Page 1

Administrator's Manual
AudioCodes High Definition IP Phones Series
405/405HD, 420HD, 430HD,
440HD IP Phones
Version 2.2.16
Page 2

Page 3
Administrator's Manual Contents
Table of Contents
1 Introduction ....................................................................................................... 19
Configuration Tools................................................................................................ 21
2 IP Phone User Interface .................................................................................... 23
2.1 Accessing the Administration Menu ...................................................................... 23
2.2 Changing Display Language ................................................................................. 24
3 Web Interface ..................................................................................................... 25
3.1 Accessing Web Interface ...................................................................................... 25
3.2 Getting Started with the Web ................................................................................ 26
3.3 Configuring the Web Interface's Port .................................................................... 27
3.4 Configuring User Login Credentials ...................................................................... 27
4 Configuration File.............................................................................................. 29
4.1 Introduction........................................................................................................... 29
4.2 File Syntax ........................................................................................................... 29
4.3 Linking Multiple Files ............................................................................................ 29
4.4 Downloading the Configuration File from the Phone ............................................. 30
4.5 Creating Configuration Files using VoIProvision Utility ......................................... 30
4.5.1 Configuration File Format .................................................................................... 30
4.5.2 Global Configuration File ..................................................................................... 30
4.5.3 VoIProvision Utility Overview ............................................................................... 31
4.5.4 CSV File .............................................................................................................. 31
4.5.5 Template File ...................................................................................................... 31
4.5.6 Generated Configuration Files ............................................................................. 31
4.5.7 Starting the VoIProvision Utility ............................................................................ 32
4.5.8 Usage ................................................................................................................. 32
4.6 Using the Encryption Tool..................................................................................... 32
4.6.1 Encrypting Configuration Files ............................................................................. 32
4.6.2 Encrypting Passwords in the Configuration File ................................................... 33
5 Device Manager Pro .......................................................................................... 35
Automatic Provisioning ......................................................................................... 37
6 Introduction ....................................................................................................... 39
7 Updating the Configuration File Manually ...................................................... 41
8 Setting up Network for Auto Provisioning ...................................................... 43
9 Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files .................................................. 45
9.1 Provisioning Hunt Order ....................................................................................... 45
9.2 Dynamic URL Provisioning ................................................................................... 45
9.2.1 Provisioning using DHCP Option 160................................................................... 48
9.2.2 Technician's Digit Key Code ................................................................................ 49
9.2.3 Provisioning using DHCP Option 66/67 ................................................................ 50
9.2.4 Provisioning using DHCP Option 43 .................................................................... 50
9.2.5 Provisioning using the User-Class Option ............................................................ 51
9.2.6 SIP SUBSCRIBE and NOTIFY Messages ............................................................ 60
Version 2.2.16 3 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 4
400HD Series IP Phones
9.2.7 Hardcoded Domain Name for Provisioning Server ............................................... 62
9.2.8 Cached Address of Last Provisioning Server Used .............................................. 62
9.2.9 Redirect Server ................................................................................................... 63
9.3 Static URL Provisioning ........................................................................................ 64
Quick Setup ............................................................................................................. 67
10 Quick Setup ....................................................................................................... 69
Networking .............................................................................................................. 71
11 Introduction ....................................................................................................... 73
12 Configuring Date and Time Manually .............................................................. 75
12.1 Configuring Daylight Saving Time ......................................................................... 76
12.2 Configuring the NTP Server .................................................................................. 79
12.3 Configuring NTP Server via DHCP ....................................................................... 81
13 Configuring IP Network Settings ..................................................................... 83
13.1 Configuring Static IP Address ............................................................................... 83
13.1.1 Configuring Static IP Address on the Phone ........................................................ 83
13.1.2 Configuring IP Network Settings .......................................................................... 84
13.2 Configuring Partial DHCP ..................................................................................... 86
14 Configuring LAN and PC Port Settings ........................................................... 89
15 Configuring VLAN Settings .............................................................................. 91
15.1 Configuring Manual or Automatic VLAN Assignment ............................................ 92
15.1.1 Configuring Manual VLAN Assignment to the Phone............................................ 92
15.1.2 Configuring Automatic VLAN Assignment to the Phone........................................ 92
15.1.3 Configuring VLAN via DHCP Provisioning Path ................................................... 92
VoIP Settings .......................................................................................................... 93
16 Configuring SIP Settings .................................................................................. 95
16.1 Configuring General SIP Settings ......................................................................... 95
16.2 Configuring Proxy and Registration ...................................................................... 99
16.2.1 Configuring Proxy Redundancy ......................................................................... 102
16.2.2 Device Registration Failover/Failback ................................................................ 105
16.2.2.1 Failover .............................................................................................. 105
16.2.2.2 Failback .............................................................................................. 106
16.2.3 Preventing Unregistering after Changing Settings and Reloading ....................... 106
16.3 Configuring a Line .............................................................................................. 107
16.4 Configuring Shared Call Appearance.................................................................. 108
16.5 Configuring SIP Timers ...................................................................................... 109
16.6 Configuring SIP QoS .......................................................................................... 111
16.7 Configuring SIP Reject Code .............................................................................. 112
17 Configuring Dialing ......................................................................................... 113
17.1 Configuring Voice Dialing through VocaNOM ..................................................... 113
17.2 Configuring General Dialing Parameters ............................................................ 114
Administrator's Manual 4 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 5

Administrator's Manual Contents
17.3 Configuring Auto Redial ...................................................................................... 116
17.4 Configuring Dial Tones ....................................................................................... 117
17.5 Configuring DTMF .............................................................................................. 119
17.6 Configuring Digit Maps and Dial Plans................................................................ 120
17.7 Configuring Headset LED to Stay On ................................................................. 122
17.8 Configuring Default Audio Device ....................................................................... 123
18 Configuring Ring Tones ................................................................................. 125
18.1 Configuring Distinctive Ring Tones ..................................................................... 125
18.1.1 Example of Configuring a Distinctive Ring .......................................................... 126
18.2 Configuring CPT Regional Settings .................................................................... 127
18.3 Uploading Ring Tones ........................................................................................ 129
18.4 Configuring Beeps to Headsets when a Call Comes in to a Call Center ............. 130
18.5 Configuring the Phone to play Fast Busy Tone if Automatically Disconnected on
Remote Side ................................................................................................................ 131
18.6 Configuring the Beep (Ring) to Play via an Answering Device ............................ 132
19 Configuring Media Settings ............................................................................ 133
19.1 Configuring Media Streaming ............................................................................. 133
19.2 Configuring RTP Port Range and Payload Type ................................................. 134
19.3 Configuring RTP QoS ......................................................................................... 135
19.4 Configuring RTP/SRTP Capability Negotiation ................................................... 135
19.5 Configuring Codecs ............................................................................................ 136
19.6 Configuring OPUS Management ........................................................................ 138
20 Configuring Voice Settings ............................................................................ 139
20.1 Configuring Gain Control .................................................................................... 139
20.2 Configuring Jitter Buffer ...................................................................................... 139
20.3 Configuring Silence Compression ....................................................................... 140
20.4 Configuring Noise Reduction .............................................................................. 141
20.5 Configuring Echo Cancellation............................................................................ 142
21 Configuring Extension Lines.......................................................................... 143
21.1 On the Phone ..................................................................................................... 143
21.2 Using the Web Interface and Configuration File .................................................. 144
22 Configuring Supplementary Services ........................................................... 147
22.1 Selecting the Application Server ......................................................................... 147
22.2 Configuring Call Waiting ..................................................................................... 148
22.3 Configuring Call Forwarding ............................................................................... 149
22.4 Configuring a Conference ................................................................................... 150
22.5 Allowing the Initiator to Drop out of a Conference ............................................... 150
22.6 Configuring Automatic Dialing ............................................................................ 151
22.7 Configuring Automatic Answer............................................................................ 152
22.8 Configuring Do Not Disturb (DnD) ...................................................................... 154
22.9 Configuring Call Pick Up ..................................................................................... 155
22.10 Configuring Message Waiting Indication ............................................................. 156
22.11 Configuring Busy Lamp Field .............................................................................. 157
22.12 Configuring Advice of Charge ............................................................................. 159
Version 2.2.16 5 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 6
400HD Series IP Phones
22.13 Configuring a Tone to Alert to Long Hold ............................................................ 159
22.14 Disabling the HOLD Key ..................................................................................... 160
22.15 Configuring Onhook Disconnect when Held........................................................ 160
22.16 Configuring Ringing on the Default Audio Device ............................................... 161
22.17 Allowing an Incoming Call when the Phone is Locked ........................................ 162
22.18 Allowing Call Center Agents to Record Welcome Greetings ............................... 162
22.19 Enabling the Electronic Hook Switch .................................................................. 163
22.20 Disabling the Hard Mute Key on the Phone ........................................................ 164
22.21 Configuring Attended and Semi-Attended Call Transfer ..................................... 165
22.22 Configuring Blind Transfer .................................................................................. 165
22.23 Creating a Speed Dial File for Configuration File ................................................ 166
23 Configuring Volume Levels ............................................................................ 167
23.1 Configuring Gain Control .................................................................................... 167
23.2 Configuring Tone Volume ................................................................................... 169
23.3 Configuring Ringer Volume ................................................................................. 170
23.4 Configuring Speaker Volume .............................................................................. 171
23.5 Configuring Handset Volume .............................................................................. 174
23.6 Configuring Headset Volume .............................................................................. 176
Advanced Phone Settings ....................................................................................179
24 Configuring the Phone Directory ................................................................... 181
24.1 Configuring the Corporate Directory ................................................................... 181
24.1.1 Configuring the LDAP-based Corporate Directory .............................................. 181
24.1.2 Loading a Text-based Corporate Directory File .................................................. 183
24.2 Modifying the Local Phone Directory .................................................................. 185
25 Configuring Keys ............................................................................................ 187
25.1 Configuring Function Keys .................................................................................. 187
25.1.1 430HD Phone .................................................................................................... 187
25.1.2 440HD Phone .................................................................................................... 188
25.1.3 Configuring Additional Function Keys................................................................. 189
25.2 Configuring Programmable Keys ........................................................................ 190
25.2.1 430HD and 440HD Phones ............................................................................... 190
25.2.1.1 Configuring Multiple Extension Lines .................................................. 191
25.2.1.2 Configuring a Key Event ..................................................................... 193
25.3 Configuring Speed Dials ..................................................................................... 194
25.3.1 420HD and 405/405HD Phone Models .............................................................. 194
25.3.2 Deleting Speed Dials ......................................................................................... 195
25.3.3 Saving Configured Speed Dials ......................................................................... 195
25.3.4 Creating a Speed Dial File for the Configuration File .......................................... 196
25.4 Configuring Softkeys .......................................................................................... 197
25.4.1 Configuring Programmable Softkeys (PSK) ....................................................... 200
25.5 Configuring Navigation Control Button Positions ................................................ 201
25.5.1 Saving Configured Keys .................................................................................... 202
25.5.2 Loading Saved Keys to Phones ......................................................................... 202
Administrator's Manual 6 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 7
Administrator's Manual Contents
26 Disabling Hard Keys and Softkeys ................................................................ 203
27 Configuring Paging ......................................................................................... 205
27.1 Configuring a Key for Paging using the Web Interface ........................................ 205
27.1.1 Configuring Barge-in .......................................................................................... 206
27.2 Configuring Paging Using the Configuration File ................................................ 207
28 Configuring Feature Key Synchronization .................................................... 209
Security ..................................................................................................................211
29 Implementing X.509 Authentication ............................................................... 213
29.1 Factory-Set Certificates and AudioCodes Trusted Root CA ................................ 213
29.2 User-Generated Certificates ............................................................................... 214
29.3 External Trusted Root CAs ................................................................................. 215
30 Loading a Certificate ....................................................................................... 217
30.1 Loading the Trusted Root CA Certificate to the Phone ....................................... 217
30.1.1 Loading Trusted Root CA Certificate Using Configuration File ............................ 217
30.2 Loading the Client Certificate to the Phone ......................................................... 218
30.2.1 Loading the Client Certificate to the Phone using the Configuration File ............. 218
30.2.2 Enabling Server-side Authentication (Mutual Authentication) .............................. 219
30.3 Generating a Certificate Signing Request ........................................................... 220
30.4 Using Previously Loaded Certificates ................................................................. 221
31 Configuring SIP TLS ....................................................................................... 223
31.1 Configuring TLS ................................................................................................. 223
31.1.1 Configuring SIP TLS using the Web Interface .................................................... 223
32 Configuring 802.1x .......................................................................................... 225
32.1 Configuring 802.1x in the Phone Screen ............................................................ 225
32.1.1 Configuring EAP-MD5 Mode .............................................................................. 226
32.1.2 Configuring EAP-TLS Mode ............................................................................... 226
32.2 Configuring 802.1x Using Web and Configuration File ........................................ 227
32.2.1 Configuring EAP MD5 Mode .............................................................................. 227
32.2.2 Configuring EAP TLS Mode ............................................................................... 228
33 Configuring SRTP ........................................................................................... 229
34 Configuring HTTP/S ........................................................................................ 231
35 Logging into a Remote HTTP/S Server from the Phone .............................. 233
36 Securing the Web Interface using HTTP/S .................................................... 235
36.1 Provisioning ........................................................................................................ 236
37 MAC-Based Authenticaton ............................................................................. 237
Maintenance ...........................................................................................................239
Version 2.2.16 7 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 8
400HD Series IP Phones
38 Changing Administrator Login Credentials .................................................. 241
39 Restarting Phones........................................................................................... 243
39.1 Restarting from the Phone .................................................................................. 243
39.2 Restarting the Phone using the Web Interface .................................................... 244
40 Restoring Phone Defaults .............................................................................. 245
40.1 Restoring Factory Defaults from the Phone's Screen.......................................... 245
40.2 Restoring Factory Defaults using the Web Interface ........................................... 246
Status and Monitoring ...........................................................................................247
41 Determining Network Status .......................................................................... 249
41.1 Determining LAN Status ..................................................................................... 249
41.2 Determining Port Status...................................................................................... 249
41.3 Determining 802.1x Status ................................................................................. 249
42 Determining VoIP Status ................................................................................ 251
42.1 Determining Phone Status .................................................................................. 251
42.2 Determining Line Status ..................................................................................... 251
42.3 Determining Memory Status ............................................................................... 252
42.4 Viewing Current Call Information ........................................................................ 253
43 Viewing Call History ........................................................................................ 255
44 Accessing System Information ...................................................................... 257
44.1 Accessing Phone Firmware Version ................................................................... 257
44.1.1 Accessing Firmware Version using the Web Interface ........................................ 257
44.1.2 Accessing Firmware Version from the Phone's Screen ...................................... 257
44.2 Viewing Phone Firmware Release Information ................................................... 258
44.2.1 Viewing Firmware Release Information in the Web Interface .............................. 258
44.2.2 Viewing Firmware Release Information on the Phone ........................................ 259
45 Monitoring Quality of Experience .................................................................. 261
45.1 Configuring Remote Voice Quality Monitoring .................................................... 261
45.1.1 Configuring RTCP Extended Report .................................................................. 261
45.1.2 Configuring Voice Quality Monitoring ................................................................. 262
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting ........................................................................263
46 Diagnosing Phone Hardware ......................................................................... 265
46.1 Testing Keypad and Hook .................................................................................. 266
46.2 Testing Handset ................................................................................................. 267
46.3 Testing the Headset ........................................................................................... 267
46.4 Testing Hands Free ............................................................................................ 267
47 Recovering Firmware ...................................................................................... 269
48 Configuring System Logging (Syslog) .......................................................... 271
48.1.1 Analyzing and Debugging Traffic using Regular Syslog...................................... 271
48.1.2 Analyzing and Debugging Traffic using 'Lightweight Syslog' ............................... 273
Administrator's Manual 8 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 9

