Page 1

Application Note
Slave Controller
Section I – Technology
(Online at http://www.beckhoff.com)
Section II – Register Description
(Online at http://www.beckhoff.com)
Section III – Hardware Description
(Online at http://www.beckhoff.com)
Application Note – PHY Selection Guide
Requirements to Ethernet PHYs used for EtherCAT
Ethernet PHY Examples
EtherCAT over optical links (FX)
Version 2.3
Date: 2014-02-03
Page 2

DOCUMENT ORGANIZATION
Version
Comment
1.1pre
First preliminary release
1.2
Ethernet PHY requirements revised (e.g., link loss reaction time)
Added Micrel KSZ8001L
Added National Semiconductor DP83848, DP83849, and DP83640
Editorial changes
1.3
Added restriction to enhanced link configuration: RX_ER has to be asserted
outside of frames (IEEE802 optional feature)
Removed National Semiconductor DP83848 and DP83849 temporarily for
further examination
1.4
Updated/clarified PHY requirements, PHY link loss reaction time is mandatory
Added National Semiconductor DP83848, DP83849 with comments
Added PHYs which require Enhanced Link detection to be activated
Editorial changes
1.5
PHY startup should not rely on MDC clocking
Added Micrel KSZ8041NL/TL Rev. A4 to list of example Ethernet PHYs for
EtherCAT with Enhanced Link Detection requirement
ESD tolerance and baseline wander compensation recommendations added
Editorial changes
1.6
Completely revised and enhanced compatibility table
Editorial changes
1.7
Added restrictions for ET1100/ET1200 and PHYs which require Enhanced Link
Detection: PHY address offset must be 0
PHY address offset for Teridian PHYs and Micrel KSZ8041 corrected
1.8
Added Micrel KSZ8051 PHYs
Link loss reaction time of Broadcom BCM5241is higher than data sheet reports
Clarified suitability of some Micrel/National Semiconductor PHYs for ET1100,
ET1200
Changed footnote: Microchip PIC10 is expected to be not suitable for
management address conversion during an access (PIC10 remains suitable for
adding an extra MCLK cycle)
2.0
Micrel KSZ8051: update to rev. A2
Micrel KSZ8721: LED1 speed behavior comments added
Texas Instruments (formerly National Semiconductor) DP83848/DP83849
comment on clock supply added
Renesas µPD60610, µPD60611, µPD60620, µPD60621 added
SMSC LAN8700 added
STMicroelectronics STE802RT1A/B PHYs added
Texas Instruments DP83620/ DP83630 added
Added chapter about EtherCAT over optical links
Added chapter about Gigabit Ethernet PHYs
Enhanced recommendations for Ethernet PHYs
Added recommendations to FX transceivers used for EtherCAT
2.1
Added Texas Instruments TLK105, TLK106, and TLK110
Added Micrel KSZ8081MNX,KSZ8081 MLX
Removed Micrel KSZ8721: not recommended for new designs by Micrel (Micrel
recommends KSZ8051 or KSZ8081 instead)
Renesas µPD60610, µPD60611, µPD60620, µPD60621 updated
Added IC Plus Corp. IP101G
IEEE802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet must not be used
Added required PHY signals table
Updated to ET1100-0003/ET1200 -0003
Trademarks
Beckhoff®, TwinCAT®, EtherCAT®, Safety over EtherCAT®, TwinSAFE® and XFC® are registered trademarks of and licensed by
Beckhoff Automation GmbH. Other designations used in this publication may be trademarks whose use by third parties for their
own purposes could violate the rights of the owners.
Patent Pending
The EtherCAT Technology is covered, including but not limited to the following German patent applications and patents:
DE10304637, DE102004044764, DE102005009224, DE102007017835 with corresponding applications or registrations in
various other countries.
Disclaimer
The documentation has been prepared with care. The products described are, however, constantly under development. For that
reason the documentation is not in every case checked for consistency with performance data, standards or other
characteristics. In the event that it contains technical or editorial errors, we retain the right to make alterations at any time and
without warning. No claims for the modification of products that have already been supplied may be made on the basis of the
data, diagrams and descriptions in this documentation.
Copyright
© Beckhoff Automation GmbH 02/2014.
The reproduction, distribution and utilization of this document as well as the communication of its contents to others without
express authorization are prohibited. Offenders will be held liable for the payment of damages. All rights reserved in the event of
the grant of a patent, utility model or design.
DOCUMENT ORGANIZATION
The Beckhoff EtherCAT Slave Controller (ESC) documentation covers the following Beckhoff ESCs:
ET1200
ET1100
EtherCAT IP Core for Altera® FPGAs
EtherCAT IP Core for Xilinx® FPGAs
ESC20
The documentation is organized in three sections. Section I and section II are common for all Beckhoff ESCs,
Section III is specific for each ESC variant.
The latest documentation is available at the Beckhoff homepage (http://www.beckhoff.com).
Section I – Technology (All ESCs)
Section I deals with the basic EtherCAT technology. Starting with the EtherCAT protocol itself, the frame
processing inside EtherCAT slaves is described. The features and interfaces of the physical layer with its two
alternatives Ethernet and EBUS are explained afterwards. Finally, the details of the functional units of an ESC
like FMMU, SyncManager, Distributed Clocks, Slave Information Interface, Interrupts, Watchdogs, and so on,
are described.
Since Section I is common for all Beckhoff ESCs, it might describe features which are not available in a specific
ESC. Refer to the feature details overview in Section III of a specific ESC to find out which features are
available.
Section II – Register Description (All ESCs)
DOCUMENT HISTORY
Section II contains detailed information about all ESC registers. This section is also common for all Beckhoff
ESCs, thus registers, register bits, or features are described which might not be available in a specific ESC.
