Page 1

WL230USB Wireless B+G USB Adapter
Page 2

User Manual
© Copyright 2007
All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, republished, or retransmitted in any form
or by any means whatsoever, whether electronically or mechanically, including, but not limited to, by way
of photocopying, recording, information recording, or through retrieval systems without the express written
permission of the owner. The owner reserves the right to revise this document at any time without the
obligation to notify any person and/or entity of such revisions and/or changes. All other company or
product names mentioned are used for identification purposes only and may be trademarks of their
respective owners.
Page 2 of 37
Page 3

User Manual
Contents
About the Product ......................................................................................................4
System Requirements .................................................................................5
Device Design.............................................................................................. 5
Getting Started........................................................................................................... 6
Check Package Contents..............................................................................6
Remove or Disable Conflicts ........................................................................ 7
Internet Sharing, Proxy, and Security Applications.................................................7
Configuring TCP/IP Settings .....................................................................................8
Configuring Internet Properties ...............................................................................8
Removing Temporary Internet Files ........................................................................9
Installation...............................................................................................................10
For Windows Vista ..................................................................................... 10
For Windows XP......................................................................................... 11
For Windows 2000..................................................................................... 12
For Windows Me ........................................................................................13
For Windows 98SE...................................................................................... 14
For Macintosh ............................................................................................ 15
About the Wireless B+G Utility ................................................................................. 21
Configuration Tab...................................................................................... 21
Advance...................................................................................................................23
Security Enable (Privacy Configuration) ................................................................24
Site Survey Tab.......................................................................................... 34
About Tab .................................................................................................. 35
Certifications ............................................................................................................ 36
Page 3 of 37
Page 4

User Manual
About the Product
WL230USB provides wireless connectivity to desktop and laptop computers. The device
performs the function of a radio broadcaster and receiver to communicate with a
wireless network. This gives the computer connected with WL230USB the capability to
communicate with other devices and use the Internet service available in the wireless
network.
WL230USB is capable of connecting with wireless networks that utilize the Wireless B and
Wireless G protocols. Wireless B broadcasts data at a speed of up to 11 Megabits per
second (Mbps) while Wireless G promises a speed of up to 54 Mbps. Bear in mind that
these speeds have nothing to do with the speed of your Internet connection. Nowadays,
most high-speed Internet connections provide 3 to 5 Mbps, which is lower than the
speed of the Wireless B protocol.
WL230USB is easy to setup - connect it to a USB port, install the necessary driver
software, and then connect to a wireless network. USB ports look physically the same but
there are generally two variants namely USB 1.1 and USB 2.0. Connect the device to a
USB 2.0 port because it provides twice the speed of a USB 1.1 port. In most cases
especially for desktop computers, USB 2.0 ports are placed behind the computer case.
Connecting WL230USB behind the computer case impedes signal strength because the
device is partly hidden. In situations like this, use the USB Extension to help place
WL230USB more prominently to the host access point.
Page 4 of 37
Page 5

