Page 1
AV250T Service Manual
Contents
chapter One Brief Introduction to Product
General description
Chapter Two Operating Principle
Section One Overall structure
Section Two Volume board
Section Three Signal processing board
Section Four CPU board
Section Five Panel control and display circuit
Section Six Power amplifier board
Section Seven Power board
Section Eight Video board
Chapter Three Servicing Process
1. No output for Karaoke
2. Power supply not connected
3. No on screen display (OSD)
4. No output
Schematic & PCB wiring diagram
Spare parts list
Page 2
Chapter One Brief Introduction to Product
General Description
AV110T is a 5.1CH audio power amplifier for home theatre usage, with the
main features and functions shown as follows:
1) Two-way audio signal input: VCD, DVD;
2) With 5.1CH input terminal, capable of connection with AC-3, DTS decode
output signal;
3) One way subwoofer signal line output, capable of connecting with active
subwoofer speaker;
4) Automatically signal search when power on;
5) 6CH digital volume control and separate channel level adjustment;
6) Three sound field modes: Hi-Fi, Standard and Cyber Logic;
7) Six preset EQ modes, multi-band electronic equalization adjustment snd
scene surround function;
8) Save/Call of user-set parameter;
9) Digital Karaoke, with microphone volume, echo and delay adjustment;
10) Auto mute function;
11) Dynamic display screen; multiple spectrum display modes; English
intelligent operation interface;
12) Bass enhancer function;
13) Digital tuning function;
14) Video switch function;
15) Headphone output function;
16) Full remote control operation.
Page 3
Chapter Two Operating Principle
Section One Overall structure
The whole unit of AV250T is mainly composed of the following parts:
2.1.1 Volume board: input selection, Cyber Logic and bass enhancer control.
2.1.2 Signal processing board: Karaoke signal processing and front stage
amplifying of 5.1Ch signal.
2.1.3 CPU board: whole machine control unit, breadth sampling circuit and
auto searching circuit.
2.1.4 Control panel: VFD display, remote control and keyboard scanning and
fulfill man-machine conversation function.
2.1.5 Power amplifier board: perform power amplifying for 5.1CH signal or
other analog signals.
2.1.6 Power board: supply the working voltage required by each unit circuit,
and over-current/over-voltage protection unit.
2.1.7 Digital tuner: receive radio signal and then send to power amplifier to
perform signal-amplifying processing.
2.1.8 Video input and output board: fulfill video input/output and video switch
function.
Section Two Volume board
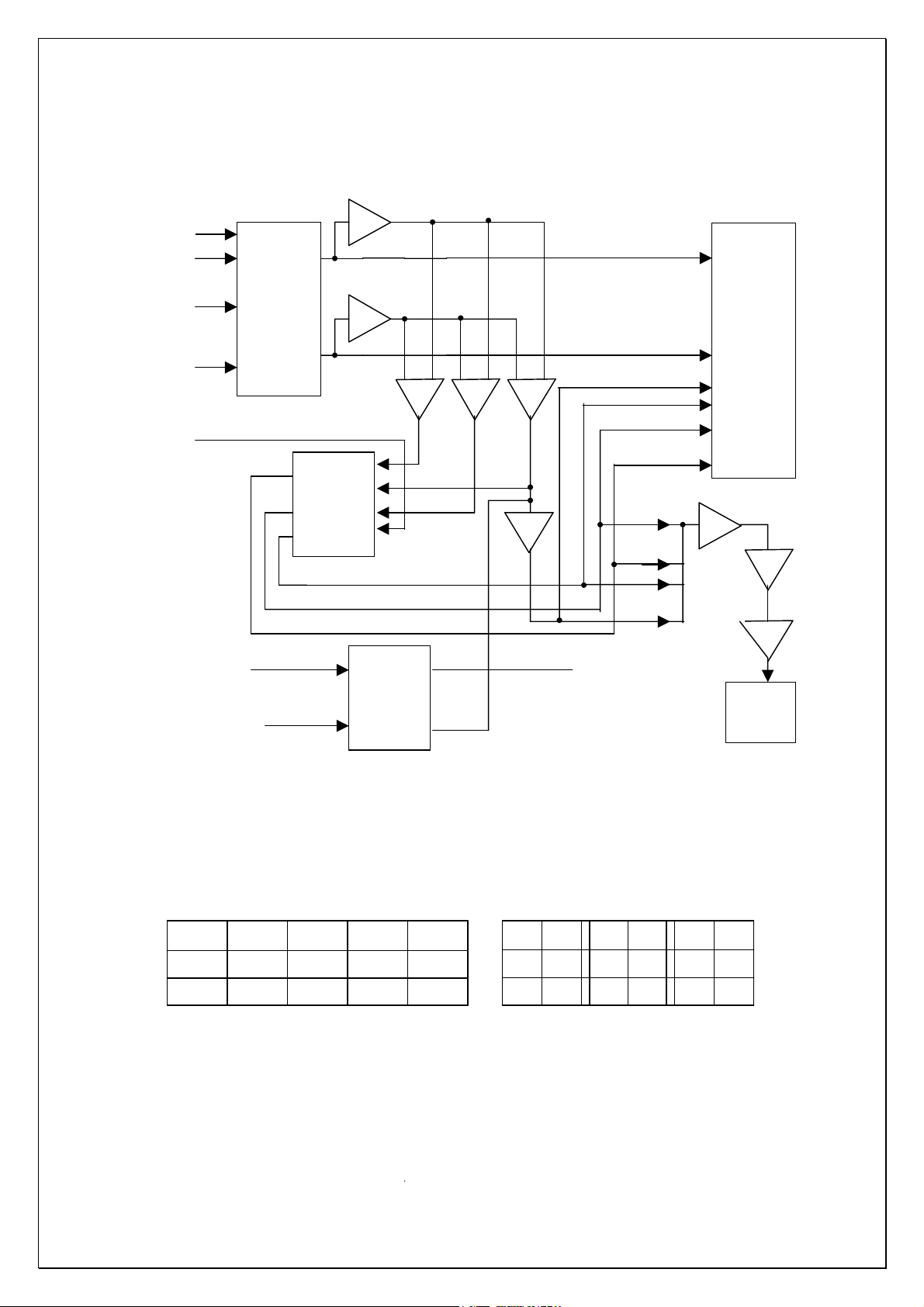
AV250T has 4 kinds of input modes in all: FM/AM, VCD, DVD and 5.1CH.
Page 4
By sampling from L/R channel of AV250T, after Cyber Logic function, C, SL
A
A
L
and SW channel signals are achieved. In this circuit, electronic analog switch
is adopted to fulfill the switch in all states, and the signal flow chart is as
FM/AM
VCD
5.l input
L, R
Channel
5.1 input
C, SR, S
channel
CD4052
Input
selection
SL
SR
c
CD4053
Electronic
switch
L
R
SW
C
SR
SL
15
13
6
11
8
9
N106
M62446
Electronic
volume
adjustment
N108B
N103A
N103B
5.1 input
SW CH
SW1
CD4053
Electronic
switch
SW
Send to L/R
SEARCH
N100
CPU
follows:
2.2.1 Input selection and sound field processing mode
The input selection of AV250T is achieved via electronic switches CD4052
and CD4053, and the truth tables are as follows:
CD4052 Truth table
Tuner VCD DVD 5.1
B
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
1
CD4053 Truth table
XBYC
0
X0
X1 1
Y0
Y1
0
1
Z
Z0
Z1
5.1CH input mode: Now A/B/5.1CH control pins of M62446 are in high level.
L/R channel signals of 5.1 input terminal is outputted from pin 3/13 of N101
and sent to IC N106 for volume and tone adjustment; meanwhile, C/SR/SL
signals of 5.1CH input terminal are outputted from pin 14/15/4 of N102 and
then respectively sent to IC N106 for independent volume adjustment. And SW
signal of 5.1CH is outputted via pin 4 of N103 and then sent to M62446 after
being amplified by N107A.
Page 5
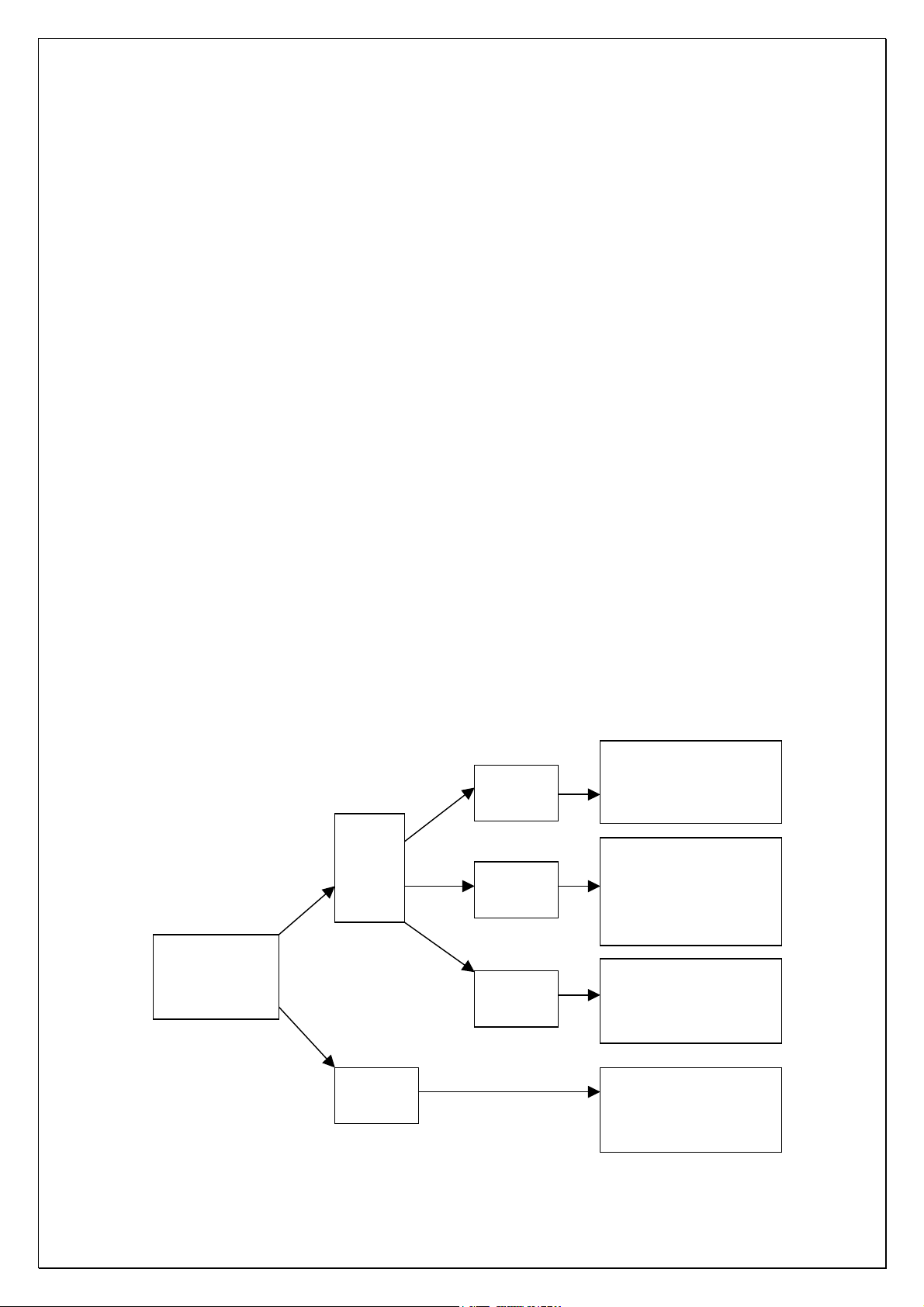
Three analog input modes: AV250T totally has three analog input modes:
T
g
digital tuning demodulation signal, VCD and DVD, which are controlled via A/B
signal respectively.
AV250T totally has three sound field modes: Standard, Cyber Logic and Hi-Fi.
1. Standard: Under the control of overall CPU, when bass enhancer is off, L/R
channel and subwoofer output are available; when bass enhancer is on,
only L/R channel output is available.
2. Hi-Fi: Under the control of overall CPU, only L/R channel output is available
to M62446.
3. Cyber Logic: Pin 9/10 of electronic switch N101 (CD4052) select a group of
analog L/R channel input signals according to the truth table. L/R signals
are outputted from pin 13/3 via the internal electronic switch of N101, and
divided into two ways. One way is respectively sent into pin 13/15 of
M62446 for electronic volume and tone adjustment. The other way
produces SW/S-SR/S-SL and S-C signals via buffer, adder-subtractor and
low-pass filter. S-C/S-SR/S-SL signals are sent to pin 12/2/5 of N102. N102
select Cyber Logic signal input (see CD4053 truth table) from Cyber Logic
and 5.1Ch signals, outputs C/SR/SL signals from pin 14/15/4 and sends
into pin 11/8/9 of M62446 for volume adjustment. Still another way of SW
signal directly sends to pin 6 of M62446 after being outputted from N107A.
5.1CH signal sent into M62446 is outputted from pin 31-36 after volume
and tone adjustment, and then outputted to signal board by XS20 power
distributor.
The relation between sound sources in input circuit and sound processing
modes is as the following figure.
Press INPU
button to select
circularly
Two
analog
input
modes
Hi-Fi
Standard
Cyber
Lo
ic
Only L/R channel output.
Sound field and EQ setup
invalid
Only L/R/SW channel
output. Concert hall
sound field and EQ setup
available
6CH output. Theatre
sound field and EQ setup
available
5.1 input
mode
6CH output. Theatre
sound field and EQ
setup available
Page 6
2.2.2 Control circuit
Pin 23/26/27 of CPU (N100) output data, PVST and clock signals send to pin
39/40/41 of M62446, control pin 1/2/3/4 of M62446 output control level, so as
to select input signal and spectrum sampling signal. It is worth noting that
PVST signal is a latch control signal. When data and clock of CPU are sent to
M62446, an identification signal will be added, indicating that this signal can
only be used by M62446 while other IC of I2C bus cannot use current data and
clock signal.
2.2.3 Frequency spectrum sampling circuit
Only S-C/S-SR/S-SL/SW signals are sampled during frequency spectrum
sampling in AV250T and added to pin 14 of N103 via a 150K sampling resistor.
Another S-C cyber logic signal is added to pin 1 of N103, called S-C'. 5.1CH
and LR-T of M62446 select sampling signals. When cyber logic is selected, the
control signal of 5.1CH is of low level while pin 9/11 of N103 is of low level.
According to the truth table, it is known that the outputs are X0/Z0. Sampling
signal is grounded while LR-T is of H level. Select Y1, S-C'signal is outputted
from pin 15 of N103 to N108B, adding to OK-R signal for the amplification of
frequency spectrum signal, and then sent to frequency point gating and auto
search circuits via XS20.
2.2.4 Tuning function
The tuning function directly controls tuner and receives audio frequency signal
mainly via CPU and then outputs after amplification via power amplifier. The
clock and data line of tuner are shared with LM62446 and the other two control
lines are connected to CPU directly. L, R signal processed by the tuner can be
sent to N101 IC CD4052 directly to input the selected channel.
Section Three Signal processing board
The signal processing board superposes, mixes and amplifies 5.1CH signal
sent from the volume board, voice signal from the voice board and Karaoke
signal.
2.3.1 Karaoke circuit of AV250T
This circuit processes human voice through power amplifier and reproduces it
via speaker. It includes human voice beautification circuit, wide sound field
processing circuit, Karaoke echo and delay adjusting circuit.
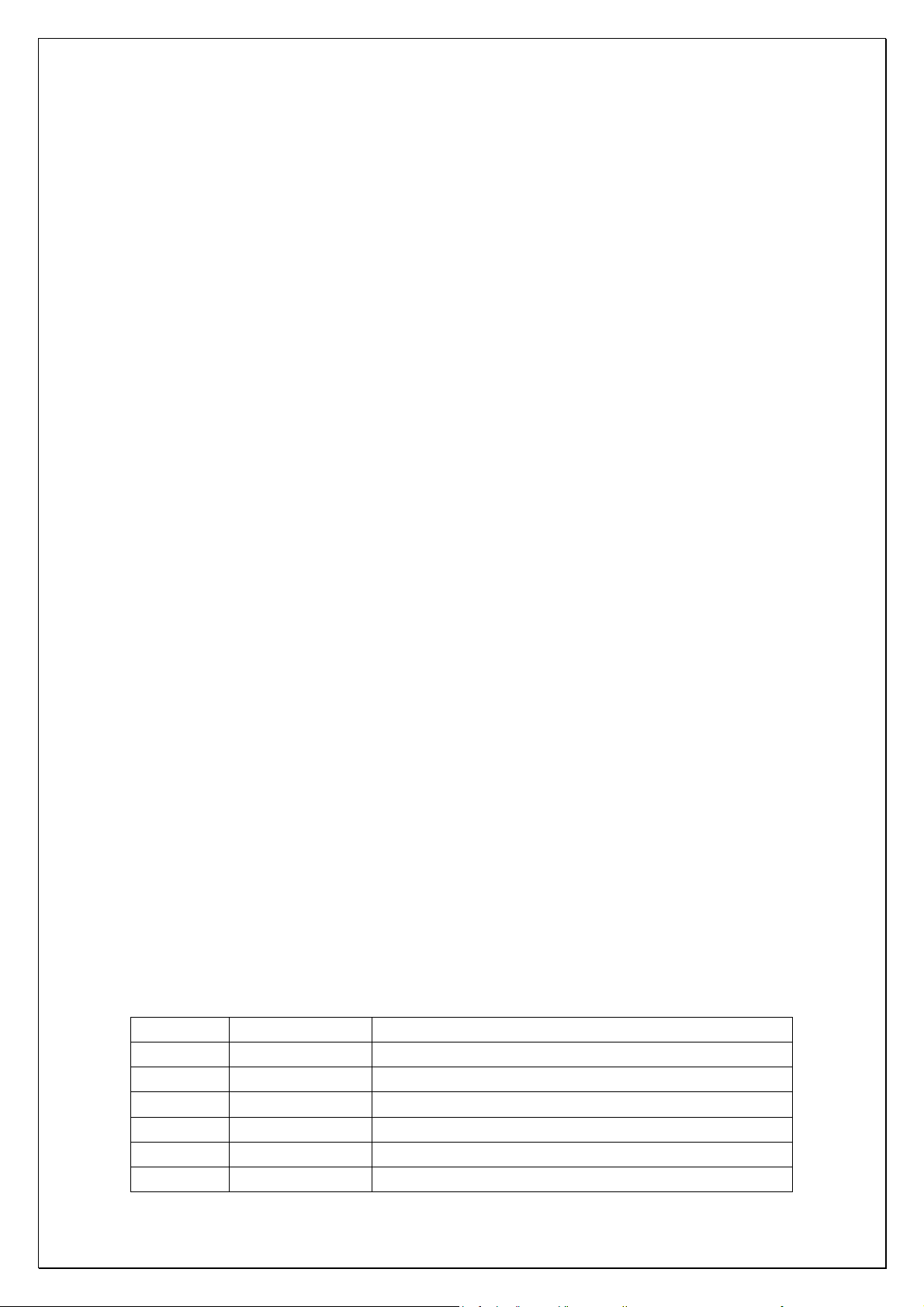
IC and its functions for Karaoke:
S.N. of IC Name of IC Functions of IC
N201 PT2308 Transmittal, pre-amplification for Karaoke signal
N200 PT2315 Karaoke volume control, including tone control
N205 CD4053 Electronic switch
N209 PT2399 Karaoke echo processing
N207 CD4051 Karaoke delay adjustment
N208 CD4051 Karaoke echo adjustment
Page 7
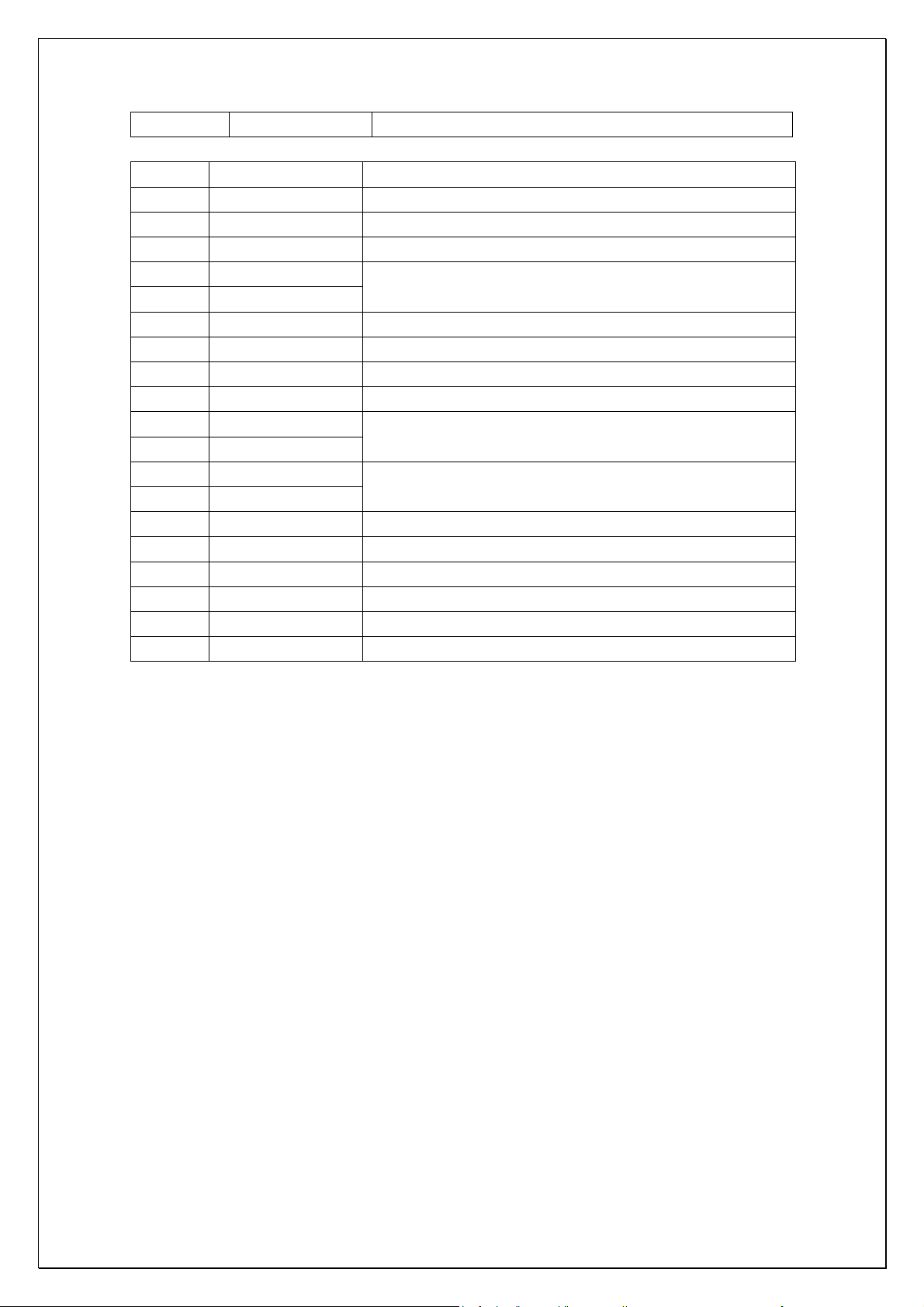
N204 4558 Phase inverter
PT2315 functional pin
S.N. Name of pin Description
1 REF Reference voltage (1/2VDD)
2 VDD Power supply
3 AGND Analog
4 TREB L
5 TREB R
6 RIN R channel input
7 LOUD-R Loudness control pin of R channel
9 LOUD-L Loudness control pin of LR channel
11 LIN L channel input
12 BIN L
13 BOUT L
14 BIN R
15 BOUT R
16 RFOUT R channel output
17 LFOUT L channel output
18 DGND Digital
19 DATA Control data of sequence transmission (DATA)
20 LCK Clock input of sequence transmission
8,10 NC Not connected
2.3.2 Flow chart of Karaoke signal
When the microphone is inserted, MIC signal is sent via MIC to the transmittal
circuit combined by N201A for amplification. Amplified MIC signal gives CPU a
MIC identification signal after N202A amplification, followed by VD201
rectification and filtering control triode V200. CPU sends PKM signal, which is
of low level, causing cutoff of triode V103/V105 and enabling output of MIC
signals; another way reaches pin 6 and 11 of PT2315 after C219/C222
coupling, outputs from pin 16/17 after internal volume and tone control, mixed
into one way and sent to N202B and then reversely send to N203B for
amplification. Signals amplified by N203B are divided into two ways: one way
is directly outputted; and the other way is outputted from pin 14 after being
coupled by R222/C247 to PT2399 for internal delayed echo adjustment,
reversed by N204B and outputted by mixing with karaoke signal. While OK-R
is outputted from pin 14 after being gated by N205 and superposed to L/R
channel.
In this circuit, the bass boost network made up of triode V201 connected to the
negative terminal of N202B is primarily for bass boost of 75HZ low frequency
signal.
During delay adjustment for PT2399, first control signal is given to CPU, which
controls N207 after being expanded via N211 IC CD4094 and connects with
pin 6 of PT2399 by selecting different resistance values for purpose of delay
Treble control pin of L/R channel
Bass control input/output pin of L channel
Bass control input/output pin of R channel
Page 8
adjustment.
Echo control is to change the resistance value at the connection point to R229,
so as to change the superposition on through connect signal for echo control.
The wide sound field processing control signal of SOK’s karaoke is in wide
sound field mode when it is high level, and now the signal of OK-R is the OK
signal inverted by N204A.
A sense signal of OK-SW on the MIC plug detection together with the network
made up of V200. When MIC is not plugged, it is low level; when plugged, it is
of high level.
Karaoke auto mute function is also available. When P-KT fails to detect signal
for a continuous period, CPU will send a P-KM signal to mute karaoke and
avoid MIC receiving noise, which may affect on sound effect.
Signal flow chart of scene mode
AV250T has a special function that switching between 5 scene modes is
available without karaoke, which is fulfilled through part of karaoke.
When pin 9/10 of N205 are of high level, sampled L/R/C signals are outputted
via pin 3 through N205 gating. After amplification by N203, one way is
connected directly; and another way is sent to internal of PT2399 for echo
delay adjustment (controlled by IC CD4049), with the adjusted effect
superposed to L/R/C channel to form different scene modes.
In this circuit, MIC shall not be inserted and is only available in 5.1CH mode.
N203A is for the purpose of reversal.
In addition, this device is added headphone output function. PHSW is low level
and each channel has output when headphone is not inserted. But when
headphone is inserted, PHSW will be high level for the mechanical settings
thus LRM and SCM signals change into high level at the same time to realize
muting in each channel, so the signal is only outputted from headphone, that is,
there is not signal output with each channel when connecting with headphone
output.
2.3.3 Bass enhancer circuit
P-BURST is the switch signal of bass enhancer. When it is of high level and
added to the base electrode of V102, V102 will be switched into conduction.
When the collector electrode outputs low level, V107 will be cutoff; when the
collector electrode is of low level, V100 will also be cutoff. SW signal is
normally outputted to external terminal. Meanwhile, the high level signal of
P-BURST is added to the emitter electrode of V108. V108 is positively biased
and switched into conduction. The collector electrode adds high level to the
base electrode of V101. V101 is positively biased and switched into conduction,
and ground SW signal, not superposing it to L/R signal.
In reverse, when P-BURST is of high level, V100 will be switched into
conduction and SWM cannot be outputted from external terminal. Meanwhile,
V101 is cut off and SW signal is superposed to L/R channel signal.
The bass enhancer of AV250T can be divided into three steps. This principle is
to change the volume of bass enhancer by changing the SW output volume of
Page 9
M62446.
2.3.4 Mixing and amplification circuit of 5.1 signal and karaoke signal
When L/R channel signal of 5.1 signal is superposed with SW signal and
amplified by N101B/N100B, it is sent to the reverse phase of N101A/N100A.
Meanwhile, OK-R/OK-L signals are also respectively added to the reverse
phases of N101A/N100A. After mixing and amplification by N100A/N101A,
they are respectively outputted from pin 1 of N100A/N101A to power
amplification circuit for power amplification.
Meanwhile, the C-1 signal sent by volume board is added to the reverse phase
of pin 6 of N102B and added to the reverse phase of N102A after amplification.
Now C1-1 signal after electronic echo processing is also added to the reverse
phase of N102A and sent to power amplification circuit after mixing and
amplification.
SR-1/SL-1 of another volume board is also added to the reverse phase of
N103B and N104B for amplification and then sent to N103A and N104A for
further amplification, and later sent to power amplification circuit.
One way of 5.1 signal after being mixed and amplified is sent to power
amplification circuit passing through XS9, and the other way forms DIST
(distortion error detecting signal) signal passing through
R111-R113/R142/R145/VD100-VD104, which will be added to CPU for
automatic gain adjustment, so as to control volume output.
Section Four CPU board
2.4.1 CPU control unit
N100, the overall CPU, is the overall control center, inputting all kinds of
control instructions to controlled circuits to achieve all kinds of control functions.
It adopts +5V supply with pin 40 as its supply pin. Pin 18 and pin 19 connect
externally with 12M crystal oscillator to provide working clock frequency for
itself. Pin 9 is its reset pin. When starting, +5V charges C106 via R100. The
voltage of two ends of capacitance cannot be mutated, thus B-pole of triode
V100 is low level, that is, V100 conduction gives a high-level reset signal to
CPU. When capacitance C106 finishes charge, V100 stops and then reset
finishes. The form of this reset circuit is to reset high level and keep low level.
When the machine is working, the static information of Power-on logo on
screen and Chinese characters are stored in CPU internal static memory.
N101, a status memory, can record the current working status of machine
when powering off and show the status when next time power on, avoiding
users to re-adjust. The sound field mode set by users is also stored in it and
can be called when necessary.
2.4.2 Detect input signal and automatically search circuit
DISPLAY signal from volume board is sent to N103A to amplify and limit level,
and then sent to inverse end of voltage comparator N103B after capacitance