Administrator's Manual Contents
49 Viewing Error Messages Displayed in the Phone Screen ............................ 275
50 Debugging using Packet Recording Parameters ......................................... 277
51 Creating a Crash Dump File ........................................................................... 279
52 Configuring Port Mirroring ............................................................................. 281
53 Enabling Tracing ............................................................................................. 283
Appendices ............................................................................................................285
A Configuring Phones in Server-Specific Deployments ................................. 287
A.1 BroadSoft's BroadWorks .................................................................................... 287
A.1.1 Configuring BLF ................................................................................................ 288
A.1.2 Configuring Call Forwarding .............................................................................. 289
A.1.3 Configuring DnD ................................................................................................ 291
A.1.4 Configuring FKS ................................................................................................ 292
A.1.5 Using SIP Authentication for Xsi Access ............................................................ 292
A.1.6 Configuring Phones to Connect to the Xsi Interface using HTTP/S Authentication292
A.1.7 Configuring Shared Call Appearance ................................................................. 295
A.1.8 Setting up a Remote Conference ....................................................................... 298
A.1.9 Loading the Corporate Directory to the Phone ................................................... 299
A.1.10 Adding a Contact to the Corporate Directory ...................................................... 300
A.1.11 Deleting a Contact from the Corporate Directory ................................................ 300
A.1.12 Disabling Handset Mode .................................................................................... 300
A.1.13 Displaying a Message in Agents' Phone Screens ............................................... 301
A.1.14 Changing Phone Screen Backlight Timeout ....................................................... 301
A.2 Asterisk, Coral and Metaswitch........................................................................... 302
A.2.1 Configuring BLF ................................................................................................ 302
A.3 Genesys SIP Server for Contact Centers ........................................................... 303
A.3.1 Using DHCP to Auto Provision Phones .............................................................. 303
A.3.2 Verifying Firmware Version ................................................................................ 303
A.3.3 Accessing a Phone's Web Interface ................................................................... 303
A.3.4 Configuring Dual Registration to Ensure SIP Business Continuity for Agents ..... 304
A.3.5 Disabling the Web Interface ............................................................................... 308
A.3.6 Forcing a Reboot on Provisioning ...................................................................... 308
A.3.7 Provisioning using TFTP / FTP / HTTP / HTTPS in DHCP Options 66/67 ........... 308
A.3.8 Enabling Agents to Sign in with Phone Numbers................................................ 309
A.3.9 Locking Agents' Phones' Alphabetical Keys ....................................................... 309
A.3.10 Playing a Beep on an Incoming Call .................................................................. 310
A.3.11 Enabling Proactive Mute .................................................................................... 310
A.3.12 Configuring Automatic Answer ........................................................................... 311
A.3.13 Regulating the 'Logged out' Message ................................................................ 311
A.3.14 3PCC (Third Party Call Control) ......................................................................... 312
A.3.15 Disabling Handset Mode .................................................................................... 313
A.3.16 Changing Phone Screen Backlight Timeout ....................................................... 313
A.3.17 Displaying a Message on Agents' Phones ......................................................... 314
A.3.18 Configuring a Redundant (Backup) Genesys Server .......................................... 314
A.4 Genband: KBS Softswitch Solution ..................................................................... 315
A.4.1 Configuring Shared Line Appearance ................................................................ 316
A.4.2 Configuring Call Pickup ..................................................................................... 318
A.4.3 Setting up a Remote Conference ....................................................................... 320
A.4.4 Configuring Parameters Mandatory for Phones in a Genband Environment ....... 321
B Configuring Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) ............................................ 323
B.1 Softkey Display and Command Menu Options .................................................... 328
Version 2.2.16 9 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 10

400HD Series IP Phones
C Recovering AudioCodes' IP Phone................................................................ 329
C.1 Identifying that the Phone is in Recovery Mode .................................................. 329
C.2 Verifying that the Phone is in Recovery Mode .................................................... 329
C.3 Recovering the Phone ........................................................................................ 330
C.4 Verifying that the Phone is Downloading the Image File ..................................... 333
C.4.1 Verifying Using Wireshark.................................................................................. 333
C.4.2 Verifying Using tftpd64....................................................................................... 334
C.4.3 Verifying on the Phone ...................................................................................... 335
D Deploying AudioCodes IP Phones - Use Case ............................................. 337
D.1 Preparing Configuration (cfg) Files for the Enterprise Customer ......................... 337
D.1.1 Saving the Phone's Default Configuration to File ................................................ 337
D.1.2 Preparing a global.cfg Configuration File............................................................ 338
D.1.3 Generating MAC-specific <private>.cfg Configuration Files ................................ 338
D.2 Preparing the DHCP Server to Automatically Provision Phones ......................... 341
D.3 Making Sure Phones are Correctly Provisioned .................................................. 341
E Supported SIP RFCs and Headers ................................................................. 343
E.1 SIP Compliance Tables ...................................................................................... 345
E.1.1 SIP Methods...................................................................................................... 345
E.1.2 SIP Headers ...................................................................................................... 346
F Specifications .................................................................................................. 349
G RTCP-XR Parameters ...................................................................................... 353
H Example SIP - PUBLISH Message .................................................................. 355
Administrator's Manual 10 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 11

Administrator's Manual Contents
List of Figures
Figure 2-1: Language ........................................................................................................................ 24
Figure 3-1: Web Interface Login ........................................................................................................ 25
Figure 3-2: Web Interface Areas........................................................................................................ 26
Figure 3-3: User Account .................................................................................................................. 27
Figure 7-1: Configuration File (430HD) .............................................................................................. 41
Figure 7-2: Load New Configuration File ........................................................................................... 41
Figure 9-1: Automatic Provisioning – Dynamic URL ........................................................................... 45
Figure 9-2: Automatic Provisioning - DHCP Option 160 ..................................................................... 48
Figure 9-3: Provisioning using DHCP Option 43 in the DHCP Server ................................................. 51
Figure 9-4: DHCP Options Assigned to IPv4 Addresses .................................................................... 52
Figure 9-5: Defining User Classes ..................................................................................................... 52
Figure 9-6: DHCP User Classes ........................................................................................................ 52
Figure 9-7: New Class ....................................................................................................................... 53
Figure 9-8: Packet Bytes Window ...................................................................................................... 53
Figure 9-9: DHCP User Classes ........................................................................................................ 54
Figure 9-10: Set Predefined Options ................................................................................................. 54
Figure 9-11: Predefined Options and Values ..................................................................................... 55
Figure 9-12: Option Type – Add AudioCodes 160 Option................................................................... 55
Figure 9-13: Predefined Options and Values – Add OVOC Server Location ....................................... 56
Figure 9-14: 'Scope Leased' Folder - Configure Options .................................................................... 56
Figure 9-15: Configure Options 1 ...................................................................................................... 57
Figure 9-16: Configure Options 2 ...................................................................................................... 57
Figure 9-17: Server Options .............................................................................................................. 59
Figure 9-18: Three Scope Options Created ....................................................................................... 59
Figure 9-19: Redirect Server Configuration Process .......................................................................... 63
Figure 9-20: Automatic Provisioning – Static URL.............................................................................. 64
Figure 10-1: Quick Setup .................................................................................................................. 69
Figure 12-1: Date and Time............................................................................................................... 75
Figure 12-2: NTP & Time Settings ..................................................................................................... 76
Figure 12-3: Daylight Saving Time .................................................................................................... 76
Figure 12-4: NTP & Time Settings ..................................................................................................... 79
Figure 12-5: NTP and Time Settings ................................................................................................. 81
Figure 13-1: Network Settings ........................................................................................................... 84
Figure 14-1: Network Settings - Port Mode ........................................................................................ 89
Figure 15-1: Network Settings - VLAN Settings ................................................................................. 91
Figure 16-1: Signaling Protocols- SIP General................................................................................... 95
Figure 16-2: SIP Proxy and Registrar ................................................................................................ 99
Figure 16-3: Proxy Redundancy ...................................................................................................... 102
Figure 16-4: Line Settings ............................................................................................................... 107
Figure 16-5: Shared Call Appearance ............................................................................................. 108
Figure 16-6: Signaling Protocols - SIP Timers ................................................................................. 109
Figure 16-7: Quality of Service ........................................................................................................ 111
Figure 16-8: General Parameters - Reject Code .............................................................................. 112
Figure 17-1: Web Interface - VocaNOM........................................................................................... 113
Figure 17-2: Web Interface Dialing .................................................................................................. 114
Figure 17-3: Automatic Redial On Busy ........................................................................................... 116
Figure 17-4: Dialing Page - Tones ................................................................................................... 117
Figure 17-5: Services Page - Tones ................................................................................................ 117
Figure 17-6: DTMF Transport Mode ................................................................................................ 119
Figure 17-7: Digit Map and Dial Plan ............................................................................................... 120
Figure 17-8: Default Audio Device ................................................................................................... 123
Figure 18-1: Distinctive Ringing ....................................................................................................... 125
Figure 18-2: Distinctive Ringing ....................................................................................................... 126
Figure 18-3: Example of the Alert-Info Header ................................................................................. 126
Figure 18-4: Tones - Regional Settings ........................................................................................... 127
Figure 18-5: Upload Ringing Tone ................................................................................................... 129
Figure 19-1: Media Streaming ......................................................................................................... 134
Version 2.2.16 11 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 12

