RGT
ANG
CN101 HEADER, P5.08, 3 POLE, RGT
ANG
CN200 HEADER, P5.08, 3 POLE, RGT
ANG
CN201 HEADER, P5.08, 3 POLE, RGT
ANG
CN600 HEADER, P2.5MM, 9 POLES NELTRON 2317SJ-09 4
CN700 B-B CONN, 30 PIN, 1MM KEL 87BFN-030R 4
XTAL700 10.000MHz, 30ppm, 2 0pF,
HC-49/S
Name
DINKLE 2EHDRC-03P 4
DINKLE 2EHDRC-03P 4
DINKLE 2EHDRC-03P 4
DINKLE 2EHDRC-03P 4
Raltron AS-10.000-20 4
42
Page 43

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly
Resistors
Designator
R100 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R101 1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K 4
R102 1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K 4
R103 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R104 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R105 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R106 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R107 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R108 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R109 110 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07110R 4
R110 110 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07110R 4
R111 110 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07110R 4
R200 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R201 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R202 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R203 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R204 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R205 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R206 1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K 4
R208 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R210 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R211 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R212 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R213 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R214 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R215 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R216 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R219 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R220 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R300 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R301 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R302 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R303 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R306 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R307 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R309 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R310 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R311 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R312 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R313 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R316 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R318 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R321 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R401 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R402 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R403 8.2 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078R2 4
R404 8.2 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-078R2 4
R407 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R408 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
43
Page 44

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly
Resistors (continued)
Designator
R409 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R410 220K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07220K 4
R450 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R451 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R452 560K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07560K 4
R457 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R458 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R459 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R460 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R461 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R462 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R463 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R464 180 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07180R 4
R465 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-074K7 4
R466 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R467 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R468 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R469 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R470 68K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0768K 4
R475 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R476 820 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07820R 4
R477 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R478 390 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07390R 4
R479 820 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07820R 4
R480 12K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0712K 4
R481 1.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K2 4
R482 120 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07120R 4
R483 1.2K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-071K2 4
R535 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R536 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R537 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R538 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR-07R00 4
R539 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R540 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R541 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
R542 33 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0733R 4
Resistor Arrays
Designator
RA100 10K, ARRAY, 10 PI N, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA101 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA102 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA103 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA104 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA105 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA106 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA107 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA108 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
44
Page 45

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly
Resistor Arrays (continued)
Designator
RA109 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA110 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA111 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA200 10K, ARRAY, 10 PIN, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA201 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA202 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA203 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA204 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA205 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA206 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA207 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA208 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA209 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA210 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA211 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA212 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA213 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA214 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA215 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA216 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA217 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA218 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA219 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA220 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA221 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA222 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA223 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA224 10K, ARRAY, 10 PIN, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA300 10K, ARRAY, 10 PIN, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA301 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA302 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA303 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA304 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA305 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA306 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA307 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA308 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA309 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA310 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA311 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA312 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA313 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA314 10K, ARRAY, 10 PIN, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA315 10K, ARRAY, 10 PIN, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA316 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA317 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA318 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA319 33 OHM, ARRAY, 8 PIN, 5% Yageo YC164-JR-0733R 4
RA400 10K, ARRAY, 10 PIN, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
45
Page 46

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly
Resistor Arrays (continued)
Designator
RA401 10K, ARRAY, 10 PI N, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA450 10K, ARRAY, 10 PI N, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA530 10K, ARRAY, 10 PI N, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA531 10K, ARRAY, 10 PI N, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA532 10K, ARRAY, 10 PI N, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
RA533 10K, ARRAY, 10 PI N, 8R, 5% Yageo YC158TJR-0710K 4
Designator
C100 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C101 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C102 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C103 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C104 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C105 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C106 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C107 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C108 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C109 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C110 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C111 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C112 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C113 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C114 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C115 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C116 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C117 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C118 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C119 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C120 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C121 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C122 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C123 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C124 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C125 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C126 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C127 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C128 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C129 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C130 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C131 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C132 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C133 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C134 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C135 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C136 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C137 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C138 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
Capacitors
46
Page 47

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C139 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C140 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C141 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C142 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C143 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C144 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C145 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C146 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C147 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C148 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C149 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C150 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C151 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C152 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C153 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C154 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C155 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C156 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C157 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C158 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C159 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C160 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C161 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C162 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C163 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C164 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C165 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C166 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C167 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C168 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C169 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C170 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C171 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C172 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C173 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C174 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C175 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C176 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C200 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C201 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C202 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C203 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C204 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C205 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C206 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C207 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C208 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C209 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C210 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
47
Page 48

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C211 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C212 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C213 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C214 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C215 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C216 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C217 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C218 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C219 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C220 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C221 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C222 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C223 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C224 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C225 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C226 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C227 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C228 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C229 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C230 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C231 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C232 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C233 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C234 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C235 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C236 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C300 22pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C301 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C302 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C303 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C304 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C305 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C306 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C307 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C308 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C309 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C310 22pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C311 22pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C312 22pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C220JBNC 4
C313 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C314 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C315 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C316 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C317 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C318 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C319 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C320 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C321 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C322 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
48
Page 49

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C323 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C324 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C325 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C326 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C327 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C328 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C329 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C330 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C331 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C332 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C333 0.047uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B471KBNC 4
C334 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C335 0.047uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B471KBNC 4
C336 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C337 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C338 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C339 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C340 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C341 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C342 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C343 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C345 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C346 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C348 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C349 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C350 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C351 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C352 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C353 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C354 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C400 0.047uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C402 0.047uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B561KBNC 4
C404 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C405 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C406 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C407 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C408 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C409 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C410 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C411 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C412 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C413 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C414 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C450 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C451 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C452 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C453 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C454 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C455 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
49
Page 50

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C456 0.047uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B471KBNC 4
C457 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C458 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C459 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C460 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C461 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C462 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C463 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C464 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C465 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C466 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C467 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C468 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C469 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C470 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C471 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C472 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C473 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C474 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C478 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C479 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C480 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C481 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C482 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C483 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C484 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C485 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C486 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C487 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C488 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C489 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C490 10uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100M C R1GB 4
C492 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C493 100uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON U WX1 C101MCR1GB 4
C493 100uF, ELEC, 16V, 55C, 20% NICHICON U WT1 C101MCR1GB 4
C494 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C495 0.047uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B473KBNC 4
C496 0.047uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 10% Samsung CL10B102KBNC 4
C497 470uF, TANT, 4V, 55C, 20% NICHICON F930G477MNC 4
C498 100uF, ELEC, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON U WX1 C101MCR1GB 4
C498 100uF, ELEC, 16V, 55C, 20% NICHICON U WT1 C101MCR1GB 4
C499 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C500 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C501 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C502 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C503 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C504 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C505 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C506 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
50
Page 51

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
C507 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C531 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C532 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C533 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C534 47pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 55C, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C535 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C536 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C537 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C538 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C539 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C540 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
Designator
L100 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L300 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L301 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L302 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L400 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L401 XFMR, 10BASE-T, SOIC-16 E&E 821-M0542 4
L402 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC102R1H3D 4
L403 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC102R1H3D 4
L404 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC102R1H3D 4
L405 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC102R1H3D 4
L450 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC102R1H3D 4
L451 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC102R1H3D 4
L452 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC102R1H3D 4
L453 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC102R1H3D 4
L454 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC102R1H3D 4
L455 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC102R1H3D 4
L456 POWER IND, 5.2uH, 30% SUMIDA CDRH104R-5R2NC 4
L457 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
L458 EMI FILTER, 50V, 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D 4
Inductors
Diodes
Designator
D450 SCHOTTKY, SC59 Toshiba 1SS396 4
D451 SCHOTTKY, SC59 Toshiba 1SS396 4
D453 RECT, 400V, 1A, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
D454 RECT, 400V, 1A, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
D455 RECT, 400V, 1A, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
D456 SCHOTTKY, SC59 Toshiba 1SS396 4
D457 SCHOTTKY, SC59 Toshiba 1SS396 4
D458 SCHOTTKY, SC59 Toshiba 1SS396 4
D459 SCHOTTKY, SC59 Toshiba 1SS396 4
D461 RECT, 400V, 1A, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
D462 RECT, 400V, 1A, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
D463 RECT, 400V, 1A, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
51
Page 52

Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Note
ELECTRICAL PART LIST
ESP-88 Digital Signal Processor (DSP) PCB Assembly
Transistors
Designator
Q450 PNP, 50V, 100Ma, SOT-2 3 KEC KRA102S 4
Q451 PNP, 50V, 100Ma, SOT-2 3 KEC KRA102S 4
Q452 PNP, 50V, 100Ma, SOT-2 3 KEC KRA102S 4
Q453 PNP, 50V, 100Ma, SOT-2 3 KEC KRA102S 4
Q454 PNP, 50V, 100Ma, SOT-2 3 KEC KRA102S 4
Q455 PNP, 50V, 100Ma, SOT-2 3 KEC KRA102S 4
Q456 PNP, 50V, 100Ma, SOT-2 3 KEC KRA102S 4
Q457 PNP, 50V, 100Ma, SOT-2 3 KEC KRA102S 4
Q458 NPN, 50V, 100mA, SO T-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Designator
M100 SDRAM, TSOP-54 ELPIDA EDS1216AATA-75 4
M101 DSP, QFP-208 TI TMS320C6713BPYP 4
M200 PROG GATE ARRAY, QFP-208 XILINX XC2S150E6PQ208C 4
M201 OCTAL BUFFER DR, TSSOP20 ONSemi MC74VHC541DT 4
M202 OCTAL BUFFER DR, TSSOP20 ONSemi MC74VHC541DT 4
M300 MICROPROCESSOR, QFP-176 Renases HD6417706F133 4
M301 SDRAM, TSOP-54 ELPIDA EDS1216AATA-75 4
M302 FLASH MEMORY, TSOP-48 SPANSION S29GL064M90TAIR 4
M400 HEX INVERTER, TSSOP-14 ONSEMI MC74VHC04DT 4
M401 ETHER LAN CONT, TQFP-100 Cirrus CS8900A-CQ3 4
M450 TRANSCEIVER, SOIC-16 Harris/Intersil HIN202ECB 4
M452 OCTAL BUFFER DR, TSSOP20 ONSemi MC74VHC541DT 4
M453 VOLT DET, SOT-23-5 SEIKO S-80947CNMC-G9H-T2 4
M454 VOLT DET, TSOP-5 ONSEMI NCP303LSN11T1 4
M455 VOLT DET, SOT-23-5 SEIKO S-80917CNMC-G8M-T2 4
M456 VOLT DET, SOT-23-5 SEIKO S-80917CNMC-G8M-T2 4
M457 VOLT DET, Vd=3.0V SEIKO S-80930CNMC-G80-T2 4
M458 VOLT DET, SOT-23-5 SEIKO S-80940CNMC-G9A-T2 4
M460 REG, 3.3V, 1A, TO-252 NEC UPC2933T 4
M461 REG, SOT-223, TI NEC LM317DCY 4
M462 REG, SOT-223, TI NEC LM317DCY 4
M463 PWM SWITCHER TI TPS54312PWP 4
Integrated Circuits
Miscellaneous
Designator
CN452 CONN, SMT, 1.0MM, 100 PIN KEL 87BFN-100R 4
CN530 CONN, SMT, 100P Molex 52584-1079 4
X200 50.000MHz, 100ppm, 50pF KDS DSO531SVL 50MHz 4
X201 24.576MHz, 100ppm, 50pF KDS DSO531SVL
24.576MHz
4
52
Page 53

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part
Note
ESP-88 General Input/Output (GIO) PCB Assembly
Resistors
Designator
R100 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R101 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R102 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R103 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R104 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R105 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R106 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R107 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R108 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R109 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R110 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R111 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R112 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R113 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R114 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R115 5.1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-075K1 4
R116 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R117 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R118 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R119 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R120 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R121 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R122 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R123 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R125 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R126 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R129 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR- 07R00 4
R130 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR- 07R00 4
R132 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R133 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R134 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-0710K 4
R135 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R136 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R137 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R138 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R139 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R140 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R141 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R142 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07100R 4
R144 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo RC0603JR- 07R00 4
R145 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
R146 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo RC0603FR-07330R 4
Number
53
Page 54

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part
Note
ESP-88 General Input/Output (GIO) PCB Assembly
Capacitors
Designator
C100 10uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C101 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 55C, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C102 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 55C, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C103 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 55C, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C104 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 55C, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C105 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 55C, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C106 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 55C, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C107 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 55C, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C108 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 55C, 10% Samsung CL10B103KBNC 4
C109 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C110 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C111 10uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C112 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C113 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C114 10uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C100MCR1GB 4
C115 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C116 12pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C120JBNC 4
C117 12pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C120JBNC 4
C118 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C119 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C120 47uF, 16V, 40C, 20% NICHICON UZT1C470MCR1GB 4
C121 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C122 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C123 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C124 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C125 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C126 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C127 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C128 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C129 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C130 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, -30C, 20% Samsung CL10F104ZBNC 4
C131 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C132 47pF, 0603, 50V, 55C, NPO, 5% Samsung CL10C470JBNC 4
C403 1000pF, CER, Y5P, 2KV, 55C,
Panasonic ECKD3D102KBP 4
10%
Number
54
Page 55

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part
Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part
Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part
Note
ESP-88 General Input/Output (GIO) PCB Assembly
Inductors
Designator
L100 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L101 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L102 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L103 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L104 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L105 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L106 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L107 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L108 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L109 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L110 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L111 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L112 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L113 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L114 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L115 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L116 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L117 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
L118 EMI FILTER, SMD 300mA, 20% Murata NFM21CC223R1H3D
Number
Diodes
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
Designator
D108 RECTIFIER, 400V, 1A, SOD-106 ROHM 1SR154-400 4
D464 LED, RIGHT ANGLE, RED/GREEN KINGBRIGHT W42WUM/EGW 4
D465 LED, RIGHT ANGLE, RED/GREEN KINGBRIGHT W42WUM/EGW 4
D466 LED, RIGHT ANGLE, RED/GREEN KINGBRIGHT W42WUM/EGW 4
D467 LED, RIGHT ANGLE, RED/GREEN KINGBRIGHT W42WUM/EGW 4
Number
Designator
Q100 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q101 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q102 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q103 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q104 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q105 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q106 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q107 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q109 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q110 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q111 NPN, 50 V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q112 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Q113 NPN, 5 0V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC KRC102S 4
Transistors
Number
55
Page 56

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part
Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part
Note
ESP-88 General Input/Output (GIO) PCB Assembly
Integrated Circuits
Designator
M100 VOLTAGE DETECTOR, TSOP-5 ONSEMI NCP303LSN30T1 4
M100 VOLTAGE DETECTOR, SOT-23-5 SEIKO S-80930CNMC-G80-
T2
M101 REGULATOR, 3.3V, 1A, TO-252 NEC UPC2933T 4
M102 FLASH, MCU, 32K, LQFP64 RENASES HD64F3664FP 4
M451 TRANSCEIVER, PDIP-8 TI SN75176BP 4
Number
4
Miscellaneous
Designator
CN100 HEADER, RT ANG, 9 POS, P3.81 Dinkle ECH381R-09P 4
CN101 HEADER, RT ANG, 9 POS, P3.81 Dinkle ECH381R-09P 4
CN102 SHROUDED HEADER, TOP
ENTRY, 8 CKT, P=2.5
CN400 JACK, MODULAR, TM5RJ2-88 HIRO SE TM5RJ2-88 4
CN450 HEADER, RIGHT ANGLE,
P2.74MM, 9 PINS
CN450 HEADER, RIGHT ANGLE,
P2.74MM, 9 PINS
CN451 HEADER, RIGHT ANGLE,
P5.08MM, 3 POLES, 2EHDRC-03P
XTAL300 32.768KHz, 20ppm, 12.5pF,
D3X8MM
XTAL301 16.000MHz, 30ppm, 20pF, HC-
49/S
XTAL400 20.000MHz, 30ppm, 20pF, HC-
49/S
XTAL100 CRYSTAL, 10.000MHz, 30ppm ,
BT450 COIN CELL, LITHIUM BATTERY
20pF, HC-49/S
WITH SOLDERING TAB, BR2325
Neltron 2317SJ-08 4
Omron XM2C-0912-112 4
WIESON 3170-09MANS4DW 4
DINKLE 2EHDRC-03P 4
Raltron R38-32.768-12.5 4
Raltron AS-16.000-20 4
Raltron AS-20.000-20 4
Raltron AS-10.000-20 4
PANASONIC BR2325-1HCE 4
Number
56
Page 57