coupling. It inputs from pin 7 of N103B and then is sent to pin 16 of CPU via
Page 10
VD103, V101, R109 and R107. When N103B inputs a high level, VD103 is in
A
3
reverse cut-off status, B-pole of switch tube V101 is high level and is in
conducting status, then gets an about +5V high level (signal input) to CPU after
VD101’s stabilization and stop searching. When the output end of N103B
outputs a low level, VD103 is in conducting status, B-pole of switching tube
V101 is low level and is in cut-off status, and then CPU detects the low level
(no signal input). Its working principles are as follows:
① After starting up, under CPU internal program’s control, a data signal is
outputted via pin 23 to M62446, and then M62446 scans each input port of
N101, N102 and N103 by emitting high and low levels. When the input ports
have no signal input, it automatically becomes standby status. When any of
ports has signal input, channel paths of input N101, N102 and N103 has A/C
signal which is amplified and limited level by N108B and N103A of CPU board,
then compares with pin 5 of N103B and gets plus-minus level close to supply
power. The co-phase voltage of N103B is about 0.1V. After the direct current
voltage is over 0.1V, the output end of N103B outputs low level is close to
negative-power voltage, VD103 positive-bias conducts, switch tube V101
(S9014) stops, emitter outputs a low level to pin 16 of CPU which by controlling
IC M62446 makes search level lock on the port through which signal inputs, to
enter normal play.
② When pressing “SEARCH” button on the remote controller, it is
converted from optical signal to electric signal by the remote control receiver of
panel. Pin 14 of CPU emits a high level to conduct V102 and search according
to the same previous process.
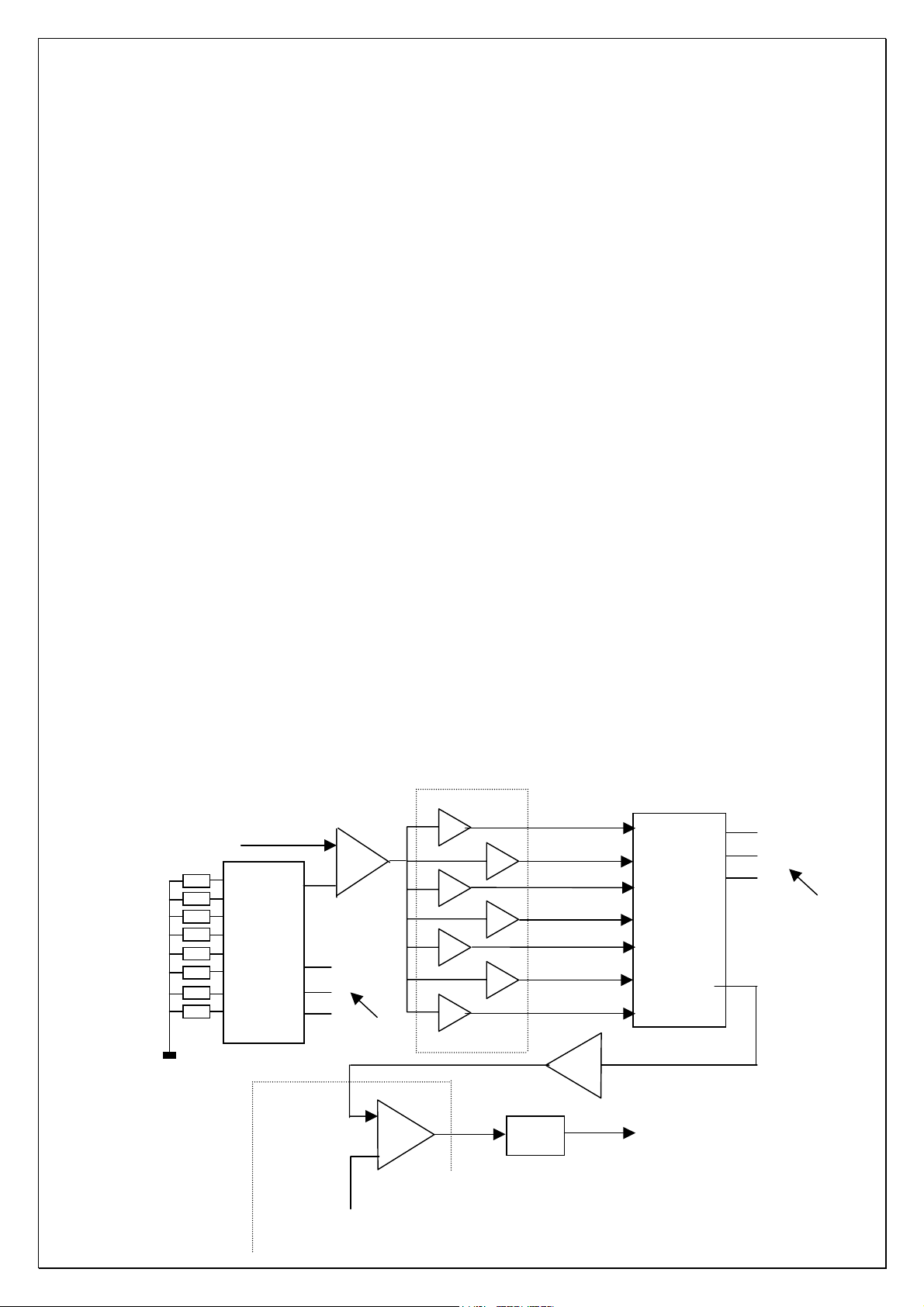
2.4.3 Spectrum Analysis Circuit (see the following figure)
Spectrum analysis circuit is divided into three parts:
DISPLAY
N104
CD4051
uto
spectru
m and
gain
adjustme
N105C
+
}
CPU
.
7-segment
band-pass
35HZ
134HZ
300HZ
1KHZ
2.2KHZ
6.3KHZ
16KHZ
N108
CD4051
Frequency
point
gating
}
3
-
+
N102A
V105
Pin 12 of CPU
CPU
.
Page 11
A
A
+5V
V103
V104
Pin 28 of CPU
/D conversion
Automatic spectrum gain adjustment circuit: To avoid two situations that
spectrum display amplitude is too low when input signal is too weak or
spectrum display is in full screen when input signal is too strong, AV250T sets
automatic spectrum gain adjustment circuit, using a single-track
one-from-eight electronic analog switch, its true value diagram is as follows:
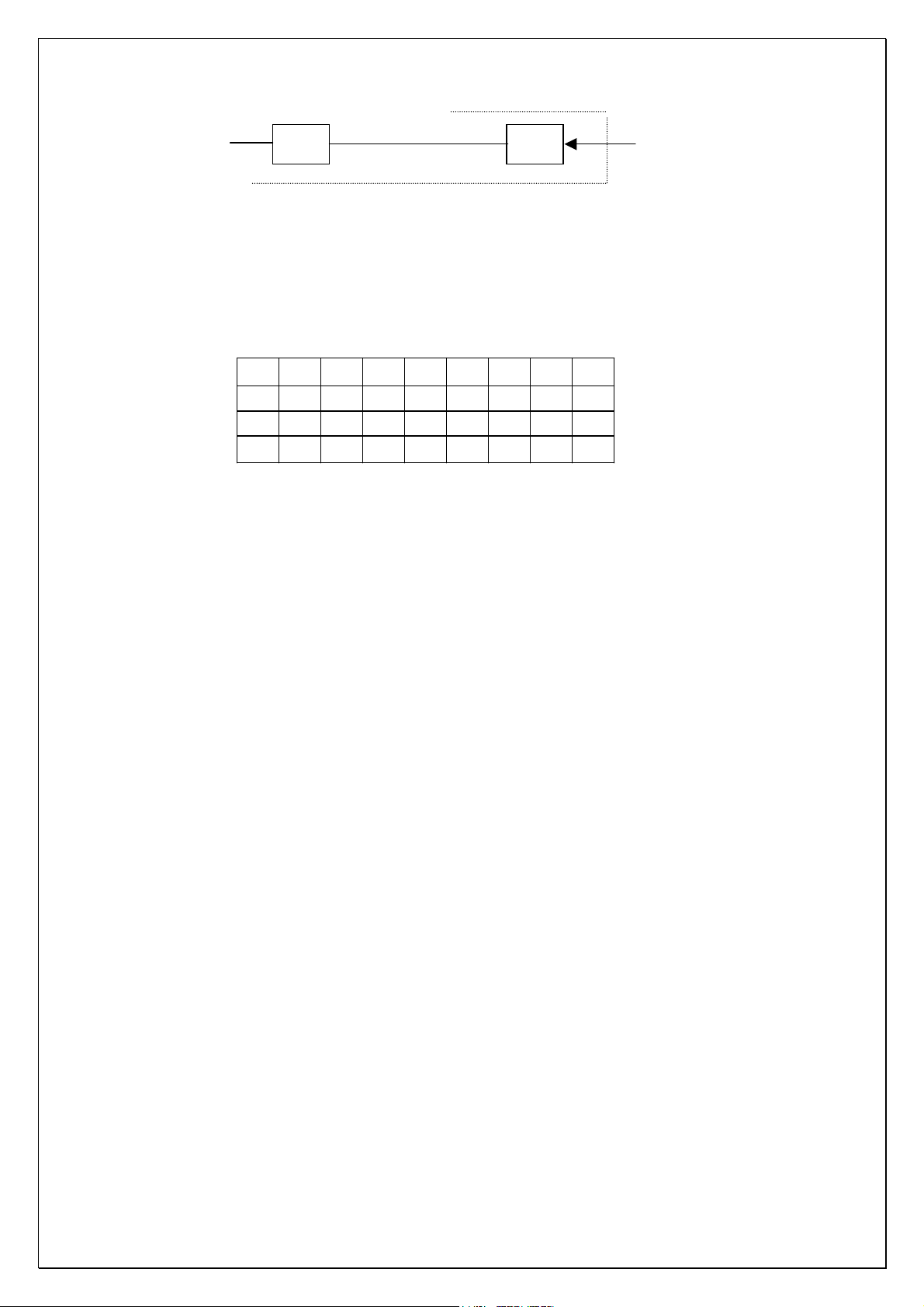
CD4051Truth table
X0 X1 X2 X3
1
0
0
0
0
0 0 0
B
C
0
1
X4 X5 X6 X7
1
0
1
0
1
1
01
1
1
0
1
1
1
Its main working principle is to change the value of inverse ground resistance
of transmittal N104 to change the transmittal gain multiple. Let’s see the
detailed work of the whole circuit. We’ve referred that spectrum analysis signal
source (DISPLAY) is sent to the co-phase input end of transmittal N105C to
amplify. Its amplification factor is determined by the value of the resistance
connecting with the electronic switch of its inverse end N104. When the main
volume is large, CPU will automatically increase the value of ground resistance
and decrease the amplification factor; when the main volume is small, CPU will
automatically decrease the value of ground resistance and increase the
amplification factor.
Amplitude sampling circuit: signal amplified by N105C is sent via C115
coupling to seven band-pass filters composed of transmittals. By setting its
capacity of feedback capacitance, its frequency-band range can be determined.
The frequency value of superscript of the output points is the central
frequency-point of the frequency band. The output end of each band-pass filter
is connected with a half-wave rectifier circuit. The amplified A/C signal is
rectified to direct current. The circuit is mainly to achieve frequency-point
sample. It can display the amplitude of all frequency-points of the whole sound
signal via direct-current voltage. If the low frequency of sound signal is stronger,
the current voltage of output end of 35HZ and 100HZ band-pass filter is higher.
When high frequency is stronger, the current voltage of 10K and 16K
band-pass filter is higher. The output ends of the seven band-pass filter are
connected with the seven input ends of electronic switch N108 (CD4051).
These electronic switches will quickly circularly-switch among frequency points
(referring to previous true value diagram). Pin 3 output end of N108 will output
a string voltage value representing frequency point signal amplitude (see next
diagram).
Page 12
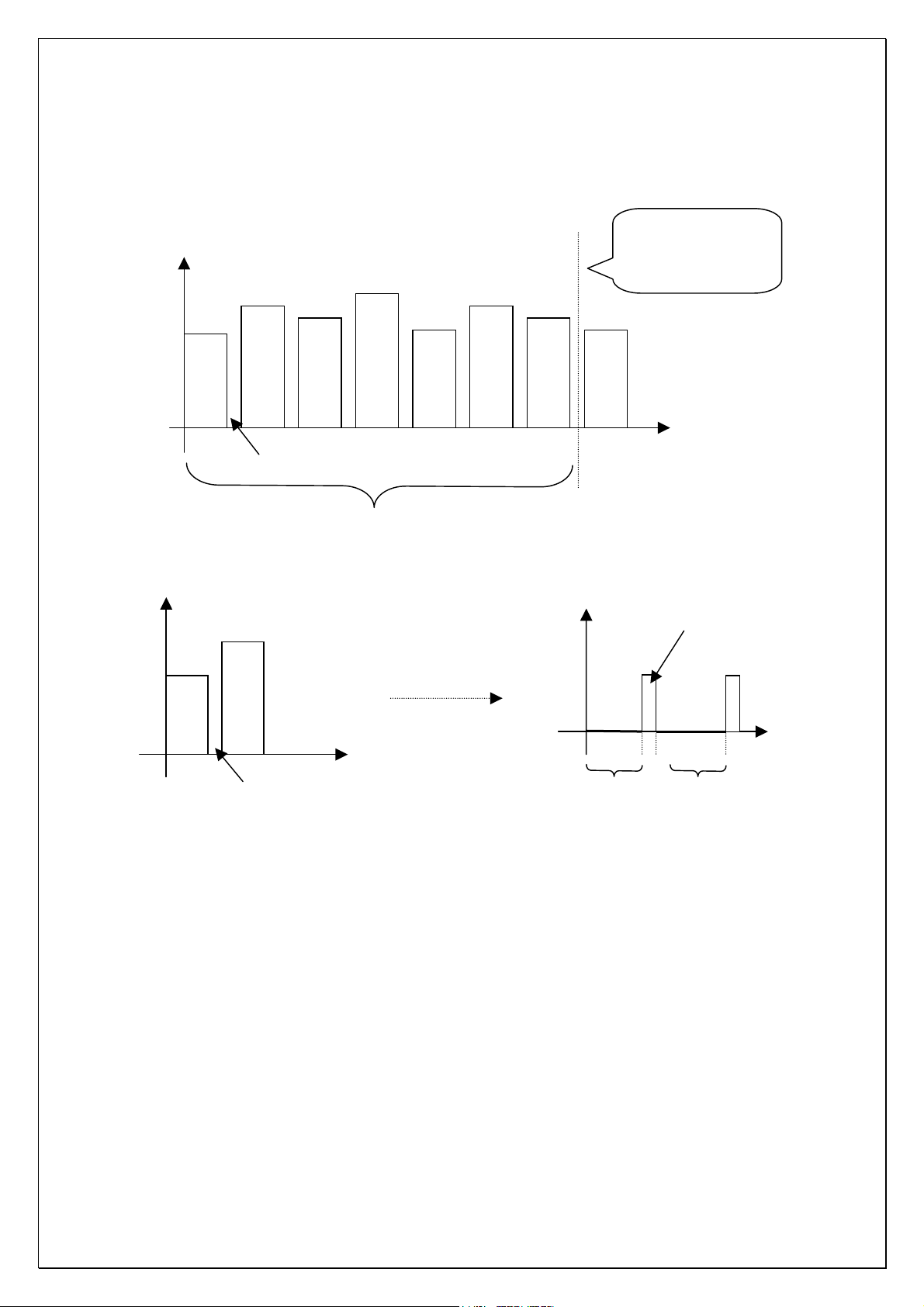
V
35HZ
100HZ
300HZ
1KHZ
3KHZ
10KHZ
16KHZ
Note: the voltage
amplitude in diagram
is uncertain.
35HZ
Interval of switch
T
Frequency point cycle gating period
V
35H
100HZ
V
Discharge of high level
Interval of switch
T
Time for charge Time for charge
35H
100HZ
T
A/D conversion and output circuit display (two situations):
1. When no signal input, pin 28 of CPU sends a high level to B-pole of V104.
The positive end of N102B is low voltage, the inverse end of N102B gets
partial voltage of R189 and R172, making N102B output a low level, that is,
triode V105 stops and C-pole of V105 will give a high level to pin 12 of CPU to
let CPU not conduct AD conversion (pin 6/7/8 of CPU are inactive and keep
high level).
2. When the machine has detected the signal (the inverse end of N102B has
a current voltage representing 35HZ signal amplitude), pin 28 of CPU is
converted into low level and +5V voltage charges for C137 via V103. When
reaching the voltage value of inverse end, the comparator converts and N102B
outputs high level. Once CPU receives low-level signal, it stops 35HZ level
gating and converts into next frequency point 100HZ. During conversion, pin
28 of CPU outputs an instant high level to conduct V104, leak the voltage
Page 13
capacity of C137 and make the co-phase end of N102B restart to charge
r
r
A
100HZ from 0-level. When the charge of 100HZ finishes, the charge and
discharge of next frequency point begin, and such process occurs circularly
under the control of CPU. The charge time form 0-level to the occurrence of
output conversion represents the signal amplitude of current frequency
point—the larger the amplitude, the longer the time and the amplitude
displaying in screen is higher; the smaller the amplitude, the shorter the time
and the amplitude displaying in screen is lower. Digital pulse outputted from
N102B output end is added by V105’s inverse to pin 12 of CPU which handle it
and output to panel to display dynamic frequency in screen. The display of
original frequency points is sequential. However, the above circular process is
extremely quick, thus, what we see in screen is the progress of the whole
spectrum displaying synchronously.
Section Five Panel control and display circuit
The panel control and display circuit of AV110 adopts the special IC 101
(PT6311), whose external buttons of pin 10/11/12/13 scan buttons matrix. After
receiving the control command of users to the machine, processing is done
inside and then outputted by two ways: one way is sent to display screen to
display the working status; and the other way is transmitted to CPU through pin
5/6/8/9 to ask for performing and finishing the corresponding control function.
N102 is remote control receiver, which transforms the received infrared remote
control signal into electronic signal and then send it to pin 13 of CPU so as to
complete remote control function.
Section Six Power amplifier board
1. L/R channel power amplifying circuit: L/R channel power amplifying
circuit of AV250T (RU) is composed of discrete components, with the
composed frame diagram shown as follows. (Take L channel as an example)
V101
V115
Mute
C negative
feedback
R121, R108, C105
L-in
Differential
amplifying stage
V102, V103
Mirror image constant source
V104, V107, VD102, VD103
Voltage
amplifying
stage
V105
Composite powe
amplifying V132,
V112
Temperature
.
compensation stage
V106
Composite powe
amplifying V133, V113
Relay
Speaker
Page 14
L channel signal is sent to pole B of differential amplifying stage V102 after
being coupled by R101, R103 and C101; V102 and V103 compose single
ended input/output differential amplifying circuit. Sound signal outputs from
pole C of V102 to pole B of voltage amplifying stage V105, and then outputs to
composite power amplifying stage after voltage amplifying. V104, V107,
VD102 and VD103 compose mirror image constant source circuit. VD102,
VD103 provide V104, V107 with constant base electrode current. Emitter
resistor of V104 determines working current of differential amplifying stage;
and emitter resistor of V107 determines working current of voltage amplifying
stage. V132 and V112 compose multiple unit tube amplifying to supply strong
current amplifying capacity for final stage of power amplifier, which composes
waveform positive half cycle amplifying. V133 and V113 compose waveform
negative half cycle amplifying and the circuit structure is the same with the
above. The function of temperature compensation tube V106 in circuit has two:
it is the base bias of geminate transistors firstly and its working state
determines the static working current of composite power amplifying stage,
that is, through adjusting the gating degree of V106, we may set the static
working point of composite power amplifying stage. The usual means is to
change the base electrode resistor of V107; it may also automatically adjust
the working state of composite power amplifying stage after the temperature
increases, with the adjustment process shown as follows:
Total current of output stage = working current + leakage current
When temperature increases, the increase of leakage current leads to drift
of static working point, and meanwhile leakage current of V106 increases. The
decrease of Uce makes the bias current of output stage decrease, the working
state change and the working current of back stage decrease to achieve the
function of temperature compensation.
Introduce voltage negative feedback into power amplifier circuit of AV250T,
composed of R121, R109, C105, which is capable of stabilizing static working
point of differential stage. AV250T adopts direct output means and R111, C116
connected to output terminal compose Joubert Network, capable of avoiding
high frequency self-excitation caused by the AC inductive reactance of
speakers voice coil.
Mote control: when pressing MUTE button on remote controller, a mute
signal, achieved through signal photoelectric conversion performed by remote
control receiver, is sent to CPU, and then a high level mute order is outputted
from pin 35, 36 of CPU to make V115, V101 and V116 on, left/right channel
signal has short circuit to ground to fulfill mute control function.
C, SR, SL power amplifying circuit: compared with the former models,
the three channels of AV250T adopt special power amplifiers LM1876 and IC
LM1875. As for LM1876, it has 15 pins in all, in which pin 2, 15, 4 are its
positive/negative power pin; and pin 7, 8, 12, 13 are its in-phase or reverse
input terminal. The rated output power of each channel of this power IC may be
up to 20W, with auto mute function when power on; as for 1875, it has 5 pins in
Page 15
all. It is a good performance power amplifying IC, with very simple application
r
circuit and 15W power output in rated state. Pin 5 and 3 are positive and
negative power supply pin.
Section Seven Power board
Power board supplies working voltage required by each unit circuit and
over-current/over-voltage protection unit. Protection unit circuit is emphasized
here.
The protection means of L, R, and C channel is fulfilled through
disconnecting relay Y100 when starting up so as to disconnect the output. SR
and SL channel achieves protection function through mute. AV250T is with
power-on protection, central point over-voltage-over-current protection and
standby protection.
1. Power-on delay attracting protection circuit:
The working of circuit is unstable when power on and the generated
percussive current does great harm to speaker and power amplifying circuit, so
delay attracting protection circuit is set. This circuit is divided into two steps:
1) C, L, R. The working process is: a 22V voltage is achieved after AC
outputted by transformer being rectified and filtered by VD113, C110, and
then charges C115 through R108 to make VD111 struck through reversely
and make V105 and V104 in-phase on to finally make Y100 attract to reach
delay effect.
2) Surround left and right channels perform anti-percussion protection when
power on: after machine system resets, pin 33 of CPU outputs a high level
to pin 9, 14 of LM1876 through R164 to make LM1876 output mute. After
delay start-up of machine succeeds, pin 33 of CPU converses to low level
immediately and outputs normally through SL/SR channel.
2. Central point over-voltage protection:
An over-voltage sampling resistor is connected to the output terminal of
each channel. L channel is R116, R channel is R117, C is R118, SR and SL
channels are R119 and R120 respectively. Only when one channel’s central
point voltage is above +3.5V or below -3.5V, V101 or V102 is on to make their
C pole voltage decrease, then V103 on, relay disconnected and protection
circuit start up finally.
Over-voltage
sampling resisto
is connected to
each channel
L
channel
is R116
When above
+3.5V
When below
+3.5V
V101 on
V102 on
C pole
voltage
decrease
V103
on
Relay
disconnect
and protection
start up
Page 16
Over-current and short circuit protection:
r
An over-current sampling triode is connected to the output load resistor of
L/R channel. Sampling tube of L channel is V114 and load resistance is R126
and R127. The other three channels’ power amplifying IC is with over-current
protection inside. Only L channel appears over current, the pressure drop
produced on R126 and R127 will increase quickly. Once the pressure drop on
R129 is above 0.7V, V114 will be on, and V103 is also on. Finally relay
disconnects and protection circuit starts up.
Over-current
sampling
triode is
connected to
each channel
L
channel
is V114
Pressure drop
on R126,
R127
increases
when ove
current
V114
is on
C pole
voltage
decrease
V103
is on
Relay
disconnects
and protection
starts up
The same, when R channel has over current, voltage on R159 will be above
0.7V to make V129 on, and then V103 on. Finally relay disconnects to reach
the purpose of protecting speaker.
4. Standby protection:
When standby time is up to 10 minutes and standby by force is needed,
PRC signal outputted from pin 34 of CPU is high level, which makes V100
saturated and on through VD108, R101 to make V103 on. Finally relay
disconnects to reach the result of standby and energy saving.
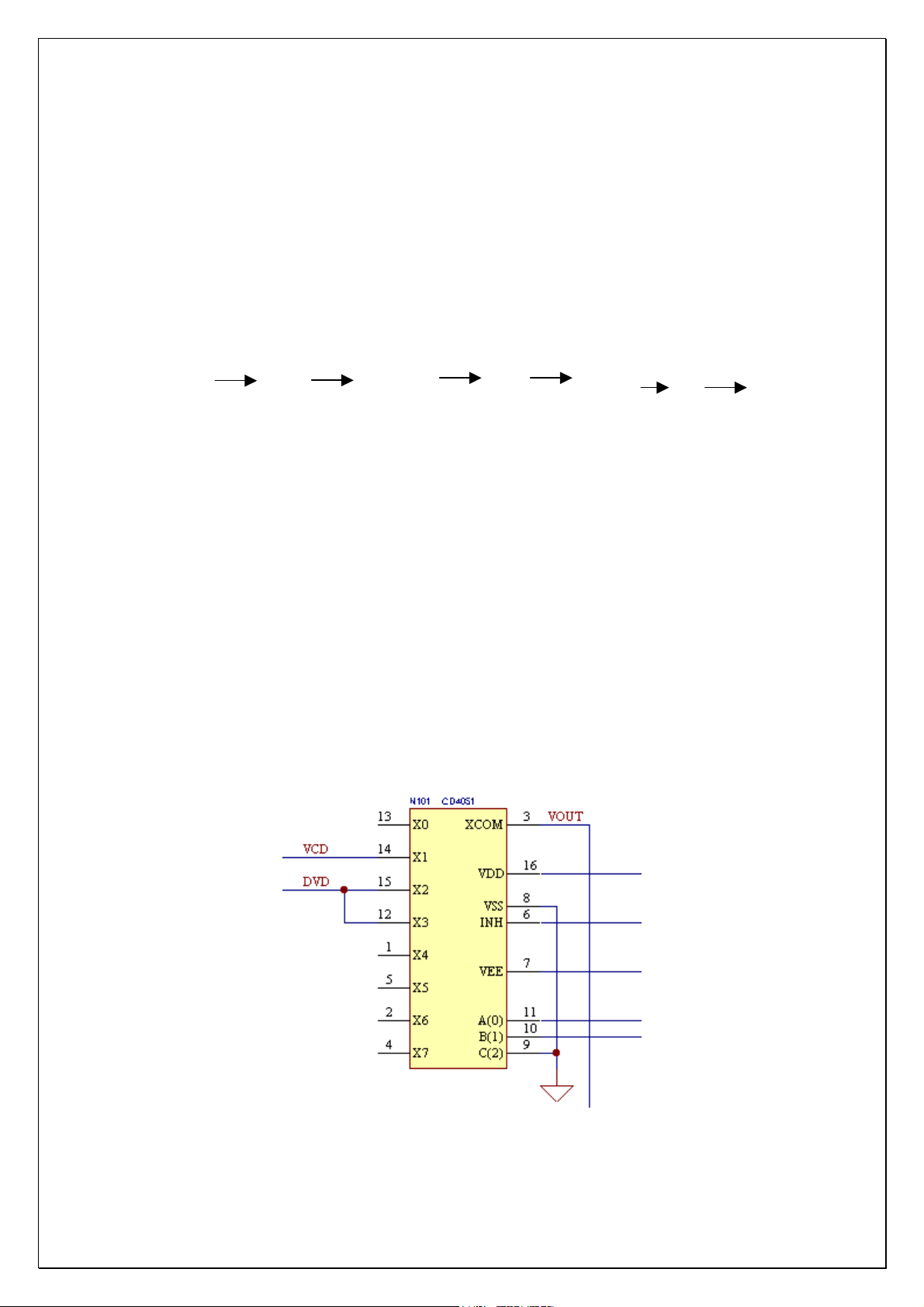
Section Eight Video board
Video board fulfills the functions of input, output and switch of the video, with
the schematic diagram shown as the following figure:
This switch function is realized through an electronic switch IC CD4051. When
high and low level of control signal A and B are changing, IC CD4051 switches
between VCD and DVD, and video signal is outputted by pin 3 VOUT.
Page 17
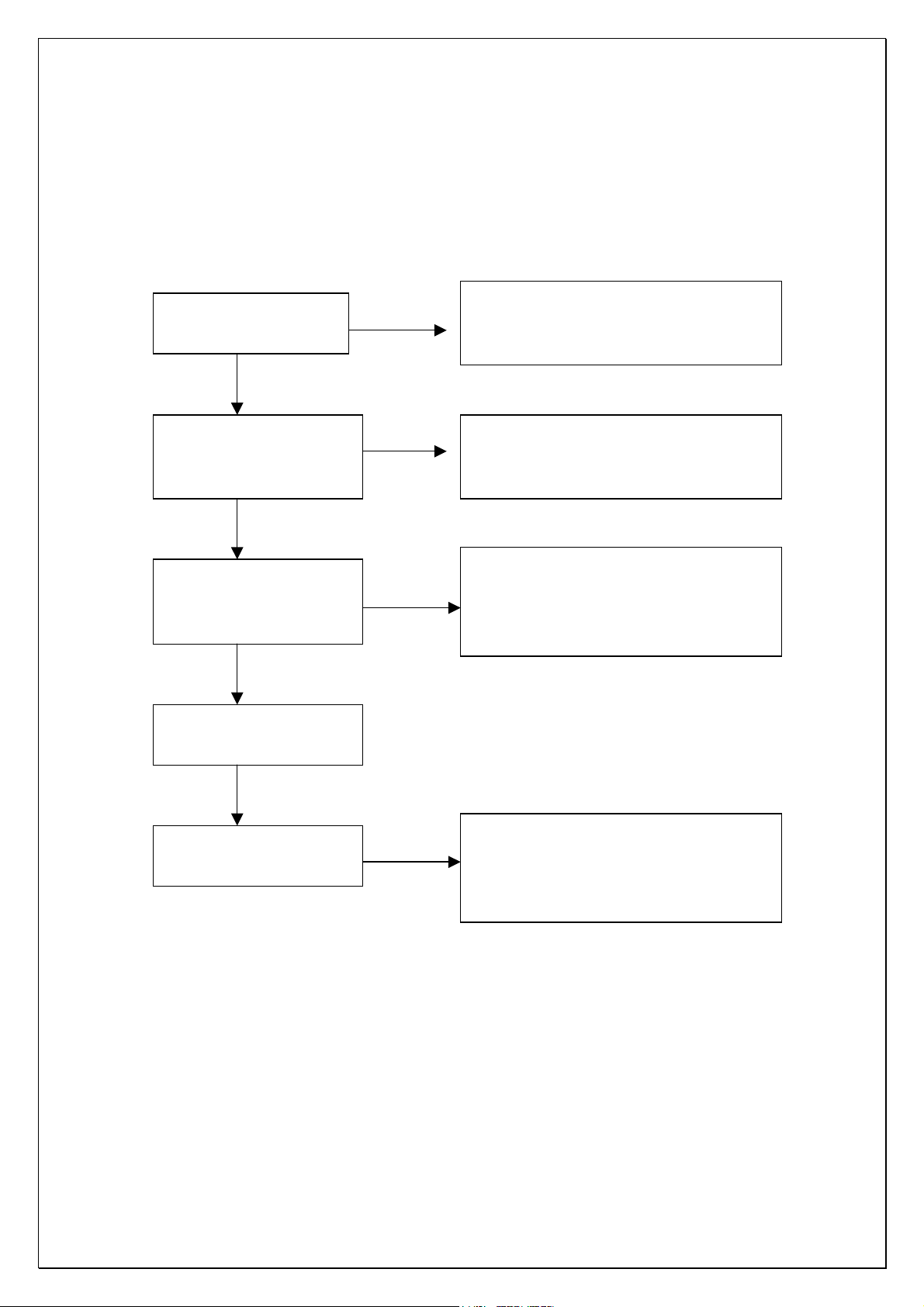
Chapter Three Servicing Process
f
f
f
r
1. No output for Karaoke
Firstly confirm whethe
microphone is good.
Whether the pre-amplification
circuit and checking circuit o
microphone work normally.
Whether the microphone
volume adjustment works
normally.
Whether high/low frequency
boost circuit works normally.
Whether mute circuit o
microphone works normally.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Note: For MIC size is disordered on the market,
that MIC is too long or too short will both lead to
no output of microphone.
Note: here please check whether the
microphone checking signal P-KT is able to
overturn when signal output is available.
Note: check whether the periphery circuit o
volume boost IC2315 or IC M62429 is normal,
and whether the voltage and data line has
abnormalities.
Note: check whether the triode in the
microphone mute circuit has damage, and
whether the mute control signal line P-KM is
normal.
Page 18