400HD Series IP Phones
Figure 19-2: Quality of Service ........................................................................................................ 135
Figure 19-3: Media Streaming - Codecs .......................................................................................... 136
Figure 19-4: Media Streaming - Codecs .......................................................................................... 138
Figure 20-1: Voice – Jitter Buffer ..................................................................................................... 139
Figure 20-2: Voice - Silence Compression ....................................................................................... 140
Figure 20-3: Voice - Noise Reduction .............................................................................................. 141
Figure 21-1: Line Settings ............................................................................................................... 144
Figure 22-1: Services ...................................................................................................................... 147
Figure 22-2: Services - Call Waiting ................................................................................................ 148
Figure 22-3: Services - Call Forward ............................................................................................... 149
Figure 22-4: Services - Conference ................................................................................................. 150
Figure 22-5: Dialing - Automatic Dialing........................................................................................... 151
Figure 22-6: Services - DnD ............................................................................................................ 154
Figure 22-7: Services - BLF Support - Call Pick Up ......................................................................... 155
Figure 22-8: Services - MWI ............................................................................................................ 156
Figure 22-9: Services - BLF............................................................................................................. 157
Figure 22-10: Services – AOC Support............................................................................................ 159
Figure 22-11: VoIP- Services – General Parameters ....................................................................... 163
Figure 23-1: Voice - Gain Control .................................................................................................... 167
Figure 24-1: LDAP .......................................................................................................................... 181
Figure 24-2: Corporate Directory ..................................................................................................... 184
Figure 24-3: Directory - Add Contact ............................................................................................... 185
Figure 25-1: 430HD Phone Personal Settings - Function Keys ........................................................ 187
Figure 25-2: 440HD Phone Personal Settings - Function Keys ........................................................ 188
Figure 25-3: Programmable Keys (430HD/440HD Phones) ............................................................. 190
Figure 25-4: Line Settings ............................................................................................................... 191
Figure 25-5: Programmable Keys .................................................................................................... 191
Figure 25-6: Personal Settings – Speed Dials (420HD and 405/405HD Phones) ............................. 194
Figure 25-7: Softkeys (420HD and 405/405HD Phone) .................................................................... 198
Figure 25-8: Navigation Keys .......................................................................................................... 201
Figure 25-9: Load and Save ............................................................................................................ 202
Figure 27-1: Services - Enable Paging ............................................................................................ 205
Figure 27-2: Enable Barge-in .......................................................................................................... 206
Figure 29-1: Certificate .................................................................................................................... 215
Figure 30-1: Root CA Certificate...................................................................................................... 217
Figure 30-2: Client Certificate .......................................................................................................... 218
Figure 30-3: Certificate Signing Request ......................................................................................... 220
Figure 31-1: Signaling Protocols - SIP General................................................................................ 224
Figure 32-1: Web Interface –801.1X Settings - EAP-MD5 ................................................................ 227
Figure 32-2: Web Interface –801.1X Settings - EAP-TLS ................................................................. 228
Figure 33-1: SRTP .......................................................................................................................... 229
Figure 36-1: Securing Web Interface Management with HTTP/S ..................................................... 235
Figure 36-2: Automatic Provisioning ................................................................................................ 236
Figure 38-1: Users – Administrator Account .................................................................................... 241
Figure 39-1: Restart System............................................................................................................ 244
Figure 39-2: Confirmation Box ......................................................................................................... 244
Figure 40-1: Restore Defaults ......................................................................................................... 246
Figure 40-2: Confirmation to Restore Defaults ................................................................................. 246
Figure 41-1: LAN Information .......................................................................................................... 249
Figure 41-2: Port Mode Status ........................................................................................................ 249
Figure 41-3: 802.1X Status ............................................................................................................. 249
Figure 42-1: VoIP Status - Phone Status ......................................................................................... 251
Figure 42-2: Line Status .................................................................................................................. 251
Figure 42-3: Memory Status ............................................................................................................ 252
Figure 42-4: Memory Status – Linux meminfo Command – Displayed Information ........................... 253
Figure 42-5: Web Interface –Line 1 Call Information ........................................................................ 253
Figure 43-1: Call History.................................................................................................................. 255
Figure 44-1: System Information–Firmware Version ........................................................................ 257
Figure 44-2: System Information – Release Information .................................................................. 258
Administrator's Manual 12 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 13

Administrator's Manual Contents
Figure 45-1: Media Streaming - RTCP-XR....................................................................................... 261
Figure 46-1: Diagnostic Tests Displayed on the Phone .................................................................... 265
Figure 46-2: Keypad and Hook Test– On-Hook (e.g., 440HD) ......................................................... 266
Figure 46-3: Keypad Test – Off-Hook (e.g., 440HD) ........................................................................ 266
Figure 48-1: Web Interface –System Logging .................................................................................. 271
Figure 50-1: Recording ................................................................................................................... 277
Figure 51-1: Crash Dump ................................................................................................................ 279
Figure 52-1: Web Interface –Port Mirroring ...................................................................................... 281
Figure 53-1: Tracing System Key Behavior...................................................................................... 283
Figure A-1: BLF Configuration in a BroadSoft Environment ............................................................. 288
Figure A-2: Configuring Call Forwarding using BroadSoft's BroadWorks .......................................... 290
Figure A-3: Configuring DnD in BroadSoft's BroadWorks - Status .................................................... 291
Figure A-4: Configuring DnD in BroadSoft's BroadWorks ................................................................. 291
Figure A-5: Services........................................................................................................................ 292
Figure A-6: Services - Feature Key Synchronization ........................................................................ 292
Figure A-7: Shared Call Appearance with Multiple Call Appearance ................................................ 295
Figure A-8: BroadSoft Server - Assigning Shared Calls Appearance to a User ................................ 295
Figure A-9: BroadSoft Server – Shared Call Appearance Add ......................................................... 297
Figure A-10: Line Settings - Shared Line ......................................................................................... 297
Figure A-11: Services - Conference................................................................................................. 298
Figure A-12: Directory ..................................................................................................................... 299
Figure A-13: Directory – Delete a Contact ....................................................................................... 300
Figure A-14: BLF Configuration for Application Server Type - Asterisk ............................................. 302
Figure A-15: Signaling Protocol – SIP Proxy and Registrar .............................................................. 304
Figure A-16: Signaling Protocol – SIP Proxy and Registrar – Secondary Proxy................................ 305
Figure A-17: Registering a Phone on the Redundant Genesys Server ............................................. 314
Figure A-18: Call Answer Groups .................................................................................................... 316
Figure A-19: Call Answer Groups - Add Group ................................................................................ 316
Figure A-20: Call Answer Group - Type ........................................................................................... 317
Figure A-21: Call Answer Group – Group Name .............................................................................. 317
Figure A-22: Call Answer Groups .................................................................................................... 318
Figure A-23: Call Answer Group ...................................................................................................... 318
Figure A-24: Number....................................................................................................................... 319
Figure A-25: Advanced ................................................................................................................... 319
Figure A-26: Services - Conference................................................................................................. 320
Figure A-27: Services - BLF Support ............................................................................................... 322
Figure B-1: ACD ............................................................................................................................. 324
Figure B-2: ACD – Unavailable Reason Code ................................................................................. 324
Figure C-1: Identifying Recovery Mode............................................................................................ 329
Figure C-2: Verifying Recovery Mode in Wireshark .......................................................................... 330
Figure C-3: Source Ethernet MAC Address in Wireshark Identical to Phone Base's ......................... 330
Figure C-4: Recovering the Phone - Configure the PC NIC to which the Phone is Connected .......... 331
Figure C-5: Verifying with Wireshark that the Phone is Downloading Phone .img File ...................... 333
Figure C-6: Verifying .img File Download with Wireshark – Filtering by TFTP .................................. 334
Figure C-7: Verifying .img File Download using tftpd64 .................................................................... 334
Figure C-8: Verifying .img File Download using tftpd64 .................................................................... 335
Figure C-9: Verifying .img File Download on the Phone ................................................................... 335
Version 2.2.16 13 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 14

400HD Series IP Phones
List of Tables
Table 2-1: Language Display Parameters .......................................................................................... 24
Table 3-1: Port Parameters ............................................................................................................... 27
Table 3-2: User Name and Password Parameters ............................................................................. 27
Table 4-1: Example of CSV File ........................................................................................................ 31
Table 5-1: OVOC Server Parameters ................................................................................................ 35
Table 9-1: DHCP Automatic Provisioning Parameters ....................................................................... 46
Table 9-2: Auto Provisioning via DHCP Option 66/67 ........................................................................ 50
Table 9-3: DHCP User Class Entry for Each AudioCodes Phone Model Deployed ............................. 54
Table 9-4: Static URL Automatic Provisioning Parameters................................................................. 65
Table 12-1: Date Display Format ....................................................................................................... 75
Table 12-2: Daylight Saving Time Parameters ................................................................................... 76
Table 12-3: NTP Server Parameters ................................................................................................. 79
Table 12-4: NTP Server and GMT Parameters .................................................................................. 82
Table 13-1: Network Settings Parameters ......................................................................................... 85
Table 13-2: Partial DHCP Parameters ............................................................................................... 86
Table 14-1: Port Settings................................................................................................................... 89
Table 15-1: VLAN Settings ................................................................................................................ 91
Table 16-1: SIP General Parameters ................................................................................................. 96
Table 16-2: Proxy and Registrar Parameters ..................................................................................... 99
Table 16-3: SIP Proxy Server Redundancy Parameters .................................................................. 103
Table 16-4: Device Registration Failover Parameters ...................................................................... 105
Table 16-5: Device Registration Failback Parameter ....................................................................... 106
Table 16-6: Preventing Unregistering .............................................................................................. 106
Table 16-7: Line Settings ................................................................................................................ 107
Table 16-8: SIP Timers Parameters ................................................................................................ 109
Table 16-9: SIP QoS Parameters .................................................................................................... 111
Table 16-10: Reject Code Parameter .............................................................................................. 112
Table 17-1: Voice-Dialing Parameter Descriptions ........................................................................... 113
Table 17-2: Dialing Parameters ....................................................................................................... 114
Table 17-3: Automatic Redial On Busy Parameters ......................................................................... 116
Table 17-4: Dial Tones Parameters ................................................................................................. 117
Table 17-5: DTMF Transport Mode ................................................................................................. 119
Table 17-6: Digit Map and Dial Plan Parameters ............................................................................. 120
Table 17-7: Headset LED Parameter ............................................................................................... 122
Table 17-8: Audio Device Parameter ............................................................................................... 123
Table 18-1: Distinctive Ringing Parameters ..................................................................................... 125
Table 18-2: Regional Parameters .................................................................................................... 127
Table 18-3: Ring Tone Parameters.................................................................................................. 130
Table 18-4: Configuring Beeps to be Played to Headsets when Calls Come in ................................ 130
Table 18-5: Configuring the Phone to Play a Fast Busy Tone when Automatically Disconnected on
Remote Side ................................................................................................................................... 131
Table 18-6: Configuring the Beep (Ring) to Play via an Answering Device ....................................... 132
Table 19-1: Media Streaming Parameters ....................................................................................... 133
Table 19-2: RTP Port Range and Payload Type Parameters ........................................................... 134
Table 19-3: RTP QoS Parameter .................................................................................................... 135
Table 19-4: RTP/SRTP Capability Negotiation Parameter ............................................................... 135
Table 19-5: Codec Parameters ....................................................................................................... 136
Table 19-6: OPUS Management Parameter .................................................................................... 138
Table 20-1: Jitter Buffer Parameters ................................................................................................ 139
Table 20-2: Silence Compression Parameters ................................................................................. 140
Table 20-3: Noise Reduction Parameters ........................................................................................ 141
Table 21-1: Line Parameters ........................................................................................................... 144
Table 22-1: General Supplementary Services Parameters............................................................... 147
Table 22-2: Call Waiting Parameters ............................................................................................... 148
Table 22-3: Call Forward Parameters .............................................................................................. 149
Table 22-4: Conference Parameters................................................................................................ 150
Administrator's Manual 14 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 15