System Requirements
Pentium® 233 processor or higher
128MB RAM
20MB available hard disk space (system files and modem driver only)
A free USB Port
CD-ROM drive
Device Design
User Manual
The LED lights up when the device is connected to a wireless network. The LED flickers
when the device is scanning for all available networks or transmitting/ receiving data.
Page 5 of 37
Page 6
User Manual
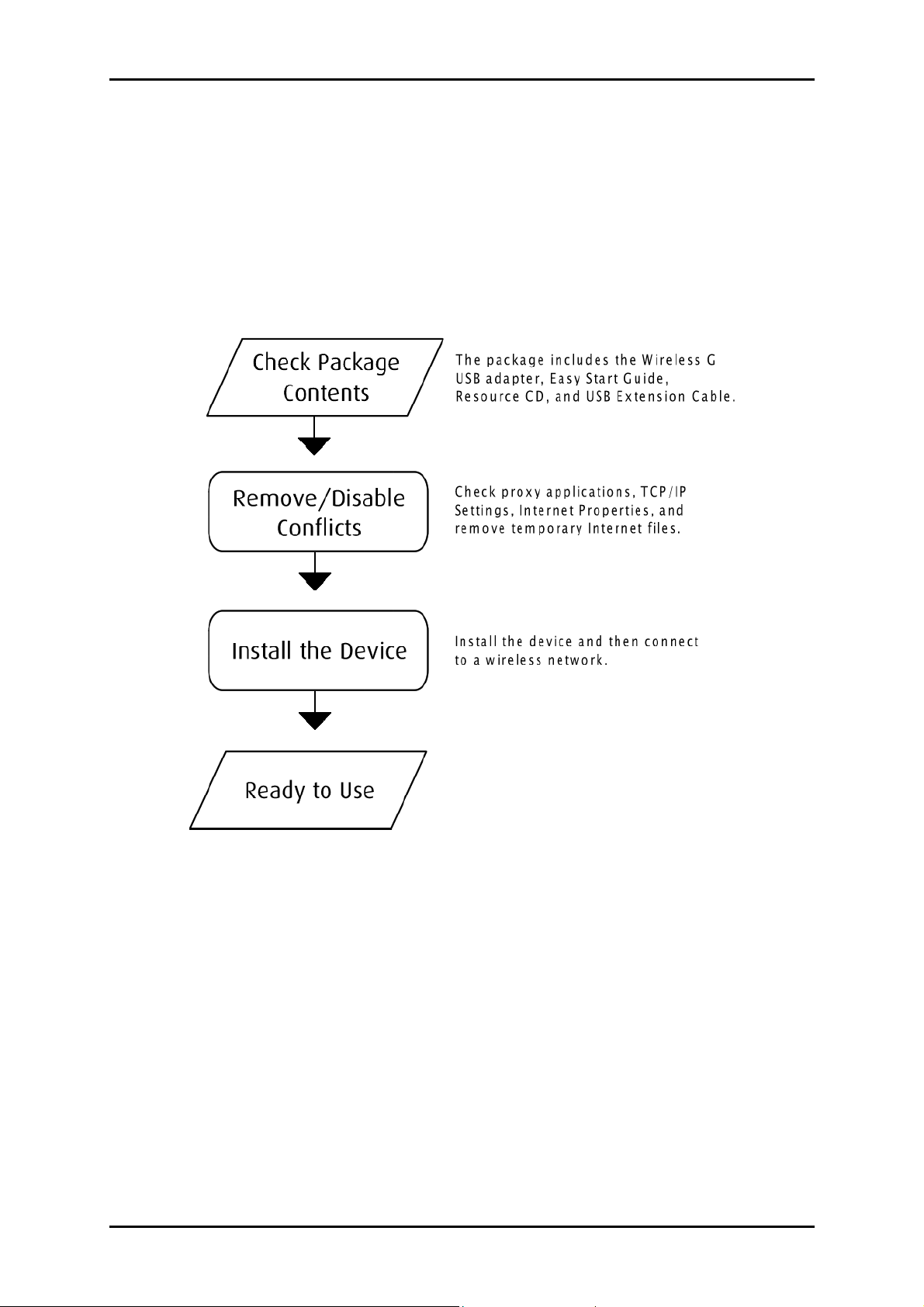
Getting Started
Setting up the device is easy. The flowchart below provides an outline of the steps you
need to go through. There are brief descriptions beside each step to help you along.
Detailed instructions are provided in the subsequent pages.
Check Package Contents
Package contents include:
Wireless B+G USB Adapter
Easy Start Guide
Resource CD
USB Extension Cable
Page 6 of 37
Page 7

User Manual
Remove or Disable Conflicts
To make sure the router installation moves on smoothly, you need to remove or disable
conflicts that may interfere with the installation. Probable conflicts may include:
Internet sharing applications
Proxy software
Security software
TCP/IP settings
Internet properties
Temporary Internet files
Internet Sharing, Proxy, and Security Applications
Internet sharing, proxy software, and firewall applications may interfere with the router
installation. These should be removed or disabled before you install and configure the
router.
If you have any of the following or similar applications installed on your computer,
remove or disable them according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Internet Sharing Applications
Internet Sharing Applications Proxy Software
Internet Sharing ApplicationsInternet Sharing Applications
Microsoft Internet Sharing WinGate Symantec
WinProxy Zone Alarm
Proxy Software Security Software
Proxy SoftwareProxy Software
Security Software
Security SoftwareSecurity Software
Page 7 of 37
Page 8