2. Power supply not connected
r
Check whether the power cord
socket has been well connected.
Yes
Whether fuse FL100 is
2. The primary internal circuit
complete and good.
Yes
Check the primary coil
resistance numerical
value of transformer.
Yes
No
No
Check whether the secondary
voltage of transformer is normal.
In most cases, primary short-circuit
of transformer will burn out this fuse.
1. If primary internal short
circuit of transformer occurs,
the resistance numerical value
will decrease, fuse will be burnt
and power supply will not be
connected.
opening of transformer leads
to disconnection of power
supply.
No
The short-circuit and circuit
opening inside the transforme
secondary coil lead to abnormal
output of secondary voltage.
Whether the input and
output of three-terminal
voltage regulator are
abnormal.
Whether power supply
voltage of pin 40 of CPU
is normal.
Whether the
secondary fuse is
complete and good.
Whether the output
voltage of rectifier tube
is normal.
Whether the control panel
IC and display screen
voltage is normal.
Page 19

3. No on screen display (OSD)
f
f
f
r
g
r
No
Note: The abnormality o
the secondary output
voltage of transforme
may probably cause no
OSD.
Check whether the
filament voltage o
display screen is normal.
No
Whether the power o
control panel IC is
normal.
No
Yes
Yes
Check whether the data line
between CPU and control
panel drive IC and clock line
signals are normal.
Yes
Note: If display screen has
air leakage, it will cause no
OSD and now the filament
voltage is close to be low.
No
Whether CPU powe
supply is normal.
Yes
No
Whether signals from control
panel drive IC to display screen
pin are normal.
Can judge that the
Ye s
problem occurs in CPU
board.
Yes
May probably cause
the badness of control
panel drive IC.
Can judge that
display screen is
not
ood.
Page 20