Refer to the register overview and to the feature details overview in Section III of a specific ESC to find out
which registers and features are available.
Section III – Hardware Description (Specific ESC)
Section III is ESC specific and contains detailed information about the ESC features, implemented registers,
configuration, interfaces, pinout, usage, electrical and mechanical specification, and so on. Especially the
Process Data Interfaces (PDI) supported by the ESC are part of this section.
Additional Documentation
Application notes and utilities like pinout configuration tools for ET1100/ET1200 can also be found at the
Beckhoff homepage.
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide II
Page 3

CONTENTS
Version
Comment
2.2
Update to EtherCAT IP Core V3.0.2/V3.00c with FX support
RX_ER is required for EtherCAT
Editorial changes
2.3
Renesas µPD60610/µPD60611: Auto-TX-Shift required (data sheet was
updated)
Renesas µPD60610/µPD60611/ µPD60620/µPD60621: MI link detection and
configuration can only be enabled with certain IP Core versions
Texas Instruments TLK105/TLK106/TLK110: MI link detection and configuration
must not be enabled
Micrel PHYs: added notes for an internal pull-up resistor at MCLK pin
Added note for PHYs with Enhanced link detection recommendation
Editorial changes
CONTENTS
1 Overview 1
2 Ethernet PHY Requirements 2
3 PHY Connection 3
3.1 Required Ethernet PHY signals 3
4 Example Ethernet PHYs 4
4.1 Enhanced Link Detection 4
4.2 Auto TX Shift 4
4.3 Example Ethernet PHYs 5
5 EtherCAT over Optical Links (FX) 7
6 Gigabit Ethernet PHYs 9
7 Appendix 9
4.4 Examples of Ethernet PHYs assumed to be incompatible with EtherCAT requirements
7
5.1 ESCs with native FX support 7
5.2 ESCs without native FX support 7
5.2.1 Standard Link Detection 7
5.2.1.1 Issue: Temporary Enhanced Link Detection while EEPROM is loading
8
5.2.1.2 Minimum solutions with Standard Link Detection 8
5.2.2 Enhanced FX Link Detection 8
5.2.2.1 Proposed solutions with Enhanced Link Detection 9
7.1 Support and Service 9
7.1.1 Beckhoff’s branch offices and representatives 9
7.2 Beckhoff Headquarters 9
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide III
Page 4
Overview
DVI
IPC
..
..
DVI
IPC
..
..
DVI
IPC
..
..
EtherCAT Segment (Slaves)Master
vom Masterfrom Master
to Master
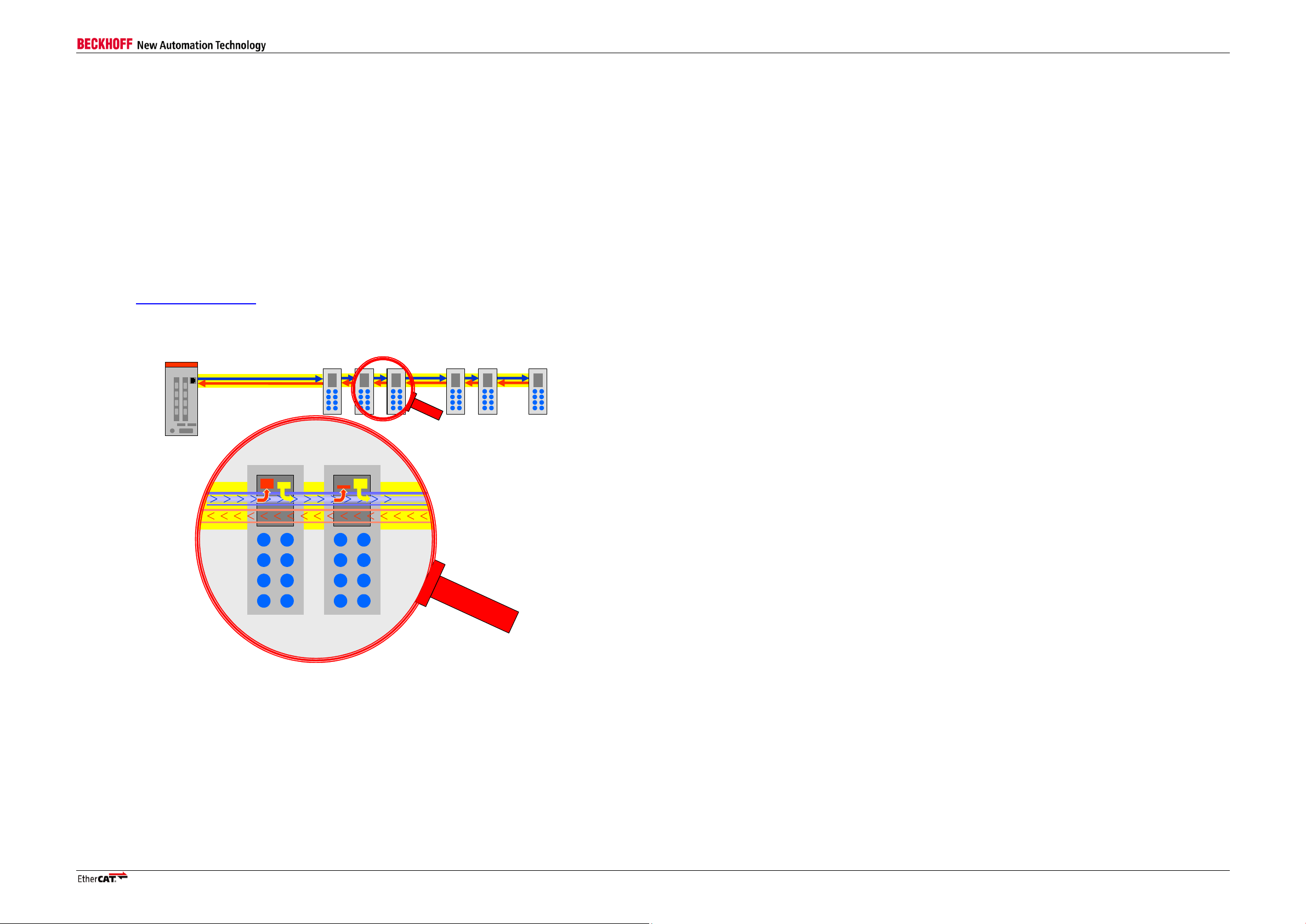
1 Overview
An EtherCAT Slave Controller (ESC) takes care of the EtherCAT communication as an interface between the
EtherCAT fieldbus (Ethernet) and the slave application. EtherCAT uses standard Fast Ethernet. Transmission
speed for EtherCAT is fixed to 100 Mbit/s with Full Duplex communication. EtherCAT Slave Controllers process
Ethernet frames on the fly.