User Manual
Configuring TCP/IP Settings
Use the default TCP/IP settings to allow the router to provide a network address to the
computer,
To set the TCP/IP properties:
1. Select Start > Run. This opens the Run dialog box.
2. Enter control ncpa.cpl and then click OK. This opens the Network Connections in
your computer.
3. Right-click LAN and then select Properties. This opens the Local Area Connection
Properties dialog box.
4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and then click Properties. This opens the Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP) dialog box.
5. Select Obtain an IP address automatically.
6. Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) dialog box.
7. Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box.
Configuring Internet Properties
To set the Internet Properties:
1. Select Start > Run. This opens the Run dialog box.
2. Enter control inetcpl.cpl and then click OK. This opens the Internet Properties
dialog box.
3. Click Connections tab.
4. In the Dial-up and Virtual Private Network settings pane, select Never dial a
connection.
5. Click OK to close the Internet Properties dialog box.
Page 8 of 37
Page 9

User Manual
Removing Temporary Internet Files
Temporary Internet files are files from Web sites that are stored in your computer. Delete
these filed to purge the Internet cache and remove footprints left by the Web pages you
visited.
To remove temporary Internet files:
1. Select Start > Run. This opens the Run dialog box.
2. Enter control and then click OK. This opens the Control Panel.
3. Double-click Internet Options. This opens the Internet Options dialog box.
4. In the Temporary Internet Files pane, click Delete Cookies.
5. Click Delete Files.
6. Click OK to close the Internet Properties dialog box.
Page 9 of 37
Page 10

User Manual
Installation
For Windows Vista
To install the driver software in Windows Vista:
1. Connect WL230USB to an available USB port.
2. The Found New Hardware opens after you connect WL230USB to the USB port.
Select Locate and install driver software (recommended).
3. Select Don’t search online.
4. Insert the Resource CD into the CD-ROM and then click Next.
5. Select Install this driver software anyway when a message informing you that
Windows cannot verify the publisher of the software.
6. Click Next.
7. Click Close.
8. A new icon appears in the system tray - . Click this icon.
9. Select Connect to a network. This opens the Connect to a network dialog box.
10. Select a wireless network and then click Connect.
If wireless security is activated for the wireless network, enter the security key
and then click Connect.
Page 10 of 37
Page 11

User Manual
For Windows XP
To install the driver software in Windows XP:
Warning…
Warning…
Warning…Warning…
Do not connect the device until the Utility is not completely installed.
1. Insert the Resource CD to the CD-ROM. This opens the WL230USB Wireless B+G
Utility Setup. If the Utility did not open automatically, select Start > Run. Enter
d:\setup.exe, where d is the CD-ROM drive.
2. Click Next.
3. Click Next.
4. Click Next. The Setup Status displays the installation progress.
5. Click Finish.
6. Connect WL230USB to an available USB port. This opens the Found New Hardware
Wizard.
7. Select No, not this time and then click Next.
8. Select Install the software automatically (Recommended) and then click Next.
9. Click Continue Anyway when the Hardware Installation dialog box appears.
10. Click Finish.
11. A new icon appears in the System tray - . Double-click this icon to open
WL230USB Wireless B+G Utility.
12. Click Site Survey.
13. Select an ESSID and then click Join. The Privacy Configuration dialog box opens
when a network key is required from the selected ESSID. Enter the Network key,
confirm the Network key, and then click OK. The System tray icon changes to
either of the following:
Page 11 of 37
Page 12
User Manual
• - You have a good connection to a wireless network.
• - You have a weak connection to a wireless network.
For Windows 2000
To install the driver software in Windows 2000:
Warning…
Warning…
Warning…Warning…
Do not connect the device until the Utility is not completely installed.
1. Insert the Resource CD to the CD-ROM. This opens the WL230USB Wireless B+G
Utility Setup. If the Utility did not open automatically, select Start > Run. Enter
d:\setup.exe, where d is the CD-ROM drive.
2. Click Next.
3. Click Next.
4. Click Next. The Setup Status displays the installation progress.
5. Click Finish.
6. Connect WL230USB to an available USB port.
7. Click Yes when the Digital Signature Not Found dialog box opens.
8. A new icon appears in the System tray - . Double-click this icon to open
WL230USB Wireless B+G Utility.
9. Click Site Survey.
10. Select an ESSID and then click Join. The Privacy Configuration dialog box opens
when a network key is required from the selected ESSID. Enter the Network key,
confirm the Network key, and then click OK.
The System tray icon changes to either of the following:
Page 12 of 37
Page 13