4. No output
r
r
r
r
Check whether the analog
electronic switch IC can be
gated in this path when there
is signal input.
No
Note: check whether IC powe
cord is normal, and signal
cords P-INA and P-INB which
control IC gating are normal.
Check whether tone adjustment
IC62446 or 75347 front stage
has signal input.
Yes
Check whether power-on
checking circuit works normally.
Yes
Yes
Check whether tone adjustment
IC62446 or 75347 front stage
has signal input.
No
Yes
Check periphery circuit of IC is
normal; IC power supply; and
whether CPU control signals
P-VDA, P-VCK and P-VST are
normal.
Whether powe
amplifier board
has signal input.
Whether power amplifie
board has signal input.
Check whether powe
tube has abnormalities
of punch hole.
Whether main channel mute control
line P-LRM and center surround
mute control line P-CSM are normal.
Page 21

Schematic & PCB wiring diagram
CPU board schematic & PCB wiring diagram
N107A
4558
10
11
12
13
14
15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
P_SELECT
C
R184
VD119
5.6K
1
R173
5.6K
P_DIST
R185
1N4148
4.7K
L100
D+5V
100uH
R203 470
P_DST1
-12V
GND
+12V
D+5V
GND
R+5V
P_DST1
P_DST2
P_DDA
P_DCK
P_KT
P_GNC
P_BURST
P_REM
+5V
+5V
+12V
R169
470K
R170
1K
R172
10K
VD116
1N4148
C109
2.2u/50V
-12V
R204 470
P_DST2
R205 470
P_DDA
R206 470
P_DCK
P_KT
P_ADSELA
P_ADSELB
P_ADSELC
RESET
R207 0
P_BURST
R208 470
P_BCK
P_ADINT0
P_REM
P_SELECT
P_DIST
P_SEARCH
P_LDA
R209 22
R210 1M
R193
P_LDA
G100
4.7K
C103
30P
12M
R187
P_KT
10K
VD117
3.3V
N102B
6
4558
R177
7
5
1K
C138
V103
2N5401
R174
4.7K
+12V
R110
22K
VD102
1N4148
R108
10K
0.22u/16V
V104
R175
C137
0.1u
2.2K
9014
V101
9014
R109
15K
R107
100
VD101
4.7V
C
F
10-Mar-2006
李林存
设 计 审 核 批 准
更 改 更 改 单 号 签 名 日 期
123456
数 量
标 准 化
BBK
第 张 共 张 版次:
1
东莞市步步高视听电子有限公司
1
1.0
C134
R162
154
10K
13
12
R163
4.7K
C131
R157
683
10K
9
10
R158
4.7K
103
C128
R152
C143
223
10K
2
3
R153
4.7K
C144
103
C125
R148
103
10K
6
5
R149
4.7K
R143
C122
10K
472
6
5
R144
4.7K
C145
C119
R138
152
103
10K
2
3
R139
4.7K
C146
103
C116
R133
561
10K
13
12
R134
4.7K
C115
10u/16V
C114
R132
DISPLAY
22K
10u/16V
R129
13
X0
470K
R128
14
X1
180K
R127
15
X2
75K
R126
12
X3
27K
R125
1
X4
10K
R124
5
X5
4.3K
R123
2
X6
2.2K
4
R122
X7
1.5K
F
E
C135
154
R164
R165
VD114
100K
1K
1N4148
14
N106D
LM324
C132
683
R159
100K
8
N106C
LM324
C129
223
R154
100K
-12V
1
N106A
LM324
4 11
+12V
C126
103
R150
100K
7
N106B
LM324
C123
472
R145
100K
7
N105B
LM324
C120
152
-12V
R140
100K
1
N105A
LM324
4 11
+12V
C117
561
R135
100K
14
N105D
LM324
R131
10K
3
X
16
VCC
8
GND
6
INH
7
VEE
11
A
10
B
9
C
N104
CD4051
35Hz
C136
R166
10K
2.2u/50V
R160
VD113
1N4148
1K
134Hz
R161
C133
10K
2.2u/50V
R155
VD112
1K
1N4148
300Hz
R156
C130
10K
2.21u/50V
R151
VD111
1K
1N4148
1KHz
R186
C127
10K
2.2u/50V
R146
VD110
1K
1N4148
2.2KHz
R147
C124
10K
2.2u/50V
R141
VD109
1K
1N4148
6.3KHz
R142
C121
10K
2.2u/50V
R136
VD108
1K
1N4148
16KHz
R137
C118
10K
2.2u/50V
N105C
LM324
10
8
9
R130
470K
R118
+6.8V
C113
470/0.25W
10P
C111
10u/16V
C112
10u/16V
R120
0
R117
+12V
VD106
10K
6.8V
VD107
6.8V
-12V
R119
-6.8V
P_GNA
470/0.25W
P_GNB
P_GNC
E
D
DIST
C139
R180
22u/25V
22K
+12V
+12V
C140
100u/16V
C141
100u/16V
-12V
N108
13
3
X0
X
14
X1
16
VCC
+6.8V
15
X2
8
GND
12
6
X3
INH
1
7
X4
VEE
5
2
4
C149
103
3
2
C150
-6.8V
X5
11
P_ADSELA
X6
A
10
P_ADSELB
B
9
P_ADSELC
X7
C
CD4051
+12V
84
C110
N103A
4.7u/16V
4558
6
1
5
47K
-12V
R115
103
470k
R116
R114
1.5K
D
C151 103
+12V
84
R181
100
3
2
-12V
C152 103
R182
220
R183
22K
XP100
CON15
103
C147
+12V
84
4558
N102A
3
R167
2
100K
C148
-12V
103
+5V
VD115
1N4148
VD103
N103B
1N4148
4558
7
+12V
R111
R113
4.7K
180K
V102
9014
R112
2.2K
R189
10K
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
VD118
1N4148
C100
47u/16V
N100
W78E58
1
P10(T2)
2
P11(T2)
3
P12
4
P13
5
P14
6
P15
7
P16
8
P17
9
RST
P30(RXD)
P31(TXD)
P32(INT0)
P33(INT1)
P34(T0)
P35(T1)
P36(WR)
P37(RD)
XTAL2
XTAL1
GND20P20(A8)
C104
30P
B
A
123456
C102
+5V
104
L101
RH-357508
C155
C142
103
104
40
Vcc
39
P00(AD0)
38
P01(AD1)
37
P02(AD2)
36
P03(AD3)
35
P04(AD4)
34
P05(AD5)
33
P06(AD6)
32
P07(AD7)
31
EA/Vpp
30
R16810K
ALE
29
PSEN
28
P27(A15)
27
P26(A14)
26
P25(A13)
25
P24(A12)
24
P23(A11)
23
P22(A10)
22
P21(A9)
21
+5V
R179
10K
P_ADINT0
P_KCK
V105
P_KDA
9014
R178
10K
P_CHARGE
P_SEARCH
B
012345678
012345678
RESET
RR100
8*4.7K
P_GNA
P_GNB
P_GNC
P_CSM
P_LRM
R202 470
P_RC
R201 470
P_RLY
R200 100
P_SCART
C156
C108
104
P_CHARGE
R199 470
R195 470
R196 470
R192 470
R191 470
R198 470
R197 470
RR101
8*4.7K
+5V
8
7
6
5
221
P_VCK
P_VST
P_KM
P_HOLD
P_VDA
P_KCK
P_KDA
R194 100
N101
A0
VDD
A1
TEST
A2
SCL
VSS4SDA
24C02
+5V'
XP101
DISP
1
DIST
2
P_CSM
3
P_LRM
4
P_RC
5
P_RLY
6
P_SCART
7
P_VCK
8
P_VST
9
P_KM
10
P_KCK
11
P_KDA
12
P_LDAP_BCK
13
P_HOLD
14
P_VDA
15
CON15
C154
221
R104
1
0
2
3
R+5V
R100
R101
C105
22K
4.7K
103
V100
9014
C107
104
R211
C106
4.3K
4.7u/16V
A
Page 22