Administrator's Manual Contents
Table 22-5: Allowing a Conference Initiator to Drop Out when On-Hooking ...................................... 150
Table 22-6: Automatic Dialing Parameters....................................................................................... 151
Table 22-7: Automatic Answer Parameters...................................................................................... 152
Table 22-8: Do Not Disturb Parameters ........................................................................................... 154
Table 22-9: Call Pick Up Parameters ............................................................................................... 155
Table 22-10: MWI Parameters ........................................................................................................ 156
Table 22-11: BLF Parameters ......................................................................................................... 157
Table 22-12: AOC Parameters ........................................................................................................ 159
Table 22-13: Reminder Tone after Long Hold .................................................................................. 159
Table 22-14: Disabling the HOLD Key ............................................................................................. 160
Table 22-15: Onhook Disconnect when Held ................................................................................... 160
Table 22-16: Configuring Ringing on the Default Audio Device ........................................................ 161
Table 22-17: Allowing an Incoming Call when the Phone is Locked ................................................. 162
Table 22-18: Letting Call Center Agents Record Welcome Greetings .............................................. 162
Table 22-19: EHS Parameter .......................................................................................................... 163
Table 22-20: Disabling the Hard Mute Key on the Phone ................................................................. 164
Table 22-21: Configuring a Softkey with Attended and Semi-Attended Call Transfer Functionality ... 165
Table 22-22: Configuring a Softkey with Blind Transfer Functionality ............................................... 165
Table 23-1: Automatic Gain Control Parameters .............................................................................. 167
Table 23-2: Tone Volume Parameter ............................................................................................... 169
Table 23-3: Ringer Volume Parameters........................................................................................... 170
Table 23-4: Speaker Parameters ..................................................................................................... 171
Table 23-5: Handset Gain Parameters ............................................................................................ 174
Table 23-6: Headset Gain Parameters ............................................................................................ 176
Table 24-1: LDAP Parameters ........................................................................................................ 181
Table 24-2: Provisioning Parameters ............................................................................................... 184
Table 25-1: 430HD Phone Function Keys Parameters ..................................................................... 188
Table 25-2: 440HD Phone Function Keys Parameters ..................................................................... 189
Table 25-3: Programmable Keys Parameters (430HD/440HD Phones)............................................ 190
Table 25-4: Configuring a Key Event ............................................................................................... 193
Table 25-5: Speed Dials Parameters ............................................................................................... 195
Table 25-6: Default Softkeys ........................................................................................................... 197
Table 25-7: Softkeys Parameters (420HD/405/405HD Phone) ......................................................... 198
Table 25-8: SoftKey Parameters ..................................................................................................... 199
Table 26-1: Parameters that can be Configured to Disable Hard Keys / Softkeys ............................. 203
Table 27-1: Paging Function Key Parameters ................................................................................. 205
Table 27-2: Barge-in Parameters .................................................................................................... 206
Table 27-3: Configuration File Paging Parameters........................................................................... 207
Table 28-1: Feature Key Synchronization Parameters ..................................................................... 209
Table 30-1: Root CA Certificate Parameters .................................................................................... 217
Table 30-2: Client Certificate Parameters ........................................................................................ 218
Table 30-3: Server-side Authentication ............................................................................................ 219
Table 31-1: SIP-over-TLS Parameters ............................................................................................ 223
Table 32-1: EAP TLS Parameters ................................................................................................... 226
Table 32-2: EAP MD5 Parameters .................................................................................................. 228
Table 33-1: SRTP Parameters ........................................................................................................ 229
Table 35-1: HTTP/S Login Authentication ........................................................................................ 233
Table 37-1: Authentication .............................................................................................................. 237
Table 38-1: Username and Password Parameters........................................................................... 241
Table 42-1: Memory Status – Linux Commands .............................................................................. 252
Table 45-1: RTCP_XR Parameters ................................................................................................. 262
Table 45-2: Voice Quality Monitoring Parameters ............................................................................ 262
Table 48-1: Syslog Parameters ....................................................................................................... 271
Table 49-1: Error Messages Displayed in the Phone Screen ........................................................... 275
Table 50-1: Recording Parameters .................................................................................................. 277
Table 51-1: Crash Dump Parameters .............................................................................................. 279
Table 52-1: Port Mirroring Parameters ............................................................................................ 281
Table 53-1: Tracing Parameters ...................................................................................................... 284
Table A-1: Features Supported in a BroadSoft Environment ............................................................ 287
Version 2.2.16 15 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 16

400HD Series IP Phones
Table A-2: Connecting Phones to BroadWorks over HTTP/S – Configuration File Parameters ......... 293
Table A-3: BroadSoft Server - Shared Call Appearance – Identity/Device Profile Type .................... 296
Table A-4: BroadSoft Server - Shared Call Appearance Add ........................................................... 297
Table 53-5: Remote Conference Parameters .................................................................................. 298
Table A-6: BroadSoft Server - Shared Call Appearance Add ........................................................... 300
Table 53-7: Displaying a Message in Agents' Phone Screens .......................................................... 301
Table 53-8: Backlight Timeout ......................................................................................................... 301
Table A-9: SIP Proxy and Registrar Parameters .............................................................................. 305
Table A-10: Disabling the Web Interface ......................................................................................... 308
Table A-11: Forcing a Reboot on Provisioning ................................................................................. 308
Table A-12: Enabling Agents to Sign in with Phone Numbers .......................................................... 309
Table A-13: Locking Agents Phones Alphabetical Keys ................................................................... 309
Table A-14: Playing a Beep on an Incoming Call ............................................................................. 310
Table A-15: Enabling Proactive Mute .............................................................................................. 310
Table 53-16: Automatic Answer....................................................................................................... 311
Table A-17: Regulating the 'Logged out' Message ........................................................................... 311
Table A-18: 3PCC Parameters ........................................................................................................ 312
Table A-19: Enabling 3PCC Calls .................................................................................................... 312
Table A-20: BroadSoft Server - Shared Call Appearance Add ......................................................... 313
Table 53-21: Backlight Timeout ....................................................................................................... 313
Table 53-22: Displaying a Message on Agents' Phones................................................................... 314
Table 53-23: Redundant Genesys Server - Parameters ................................................................... 315
Table A-24: Retransmission Timer T1 - Parameter .......................................................................... 315
Table 53-25: Remote Conference Parameters................................................................................. 320
Table 53-26: Parameters Mandatory for Phones in a Genband Environment ................................... 321
Table B-1: ACD Parameters ............................................................................................................ 325
Table B-2: BroadSoft-Softkey Display States and Command Menu Options .................................... 328
Table 53-3: Configuring tftpd64 Settings .......................................................................................... 331
Table D-1: CSV File Description ...................................................................................................... 338
Table E-1: Supported IETF RFCs .................................................................................................... 343
Table E-2: Supported SIP Methods ................................................................................................. 345
Table E-3: Supported SIP Headers ................................................................................................. 346
Table F-1: IP Phone Specifications.................................................................................................. 349
Table G-1: RTCP-XR Parameters ................................................................................................... 353
Administrator's Manual 16 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 17
Administrator's Manual Notices
440HD IP Phone User’s Manual
440HD IP Phone Quick Guide
430HD IP Phone User’s Manual
430HD IP Phone Quick Guide
420HD IP Phone User’s Manual
420HD IP Phone Quick Guide
405 and 405HD IP Phone User’s Manual
405 and 405HD IP Phone Quick Guide
Device Manager Pro Administrator’s Manual
One Voice Operations Center (OVOC) IOM Manual
OVOC User’s Manual
Notice
Information contained in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable at the time of
printing. However, due to ongoing product improvements and revisions, AudioCodes cannot
guarantee accuracy of printed material after the Date Published nor can it accept responsibility
for errors or omissions. Updates to this document can be downloaded from
https://www.audiocodes.com/library/technical-documents.
This document is subject to change without notice.
Date Published: Apr-12-2020
WEEE EU Directive
Pursuant to the WEEE EU Directive, electronic and electrical waste must not be disposed of
with unsorted waste. Please contact your local recycling authority for disposal of this product.
Customer Support
Customer technical support and services are provided by AudioCodes or by an authorized
AudioCodes Service Partner. For more information on how to buy technical support for
AudioCodes products and for contact information, please visit our Web site at
https://www.audiocodes.com/services-support/maintenance-and-support.
Stay in the Loop with AudioCodes
Abbreviations and Conventions
Each abbreviation, unless widely used, is spelled out in full when first used.
Related Documentation
Document Name
Version 2.2.16 17 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 18
400HD Series IP Phones
11947
Version 2.2.2.
11948
Version 2.2.4. 405. CC features: Supervisor Listen, Select Ring Audio Device, Disable
Slovak, Czech, Turkish.
11949
Version 2.2.8 – preliminary. Proxy and Registrar parameter values, Headset LED, ring-tone,
Handset Mode, Displaying a Message in Agents’ screens, hide ACW softkey, 3PCC restored.
11950
Version 2.2.8 – official. Multiple lines. Dual registration (Genesys), 3PCC. Voip/talk_event.
Unregister_on_voip_reload. Lightweight Syslog. Recovering phone.
11951
Version 2.2.12. 3DES. Multiple Lines. System/syslog/mode. Locking A-B keys – applicability.
User-Class. Distinctive Ring Tone. 405HD. 430HD with high resolution screen.
11953
Version 2.2.14. Call Log sync. Technician’s Digit Key Code. XSI. EMS > OVOC server.
Xsi
over HTTP/S.
11955
SIP SUBSCRIBE and NOTIFY Messages. USB Headsets. VocaNOM. Disable HOLD key.
headsets.
11956
PAI on Replay. Automatic Answer: new Note. Tone after long hold. Client Certificate: modified
descriptions. Server-side Authentication: modified descriptions. Plantronics link.
11959
Preventing Unregistering. DTMF level. Voip/media/srtp/NegotiationMode. SRTCP. Device
Remove the ‘lifetime’ parameter. OpenSSL. ‘provisioning/period/type’ description improved.
11970
personal_settings/menu/callautoanswering/enabled. Configuring parameters mandatory for
Genband.
11971
voip/ring_via_answer_device/enabled
11972
Beep (Ring) via Answering Device. Network/lan/_802_1x/eap_type.
Voip/services/enhanced_ACD/enabled.
11974
RTP/SRTP Capability Negotiation
Document Revision Record
LTRT Description
Hands-Free Mode, Greeting Recording, BroadSoft-based ACD Hoteling, SHA2, Blind
Transfer, Drop From Local Conference, Factory-Set Certificates and AudioCodes Trusted
Root CA, Factory-Installed Certificates Status Displayed, Send DTMF via SIP and via RTP
Together, HTTP/S Provisioning, CDP Enhanced, Restoring Phone Settings to Defaults;
RTP Port Range (media_port), Codec Type updated, Media Streaming – Codecs updated,
DnD Activate, Function Keys pgs, Firmware Release Information, RTCP-XR, Disabling
Removed Redundant Outbound proxy; new note recommending DNS queries. OPUS
payload. Auto_answer_use_180. Paging. Barge-in. voip/services/group_paging/codec.
Voip/services/group_paging/end_income_paging_timeout. System Logging. BroadWorks
Disable mute key. Disabling Hard Keys and Softkeys. SRTP. Backlight timeout. USB
Manager Pro. USB Headset. Recovery Mode notification. DIGICert. Genband support.
Network/lan/_802_1x/eap_identity. Network/lan/_802_1x/eap_identity.
Voip/services/sla/barging/enable. Voip/sla/group/0/description. Voip/sla/group/0/enabled.
Voip/sla/group/1/description. Voip/sla/group/1/enabled. Combined ACD/Hoteling.
Documentation Feedback
AudioCodes continually strives to produce high quality documentation. If you have any
comments (suggestions or errors) regarding this document, please fill out the Documentation
Feedback form on our Web site at https://online.audiocodes.com/documentation-feedback.
Administrator's Manual 18 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 19

Administrator's Manual 1. Introduction
1 Introduction
This manual is intended for the system administrator responsible for setting up and
configuring the 420HD, 430HD, 440HD, 405 and 405HD IP phones.
AudioCodes' IP phones are based on AudioCodes' proprietary High Definition (HD) voice
technology, providing clarity and a rich audio experience in Voice-over-IP (VoIP) calls. The
phones are fully-featured telephones that provide voice communication over an IP network,
allowing you to place and receive phone calls, put calls on hold, transfer calls, make
conference calls, and so on.
The phone offers a wide variety of management and configuration tools:
Phone screen - easy-to-use, menu-driven screen providing basic phone configuration
and status capabilities
Web interface - provides a user-friendly Web interface that runs on a Web browser
(Microsoft® Internet Explorer is the recommended browser).
Configuration file - text-based file (created using any plain text editor such as Microsoft's
Notepad) containing configuration parameters and which is loaded to the phone using
the Web interface or a TFTP, FTP, HTTP or HTTPS server.
Device Manager Pro (see the Device Manager Pro Administrator's Manual).
For a detailed description on hardware installation and for operating the phone's call
features, see the User's Manual.
Note:
• Boldened parameters enclosed in square brackets [ ] in the tables in this document
indicate configuration file parameters.
• Web interface parameters are displayed in regular font above their web counterparts.
Version 2.2.16 19 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 20

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 20 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 21

Part I
Configuration Tools
Page 22

Page 23

Administrator's Manual 2. IP Phone User Interface
2 IP Phone User Interface
The phone provides a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) based screen, offering an intuitive,
menu-driven interface for configuring the phone. The administrative tasks are performed in
the phone's Administration menu.
Note: Screenshots of the 440HD are shown in this document. Screenshots of the 420HD
and 405/405HD are only shown if they significantly differ.
2.1 Accessing the Administration Menu
Here's how to access the Administration menu on the phone.
Note:
• The phone is password protected. The default password is 1234. To change the login
password, use the phone's Web interface or Configuration file.
• After entering the password, the access session is applied to all the submenus.
• To change the Administration screen's login password, use the phone's Web
interface or use the configuration file.
To access the Administration screen:
1. Press the MENU key on the phone and navigate down to Administration.
Note: Alternatively, after pressing the MENU key you can press an item's number to
navigate to the item, for example, press 6 to navigate to Administration.
2. Press Select; you're prompted for a password.
3. Enter the administration password (Default: 1234) and then press the OK softkey.
Version 2.2.16 23 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 24