User Manual
• - You have a good connection to a wireless network.
• - You have a weak connection to a wireless network.
For Windows Me
To install the device in Windows Me:
Warning…
Warning…
Warning…Warning…
Do not connect the device until the Utility has been completely installed.
1. Insert the Resource CD to the CD-ROM. This opens the WL230USB Wireless B+G
Utility Setup. If the Utility did not open automatically, select Start > Run. Enter
d:\setup.exe, where d is the CD-ROM drive.
2. Click Next.
3. Click Next.
4. Click Next. The Setup Status displays the installation progress.
5. Click Finish.
6. Connect WL230USB to an available USB port.
7. A new icon appears in the System tray - . Double-click this icon to open
WL230USB Wireless B+G Utility.
8. Click Site Survey.
9. Select an ESSID and then click Join. The Privacy Configuration dialog box opens
when a network key is required from the selected ESSID. Enter the Network key,
confirm the Network key, and then click OK.
The System tray icon changes to either of the following:
• - You have a good connection to a wireless network.
Page 13 of 37
Page 14

User Manual
• - You have a weak connection to a wireless network.
For Windows 98SE
To install the device in Windows 98SE:
Warning…
Warning…
Warning…Warning…
Do not connect the device until the Utility has been completely installed.
1. Insert the Resource CD to the CD-ROM. This opens the WL230USB Wireless B+G
Utility Setup. If the Utility did not open automatically, select Start > Run. Enter
d:\setup.exe, where d is the CD-ROM drive.
2. Click Next.
3. Click Next.
4. Click Next. The Setup Status displays the installation progress.
5. Click Finish.
6. Connect WL230USB to an available USB port.
7. Click OK when the Insert Disc dialog box opens and then insert your Windows
98SE CD in the CD-ROM.
8. A new icon appears in the System tray - . Double-click this icon to open
WL230USB Wireless B+G Utility.
9. Click Site Survey.
10. Select an ESSID and then click Join. The Privacy Configuration dialog box opens
when a network key is required from the selected ESSID. Enter the Network key,
confirm the Network key, and then click OK.
The System tray icon changes to either of the following:
Page 14 of 37
Page 15

• - You have a good connection to a wireless network.
• - You have a weak connection to a wireless network.
For Macintosh
These instructions are provided for installing WL230USB in the Mac OS X platform.
Minimum requirements include:
• G4 or higher
• 128MB RAM
User Manual
• 20MB free hard disk space
• A free USB Port
• CD-ROM drive
• Mac OS 10.3 and above
Install the Driver and the Utility
A driver is a software program created to allow your device to work in your computer.
The Utility, on the other hand, is used to configure and control the device functions.
Note:
Note: Do not connect WL230USB until you complete the driver software installation.
Note:Note:
To install the driver and utility:
1. Exit all programs.
2. Insert the Resource CD into your CD-ROM. A disk image file appears on the
desktop entitled WL230USB.
3. Double-click WL230USB and then open Mac Driver.
4. Open the open folder entitled with the version of your operating system.
Page 15 of 37
Page 16

User Manual
5. Double-click WL230USB_MacUSB_install.dmg. This creates a new object on the
desktop called WL230USB_MacPkg_install.
6. Double click WL230USB_MacPkg_install file to start the installation of the Mac
driver. This opens the Introduction step.
7. Click Continue in the Introduction step.
8. Click Continue in the Read Me step.
9. Select a destination and then click Continue.
10. Click Install in the Installation Type step.
Page 16 of 37
Page 17