Power Amplifer board schematic & PCB wiring diagram
TC103
0.47u/50V
TC109
0.47u/50V
B
N101
R183
Vs+
47/3W
R184
Vs-
47/3W
L7812
1
Vin
C146
220u/35V
C147
220u/35V
2
Vin
N102
L7912
Vs+
10u/100V
Vs-
N105
R190
-Vs
22K
5
N/M
TC104
3.3U/16V
TC110
3.3U/16V
S/M
R191
6
IN
820
+Vs
7
N/P
OUT
R192
22K
TDA7298
47K
R193
22p
C160
N106
R194
-Vs
22K
5
N/M
S/M
R195
6
IN
820
+Vs
7
N/P
OUT
R196
22K
TDA7298
47K
R197
C163
22p
B
C103
47u/100V
C113
47u/100V
R1052KR106
V102
2N5551
C104
220p
R107 47
V104
2N5551
C107
47u/100V
R1352KR136
V117
2N5551
C114
220p
R137 47
V119
2N5551
C117
47u/100V
Vs+
C127
53
47n
N104
LM1875
C128
47n
Vs-
D
2K
C108
33p/500V
V103
2N5551
R111
R114 4.7K
33K/0.5W
R108
V106
47
2N5551
R109 1K
R115
2.2K
C105
100u/16V
R112
1K
VD102
1N4148
R110
510
VD103
1N4148
2K
C118
33p/500V
V118
2N5551
R141
R144 4.7K
R138
33K/0.5W
V121
47
2N5551
R139 1K
R145
2.2K
C115
100u/16V
R142
1K
VD105
1N4148
R140
510
VD106
1N4148
4
E
11-Mar-2006
卢建强
设 计 审 核 批 准
F
更 改 更 改 单 号 签 名 日 期
123456
数 量
C101
R103
R101
1K
10K
10u/16V
V101
标 准 化
XP9
SWM
1
L1
2
R1
3
C1
4
SL1
5
SR1
6
GND
7
CON7
XP13
GND
1
P_Rly
2
P_RC
3
P_LRM
4
P_CSM
5
CON5
BBK
第 张 共 张 版次:
5
东莞市步步高视听电子有限公司
12
R165
4.7K
C122
22u/16V
VD101
1N4148
Vs+
R163
10K
R166
10K
VD115
1N4148
S8050
R161
4.7K
V115
2N5401
R162
C121
V116
10K
22u/16V
S8050
R164
10K
C124
R167
4.7K
10u/16V
V131
S8050
V130
2N5401
V136
R168
S8050
10K
R104
R102
47K
100K
R131
10K
C111
R133
1K
10u/16V
R134
R132
47K
100K
1
2
R169
R171
47K
C125
33K
R170
820
C126
4.7u/16V
68p
0.0
F
E
D
C
R117
220/0.5W
V132
R113
2SC5248
150
V105
2N5401
R121
C109
33K
47n
V107
2N5551
R116
V133
150
2SA1964
R125
220/0.5W
R147
V134
220/0.5W
2SC5248
R143
150
V120
2N5401
R151
C119
33K
47n
V122
2N5551
V135
R146
150
2SA1964
R155
220/0.5W
R185
10K
VD116
TC101
1N4148
10u/16V
100/0.25W
100/0.25W
100/0.25W
100/0.25W
Vc+
V112
2SC5200
R128
4.3K
R126
R120
0.25/7W
R122
R127
0.25/7W
R130
4.3K
V113
2SA1943
V127
2SC5200
R158
4.3K
R156
R150
0.25/7W
R152
R157
0.25/7W
R160
4.3K
V128
2SA1943
V137
C9015
R186
10K
VD104
1N4148
V114
2N5551
R129
C110
1.5K
0.47u/16V
Vc-
Vc+
VD107
1N4148
V129
2N5551
R159
C120
1.5K
0.47u/16V
Vc-
R189
R187
100K
10K
TC102
R188
10u/25V
22K
Vs-
C
A
123456
XS7
SWM
1
Rly0
2
P_RC
3
Over
4
CON4
C148
100u/16V
3
Vout
GND
2
1
GND
3
Vout
C149
100u/16V
VD111
C141
C139
1N5404
47n
4700u/35V
VD112
C159
1N5404
VD113
1N5404
C142
C140
VD114
4700u/35V
47n
1N5404
C161
Vs-
473
4
47u/35V
TC105
3
TC106
47u/35V
2
1
C162
Vs+
473
C164
Vs-
473
4
47u/35V
TC107
3
TC108
47u/35V
2
1
C165
Vs+
473
XP6
C150
+12V
1
47n
DGND
2
DGND
3
-12V
4
C151
CON4
47n
FL101
T6.3A250V
XS5
C143
0.1u
1
2
3
C144
CON3
0.1u
FL102
T6.3A250V
XS8
L2
1
R2
2
C2
3
SL2
4
SR2
5
6
Vc+
GND
7
8
9
Vc-
CON9
A
Front Panel schematic & PCB wiring diagram
Page 23

F
10-Mar-2006
更 改 更改单号 签 名 日 期
李林存
设 计 审 核 批 准
123456
数 量
标 准 化
东莞市步步高视听电子有限公司
第 张 共 张 版次:
BBK
10
12 0.0
E
XS101
5
4
3
2
1
CON5
R101
2.2/0.25W
VD102
1N4004
R103 270/0.5W
C109
100u/35V
R102
VD101
4.7k/0.25W
5.6V
VD103
C101
C110
30V
47u/35V
VD104
LED
XP103
1
2
3
CON3
VD105
LED
D
VFD101
VFD210T
1
26
SG13/GR16
SG14/GR15
SG15/GR14
SG16/GR13
SG17/GR12
SG18/GR11
VDD
VEE
SG19/GR10
SG20/GR10
GR8
GR7
GR6
R113
180
+5V
R114
180
23
SG10/KS1024SG11/KS1125SG12/KS12
GR540GR441GR342GR243GR144VDD45LED546LED447LED348LED249LED150GND51OSC
G11
G12
G13
G14
G15
+5V
Ve
27
G1
28
47n
29
G2
30
G3
31
G4
32
G5
+5V
33
Ve
34
35
G6
36
G7
37
G8
38
G9
39
G10
N101
PT6311
XS103
1
2
3
CON3
C
B
A
123456
P116P215P314P413P512P611P710P89P98P107P116P125P134F2F
14
VDD
K4
SG1/KS115SG2/KS216SG3/KS317SG4/KS418SG5/KS519SG6/KS620SG7/KS721SG8/KS822SG9/KS9
K3
K2
K1
STB
CLK
NC
DIN
DOUT
SW4
SW3
SW2
SW1
52
R117
47k
R118
180
R116
180
R115
180
29
G10
G11
G12
G13
G14
G15
C102
47n
S101
S102
S103
KEY
KEY
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
C103
1
221
VD108
LED
VD107
LED
VD106
LED
KEY
R108
R109
C104
10k
10k
221
+5V
3
C106
2
47u/16V
F46F45G143G242G341G440G539G638G737G836G935G1034G1133G1232G1331G1430G15
G1G2G3G4G5G6G7G8G9
+5V
S104
S105
KEY
KEY
R104 100
R106 10k
R105 100
R107 10k
R112 10k
C108
47u/16V
+5V
XP102
8
REM
CK3
7
DA3
6
5
ST3
4
ST4
3
DGND
2
1
+5V
CON8
R111 100
R110
C105
10k
221
N102
REMOT
VS
1
OUT
GND
+5V
C107
47n
F
F
10-Mar-2006
更 改 更改单号 签 名 日 期
李林存
设 计 审 核 批 准
123456
数 量
标 准 化
AV110T咪座板原理图
东莞市步步高视听电子有限公司
第 张 共 张 版次:
BBK
1
11.0
F
E
E
D
D
C
C
B
B
A
A
123456
D+5V
84
N100A
PT2308
3
C103
R103 4.7K
10u/16V
R101
47K
R100 22K
D+5V
R105
47K
C105 10u/16V
R106
47K
C102
100u/16V
R104 4.7K
C104 10u/16V
R102
47K
XP12
4
MIC1
GND
3
2
GND
1
MIC-DET
CON4
D
XP24
D+5V
1
DGND
2
R
3
L
4
PH_SW
5
CON5
MIC1
E
C106 330u/16V
1
2
R107 10K
N100B
PT2308
5
6
R108 10K
R109
47K
PH_R
PH_L
C107
7
330u/16V
R110
47K
X100
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
MIC
PH_SW
C101 103
C100 103
C
B
A
Power board schematic & PCB wiring diagram
Page 24

F
更 改 数 量 更改单号 签 名 日 期
设 计 审 核
1
23
标 准 化
批 准
4
第 张 共 张
东莞市步步高视听电子工业有限公司
BBK
5
E
D
C
B
A
1
C100
22n
VD100
1N5404
VD101
FL100
XS1
T6.3AL250V
2
1
CON2
~220V 50HZ
XP7
OVER
4
P_RC
3
RLY0
2
SWM
1
From AMPFrom AMP
CON4
XP8
1
L2
2
R2
3
C2
4
SL2
5
SR2
6
VC+
VC+
7
GND
8
GND
9
VC-
VC-
CON9
XS2
1
TO SWITCH
2
C102
CON2
CT7 472
XS3
1
TO TRANS
2
CON2
VD113
1N4004
R102
1K
C126
VD108
2.2u/16V
R101
V100
C9014
10K
RLY0
IN4148
R103
SWM
47K
R111
4.7/1W
C116 0.1u
R112
4.7/1W
C117 0.1u
R113
4.7/1W
C118 0.1u
R114
4.7/1W
C119 0.1u
R115
4.71W
C120 0.1u
From TRANS
XS4
1
~V1
2
0
3
~V1
4
V-RLY
CON4
C110
100u/35V
R100
47/3W
R104
10K
L100
0.7UH
L101
0.7UH
R121
2K/0.25W
C122
104
R105
10K
C113
V101
V102
220u/16V
C9014
C9014
C114
220u/16V
R116
51K
R117
51K
R118
47K
R119
56K
R120
56K
R122
2K/0.25W
FL101
C103
T8AL250V
0.22u
C104
0.22u
FL102
T8AL250V
VD110
IN4148
R106
R108
4.7K
100K
R107
100K
V103
C9015
C121
R109
103
10k
1
1
2
2
XL101A
XL101A
WP6
WP6
1N5404
C101 22n
VD102
1N5404
VD103
1N5404
VD104
1N5404
VD105
1N5404
C105 22n
VD106
1N5404
VD107
1N5404
C111 22n
VD111
R110
5.1V
C115
56K
47U/25V
XL101A
Y100
1
1
9
5
2
2
10
6
3
11
7
4
SWM
12
8
RLY0
13 14
RELAY-4
VD112
1N4148
Vc+
C108
8200u/63V
C106
0.1u
C107
C109
0.1u
8200u/63V
Vc-
C123
103
C112
103
XL100A
XL100A
1
1
2
2
WP6
WP4
WP4
V105
C9014
V104
C8050
2
3
45
版次:
6
F
E
D
C
Video board schematic & PCB wiring diagram
1
更 改 数 量 更改单号 签 名 日 期
设 计 审 核
A
6
B
A
65432
A
标 准 化
B
批 准
C
D
广东步步高电子工业有限公司
第 张
BBK
E
共 张 版 次:
F
1
B
XC101
1
VCD
2
R101 100
3
DVD
4
R102 100
5
VOUT
6
AV3
R107 10k
220u/16V
VCD
DVD
TC103
+5V
VOUT
R105
100
V101
A1015
N101 CD4051
13
14
15
12
TC101
100u/16V
R106
22K
R108
1
3
XCOM
X0
X1
16
VDD
X2
8
VSS
6
INH
X3
1
X4
7
VEE
5
X5
2
11
X6
A(0)
10
B(1)
4
9
X7
C(2)
C102
103
+5V
C103
103
C104
103
R103 22
R104 100
XS101
1
DGND
2
INH
3
V-A
4
V-B
5
-12V
6
CON6
+5V
C101
TC104
103
220u/16V
C
D
E
F
2
34 56
Page 25

Signal Processing Board schematic & PCB wiring diagram
D
10-Mar-2006
李林存
设 计 审 核 批 准
F
E
更 改 更 改 单 号 签 名 日 期
123456
数 量
C100
10u/16V
V107
V100
R115
100K
S8050
R162
10K
R116
100K
VD110
VD111
R118
100K
1N4148
1N4148
VD109
VD105
1N4148
1N4148
N107 7805
1
3
Vin
Vout
GND
C128
C134
47n
220u/16V
2
BBK
BURST
L-1
R-1
C-1
XP20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
CON10
DISP
OK-R
OK-L
KM
C1-1
FAN
XS23
1
2
3
CON3
标 准 化
第 张 共 张 版次:
1
东莞市步步高视听电子有限公司
1
R109
1K
R169 4.7K
BURST
C115
22u/16V
SR-1
SL-1
C-1
R-1
L-1
SW1
DISP
OK-R
OK-L
KM
C1-1
XS24
1
2
3
CON3
FAN
VD106 1N4004
R170 1
R171 1
VD107 1N4004
R152 2.2K
R110 1K
R151 2.2K
R167
4.7K
2N5401
R139
10K
V102
9014
+12V
V108
2N5401
V101
S8050
R163
10K
V104
S8050
V103
2N5401
R153
V105
S8050
4.7K
R143
C119
10K
22u/16V
VD108
1N4148
V110
9014
R106
22/0.5W
V109
S8050
C130
1000u/16V
1.0
C129 47n
C101
10u/16V
C142 100u/16V
D+5V
C143
C144
47n
C
C103 47P
R120 20K
R132 20K
N100B
R127 82K
4558
6
C113
7
4.7u/16V
5
C105 47P
R133 20K
R128 20K
N101B
R122 82K
4558
6
C114
7
4.7u/16V
5
C107 47P
R134 22K
R129 22K R12430K
N102B
4558
6
C118
7
4.7u/16V
5
+12V +12V
C124
47u/16V
D+5V
C125
47u/16V
47n
R121 18K
R137 12K
R123 18K
R140 12K
R108 12K
R158
220
R161
220
C121
47n
C122
47n
-12V-12V
B
C104 47P
R101 43K
-12V
N100A
4558
2
1
C106 47P
R102 43K
C108 47P
R103 22K
R1
C13110u/ 16V
8 4
+12V
-12V
N101A
4558
1
L1
C13210u/ 16V
8 4
+12V
-12V
N102A
4558
1
C1
8 4
+12V
SR1
SL1
P_TDO
C137
C135
C138
103
103
103
3
2
3
2
3
R111 560
R112 560
R113
R142 39K
R145 39K
A
LINE OUT
1
R100
47K
XS9
SWM
L1
R1
C1
SL1
SR1
CON7
XS13
P_RLY
P_RLY
RLYC
RLYC
LRM
LRM
SCM
SCM
CON5
VD100
1N4148
VD101
1N4148
560
VD102
1N4148
VD103
1N4148
VD104
1N4148
R104
R105
47K
47K
P_TCE
P_TCE
P_TDO
P_CLK
P_CLK
P_DATA
P_DATA
P_LT62446
P_LT62446
A+5V
+12V
-12V
123456
XC100
SW-OUT
2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
From AMP Board
1
2
3
4
5
DIST
DIST
XP22
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
CON9
F
E
D
C
B
A
Page 26

