Page 1

AV225T
service manual
Page 2

Catalog
Chapter One About Maintenance
1.1 Safety precautions
1.1.1 Power supply
1.1.2 Precautions for antistatic
1.1.3 About placement position
1.2 Maintenance method
1.2.1 Visualized method
1.2.2 Electric resistance method
1.2.4 Current method
1.2.5 Cutting method
1.2.4Currentmethod
1.2.5Cuttingmethod
1.2.6 Element substitution method
1.2.7 Comparison method
1.3 Required device for maintenance
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
3
3
3
Chapter Two Operation Instructions
2.1 Control button locations and explanations
2.1.1 Front panel illustratlons
2.1.2 Rear panel illustration
2.1.3 llustrations to the
i
2.2 asic operations remote control
B
2.2.1 urn on/off this unit
T
2.2.2 tp function
O
2.2.3 Select Input Sound Source
2.2.4 Bass Enhancer
2.2.5 Select Sound Field
2.2.6 Adjust Volume
2.2.7 Adjust Level
2.2.8 EQ function
4
4
5
5
5
6
6
6
7
7
8
9
9
10
Page 3

2.2.9 Parameter Processing
11
2.2.10 Adjust Karaoke
2.2.11 Tuning Function
2.2.12 Other Operations
Chapter Three Principle and Servicing
Section One Principle of the Player
3.1.1 Composition of the player
3.1.2 Function and features
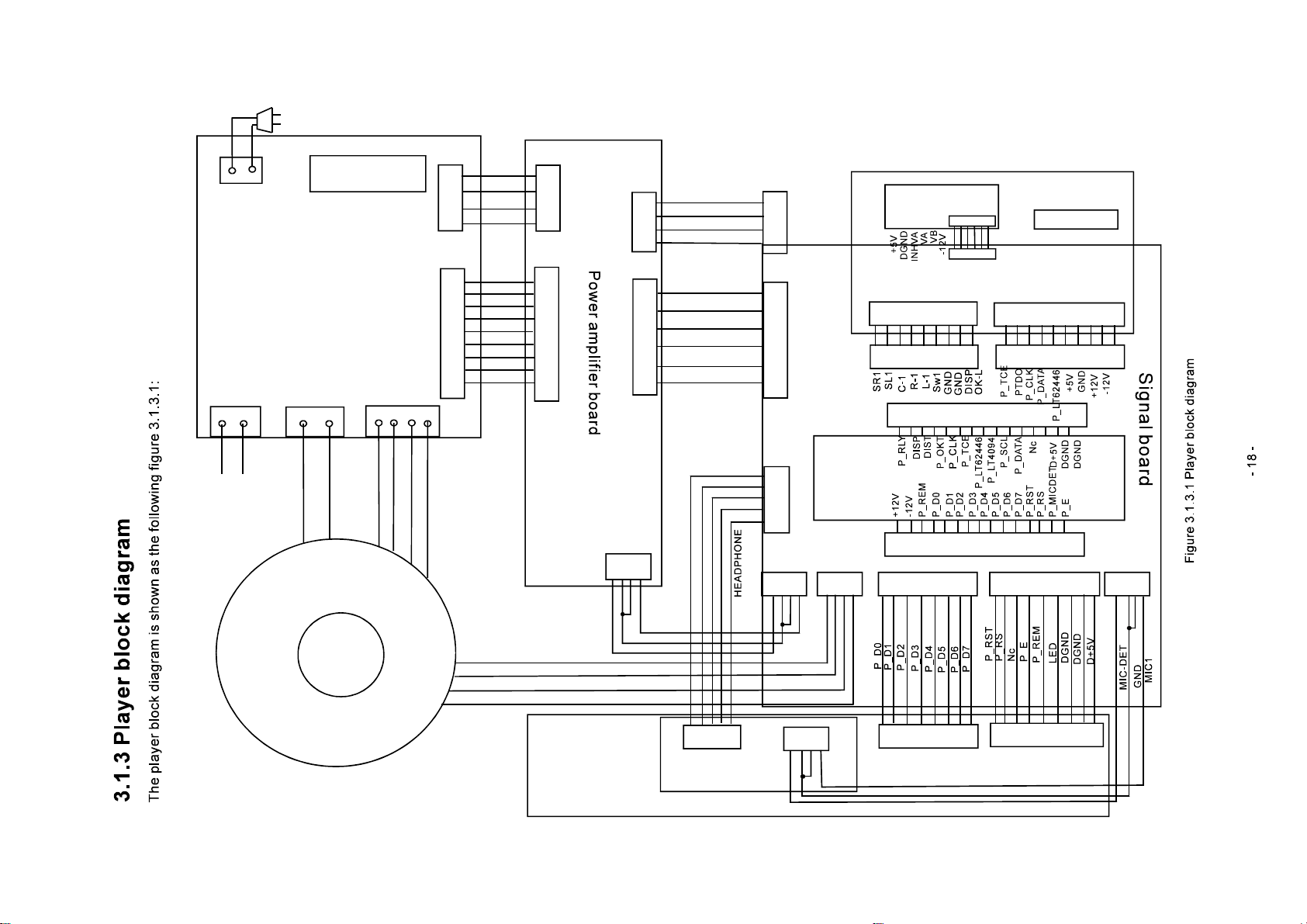
3.1.3 Player block diagram
3.1.4 The player signal flow chart
Section Two Unit Circuit Principle
3.2.1 Volume board circuit
3.2.2 Signal processing board circuit
3.2.3 MCU board circuit
3.2.4 Control panel circuit
12
13
15
17
17
17
17
18
19
20
20
23
25
29
3.2.5 Power board circuit
3.2.6 Power amplifier board and protection circuit
3.2.7 MIC, headphone board
3.2.8 Video in/out board circuit
Section Three Servicing Cases
3.3.1 Servicing instances
3.3.2 Troubleshooting process
Section Four Servicing Parameters
3.4.1 Signal waveform diagram
3.4.2 Key point voltage
Section Five Function Introduction to IC
3.5.1 function introduction to 4558
3.5.2 function introduction to Pt2399
3.5.3 function introduction to Cd4051
3.5.4 function introduction to Cd4052
30
31
34
34
36
36
41
49
49
56
57
57
58
59
60
3.5.5 function introduction to Cd4053
3.5.6 function introduction to Sm79164
3.5.7 function introduction to Pt2308
3.5.8 function introduction to Pt2222
61
62
65
66
Page 4

3.5.9 function introduction to Lm1875
67
3.5.10 function introduction to TDA7265
3.5.11 function introduction to M62446
3.5.12 function introduction to AT24C02
3.5.13 function introduction to L7805
3.5.14 function introduction to 7812
3.5.15 function introduction to 7912
3.5.16 function introduction to LM324
3.5.17 function introduction to Pt2315
3.5.18 function introduction to 74VHC245
3.5.19 function introduction to Cd4094
Chapter Four Disassembly and Assembly Process
Chapter Cinque PCB board & Circuit diagram
Section One PCB board
Section Two circuit diagram
68
69
70
71
72
72
73
74
75
77
79
87
87
96
Chart 6 BOM List
6.1 olume board
V
6.2 olume board ai segment
V
6.3 ignal disposal board
S
6.4 ignal disposal board ai segment
S
6.5 pu board
C
6.6 pu board-smd
C
6.7 mplifier board
A
6.8 urface control board
S
6.9 ideo input output board
V
6.10 Microphone holder board
6.11 ower board
P
6.12 emote coneroller
R
6.13 anel units
P
6.14 ofeware program
S
105
105
105
106
108
110
111
112
116
117
117
118
120
120
121
6.15 n lasel
S
6.16 Supplement module
121
121
Page 5

ChapterOneAboutMaintenance
1.1Safetyprecautions
1.1.1Powersupply
Whenservicingaudiopoweramplifier,theservicingpersonnelpayspecialattentiontothepower
boardwith220VAC,orelsetheimproperoperationwillleadtobodydamage.Thealternatecurrent
whichoutputstopoweramplifierboardthroughpowerboardisalsouptovoltagewithabout50V;when
servicing,short-circuitandjointweldingcannotoccur,orelsetheelementswillbeburntoutandtrouble
rangewillbeenlarged.
1.1.2Precautionsforantistatic
Movementandfrictionwillbothbringstaticelectricitywhichcausesseriousdamagestointegrated
IC.Thoughstaticchargeislittle,whenalimitedquantityofelectricchargeisaddedtolargescaleintegratedIC,asthecapacitanceisverysmallinthemeantime,nowtheintegratedICisverymuch
easytobestruckthroughbystaticelectricityortheperformancewilldecrease.Thusstaticelectricity
preventionisofextraordinaryimportance.Thefollowingareseveralmeasurestopreventstatic
electricity:
1.Useapieceofelectricconductionmetalwiththelengthofabout2metrestoinsertintotheearth,
andFetchtheleadwirefromthetopofthesurplusmetalandconnecttotherequiredstaticelectricity
device.Thelengthanddepthofthemetalembeddedundertheearthshouldbedeterminedaccordingto
thewettabilityofthelocalsoil.Forhumidplaces,itmaybeshorter,andlongeranddeeperfordryplaces.
Ifpossible,itcanbedistributedandlayedintermsof“#”shape.
2.Onoperatingtable-board,theantistatictablecushionshouldbecoveredandgrounded.
3.Alldevicesandequipmentsshouldbeplacedontheantistatictablecushionandgrounded.
4.Maintenancepersonnelshouldwearantistaticwristringwhichshouldbegrounded.
5.Placesaroundtheoperatingpositionshouldalsobecoveredwithelectricconductioncushionor
Paintedwithantistaticpaint.
-1-
Page 6

1.1.3Aboutplacementposition
1.
Audiopoweramplifiercannotbeinstalledinplaceswithhightemperatureandhumidity.
2.Positionsforplacementshouldbestableandsecure.
1.2Maintenancemethod
1.2.1Visualizedmethod
Directlyviewwhetherabnormalitiesofcollision,lackofelement,jointwelding,sheddingwelding,
rosinjoint,copperfoilturningup,leadwiredisconnectionandelementsburningupamongpinsof
elementsappear.Checkpowersupplyofthemachineandthenusehandstotouchthecasingofpartof
elementsandcheckwhethertheyarehottojudgethetroublespot.Youshouldpaymoreattentionwhen
usingthismethodtocheckinhighvoltageparts.
1.2.2Electricresistancemethod
Setthemultimeterinresistancepositionandtestwhetherthenumericalvalueofresistanceofeach
pointinthecircuithasdifferencefromthenormalvaluetojudgethetroublespot.Butinthecircuitthe
testednumericalvalueofresistanceisnotaccurate,andthetestednumericalvalueofintegratedIC's
pinscanonlybeusedforreference,sotheelementsshouldbebrokendownfortest.
1.2.3Voltagemethod
Voltagemethodisrelativelyconvenient,quickandaccurate.Setthemultimeterinvoltageposition
andtestpowersupplyvoltageoftheplayerandvoltageofacertainpointtojudgethetroublespot
accordingtothetestedvoltagevariation.
1.2.4Currentmethod
Setthemultimeterincurrentpositionandtestcurrentoftheplayerofacertainpointtojudgethe
troublespot.Butwhentestingincurrentmethod,themultimetershouldbeseriesconnectedinthe
circuit,whichmakesthismethodtootrivialandtroublesome,soitislessfrequentlyusedinreality.
1.2.5Cuttingmethod
Cuttingmethodshouldbecombinedwithelectricresistancemethodandvoltagemethodtouse.
Thismethodismainlyusedinphenomenaofshortcircuitandcurrentleakageofthecircuit.When
cuttingtheinputterminalvoltageofacertainlevel,ifvoltageoftheplayerrisesagain,itmeansthatthe
troubleliesinthislevel.
-2-
Page 7

1.2.6Elementsubstitutionmethod
Whensomeelementscannotbejudgedgoodorbad,substitutionmethodmaydeadopteddirectly.
1.2.7Comparisonmethod
AsamegoodPCboardisusuallyusedtotestthecorrectvoltageandwaveform.Comparedthese
datawiththosetestedthroughfaultPCboard,thecauseoftroublesmaybefound.
Throughtheabovemaintenancemethod,theoreticalknowledgeandmaintenanceexperience,all
difficultiesandtroubleswillbereadilysolved.
1.3Requireddeviceformaintenance
AudioGenerator
◆
Digitaloscillograph(100MHE)
◆≥
SMDreworkstation
◆
Multimeter
◆
Solderingiron
◆
Pointed-monthpincers
◆
Cuttingnippers
◆
Forceps
◆
Electricscrewdriver
◆
Terminalsconnectingcord
◆
Headphone
◆
Microphone
◆
-3-
Page 8