400HD Series IP Phones
2.2 Changing Display Language
Here's how to change the language in the phone screen. Language can be configured using
the Web interface or configuration file.
To choose a language using the Web interface:
1. Open the Language page (Configuration tab > Personal Settings menu > Language).
Figure 2-1: Language
2. Select the language according to the parameter in the table below, and then click
Submit; the phone reboots and changes the screen language.
To choose a language using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Table 2-1: Language Display Parameters
Parameter Description
Phone Display Language
[personal_settings/language]
[personal_settings/lcd_contrast]
[personal_settings/blf_lcd_contrast]
Determines the screen language. See the
Release Notes for the list of languages
supported.
Determines the screen contrast. Configure to a
level that is comfortable for the user.
Range: 0-35 (430HD / 440HD) and
0-30 (420HD). The default depends on the
hardware revision.
Applies only to 440HD phone. Determines the
sidecar BLFs contrast. Configure to a level
comfortable for the user.
Range: 0-39. Default: 16.
Administrator's Manual 24 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 25
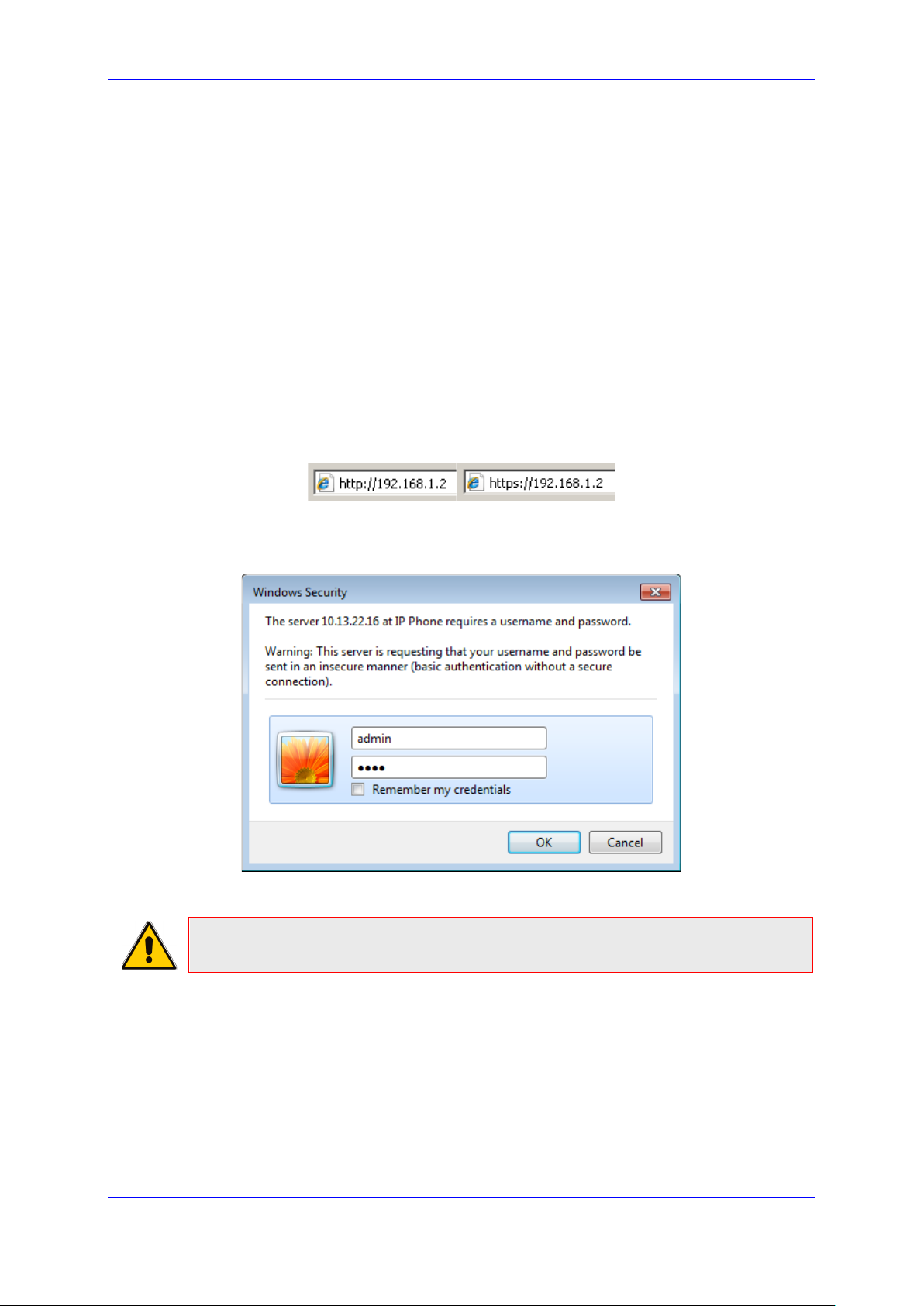
Administrator's Manual 3. Web Interface
3 Web Interface
This section describes the phone's Web interface. You can use the Web interface to
configure the device.
3.1 Accessing Web Interface
You can use any standard Web browser (such as Microsoft Internet Explorer) to access the
phone's Web interface. The IP address used for accessing the Web interface is the phone's
IP address, received from a DHCP server or manually configured (static IP address).
To access the phone's Web interface:
1. Connect the LAN port of your phone to the IP network (using the Cable or ADSL modem
from your Internet Service Provider).
2. Determine the phone's IP address obtained from the DHCP server.
3. Open a Web browser, and then in the URL address field, enter the phone's IP address
(for example, http://192.168.1.2 or https://192.168.1.2), as displayed below:
The Web login window appears:
Figure 3-1: Web Interface Login
Note: The administrator's default login user name and password are admin and 1234
respectively.
4. Alternatively, if your DHCP and DNS servers are synchronized, you can access the
phone Web browser by using the following method:
http://<Phone Model>-<MAC Address>.<Domain Name>
E.g. http://440hd-001122334455.corp.YourCompany.com
5. Enter the User name and Password, and then click OK.
Version 2.2.16 25 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 26
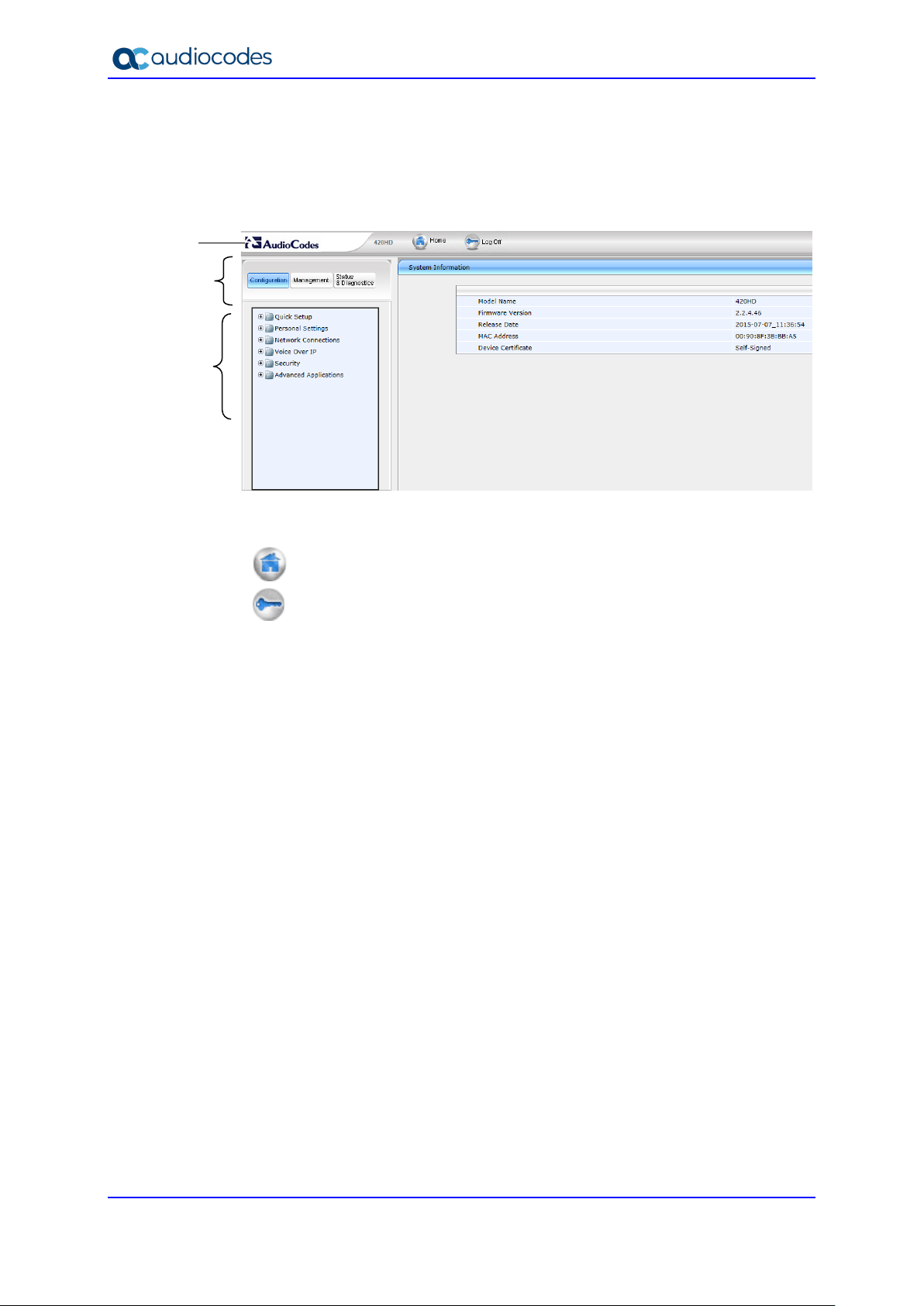
400HD Series IP Phones
Navigation
Bar
Toolbar
Navigation
Tree
3.2 Getting Started with the Web
The areas of the Web interface are shown below:
Figure 3-2: Web Interface Areas
The Web interface is composed of the following main areas:
Toolbar: displays AudioCodes logo and provides the following buttons:
• Home: opens the Home page
• Log off: closes the Web interface
Navigation bar: provides tabs for accessing the configuration menus:
• Configuration: provides menus for configuring the phone.
• Management: provides menus for various management tasks such as firmware
upgrade and changing the login username and password.
• Status& Diagnostics: provides menus for displaying information on the status of the
phone, such as call history.
Navigation tree: tree-like, hierarchical structure of menus pertaining to the selected tab
on the Navigation bar.
Configuration pane: displays the configuration parameters pertaining to a selected
menu in the Navigation tree.
Administrator's Manual 26 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 27
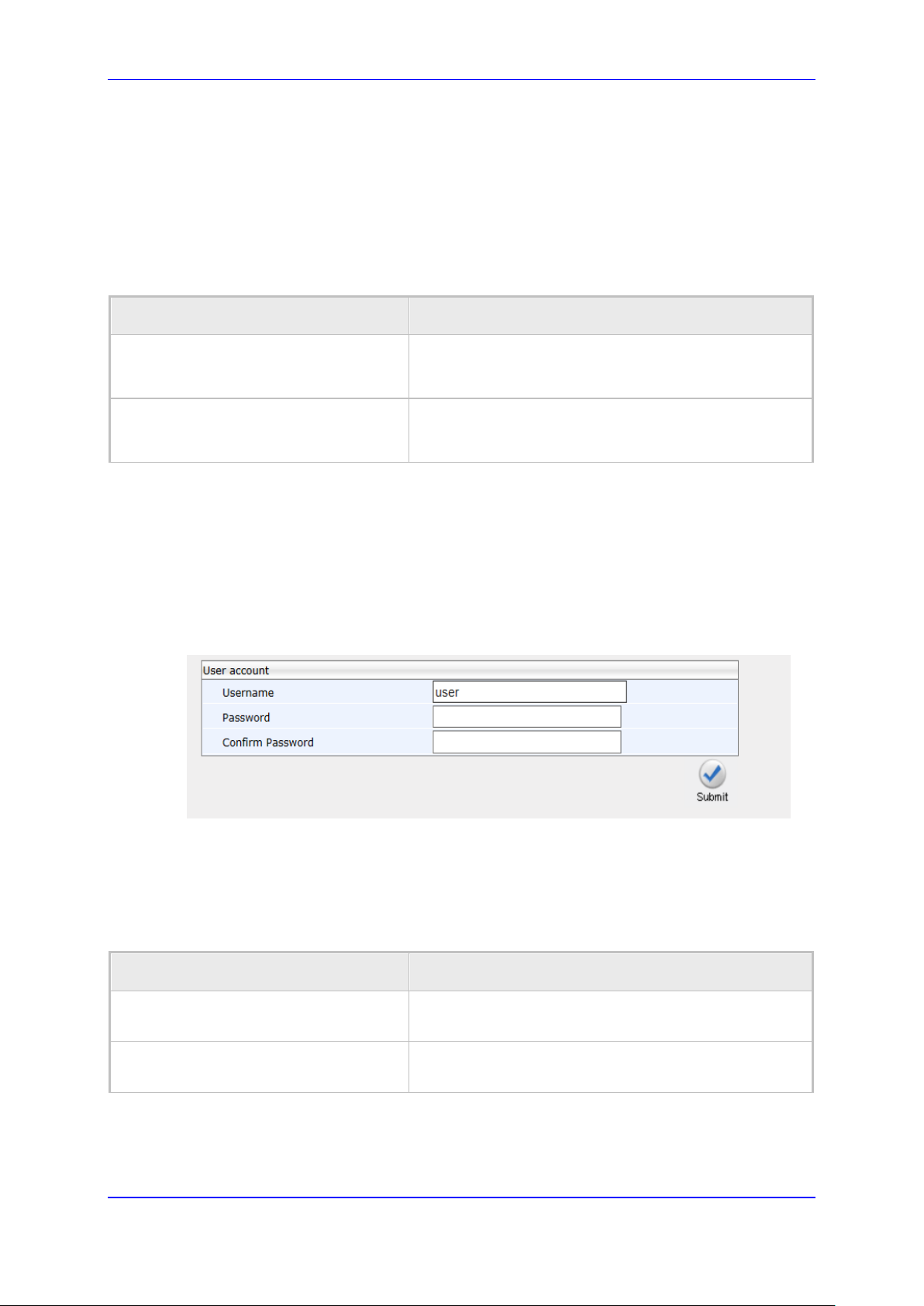
Administrator's Manual 3. Web Interface
3.3 Configuring the Web Interface's Port
Here's how to assign a port number to the Web interface, using the configuration file.
To configure the Web interface port using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Table 3-1: Port Parameters
Parameter Description
[system/http_server_port]
[system/https_server_port]
Assigns a port number to the Web interface.
The HTTP server by default uses port number 80.
Range: 0-65535.
Assigns a port number to the Web interface.
The HTTPS server by default uses port number 443.
Range: 0-65535.
3.4 Configuring User Login Credentials
Here's how to configure the phone user's name and password.
To configure the phone user's name and password using the Web interface:
1. Open the User Account page (Management menu > Administration > Users):
Figure 3-3: User Account
2. Configure using the table below as reference, and click Submit.
To configure using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Table 3-2: User Name and Password Parameters
Parameter Description
Username
[system/web_user_name]
Password
[system/web_user_password]
Version 2.2.16 27 400HD Series IP Phones
The phone user name. Default: admin.
Applies only to the Web interface.
The encrypted phone password. Default: 1234.
Applies only to the Web interface, and phone screen.
Page 28

