Page 1

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Publication#:
Document Release:
Release Date:
N0064485
1.0
July 13, 2006
Page 2

Important Notice
Nortel reserves the right to make changes in the contents of this publication including
functions and specifications identified herein without notice.
The material contained in this document is intended for Nortel personnel and licensed
customers with a non-disclosure agreement or standard contract.
In the absence of a written agreement to the contrary, Nortel assumes no liability for
applications assistance, customer's product/application/concepts, or infringements of
patents or copyrights of third parties arising from the use of systems and architectures
described herein. Nor does Nortel warrant or represent that any license, either
expressed or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, or other
combination of technology, architecture, or software as might be or is already in use.
This document should not be reproduced, disseminated, or otherwise disclosed
without prior written consent from a Nortel officer.
This document has been copyrighted by Nortel and may not be duplicated.
Copyright © 2006 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved
Page 3

Revision History
July 2006 Standard 1.0.
Revision History
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 3
Page 4

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Page 4 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 5

Table of Contents
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Scope . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
How to Get Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Finding the latest updates on the Nortel Web site . . . . . . . . . 8
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center 9
Getting Help from a specialist by using an Express Routing
Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller . . . . . . . 9
How to Use This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Organization of This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Conventions Used in This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Solaris and Windows Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Two-Button (Windows) vs. Three-Button (Solaris) Mouse . 14
Trademark Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
The BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
New or Updated Features of BCM-IVR 2.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Pre-Requisites for the BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Application Developer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
System Administrator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Transition Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Transition Issues for the Application Developer . . . . . . . . . 20
PeriProducer 3.00 Block Changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Discontinued Features and Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Other PeriProducer Changes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Transition Issues for the System Administrator . . . . . . . . . . 37
Documentation Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Administrator on the Windows Workstation . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Windows Workstation Operating System Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . 40
BCM-IVR 1.X Uninstall Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Uninstall Procedures with MPS 2.1 Software and Document CD
40
BCM-IVR 2.1 Installation Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Installing PeriProducer 3.00 and PeriStudio 2.20. . . . . . . . . 43
BCM-IVR 2.1 Toolkit Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
License Service Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
PeriView 2.1 and PeriView 2.1 Consolidator Installation . . . . . . 53
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 5
Page 6

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Installing BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriView Consolidator . . . . . . . . . 54
Launching Applications in PeriView . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Loading Application .vex files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Loading User Defined Call Function Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Assigning and Starting Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Administrator on the BCM 4.0 Platform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Numbering components using Element Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Enabling Host Communications with Element Manager . . . . . . 75
Application Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Developer Upgrade on Windows Workstation . . . . . . . . . . 81
Porting PeriProducer 2.30 Applications to PeriProducer 3.00 . . 82
Application Porting Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Converting Standard PeriProducer 2.30 Applications to
PeriProducer 3.00 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Porting Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Conversion Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Known Conversion Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Set Resource Label in 2.30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Unsupported 2.30 Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Resource Block Conversions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Flushing the Speak Prompt Buffer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
System Transfer Connection ID Datacard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Developer Upgrade on Fedora Workstation . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Installing Fedora . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Installing Nortel IVR Plugin Development Environment . . . . . . 89
Building C/C++ Call Functions Libraries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
makecall_tux Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Database Access Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
VMST 3 on the BCM Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Install Patches on the Windows Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Configuring periq on the Windows Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Configuring sqlclnt on Windows Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Page 6 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 7

Preface
Page 8
BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Scope
Business Communications Manager (BCM) with Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
capabilities is a communications platform that delivers multimedia voice processing,
business telephony applications, and data networking services.
The BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade manual explains how to upgrade a BCM-IVR 1.X system
to a BCM-IVR 2.1 system. It further explains how to port existing applications to run
on the upgraded BCM-IVR 2.1. This manual is not intended to replace individual
software manuals. It is meant only to be used as a supplement to them.
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for both IVR Application Developers and BCM-IVR System
Administrators. This manual assumes that the reader is familiar with:
• BCM application development;
• site-specific operating procedures relating to the BCM;
• specific application functions performed by the BCM; and
• other equipment to which the BCM may be connected.
How to Get Help
Basic knowledge of your operating system software is also assumed.
This section explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Finding the latest updates on the Nortel Web site
The content of this documentation was current at the time the product was released.
To check for updates to the latest documentation for the MPS 500 and 1000, click one
of the following links:
MPS 500 Takes you directly to the Nortel page for MPS 500 documentation at
www130.nortelnetworks.com/cgi-bin/eserv/cs/main.jsp?cscat=DOCUMENTATION&resetFilter=1&tranProduct=12605
MPS 1000 Takes you directly to the Nortel page for MPS 1000 documentation at
www130.nortelnetworks.com/cgi-bin/eserv/cs/main.jsp?cscat=DOCUMENTATION&resetFilter=1&tranProduct=11721
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel Technical
Support web site:
www.nortel.com/support
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and tools to
address issues with Nortel products:
Page 8 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 9

Preface
• download software, documentation, and product bulletins
• search the Technical Support web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base for
answers to technical issues
• sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation for
Nortel equipment
• open and manage technical support cases
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you do not find the information you require on the Nortel Technical Support web
site, and have a Nortel support contract, you can also get help over the phone from a
Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Outside North America, go to the following web site to obtain the phone number for
your region:
www.nortel.com/callus
Getting Help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some Nortel Technical Solutions Centers, you can use an Express Routing
Code (ERC) to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel product or service.
To locate the ERC for your product or service, go to:
www.nortel.com/erc
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor or
authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that distributor or reseller.
How to Use This Manual
This manual uses many standard terms relating to computer systems, software
application functions, and the Internet. However, it contains some terminology that
can be explained only in the context of the MPS Series. Refer to the Glossary of
Nortel’s Media Processing Server Series Terminology for definitions of MPS Series
specific terms.
Read this manual from start to finish at least once. When you are familiar with the
document, you can use the Table of Contents to locate topics of interest for reference
and review.
If you are reading this document online, use the cross-reference links (shown in blue)
to quickly locate related topics. Position your cursor over the cross-reference link and
click once. Click any point in a Table of Contents entry to move to that topic. Click
the page number of any Index entry to access that topic page.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 9
Page 10

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Familiarize yourself with various specialized textual references within the manual, see
Conventions Used in This Manual on page 12.
Periphonics is now part of Nortel. The name Periphonics, and variations thereof,
appear in this manual only in reference to a product (for example, the PERImps
package, the perirev command, and so on).
Page 10 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 11

Organization of This Manual
This manual is organized according to the needs and requirements of two distinct
BCM-IVR users: System Administrators and Application Developers.
Chapter 1 — Introduction to the BCM - IVR Upgrade
Overviews the upgraded Business Communication Manager (BCM) with Interactive
Voice Response capabilities. Explains how to access documentation on Helmsman.
Chapter 2 — Administrator Upgrade on Windows Workstation
Discusses prerequisites and steps necessary to upgrade the BCM-IVR PeriView
Consolidator workstation.
Chapter 3 — Administrator Upgrade on BCM 4.0 Platform
Discusses how to manage BCMs using Element Manager. Explains how to add BCMs
to the Element Manager administration list.
Chapter 4 — Developer Upgrade on Windows Workstation
Discusses steps necessary to port PeriProducer 2.30 applications to PeriProducer 3.00,
as well as porting events and conversion issues.
Preface
Chapter 5 — Developer Upgrade on Fedora Workstation
Discusses steps necessary to configure the Fedora workstation to compile C/C++ code
for User Defined External Call Functions.
Chapter 6 — Database Access Configuration
Discusses how to configure the Windows workstation for external database access.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 11
Page 12
BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Conventions Used in This Manual
This manual uses different fonts and symbols to differentiate between document
elements and types of information. These conventions are summarized in the
following table.
Conventions Used in This Manual (Sheet 1 of 2)
Notation Description
Normal text
important term
system
command
command,
condition
and alarm
file name /
directory
on-screen field
<KEY NAME>
Book Reference
Normal text font is used for most of the document.
The Italics font introduces new terms, highlights meaningful words
or phrases, or distinguishes specific terms from nearby text.
This font indicates a system command or its arguments. Enter
such keywords exactly as shown (that is, do not fill in your own
values).
Command, Condition and Alarm references appear on the screen
in magenta text and reference the Command Reference Manual,
the MPS Developer User’s Guide, or the Alarm Reference Manual,
respectively. Refer to these documents for detailed information
Commands, Conditions, and Alarms.
about
This font highlights the names of disk directories, files, and
extensions for file names. It also shows what is displayed on a
text-based screen (for example, to show the contents of a file.)
This font indicates field labels, on-screen menu buttons, and action
buttons.
A term that appears within angled brackets denotes a terminal
keyboard key, a telephone keypad button, or a system mouse
button.
This font indicates the names of other publications referenced
within the document.
cross-reference
!
A cross-reference appears on the screen in blue. Click the crossreference to access the referenced location. A cross-reference that
refers to a section name accesses the first page of that section.
The Note icon identifies notes, important facts, and other keys to
understanding.
The Caution icon identifies procedures or events that require
special attention. The icon indicates a warning that serious
problems may arise if the stated instructions are not followed
implicitly.
Page 12 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 13