User Manual
11. When the Macintosh Administrator authentication window appears, enter the
administrator Name and password or phrase, and then click OK.
12. Click Continue Installation when a message appears informing you that the
computer will restart after the installation.
13. Click Restart to finish installing the driver software.
Page 17 of 37
Page 18

User Manual
14. Click Restart to finish installing the driver software.
Connect the Device and Set the Network Settings
To connect the device and update the network settings:
1. Connect WL230USB to a USB port.
2. Go to System Preferences and then select Network.
3. Select Automatic as the Location.
4. Show the latest installed Ethernet Adapter.
5. Click TCP/IP.
6. Select Using DHCP to Configure Ipv4.
Page 18 of 37
Page 19

7. Click Apply Now.
8. Close the screen.
Connect to a Wireless Network
1. Go to System Preferences. WL230USB appears in the category entitled Other.
User Manual
2. Double-click WL230USB.
3. Double click on an available network.
4. Click No to enter the security key setting. This opens the WEP key setting screen.
Otherwise, click Yes if there is no security implemented in the available wireless
network.
Page 19 of 37
Page 20

User Manual
5. Select the Key Length, Key Format, Default Key, and Key Value for the wireless
network.
6. Click Apply.
7. Click OK.
Uninstall
To uninstall:
1. Exit all programs.
2. Insert the Resource CD into your CD-ROM. A disk image file appears on the
desktop entitled WL230USB.
3. Double-click WL230USB and then open Mac Driver.
4. Double click WL230USB_MacPkg_uninstall.
5. Remove the device and then reboot the system.
Page 20 of 37
Page 21

User Manual
About the Wireless B+G Utility
WL230USB Wireless B+G Utility is used to configure the device settings and connect to a
wireless network. It works on Windows 98SE, Me, 2000, and XP.
Note:
Note: WL230USB Wireless B+G Utility is not used in Windows Vista.
Note:Note:
Configuration Tab
The Configuration Tab provides all basic and advanced configuration settings for wireless
network connection.
Profile
Profile
ProfileProfile
A Profile is a name identifier to wireless network connections that have been saved. Profiles are
created to avoid reentering of the parameters required every time you want to connect to a
wireless network.
Page 21 of 37
Page 22

User Manual
SSID
SSID
SSIDSSID
The SSID is represents the name of the wireless network. An SSID is case sensitive and can have a
maximum of 32 characters.
Network Type
Network Type
Network TypeNetwork Type
WL230USB supports two network types:
• Infrastructure
Infrastructure Used for connecting to a wireless network
InfrastructureInfrastructure
• Adhoc
Adhoc used for setting up a group of wireless stations for file and printer sharing
Adhoc Adhoc
Transmit Rate
Transmit Rate
Transmit RateTransmit Rate
The default Transmit Rate value is Auto. This setting allows your device to automatically switch the
data transmission rate based on the conditions available in your environment. When the quality
drops below a certain level, the WL230USB will automatically switch to a lower data rate.
Otherwise, when the quality improves, the Wireless USB Adapter will gradually increase the data
rate until it has reached the highest available transmit rate.
Status
Status
StatusStatus
Status provides a general overview of the connection quality. Status parameters include:
• State
State Displays the Network Type, wireless network name (ESSID), and MAC address of the
StateState
access point. When operating in Ad-Hoc mode, State displays the virtual MAC address
used by computers participating in the Ad-Hoc network.
• Current Channel
Current Channel Displays the channel used.
Current ChannelCurrent Channel
• Current Tx Rate
Current Tx Rate Displays the highest transmit rate of the wireless network.
Current Tx RateCurrent Tx Rate
• Throughput
Throughput Displays the short term transmit and receive throughput in bytes/second.
ThroughputThroughput
• Link Quality
Link Quality Displays the link quality. There are 5 states of link quality:
Link QualityLink Quality
o 100%~80% Excellent link
o 80%~60% Good link quality
o 60%~40% Fair link quality
o Below 40% Poor or no connection
• Signal Strength
Signal Strength Displays the signal strength measurement. There are 5 states of signal
Signal StrengthSignal Strength
strength:
o 100%~80% Excellent signal strength
o 80%~60% Good signal strength
Page 22 of 37
o 60%~40% Fair signal strength.
o Below 40% Poor or no signal strength
• Rescan
Rescan Click to perform a new scan of all available wireless networks.
RescanRescan
Page 23