F
10-Mar-2006
李林存
设 计 审 核 批 准
更 改 更 改 单 号 签 名 日 期
123456
东莞市步步高视听电子有限公司
XS25
D+5V
5
DGND
4
R-1
3
L-1
2
数 量
标 准 化
BBK
第 张 共 张 版次:
1
HEADPHONE
1
CON5
C217
R207 5.1K
10u/16V
XS12
MIC1
1
GND
2
GND
3
MIC-DET
4
CON4
P_LT4094
P_DATA
P_CLK
1
1.0
E
-12V
N201A
4558
+12V
N210 CD4094
STR
DATA
CLK
Qs
Q`s
VSS
OUTB
VDD
N211 CD4094
STR
DATA
CLK
Qs
Q`s
VSS
OUTB
VDD
N207 CD4051
X0
X1
X215VDD
X3
X4
X5
X6
X7
+12V
R204
100/0.25W
C211
VD200
47n
9.1V
C208
100u/16V
C219 10u/16V
C236 10P
R240 220K
C252
R213 2K
1
10u/16V
-12V
N202A
4558
2
3
8 4
+12V
4
Q1
FAN
5
Q2
6
Q3
7
BURST
Q4
BURST
14
RELAY
Q5
RELAY
13
LRM
Q6
LRM
12
SCM
Q7
SCM
11
KM
Q8
KM
4
Q1
5
Q2
6
Q3
7
Q4
14
Q5
13
Q6
12
Q7
11
Q8
3
XCOM
INH
VSS
VEE
A(0)
B(1)
C(2)
R259 1
6
R215 2K
16
+6.8V
R272 3.3K
8
R270 6.8K
7
-6.8V
R266 8.2K
11
R271 12K
10
R261 18K
9
R269 33K
D+5V
C200 151
R200 39K
2
3
8 4
R285
10K
1
2
3
9
10
8
15
16
D+5V
1
2
3
9
10
8
15
16
D+5V
13
R254 15K
14
R218 20K
R223 27K
12
R260 30K
1
R255 36K
5
R262 43K
2
R256 62K
4
R257 120K
D
C202 47u/16V
N200 PT2315
1
REF
CLK
2
VDD
DATA
3
AGND
DGND
C225
4
TREBL
LOUT
5.6n
C226
5
TREBR
ROUT
5.6n
6
RIN
BOUT_R
7
BIN_R
LOUD_R
8
NC
BOUT_L
9
BIN_L
LOUD_L
NC10LIN
VD201
R209 1K
1
1N4148
C205
47u/16V
VD203
1N4148
N208 CD4051
3
13
XCOM
X0
6
14
INH
X1
16
X215VDD
+6.8V
8
12
VSS
X3
1
7
X4
VEE
-6.8V
5
11
X5
A(0)
2
10
X6
B(1)
4
9
X7
C(2)
P_RLY
DISP
DIST
P_OKT
P_CLK
P_CLK
P_TCE
P_LT62446
P_LT62446
P_LT4094
P_SCL
P_DATA
P_DATA
DGND
D+5V
D+5V
DGND
DGND
R233 200K
R234 200K
R235 200K
+12v
84
N203A
4558
3
2
-12v
R253 10K
R250 2K
R251 2K
R252 2K
+6.8V +12V
C215
10u/16V
C216
10u/16V
-6.8V -12V
+12V +12V
C235
101
N204A
4558
1
C245 4.7u/16V
C246 4.7u/16V
C203
47u/16V
C204
47u/16V
+12V
-12V
A
P_RLY
123456
DISP
DIST
P_TCE
L-1
L-1
R-1
R-1
C-1
1
C1-1
C1-1
OK-L
OK-L+6.8V
OK-R
OK-R
R236 510
R239
680
R274
680
R273 510
C209
47n
C210
47n
-12V-12V
XS6
+12V
1
DGND
2
DGND
3
-12V
4
CON4
R230 15K
R2482KR249
4.7u/16V
R227
10K
R229
100K
B
XS101
1
2
XS103
REM
CK3
DA3
ST3
DGND
DGND
+12V
+12V
CON8
6
5
12
13
2
1
5
3
6
11
10
R238
10K
2K
C249
N204B
4558
6
5
3
4
8
5
7
6
6
7
5
8
4
9
3
10
2
11
1
12
13
14
15
CON15
R231 47K
N203B
4558
7
N205
CD4053
14
X0
X
X1
15
Y0
Y
Y1
4
Z0
Z
Z1
16
VDD
INH
8
A
Vss
B
7
C9VEE
-6.8V
R268 10K
R267 10K
-12v
2
7
3
8 4
+12v
C
XS100
+12V
1
-12V
2
3
4
5
103
R216
5.6K
A+5V
C212
47n
C207 47u/16V
C239
103
6
7
8
9
10
P_MICDET
11
ST3
12
CK3
13
14
P_TDO
DA3
15
CON15
N209
PT2399
1
VCC
2
REF
3
AG
4
DG
R258
5
CLK
56K
6
VCO
C213
7
CC1
0.22u
C214
CC08P1-O
0.22u
N202B
4558
5
7
6
R228
100K
C234
3.9n
R247 3.9K
+12V
R242
R211
330
1K
V201
9014
C231
C240
68n
0.47u/16V
R210
R244
150K
16
F1-I
15
F1-O
14
F2-O
13
F2-I
12
P2-O
11
P2-I
10
P1-I
9
R202
R246
1K
20K
39K
-12V
C247 4.7u/16V
R222 10K
C242
5.6n
C248 4.7u/16V
R221 12K
R284 22K
C250
R224 10K
561
C251
R232 15K
R264
561
4.7K
R225 10K
C233
R226 15K
0.1u
C238
103
C243 5.6n
C232
0.1u
20
P_SCL
19
P_DATA
18
17
R220 10K
C221
16
10u/16V
C227
15
68n
C228
14
68n
13
12
11
P_OKT
C237
V200
9014
R241
47K
+12V
R263
220/0.5W
C206 47u/16V
VD202
5.1V
F
E
D
C
B
A
Page 27

Volume Board schematic & PCB wiring diagram
2
3
6
5
A+6.8V
R150 22K
C112 101
C
R156
R155
R154
R153
22K
22K
22K
22K
1
B
B
A
INH
5.1CH
C116
47n
R157
100K
R160
100K
R161
100K
R162
100K
R158
100K
R159
100K
V-TU
C113
221
-12V
N107A
4558
1
8 4
+12V
N107B
4558
7
OUT4
2
A
OUT3
3
INH
OUT2
4
5.1CH
OUT1
5
AVDD
6
C117
SWIN
4.7u/16V
7
GNDS
8
C118
SRIN
4.7u/16V
9
C119
SLIN
4.7u/16V
10
GNDC
11
C120
CIN
4.7u/16V
12
GNDR
13
C121
RIN
4.7u/16V
14
GNDL
15
C122
LIN
4.7u/16V
16
BYPASR
17
BYPASL
C123
18
LTRE
822
19
LBASS3
C124
15n
20
LBASS2
C125
0.33u
LBASS121RBASS1
S8050
V106
C152
C153
47u/16V
47n
VD112
9.1V
R196 100K
C114 22P
R191
6
100K
5
R170 75K
R169 68K
R168 27K
2
C145
3
10n
R167
100K
C
10-Mar-2006
卢建强
设 计 审 核 批 准
更 改 更 改 单 号 签 名 日 期
123456
数 量
标 准 化
BBK
第 张 共 张 版次:
1
东莞市步步高视听电子有限公司
1
1.0
F
R130 1K
TUNER_R
R132 47K
R152 47K
R197 1K
TUNER_L VCD-L
R111 1K
XC101A
3
R112 47K
R
2
R113 47K
VCD
1
R114 1K
L
R115 1K
XC101B
6
R116 47K
R
5
R117 47K
DVD
4
R118 1K
L
R119 1K
XC102A
3
R120 47K
R
2
R121 47K
1
R122 1K
L
R103 1K
XC102B
6
R104 47K
R
5
R105 47K
4
R106 1K
L
R107 1K
XC102C
9
R108 47K
R
8
R109 47K
7
R110 1K
L
C144
C149
C150
103
103
103
N104B
6
4558
5
C105
221
C107
-12V
47u/16V
N104A
2
4558
3
C108
C106
47u/16V
221
8 4
+12V
F
E
VCD-R
DVD-R
5.1CH-R
DVD-L
5.1CH-L
B
B
A
A
S-C
5.1CH-C
S-SR
5.1CH-SR
S-SL
5.1CH-SL
5.1CH
5.1CH
SW
R1241KR125
R126
1K
1K
C148
103
R137 56K
7
1
R138 56K
R139 100K
C109 101
R140 47K
R141 22K
R142 33K
2
3
R143
27K
6
5
E
D
N101
CD4052
12
X0
14
13
X1
X
15
X2
11
X3
3
Y
1
Y0
5
Y1
2
Y2
4
16
A+6.8V
Y3
VDD
6
INH
8
VSS
9
B
7
A-6.8V
VEE
10
A
N102
CD4053
12
14
X0
X
13
X1
2
15
Y0
Y
1
Y1
5
4
Z0
Z
3
Z1
16
VDD
A+6.8V
6
INH
11
8
A
Vss
10
B
7
C9VEE
A-6.8V
R134
R135
R136
150K
150K
N103
CD4053
12
14
X0
X
13
X1
2
15
Y0
Y
1
Y1
5
4
Z0
Z
3
Z1
16
VDD
6
INH
11
8
A
Vss
10
B
7
C9VEE
R195
56K
S-C
-12V
N105A
4558
C111
1
4.7u/16V
8 4
+12V
C110 101
N105B
4558
7
S-SR S-SL
150K
R133
150K
A+6.8V
A-6.8V
R149 22K
R148 30K
R144 47K
R145 22K
R146 33K
D
C115
47u/16V
R147
27K
D+5V
R163 100
R164 100
R165 100
C139
101
TUNER_L
V-TU
TUNER_R
INH
A
B
DISP
OK-R
-12V
A-6.8V A+6.8V
R129
220/0.5W
VD100
6.8V
C101
C103 47n
47u/16V
A
XS22
1
2
P_CLK
3
P_DATA
P_LT62446
+5V
GND
INH
A
B
-12V
A
123456
4
5
6
7
8
+12V
9
-12V
CON5
XS19
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
CON11
XP101
1
2
3
4
5
6
CON6
XS20
SR1
1
SL1
2
C-1
3
R-1
4
L-1
5
SW1
6
7
8
9
10
CON10
+12V
R131
220/0.5W
VD101
6.8V
C104
47u/16V
B
C143
C142
47n
47u/16V
L101 100uH
42
DVDD
41
CLK
40
DATA
39
LATCH
DGND
AGND
N106
SWOUT
M62446
SROUT
SLOUT
COUT
ROUT
LOUT
AVSS
CR1
CR2
RTRE
RBASS3
RBASS2
R198 1K
C154
47u/16V
N108B
4558
7
C146
3.9n
-12V
N108A
C147
4558
1
47u/16V
8 4
+12V
C141
C138 4.7u/16V
C137 4.7u/16V
C136 4.7u/16V
C135 4.7u/16V
C134 4.7u/16V
C133 4.7u/16V
C140
101
101
SR1
SL1
C-1
R-1
L-1
A-6.8V
C131 47n
C132
47u/16V
C128
822
C127
15n
C126
0.33u
R174
47K
R175
47K
R176
47K
R177
47K
R178
47K
C102 47n
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
CL1
C130
4.7u/16V
28
CL2
27
C129
4.7u/16V
26
25
24
23
22
+12V
DISP
B
Spare parts list
Signal processing Board
MATERIAL
CODE
0880230 IC PT2399 DIP PCS 1 N209
MATERIAL
NAME
SPECS &
MODEL
UNIT QTY LOCATION
Page 28

0880417 IC CD4053BCN DIP PCS 1 N205
0881430 IC CD4053BE DIP PCS 1 N205
0880379 IC
LM7805 GOLD
SEALED TO-220
PCS 1 N107
MC7805CT
0880247 IC
GOLD SEALED
PCS 1 N107
TO-220
0880499 IC
L7805CV GOLD
SEALED TO-220
PCS 1 N107
0881743 IC F4558 DIP PCS 4 N201~N204
0882161 IC AZ4558 DIP PCS 4 N201~N204
0880445 IC 4558C DIP PCS 4 N201~N204
0880124 IC NJM4558D DIP PCS 4 N201~N204
0881393 IC IL4558N DIP PCS 4 N201~N204
0882223 IC NE5532 DIP PCS 3 N100~N102
0880807 IC PT2315 SOP PCS 1 N200
0880271 IC CD4051 DIP PCS 2 N207,N208
0881428 IC CD4094BCN DIP PCS 2 N207,N208
0880444 IC TC4094BP DIP PCS 2 N210,N211
CD11
0880654 IC
16V1000U±20%
PCS 2 N210,N211
10×16 5
0882338 IC
1/2W22Ω±5%
SHAPED 12.5
PCS 2 N210,N211
15P
40mm2.54mm
0260030 CD
OUTSIDE
DISTANCE
PCS 1 C130
BETWEEN GLUE
CORE 28.4mm
0010226
1970064
2120296
METAL
OXIDE
FILM
RESISTOR
NEEDLE
NETWORK
S
FLAT
CABLE
5P140 2.5
2PLUG WITH
PCS 1 R106
NEEDLE
10P75 2.5
2PLUG WITH
NEEDLE
PCS 2
IN-PHASE
9P75 2.5 2PLUG
WITH NEEDLE
PCS 1 XP25
BETWEEN
XS100~XP100,
BETWEEN
XS101~XP101
Page 29

IN-PHASE
2121187
2121561
1940002 SOCKET 7P 2.5mm PCS 2 XS23,XS24
1940003 SOCKET 8P 2.5mm PCS 2 XS6,XS12
1940004 SOCKET
1940007 SOCKET 14×8×16 AV130 PCS 1 XS9
1940009 SOCKET AV100 PCS 1 XS103
1910034
3580092
3870591
3026724
4000197
4000462
5447830
5447837
FLAT
CABLE
FLAT
CABLE
TERMINAL
SOCKET
HEAT
RADIATIO
N BOARD
GROUNDI
NG PIECE
PLASTIC
BRACKET
SELF-TAP
PING
SCREW
SELF-TAP
PING
SCREW
SEMI-FINIS
HED PCB
SEMI-FINIS
HED PCB
3P 2.5mm PCS 1 XP20
4P 2.5mm PCS 1 XP22
AV1-8.4-5G
BLACK
H=28.4mm
AV230
BT3×8 NICKEL PCS 1
BT 3×6H WHITE
NICKEL
3110T-2
AV250T(RU) AI
7228-1
AV250T(RU)
PCS 1
PCS 1
PCS 1
PCS 1 XS13
PCS 1 XC100
STICK TO 7805(N107)
PCS 2
PCS 2
PCS 4
SIGNAL PROCESSING
BOARD/CPU BOARD
2 PCS FOR PLASTIC
BRACKET/SIGNAL
PROCESSING BOARD,
2PCS FOR PLASTIC
BRACKET/CPU BOARD
HEAT RADIATION
BOARD/IC
MATERIAL
CODE
2100003
2100004
MATERIAL
NAME
CONNECTI
ON CORDS
CONNECTI
ON CORDS
SPECS &
MODEL
Φ0.6 SHAPED
7.5mm
Φ0.6 SHAPED
10mm
UNIT QTY LOCATION
W1,W3~W33,W34,W36~
PCS 60
PCS 13 W60~W70,W90,W2
W42,W44~W48,W50,
W52~W59,W78,W82,
W84,W85,W92,W93
Page 30

2100007
2100017
00000029
00000119
00000139
00000179
00000189
00000199
00000229
00000269
00000279
00000309
00000329
00000349
00000359
CONNECTI
ON CORDS
CONNECTI
ON CORDS
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
Φ0.6 SHAPED
15mm
Φ0.6 SHAPED
20mm
PCS 8 W71~W77,W91
PCS 4 W79~W81,W83
1/6W1Ω±5% PCS 1 R259
1/6W220Ω±5% PCS 2 R158,R161
1/6W330Ω±5% PCS 1 R242
1/6W510Ω±5% PCS 2 R236,R273
1/6W560Ω±5% PCS 3 R111~R113
1/6W680Ω±5% PCS 2 R239,R274
1/6W1K±5% PCS 5 R110,R109,R209~R211
1/6W2K±5% PCS 7 R248~R252,R213,R215
1/6W2.2K±5% PCS 2 R151,R152
1/6W3.3K±5% PCS 1 R272
1/6W3.9K±5% PCS
R247
1
1/6W4.7K±5% PCS 4 R153,R169,R264,R167
1/6W 5.1K±5% PCS 1 R207
Page 31

00000369
00000379
00000389
00000409
00000419
00000439
00000449
00000459
00000469
00000489
00000499
00000509
00000519
00000589
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
1/6W5.6K±5% PCS 1 R216
1/6W6.8K±5% PCS 1 R270
1/6W8.2K±5% PCS 1 R266
R139,R220,R222,R238,
1/6W10K±5% PCS 13
R253,R267,R268,R143,
R162,R163,R224,R225,
R227
1/6W12K±5% PCS 4 R271,R221,R137,R140
1/6W15K±5% PCS 4 R232,R254,R226,R230
1/6W18K±5% PCS 3 R261,R121,R123
1/6W20K±5% PCS 5
R202,R129,R218,R120,
R128
1/6W22K±5% PCS 4 R284,R132,R133,R134
1/6W27K±5% PCS 1 R223
1/6W30K±5% PCS 2 R260,R124
1/6W33K±5% PCS 1 R269
1/6W39K±5% PCS 4 R246,R200,R142,R145
1/6W82K±5% PCS 2 R127,R122
Page 32

