Avaya BCM 4.0 Installation Guide

BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide
BCM
Business Communications Manager
Document Status: Standard
Document Version: 01.
Part Number: N0060609
Date: May 2009
30

Copyright © 2006–2009 Nortel Networks, All Rights Reserved.
LEGAL NOTICE
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and
recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The
information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks.
Trademarks
Nortel, the Nortel logo, and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.

Task List
New in this release . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Getting started with BCM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Device description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Installing an analog station media bay module (ASM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
To configure the MBM ...................................................................................................27
Installing the analog terminal adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
To connect the ATA2 .....................................................................................................31
To mount the ATA2 on a wall ........................................................................................31
To measure the insertion loss from the CO to the analog device..................................32
To measure the insertion loss from the analog device to the CO..................................33
Using an analog telephone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
To make external calls...................................................................................................35
To make internal calls....................................................................................................35
To answer calls..............................................................................................................36
To make or answer a second call ..................................................................................36
To answer a second call while on another call ..............................................................36
To hold a call and make a second call ..........................................................................36
To cancel MWI...............................................................................................................37
To reply to internal messages .......................................................................................37
To reply to external messages ......................................................................................37
3
ISDN overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Telephone button icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
IP telephone overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Registering Nortel 20XX and 11XX IP telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
To access the local configuration menu on an IP telephone .........................................75
To deregister a IP telephone from the IP record ...........................................................80
Relocating telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
To enable Set relocation and relocate digital telephones..............................................81
To keep an IP telephone active after it is disconnected ................................................82
To move an IP telephone without changing the DN ......................................................82
To move a Nortel IP telephone and change the DN......................................................82
ASM8, ASM8+, and GASM wiring chart and switch settings . . . . . . . . . . 85
DSM16 and DSM32 wiring charts and switch settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
DTM wiring chart and switch settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide

4 Task List
BRIM wiring chart and switch settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
N0060609N0060609

Contents
New in this release. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Other Changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Chapter 1
Getting started with BCM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
About this guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Purpose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
About BCM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
BCM key hardware elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Symbols and conventions used in this guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Related publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
How to get Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5
Chapter 2
Device description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Analog devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Digital devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Wireless devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
IP devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
ISDN devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Chapter 3
Installing an analog station media bay module (ASM). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Installing an MBM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Configuring the media bay module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Wiring the ASM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Installing analog devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Chapter 4
Installing the analog terminal adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Configuration overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Analog telephone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide

6 Contents
Installing the ATA2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Configuring the ATA2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Chapter 5
Using an analog telephone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Making and answering calls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Call Display Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Message Waiting Indication (MWI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Feature list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Other documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Chapter 6
ISDN overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Analog data device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Connecting the ATA2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Mounting the ATA2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Test insertion loss measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Replying to messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Welcome to ISDN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Analog versus ISDN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Types of ISDN service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
ISDN layers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
ISDN bearer capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Services and features for ISDN BRI and PRI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
PRI services and features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
BRI services and features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Service provider features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Network name display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Name and number blocking (ONN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Call by Call Service Selection for PRI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Emergency 911 dialing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
2-way DID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Dialing plan and PRI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
ISDN hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
PRI hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
BRI hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
S Reference Point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
T Reference Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Clock source for ISDN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
ISDN BRI NT1 equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
ISDN standards compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Planning your ISDN network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
N0060609N0060609

Contents 7
Ordering ISDN PRI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Ordering ISDN BRI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Supported ISDN protocols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Chapter 7
Telephone button icons. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Telephone features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Call Display Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
ETSI feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Chapter 8
IP telephone overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
IP telephones and VoIP trunks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Creating the IP telephony network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Networking with BCM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Key IP telephony concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Chapter 9
Registering Nortel 20XX and 11XX IP telephones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Determining the registration process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Registering the telephone to the system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Configuring telephone settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Troubleshooting IP telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Operation issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Deregistering IP telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Chapter 10
Relocating telephones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Moving digital telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Keeping an IP telephone active . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Moving IP telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
User card list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Appendix A
ASM8, ASM8+, and GASM wiring chart and switch settings . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Appendix B
DSM16 and DSM32 wiring charts and switch settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Appendix C
DTM wiring chart and switch settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Appendix D
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide

8 Contents
BRIM wiring chart and switch settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
N0060609N0060609

New in this release
The following section details what is new in Business Communications Manager Telephony
Device Installation Guide (N0060609) for release 4.0.
Navigation
• “Features” on page 9
• “Other Changes” on page 9
Features
This release contains no new features.
Other Changes
New in this release 9
See the following sections for information about changes that are not feature-related:
Revision history
April 2009
May 2009
Standard 1.2. This document is up-issued to update technical content in the
section Determining the registration process.
Standard 01.03. This document is up-issued to add IP phone 1110.
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide

10 New in this release
N0060609N0060609

Chapter 1
Getting started with BCM
Refer to the following topics for general BCM information:
• “About BCM”
• “Symbols and conventions used in this guide” on page 13
• “Related publications” on page 15
• “How to get Help” on page 17
About this guide
The BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide describes how to configure, and maintain
analog, digital, IP, and ISDN devices running on the Business Communications Manager 4.0
(BCM) software.
11
Purpose
The concepts, operations, and tasks described in this guide relate to the installation and
configuration of devices used with the BCM system. This guide provides task-based information
on how to configure devices for use with the BCM.
Use Element Manager, Startup Profile, and Telset Administration to configure various BCM
parameters.
In brief, the information in this guide explains:
— installation and configuration of components
— registration and relocation of telephones and devices
— programming loops, configuring digital telephones
— managing system-wide call appearance (SWCA) keys
— setting up central answering positions (CAP)
Audience
The BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide is directed to installers responsible for
installing, configuring, and maintaining BCM systems.
To use this guide, you must:
• be an authorized BCM installer/administrator within your organization
• know basic Nortel BCM terminology
• be knowledgeable about telephony and IP networking technology
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide

12 Chapter 1 Getting started with BCM
Organization
This guide is organized for easy access to information that explains the concepts, operations, and
procedures associated with the BCM system.
About BCM
The BCM system provides private network and telephony management capability to small and
medium-sized businesses.
The BCM system:
• integrates voice and data capabilities, VoIP gateway functions, and QoS data-routing features
into a single telephony system
• enables you to create and provide telephony applications for use in a business environment
BCM key hardware elements
BCM includes the following key elements:
• BCM200 main unit
• BCM400 main unit
• BCM1000 main unit
• BCM expansion unit (compatible with BCM400 main unit)
• BCM400 expansion gateway
• media bay modules (MBM):
— 4x16
— ASM8, ASM8+
— BRIM
—CTM4, CTM8
— DDIM
— DSM16+, DSM32+
—DTM
—FEM
— GASM
—GATM4, GATM8
BCM features
BCM 4.0 supports the complete range of IP telephony features offered by existing BCM products.
N0060609N0060609
Note: You enable the following features by entering the appropriate keycodes (no
additional hardware is required)
Chapter 1 Getting started with BCM 13
BCM applications
BCM 4.0 supports many applications provided on the existing BCM platforms.
Note: You enable the following features by entering the appropriate keycodes (no
additional hardware is required)
• Voice Messaging for standard voice mail and auto-attendant features
• Unified Messaging providing integrated voice mail management between voice mail and
common e-mail applications
• Fax Suite providing support for attached analog fax devices
• Voice Networking features
• LAN CTE (computer telephony engine)
• VEWAN (Voice Enabled WAN)
• IVR (Integrated Voice Response)
•IP Music
• Intelligent Contact Center
Symbols and conventions used in this guide
These symbols are used to highlight critical information for the BCM system:
Caution: Alerts you to conditions where you can damage the equipment.
Danger: Alerts you to conditions where you can get an electrical shock.
Warning: Alerts you to conditions where you can cause the system to fail or work
improperly.
Note: Alerts you to important information.
Tip: Alerts you to additional information that can help you perform a task.
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide
14 Chapter 1 Getting started with BCM
Security Note: Indicates a point of system security where a default should be
changed, or where the administrator needs to make a decision about the level of
!
security required for the system.
Warning: Alerts you to ground yourself with an antistatic grounding strap
before performing the maintenance procedure.
Warning: Alerts you to remove the BCM main unit and expansion unit power
cords from the ac outlet before performing any maintenance procedure.
The following conventions and symbols are used to represent the Business Series Terminal display
and dialpad.
Convention Example Used for
Word in a special font (shown in
the top line of the display)
Underlined word in capital letters
(shown in the bottom line of a
two-line display telephone)
Dialpad buttons Buttons you press on the dialpad to select a
Pswd:
PLAY
Command line prompts on display telephones.
Display option. Available on two line display
telephones
option on the display to proceed.
particular option.
. Press the button directly below the
The following text conventions are used in this guide to indicate the information described:
Convention Description
bold Courier
text
Indicates command names and options and text that you must enter.
Example: Use the
Example: Enter
info command.
show ip {alerts|routes}.
italic text Indicates book titles.
plain Courier
text
FEATURE
HOLD
Indicates command syntax and system output (for example, prompts
and system messages).
Example:
Set Trap Monitor Filters
Indicates that you press the button with the coordinating icon on
whichever set you are using.
RELEASE
N0060609N0060609

Related publications
This section provides a list of additional documents referred to in this guide. There are two types
of publications: Technical Documents and User Guides.
Technical Documents
BCM 4.0 System Overview (N0060607)
System Installation
BCM 4.0 for BCM1000 Installation and Maintenance Guide Addendum (N0060603)
BCM200/400 BCM 4.0 Installation and Maintenance Guide (N0060612)
System Programming
BCM 4.0 Administration Guide (N0060598)
BCM 4.0 Device Configuration Guide (N0060600)
BCM 4.0 Networking Configuration Guide (N0060606)
Chapter 1 Getting started with BCM 15
BCM 4.0 Telset Administration Guide (N0060610)
Telephones and Peripherals
BST Doorphone Installation and Configuration Guide (P1013654)
T24 KIM Installation Card (P0603481)
IP Key Expansion Module (KEM) User Guide
Digital Mobility
DECT Deployment and Demonstration Tool
Digital Mobility System Installation and Configuration Guide (N0000623)
T7406 Cordless Handset Installation Guide (P0606142)
2G4 Deployment and Demonstration Tool (N0027187)
IP Telephony
i2050 Software Phone Installation Guide (N0022555)
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Configuration Guide (N0060634)
Call Pilot
BCM 4.0 Unified Messaging Configuration Guide (N0060611)
CallPilot Fax Set Up and Operation Guide (P0606017)
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide

16 Chapter 1 Getting started with BCM
CallPilot Manager Set Up and Operation Guide (N0027247)
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide (N0027249)
CallPilot Programming Record (N0027404)
CallPilot Reference Guide (N0060617)
CallPilot Telephone Administration Guide (N0060618)
User Guides
Telephones and Peripherals
BCM 4.0 Telephone Features User Guide (N0060608)
BST Doorphone User Guide (P0605668)
Central Answering Position (CAP) User Guide (P0603480)
Hospitality Features Card (N0027326)
System-wide Call Appearance (SWCA) Features Card (N0027186)
T7000 Telephone User Card (P0912061)
T7100 Telephone User Card (P0609621)
T7208 Telephone User Card (P0609622)
T7316 Telephone User Card (P0935248)
T7316E Telephone User Card (P0609623)
Digital Mobility
DECT 413X/414X Handset User Guide (N0028550)
Digital Mobility Phone 7420 User Guide (N0000635)
Digital Mobility Phone 7430/7440 User Guide (N0028550)
T7406 Cordless Telephone User Card (P0942259)
IP Telephony
IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 User Guide (N0060623)
IP Phone 2001 User Guide (N0027313)
IP Phone 2002 User Guide (N0027300)
IP Phone 2004 User Guide (N0027284)
IP Phone 2007 User Guide (N0064498)
IP Phone 1120E User Guide (NN-10300-062)
N0060609N0060609

IP Phone 1140E User Guide (NN-10300-064)
BCM WLAN 2210/2211/2212 Handset User Guide (N0009103)
How to get Help
This section explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site
The best source of support for Nortel products is the Nortel Support Web site:
http://www.nortel.com/support
This site enables customers to:
• download software and related tools
• download technical documents, release notes, and product bulletins
• sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation
• search the Support Web site and Nortel Knowledge Base
• open and manage technical support cases
Chapter 1 Getting started with BCM 17
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you have a Nortel support contract and cannot find the information you require on the
Nortel Support Web site, you can get help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Outside North America, go to the Web site below and look up the phone number that applies
in your region:
http://www.nortel.com/callus
When you speak to the phone agent, you can reference an Express Routing Code (ERC) to more
quickly route your call to the appropriate support specialist. To locate the ERC for your product or
service, go to:
http://www.nortel.com/erc
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor or authorized
reseller, you can contact the technical support staff for that distributor or reseller.
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide

18 Chapter 1 Getting started with BCM
N0060609N0060609

Chapter 2
Device description
This chapter describes the telephony devices (telephones) that BCM supports.
Analog devices
BCM 4.0 supports analog telephones (single-line telephones), cordless telephones, fax machines,
answering machines, and modems (with a maximum speed of 28.8 kbit/s). You must install an
analog station media bay module (ASM8, ASM8+, and GASM) for analog devices (see Installing
an analog station media bay module (ASM)). To connect a standard analog voice device or data
communication device to the BCM system through a digital station module, you must install an
ATA2 (see Installing an analog station media bay module (ASM)).
Digital devices
19
BCM 4.0 supports the following digital devices:
• T7000(International only): four memory buttons, without display or indicators
• T7100: one-line display, one memory button without indicator
• T7208: one-line display, eight memory buttons with indicators
• T7316: two-line display, three display buttons, 16 memory buttons with indicators, eight
memory buttons without indicators.
The T7316 supports separate mute key and a headset key under the dial pad.
• T7316E: two-line display, three display buttons, 16 memory buttons with indicators, eight
memory buttons without indicators; handsfree, mute, and headset buttons (located under the
dial pad)
• T7406 cordless telephone system: six memory buttons with indicators and a two-line display
with three display buttons.
The T7406 provides cordless mobility in a small office environment. Each base station
supports three telephones. Function is based on the 7316 telephone. The base station connects
to a digital station media bay module on the system.
• Key Indicator Module (KIM): 24 memory buttons with indicators
• BST Doorphone: used as an intercom to control access to your building. Press the Call button
on the BST Doorphone to call one or more telephones, or to send a distinctive chime to
telephones in an assigned page zone. Place an internal call from any telephone on the system
to the BST Doorphone to set up a two-way voice call. Install a Door Opening Controller to
permit the activation of locks on doors or gates.
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide

20 Chapter 2 Device description
Wireless devices
BCM 4.0 supports the following wireless devices:
• Dect 413x series handsets: three display softkeys, four-line handset display, text messaging
• Dect 414x series handsets: three display softkeys, four-line handset display, loudspeaker
capability, text messaging
• Digital Mobility Phone 7420: three display softkeys, four-line handset display
• Digital Mobility Phone 7430: three display softkeys, four-line handset display, text
messaging
• Digital Mobility Phone 7440: three display softkeys, four-line handset display, loudspeaker
capability, text messaging
• WLAN Handsets 2210/2211/2212: Voice over IP (VoIP) technology, Push-to-Talk (enables
two-way communication with another BCM user)
The handsets communicate with the BCM system and with the WLAN IP Telephony Manager
2245. Just like wired telephones, the wireless handsets receive calls directly, receive
transferred calls, transfer calls to other extensions, and make outside and long-distance calls
(subject to corporate restrictions). The handsets interoperates with other IP Line and IP Trunk
features and devices, such as IP Peer, and the IP Phone 20xx and IP Softphone 2050 series of
IP Phones.
IP devices
BCM 4.0 supports the following IP devices:
• IP Phone 2001: connects through an IP link to the BCM system. The IP Phone 2001 has a
single-line text display with a row of display keys on the second display line. The IP Phone
2001 can be used to call through any type of BCM line.
• IP Phone 2002: connects through an IP link to the BCM system. The IP Phone 2002 has a
two-line text display with a row of display keys on the third display line, and four memory
keys with indicators. The IP Phone 2002 can be used to call through any type of BCM line.
• IP Phone 2004: connects through an IP link to the BCM system. The IP Phone 2004 has a
six-line text display with a row of display keys on the eighth display line, and six memory
keys with indicators. The IP Phone 2004 can be used to call through any type of BCM line.
• IP Phone 2007: connects to a LAN through an Ethernet connection. The IP Phone 2007
supports call processing features, and can work with an External Application Server to display
web-based and interactive applications on the large, color LCD touch screen.
• IP Softphone 2050: provides Voice over IP (VoIP) services using a telephony server and your
company’s local area network (LAN).
• IP Audio Conference Phone 2033: provides audio conferencing. The keypad provides many
of the set features of the basic Business Series telephones without display or memory buttons.
The audio conference phone comes with three microphones. Installation instructions are
provided with the audio conference phone.
• IP Phone 1110: has a graphical, high-resolution LCD display, backlit, with adjustable
contrast. It has three user-defined feature keys and four soft keys.
N0060609N0060609
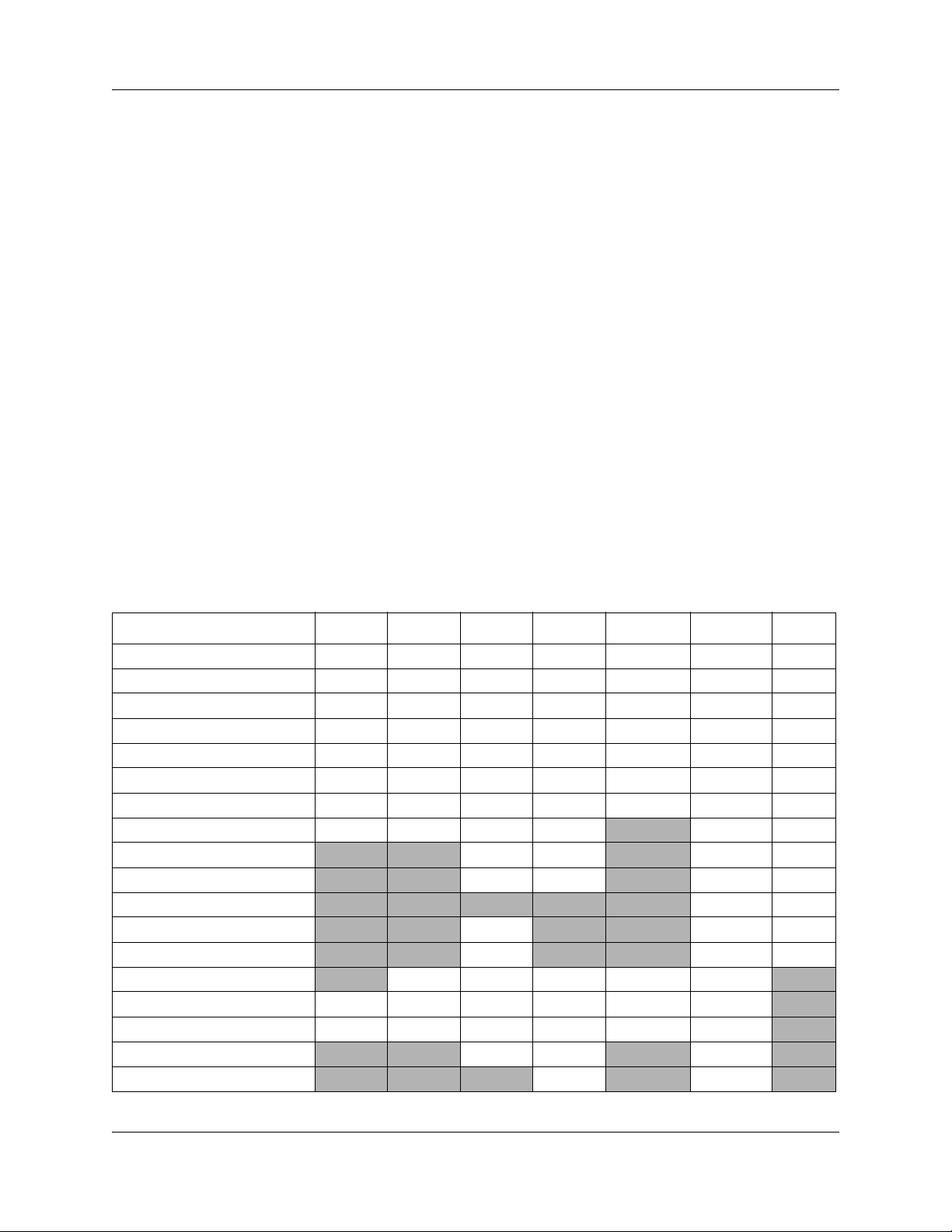
The IP Phone 1110 brings voice and data to the desktop by connecting directly to a local area
network (LAN) though an Ethernet connection.
• IP Phone 1120/1120E: has a graphical, high-resolution LCD display, backlit, with adjustable
contrast. It also has four user-defined feature keys and four soft keys.