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 28 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 29

Administrator's Manual 4. Configuration File
4 Configuration File
This section describes the configuration file and the parameters you can configure in it.
4.1 Introduction
The configuration file can be loaded to the phone using the automatic provisioning
mechanism, or manually from your local computer using the Web interface. The subsections
below describe configuration file syntax and linking additional configuration files to a
configuration file.
4.2 File Syntax
The configuration file can be created using a standard ASCII, text-based program such as
Notepad. The configuration file is a .cfg file with the file name being the phone's MAC
address: <phone's MAC address>.cfg.
The syntax of the configuration file is as follows:
<parameter name>=<value>
Make sure the configuration file conforms to these guidelines:
No spaces on either side of the equals (=) sign.
Each parameter must be on a new line.
Below is an example of part of a configuration file:
system/type=440HD
voip/line/0/enabled=1
voip/line/0/id=1234
voip/line/0/description=440HD
voip/line/0/auth_name=1234
voip/line/0/auth_password=4321
4.3 Linking Multiple Files
The Configuration file allows you to include links (URL and/or file name) to other
Configuration files that provide additional parameter settings. This is especially useful in
deployments with multiple phones, where the phones share common configuration but
where each phone has some unique settings. In such a scenario, a phone's Configuration file
can include unique parameter settings as well as links to additional Configuration files with
settings common to all phones.
Linking additional files is achieved by using the include function in the phone's Configuration
file. For example, the below Configuration file provides links to additional Configuration files
(shown in bolded font):
system/type=440HD
include 440HD_<MAC>_voip.cfg
include vlan_conf.cfg
include network_conf.cfg
include provisioning_conf.cfg
Version 2.2.16 29 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 30
400HD Series IP Phones
In addition, the Configuration file can provide URL paths (FTP, TFTP, HTTP, or HTTPS) to
where the additional files are located, as shown in the example below (shown in bolded font):
system/type=440HD
include http://10.10.10.10/440HD_<MAC>_voip.cfg
include https://remote-pc/vlan_conf.cfg
include tftp://10.10.10.10/440HD_<MAC>_network.cfg
include ftp://remote-pc/provisining_conf.cfg
Note: If no URL is provided in the Configuration file, the files are retrieved according to
the provisioning information (e.g. DHCP Option 160 as well as Option 66/67).
4.4 Downloading the Configuration File from the Phone
For more information, see Maintenance.
4.5 Creating Configuration Files using VoIProvision Utility
When installing AudioCodes' phones, the network administrator typically configures each
installed phone automatically. Using DHCP options or other methods, the phone can be
instructed to download a configuration file. This file is typically unique to each phone, based
on the MAC address. This MAC-specific configuration file is generated with phone specific
configuration parameters; such as, the extension ID, name and authentication password.
Not all of the iPBX and SoftSwitch vendors (and especially the full solution vendors) include
provisioning in their interoperability programs. As an IP phone vendor, AudioCodes is
required to provide a standalone provisioning tool that will enable the provisioning of its
phones in such environments.
AudioCodes provides a tool that assists in the automatic generation of configuration files.
These files can be generated for the initial configuration of the phones and then later
regenerated for subsequent configuration updates as required.
4.5.1 Configuration File Format
The detailed format of the phones' configuration files are described in the appendix. The
following is an output example of an automatically generated MAC-specific file:
system/type=440HD
voip/line/0/enabled=1
voip/line/0/id=56832432
voip/line/0/auth_name=3423fdwer2tre
voip/line/0/auth_password=123456
include global.cfg
4.5.2 Global Configuration File
In addition to the MAC-specific files, it is recommended to maintain a single global
configuration file, which contains parameters that are common to all phones in the specific
site. The MAC-specific files can call the global file (using the 'include' method) as illustrated
in the above example. For more information, see 'Linking Additional Files using “Include”' in
the Administrator's Manual.
Administrator's Manual 30 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 31

Administrator's Manual 4. Configuration File
4.5.3 VoIProvision Utility Overview
The VoIProvision utility is a generic tool that automatically generates multiple MAC-specific
configuration files (.cfg). The utility generates a separate .cfg file for each phone.
To execute the utility, the user needs to prepare a csv file and a template file. The csv file
contains the tagged records for each phone and the template file maps these tagged records
to a configuration file format, which can be read by the phone.
4.5.4 CSV File
The csv file contains a list of tags and a list of the tag's values. The first line in the file contains
the list of tags (comma-separated) and each of the other lines contains a list of v alues, where
each line record represents an individual phone.
The csv file is usually exported from the customer's IP-PBX or some other database and
typically contains the list of phones (e.g. MAC, extension ID, user name and password of
each phone).
Table 4-1: Example of CSV File
[mac] [name] [id] [password]
00908F123456 Jonathan 4071 12345
00908F123457 David 4418 12345
When opened as a text file, the csv file appears similar to the example below:
[mac],[name],[id],[password]
00908F123456,Jonathan,4071,12345
00908F123457,David,4418,12345
4.5.5 Template File
The template file defines the format of the generated configuration files, but contains tags
instead of actual values. The VoIProvision utility reads the template file and replaces each
tag with actual values from the csv file.
Example of a template file:
system/type=440HD
voip/line/0/enabled=1
voip/line/0/id=[id]
voip/line/0/auth_name=[name]
voip/line/0/auth_password=[password]
include global.cfg
4.5.6 Generated Configuration Files
The generated configuration (.cfg) files use a similar format to the template file; however the
tags are replaced with the actual values that are read by the VoIProvision utility from the csv
file. One of the tags defined in the csv file, should be used as the .cfg file name (in order for
the VoIProvision utility to generate a separate .cfg file for each line record in the csv file).
Typically the tag which defines the MAC address is used as the .cfg file name.
Version 2.2.16 31 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 32

400HD Series IP Phones
4.5.7 Starting the VoIProvision Utility
The VoIProvision utility can run on both the Linux and Windows platforms. The VoIProvision
utility initially parses the csv file to generate the list of tags. The VoIProvision then reads each
line record of values in the csv file and for each line record, does the following:
Parses the line record to create a list of values
Opens the template file
Generates the .cfg file name and create a new .cfg file
Reads the template file, associates the mapped tags with actual values from the csv file
and writes the result to the .cfg file
Closes the .cfg file and template file
4.5.8 Usage
USAGE: VoIProvision<csv file><template file><.cfg file>
Note the following:
The first line of the csv file contains the list of tags (e.g.,
[mac],[name],[id]).
The remainder of the csv file contains a line record per .cfg file (e.g.
00908f112233,4071,Ethan).
There is no restriction on the format of the tags (e.g., [tag] or @tag@).
The template file defines the .cfg file format. During VoIProvision
run-time, the mapped tags in the template file are associated to actual
values that are read from the csv file.
Currently only a single tag can be defined per line record in the template
file.
The .cfg file name should represent the string of one of the predefined
tags in order to generate a separate .cfg file per csv line record
(e.g., [mac].cfg).
4.6 Using the Encryption Tool
AudioCodes' phones use the Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) algorithm for
encryption. Here's how to use the encryption tool.
4.6.1 Encrypting Configuration Files
Here's how to encrypt the configuration file. For example, you may wish to encrypt the
configuration file when it is send over an unsecure network.
To encrypt the configuration file:
At the command line prompt, specify the following:
encryption_tool.exe –f <filename>.cfg
where <file name>.cfg specifies the name of the Configuration file that you wish to
encrypt.
Once the Configuration file is encrypted, it receives the suffix '.cfx' (e.g. Conf.cfx). This is
the file that you should specify in the 'Configuration URL' and the 'Dynamic Configuration
URL' fields when performing automatic provisioning (see Part II 'Automatic
Provisioning').
Administrator's Manual 32 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 33

Administrator's Manual 4. Configuration File
4.6.2 Encrypting Passwords in the Configuration File
Here's how to encrypt phone passwords used in the configuration process, for example, the
'System' password and the 'SIP Authentication' password.
To encrypt passwords:
1. At the command line prompt, specify the following:
encryption_tool.exe –s <password_string>
where <password_string> specifies the string of the password that you wish to encrypt.
Once the password is encrypted, a string is generated with the following syntax:
{"<encrypted_string>"}
For example:
{"0qrNRpSJ6aE="}
2. Copy the generated string (including the {“ “}) with the syntax specified above to the
relevant parameter in the Configuration file.
For example, if you encrypted the SIP authentication password, the following is
displayed in the relevant line in the configuration file:
voip/line/0/auth_password={"0qrNRpSJ6aE="}
Note: It's recommended to encrypt the 'System' password using this procedure. If you
choose not to, the 'System' password is by default encrypted using MD5.
Version 2.2.16 33 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 34

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 34 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 35

Administrator's Manual 5. Device Manager Pro
For more information on the Device Manager Pro, see the Device Manager Pro
5 Device Manager Pro
Network administrators can provision an enterprise's phones from the server of the One
Voice Operations Center (OVOC) module, Device Manager Pro.
Note:
• Device Manager Pro and OVOC share the same server location.
• For more information on using Device Manager Pro to provision phones, see the
Device Manager Pro Administrator's Manual.
To configure provisioning phones from the OVOC server using the configuration
file:
1. Open the Configuration File page in the Web interface (Management tab > Manual
Update > Configuration File).
2. Configure the OVOC server parameters using the table below as reference.
Table 5-1: OVOC Server Parameters
Parameter Description
[ems_server/keep_alive_period]
[ems_server/provisioning/url]
[ems_server/user_name]
[ems_server/user_password]
Note:
AudioCodes’ Device Manager Pro also supports headset management capability in
addition to phone management capability. IGS-1071The management interface displays
(for example) in the Devices Status page:
• Column 'USB Headset Type' displaying a headset connected to a phone’s USB port
• Column 'IPP Model' displaying the USB icon
The OVOC server sends a keep alive message at a
configured interval to verify that its link with the network
is operating. If no reply is received, the link is determined
to be down or not working.
Default: 60 minutes
Defines the URL of the OVOC server, for example,
http://10.1.8.23:8081
Defines the username of the administrator who'll use the
OVOC server for provisioning, for example, John Smith.
Defines the password (encrypted) of the network
administrator who'll provision the phones from the
OVOC server, f or example:
{"Y6QYmP53BDkoTvuIFjEBuQ=="}
Administrator's Manual.
Version 2.2.16 35 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 36

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 36 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 37

