Page 1

BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
BCM 5.0
Business Communications Manager
Document Status:Standard
Document Number: NN40170-700
Document Version: 01.01
Date: August 2009
Page 2

Copyright © 2009 Nortel Networks, All Rights Reserved.
All rights reserved.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and
recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The
information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks.
Trademarks
Nortel, the Nortel logo, and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Sourced in Canada
Page 3

Task List
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Initial Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Hardware Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
To verify the keycodes using Element Manager............................................................28
To verify the keycodes using Telset ..............................................................................28
To restart the system .....................................................................................................29
Viewing the POST log file ..............................................................................................31
To test the main unit ......................................................................................................33
To troubleshoot the main unit ........................................................................................33
To test the expansion unit .............................................................................................34
To troubleshoot the expansion unit ...............................................................................34
Testing an MBM ............................................................................................................35
Determining why a BCM450 MBM does not appear in Element Manager ....................35
Determining why a BCM50 MBM does not appear in Element Manager ......................36
Troubleshooting the FEM on the BCM450 ....................................................................36
To determine why the ATA 2 does not function.............................................................36
To determine why there is no dial tone at the ATA2......................................................37
To check the ATA2 wiring..............................................................................................37
To perform a Level 1 reset (configuration reset) ...........................................................41
To perform a Level 2 reset (software reset) ..................................................................41
3
Software Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
To check line programming ...........................................................................................44
To restore data from an archive ....................................................................................52
To restore the factory configuration...............................................................................53
To view the BCM software inventory .............................................................................54
To obtain updates from the Nortel Technical Support Web page..................................54
Advanced Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Troubleshooting example 1 ...........................................................................................55
Troubleshooting example 2 ...........................................................................................57
Troubleshooting example 3a .........................................................................................64
Troubleshooting example 3b .........................................................................................64
Troubleshooting example 4 ...........................................................................................65
Troubleshooting example 5 ...........................................................................................66
Troubleshooting example 6 ...........................................................................................71
Troubleshooting example 7 ...........................................................................................71
Recovery trees . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Downloading Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
To download software from the BCM Web page ...........................................................82
Troubleshooting Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Accessing the CLI through a serial connection .............................................................85
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 4

4 Task List
Accessing the CLI through the OAM port ......................................................................85
Understanding System Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
To set Release Reasons ...............................................................................................89
Useful Troubleshooting Links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
To use the Knowledge and Solution Engine..................................................................92
Frequently Asked Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
To perform a backup .....................................................................................................93
To restore data from the BCM .......................................................................................94
Completing a warm or cold reset...................................................................................95
Recovering a lost password ..........................................................................................95
To view an alarm ...........................................................................................................96
To acknowledge an alarm .............................................................................................97
Using the Element Manager to transfer log files............................................................98
Capturing the current configuration ...............................................................................99
Viewing the system health ...........................................................................................100
Viewing specific process states ...................................................................................100
Verify the current software revision .............................................................................101
Viewing the system ID and serial number ...................................................................101
Contacting Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 5

Contents
Chapter 1
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Purpose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Acronyms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Symbols and conventions used in this guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Chapter 2
Initial Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Proper installation and routine maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Network configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Site network map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Logical connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Device configuration information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Other important data about your network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Normal behavior on your network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5
Chapter 3
Hardware Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
LAN IP Packet Capture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Troubleshooting BCM hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Check the power source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Check LED indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Check the wiring connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Verify the keycodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Restart or shut down the system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Power on self test (BCM450 only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Testing basic hardware functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Reset to factory settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Command Line Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Monitoring the boot process (BCM450 only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Chapter 4
Software Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Verify the software version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 6

6 Contents
Verify the keycodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Check the programming of lines and phones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Restoring system data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Verify the software inventory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Chapter 5
Advanced Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Example 1: Cannot dial out from an analog trunk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Example 2: Cannot dial out from a SIP or H323 VoIP trunk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Example 3: IP set is not registering with the BCM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Example 4: Cannot install keycode or invalid keycode application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Example 5: Cannot dial out from digital trunk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Example 6: MeetMe Conferencing commands do not work, or conferencing is busy . 70
Example 7: Unable to apply a software update from a USB storage device . . . . . . . . 71
Example 8: Element Manager incorrectly shows expansion cabinet as empty . . . . . . 72
Example 9: HDD-2 LED is Off after installing second hard disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Example 10: VLAN interfaces cannot communicate with external devices . . . . . . . . . 72
Check line programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Trunk/Line data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Restrictions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Assigned DNs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Viewing the inventory of BCM software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Obtaining software updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Chapter 6
Recovery trees . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
System is not processing calls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Start-up profile fails . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Cannot access BCM450 through Element Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
BCM450 shuts down unexpectedly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Chapter 7
Downloading Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Downloading software from the BCM system webpage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Downloading software from the Nortel web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 7

Contents 7
Chapter 8
Troubleshooting Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Service Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Status and Metrics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Command Line Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Accessing the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Using the Configuration CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Using the Maintenance CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Chapter 9
Understanding System Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Alarms, logs, and traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Reporting for dropped calls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Chapter 10
Useful Troubleshooting Links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Partner Bulletins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Knowledge and Solution Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Using the Knowledge and Solution Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Chapter 11
Frequently Asked Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Backup, restore, and reset operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
How do I back up the database? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
How do I restore the BCM from a previous backup? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
How do I complete a Warm Reset or Cold Reset? Is it safe and will I lose customer data? 94
Password protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
How do I recover a lost password for the BCM? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Fault management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
How do I view Alarms? Can I acknowledge and clear them? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
System and status information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
How do I capture the logs from the BCM? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
How do I capture the current BCM configuration? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
How do I find the BCM system health? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
How do I show specific process states? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
How do I verify current software revision? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
How do I find the BCM450 System ID and Serial Number? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Connectivity problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
What is an Ethernet loop, and how do I avoid creating one? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 8

8 Contents
IP addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Chapter 12
Contacting Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Gathering critical information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Getting help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Can I modify the IP address of the OAM port? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
What are the default IP addresses of the BCM ports? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 9

Chapter 1
Introduction
Business Communications Manager (BCM) 5.0 provides private network and telephony
management capability to small and medium-sized businesses. The BCM system integrates voice
and data capabilities, and IP Telephony gateway functions into a single telephony system. It also
enables you to create and provide telephony applications for use in a business environment.
Purpose
This guide provides procedural information to help you troubleshoot and isolate problems in your
BCM network.
Audience
9
The BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide is for use by network administrators responsible for
maintaining BCM networks. This guide is also useful for network operations center (NOC)
personnel supporting a BCM managed services solution. The following are the considerations to
use this guide:
• be an authorized BCM administrator within your organization
• know basic Nortel BCM terminology
• be knowledgeable about telephony and IP networking technology
Organization
This guide is organized for easy access to information that explains the troubleshooting procedures
associated with using the BCM system. This guide contains information on the following topics:
• Initial Troubleshooting on page 15
• Hardware Troubleshooting on page 17
• Software Troubleshooting on page 43
• Advanced Troubleshooting on page 55
• Recovery trees on page 73
• Downloading Software on page 79
• Troubleshooting Tools on page 83
• Understanding System Messages on page 89
• Useful Troubleshooting Links on page 91
• Frequently Asked Questions on page 93
• Contacting Technical Support on page 105
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 10
10 Chapter 1 Introduction
Acronyms
The following is a list of acronyms used in this guide.
Table 1 List of acronyms
Acronym Description
3DES Triple Data Encryption Standard
AES Analog Encryption Standard
AIS Alarm Indication Signal
BCM Business Communications Manager
BFT Base Function Tray
BRI Basic Rate Interface
CbC Call by Call
CDR Call Detail Recording
CFA Carrier Failure Alarms
CIF Chassis Interface Card
CLID Calling Line Identification
CPE Customer Premises Equipment
CSU Channel Service Unit
DES Digital Encryption Standard
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DN Directory Number
DNS Domain Name Server
DNIS Dialed Number Identification Service
DTM Digital Trunk Module
ES Errored Seconds
HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol
IP Internet Protocol
ISDN Integrated Switched Digital Network
LAN Local Area Network
MBM Media Bay Module
MIB Management Information Base
MGS Media Gateway Server
MOS Mean Opinion Score
MPS Media Path Server
NAT Network Address Translation
NCM Network Configuration Manager
NOC Network Operations Center
NTP Network Time Protocol
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 11
Table 1 List of acronyms
Acronym Description
OOF Out of Frame
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol
PRI Primary Rate Interface
PBX Private Branch Exchange
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network
PVQM Proactive Voice Quality Monitoring
QoS Quality of Service
RAI Remote Alarm Indication
RTP Real-time Transport Protocol
SFTP Secure File Transfer Protocol
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
SSH Secure Shell
SSL Secure Socket Layer
UAS Unavailable Seconds
UPS Uninterrruptable Power Supply
USB Universal Serial Bus
VoIP Voice over Internet Protocol
VLAN Virtual Local Area Network
VPN Virtual Private Network
WAN Wide Area Network
Chapter 1 Introduction 11
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 12

12 Chapter 1 Introduction
Symbols and conventions used in this guide
These symbols are used to highlight critical information for the BCM system:
Caution: Alerts you to conditions where you can damage the equipment.
Danger: Alerts you to conditions where you can get an electrical shock.
Warning: Alerts you to conditions where you can cause the system to fail or work
improperly.
Note: A Note alerts you to important information.
Tip: Alerts you to additional information that can help you perform a task.
Security note: Indicates a point of system security where a default should be changed,
or where the administrator needs to make a decision about the level of security required
!
for the system.
Warning: Alerts you to ground yourself with an antistatic grounding
strap before performing the maintenance procedure.
Warning: Alerts you to remove the BCM main unit and expansion unit
power cords from the ac outlet before performing any maintenance
procedure.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 13

Chapter 1 Introduction 13
Related publications are listed below. For more information, see Nortel Business Communication
Manager Documentation Roadmap (NN40170-119).
Nortel Business Communications Manager 5.0 Administration and Security (NN40170-603)
Nortel Business Communications Manager 450 5.0 Installation—System (NN40170-303)
Nortel Business Communications Manager 450 5.0 Maintenance (NN40170-503)
BCM50 5.0 Installation and Maintenance (NN40170-305)
Keycode Installation Guide (NN40010-301)
Nortel Business Communications Manager 5.0 Configuration—Devices (NN40170-500)
Nortel Business Communications Manager 5.0 Configuration—System (NN40170-501)
Telset Administration Guide (NN40070-604)
CallPilot Telephone Administration Guide (NN40170-601)
CallPilot Contact Center Telephone Administration Guide (NN40170-600)
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 14

14 Chapter 1 Introduction
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 15

Chapter 2
Initial Troubleshooting
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms running
BCM 5.0.
You can better troubleshoot the problems on your network and reduce their impact by preparing
for such events in advance. To do this, you must know the following:
• that your system is properly installed and routinely maintained
• the configuration of your network
• the normal behavior of your network
Navigation
• Proper installation and routine maintenance on page 15
• Network configuration on page 15
• Normal behavior on your network on page 16
15
Proper installation and routine maintenance
For more information about detailed installation information, see Nortel Business
Communications Manager 5.0 Installation—System (NN40170-303).This document also outlines
the routine tasks required for operating the BCM50 and BCM450.
Network configuration
To keep track of your network’s configuration, gather the information described in the following
sections. This information, when kept up-to-date, is extremely helpful when you experience
network or device problems.
• Site network map on page 15
• Logical connections on page 16
• Device configuration information on page 16
• Other important data about your network on page 16
Site network map
A site network map identifies where each device is physically located on your site, which helps
locate the users and applications that are affected by a problem. You can use the site network map
to systematically search each part of your network for problems.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 16

16 Chapter 2 Initial Troubleshooting
Logical connections
With virtual LANs (VLANs), you must know how your devices are connected logically as well as
physically.
Device configuration information
You should maintain online and paper copies of your device configuration information. Ensure
that all online data is stored with your site’s regular data backup. If your site does not have a
backup system, copy the information onto a backup disk (such as a CD or zip disk) and store the
backup disk at an offsite location.
Other important data about your network
For a complete picture of your network, have the following information available:
• All passwords—Store passwords in a safe place. It is a good practice to keep records of your
previous passwords in case you must restore a device to a previous software version and need
to use the old password that was valid for that version.
• Device inventory—It is a good practice to maintain a device inventory, which list all devices
and relevant information for your network. The inventory allows you to easily see the device
type, IP address, ports, MAC addresses, and attached devices.
• MAC address-to-port number list—If your hubs or switches are not managed, you must
keep a list of the MAC addresses that correlate to the ports on your hubs and switches.
• Change control—Maintain a change control system for all critical systems. Permanently store
change control records.
• Contact details—It is a good practice to store the details of all support contracts, support
numbers, engineer details, and telephone and fax numbers. Having this information available
when troubleshooting can save a lot to time.
Normal behavior on your network
When you are familiar with the performance of your network when it is fully operational, you can
be more effective at troubleshooting problems that arise. To understand the normal behavior of
your network, monitor your network over a long period of time. During this time you can see a
pattern in the traffic flow, such as which devices are typically accessed or when peak usage times
occur.
To identify problems, you can use a baseline analysis, which is an important indicator of overall
network health. A baseline serves as a useful reference of network traffic during normal operation,
which you can then compare to captured network traffic while you troubleshoot network
problems. A baseline analysis speeds the process of isolating network problems. By running tests
on a healthy network, you compile normal data for your network. This normal data can then be
used to compare against the results that you get when your network is experiencing trouble. For
example, ping each node to discover how long it typically takes to receive a response from devices
on your network. Capture and save each device’s response time and when you are troubleshooting
you can use these baseline response times to help you troubleshoot.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 17

Chapter 3
Hardware Troubleshooting
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and BCM450 platforms running BCM
5.0.
Perform the tasks in this chapter to troubleshoot problems related to the BCM50 and BCM450
hardware components.
Navigation
• Troubleshooting BCM hardware on page 18
• Power on self test (BCM450 only) on page 31
• Testing basic hardware functionality on page 32
• Monitoring the boot process (BCM450 only) on page 41
17
LAN IP Packet Capture
Use the LAN IP packet capture feature to help isolate and resolve voice applications set up issues.
You must have DataAdmin privileges to use the LAN Packet capture feature.
You can initiate IP packets capture on the BCM LAN and store captured IP packets in the output
file on BCM filesystem or a USB flash drive. LAN IP Packet Capture is accessed through
Business Element Manager at Administration > Utilities > LAN IP Packet Capture. Packets can be
captured at the OAM port or any of the LAN ports.
On the Configuration tab, you can select to store the output file on a network drive, a USB flash
drive, or on the BCM system. The configuration options will change depending on where you want
to store the output file.
The Filters tab allows you to set filters to reduce or increase the amount of data captured.
The table Reset functions on page 18 lists the fields on the LAN IP Packet Capture panel.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 18
18 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
Table 1 Reset functions
Variable Description
Port The port you want to capture from. If LAN is selected,
all LAN ports will be captured.
Mode Promiscuous: gives IP Packet Capture access to all
packets on the LAN.
Non-promiscuous: gives IP Packet Capture access
only to packets coming to or from the BCM.
Output format Allows you to select the output format. The options
are:
Raw: The raw packet data.
Text: converts the data to a text file.
Duration (sec) : The duration (in seconds) of the capture.
Start Starts the capture
Stop Stops the capture
Status View the status of the capture
IP packets going to WAN port will not be captured if entering one of the router ports regardless of
Promiscuous mode state. Any packets entering any of the LAN ports will always be captured if
promiscuous mode is ON.
If you are using a USB flash drive and it is disconnected during the capture, the capture session
does not stop. Stop the capture manually before disconnecting the USB drive.
Troubleshooting BCM hardware
Complete the following tasks, in the order shown below, to troubleshoot some of the common
problems that you may encounter with the BCM50 and BCM450 hardware:
• Check the power source on page 18
• Check LED indicators on page 19
• Check the wiring connections on page 27
• Verify the keycodes on page 28
• Restart or shut down the system on page 29
Check the power source
Begin troubleshooting the hardware by checking the power source:
• check the connection between the power supply and the main unit
• check the connection from the power supply to the electrical outlet
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 19

Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 19
Check LED indicators
After checking the power source, check the LED indicators. This section describes the operation of
the BCM450 system LEDs:
• BCM450 system status LEDs on page 19
• BCM50 system status LEDs on page 19
• LAN port LEDs on page 21
• ADSL router LEDs (BCM50a and BCM50ba only) on page 22
• Ethernet router LEDs (BCM50e and BCM50be only) on page 23
• BRI port LEDs on main unit (BRI series only) on page 24
• Media bay module LEDs on page 25
• DTM LEDs on page 26
• BRIM LEDs on page 27
Not all MBMs are supported on all platforms. For details on which MBMs are supported on each
platform, see Nortel Business Communications Manager 450 5.0 Installation—System
(NN40170-303), Nortel Business Communications Manager 450 5.0 Maintenance
(NN40170-503), or BCM50 5.0 Installation and Maintenance Guide (NN40170-305).
BCM450 system status LEDs
The chassis of the BCM450 contains two LEDs: a Status LED and a Power LED. The Power LED
is located at the bottom left of the chassis; the Status LED is immediately above it. The table “LED
states with descriptions of LED combinations” on page 20 describes the meaning of the system
status LEDs in the following situations:
• start-up sequence: LED indicators during the normal start-up process
• safe-mode start-up sequence: LED indicators during a safe-mode start-up
• shutdown sequence: LED indictors during a shutdown or failure
• start-up profile sequence: LED indicators during an initial installation or staging
BCM50 system status LEDs
The information in this section applies to the BCM50 platform only.
The two system status LEDs on the BCM50 main units (BCM50, BCM50a, BCM50e, BCM50b,
BCM50ba, and BCM50be) show the current state of the BCM50 system.
You can view the system status LEDs on the faceplate and on the top of the main unit, as shown in
the figure Location of system status LEDs on a BCM50 main unit on page 20. The bottom LED is
the power LED, and the top LED is the status LED. Under normal operating conditions, both
LEDs are solid green.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 20