Conventions Used in This Manual (Sheet 2 of 2)
Notation Description
Preface
(1): Windows and the flying Window logo are either trademarks or registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
(2): Solaris® is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the U.S. and other
countries.
Solaris and Windows Conventions
This manual depicts examples (command line syntax, configuration files, and screen
shots) in Solaris format. Windows-specific commands, procedures, or screen shots are
shown when required. The following table lists general operating system conventions
used with either the Solaris or Windows operating system.
The flying Window icon identifies procedures or events that apply
to the Windows operating system only.
The Solaris icon identifies procedures or events that apply to the
Solaris operating system only.
(2)
(1)
Solaris Windows
Environment $PPROHOME %PPROHOME%
Paths $PPROHOME/bin %PPROHOME%\bin
Command <command> & start /b <command>
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 13
Page 14
BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
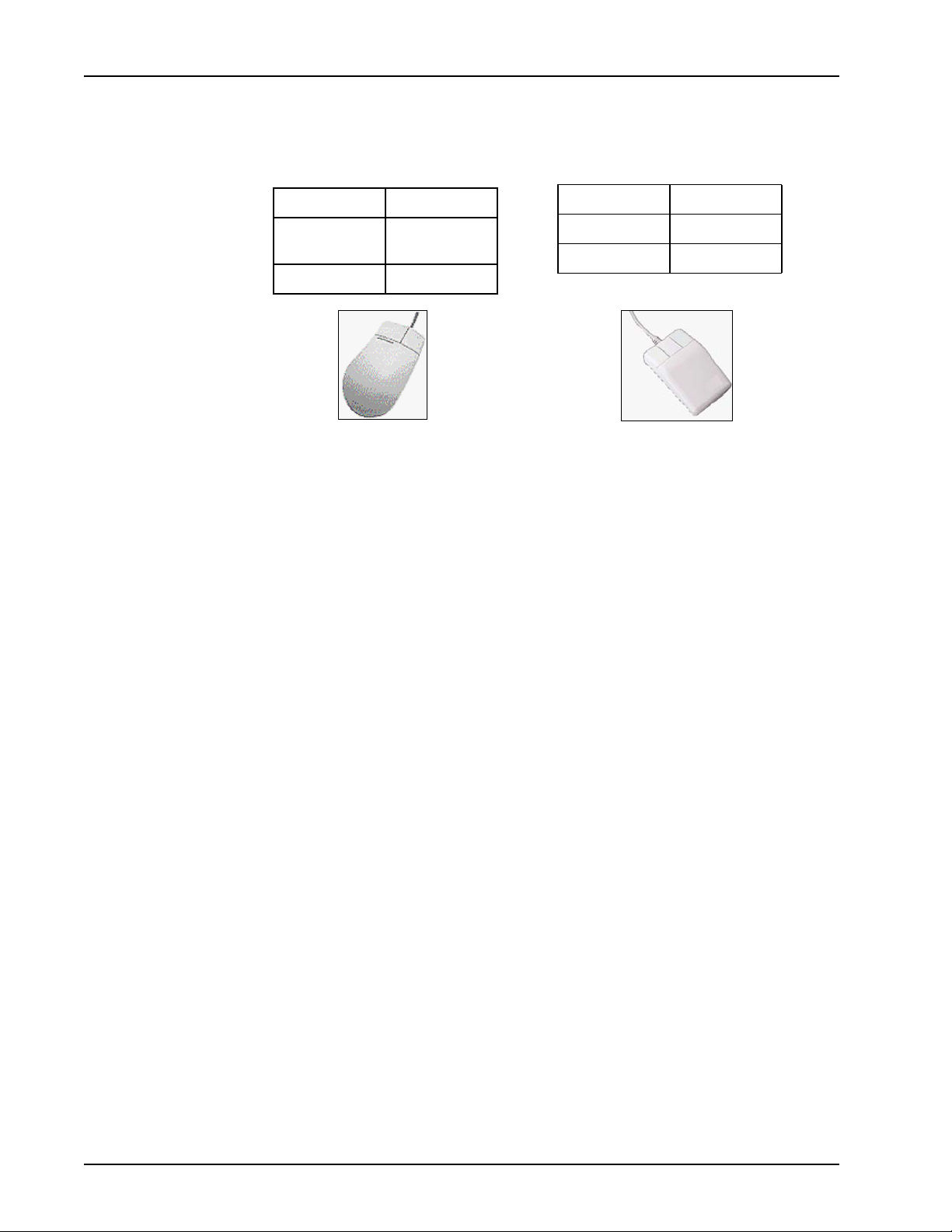
Two-Button (Windows) vs. Three-Button (Solaris) Mouse
<SELECT> Left button
<ADJUST> Left and Right
<MENU> Right button
Trademark Conventions
The following trademark information is presented here and applies throughout for
third party products discussed within this manual. Trademarking information is not
repeated hereafter.
Solaris
other countries.
Solaris, SunOS, OpenWindows, SPARC, and UltraSPARC are trademarks or
registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and other
countries.
®
<SELECT> Left button
<ADJUST> Middle button
together
<MENU> Right button
and Motif® are registered trademarks of The Open Group in the U.S. and
Microsoft, MSSQL, Windows, Internet Explorer, and the Flying Windows logo are
either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
®
Oracle
Sybase
Informix
is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation.
™
and SYBASE™ are trademarks of Sybase, Inc. or its subsidiaries.
®
and INFORMIX® are registered trademarks of Informix Corporation or its
affiliates.
Page 14 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 15
BCM - IVR 2.1
Upgrade Overview
This chapter covers:
1. The BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade
2. New or updated features of
BCM-IVR 2.1
3. Pre-requisites for the BMCIVR 2.1 upgrade
4. Transition issues
5. Documentation issues
Page 16

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
The BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade
Business Communication Manager 4.0 (BCM) is a fully integrated communication
system for small businesses, government networks, retail networks, and enterprise
branch offices.
The BCM 4.0 offers interactive voice response capabilities through Interactive Voice
Response 2.1 (IVR 2.1). IVR 2.1 is a suite of products that allows businesses to create
applications callers can use to access information by responding to a series of prompts
through their touchtone phones.
The IVR applications are developed for specific customer needs and in many cases are
integrated with databases to enable real-time queries and updates. Some examples of
IVR applications are:
• A pharmacy’s application that lets customers access their accounts,
receive real-time status on their prescription refills, and request
prescription refills.
• A bus station’s IVR application that lets customers book seats on a trip or
review projected departure times.
• A bookstore’s application that lets customers hear store hours, purchase
books, and check the delivery of an existing order.
The collection of hardware and software that creates and administers IVR applications
on BCMs is collectively referred to as the BCM-IVR 2.1 system.
New or Updated Features of BCM-IVR 2.1
In previous BCM-IVR systems (such as the BCM-IVR 1.X system), both the BCM
3.X and the IVR 1.X operated on an Embedded Windows NT platform. The IVR 1.X
development and administration tools (PeriProducer 2.X, PeriStudio 1.X,
PeriReporter, and PeriView) ran on a Windows NT/2000 platform.
The BCM-IVR 2.1 system requires both the Nortel Carrier Grade Linux (NCGL)
platform and the Windows 2000 platform. The BCM 4.0 operates on the NCGL
platform. The BCM 4.0 runs IVR applications developed and administered with the
latest releases of IVR development and administration tools: PeriProducer 3.00,
PeriStudio 2.20, PeriView 2.1, and PeriReporter 1.21. These IVR development and
administration tools run on the Windows 2000 platform.
In the BCM-IVR 2.1 system, BCMs are managed with Element Manager, not Unified
Manager (for more information about Element Manager, see BCM 4.0 Networking
Configuration Guide).
In the BCM-IVR 2.1 system, PeriView and PeriView Consolidator reside on a
Windows 2000 workstation, and BCM 4.0 resides on an NCGL workstation. The
BCMs IVR capabilities are managed from any user PC by pointing the user PC web
browser to the PeriView/PeriView Consolidator workstation. A third workstation with
Page 16 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 17
Fedora Core 3 is required if IVR applications use C/C++ external call functions.
As such, the configuration of the new BCM-IVR 2.1 system differs from that of the
BCM-IVR 1.X system.
BCM-IVR 1.X Configuration
The following figure shows a graphical representation of a typical BCM-IVR 1.X
configuration.
Typical BCM-IVR 1.X
System Configuration
Windows Workstation
Developer and Administrator
Workstations could be the same
machine.
BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
Developer Workstation
Windows NT/2K
Software Tools:
PeriProducer 2.3
PeriStudio 2.1
Administrator
Workstation
Windows NT/2K
Software Tools:
PeriView 1.0
PeriReporter
BCM 3.X
with
BCM-IVR 1.X
on Embedded Win-
dows NT
Software Tools:
Unified Manager
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 17
Page 18
BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
BCM-IVR 2.1 Configuration
The following figure shows a typical BCM-IVR 2.1 system configuration.
Windows Workstation
The Developer and
Administrator
Workstations could be the
same machine.
Developer
Workstation
Windows 2K
Typical BCM-IVR 2.1 System
Configuration
Software Tools:
PeriProducer 3.00
PeriStudio 2.20
Administrator
Workstation
Windows 2K
Software Tools:
PeriView
Consolidator 2.1
PeriReporter
Element Manager
C/C++ Call Function
Workstation running
Fedora
BCM 4.0
with
BCM-IVR 2.1
on NCGL
The BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
describes the installation and
configuration of items in this box.
Page 18 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 19

Pre-Requisites for the BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade
Application Developer
Application Developers create applications that run on the BCM-IVR system.
Application Developers must upgrade their developer workstation and install Fedora
Core 3 to upgrade any external C/C++ Call Functions in existing applications.
Chapters 4 and 5 are intended for Application Developers.
An Application Developer must obtain the following CDs to upgrade the BCM-IVR
system:
• MPS 2.1 Software, Documentation and Update CD—MPS 2.1 Patch Bundle
9, PeriProducer 3.00, PeriStudio 2.20, PeriView 2.1 and PeriReporter 1.21
and supporting documentation
• BCM-IVR Toolkit CD—contains BCM Toolkit for PeriProducer 3.00, NCGL
Development Environment, userdb.xml.BCM, BCM-IVR Integration
Supplement, PeriProducer for the BCM Guide, BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade
Guide, ReadMe_1st.
BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
An Application Developer must have a Windows 2000 operating system.
If the IVR applications use C/C++ call functions, an Application Developer must also
have a PC with Fedora installed. See “Overview” on page 88.
System Administrator
System Administrators monitor and maintain the BCM-IVR system. System
Administrators must uninstall existing PERI packages, install BMC/IVR 2.1 PERI
packages, and install PeriView Consolidator. System Administrators are also
responsible for managing the BCMs using Element Manager. Chapters 2 and 3 are
intended for System Administrators.
A System Administrator must obtain the following CDs in order to upgrade the BCMIVR system:
• MPS 2.1 Software, Documentation and Update CD—MPS 2.1 Patch Bundle
9, PeriProducer 3.00, PeriStudio 2.20, PeriView 2.1 and PeriReporter 1.21
and supporting documentation
• BCM-IVR Toolkit CD—contains BCM Toolkit for PeriProducer 3.00, NCGL
Development Environment, userdb.xml.BCM, BCM-IVR Integration
Supplement, PeriProducer for the BCM Guide, BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade
Guide, ReadMe_1st.
A System Administrator must have a Windows 2000 operating system.
Before proceeding with this upgrade, the System Administrator must obtain ported
IVR applications from the Application Developer. See “Porting PeriProducer 2.30
Applications to PeriProducer 3.00” on page 82.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 19
Page 20

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Transition Issues
Transition Issues for the Application Developer
In upgrading from BCM-IVR 1.X to BCM-IVR 2.1, Application Developers may
encounter transition issues due to new or obsolete PeriProducer features.
Database Access Modes
BCM-IVR 2.1 supports VTCPD and Host database access.
BMC/IVR 2.1 no longer supports native mode or Open Database Connectivity access
(ODBC). Existing applications configured for native mode or ODBC access must be
reconfigured.
For more information about configuring your BCM-IVR 2.1 system for database
access. See “Database Access Configuration” on page 91.
New PeriProducer 3.00 Blocks
PeriProducer 3.00 introduces several new toolkit blocks; however, some are not
supported in the BCM environment. The following table lists the new blocks and
whether they are supported in the BCM Environment.
New PeriProducer 3.00 Blocks
Block Function
Abort Abort input/output
Bridge Not supported
Call Control Send data to telephony protocol layer/perform a hookflash
(moved from Originate block in PeriProducer 2.30)
Call Conferencing Not supported
Call Progress Detection Manage call progress detection functions
Edit Sequence Manage touch tone input editing and user edit sequences
Line Operations Perform phone line operations (such as offer call, accept
call, get line/application resource from pool)
Media Operations Not supported
Select Input Not currently implemented
See the PeriProducer 3.00 User’s Guide for full descriptions of the blocks.
Blocking/Non-blocking Execution
Many PeriProducer blocks provide the option of choosing blocking (execution waits
at that block until it receives success/failure message) or non-blocking (execution
Page 20 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 21

BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
continues to next block without waiting for message) execution. A Wait checkbox
enables/disables blocking execution for the applicable blocks. See Blocking/Nonblocking Operation in the PeriProducer 3.00 User’s Guide for details.
Call Progress Detection
Using Call Progress Detection (CPD) is updated in PeriProducer 3.00. CPD is
controlled by dynamically enabling and disabling specific tone/event detection in the
Call Progress Detection block. All CPD events return to the application as the cpd
condition with the specific event (Busy, Reorder, and so on) in the condition data. See
the PeriProducer 3.00 User’s Guide for details.
PeriProducer 3.00 Block Changes
Many PeriProducer 3.00 blocks have amended or improved function.
Connection IDs (Caller I/O blocks)
Phone line and resource numbers are replaced with Connection IDs (CIDs).
Connection IDs indicate the component name and the line number of the connection.
For example, the CID mps24.1 indicates the connection is from line one on
component mps24. The default Connection ID for the current phone line is available
in the System folder’s DefaultCID data card. The CID for an operation is supplied by
the system (for example, when a resource is allocated).
Accessory Toolkit Blocks
The Table Search, Table Sort, Date Calculations, and Send email blocks are moved
from the main toolkit to the accessory toolkit.
Answer Block
Continue on Ring Detect Removed
The Continue on Ring Detect option is removed.
Get Phone Number Options Removed
The Get Dialed Phone Number and Get Caller’s Phone Number options are supported
only with certain protocols. See the BCM 4.0 Networking Configuration Guide for
more details.
Disconnect Block
Abandoned Call Counter Removed
The MPS does not automatically track system abandoned calls. The Mark as
abandoned option is removed. To track abandoned calls, create application statistics
and use MPS Reporter to display the reports
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 21
Page 22
BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
System Block
Diagnostic Functions Removed
The diagnostics function is removed.
Condition Data
The Get Condition Data function is added. This function replaces using the conditiondata call function. Get Condition Data requires a folder with the same structure, data
names, and data types expected with the condition.
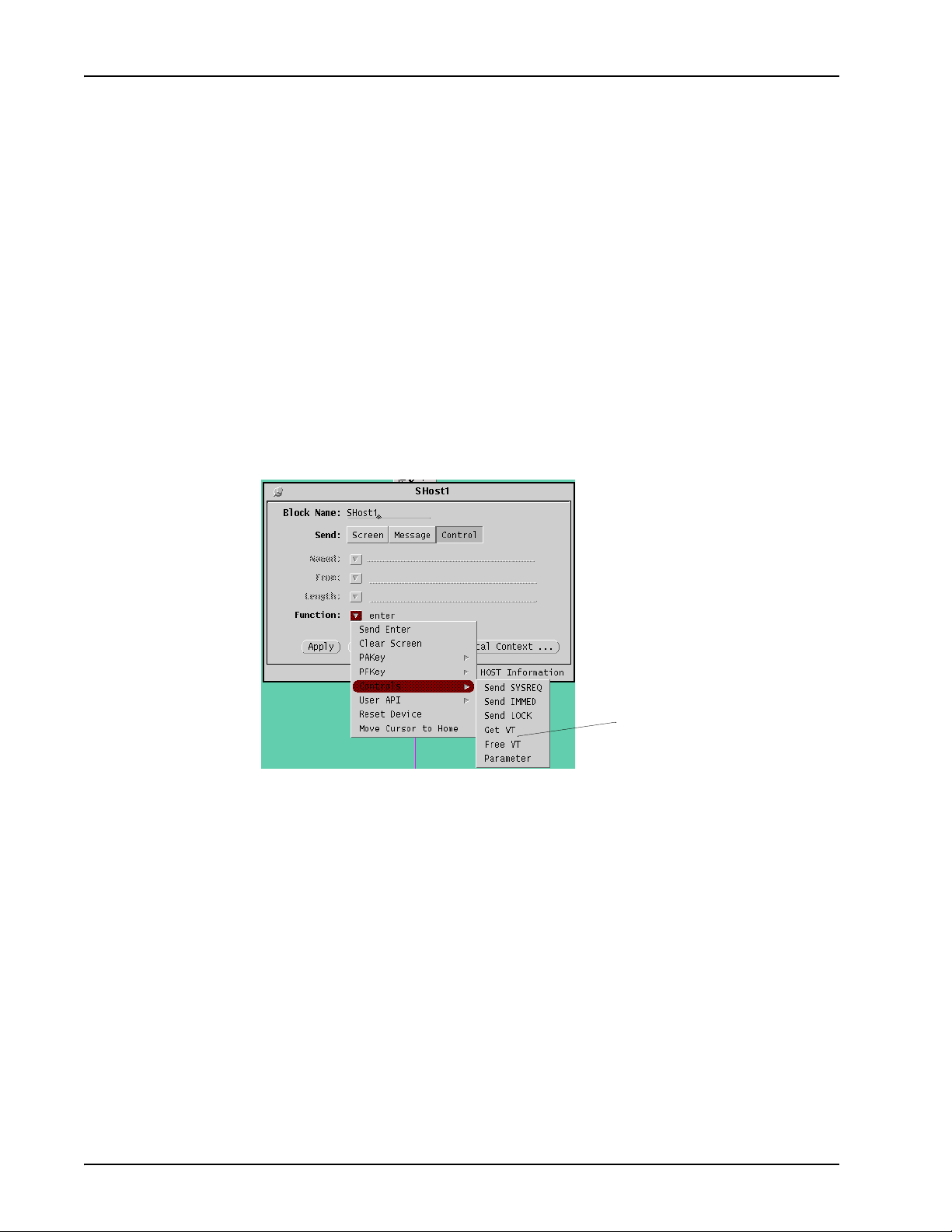
Send Host Block
Virtual Terminal (VT) Allocation
VT allocation functions are available from the Send Host block. These functions
replace the VT allocation Environment block options.
new VT options
Setting Host Environment Parameters
Host environment parameters are sent from the Send Host block. This function
replaces the Environment block "host" option.
Page 22 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 23
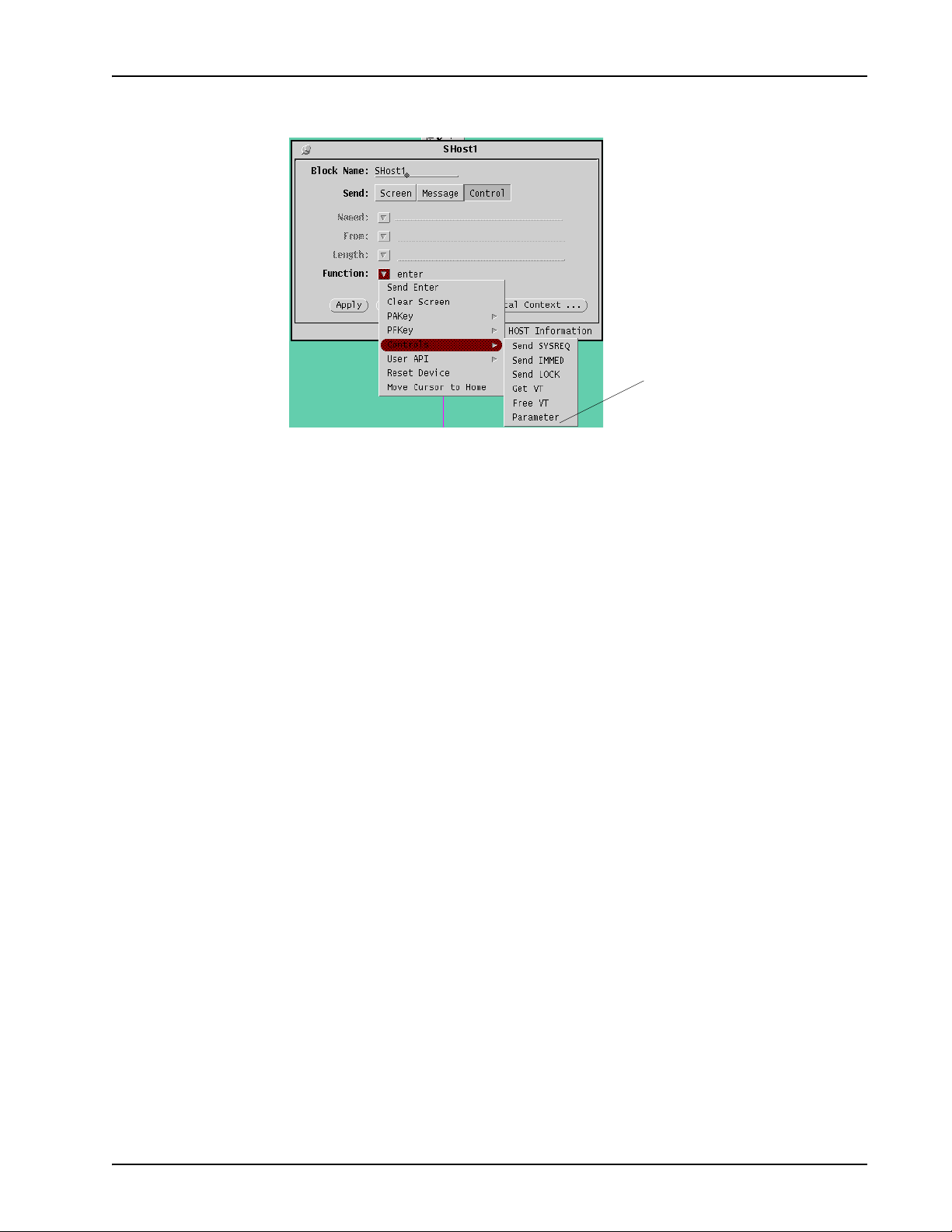
Receive Host Block
BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
parameter option
Asynchronous Operation
The Asynchronous checkbox is replaced by the Wait checkbox. Receive Host operates
asynchronously when the Wait checkbox is unchecked.
Send Fax Block
Fax Composition Removed
The Fax Composition feature is not supported. All controls and options used to create
and store composed faxes are removed.
Send Fax from TIFF File
PeriProducer 3.00 supports sending faxes directly from TIFF format files. TIFF faxes
no longer need to be imported into a MultiMedia File and accessed by a media storage
token.
Fax Mode Removed
PeriProducer 3.00 supports only Group 3 faxes.
Receive Fax Block
Receive Fax Direct into TIFF File
Applications can save an incoming fax directly to a TIFF-format file. In previous
versions of PeriProducer, faxes were stored in MultiMedia Files and had to be
exported to individual TIFFs.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 23
Page 24

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Local Station ID
The user can specify the Local Station ID (which typically represents the phone
number of the station receiving the fax) in the block. The Local Station ID is typically
displayed on the transmitting fax machine.
Fax Mode Removed
PeriProducer 3.00 supports only Group 3 faxes.
Originate Block
Moved Functions
All bridging functions are moved to the new 3.00 Bridge Block. Hookflash is moved
to the Call Control Block. The End Transfer function is deleted and the user can use
the Disconnect block instead.
Record Block
Asynchronous Recording
Asynchronous recording provides an unlimited duration message. Asynchronous
recording is explicitly started and stopped by Begin and End functions of the Record
block.
Moved Functions
Element deletion functions are moved to the Media Operations block.
Resource Block
Asynchronous Execution Changes
There is no longer an Async checkbox in the Resource block. To perform the resource
receive asynchronously, clear the Wait box.
Discontinued Features and Functions
Fax Composition
Fax composition is not supported in PeriProducer 3.00. Faxes to be sent must be
created by external applications or received (and stored for later use) by the BCM.
Hardware Properties Window
The Hardware Properties Window is removed.
Page 24 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 25

BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
Unsupported Resources
PeriProducer 3.00 no longer supports the following resources:
•mps
•abb
•asdi
•ast
•iwr
•ppd
•modem
•mts
•iscp
•ctx
•lcr
Obsolete Functions
The Media Operations block in PeriProducer has rendered obsolete the file-tomessage, message-to-item and message-to-file functions.
Other PeriProducer Changes
Enhanced Condition Data
Condition Data is now returned as a data structure consisting of different field/value
pairs. To access the expanded condition data, use the System block’s "Get Condition
Data" function and specify the appropriate response folder (templates provided in
%PPROPATH%\sample\folders). To access all of the condition data, the folder
must have data cards defined as the same name and type as the associated condition
data field. The data for one field only can be obtained by specifying a datacard whose
name matches the desired field.
The condition data for many conditions have a Status field. The Status field value is
automatically copied into the System folder’s ConditionData card.
Environment Options
Many PeriProducer 2.30 Environment options are rendered obsolete or replaced by
new environment options, block built-in functions or both, in PeriProducer 3.00. The
following table lists the 2.30 Environment options and the analogous 3.00 option (if
any). Comments are provided where appropriate.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 25
Page 26

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
2.30 Environment Option 3.00 Equivalent
Phone Environment
answer Unsupported as environment option. Use the Answer block
first DtmfFirst (Application and System Environment options)
inter DtmfInter (Application and System Environment options)
keepterm Unsupported as environment option. Use the "Retain" option
termchar Unsupported as environment option. Use the Edit Sequence
total LineTotalCall (Application and System Environment options)
typeahead Unsupported
Phone Line Task Environment
Environment Options Conversions Sheet 1 of 3
(Answer function) to answer a call.
(for the termination character) in Edit Sequence block.
block to enable/set a termination character.
backsp Unsupported as environment option. Use the Edit Sequence
block to enable/set a backspace edit sequence.
delete Unsupported
eXtext Unsupported. Use the Edit Sequence block to enable/set
user edit sequences.
Phone Resource Server Environment
prs Unsupported
tstop Unsupported as environment option
Message Recording Environment
intersil RecInterSil (Application and System Environment options)
Call Progress Detection Environment
cpansup Unsupported
pickup Unsupported
Speech Management Environment
clear Supported for legacy applications only. Use the Abort block
with the "Caller I/O Only" option enabled.
vioabort Unsupported as environment option. Use the Abort block.
Host Environment
er er
freevt Supported for legacy applications only. Use the Send Host
block "Free VT" (in Control > Function > Controls) option.
Page 26 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 27

BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
Environment Options Conversions Sheet 2 of 3
2.30 Environment Option 3.00 Equivalent
getvt Supported for legacy applications only. Use the Send Host
block "Get VT" (in Control > Function > Controls) option.
headermode headermode
hostctl hostctl
intime intime
parameter Supported for legacy applications only. Use the Send Host
block "parameter" (in Function > Controls) option.
refer refer
rfno rfno
session session
setaid setaid
unlocks unlocks
usepool usepool
Advanced Phone Line Management
phone Unsupported as environment option
Optional Exception Conditions
rngback Unsupported as environment option
uedit3 Unsupported as environment option (in the context of taking
a digital system out of wait for an outdial complete message)
Generic Environment Options
Phone Line Manager
Options
Vengine Options Vengine Options
VENGINE Environment
alarmdbtask alarmdbtask
apprestart apprestart
centurymark centurymark
debug debug
deltimedcall deltimedcall
hnowait Unsupported (a corresponding VENGINE runtime option is
Superseded by "Application and System Options"
available)
intermsg intermsg
maxmessage Unsupported
mode mode
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 27
Page 28

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
2.30 Environment Option 3.00 Equivalent
notice notice
numset numset
rscertime rscertime
rscintime rscintime
setvpsline setvpsline
softterm softterm
speak speak
timedcall timedcall
unnotice unnotice
vmstimedcall vmstimedcall
vpsrcvtime vpsrcvtime
webtimeout webtimeout
Environment Options Conversions Sheet 3 of 3
Conditions
When a PeriProducer 2.30 application is opened in 3.00, PeriProducer attempts to
automatically convert handle conditions to their counterparts in 3.00. Condition
conversions shown with a preceding dollar sign ("$") are displayed in the application
as the 2.30 condition but are automatically converted to the appropriate 3.00 condition
at runtime.
The following table lists the 2.30 condition, the corresponding 3.00 condition (if any),
and, if applicable, how PeriProducer 3.00 converts the condition when a 2.30
application is ported to 3.00.
Conditions Conversion Sheet 1 of 10
2.30 Condition 3.00 Condition Conversion
abend abend abend
addfail importfail w/Status
"ErrInUse" in condition data
addsucc importcmp importcmp
altlinkdown altlinkdown altlinkdown
ansfail answerfail answerfail
$addfail
asrdet asrdet asrdet
asyncdata Unsupported
asyncfail Unsupported
Page 28 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 29

BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
Conditions Conversion Sheet 2 of 10
2.30 Condition 3.00 Condition Conversion
autofail detinputfail detinputfail
autotim autotim autotim
avserr avserr avserr
badoperation badoperation badoperation
badparameter badparameter badparameter
calltim calltim calltim
carloss Unsupported
ccs7cc ccs7cc ccs7cc
chartim getinputfail w/Status
"ErrInter" field in condition
data
cmrhigh Unsupported
cmrlow Unsupported
comfail comfail comfail
conn answercmp answercmp
crefer Unsupported
crepeat Unsupported
crepmax Unsupported
cticond cticond cticond
ctidown ctidown ctidown
ctifail ctifail ctifail
ctiup ctiup ctiup
ctxcc Unsupported
ctxfailcc Unsupported
ctxokcc Unsupported
getinputfail
cvoice Unsupported
dcdown Unsupported
dcup Unsupported
deadlock deadlock deadlock
delcomp delcmp delcmp
delfail delfail delfail
dialtn Unsupported
disable Unsupported
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 29
Page 30

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
2.30 Condition 3.00 Condition Conversion
disc Dependent upon event that caused disc condition.
Conditions Conversion Sheet 3 of 10
disc (caller hangup) $disc
disccmp (system-initiated
disconnect)
discfail discfail w/Status field in
condition data
dtmfzl recordfail w/Status
"ErrZeroLengthDTMF" in
condition data
dupkey dupkey dupkey
dupvalidx dupvalidx dupvalidx
enable Unsupported
endfail discfail $endfail
endfile endfile endfile
error error error
ertimeout Dependent upon event that caused ertimeout condition
ertimeout (gen’d by
VENGINE)
hrcvmapfail w/Status
"ErrTimeout" in condition
data (failed receive map)
$disc
$discfail
recordfail
$ertimeout
$ertimeout
hrcvtxtfail w/Status
"ErrTimeout" in condition
data (failed receive text)
expired expired expired
faxdet faxdet faxdet
forcefree forcefree forcefree
forward Unsupported
fromphone fromphone fromphone
frstim getinputfail w/Status
"ErrFirst" in condition data
ftomfail Unsupported
ftomsucc Unsupported
$ertimeout
getinputfail
Page 30 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 31

BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
Conditions Conversion Sheet 4 of 10
2.30 Condition 3.00 Condition Conversion
getfail Dependent upon event that caused getfail condition
getfail (gen’d by VENGINE) $getfail
getrsrcfail (failed resource
get request)
rcvfaxfail w/Status
"ErrNoFaxAvail" in condition
data (failed receive fax when
fax not available)
sndfaxfail w/Status
"ErrNoFaxAvail" in condition
data (failed send fax when
fax not available)
getvtfail hgetvtfail hgetvtfail
getvtpass hgetvtcmp hgetvtcmp
gotres Dependent upon event that caused gotres condition
getrsrccmp $gotres
rcvfaxcmp $gotres
sndfaxcmp $gotres
green Unsupported
hctloff hctloff hctloff
hctlon hctlon hctlon
$getfail
$getfail
$getfail
heldres Unsupported
hkfcomp hookflshcmp hookflshcmp
hkffail hookflshfail hookflshfail
hostasyncevt hostasyncevt hostasyncevt
hostdown hostdown hostdown
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 31
Page 32

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
2.30 Condition 3.00 Condition Conversion
hostfail Dependent upon event that caused hostfail condition
Conditions Conversion Sheet 5 of 10
hrcvmapfail w/Status
"ErrNoData" or "ErrTimeout"
in condition data (failed to
receive map)
hrcvtxtfail w/Status
"ErrNoData" or "ErrTimeout"
in condition data (failed to
receive text)
hsndmapfail (failed to send
map)
hsndtxtfail (failed to send
text)
hsndaidfail (failed to send
AID key)
hostup hostup hostup
hstatdata hstatdata hstatdata
idle Unsupported
inf Dependent upon event that caused inf condition
inf (gen’d by VENGINE) $inf
rcvfaxfail w/Status
"ErrNoFaxAvail" in condition
data (failure to receive fax)
$hostfail
$hostfail
$hostfail
$hostfail
$hostfail
$inf
recordfail w/Status
"ErrZeroLengthDTMF" or
"ErrZeroLengthSilence" in
condition data (failure to
record CMR message)
intertimeout intertimeout (gend’ by
VENGINE)
invreq invreq invreq
ioerr ioerr ioerr
iscpf iscpf iscpf
isdncc Unsupported
iupdbusy Unsupported
iupdcomp Unsupported
iupdfail Unsupported
lengerr lengerr lengerr
linkdown linkdown linkdown
$inf
$intertimeout
Page 32 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 33

BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
Conditions Conversion Sheet 6 of 10
2.30 Condition 3.00 Condition Conversion
lockfail lockfail lockfail
logdeny logdeny logdeny
lost Unsupported
marshall mailshall marshall
mmfhigh mmfhigh mmfhigh
mmflow mmflow mmflow
modvar modvar modvar
mpscc Unsupported
mpsinfo Unsupported
mpsoc Unsupported
mpsof Unsupported
mtoffail exportfail exportfail
mtofsucc exportcmp exportcmp
nilobjref nilobjref nilobjref
nonexistobj nonexistobj nonexistobj
norecfound norecfound norecfound
norestart norestart norestart
nospace nospace nospace
notfnd notfnd notfnd
notimpl notimpl notimpl
notlogon notlogon notlogon
notopen notopen notopen
oa speakcmp w/Status "Abort"
in condition data
oc Dependent upon event that caused oc condition
speakcmp w/Status "Done"
in condition data (completed
speak request)
sndfaxcmp (completed send
fax)
speakcmp
$oc
$oc
sndrsrccmp (completed
send resource)
$oc
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 33
Page 34

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
2.30 Condition 3.00 Condition Conversion
of Dependent upon event that caused of condition
Conditions Conversion Sheet 7 of 10
of (gen’d by VENGINE) $of
sndfaxfail w/Status
"ErrNoFaxAvail" in condition
data (failed send fax)
sndrsrcfail (failed send
resource)
speakfail (failed speak
request)
ofaxdet Unsupported
orberr orberr orberr
oscoc sndrsrccmp
oscof sndrsrcfail
outbad origfail w/Status
"ErrInvalidLineState" in
condition data
outbsy origfail w/Status "ErrBusy" in
condition data
outcomp origcmp origcmp
outfail origfail w/Status "ErrBusy",
"ErrInvalidLineState",
ErrNoAnswer", or
"ErrRejected" in condition
data
$of
$of
$of
origfail
origfail
$outfail
outnoa origfail w/Status
"ErrNoAnswer" in condition
data
outrej origfail w/Status
"ErrRejected" in condition
data
outvoa Unsupported
pgid pgid pgid
pgml pgml pgml
pgun pgun pgun
prsfree Dependent upon event that caused prsfree condition
prsfree (gen’d by VENGINE) $prsfree
freersrccmp (completed free
resource)
qiderr qiderr qiderr
origfail
origfail
$prsfree
Page 34 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 35

BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
Conditions Conversion Sheet 8 of 10
2.30 Condition 3.00 Condition Conversion
qzero qzero qzero
rcverr rcvrsrcfail $rcverr
rcvnull Dependent upon event that caused rcvnull condition
rcvnull (gen’d by VENGINE) $rcvnull
hrcvmapfail w/Status
"ErrNoData" in condition
data (failed receive map)
hrcvtxtfail w/Status
"ErrNoData" in condition
data (failed receive text)
rcvoice Unsupported
rdcdown Unsupported
rdcup Unsupported
rdisable Unsupported
red Unsupported
refbad transferfail w/Status
"ErrInvalidLineState" in
condition data
refbeg transfercmp transfercmp
refcan disccmp $refcan
reffail transferfail w/Status
"ErrInvalidLineState" or
"ErrRejected" in condition
data
$rcvnull
$rcvnull
transferfail
$reffail
refrej transferfail w/Status
"ErrRejected" in condition
data
reftim calltim $reftim
renable Unsupported
reorder Unsupported
resumefail resumefail resumefail
rgreen Unsupported
ring alertcmp alertcmp
rinfail alertfail alertfail
rlost Unsupported
rngback Unsupported
transferfail
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 35
Page 36

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
2.30 Condition 3.00 Condition Conversion
rred Unsupported
rscoc rscoc rscoc
rscof rscof rscof
rsilence Unsupported
rvoice Unsupported
rxdcdown Unsupported
rxdcup Unsupported
rxdisable Unsupported
ryellow Unsupported
sentcp sndtonecmp sndtonecmp
serverdown serverdown serverdown
setfail ctrlrsrcfail $setfail
Conditions Conversion Sheet 9 of 10
setres ctrlrsrccmp ctrlrsrccmp
silence Unsupported
silzl recordfail w/Status
"ErrZeroLengthSilence" in
condition data
softterm softterm softterm
sqlerr sqlerr sqlerr
sslfail sslfail sslfail
stoptim Unsupported
stpring Unsupported
tcapcc tcapcc tcapcc
tftprecfail tftprecfail tftprecfail
tftprecsucc tftprecsucc tftprecsucc
tftpsendfail tftpsendfail tftpsendfail
tftpsendsucc tftpsendsucc tftpsendsucc
timeres timeres timeres
toomanyrows toomanyrows toomanyrows
recordfail
tophonefail tophonefail tophonefail
ttdata getinputcmp getinputcmp
ttdet ttdet ttdet
Page 36 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 37