This application note provides an overview of the requirements to Ethernet PHYs used for EtherCAT devices.
An example list of Ethernet PHYs currently expected to be suitable for EtherCAT is also provided.
This application note applies to the following Beckhoff EtherCAT Slave Controllers:
ET1200-0003
ET1100-0003
EtherCAT IP Core for Altera®/Xilinx® FPGAs V3.0.2/V3.00c and later
ESC10/20
Refer to the ESC data sheets for further information. The ESC data sheets are available from the Beckhoff
homepage (http://www.beckhoff.com).
Figure 1: EtherCAT Segment
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide 1
Page 5

Ethernet PHY Requirements
1
2
3
4
2 Ethernet PHY Requirements
ESCs which support Ethernet Physical Layer use MII interfaces, some do also support the RMII interface. Since
RMII PHYs include TX FIFOs, they increase the forwarding delay of an EtherCAT slave device as well as the
jitter. RMII is not recommended due to these reasons.
EtherCAT and Beckhoff ESCs have some general requirements to Ethernet PHYs, which are typically fulfilled
by state-of-the-art Ethernet PHYs.
The MII interfaces of Beckhoff ESCs are optimized for low processing/forwarding delays by omitting a
transmit FIFO. To allow this, the Beckhoff ESCs have additional requirements to Ethernet PHYs, which
are easily accomplished by several PHY vendors.
Refer to Section III of the ESC documentation for ESC specific information about supported features.
Requirements to Ethernet PHYs used for EtherCAT:
The PHYs have to comply with IEEE 802.3 100BaseTX or 100BaseFX.
The PHYs have to support 100 Mbit/s Full Duplex links.
The PHYs have to provide an MII (or RMII1) interface.
The PHYs have to use autonegotiation in 100BaseTX mode.
The PHYs have to support the MII management interface.
The PHYs have to support MDI/MDI-X auto-crossover in 100BaseTX mode.
PHY link loss reaction time (link loss to link signal/LED output change) has to be faster than 15 µs to
enable redundancy operation2.
The PHYs must not modify the preamble length.
The PHYs must not use IEEE802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet.
The PHYs must offer the RX_ER signal (MII/RMII) or RX_ER as part of the RX_CTL signal (RGMII).
Additional requirements to Ethernet PHYs used with Beckhoff ESCs:
The PHYs have to provide a signal indicating a 100 Mbit/s (Full Duplex) link3, typically a configurable
LED output. The signal polarity is active low or configurable for some ESCs.
The PHY addresses should be equivalent to the logical port number (0-3). Some ESCs also support a
fixed offset (e.g. offset 16, PHY addresses are logical port number plus 16: 16-19), or even an arbitrary
offset. If none of these possibilities can be used, the PHY address should be configured to logical port
number plus 1 (1-4), although some features (e.g., Enhanced Link Detection) can not be used in this case,
because apart from the optional configurable PHY address offset, the PHY addresses are hard-coded inside
the ESCs.
PHY configuration must not rely on configuration via the MII management interface, i.e., required features
have to be enabled after power-on, e.g., by default or by strapping options. PHY startup should not rely on
MII management interaction, i.e., MDC clocking, since many ESCs do not communicate with the PHY via
management interface unless the EtherCAT master requests this (only the EtherCAT IP Core with MI Link
detection and configuration will communicate without master interaction).
Additional requirements to Ethernet PHYs used with Beckhoff ESCs using the MII Interface:
All PHYs connected to one ESC and the ESC itself must share the same clock source. This can be
achieved by sourcing the PHYs from an ESC clock output or by sourcing the PHYs and the ESC from the
same quartz oscillator. The ESC10/20 uses TX_CLK as a clock source, both PHYs have to share the same
quartz oscillator.
The TX_CLK signals of the PHYs must have a fixed phase relation to the clock input of the PHYs with a
tolerance of ±5 ns4, because a TX FIFO is omitted. During operation the phase relation can not change
since the PHYs and the ESC have to share the same clock source. The phase offset is compensated inside
the ESC either manually by configuration or automatic:
Manual TX Shift compensation: ET1100, ET1200, and IP Core provide a TX Shift configuration option
(configurable TX_EN/TXD signal delay by 0/10/20/30 ns) which is used for all MII ports. Thus, all PHYs
connected to one ESC must have the same fixed phase relation between TX_CLK and their clock input.
This is typically true if the same PHY model is used for all ports. The phase relation has to be the same
each time the PHYs are powered on. As the ESC10/20 use TX_CLK as device clock source, configuration
is not necessary, but the requirements for manual TX Shift compensation have to be fulfilled anyway.
Automatic TX Shift compensation: The IP Core supports automatic TX Shift compensation individually for
each port. With automatic TX Shift compensation, the PHYs are not required to have the same fixed phase
relation each time they are powered on.