Part II
Automatic Provisioning
Page 38

Page 39

Administrator's Manual 6. Introduction
6 Introduction
By default, the phone is ready for out-of-the-box deployment using its automatic provisioning
capabilities.
The phone offers a built-in mechanism for automatically upgrading its software image and
updating its configuration. This method is used to upgrade the phone firmware and update its
configuration, by remotely downloading an updated software image and configuration file.
The automatic update mechanism helps you keep your software image and configuration
up-to-date, by performing routine checks for newer software versions and configuration files,
as well as allowing you to perform manual checks.
The automatic update mechanism is as follows:
Before connecting the phone, verify that the provisioning server is running and that the
firmware and configuration files are located in the correct location.
Connect your phone to the IP network, and then connect the phone to the power outlet.
During DHCP negotiation, the phone requests for DHCP options 66/67/160 to receive
provisioning information. The DHCP server should respond with Option 160 providing
the provisioning URL or Options 66 and 67 providing the TFTP IP address and firmware
file name respectively.
The phone then checks whether new firmware is available by checking the firmware file
header. If the version is different from the one currently running on the phone, the phone
downloads the complete image and burns it to its flash memory.
If a new firmware is unavailable, the phone then checks whether a new configuration is
available. If a configuration file is available on the server, the phone downloads it and
updates the phone's configuration after verifying that the configuration file is related to
the phone model. When a configuration update is needed, the phone might reboot.
Note:
• In the DHCP Discover message, the phone publishes its model name in Option fields
60 and 77 (e.g. 440HD). If the administrator wants to provide different provisioning
information to different phone models, the administrator can set up a policy in the
DHCP server according to the phone model name.
• If the phone is powered off for some reason during the firmware upgrade process, the
phone will be unusable and the recovery process must be performed.
• You can only use firmware files with an .img extension and configuration files with a
.cfg extension.
• To "force" the firmware or configuration file to be retrieved immediately regardless of
the 'Check Period' value, click the Check Now button on the relevant page on the
Web interface.
• An additional auto-provisioning mechanism is supported if the provisioning
environment does not provide all the required information (e.g. DHCP options).
Note: Automatic mass provisioning of phones using DHCP can alternatively be
performed from the OVOC’s IP Phones Manager Pro module. For more information, see
the Device Manager Pro Administrator's Manual.
Version 2.2.16 39 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 40

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 40 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 41

Administrator's Manual 7. Updating the Configuration File Manually
7 Updating the Configuration File Manually
The phone enables you to view, save, and load its configuration file to backup and restore
the current configuration.
To manually update the configuration file:
1. Open the Configuration File page (Management tab > Manual Update menu >
Configuration File). The current configuration file settings are displayed in the text pane.
Figure 7-1: Configuration File (430HD)
2. Click the Loading new Configuration File button; the following page appears:
Figure 7-2: Load New Configuration File
3. Click the Browse button and then select the required configuration file located on your
local PC; the phone verifies that the configuration file is related to the phone model. The
configuration file is then loaded to the phone. Once loaded, the phone reboots
(indicated by a message displayed on the phone's screen). The phone is now updated
with the new configuration.
Note: The configuration file name must have the extension .cfg.
Version 2.2.16 41 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 42

400HD Series IP Phones
To save the configuration file:
In the Configuration File page, click the Saving Current Configuration File button, and
then save the current phone configuration file to a folder on your local PC.
Note: When creating a new configuration file, make sure the system/type parameter in
the configuration file is set to the correct phone model (e.g., 430HD).
Administrator's Manual 42 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 43

Administrator's Manual 8. Setting up Network for Auto Provisioning
8 Setting up Network for Auto Provisioning
The phone supports dynamic VLAN discovery, dynamic IP addressing (DHCP), and NTP (as
client).
Note: For manual configuration of Network Settings, see Section 13.
Version 2.2.16 43 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 44

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 44 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 45

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
9 Obtaining Firmware and Configuration
Files
The Web interface allows you to:
Automatically update firmware and configuration files
Manually update firmware and configuration files
9.1 Provisioning Hunt Order
The phone always attempts to use the first provisioning method listed below (DHCP Option
160). If it cannot use this method, it attempts to use the second method listed below, and so
on, until it reaches a successful provisioning method. This is called the provisioning 'hunt
order'. The 'hunt order' is:
1. DHCP Option 160 (see Section 9.2.1)
2. DHCP Options 66-67 (see Section 9.2.2)
3. DHCP Options 43 (see Section 9.2.4)
4. SIP SUBSCRIBE and NOTIFY Messages (see Section 9.2.6)
5. Static and Globally Accessible Domain (see Section 9.2.7)
6. Cached Addresses of the Last Provisioning Server Used on Reboots (see Section
9.2.8)
7. AudioCodes Redirect server (see Section 9.2.9)
9.2 Dynamic URL Provisioning
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) can be used to automatically provision the
phone. The DHCP feature can be configured using the Web interface or configuration file.
To configure DHCP using the Web interface:
1. Open the Automatic Update page (Management tab > Automatic Update menu >
Automatic Provisioning).
Figure 9-1: Automatic Provisioning – Dynamic URL
2. Configure the parameters using the table below as reference, and then click Submit.
Version 2.2.16 45 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 46

400HD Series IP Phones
440HD_<MAC Address>_conf.cfg.
To configure DHCP using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Table 9-1: DHCP Automatic Provisioning Parameters
Parameter Description
Provisioning Method
[provisioning/method]
DHCP Option Value
[provisioning/url_option_value]
Defines the provisioning method:
[Disable] Disable - Automatic update is disabled.
The phone attempts to upgrade its firmware and
configuration
[Dynamic] DHCP Options (Dynamic URL) (default)
- Using DHCP option 160 as well as option 66/67
for provisioning
[Static] Static URL - Using Static URL for
provisioning
Determines the DHCP option number to be used for
receiving the URL for provisioning.
The default value is 160.
The phone supports DHCP Option 160 for complete
URL as well as Options 66/67 for TFTP usage. Option
160 has the highest priority and if absent, Options
66/67 are used.
The following syntax is available for DHCP option 160:
<protocol>://<server IP address or host name>
<protocol>://<server IP address or host
name>/<firmware file name>
<protocol>://<server IP address or host
name>/<firmware file name>;<configuration file
name>
<protocol>://<server IP address or host
name>/;<configuration file name>
Where <protocol> can be one of the following: ftp, tftp,
http or https.
For example:
ftp://192.168.2.1 – retrieved firmware file
is440HD.img and the configuration file name is
<MAC address>.cfg. For example,
001122334455.cfg
tftp://192.168.2.1/different_firmware_name.img -
retrieved firmware file is
Different_Firmware_Name.img and the
configuration file name is <MAC address>.cfg. For
example, 001122334455.cfg
http://192.168.2.1/different_firmware_name.img;
<MODEL>_<MAC>_conf.cfg - retrieved firmware
file is different_firmware_name.img and the
configuration file name is <Model type>_<MAC
address>_conf.cfg. For example,
440HD_001122334455_conf.cfg
• https://192.168.2.1/;<MODEL>_<MAC>_conf.cfg -
if the model is 440HD, the retrieved firmware file is
440HD.img and the configuration file name is
Administrator's Manual 46 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 47

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
For example, 440HD_001122334455_conf.cfg
defined, the phone will check only on powerup.
Note: This parameter is applicable only when type is
Parameter Description
The following syntax is available for DHCP Options
66/67:
Option 66 must be a valid IP address or host name
of a TFTP server only.
Option 67 must be the firmware name.
If Option 67 is absent, the phone requests for the
440HD.img image file. For example:
Option 66: 192.168.2.1 or myTFTPServer
Option 67: 440HD_2.2.2.img
Note:
This parameter is applicable only when method is
configured to Dynamic.
It is recommended to leave the parameter at its
default value to avoid conflict with other DHCP
options settings.
Random Provisioning Time
[provisioning/random_provisioning_time]
Defines the maximum random number to start the
provisioning process.
This is used for periodic checking of firmware and
configuration files to avoid multiple devices from
starting the upgrade process at the same time. When
the device is meant to start the upgrade, the device
randomly selects a number between 1 and the value
set for random_provisioning_time and performs the
check only after the random time.
The valid range is 0-65535. The default value is 120.
Check Period
[provisioning/period/type]
Every (Check Period = Hourly)
[provisioning/period/hourly/hours_interval]
Every day at
[provisioning/period/daily/time]
Defines the period type for automatic provisioning:
[every5minutes] Minimum definable time. Sets the
interval at every five minutes.
[every15minutes] Sets the interval at every five
minutes.
[hourly] Hourly - Sets an interval in hours.
[daily] Daily (default) - Sets an hour in the day.
[weekly] Weekly - Sets a day in the week and an
hour in the day.
[powerup] Irrespective of what value is defined, the
phone always checks on powerup, but if powerup is
The interval in hours for automatically checking for
new firmware and configuration files.
The valid range is 1 to 168. The default is 24.
Note: This parameter is applicable only when type is
configured to hourly.
The hour in the day for automatically checking for new
firmware and configuration files.
The format of this value is hh:mm, where hh is hour
and mm is minutes. For example, 00:30.
The default time is 00:00.
Version 2.2.16 47 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 48

400HD Series IP Phones
configured to daily.
Parameter Description
Every (Check Period = Day)
[provisioning/period/weekly/day]
The day in the week for automatically checking for new
firmware and configuration files.
[Sunday] Sunday (default)
[Monday] Monday
[Tuesday] Tuesday
[Wednesday] Wednesday
[Thursday] Thursday
[Friday] Friday
[Saturday] Saturday
Note: This parameter is applicable only when type is
configured to weekly.
Every (Check Period = Weekly)
[provisioning/period/weekly/time]
The hour in the day for automatically checking for new
firmware and configuration files.
The format of this value is: hh:mm, where hh is hour
and mm is minutes. For example: 00:30
The default time is 00:00.
Note: This parameter is applicable only when type is
configured to weekly.
9.2.1 Provisioning using DHCP Option 160
Phones can get a provisioning URL from DHCP Option 160, 66/67 or 43. Option 160 has the
highest priority, following by Option 66/67, and then Option 43. DHCP Option 160 can be
configured using the Web interface.
To configure DHCP Option 160 using the Web interface:
1. Open the Automatic Update page (Management tab > Automatic Update menu >
Automatic Provisioning).
Figure 9-2: Automatic Provisioning - DHCP Option 160
2. From the 'Provisioning Method' dropdown, select DHCP Option (Dynamic URL).
3. In the 'DHCP Option Value' field, enter 160.
4. Configure the remaining parameters, and then click Submit.
5. After reboot, confirm that the firmware and configuration files hav e been updated.
Administrator's Manual 48 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 49

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
9.2.2 Technician's Digit Key Code
Technicians installing phones at customer sites do not need to connect laptops to phones to
provision them. After connecting phones to the network, technicians can enter a specific digit
key code which changes the phones' provisioning URL to the server's URL. If the code that
the technician enters matches, the phones are automatically provisioned from that server.
Note: The feature requires software customization.
Version 2.2.16 49 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 50

400HD Series IP Phones
1
2
3
4
9.2.3 Provisioning using DHCP Option 66/67
Phones can get a provisioning URL from DHCP Option 66/67. Option 160 has the highest
priority, following by Option 66/67, and then Option 43. The table below shows the behaviors
for Option 66/67.
Table 9-2: Auto Provisioning via DHCP Option 66/67
Option 66 Option 67 Result Comment
Doesn’t exist or empty Any No U RL f rom Option 66/67 When Option 66
doesn’t exist, or it’s
empty, the phone
cannot get a URL
from Option 66/67.
Server address exists but there is no
protocol header such as TFTP, FTP,
HTTP, HTTPS.
File names do not exis t.
Example:
Audiocodes.com
192.168.0.11
Server address exists
File names do not exis t.
Example:
http://Audiocodes.c om
http://192.168.0.11
Server address exists.
File names exist.
Example:
http://Audiocodes.c om/abc.image;efg
.cfg
Non-existent Firmware URL:
Tftp://audiocodes.c om/<hardwar e
type>.img
Configuration file url:
Tftp://audiocodes.c om/.<mac>cf g
Contains names.
Example:
abc.img;efg.cfg
Non-existent Firmware URL:
Contains names.
Example:
abc.img;efg.cfg
Any Firmware URL:
Firmware URL:
Tftp://audiocodes.c om/abc.img
Configuration file URL:
Tftp://audiocodes.c om/efg.cfg
http://audioc odes.c om/<hardwar e
type>.img
Configuration file URL:
http://audioc odes.c om/.<mac>cfg
Firmware URL:
http://audioc odes.c om/abc.img
Configuration file URL:
http://audioc odes.c om/efg.cfg
http://audioc odes.c om/abc.img
Configuration file URL:
http://audioc odes.c om/efg.cfg
When protocol is
not specified, tftp is
added as the
def au lt pr ot oc ol.
If any file name
exists in Option 66,
the names in
Option 67 ar e
ignored.
To operate with DHCP Options 66 and 67:
Configure DHCP Options 66 and 67 in the DHCP server, instead of configuring Option
160. See the DHCP server related documentation for detailed information.
9.2.4 Provisioning using DHCP Option 43
Phones can get a provisioning URL from DHCP Option 43. Option 160 has the highest
priority, following by Option 66/67, and then Option 43.
To operate with DHCP Options 43:
Configure DHCP Options 43 in the DHCP server. Use the example in the figure below
as reference.
Administrator's Manual 50 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 51