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part Number Note
Reference
Description Vendor Vendor Part Number Not e
ESP-88 Output PCB Assembly
Inductors
Designator
L900 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L901 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L902 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L903 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L904 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L905 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L906 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L907 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L908 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L909 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L910 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
L911 NFM39R12C223 MURATA NFM39R12C223 4
Designator
CN900 STLZ950/3G-5.08 FENIXCN901 STLZ950/3G-5.08 FENIXCN902 STLZ950/3G-5.08 FENIXCN903 STLZ950/3G-5.08 FENIXCN904 0T1-400334 CT 0T1-400334 4
ESP-88 LED PCB Assembly
Miscellaneous
Name
Name
STLZ950/3G-5.08 4
CONTACT
STLZ950/3G-5.08 4
CONTACT
STLZ950/3G-5.08 4
CONTACT
STLZ950/3G-5.08 4
CONTACT
Diodes
Designator
D920 LED, RED/GREEN SHARP GL3ED8(R/G) 4
D921 LED, RED/GREEN SHARP GL3ED8(R/G) 4
D922 LED, RED/GREEN SHARP GL3ED8(R/G) 4
D923 LED, RED/GREEN SHARP GL3ED8(R/G) 4
D924 LED, RED/GREEN SHARP GL3ED8(R/G) 4
D925 LED, RED/GREEN SHARP GL3ED8(R/G) 4
D926 LED, RED/GREEN SHARP GL3ED8(R/G) 4
D927 LED, RED/GREEN SHARP GL3ED8(R/G) 4
57
Page 58

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part
Note
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part
CC-64 Control Center
Resistors
Designator
Name
RA100 NETWORK, 10K, 10 PIN/8R, 5% Yageo
RA400 NETWORK, 10K, 10 PIN/8R, 5% Yageo
RA401 NETWORK, 10K, 10 PIN/8R, 5% Yageo
RA500 NETWORK, 10K, 10 PIN/8R, 5% Yageo
R100 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R101 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R102 47 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo
R103 47 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo
R104 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R105 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R106 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R107 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R108 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R109 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R200 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R201 47 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo
R202 47 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo
R203 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R204 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R205 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R206 100 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R208 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R209 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R210 330 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R212 47 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo
R216 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R300 56K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R400 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R401 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R402 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R403 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R404 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo
R500 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo
R501 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R502 0 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo
R505 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R506 1K, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
R509 680 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo
Capacitors
YC158TJR-0710K
YC158TJR-0710K
YC158TJR-0710K
YC158TJR-0710K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603JR-0747R
RC0603JR-0747R
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-07330R
RC0603JR-0747R
RC0603JR-0747R
RC0603FR-07330R
RC0603FR-07330R
RC0603FR-07100R
RC0603FR-07100R
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-074K7
RC0603FR-07330R
RC0603JR-0747R
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-0756K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603JR-07R00
RC0603JR-07R00
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603JR-07R00
RC0603FR-0710K
RC0603FR-071K
RC0603FR-07680R
Number
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
Designator
Name
C100 12pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 125C, 5% Samsung
C101 12pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 125C, 5% Samsung
C102 10uF, SMD E CAP, 16V, 105C, 20% Nichicon
C103 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C104 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
58
Number
CL10C120JBNC
CL10C120JBNC
UZT1C100MCR1GB
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
4
4
4
4
4
Page 59

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part
CC-64 Control Center
Capacitors (continued)
Designator
Name
C105 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C106 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C107 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C108 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C109 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C110 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C200 1000pF, CER, Y5P, 2KV, 125C, 10% Panasonic
C201 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C202 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C203 12pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 125C, 5% Samsung
C204 12pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 125C, 5% Samsung
C205 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C206 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C207 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C208 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C209 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C210 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C211 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C213 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C214 1000pF, CER, Y5P, 2KV, 125C, 10% Panasonic
C300 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C301 22pF, 0603, NPO, 50V, 125C, 5% Samsung
C302 10uF, SMD E CAP, 16V, 105C, 20% Nichicon
C400 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C401 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C402 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C403 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C404 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C405 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C406 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C407 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C408 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C409 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C410 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C411 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C412 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C413 0.01uF, 0603, X7R, 50V, 125C, 10% Samsung
C500 220uF, SMD E CAP, 10V, 105C, 20% Nichicon
C501 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C502 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C503 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C504 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C505 220uF, SMD E CAP, 10V, 105C, 20% Nichicon
C507 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C508 0.1uF, 0603, Y5V, 50V, 85C, 20% Samsung
C509 10uF, E CAP, 16V, 105C, 20% Nichicon
Number
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
ECKD3D102KBP
CL10B103KBNC
CL10B103KBNC
CL10C120JBNC
CL10C120JBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
ECKD3D102KBP
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10C220JBNC
UZT1C100MCR1GB
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10B103KBNC
CL10B103KBNC
CL10B103KBNC
CL10B103KBNC
CL10B103KBNC
CL10B103KBNC
CL10B103KBNC
CL10B103KBNC
CL10B103KBNC
CL10B103KBNC
UWT1A221MCL1GS
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
UWT1A221MCL1GS
CL10F104ZBNC
CL10F104ZBNC
UZT1C100MCR1GB
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
59
Page 60

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part
CC-64 Control Center
Diodes
Designator
Name
D100 SWITCHING, KDS181, SOT-23 KEC
D101 SWITCHING, KDS181, SOT-23 KEC
D102 SWITCHING, KDS181, SOT-23 KEC
D200 LED, YELLOW, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D201 LED, AMBER, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D202 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D300 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D301 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D302 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D303 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D304 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D305 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D306 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D307 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D308 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D309 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D310 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D311 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D312 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D313 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D314 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D315 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D316 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D317 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D318 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D319 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D320 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D321 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D322 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D323 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D324 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D325 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D326 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D327 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D328 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D329 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D330 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D331 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D332 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D333 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D334 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D335 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D336 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D337 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D338 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
60
Number
KDS181
KDS181
KDS181
17-21 UYC/S530-
A2/TR8
17-21 UYOC/S530A2/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
Page 61

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part
CC-64 Control Center
Diodes (continued)
Designator
Name
D339 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D340 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D341 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D342 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D343 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D344 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D345 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D346 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D347 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D348 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D349 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D350 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D351 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D352 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D353 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D354 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D355 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D356 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D357 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D358 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D359 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D400 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D401 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D402 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D403 LED, GREEN, SMD, 0805 Everlight
D500 TVSSMAJ5.0CA-TR, SMA, ST ST
D501 TVSSMAJ5.0CA-TR, SMA, ST ST
Inductors
Number
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
17-21 VGC/TR8
SMAJ5.0CA-TR
SMAJ5.0CA-TR
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
Designator
Name
L200 10-BASE T LOW PASS FILTER YCL
L200 10-BASE T LOW PASS FILTER BEL-FUSE
L201 CHIP, EMI FILTER, 50V/2A, 20% Panasonic
L202 CHIP, EMI FILTER, 50V/2A, 20% Panasonic
L502 CHIP, EMI FILTER, 50V/2A, 20% Panasonic
L503 CHIP, EMI FILTER, 50V/2A, 20% Panasonic
Designator
Transistors
Name
Q100 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC
Q101 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC
Q102 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC
Q103 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC
Q202 PNP, 60V, 1A, SOT-89, KTA1668 KEC
Q500 PNP, 50V, 100mA, SOT-23 KEC
61
Number
20F001N
A556-2006-02
EXCCET103U
EXCCET103U
EXCCET103U
EXCCET103U
Number
KRA102S
KRA102S
KRC102S
KRA102S
KTA1668Y
KRC102S
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
Page 62