Recommendations to Ethernet PHYs used for EtherCAT:
Receive and transmit delays should be deterministic, and as low as possible.
Maximum cable length should be ≥ 120 m to maintain a safety margin if the standard maximum cable length
of 100 m is used.
ESD tolerance should be as high as possible (4kV or better)
Baseline wander should be compensated (the PHYs should cope with the ANSI X3.263 DDJ test pattern for
baseline wander measurements at maximum cable length)
The PHYs should detect link loss within the link loss reaction time of 15 µs also if only one of the RX+ and
RX- lines gets disconnected.
The PHYs should maintain the link state regardless of the received symbols, as long as the symbols are
valid.
Ethernet PHYs for 100BaseFX should implement Far-End-Fault (FEF) completely (generation and
detection).
MDC should not incorporate pull-up/pull-down resistors, as this signal is used as a configuration input signal
by some ESCs.
Restriction of Autonegotiation advertisement to 100 Mbit/s / Full Duplex is desirable (configured by
hardware strapping options).
Power consumption should be as low as possible.
I/O voltage: 3.3V should be supported for current ASIC and FPGA ESCs, additional 2.5V/1.8V I/O support is
recommended for recent FPGA ESCs.
Single power supply according to I/O voltage.
The PHY should use a 25 MHz clock source (quartz oscillator or ESC output).
Industrial temperature range should be supported.
NOTE: The following requirements defined by IEEE802.3 have to be observed:
a) the preamble length should be maintained. Accumulating preamble reduction below 2 bytes including Start-of-FrameDelimiter/SFD (0x55 5D) must not occur for single or cascaded ESCs. ESCs can not regenerate preambles to 8 bytes
including SFD because of the on-the-fly processing: received and transmitted preamble length is identical.
b) receive and transmit delays should comply with the standard (RX delay should be below ~320 ns, TX delay below ~140
ns),
c) MII Management interface should not require additional MCLK cycles or continuous MCLK.
Recommendations to FX transceivers used for EtherCAT:
The transceiver should have an input for disabling the transceiver/transmitter (for Enhanced FX link
detection; e.g. enable, power-down or reset).
RMII is only supported by the EtherCAT IP Core
This can either be achieved by a PHY with such a link loss reaction time or by activating Enhanced link detection if the
PHY asserts RX_ER both inside and outside of frames for each invalid symbol. Enhanced link detection requires proper
PHY address configuration.
If a combined signal (100 MBit/s link with Full Duplex) is not available, a signal indicating 100 Mbit/s speed might be used.
Take care that the speed signal is inactive (10 Mbit/s) in case of no link. If only a Link signal is available, this might be used.
Never use (combined) activity signals. Some PHYs toggle the 100 Mbit/s speed signal during autonegotiation, this is a
problem for hot-connecting. Use the link signal in this case.
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide 2
The ±5ns tolerance is valid for PHYs using the IEEE802.3 TX specification (TX signal change is allowed in a time window
of 25 ns, TX signals are stable in a window of 15 ns). If the PHY has a larger window for changing the TX signals (25 ns + x),
the tolerance will be ±(5ns + x/2).
Page 6

PHY Connection
Ethernet PHY
25 MHz
OSC_OUT
OSC_IN CLK25OUT
RX_DV
RXD[3:0]
RX_ER
TX_EN*
TXD[3:0]*
RX_CLK
RX_DV
RXD[3:0]
RX_ER
TX_EN
TXD[3:0]
RX_CLK
TX_CLK
CLK25
CRS
TX_ER
COL
LINK_MII LINK_STATUS
25 MHz
Option: one quartz oscillator for
ESC and PHYs
MDIO
MDC*
MDIO
MDC
4K7
V
CC I/O
* Configuration input (ESC dependent)
TX signal delay
configuration
0 ns
10 ns
20 ns
30 ns
TX_CLK
IP Core opt. with
Auto-TX-Shift:
ESC
5
Signal
Required
Comment
CLK25
Mandatory
Shared 25 MHzclock source between ESC and PHY
LINK_STATUS
Mandatory
LINK LED signal, required for fast link loss reaction time
RX_CLK
Mandatory
RX_DV
Mandatory
RXD[3:0]
Mandatory
RX_ER
Mandatory
Required for error detection and error source localization
COL
Not used
EtherCAT uses full duplex only
CRS
Not used
EtherCAT uses full duplex only
TX_CLK
Optional
Optional for automatic TX Shift compensation
TXD[3:0]
Mandatory
TX_ER
Not used
Connect to GND
MDIO
Optional
Recommended especially for debugging
MDC
Optional
Recommended especially for debugging
Signal
Required
Comment
REF_CLK
Mandatory
Shared 50 MHz clock source between ESC and PHY
LINK_STATUS
Mandatory
LINK LED signal, required for fast link loss reaction time
CRS_DV
Mandatory
RXD[1:0]
Mandatory
RX_ER
Mandatory
Required for error detection and error source localization
TX_EN
Mandatory
TXD[1:0]
Mandatory
MDIO
Optional
Recommended especially for debugging
MDC
Optional
Recommended especially for debugging
3.1 Required Ethernet PHY signals
3 PHY Connection
Figure 2 shows the principle connection between ESC5 and PHY. The clock source of Ethernet PHYs and ESC
has to be the same quartz or quartz oscillator. TX_CLK is usually not connected unless automatic TX Shift
compensation is used, because the ESCs do not incorporate a TX FIFO. The TX signals can be delayed inside
the ESC for TX_CLK phase shift compensation. LINK_STATUS is an LED output indicating a 100 Mbit/s (Full
Duplex) link.
Refer to ESC data sheet Section III for details about Ethernet PHY connection of a specific ESC.