Advance
The Utility provides advanced configuration options.
User Manual
Advanced Configuration options include:
Power Save
Power Save
Power SavePower Save
The Power Save option is designed to conserve computer battery life. When Power Save is
enabled, your Wireless USB Adapter will go into sleep mode to minimize power consumption.
Note:
Note: When power saving mode is enabled, the Access Points you use need to
Note:Note:
support power saving as well so that the communication can be established.
RTS Threshold
RTS Threshold
RTS ThresholdRTS Threshold
RTS Threshold is a mechanism implemented to prevent the “Hidden Node” problem. If the “Hidden
Node” problem is an issue, please specify the packet size. The RTS mechanism will be activated if
the data size exceeds the value you set. It is highly recommended that you set the value ranging
from 0 to 1500. The default value is Disable.
Note
Note:::: Enabling RTS Threshold would cause redundant network overhead that could
NoteNote
negatively affect the throughput performance instead of providing a remedy.
Fragmentation Threshold
Fragmentation Threshold
Fragmentation Threshold Fragmentation Threshold
Threshold Fragmentation mechanism is used for improving the efficiency during high traffic. It
chunks down large pieces of data into smaller packets which are more manageable during
transmission.
Page 23 of 37
Page 24

User Manual
Security Enable (Privacy Configuration)
Security is applied to wireless networks to ensure integrity and limit unauthorized access
within the network. To open this, select Security Enable and then click Config. A dialog
box called Privacy Configuration opens displaying the Security and Certification tabs.
If you do not enable any wireless security on your IEEE 802.11g Wireless LAN USB
Adapter, the wireless communications are accessible to any wireless networking device
that is in the coverage area.
Data Encryption with WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption scrambles all data packets transmitted
between the wireless LAN adapter and the AP or other wireless station to keep network
communications private.
Both the wireless stations and the access points must use the same WEP key for data
encryption and decryption.
Page 24 of 37
Page 25

User Manual
The IEEE 802.11g Wireless LAN USB Adapter allows you to configure up to four 64-bit, or
128-bit WEP keys and only one key is used as the default key at any one time. The Key
index
index field allows you specify which of the four keys you use to transmit data on your
indexindex
wireless LAN. You can change the default key by clicking on the up or down arrow and
make sure the default key is set up exactly the same on the Wireless LAN stations as
they are on the wireless Access Points.
For 64bit encryption you may choose:
• Alpha
Alphanumeric
numeric
AlphaAlpha
numericnumeric
and “0-9” (e.g. MyKey).
• Hexadecimal
Hexadecimal: entering
HexadecimalHexadecimal
9” (e.g. 11AA22BB33).
• For 128bit encryption you may choose:
• Alphanumeric
Alphanumeric
AlphanumericAlphanumeric
::::
entering
::::
entering
5 characters
5 characters
5 characters 5 characters
10 hexadecimal digits
10 hexadecimal digits
10 hexadecimal digits 10 hexadecimal digits
13 characters
13 characters
13 characters 13 characters
(case sensitive) ranging from “a-z”, “A-Z”
(case sensitive) ranging from “a-z”, “A-Z”
in the range of “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-
Key
Key Key
and “0-9” (e.g. MyKey12345678).
• Hexadecimal
Hexadecimal: entering 26
HexadecimalHexadecimal
9” (e.g. 00112233445566778899AABBCC).
26
hexadecimal digits
hexadecimal digits
26 26
hexadecimal digits hexadecimal digits
in the range of “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-
IEEE 802.1x
The IEEE 802.1x standard outlines enhanced security methods for both the authentication
of wireless stations and encryption key management. Authentication can be done using
an external RADIUS server.
EAP Authentication
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) is an authentication protocol which runs on the
top of IEEE 802.1x transport mechanism in order to support multiple types of user
authentication. By using EAP to interact with an EAP-compatible RADIUS server, an access
point helps a wireless station and a RADIUS server perform authentication.
Page 25 of 37
Page 26