The IP Phone 1120 brings voice and data to the desktop by connecting directly to a local area
network (LAN) though an Ethernet connection.
• IP Phone 1140/1140E: has a graphical, high-resolution LCD display, backlit, with adjustable
contrast. It also has six user defined feature keys and four soft keys .
The IP Phone 1140 brings voice and data to the desktop by connecting directly to a LAN
through an Ethernet connection.
• IP Key Expansion Module (KEM): 24 programmable keys (with labels) for IP Phone 2002
or 2004 models; maximum of four IP KEMs for one phone.
ISDN devices
Refer to ISDN overview for information on ISDN devices (hardware).
Chapter 2 Device description 21
Table 1 is a matrix of telephony devices and the BCM releases with which they are compatible.
Table 1 also shows what media bay module (MBM) is needed to support each device.
Table 1 Telephony devices release compatibility matrix (Sheet 1 of 2)
Device BCM 3.5 BCM 3.6 BCM 3.7 BCM 4.0 BCM50 1.0 BCM50 2.0 MBM
T7000 (EU only) XXXXX X DSM
T7100 XXXXX X DSM
T7208 XXXXX X DSM
T7316 XXXXX X DSM
T7316E XXXXX X DSM
T7406 (North America only)XXXXX X DSM
T 24 KIM XXXXX X DSM
BST Doorphone XXXX
Dect 413x
Dect 414x
Digital Mobility Phone 7420
Digital Mobility Phone 7430
Digital Mobility Phone 7440
IP Phone 2001
IP Phone 2002 XXXXX X
IP Phone 2004 XXXXX X
IP Phone 2007 XX X
IP Phone 1110 X X
XXXX X
XX XDSM
XX XDSM
X XDSM
X XDSM
XDSM
XDSM
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide
22 Chapter 2 Device description
Table 1 Telephony devices release compatibility matrix (Sheet 2 of 2)
Device BCM 3.5 BCM 3.6 BCM 3.7 BCM 4.0 BCM50 1.0 BCM50 2.0 MBM
IP Phone 1120E X X
IP Phone 1140E X X
IP Softphone 2050 XXXXX X
IP Audio Conference Phone
2033
IP KEM X X
WLAN 2210 Handset XX X
WLAN 2211 Handset XX X
WLAN 2212 Handset X X
X X
Table 2 shows the types of lines supported by different MBMs and the number of lines those
MBMs support.
Table 2 MBM trunk requirements
Type of lines Type of MBM Number of lines per MBM
T1 digital digital trunk MBM (DTM) 24
PRI digital lines (NA) DTM 23
E1 digital lines DTM 30
PRI digital lines (EMEA) DTM 30
Analog lines caller ID trunk module 4 (CTM4)
(North American systems only)
Analog lines CTM8 (North American systems
only)
Analog lines global analog trunk module 4
(GATM4)
Analog lines GATM8 8
Analog lines 4x16 combination MBM (North
American systems only)
Analog lines ADID 4 4
Analog lines ADID 8 8
BRI ISDN lines BRIM S/T 4 ISDN loops (to a maximum of 8 lines)
Integrated BRI lines BRIM S/T 2 ports (replace 4 analog lines on the RJ-21
4
8
4
4 (also requires a full DS30 channel for the DNs)
telephony connector)
Table 3 MBM station requirements (Sheet 1 of 2)
Type of extension Type of MBM Number of extensions per MBM
Digital extensions DSM16/DSM16+ 16
Digital extensions DSM32/DSM32+ 32
N0060609N0060609
Chapter 2 Device description 23
Table 3 MBM station requirements (Sheet 2 of 2)
Type of extension Type of MBM Number of extensions per MBM
Digital extensions 4x16 16
Analog extensions ASM8 8
Analog extensions GASM8 8
Cordless handsets (DECT) (selected
profiles only)
Digital extensions are for digital or IP telephones. You do not need to include IP telephones when you calculate the
number of required DSM MBMs.
DSM 32
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide

24 Chapter 2 Device description
N0060609N0060609

Chapter 3
Installing an analog station media bay module (ASM)
The analog station media bay modules (ASM8, ASM8+, and GASM) can connect to a maximum
of eight analog telecommunication devices. These devices are standard analog telephones,
cordless telephones, fax machines, answering machines, or modems. The maximum speed for a
modem connection is 28.8 kbit/s.
The ASM8 is available in North America only; the ASM8+ and GASM8 are available in North
America, the United Kingdom, Australia, and Poland.
In addition to ASM8 features, the ASM8+ and GASM offer the following features:
• Visual Message Waiting Indicator (VMWI) — LED indicates to the end user that a message is
waiting.
• Disconnect supervision (Open Switch Interval [OSI] as per EIA/TIA 464) — indicates to the
attached device, in an established communication, that the connected device should release the
call (see disconnect supervision note).
• Caller ID — provides the name, phone number, and other information about the caller to the
end user at the start of the call.
• Firmware downloading capability — allows the system to upgrade the ASM8+ and GASM
firmware at customer sites.
• Enhanced ringing capability — ASM8+ and GASM provide a ringing voltage of 2 REN/65 V
rms per port.
• Calling line identification (CLID)
• The GASM8 is designated as an ONS (on-premise station) port.
25
Disconnect supervision note: When disconnect happens from the central office,
the ASM8+ provides an open switch interval (OSI) to the off-hook station of 850
ms (TIA/EIA 464 section 5.4.10.2.4; minimum is 600 ms) as a disconnect signal.
If the station remains on-hook after the disconnect signal, the ASM8+ disconnects
the station equipment from the network without returning a tone to it (TIA/EIA
464 section 5.4.10.2.5[1]). After the station equipment goes on-hook, the ASM8+
station interface is restored to on-hook (idle).
It is important to ensure that the device, application, or interface card connected to
an ASM8+ station interface conform to these on-hook and off-hook conditions.
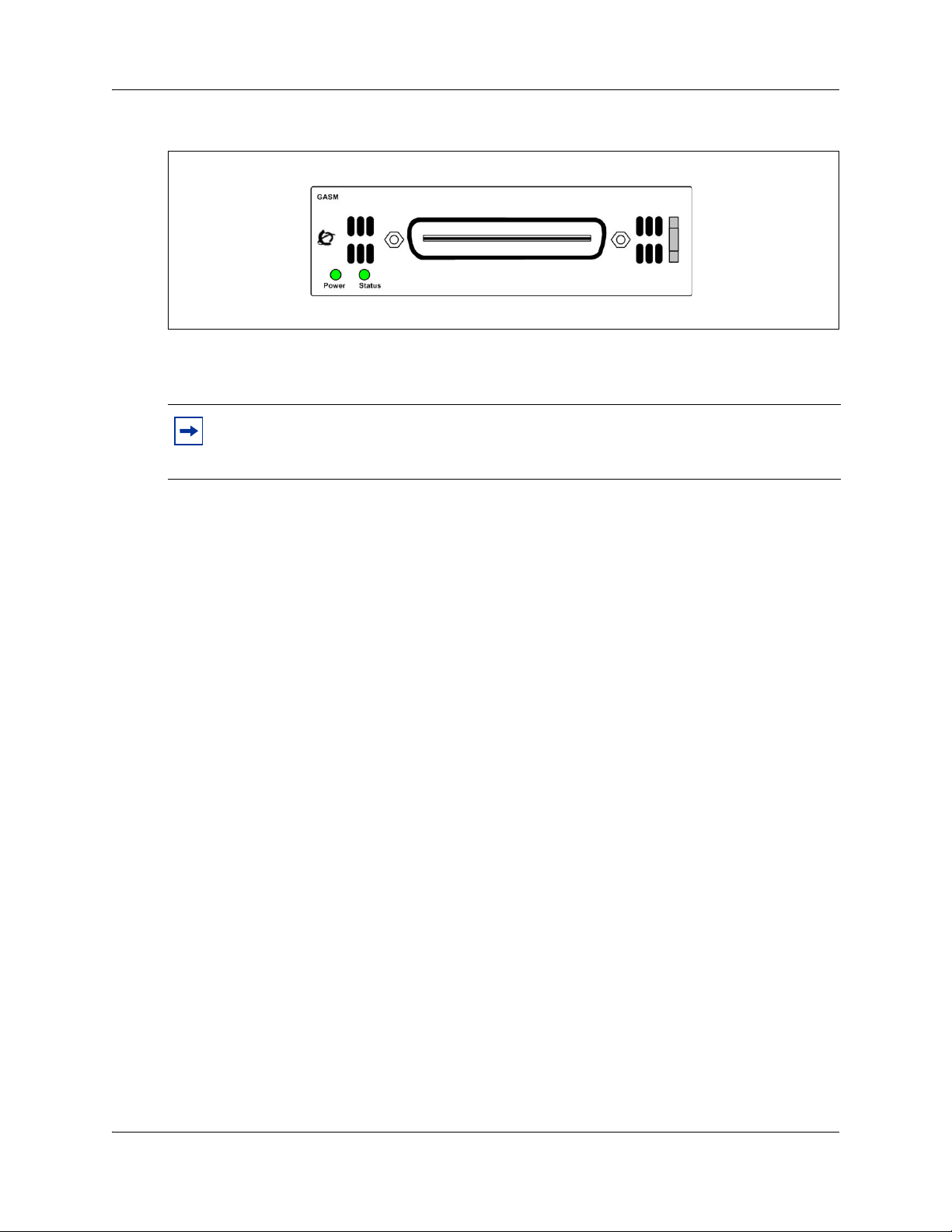
The ASM8, ASM8+, and GASM each have one RJ-21 connector on the faceplate. Figure 26
shows the GASM.
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide
26 Chapter 3 Installing an analog station media bay module (ASM)
Figure 1 GASM faceplate LEDs and connectors