Table 1: Required Ethernet PHY signals using MII
Table 2: Required Ethernet PHY signals using RMII
Figure 2: PHY Connection
ESC10/20 uses TX_CLK of a PHY as the clock source of the ESC. FPGAs with IP Core only support the quartz oscillator
alternative.
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide 3
Page 7

Example Ethernet PHYs
4 Example Ethernet PHYs
In this chapter, some example Ethernet PHYs which are assumed to fulfill the EtherCAT requirements are
presented, as well as an overview of Ethernet PHYs which are assumed to not fulfill these requirements. These
lists represent a current collection of information from data sheets, vendors, and basic hardware tests for some
devices, and they represent the best of current knowledge. These lists do not imply any kind of certification for
EtherCAT, since none of these PHYs has been tested thoroughly to fulfill each individual EtherCAT or
IEEE802.3 requirement. These lists are only intended for sharing current information about Ethernet PHYs for
EtherCAT, and they are still work-in-progress.
The Ethernet PHYs were either judged by a brief overview of their data sheets or by additional basic hardware
communication tests (basic hardware communication tests are indicated in the table).
The example Ethernet PHYs for EtherCAT shown in the following tables are sorted alphabetically by vendor
name, not by preference. The selection of Ethernet PHYs was restricted to 1-4 port 10/100 Mbit/s Ethernet
PHYs. These tables are incomplete in terms of Ethernet PHY vendors and Ethernet PHY devices – they just
give some examples, and it is likely that other devices and devices from different vendors meet the
requirements as well.
It can not be guaranteed that the mentioned Ethernet PHYs, future revisions of them, or product changes are or
will be fully EtherCAT compatible or not, nor that they are compatible with individual ESCs – because of ESC
specific options (e.g., configurable link polarity, supported PHY address offsets, Enhanced Link detection,
automatic TX Shift compensation). As far as known, restrictions and features of the PHYs impacting their
EtherCAT usage are added to the tables.
Table 1 indicates for which ESC the PHY is assumed to be suitable, and which features have to be enabled and
which settings have to be made for the ESC/PHY combination.
4.1 Enhanced Link Detection
Some Ethernet PHYs require Enhanced Link Detection to be activated in order to achieve sufficient link loss
reaction times.
PHYs which require Enhanced Link Detection to be activated are marked in the following table. Enhanced Link
Detection is generally recommended because additional faults are detected and link loss reaction time is
improved.
4.2 Auto TX Shift
Some Ethernet PHYs cannot guarantee a fixed phase relation between their clock input and TX_CLK. The Auto
TX Shift feature compensates these phase shift variations, as long as the phase shift is at least constant while
the link is up. Auto TX Shift is not equivalent to a TX FIFO, it is just a controlled output phase for the TX signals.
ESC and PHY have to share the same clock source anyway.
PHYs which require Auto TX Shift to be activated are marked in the following table.
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide 4
Page 8

Example Ethernet PHYs
Vendor / Device
ET1200
suitable
ET1100
suitable
IP Core
suitable
# Ports
Basic
HW
test6
TX_CLK fixed
phase7
PHY
addr.8
PHY addr.
offset9
Link loss
reaction time
Enhanced Link
Detection
Auto-TX-Shift
(IP Core only)
Comments
Broadcom
BCM5221
X X X 1
yes
(Data sheet10)
0-31 0 1.3 µs
recommended11
Requires additional write clock on MDC. Quartz oscillator required. Internal pull-down at MDC.
BCM5222
X X X 2
yes (Data sheet)
0-31 0 1.3 µs
recommended11
Requires additional write clock on MDC. Quartz oscillator required. Internal pull-down at MDC.
BCM5241
X X X 1 yes
yes (Data sheet)
0-7, 8,
16, 24
0
45 µs
required
Requires additional write clock on MDC. Quartz oscillator required. Internal pull-up at MDC. XTALI
voltage ≤ 1.8V.
Cortina Systems
LXT973
(X12)
(X12) X 2
yes
Measurement12
0-31 0 1.9 ms
required
provisionally
12
Davicom Semiconductor
DM9161B
X 1 0-31 0
provisionally
provisionally
IC Plus Corp.
IP101ALF
X 1 0-31 0
provisionally
provisionally
Link signal depends on PHY address.
IP101G
X 1 0, 1, x
0 provisionally
provisionally
Link signal depends on PHY address. Max. 3 ports usable because of PHY addresses.
Marvell
88E3015/
88E3018
- - X 1
no
0-31 0
provisionally
required
Micrel
KSZ8001L
X X X 1
yes (Vendor)
1-31
ET1100/
ET1200: 0
IP: 16
provisionally
PHY addr. 0 = Broadcast.
ET1100/ET1200: if port 0 is used, set PHY addresses to 1-4, PHY address offset to 0. Disable
Enhanced link detection or add CPLD/uC for address conversion.
IP Core: Set PHY address offset = 16 and use PHY addresses 16-19.
The KSZ8001 might have a pull-up resistor at the MCLK pin, which might interfere with an external pulldown resistor for strapping.
KSZ8041TL Rev. A4
KSZ8041NL Rev. A4
X X X 1
yes (Vendor)
1-7
ET1100/
ET1200: 0
IP: 1
10 µs
recommended11
PHY addr. 0 = Broadcast. Enable 8 byte preamble with CONFIG[2:0]=100 (was PCS Loopback in Rev.
A3).
ET1100/ET1200: if port 0 is used, set PHY addresses to 1-4, PHY address offset to 0. Disable
Enhanced link detection or add CPLD/uC for address conversion.
IP Core: Set PHY address offset = 1 and use PHY addresses 1-4.
The KSZ8041 might have a pull-up resistor at the MCLK pin, which might interfere with an external pulldown resistor for strapping.