00000529
00000549
00000559
00000599
00000609
00000629
00000659
00000669
00001759
00003459
00003519
00003609
00006239
00102289
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
METAL
OXIDE
FILM
RESISTOR
1/6W47K±5% PCS 6
R100,R103,R241,R231,
R104,R105
1/6W56K±5% PCS 1 R258
1/6W62K±5% PCS 1 R256
1/6W100K±5% PCS 5
R115,R116,R228,R229,
R118
1/6W120K±5% PCS 1 R257
1/6W150K±5% PCS 1 R244
1/6W200K±5% PCS 3 R233,R234,R235
1/6W220K±5% PCS 1 R240
1/4W100Ω±5% PCS 1 R204
1/6W36K±5% PCS 1 R255
1/6W43K±5% PCS 3 R262,R101,R102
1/6W 7.5K±5% PCS 1 R108
1/2W220Ω±5% PCS 1 R263
1/4W1Ω±5% PCS 2 R170,R171
Page 33

02600019 CD
02600029 CD
02601819 CD
02601889 CD
02603909 CD
02604379 CD
02604389 CD
PORCELAI
02003069
N
CAPACITO
R
PORCELAI
02003079
N
CAPACITO
R
PORCELAI
02003109
N
CAPACITO
R
PORCELAI
02003159
N
CAPACITO
R
PORCELAI
02003299
N
CAPACITO
R
PORCELAI
02003309
N
CAPACITO
R
CD11
16V22U±20%
5×11 C5
CD11
16V47U±20%
5×11 C5
CD11
16V220U±20%
6×12 C5
CD11
16V100U±20%
6×12 C5
CD11
50V0.47U±20%
5×11C5
CD11
16V4.7U±20%
5×11C5
50V 47P±10%
SHAPED 5mm
50V 101±10%
SHAPED 5mm
50V 103±10%
SHAPED 5mm
50V 10P ± 10 %
SHAPED 5mm
50V561±10%
SHAPED 5mm
50V151±10%
SHAPED 5mm
100V 683 ±10%
SHAPED 5mm
PCS 2 C119,C115
PCS 8 C124,C125,C202~C207
PCS 1 C134
PCS
C142,C208
2
PCS
C240
1
C131,C100,C101,C132,
PCS 10
C215~C217,C219,C221,
C252
PCS 8
C113,C114,C118,C245~
C249
PCS 6 C103~C108
PCS 1 C235
PCS 6
C237~C239,C135,C138,
C137
PCS 1 C236
PCS 2 C250,C251
PCS 1 C200
Page 34

02100689
V
02101439
02101489
02102209
02101579
02102219
02101049
02101459
TERYLENE
CAPACITO
R
TERYLENE
CAPACITO
R
TERYLENE
CAPACITO
R
TERYLENE
CAPACITO
R
TERYLENE
CAPACITO
R
TERYLENE
CAPACITO
R
100V392±10%
C5
100V 473 ±10%
SHAPED 5mm
100V 473 ±5%
SHAPED 5mm
100V 562±10%
SHAPED 5mm
100V 562±5%
SHAPED 5mm
CL21X100V224
K C5BD
METAL
POLYESTE
R FILM
CAPACITO
CL21X 100
104K C5
R
METAL
POLYESTE
R FILM
1N4004 PCS 2 C232,C233
CAPACITO
R
PCS 3 C227,C228,C231
PCS 1 C234
PCS 10
PCS 10
C121,C122,C128,C129,
C143,C144,C209~C212
C121,C122,C128,C129,
C143,C144,C209~C212
PCS 4 C225,C226,C242,C243
PCS 4 C225,C226,C242,C243
PCS 2 C213,C214
05700049 DIODE 1N4148 PCS 2 VD106,VD107
VD201,VD203,VD108,
0570006 DIODE 5.1V 1/2W PCS 12
VD100~VD105,VD109~
VD111
VOLTAGE
05800069
REGULAT
9.1V 1/2W PCS 1 VD202
OR DIODE
VOLTAGE
05800099
REGULAT
2N5401 PCS 1 VD200
OR DIODE
07800259 TRIODE 9014C PCS 3 V103,V107,V108
07800329 TRIODE 8050D PCS 4 V102,V200,V201,V110
07801389 TRIODE 3110T-2 PCS 5
V105,V101,V104,V100,
V109
Page 35

01564101 PCB PCS 1
CPU Board
MATERIAL
CODE
0100008
0390168
0390353
0000279
0260019 CD
0260025 CD
0260049 CD
0260067 CD
0260096 CD
0260127 CD
0210111
MATERIAL
RESISTOR
NETWOR
K
INDUCTO
R
MAGNETI
C BEADS
INDUCTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
METAL
POLYEST
ER FILM
CAPACITO
R
NAME
SPECS &
MODEL
1/6W 4.7K ±5%
9P
100UH ± 10 %
0410 SHAPED
12.5mm
RH-357508
SHAPED 12.5mm
1/4W470Ω±5%
SHAPED 10
CD11
16V10U±20%5×1
1 2
CD11
16V47U±20%5×1
1 2
CD11
50V0.22U±20%5×
11 2
CD11
50V2.2U±20%5×1
1 2
CD110
16V100U±20%6×
12 2.5
CD11
16V4.7U±20%5×1
1 2
CL21X 63V 104±
5% 5
UNIT QTY LOCATION
PCS 1 RR100
PCS 1 L100
PCS 1 L101
PCS 2 R118,R119
PCS 5
PCS 1 C100
PCS 1 C138
PCS 8
PCS 2 C140,C141
PCS 2 C110,C106
PCS 1 C137
C111,C112,C114,C115,
C139
C118,C121,C124,C127,
C130,C133,C136,C109
Page 36

VD102,VD103,VD108,
VD109,VD110,VD111,
0570006 DIODE 1N4148 PCS 13
VOLTAGE
05800019
05800059
05800459
0780025 TRIODE 2N5401 PCS 1 V103
REGULAT
OR DIODE
VOLTAGE
REGULAT
OR DIODE
VOLTAGE
REGULAT
OR DIODE
3.3V 1/2W PCS 1 VD117
4.7V 1/2W PCS 1 VD101
6.8V 1/2W PCS 2 VD106,VD107
VD112,VD113,VD114,
VD115,VD116,VD118,
VD119
0780032 TRIODE 9014C PCS 5
0880013 IC LM324N DIP PCS 2 N105,N106
0880271 IC CD4051 DIP PCS 2 N104,N108
0881428 IC CD4051BE DIP PCS 2 N104,N108
0880664 IC 24C02 DIP PCS 1 N101
0881743 IC F4558 DIP PCS 3 N102,N103,N107
0882161 IC AZ4558 DIP PCS 3 N102,N103,N107
0880445 IC 4558C DIP PCS 3 N102,N103,N107
0880124 IC NJM4558D DIP PCS 3 N102,N103,N107
0881393 IC IL4558N DIP PCS 3 N102,N103,N107
CERAMIC
0970002
0890277
1850005
5447838
RESONAT
OR
SOFTWAR
E
PROGRA
M CPU
DUAL
LINE IC
SOCKET
SEMI-FINI
SHED PCB
12.0MHz PCS 1 G100
CPU250T(RU)-0 PCS 1
40P DIP
7228-1-SMD
AV250T(RU)
PCS 1 N100
PCS 1
V101,V104,V102,V105,
V100
MATERIAL
CODE
MATERIAL
NAME
SPECS & MODEL
UNIT QTY LOCATION
Page 37

0090001
0090004
0090011
0090014
0090016
0090017
0090019
0090023
0090024
0090026
0090027
0090029
0090034
0090109
0090009
0090181
0090184
0090199
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
1/16W 0Ω ±5%
0603
1/16W 22Ω ±5%
0603
1/16W 470Ω ±5%
0603
1/16W 1K ±5%
0603
1/16W 1.5K ±5%
0603
1/16W 2.2K ±5%
0603
1/16W 4.7K ±5%
0603
1/16W 10K ±5%
0603
1/16W 15K ±5%
0603
1/16W 22K ±5%
0603
1/16W 27K ±5%
0603
1/16W 47K ±5%
0603
1/16W 100K ±5%
0603
1/16W 1MΩ ±5%
0603
1/16W 330Ω ±5%
0603
1/16W 100Ω ±5%
0603
1/16W 4.3K ±5%
0603
1/16W 180K ±5%
0603
PCS 1 R104
PCS 1 R209
PCS 33
R191,R192,R195~R208,
R215~R231
R136,R141,R146,R151,
PCS 9
R155,R160,R165,R170,
R177
PCS 2 R122,R114
PCS 3 R112,R123,R175
R111,R134,R139,R144,
PCS 11
R149,R153,R158,R163,
R174,R185,R101
R108,R117,R125,R131,
R133,R137,R138,R142,
R143,R147,R148,R152,
PCS 26
R156,R157,R161,R162,
R166,R172,R178,R179,
R186,R187,R189,R212,
R213,R214
PCS 1 R109
PCS 4 R100,R110,R132,R183
PCS 1 R126
PCS 2 R115,R180
PCS 8
R135,R140,R145,R150,
R154,R159,R164,R167
PCS 1 R210
PCS 1 R182
PCS 2 R107,R181
PCS 2 R124,R211
PCS 2 R128,R113
Page 38

0090208
0090225
0090242
0310067
0310072
0310594
0310188
0310191
0310471
0310198
0310202
0310206
0310634
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
RESISTOR
SMD
CAPACIT
OR
SMD
CAPACIT
OR
SMD
CAPACIT
OR
SMD
CAPACIT
OR
SMD
CAPACIT
OR
SMD
CAPACIT
OR
SMD
CAPACIT
OR
SMD
CAPACIT
OR
SMD
CAPACIT
OR
SMD
CAPACIT
OR
1/16W 470K ±5%
0603
1/16W 5.6K ±5%
0603
1/16W 75K ±5%
0603
50V 152 ±10%
0603
50V 103 ±10%
0603
25V 104±10%
X7R 0603
50V 10P ±5%
NPO 0603
50V 30P ±5%
NPO 0603 PCS 2 C103,C104
50V 561±5% NPO
0603
50V 472 ±10%
0603
50V 223 ±10%
0603
50V 683 ±10%
0603
25V 154 ±10%
X7R 0603 PCS 2 C134,C135
PCS 4 R129,R130,R116,R169
PCS 2 R173,R184
PCS 1 R127
PCS 2 C119,C120
C105,C142,C143,C144,
PCS 14
PCS 4 C102,C107,C108,C155
PCS 1 C113
PCS 2 C116,C117
PCS 2 C122,C123
PCS 2 C128,C129
PCS 2 C131,C132
C145,C146,C147,C148,
C149,C150,C125,C126,
C152,C151
1632936 PCB 7110T-0 PCS 1
Volume Board
MATERIAL
CODE
MATERIAL
NAME
SPECS & MODEL
UNIT QTY LOCATION
Page 39

0881743 IC F4558 DIP PCS 1 N108
0882161 IC AZ4558 DIP PCS 1 N108
0880445 IC 4558C DIP PCS 1 N108
0880124 IC NJM4558D DIP PCS 1 N108
0881393 IC IL4558N DIP PCS 1 N108
0882223 IC NE5532 DIP PCS 3 N104,N105,N107
0880417 IC CD4053BCN DIP PCS 2 N103,N102
0881430 IC CD4053BE DIP PCS 2 N103,N102
0881429 IC CD4052BE DIP PCS 1 N101
0880443 IC CD4052BCN DIP PCS 1 N101
0881380 IC
0390425
1910117
1910118
1940072
2120325
1940029 SOCKET 9P 2.5mm PCS 1 XS22
1940030 SOCKET 10P 2.5mm PCS 1 XS20
3870591
5447608
INDUCTO
R
TERMINA
L SOCKET
TERMINA
L SOCKET
CABLE
SOCKET
FLAT
CABLE
GROUNDI
NG PIECE
SEMI-FINI
SHED
PCB
M62446AFP
SOP
100UH ±10%
0307 SHAPED
12.5
AV6-8.4-13/ES
AV4-8,4-13/ES PCS 1 XC101
6/5P 1.25mm
DUAL LINE
STRAIGHT PLUG
6P140 2.5 2PLUG
WITH NEEDLE
AV100 PCS 2
2110T-0
AV110T(RU) AI
PCS 1 N106
PCS 1 L101
PCS 1 XC102
PCS 1 XS19
PCS 1 XP101
PCS 1
MATERIAL
CODE
2100003
00000099
MATERIAL
NAME SPECS & MODEL
CONNECT
ION
CORDS
CARBON
FILM
Φ 0.6 SHAPED
7.5mm
1/6W100Ω±5%
UNIT QTY LOCATION
PCS 73 W1~W73
PCS 3 R163,R164,R165
Page 40

00000229
00000469
00000489
00000499
00000509
00000529
00000549
00000569
00000579
00000599
00000629
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
RESISTO
R
CARBON
FILM
R103,R106,R107,R110,
1/6W1K±5% PCS 16
R111,R114,R115,R118,
R119,R122,R124~R126,
R197,R130,R198
1/6W22K±5% PCS 8
R141,R145,R149,R150,
R153,R154,R155,R156
1/6W27K±5% PCS 3 R143,R147,R168
1/6W30K±5% PCS 1 R148
1/6W33K±5% PCS 2 R142,R146
R104,R105,R108,R109,
1/6W47K±5% PCS 19
R112,R113,R116,R120,
R117,R132,R121,R144,
R140,R152,R174~R178
1/6W56K±5% PCS 3 R137,R138,R195
1/6W68K±5% PCS 1 R169
1/6W75K±5% PCS 1 R170
1/6W100K±5% PCS 10
R139,R157~R162,R167,
R191,R196
1/6W150K±5% PCS 4 R133,R134,R135,R136
Page 41

RESISTO
R
CARBON
00006239
FILM
RESISTO
R
02600029 CD
02604389 CD
PORCELA
02003059
IN
CAPACIT
OR
PORCELA
02003079
IN
CAPACIT
OR
PORCELA
02003089
IN
CAPACIT
OR
PORCELA
02003109
IN
CAPACIT
OR
PORCELA
02003149
IN
CAPACIT
OR
TERYLEN
02101439
E
CAPACIT
OR
TERYLEN
02101449
E
CAPACIT
OR
TERYLEN
02101489
E
CAPACIT
1/2W220Ω±5%
PCS 2 R129,R131
CD11
16V47U±20%
5×11 C5
CD11
16V4.7U±20%
5×11C5
50V 22P±10%
SHAPED 5mm
50V 101±10%
SHAPED 5mm
50V 221±10%
SHAPED 5mm
50V 103±10%
SHAPED 5mm
50V 822±10%
SHAPED 5mm
PCS 10
PCS 15
PCS 1 C114
PCS 6
PCS 3 C105,C106,C113
PCS 2 C144,C148
PCS 2 C123,C128
C101,C104,C107,C108,
C115,C132,C142,C147,
C152,C154
C111,C117,C118,C119,
C120,C121,C122,C129,
C130,C133,C134,C135,
C138,C136,C137
C109,C110,C112,C139,
C140,C141
100V392±10% C5
PCS 1 C146
100V 153 ±10%
C5
100V 473 ±10%
SHAPED 5mm PCS 6
PCS 2 C124,C127
C102,
C103,C116,C131,C143,
C153
Page 42

OR
02102209
02101599
02102239
02101419
05800459
05800099
TERYLEN
E
CAPACIT
OR
TERYLEN
E
CAPACIT
OR
TERYLEN
E
CAPACIT
OR
METAL
POLYEST
ER FILM
CAPACIT
OR
VOLTAGE
REGULAT
OR DIODE
VOLTAGE
REGULAT
OR DIODE
100V 473 ±5%
SHAPED 5mm
100V 103 ±10%
SHAPED 5mm
100V 103 ±5%
SHAPED 5mm
CL21X100V334K
C5
6.8V 1/2W PCS 2 VD100,VD101
9.1V 1/2W PCS 1 VD112
C102,
PCS 6
PCS 1 C145
PCS 1 C145
PCS 2 C125,C126
C103,C116,C131,C143,
C153
07801389 TRIODE 8050D PCS 1 V106
1564053 PCB 2110T-0 PCS 1
Power Amplifer Board
MATERIAL
CODE
2100003
2100004
2100006
2100007
MATERIAL
NAME
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CONNECTI
ON
SPECS &
MODEL
Φ0.6 SHAPED
7.5mm
Φ0.6 SHAPED
10mm
Φ0.6 SHAPED
12.5mm
Φ0.6 SHAPED
15mm
UNIT QTY LOCATION
W16,W18,W27,W40,W42
PCS 13
PCS 19
PCS 7
PCS 10
,W43,W54,W55,W61,
W72,W76,W77,W78
W8,W9,W15,W21,W24,
W36,W41,W45,W46,W48
,W51,W57,W63,W65,W6
9,W71,W73,W74,W80
W3,W20,W35,W59,W62,
W66,W70
W2,W14,W19,W26,W50,
W53,W67,W79,W81,W82
Page 43