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part
Reference
Description Vendor
Vendor Part
CC-64 Control Center
Integrated Circuits
Designator
M100 QUAD 2-INPUT AND, TSSOP14 ON Semi
M101 CMOS, SRAM, TSOP44 Samsung
M102 MCU, FLASH, UNPROG, FP-100B Hitachi
M200 HEX INVERTER, TSSOP14 ON Semi
M201 EEPROM, DIP8, ATMEL ATMEL
M202 ETHERNET CONT, PQFP-100 Realtek
M300 LED DISPLAY DRIVER, QSOP16 MAXIM
M400 DECODER, TSSOP16 ONSEMI
M401 OCTAL BUFFER DRIVER, TSSOP20 ON Semi
M402 OCTAL BUFFER DRIVER, TSSOP20 ON Semi
M403 OCTAL D-TYPE F-F, TSSOP20 ON Semi
M404 IDENTITY COMP, TSSOP20 Fairchild
M500 DC/DC CONVERTER, DIP-24 Cincon Elec
M501 VOLTAGE DETECTOR, TSOP-5 ONSemi
M501 VOLTAGE DETECTOR, SOT-23-5 Seiko
M503 OCTAL BUFFER DRIVER, TSSOP20 ON Semi
M504 OCTAL D-TYPE FLIP-FLIP,
Name
ON Semi
MC74VHC08DT
K6R1016C1D-TC10
HD64F3069RF25
MC74VHC04DT
AT93C46-10PI-2.7
RTL8019AS
MAX6951CEE
MC74VHC138DT
MC74VHC541DT
MC74VHC541DT
MC74VHC574DT
74ACT521MTC
EC5A-12S05
NCP303LSN47T1
S80947CNMC-G9H-
T2
MC74VHC541DT
MC74VHC574DT
TSSOP20
Miscellaneous
Number
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
Designator
Name
CN100 CONNECTOR, 6POLE, P2.5MM Neltron
CN200 MODULAR JACK, 7006- 8P8C- M-01 Neltron
CN501 WIRE TO BOARD HEADER,
Dinkle
P5.08MM, 2POLE, 2EHDVC-02P
CN503 PCB SOCKET, DUAL ROW,
Neltron
P2.54MM, 16POLE, H=7.1MM
E400 ENCODER, SW, 5P, 5V/10mA ALPS
E401 ENCODER, SW, 5P, 5V/10mA ALPS
E402 ENCODER, SW, 5P, 5V/10mA ALPS
E403 ENCODER, SW, 5P, 5V/10mA ALPS
E404 ENCODER, SW, 5P, 5V/10mA ALPS
JP500 HEADER, P2.54MM, 3PIN, H=6.0MM Neltron
JP501 HEADER, P2.54MM, 3PIN, H=6.0MM Neltron
LCM HEADER, P2.54MM, 16PIN,
Neltron
H=6.0MM
SW400
SW401
TACT SW, SMT, 12V/50mA, 160g,
H=5MM, TD-06XA
Wealth
Metal
SW402
SW403
XTAL100 20.000 MHz +/-30ppm, 20pF, HC-49/S Raltron
XTAL200 20.000 MHz +/-30ppm, 20pF, HC-49/S Raltron
/JP500 JUMPER, CAP, 2 PIN, 6MM Computime
/JP501 JUMPER, CAP, 2 PIN, 6MM Computime
/LED PCB FLAT CABLE, 18P, 2651, #26AWG,
Computime
L=39MM, GREY, UL&CSA
62
Number
2317SJ-06
7006-8P8C-M-01
2EHDVC-02P
2214S-16G
EC11E15244EF
EC11E15244EF
EC11E15244EF
EC11E15244EF
EC11E15244EF
2211S-03G
2211S-03G
2213S-16G
TD-06XAX
AS-20.000-20
AS-20.000-20
22Z02-0611
22Z02-0611
3618BA00396K0Z04
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
Page 63

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor Name Vendor Part
Note
Reference
Description Vendor Name Vendor Part
Note
Reference
Description Vendor Name Vendor Part
Note
CC-16 Zone Controller
Resistors
Designator
R1 715 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo Corporation RC0603FR-07715R
R2 240 OHM, 0603, 1/10W, 1% Yageo Corporation RC0603FR-07240R
R3 100K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-07100K 4
R4 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R5 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R8 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R6 120 OHM, 1206, 1/4W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC1206JR-07120R 4
R7 1. 2K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo Corpor ation RC0603JR-071K2 4
R9 1. 2K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yag eo Corpor ation RC0603JR-071K2 4
R11 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R12 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R13 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R14 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R15 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R16 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R17 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R18 10K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0710K 4
R10 47K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-0747K 4
R22 4.7K, 0603, 1/10W, 5% Yageo Corporation RC0603JR-074K7 4
Capacitors
Number
4
4
Designator
C1 47uF, 50V, SMD, ECAP,
+105/-55C, 20%, D6.3x7.7
C2 100uF, 16V, SMD, ECAP,
+105/-55C, 20%, D6.3X5.4
C3 20pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 5% Teamyoung Corp 0603N200J500BB 4
C4 20pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 5% Teamyoung Corp 0603N200J500BB 4
C5 220pF, 0603, 50V, NPO, 5% Teamyoung Corp 0603N221J500BB 4
C6 0.1uF, 0603, X7R, 16V, 10% Teamyoung Corp 0603B104K160BB 4
C7 0.1uF, 0603, X7R, 16V, 10% Teamyoung Corp 0603B104K160BB 4
C8 0.1uF, 0603, X7R, 16V, 10% Teamyoung Corp 0603B104K160BB 4
C9 0.1uF, 0603, X7R, 16V, 10% Teamyoung Corp 0603B104K160BB 4
C10 0.1uF, 0603, X7R, 16V, 10% Teamyoung Corp 0603B104K160BB 4
C11 0.1uF, 0603, X7R, 16V, 10% Teamyoung Corp 0603B104K160BB 4
C12 0.1uF, 0603, X7R, 16V, 10% Teamyoung Corp 0603B104K160BB 4
Nichicon Corp
Nichicon Corp
Number
UUD1H470MCR1GS
UWT1C101MCR1GB
4
4
Diodes
Designator
- RECT, 400V/1A, SOD-106 Rohm Semi 1SR154-400 4
D1 SCHOTTKY BARR, SOD-80C Philips Semi BAS85 4
D2 SCHOTTKY BARR, SOD-80C Philips Semi BAS85 4
D3 SCHOTTKY BARR, SOD-80C Philips Semi BAS85 4
D4 SCHOTTKY BARR, SOD-80C Philips Semi BAS85 4
Number
63
Page 64

ELECTRICAL PART LIST
Reference
Description Vendor Name Vendor Part
Note
Reference
Description Vendor Name Vendor Part
Note
CC-16 Zone Controller
Integrated Circuits
Designator
U1 REG, 1.5A, TO-263 NS National Semi LM317S 4
U2 XCVR, SO-8, MAXIM Maxim Integrated MAX485ECSA 4
U3 EEPROM, 16Kx8, MSOP-8 Microchip Tech Inc 24LC128-I/MS 4
U4 MCU, SSOP28, 10MHz Microchip Te ch Inc PIC16F873A-I/SS 4
Number
Miscellaneous
Designator
LCM LCD MODULE, BSE002A,
122X32 DOT
CN1 TERMINAL BLOCK, 6P,
ELK508A-06P, P=5.08MM
CN2 HEADER, P2.54MM, DUAL,
20PIN, H7.5MM
SW1 DIP SWITCH, 8 POLE, SPST,
ON/OFF, DS-08B
X1 CRYSTAL, 9.8304MHz +/-
30ppm, 20pF, HC-49/S
ShanTou Goworld
Co Ltd
Dinkle Enterprise
Co Ltd
Neltron Industrial
Co Ltd
Diptronics
Manufacturing Inc.
Raltron Electronics AS-9.8304- 20 4
Number
SM4353 4
ELK508A-06P 4
2213S-20G 4
DS-08B 4
64
Page 65

DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURES
ControlSpace® ESP-88 Chassis
Refer to Figure 4 for the following procedures
1. Top Cover Removal
1.1 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver,
remove the eight screws (2, 3) that secure
the top cover (1). There are six around the
back and side edges of the cover and two at
the front lip.
1.2 Lift off the top cover.
2. Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS)
Removal
2.1 Perform procedure 1.
2.2 Disconnect the power supply AC wiring
harness located toward the rear of the
chassis (22). Disconnect the green ground
wire from the GND terminal on the power
supply. Disconnect the DC output connector
located toward the front of the chassis. This
cable harness connects to the motherboard.
2.3 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver,
remove the four screws that secure the
power supply to the chassis. These screws
are located on the bottom of the chassis. Lift
out the power supply.
4. GPIO Board Removal
4.1 Perform procedure 1.
4.2 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver,
remove the two screws (3) that secure the
GPIO card (31) to the back of the chassis
(22).
4.3 Unplug the wire harness at CN102. Lift
out the GPIO card.
Note: The chassis can support up to two
GPIO cards at the end of the chassis nearest the power supply.
5. DSP PCB Removal
5.1 Perform procedure 1.
5.2 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver,
remove the two screws (3) that secure the
DSP card (30) to the back of the chassis
(22).
5.3 Lift up on the back of the DSP card until
it unplugs from the motherboard (12) connector. Lift out the DSP card.
Re-assembly Note: When re-installing the
card, ensure that the LEDs at the front edge
of the card align with the openings in the
front panel.
6. Mic/Line Input PCB Removal
3. DC Fan Removal
3.1 Perform procedure 2.
3.2 Unplug the DC fan wiring harness from
the motherboard at CN205.
3.3 Remove the four screws (27) that secure
the DC fan (28) to the chassis (22). Lift out
the fan. Take care to not lose the nylon
locknuts (29).
6.1 Perform procedure 1.
6.2 Remove the one screw (3) that secures
the LED PCB (25) to the front panel (21).
This screw is located in the middle of the
LED PCB at the front end of the Mic/Line
Input PCB (10).
6.3 Remove the two screws (3) that secure
the back of the Mic/Line PCB to the chassis
(22). These screws are located at the back
of the chassis.
65
Page 66

DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURES
6.4 Lift out the Mic/Line PCB assembly.
Unplug the wiring harness for the Line
Output PCB.
Re-assembly Note: When re-installing the
Mic/Line PCB assembly, ensure that the
LEDs located on the front of the LED PCB
are aligned with the openings in the front
panel.
7. Line Output PCB Removal
7.1 Perform procedure 1.
7.2 Remove the two screws (3) that secure
the Line Output PCB assembly (9) to the
chassis (22). Lift out the PCB assembly.
8. Motherboard PCB Removal
8.1 Perform procedure 1.
8.2 Remove all installed cards that plug into
the motherboard (12) using the applicable
disassembly procedures.
8.3 Disconnect all GPIO and DC Switching
Power Supply wiring harnesses from the
motherboard PCB.
8.4 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver,
remove the twelve screws (3) that secure the
motherboard to the chassis (22).
ControlSpace® CC-16 Control Center
Refer to Figure 5 for the following procedures.
1. Front Plate Removal
1.1 Grasp the edge of the front plate (1) and
pull it away from the rest of the unit. The
snaps should release and the front panel
should come off easily.
2. Main PCB Removal
2.1 On the back of the unit, release the two
white clasps that secure the main PCB (5) in
place and gently pull off it off the mounting
frame (6).
3. LCD PCB Removal
3.1 Perform procedure 2.
3.2 If necessary, remove the front plate (1)
using procedure 1.
3.3 On the back of the mounting frame (5),
release the two white plastic clips that
secure the insert plate (3) and lift it off.
3.4 On the front of the mounting frame,
release the four white plastic clips that
secure the LCD PCB (4) in place. Lift out the
PCB.
66
Page 67

DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURES
ControlSpace® CC-64 Control Center
Refer to Figure 6 for the following procedures.
1. Front Panel Removal
1.1 Grasp the edge of the front panel (2) and
pull it away from the rest of the unit. The
snaps should release and the front panel
should come off easily.
2. EMC Shield Removal
2.1 Place the unit face down onto a soft
surface.
2.2 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver,
remove the four screws (11) that secure the
EMC shield (1).
2.3 Lift off the EMC shield.
5. LCM Display Module Removal
5.1 Perform procedure 3, but do not
unsolder the ribbon cable connection to the
Main PCB (8). You can swing the Main PCB
out of the way to allow access to the LCM
display module (6) screws.
5.2 Remove the four screws (10) that secure
the LCM display module in place.
5.3 Lift off the LCM display module. Take
care to not lose the four nylon washers (12)
on the screws or the four nylon spacers
under the LCM display module.
3. Main PCB Removal
3.1 Pull off the five control knobs (3) from
the front of the unit.
3.2 Perform procedure 2.
3.3 Unsolder the ribbon cable connections
located at the left side of the main PCB (8)
near the RJ-45 connector.
3.4 Remove the four screws (11) that secure
the Main PCB.
3.5 Slide the Main PCB off of the posts and
lift it off.
4. LED PCB Removal
4.1 Perform procedure 3.
4.2 Remove the five screws (11) that secure
the LED PCB (7) to the front panel (9).
4.3 Slide the PCB off of the posts and lift it
off.
67
Page 68

Front Panel Indicators and Features
1. Status Indicator
Green = Netlist loaded, operating
Yellow = DSP resource shortage (delay
or cycles)
Red = Error in netlist
Off = No netlist loaded
2. Power Indicator
Green = Power on
Red = Fatal error
3. Audio Input Indicator
Green = Input signal > -36dBu/-60dBFS
Yellow = Input signal >/= +4dBu/-20dBFS
Red = Clipping, input signal >/= +18.0dBu/-
6.0dBFS
4. Audio Output Indicator
6. Serial Indicator
Red = RS232: Rx/Tx
Yellow = RS485: CC-16 controller command
received
Green = RS485: CC-16 controller command
transmitted
7. Ethernet Indicator
Green = Link
Yellow = Tx activity
Red = Rx activity
8. Front Door
Shown open
9. Audio Output Label Area
Apply labels in this area to indicate the
names of the output signals (e.g. “Center
Fill”)
Green = Output signal > -36dBu/-60dBFS
Yellow = Output signal >/= +4dBu/-20dBFS
Red = Clipping, output signal >/= +18.0dBu/-
6.0dBFS
5. Front Door
Shown closed, pull to open
10. Audio Input Label Area
Apply labels in this area to indicate the
names of the output signals (e.g. “Podium
Mic”)
68
Page 69

Rear Panel Controls and Connections
1. Mic/Line Inputs
Four balanced mic/line inputs (audio input
connectors are green) in slots 1 and 3.
These are inputs S1-1 through S1-4 and S31 through S3-4 in the ControlSpaceTM
Designer software
2. Line Outputs
Four balanced line outputs (audio output
connectors are orange) in slots 2 and 4.
These are outputs S2-1 through S2-4 and
S4-1 through S4-4 in the Designer software
3. RS-232C Connector
DB-9 male (DTE)
4. RS-485 Connector
Connect ControlSpace CC-16 controllers
6. GPIO slot 2
For optional second GPIO card
7. Power Switch
ON/OFF AC power
8. AC Cord Inlet
Connect the AC cord appropriate for your
area
9. Ethernet LAN Connector
Connect to your PC with enclosed crossover
cable. Or, connect directly to a hub or router
with a straight-through cable
10. Audio Slots 5 - 8
For optional audio cards
5. GPIO Card
Eight general purpose control inputs
Eight general purpose control outputs
RS-232C Serial Port
The ESP-88 features a serial port that can
be used to send control signals to other
equipment (such as a video switcher). The
serial port is a DB9 male. The pin-out is
shown at right.
69
Page 70