User Manual
The type of authentication you use depends on the RADIUS server and an intermediary
AP that supports IEEE 802.1X. You must first have a wired connection to the network and
obtain the certificate from a certificate authority (CA). A certificate can be used to
authenticate users and a CA issues certificates and guarantees the identity of each
certificate owner.
WPA(2)
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA2 is a wireless
security standard that defines stronger encryption, authentication and key management
than WPA.
WPA
WPA:::: Allows you to gain access to a more secured wireless network that requires mutual
WPAWPA
authentication between client and access point with a Radius authentication server or
other authentication server on the network. WPA uses 802.1X and Extensible
Authentication Protocol (EAP) for authentication. WPA offers Enterprise and individual
needs to meet the different market segments. This product supports various EAP types
(TLS and PEAP), which require different credential authentication. In order to access the
wireless network, you must select EAP type your service provider supplied in the section
of IEEE802.11
IEEE802.11XXXX Authentication
IEEE802.11 IEEE802.11
Authentication. Choose WPA2 if needed from Authentication Mode.
Authentication Authentication
Page 26 of 37
Page 27

User Manual
WPA
WPA----PSK
PSK:::: WPA offers a Personal mode of operation. In the Personal mode of operation, a
WPAWPA
PSKPSK
pre-shared key is used for authentication. WPA-PSK allows you to gain access to a
secured wireless network that the station and the access point use the same pre-shared
key to authenticate. You must type a mixture of numbers and letters in the Pre
key
key section of this menu. You may input either 8-63 ASCII characters or 64 HEX
key key
Pre----shared
shared
PrePre
shared shared
characters. Choose WPA-PSK if needed from Authentication Mode.
WPA2
WPA2:
: WPA2 provides a stronger encryption mechanism than WPA. WPA2 is the second
WPA2WPA2
: :
generation of WPA security, providing personal and enterprise users with a high level of
assurance that only authorized users can access to their wireless network. There is no
difference between WPA and WPA2. The only difference is that WPA2 provides a stronger
data encryption via the AES, contrast to WPA, which uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
(TKIP). Choose WPA2 if needed from Authentication Mode.
Page 27 of 37
Page 28

User Manual
WPA2
WPA2----PSK
WPA2WPA2
PSK:
: Like WPA, WPA2-Personal offers authentication via a pre-shared key. Pre-
PSKPSK
: :
shared key is usually used for Personal authentication. Personal mode requires only an
access point and client on the network. Similarly, you need to type a mixture of numbers
and letters in the Pre
Pre----shared key
shared key section of this menu. You may input either 8-63 ASCII
PrePre
shared key shared key
characters or 64 HEX characters. Choose WPA2-PSK if needed from Authentication Mode.
Page 28 of 37
Page 29

User Manual
Encryption Mode
WPA improves data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), Message
Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE 802.1X. WPA2 use Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in
the Counter mode with Cipher block chaining Message authentication code Protocol
(CCMP) to offer stronger encryption than TKIP.
The encryption mechanism used for WPA(2) and WPA(2)-PSK are the same. The only
difference between them is that WPA(2)-PSK uses a simple common password, instead
of user specific credentials. The common password approach makes WPA(2)-PSK
susceptible to brute-force password-guessing attacks but it’s still an improvement over
WEP as it employs a consistent, single, alphanumeric password to derive a PMK which is
used to generate unique temporal encryption keys.
IEEE 802.1X Authentication
WPA and WPA2 apply IEEE 802.1X and Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to
authenticate wireless stations using an external RADIUS database. WPA2 reduces the
number of key exchange messages from six to four (CCMP 4 way handshake) and
shortens the time required to connect to a network. Other WPA2 authentication features
that are different from WPA include key caching and pre-authentication.
After you select the EAP type, you need to click Certification Tab
setting. The following describes configuration of each available EAP type.
Certification Tab to make advanced
Certification TabCertification Tab
Page 29 of 37
Page 30