20 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
Figure 1 Location of system status LEDs on a BCM50 main unit
The table LED states with descriptions of LED combinations on page 20 describes the meaning of
the system status LEDs after the system turn on and is in service.
During BCM50 system startup or restart, the system status LEDs move through a sequence of state
changes. If either the power LED or status LED is yellow, the system is initializing and is not
ready for service. The table LED states with descriptions of LED combinations on page 20 shows
the key states indicating service availability.
Table 2 LED states with descriptions of LED combinations
Power LED Status LED LED combinations description
Start-up sequence
Solid yellow Solid yellow Power is applied to the system.
Solid yellow Off POST (Power On Self Test) (duration 9 seconds)
Solid yellow Solid yellow System initialization (duration 14 seconds)
Solid green Solid yellow Kernel initialization (duration 8 seconds) or Safe OS
Solid green Blinking green Services initialization (duration 1 minute)
Solid green Solid green System running
Solid green Solid red Services initialization FAILURE
Safe Mode start-up sequence
Solid red Solid green System is running with manufacturing settings enabled
Solid red Solid red System is running in Software Reset mode
Solid red Blinking yellow System is running in Configuration Reset mode
Shutdown sequence or FAILURE
Solid green Blinking yellow Graceful shutdown in progress (trigger: Element Manager
Off Solid yellow Graceful shutdown completed.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
or UPS)
Page 21
Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 21
Table 2 LED states with descriptions of LED combinations
Power LED Status LED LED combinations description
Solid red Blinking yellow Overheat detected; thermal shutdown completed
Solid red Solid red Power spike or rail power fluctuation detected
Blinking red Solid red Rail power fluctuation; power monitor shutdown completed
Solid yellow Solid red Power spike shutdown completed (temperature and rail
power OK)
Off Off No power; system is shut down (power cable is
disconnected)
Start-up profile (LED combinations seen only during initial system install or staging)
Blinking yellow Blinking yellow Start-up profile executing
Solid green Solid green Start-up profile successfully applied
Blinking yellow Blinking red Start-up profile FAILURE
LAN port LEDs
Each LAN port on the main unit and expansion unit has two LEDs. These LEDs indicate the status
of the connection for that LAN port. The table LAN port LED locations on the BCM450 main unit
on page 21 shows the location of these LEDs on the main unit.
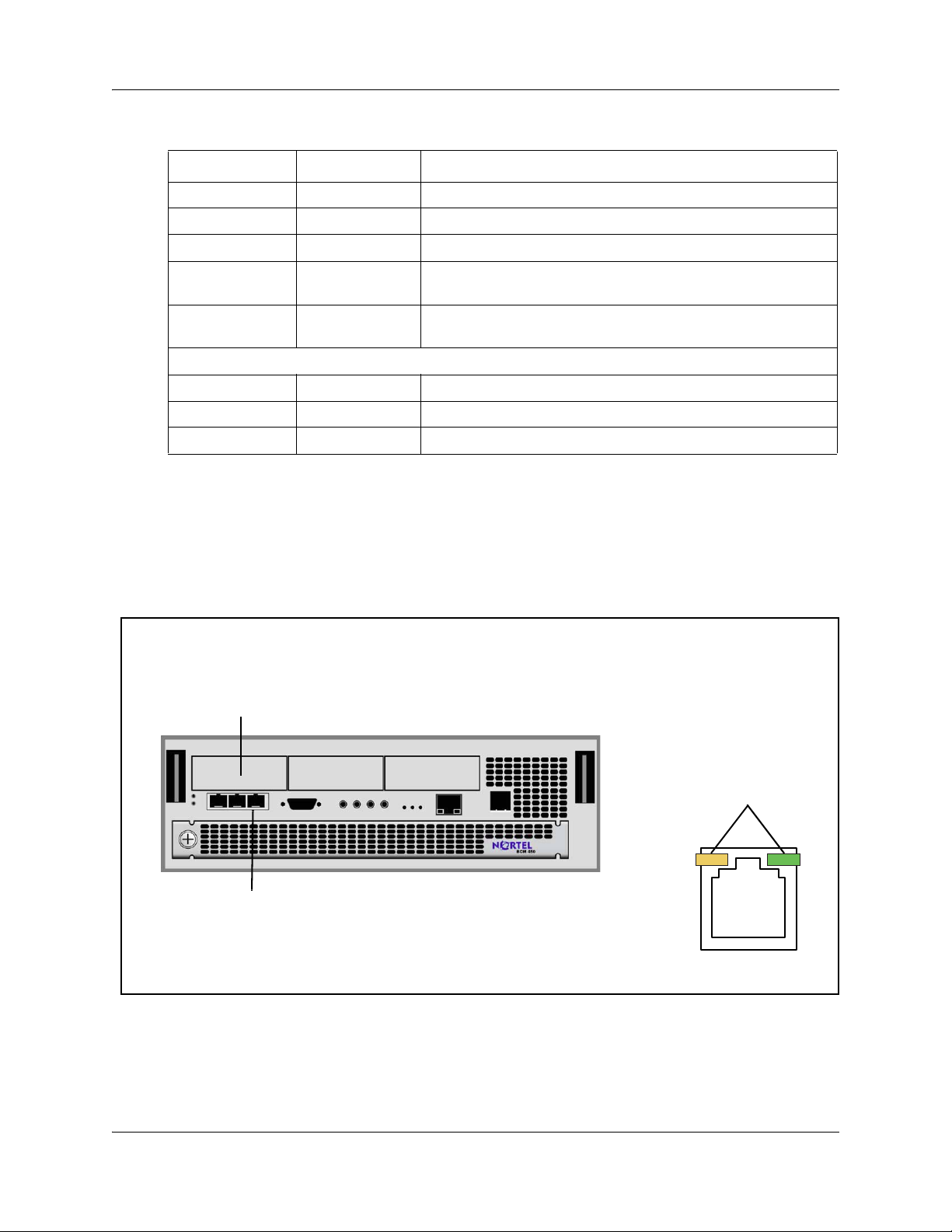
Figure 2 LAN port LED locations on the BCM450 main unit
LAN port
LAN port LEDs
LAN port
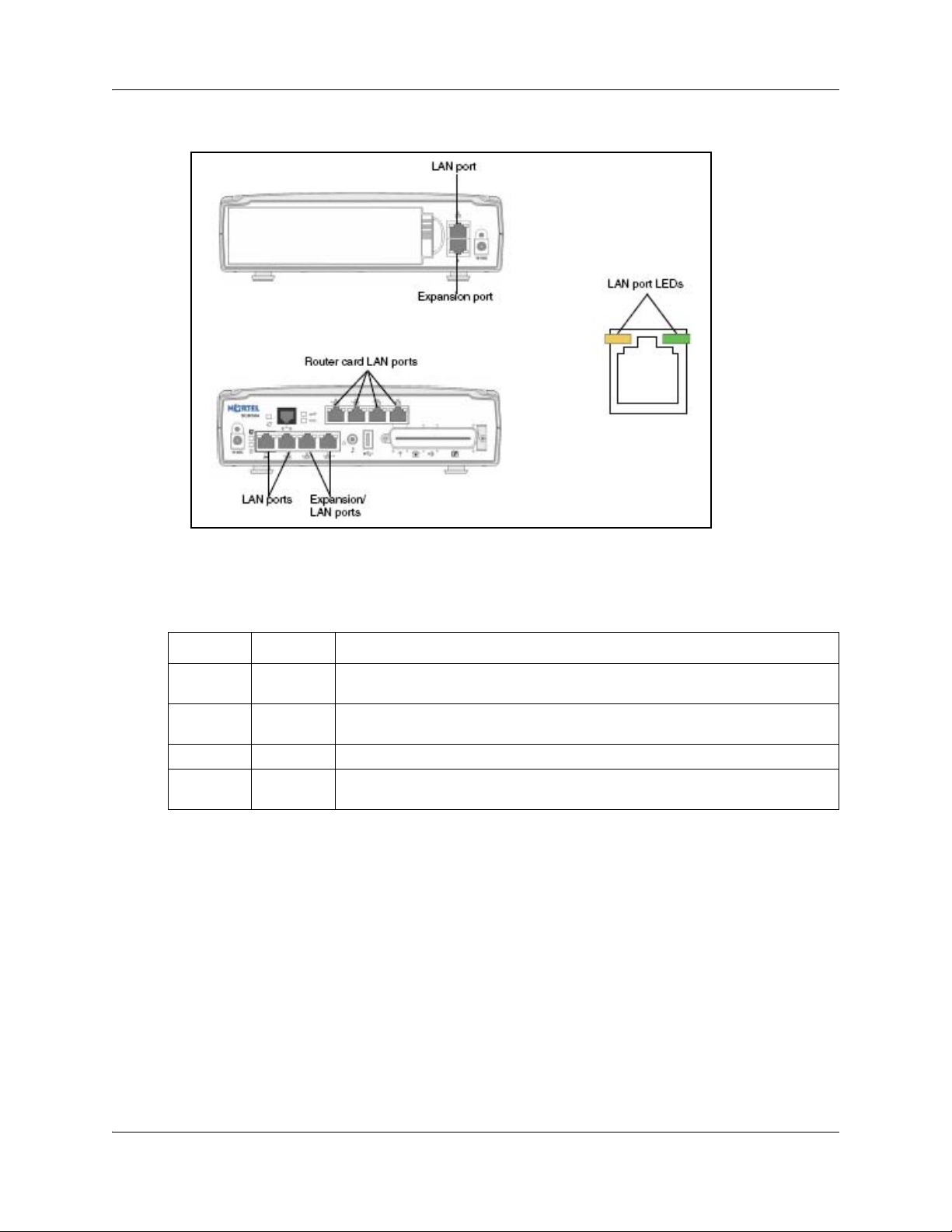
The figure LAN port LED locations on the BCM50 main unit on page 22 shows the LAN port
LED locations on the BCM50 main unit. The expansion ports on the BCM50 main unit also
function as LAN ports. The expansion port LEDs indicate LAN activity only. The LEDs do not
indicate expansion unit presence. The LEDs do not light.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 22
22 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
Figure 3 LAN port LED locations on the BCM50 main unit
The table LAN port and expansion port LED indicators on page 22 describes the possible LED
states for the LAN ports LEDs.
Table 3 LAN port and expansion port LED indicators
LED Status Description
Ye l l o w (l e ft
LED)
Green (right
LED)
Both LEDs Off No connection.
Any LED Flashing The LAN port is sending or receiving network data. The frequency of the flashes
On
On
The LAN port is operating at 10 Mb/s.
The LAN port is operating at 100 Mb/s.
increases with increased traffic.
ADSL router LEDs (BCM50a and BCM50ba only)
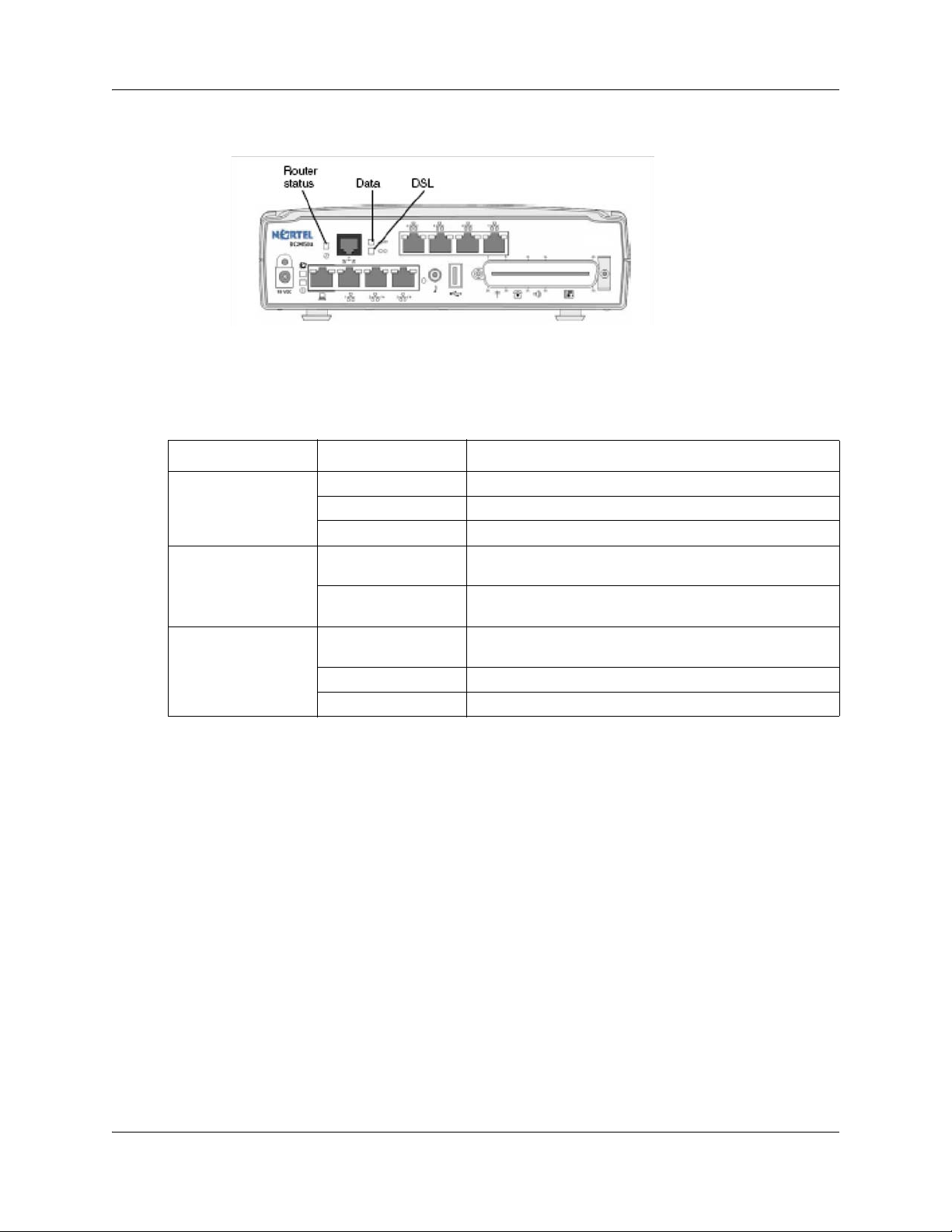
The three ADSL router LEDs on the faceplate of the BCM50a and BCM50ba main units monitor
router status, data, and DSL. The figure ADSL router LEDs on the BCM50a and BCM50ba main
units (BCM50a shown) on page 23 shows the location of the three ADSL router LEDs.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 23
Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 23
Figure 4 ADSL router LEDs on the BCM50a and BCM50ba main units (BCM50a shown)
The table ADSL router LED descriptions on page 23 describes the possible ADSL router LED
states.
Table 4 ADSL router LED descriptions
LED Status Description
Router status On The router card is functioning properly.
Off The router card is not ready or has malfunctioned.
Flashing The router card restarts.
Data Flashing The router card is sending or receiving data through the
WAN port.
Off The router card is not sending or receiving data through the
DSL On The router card is linked successfully to a digital subscriber
Off The DSL link is not functioning.
Flashing The router card is initializing the DSL line.
WAN port.
line access multiplexer (DSLAM).
Ethernet router LEDs (BCM50e and BCM50be only)
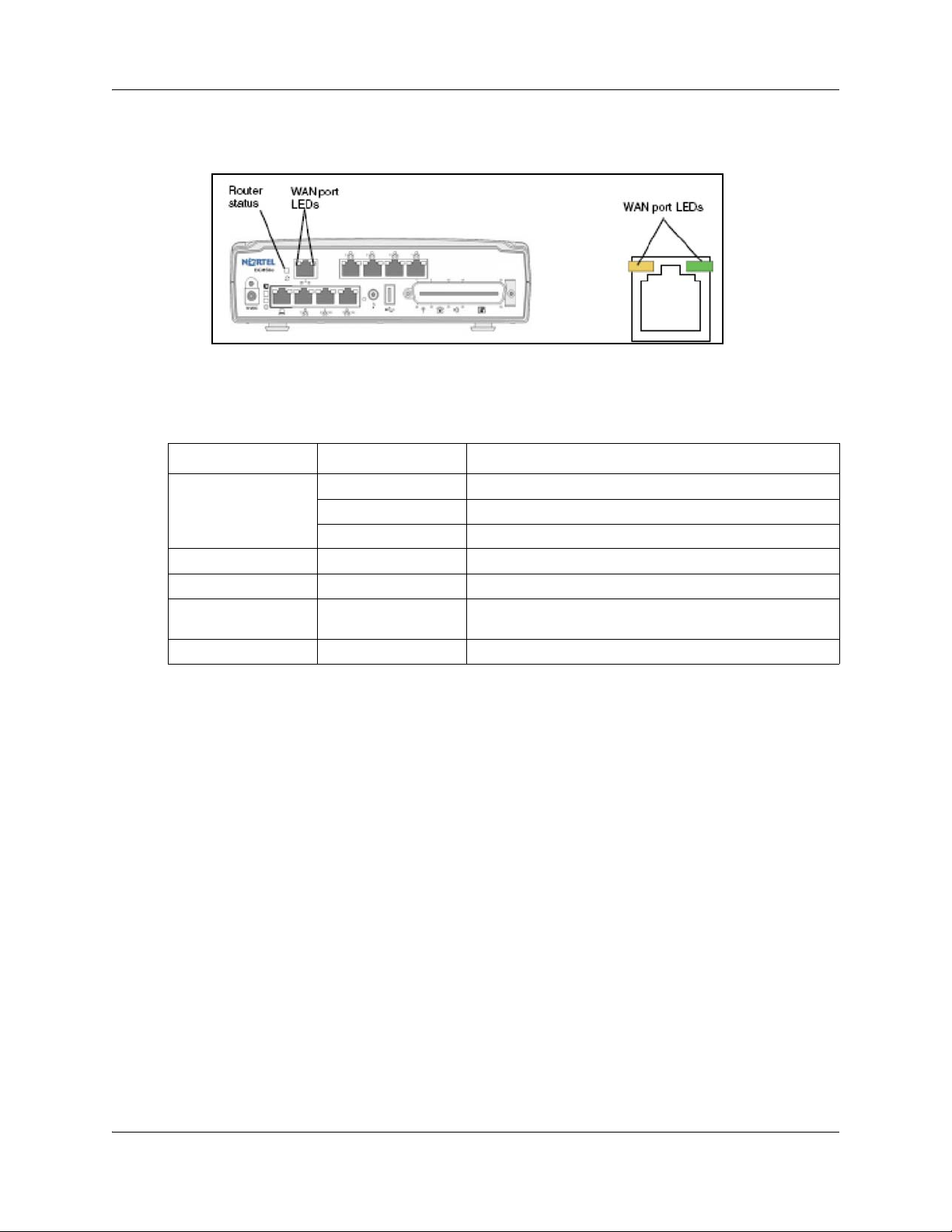
The three Ethernet router LEDs on the BCM50e and BCM50be main units monitor the router
status and the WAN port. The figure Ethernet router LEDs on the BCM50e and BCM50be main
units (BCM50e shown) on page 24 shows the location of the three Ethernet router LEDs.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 24
24 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
Figure 5 Ethernet router LEDs on the BCM50e and BCM50be main units (BCM50e shown)
The table LAN port LED indicators on page 24 describes the possible Ethernet router LED states.
Table 5 LAN port LED indicators
LED Status Description
Router status On The router card is functioning properly.
Off The router card is not ready or malfunctioned.
Flashing The router card restarts.
WAN port yellow On The WAN port is operating at 10 Mb/s.
WAN port green On The WAN port is operating at 100 Mb/s.
Any WAN port LED Flashing The WAN port is sending or receiving network data. The
frequency of the flashes increases with increased traffic.
Both WAN port LEDs Off No connection.
BRI port LEDs on main unit (BRI series only)
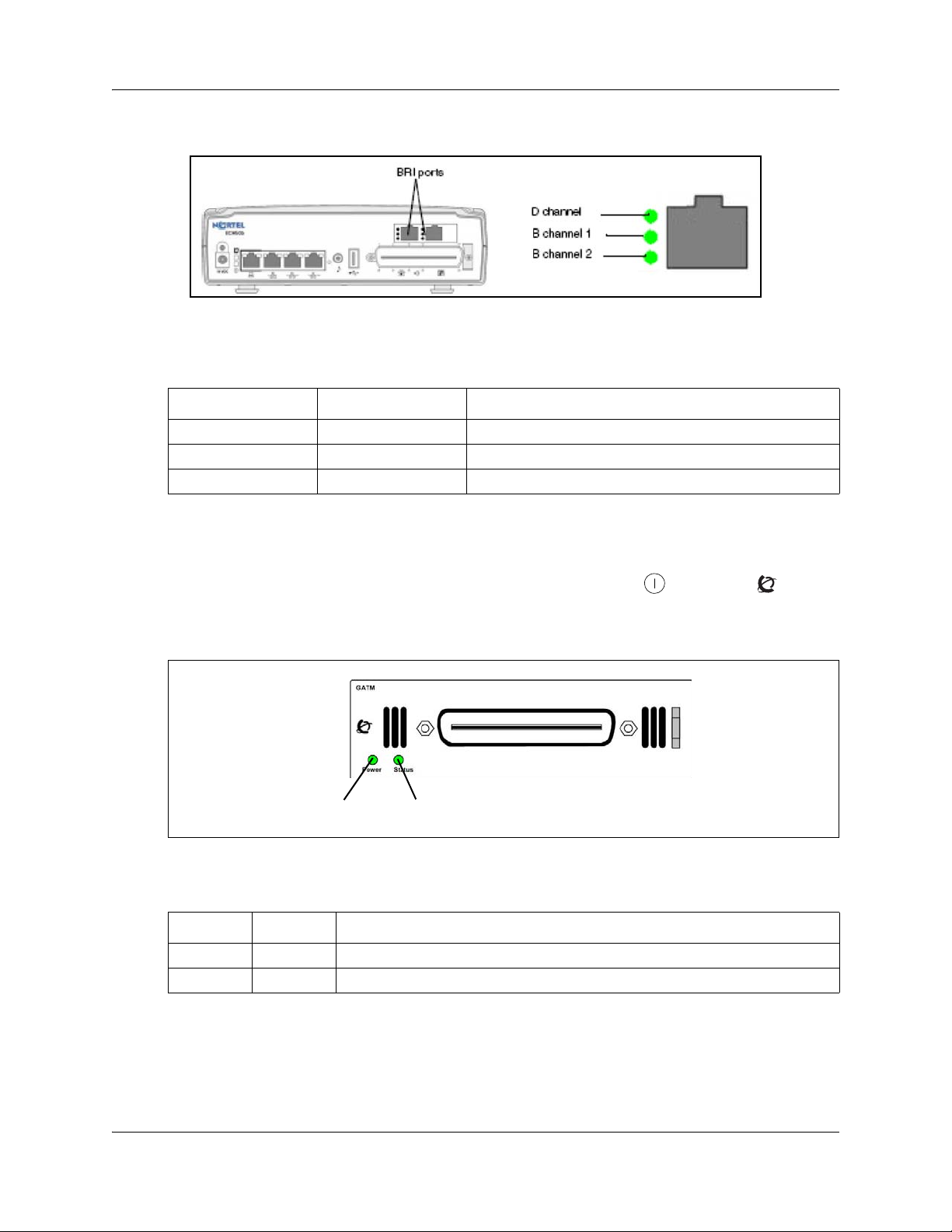
The three BRI port LEDs on the BCM50b, BCM50ba, and BCM50be main units monitor the BRI
port status. The figure BRI port LEDs on the BCM50b, BCM50ba, and BCM50be main units
(BCM50b shown) on page 25 shows the location of the BRI ports and LEDs.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 25
Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 25
Figure 6 BRI port LEDs on the BCM50b, BCM50ba, and BCM50be main units (BCM50b shown)
The table BRI port LED indicators on page 25 describes the possible BRI port LED states.
Table 6 BRI port LED indicators
LED (channel) Status Description
D On (green) D channel is functioning through this BRI port.
B1 On (green) B channel 1 is functioning through this BRI port.
B2 On (green) B channel 2 is functioning through this BRI port.
Media bay module LEDs
The two media bay module (MBM) LEDs on an expansion unit show the power and status of the
MBM. The figure MBM LEDs on page 25 shows the location of the
LEDs on an MBM. The power and status LEDs are in the same location on all MBMs.
Figure 7 MBM LEDs
Power Status
The table MBM LED descriptions on page 25 describes the possible MBM LED states.
Table 7 MBM LED descriptions
Power Status Description
Off Off The MBM has no power, or a failure occurred on the MBM power converter.
On Off BCM450 to expansion unit failure or system initialization.
(Power) and (Status)
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 26
26 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
Table 7 MBM LED descriptions
Power Status Description
On Blinking Hardware is working, but an operational problem exists such as:
• no link to the main unit is detected
• frame alignment is lost on messages from the main unit
• bandwidth not allocated
• MBM is in maintenance state
• MBM is in download state (GASM, GATM4/GATM8)
Blinking Blinking The MBM has power, but a hardware problem exists such as:
• partial failure of power converter
• thermal overload
• fan failure
On On The MBM is ready to operate.
DTM LEDs
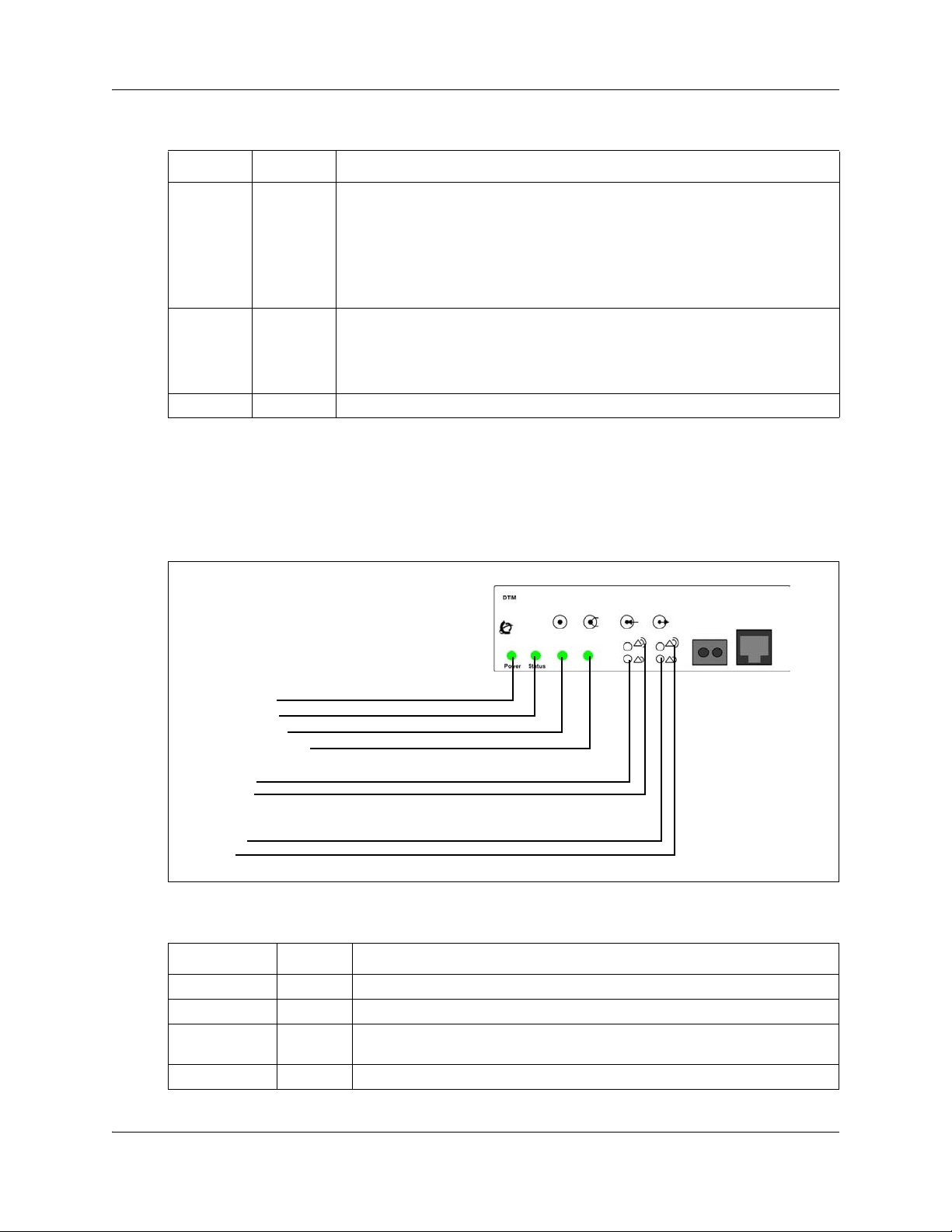
The DTM has additional LEDs that are not on most other MBMs. Figure 8 on page 26 shows the
location of the DTM LEDs.
Figure 8 DTM LEDs
Power LED
Status LED
In service LED
Loopback test LED
Receive LEDs
Error
Alarm
Transmit LEDs
Error
Alarm
The table DTM LED functions on page 26 describes the functions of the DTM LEDs.
Table 8 DTM LED functions (Sheet 1 of 2)
LED Status Descriptions
Power – See “Media bay module LEDs” for details.
Status – See “Media bay module LEDs” for details.
In service Flashing The T1, ETSI, or PRI trunks are out of service because a loopback test is
Loopback test On A continuity loopback test is running.
running or the DTM is initializing.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 27
Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 27
Table 8 DTM LED functions (Sheet 2 of 2)
LED Status Descriptions
Receive alarm On A problem with the received digital transmission. This half-duplex link does
not work.
Receive error On A small error as a result of degraded digital transmission. Possible causes are
Transmit alarm On The DTM cannot transmit. The DTM sends an alarm indication signal (AIS) to
Transmit error On The DTM is sending a remote alarm indication (RAI) carrier failure alarm
All LEDS Flashing The DTM is initializing.
an ohmic connection, water ingress, or too long a loop.
the terminating switch. This half-duplex link does not work.
(CFA) to the terminating switch. If the transmit alarm is not on, this error
indicates a far-end or cable problem.
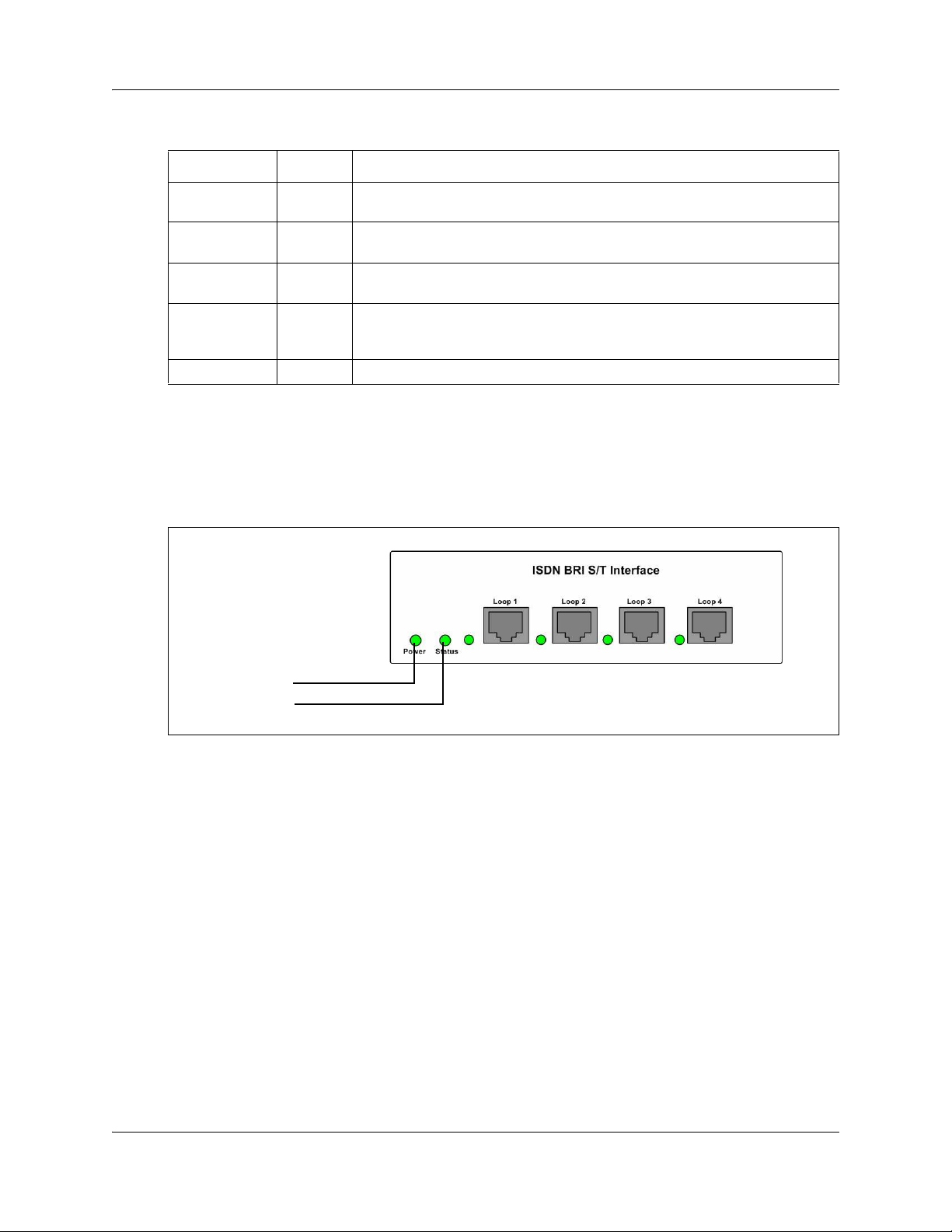
BRIM LEDs
The BRIM has one additional LED beside each RJ-48C jack. These LEDs are on when the ISDN
line is active. The figure BRIM LEDs on page 27 shows the location of the LEDs on a BRIM.
Figure 9 BRIM LEDs
Power LED
Status LED
For more information on the power and status LED functions, see Media bay module LEDs on
page 25.
Check the wiring connections
After you check the power source and the LEDs, begin to check the wiring. Check the connections
between the following components:
• the expansion unit and the main unit
• the main unit and to the MBMs—make sure that the cables are properly seated and are
connected to the correct ports
• for the BCM450, the power supply and the AC power outlet
• for the BCM50, the power supply and the main unit and the AC power outlet
• if you are using a UPS, check the connection from:
— the USB port on the BCM450 to the USB port on the UPS
— the UPS and the electrical outlet
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 28