Chapter Two Operation Instructions
2.1 CONTROL BUTTON LOCATIONS AND EXPLANATIONS
2.1.1 FRONT PANEL ILLUSTRATLONS
1
POWER SWITCH
Power on/off this unit
2
LCD Screen
Buttons operation indication and spectrum
display when working
3
IR sensor
Receive the infrared signals transmitted from
the remote control
4
MASTER VOLUMEPress this button to synchronously lower all
6CH volumes
5
INPUT
Sound source input button
6
MIC VOLUME+
Press this button to increase the volume of
MIC
7
MIC VOLUMEPress this button to lower the volume of MIC
8
TUNING
Select other frequency radio stations upwards
9
Tuning
Select other frequency radio stations
downwards
10
BAND
Select FM/AM tuner BAND
11
PRESET
Select the latter preset radio station
12
PRESET
Select the previous preset radio station
13
MODE
Select tuner mode:manual/auto
14
MASTER VOLUME+
Press this button to synchronously increase
all 6CH volumes
15
STANDBY
Standby
16
COVER OF PHONE JACK AND
MICROPHONE JACK
- 4 -
Page 9
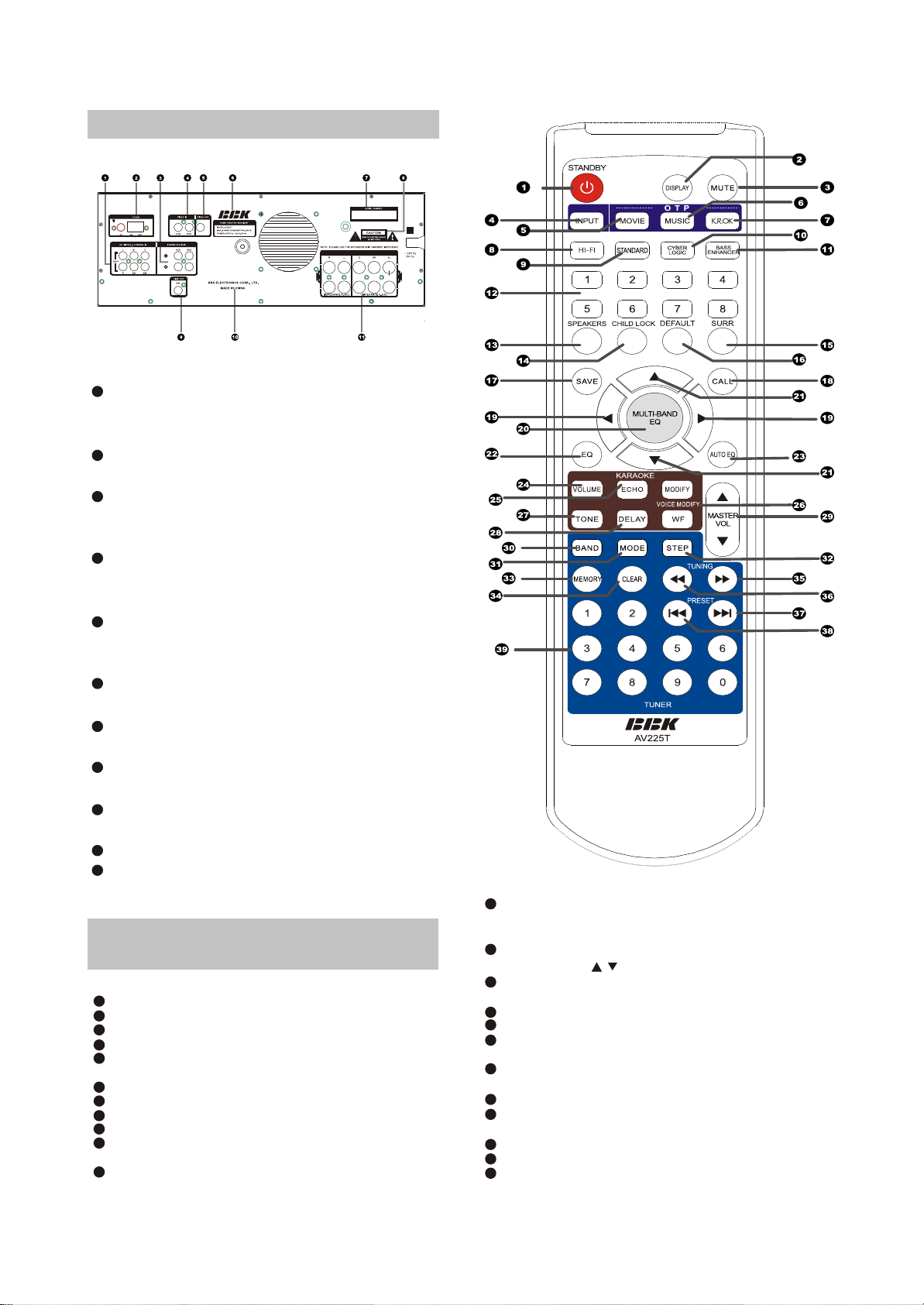
2.1.2 REAR PANEL ILLUSTRATION
1
AC-3/DTS 5.1CH INPUT
5.1CH audio signals input terminals that
connect to DVD, AC-3/DTS
2
AM/FM antenna terminal
Connect AM/FM antenna outside
3
Stereo Audio jack
The terminals that connect with VCD, DVD
stereo audio signals input
4
Video input
The terminals that connect with VCD,DVD
Video signals input
5
Video output jack
The terminals that connect with TV Video
signal output
6
Data
The data plate of this unit
7
SERIAL NO. Mark
The manufacturing records
8
CAUTION mark
Remind the user of dangerous voltage inside
9
Line-out
Subwoofer signals line-out jack
10
This unit's manufacturer
11
Terminals
Connect with SPEAKER terminals
2.1.3 ILLUSTRATIONS TO THE
REMOTE CONTROL
1
STANDBY button: Power on, STANDBY switch button
2
DISPLAY button: Select audio spectrum display modes
3
MUTE button: Mute On/Off button
INPUT button: Select input signal sources manually
4
MOVIE button: OTP button to set standard movie
5
theater surround mode
6
MUSIC button: OTP button to set standard concert mode
7
K.R.OK: OTP button to set standard Karaoke mode
8
HI-FI button: Select the Hi-Fi sound field
9
STANDARD button: Select the standard sound field
10
CYBER LOGIC button: Select the cyber logic sound
field
11
BASS ENHANCER button: Select the bass enhancing
effect
12
Number buttons 1~8: Select 8 preset working modes
with the help of SAVE/CALL button, capable of storing
and calling the user-set working mode parameters
13
SPEAKERS button: Adjust the separate channel level
with the help of / keys
14
CHILD LOCK button: Lock the functions of the front
panel controls
15
SURR. Button: Select the surround sound field
16
DEFAULT button: Restore the factory default settings
17
SAVE button: Store the current working mode
parameters with the help of number buttons 1~8
18
CALL button: Call the user-stored working mode
parameters with the help of number buttons 1~8
19
EQ select button: Select the equalization frequency
20
MULTI-BAND EQ button:Adjust multi-band electronic
equalization
21
Adjust button: Adjust level and multi-band EQ
22
EQ button: Circularly call the preset EQ modes
AUTO EQ button: Analyze the current signal spectrum,
23
automatically set EQ parameters
- 5 -
Page 10
24
VOLUME button: Adjust the karaoke level with / keys
25
ECHO button: Adjust the karaoke ECHO with / keys
26
VOICE MODIFY:
MODIFY button: Select Karaoke voice modify
WF button: Karaoke wide sound field On/Off
27
TONE button: Adjust the karaoke BASS/Treble tone
levelwith / keys
28
DELAY button: Adjust the karaoke delay time with /
keys
29
MASTER VOL button: Synchronously increase/decrease
6 channels' volume
30
BAND button: Select FM/AM tuner band
31
MODE button: Select tuner mode:manual/auto
32
STEP button: Select AM tuning step:9K/10K
33
MEMORY button: Memory the received radio station
with the help of number buttons 0~9
CLEAR button: Clear the preset radio station with the
34
help of number buttons 0~9
35
TUNING : Scan other frequency radio station upwards
36
TUNING : Scan other frequency radio station
downwards
37
PRESET : Select the latter preset radio station
38
PRESET : Select the previous preset radio station
39
NUMBER 0~9 :Save the received radio station programs
or directly call the preset programs with the help of
MEMORY button
2.2 BASIC OPERATIONS
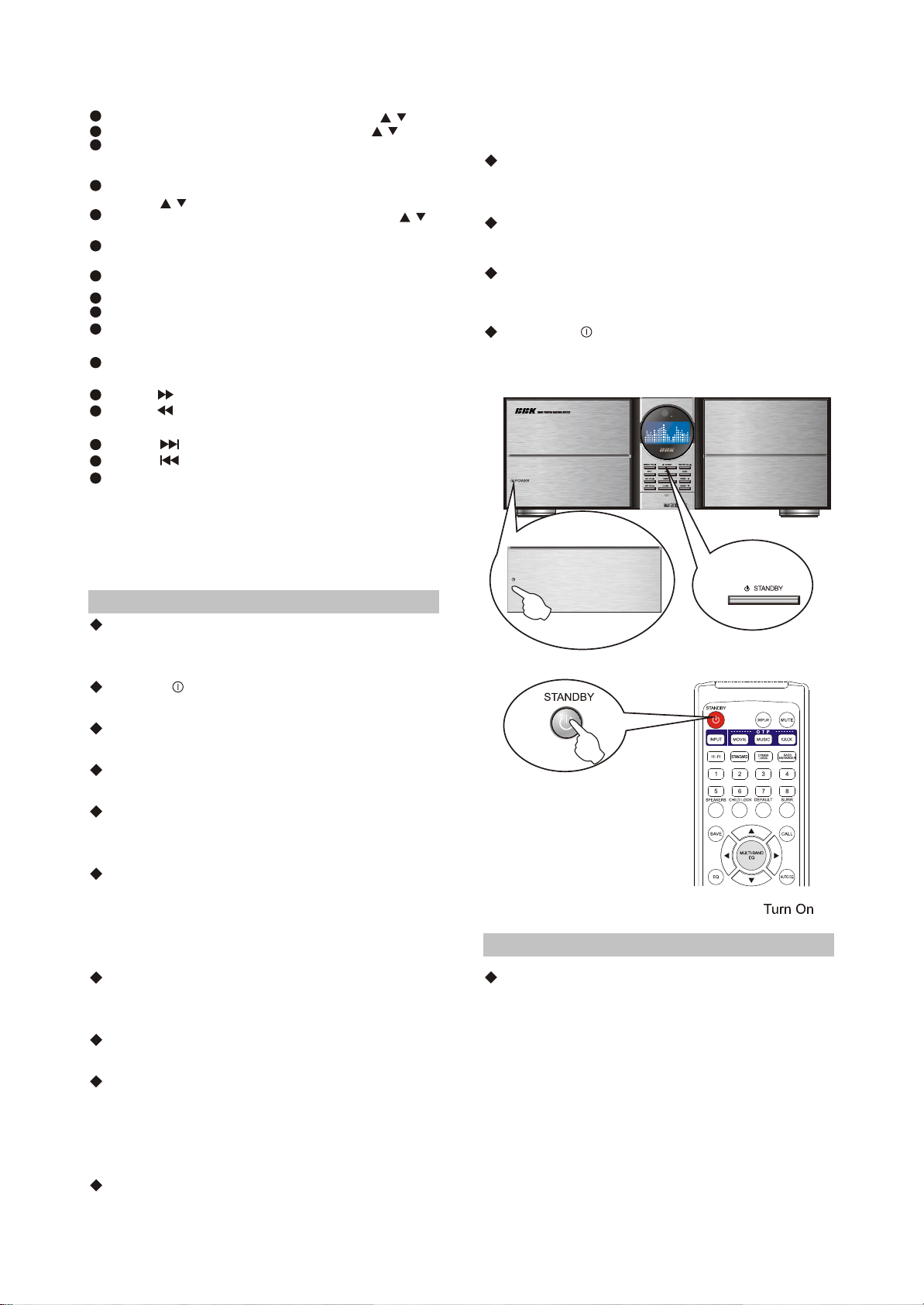
2.2.1 TURN ON/OFF THIS UNIT
Please check the connection cords before
turning this unit on. If all connections are correct,
you can connect this unit to power.
Press the POWER button, this unit enters the
standby mode .
When this unit is in the standby mode, it
detects the input signals automatically.
When there is signal input, this unit turns on
automatically.
When the input signal is too small, this unit
might not detect the signal and will not turn on
automatically.
When there is signal input and the unit cannot
turn on automatically, press the STANDBY
button on the front panel or remote control to
operate manually and select input signals by
using the INPUT button.
When the unit is in the standby mode, press
the STANDBY button on the front panel or
remote control to turn on this unit.
Press the STANDBY button on the front panel
or remote control.
After turning on this unit, it detects the input
signal automatically. When there is signal input,
it receives the input signal automatically.
Otherwise, the unit will automatically search
signals all the time.
When there is signal input but it cannot receive
The signal automatically, press the INPUT button
on the remote control to select the input signal.
When the unit is in normal working mode,
press the STANDBY button on the front panel or
remote control if you want to enter standby mode.
Please turn off the power when you are not
going to use the unit for a long time.
Please turn off the power every time after you
use the unit.
Press the " POWER" button on the front
panel to power off this unit.
POWER
2.2.2 OTP function
We have set the OTP function to simplify the
operation of testing sound effects.If the played
disc is movie or story, you just press the MOVIE
button and the system will automatically set
standard movie mode.If the played disc is music,
you just press the MUSIC button and the system
will automatically set standard music mode.If
you want to sing Karaoke, you just press the
- 6 -
Page 11
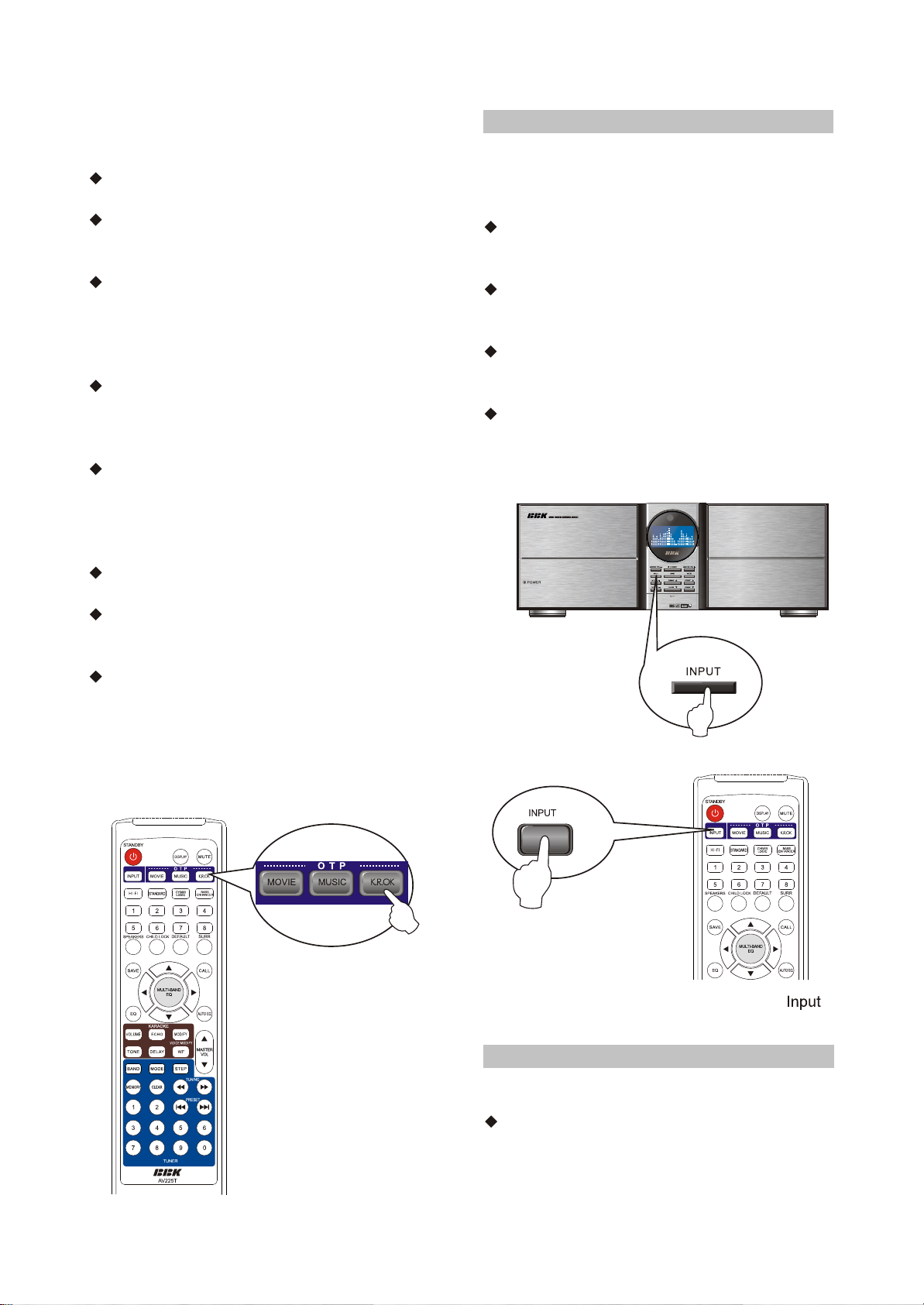
K.R.OK button after inserting microphone and
The system will automatically set standard
Karaoke mode.
Press the MOVIE button to set standard
theater surround mode.
Automatically detect the input signal source. If
many signal sources input, it will select the
current signal input preferentially.
Automatically set the parameters of surround.
If 5.1CH input signal is detected, it will
automatically adopt standard mode; if 2CH
signal source is detected, it will automatically
adopt Cyber Logic.
Press the MUSIC button to set standard music
modeAutomatically detect the input signalsource.
If many signal sources input, it will select the
current signal preferentially.
Automatically set the parameters when
enjoying music. If 5.1CH input signal is detected,
it will automatically adopt standard mode;if 2CH
signal source is detected, it will automatically
adopt Hi-Fi mode.
Press the K.R.OK button to set standard
Karaoke mode.
Automatically detect the input signal source. If
many signal sources input, it will select the
current signal preferentially.
Automatically set the parameters of Karaoke
mode.
NOTE: If the signal is too weak or in the blank
segment of music
when operating, the system will probably appear
wrong indications.
2.2.3 Select Input Sound Source
This unit utilizes two input lines of stereo audio
sources: VCD, DVD; one line 5.1 channel signal
input. Select the input signal source manually
through the remote control.
Press the INPUT button on the remote control,
and "INPUT TUNER" splays, which means
TUNER has been selected.
Press the INPUT button on the remote control,
and "INPUT VCD" displays, which means VCD
2CH input jack has been selected.
Press the INPUT button on the remote control,
and "INPUT DVD" displays, which means DVD
2CH input jack has been selected.
Press the INPUT button on the remote control,
and "INPUT 5.1CH" displays, which means
5.1CH input jack has been selected.
2.2.4 Bass Enhancer
In order to strengthen the low frequency of music,
you may start up Bass Enhancer function.
Press the "BASS ENHANCER" button on the
front panel or remote control, "BASS driver 0",
“BASS driver 1 ", "BASS driver 2 " or”BASSdriver
3" will display.
- 7 -
Page 12
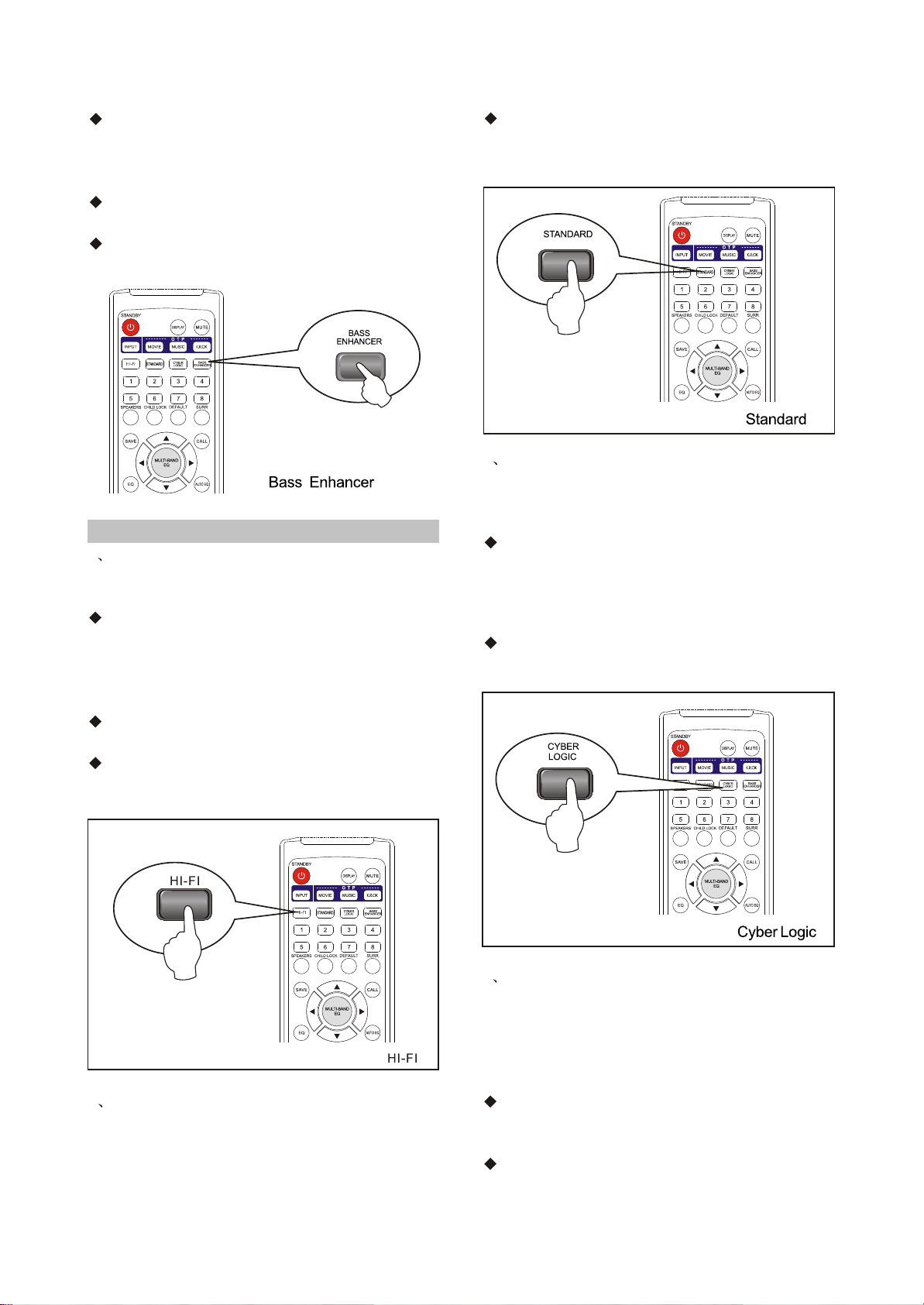
The display "BASS driver 1-3" means the first,
second and third Bass Enhancer; the subwoofer
signal adds into the master channelsignal; turn
off the subwoofer line output.
The display "BASS driver 0 " means turn off
Bass Enhancer; normal subwoofer line output.
Bass Enhancer function cannot be started up
in Hi-Fi mode.
2.2.5 Select Sound Field
1 HI-FI
In 2CH signal input, you may select the Hi-Fi
mode to keep the originally musical features.
Press the HI-FI button on the remote control
and "HI-FI" will displays, which means the
system enters the Hi-Fi mode; if "NVALID"
displays, it means the system cannot enter the
Hi-Fi mode.
Bass Enhancer function and operations
related to EQ are invalid in Hi-Fi mode.
Pressing the HI-FI button is invalid in
5.1channel input.
Press the STANDARD button on the remote
control and "STANDARD" will display, which
means the system enters standard sound field.
3 Cyber Logic
In order to make 2 channel input signals have
multi-channel sound field effect, you may select
Cyber Logic sound field.
Press the CYBER LOGIC button on the remote
control and "CYBER LOGIC" will display, which
means the system enters Cyber Logic sound
field: if "INVALID" displays, it means the system
cannot enter Cyber Logic
Cyber Logic mode is invalid in 5.1 channel
signal input.
2 Standard
In order to keep the correspondence with input
signals and adjust output timbre according to
personal habit, you may select the standard
sound field.
4 Surround
In order to cater for different listening
Environments and meet different sound effect
requirements of customers, you may select
different surround modes in 5.1 channel signal
input status.
Press the SURR button on the remote control
in 5.1 channel signal source input, the surround
will display.
Press the SURR button on the remote control
Repeatedly; you may select the environment
- 8 -
Page 13
Modes between Affectional movie, Sowordsmen
movie, Gunfignt movie, Sci-fi movie and music.
The environment surround is invalid in 2-
channel signal input status.
The environment surround is invalid if
microphone is inserted.
2.2.6 Adjust Volume
1 Master Volume
When the current sound is too high, too low or
unsuitable, you may press the MASTER VOL on
the front panel or remote control to adjust the
volume of all channels.
Press the "+" button of master volume on the
front panel or remote control to increase all
channels' volume simultaneously; the max
volume is 60.
Press the "-" button of master volume on the
front panel or remote control to decrease all
channels' volume simultaneously; the min
volume is 0.
The master volume displays as the example:
"VOL: 20”
2.2.7 Adjust Level
1 Left channel level
When sound of left and right channels is
imbalance, you may adjust R channel level to
make it in balance with L channel.
Press the SPEAKERS button on the remote
control and "L: 00" will display. Operate as
follows:
Press the " " button on the remote control to
Increase the volume of L channel. The max level
is +60.Press the “ " button on the remote
control to decrease the volume of L channel. The
min level is -60.
2 Right channel level
When sound of left and right channels is
imbalance, you may adjust L channel level to
make it in balance with R channel.
Press the SPEAKERS button on the remote
control and "L: 00" will display. Operate as
follows:
Press the " " button on the remote control to
Increase the volume of L channel. The max level
is +60.Press the “ " button on the remote
control to decrease the volume of L channel. The
min level is -60.
3 Center level
When sound of left and right channels is
imbalance, you may adjust R channel level to
make it in balance with L channel.
Press the SPEAKERS button on the remote
control and "R: 00" will display. Operate as
follows:
Press the “ " button on the remote control to
increase the volume of R channel. The max level
is +60.Press the “ " button on the remote
control to decrease the volume of R channel.
The min level is -60.
4 Surround Left level
When sound of center channel is unsuitable,
you may adjust center level to make it suitable to
the sound field.
Press the SPEAKERS button on the remote
control and "C: 00" will display. Operate as
follows:
Press the “ " button on the remote control to
increase the volume of C channel. The max level
is +60.Press the “ " button on the remote
control to decrease the volume of C channel.
The min level is -60.
NOTE: The center level cannot be adjusted only
when left and right channels have output.
5 Surround Right level
When sound of surround left is unsuitable, you
- 9 -
Page 14
may adjust surround left level to make it suitable
to the sound field.
Press the SPEAKERS button on the remote
control and "SL: 00" will display. Operate as
follows:
Press the " " button on the remote control to
increase the volume of surround left. The max
level is +60.Press the " " button on the remote
control to decrease the volume of surround left.
The min level is -60.
NOTE: The surround left level cannot
beadjusted only when left and right channels
have output.
When sound of surround right is unsuitable,
you may adjust surround right level to make it
suitable to the sound field.
Press the SPEAKERS button on the remote
control and "SR: 00" will display. Operate as
follows:
Press the " " button on the remote control to
increase the volume of surround right. The max
level is +60.Press the " " button on the remote
control to decrease the volume of surround right.
The min level is -60.
NOTE: The surround right level cannot be
adjusted only when left and right channels have
output.
6 Subwoofer level
When sound of subwoofer is unsuitable, you
may adjust the volume of subwoofer speaker
and the level of subwoofer channel to make it
balanced to the sound field.
Press the SPEAKERS button on the remote
control and "SW: 00" will display. Operate as
follows:
Press the " " button on the remote control to
increase the volume of subwoofer. The max level
is +60.
Press the " " button on the remote control to
decrease the volume of subwoofer. The min level
is -60.
NOTE: The subwoofer level cannot be adjusted
only in Hi-Fi and Bass Enhancer conditions.
2.2.8 EQ function
Due to the personal like to music, you may adjust
EQ to meet your own needs. If the music tempo
is not enough or full, adjust bass; if the voice is
unclear, adjust middle frequency; if the
musical details are not rich, adjust treble.
1 Pre-set EQ
When the sound of master volume is too weak
or unclear, you may directly use pre-set EQ
mode to make it accordant with the current music.
This unit utilizes 8 EQ modes: Rock, Jazz,
Classical, Pop, Disco, Rap and Blues.
Press the EQ button on the remote control to
display the EQ curve.
Press the EQ button repeatedly to select the
EQ mode accordant with the current music.
EQ mode cannot be adjusted in Hi-Fi mode.
2 Multi-band EQ
When the sound of master volume is too weak
or unclear, you may set EQ mode yourself to
meet you own taste.
Press the "AUTO EQ" button on the remote
control to display the current EQ curve. There is
a cursor flashing in the current frequency.
Press the " " button on the remote control to
select the high
frequency. The flashing cursor moves rightwards
until the rightmost.
Press the " " button on the remote control to
select the low frequency. The flashing cursor
moves leftwards until the leftmost.
Press the " " button on the remote control and
the current frequency level increases until the
maximum.
Press the " " button on the remote control and
the current frequency level decreases until the
minimum.
EQ mode cannot be adjusted in Hi-Fi mode.
3 Auto EQ
When the sound of master volume is
unsuitable to you listening, you may select auto
EQ.
The unit will automatically analyze the current
spectrum to set the current EQ according to the
current music.
- 10 -
Page 15
Press the AUTO EQ button on the remote
control to display the analyzing curve.
EQ function
Auto EQ setup is invalid in Hi-Fi mode.
2.2.9 Parameter Processing
To memory the current parameter for later use,
or use the defauly parameter, the Memory and
Call functions will be used. The current
parameters to be adjusted include: Channel
Level, EQ, Bass Enhancer, Sound Field,
Environment Surround, MIC Volume, MIC Treble,
MIC Bass, MIC Delay, MIC Echo and Voice
Modification.
1 Call Default parameter
control and "CALL 1-8" displays.
according to the default parameters.
2 Memory Parameters
first to display "SAVE "
control again under the display "SAVE "
corresponding number buttons and "SAVE 1-8"
displays.
3 Call parameters
first to display "CALL "
control again under the display "CALL "
buttons before will be adopted currently and
"CALL 1-8" displays.NOTE: Due to some
unexpected reasons, the user-memorized
parameters will probably be lost, so please
adjust again and then memorize. The system will
automatically check the parameter saved ast
time when switching on this unit. When the
Press the number buttons 1-8 on the remote
Setup will be processed automatically
Press the "SAVE" button on the remote control
Press the number buttons 1-8 on the remote
The current parameter is memorized into the
Press the "CALL" button on the remote control
Press the number buttons 1-8 on the remote
The parameters memorized in the number
channel level is too high or too low, the system
will adjust automatically
- 11 -
Page 16
2.2.10 Adjust Karaoke
1 Microphone Volume
When inserting microphones to sing Karaoke,
press the MIC VOL button to adjust the volume
of microphonewhen the microphone voice is too
high, too low or unsuitable.
Press the " " button of MIC VOL on the front
panel to increase the volume of microphone
The maximum volume is 30.
Press the " " button of MIC VOL on the front
panel to decrease the volume of microphone
The minimum volume is 0.
Press the "VOLUME" on remote control,then
press " "" " to adjust karaoke volume.
The microphone volume displays as "MIC VOL
20".
The microphone volume cannot be adjusted
when not inserting microphones.
2 Bass
When inserting microphone to sing Karaoke, you
may adjust microphone bass when the sound
tempo is not full or rich.
Press the "TONE" button on the remote control
once then press" " or " " to adjust the bass of
microphone. The adjustable range is 6.
The microphone bass displays as "MIC BASS
+2”
The microphone bass cannot be adjusted
when not inserting microphone.
3 Treble
When inserting microphone to sing Karaoke, you
may adjust microphone treble when the sound is
unclear.
Press the "TONE" button on the remote
control twice, then press " " or " " to adjust
the treble of microphone. The adjustable range
is 6
The microphone treble displays as "MIC
TREBL+2”
The microphone treble cannot be adjusted
when not inserting microphone.
4 Echo
When inserting microphone to sing Karaoke, you
may adjust microphone echo when the sound is
weak or not full.
Press the "ECHO" button on the remote
control then press or to adjust the echo of
" "
" "
microphone. The adjustable range is 0~7.
The microphone echo displays as "MIC ECHO
2”
The microphone echo cannot be adjusted
when not inserting microphone.
- 12 -
Page 17
5 Delay
When inserting microphone to sing Karaoke, you
may adjust microphone delay when the sound is
not full.
Press the "DELAY" button on the remote
" "
control then press of to adjust the delay
" "
of microphone. The adjustable range is 0~7..
The microphone delay displays as "MIC
DELAY 2”
The microphone delay cannot be adjusted
when not inserting microphone.
7 Wide Field
When inserting microphone to sing Karaoke, you
may select to switch on/off Karaoke wide field
when the sound field is not wide.
Press the "WF" button on the remote control to
display "MIC WIDE ON", which means Karaoke
Wide Sound Field is switched on.
Press the "WF" button on the remote control
again to display "MIC WIDE OFF", which means
Karaoke Wide Sound Field is switched off.
The karaoke WF button cannot be selected
when not inserting microphone.
NOTE: If noise appears when adjusting Karaoke,
please refer to TROUBLESHOOTING for details.
6 Modify
When inserting microphone to sing Karaoke, you
may select microphone euphonize mode when
the sound is unsuitable.
Pressing the "MODIFY" button on the remote
control can circularly select the euphonized
¡ï
voice"NATURAL", "Full", "Fruity", "Bright" and
"Ringing".
The MODIFY button cannot be selected when
not inserting microphone.
2.2.11 Tuning Function
Auto Tuning One:
1 Press INPUT button on the front panel or
remote control to select TUNER as the input
sound source.
2 Press BAND button on the front panel or
remote control to select receiving wave band.
7 Wide Field
When inserting microphone to sing Karaoke, you
may select to switch on/off Karaoke wide field when
the sound field is not wide.
- 13 -
Page 18
3 Press TUNING / button on the front panel
or remote control for above 5 seconds to
automatically tune upwards/downwards until
your needed radio station programs. When
programs are searched, it will stop searching
automatically.
3¡¢
NOTE: 1. This operation will search and save
automatically, so the user-preset programs will
be covered.
2. Pressing TUNING / button may
stop the function in the course of this operation.
If the tuning searching stops in imperfect radio
station (because of weak radio station signals or
radio wave interferes), please change into
manual tuning method.
Clear Radio Station
If you do not need the preset radio station, you
may clear it by using CLEAR button on the
remote control with the help of number buttons
0~9.
1 Press CLEAR button on the remote control.
2 Press the serial number of the radio station
that you want to clear in the course of the
screen's displaying”CLEAR " to finish this
operation.
If the tuning searching stops in imperfect radio
station or radio wave interferes, please continue
operating.
If the tuning searching stops in imperfect radio
station (because of weak radio station signals),
please change into manual tuning method.
4 The following save and call operations are
the same with manual tuning operations.
Auto Tuning Two:
1 Firstly select TUNER as the current input
sound source according to the operations oF
"Manual Tuning", and then select the wave band
to be received.
2 Press MEMORY button on the front panel or
remote control, and then press TUNING /
button for above 0.5 seconds during the course
of displaying MEMORY to enter the radio station
auto searching status.
NOTE: 1. This operation is beyond retrieve, so
please take care to operate.
2. If you clear the radio station
incautiously, you may save again according to
the select operation.
The Explanation of MODE button
This unit has two working modes in the receiving
status: AUTO/MANUAL
1 In AUTO working mode, if you select FM
wave band, this unit will automatically recognize
the radio station program is mono signal or
stereo signal and keep the mono or stereo
receiving status.
2 If the received radio station program has
louder noise or cacophony in stereo status, you
may switch to MANUAL working mode.In this
way, the unit is in mono receiving status to
decrease noise and cacophony generally.
You may switch the two working modes through
MODE button on the remote control.
- 14 -
Page 19
Antenna Connection
You may use our accessional AM and FM indoor
antenna when in bad receiving effect. Generally
speaking, these antennae can supply enough
signal strength.
Connect to AM Round Antenna
1 Push the jack button to open it.Push the jack
button to open it.
2 Connect the AM round antenna cord to AM
ANT and GND terminals.
3 Let go of the button to clamp the speaker
cord. Pull the cord lightly to check the connection
is right or not.
NOTE: 1. AM round antenna should be placed far
away from the equipment. You may put up on the
wall or on the bookshelf.
2. AM round antenna and outdoor antenna can
be used at the same time.
Connect to FM Antenna
Connect to the indoor FM antenna
Connect the accessional indoor FM antenna to
75 UNBAL.FM ANT terminal.
NOTE:Do not use the outdoor and indoor FM
antennae at the same time.
How to Connect
Push the jack button to open it.
Insert the speaker cord.
Let go off the button to clamp
thespeaker cord.
4 Connect the AM round antenna to the stand.
AM round antenna
5 Adjust the direction of AM round antenna
to get the best receiving effect.
GND (Grounding) terminal
In order to ensure the safety and decrease the interference,
please well connect the GND terminal. The better grounding
method is insert the metal pole into wet ground.
2.2.12 Other Operations
1 Mute
Mute the sound to make your conversation or
answering telephone not be affected by music.
Press the MUTE button on the remote control
to mute the sound and the display "MUTE"
flickers.
Rotate
Mute
- 15 -
Page 20
2 Child Lock
To prevent the children wrongly pressing the
front panel buttons, you may lock the buttons on
Other Operations
the front panel.
Press the CHILD LOCK button on the remote
control to display "LOCK". The buttons on the
front panel are invalid and now "LOCKED"
displays.
Press the CHILD LOCK button on the remote
control again to display"UNLOCK" and the fronta
pnel buttons can be normally used.
The DISPLAY button cannot be selected when
no signals input.
3 Display
To make the display spectrum colorful, we have
set many kinds of spectrum display means. You
may press the DISPLAY button to select.
After switching on the unit, it will automatically
select a kind of spectrum display mode every
third moment or so.
Pressing the DISPLAY button on the remote
control can cancel auto switch and select your
favorite display mode.
Pressing the DISPLAY button on the remote
control repeatedly can select many kinds of
spectrum display effects until auto switch.
4 Default
When the system parameters adjusted disorderly,
you may restore the default settings.
Press the DEFAULT button on the remote
control to display "DEFAULT".
The unit automatically sets the default
parameters.
Default
- 16 -
Page 21