BCM - IVR 2.1 Upgrade Overview
Conditions Conversion Sheet 10 of 10
2.30 Condition 3.00 Condition Conversion
ttfail getinputfail w/Status
"ErrFirst" in condition data
uedit0 - uedit3 uedit0 - uedit3 uedit0 - uedit3
unexdata unexdata unexdata
unexhost unexhost unexhost
unexphone unexphone unexphone
valueperr valueperr valueperr
voice Unsupported
vrto vrto vrto
webfail webfail webfail
webtimeout webtimeout webtimeout
xdisable Unsupported
xmtcomp Unsupported
xmtfail Unsupported
yellow Unsupported
$ttfail
Miscellaneous
VRAM Language
VRAM is no longer supported.
Downward Porting of .ppr Source Code
Source code cannot be ported to previous versions of PeriProducer.
MPS Release Level
You must use PeriProducer 3.00 on MPS 2.1 or later.
Transition Issues for the System Administrator
Minor changes to PeriView and PeriView Consolidator impact how System
Administrators administer IVR scripts on the BCMs; however, no functionality has
been lost (see the PeriView 2.1 Users Guide).
System Administrators now manage BCMs through Element Manager (see the BCM
4.0 Networking Configuration Guide).
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 37
Page 38

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Documentation Issues
Issue
Documentation currently refers to hardware as the MPS.
Wherever the documentation uses MPS, assume that this refers to the BCM-IVR,
unless otherwise noted.
Page 38 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 39

Administrator on the
Windows
Workstation
This chapter covers:
1. Windows Workstation
Operating System Upgrade
2. BCM-IVR 1.X Uninstall
Procedures
3. BCM-IVR 2.1 Installation
Procedures
4. BCM-IVR 2.1 Toolkit
Installation
5. PeriView 2.1 and PeriView
2.1 Consolidator Installation
6. Launching Applications in
PeriView
Page 40

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Windows Workstation Operating System Upgrade
If either the Application Developer workstation or the System Administrator
workstation is currently running on Windows NT, both workstations must be upgraded
to the Window 2000 operating system. For more information about upgrade
prerequisites, see Pre-Requisites for the BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade on page 19.
BCM-IVR 1.X Uninstall Procedures
Uninstall Procedures with MPS 2.1 Software and Document CD
If BCM-IVR 1.X is already on the Windows Workstation, follow these procedures to
remove the BCM-IVR 1.X PERI packages prior to installing BCM-IVR 2.1.
1. Ensure PERI packages are installed on the box by either:
a. running the following command:
C:\perl -S perirev.plx outfile=STDOUT
The preceding command produces an output similar to the following sample.
PERIase 4.7.1
PERIMPSPatch Bundle 7
PERIrel5Patch Bundle 27 BundleCutDate-20031007
PkgCutDate-20020122
PERIfw 1
PERIMPSPatch Bundle 7
PERIrel5Patch Bundle 27 BundleCutDate-20031007
PkgCutDate-20011214
PERIgase 1.0.0
PERIMPSPatch Bundle 7
PERIrel5Patch Bundle 27 BundleCutDate-20031007
PkgCutDate-20020104
PERIglobl 1.1.1
PERIrel5Patch Bundle 27 BundleCutDate-20031007
PkgCutDate-20010611
PERIgrs 2.2
PkgCutDate-20030729
PERIperl 1.0.1
PERIrel5Patch Bundle 27 BundleCutDate-20031007
PkgCutDate-20020116
PERIplic 1.1.1
PERIMPSPatch Bundle 7
PERIrel5Patch Bundle 27 BundleCutDate-20031007
PkgCutDate-20021004
Page 40 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 41

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
PERIppro 2.30
PERIpstu 2.20
PERIrdb 1.2
PERIview 1.0.0
b. by clicking Setting > Control Panel > Add/Remove
PERIMPSPatch Bundle 7
PERIrel5Patch Bundle 27 BundleCutDate-20031007
PkgCutDate-20010427
PERIMPSPatch Bundle 7
PERIrel5Patch Bundle 27 BundleCutDate-20031007
PkgCutDate-20010427
PERIMPSPatch Bundle 7
PERIrel5Patch Bundle 27 BundleCutDate-20031007
PkgCutDate-20020117
PERIMPSPatch Bundle 7
PkgCutDate-20020516
.
The Add/Remove list contains the list of all PERI packages to be uninstalled.
2. Back up old license files by copying C:\Program
Files\Nortel\PERIplic\etc\plservrc to a safe location.
If you are upgrading your operating system from Windows NT to Windows 2000,
back up old license files to an external media other than the Windows Workstation.
3. Insert the MPS 2.1 Software, Documentation and Update CD and run
PERIinstaller\setup.exe.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 41
Page 42

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
4. Select Uninstall when the Select Components window appears.
5. The following window appears. Select YES.
6. After the system has rebooted, select Add/Remove Programs from the
Control Panel menu to confirm that all PERI packages are removed.
Page 42 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 43

BCM-IVR 2.1 Installation Procedures
The installation of the BCM-IVR 2.1 is a three-part process:
a. Installation of PeriProducer 3.00 and PeriStudio 2.20
b. Installation of the BCM-IVR 2.1 Toolkit
c. Installation of the License
During these installation procedures, you may be prompted to reboot a number of
times. As well, the system may reboot automatically after installing a number of
packages.
Installing PeriProducer 3.00 and PeriStudio 2.20
1. From the MPS 2.1 Software, Documentation and Update CD, run
PERIinstaller/setup.exe.
2. Select Install when the Select Components window appears.
Administrator on the Windows Workstation
3. The Configurations window appears. Select the configuration you wish
to install and click Next.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 43
Page 44

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
4. Select Typical when prompted to select the type of installation. Click
Next.
Nortel highly recommends Typical installation. Only users with the most advanced
understanding of BCM-IVR systems and PERI packages should attempt Custom
installation.
Page 44 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 45

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
After selecting Typical Installation, the following window appears.
Click Yes.
In a Typical Installation, the PERI packages install in the following order:
PERIperl > Auto Reboot > PERIfw > PERIglobl > PERIgrs >
PERIppro > PERIpstu > PERIplic > PERIrdb > Auto Reboot
5. From the MPS 2.1 Software, Documentation and Update CD, install any
PERI patch or patch bundles (for example,
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9.exe) in the Patch folder. If the patch
or patch bundle installs successfully, the following message appears:
6. If the Windows Workstation is used as a statistics collector node (see MPS
2.1 PeriReporter User Guide), install any patches in the Patches >
Collector folder on the MPS 2.1 Software, Documentation, and Update
CD.
7. When all of the patch bundles (if any) have been successfully installed,
open the Services window.
Note the presence of the Nortel Networks License Service and the PeriView Data
Provider Service. The Nortel Networks Startup Service is not present.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 45
Page 46

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
You must manually install the Nortel Networks Startup Service.
8. Install the Nortel Startup Service by entering the following command:
perisvc -install -dispname “Nortel Networks Startup
Service”
9. Confirm that srp is running by entering the following command:
srp -status
The preceding command produces an output similar to the following:
C:\WINNT\system32>vsh
vsh#common.0,gen/JVARGH-2 {1} -> srp -status
Page 46 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 47

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
NODE:PORT USER PID LINE STATE ENTERED
STATE FLAGS CMDLINE
JVARGH-2:5999 SYSTEM 15900 - RUNNING Sep 15
15:52:40
C srp
Confirm that Nortel Networks Startup Service is running by opening Services.
10. Ensure PERI packages are installed on the Windows workstation by
running the following command:
C:\>perl -S perirev.plx outfile=STDOUT
C:\>perl -S perirev.plx outfile=STDOUT
PERIase 5.0.0
PERIfw 1
PERIglobl 2.2.0
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9 BundleCutDate-20050223
PkgCutDate-20020917
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9 BundleCutDate-20050223
PkgCutDate-20011214
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9 BundleCutDate-20050223
PkgCutDate-20020917
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 47
Page 48

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
C:\>perl -S perirev.plx outfile=STDOUT
PERIgrs 2.2
PERIperl 1.0.1
PERIplic 1.2.0
PERIppro 3.00
PERIpstu 2.20
PERIrdb 2.0
BCM-IVR 2.1 Toolkit Installation
Introduction
When all the PERI packages for BCM-IVR 2.1 are successfully installed, you can
install the BCM-IVR 2.1 Toolkit.
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9 BundleCutDate-20050223
PkgCutDate-20030729
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9 BundleCutDate-20050223
PkgCutDate-20020116
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9 BundleCutDate-20050223
PkgCutDate-20030213
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9 BundleCutDate-20050223
PkgCutDate-20021017
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9 BundleCutDate-20050223
PkgCutDate-20030220
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9 BundleCutDate-20050223
PkgCutDate-20030310
If you already had the BCM-IVR Toolkit installed prior to upgrading to BCM-IVR
2.1, Nortel recommends that you remove it prior to installing BCM-IVR 2.1 Toolkit.
Previous versions of BCM-IVR Toolkit were not removed during the uninstall
procedures described on page 40.
The BCM-IVR Toolkit is a graphical user interface (GUI) designed to allow
applications to perform BCM platform-specific operations. The BCM-IVR Toolkit
contains the feature extensions shown in the BCM-IVR Toolkit Feature Summaries
table on page 49.
Page 48 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 49

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
Table 1: BCM-IVR Toolkit Feature Summaries
Set Call Data: Associates data (for example, PIN,
Credit Card Number, and so on) with a specific call.
Up to five strings of data can be stored per call.
Get Call Data: Retrieves data that was previously
stored using Set Call Data.
Park Call: Suspends a call so that another device on
the BCM system can retrieve the call. A parked call is
connected to either a silence audio stream or the
Music On Hold input of the BCM until it is retrieved.
Check Park Status: Checks the status of a parked
call in the system. The Check Park Status operation
indicates whether a timeout has occurred, the call has
been automatically unparked and returned to the
application, or the caller has disconnected.
Begin Page: Attaches the voice port to a paging
system. When combined with the Park function,
BCM-IVR system parks a call and issues a page
advising personnel of the call (and the code to
retrieve it).
End Page: Disconnects the voice port from the
paging system.
For more information about the functionality of the BCM-IVR Toolkit, see the
PeriProducer Toolkit for the BCM-IVR
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 49
Page 50

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Installing the BCM-IVR Toolkit
1. On the BCM-IVR Toolkit CD, open READ_1st.htm.
2. Click the BCM Toolkit link to execute the toolkit installation.
3. Reboot the system.
The BCM-IVR Toolkit has six block functions.
License Service Installation
The following steps apply to users who are upgrading from IVR 1.X tools to IVR 2.1
tools (PeriProducer 2.1 and PeriStudio 2.1 to PeriProducer 3.00 and PeriStudio 2.20).
Users who are installing IVR 2.1 for the first time should consult the IVR Installation
and Configuration Guide.
1. Obtain the MAC address of the IVR workstation where the IVR
development tools (for example, PeriStudio 2.20 and PeriProducer 3.00)
reside by issuing the following command at the dos prompt:
c:\> plicnum
The plicnum command produces an output containing the MAC address of the
workstation.The command output is similar to the following sample output:
Interface Address (Interface #0) --> 0:6:5b:da:51:3f
Interface Host Name --> BCMWKSTN-1
Page 50 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 51