Rear Panel Controls and Connections
Mic/Line Inputs
The ESP-88 (base model) includes two “4x4”
Mic/Line cards. Each of these cards occupy
two slots. The input connectors (green) and
the input LEDs appear in the first slot. The
output connectors (orange) and LEDs
appear in the second slot. A microphone or
line level audio source can be connected to
the Mic/Line inputs using one of the following
cable types.
Inputs
Switches and potentiometers can be connected to the control inputs to control various functions in the system. For example,
simple ON/OFF switches can be connected
and then programmed to invoke presets,
select scenes, or invoke a snapshot of a
control. Likewise, 10k linear potentiometers
can be connected to control gains in the
system.
Inputs contain a 5k ohm pull-up resistor
allowing SPST switches to be wired from
input to ground. Potentiometers can be
wired in series from the control input to
ground.
General Purpose Inputs/Outputs
The ESP-88 (base model) includes one
GPIO card in slot 1 providing eight control
inputs and eight control outputs. A second
card can be added to GPIO slot 2.
Outputs
LEDs and relays can be connected to general purpose outputs to indicate state
changes in the system (e.g. preset or scene
changes).
70
Page 71

TEST PROCEDURES
Audio Processor ESP-88 Standard Version
1. Electrical Tests
Required Items
• Audio Precision ATS-2 test station
• Aubit ESP-88 test switchbox with cables
and adapters
• Bose
• IBM Compatible PC with Microsoft
®
CC-16 or CC-64 controller
Windows® XP
®
• LAN Ethernet crossover cable
• DB9F to DB9F Null Modem cable
• Bose
®
ControlSpaceTM software
• ATS-2 test station software
• Microsoft Excel
Test Setup Procedures
1. Ensure that the PC has valid IP address
[192.168.0.1 – 192.168.0.99]. To set your IP
address, click on START go to the CONTROL PANEL and click on NETWORK &
DIAL UP CONNECTIONS. Click on MAKE
NEW CONNECTION. Make a LAN connection. Click on PROPERTIES, then click on
INTERNET PROTOCOL TCP/IP. Set the IP
address to be between 192.168.0.1 and
192.168.0.99. The subnet mask will remain
255.255.255.0 and leave DNS settings
window blank. Click OK.
Once you open the ControlSpace software,
you should see a blank project window like
the one shown below.
d. Click on “Scan”.
2. Connect the ESP-88 chassis under test to
the AuBit switcher and the ATS-2 test station
as shown in Figure 7.
3. If not installed on the PC, install the Bose
ControlSpace Designer software. Once the
software is installed, click on the icon to start
the program.
4. Once the software opens, load the ESP88
TEST connection.csp file. This is a test file
that is has the ESP-88 chassis pre-configured as a straight pass-through to allow test.
If you don’t have this file, perform the following steps to set up the software and hardware for test.
e.The connected ESP will appear on
“Project view”. This case has no Technic.
71
Page 72

TEST PROCEDURES
If there is no CC-16 or CC64 controller
connected, connect it now. You will also
need the power supply for the controller.
Click on the Properties view
.
This setup is a straight-through connection
for this test. Click the connect icon.
When the connection is completed, the
background color will change.
Check Firmware Version on properties
dialog box. Select ESP 1 view.
Click the connect icon again. At this point
the ESP is settled to the proper configuration
for this test.
After disconnect, the ESP-88 chassis must
be powered off and powered on again.
This power off sequence is needed by the
time test. It is recommended to use same
PC that set this configuration and to run the
ATS2 macro that will be described later.
This will avoid the time difference between
the two PC’s.
72
Page 73

TEST PROCEDURES
4-2. Test Setup for the ControlSpace® ESP-88 Chassis
ESP-88 Chassis
1
2
3
4
OUTPUT INPUT
AuBit Switchbox
CHANNEL
OUT
12345678
IN
12345678
1
2
3
4
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
OUTPUT INPUT
PHANTOM
INDICATOR
OPEN
OPEN
PCB
OPEN
OPEN
CH A CH B
LOAD
600
CC-16
DSP
LOAD
600
COM
OUTA
OUT
CHA
GIO
COM
OUTB
OUT
CHB
ETHERNET
LAN CABLE
BLANK
B
A
DB9
SERIAL
PORT
GIO
LOOP-BACK
ADAPTER
PHANTOM
CUTTER PCB
PC
TO ATS-2
CONTROL
AC
DB-9 to
ATS-2 AUX
CONTROL OUT
AC
ATS-2 Front Panel
ATS-2 Back Panel
CONTROL
Figure 7. ATS-2, ESP-88 and AuBit Switchbox Test Setup Diagram
ATS-2
CABLE
AUX CONTROL
OUT IN
ANALOG OUT ANALOG INPUT
CH A CH B
CH A
DB9 to AuBit
73
CH B
Page 74

TEST PROCEDURES
Switcher
Table of connection between the ESP-88 and AuBit switcher
Outputs
OUT CH1 Slot1 Input CH1 IN CH1 Slot2 Output CH1
OUT CH2 Slot1 Input CH2 IN CH2 Slot2 Output CH2
OUT CH3 Slot1 Input CH3 IN CH3 Slot2 Output CH3
OUT CH4 Slot1 Input CH4 IN CH4 Slot2 Output CH4
OUT CH5 Slot3 Input CH1 IN CH5 Slot4 Output CH1
OUT CH6 Slot3 Input CH2 IN CH6 Slot4 Output CH1
OUT CH7 Slot3 Input CH3 IN CH7 Slot4 Output CH1
OUT CH8 Slot3 Input CH4 IN CH8 Slot4 Output CH1
OUT OPT-1L NC IN OPT-1L NC
OUT OPT-1R NC IN OPT-1R NC
OUT OPT-2L Phantom Checker CHA IN OPT-2L 600ohm Load
OUT OPT-2R Phantom Checker CHB IN OPT-2R 600ohm Load
COM-L ATS-2 Anal og Output A COM-L ATS-2 Analog Input A
COM-R ATS-2 Analog Output B COM-R ATS-2 Analog Input B
ESP-88 ESP-88 Switcher Inputs
Caution ! COM-L and COM-R shall be connected with “Phantom cutter”.
ESP-88 Chassis Configuration for test
ESP Slot Card Description
GIO2 Blank Empty slot
GIO1 GIO With 2.2k ohm Loop back cable.
DSP DSP Main Card Main card only - no expansion card
IO Slot 1 4x4 Main card MIC/Lin e Input card
IO Slot 2 4x4 Output card Line ou tput card
IO Slot 3 4x4 Main card MIC/Lin e Input card
IO Slot 4 4x4 Output card Line ou tput card
IO Slot 5 Blank Empty slot
IO Slot 6 Blank Empty slot
IO Slot 7 Blank Empty slot
IO Slot 8 Blank Empty slot
74
Page 75

TEST PROCEDURES
Test Connection Photographs
Phantom Cutter Connection of Phantom Cutter
GIO 2.2k ohm loop back cable
75
Page 76

TEST PROCEDURES
Test
Test Gain or test item Test Channel 1k 20 20k
4-3. The order of testing. The table below lists the tests that are automatically performed by the
ATS-2 test station test macro.
No
1 Input 1/2 ~ Output 1/2 Do Do Do
2 Input 3/4 ~ Output 3/4 Do Do Do
3 Input 5/6 ~ Output 5/6 Do Do Do
4
5 Input 1/2 ~ Output 1/2 Do - 6 Input 3/4 ~ Output 3/4 Do - 7 Input 5/6 ~ Output 5/6 Do - 8
9 Input 1/2 ~ Output 1/2 Do - 10 Input 3/4 ~ Output 3/4 Do - 11 Input 5/6 ~ Output 5/6 Do - 12
13 Input 1/2 ~ Output 1/2 Do - 14 Input 3/4 ~ Output 3/4 Do - 15 Input 5/6 ~ Output 5/6 Do - 16
17 Input 1/2 ~ Output 1/2 Do Do Do
18 Input 3/4 ~ Output 3/4 Do Do Do
19 Input 5/6 ~ Output 5/6 Do Do Do
20
21 Input 1/2 ~ Output 1/2 Do - 22 Input 3/4 ~ Output 3/4 Do - 23 Input 5/6 ~ Output 5/6 Do - 24
25 Input 1/2 ~ Output 1/2 Do Do Do
26 Input 3/4 ~ Output 3/4 Do Do Do
27 Input 5/6 ~ Output 5/6 Do Do Do
28
29 Input 1/2 ~ Output 1/2 Do Do Do
30 Input 3/4 ~ Output 3/4 Do Do Do
31 Input 5/6 ~ Output 5/6 Do Do Do
32
33 6 Phantom test (Hand Pass/Fail) Input 1 ~ 8 - - 34 7 GIO GIO bit 0 ~ 7 - - 35 8 Time ESP internal time - - 36 9 LAN
37 10 RS232C
38 11 RS485(Hand Pass/Fail)
No
5-1 Input 0dB / Output +4dBu
Input 7/8 ~ Output 7/8 Do Do Do
5-2 Input +14dB / Output +4dBu
Input 7/8 ~ Output 7/8 Do - -
5-3 Input +24dB / Output +4dBu
Input 7/8 ~ Output 7/8 Do - -
5-4 Input +42dB / Output +4dBu
Input 7/8 ~ Output 7/8 Do - -
5-5 Input 48dB / Output +4dBu
Input 7/8 ~ Output 7/8 Do Do Do
5-6 Input 54dB / Output +4dBu
Input 7/8 ~ Output 7/8 Do - -
5-7 Input 64dB / Output +4dBu
Input 7/8 ~ Output 7/8 Do Do Do
5-8 Input 0dB / Output -10dBu
Input 7/8 ~ Output 7/8 Do Do Do
76
Page 77