ChapterThreePrincipleandServicing
SectionOnePrincipleofthePlayer
AV225T(RU)isanadvancedpoweramplifierwithcompletefunctions.Basedontheformerpower
amplifiers,itadoptsLCDscreen,withskybluebackgroundmatchedwith16differentkindsofspectrum
displaystyles,inaddition,thisplayeriswithtuningfunctionanditisanexcellentselectionforuserswho
lovelisteningtoradio.
3.1.1Compositionoftheplayer
1.Volumeboard:selectinputsignalsource,CyberLogicandbassenhancercontrol.
2.Signalprocessingboard:Karaokesignalprocessingand5.1CHsignalamplifying.
3.MCUboard:playercontrol,frequencypointgating,andautosearchcircuit.
4.Controlpanel:LCDdisplay,remotekeyboardandbackgroundlightdisplay.
5.Powerboard:supplytheworkingvoltagerequiredbyeachunitcircuitandperformplayer
protectionfunction.
6.Poweramplifierboard:performpoweramplifyingto5.1CHanalogsignal.
7.Digitaltuner:receiveradiosignalandthensendtopoweramplifierforsignalprocessing.
8.MIC,headphoneboard:MICsignalinput,headphoneamplifyingoutputcircuit.
9.Videoinputandoutputboard:fulfiltheswitchofVCD,DVDchannel.
3.1.2Functionandfeatures
Built-in5CHpoweramplifying,applicabletoAC-3/DTSandstereomusicreplay.Mainchannel
◆
80W,central/surround15Wwithstrongpower.
◆
AC-3/DTS,VCD,DVDinputjackandsubwooferoutputjack.
◆
6CHvolumecontrolandseparatelevelcontrol,with7-bandelectronicequalization.
◆
Bassenhancersystem,CyberlogicfunctionandHi-Fiplaybackfunction.
◆
Q-playfunctionofmovie,musicandKaraoke.
◆
MultipleEQmodes,applicabletodifferentmusicstyles.
◆
Autospectrumanalysiscompensationfunctionperformscompensationtosignalsautomatically.
◆
CompleteKaraokefunction,includingseparateMICvolumecontrol,high/lowtoneadjustment,
voicecompensation,delayandechoadjustment,Karaokewidesoundfieldfunction.
-17-
Page 22
XS1
Powerboard
XS2
220V
XS3
Signaloutput
XL100
XS4
XS7
XS8
SWM
RLY0
P_RC
OVER
L2
R2
C2
SL2
SR2
VC+
GND
GND
VC-
XP7
XP8
XP13
XP9
RLY
P_RC
P_LRM
P_CSM
SWM
L1
R1
C1
SL1
SR1
XS13
XS9
Videoboard
Volumeboard
XS20
XP20
Xp101
XS101
XP101
Tunersocket
XS22
XP22
SWITCH
Transformer
elementary
Transformer
Sublevelcoil
Sublevelcoil
XP23
+12V
GND
GND
-12V
Controlpanel
DGND
+12V
GND
-12V
XP25
MICholder
board
D+5V
L1
R1
XS25
CPUboard
XP12
XP100
XS6XS23
XS102
XP102
XS103
XP103
XS12
Page 23
TUNER(L/R)
VCD(L/R)
DVD(L/R)
5.1CH(L/R)
Volume board
5.1CH(C/SL/SR)
5.1CH(SW)
Input selection
DLSPLY
A
B
L/R
Follow buffering
L/R
5.1CH(C/SL/SR)
5.1CH(SW)
S-C C/SL/SR/SW
MIC
Mix
Cyber logic
S-C/S-SL/S-SR
S-C
D-SW
A
B
5.1CH
LR_T
Channel selection
LR_T
5.1CH
C/SL/SR
Mix
SW
Electronic volume
L/R
C
SL/SR
L/R/C
Headphone
amplifier
MIC
MIC, headphone
board
MIC input
Signal board
1
VCD
2
3
DVD
4
5
6
V-OUT
Video in/out board
C/SL/SR
C/SL/SR
Power amplifier board
CD4051
B
A
Mute
LR
Power amplifying
Load
test
SL
SR
AGND
+12V
-12V
Preposition power
L
R
C
VS+ GND VS-
Power
SW-OUT
OK
volume
tone
Amplifying
amplifying
Program
Amplifying
+6.8V
AGND
-6.8V
Switch in bass
enhancer and line output
filtering
compare
Bandpass
Dual-limit
boost
Low frequency
Detect
switch
channel
Detect
EEPROM
24C02
echo
Electronic
Echo
adjustment
Delay
adjustment
Sampling
intermit
P_SELECT
P_SEARCH
Reset
circuit
CPU board
Reverse
VSTNDANCK
P_CHARGE
CPU
DIST
MIC direct connection
P_DO-P_D7
RST/RS/RW/PE
P REM
PT2222 remote control
buttons array
DVD all-in-one input
amplifying
Preposition
MIC
+12V
AGND
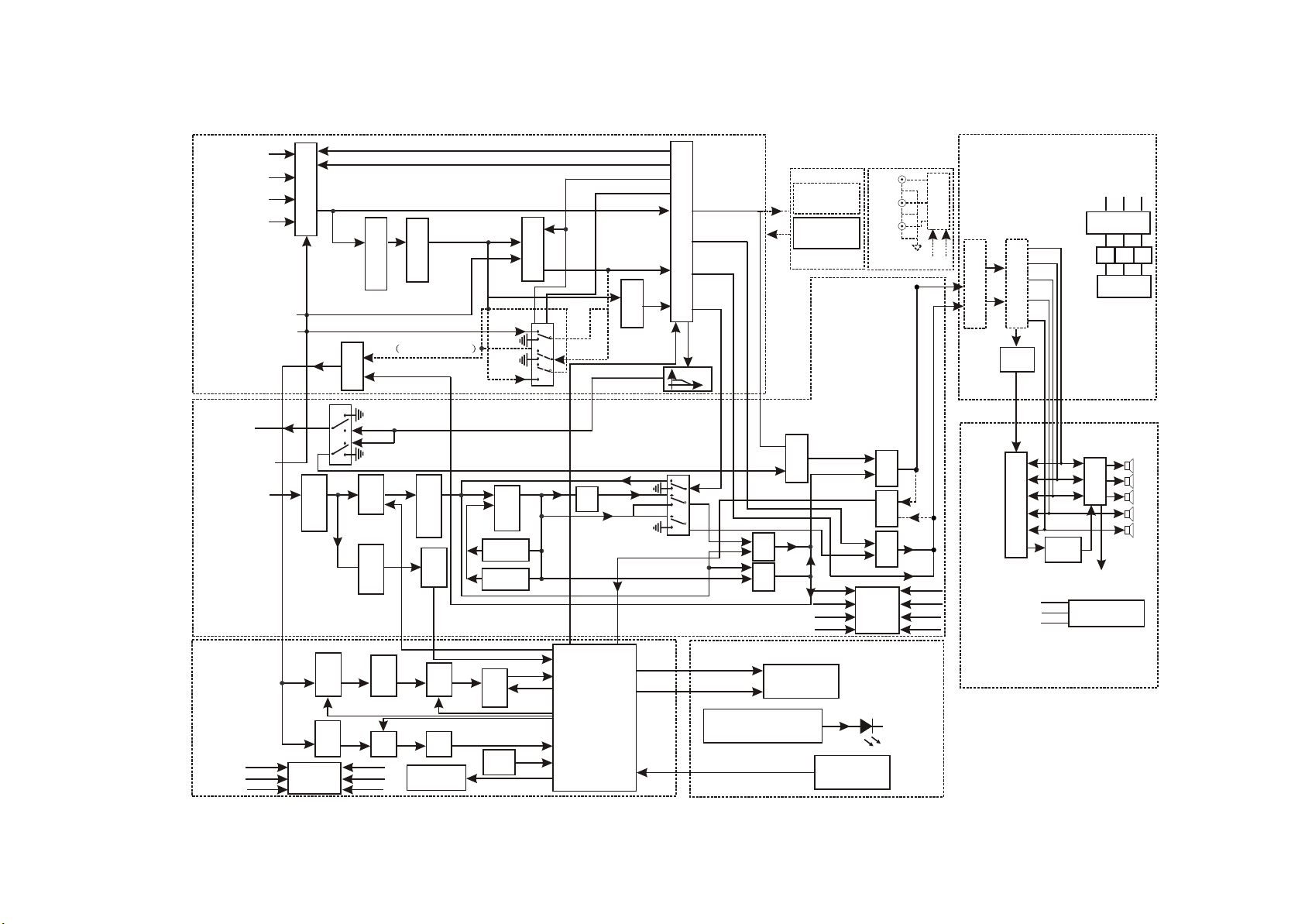
3.1.4 The player signal flow chart
The player signal flow chart is shown as the following figure 3.1.4.1:
-12V
Power
±6.8V
Mixed
L/R
SW
Mixed
Clipping
OK-R
Mixed
Clipping
OK-L
LCD display
OKL/OKR
C
SR/SL
+12V
Power
AGND
±6.8V
-12V
-VS
Remote control
receiving
Mixed Mixed Mixed
+6.8V
AGND
-6.8V
+5V
+5V
Control panel
Protection circuit
Relay
drive
Relay
SW mute and relay state detect
VC+
AGND
VC-
Main power
amplifier power
Power board
L
R
C
SL
SR
- 19 -
Figure 3.1.4.1 The player signal flow chart
Page 24
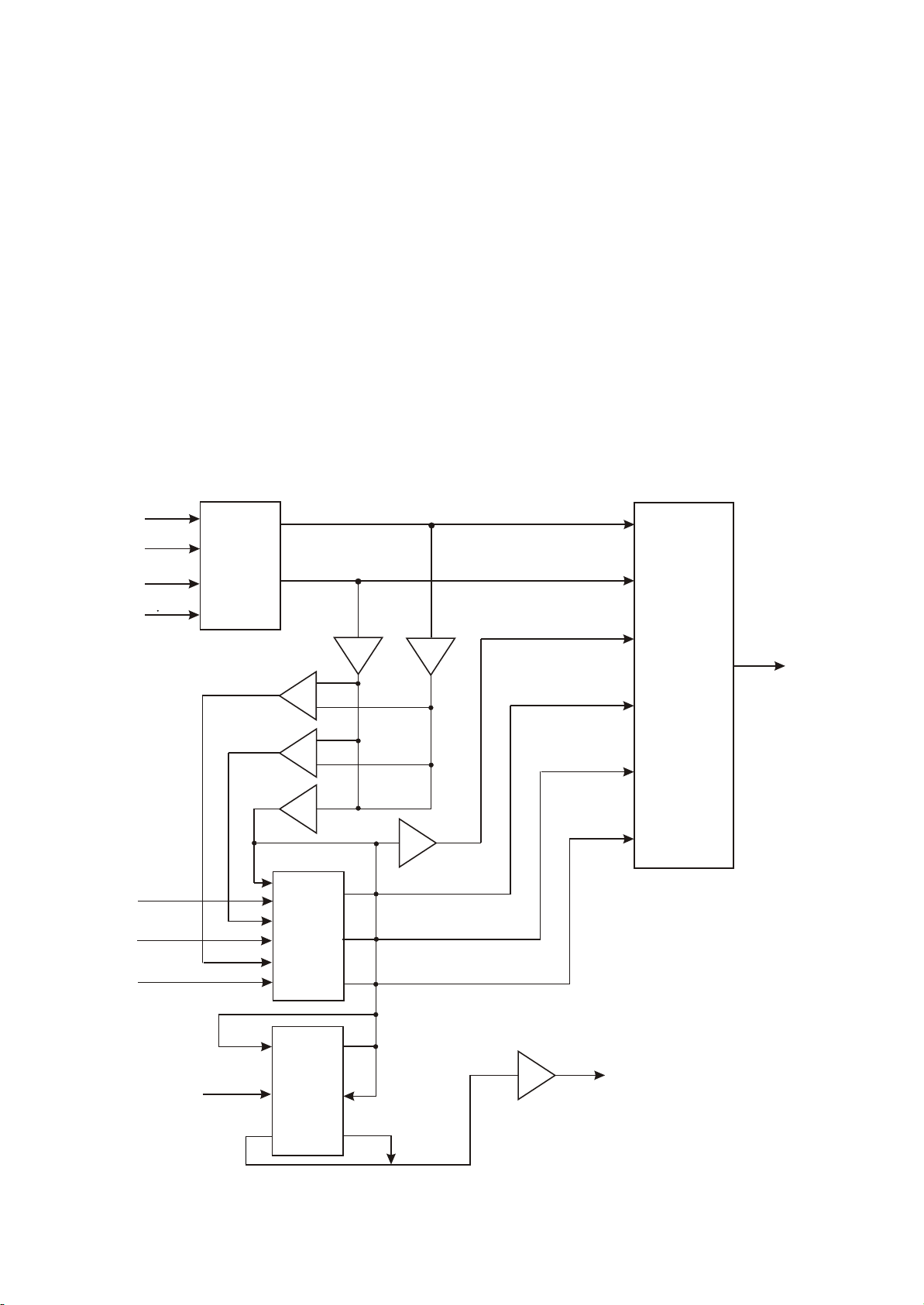
Section Two Unit Circuit Principle
3.2.1 Volume board circuit
AV225T (RU) has 4 kinds of input means in all: tuning input, VCD, DVD stereo input and 5.1CH
input. The Cyber logic function of AV225T (RU) is to achieve C, SR, SL and SW signal through buffer and
processing of adder and subtracter after sampling from L, R channels. In this circuit, electronic
simulation switch is adopted to fulfil the switch in all kinds of state. Signal flow is shown as the following
figure 3.2.1.1:
Tuner
VCD
DVD
1CH
5
C
SR
SL
N101
CD4052
Electronic
switch
N10
SL
N105B
SR
N10
S SR
S SL
S-C
SW
7B
5A
S-C
L
R
N104A
CD
4053
Electronic
switch
N102
CD
4053
Electronic
switch
N103
N104B
N106
OUT
M62446
SWIN
N107A
N108B
DISPLY
Figure 3.2.1.1 Volume board signal flow chart
- 20 -
Page 25
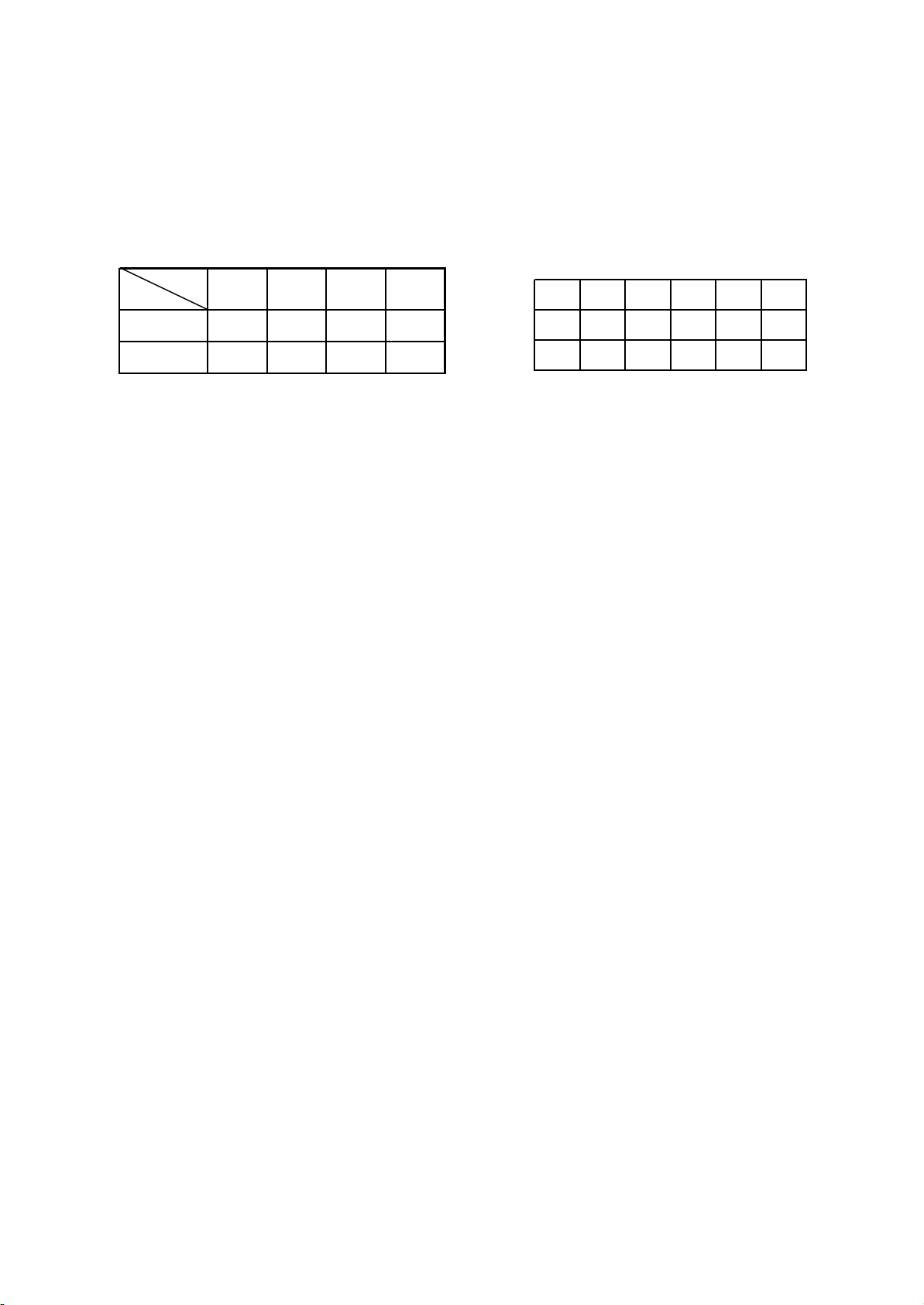
1. Input selection and sound field processing mode
A X B Y C Z
0 X0 0 Y0 0 20
1 X1 1 Y1 1 Z1
Mode
Pin
Tuner VCD DVD 5.1
A 0 1 0 1
B 0 0 1 1
The input selection of AV225T (RU) is fulfilled through electronic switch CD4052 and CD4053, and
the truth value table is shown as follows:
CD4052 Truth value table
CD4053 truth value table
(1) 5.1CH input state: now A, B, 5.1CH of M62446 are in high level, L and R channel signals of
5.1CH input terminal are outputted from pin 3, 13 of N101 respectively and then sent to IC N106 for
volume and tone adjustment; meanwhile C, SR, SL signals of 5.1CH input terminal are outputted from
pin 14, 15, 4 of N102 and then sent to IC N106 for separate volume adjustment; in addition, SW signal of
5.1CH is outputted through pin 4 of N103, amplified by N107A and then sent to M62446.
(2) 3 kinds of analog input modes: AV225T (RU) has 3 kinds of analog input modes: tuning signal,
VCD and DVD are controlled through signals A, B separately. Please refer to CD53 truth value table for
reference.
(3) AV225T (RU) has 3 kinds of sound field modes in all: standard, Cyber logic and Hi-Fi.
A. Standard: under the control of the player MCU, when bass enhancer is off, left channel, right
channel and subwoofer have output; when bass enhancer is on, only left and right channels have output.
B. Hi-Fi: under the control of MCU, only left and right channels of M62446 have output; when bass
enhancer is off, volume adjustment is off.
C. Cyber logic: pin 9, 10 of electronic switch N101 (CD4052) select a group of analog left and right
channel input signals according to the truth value table, the left and right channel signals are outputted
from pin 3, 13 through the electronic switch inside N101 and divided into 2 ways: one way is sent to pin
13, 15 of M62446 for electronic volume and tone adjustment, and the other way gets SW, S-SR, S-SL
and S-C signals though buffer and adder and subtracter, in which S-C, S-SR and S-SL signals are sent
to pin 12, 2, 5 of N102, under the control of 5.1CH signal, N102 selects Cyber logic signal input (see
Cd4053 truth value table) from Cyber logic and 5.1CH signal, central, right surround and left surround
signals are outputted from pin 14, 15 and 4 respectively and then sent to pin 11, 8 and 9 of M62446 for
volume adjustment. Another SW signal is outputted from N107A and then sent to pin 6 of M62446.
5.1CH signal sen t to M62446 outputs from pin 31, 36 after volume adjustment, and then is outputted by
XS20 flat cable holder to signal board.
(4) The relationship between the switch in all kinds of sound sources and sound handling mode in
input circuit is show as the following figure 3.2.1.2:
- 21 -
Page 26
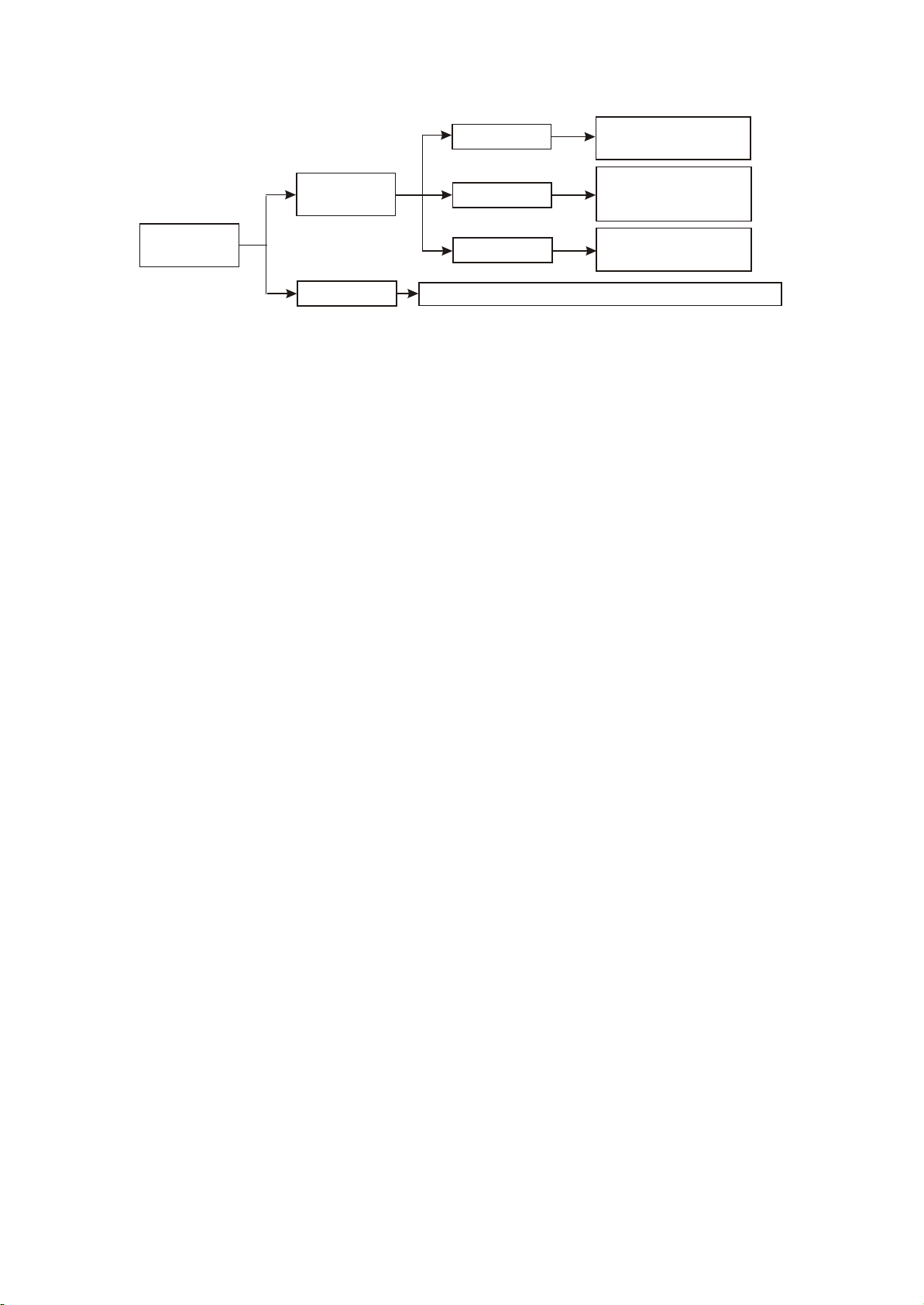
Only L/R channel has output,
sound field and EQ setup is
invalid
Only L, R and SW channel
has output, capable of
performing sound field and
EQ setup
6CH output, capable of
performing cinema sound
field and EQ setup
Press INPUT
button to select
circularly
Hi-Fi mode
2 kinds of analog
input modes
5.1CH input mode
Figure 3.2.1.2 Illustration between input circuit
Standard mode
Cyber logic mode
6CH output, capable of performing cinema sound field and EQ setup
2. Control circuit
The latched, data and clock signals outputted by MCU (N100) pin are sent to pin 39, 40, 41 of
M62446, pin 1, 2, 3, 4 of M62446 output control level to select the input signal and spectrum sampling
signal. Other functions, such as volume and tone adjustment, are also controlled by the three control
signals. The display of display screen is controlled by CPU directly.
3. Spectrum sampling circuit
The spectrum sampling in AV225T (RU) is sent from pin 13 of N103 to N108B for amplification, and
then sent to spectrum gating circuit. 5.1CH of M62446 selects sampling signal. When selecting Cyber
Logic, 5.1CH control signal is low level, now pin 9, 11 of N103 is low level, and it is known from the truth
value table that the output is X0 and Z0 and this two sampling signals are grounded. It is known from
Cyber logic principle, centre, surround and subwoofer channels are all produced by left and right
channel signals, but in S-C signal, complete left and right channel signals are included, so it is ok to
sample from S-C only. Therefore, S-C signal is outputted through R195 (pin 13 of N103) to N108B and
added with OK-R signal for the amplification of spectrum sampling signal, and then sent through XS20
to frequency point gating and auto search circuit; the same, when selecting 5.1CH input, 5.1CH control
signal is high level, pin 14, 15, 4 of N102 select pin 14, 4 of X1, Y1, Z1 of N103 and connect to X1, Z1,
thus, the 6-channel signals are outputted through pin 13 of N103 to N108B and added with OK-R signal
for the amplification of spectrum sampling signal, and then sent to frequency point gating and auto
search circuit through XS20.
4. Tuning function
This player has tuning function, which provides a good selection for users. It directly controls digital
tuner through MCU to receive audio signal, and then output after amplification by power amplifier. The
clock and data line of digital tuner is commonly used together with M62446, the other two control lines
are directly connected to MCU, L, R signals after being handled by digital tuner are directly sent to pin 1
and 12 of N101 CD4052 for gating input.
- 22 -
Page 27
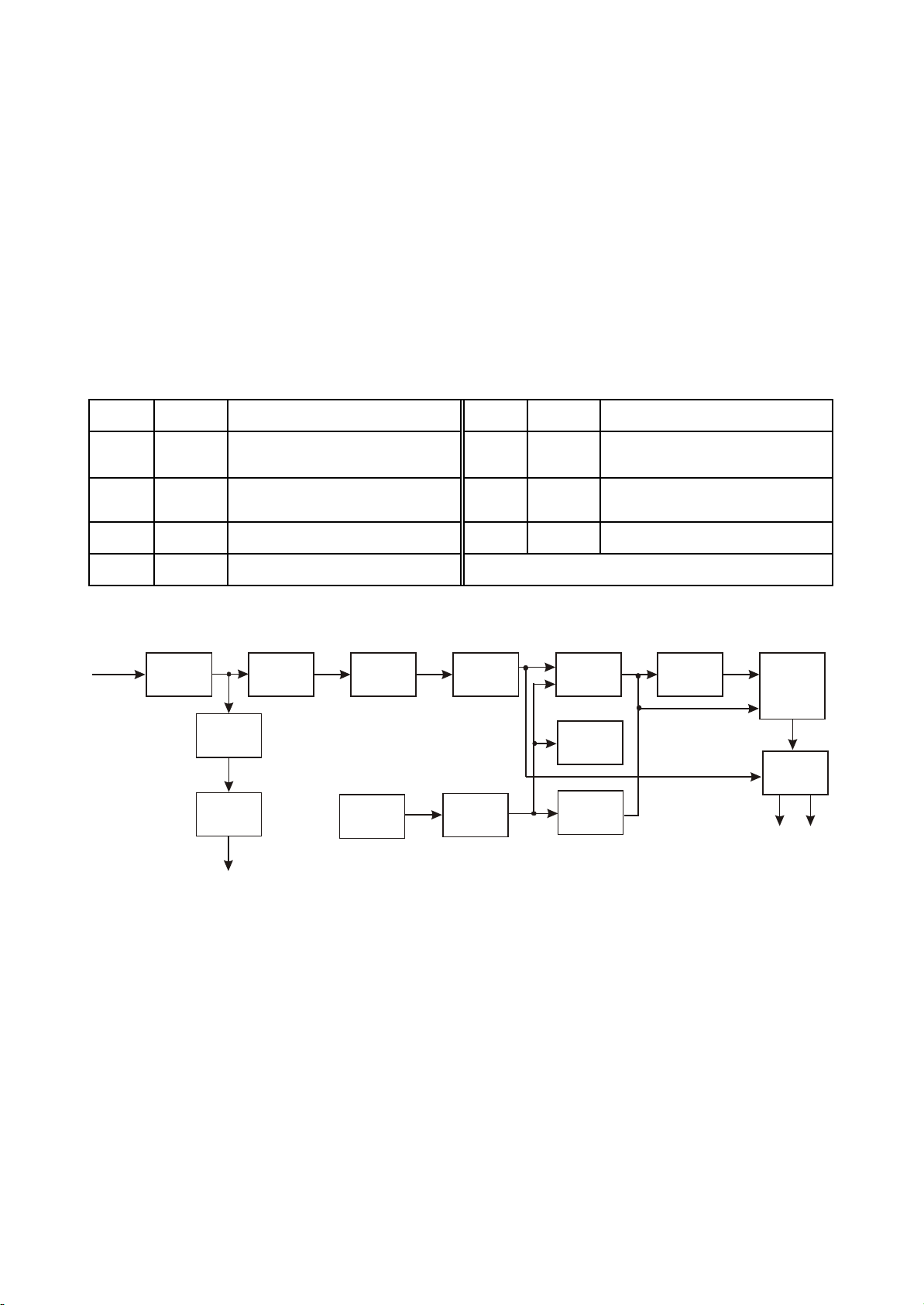
3.2.2 Signal processing board circuit
IC SN IC name IC function IC SN IC name IC function
N201 4558
Operational amplifier performs
preamplification to voice signals
N207 CD4051 Karaoke delay adjustment
N200 PT2315
Karaoke volume adjustment,
including tone adjustment
N208 CD4051 Karaoke echo adjustment
N205 CD4053 Electric switch N204 4558 Inverter
N209 PT2399 Karaoke echo settlement
The signal board performs mixed amplification to 5.1CH signal sent from volume board, voice signal
sent from microphone, headphone board and Karaoke echo signal.
1. AV225T (RU) Karaoke circuit
(1) Function: this circuit is to reset by loudspeaker after handling voice and being amplified by
power amplifier. It includes voice beautification circuit, wide sound field processing circuit and Karaoke’s
echo and delay adjustment circuit.
(2) Function of IC of Karaoke circuit is shown as the following table:
(3) Karaoke signal flow chart
MIC
N20A1
N202A
V200
N200
P_OKT
N202B N203B
N100
Figure 3.2.2.1 Karaoke signal flow chart
N211
N100
N209
N207
N208
N204
Directly connected
OK
N205
Mixed
output
Shown as in the figure 3.2.2.1, when microphone is inserted, MIC signal is sent to N201A
operational amplifying circuit for amplification. One path of MIC signal after being amplified gives MCU a
microphone input identification signal P_OKT through VD201 rectification filtering control triode V200
after being amplified by N202A; when there is signal input, P_OKT is low level, MCU makes N210
CD4094 send out KM low level signal to make triode V103, V105, V104 ccutoff and then to make MIC
signal can output; the other path is coupled by C219 to pin 6 of PT2315, and then output from pin 16
after internal volume adjustment to N202B and N203B for amplification. The signal after being amplified
of N203B is divided into two paths, one path outputs directly, and the other path is coupled byR222,
C247 to PT2399 inside for delay and echo adjustment and then outputs from pin 14, and then mix output
- 23 -
Page 28
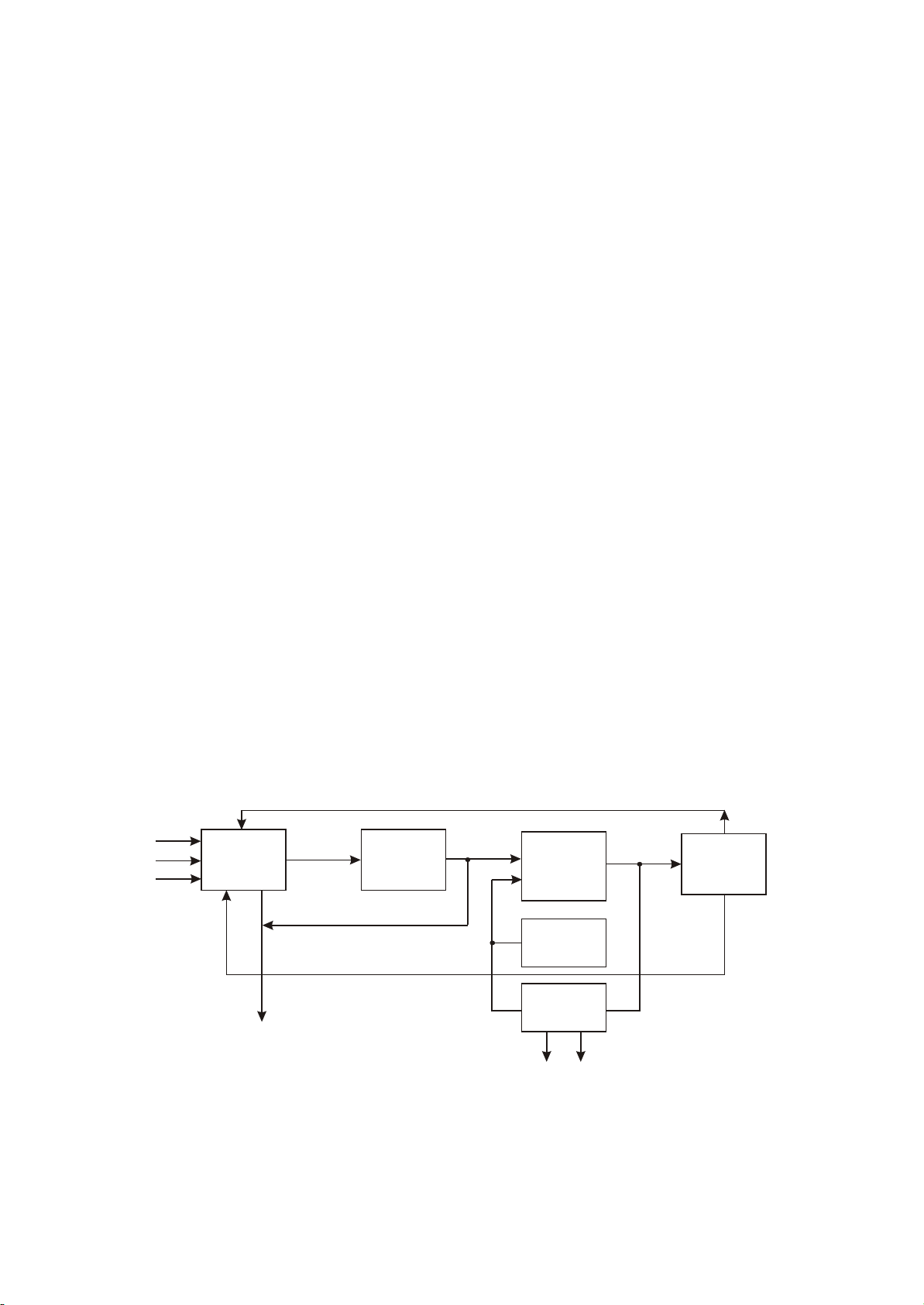
Together with direct connection OK signal through N204B, while OK-R is outputted from pin 14 after
being gated by N205 and then overlapped to left and right channels.
In this circuit, the low frequency exalt network composed by triode V201 connected to the reverse
end of N202B is mainly to exalt 75HZ low frequency signal.
When performing delay adjustment to PT2399, firstly give control signal to MCU, and MCU controls
N207 after being extended by N211 IC CD4094, then selects different resistance value to connect into
pin 6 of PT2399 to reach the purpose of delay adjustment.
Similarly, through changing the resistance value in R229 to change the echo level overlapped to
direct connection signal, the echo adjustment is realized.
The wide sound field control signal of Karaoke is sent by N211 to pin 11 of N205, when it is high
level, pin 14 of N205 is connected to X1, now the phase of OK-R signal is reverse from that of OK-L,
sound field is widened and Karaoke is in wide sound filed state. On the contrary, the phase of OK-R
signal is the same with that of OK-L, Karaoke is in the narrow sound field state.
In addition, microphone plug has a detect signal P_MICDET, and it composes the detection to
microphone inserting together with the circuit composed of V202. When microphone is not inserted, it is
low level, V202 cutoff; when microphone is inserted, it is high level, V202 is on, now turn off scene
surround mode and forbid tuning.
Otherwise, there is OK auto mute function. When P-KT cannot detect any signal in a continuous
period, MCU will send out a control signal to make KM be high level, triode V103, V105, V104 is on to
mute OK signal to advance SNR of the player and better listening effect.
(4) Scene mode signal flow
AV225T (RU) has a special function, that is, it may realize switch in 5 kinds of scene mode when there
is no Karaoke, which is fulfilled by Karaoke part. Signal flow chart is shown as in the figure 3.2.2.2:
R- 1
L -1
C- 1
N205
Mixed output
N203B
N209
N207
N208
N204B
Figure 3.2.2.2 Scene mode signal flow chart
When pin 9 and 10 of N205 is in high level, the sampled L, R, C signals are outputted by pin 3
through N205 gating, after being amplified by N203B, one path is sent to PT2399 inside for echo and
delay adjustment (controlled by IC CD4094), the effect after adjustment is overlapped to L, R, C channel
- 24 -
Page 29