28 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
— the connection from the power supply to both the UPS and the BCM450 main unit
• the lines and extensions connected through the RJ-21 telephony connector
• the auxiliary equipment—connections at the auxiliary terminal block, or at the patch panel
• For more information on wiring connections, refer to Nortel Business Communications
Manager 450 5.0 Installation—System (NN40170-303) or BCM50 5.0 Installation and
Maintenance (NN40170-305).
Verify the keycodes
If a specific feature is not functioning, verify that the feature is included in your installed
keycodes. This section provides procedure for verifying the installed keycodes using either
Element Manager or Telset. For more detailed information about retrieving and entering the
keycode for your system, see the Keycode Installation Guide (NN40010-301).
To verify the keycodes using Element Manager
1 In the Task Navigation Panel, select the Configuration tab.
2 Select the System folder and click the Keycodes task.
The Keycodes panel displays and the installed features appear in the Keycodes list.
3 To enter a new keycode, click Load File.
4 Browse to where you saved the keycode file you downloaded from KRS.
5 Click Open.
The file uploads and the feature appears in the Keycodes list.
To verify the keycodes using Telset
1 Select Feature 9*8 from a two-line display telephone.
2 Enter the following user ID and password:
User ID: SETNNA
Password: CONFIG
The numerical values of the user ID and password are 738662 and 266344, respectively.
3 Press NEXT to scroll through the menu and select Feature Codes.
4 Press OK.
The system ID (SID) displays.
5 Press NEXT.
6 Enter your sequence ID.
7 Press NEXT to scroll through the list and perform one or both of the following tasks:
a To activate features, select Feature List.
• Press SHOW to view the available features.
• Use the soft keys to activate features for your system.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 29
Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 29
b To enter a new keycode, select Entitlement Code.
• Press SHOW to view the current keycode.
• Use the soft keys to modify the keycode for your system.
Restart or shut down the system
You can use the BCM 5.0 Reset utility to:
• perform a warm reset of telephony services
• perform a cold reset of telephony services
You can also perform a Configuration Reset, which restores the configuration settings to factory
default, or a Software Reset which restores both the software and configuration settings to factory
default. For more information on Configuration and Software resets. Use this procedure to restart
the system.
To restart the system
Perform this procedure to restart the system from the Element Manager.
1 Select Administration > Utilities > Reset.
2 Click the appropriate reset button.
The table Reset functions on page 29 lists the Reset functions.
Table 9 Reset functions
Function Description Impact
Warm Reset Telephony
Services
Cold Reset Telephony
Services
Restarts telephony services running
on the BCM450 system
Resets telephony programming of
the BCM450 system to the factory
defaults for that software level
Restarts all telephony services,
including LAN CTE, voice mail, and
IP telephony. This operation does not
affect configuration parameters or
programming.
Affects all telephony services,
including LAN CTE, voice mail, and
IP telephony.
Telephony services restart with all
telephony programming at default
values for the specified region,
template, and start DN, for the
current software release level.
A cold reset erases voice message
mailboxes and messages if the DN
length is not set to system defaults.
For information about setting the DN
length, refer to Nortel Business
Communications Manager 5.0
Configuration—Devices
(NN40170-500).
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 30
30 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
Table 10 BCM50 hardware reset functions
Reset Level Description Impact
Level 1 This reset erases all the
customer-specific data and
restores the default
configuration for all
components.
The LED illuminates yellow to
denote Level 1 reset.
Level 2 This reset erases all the
customer-specific data and
software releases and
patches.
This also resets the router
firmware to the original
configuration settings.
The LED illuminates red to
denote Level 1 reset.
Reboot
You can use the Reboot utility to:
Only the system and user
configuration data is erased
and replaced with default
values.
The software components are
not altered, that is, the system
will have the latest release and
patch level of the software
installed.
There will be no Ethernet
connectivity during this
operation.
The system re-installs the
original factory configuration
settings.
There will be no Ethernet
connectivity during this
operation.
• reboot the BCM450 system
• shut down the system
• reboot the integrated router (BCM50a/e only)
• create a scheduled reboot to take place at a specified time. This can be configured to occur
once, daily, weekly or monthly.
The table Reboot functions on page 30 lists the Reboot functions.
Table 11 Reboot functions
Function Description Impact
Reboot BCM450
System
System Shutdown Shuts down the BCM450. Stops all services in preparation for
Add (Scheduled Reboot
tab)
Restarts the operating system of the
BCM450 system.
Allows you to create a new Scheduled
Reboot.
Temporarily stops all services on the
system. Restarts all services.
This operation does not affect configuration
parameters or programming.
removing power from the system.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 31

Table 12 LED Status
LED Status Description
Blinking power LED Indicates a user input
window; the BCM50 system is
waiting for user input.
Solid power LED Indicates caution for extreme
action.
Red/Green Level of reset
Blinking status LED Indicates an interim state, the
system is trying to establish
user input.
Solid status LED Indicates confirmation of user
selection
Note: Power LED has priority over Status LED.
Power on self test (BCM450 only)
Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 31
The information in this section applies to the BCM450 platform only.
The power on self test (POST) feature tests basic hardware functionality when the BCM450
system powers up, and stores the results in a log file. You can view the log file for hardware
failures.
Viewing the POST log file
1 Use Element Manager to transfer the log files to your PC. For more information about how to
transfer log files, see Nortel Business Communications Manager 5.0 Administration and
Security (NN40170-603).
2 View the bootloader.log file.
3 Check the log file for errors. The figure Example: Bootloader.log file with no errors on page
32 shows a bootloader.log file with no errors.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 32

32 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
Figure 10 Example: Bootloader.log file with no errors
The figure Example: Boot file with errors on page 32 shows a file with errors.
Figure 11 Example: Boot file with errors
Testing basic hardware functionality
This section describes how to test the components of the BCM system, and how to troubleshoot
them if they fail the test.
The table Procedures to test and troubleshoot BCM platform components on page 32 lists the
procedures to use to help isolate and identify problems with your BCM hardware:
Table 13 Procedures to test and troubleshoot BCM platform components
Procedure Supported on BCM450 Supported on BCM50
To test the main unit on page 33 yes yes
To troubleshoot the main unit on page 33 yes yes
To test the expansion unit on page 34 yes yes
To troubleshoot the expansion unit on page 34 yes yes
Testing an MBM on page 35 yes yes
Determining why a BCM450 MBM does not appear in
Element Manager on page 35
Determining why a BCM50 MBM does not appear in
Element Manager on page 36
Troubleshooting the FEM on the BCM450 on page 36 yes no
yes no
no yes
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 33

Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 33
Table 13 Procedures to test and troubleshoot BCM platform components
Procedure Supported on BCM450 Supported on BCM50
To determine why the ATA 2 does not function on page 36yes yes
To determine why there is no dial tone at the ATA2 on
page 37
To check the ATA2 wiring on page 37 yes yes
Reset to factory settings on page 37 yes yes
To perform a Level 1 reset (configuration reset) on page 41yes yes
To perform a Level 2 reset (software reset) on page 41 yes yes
yes yes
To test the main unit
If you have the digital station feature included in your installed keycode, use the following test to
ensure the main unit is operating properly:
1 Go to an extension that is connected to the RJ-21 telephony connector on the main unit.
2 Check for a dial tone.
3 Use this extension to make a call to another extension on the system.
4 If this system has an expansion unit with a media bay module (MBM) that supports
extensions, repeat steps 3 and 4 for an extension connected to the expansion unit.
5 Go to an extension that has access to one of the lines on the main unit.
6 Select the line or line pool to which the line belongs.
7 Check for a dial tone.
8 Make a call using the line or line pool.
9 If this system has an expansion unit with an MBM that supports lines, repeat steps 6 to 8 with
an extension that can access one of the lines connected to the expansion unit.
To troubleshoot the main unit
If a test fails, perform the following procedure:
1 Verify that any nonfunctional feature is included in your installed keycode.
2 Check the wiring to the main unit and to the MBMs. Make sure that the cables are properly
seated and are connected to the correct ports.
3 Restart the BCM system.
4 Check LEDs.
5 Use Element Manager or the Telset Administration feature to check the programming for the
lines or extensions that failed the call test.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 34

34 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
6 If the programming is incorrect, use the Backup and Restore Utility to load a recent backup of
system programming. If a recent backup is not available, correct the programming using
Element Manager or the Telephone Administration feature.
To test the expansion unit
Use the following test to ensure the expansion unit is operating properly:
1 Make sure that the BCM450 system is fully booted.
2 Check the power and status LEDs on the MBM that is inserted in the expansion unit. Both
LEDs must be solid green. If either LED is not solid green, a problem exists with the MBM or
the expansion unit.
3 If the expansion unit has an MBM that supports extensions, go to an extension that is
connected to the MBM.
4 Check for a dial tone.
5 Use this extension to make a call to another extension on the system.
6 If the expansion unit has an MBM that supports lines, go to an extension that has access to one
of the lines on the MBM.
7 Select the line or line pool to which the line belongs.
8 Check for a dial tone.
9 Make a call using the line or line pool.
To troubleshoot the expansion unit
1 Check that the correct feature for the expansion unit is included in your installed keycode.
2 Check that the expansion port is connected to the proper connector.
3 Check the wiring to the MBM. Make sure that the cables are properly seated and are connected
to the correct ports with proper LED indications.
4 Check that the switches on the MBM are all set to on.
If the MBM is a GASM or GATM, all the switches on the right are not on.
To check the MBM switches, you must remove the MBM from the expansion unit.
5 Perform a firmware download to ensure that the correct version is loaded on the ASM/GASM
or GATM unit.
6 Use Element Manager or Telset Admin to check the programming for the lines or extensions
connected to the MBM.
7 Restart the system to ensure that the BCM450 main unit functions correctly.
8 If the programming is incorrect, use the Backup and Restore Utility to load a recent backup of
system programming. If a recent backup is not available, correct the programming using
Element Manager or the Telephone Administration feature.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 35

Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 35
Testing an MBM
Perform the following procedure to test an MBM installed in the main unit or
expansion cabinet.
For BCM450, if you are experiencing an issue with an FEM, ensure all DIP
switches are set to the On position. The FEM is not supported on the BCM50
platform.
1 Check the Power and Status LEDs on the MBM. Both LEDs must be solid green. If either
LED is not solid green, a problem exists with the MBM.
2 Go to an extension on the MBM if it is a station MBM.
OR
Go to an extension that has access to one of the lines on the MBM if it is a trunk MBM. Select
the line or line pool to which the line belongs.
3 Check for a dial tone.
4 Use this extension to make a call to another extension on the system if it is a station MBM.
OR
Make a call using the line or line pool if it is a trunk MBM.
5 Use this extension to make a call to an external telephone number if you are testing a station
MBM.
Determining why a BCM450 MBM does not appear in Element
Manager
Use the following procedure if an installed MBM does not appear in Element Manager.
1 Check that the correct feature is included in your installed keycode.
2 Check that both the Power and Status LEDs on the MBM are solid green.
3 If the Power LED is off, and the MBM is installed in the expansion cabinet, check that the
power supply cable is properly seated in the expansion cabinet and the power supply is
connected to a working power outlet.
4 Ensure that the MBM is properly seated in the MBM bay.
5 If the Status LED is not solid green, and the MBM is installed in the expansion cabinet, check
that the Expansion cable is properly seated in the Expansion port on the expansion cabinet and
on the main unit.
6 Ensure that the MBM is enabled using either Element Manager or Telset Administration. If the
MBM is enabled, disable and re-enable it.
7 Ensure that all DIP switches are set correctly.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 36

36 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
Determining why a BCM50 MBM does not appear in Element
Manager
1 Check that the correct feature for the expansion unit is included in your installed keycode.
2 Check that both the Power and Status LEDs on the MBM are solid green.
• If the Power LED is off, check that the power supply cable is properly seated in the
expansion unit, and the power supply is connected to a working power outlet. Also check
that the MBM is properly seated in the expansion unit.
• If the Status LED is not solid green, check that the expansion cable is properly seated in
the expansion port on the expansion unit and on the main unit.
3 Check that the MBM and expansion unit are enabled using either Element Manager or Telset
Administration. If the units are enabled, disable them, and then reenable them.
4 Check that all the switches on the MBM are on. If the MBM is a GASM or GATM, all the
switches on the right are not set to on. To check the MBM switches, you must remove the
MBM from the expansion unit. For more information, see the BCM50 Installation and
Maintenance Guide.
Troubleshooting the FEM on the BCM450
This procedure applies to the BCM450 only.
Perform the following procedure to troubleshoot an installed fibre expansion module (FEM).
1 Ensure that all six connector LEDs are lit.
2 If all six LEDs are not lit, ensure that all six DIP switches are set to the On (up) position.
To determine why the ATA 2 does not function
1 Check for a dial tone using an analog device.
2 Check that AC power is connected to the ATA 2 unit.
3 Check that the correct feature for digital sets is included in your installed keycode.
4 Verify that the ATA2 is connected to a digital station port.
5 Allow sufficient startup time (30–60 sec).
6 Plug an analog device into the phone port of the ATA2 and check for a dial-tone.
7 In Element Manager, verify that the ATA 2 is correctly configured:
a Select Configuration, Telephony, Sets, All DNs.
b Select the appropriate DN from the list and click the ATA settings tab.
The options for the Device Type are Modem or Telephone.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 37

Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 37
To determine why there is no dial tone at the ATA2
1 If you hear no dial tone, replace a single-line telephone for the data communication device.
2 If you hear no dial tone at the ATA2 unit:
a Disconnect the line side of the ATA2. Connect a digital telephone to the ATA2 port.
b Check that the connection from the ATA2 to the hardware works correctly.
To check the ATA2 wiring
1 Use an analog phone to test the ATA2.
2 Check the following connections:
a ATA 2 to the terminal
The resistance must be 200 ohms or less for data applications and 1300 ohms or less for
voice applications.
b BCM450 hardware to the ATA2
The wiring must be equivalent to 800 m of 0.5 mm wire (2600 ft. of 24-AWG) or less. Do
not use bridge taps and loading coils between the hardware and ATA2.
Reset to factory settings
This section describes how to reset the BCM system to the factory settings or a stable working
condition using the reset switch. When the BCM450 is in this condition, you can make further
modifications.
You can perform a Configuration Reset (previously known as a Level 1 reset), which restores
configuration settings to the factory default, or a Software Reset (previously known as a Level 2
reset), which resets the software and configuration to the factory default. Configuration and
Software resets are performed through the Command Line Interface (CLI) (see).
The figure Reset switch location on BCM450 on page 38 shows the location of the reset switch on
the BCM450.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 38

38 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
Figure 12 Reset switch location on BCM450
Reset button
The figure Reset switch location on BCM50 on page 38 shows the location of the reset switch on
the BCM50.
Figure 13 Reset switch location on BCM50
Some possible situations in which you use the reset feature are:
• If the system is configured incorrectly to an extent that it is no longer functional. The customer
must use a Configuration reset to return to the default system programming and restore a
previous configuration or reconfigure the system.
• If distributors want to reuse systems, they must first erase all customer-specific data using a
Configuration or Software reset.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 39

Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 39
Reset levels
Reset to factory settings is a stand-alone feature that has the following levels of reset:
• Configuration Reset (previously known as Level 1) reset erases all customer-specific data
and restores the default configuration for all components. This reset leaves the software
components untouched. That is, the system has the latest release and patch level of the
software installed. Only the system and user configuration data is erased and replaced with
default values. For the BCM50, no Ethernet connectivity to the system occurs during this
operation.
• Software Reset (previously known as Level 2) reset erases all customer and system
configuration data and all software releases and patches. This reset reinstalls the original
factory configuration settings. For BCM50, a Software reset also resets the router firmware to
what was shipped from the factory. No Ethernet connectivity to the system occurs during this
operation.
Warning: If you perform a software reset to solve an undetermined problem and
still have access to Element Manager, you must retrieve all the log files for
technical support before performing the software reset. A software reset erases all
log files from the system.
Command Line Interface
You can use the Command Line Interface (CLI) to configure basic settings, as well as shut down,
reboot, or perform a Configuration or Software Reset on your BCM450 or BCM50 system. Two
CLI modes are available: Maintenance CLI, and Configuration CLI.
Your user account must be assigned the System-CLI privilege in order to access the CLI.
Before performing a Configuration or Software reset, review all the effects of the levels of reset.
See Reset levels on page 39.
This section contains information about the following topics:
• Configuration CLI on page 39
• Maintenance CLI on page 40
Configuration CLI
The Configuration CLI displays when the system is in Main OS mode. The options available on
the Configuration CLI are
• 0—Exit. The system exits the CLI to the login prompt.
• 1—Reboot. The system reboots to the Main OS.
• 2—Shutdown. The system shuts down. You need physical access to the BCM hardware to
restart the system.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 40

40 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
• 3—Safe OS. The system reboots to the Safe OS and waits 1 minute for you to login. When
you login within 1 minute, the Maintenance CLI displays. If you do not login within 1
minute, the system changes to the Main OS.
• 4—Configuration Reset. A Level 1 reset occurs. The system resets all configuration data
to the factory defaults.
• 5—Software Reset. A Level 2 reset occurs. The system resets all configuration data and
software to the factory defaults.
• 6—IP Configuration. You can configure the following basic IP settings:
— 0—Return to Previous Menu. The system returns to the main menu.
— 1—Hostname. Provision the hostname of the system.
— 2—IP Address. Provision the IP address of the system.
— 3—Subnet Mask. Provision the subnet mask for the IP address.
— 4—Default Gateway. Provision the default gateway for the system.
— 5—DHCP Client Mode. Enable or disable the DHCP client.
— 6—Commit Changes. Save changes to the IP settings.
— 7—Reload Settings. Reload the existing IP settings.
Maintenance CLI
The Maintenance CLI displays when the system is in Safe OS mode. The Safe OS is a diagnostic
mode that you can use if the Main OS is experiencing problems. No applications or telephony
services are running when the BCM 5.0 is in Safe OS mode. The options available on the
Maintenance CLI are
• 0—Exit. The system exits to the Safe OS login prompt.
• 1—Reboot into Main OS. The system reboots to the Main OS.
• 2—Shutdown. The system shuts down. You need physical access to the BCM450
hardware to restart the system.
• 3—Reboot into Safe OS. The system reboots to the Safe OS and waits 1 minute for you to
login. If you do not login within 1 minute, the system changes to the Main OS.
• 4—Transition to Main OS. The system changes from the Safe OS to the Main OS without
restarting.
• 5—Configuration Reset. A Level 1 reset occurs. The system resets all configuration data
to the factory defaults.
• 6—Software Reset. A Level 2 reset occurs. The system resets all configuration data and
software to the factory defaults.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 41

Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting 41
To perform a Level 1 reset (configuration reset)
1 Access the CLI. For information about how to access the CLI, see Command Line Interface on
page 84.
2 From the Configuration CLI, select option 4—Configuration Reset. If you are using the
Maintenance CLI, select option 5—Configuration Reset.
3 The LEDs progress through the start-up and shut down sequence. This process can take more
than 2 minutes.
4 A Status LED that is flashing yellow, and a Power LED that is solid red, indicates that a
configuration reset is in progress. This process can take more than 2 minutes.
5 The system restarts to the Main OS. This process can take more than 2 minutes.
To perform a Level 2 reset (software reset)
1 Access the CLI. For information about how to access the CLI, refer to Command Line
Interface on page 84.
2 From the Configuration CLI, select option 5—Software Reset. If you are using the
Maintenance CLI, select option 6—Software Reset.
3 The LEDs will progress through the start-up and shut down sequence. This process can take
more than 2 minutes.
4 A Status LED that is flashing yellow, and a Power LED that is solid red, indicates that a
software reset is in progress. This process can take more than 5 minutes.
5 The system restarts to the Main OS. This process can take more than 2 minutes.
Monitoring the boot process (BCM450 only)
1 Connect a serial cable with a 9-pin female connector from the serial port on a PC to the serial
port on the BCM450.
2 Ensure that you use the following settings:
• bits per second: 115200
• data bits: 8
•parity: N
• stop bits: 1
• no flow control
3 Use a terminal emulation program, such as Hyperterminal or Nortel CLI Manager, to establish
a connection to the BCM450.
4 Restart the system and observe the boot process. Figure 14 shows an example of a boot
process when there is failed or missing memory; Figure 15 shows an example of a boot
process when there is a failed or missing hard drive.
5 If the system starts normally, the CLI login prompt displays when the boot cycle is complete.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 42

42 Chapter 3 Hardware Troubleshooting
Figure 14 Boot process with failed or missing memory
Figure 15 Boot process with failed or missing hard drive
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 43

Chapter 4
Software Troubleshooting
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms running
5.0.
Use the information in this chapter to troubleshoot problems related to the BCM software
components.
Navigation
Complete the following tasks, in the order shown below, to troubleshoot some of the common
problems that you can encounter with the BCM software:
• Verify the software version on page 43
• Verify the keycodes on page 43
• Check the programming of lines and phones on page 43
• Restoring system data on page 52
• Verify the software inventory on page 53
43
Verify the software version
In the Element Manager, select Help, About. A panel displays and provides information about the
Element Manager, such as the Release level.
Verify the keycodes
If a specific feature is not functioning, verify that the feature is included in your installed
keycodes. For information about how to verify the installed keycodes, see Verify the keycodes on
page 28.
Check the programming of lines and phones
You can use the Element Manager to view the programming of lines and phones. When you view
the lines, the information on the panels may vary, depending on the type of line.
The Element Manager displays line information in two sections:
• The main section, Trunk/Line data, is located at the top of the screen and provides a table of
lines and the current or default settings.
• The bottom section contains three tabs. The contents of the tabs may vary, depending on the
line selected in the top table.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 44

44 Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting
—The Properties tabbed panel provides the settings for individual line characteristics.
—The Preferences tab shows information that may vary from trunk to trunk
—The Restrictions tabbed panel allows you to define which restrictions will be active for
individual lines. Note that lines that are assigned to the same line pool will automatically
assign the same restrictions.
—The Assigned DNs tabbed panel provides a quick way to assign lines to telephones. You
must use the DN records panels to assign line pools to telephones.
Check line programming
Use the following procedure to check line programming in your BCM system.
To check line programming
1 In the Task Navigation Panel, select the Configuration tab.
2 Select Telephony > Lines.
3 Verify that the programming for all lines is correct; see Trunk/Line data on page 44 for an
explanation of the fields on the panel.
4 Select a line, and then select a tab:
a Select the Properties tab and verify that the settings are correct; see Properties on
page 46 for an explanation of the fields on the tab.
b Select the Preferences tab and verify that the settings are correct; see Preferences on
page 47 for an explanation of the fields on the tab.
c Select the Restrictions tab and verify that the settings are correct; see Restrictions on
page 50 for an explanation of the fields on the tab.
d Select the Assigned DNs tab and verify that the settings are correct; see Assigned
DNs on page 51 for an explanation of the fields on the tab.
5 Repeat step 4 for the remaining lines.
6 Correct any programming problems, or restore the system data; for more information, see
Restoring system data on page 52.
Trunk/Line data
The top-level Table View panel shows line records for all lines active on the system, and the
common assigned parameters.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 45

The table Trunk/Line Data main panel on page 45 describes the fields found on the Trunk/Line
Data main panel.
Table 14 Trunk/Line Data main panel (Sheet 1 of 2)
Attribute Value Description
Line This list contains all the
possible line numbers for
the system, including target
lines.
Configure only those lines that are active on the system.
(Click the Active check box and ensure that the Inactive
check box is empty).
Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting 45
Trunk Type PSTN-based lines, VoIP,
Target
Name <maximum of seven
alphanumeric characters>
Control Set DN <control telephone DN>
Default: 221 (default Start
DN)
Tips: External lines and telephones must be programmed to use one of the Scheduled
Services: Ringing, Restriction, and Routing Services.
For maximum flexibility, Nortel recommends that you create two different control
telephones, one for the lines and one for the telephones.
You can turn on a service manually or automatically for all external lines from an assigned
control telephone. However, you cannot combine schedules. A service can only be active
as normal service or one of the six schedules at any one time. Several schedules can be
active at one time, but they must use different services.
Line Type Public
Private to: <telephone DN>
Pool A to O,
BlocA to BlocF
There are three main categories of lines:
PSTN-based lines: (analog, T1, PRI, BRI)
Voice over IP (VoIP) trunks, which connect through the LAN
or WAN.
Target lines, which are internal channels that provide direct
dial capability.
Identify the line in a way that is meaningful to your system,
such as by the type of line and line pool or the DN it is
attached to in the case of target lines.
Enter a telephone DN for a telephone that you want to use
to turn service off or on for other telephones using this line.
The control telephone must have the line assigned, or must
be assigned to the line pool the line is in.
Define how the line is used in relation to other lines in the
system.
• Public line: can be accessed by more than one
telephone.
• Private line: can be assigned only to one telephone and
the prime telephone for that line. Enter the internal
number of the telephone.
• Pool A - O (analog and T1 lines) BlocA to BlocF
(PRI and VoIP lines): assigns the line to one of the line
pools. If a line is assigned to a line pool, but is not
assigned to any telephone, that line is available only for
outgoing calls.
Bloc line pools must be used in conjunction with routes
and destination codes. Target lines cannot be put into
line pools.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 46

46 Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting
Table 14 Trunk/Line Data main panel (Sheet 2 of 2)
Attribute Value Description
Prime set DN: <telephone DN>
None
Pub.
Received #
(Target lines
only)
<digits associated with a
specific target line>
Assign a telephone to provide backup answering for calls
on the line. For an Auto Answer line, calls are redirected if
the received number is invalid or the target line is busy, and
if the
If busy parameter is set To prime.
Each line can be assigned only one prime telephone.
Specify the digits the system will use to identify a call from
the public network to this target line.
• A received number cannot be the same as, or be the
start digits, of a line pool access code, a destination
code, the DISA DN or the Auto DN.
• If you are configuring auto-answer BRI trunks to map to
target lines, the received number should be the same as
the Network DN supplied by your service provider. The
call will be directed to the prime telephone for the
incoming line if the Network DN is not used.
Priv.
Received #
(Target lines
only)
Distinct ring None
<digits associated with a
specific target line>
Pattern 2
Pattern 3
Pattern 4
Properties
Specify the digits the system will use to identify a call from
the private network to this target line.
• A received number cannot be the same as, or be the
start digits, of a line pool access code, a destination
code, the DISA DN or the Auto DN.
• If you are configuring auto-answer BRI trunks to map to
target lines, the received number should be the same as
the Network DN supplied by your service provider. The
call will be directed to the prime telephone for the
incoming line if the Network DN is not used.
Choose the distinctive ring pattern that you want to assign
to the line. This allows you to provide selective service to
calls with differing answer priorities.
When more than one line with the distinct ring settings rings
at a telephone, the line with the highest priority rings first.
• Pattern 4 has the highest ring priority
• Pattern 3 has second highest ring priority
• Pattern 2 has third highest ring priority
• None has the lowest ring priority.
By default, all telephones and lines are set to None.
The Properties tab shows basic line properties. Not all fields apply to all types of lines.
The Properties tab is shown in the figure Properties details panel on page 47.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 47

Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting 47
Figure 16 Properties details panel
The table Properties line settings on page 47 defines the fields on this panel and indicates the lines.
Table 15 Properties line settings
Attribute Value Description
Legend: Loop = analog/digital loop; GS = ground start; DID = DID; E&M = E&M; BRI = BRI; DPNSS
= DPNSS; VoIP = VoIP; TL = Target. Note: PRI fields are all included under the main table.
Loss package
Line Tuning Digit drop-down menu Select the line tuning digit to use. When a trunk is connected,
Loop (analog
only)
Short CO
Medium CO
Long CO
Short PBX
Long PBX
Select the appropriate loss/gain and impedance settings for
each line.
the BCM 5.0 starts a call and sends this digit to the CO to turn
off the dial tone signal, and then tests the line to optimize the
trunk levels. The default digit is 1. You may need to change the
default digit if your CO uses the digit 1 to route the call to a
special service or to a second dial tone or busy/re-order tone.
Select the digit that will result in silence on the trunk.
Preferences
The Preferences tab shows information that may vary from trunk to trunk. Most of this information
needs to coordinate with the line service provider equipment.
The figure Preferences details panel on page 48 shows the Preferences tab.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 48