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
Record the MAC address shown in the Interface Address field.
2. Contact Nortel Technical Support at 1-800-4NORTEL. Select Option 5 >
Option 1. Tell the Nortel Technical Support prime that you need to
produce a BCM PeriProducer keycode or BCM PeriStudio keycode
(license files). These files are necessary to enable License Service
installation.You must provide the Nortel Technical Support prime with
the following information:
a. The MAC address of the workstation where the IVR development
tools reside,
b. The existing IVR 1.X license file that you backed up to a safe place
(see instructions page 41). You must send the existing license file by
email to the Nortel Technical Support prime, and
c. The authorization numbers you received when you purchased the
PeriProducer (NTAB4211) and PeriStudio (NTAB4210) tools.
The Nortel Technical Support prime will send you the necessary keycode for license
service installation by email after receiving all the necessary information listed above
(see a, b and c).
3. When you receive the keycode file, save it to:
c:\Program Files\Nortel\PERIplic\etc
4. Select Start > Settings > Control Panel > System. Point the
LSHOST System variable to the license server. In the following example,
the local host is BCMWKSTN-1:
5. Select Settings > Control Panel > Admin Tools > Services and
start the licensing service.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 51
Page 52

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
6. Confirm that the license server obtained the appropriate licenses and
activated them on the workstation by entering the command:
The preceding command produces an output similar to the following sample output
from a workstation with hostname BCMWKSTN-1:
C:\>plicmon BCMWKSTN-1
Available Licenses from Server : BCMWKSTN-1
Product: PERIPRO 1.1
Product: PERISTUDIO 1.3
Licensed to ethernet: 0:6:5b:da:51:3f
Product: plicd 1.2
C:\>plicmon <hostname>
Licensed to ethernet: 0:6:5b:da:51:3f
Maximum users is: 355 Refresh every 360 seconds
Maximum users is: 355 Refresh every 360 seconds
Licensed to ethernet: 0:6:5b:da:51:3f
Maximum users is: 355 Refresh every 360 seconds
7. Select Start > Settings > Control Panel > Vision
Communications > Tranports and confirm that TCP-Unix is
enabled.
Page 52 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 53

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
8. Restart the XVision server.
9. Go to Start > Programs > Nortel and launch the licensed package.
PeriView 2.1 and PeriView 2.1 Consolidator Installation
Overview
PeriView 2.1 is an integrated systems management application suite that provides full
administration and control over BCM self-service platforms. It is used by BCM-IVR
2.1 System Administrators to manipulate and view network activity and to deploy and
maintain applications in the network environment.
PeriView Consolidator is the communications hub for BCM-IVR system
administration. The System Administrator remotely manages the BCM-IVR system
by pointing any User PC web browser to the PeriView Consolidator workstation. The
PeriView Consolidator workstation communicates with and collects data from the
BCMs. The System Administrator also administers the BCM-IVR 2.1 system directly
from the PeriView Consolidator workstation.
For additional information, see BCM-IVR 2.1 Configuration on page 18.
The PeriView Consolidator Workstation runs both the Apache Web Server and the
MPS Manager Data Provider (MMDP). The PeriView Consolidator MMDP
communicates with MMDPs running on the BCMs and collects information.
The BCM MMDPs always run in service mode. An MMDP process in service mode
allows another, higher-level MMDP process such as PeriView Consolidator to
establish a constant and persistent connection.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 53
Page 54

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Installing BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriView Consolidator
1. From MPS 2.1 Software, Documentation and Update CD, select
Preinstall and install the JAVA runtime or SDK.
2. From the MPS 2.1 Software, Documentation and Update CD, select
PERIinstaller/setup.exe.
3. Select periview-workstation.
4. When prompted to select an installation type, select T
YPICAL.
Page 54 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 55

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
When the following message appears, click Y
ES.
During a Typical PeriView Consolidator installation, packages are installed in the
following order:
PERIperl > Auto Reboot > PERIfw > PERIglobl > PERIgrs >
PERIppro > PERIpstu > PERIplic > PERIrdb > PERIpdp >
PeriView > Auto Reboot
If PeriView Consolidator is being installed on the BCM-IVR 2.1 Developer
Workstation, only PERIpdp and PeriView need to be installed because the other
packages were installed in the PeriProducer and PeriStudio upgrade steps (on page
43).
5. Select Yes to Apache Web Server installation during the PERIdist
installation if Apache Web Server is not already installed on the PeriView
Consolidator Workstation.
6. Select Yes when prompted to install web-based PeriView during the
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 55
Page 56

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
PeriView installation.
You may be required to stop Microsoft Internet Information Server during the
installation of web-based PeriView.
7. Install any PERI service patches on the MPS 2.1 Software,
Documentation and Update CD (for example,
MPS2.1Patch_Bundle_9.exe). When the following message appears,
patches are successfully installed:
Click OK.
8. Confirm installation of PeriView and PERIpdp 2.1 from the command
line by entering:
C:\>perl -S perirev.plx outfile=STDOUT
9. In C:\Program Files\Nortel\PERIpdp\etc, back up the
userdb.xml file.
10. Copy the file userdb.xml.BCM from the BCM-IVR Toolkit CD
Page 56 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 57

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
to overwrite
C:\Program Files\Nortel\PERIpdp\etc\userdb.xml.
The userdb.xml.BCM file contains the administrative plugins required for BCMIVR management.
11. Restart Apache and PeriView Data Provider services. Ensure the
PeriView Consolidator host name appears in C:\Program
Files\Nortel\PERIpdp\etc\mmdp.cfg, as shown here:
12. If you are managing the BCM-IVR system from a browser located outside
the local host, change permissions in
C:\ProgramFiles\Nortel\PERIdist\apache\conf\httpd.conf
13. From Services, restart Apache web browser.
14. Ensure PeriView Consolidator is running by pointing the Apache web
browser to the PeriView URL:
http://<Consolidator IP>/periview/Periview.html
a. In the UserID box, enter Administrator.
b. In the Password box, enter root.
c. Check that the Host box contains the PeriView Consolidator IP
address.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 57
Page 58

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
d. Check that the Port box contains “9191”.
e. Click OK to log on.
You are now ready to add the BCM nodes to the system.
15. Click C
ONTROL CENTER on the Management toolbar.
16. Select MMDP Configuration.
Page 58 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 59

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
17. Click Add to add a data provider.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 59
Page 60

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
18. In the Add Data Provider dialog box, enter the host name of the new
data provider (for example, BCM1000) in the Data Provider Name
box.
To ensure the Data Provider host name translates to its corresponding IP address,
make a DNS entry or place an entry in the consolidator host file:
C:\winnt\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
19. Select the BCM1000 as the Service Data Provider by selecting Service
Data Provider. Select the PeriView Consolidator workstation as the
Parent Data Provider.
20. At the bottom of the window, select the Will the Data Provider
monitor local components checkbox. This triggers the BCM1000’s
MMDP process to connect to the local srp to get state information.
21. Click Add.
The MPS Manager Data Provider Configuration Tool window appears showing
a hierarchy of two MMDPs. The PeriView Consolidator MMDP (i.e. Windows 2000
MMDP) appears above the BCM1000 MMDP, indicating that it is the parent service
provider.
Page 60 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 61

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
Select BCM1000 from the Data Providers list box in the upper left of the window or in
the hierarchy. The BCM1000 is listed as a monitored system.
22. Click S
AVE. If the information from the subsequent steps is entered
correctly, the BCM1000 IP address and node are contacted. The icons
representing the BCM-IVR Service Data Providers (i.e. BCM1000) turn
green when a connection is established.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 61
Page 62

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Launching Applications in PeriView
This section describes how to launch an IVR application from the user PC and send it
to the BCM. The section includes the following procedures:
• loading application .vex files (Loading Application .vex fileson page 62)
• loading user-defined call function files (Loading User Defined Call Function
Fileson page 65)
• assigning and starting applications (Assigning and Starting Applicationson
page 66).
Loading Application .vex files
Prior to launching an application in PeriView, ensure that all system connections are
established and running. All elements of the system (such as the BCMs and the
Windows host workstation) that are running appear as green icons in the left area of
the PeriView launch screen.
1. Ensure Windows host SRP is running using Settings>Control
Panel>Services Startup.
2. Launch PeriView.
3. In the PeriView launch screen, click Application Configuration to
start the IVR setup.
In the preceding fiugure, the Windows host workstation is JVARGH. The icon
representing the host worktation JVARGH is green in the left area of the PeriView
launch screen.
Page 62 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 63

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
4. Click Choose. The Choose Application window appears showing
folders on the selected node.
5. From the Select Node list, select the Windows host.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 63
Page 64

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
6. Browse the .vex folder. In the following figure, the .vex folder is located
in C:\Program Files\Nortel\PERIppro\sample and
contains only one application (numdemo.vex). Files with .vex
extensions are the compiled output of PeriProducer source files.
7. Select the desired .vex file. Click Load then click Save.
Note that PeriView automatically creates the .acfg file when a .vex file is loaded
to the Application Configuration utility.
Page 64 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 65

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
Note that you cannot have two MPS components with the same component number of
the same network.
Loading User Defined Call Function Files
Code for User Defined Call Functions is compiled on a Fedora NCGL workstation. A
.so file is generated and sent to the Windows host for transfer to the BCM. C/C++ Call
Function files are those with .so extensions. See “Building C/C++ Call Functions
Libraries” on page 89.
To deploy User Defined Call Functions (C/C++ Call Function files) to the BCM, click
Change Option in the Application Configuration window.
Click Add. Browse the Windows host folder where .so files are located and select
the desired .so file.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 65
Page 66

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Click Deploy to assign the .so file to the BCM.
Assigning and Starting Applications
1. Return to the PeriView launch screen and click APPLICATION
ANAGEMENT. The Application Management window appears.
M
In the Choose pane of the Application Management window, you can select the
desired BCM nodes and line numbers
Page 66 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 67

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
2. In the Choose field, select the Filter tab and select the desired BCM
component from the Components list.
3. Enter the BCM component number in the T
4. In the L
INES boxes, select the lines where the IVR application runs. In the
YPE box.
following example, the IVR application runs on lines 1 to 2:
5. Select the application to be deployed to the BCM from the A
PP list.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 67
Page 68

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
6. To enter the information in the Choose pane in the for a location listed
in the Locations list, select the desired selection in the Locations l is t.
Page 68 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 69

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
The application selected is represented by a Telephone icon in the Locations list.
Note that the Telephone icon is yellow. This indicates that no applications are
currently running on the selected BCMs.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 69
Page 70

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
7. In the Action pane, select Assign and Start .
Note that the application Telephone icon is yellow, indicating that no application is
currently running on the selected BCM ports.
8. Click Apply to activate the selected application to the desired BCM
ports.
Page 70 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 71

Administrator on the Windows Workstation
The application Telephone icon changes from yellow to green when the application is
successfully assigned and started.
The PeriView launch screen shows the application running on two BCM ports.
To validate the IVR application, use any phone connected to your BCM system to call
the IVR DN. If you do not know the IVR DN, proceed to step 9.
9. You can obtain the IVR DN by using the vsh command.
a. From the Interactive Voice Response panel, select the
Advanced Commands tab. The Advanced Commands tab
appears.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 71
Page 72

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
b. From the Command list, select the vsh command.
c. In the Arguments box, type the arguments you want to add to the
d. Click Run Command. The output appears in the Results panel.
The IV R D N a ppear s i n t he Por t G roup D N l in e of th e o ut put.
vsh command (bim repvoicecti).
When you obtain the IVR DN, validate the IVR application by using any phone
connected to your BCM to call the IVR DN.
Page 72 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 73

Administrator on the
BCM 4.0 Platform
This chapter covers:
1. Numbering Components
using Element Manager
2. Enabling Host
Communications with
Element Manager
Page 74