To form various scene modes. Seen from this, its principle is the same with that of Karaoke. In scene
mode, it functions only when microphone is not inserted and in 5.1CH mode at the same time.
2. Bass enhancer circuit
BURST sent out by N210 is bass enhancer on/off signal. When it is high level, it is added to base
electrode of V102, V102 is on, base electrode outputs low level, V107, V100 are cutoff, SW signal
outputs to external terminal normally, at the same time, BURST high level signal is added to emitting
electrode of V108, V108 is on, collector electrode output high level is added to the base electrode of
V101, V101 is on to make SW signal grounding and it will not be overlapped to left and right channel
signals.
Reversely, when BURST is low level, V100 is on, SWM signal cannot output from external terminal,
at the same time V101 is cutoff, SW signal is overlapped to left and right channel signal.
Bass enhancer of AV225T (RU) is divided into 3 levels, the principle is to change the high/low of
bass enhancer level through changing SW output volume of M62446.
Meanwhile, SWM signal is added to relay through XS9, when relay is disconnected, SWM signal is
grounded to make subwoofer terminal have no output to avoid the concussion to speakers at the
moment of power-on.
3. 5.1 signal and Karaoke signal mixed amplification circuit
Left and right channel signals of 5.1 signal, after being mixed with SW signal and being amplified by
N101B, N100B, are sent to the reverse end of N101A, N100A, at the same time, OK-R, OK-L signals are
respectively added to the reverse end of N101A, N100A and then output from pin 1 of N100A, N101A to
power amplifying circuit for amplification after the mixed amplification of N100A, N101A.
Meanwhile, the centre C-1 signal sent from volume board is added to the pin 6 reverse end of
N102B, and then added to the reverse end of N102A after amplification. Now the C1-1 signal after
processed by echo (scene surround mode) is also required to add to the reverse end of N102A and
mixed amplifying with it, then sent to centre channel power amplification circuit.
Surround SR-1, SL-1 signal of the other path volume board is directly sent to surround channel
power amplification circuit.
One path of 5.1 signal after mixed amplification is sent to power amplification circuit through XS9,
the other path forms DIST signal (distortion detect signal) to MCU board through R111, R112, R142,
R145, VD100-VD104 to perform auto gain adjustment to control the volume output.
3.2.3 MCU board circuit
MCU board is composed of player control circuit, auto search input signal and spectrum analysis
circuit.
- 25 -
Page 30