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Setting
Item Setting
4-4. Fundamental Setting of ATS-2
4-4-1.Analog Generator Setting.
Instrument Audio Analyzer
Wave form Sine(Normal)
Frequency 1kHz
Out puts A/B-ON
Track Track-A
Amplitude +4.00dBu
Configuration Bal XLR
Z-Out(Ohms) 40
4-4-2.Analog Input Setting.
Source XLR-Bal (Both A/B
Input Analog
Level Set the units "dBu"
Frequency Set the units "kHz"
Range Check both
Measurement
Function
Function Set the units "%"
Range Check both
Detect Auto-RMS
Band width 22Hz~20kHz LPF
BP/BR filter
frequency
Filte r "A" we ightin g
Channel)
Peak Monitor Set the units "dBu"
Auto Range Check
DC No Check
4-4-3.Analyzer Setting.
THD+N Ratio
Sweep Track
77
Page 78

TEST PROCEDURES
4-5.Automatic test setting on ATS2.
Load the ATS2 macro file “ESP88 TestMacro.atsb”. Click on the Macro Editor button. The Macro
Editor window shown at the bottom of the page will open. CAUTION: Do not change any of the
text in the Macro Editor window, or you will change the test parameters, corrupting the test file
and causing the test to fail.
Click on the START/RESUME button in the Macro Editor window toolbar.
78
Page 79

TEST PROCEDURES
4-6. About Automatic test setting on ATS2.
This macro file “ESP88 TestMacro.atsb” can
measure all items listed in section 4-3. The
order of testing.
Audio quality can be measured and logged
automatically.
When you click on the START/RESUME
button in the Macro Editor window toolbar,
the dialog box shown at right will appear on
the screen. Make sure the ESP 8X8 Version
radio button is checked. Input the serial
number, lot number, tester ’s name and push
START TEST button.
Once you click the start button, the file save
dialog box will appear. The serial number is
used for the file name. There is no need to
change the file name, but if you wish to
change the directory you save to, select the
proper directory.
If a test fails, the dialog box at right will
appear on the screen and ask if you would
like to continue or not.
This message show the ESP that is tested
has a fault. If you would like to get information for repair by saving a log file, you can
continue by pushing the YES button to
generate a log file. You can terminate the
test by pushing the NO button to end the
test.
The dialog box at right shows the progress
of the test.
This “Auxiliary Control I/O” dialog box shows
the status of Aubit switcher.
79
Page 80

TEST PROCEDURES
4-7. Phantom Power test on the ATS2.
The Phantom test is done by the Phantom checker hardware.
This test will proceed automatically.
4-8. RS485 test on the ATS2.
The RS485 test is performed by checking to see if the unit can see the CC-16 controller that is
connected to the RS485 connector.
The CC-16 icon will appear in the ControlSpace
ESP-88.
®
test window when the CC-16 is connected to
This test will proceed automatically.
When “EC16” is detected, “Pass” is logged to the log file automatically.
When “EC16” is not detected, “Fail” is logged to the log file automatically.
The address of the CC-16 should set anywhere from 1 to 15. Refer to the diagram below.
When the CC-16 controller is detected by the software through the chassis, this test will pass.
CC-16 DIP Switch Settings
80
Page 81

TEST PROCEDURES
4-9. Test log file.
This test will be saved automatically as a text file with the file name specified in step 4.6.
The text file format is as shown below.
81
Page 82

TEST PROCEDURES
4-10. Pass/Fail evaluation and report of this test.
The log file data must be checked for each item.
The Excel test file “ESPTestReporter.xls” can check all of the items that are logged. This file has
a macro to load the data from the log data text (.txt) file.
The example above shows a test that failed because of no data.
The method to load the log data is below.
- Open the Excel test file, “ESPTestReporter.xls”. Be sure to click ENABLE MACROS when the
dialog box opens.
- Once the file is open, click on TOOLS / MACRO / MACROS. When the macro dialog box
opens, you should see a macro named “TestLogOpen”. Select this macro and click RUN. When
the File Open dialog box opens, browse to the location of the test text (.txt) file you created and
select it. Click OPEN. At this point the test data will automatically be loaded into the Excel sheet.
If the item is passed, the corresponded cell will be changed to TRUE.
If the item is failed, the corresponded cell will be kept to FALSE.
After loading , pass/fail will be summed to the RESULT cell.
The macro will default to a blank sheet after the results have been loaded. You must open the
.xls file that was created as a result of loading the test text (.txt) file. It will be the same name as
the .txt file with an .xls extension. Once you open this file in Excel you will be able to view the
results, PASS or FAIL, and view the parameters measured. All tests must be passed.
82
Page 83

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
This is an example of the PASSED ESP-88 chassis test data in Excel format.
5. Testing method and criteria.
Note: The information in the following pages is provided for reference only. You will not need to
set the ATS2 manually to perform these tests.
This section describes the settings and criteria of each of the tests to be performed.
The setting of the ATS-2 test station will be done automatically by the ATS2 Macro.
5-1. Gain at 0dB
ESP Setting: Set all channel gains to = 0dB. (Command on COM = ^BA{1/2}{L/R}00^C)
AMPL(1kHz)
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude +4.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +5.5dBu +2.5dBu
83
Page 84

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Noise Test
ATS2 Settings
Frequency -Amplitude Off
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Level -77dBu -200dBu
FRQ20kHz
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 20kHz
Amplitude +4.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +4.5dBu +1.5dBu
FRQ20Hz
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 20Hz
Amplitude +4.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +5.5dBu +2.5dBu
THDN
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude +4.00dBu
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Function(THD+N) 0.015% 0
84
Page 85

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
19.5dBu
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude +23.5dBu (Nominal +19.5dB)
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Function(THD+N) 1.5% 0
Perform these tests for channels 1 through 8.
5-2.Gain at 14dB
ESP Setting: Set all channel gains to = 14dB.
(Command on COM = ^BA{1/2}{L/R}14^C)
AMPL(1kHz)
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude -10.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +5.5dBu +2.5dBu
Noise
ATS2 Settings
Frequency -Amplitude Off
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Level -77dBu -200dBu
Perform this test on channels 1 through 8.
85
Page 86

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
5-3.Gain 24dB
ESP-88 Chassis Settings: Set all channel gains to = 24dB.
(Command on COM = ^BA{1/2}{L/R}24^C)
AMPL(1kHz)
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude -20.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +5.5dBu +2.5dBu
Noise
ATS2 Settings
Frequency -Amplitude Off
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Level -77dBu -200dBu
Perform this test on channels 1 through 8.
5-4.Gain 42dB
ESP Settings: Set all channel gains to = 42dB.
(Command on COM = ^BA{1/2}{L/R}42^C)
AMPL(1kHz)
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude -38.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +5.5dBu +2.5dBu
86
Page 87

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Noise
ATS2 Settings
Frequency -Amplitude Off
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Level -73dBu -200dBu
Perform this test on channels 1 through 8.
5-5. Gain 48dB
ESP Settings: Set all channel gains to = 48dB.
(Command on COM = ^BA{1/2}{L/R}48^C)
AMPL(1kHz)
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude -44.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +5.5dBu +2.5dBu
Noise
ATS2 Settings
Frequency -Amplitude Off
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Level -68dBu -200dBu
87
Page 88