KSZ8051 MLL Rev. A2
KSZ8051 MNL Rev. A2
X X X 1
yes (Vendor)
0-7 0 5.3 µs
recommended11
Enable B_CAST_OFF to support PHY addr. 0 (otherwise PHY addr. 0 = Broadcast).
Rev. A2 has a fixed TX_CLK phase.
The KSZ8051 might have a pull-up resistor at the MCLK pin, which might interfere with an external pulldown resistor for strapping.
KSZ8081MNX
KSZ8081MLX
X X X 1
yes (Data sheet)
0-7 0 4.4 µs
recommended11
Enable B_CAST_OFF to support PHY addr. 0 (otherwise PHY addr. 0 = Broadcast).
The KSZ8081 has a pull-up resistor at the MCLK pin, which might interfere with an external pull-down
resistor for strapping.
Realtek
RTL8201N
- - X 1
no
1-31
16 provisionally
required
PHY addr. 0 = Power down.
RTL8201DL
- - X 1
no
0-7 0
provisionally
required
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
4.3 Example Ethernet PHYs
Table 3: Example Ethernet PHYs assumed to fulfill EtherCAT requirements
The following requirements were not part of the basic hardware test: MDI/MDI-X auto-crossover, MII management interface, TX clock phase relation, and preamble length maintenance. These requirements are assumed to be fulfilled either according to the data
sheet or vendor notice. Hardware tests are typically performed with only one of the ESC types, e.g., IP Core.
Information about fixed phase shift between TX_CLK and PHY clock source from data sheet or from vendor
PHY address range supported by PHY. Special PHY addresses are excluded (Broadcast/Isolate/Power down).
Suggested PHY address offset. ET1100 and ET1200 only support a PHY address offset of 0 or 16. A PHY address offset of 0 means PHY addresses 0-3 are used, an offset of 16 means PHY addresses 16-19 are used, etc..
Only for XTALI, not approved for REF_CLK. According to Broadcom, a quartz oscillator can be connected to XTALI as well.
Recommended for IP Core only. Do not enable for ET1100/ET1200.
Measurements from the vendor with some LXT973 indicated that there is a fixed TX_CLK phase relation, but a general statement could not be made. It is assumed that Auto-TX-Shift is not required and that ET1200/ET1100 are supported, but provisionally Auto-
TX-Shift should be turned on.
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide 5
Page 9

Example Ethernet PHYs
Vendor / Device
ET1200
suitable
ET1100
suitable
IP Core
suitable
# Ports
Basic
HW
test6
TX_CLK fixed
phase7
PHY
addr.8
PHY addr.
offset9
Link loss
reaction time
Enhanced Link
Detection
Auto-TX-Shift
(IP Core only)
Comments
Renesas
µPD60610/µPD60611
- - X 1
no
0/8/16
/24
0
3 x RX_ER
(120 ns)
not necessary
required
Link loss reaction time configurable via MII management interface. Enhanced Link Detection cannot be
used with more than 1 port, because PHY addresses are not consecutive.
MI Link detection and configuration can only be enabled for tolerant IP Cores (starting with
V2.4.3/V2.04d and V3.0.2/V3.00c)
µPD60620/µPD60621
X X X 2
yes (Data sheet)
0/8/16
/24+1
0
3 x RX_ER
(120 ns)
not necessary
Link loss reaction time configurable via MII management interface; Set P1TXCL=0 for fixed TX_CLK
phase shift. Enhanced Link Detection cannot be used with more than 1 port, because PHY addresses
are not consecutive.
EtherCAT support starts with order number UPD60620AGK-GAK-AX / UPD60621AGK-GAK-AX.
MI Link detection and configuration can only be enabled for tolerant IP Cores (starting with
V2.4.3/V2.04d and V3.0.2/V3.00c)
SMSC/Microchip
LAN8187
- - X 1
no (Vendor)
0-31 0
provisionally
required
Link signal depends on PHY address.
LAN8700
- - X 1
no (Vendor)
0-31 0
provisionally
required
Link signal depends on PHY address.
LAN8710
X 1
no
0-7 0
provisionally
provisionally
STMicroelectronics
STE101P
- - X13 1 1-31
16 provisionally
provisionally
PHY addr. 0 = Isolate. MDC clock transition required to complete reset phase (MI Link Detection and
Configuration required). Link signal depends on PHY address.
STE802RT1A/B
- - X13 1
yes (Vendor)
1-31
16 provisionally
PHY addr. 0 = Isolate. MDC clock transition required to complete reset phase (MI Link Detection and
Configuration required).
Teridian
78Q2123
78Q2133
X 1 0/1 0
provisionally
provisionally
PHY addr. 0 = Broadcast. Only for single port devices, because only one PHY address can be used.
Texas Instruments
DP83620/
DP83630/
DP83640
X X X 1
yes (Vendor)
1-31
ET1100/
ET1200: 0
IP: 16
250 µs (conf.
to ~1.3 µs)
required
PHY addr. 0 = Isolate. Do not use SCMII mode. Use LED_LINK for link detection. Reset controller
required if clock sourced by ESC.
ET1100/ET1200: if port 0 is used, set PHY addresses to 1-4, PHY address offset to 0, add CPLD/uC
for address conversion.
IP Core: Set PHY address offset = 16 and use PHY addresses 16-19.
DP83848
X X X 1 yes
yes (Vendor)
1-31
ET1100/
ET1200: 0
IP: 16
250 µs
required
PHY addr. 0 = Isolate. Use LED_LINK for link detection.
ET1100/ET1200: if port 0 is used, set PHY addresses to 1-4, PHY address offset to 0, add CPLD/uC
for address conversion. X1 must be stable for min. 167 µs, need reset controller if CLK25Out is used
and resets are connected.