CORDS
2100010
2100016
2100017
2100024
0000125
0000128
0000129
0000132
0000131
0000133
0000137
0000140
0000141
0000142
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
Φ0.6 SHAPED
5mm
Φ0.6 SHAPED
18mm
Φ0.6 SHAPED
20mm
Φ0.6 SHAPED
22mm
1/6W510Ω±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W820Ω±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W1K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W2.2K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W1.5K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W4.7K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W10K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W22K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W27K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W33K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
PCS 6
W1,W33,W47,W49,W60,
W68
PCS 4 W39,W52,W58,W75
PCS 2 W28,W56
PCS 8 W5,W6,W7,W10,W11,
W12,W13,W64
PCS 2 R110,R140
PCS 3 R170,R191,R195
PCS 6
R103,R109,R112,R133,
R139,R142
PCS 2 R115,R145
PCS 2 R129,R159
PCS 5
R161,R167,R114,R144,
R165
R101,R131,R162,R163,
PCS 10
R168,R164,R166,R185,
R186,R189
PCS 5
R190,R192,R194,R196,
R188
PCS 1 R171
PCS 2 R121,R151
Page 44

CARBON
0000144
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
0000146
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
0000276
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
0000379
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
0000452
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
0000533
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
0000495
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
0000556
FILM
RESISTOR
0040069
CEMENT
RESISTOR
METAL
0010321
OXIDE
FILM
RESISTOR
METAL
0010210
OXIDE
FILM
RESISTOR
METAL
0010268
OXIDE
FILM
RESISTOR
0260389 CD
CD
0260036
1/6W47K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W100K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/4W100Ω±5%
SHAPED 10
PCS 5
PCS 3 R102,R132,R187
PCS 4 R120,R122,R150,R152
R104,R134,R169,R193,
R197
1/6W6.8K±5% PCS 4 R105,R106,R135,R136
1/6W150Ω±5%
SHAPED 7.5
PCS 4 R113,R116,R143,R146
1/2W220Ω±5%
SHAPED R
PCS 4 R117,R125,R147,R155
12.5×8
1/6W4.3K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W47Ω±5%
SHAPED 7.5
PCS 4 R128,R130,R158,R160
PCS 4 R107,R108,R137,R138
7W0.25Ω±5%
SQM SHAPED
PCS 4 R126,R127,R156,R157
R 10×5
1/2W33K±5%
SHAPED 12.5
3W47 Ω±5 %
SHAPED R 20×8
3W22Ω±5%
SHAPED R 20×8
CD1150V0.22U
±20%5×11C5
PCS 2 R111,R141
PCS 1 R184
PCS 1 R183
PCS 3 C124,TC103,TC109
CD11
25V10U±20%
PCS 3 C101,C111,TC102
5×11 2
Page 45

0260021 CD
0260027 CD
0260063 CD
0260302 CD
0260447 CD
0260234 CD
0260465 CD
0260487 CD
PORCELAI
N
CAPACITO
0200018
0200066
0200333
0210147
0210025
R
PORCELAI
N
CAPACITO
R
PORCELAI
N
CAPACITO
R
TERYLENE
CAPACITO
R
TERYLENE
CAPACITO
R
CD11
16V22U±20%
5×11 2
CD11
16V100U±20%
6×12 2.5
CD11
50V1U±20%
5×11 2
CD11 100V47U±
20%8×15 3.5
LUA 35V4700U±
20%18×35 7.5
CD11
35V4700U±20%
19×35 7.5
CD11 100V10U±
20%6.3×11 2.5
CD11K35V220U±
20% 8×16 3.5
50V 22P ±10%
NPO 2.5mm
50V 221 ±10%
2.5mm
500V33P±10%
NPO SHAPED
5mm
100V 473 ±10%
5mm
100V 473 ±5%
6mm
PCS 5
PCS 4 C105,C115,C148,C149
PCS 2 C110,C120
PCS 4 C103,C107,C113,C117
PCS 2 C141,C142
PCS 2 C141,C142
PCS 1 C159
PCS 2 C146,C147
PCS 2 C160,C163
PCS 2 C104,C114
PCS 2 C108,C118
PCS 12
PCS 12
C121,C122,C125,TC104,
TC110
C109,C119,C127,C128,
C139,C140,C150,C151,
C161,C162,C164,C165
C109,C119,C127,C128,
C139,C140,C150,C151,
C161,C162,C164,C165
0570006 DIODE 1N4148 PCS 8 VD101~VD107,VD115
0570020 DIODE 1N5404 PCS 4
0780025 TRIODE 2N5401 PCS 5
VD111,VD112,VD113,
VD114
V105,V115,V120,V130,
V137
Page 46

V102~V104,V106~V107,
0780026 TRIODE 2N5551 PCS 12
0780138 TRIODE 8050D PCS 4 V101,V116,V131,V136
0780070 TRIODE 2SA1964E PCS 2 V133,V135
0780255 TRIODE 2SA940 PCS 2 V133,V135
0780257 TRIODE KSA940 PCS 2 V133,V135
V114,V117~V119,V121~
V122,V129
0780072 TRIODE
0780021 TRIODE 2SC2073 PCS 2 V132,V134
0780258 TRIODE KSC2073 PCS 2 V132,V134
0780097 TRIODE 2SC5200R PCS 2 V112,V127
0780071 TRIODE 2SC5200O PCS 2 V112,V127
0780096 TRIODE 2SA1943R PCS 2 V113,V128
0780069 TRIODE 2SA1943O PCS 2 V113,V128
0882646 IC
0880131 IC
0880380 IC
0881418 IC
0880324 IC
0880325 IC
0880381 IC
0882618
0882913 IC
IC
2SC5248E
CW7812CS
TO-220
L7812CV GOLD
SEALED TO-220
LM7812 GOLD
SEALED TO-220
UA7812C GOLD
SEALED TO -
220
MC7812CT
GOLD SEALED
TO-220
MC7912CT
GOLD SEALED
TO-220
LM7912CT
GOLD SEALED
TO-220
CD1875CZ
TO-220
TDA2052V
GOLD SEALED
TO-220
PCS 2 V132,V134
PCS 1 N101
PCS 1 N101
PCS 1 N101
PCS 1 N101
PCS 1 N101
PCS 1 N102
PCS 1 N102
PCS 1 N104
PCS 2 N105,N106
1940003 SOCKET 4P 2.5mm PCS 1 XS7
1940040 SOCKET 3P 3.96mm PCS 1 XS5
1940155 SOCKET 9P 3.96mm PCS 1 XS8
Page 47

4P140 2.5
A
2PLUG WITH
NEEDLE
PCS 1 XP6
2120267
FLAT
CABLE
5P 125 2.5
2121182
FLAT
CABLE
2PLUG WITH
NEEDLE
PCS 1 XP13
IN-PHASE
7P 145 2.5
2121183
FLAT
CABLE
2PLUG WITH
NEEDLE
PCS 1 XP9
IN-PHASE
2300005 FUSE T6.3AL 250V PCS 2 FL101,FL102
3870057
3580085
3580092
3580215
3870603
4000516
4000453
4000462
FUSE
HOLDER
HEAT
RADIATIO
N BOARD
HEAT
RADIATIO
N BOARD
LARGE
HEAT
RADIATOR
PCB
BRACKET
SELF-TAP
PING
SCREW
SELF-TAP
PING
SCREW
SELF-TAP
PING
SCREW
0 PCS 4 FL101,FL102
15.4×10.7×45
AV220
PCS 1 SRQ1
14×8×16 AV130 PCS 1 STICK TO 7912
261×128×80
AV250T
PCS 1
3PCS FOR POWER
AV130 PCS 3
AMPLIFIER
BOARD/HEAT
RADIATOR
4PCS FOR POWER
PIPE/LARGE HEAT
PT 3×12H WHITE
NICKEL
PCS 7
RADIATOR; 1PC FOR
CD1875/LARGE HEAT
RADIATOR; 2PCS FOR
TDA2052/LARGE HEAT
RADIATOR
3PCS FOR PCB
BT 3×8H WHITE
NICKEL
PCS 4
BRACKET/HEAT
RADIATOR; 1PC FOR
7812/HEAT RADIATION
BOARD
3PCS FOR PCB
BT 3×6H WHITE
NICKEL
PCS 4
BRACKET/POWER
MPLIFIER BOARD;
1PC FOR 7912/HEAT
Page 48

4450012
4490001
5230395
5230979
5230928
5232006
SCREW
SPACER
SPRING
SPACER
INSULATIO
N SPACER
CASING
MIC
SPACER
MICA
SPACER
SOFT
SPONGE
SPACER
RADIATION BOARD
4PCS FOR
SELF-TAPPING
SCREW/POWER PIPE;
Φ3×7.2×0.5 PCS 7
Φ3 PCS 7
Φ3×6×3 PCS 3
28×22×0.1 PCS 4
18×13×0.1 PCS 3
80×12×1.5
SINGLE-SIDED
SOFT
PCS 1
1PC FOR TAPPING
SCREW/CD1875; 2PCS
FOR TAPPING
SCREW/TDA2052
4PCS FOR
SELF-TAPPING
SCREW/POWER PIPE;
1PC FOR TAPPING
SCREW/CD1875; 2PCS
FOR TAPPING
SCREW/TDA2052
1PC FOR
CD1875/SELF-TAPPING
SCREW
4PCS FOR POWER
PIPE/HEAT RADIATOR
1PC FOR
CD1875/LARGE HEAT
RADIATOR; 2PCS FOR
TDA2052/LARGE HEAT
RADIATOR
FLAT CABLE XP9,
XP13/HEAT RADIATOR
1564051
PCB 4320T-0 PCS 1
Video Board
MATERIAL
CODE
0000120
0000122
0000140
MATERIAL
NAME
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
SPECS &
MODEL
1/6W22Ω±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W100Ω±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W22K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
UNIT QTY LOCATION
PCS 1 R103
PCS 4 R101,R102,R104,R105
PCS 1 R106
Page 49

RESISTOR
CARBON
0000137
0000599
0200174
0260027 CD
0260028 CD
0880271 IC CD4051 DIP PCS 1 N101
0881428 IC CD4051BE DIP PCS 1 N101
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
PORCELAI
N
CAPACITO
R
1/6W10K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W1Ω±5%
SHAPED 7.5
50V 103 ±10%
2.5mm
CD11
16V100U±20%6×
12 2.5
CD11
16V220U±20%6×
12 2.5
PCS 1 R107
PCS 3
PCS 4 C101,C102,C103,C104
PCS 1 TC101
PCS 2 TC103,TC104
R108,焊在 PCB 背后
0780043 TRIODE 2SA1015 PCS 1 V101
1940006 SOCKET
1910239
1564076 PCB C210T-0 PCS 1
TERMINAL
SOCKET
6 芯 2.5mm
AV3-8.4-14/ES-10 PCS 1 XC101
PCS 1 XS101
Front Panel Board
MATERIAL
CODE
3004192
3071946
3071947
3071948
3071949
MATERIAL
NAME
SURFACE
CASING
LIGHT
CONDUCT
RING 1
LIGHT
CONDUCT
RING 2
LIGHT
CONDUCT
STRIP
BUTTON
BRACKET
SPECS &
MODEL
AV250T SILVERY PCS 1
AV250T
TRANSPARENT
WHITE
AV250T
TRANSPARENT
WHITE
AV250T
TRANSPARENT
WHITE
AV250T PCS 1
UNIT QTY LOCATION
PCS 1 POWER SWITCH
PCS 1 Q-PLAY
PCS 2
PACK TO BUTTON
BRACKET
Page 50

3871823
Y
Y
3071950
3871821
3871822
3110527
3110380
3029205
4000048
4000120
5447833
5447834
5447835
MIC
PREFORM
DECORATI
ON GLASS
ALUMINU
M
DECORATI
ON
BOARD
ALUMINU
M
DECORATI
ON STRIP
ALUMINU
M-ALLOY
POWER
BUTTON
POWER
BUTTON
DECORATI
ON
CASING
POWER
BUTTON
SELF-TAP
PING
SCREW
SELF-TAP
PING
SCREW
SEMI-FINI
SHED PCB
SEMI-FINI
SHED PCB
SEMI-FINI
SHED PCB
AV250T PCS 1 MIC SOCKET/PANEL
AV250T GLASS
FACE
AV250T SILVERY PCS 1
AV250T SILVERY PCS 2
AV168 SILVER
WHITE
AV138 SILVER
WHITE
AV138 PCS 1
PB 3×8
COLORFUL ZINC
PB 3×10
COLORFUL ZINC
6250T-0
AV250T(RU)
D250T-0
AV250T(RU)
9250T-0
AV250T(RU)
PCS 1
PCS 1
PCS 1
PCS 9
PCS 5
PCS 1
PCS 1
PCS 1
STICK TO LIGHT
CONDUCT STRIP
7PCS FOR
PANEL/CONTROL
PANEL; 2PCS FOR
PANEL/POWER SWITCH
BOARD
2PCS FOR POWER
SWITCH/PANEL; 3PCS
FOR PANEL/MIC
HOLDER PREFORM
Power Board
MATERIAL
CODE
MATERIAL
NAME
SPECS &
MODEL
UNIT QTY LOCATION
Page 51

2100003
2100004
2100007
2100008
2100017
0000129
0000137
0000144
0000146
0000289
0000294
0000301
0000436
0000302
0000305
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CONNECTI
ON
CORDS
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
FILM
Φ 0.6 SHAPED
7.5mm
Φ 0.6 SHAPED
10mm
Φ 0.6 SHAPED
15mm
Φ 0.6 SHAPED
6mm
Φ 0.6 SHAPED
20mm
1/6W1K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W10K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W47K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1/6W100K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
PCS 4 W14,W16,W17,W22
PCS 10
PCS 6
W7,W8,W10,W11,W1,W2
,L102,L103,L104,W13
W5,W12,W15,W4,W9,
W19
PCS 2 W20,W21
PCS 3 W18,W3,W6
PCS 2 R101,R102
PCS 2 R104,R105
PCS 1 R103
PCS 1 R107
1/4W4.7K±5%
SHAPED 10 PCS 1 R106
1/4W10K±5%
SHAPED 10
PCS 1 R109
1/4W47K±5%
SHAPED 10 PCS 3 R118,R119,R120
1/4W2K±5%
SHAPED 10
1/4W51K±5%
SHAPED 10
1/4W100K±5%
SHAPED 10
PCS 2 R121,R122
PCS 2 R116,R117
PCS 1 R108
Page 52

RESISTOR
CARBON
0000476
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
0000499
FILM
RESISTOR
CARBON
0000622
FILM
RESISTOR
0260028 CD
0260039 CD
0260452 CD
0260572 CD
PORCELAI
0200138
N
CAPACITO
R
PORCELAI
0200174
N
CAPACITO
R
CERAMIC
0200338
CAPACITO
R
TERYLEN
0210022
E
CAPACITO
R
TERYLEN
0210029
E
CAPACITO
R
0210031
TERYLENE 100V 224 ±10%
1/6W56K±5%
SHAPED 7.5
1W4.7 Ω ±5%
SHAPED R 15×9
2W22 Ω ±5%
SHAPED R 20×8
CD11
16V220U±20%6×
12 2.5
CD11
25V47U±20%5×1
1 2
CD11
35V220U±20%
8×14 3.5
CD293
63V15000u±20 %
35×70 10
50V 104 ±20%
5mm
50V 103 ±10%
2.5mm
CT7 400VAC 472
±20% 2E4 10mm
100V 223 ±5%
5mm
100V 104 ±5%
7mm
8mm
PCS 1 R110
PCS 5 R111~R115
PCS 1 R100
PCS 2 C113,C114
PCS 1 C115
PCS 1 C110
PCS 2 C108,C109
PCS 1 C122
PCS 4 C121,C112,C123,C126
PCS 1 C102
PCS 4 C100,C101,C105,C111
PCS 7 C106,C107,C116~C120
PCS 2 C103,C104
Page 53

CAPACITO
R
TERYLEN
0210213
E
CAPACITO
100V 224 ±5%
8mm
PCS 2 C103,C104
R
0410007
INDUCTO
R COIL
0.7UH
SC-0.8×8.0×11.5
PCS 2 L100,L101
0570004 DIODE 1N4004 PCS 1 VD113
0570006 DIODE 1N4148 PCS 3 VD112,VD108,VD110
0570020 DIODE 1N5404 PCS 8 VD100~VD107
VOLTAGE
05800069
REGULAT
5.1V 1/2W PCS 1 VD111
OR DIODE
0780032 TRIODE 9014C PCS 4 V100,V101,V102,V105
0780033 TRIODE
9015C(200-600)
TO-92
PCS 1 V103
0780138 TRIODE 8050D PCS 1 V104
1250025 RELAY
2120535
2121040
FLAT
CABLE
FLAT
CABLE
JH1806-012-(3H1
+1Z1) DC12V
4P60 2.5 2PLUG
WITH NEEDLE
PCS 1 Y100
PCS 1 XP7
9P60 3.96 1PLUG PCS 1 XP8
1940037 SOCKET 4P 3.96mm PCS 1 XS4
1940074 SOCKET 2P 7.92mm PCS 3 XS1~XS3
2010003
2010004
SPEAKER
S CORD
SPEAKER
S CORD
WP4-10A PCS 1 XL100
WP6-10A PCS 1 XL101
2300005 FUSE T6.3AL 250V PCS 1 FL100
2300008 FUSE T8AL 250V PCS 2 FL101,FL102
3020402
3870057
3540076
FUSE
HOLDER
FUSE
HOLDER
SCREEN-S
HIEDED
PIECE
BLX-2 PCS 1 FL100
0 PCS 4 FL101,FL102
AV100 OUTPUT
TERMINAL
PCS 1
Page 54

3870591
5180263
5180388
GROUNDI
NG PIECE
GLUE
STICKER
GLUE
STICKER
AV100 PCS 2
STICK TO FL101,
T8AL 250V PCS 2
T6.3AL250V 18×3 PCS 1
BESIDE FL102,
COVER T6.3AL250V
STICK BESIDE FL100,
COVER T4AL250V
1564105 PCB @5100-5 CQC PCS 1
 Loading...
Loading...