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Numbering components using Element Manager
Element Manager is a management application for performing all day-to-day BCM
administration, configuration and management functions. Element Manager resides on
the System Administrator’s Windows 2000 workstation.
Using Element Manager’s graphical user interface, the System Administrator can
easily configure and manage BCM nodes—whether from a PC directly connected to
the BCM or over a LAN, internet, or dial-up connection (ISDN or analog).
With Element Manager, all management tasks, including configuration changes,
alarm monitoring, adding features with keycodes and managing backups, can be
performed remotely.
In order to manage the BCMs using Element Manager, the BCMs must added to
Element Manager’s administration list.
1. Launch Element Manager.
2. In the Task Navigation pane, expand the Applications folder and
select IVR.
Page 74 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 75

Administrator on the BCM 4.0 Platform
3. The Interactive Voice Response window with three tabs appears.
Select Basic Settings.
To administer many IVR systems on different BCMs, IVR systems must be assigned
different node numbers. To change a node number, type in the new number and select
the Tab key on your keyboard to exit from the box.
4. IVR service shuts down and restarts after a node number change.
Enabling Host Communications with Element Manager
The Nortel IVR Keycode files enable host access. You do not have access to IVR Host
Access Service without loading the necessary Keycode files in Element Manager.
The keycode files (license files) for Host Access Licensing in BCM/IVR 2.1 are
different from those in BCM/IVR 1.X.
Contact your Nortel Technical Support organization to obtain the new license file for
host access.
Prior to contacting your Nortel Technical Support organization, obtain the MAC
address for the BCM interface that communicates with the Host:
1. Launch Element Manager
2. In the Task Navigation Panel, click the Configuration tab.
3. Expand the Resources folder and click Network Interfaces.
4. Select the LAN interface you want to use to communicate with the
external host (for example, LAN 1). The Details for Protocol appears
with the Interface tab displayed
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 75
Page 76

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
5. Record the information that appears in the MAC Address box. This is
the MAC address of your BCM.
Retrieving existing Host Communications License File
1. Create a shared folder on the PC that will receive the Host
Communications License File from the BCM.
Page 76 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 77

Administrator on the BCM 4.0 Platform
2. Log on to Unified Manager on your BCM 3.X system.
3. Click Maintenance.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 77
Page 78

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
4. Select Attach Shared Volume. Select the shared folder you created
previously (see page 76) to be accessible by the BCM.
Page 78 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 79

Administrator on the BCM 4.0 Platform
5. Return to the Maintenance page and select Execute a Command.
Copy the Host Communications License File from the BCM to the shared
folder that you previously created by entering the command in the
Command box.
Getting and Applying the License File
Contact Nortel Technical Support (1-800-4Nortel). Select option 5 > option 1.
Tell the Nortel Technical Support prime that you need assistance in producing a
keycode for BCM/IVR. When you are connected with a Level 2 Nortel Keycode
Support Prime, tell the support prime that you need to produce a BCM Host
Communications keycode (license file).
To receive the BCM Host Communications keycode, you must provide the Level 2
Nortel Keycode Support Prime with the following:
• the BCM MAC address
• the existing IVR 1.X license file (you must send an email with the existing
license file attached to the Level 2 Nortel Keycode Support Prime)
• the Authorization numbers obtained from purchasing the PeriProducer
(NTAB4211) and PeriStudio (NTAB4210).
When you receive an email containing the keycode from the Level 2 Nortel Technical
Support Prime, you are ready to load the keycode to the Keycode directory in Element
Manager.
1. Launch Element Manager.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 79
Page 80

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
2. In the Task Navigation panel, select the Configuration tab.
3. Expand the Applications folder and click IVR.
4. Enter the node number for the IVR.
5. Click Load File in the Host Access Licenses pane and load the
keycode received from the Level 2 Nortel Technical Support Prime.
After the keycode is installed, the IVR service restarts automatically.
You can now make IVR configuration changes, if any.
For IVR configuration changes, see the Interactive Voice Response Installation and
Configuration Guide.
For BCM configuration changes, see the BCM 4.0 Configuration And Installation
Guide.
Application Resources
For more information about Application Resources, including Service Manager,
Keycode, IVR Advanced Commands, and the Advanced Commands Settings screen,
see the Interactive Voice Response Installation and Configuration Guide.
Page 80 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 81

Developer Upgrade
on Windows
Workstation
This chapter covers:
1. Porting PeriProducer 2.30
Applications to
PeriProducer 3.00
2. Porting Events
3. Conversion Logs
4. Known Conversion Issues
5. Assign and Start
PeriProducer 3.00
Applications
Page 82

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Porting PeriProducer 2.30 Applications to PeriProducer 3.00
To upgrade to PERI products on the Windows Workstation, see Administrator on the
Windows Workstation on page 39.
BCM 4.0 runs IVR applications that are developed with and use PeriProducer 3.00.
PeriProducer 3.00 supports legacy (PeriProducer 2.30) applications. The legacy
applications are converted automatically when they are loaded into PeriProducer 3.00.
Application Porting Considerations
Consider the following when porting the legacy applications:
• Make a copy of the source file and port the copy.
• Back up the source file on another system, external media, or both.
• Save the ported copy as a different name (such as <original_name>300).
Converting Standard PeriProducer 2.30 Applications to PeriProducer 3.00
Porting Events
Applications that used the standard PeriProducer 2.30 are automatically converted by
PeriProducer 3.00. No other setup or configuration procedures are required to convert
the PeriProducer 2.30 legacy applications.
Load into PeriProducer 3.00
Load the PeriProducer 2.30 application into PeriProducer 3.00 as you would any other
application. Conversion takes place automatically. The PeriProducer logo indicates
that the application is changed and needs to be saved.
Using the PeriProducer Command Line to Port Applications
Use the following command line syntax to convert a legacy application:
peripro -c <application>
The preceding command converts the selected .ppr file to an executable .vex file.
For example, to convert numdemo.ppr, enter peripro -c numdemo. You can also
use filename wildcards (e.g. peripro -c num*) to batch-convert applications.
The previous example converts all applications in the current directory whose names
start with num.
During application porting, the following events occur:
• Conditions and environment options are converted when possible. See
“Other PeriProducer Changes” on page 25. See PeriProducer for the
BCM for more information about BCM-specific changes to PeriProducer.
• Blocks are converted to their nearest possible counterparts in 3.00. See
Page 82 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 83

Conversion Logs
Developer Upgrade on Windows Workstation
“PeriProducer 3.00 Block Changes” on page 21. See PeriProducer for
the BCM for more information about BCM-specific changes to
PeriProducer.
• Resources are rendered obsolete. See PeriProducer for the BCM for
more information about BCM-specific changes to PeriProducer.
• The original file is renamed by changing its extension to .p2x
• The PeriPro 2.30 Runtime Behavior is enabled by default. See the
PeriProducer User’s Guide for more information about the 2.30 Runtime
Behavior option.
• A file with name conversionlog_ <application>.txt is created
and contains messages pertaining to the conversion process. A similar file
is created with the extension .html and is in HTML format.
The conversion logs are detailed lists of issues encountered during conversion of
PeriProducer 2.30 applications to PeriProducer 3.00. The conversion logs are written
to the same directory as the source (2.30) application. The logs are named
conversion_appname.txt (in plain text format) and
conversion_appname.html.
Each log entry indicates an application function that required some translation to
become PeriProducer 3.00-compatible. A conversion log is divided into three
categories:
1. Information: An information message indicates a conversion event that
does not affect the functionality of the application. For example, an
information message generates from the conversion of a 2.30 condition
name to a new 3.00 condition name. The application containing the
condition reacts the same way in PeriProducer 3.00; however, it uses a
different condition name.
2. Warning: A warning message indicates that an application successfully
converted but may not work as expected in 3.00. A typical warning
message generates to indicate an obsoleted block setting that does not
affect application function.
3. Severe: This category indicates something requiring manual application
editing for the application to run under PeriProducer 3.00. Severe
messages can include:
• using features or resources no longer supported (see PeriProducer for the
BCM for more information about features and resources that are not
supported in the BCM environment)
• obsolete environment settings, conditions, system datacards that do not
have an equivalent in PeriProducer 3.00 (see “Discontinued Features and
Functions” on page 24).
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 83
Page 84

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Known Conversion Issues
Set Resource Label in 2.30
PeriProducer 2.30 uses a Resource block Set operation to change the external resource
(for example, OSCAR) label. PeriProducer 3.00 converts the Resource (Set) block to
an Environment block that sets the RscLabel parameter and enables the Wait option.
If the Resource (set) block had the failure connector enabled, the Environment block
has the failure connector enabled and connects to the same failure path as in the 2.30
application.
If the 2.30 application explicitly handled the setfail (or setres) condition for a
Resource set (instead of using the failure connector), you must manually edit the
converted application to explicitly handle the envfail (or envcmp) condition. The
setfail (or setres) condition in 2.30 automatically converts to
ctrlrsrcfail (or ctrlrsrccmp) in 3.00. If the resource label change fails in
3.00, the envfail condition occurs, not the ctrlrsrcfail.
Unsupported 2.30 Resources
Several resources from PeriProducer 2.30 are not supported in PeriProducer 3.00. (See
“Unsupported Resources” on page 25.) When an unsupported resource is encountered
during conversion, the unsupported resource is reported in the conversion log file. In
the application, the resource is changed from the resource name to “Unsupported” in
the associated Resource block. Depending on the resource type, you may not be able
to use the application with PeriProducer 3.00.
Resource Block Conversions
If Wait is enabled or a failure connector is available on a 2.30 Resource block, Wait is
enabled on the 3.00 converted block.
Flushing the Speak Prompt Buffer
The PeriProducer 2.30 System block Start Reprompt List function flushes the list of
previously spoken output. This function is still supported in PeriProducer 3.00.
However, Nortel recommends that to flush the output list buffer, use a Resource block
with the Resource field set to Player, the CID field set to System.Default.CID, the
Operation set to Control, and the Send From field set to System.Constants.Flush. This
suggestion action appears in a 2.30 application’s conversion log file.
System Transfer Connection ID Datacard
PeriProducer 3.00 introduces the system datacard TransferCID. The system returns
the Connection ID (CID) of the line that is used for a transfer operation back to the
TransferCID datacard. TransferCID must not be used in PeriProducer 3.00-native
applications to specify a CID for a transfer operation.
Page 84 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 85

Developer Upgrade on Windows Workstation
TransferCID is populated only if the transfer operation is performed synchronously
(Originate block with Wait enabled). If Wait is not enabled, TransferCID stays empty.
During 2.30 to 3.00 conversions, PeriProducer may use TransferCID in this capacity
(to specify a CID instead of receiving a value from the system). However, this is done
only when converting applications.
Assign and Start PeriProducer 3.00 Applications
See “Launching Applications in PeriView” on page 62.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 85
Page 86

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Page 86 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 87

Developer Upgrade on
Fedora Workstation
This chapter covers:
1. Overview
2. Installing Fedora
3. Installing Nortel IVR Plugin
Development Environment
4. Building C/C++ Call
Functions Libraries
Page 88

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Overview
Some application developers create their own Call Functions using the C-language to
supplement the base language constructs.
To run applications that use User Defined Call Functions, Call Functions must be
compiled into shared libraries to be available to VENGINE at runtime. In the
BCM/IVR 2.1 system, Call Functions must be compiled on a Fedora workstation
using the makecall script. Compiled code is then transferred to the Windows
workstation to run on the BCM.
For more information about User Defined Call Functions, see User Defined Call
Functions in the PeriProducer Environment.
The following graphic shows the path to incorporating user-defined call functions in
the BCM/IVR 2.1 system:
Windows User PC
Workstation
User PeriView to install
compiled C/C++ code
The compiled C/C++ code
is transferred back to the
Windows User PC
BCM Linux
Machine
Fedora 3 PC
Run makecall_tux
to compile C/C++
code.
Installing Fedora
Fedora Core 3 is available for download at http://fedora.redhat.com.
Page 88 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 89