48 Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting
Figure 17 Preferences details panel
The table Preferences details fields for lines on page 48 defines the fields on this panel and
indicates the lines.
Table 16 Preferences details fields for lines (Sheet 1 of 3)
Attribute Value Description
Legend: Loop = analog/digital loop; GS = ground start; DID = DID; E&M = E&M; BRI = BRI; DPNSS
= DPNSS; VoIP = VoIP; TL = Target and DASS2. Note: PRI fields are all included under the main
panel.
Auto privacy
Full autohold
Loop GS DID E&M BRI Vo IP
<check box> Define whether one BCM450 user can select a line in use at
another telephone to join an existing call.
Loop BRI DPNSS VoI P
Aux. ringer
<check box> Enables or disables Full autohold.
When enabled, if a caller selects an idle line but does not dial
any digits, that line is automatically placed on hold if you then
select another line.
Full autohold is always in place for T1 E&M trunks because it
has no meaning for incoming-only T1 DID trunks.
The default setting should be changed only if Full autohold is
required for a specific application.
Loop GS DID E&M BRI DPNSS VoIP TL
<check box> Turn the auxiliary ringer on or off for all telephones using this
line.
When programmed on a line, the auxiliary ringer will ring every
time a call is received.
Note: When programmed only on a telephone, no ring occurs for a transferred call.
An auxiliary ringer can also be programmed in Services to ring for a line placed into
a scheduled Ringing service.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 49
Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting 49
Table 16 Preferences details fields for lines (Sheet 2 of 3)
Attribute Value Description
Legend: Loop = analog/digital loop; GS = ground start; DID = DID; E&M = E&M; BRI = BRI; DPNSS
= DPNSS; VoIP = VoIP; TL = Target and DASS2. Note: PRI fields are all included under the main
panel.
ANI Number
DNIS Number
Distinct Rings in
use
Answer mode
Answer with DISA
If busy
DID E&M
<check box> Define whether the telephone number of the caller will be
shown for this line.
For T1 E&M and T1 DID trunks connected to a DTM, this setting
only appears if Signaling is set to WinkStart.
The central office must deliver ANI/DNIS in DTMF mode. No
additional equipment is required.
E&M
<check box> Defines whether the digits dialed by an external caller on this
line will be shown.For T1 E&M trunks connected to a DTM, this
setting only appears if Signaling is set to WinkStart and Answer
mode is set to Manual.
<read-only> Indicates if a special ring has been assigned. See Distinct Ring
on the main table.
Loop GS E&M BRI DPNSS
Manual
Auto
Note: You require Disconnect supervision on the line if loop start trunks are to
operate in auto-answer mode.
Loop GS E&M BRI
<check box> Define whether the system prompts a caller for a six-digit class
To Prime
Busy Tone
Tips: The duration of an open switch interval (OSI) before BCM450 disconnects a
call is programmed by the Disconnect timer setting.
Define whether a trunk is manual or automatic answer.
Auto answer mode allows the trunk to be a shared resource by
the system telephones. This shared resource is created through
routing to target lines or using DISA.
For auto answer trunks being used to allow remote call-in from
system users, the trunk can be configured to answer with a
straight dial tone, if DISA has not been enabled. It can also be
configured to answer with a stuttered dial tone if DISA is
enabled and the caller is expected to enter a CoS password.
The CoS password defines which system features the caller is
permitted to access.
Manual answer trunks are assigned to one or more telephones.
The assigned telephones exclusively own the line.
of service (CoS) password.
start, T1 E&M lines that have auto-answer mode, and analog
trunks. Set this option to No for T1 E&M lines on a private
network that have auto-answer mode.
Define whether a caller receives a busy tone or the call
forwards to the prime telephone when the target line is busy.
Busy tone only works for PRI trunks.
This setting appears for T1 loop
TL
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 50

50 Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting
Table 16 Preferences details fields for lines (Sheet 3 of 3)
Attribute Value Description
Legend: Loop = analog/digital loop; GS = ground start; DID = DID; E&M = E&M; BRI = BRI; DPNSS
= DPNSS; VoIP = VoIP; TL = Target and DASS2. Note: PRI fields are all included under the main
panel.
Voice Message
Center
Redirect to
Warning: Enable modules
If you disabled any trunk media bay modules prior to performing programming, enable them now to
ensure your system will function properly.
Loop GS DID E&M BRI DPNSS VoIP TL
Center 1 Center 5
Loop GS DID E&M TL
<dial string> Enter a dial string (including destination code) to redirect the
If this line connects t o a remote voice mail, either through the
private network or at the Central Office, indicate which Center
number has been configured with the contact number.The
system calls that number to check voice mail messages when a
message indicator is presented to a telephone.
line to an external telephone, such as a call attendant on
another system.
If you want to stop redirection, you need to delete the dial string
and allow the record to update.
Warning: If the dialstring is set up, the line will immediately be
redirected out of the system not ringing any telephone.
Restrictions
Assigning Line restrictions and Remote Access Package restrictions are part of the configuration
for controlling calls out of the system (line restrictions) and into the system from a private network
node or from a remote user calling in over the PSTN lines (Remote Access Packages).
The figure Restrictions tab on page 51 shows the restrictions for a line.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 51

Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting 51
Figure 18 Restrictions tab
The table Restrictions on page 51 describes the fields on this panel.
Table 17 Restrictions
Attribute Values Description
Use remote package <remote package #> If the line is being used to receive external calls or calls
from other nodes on the private network, ensure that
you indicate a remote package that provides only the
availability that you want external callers to have. This
attribute is typically used for tandeming calls.
Schedule Default: Normal, Night, Evening, Lunch, Sched 4, Sched 5, Sched 6
Line Restrictions Use Filter
Remote Restrictions
- Use Filter
<00-99> Enter the restriction filter number that applies to each
schedule.
(controls outgoing calls)
<00-99> Enter the restriction filter that applies to each schedule.
This setting provides call controls for incoming calls over
a private network or from remote user dialing in over
PSTN)
Assigned DNs
The Assigned DNs tabbed panel displays the DN properties for lines that are assigned to
telephones.
This information can also be configured on the DN record. Any information added, deleted or
modified in this table reflects in the DN record.
Note: Lines that do not allow single-line assignment, such as PRI lines and VoIP lines,
will not display this tabbed panel.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 52

52 Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting
Restoring system data
If the programming of lines and extensions is incorrect, you can restore from an archive file, or
you can restore the system to factory defaults. This section provides the procedures to follow to
restore system data from an archive file, and to restore factory defaults. For information about the
effects of performing a restore operation, or about optional components, see Nortel Business
Communications Manager 5.0 Administration and Security (NN40170-603).
Restoring data from an archive
Caution: A backup operation can interrupt services running on the BCM. A
warning displays whenever the backup will cause a service interruption. If you
want to perform a backup that does not affect the system, you can exclude
services that would be affected. Alternatively, you can include these services and
perform a backup at a time when the system is typically not in use.
To restore data from an archive
1 In the task panel, click the Administration tab.
2 Open the Backup and Restore folder, and then click Restore.
The Restore panel opens. The Restore From selection field has BCM as a default value.
3 In the Restore From selection field, select the location of the archive file to restore:
• BCM
• My Computer
• Network folder
• FTP server
• SFTP server
• USB storage device
• Factory Default
4 Click the Restore button.
The Select Components to Restore window opens.
5 Select the optional components that you want to include from the backup file.
6 Click the OK button.
A warning window opens and displays information about components that will be affected by
the restore operation. Read the warning carefully before proceeding.
7 Click the Yes button to proceed.
A progress window opens. When the operation is complete, the Restore Complete window
opens.
8 Click the OK button.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 53

Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting 53
Restoring the factory configuration
Caution: A restore operation is a service-affecting operation. A number of
services running on the BCM system are stopped and then restarted using the
restored configuration or application data. A reboot is required if you choose
Keycodes as a restore option. It will take several minutes before Voicemail is
working again.
To restore the factory configuration
Your BCM is delivered with a backup file that was created at the factory. This file can be a helpful
starting point if you decide to completely reconfigure your BCM and you want to erase the settings
programmed on your device. Although you can select individual components to restore, Nortel
recommends that you restore all components when using this option.
1 In the task panel, click the Administration tab.
2 Open the Backup and Restore folder, and then click Restore.
The Restore panel opens.
3 In the Restore From selection field, select Factory Default.
A warning dialog box displays.
4 Click the Restore button.
The Select Components to Restore panel opens.
5 Select the optional components that you want to include from the backup archive.
6 Click the OK button.
A warning window opens and displays information about components that will be affected by
the restore operation. Read the warning carefully before proceeding.
7 Click the Yes button to proceed.
A progress window opens. When the operation is complete, the Restore Complete window
opens.
8 Click the OK button.
Verify the software inventory
This section provides information about how to verify the level of software components and obtain
updates to your software inventory. For information about applying software updates, see Nortel
Business Communications Manager 5.0 Administration and Security (NN40170-603).
Viewing the inventory of BCM software
BCM software is organized into software components that you can individually update as
required. The version of each software component is tracked so that you can determine the exact
software release level of a BCM to the component level.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 54

54 Chapter 4 Software Troubleshooting
You can view the complete inventory of software installed on the BCM. The Software Inventory
table displays all the software components installed on the system, the functional group and the
software version of each component.
The table Information displayed in the Software Component Version Information table on page 54
lists the information displayed in the Software Component Version Information table.
Table 18 Information displayed in the Software Component Version Information table
Column Description
Component The name of the software component installed on the BCM450. For
example, backup-recovery.
Group The functional group to which the software component belongs. For
Version The version of the software component.
example, Operating System.
You can change the order of the information displayed in the table by clicking a column heading
and dragging it to a new place in the table. You can also sort the information in a column by
descending or ascending order, by clicking the column heading.
To view the BCM software inventory
1 In the task panel, click the Administration tab.
2 Open the Software Management folder, and then click the Software Inventory task.
The Software Inventory panel opens.
3 View the details in the Software Component Version Information table.
Obtaining software updates
Before you can apply a software update to your BCM, you must obtain the software update and
unzip the file. Authorized Nortel partners can download BCM software updates from the Nortel
Technical Support web page.
To obtain updates from the Nortel Technical Support Web page
1 In your web browser, enter www.nortel.com/cs and then click the Go button.
The Nortel Technical Support Web page opens.
2 Download the required updates.
3 Create a directory for each update and unzip the downloaded file into a directory.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 55

Chapter 5
Advanced Troubleshooting
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and BCM450 platforms running BCM
5.0.
This chapter contains examples of advanced troubleshooting procedures. You must be a system
administrator to perform these procedures.
Navigation
• Example 1: Cannot dial out from an analog trunk on page 55
• Example 2: Cannot dial out from a SIP or H323 VoIP trunk on page 57
• Example 3: IP set is not registering with the BCM on page 63
• Example 4: Cannot install keycode or invalid keycode application on page 65
• Example 5: Cannot dial out from digital trunk on page 66
• Example 6: MeetMe Conferencing commands do not work, or conferencing is busy on page
70
• Example 7: Unable to apply a software update from a USB storage device on page 71
• Example 8: Element Manager incorrectly shows expansion cabinet as empty on page 72
55
Example 1: Cannot dial out from an analog trunk
When you cannot dial out from an analog trunk, you may experience the following problems in
your network:
• you are unable to reach a destination number when you dial it
• there is no dial tone
• instead of a dial tone, you hear a re-order or fast-busy tone
• you hear a “wrong number” message from the central office.
Use the following procedure when you cannot dial out from an analog trunk.
Troubleshooting example 1
1 Check that the LED indicators on the BCM Chassis and the MBM are solid green.
2 Using an analog test set, verify that a dial tone is present at the MBM termination point.
3 From the Element Manager, select Configuration > System > Keycodes to view the list of
installed features.
4 Verify that the appropriate keycode is active. For analog trunk modules, the keycode is Exp
Port, and for BCM50 built-in trunks (main chassis), the keycode is Int Analog Trunk.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 56

56 Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting
5 Select Configuration, Resources > Telephony Resources and select the appropriate trunk.
Verify that the trunk is active.
6 Select Configuration, Telephony > Lines > Active Physical Lines. Select the appropriate
line and verify that it is provisioned correctly. The Line Type should be Pool A, the Trunk
Mode should be Supervised, and the Dial Mode should be Tone.
7 Select Configuration, Telephony > Sets > Active Sets. Select the appropriate set and verify
that it is provisioned correctly. On the Line Assignment tab, verify that the Appearance
Type is one of the following: appear only, appear and ring, or ring only.
8 Select Administration > Utilities > BCM Monitor and click the Launch BCM Monitor
button.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 57

Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting 57
9 Select the BCM Info tab and verify the status of the line.
Example 2: Cannot dial out from a SIP or H323 VoIP trunk
When you cannot dial out from a SIP or H323 VoIP trunk, you may experience the following
problems in your network:
• you are unable to reach a destination number when you dial it
• there is no route to the destination
Use the following procedure when you cannot dial out from a SIP or H323 trunk.
Troubleshooting example 2
1 Check that the LED indicators on the BCM Chassis are solid green.
2 From the Element Manager, select Configuration > System > Keycodes to view the list of
installed features.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 58

58 Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting
3 Verify that the appropriate keycode is active. For H323 trunks, the keycode is VoIP GW
Trunk, and for SIP trunks, the keycode is SIP GW Trunk.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 59

Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting 59
4 Select Configuration > Telephony > Line > Active VoIP Lines. Select the appropriate line
and verify that the Control Set and Prime Set are provisioned correctly.
5 Select Configuration > Resources > Telephony Resources and select the appropriate trunk.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 60

60 Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting
6 Click the Add button to open the Add Remote Gateway dialog box. Verify that the remote
gateway is configured correctly.
7 Select Configuration > Telephony > Dialing Plan > Routing and select the Routes tab.
Verify that the route is configured correctly.
8 Select Configuration > Telephony > Dialing Plan > Routing and select the Destination
Codes tab. Verify that the destination code is configured correctly.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 61

Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting 61
Note: Ensure that the Absorbed Length is configured to the expected dialing plan.
9 Select Configuration > Telephony > Sets > Active Sets and select the Line Access tab.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 62

62 Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting
10 Highlight the appropriate set and select the Line Pool Access tab. Verify that the set has
access to VoIP trunks
11 Select Configuration > Telephony > Dialing Plan > Private Network and ensure that the
Private Network Type is set to CDP or UDP.
Note: In this example, the dialing plan is configured for a CDP Network with the
recommended minimum 4 digit Private DN length.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 63

Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting 63
Example 3: IP set is not registering with the BCM
When an IP set cannot register with the BCM, you notice the following problem in your network:
• the IP set is not registered and repeatedly tries to connect to the BCM
If an IP phone is not registering with the BCM, there are three possible causes:
• there are not enough licenses for the number of IP phones connected to the system
• the number of IP sets connected exceeds the maximum: the maximum for BCM450 is 300 and
the maximum for BCM50 is 32
• the phone is not correctly configured
Verify that the number of phones does not exceed the number of licenses. If there are too many
phones for the number of licenses, disconnect unnecessary phones, or increase the number of
licenses.
If the number of IP sets connected to the BCM exceeds the maximum number of IP set licenses or
keycodes, it is possible that after a system reboot, not all of the supported IP sets can register. To
resolve this problem, refer to the procedure Troubleshooting example 3a on page 64.
If the number of phones connected does not exceed the number of licenses, and does not exceed
the maximum number of IP sets supported, use the procedure Troubleshooting example 3b on
page 64 to verify the configuration of the IP phone.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 64

64 Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting example 3a
1 Select Configuration > Telephony Resources deregister the offline sets.
OR
2 To connect more than the maximum number of IP sets, configure unused Application DNs for
these sets by selecting Configuration > Telephony Resources > Application Sets.
3 Decrease the Application DNs and increase the IPSet DN count.
Troubleshooting example 3b
1 Select Configuration > Resources > Telephony Resources and select the appropriate IP set
from the list.
2 On the IP Terminal Global Settings tab, ensure that the Enable Registration checkbox is
selected.
3 Verify that the Global password on the BCM is the same password that you are using the
register the IP set (the default password is 2264). If this field is left blank, no password prompt
occurs during phone registration.
4 Verify S1/S2 IP address & Port settings on phone (Port 7000 for BCM)
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 65

Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting 65
Example 4: Cannot install keycode or invalid keycode application
When you cannot install a keycode, or have an invalid keycode application, you will see the
following message: “Error Happened. Error detail; Invalid Keycode File.”
Use the following procedure when you cannot install a keycode, or when a keycode application is
invalid. For more information about keycodes, see Keycode Installation Guide.
Troubleshooting example 4
1 Verify that the keycode is generated against the right system ID in the Keycode Retrieval
System (KRS). Access the KRS using one of the following methods:
a Connect to http://www.nortel.com/support/tools/krs/
b In Element Manager, select Configuration > System > Keycodes and click the
Connect to Nortel Keycode Retrieval System button.
2 In the Element Manager, select Help, About. Verify that the installed version is the latest
version of the software.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 66

66 Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting
Example 5: Cannot dial out from digital trunk
When you cannot dial out from a digital trunk, you may experience the following problems in your
network:
• you are unable to reach a destination number when you dial it
• there is no route to the destination
Use the following procedure when you cannot dial out from a digital trunk.
Troubleshooting example 5
1 Check that the LED indicators on the BCM Chassis are solid green.
2 Verify the physical connection from the carrier demarcation; ensure that the cable is securely
connected.
3 Verify the physical connection from the carrier demarcation to the BCM equipment; ensure
that the cable is securely connected.
4 If you are using SL-1 or ETSI QSIG, verify that the MCDN keycode is active. From the
Element Manager, select Configuration > System > Keycodes to view the list of installed
features.
5 Verify that the digital trunk parameters are configured according to the parameters specified
by your carrier or central office.
6 Select Configuration > Resources > Telephony Resources and click the Trunk Port
Details tab. Verify that the trunk port details and state are correctly provisioned.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 67

Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting 67
7 Select the Provision Lines tab and verify that the lines are correctly provisioned.
8 Select Configuration > Telephony > Dialing Plan > Routing and select the Routes tab.
Verify that the route is configured correctly
9 Select Configuration > Telephony > Dialing Plan, > Routing and select the Destination
Codes tab. Verify that the destination code is configured correctly.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 68

68 Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting
Note: Ensure that the Absorbed Length is configured to the expected dialing plan.
10 Select Administration > Telephony Metrics > Trunk Module Metrics and select the DTM
module. Verify that the State of the DTM module is Enabled.
11 Select the CSU Alarm History tab and check the alarm status of the module.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 69

Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting 69
12 Select Administration > Telephony Metrics > CBC Limit Metrics and verify calls were not
denied due to exceeding CBC limits.
13 Select Administration > Utilities > BCM Monitor and click the Launch BCM Monitor
button.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 70

70 Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting
14 Select the Line Monitor tab and verify the status of the line; select the UIP tab and verify the
call set up.
Example 6: MeetMe Conferencing commands do not work, or conferencing is busy
Use the following procedure to troubleshoot problems with MeetMe Conferencing.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 71

Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting 71
Troubleshooting example 6
1 Select Configuration > Resources > Application Resources and then select the VoiceMail +
CC application.
2 Increase the maximum number of application resources (voice ports) for Voice Mail + CC.
Example 7: Unable to apply a software update from a USB storage device
Use the following procedure when a software update from a USB storage device fails. When the
update fails, the BCM generates alarm 1003.
Troubleshooting example 7
1 Verify that only one USB storage device is attached to the BCM in the bottom USB port.
2 If a second USB storage device is attached, remove it.
3 Verify that there is only one partition on the USB storage device, and that the software update
is on the first partition. The BCM will recognizes only the first partition.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 72

72 Chapter 5 Advanced Troubleshooting
Example 8: Element Manager incorrectly shows expansion cabinet as empty
Use the following procedure when a module is installed in the expansion cabinet, but the Element
Manager shows the expansion cabinet as empty, and the MBM is not active.
1 Select Configuration > Resources > Telephony Resources.
2 Double-click the Module Type field for the expansion cabinet.
3 Select the module from the list.
4 Configure the module and select Enable.
Example 9: HDD-2 LED is Off after installing second hard disk
When you apply a RAID upgrade kit to an existing BCM450 5.0 software system, the LED
indicator of HDD-2 remains off after installing the second hard disk.
Perform the following actions when this occurs:
1 Verify if the version of the running software is BCM450 5.0 or greater. BCM450 1.0 systems
are incompatible with RAID upgrade kit.
2 Verify if the hard disk is seated properly.
If not, shut down the system, remove the second hard disk, and reset it, ensuring the hard disk
tray is firmly locked to the rear SATA connection. When the hard disk clips into the correct
position as the hard disk tray locks itself firmly into position, the front of the second hard disk
tray must be flush with the first hard disk tray.
Example 10: VLAN interfaces cannot communicate with external devices
When VLAN interfaces cannot communicate with external devices, you can notice the following
problems in your network:
• The network is not connected to the appropriate BCM LAN port.
• The remote VLAN endpoint is not configured with the same VLAN ID as on the BCM.
• The remote VLAN endpoint is configured on the same VLAN ID as on the BCM but their
subnet IP address differ.
Use the following procedure when VLAN interfaces cannot communicate with external devices:
1 Select the Ethernet Activity option from the Element Manager.
2 Verify the BCM LAN port connectivity and traffic forwarding statistics.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Note: The statistics of the Layer 2 switch ports do not differentiate between
normal LAN traffic and VLAN traf fic .
Page 73

Chapter 6
Recovery trees
The information in this chapter applies to the BCM450 platform only.
This chapter provides recovery trees for common troubleshooting scenarios.
Navigation
• System is not processing calls on page 73
• Start-up profile fails on page 74
• Cannot access BCM450 through Element Manager on page 75
• BCM450 shuts down unexpectedly on page 77
System is not processing calls
73
Use the following flowchart when the BCM450 is not processing calls.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 74

74 Chapter 6 Recovery trees
Figure 19 System is not processing calls
Start-up profile fails
Use the following flowchart when the start-up profile of the BCM450 fails.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 75

Figure 20 Start-up profile fails
Chapter 6 Recovery trees 75
Cannot access BCM450 through Element Manager
Use the following flowchart when you cannot access the BCM450 through Element Manager.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 76
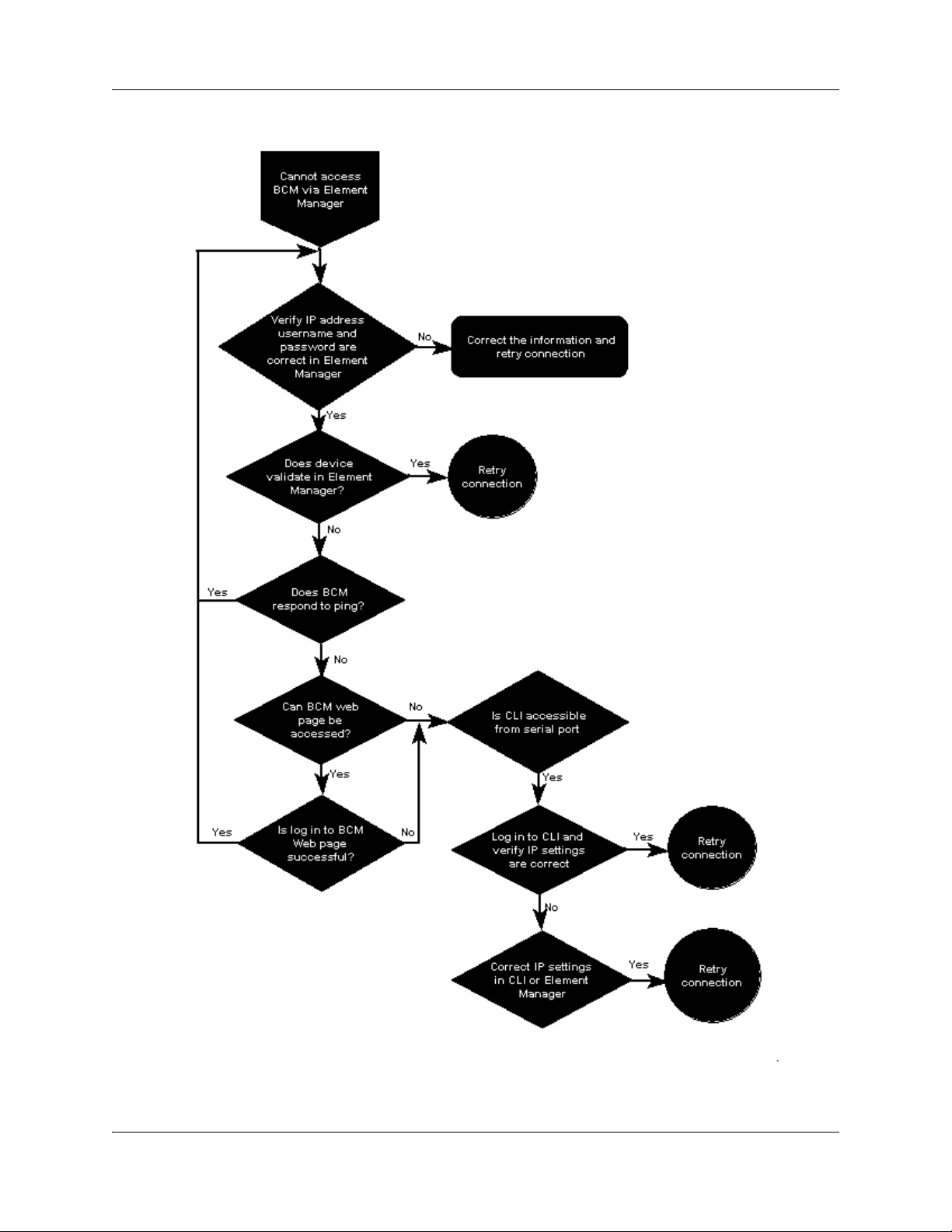
76 Chapter 6 Recovery trees
Figure 21 Cannot access BCM450 through Element Manager
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 77

BCM450 shuts down unexpectedly
Use the following flowchart when the BCM450 shuts down unexpectedly.
Figure 22 Unexpected shutdown
Chapter 6 Recovery trees 77
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 78

78 Chapter 6 Recovery trees
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 79

Chapter 7
Downloading Software
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and BCM450 platforms running the
BCM 5.0.
Use the information in this chapter to download BCM software.
Navigation
• Downloading software from the BCM system webpage on page 79
• Downloading software from the Nortel web site on page 82
Downloading software from the BCM system webpage
The BCM system web page facilitates the download of applications, documentation, and other
information necessary for running the BCM platform and its services. You connect to the BCM
system web page by typing the IP address of your BCM system device into your browser. A valid
user name and password are required in order to access the web page.
79
The BCM system web page contains the following links:
• Quick Link - Provides links to frequently used applications, including Mailbox Manager,
Activity Reporter Basic, and CallPilot Manager.
• User Applications - Applications listed in Table 19 that are available to the end users of
the BCM platform.
• Business Applications - Applications listed in Table 19 that are available to business users
of the BCM platform.
• Administrator Applications - Applications listed in Table 19 that are available to BCM
platform administrators.
• Documentation - Documentation for the BCM450 end users to explain the end-user
applications and BCM platform-specific tasks.
Table 19 Applications available on BCM system Web page
Application User Administrator
User Applications
Mailbox Manager Y Y
Desktop Assistant Pro Y Y
CallPilot Unified Messaging Y Y
Personal Call Manager Y Y
LAN CTE Client Y Y
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 80

80 Chapter 7 Downloading Software
Table 19 Applications available on BCM system Web page
Application User Administrator
IP Software Phone 2050 Y Y
Mobile Voice Client 2050 Y Y
Business Applications
Reporter Applications
Activity Reporter Basic N Y
Activity Reporter N Y
Contact Center Applications
Reporting for Contact Center N Y
Contact Center Reporting
Server
Multimedia Contact Center N Y
IP View Softboard N Y
Administrator Applications
Administrator Management Tools
CallPilot Manager N Y
Business Element Manager N Y
Desktop Assistant Pro AE N Y
NCM for BCM N Y
BCM Monitor N Y
CDR Clients N Y
BCM
MIBs N Y
RADIUS Dictionary
SSH Client (PuTTY) N Y
BCM Logs N Y
Digital Mobility Tools
Digital Mobility Controller N Y
Digital Mobility Service Tool N Y
Templates
Startup Profile Template N Y
Factory Default Programming
Record
NY
NY
Table 20 Applications available on BCM50 Web page
Application User Administrator
User Applications
Mailbox Manager Y Y
Desktop Assistant Pro Y Y
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 81

Chapter 7 Downloading Software 81
Table 20 Applications available on BCM50 Web page
Application User Administrator
CallPilot Unified Messaging Y Y
Personal Call Manager Y Y
LAN CTE Client Y Y
IP Software Phone 2050 Y Y
Mobile Voice Client 2050 Y Y
Nortel VPN Client N Y
Business Applications
Reporter Applications
Activity Reporter Basic N Y
Activity Reporter N Y
Contact Center Applications
Reporting for Contact Center N Y
Contact Center Reporting
Server
Multimedia Contact Center N Y
IP View Softboard N Y
Administrator Applications
Administrator Management Tools
CallPilot Manager N Y
Business Element Manager N Y
Desktop Assistant Pro AE N Y
NCM for BCM N Y
BCM Monitor N Y
CDR Clients N Y
BCM
MIBs N Y
RADIUS Dictionary
SSH Client (PuTTY) N Y
BCM Logs N Y
Digital Mobility Tools
Digital Mobility Controller N Y
Digital Mobility Service Tool N Y
Templates
Startup Profile Template N Y
Factory Default Programming
Record
NY
NY
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 82

82 Chapter 7 Downloading Software
To download software from the BCM Web page
1 Connect to the BCM Web page
— If the BCM is installed on the network use a browser and type in the BCM IP address as
the URL in the following format:
http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
— If the BCM is installed but not yet configured, connect directly to the BCM through the
OAM port and, using a browser, type the following:
http://10.10.11.1/
2 Enter the user name and password to be authenticated on the BCM Web page.
3 Select the link for the type of application that you want to download.
4 Select the link for the specific application or tool that you want to download and select the
download link.
Downloading software from the Nortel web site
To download software from the Nortel Web site, see the following web site:
http://www.nortel.com/downloadingcontent
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 83

Chapter 8
Troubleshooting Tools
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms running
BCM 5.0.
The BCM system provides several tools that you can use to diagnose problems.
Navigation
• Service Management on page 83
• Status and Metrics on page 83
• Utilities on page 84
• Command Line Interface on page 84, for BCM450 only
83
Service Management
You can use the Element Manager to view a list of the services that are running on your BCM
system.
For more information about service management on BCM 5.0, see BCM 5.0 Administration and
Security Guide (NN40170-603).
Status and Metrics
You can use the Element Manager to view detailed information about the performance of the BCM
and about the performance of system resources.
You monitor system status using the following tools:
• QoS Monitor—QoS Monitor monitors the quality of service (QoS) of IP trunk services.
• UPS Status—The Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) feature provides monitoring of the
power source and the battery backup.
• NTP Metrics—The Network Time Protocol (NTP Metrics) feature provides an overview of
the integrity of the NTP time source
For information about monitoring the system status, see the BCM 5.0 Administration and Security
Guide (NN40170-603).
You can monitor system performance using the following tools:
• Activity Reporter Basic—Generate reports about call activity and voice mail receive statistics.
• Trunk Module Metrics— View the status of digital trunk modules as well as identify any
device or lines connected to the system.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 84

84 Chapter 8 Troubleshooting Tools
• CbC Limit Metrics—Use the CbC Limit metrics panel to monitor denied call activity for each
service on each line pool.
• Hunt Group Metrics—Access the Hunt Group metrics to evaluate total call processing by hunt
group member.
• PSTN Fallback Metrics—View how many fallback attempts and fallback failures occur within
a specific period using the PSTN Fallback Metrics panel.
• Proactive Voice Quality Management—Proactive Voice Quality Management (PVQM)
metrics allow you to monitor the quality of VoIP calls. You can also use the PVQM metrics to
diagnose infrastructure problems in your network.
For more information about monitoring system performance, see Nortel Business Communications
Manager 5.0 Administration and Security (NN40170-603).
Utilities
BCM provides the following utilities:
• BCM Monitor—BCM Monitor is a stand-alone diagnostic application that the system
administrator can use to view real-time system and IP telephony information about BCM
systems.
• Ping—Ping (Packet InterNet Groper) is a utility that you can use to verify that a route exists
between the BCM and another device.
• Route trace—You can use Trace Route to measure round-trip times to all hops along a route.
This helps you to identify bottlenecks in the network.
• Ethernet activity—The Ethernet Activity panel is a utility that you can use to view ethernet
activity in the BCM system.
For more information about utilities, see Nortel Busines Communications Manager 5.0
Administration and Security (NN40170-603).
Command Line Interface
The information in this section applies to the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms running BCM
5.0.
You can use the Command Line Interface (CLI) to configure basic settings, as well as shut down,
reboot, or reset the BCM450 system. Two CLI modes are available: Maintenance CLI, and
Configuration CLI.
This section contains information about the following topics:
• Accessing the CLI on page 85
• Using the Configuration CLI on page 86
• Using the Maintenance CLI on page 86
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 85

Chapter 8 Troubleshooting Tools 85
Accessing the CLI
There are two methods of accessing the CLI:
• through a serial connection
• through the OAM port
For either method, your user account must be assigned the System-CLI privilege before you can
access the CLI.
Accessing the CLI through a serial connection
Caution: The CLI is intended for use by experienced technicians, or as directed
by Nortel Technical Support. Improper use of the CLI may result in data loss.
1 Connect a serial cable with a 9-pin female connector from the serial port on a PC to the serial
port on the BCM450.
2 Ensure that you use the following settings:
• bits per second: 115200
• data bits: 8
•parity: N
• stop bits: 1
• no flow control
3 Use a terminal emulation program, such as Hyperterminal or Nortel CLI Manager, to establish
a connection to the BCM450.
4 Log into the BCM450 by entering your username and password. Your user account must be
assigned the System-CLI privilege in order to access the CLI.
Accessing the CLI through the OAM port
Caution: The CLI is intended for use by experienced technicians, or as directed
by Nortel Technical Support. Improper use of the CLI may result in data loss.
1 Connect an Ethernet cable from the Ethernet port on a PC to the OAM Ethernet port on the
BCM450.
2 Set the IP address of the PC to 10.10.11.2.
3 Use putty to establish an SSH connection to the default IP address of the OAM port:
10.10.11.1.
4 Log into the BCM450 by entering your username and password. Your user account must be
assigned the System-CLI privilege in order to access the CLI.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 86