1. The player MCU control
N100 is the control centre of the player, various control instruction are outputted by it to each
controlled circuit to fulfil each control function. +5V power supply is adopted, and pin 40 is its power
supply pin. Pin 18, 19 externally connects with 12M crystal oscillator to provide itself with working clock
frequency. Pin 9 is its reset pin, when power on, +5V charges C106 through R100. The voltage on the
two ends of capacitor cannot change suddenly, so B-pole of triode V100 is low level, that is, V100 is not
on, a high level reset signal is given to MCU. When capacitor C106 charging finishes, V100 is on, now
reset finishes. Form of this kind of reset circuit is high level reset, and low level is kept.
When the player is working, information of power-on picture and Chinese characters when
operating displayed on display screen are all saved in the static memorizer inside MCU. N101 is a state
memorizer and it can save the working state of the player at the time of power-off and then call these
states until power-on next time to avoid the adjustment of users again. All kinds of user-set sound field
modes are also saved in it and can be called when necessary.
2. Input signal detecting, search circuit automatically
DISPLAY signal from volume board is sent to N103A for amplification, after being coupled by
capacitor C110, sent to the reverse end of voltage comparator N103B, outputted from pin 7 of N103B,
then sent to pin 16 of the player MCU through VD103, V101, R109, R107. When N103B outputs a high
level, Vd103 is in reverse cutoff state, B-electrode of switch pipe V101 is high level, now switch pipe
V101 is in on state, and then a +5V P_SEARCH high level is achieved through VD101 voltage regulating
to MCU, which means there is no signal input, and the search continues. When output terminal of N103B
outputs a low level, VD103 is in positive direction on state, B-electrode of switch pipe V101 is low level,
now switch pipe is in curoff state, MCU detects that P_SEARCH is low level, which means there is signal
input, at the same time, the search stops. The working principle is as follows:
(1) After power-on, under the control of MCU internal program, data signal is outputted to M62446,
then M62446 sends out high/low level to perform scanning to N101, N102, N103 each input port of
volume board, at the same time, P_SELECT is high level, V102 is on, now the in-phase end voltage of
comparator N103B is about 0.1V. When these input ports have no signal output, voltage of pin 6 of
N103B is less than 0.1V, pin 7 outputs 12V, Vd103 is in reverse cutoff state. It is known from the above
analysis, P_SEARCH is high level, which means there is no signal input. After all ports being searched
once, it enters standby state automatically; when a certain port has signal input, this signal is compared
with pin 5 of N103B through N108B of volume board and MCU board N103A amplification, if voltage of
pin 6 of N103B is more than 0.1V, pin 7 outputs -12V, Vd103 is in positive direction on state, now,
P_SEARCH is low level, which means there is signal input, through controlling IC M62446, MCU locks
this port that has signal input to enter normal playback.
(2) When pressing “GOTO” button on remote controller, through remote control receiver on the
panel, the switch from light signal to electric signal is performed, thus, pin 11 of MCU sends out a high
- 26 -
Page 31

Level to make V102 in on state, and search also according to the above program.
3. Spectrum analysis circuit
(1) Spectrum analysis circuit is composed of auto spectrum gain adjustment circuit, frequency point
gating circuit, A/D conversion circuit and display output circuit, shown as in the following figure 3.2.3.1:
DISPLAY
N104
CD4051
Auto spectrum
Gain adjustment
+5V
N105C
B
+
-
3
}
A/D conversion
CPU
-
V105
+
V104V103
Figure 3.2.3.1 Spectrum analysis circuit
35HZ
134HZ
300HZ
N102A
1KHZ
2.2KHZ
6.3KHZ
16KHZ
CD4051
Frequency
point gating
Pin 12 of MCU
Pin 14 of MCU
N108
}
MCU
3
(2) Auto spectrum gain adjustment circuit: in order to avoid the two conditions that when input signal
is too weak, screen display range is too low, or when input signal is too strong, full screen will appear,
AV225T (RU) has set auto spectrum gain adjustment circuit and adopted a single-channel 1-selected-
from-8 electronic analog switch N104 CD4051, with its truth value table shown as follows:
X0 X1 X2 X3
0
A
B
C
1
0 0
0 0 0 0
0
1
X4 X5 X6 X7
0
1
1
1
0
0
1 1 1 1
0
1
1
1
Through changing the resistance value of the reverse end grounding resistor of operation amplifier
N104, gain of the operation amplifier is changed. See the details of the working of the entire circuit. The
spectrum analysis signal source (DISPLAY), mentioned above, is sent to the in-phase input terminal of
operational amplifier N105C for amplification, and its amplified multiple depends on the ratio of the
resistor connected by feedback resistor R130 and N104 electronic switch. When main volume is too high,
through the control of MCU, N104 increases the resistance value of grounding resistor automatically and
- 27 -
Page 32

Decreases the amplified multiple; when main volume is too small, N104 decreases the resistance value
of grounding resistor automatically and increases the amplifies multiple.
(3) Frequency point gating circuit: the signals after being amplified by N105C, through C115
coupling, are sent to the 7 bandpass filters composed by operational amplifier, the corresponding
frequency range can be confirmed through setting the capacity of its feedback capacitor. On the output
end of each filter, a half-wave rectification circuit is connected, through rectification filtering to the AC
signal after being amplified DC voltage is achieved. This circuit is mainly to realize frequency point
sampling function, which can represent the range of each frequency point in a complete sound signal.
If the low frequency part in sound signal is strong, the DC voltage on the output terminal of 35HZ,
100HZ filter will be higher, similarly, when high frequency part is strong, the DC voltage on10K, 16K filter
will be higher. The output terminal of this 7 filters is connected to 7 input terminals of electronic switch
N108 (Cd4051) to make this electrtonic switch quickly and circularly gating in each frequency point. On
the output terminal of pin 3 of N108 will output a series voltage values that stand for each frequency
point signal range, shown as in the following figure 3.2.3.2:
V
35HZ
100HZ
300HZ
1KHZ
3KHZ
10KHZ
16KHZ
Note: the voltage range
in the figure is uncertain.
35HZ
T
Time interval of swich
Frequency point circular gating cycle
Figure 3.2.3.2 Frequency point signal range voltage value
(4) A/D conversion, display output circuit (two cases divided)
1) When there is no signal input, MCU sends a P_CHARGE high level signal to B-electrode of V104,
the positive direction end of comparator N102B is low voltage, for the reverse end of N102B gets the
partial pressure of R169, R172, thus it will make N102B output voltage with -12V about to make triode
V105 cutoff; C-electrode of V105 will give a high level P_ADINT0 to pin 12 of MCU to inform MCU of not
performing A/D conversion. (Pin 9, 10 of N108 has no action and keep in high level)
2) When machine detects signal, MCU sends a P_CHARGE low level signal to B-electrode of V104,
+5V voltage charges C137 through V103; when the voltage value of reverse end is reached, comparator
turns over, pin 7 of N102B outputs 12V voltage to make V105 on, C electrode is low level, after MCU
- 28 -
Page 33

Receives low level signal, 35Hz level gating is immediately finished, and then switches to next
frequency Point 100Hz. During the course of conversion, P_CHARGE outputs an instant high level to
make V104 on, releases the voltage on C137, and makes the in-phase end of N102B begin the process
of 100Hz charging from 0 level. When 100Hz charging finishes, switch into the charge/discharge
process of the next frequency point, and this kind of process circles continuously under the control of
MCU. This period of charge, from 0 level to the point that turn over happens, stands for the signal range
of the current frequency point. The range is larger, time is longer and range displayed on screen is
higher; the range is smaller, time is shorter and range displayed on screen is lower. The digital pulse
outputted from the output terminal of N102B adds to pin 12 of MCU through V105 phase, MCU handles it
and outputs to panel and makes dynamic spectrum display on display screen. Originally speaking the
display of each frequency point performs one by one according to the sequency, for the above
circulation process is fast, on the screen we will see the process of a whole spectrum displays. Shown
as in the figure 3.2.3.3, the charge time parameter is frequency point signal range voltage value cyclic
parameter in the figure 3.2.3.2:
V
35HZ
100HZ
Frequency point signal range voltage
value switches into time interval
V
High level discharge
5HZ
3
100HZ
T
T
Switch time interval
Figure 3.2.3.3 Illustration of "Frequency point signal range
voltage value switches into time interval"
Charge time Charge time
3.2.4 Control panel circuit
Front panel control circuit is the window of man-machine conversation of the player, and it can
transmit various operation instructions to MCU to fulfil various operation. At the same time, it is also a
window of the player. Users control the working state of the player through it and it is also an important
composition of the appearance. Control panel circuit block diagram is shown as in the figure 3.2.4.1:
Drive circuit
MCU
Figure 3.2.4.1 Control panel circuit block diagram
LCD display
Power
Remote control
receiving
- 29 -
Button
Page 34

1. Power supply circuit
Control panel power supply of AV225T (RU) has two groups voltage of +3.3V and +5V. The +5V
voltage from signal board after voltage regulating supplies power for N102, N103 (74VHC245) and N101
PT2222 respectively through the voltage reduction of three diode VD105, VD106 and VD107.
2. LCD display drive and buttons circuit
This circuit is composed of N101, N102, N103 and LCD. The display is directly controlled by P0 port
of MCU, LCD is banded with IC inside. For working voltage of display screen is 3.3V, but the control
line level sent out by MCU is 5V, between MCU and LCD display screen, two IC 74VHC245 are used
to perform level conversion to change the +5V control level from MCU into +3.3V control level to control
the display of display screen.
Buttons circuit of this player is equal to a remote controller. Signal of buttons matrix is received by
PT 2222 and then makes infrared light emitting diode VD100 send out signal through the control of
triode gating by pin 7 , then send to MCU for processing after being received by remote control receiver.
3.2.5 Power board circuit
Power board provides each unit circuit of the player with required various working voltage. Shown
as in the figure 3.2.5.1, AV225T (RU) adopts a large power round transformer to supply power for main
channel, central and surround channel power amplifier.
9.8 V
220V 50HZ
Figure 3.2.5.1 Power board power supply block diagram
Panel display,
MCU power supply
Rectification
31V
filtering
Rectification
15V
filtering
Fan
Left/right channel
power amplifying
level
C , SL, SR channel
power amplifying
level
1. The two groups AC 31V outputted by the first time grade of transformer, through rectification
filtering of 8 In5404 and 2 large electrolytic capacitor (15000uF/68V), gets +/-43V voltage to supply
power for left and right channels.
2. The two groups AC 15V voltage outputted by the second time grade of transformer, through
rectification filtering of 4 In5404 and 2 electrolytic capacitor (4700uF/35V), gets +/- 21V voltage to
- 30 -
Page 35

Supply power for SL/SR/C channels. In addition, for other IC and operational amplifiers, power is
achieved also through voltage regulation of 3-end voltage regulator L7812, L7912 by it to supply power
for other IC.
3.2.6 Power amplifier board and protection circuit
1. L/R channel power amplifying circuit
L, R channel power amplifying circuit of AV225T (RU) is composed of discrete components. The
composed block diagram is shown as in the figure 3.2.6.1: (take L channel as instance)
L IN
V101
V116
Mute
AC negative
feedback
R
121,R109,C105
Difference
amplification
Stage
V102
Constant current source V104, V107,
Vd102, Vd103
,V103
Voltage
amplification
stage V105
Figure 3.2.6.1 L input block diagram
Composite power
amplifying
V132 V112
Temperature
compensation
stage V106
Composite power
amplifying V133,
V113
Relay
Speaker
L channel signal, through R101, R103, C101 coupling, is sent to B electrode of V102; V102 and
V103 are composed difference amplifying circuit of single ended input and single ended output. Sound
signal outputs from C electrode of V102 to B electrode of voltage amplifying stage, and then outputs to
composite power amplifying stage after voltage amplification. V104, V107, VD102 and VD103 compose
constant current source circuit. VD102 and VD103 provide constant base electrode current for V104 and
V107. The emitter electrode resistor of V104 decodes working current of difference amplifying stage, the
emitter electrode resistor of V107 decides working current of voltage amplifying stage. V132 and V112
compose multiple unit tube amplifying to make the final stage of power amplifier have strong current
amplification capacity and they compose waveform positive half cycle amplification. V133 and V113
compose the negative half cycle amplifying of waveform and its circuit structure is the same with that of
upper tube. The function of temperature compensation tube V106 in the circuit has two: firstly, it is the
base electrode bias of upper/lower multiple unit tube and its working state decides the static working
current of composite power amplifying stage, that is, we can set the static working point through
adjusting the on degree of V106, and the usual method is to change the base electrode resistor of V106;
secondly, it can automatically adjust the working state of composite power amplifying stage when
temperature increases, and the adjustment process is as follows:
- 31 -
Page 36

Total current of output stage = working current + leakage current
When temperature increases, the increase of leakage current leads to the drift of static working
point (unfavourable), at the same time, the leakage current of V106 increases, Uce decreases to make
the bias current of output stage decrease to make working state change and working current of back
stage decrease to reach the purpose of temperature compensation.
Introduce voltage negative feedback to power amplifying circuit of AV225T (RU) and it is composed
of R121, R109 and C105, which can stabilize static working point of difference stage. AV225T (RU)
adopts direct output means, R111, C116 (on power board) connected with output end compose Zobel
Network to prevent the high frequency self-exitation caused by the AC inductive reactance of speaker
voice coil.
2. Mute circuit
When pressing MUTE button on remote controller, after the photoelectric conversion performed by
infrared receiver, a mute signal is achieved to send to MCU, which sends out P_LR high level and
P_CSM high level mute instruction at the same time. P_LRM high level make 2N5401 (V115), S8050
(V101), S8050 (V116) on, left/right channel signal is short circuited to ground to fulfil the mute control
function of left/right channel; P_CSM high level makes 9014 (V150)on, 2N5401 (V130) and S8050 (V131)
on, centre channel signal is short circuited to ground and centre channel mute control function is fulfilled;
at the same time, the on of 9014 (V150) makes 9014 (V151) cutoff, voltage of pin 5 of TDA7265 is
positive power voltage, TDA7265 internal mute circuit works to reach surround mute function. When
headphone is inserted, HEADPHONE controls LRM and SCM through VD203 and VD204 to make
main channel, centre and surround channel mute.
3. C, SR, SL power amplifying circuit
Compared with the former models, the three channels of AV225T (RU) adopt power amplifying IC
CD1875CZ (N104) and TDA7265 (N106) special for audio. As for TDA7265 (N106), it has 11 pins in all,
pin 3, 1 and 6 are its positive and negative power pins respectively; pin 10, 8 are its reverse input end,
the rated output power of each channel of this power IC may be up to 15W and it is with function of auto
mute when power on; it has 5 pins in all, and it is a good-performance power amplifying IC, the
application circuit is simple and has 15W power output in rated state. Pin 5 and 3 are positive/negative
power pins.
4 Protection circuit
Protection circuit of AV225T (RU) power amplifier is on power board. Protection means of L, R, C
channel is through disconnecting relay Y100 when protection starts up to disconnect its output. SR, SL
channel fulfils the protection function through mute. AV225T (RU) is with power-on delay protection,
central point over-voltage and over-current protection, standby protection.
- 32 -
Page 37

(1) Power-on delay attracting protection circuit: when power on, working of circuit is stable, and the
produced current has great damage to speaker and power amplifier, so delay attracting protection circuit
is set. Power-on delay attracting protection circuit is divided into 2 steps: 1. C, L, R channel working
process: the AC outputted from transformer, through rectification filtering of Vd113, C110, gets +22V
voltage to make VD111 reverse broken-down through charge to C115 by R108 to make Vd111 reverse
broken down to make V105, V104 positive direction on to make relay Y100 attracting to realize delay
attracting effect. SR, SL channels performs concussion protection when power-on/off through the
following means: after machine system resets, MCU outputs a P_CMS high level signal to make V150
on and make V151 cutoff; pin 5 of TDA7265 is power voltage, TDA7265 outputs mute. After delay start-
up of machine succeeds, the output signal P_CMS of MCU switches into low level immediately, V150 is
cutoff to make V151 on, voltage of pin 5 of TDA7265 is about 5V lower than power voltage, SL/SR
channel resumes normal output.
(2) Over-voltage protection: on each channel’s output end, a over-voltage sampling resistor is
connected, L channel is R116, R channel is R117, C is R118, SR and SL are R120 and R119 respectively.
When just one channel’s central point voltage is more than +3.5V or less than -3.5V, V101 or V102 is on
to make their C electrode voltage decrease, B electrode of V103 is pulled down to make V103 on, relay
is disconnected finally and over-voltage protection is fulfilled. Working process is shown as the following
figure 3.2.6.2:
Over-voltage
sampling resistor
is connected to
each channel
L channel
is R116
When more
than +3.5V
When less
than -3.5V
Figure 3.2.6.2 Over-voltage protection flow chart
V101 is on
V102 is on
Voltage
of C
electrode
decreases
V103
is on
Relay
disconnects
and protection
starts up
(3) Over-current and short-circuit protection: on the output load resistor of L, R channel, a over-
current sampling triode is connected. Sampling triode of L channel is V114 (on power amplifier board),
load resistor is R126, R127 (on power amplifier board). C, SR, SL channel power amplifying IC is with
over-curent protection function inside. Only over-current appears in L channel, the voltage decrease
that produces on R126, R127 will increase. Once the voltage decrease of R129 (on power amplifier
board) is more than 0.7V, V114 will be on, V103 is also on, and relay is disconnected finally and short-
circuit protection is finished. Working process is shown as the following figure 3.2.6.3:
Over-current
sampling triode
is connected to
each channel
L channel
is V114
Figure 3.2.6.3 Over-current and short-circuit protection flow chart
Voltage decrease
on R126, R127
increases when
over-current
- 33 -
V114 is
on
C electrode
voltage
decreases
V103
is on
Relay
disconnects
and protection
starts up
Page 38

Similarly, when over-current appears in R channel, (on power amplifier board) voltage on R159 will
be more than 0.7V to make (on power amplifier board) V129 on, and also make V103 on, relay is
disconnected finally to reach the purpose of protecting speaker.
3.2.7 MIC, headphone board
MIC signal is directly sent to signal processing board through flat cable XP12, the principle has
been specified in section 3, so it is omitted here. The main element of headphone part is headphone
amplifier N100 PT2308. It is a dual-channel operational amplifier, has 8 pins in all and adopts signal
power (+5V) to supply power. Pin 1 and 7 are two channels’ signal output ends; pin 2 and 6 are two
channels’ reverse input ends; pin 3 and 5 are two channels’ in-phase input ends; pin 8 and 4 are positive
and negative power pins.
When no headphone is inserted, headphone detect signal PH_SW is low level, now the mute
control signals P_LRM and P_CSM of main channel, centre and surround channels are low level, these
5 channels all have normal output; when headphone is inserted, PH_SW is high level, now diode VD203
and VD204 on signal board make the mute control signals P_LRM and P_CSM of main channel, centre
and surround channels be high level, and make main channel, centre and surround channels have no
output on account of mute. Please refer to mute circuit part for the principle. At the same time, triode
V111 is made on through the resistor R166 on signal board, so V110 and V109 are cutoff to cut the
power supply loop of fan; when volume is more than 45dB, fan tunning is forbidden to facilitate to listen
with headphone.
Please be noted here that headphone detect signal PH_SW is not connected with MCU, but is set
by machinery structure of headphone jack.
3.2.8 Video in/out board circuit
AV225T (RU) is with two-channel composite video input (VCD, DVD or 5.1CH) and one-channel
composite video output (VCD, DVD or 5.1CH).
Input/video switch of video signal is realized through a electronic switch CD4051 (N101), the truth
value table is shown as follows:
X0 X1 X2 X3
A
B
C 0
1
0
0
0
0 0 0
X4 X5 X6 X7
1
0
1
- 34 -
0
1
0
1
0 1
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
Page 39

When select VCD channel, pin 1 and 2 of N106 (M62446) of volume board sends out two control
signals of A and B, and one INH control signal. A=1, B=0, INH=0, known from Cd4051 truth value table
that output pin of CD4051 (pin 3) selects X1, ie, VCD channel, now, in terms of volume board working
principle in section 2, A and B also control gating of audio part CD4052, that is, audio channel also
selects VCD channel, thus, the synchronous switch of audio and video of VCD channel is realized.
Similarly, for the synchronous switch of audio and video of DVD channel, pin 1 and 2 of N106
(M62446) of volume board send out 0, 1 and INH=0 control signal of A and B to fulfil the corresponding
switch. When 5.1CH is selected, A=1, B=1, INH=0, the audio/video switch in 5.1CH is fulfilled.
At last, composite video signal outputs through triode V101 (1015) .
When INH=1, CD4051 gas no output.
- 35 -
Page 40

Section Three Servicing Cases
3.3.1 Servicing instances
Instance 1 Trouble symptom: power-on protection
Description: relay not attracting and display “System abnormal, auto protection”.
Analysis and troubleshooting: system protection after power-on, relay not attracting; shown as in
the figure 3.3.1.1, test whether L, R, C, SL, SR of power board flat cable holder XP8 has DC output, pin 1
of power board flat cable holder XS7 is tested high level, pin 2 is low level, C electrode of triode V101 is
high level, known from the above test that protection is not caused by over-current and over-voltage
(you may also unplug XP7 and XP8 flat cable holder and check whether it also has protection). The
anode voltage of diode VD112 is tested 0, so relay is judged abnormal. It is normal after changing relay
and trouble is removed.
OVER
P_RC
RLY0
SWM
L2
R2
C2
SL2
SR2
VC+
GND
GND
VC-
XP8
CON9
XP7
CON4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
R105
10K
V101
C9014
C110
220u/35V
V102
C9014
R116
51K
R117
51K
R118
47K
R119
47K
R120
47K
C122
104
C113
220u/16V
C114
220u/16V
1
2
XL101A
R106
WP6
4.7K
R109
VD110
IN4148
R108
100K
R107
100K
V103
C9015
C121
103
10k
1
2
XL101A
WP6
C115
47U/25V
9
10
11
12
13 14
VD111
5.1V R110
RELAY-4
Y100
VD112
1N4148
56K
1
5
2
6
3
7
4
SWM
8
RLY0
XL101A
1
2
WP6
V104
C8050
XL100A
1
2
WP4
XL100A
1
2
WP4
V105
C9014
VD113
R100
47/3W
1N4004
R102
1K
RLY0
SWM
VD108
IN4148
R101
1K
R111
4.7/1W
R112
4.7/1W
R113
4.7/1W
R114
4.7/1W
R115
4.71W
R103
47K
4
3
2
1
VC+
VC-
C1160.1u
C1170.1u
C1180.1u
C1190.1u
C1200.1u
C126
R104
10K
V100
C9014
103
L100
0.7UH
L101
0.7UH
Figure 3.3.1.1 Protection circuit diagram
Note: 1. After relay being used for a period, working state may be unstable and some abnormalities
will appear. For instance, relay not attracting after power-on sometimes; each contact point not fully
contacted after relay attracting; CPU not detect RLY0 signal (this signal is low level after relay attracting);
auto protection.
- 36 -
Page 41