The ringer equivalency number (REN) per port for ASM8 is 1; the REN for ASM8+ and GASM
is 2.
Note: The termination of the analog interface can consist of any combination of devices,
subject only to the requirement that the sum of the RENs of all the devices does not exceed
the REN of the interface to which the device is connected.
Refer to the following for information on installing and configuring an ASM:
• “Installing an MBM”
• “Configuring the media bay module” on page 66
• “Wiring the ASM” on page 67
• “Installing analog devices” on page 68
For more detailed information on installing the BCM system and related components, refer to
BCM200/400 4.0 Installation and Maintenance Guide (N0060612).
Installing an MBM
MBMs are installed in BCM main units and expansion units, depending on your system
requirements.
The primary tasks to install an MBM are:
• Selecting MBMs for your system
• Assigning DS30 resources
• Setting MBM dip switches
• Installing an MBM
For more detailed information on installing an MBM, refer to BCM200/400 4.0 Installation and
Maintenance Guide (N0060612).
Configuring the media bay module
For information on installing a media bay module (MBM) and setting the dip switches, refer to the
BCM200/400 4.0 Installation and Maintenance Guide (N0060612).
N0060609N0060609
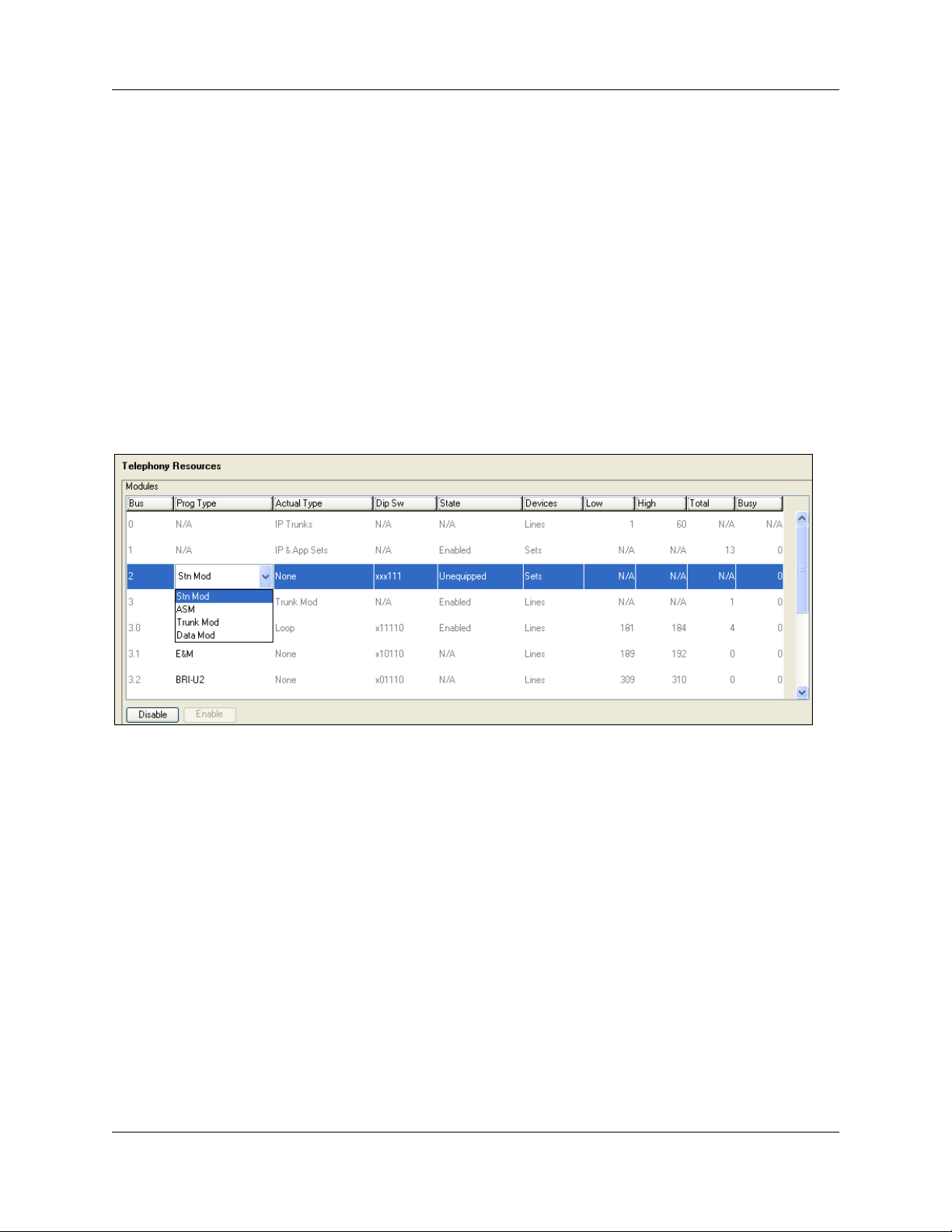
To configure the MBM
1 Open Element Manager and connect to your BCM system.
2 Click Configuration > Resources > Telephony Resources.
The Telephony Resources panel appears (see Figure 27).
3 In the Modules table, select the location of the MBM that you want to configure.
4 Double-click the Programmed type field to display the drop-down list.
5 Select the type of MBM that you installed in that location.
6 Click Enable.
7 Repeat steps 4 to 7 to enable each MBM in your system.
You can set other parameters for the MBMs depending on the type of MBM you installed.
Figure 2 Telephony Resources panel
Chapter 3 Installing an analog station media bay module (ASM) 27
Wiring the ASM
An experienced installer can wire the ASM for your system using the wiring chart, for more
information refer to the “ASM8, ASM8+, and GASM wiring chart and switch settings” on page
85.
Installing analog devices
After the ASM is correctly wired, you can connect your analog devices.
Documentation describing installation and features of your analog devices is supplied with each
piece of equipment.
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide

28 Chapter 3 Installing an analog station media bay module (ASM)
N0060609N0060609
Chapter 4
Installing the analog terminal adapter
The following provides installation instructions for the analog terminal adapter 2 (ATA2) or ATA.
The ATA2 connects a standard analog voice device or data communication device to the BCM
system through a digital station module. Examples of analog voice devices are analog telephones
and answering machines. Examples of analog data communication devices are modems and fax
machines.
The ATA2 is designated as either an ONS (on-premise station) or an OPS (off-premise station)
port.
Refer to the following topics for information on installing an ATA2:
• “Configuration overview”
• “Installing the ATA2” on page 30
• “Configuring the ATA2” on page 33
29
Configuration overview
The following describes environment configurations for connecting analog and data devices to the
main unit using an ATA2:
• “Analog telephone”
• “Analog data device” on page 30
Analog telephone
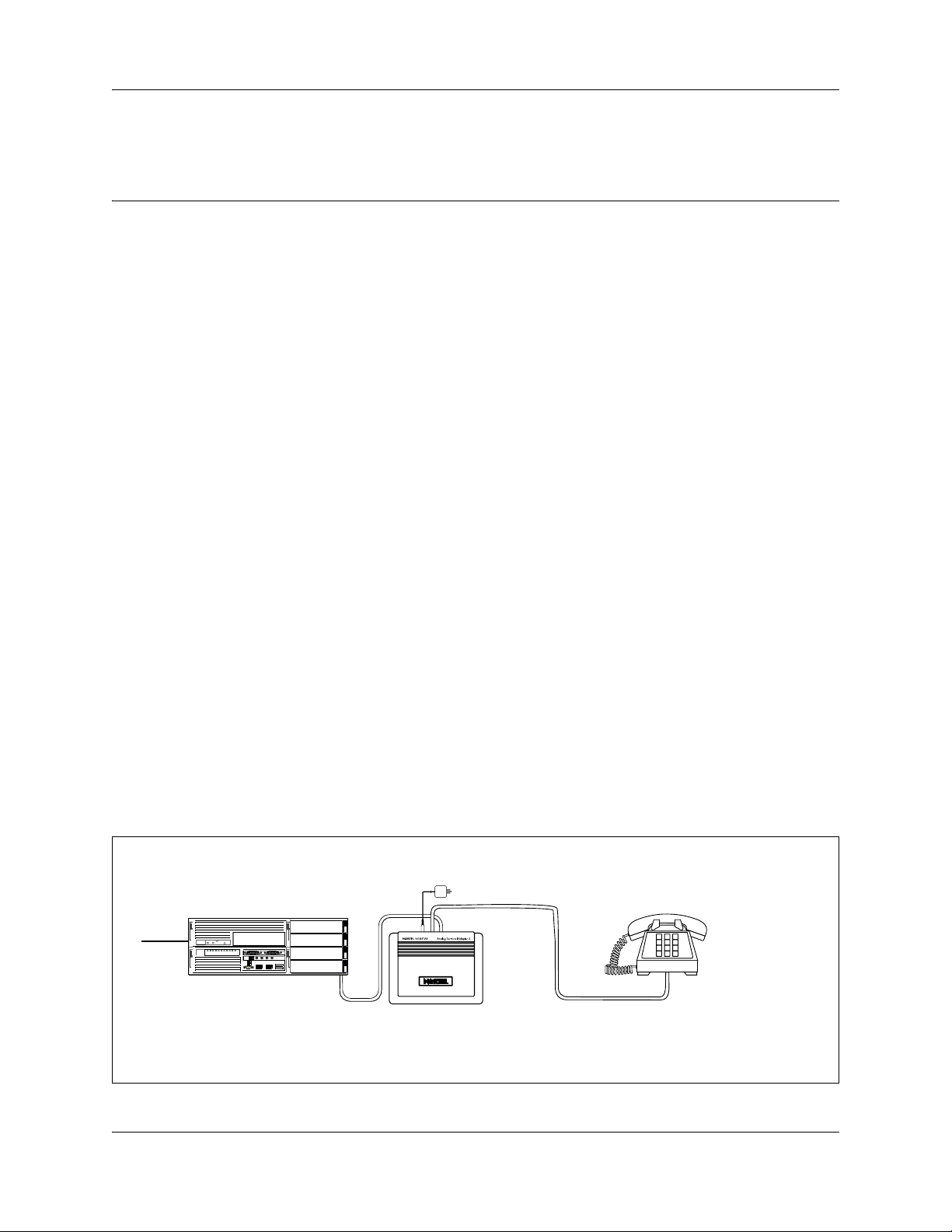
Figure 3 on page 29 shows an installation overview for connecting an analog device through an
ATA2 to the main unit.
Figure 3 Analog telephone installation overview
ATA 2 power cord
BCM main unit
Central
Office
Analog telephone
ATA 2
Line loop resistance:
135 ohms maximum
Terminal loop resistance:
1300 ohms maximum
BCM 4.0 Telephony Device Installation Guide
 Loading...
Loading...