Developer Upgrade on Fedora Workstation
Installing Nortel IVR Plugin Development Environment
Transfer the nortel.tgz file on the BCM/IVR Toolkit CD to the /tmp directory on the
Fedora Core 3 machine.
Building C/C++ Call Functions Libraries
1. On the Fedora Core 3 machine, log on as root (or use sudo) and then
change to the root directory: cd /
2. Extract the nortel.tgz file:
tar xzf /tmp/nortel.tgz (or sudo tar xzf /tmp/nortel.tgz)
3. Log on again as a regular user and access the IVR Plugin development
environment in /usr/local/nortel.
A directory tree is available in /usr/local/nortel/README.
4. To build the example, go to the /usr/local/nortel/examples
directory:
cd /usr/local/nortel/examples
makecall_tux Tool
The makecall_tux tool compiles C/C++ code into .so files that are transferred to
the Windows workstation to run on Periview:
makecall_tux [-C libname.a] [-d] {failname[.c[pp]...}
The following options are available with the makecall_tux tool:
Option Description
-C libname.a Library name. Defaults to
/usr/local/nortel/examples/lib/libcall.a
-d Prepare to sue debugger dbx [tool]
-u “ccopt”. C compiler options
-l “ldopt”. ld link options
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 89
Page 90

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
For help on using the makecall_tux tool, type:
./makecall_tux
Usage: makecall_tux [-C libname.a] [-d] {filename[.c[pp]]
...}
-C libname.a library name (default
/home/loucksv/lib/libcall.a)
-d prepare to use debugger dbx[tool]
-u '"ccopt"' C compiler options
-l '"ldopt"' ld link options
5. To compile the sample, type:
The output appears in the /usr/local/nortel/examples/lib directory.
./makecall_tux new-function.c
6. To compile your own code, run the makecall_tux command with
your own file name. For example:
The lib directory must exist before running makecall_tux.
Page 90 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 91

Database Access
Configuration
This chapter covers:
1. Overview
2. Configuring periq on the
Windows Node
3. Configuring sqlclnt on the
Windows Node
Page 92

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Overview
Some applications require access to external databases. BCM-IVR 2.1 supports Host
database access and VTCPD. The system is configured so that database requests from
applications running on BCMs are relayed to an intermediate Windows node where
periq and sqlclnt are running. The Windows node retrieves the information and
relays it back to the application running on the BCM.
The following graphic shows the interaction between the application on the BCM, the
intermediate Windows node, and the external database.
BCM 1
vmst
BCM 2
vmst
Application on
BCM 2 requests
database access
from Windows
Work st at ion
To configure the BCM-IVR 2.1 system for database access, periq and sqlclnt
must run on the Windows node. Both periq and sqlclnt are installed as
components of perirdb in a TYPICAL installation on the Windows workstation
(see Administrator on the Windows Workstation on page 39.) The Windows
workstation can serve as the intermediate Windows node.
To run the database access configuration, additional components are needed from
MPS 2.1 Patch Bundle 9 and additional database patches on the MPS 2.1 Software,
Documentation and Update CD.
Intermediate Windows Node processes
the application’s request and interfaces
with external database
Intermediate
Windows Node
with
periq &
sqlclnt
Database
VMST 3 on the BCM Node
Ensure vmst is running on the BCM node where the applications requiring database
access are running. The following command produces an output showing the list of
active vmst ports and the attached BCM components:
Page 92 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 93

[root@BCM1000 root]#vvpsactive
Install Patches on the Windows Node
To configure remote database access, you must install all the patches found in the
Patches Remote Database folder on the MPS 2.1 Software, Documentation and
Update CD. Install the patches (if any) by double clicking on the executable files in
the folder.
Configuring periq on the Windows Node
To configure periq on the Windows Node, you must edit the gen.cfg file. The
following figure shows a sample gen.cfg file:
Database Access Configuration
In the gen.cfg file, make the following entry for periq:
periq -v NodeA:3 -s16 -a sqlclnt -q odbcq32
The preceding command starts periq and connects the Windows node to vmst number
3 (running on the host BCM) through port 16. Port 16 is the default port for periq
and is configured in $ASEHOME/etc/services. The preceding command also restarts
sqlclnt services and sets the queue name as odbcq32.
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 93
Page 94

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
The following table lists periq attributes and their descriptions:
Attribute Description
-v[host:]vps host and vps number
-s # port number to vms
-P poll new connection poll (default 15 seconds
-q [name:]# [queue name:] number of tellers
-m {g|f} not route GET or FREE to tellers
-m i free tellers on ISSUE FREE from app
-m r return undelivered message to tellers
-m t time message flow
-a {rsc|ports} announce restart to service
periq Attributes
-X {a|s} debug message flow (full or short form)
-X 1 debug queueing
-r {device|file} redirect output (to /dev/tty#,/dev/console)
-H help
Configuring sqlclnt on Windows Node
In the gen.cfg file, make the following entry for sqlclnt:
sqlclnt -v 3 -s 230 -N nodeA -u sa/peri@database -m odbc
-q odbcq32 -P 16 -Q 5
This command specifies the system to start the sqlclnt service and connect it to
vmst 3 on Node A through port 230. Port 230 is one of many available to sqlclnt
and is configured in $ASEHOME/etc/services. The unencrypted connection string to
the database is sa/peri@database. Database mode is ODBC and sqlclnt is part of
queue odbcq32. The sqlclnt service communicates with periq through port 16
with a ping rate of 5 seconds.
The following table lists sqlclnt attributes and their descriptions:
sqlclnt Attributes
Attribute Description
-v # vps number
-s port port number to use
Page 94 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 95

Database Access Configuration
sqlclnt Attributes
Attribute Description
-N host VMS host machine (default - local)
-P port PeriQ port (default - any)
-m queue_type ‘oracle’, ‘sybase’, ‘odbc’, ‘db2’ or ‘mssql’
-q name associated queue name
-u
[<usr>[/<passwd>][@<s
erver><odbc
dsn%OEM>]]
-U cryptstring Crypted RDBMS connect string
-l directory Enable SQL Timing, specify directory path to place log files
-S backup user/psswd@server backup/fail over server. If connect string
-B crypststring Crypted RDBMS connect string for backup/fail over server
-c AUTOCOMMIT Enable AUTOCOMMIT
-x Transaction Timeout Transaction Timeout for a database Query (ODBC)
-L Login TimeOut Login TimeOut (ODBC)
-T poll new server connection poll (default 20 seconds)
-R # number of re-cycle attempts (default forever)
-Q ping rate Set ping rate for retrying connection to vmst (default 60 seconds)
-X {s|n} debugging level
-r {dev|file} redirect output
RDBMS connect string. If connect string contains @ or /, use \\
as escape character.
contains @ or /, use \\ as escape character
-H help
# N0064485 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 95
Page 96

BCM-IVR 2.1 Upgrade Guide
Page 96 Nortel Confidential # N0064485 Ver: 1.0
Page 97

Index
Page 98

BCM-IVR 2.0 Upgrade Guide
Symbols
$addfail 28
$disc
30
$discfail
$ertimeout
$getfail
$gotres
$hostfail
$inf
$intertimeout
$oc
$of
$outfail
$prsfree
$reftim
$ttfail
.ppr Source Code
.vex files
30
30
31
31
32
32
32
33
34
34
34
35
37
37
62
A
abend 28
20
Abort
Accessory Toolkit Blocks
acfg file
addfail
addsucc
alarmdbtask
alertcmp
alertfail
altlinkdown
ansfail
answer
Answer Block
answercmp
answerfail
Apache Web Server
Application Developer
Application Resources
Applications
64
28
28
27
35
35
28
28
26
21
Continue on Ring Detect
Get Phone Number
21
29
28
53, 55
19
CDs
External Call Functions
Fedora
Operating System
Software
Upgrade Prerequisites
19
19
19
80
Porting
82
21
19
21
19
apprestart
asrdet
asyncdata
asyncfail
autofail
autotim
avserr
27
28
28
28
29
29
29
B
backsp 26
badoperation
badparameter
BCM/IVR 2.0
Element Manager
Installation
New Features
Operating System
System Configuration
Upgrade Prerequisites
BCM/IVR 2.0 Toolkit
Begin Page
Check Park Status
End Page
Feature Summary
Get Call Data
Installation
Park Call
Set Call Data
BCM/IVR Toolkit
Description
Blocking Execution
Bridge
Business Communications Manager
Description
NCGL
29
29
16
41, 43
16
16
17, 18
19
49
49
49
49
49
48, 49
49
49
48
20
20
16
16
C
Call Conferencing 20
Call Control
Call Progress Detection
calltim
carloss
ccs7cc
centurymark
chartim
clear
26
cmrhigh
cmrlow
20
20, 21
29, 35
29
29
27
29
29
29
Page 98 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 99

Index
comfail
Conditions
conn
Connection IDs
conventions
cpansup
crefer
crepeat
crepmax
cticond
ctidown
ctifail
ctiup
ctrlrsrccmp
ctrlrsrcfail
ctxcc
ctxfailcc
ctxokcc
cvoice
29
28
Conversion Table
29
21
manual
12
26
29
29
29
29
29
29
29
36
36
29
29
29
29
28
D
Database Access Modes
Host
20
Native Mode
ODBC
VTCPD
dcdown
dcup
deadlock
debug
delcmp
delcomp
delete
delfail
deltimedcall
detinputfail
dialtn
disable
disccmp
discfail
Disconnect Block
dtmfzl
dupkey
dupvalidx
29
29
29
27
29
29
26
29
29
29
30
30
Abandoned Call Counter
30
30
30
20
20
20
27
29
21
21
E
Edit Sequence 20
Element Manager
Description
Host Communications
Keycodes
Managing BCMs
Numbering Components
enable
30
endfail
30
30
endfile
Enhanced Condition Data
Environment Options
Conversion Table
er
26
error
30
ertimeout
expired
exportcmp
exportfail
eXtext
30
30
33
33
26
16, 74
74
75
74
25
26
F
faxdet 30
65
Fedora
first
26
forcefree
forward
freevt
fromphone
frstim
ftomfail
ftomsucc
30
30
26
30
30
30
30
G
getfail 31
getinputcmp
getinputfail
getrsrccmp
getrsrcfail
getvt
27
getvtfail
getvtpass
gotres
green
31
36
29, 30
31
31
31
31
31
75
74
25
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 99
Page 100

BCM-IVR 2.0 Upgrade Guide
H
Hardware Properties Window 24
hctloff
31
hctlon
31
headermode
heldres
hgetvtcmp
hgetvtfail
hkfcomp
hkffail
hnowait
hookflshcmp
hookflshfail
hostasyncevt
hostctl
hostdown
hostfail
hostup
hstatdata
27
31
31
31
31
31
27
31
31
31
27
31
32
32
32
I
idle 32
importcmp
32
inf
inter
Interactive Voice Response
Interactive Voice Response 2.0
intermsg
intersil
intertimeout
intime
invreq
ioerr
iscpf
isdncc
iupdbusy
iupdcomp
iupdfail
IVR Keycode
28
26
Adminstrative tools
Development tools
Description
16
27
26
32
27
32
32
32
32
32
32
32
75
16
16
K
keepterm 26
L
lengerr 32
license files
License Service Installation
plicd
Line Operations
linkdown
lockfail
logdeny
lost
33
41
50
50
20
32
33
33
M
MAC ID 75
mailshall
Manual
marshall
maxmessage
Media Operations
Microsoft Internet Information Server
MMDP
mmfhigh
mmflow
mode
modvar
MPS Manager Data Provider
MPS Release Level
mpscc
mpsinfo
mpsoc
mpsof
mtoffail
mtofsucc
33
Intended Audience
Organization
8
Scope
11
33
27
20
53
33
33
27
33
37
33
33
33
33
33
33
8
53
N
nilobjref 33
Non-blocking Execution
nonexistobj
norecfound
norestart
Nortel Carrier Grade Linux
Nortel Networks License Service
Nortel Networks Startup Service
Installation
nospace
notfnd
33
33
33
46
33
33
20
16
45
46
56
Page 100 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
 Loading...
Loading...