User Manual
TLS:
TLS: Clicking the Certification
TLS: TLS:
Certification tab for TLS shows the following menu.
CertificationCertification
TLS requires the entry of Certificate Information and Login Information for mutual
authentication. This utility will auto-detect the Certificate Information for you to configure
TLS easily. You only need to enter the Login Name
Login Name in the Login information filed to
Login NameLogin Name
authenticate. If you desire to use the Server Certificate manually, you can click the check
box next to “Verify Server Certificate”
“Verify Server Certificate” and choose the usable selection in the User
“Verify Server Certificate”“Verify Server Certificate”
Certificate field using drop-down menu.
User Certificated:
User Certificated: select one of user certificates you have enrolled.
User Certificated:User Certificated:
TLS is used to create a secure tunnel through which authentication and encryption keys
can be passed and require server and client side keys. To save the information you
entered in the appropriate field, click the OK
close the menu. If you want to return to select other EAP type, click the Security
OK button. Otherwise, click the Cancel
OKOK
Cancel button to
CancelCancel
Security tab.
SecuritySecurity
Page 30 of 37
Page 31

PEAP:
PEAP: Clicking the Certification tab for PEAP displays the following menu.
PEAP:PEAP:
User Manual
PEAP requires the use of Certificate Information and User Information. This utility will
automatically identify Certificate Information and Login Information for users to configure
PEAP easily. You only need to enter User Name and Password in the User information
filed to authenticate. If you click the “Verify Server Certificate” check box, you are able to
choose one of User Certificate from the drop-down menu. Furthermore, you need to input
User Name and Password in the User Name.
To save the information you entered in the appropriate field, click the OK
Otherwise, click the Cancel
EAP type, click the Security
Cancel button to close the menu. If you want to return to select other
CancelCancel
Security tab.
SecuritySecurity
OK button.
OKOK
Page 31 of 37
Page 32

User Manual
LEAP:
LEAP: Clicking the Certification
LEAP: LEAP:
Certification tab for LEAP shows the following menu.
CertificationCertification
LEAP requires the mutual authentication between station and access points. You must
present a User Name
User Name and Password
User NameUser Name
Password in the User Information field that will be verified by
PasswordPassword
LEAP-capable server. This mutual authentication ensures that only authorized users are
allowed access to the network.
Authentication Type
The IEEE 802.11b/g standard describes a simple authentication method between the
wireless stations and AP. Two authentication types are defined: Open
Shared
Shared key mode.
SharedShared
Open system mode is implemented for ease-of-use and when security is not an issue. It
requires NO authentication, since it allows any device to join a network without
performing any security check. The wireless station and the AP do not share a secret key.
Open system mode and a
OpenOpen
Thus the wireless stations can associate with any AP and listen to any data transmitted
plaintext.
Page 32 of 37
Page 33

User Manual
Shared key mode involves a shared secret key to authenticate the wireless station to the
AP. It requires that the station and the access point use the same WEP key to
authenticate. This basically means that WEP must be enabled and configured on both the
AP and the other wireless stations with a same key.
Preamble Type
Preamble is used to signal that data is coming to the receiver.
Short preamble increases performance as less time sending preamble means more time
for sending data.
Select Long and Short
when access point or wireless stations support it; otherwise the wireless LAN adapter
uses long preamble.
Long and Short to have the wireless LAN adapter automatically use short preamble
Long and Short Long and Short
Page 33 of 37
Page 34

User Manual
Site Survey Tab
Site Survey displays the available wireless networks you can connect to. To connect to a
wireless network, select the ESSID and then click the Join. Besides showing the ESSID of
each available wireless network, it also displays the following information:
• BSSID
• Channel
• Network Type
• Security
• Signal
• Support Rates
Page 34 of 37
Page 35

User Manual
About Tab
The About tab displays the version for the Configuration Utility, Network Driver, and
Network Firmware.
Page 35 of 37
Page 36

User Manual
Certifications
FCC Certification
The United States Federal Communication Commission (FCC) and the Canadian
Department of Communications have established certain rules governing the use of
electronic equipment.
Part15, Class B
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interface, and
2. This device must accept any interface received, including interface that may cause
undesired operation. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with
the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However,
there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which can be determined by turning off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Page 36 of 37
Increase the distance between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
Page 37

User Manual
Notes…
Notes…
Notes… Notes…
1. To comply with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, a separation distance of
at least 20 cm must be maintained between the antenna of this device and all
persons.
2. This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
Page 37 of 37
 Loading...
Loading...