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
FRQ20kHz
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 20kHz
Amplitude -44.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +3.5dBu +1.0dBu
FRQ20Hz
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 20Hz
Amplitude -44.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +5.5dBu +2.5dBu
THDN
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude -44.00dBu
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Function(THD+N) 0.02% 0
19.5dBu
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude -24.5dBu (Nominal +19.5dB)
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Function(THD+N) 1.5% 0
Perform this test on channels 1 through 8.
88
Page 89

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Low e r limit
5-6.Gain 54dB
ESP Setting: Set all channel gains to = 54dB.
(Command on COM = ^BA{1/2}{L/R}54^C)
AMPL(1kHz)
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude -50.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +5.5dBu +2.5dBu
Noise
ATS2 Settings
Frequency -Amplitude Off
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Level -63dBu -200dBu
Perform this test on channels 1 through 8.
5-7.Gain 64dB
ESP Setting: Set all channel gains to = 64dB.
(Command on COM = ^BA{1/2}{L/R}64^C)
AMPL(1kHz)
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude -60.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +5.5dBu +2.5dBu
89
Page 90

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Noise
ATS2 Settings
Frequency -Amplitude Off
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Level -52dBu -200dBu
FRQ20kHz
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 20kHz
Amplitude -60.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +3.5dBu +1.0dBu
FRQ20Hz
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 20Hz
Amplitude -60.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level +5.5dBu +2.5dBu
THDN
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude -60.00dBu
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Function(THD+N) 0.12% 0
90
Page 91

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
19.5dBu
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude -40.5
dBu (Nominal +19.5dB)
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Function(THD+N) 1.5% 0
Perform this test on channels 1 through 8.
5-8.Gain 0dB and Output Level -10dB
ESP Setting: Set all channel gains to = 0dB. (Command on COM = ^BA{1/2}{L/R}00^C)
ESP Setting: Set all channel output levels to = -10dB. (Command on COM = ^BL{1/2}{L/R}0^C)
AMPL(1kHz)
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude +4.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level -9.0dBu -11.0dBu
Noise
ATS2 Settings
Frequency -Amplitude Off
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Level -77dBu -200dBu
91
Page 92

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
Item Setting
Item Upper limit Lower limit
FRQ20kHz
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 20kHz
Amplitude +4.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level -8.5dBu -11.5dBu
FRQ20Hz
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 20Hz
Amplitude +4.00dBu
B/W <10HZ / FS/2
Filter None
Test Limits
Level -8.5dBu -11.5dBu
THDN
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude +4.00dBu
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Function(THD+N) 0.02% 0
19.5dBu
ATS2 Settings
Frequency 1kHz
Amplitude +23.5dBu (Nominal +19.5dB)
B/W 22HZ / 22KHz LPF
Filter “A” Weighting
Test Limits
Function(THD+N) 1.5% 0
Perform this test on channels 1 through 8.
92
Page 93

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Pass Fail
Item Upper limi t Lower limit
Item Upper limit Lower limit
6. Phantom test
The phantom test will be done after the audio tests.
Pass/Fail is detected by “Phantom Checker”.
This phantom checker is modified a GIO used to measure the voltage of the phantom power.
Test Limits
Measured channel
Hot and Cold line
(CH 1/2/3/4)
Perform these tests for channels 1 through 4.
Refer to section “4-7. About Phantomtest on ATS2”.
7.GIO test.
This GIO test will be done by the ATS2 macro automatically.
This test requires the GIO 2.2k ohm loop back cable.
The GIO settings are as follows.
ESP Setting: Set GIO outputs.
(Command on COM = ^BO{0~7}{0/1}^C)
ESP Setting: Get the value of GIO input .
(Command on COM = ^BI^C)
Test Limits
GIO test (Full) 100% 95%
GIO test (Half) 48% 45%
More than 13V
Opposite channel
Lower than 2V
Measured channel
Lower than 13V
Opposite channel
More than 2V
Perform this test for ports 0 through 7.
8.Time test.
This time test will be done by the ATS2 macro automatically.
In this test, the time that is stored on the ESP is compared with the PC time by the ATS2 macro.
ESP Setting : Get time report from ESP.
(Command on COM = t )
Test Limits
Date diff 0 0
Time diff +3 -3
93
Page 94

TEST PROCEDURES
Item Pass Fail
Item Pass Fail
Item Pass Fail
9. LAN Test.
The configuration of ESP is done by the Local Area Network (LAN).
Therefore LAN communication can be confirmed by the ESP and can be settled by the design
tool and that can measure it in the correct situation.
Test Limits
LAN ATS2 macro can
reach this item.
10. RS-232C Test.
The measurement by ATS2 macro is done using the RS232C line.
Therefore RS232C communication can be confirmed by the ESP and it can be measured in the
correct situation.
Test Limits
RS232C ATS2 macro can
reach this item.
11. RS-485 Test.
This RS-485 test will come after above inspection.
Pass/Fail is detected by automatically.
Refer to section “4-8. About RS485 test on ATS2”.
When “EC16” could be found in the sequence of ESP setting(refer to section 4),
this test is passed.
Cannot reach.
Can not reach.
Test Limits
RS485 “EC16” could be found in
design tool.
12. Phantom Power Test
The test will prompt you to check to see if the A or B red LEDs on the phantom cutter PCB are
lit or not. Respond to the prompts as needed. If the LEDs are lit properly for all 8 channels, the
test will be completed.
13. Test Completion.
Once all of
the tests are
completed,
the dialog box
shown below
will appear.
Click the OK button to end the test. You will
get the dialog box shown above. Click OK.
94
Can not found.
Page 95

TEST PROCEDURES
TM
Once the test is complete, open the ControlSpace
that there is no connection, as shown in the examples below. This must be done so that the
chassis will not be configured for pass-through when it gets back to the customer.
Setting of outside of ESP No connection
Write no connection by “connecting”. And disconnect.
software and set the ESP-88 chassis so
Push ok button on ATS Basic Macro dialog.
Then return to first dialog, choose finish or continue.
95
Page 96

TEST PROCEDURES
Device under test According to OT1-400338
Serial Number ESP-1
Lot
Date of test 2005,03,13
Tester's Name
CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 CH5 CH6 CH7 CH8
AMPL 4.17 4.02 3.94 4.11 3.92 3.94 4.00 3.95
Nois -80.03 -80.13 -80.05 -80.04 -81.30 -81.23 -81.30 -81.32
FRQ20K
3.39 3.08 3.05 3.15 2.87 2.98 2.74 3.04
FRQ20 3.66 3.50 3.41 3.61 3.44 3.47 3.54 3.48
Result
Passed
5-1.(GV=0dB)
Device under test According to OT1-400338-1
Serial Number
Lot
Date of test
Tester's Name
CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 CH5 CH6 CH7 CH8
AMPL
Nois
FRQ20K
FRQ20
Result
FAIL
5-1.(GV=0dB)
13. Viewing the test results.
The log data that was obtained by the ATS2 macro must be evaluated by opening the Excel
sheet that was described in section “4-10. Pass/Fail evaluation and report of this test.”
When this sheet shows that the unit has passed test, it can be returned to the customer.
If the test is failed, retest or repair the ESP.
Print out the results of the Excel sheet and place it with the unit to be shipped back to the
customer. The passed Excel test sheet and text (.txt) log file should be archived so that there is
a record of the unit passing test.
96
Page 97

Figure 8. Motherboard Top Etch
Layout Diagram
Figure 9. Motherboard VCC Etch
Layout Diagram
97
Page 98

Figure 10. Motherboard GND Etch
Layout Diagram
Figure 11. Motherboard Bottom Etch
Layout Diagram
98
Page 99

Figure 12. MIC/Line Input PCB Topside Etch
Layout Diagram
Figure 13. MIC/Line Input PCB VCC Etch
Layout Diagram
99
Page 100

Figure 14. MIC/Line Input PCB GND Etch
Layout Diagram
Figure 15. MIC/Line Input PCB Bottom Etch
Layout Diagram
100
 Loading...
Loading...