IP Core: Set PHY address offset = 16 and use PHY addresses 16-19.
DP83849
X X X 2
yes (Vendor)
0-31 0 250 µs
required
Do not use SCMII mode. Use LED_LINK for link detection. X1 must be stable for min. 167 µs, need
reset controller if CLK25Out is used and resets are connected.
TLK100
- - X 1
no
0-31 0 500 µs
required
required
TX_CLK phase changes at each link up.
TLK105
X X X 1
yes (Data sheet)
0-31
0
200 µs (conf.
to <10 µs)
required
Fast Link Down mode with 10 µs reaction time is supported (requires configuration via MII
management, default is 200 µs). Recommended configuration for Fast Link Down mode in CR3:
enable Bit 3 (RX Error count) and Bit 0 (Signal/Energy loss).
MI Link detection and configuration must not be used, because register 9 is PHY specific.
TLK106
X X X 1
yes (Data sheet)
0-31
0
200 µs (conf.
to <10 µs)
required
Fast Link Down mode with 10 µs reaction time is supported (requires configuration via MII
management, default is 200 µs). Recommended configuration for Fast Link Down mode in CR3:
enable Bit 3 (RX Error count) and Bit 0 (Signal/Energy loss).
MI Link detection and configuration must not be used, because register 9 is PHY specific.
TLK110
X X X 1
yes (Data sheet)
0-31
0
200 µs (conf.
to <10 µs)
required
Fast Link Down mode with 10 µs reaction time is supported (requires configuration via MII
management, default is 200 µs). Recommended configuration for Fast Link Down mode in SWSCR3:
enable Bit 3 (RX Error count) and Bit 0 (Signal/Energy loss).
MI Link detection and configuration must not be used, because register 9 is PHY specific.
13
MI link detection and configuration required.
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide 6
Page 10

EtherCAT over Optical Links (FX)
Ethernet PHY
Port 0
nPHY_RESET_OUT(0) nRESET
ESC Transceiver Port 0
MDC/MDIO MDC/MDIO
V
CC
Vcc
nReset
Ethernet PHY
Port 1
nRESET
Transceiver Port 1
MDC/MDIO
V
CC
Vcc
nReset
nPHY_RESET_OUT(1)
4.4 Examples of Ethernet PHYs assumed to be incompatible with EtherCAT requirements
The following Ethernet PHYs are currently assumed or known to be incompatible with EtherCAT – because
they do not support MDI/MDIX-auto-crossover which became state-of-the-art for many recent PHYs:
AMD Am79C874, Am79C875 (datasheet: no MDI/MDIX-auto-crossover)
Broadcom BCM5208R (datasheet: no MDI/MDIX-auto-crossover)
BCM5214 (datasheet: only RMII/SMII interface)
Cortina Systems LXT970A, LXT971A, LXT972A, LXT972M, LXT974, LXT975 (datasheet:
no MDI/MDIX-auto-crossover)
Davicom Semiconductor DM9761 (datasheet: no MDI/MDIX-auto-crossover)
Marvell 88E3016 (datasheet: only RGMII interface)
Micrel KSZ8041 Rev. A3 (hardware test: no preamble maintenance) and maybe
previous revisions
SMSC/Microchip LAN83C185 (datasheet: no MDI/MDIX-auto-crossover)
STMicroelectronics STE100P (datasheet: no MDI/MDIX-auto-crossover)
Teridian 78Q2120C (datasheet: no MDI/MDIX-auto-crossover)
VIA Technology VT6103F, VT6303L (datasheet: no MDI/MDIX-auto-crossover)
5 EtherCAT over Optical Links (FX)
The intention of this chapter is to share current knowledge about FX operation with EtherCAT. The solutions
and comments are still work-in-progress, they are possibly subject to change or even incomplete. Most of the
presented example schematics have not been implemented in hardware, but they are expected to be working.
5.1 ESCs with native FX support
ESCs with FX support have individual PHY reset outputs for each port. This PHY reset output is intended to
hold the PHY and the transceiver in reset state while the ESC is in reset state, and additionally, to issue a reset
cycle when a link failure is detected by the enhanced link detection mechanism.
If at least one port is configured for FX operation, all ports have to use the individual PHY reset outputs. This is
especially important for enhanced link detection, since all the PHY reset outputs are used for link down
signalling instead of auto-negotiation restart, which is not used anymore – regardless of the port using FX or TX.
Figure 3: PHY reset connection for ESCs with FX support or mixed FX/TX support
5.2 ESCs without native FX support
5.2.1 Standard Link Detection
The Enhanced link detection restarts auto-negotiation between the PHYs if a certain level of receive errors is
reached. With FX PHYs, auto-negotiation is not available (it is a 100Base-TX feature). Typically, PHYs ignore
the restart auto-negotiation request. As a consequence, the EtherCAT slave controller waits endlessly for the
link to go down. Other PHYs might get into a dead-lock, because auto-negotiation is enabled by the restart autonegotiation request, but it will not complete due to the FX operation mode.
Thus, Enhanced Link Detection has to be turned off for FX links (unless Enhanced FX Link Detection is used,
which is recommended. See later for more information). It is strongly recommended to use PHYs which are
supporting Far-end-Fault (FEF) completely if Enhanced link detection is not used (refer to Section I of the ESC
data sheets for more information on FEF).