86 Chapter 8 Troubleshooting Tools
Using the Configuration CLI
The Configuration CLI displays when the system is in Main OS mode. The options available on
the Configuration CLI are:
• 0—Exit. The system exits the CLI to the login prompt.
• 1—Reboot. The system reboots to the Main OS.
• 2—Shutdown. The system shuts down. You need physical access to the BCM450 hardware to
restart the system.
• 3—Safe OS. The system reboots to the Safe OS and waits 1 minute for you to login. When
you login within 1 minute, the Maintenance CLI displays. If you do not login within 1 minute,
the system changes to the Main OS. For more information about the Safe OS, see Using the
Maintenance CLI on page 86.
• 4—Configuration Reset. A Level 1 reset occurs. The system resets all configuration data to
the factory defaults.
• 5—Software Reset. A Level 2 reset occurs. The system resets all configuration data and
software to the factory defaults.
• 6—IP Configuration. You can configure the following basic IP settings:
• 0—Return to Previous Menu. The system returns to the main menu.
• 1—Hostname. Provision the hostname of the system.
• 2—IP Address. Provision the IP address of the system.
• 3—Subnet Mask. Provision the subnet mask for the IP address.
• 4—Default Gateway. Provision the default gateway for the system.
• 5—DHCP Client Mode. Enable or disable the DHCP client.
• 6—Commit Changes. Save changes to the IP settings.
• 7—Reload Settings. Reload the existing IP settings.
Using the Maintenance CLI
The Maintenance CLI displays when the system is in Safe OS mode. The Safe OS is a diagnostic
mode that you can use if the Main OS is experiencing problems. No applications or telephony
services are running when the BCM450 is in Safe OS mode. The options available on the
Maintenance CLI are:
• 0—Exit. The system exits to the Safe OS login prompt.
• 1—Reboot into Main OS. The system reboots to the Main OS.
• 2—Shutdown. The system shuts down. You need physical access to the BCM450 hardware to
restart the system.
• 3—Reboot into Safe OS. The system reboots to the Safe OS and waits 1 minute for you to
login. If you do not login within 1 minute, the system changes to the Main OS.
• 4—Transition to Main OS. The system changes from the Safe OS to the Main OS without
restarting.
• 5—Configuration Reset. A Level 1 reset occurs. The system resets all configuration data to
the factory defaults.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 87

Chapter 8 Troubleshooting Tools 87
• 6—Software Reset. A Level 2 reset occurs. The system resets all configuration data and
software to the factory defaults.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 88

88 Chapter 8 Troubleshooting Tools
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 89

Chapter 9
Understanding System Messages
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms running
BCM 5.0.
The BCM5.0 generates alarms, logs, traps, and other system messages that you can use to
troubleshoot problems.
Alarms, logs, and traps
For information about system messages, alarms, logs, and SNMP traps, see Nortel Business
Manager 5.0 Fault and Performance (NN40170-701). For more information about specific
alarms, see Nortel Business Communications Manager 5.0 Alarms Reference (NN40170-702).
Reporting for dropped calls
89
You can specify the level of system reporting that you require for released ISDN or VoIP calls.
You can choose to have no text, a simple explanation, or a detailed explanation in the dropped call
notification.
Use this procedure to set the level of reporting for dropped calls.
To set Release Reasons
To set Release reasons, follow these steps:
1 Click Administration > Utilities > Diagnostic settings.
2 Click the Telephony tab.
The Release Reasons panel appears.
3 From the Release Reason drop-down menu, select the level of reporting that you require.
Table 21 lists the possible values for Release reasons.
Table 21 Release reasons
Attributes Values Description
None Default Value No text will accompany a dropped call notification.
Simple Cause Code:
Off
On
Off: no text is provided
On: the code only is provided
Note: if you select Simple text, you must turn off the Cause code. This is for
diagnostic purposes only.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 90

90 Chapter 9 Understanding System Messages
Table 21 Release reasons
Attributes Values Description
Detailed No setting A detailed explanation of the Cause code is provided.
Cause
Code
check box This check box appears when you select Simple in the Release Reason
Text drop-down menu. When you select the check box, only the cause code
accompanies a dropped call notification.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 91

Chapter 10
Useful Troubleshooting Links
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms running
BCM 5.0.
Use the information in this chapter to find additional reference information when you are
troubleshooting a problem with the BCM5.0. As part of your initial troubleshooting, Nortel
recommends that you check these resources for information about known issues and for solutions
related to the problem you are experiencing.
Navigation
• Partner Bulletins on page 91
• Knowledge and Solution Engine on page 91
91
Partner Bulletins
To locate Partner Bulletins, visit the Nortel Partner Information Center:
http://www.nortel.com/pic
Knowledge and Solution Engine
The Knowledge and Solution Engine allows you to search an entire database of Nortel technical
documents, troubleshooting solutions, software, and technical bulletins.
The document types available from the Knowledge and Solution Engine include the following:
• Bulletins: Includes a listing of technical bulletins.
• Documentation: Includes all technical documentation written for Nortel
• products (such as installation guides, administration guides, release
• notes).
• Service Requests: Includes technical support cases created within the past year. The
availability of service requests is based on your customer entitlement.
• Software: Includes software patches and software releases.
• Solutions: Includes troubleshooting solutions written by the Nortel Technical Support team.
When searching through the Knowledge and Solution Engine, enter a natural language query (that
is, a query in the form of a statement or a question).
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 92

92 Chapter 10 Useful Troubleshooting Links
Using the Knowledge and Solution Engine
Use the following procedure to access the Knowledge and Solution Engine.
To use the Knowledge and Solution Engine
1 Go to the Nortel Web site: www.nortel.com
2 Log in using user name and password.
3 Select SUPPORT & TRAINING.
4 Select ONLINE SELF-SERVICE, and then select Knowledge Base.
The Online Self-Service page appears and shows the Knowledge and Solution Engine. For
information on performing your search, click the Search Tips link.
To view an interactive tutorial for the Knowledge and Solution Engine, go to the Help &
Contact section, click the Help Using This Site link and then scroll to find the Knowledge
Base tutorial.
5 Enter your problem statement or question in the text box. Ensure that you leave spaces
between the words in the statement or question.
6 From the ALL TYPES drop-down list, select the document type you would like to search
against. The default is ALL TYPES, which searches on all available documents (bulletins,
documentation, services requests, software, and solutions).
7 Click > (the arrow adjacent to the text box) or press Enter to start your search. The page
reloads and provides the option to narrow your search by product family.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 93

Chapter 11
Frequently Asked Questions
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms running
BCM 5.0.
This chapter provides answers to frequently asked questions.
Navigation
• Backup, restore, and reset operations on page 93
• Password protection on page 95
• Fault management on page 96
• System and status information on page 97
• Connectivity problems on page 101, for BCM450 only
• IP addresses on page 102
93
Backup, restore, and reset operations
This section contains answers to the following questions:
• How do I back up the database? on page 93
• How do I restore the BCM from a previous backup? on page 94
• How do I complete a Warm Reset or Cold Reset? Is it safe and will I lose customer data? on
page 94
How do I back up the database?
Use the following procedure to back up the BCM450 database.
To perform a backup
1 In the task panel, click the Administration tab.
2 Open the Backup and Restore folder, and then click Backup.
The Backup panel opens and displays the Immediate Backup tab. In the Backup To
selection field, choose a destination for the backup archive.
3 Click the Backup button.
The Backup window opens.
4 In the Optional Components table, select or clear the check box for each component to
include or exclude these components from the backup operation.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 94

94 Chapter 11 Frequently Asked Questions
5 Click the OK button.
A warning window opens. Read the warning carefully before proceeding.
6 Click the Yes button to proceed.
A progress window opens. When the backup is complete, the Backup Complete message
appears.
7 Click the OK button.
How do I restore the BCM from a previous backup?
Use the following procedure to restore the BCM database.
To restore data from the BCM
1 In the task panel, click the Administration tab.
2 Open the Backup and Restore folder, and then click Restore.
The Restore panel opens. In the Restore From field, select the location of the backup archive
to use.
3 Click the Restore button.
The Select Components to Restore window opens.
4 Select the optional components that you want to include from the backup file.
5 Click the OK button.
A warning window opens and displays information about components that will be affected by
the restore operation. Read the warning carefully before proceeding.
6 Click the Yes button to proceed.
A progress window opens. When the operation is complete, the Restore Complete window
opens.
7 Click the OK button.
How do I complete a Warm Reset or Cold Reset? Is it safe and will I lose customer data?
You can use the Reset utility in Element Manager to:
• reboot the BCM system
• perform a warm reset of telephony services
• perform a cold reset of telephony services
• for the BCM450, shut down the system
• for the BCM50, perform a cold reset of the router
For a description of the impact on the system of each of these resets, see Reset functions on page
29.
Use this procedure to perform a warm or cold reset.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 95

Completing a warm or cold reset
1 Select Administration, Utilities, Reset, and click one of the following buttons:
a Reboot BCM450 System will restart the operating system of the BCM450
b Warm Reset Telephony Services will restart telephony services. Customer data will
be retained.
c Cold Reset Telephony Services will reset telephony programming to factory
defaults. Customer data will be lost.
d Shutdown System will stop all services and shut down the system. Restarting the
system requires physical access to the BCM450.
e Cold Reset Router resets the router programming to the factory defaults. This applies
to BCM50 only.
Password protection
This section answers the following frequently asked question:
Chapter 11 Frequently Asked Questions 95
• How do I recover a lost password for the BCM? on page 95
How do I recover a lost password for the BCM?
There is a Nortel support default user which cannot be deleted or modified. This account is set up
to allow Nortel troubleshooting technicians to access areas of the system that are not available to
other users. You can change the default challenge key, but be sure to retain a record of the change
so that Nortel support technicians can access your system.
Recovering a lost password
1 Select Configuration, Administrator Access, Security Policies, and select the Entry Policy
tab.
2 With the Challenge Key available, contact Nortel Technical Support and request help to
recover the lost password.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 96

96 Chapter 11 Frequently Asked Questions
Fault management
This section answers the following frequently asked question:
• How do I view Alarms? Can I acknowledge and clear them? on page 96
How do I view Alarms? Can I acknowledge and clear them?
When you view an alarm on the alarms panel, you can change the order of the columns in the table
and you can sort alarms. For example, you may want to sort alarms by Component ID and Alarm
ID.
Use the following procedures to view alarms and to acknowledge alarms.
To view an alarm
1 Click the Administration tab.
2 Open the General folder, and then click the Alarms task.
The Alarms page opens.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 97

Chapter 11 Frequently Asked Questions 97
3 In the Alarms Panel table, select an alarm.
The Alarm Details panel displays below the Alarms table.
4 To change the order of columns in the Alarm table, select a column and drag it left or right to
the desired location, and release it.
5 To view a column by ascending or descending order, click the column heading.
To acknowledge an alarm
1 Click the Administration tab.
2 Open the General folder, and then click the Alarms task.
The Alarms panel opens.
3 In the Alarms table, select the alarm you want to acknowledge.
The Alarm Details panel is displayed below the Alarms table.
4 On the Alarms Details panel, click the Acknowledge Alarm button.
A check box appears in the Alarm ACKed column in the Alarms table for this alarm.
Acknowledging the alarm does not clear the alarm; it indicates only that the alarm has been
noted.
System and status information
This section answers to the following frequently asked questions:
• How do I capture the logs from the BCM? on page 97
• How do I capture the current BCM configuration? on page 99
• How do I find the BCM system health? on page 100
• How do I show specific process states? on page 100
• How do I verify current software revision? on page 100
• How do I find the BCM450 System ID and Serial Number? on page 101
How do I capture the logs from the BCM?
You can capture or transfer logs from the BCM using Element Manager, or from the BCM Web
page.
When you use the BCM Web page to transfer log files, you cannot choose the log file categories
that you will transfer; all the log files in all the categories will be transferred.
Use the following procedures to transfer log files.
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 98

98 Chapter 11 Frequently Asked Questions
Using the Element Manager to transfer log files
1 Click the Administration tab, and then open the Logs folder.
2 Click the Log Management task.
The Log Management panel opens.
3 Click the Immediate Log Transfer tab.
4 In the Transfer To selection field, select a storage location.
5 Click the Transfer button.
The Transfer To window opens.
6 Select the log file categories that you want to include in the log file transfer. All the log files
associated with the selected categories will be transferred.
7 Click the OK button.
A transfer window opens and displays applicable warnings.
8 Click the Yes button to initiate the transfer.
A Save dialog box displays.
9 Specify a filename and location for the log file and click Save.
The Progress Update window opens. When the log files are transferred, the Transfer
Complete window opens.
10 Click the OK button.
The log archive is saved in the location you specified.
Using the BCM Web Page to transfer log files
1 In your Web browser, type the IP address of the BCM, and then click Go.
The login screen opens.
2 Log on to the BCM using the same user name and password that you use to log on to a BCM
using the Element Manager.
The BCM Web pages appear.
3 Click the Administrators Applications link.
4 Click BCM Logs.
5 Click the Retrieve Log Files link.
The Retrieve Log Files panel appears.
6 Click one of the three options for file transfer: Transfer to My Computer, Store on USB
Memory, or Send to.
7 If you select the Send to radio button, select a destination from the drop-down list, otherwise,
go to the next step.
8 Click Submit. The web page shows the status as Working; when complete, it shows Success.
9 Click the Click Here to Download Logs link.
The File Download screen opens.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
Page 99

Chapter 11 Frequently Asked Questions 99
10 Click the Save button.
The Save As screen opens.
11 Specify the location where you want to save the log file transfer, and enter a name for the file
in the File Name field.
12 Click the Save button.
The file is saved.
How do I capture the current BCM configuration?
You can create a programming file that contains the current settings of all or part of your Element
Manager data. These files can be saved in either HTML or Excel spreadsheet format. You can
access the programming record in the same way you access any other HTML file or by using
Excel, version 2002 or later, for the spreadsheet format.
A programming record that contains the factory default settings is available in Excel format from
the BCM web page.
Note: It may take several hours to save programming records, depending on the
size of the system. Nortel recommends that you saving programming records
during periods of low system use.
Use the following procedure to capture the current programming record.
Capturing the current configuration
1 Select the item on the task navigation panel for which you want to save the data into an HTML
report or Excel workbook. An item can be a task item, task bullet, or a folder.
2 Click on Session, device IP address, Save Programming Record, Save Selected Data.
A warning dialog box appears; review the warning and click Yes. A Save dialog box appears.
Figure 23 Save dialog box
BCM 5.0 Troubleshooting Guide
Page 100

100 Chapter 11 Frequently Asked Questions
3 In the Save: field choose the path where you want the file stored.
4 In the Files of type: field, choose the format in which you want to save the data (HTML or
Microsoft Excel spreadsheet).
5 Enter a File name. Nortel recommends that you make the current date and system name part of
the file name.
6 Click on Save.
Note: The Save All Data selection can take up to 45 minutes to complete. Your
computer must stay connected to the element during this time, as the Save All
Data function is actively writing into the file specified until the function is
complete.
How do I find the BCM system health?
You can use the BCM Monitor to view information about system health.
The Usage Indicators tab on the BCM Monitor displays real time information about the BCM450
system, including:
• BCM system data, including CPU and memory use
• resources used on the Media Card, including signaling channels, media channels, voice bus
channels, and DSP resources
• active telephony devices, such as IP trunks, IP sets. voice ports, and media gateways
The information is displayed as an absolute figure and as a percentage of the resource used. Use
this procedure to access system health information.
Viewing the system health
1 Select Administration, Utilities, BCM Monitor and click the Launch BCM Monitor
button.
1 Select the Usage Indicators tab.
How do I show specific process states?
Use the following procedure to view specific process states.
Viewing specific process states
1 Select Administration, General, Service Manager.
The Service Manager page opens. Services are displayed in the Services table.
How do I verify current software revision?
Use the following procedure to view the current software revision.
NN40170-700NN40170-700
 Loading...
Loading...