2. Power-on protection causes: over-current protection, over-current protection and CPU not detect
RLY0 signal: test whether each output channel has DC output; when power-on protection trouble
appears, make clear which kind of reason caused this. The common protection is that abnormal centre
or surround power IC causes that output signal has DC.
Instance 2 Symptom: no sound output
Description: system not detect signal after power on, no output when switching various sound
sources
Analysis and troubleshooting: select VCD channel after power on, input sine wave signal, shown as
in the figure 3.3.1.2; test volume board capacitor C133, C134, no signal; test volume board capacitor
C122, C121, also no signal; pin 5 and 14 of N101 have signal; test power voltage of pin 7 and 8 of N101,
normal; it is known primarily that N101 has input but no output, change N101 and N101 still has no
output after changing, so it is judged that N101has no problem, it is that A, B signal of N106 have trouble
when this channel has not been selected; change N106, output is normal after changing and trouble is
removed.
N101
CD4052
12
5.1CH
X0
14
X1
15
X2
11
X3
1
Y0
5
Y1
2
Y2
4
Y3
6
INH
B
9
B
A
10
A
N102
CD4053
12
X0
13
X1
2
Y0
1
Y1
5
Z0
3
Z1
6
INH
11
A
10
B
C9VEE
VDD
Vss
VDD
VSS
VEE
X
Y
13
X
3
Y
16
A+6.8V
8
7
A-6.8V
14
15
4
Z
16
A+6.8V
8
7
A-6.8V
R134
R135
R136
150K
150K
150K
R133
150K
C115
47u/16V
A+6.8V
C116
47n
B
A
INH
5.1CH
R157
100K
R160
100K
R161
100K
R162
100K
R158
100K
R159
100K
R153
22K
B
A
INH
5.1CH
R154
22K
C124
15n
C125
0.33u
R155
22K
C123
822
C117
4.7u/16V
C118
4.7u/16V
C119
4.7u/16V
10
C120
4.7u/16V
12
13
C121
4.7u/16V
14
15
C122
4.7u/16V
16
17
18
19
20
R156
22K
11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
OUT4
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
AVDD
SWIN
N106
GNDS
M62446
SRIN
SLIN
GNDC
CIN
GNDR
RIN
GNDL
LIN
BYPASR
BYPASL
LTRE
LBASS3
LBASS2
LBASS121RBASS1
DVDD
CLK
DATA
LATCH
DGND
AGND
SWOUT
SROUT
SLOUT
COUT
ROUT
LOUT
AVSS
CL1
CL2
CR1
CR2
RTRE
RBASS3
RBASS2
C143
47n
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
C130
4.7u/16V
28
27
C129
4.7u/16V
26
25
24
23
22
C142
47u/16V
C138 4.7u/16V
C137 4.7u/16V
C136 4.7u/16V
C135 4.7u/16V
C134 4.7u/16V
C133 4.7u/16V
C13147n
C128
822
C127
15n
C126
0.33u
L101100uH
C141
101
SR1
SL1
C-1
R-1
L-1
A-6.8V
C132
47u/16V
C140
101
C139
101
5.1CH
VCD-R
DVD-R
5.1CH-R
VCD-L
DVD-L
5.1CH-L
B
A
S-C
5.1CH-C
S-SR
5.1CH-SR
S-SL
5.1CH-SL
Figure 3.3.1.2 Volume circuit diagram
Note: when there is no output, firstly make sure whether signal input can be detected; if signal input
can be correctly detected, it means that signal source conversion circuit has no problem, then make
sure whether it is a certain channel has no output or all have no output; if all have no output, it is
probably that power supply of certain part is abnormal, also it is mute signal that abnormal, etc. For
Cd4052 and Cd4053 belong to the electronic switch with high conversion frequency, they are easy to be
damaged; after being damaged, +6.8V and -6.8V voltage may probably be pulled down, or gating signal
A, B of 62446 will be pulled down, and then troubles, such as signal not detected and no output, will
appear.
- 37 -
Page 42

Instance 3 Symmtom: no output
Description: after power on, connect to 5.1CH, main channel has no output, central and surround
have output, power board FL101, FL102 fuse is burnt down.
Analysis and troubleshooting: change fuse of FL101, FL102 and power on again. Fuse is burnt
down, power off, test resistance to ground of power board Vc+, Vc- and find that resistance is 0 ohm;
unplug power board flat cable holder XS8, shown as in the figure 3.3.1.3; test resistance to ground of
power amplifier board Vc+, Vc-, it is also 0 ohm, the trouble lies in power amplifier board by primary
judgment, test resistance in each pin of power amplifier board power tube V112, they are all 0 ohm,
resistance in each pin of power tube is 0 ohm, V112 and V113 have been broken down, change V112,
V113, change fuse, output is normal after power on again, and trouble is removed.
C101
10u/16V
R104
47K
C103
47u/100V
R1052KR106
V102
2N5551
C104
220p
R107 47
V104
2N5551
C107
47u/100V
2K
V103
2N5551
R108
47
R109 1K
C105
100u/16V
VD102
1N4148
R110
VD103
510
1N4148
C108
33p/500V
R111
R114 2.7K
33K/0.5W
V106
2N5551
R115
1.2K
R112
1K
R117
220/0.5W
R113
150
V105
2N5401
V107
2N5551
R116
150
R125
220/0.5W
C109
47n
V132
2SC5248
R121
33K
V133
2SA1964
R120
100/0.25W
R122
100/0.25W
P+30V
V112
2SD1047C
R128
4.3K
R126
0.25/7W
R127
0.25/7W
R130
4.3K
V113
2SB817C
P-30V
R129
2.7K
P+30V
P-30V
C110
1u/16V
V114
2N5551
VD104
1N4148
Figure 3.3.1.3 Power amplifier output circuit diagram
Note: when a certain channel has no output, firstly confirm whether voltage of power amplifying
circuit of each channel is normal. We often test stage by stage from the final stage of signal output and
then analyse. Vibration exists in the course of moving machines, the line of PCB board of signal board
will probably be broken off, or copper surface of element pin will fall off, so you should consider when
analysing problems.
Instance 4 Symptom: microphone has no output
Description: insert microphone after power on, that MIC input has been detected displays, but
microphone has no output.
Analysis and troubleshooting: after power on, insert microphone, microphone inputs sine wave
signal, shown as in the figure 3.3.1.4; test base electrode of signal board triode V105, it is low level, MIC
mute signal is normal, test signal board capacitor C245, C246, they both have no signal, test pin 7 of
signal board N202, there is no signal, considering that MIC input can be detected, test signal board
- 38 -
Page 43

Capacitor C219, there is signal, power supply voltage of N200 is normal, the trouble lies in N200
PT2315 by primary judgment; change PT2315 and trouble is removed.
+12V
MIC1
GND
GND
MIC-DET
XS12
1
2
3
4
CON4
C217
10u/16V
R243
10K
R2075.1K
V202
9014
2
3
P_MICDET
C200151
R20039K
-12V
N201A
4558
8 4
+12V
R204
100/0.25W
C208
2
C211
47n
C23610P
R240220K
-12V
N202A
4558
VD200
9.1V
100u/16V
C21910u/16V
R2132K
1
C252
10u/16V
3
8 4
+12V
Figure 3.3.1.4 MIC circuit diagram
C20247u/16V
1
2
3
C225
4
5.6n
C226
5
5.6n
6
7
8
9
10
VD201
1
1N4148
N200PT2315
REF
VDD
AGND
TREBL
TREBR
RIN
BOUT_R
LOUD_R
NC
BOUT_L
LOUD_L
NC
R2091K
C205
47u/16V
CLK
DATA
DGND
LOUT
ROUT
BIN_R
BIN_L
LIN
20
19
18
17
C221
16
10u/16V
C227
15
C228
14
13
12
11
R241
47K
68n
68n
V200
9014
P_SCL
P_DATA
R22010K
P_OKT
C237
R216
103
5.6K
Note: when changing PT2315, microphone still has no output sometimes. Considering that PT2315
and N101 24C02 of CPU board commonly use P_DATA and clock line P_SCL, when 24C02 is abnormal,
the communication between CPU and PT2315 may probably be affected to cause no output for
microphone, so 24C02 is required to change sometimes.
Instance 5 Symptom: no sound output
Description: signal input may be detected after power on, but no signal output, no output when
switching various sound sources.
Analysis and troubleshooting: after power on, VCD channel inputs sine wave signal, check power
amplifier board Vc+, Vc- , Vs+ and Vs-, power supply is normal, test volume board capacitor C133.C134,
there is signal, test pin 4 and 5 of volume board flat cable holder XS20, there is signal, so it is sure that
volume board working is normal; test pin2 and 3 of signal board socket XS9, there is no signal, trouble
lies in signal board by primary judgment; test power supply voltage +12V and -12V of pin 4 and 8 of
N100, normal, left channel output is normal after changing N100, right channel output is normal after
changing N101, centre has no output when adjusting to Cyber logic state, test pin 3 of volume board flat
cable holder XS20, there is signal, test pin 4 of signal board socket XS9, there is no signal, test N102,
power supply is normal, change N102 and output is normal, so trouble is removed.
Note: because of unstable voltage, 4558 of some part will be burnt down, +12V, -12V is pulled down,
then whole system working is abnormal, so several 4558 are required to change sometimes.
- 39 -
Page 44

Instance 6 Symptom: no OSD (on screen display)
Description: after power on, relay attracting, output signal is normal, LCD has no display,
background light of display screen is lighted when pressing buttons.
Analysis and troubleshooting: because background light is bright, it is confirmed that +5V voltage of
control panel is normal. When using remote controller, remote control function is normal, which means
that control panel +3.3V is normal; change LCD screen, display is normal and trouble is removed.
Note: when no OSD appears, firstly make sure whether display screen voltage is normal, whether
data buffer output is normal; because display screen is easy to damage, in most conditions, it is display
screen that is damaged.
Instance 7 Symptom: power not on
Description: not any reaction after power on, relay not attracting, no OSD
Analysis and troubleshooting: power on and observe that each fuse is normal, secondary stage
voltage of transformer is tested 0, primary stage voltage of transformer is tested normal, primary stage
resistance is tested infinite, so it is judged that transformer has been burnt down; change transformer
and trouble is removed.
Note: when power not on, firstly confirm that whether it is power not on or no OSD, whether part of
voltage or all voltage is abnormal; if it is that power not on, test step by step from power socket until the
trouble is found.
Instance 8 Symptom: remote controller has no function
Description: after power on, panel buttons have no function, remote controller has no function.
Analysis and troubleshooting: after power on, remote controller has no function, change its battery
and it also has no function, test pin 3 P_REM signal of CPU board socket XP100, when remote
controlling, this signal has no pulse waveform, test voltage of control panel resistor R102, it is +5V, when
checking the welding point of N100 remote control receiver, we found that pin has rosin joint, after
adding tin, remote control is normal and trouble is removed.
Note: buttons function and remote control function are all fulfilled by infrared receiver, when buttons
and remote control have no function, trouble may lie in remote control receiver.
Instance 9 Symptom: Microphone has no delay and echo
Description: after power on, insert microphone, set echo and delay in maximum, beat microphone
and there is no echo and no delay.
Analysis and troubleshooting: test pin 7 of signal board N204, there is no signal, test power supply
of N209 PT2399, it is normal; change PT2399, trouble is not removed; test resistance of signal board
capacitor C242, C243, C238, we find that resistance of C243 only has 2.5K; change capacitor C243 and
trouble is removed.
Note: no echo and delay for microphone is caused by abnormal working of Pt2399; one case is that
PT2399 is abnormal itself; the other is that PT2399 peripheral circuit has trouble. Porcelain capacitor in
peripheral circuit is easy to damage.
- 40 -
Page 45

3.3.2 Troubleshooting process
1. Symptom: Karaoke has no sound
Analysis: for this kind of trouble, you may usually adopt signal injection method to check stage by
stage. If a certain stage does not give out disturbance sound, this stage has problem; this method is
generally preformed from back stage to front stage. Another is signal control method. Check stage by
stage from front stage to back stage. If a certain stage has no sound, it means that this stage has trouble.
The troubleshooting process is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.1:
Karaoke has no sound
Check signal board
Check
whether there
is sound signal on
C252,C217
Y
Check
whether there
is sound on R219,
R221
Y
Check
whether there is sound
on R230
Y
Check
whether there
is sound on C245,
C246
Y
Check
whether base
electrode of V104,
V105 is
0.7AV
N
Check N210 and MIC hole circuit
N
Check PT2315 and CPU signal
P-SCCL, P-DATA
N
Check N202 and its power
supply circuit
N
Check N203 and its power
supply circuit
N
Check whether V104 or
V105 is stricken through
Y
Check
whether E-electrode
of V103 is high
level
Y
Whether
MICDET is high
level; whether PKT is
low level
N
N
Change V103
CPU, MIC hole and V200
are damaged
Figure 3.3.2.1 Troubleshooting process for "Karaoke has no sound"
- 41 -
Page 46

2. Troubleshooting process for “No spectrum display” is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.2;
No spectrum display
Whether
V105 collector
electrode has high and
low level
variation
N
No spectrum display
Y
Check
whether VD118 is
normal
Y
Whether
positive direction
voltage of N102B has
sawtooth
waveform
Y
Y
N
N
Check CPU, I C bus
Check power supply, V105
and peripheral circuit
N
Change VD118
Check V103, V104, VD115,
VD116, C137
2
Whether
negative direction
voltage of N102B has
sawtooth
waveform
N
Check N102 and
peripheral circuit
Y
Whether
N108 and CPU
control pin working
is normal
N
Check control signal,
N108 and peripheral circuit
Y
Check 7-segment bandpass
filter, C115 and the auto
gain adjustment circuit
composed by N105
Figure 3.3.2.2 Troubleshooting flow chart for "No spectrum display"
- 42 -
Page 47

3. Troubleshooting process for “Power-on protection” is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.3:
Power-on protection
Check
whether there is
central point
voltage
Y
Check
whether protection
is fulfilled when signal is
added or main volume
is increased
Y
Check
whether power
amplifier board resistor
R111, R141 has
open-circuit
Y
Check
whether resistor R108
has open
circuit
Y
N
Check which channel outputs
DC and check this channel
Check whether the current-
N
protection diode or triode is
damaged, or capacitor C115
is not good
N
N
Change resistor
Change resistor
Check
whether RLY detect
signal is
abnormal
Y
Whether it is machine
vibration protection
N
Check whether power board
VD108 is low level, and
change V100
Y
Change relay
Figure 3.3.2.3 Troubleshooting flow chart for "Power-on protection"
- 43 -
Page 48

4. Troubleshooting process for “Cannot search automatically” is shown as the following figure
3.3.2.4:
Cannot search automatically
Whether
DISPLAY signal is
sent to the negative direction
terminal of N103A of
CPU board
N
Check CPU board spectrum sampling
Y
and amplifying circuit N103, N108B
of volume board
Whether
the in-phase
terminal of N103B is
low level
N
Whether
the in-phase
terminal of N103B is
low level
N
Whether
VD103 is normal
Y
Check VD101, CPU, V101
and peripheral circuit
Y
Check N103A amplifying and
power supply circuit
Y
Check V102 and peripheral
circuit
Y
Change VD103
Figure 3.3.2.4 Troubleshooting flow chart for "Cannot search automatically"
- 44 -
Page 49

5. Troubleshooting process for “No output (2-channel)” is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.5:
No output (2-channel)
Check
whether power
supply of each channel
is normal
Y
N
Refer to troubleshooting
of "Power not on"
Check
whether mute circuit
signal is normal
Y
Check
whether power
amplifier board XS8
has output
Y
Check
whether voltage of
power board R100
is normal
Y
Change relay
Check whether MIC holder
N
is normal and then check
mute circuit
N
N
Change VD113
whether signal of
whether 12V voltage
of signal board
Change signal board
N100, N101, N102
Check
X20 is normal
Y
Check
is normal
Y
N N
N
Check power supply circuit
Check
power supply of signal
board N106
Y
Change N106
Check power supply and
change N106
Figure 3.3.2.5 Troubleshooting flow chart for "No output (2-channel)"
- 45 -
Page 50

6. Troubleshooting process for “5.1CH has no output” is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.6:
5.1CH has no output
Change
into 2CH and check
whether it has
output
Y
Check
power supply of
N102, N103
Y
Change N102, N103
N
Refer to troubleshooting
of "2CH has no output"
N
Check power supply circuit
Figure 3.3.2.6 Troubleshooting flow chart for "5.1CH has no output"
- 46 -
Page 51

7. Troubleshooting process for “Left channel has no output” is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.7:
Left channel has no output
Check
whether power
amplifier board flat
cable XS8 has
output
Y
Check
whether power
board R113 has
output
Y
Change relay
N
whether power
amplifier board flat
cable XS9 has
whether C101 has
R125, R127 power
Check
waveform
Y
Check
waveform
Y
Check
supply
Y
N
N
Check
whether signal board
X200 is
normal
Y
Check
power supply of signal
board N100
Y
Change N100
Check power supply circuit
N
waveform of volume
power supply of N106
N
Check power circuit
Check
board C122
Y
Check
Y
Change N106
N
Check power
supply circuit
Check whether R121 has DC voltage;
check triode of amplification part of
this channel and then change it
Figure 3.3.2.7 Troubleshooting flow chart for "Left channel has no output"
- 47 -
Page 52

8. Troubleshooting process for “Power not on” is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.8:
Power not on
Check
whether each
protector tube is
normal
Y
Check
whether voltage
of power board XP8VC+
and VC- is normal ( 4.35V);
whether 20 of power amplifier
board is normal; whether
+5V of signal board
is normal
N
Check
whether AC
output of each sublevel
of transformer is
normal
N
Change transformer
Figure 3.3.2.8 Troubleshooting flow chart for :Power not on"
Check
N N
whether each
channel power is
short-circuited to
ground
Y
Check
the voltage
regulation capacitor of
short-circuited
power
N
Check the load circuit of
this channel power
Change the burnt-out
protector tube
- 48 -
Page 53

Section Four Servicing Parameters
3.4.1 Signal waveform diagram
This section collects signal waveform diagram of audio, video and each unit circuit with the purpose
of helping servicing personnel to judge where the trouble lies accurately and quickly to promote their
servicing skills. Because of the difference of oscillograph brand, model and tuning, the servicing
personnel should pay more attention to check in daily work for some difference may exist.
1. Input signal (2-channel input) waveform diagram:
2. Volume board capacitor C122 (L) waveform diagram:
- 49 -
Page 54

3. Volume board capacitor C121 R waveform diagram:
4. Volume board capacitor C120 C waveform diagram:
5. Volume board capacitor C119 (SL) waveform diagram:
- 50 -
Page 55

6. Volume board capacitor C118 (SR) waveform diagram:
7. Volume board capacitor C117 (SW) waveform diagram:
8. Waveform diagram of outputting C133 (L) after volume adjustment:
- 51 -
Page 56

9. Waveform diagram of outputting C134 R after vvolume adjustment:
10.C135 C waveform diagram in Cyber Logic state:
11. C136 (SL) waveform diagram in Cyber Logic state:
- 52 -
Page 57

12. C137 (SR) waveform diagram in Cyber Logic state:
13. Output to flat cable XS8 after power amplification, pin 1 (L) waveform diagram:
14. Output to flat cable holder Xs8 after power amplification, pin 2 R waveform diagram:
- 53 -
Page 58

15. Output to flat cable holder XS8 after power amplification, pin 3 C waveform diagram:
16. Output to flat cable holder XS8 after power amplification, pin 4 (SL) waveform diagram:
17. Output to flat cable holder XS8 after power amplification, pin 5 (SR) waveform diagram:
- 54 -
Page 59

18. P_CHARGE waveform diagram after signal being detected:
19. P_ADINTO waveform diagram after signal being detected:
Note: C138 (SW) has waveform only when bass enhancer is in off state.
- 55 -
Page 60

3.4.2 Key point voltage
1. Power board:
VC+=43.5V
VC-=-43.5V
VD113 cathode terminal 12.8V (19.3V when in standby)
Vd111 cathode terminal 6.3V (DV when in standby)
P-RC=0V (4.8V when in standby)
2. Power amplifier board:
L7812 pin 3 +12V L7912 pin 2 12V
TDA7265 pin 3 +20V Pin 6 20V
over 5.3V (0V when in standby) S-MVTE 0V (19.5V when in mute)
3. CPU board:
When in standby: V103 pin 5 2.0V (0.1V after signal being detected)
VD101 cathode terminal 3.45V (0.6V after signal being detected)
R175 (P_CHARGE) 0.65V (waveform after signal being detected)
R179 (P_ADINTO) 5.0V (waveform after signal being detected)
- 56 -
Page 61

Section Five Function Introduction to IC
3.5.1 function introduction to 4558
1. Description
The RC4558 and RM4558 devices are dual general-purpose operational amplifiers with each half
electrically similar to the A741 except that offset null capability is? not provided.
The high common-mode input voltage range and the absence of latch-up make these amplifiers ideal for
voltage-follower applications. The devices are short-circuit protected and the internal frequency compensation
ensures stability without external components.
The RC4558 is characterized for operation from 0 C to 70 C, and the RM4558 is character ized for ? ?
operation over the full military temperature range of –55 C to 125 C.
2. FEATURES
◆ Continuous-Short-Circuit Protection
◆ Wide Common-Mode and Differential
◆ Voltage Ranges
◆ No Frequency Compensation Required
◆ Low Power Consumption
◆ No Latch-Up
◆ Unity-Gain Bandwidth . . . 3 MHz Typ
◆ Gain and Phase Match Between Amplifiers
◆ Low Noise . . . 8 nV?Hz Typ at 1 kHz
◆ Designed To Be Interchangeable With
◆ Raytheon RC4558 and RM4558 Devices
3. PIN CONFIGURATION
PIN No. Symbol I/O
Description
1 1OUT O
2 1IN– I
3 1IN+ I
Output 1
Inverting Input Pin 1
Non-Inverting Input Pin 1
- 57 -
Page 62

PIN No. Symbol I/O
Description
4 VCC– I
5 2IN+ I
6 2IN– I
7 2OUT O
8 VCC+ I
Negative Power Supply
Non-Inverting Input Pin 2
Inverting Input Pin 2
Output 2
Positive Power Supply
3.5.2 function introduction to PT2399
1. DESCRIPTION
PT2399 is an echo audio processor IC utilizing CMOS Technology which is equipped with ADC and DAC,
high sampling frequency and an internal memory of 44K digital processing is used to generate the delay time,
it also feature an internal VCO circuit in the system clock, thereby , making the frequency easily adjustable.
PT2399 boast of very low distortion (THD<0.5%) and very low noise (No<-90dBV), thus producing high
quality audio output .The pin assignments and application circuit are optimized for easy PCB layout and cost
saving advantage.
2. FEATURES
◆ CMOS Technology
◆ Least External component
◆ Auto Reset Function
◆ Low Noise, No<-90dBV Typical
◆ Low Distortion, THD<0.5% Typical
◆ External Adjustable VCO
◆ Available in 16 pins DIP or SOP package
3. PIN CONFIGURATION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 VCC I Positive Power Supply
2 REF I Reference Power Supply
3 AGND I Simulative Ground
4 DGND I Digital Ground
5 CLK_O O NC
6 VCO O Voltage Controlled Oscillator
7 CC1 O External capacitor
- 58 -
Page 63

PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
8 CC0 O External capacitor
9 OP1-OUT O External capacitor 1 output
10 OP1-IN I External capacitor 1 input
11 OP2-OUT O External capacitor 2 output
12 OP2-IN I External capacitor 2 input
13 LPF2-IN I Low pass filter 2 input
14 LPF2-OUT O Low pass filter 2 output
15 LPF1-OUT O Low pass filter 1 input
16 LPF1-IN I Low pass filter 1 output
3.5.3 function introduction to CD4051
1. DESCRIPTION
The CD4051 is a single 8-channel multiplexer with three binary control inputs and inhibit input.
The three binary control input signals select 1 of 8 channels to be turned on and connect it to the single
out.
The operating voltage is as 3 to 18V and quiescent current is as low as 5 µA max. (at Vpp=5V ).
2. PIN CONFIGURATION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 X4 I/O Channel selection port 4
2 X6 I/O Channel selection port 6
3 X I/O Channel selection output
4 X7 I/O Channel selection port 7
5 X5 I/O Channel selection port 5
6 INH I Inhibit
7 VEE I/O Negative Power Supply
8 GND I GND
9 C I Channel selection binary bit C
10 B I Channel selection binary bit B
11 A I Channel selection binary bit A
12 X3 I/O Channel selection port
13 X0 I/O Channel selection port 0
- 59 -
Page 64

PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
14 X1 I/O Channel selection port 1
15 X2 I/O Channel selection port 2
16 VCC I Positive Power Supply
3. TRUTH TABLE
INH C B A ON SWITH
0 0 0 0 X0
0 0 0 1 X1
0 0 1 0 X2
0 0 1 1 X3
0 1 0 0 X4
0 1 0 1 X5
0 1 1 0 X6
0 1 1 1 X7
1 X X X NONE
3.5.4 function introduction to CD4052
1. DESCRIPTION
The CD4052 is a dual 4-channel multiplexer with two binary control inputs and inhibit input.
The two binary control input signals select 1 of 4 pairs of channels to be turned on and connect it to the
two outputs.
The operating voltage is as 3 to 18V and quiescent current is as low as 5 µA max. (at Vpp=5V ).
2. PIN CONFIGURATION
PIN No Symbol I/O Description
1 Y0 I/O Y channel selection port 0
2 Y2 I/O Y channel selection port 2
3 Y I/O Y channel selection output
4 Y3 I/O Y channel selection port 3
5 Y1 I/O Y channel selection port 1
6 INH I Inhibit
7 VEE I/O Negative Power Supply
- 60 -
Page 65

PIN No Symbol I/O Description
8 GND I GND
9 A I Channel selection binary bit A
10 B I Channel selection binary bit B
11 X3 I X channel selection port 3
12 X0 I/O X channel selection port 0
13 X I/O X channel selection output
14 X1 I/O X channel selection port 1
15 X2 I/O X channel selection port 2
16 VCC I Positive Power Supply
3. TRUTH TABLE
INH B A ON SWITH
0 0 0 X0 Y0
0 0 1 X1 Y1
0 1 0 X2 Y2
0 1 1 X3 Y3
1 X X NONE
3.5.5 function introduction to CD4053
1. DESCRIPTION
The CD4053 is a triple 2-channel multiplexer having three separate digital control inputs, A, B, and C and
an inhibit input. Each control input selects one of a pair of channels which are connected in a single-pole
double-throw configuration
The three binary control input signals select 1 of 2 pairs of channels to be turned on and connect it to the
three outputs.
2. Features
The operating voltage is as 3 to 18V and quiescent current is as low as 5 µA max. (at Vpp=5V ).
3. PIN CONFIGURATION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 by I Y1
2 bx I Y0
- 61 -
Page 66

PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
3 cy I Z1
4 c O Z
5 cx I Z0
6 INH I Enable
7 Vee I Negative Power Supply
8 Vss I GND
9 C I Select C
10 B I Select B
11 A I Select A
12 ax I X0
13 ay I X1
14 a O X
15 b O Y
16 Vdd I Positive Power Supply
4. TRUTH TABLE
INH B A ON SWITH
0 0 0 X0 Y0
0 0 1 X1 Y1
0 1 0 X2 Y2
0 1 1 X3 Y3
1 X X NONE
3.5.6 function introduction to SM79164
1. Description
The SM79164 series product is an 8 - bit single chip microcontroller with 64KB on-chip flash and 4K byte
RAM embedded. It is a derivative of the 8052 micro controller family. It has 8-channel PWM build-in. User can
access on-chip expanded RAM with easier and faster way by its ‘bank mapping direct addressing mode’
scheme. With its hardware features and powerful instruction set, it’s straight forward to make it a versatile and
cost effective controller for those applications which demand up to 32 I/O pins for PDIP pack age or up to 36
I/O pins for PLCC/QFP package, or applications which need up to 64K byte flash memory for program data.
To program the on-chip flash memory, a commercial writer is available to do it in parallel programming
method.
- 62 -
Page 67

2. Features
◆ 2.4V ~ 3.0V For V Version
◆ Working voltage: 3.0V ~ 3.6V For L Version
◆ 4.5V ~ 5.5V For C Version
◆ General 8052 family compatible
◆ 12 clocks per machine cycle
◆ 64K byte on chip program flash
◆ 4096 byte on-chip data RAM
◆ Three 16 bit Timers/Counters
◆ One Watch Dog Timer
◆ Four 8-bit I/O ports for PDIP package
◆ Four 8-bit I/O ports + one 4-bit I/O ports for PLCC or QFP package
◆ Full duplex serial channel
◆ Bit operation instruction
◆ Industrial Level
◆ 8-bit Unsigned Division
◆ 8-bit Unsigned Multiply
◆ BCD arithmetic
◆ Direct Addressing
◆ Indirect Addressing
◆ Nested Interrupt
◆ Two priority level interrupt
◆ A serial I/O port
◆ Power save modes: Idle mode and Power down mode
◆ Code protection function
◆ Low EMI (inhibit ALE)
◆ Bank mapping direct addressing mode for access on-chip RAM
◆ 8 channel PWM function with P1.0 ~ P1.7
3. PIN CONFIGURATION
DIP Symbol I/O Define Name Function
1
O P_RST Liquid crystal reset
2 P1.1/T2 O P_RS Liquid crystal data
3 P1.2 I P_MICDET Microphone detecting input
4 P1.3 O P_E Liquid crystal read control bit
5 P1.4 O P_ADSELA Selection spectrum sampling control A
- 63 -
Page 68

DIP Symbol I/O Define Name Function
6 P1.5 O P_ADSELB Selection spectrum sampling control B
7 P1.6 O P_ADSELC Selection spectrum sampling control C
8 P1.7 O P_GNB Spectrum gain control B
9 RST I RESET System reset
10 P3.0 O P_GNC Selection spectrum sampling control C
11 P3.1 I P_SELECT Mute/input detecting selection
12 P3.2 I P_ADINT0 Spectrum sampling interruption
13 P3.3 I P_REM Remote control detecting
14 P3.4 O P_CHARGE Spectrum sampling discharge control
15 P3.5 I P_DIST Distortion detecting
16 P3.6 I P_SEARCH Mute/input detecting
17 P3.7 O P_OKT OK sampling
18 XTAL2 O Crystal out Crystal out
19 XTAL1 I Crystal in Crystal in
20 GND I GND GND
21 P2.0 O P_SDA I2C data line
22 P2.1 O P_SCL I2C clock line
23 P2.2 O P_LT62446 LT62446 latched
24 P2.3 O P_LT4094 LT4094 latched
25 P2.4 O P_SCART SCART detecting
26 P2.5 O P_CLK Click line
27 P2.6 I P_ RLY Relay state input
28 P2.7 O P_GNA Selection spectrum sampling control A
29 /PSEN I Blank
30 ALE I Blank
31 /EA/Vpp I Vpp +5V pull up
32 P0.7 O P_D7 Liquid crystal data D7 bit
33 P0. 6 O P_D6 Liquid crystal data D6 bit
34 P0.5 O P_D5 Liquid crystal data D5 bit
35 P0.4 O P_D4 Liquid crystal data D4 bit
36 P0.3 O P_D3 Liquid crystal data D3 bit
37 P0.2 O P_D2 Liquid crystal data D2 bit
- 64 -
Page 69

DIP Symbol I/O Define Name Function
38 P0.1 O P_D1 Liquid crystal data D1 bit
39 P0.0 O P_D0 Liquid crystal data D0 bit
40 Vcc I Vcc Vcc
3.5.7 function introduction to PT2308
1. DESCRIPTION
PT2308L is a Class AB stereo headphone driver chip utilizing CMOS Technology specially designed for
portable digital audio applications. It is housed in an 8-pin DIP or SO package and is
functionally compatible with TDA1308. Pin assignments and application circuit are
optimized for lower cost effectiveness and easy PCB Layout
2. FEATURES
◆ CMOS Technology
◆ Low Power Consumption
◆ Wide Temperature Range
◆ Excellent Power Supply Ripple Rejection
◆ High Signal-to-Noise Ratio, S/N=110dB
◆ Low Harmonic Distortion, THD= 0.001%
◆ Large Output Voltage Swing
◆ Low Supply Voltage Available (VDD=2V)
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 OUT1 O Output Pin R
2 IN1- I Inverting Input Pin R
3 IN1+ I Non-Inverting Input Pin R
4 Vss I Negative Power Supply
5 IN2- I Inverting Input Pin L
6 IN2+ I Non-Inverting Input Pin L
7 OUT2 O Output Pin L
8 Vdd I Positive Power Supply
- 65 -
Page 70

3.5.8 function introduction to PT2222
1. DESCRIPTION
The PT2222is remote control transmitters utilizing CMOS Technology specially designed for use on
infrared remote control applications .It is pin-to-pin compatible with NEC µPD6122 respectively. PT2222 is
housed in 24 pins so and capable of controlling 64 function kens and 3 double keys. PT2222 may be paired
with PT2225to construct a powerful remote control system.
2. FEATURES
◆ CMOS Technology
◆ Low Power Consumption (Vdd=2.0~5.5V)
◆ Pin-to-Pin Consumption with µPD6122
◆ Using SEL pin, PT2222can support 128+6 function codes
◆ Customer Code can be selected (please contact PTC for details)
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 K12 I Nc
2 K13 I Nc
3 K14 I Nc
4 K15 I Nc
5 K16 I Nc
6 K17 I Nc
7 REM O Serial data output
8 VDD I Positive Power Supply
9 SEL I GND
10 OSCO O Crystal out
11 OSCI I Crystal in
12 VSS I VSS
13 LMP Emission output indication
14 KI/O7 O Keyboard matrix line control
15 KI/O6 O Keyboard matrix line control
16 KI/O5 O Keyboard matrix line control
17 KI/O4 O Keyboard matrix line control
18 KI/O3 O Keyboard matrix line control
19 KI/O2 O Keyboard matrix line control
- 66 -
Page 71

PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
20 KI/O1 O Keyboard matrix line control
21 KI/O0 Keyboard matrix line control
22 CCS I Address code control
23 K10 I Keyboard matrix row control
24 K11 I Keyboard matrix row control
3.5.9 function introduction to LM1875
1. Description
The LM1875 is a monolithic power amplifier offering very low distortion and high quality performance for
consumer audio applications.
The LM1875 delivers 20 watts into a 4 ?or 8 ?load on ? ? ±25V supplies. Using an 8 ?load and ? ±30V
supplies, over 30 watts of power may be delivered. The amplifier is designed to operate with a minimum of
external components. Device overload protection consists of both internal current limit and thermal shutdown.
The LM1875 design takes advantage of advanced circuit techniques and processing to achieve extremely
low distortion levels even at high output power levels. Other outstanding features include high gain, fast slew
rate and a wide power bandwidth, large output voltage swing, high current capability, and a very wide supply
range. The amplifier is internally compensated and stable for gains of 10 or greater.
2. Features
◆ Up to 30 watts output power
◆ AVO typically 90 dB
◆ Low distortion: 0.015%, 1 kHz, 20 W
◆ Wide power bandwidth: 70 kHz
◆ Protection for AC and DC short circuits to ground
◆ Thermal protection with parole circuit
◆ High current capability: 4A
◆ Wide supply range 16V-60V
◆ Internal output protection diodes
◆ 94 dB ripple rejection
◆ Plastic power package TO-220
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 +IN I Non-Inverting Input Pin C
- 67 -
Page 72

PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
2 -IN I Inverting Input Pin C
3 -VEE I Negative Power Supply
4 OUTPUT O Signal out C
5 VCC I Positive Power Supply
3.5.10 function introduction to TDA7265
1. DESCRIPTION
The TDA7265 is class AB dual Audio power amplifier assembled in the Multiwatt package, specially
designed for high quality sound application as Hi-Fi music centers and stereo TV sets.
2. Features
◆ WIDE SUPPLY VOLTAGE RANGE (UP TO 25V ABS MAX.)?
◆ SPLIT SUPPLY
◆ HIGH OUTPUT POWER 25 + 25W @THD =10%, RL = 8 , V? S = +20V
◆ NO POPAT TURN-ON/OFF
◆ MUTE (POP FREE)
◆ STAND-BY FEATURE (LOW Iq)
◆ SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
◆ THERMAL OVERLOAD PROTECTION
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 -Vs I Negative Power Supply
2 OUT1 O Signal out SL
3 +Vs I Positive Power Supply
4 OUT2 O Signal out SR
5 MUTE I Mute control
6 -Vs I Negative Power Supply
7 IN2+ I Non-Inverting Input Pin SR
8 IN2- I Inverting Input Pin SR
9 GND I GND
10 IN1+ I Non-Inverting Input Pin SL
11 IN1- I Inverting Input Pin SL
- 68 -
Page 73

3.5.11 function introduction to M62446
1. DESCRIPTION
The M62446FP is 6 channels electric volume controlled 3-wire serial data.
The IC is suitable for use in home-use audio systems and TV sets.
2. Features
◆ Electric volume: Volume level••••• 0dB ~ -79dB, - dB (1dB / step)?
◆ Tone control: Bass / Treble, 0dB ~ ±10dB(2dB / step)
◆ 4 Output ports: Built-in microcomputer interface circuit controlled by 16-bit serial data.
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 Out 4 O Source select control 4
2 Out3 O Source select control 3
3 Out2 O Source select control 2
4 Out1 O Source select control 1
5 AVdd I Positive Power Supply
6 SWin I SW Input
7 GNDS I SW GND
8 SRin I SR Input
9 SLin I SL Input
10 GNDC I C GND
11 Cin I C Input
12 GNDR I R GND
13 Rin I R Input
14 GNDL I L GND
15 Lin I L Input
16 BYPASSR O R bypass capacitance
17 BYPASSL O L bypass capacitance
18 LTRE O L treble capacitance
19 LBASS3 O L bass capacitance
20 LBASS2 O L bass capacitance
21 LBASS1 O L bass capacitance
22 RBASS1 O R bass capacitance
- 69 -
Page 74

PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
23 RBASS2 O R bass capacitance
24 RBASS3 O R bass capacitance
25 RTRE O R treble capacitance
26 CR2 O R capacitance
27 CR1 I R capacitance
28 CL2 O L capacitance
29 CL1 I L capacitance
30 AVSS I Negative Power Supply
31 Lout O L out
32 Rout O R out
33 Cout O C out
34 SLout O SL out
35 SRout O SR out
36 SWout O SW out
37 AGND I AGND
38 DGND I DGND
39 LATCH I Select control
40 DATA I Serial Data input
41 CLK I Serial CLK input
42 DVDD I Digital Power Supply
3.5.12 function introduction to AT24C02
1. Description
The AT24C02 provides 2048 bits of serial electrically erasable and programmable read-only memory
(EEPROM) organized as 256 words of 8 bits each. The device is optimized for use in many industrial and
commercial applications where low-power and low-voltage operations are essential. The AT24C02 is
available in space-saving 8-lead PDIP,
8-lead MAP, 8 lead TSSOP and 8-ball dBGA2 packages and is accessed via a 2-wire serial interface. In
addition, the entire family is available in 2.7V (2.7V to 5.5V) and 1.8V (1.8V to 5.5V) versions.
2. Features
◆ Low-voltage and Standard-voltage Operation
– 2.7 (VCC = 2.7V to 5.5V)
- 70 -
Page 75

– 1.8 (VCC = 1.8V to 5.5V)
◆ Internally Organized, 256 x 8 (2K),
◆ 2-wire Serial Interface
◆ Schmitt Trigger, Filtered Inputs for Noise Suppression
◆ Bi-directional Data Transfer Protocol
◆ 100 kHz (1.8V) and 400 kHz (2.5V, 2.7V, 5V) Compatibility
◆ Write Protect Pin for Hardware Data Protection
◆ 8-byte Page (1K, 2K), Write Modes
◆ Partial Page Writes are Allowed
◆ Self-timed Write Cycle (5 ms max)
◆ High-reliability
– Endurance: 1 Million Write Cycles
– Data Retention: 100 Years
◆ Automotive Grade, Extended Temperature and Lead-Free Devices Available
◆ 8-lead PDIP, 8-lead JEDEC SOIC, 8-lead MAP, 5-lead SOT23,
8-lead TSSOP and 8-ball dBGA2™ Packages
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 A0 I To Ground
2 A1 I To Ground
3 A2 I To Ground
4 VSS I To Ground
5 SDA I/O Serial Data input
6 SCL I/O Serial SCL input
7 TEST I/O Test port
8 VDD I Positive Power Supply
3.5.13 function introduction to L7805
1. Description
LM7805 is 5V voltage regulator, locates on power board in this player and is used to generate 5V stable
voltage.
2. Features
◆ Suitable for CMOS ,TTL, the other digital IC’s power supply
- 71 -
Page 76

◆ Internal thermal overload protection
◆ Internal short circuit current limiting
◆ Output current in excess of 1 A
◆ Metal Fin is fully covered with Mold Resin
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 Input I Input +18V
2 Common I Ground
3 Output O Output +12V
3.5.14 function introduction to 7812
1. Description
LM7812 is +12V voltage regulator, locates on power board in this player and is used to generate +12
stable voltage.
2. Features
◆ Suitable for CMOS ,TTL, the other digital IC’s power supply
◆ Internal thermal overload protection
◆ Internal short circuit current limiting
◆ Output current in excess of 1 A
◆ Metal Fin is fully covered with Mold Resin
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 Input I Input +18V
2 Common I Ground
3 Output O Output +12V
3.5.15 function introduction to 7912
1. Description
LM7812 is +12V voltage regulator, locates on power board in this player and is used to generate +12
stable voltage.
- 72 -
Page 77

2. Features
◆ Suitable for CMOS ,TTL, the other digital IC’s power supply
◆ Internal thermal overload protection
◆ Internal short circuit current limiting
◆ Output current in excess of 1 A
◆ Metal Fin is fully covered with Mold Resin
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 Input I Input -18V
2 Output O Output -12V
3 Common I Ground
3.5.16 function introduction to LM324
1. Description
The LM124 series consists of four independent, high gain, internally frequency compensated operational
amplifiers which were designed specifically to operate from a single power supply over a wide range of
voltages. Operation from split power supplies is also possible and the low power supply current drain is
independent of the magnitude of the power supply voltage.
Application areas include transducer amplifiers, DC gain blocks and all the conventional op amp circuits
which now can be more easily implemented in single power supply systems. For example, the LM124 series
can be directly operated off of the standard a 5 V power supply voltage which is used in digital systems and
will easily provide the required interface electronics without requiring the additional g15V power supplies.
2. Features
◆ Internally frequency compensated for unity gain
◆ Large DC voltage gain 100 dB
◆ Wide bandwidth (unity gain) 1 MHz (temperature compensated)
◆ Wide power supply range: Single supply 3V to 32V or dual supplies ±1.5V to ±16V
◆ Very low supply current drain (700 µA)–essentially independent of supply voltage
◆ Low input biasing current 45 n A (temperature compensated)
◆ Low input offset voltage 2 mV and offset current 5 n A
◆ Input common-mode voltage range includes ground
◆ Differential input voltage range equal to the power supply voltage
◆ Large output voltage swing 0V to ±1.5V
- 73 -
Page 78

3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 Output 1 O Output 1 Pin
2 Input 1- I Inverting Input Pin
3 Input 1+ I Non-Inverting Input Pin
4 V + I Positive Power Supply
5 Input 2+ I Non-Inverting Input Pin
6 Input 2- I Inverting Input Pin
7 Output 2 O Output 2 Pin
8 Output 3 O Output 3 Pin
9 Input 3- I Inverting Input Pin
10 Input 3+ I Non-Inverting Input Pin
11 GND I GND
12 Input 4+ I Non-Inverting Input Pin
13 Input 4- I Inverting Input Pin
14 Output 4 O Output 4 Pin
3.5.17 function introduction to PT2315
1. Description
PT2315 is a two-channel digital audio processor utilizing CMOS Technology . Volume, Bass, Treble and
balance controls are incorporated into a single chip. Loudness Function is also provided to build a highly
effective electronic audio processor having the highest performance and reliability with the least external
components. All functions are programmable using the IIC Bus. The pin assignments and application circuit
are optimized for easy PCB layout and cost saving advantage for audio application. Housed in a 20-pin
DIP/SO Package, PT2315is pin-to-pin compatible with TDA7315 and is very similar in performance with
performance with the later.
2. Features
◆ CMOS Technology
◆ Least External Components
◆ Treble and Bass Control
◆ Loudness Function
◆ Input/Output External Noise Reduction System/Equalizer
◆ 2 Independent Speaker Controls for Balance Function
- 74 -
Page 79

◆ Independent Mute Function
◆ Volume Control in 1.25 dB/step
◆ Low Distortion
◆ Low Noise and DC Stepping
◆ Controlled by IIC BUS Micro-Processor Interface
◆ Pin-to-Pin Compatible with TDA7315
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No.
1 REF O Reference Power Supply
2 VDD I Power Supply
3 AGND I AGND
4 TREB_L O L treble adjust capacitance
5 TREB_R O R treble adjust capacitance
6 RIN I R input
7 LOUD_R O R Loud adjust
8 NC NC
9 LOUD_L O R Loud adjust
10 NC NC
11 LIN I L input
12 BIN_L I L adjust capacitance input
13 BOUT_L O L adjust capacitance output
14 BIN_R I R adjust capacitance input
Symbol I/O Description
15 BOUT_R O R adjust capacitance output
16 ROUT O R output
17 LOUT O L output
18 DGND I DGND
19 DATA I Serial Data input
20 CLK I Serial CLK input
3.5.18 function introduction to 74VHC245
1. Description
The VHC245 is an advanced high speed CMOS octal bus transceiver fabricated with silicon gate CMOS
technology. It achieves high-speed operation similar to equivalent Bipolar Schottky TTL while maintaining the
- 75 -
Page 80