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide 7
Page 11

EtherCAT over Optical Links (FX)
Ethernet PHY
nRESET nRESET
ESC
Reset
release
delay
>170 ms
Transceiver
MDC/MDIO
RX/TX
MDC/MDIO
V
CC
Vcc
V
CC
Vcc
nReset
Ethernet PHY
nRESET nRESET
ESC
Transceiver
MDC/MDIO
RX/TX
MDC/MDIO
Power delay
>170 ms
V
CC
Vcc Vcc
Vcc
nReset
5.2.1.1 Issue: Temporary Enhanced Link Detection while EEPROM is loading
Enhanced Link Detection is enabled after Reset, and it can only be disabled by EEPROM. This takes about
170 ms. In the meantime, the FX PHYs are powering up. Since they do not need to go through an autonegotiation sequence, the link (signal detect) comes very early. It is possible that the link is detected, but
communication is not possible (RX_ERR are detected). This can trigger the ESC to restart auto-negotiation
before the EEPROM is loaded, resulting in potential PHY problems with the restart auto-negotiation request.
The recommended solution to overcome this issue is to power up the FX PHY (and the transceiver) at least
170 ms after the ESC, e.g. by an additional reset controller with delay or power sequencing (Figure 4 or Figure
5).
Another, recommended solution is the Enhanced FX Link Detection, discussed later.
5.2.1.2 Minimum solutions with Standard Link Detection
These two solutions represent the minimum solution for proper power-up and reset operation, but they have
drawbacks in detection low quality links. The preferred solution is the Enhanced FX Link Detection, see later.
5.2.2 Enhanced FX Link Detection
In order to detect erroneous links fast enough, it is desirable to use the error detection principle of Enhanced
Link Detection also for FX PHYs. One possible solution is to use the Enhanced Link Detection logic inside the
ESC, and another possible solution is to implement enhanced link detection logic with external logic, e.g. a
CPLD.
The preferred solution is to let the ESC count the RX_ERR of the PHY, and to detect the restart autonegotiation request of the ESC by some additional logic (CPLD or µController etc.) attached to the MII
management interface. This logic should reset the PHY and the Transceiver (power-down) for a short time. This
reset causes a link down, which will be detected by the local ESC (which will leave its potential dead-lock state),
and by the communication partner (link down, loop closed). If this solution is chosen, Enhanced Link Detection
can be enabled in the EEPROM.
The MII management interface is still connected to the PHY, the CPLD/µC just snoops the bus. It is possible to
use one CPLD/µC for all ports of the ESC. The PHY address has to be evaluated and individual reset outputs
for each PHY have to be used.
Take care that a reset coming from the ESC also turns at least the transceiver off, in order to enable the
communication partner to close the loop.
NOTE: Some PHYs use the “signal detect” input to switch into FX operation mode. If the transceiver is powered down, the
PHY might not enter FX mode correctly. Other PHYs might not properly keep the auto-negotiation feature turned off,
especially as the ESC tries to enable it with the auto-negotiation restart command. In such a case the PHY is required to be
put into reset or power-down state, too.
Figure 4: PHY reset release delay with transceiver power down/reset
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide 8
Figure 5: PHY power sequencing with transceiver power down/reset
Page 12

Appendix
Transceiver
Ethernet PHY
nRESET nRESET
V
CC
Auto-negotiation
restart detection
ESC
Vcc
nReset
MDC/MDIO
RX/TX
MDC/MDIO
CPLD/µC
Ethernet PHY
nRESET nRESET
V
CC
Auto-negotiation
restart detection
ESC
Transceiver
MDC/MDIO
Vcc
RX/TX
MDC/MDIO
nReset
CPLD/µC
nPOWERDOWN
5.2.2.1 Proposed solutions with Enhanced Link Detection
Figure 6: CPLD/µC detects auto-negotiation restart command and resets PHY and transceiver
7 Appendix
7.1 Support and Service
Beckhoff and our partners around the world offer comprehensive support and service, making available fast and
competent assistance with all questions related to Beckhoff products and system solutions.
7.1.1 Beckhoff’s branch offices and representatives
Please contact your Beckhoff branch office or representative for local support and service on Beckhoff products!
The addresses of Beckhoff's branch offices and representatives round the world can be found on her internet
pages: http://www.beckhoff.com
You will also find further documentation for Beckhoff components there.
7.2 Beckhoff Headquarters
Beckhoff Automation GmbH
Eiserstr. 5
33415 Verl
Germany
Phone: +49 (0) 5246 963-0
Fax: +49 (0) 5246 963-198
E-mail: info@beckhoff.com
Figure 7: CPLD/µC detects auto-negotiation restart command and powers down PHY and transceiver
NOTE: In Figure 7, the CPLD/µC is connected to the nRESET signal of the ESC/PHY to power-down/reset the transceiver
while the ESC/PHY is in reset state.
6 Gigabit Ethernet PHYs
either by strapping options of the PHY or by using the autonegotiation advertisement.
Some ESCs are capable of restricting the autonegotiation advertisement of Gigabit Ethernet PHYs to 100 Mbit/s
full-duplex if MI link detection and configuration is enabled.
Gigabit Ethernet PHYs can generally be used for EtherCAT, as long as the link speed is restricted to 100 Mbit/s,
Nevertheless, all other requirements of EtherCAT have to be fulfilled – especially the link loss reaction time
(Enhanced Link Detection might be required).
Web: www.beckhoff.com
Beckhoff Support
Support offers you comprehensive technical assistance, helping you not only with the application of individual
Beckhoff products, but also with other, wide-ranging services:
world-wide support
design, programming and commissioning of complex automation systems
and extensive training program for Beckhoff system components
Hotline: +49 (0) 5246 963-157
Fax: +49 (0) 5246 963-9157
E-mail: support@beckhoff.com
Beckhoff Service
The Beckhoff Service Center supports you in all matters of after-sales service:
on-site service
repair service
spare parts service
hotline service
Hotline: +49 (0) 5246 963-460
Fax: +49 (0) 5246 963-479
E-mail: service@beckhoff.com
Slave Controller – Application Note PHY Selection Guide 9
 Loading...
Loading...