CMOS low power dissipation. The VHC245 is intended for bi-directional asynchronous communication
between data busses. The direction of data transmission is determined by the level of the T/R input. The
enable input can be used to disable the device so that the busses are effectively isolated. All inputs are
equipped with protection circuits against static discharge.
2. Features
◆ High Speed: Tpd= 4.0 ns (typ) at Vcc= 5V
◆ High Noise Immunity: Vnih= Vnil = 28% Vcc (Min)
◆ Power Down Protection is provided on all inputs
◆ Low Noise: Volp= 0.9V (typ)
◆ Low Power Dissipation:
◆ Icc= 4 µA (Max) @ TA= 25qC
◆ Pin and Function Compatible with 74HC245
3. Truth table
Inputs
-OE T/–R
Outputs
L L Bus B Data to Bus A
L H Bus A Data to Bus B
H X HIGH-Z State
H= HIGH Voltage Level L= LOW Voltage Level X= Immaterial Any unused bus terminals during HIGH-Z
State must be held HIGH or LOW.
4. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 T/–R I Transmit/Receive Input
2 A0 I/O
3 A1 I/O
4 A2 I/O
5 A3 I/O
6 A4 I/O
Side B Inputs or 3-STATE Outputs
7 A5 I/O
8 A6 I/O
9 A7 I/O
10 Nc
- 76 -
Page 81

PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
11 B7 I/O
12 B6 I/O
13 B5 I/O
14 B4 I/O
15 B3 I/O
16 B2 I/O
17 B1 I/O
18 B0 I/O
19 -OE I Output Enable Input
20 Vcc I Power Supply
Side B Inputs or 3-STATE Outputs
3.5.19 function introduction to CD4094
1. Description
The CD4094BC consists of an 8-bit shift register and a 3-STATE 8-bit latch. Data is shifted serially
through the shift register on the positive transition of the clock. The output of the last stage (QS) can be used
to cascade several devices. Data on the QS output is transferred to a second output, Q′S, on the following
negative clock edge.
The output of each stage of the shift register feeds a latch, which latches data on the negative edge of the
STROBE input. When STROBE is HIGH, data propagates through the latch to 3-STATE output gates. These
gates are enabled when OUTPUT ENABLE is taken HIGH.
2. Features
◆ Wide supply voltage range: 3.0V to 18V
◆ High noise immunity: 0.45 VDD (typ.)
◆ Low power TTL compatibility: Fan out of 2 driving 74L or 1 driving 74LS 3-STATE outputs
3. PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 STROBE I Store control
2 DATA I Serial data
3 CLOCK I Serial clock
4 Q1 O Bit 1 output
5 Q2 O Bit 2 output
6 Q3 O Bit 3 output
- 77 -
Page 82

PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
7 Q4 O Bit 4 output
8 Vss I GND
9 Qs O Top Bit output
10 Qs’ O Non-Qs
11 Q8 O Bit 8 output
12 Q7 O Bit 7 output
13 Q6 O Bit 6 output
14 Q5 O Bit 5 output
15 Output enable I Output enable
16 Vdd I Positive Power Supply
- 78 -
Page 83

Chapter Four Disassembly and Assembly Process
In order to know the structure of audio power amplifier AV225T easily, visibly and quickly, now each
key link of the disassembly and assembly process of the player is presented in means of pictures to
prevent users from incorrect operating and damaging elements. This player is composed by control
panel components, power amplifier board components, signal board components, volume board
components, power board components and MIC board components. So please operate according to
illustration strictly.
1. Disassembly and assembly process for the unit
DDD
CCC
BBB
AAA
(1) Use electric screwdriver to unfix screws in the joint
place
of upper cover and rear cover.
GGG
EEE
FFF
CCC
BBB
AAA
(2) Use electric screwdriver to unfix left and right hand
side upper cover screws A , B and C.
BBB
(3) Take down upper casing.
BBB
AAA
(4) Pull down tuner flat cable A and video flat cable B.
- 79 -
Page 84

CCC
DDD
AAA
AAA
BBB
B B B
C CC
(5) Use electric screwdriver to unfix screws A and B in the
joint position of tuner and rear cover, and then unfix
screws C and D in the joint position of video board and
rear cover, then take them down.
AAA
BBB
AAA
CCC
(7) Use electric screwdriver to unfix screws A~E and screws
A, B in the joint position of volume board and rear cover,
and then take down volume board.
BBB
DDD EEE
(6) Pull down flat cable A, B and C on volume board.
AAA
(8) Pull down flat cable A E on signal board.
CCC
BBB
DDD
EEE
AAA
BBB
EEE
AAA
(9) Use electric screwdriver to unfix screws A, B, C, D and E
in the joint position of signal board and rear cover, and
then take down signal board.
CCC
DDD
AAA
BBB
DDD
CCC
(10) Pull down flat cable A, B C and D on power amplifier
board.
- 80 -
Page 85

EE
AA
BB
CC
DD
AA
BB
CC
(11) Use electric screwdriver to unfix screws A~D in the
point
position of bottom casing and power amplifier
board
heat radiator and screw E in the joint place
with rear cover.
AA
BB
CC
DD
(13) Pull down flat cable A, B, C and D on power board.
(12) Use electric screwdriver to unfix screws A, B and C of
power amplifier board, and then take down power
amplifier board.
A A
BB
CC
DD
(14) Use electric screwdriver to unfix screws A~D in the
joint place of rear cover and output terminal of power
amplifier output board (power board and power
amplifier output board are both in one).
AA
BB
CC
(15) Use electric screwdriver to unfix screws A~D of power
board, and then take down power board.
DD
(16) Use electric screwdriver to unfix screws on two sides
of panel.
- 81 -
Page 86

AA
BB
AA
CC
DD
EE
C C
DD
BB
(17) Use electric screwdriver or “+”-shaped screwdriver to
unfix screws A~E in the joint place of panel and
bottom casing.
(19) Use electric screwdriver to unfix screws of panel and
MIC board, and then take down PCB board.
(18) Take hold of panel by right hand, fasten the bottom
casing D with 4 fingers of left hand, hold the panel
button bracket C with thumb and exert strength
towards direction of arrow C until panel comes off from
bottom casing clasp B, then exert strength towards
direction of arrow C, left side panel falls off from
bottom casing, and then right hand panel clasp falls
off from bottom casing automatically.
(20) PCB board has been taken away.
2. Assembly process for whole unit
(1) Install panel, MIC board and use electric screwdriver to
fix screws.
(2) Take hold of panel components and exert strength
towards arrow direction (inward) until the clasp is f
astened.
- 82 -
Page 87

AA
BB
CC
DD
EE
(3) Use electric screwdriver to fix screws in two sides of
surface casing.
AA
BB
(5) Install power board and then Use electric screwdriver to
fix screws A~D in the joint place of rear cover and output
terminal of power amplifying output board (power board
and power amplifying output board are both in one).
DD
CC
(4) Use electric screwdriver to fix screws A~E in the joint
place of surface casing and bottom casing.
AA
BB
CC
DD
(6) Use electric screwdriver to fix screws of power board
and insert flat cable A D to proper position.
AA
BB
(7) Install power amplifier board, and use electric
screwdriver to fix screws A~D in the joint place of
bottom casing and power amplifier board heat radiator.
CC
DD
AA
BB
CC
(8) Use electric screwdriver to fix screws A, B, C of power
amplifier board and then insert flat cable to proper
position.
- 83 -
Page 88

AAA
AAA
(9) Install signal board and use electric screwdriver to fix
screw A of signal board.
BB
DD
AA
CC
AAA
CCC
(10) Use electric screwdriver to fix screws A, B, C, D of signal
board and then insert flat cable to proper position.
BB
BBB
DDD
AA
(11) Install volume board and use electric screwdriver to fix
screws A~D in the joint place of rear cover.
CCC
DDD
AAA
(13) Take hold of tuner by left hand, use electric screwdriver
to fix screws A, B; take hold of video board by left hand,
use electric screwdriver to fix screws C, D; insert flat
cable respectively to proper position.
BBB
(12) Use electric screwdriver to fix screws A, B of volume
board and then insert flat cable to proper position.
DDD
CCC
BBB
AAA
(14) Install upper cover, use electric screwdriver to
fix screws of left, back and right sides; power on and
test, and it is ok.
EEE
GG G
FFF
- 84 -
Page 89

3. The process of changing LED back light source
(1) Use nail to enter the gap between LCD screen and upper
edge of LED back light source, and then exert strength
to put it up.
(3) After LCD screen falls off, take hold of forceps by right
hand to move away flat cable holder of LCD screen,
and the flat cable falls off automatically.
2 Take LCD screen with thumb and forefinger of left hand,
press the whole board by right hand, take hold of the
upper edge of LCD screen and exert strength towards
arrow direction (leftwards).
AA
BB
(4) Use brand iron to weld away pin A and B of LED back
light source.
AA
CC
BB
(5) Press down LCD screen bracket clasp A, B with thumb
and forefinger of right hand, exert strength with thumb
towards direction of arrow A; after clasp A is away from
PCB board, press down towards direction of arrow C,
clasp A falls off and then clasp B falls off automatically.
(6) Separate LED back light source and LCD screen
bracket clasp.
- 85 -
Page 90

4. Process of assembling LED back light source
(1) Install LCD screen bracket clasp.
AA
BB
(3) Use brand iron to solder pin A and B of LED back light
source.
(2) Install LED back light source.
(4) Take LCD screen flat cable between thumb and
forefinger of right hand, insert it into flat cable holder,
push up flat cable plug to proper position.
(5) Take hold of LCD screen by left hand and put down
towards arrow direction.
(6) Press the LCD screen tightly.
- 86 -
Page 91

Chapter Cinque
PCB board & Circuit diagram
Section One PCB board
5.1.1 Video Board
TC103
TC101
R106
V101
R107
R105 C101
TC104
C110T-2
N101
R103
2005.11.14
R101
R102
C103
R104
XC101
R108
C102
-12V
V-B
V-A
INH
DGND
+5V
XS101
R109
- 87 -
Page 92

5.1.2 Volume Board
C105
R162
R161
C106
R150
C113
R157
R170
R169
R168
R167
C146
C145
2110T-1
2006-01-17
C144
C150
R117
DVDL DVDR
R118
R116
C107
R115
N104
W14
N107
R146
R148
W21
R149
N108
W38
W39
W40
W41
W42
W43
C108
W44
XC101
VCDL VCDR
R112
R111
R113
R114
W7
W8
W9
R144
R147
C112
R145
C111
C147
W22
R196
C114
W35
W36
W37
C138 C117
R138
R137
R139
C109
C121
W45
R155
C143
C122
C137
C136 C142
W46
L101
R177
R191
R178
W47
XS20
OK
GND
R-1
C-1
SW1
L-1
SL1
DISP
GND
SR1
XC102
C
SL
N103C110
C124
W59
W6
W12
R136
R124
R195
R133
W70
W66
W29
W30
W31
C131
R105
N102
C123
R106
W52
SR L
R103
R134
R135
SW
R152
R132
W3
W2
N101
W15
W16
W17
W18
W19 W26
W58
N105
N106
R108
W1
R109
R110
R130
W10
R107
W5
R125
W11
R126
W13
W23
W24
R143
W20
R140
R141
R142
W28
W32
W33
W69
R159
C119
W34
R154
R153
C125
C132
R156
C126
C135 C134
W48
R176
R175
R174
C133
W50
C130 C129
W51
W49
C127 C128
C139
R165
C140
R164
C141
VD100
VD101
R163
XS22
-12V
+12V
D+5V
P_VST
DGND
P_CLK
P_VDA
P_TDO
R104
C120
C101C102
W53
P_TCE
R131
R129
R122
W4
W25
W64
W68
W67
W27
R160
R158
W65
C154
C118
R121
V106
C103
R119RR120
W56
W61
C152
VD112
C115 R198
XP101
W63
W54
C149
W72
W62
W55
C116
C104
C153
W73
W71
W57
W60
-12V
D+5V
XJ2
C148
TUNER_L
TUNER_R
P_TDO
P_DATA
B
A
INH
GND
R197
XS19
1
11
+12V
GND
P_CLK
P_TCE
GND
- 88 -
Page 93

XS23
~9V
GND
~9V
XS6
+12V
DGND
DGND
-12V
XS102
P_D0
P_D1
P_D2
P_D3
P_D4
P_D5
P_D6
P_D7
XS103
P_RST
P_RS
P_E
P_REM
LED
DGND
DGND
D+5V
XS12
MIC2
AGND
MIC1
MIC-T
5.1.3 Signal Board
V109VD108
W17
C227
C211
C202
C228
N210
W59
V201
R210
W46
W42
C240
W63
R246
R211
R247
R220
R219
C221
C220
C143
W58
W57
W52
C234
W80
V110V111
W12
W50
W56
W54
C231
W34
XS101
W62
W64
W60
W61
W53
P_RLY
DISP
DSIT
P_OKT
P_CLK
P_DATA
P_LT62446
P_LT4094
P_SCL
P_SDA
NC
GND
D+5V
GND
GND
W48
W33
W55
VD206
VD205
R168
W71
R167
XP20
XP22
R153
VD202
W1
OK-R
DISP
AGND
AGND
SW
L-1
R-1
C-1
SR-1
SL-1
C206
C212
C207
C239
R258
C213
C214
W41
W18
R265
R275
W65
W70
W31
W72
R263
W73
W51
N207
N209
C138
W45
C144
W82
C250
VD204
N211
W28
VD203
C233
C232
2
R262
R254
R260
R232
R225
C251
R226
W79
R221
R224
R257
R255
R256
R223
R218
W30
W29
3215T-2 LLC
2005-06-15
W81
R235
W36
W19
W44
W32
W23
C248
W37
C242
R249
C243
R268
R284
C235
R264
C238
C249
R273
R234
R230
R248
R238
R274
R233
N205
N204
R253
C247
C216
W77
W74
W16
W20
W14
W21
W22
W27
C215
W83
XS9
XS13
VD104
VD103
VD102
VD100
VD101
N203
R222
R267
R229
R227
P_SCM
R239
P_RC
P_LRM
R250
R231
N208
R236
P_RLY
R145
R142
R113
R111
R112
R105
R104
AGND
R266
R261
R269
R271
R272
R215
R259
R270
R161
W10
R158
W4
W69
W9
V105
V104
R118
VD105
VD109
VD110
VD111
R252
R251
W68
W8
C132
XP19
XS24
V103
R143
C131
C114
C113
C246
C245
C118
SW'C'SR'L'SL'R'AGND
W75
C125
W5
C104
W6
C108
W7
FAN+
C122
C106
C119
R102
R140
R101
R137
R103
R108
FAN-
W66
C124
C121
N101
W3
N100
W13
N102
AGND
R152
W67
R139
R109
R123
R121
R124
W43
SRQ1
XS25
C130
+12V
-12V
P_REM
P_D0
P_D1
P_D2
P_D3
P_D4
P_D5
P_D6
P_D7
P_RST
P_RS
P_E
V202
W35
W78
R170
R171
VD106
VD107
C128
C203
W11
R209
R241
C205
V200
C237
VD200
XS100
R204
C200
C201
R207
C217 C218
C209
O
I
W38
G
N107
C129C134
C210
C229
C230
W15
R200
N201
R201
R208
W47
R213
R214
R217
W85
W84
C204
VD201
R242
R244
C236
R202
R240
C252
N202
W76 R216
C222
C219
C226
C225
C208
W2
R106
R228
R243
C142
1
C137
R116
R110
W40
W39
R122
R132
R129
R163
R100
V102
C105
R133
R128
C103
C107
R134
C100
R120
R127
V108
R151
C115
R169
X100
C117
R154
C135
V106
W24
V107
C101
W49
R115
W26
W25
R162
V100
XC100
V101
C116
R157
C102
XJ2
- 89 -
Page 94

5.1.4 Power Board
R103
V100
C121
XS1
05/12/2
5100-5 LJQ
XS2
SW
XS3
TRANS
R101
R104
W14
C126
V103 R107 V101
C115 C114
FL100 T4AL250V
C102
R105
V102
C113
W22
W20
C109
C112
W13
R109
C120
C119
C118
C116
R106
VD110
R108
C117
VD111
W9
W4
R120
R115
R114
R119
R118
R113
R111
R116
W15
R117
R112
W2
W1
XL101
L103
C108
VD105
W11
W10
VD104
R121
L101
L104
VD103
R122
W16
W19
L102
L100
VD102
VD112
VD101
R110
W12
W8
W7
V105
C122
VD100
C124
V104
C110
C106
Y100
R100
W5
VD107
C107
C125
XL100
W18
VD106
XP7
XP8
C111
VD108
VD113
C123
R102
SWM
RLY0
P_RC
OVER
L2
R2
C2
SL2
SR2
VC+
GND
GND
VC-
W21
XS4
C103
W17
FL101T6.3AL250V
FL102T6.3AL250V
C104 C105
- 90 -
W6
C101
W3
C100
Page 95

5.1.5 Key Scan Board
V100
VD100
N101
VD101
VD102
VD1032VD104
2004-03-30
6228-1 LJQ
R100
1
R107
G100
S107 S101
S100
S106
C105
VD109
XP104
W3
W9W11
N103
S103
S109
S102
S108
O
V
G
C102
2
1
C104
W7
W4
XP105
R102 R101
R105
W2
8
W10
7
W12
N100
C100
C101
W6
8
7
W1
C110
W5
N102
S105
S111
S104
S110
C107
V101
R106
C103
C106
C109
VD107
VD108
VD106
W8
R103
R104
XP102
C108
VD105
XP103
SOL
- 91 -
Page 96

5.1.6 MIC Board
XP12
C100
MIC-DET
GND
GND
MIC1
9215T-1
2004-08-09
XJ1
R100
XP24
C102
+5V
R101
W2
C105
R
L
DG
SW
R105
R106
C104
R104
R102
R103
MIC1
R108
W3
C103
C106
W1
R107
C101
XJ2
C107
R109R110
X100
- 92 -
Page 97

5.1.7 audio power amplifying Board
C120
C110
W2
W14
V129
V114
W61
W8
V112
W63
R113
R120
VD107
R117
VD104
C102
W69
W57
W51
W48
W75
V109
W43
W64
N
C103
R126
R119
R106
V132
R105
R109
V103
R128
W68
R118
W47
V108
SWM
W7
V102
XS7
RLY0
C109
V105
R121
P_RC
C108
R111
C105
OVER
R112
V106
R114
R115
W6
R108
C104
R104
R129
V107
R116
R107
W60
W76
V104
W5
V111
R122
R124
L2
V133
R110
C107
R130
R2
W50
P
R123
V110
VD102
VD103
C106
C2
R127
R125
VD101
R161
C121
C101
XS8
SL2
V113
W16
R101
R102
R103
V101V116R133
W45 W46
VC+
SR2
GND
R131
GND
P_RLY
V115
R132
P_RC
GND
P_LRM
P_CSM
W55
VC-
XP13
R162
C111
W67
V127
XP9
W77
W78
W66
W56
R147
C112
W9
R143
N
R150
W13
V134
R149
V124
R136
C113
T4225T-0
2006 02 22
R135
W49
R156
R148
V118
R139
R151
W33
W59
V123
V117
R158
V120
W10
C118
R141
C119
C115
R142
R138
C114
V122
R146
R137
R134
V121
R144
R145
W11
V119
R159
V125
R153
R152
W12
V135
R154
2SA1964
R140
C117
W70
W62
R160
W58
VD105
VD106
C116
V126
W26
C125
C128
R163
V130
W37
C127
W18
W42
VD108
C154
T6.3AL250V
C159
V131
C124
C145
R181
N102
7912
R184 R183
N104
R167
O
SRQ1
I
G
C149
C151
XP6
-12V
C146
W81
C147
W80
GND+12V
C148
C150
O
G
I
N1017812
VD10
W35
W20
W72
W41
W1
V151
W36
W19
W54
R165
FL101
R171
W24
R166
C123
VD110
C126
V150
C122
VD109
R170
R169
R168
R180
T6.3AL250V
FL102
V128
P
R157
W39
W15
W40
R155
C141
C142
C156
R179
W65
C132
C155
W28
R175
C139
C140
W71
N106
W22
R178
W3
C134
C131
W74
R174
W53
C137
C135
W27
W21
C157
C130C129
VD112
VD114
VD111
VD113
XS5
W73
R172
C136
W52
R177
C144 C143
W31
R164
R173
R176
- 93 -
Page 98

5.1.8 Surface layer of CPU Board
R127R128R129R126
C128
R144
R162
R152
R153 R163
C143
C144
R141
R146
R136
R151
R155
R160
R165
R158
R149
R143
R157
R148
C114
C122
C125
C131
R145
N104
C123
R159
R150
R142
R147
R137
R186
R156
C132
N108
C126
R161
R166
C136
C111
VD106
C141
C115
R125
R123
R122
R124
C127
C133
R118 R119
C124
C118
C130
C121
VD107
XP100
C139
VD119
VD117
R170
R169
C147
R172
R178
R177
N102
R183
C151
C112
RR100
R182
C102
L100
R180
R167
R181
C148
C152
L101
C105
C104
C101
C102
C107
R132
R131
C145
C113
XP104
C100
R100
1228-0
R135
C120
C117
C119
R140
VD109
VD110
VD108
VD111
VD112
VD113
VD114
C116
N105
R138
C135
R133
R139
R164
R134
C146
C134
N106
R130
C129
C140
R154
C106
2
1
28
8
7
R101
B100
2
1
1
8
7
C103
XP105
C108
C100
C155
C142
C110
VD115
R206
R225
N107
C137
C138
R224
C149R110
R185
R184
VD118
V105
R207
R223
R222
R115
R208
R220
R219
R218
VD116
V103
R203R204
C150
R117
V104
XP101
R116
R205
C109
N103
VD102
V102
DISP
P_RLY
DSIT
R104
R189
R113
VD103
VD101
V101
P_OKT
P_CLK
C108R112
R114
P_SCART
P_LT62446
R231
R230
P_LT4094
P_SCL
P_SDANCGND
R229
R228
R227
R199
R187
R217 R216
V100
R202
N101
R201
R179
R200
R215
C106
D+5V
R173
R212
R213
R198
GND
R174
R175
G100
GND
R111
R108
R109
R214
R197
P_E
P_MT
P_RS
P_RST
7228-1
P_D7
P_D6
P_D5
P_D4
R107
P_D3
P_D2
P_D1
P_D0
R192
R195
P_REM
-12V
+12V
R191
R196
R226
N100
R101
C105
R221
C103
R209
C104
R210
XP100
R100
C107
R211
- 94 -
Page 99

5.1.9 Bottom layer of CPU Board
- 95 -
Page 100

5.2.1 Video IN Board
Section Two circuit diagram
- 96 -
VCD
DVD
VOUT
XC101
AV3
1
2
R101 100
3
R102 100
4
R108 22
5
6
R107 10k
VCD
DVD
TC103
220u/16V
+5V
R105
100
VOUT
R109 1
V101
A1015
R106
22K
TC101
100u/16V
13
14
15
12
1
5
2
4
N101 CD4051
XCOM
X0
X1
X2
X3
X4
X5
X6
X7
C102
103
VDD
VSS
INH
VEE
A(0)
B(1)
C(2)
3
16
8
6
+5V
R103 22
7
11
10
9
R104 100
DGND
INH
V-A
V-B
-12V
XS101
1
2
3
4
5
6
CON6
+5V
C101
C103
103
TC104
103
220u/16V
 Loading...
Loading...