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
Figure 9-3: Provisioning using DHCP Option 43 in the DHCP Server
Note:
• 01 is the sub option
• 27 is the length (in HEX) of the provisioning path string that you configured
• The remainder is the provisioning path, in ASCII code.
Example: tftp://192.168.202.103/test.img;test.cfg
9.2.5 Provisioning using the User-Class Option
Provision using the User-Class Option if vendor phones other than those of AudioCodes are
deployed in the same enterprise as AudioCodes' phones and a DHCP Option cohabitation
issue consequently occurs.
Here's how to configure provisioning of AudioCodes phones using the User-Class Option
when other vendor phones in the enterprise point to the same DHCP server and use one of
the standard DHCP Options described in the previous sections.
To configure provisioning of AudioCodes phones using the User-Class Option:
1. Determine the DHCP server hosting the phones.
2. Determine if DHCP Options are assigned to IPv4 or IPv6 addresses.
Note:
• The examples below show DHCP server acrtplab-ad.audiocodes.local
• The examples below show IPv4 addresses
Version 2.2.16 51 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 52

400HD Series IP Phones
Figure 9-4: DHCP Options Assigned to IPv4 Addresses
3. Define a separate User Class for each AudioCodes phone model deployed (420HD,
430HD and 440HD phone models): Right-click the IPv4 server icon and from the popup
menu, select Define User Classes…
Figure 9-5: Defining User Classes
The DHCP User Classes screen opens.
Figure 9-6: DHCP User Classes
4. Click the Add… button.
Administrator's Manual 52 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 53

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
Figure 9-7: New Class
5. In the New Class screen, enter Display name and Description as shown in the figure
above, and then in the ASCII field, enter the User Class Phone Type (see the Packet
Bytes window in Wireshark below for an example of the 420HD phone, and see the
table below for the other AudioCodes phone models) to be sent from the phone during
DHCP Discover via Option 77 (supported by DHCP Server 2008). Do this for each
AudioCodes phone model so that a User Class entry for each model deployed will exist
when completed.
Figure 9-8: Packet Bytes Window
6. Make sure one DHCP User Class entry exists for each AudioCodes phone model
deployed in the enterprise.
Version 2.2.16 53 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 54

400HD Series IP Phones
Figure 9-9: DHCP User Classes
Table 9-3: DHCP User Class Entry for Each AudioCodes Phone Model Deployed
Display Name Description ASCII
420HD AudioCodes 420HD IP Phone 420HD
430HD AudioCodes 430HD IP Phone 430HD
440HD AudioCodes 440HD IP Phone 440HD
405 AudioCodes 405 IP Phone 405
7. Configure Scope Option 160. This is not a standard Scope Option, so it needs to be
created. To create it on the server, select the IP version (IPv4) and select Set
Predefined Options…
Figure 9-10: Set Predefined Options
Administrator's Manual 54 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 55

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
8. From the 'Option class' dropdown, select DHCP Standard Options, and then click the
Add… button.
Figure 9-11: Predefined Options and Values
9. Add the AudioCodes 160 Option as shown below, and then click OK.
Figure 9-12: Option Type – Add AudioCodes 160 Option
10. Add the OVOC server location using HTTP. In the figure below, it's http://<OVOC server
IP address>/firmwarefiles;ipp/dhcpoption160.cfg. See the Device Manager Pro
Administrator’s Manual for more information.
Version 2.2.16 55 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 56

400HD Series IP Phones
Figure 9-13: Predefined Options and Values – Add OVOC Server Location
Note: Make sure you defined in the enterprise's DHCP server http://<OVOC server IP
address>/firmwarefiles;ipp/dhcpoption160.cfg for DHCP Option 160.
11. Decide if the DHCP Scope Option needs to be assigned to phones in a specific VLAN
(Scope), or to the entire server (acrtplab-ad.audiocodes.local) for IPv4 addresses.
VLAN Scope
12. Assign to a specific VLAN (Scope of IP addresses such as the Scope below 172.17.0.0,
or to multiple Scopes, to be performed separately on each Scope).
a. If selecting a VLAN, expand the 'Scope Leased' folder, select 'Scope Options', and
then select Configure Options from the popup menu.
Figure 9-14: 'Scope Leased' Folder - Configure Options
Administrator's Manual 56 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 57

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
-OR-
b. Select the collapsed folder 'Scope Leased' and in the main screen, right-click
'Scope Options' and select Configure Options…
Figure 9-15: Configure Options 1
-OR Server Option
13. If assigning to the entire server (acrtplab-ad.audiocodes.local), select the 'Server
Options' folder under server IPv4, right-click 'Server Options' and select Configure
Options...
Figure 9-16: Configure Options 2
Version 2.2.16 57 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 58

400HD Series IP Phones
14. In the Server Options page (or Scope Options page) that opens, select the Advanced
tab, make sure DHCP Standard Options remains selected, and select 420HD User
Class for the first phone model to be defined. Scroll through the Available Options (all
are cleared) and select only 160 AudioCodes 160 Option.
The figure below shows the Server Options page. The Scope Options page is identical.
Note that the String value you defined for Scope Option 160 is automatically
populated so it's unnecessary to change it. Note also that if additional DHCP Options
are required (such as DNS or time server) that are different from the Servers Options for
the rest of the Scopes on the server, they can also be selected, but this is typically
not needed.
Administrator's Manual 58 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 59

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
Figure 9-17: Server Options
15. Click Apply and then follow the same procedure to add the 430HD and 440HD user
classes. After adding them, click the OK button.
You've successfully created three separate Scope Options that will only allow
AudioCodes phones to connect to the Device Manager Pro when they boot up and will
prevent other vendor phones from receiving the OVOC as their provisioning server.
Figure 9-18: Three Scope Options Created
Version 2.2.16 59 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 60

400HD Series IP Phones
9.2.6 SIP SUBSCRIBE and NOTIFY Messages
If the provisioning information (e.g. Option fields 66/67/160) is not provided by the DHCP
server, the phone sends a SIP SUBSCRIBE message to the multicast address
224.0.1.75:5060 as shown below.
Note: If the provisioning server supports using SIP SUBSCRIBE and NOTIFY messages
and the device receives the provisioning URL in the NOTIFY message, the automatic
provisioning mechanism then periodically tries to retrieve a new firmware/configuration
according to the information provided.
SUBSCRIBE sip:224.0.1.75:5060 SIP/2.0
From:
<sip:00000001@10.13.2.37:5060>;tag=87a5a8-25020d0a-13c4-50029-386d
4398-66dc40c-386d4398
To: <sip:224.0.1.75:5060>
Call-ID: 8884c8-25020d0a-13c4-50029-386d4398-3e2bcb8e-386d4398
CSeq: 1 SUBSCRIBE
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP
10.13.2.37:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bK-386d4398-6ad00ca2-7ca3606e
Expires: 0
Event:
ua-profile;profile-type="application";model="440HD";version="2.2.2
"
Max-Forwards: 70
Supported: replaces,100rel
Accept: application/url
Contact: <sip:00000001@10.13.2.37:5060>
User-Agent: AUDC-IPPhone/2.2.2
Content-Length: 0
The provisioning server or any other entity replies with a 200 OK message to the
SUBSCRIBE message (see below) and sends a NOTIFY SIP message with the provisioning
URL in the message body as shown below. (The provisioning URL can be in any format as
described in the Administrator's Manual).
If no response is received by the provisioning server, the phone resends SUBSCRIBE
messages for five seconds.
With the above method, the phone uses its built-in auto-provisioning mechanism while the
provisioning information is retrieved through the NOTIFY message.
The following code describes SIP 200 OK Response on the SUBSCRIBE Message:
SIP/2.0 200 OK
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP
10.13.2.37:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bK-386d4398-6ad00ca2-7ca3606e
Contact: <sip:10.13.2.37:5060>
To: <sip:224.0.1.75:5060>
From:
<sip:00000001@10.13.2.37:5060>;tag=87a5a8-25020d0a-13c4-50029-386d
4398-66dc40c-386d4398
Call-ID: 8884c8-25020d0a-13c4-50029-386d4398-3e2bcb8e-386d4398
CSeq: 1 SUBSCRIBE
Expires: 0
Administrator's Manual 60 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 61

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
Content-Length: 0
The following code describes SIP NOTIFY Message with Provisioning Information.
NOTIFY sip:10.13.2.37:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP
10.13.2.37:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bK-386d4398-6ad00ca2-7ca3606e
Max-Forwards: 20
Contact: <sip:10.13.4.121:5060>
To: <sip:224.0.1.75:5060>
From:
<sip:00000001@10.13.2.37:5060>;tag=87a5a8-25020d0a-13c4-50029-386d
4398-66dc40c-386d4398
Call-ID: 8884c8-25020d0a-13c4-50029-386d4398-3e2bcb8e-386d4398
CSeq: 1 NOTIFY
Content-Type: application/url
Subscription-State: terminated;reason=timeout
Event:
ua-profile;profile-type="application";model="440HD";version="2.2.2
"
Content-Length: 18
tftp://10.13.4.121
The following code describes SIP SUBSCRIBE Message to Obtain Provisioning Information.
SUBSCRIBE sip:224.0.1.75:5060 SIP/2.0
From:
<sip:00000001@10.13.2.37:5060>;tag=87a5a8-25020d0a-13c4-50029-386d
4398-66dc40c-386d4398
To: <sip:224.0.1.75:5060>
Call-ID: 8884c8-25020d0a-13c4-50029-386d4398-3e2bcb8e-386d4398
CSeq: 1 SUBSCRIBE
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP
10.13.2.37:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bK-386d4398-6ad00ca2-7ca3606e
Expires: 0
Event:
ua-profile;profile-type="application";model="440HD";version="2.2.2
"
Max-Forwards: 70
Supported: replaces,100rel
Accept: application/url
Contact: <sip:00000001@10.13.2.37:5060>
User-Agent: AUDC-IPPhone/2.2.2
Content-Length: 0
With the above method, the phone uses its built-in auto-provisioning mechanism while the
provisioning information is retrieved through the NOTIFY message.
Version 2.2.16 61 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 62

400HD Series IP Phones
9.2.7 Hardcoded Domain Name for Provisioning Server
If no higher-priority provisioning method applied, the phone automatically searches in the
DNS server for the domain named "ProvisioningServer". After the DNS server gives the
domain IP address, the phone contacts the provisioning server. The phone tries to retrieve
firmware and configuration files using URL tftp://ProvisioningServer/<Phone Model Name>/
For example:
The phone tries to obtain the following firmware file:
tftp://ProvisioningServer/440HD.img
where 440 is optional; if omitted, the phone will try to retrieve the firmware file
according to its model name.
The phone tries to obtain the following configuration file: tftp://ProvisioningServer/<MAC
address>.cfg
where MAC address is optional; if omitted, the phone will try to retrieve the
configuration file according to its MAC address.
(e.g. tftp://ProvisioningServer/440HD/001122334455.cfg)
The network administrator must configure a DNS entry called "ProvisioningServer" on the
DNS server and set it to the TFTP server IP address.
Note: If Generic Domain Name is used, the automatic provisioning mechanism
periodically tries to retrieve new firmware/configuration from Provisioning Server domain
name.
9.2.8 Cached Address of Last Provisioning Server Used
These are the addresses of the last provisioning servers used, stored in cache memory.
When the device starts up and connects to the provisioning server, it can pull firmware,
configuration and private label files from the provisioning server using the cached address of
the last provisioning server used.
After the phone creates a successful connection with a provisioning server, this server's
address is cached by the phone. The next time the phone is rebooted, if it doesn't receive
provisioning details, the device performs provisioning using the cached IP address.
Administrator's Manual 62 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 63

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
9.2.9 Redirect Server
You can use the AudioCodes Redirect server to direct you to the appropriate Provisioning
server URL to download the relevant configuration and firmware files.
After the phone is powered up and network connectivity is established, it automatically
requests provisioning information. If it doesn't get these files according to the regular
provisioning hunt order methods, it sends an HTTPS request to the AudioCodes HTTPS
Redirect server. The server responds to the phone with an HTTPS Redirect response
containing the URL of the provisioning server where the firmware and configuration files are
located. After the phone successfully connects to the provisioning server URL, the Automatic
Update mechanism commences.
Note:
• The MAC addresses of the phones and the provisioning server's URL are
pre-configured on the HTTPS Redirect server. For more information, contact
AudioCodes support.
• The default URL of the Redirect server is:
provisioning/redirect_server_url=https://redirect.audiocodes.com
This address can be reconfigured if required.
Figure 9-19: Redirect Server Configuration Process
1. Device sends HTTPS request to AudioCodes HTTPS Redirect server.
2. Redirect server sends HTTPS response with redirect URL of the provisioning server.
3. Phone sends request to redirected URL (i.e., provisioning server).
Version 2.2.16 63 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 64

400HD Series IP Phones
For security, communication between the phone and the HTTPS Redirect server is
encrypted (HTTPS) and uses the pre-installed AudioCodes factory-set certificate to
authenticate itself with the HTTPS Redirect server and to verify authenticity of the latter. If the
redirect URL (where the configuration file is stored) also uses the HTTPS protocol, the phone
can use a regular certificate or the AudioCodes factory-set certificate to authenticate itself
and to validate the server’s certificate if a trusted root certificate (regular) is configured.
Note: The phone repeats the redirect process whenever it undergoes a reset to factory
defaults.
9.3 Static URL Provisioning
Here's how to configure the phone using the Static URL method.
To configure static provisioning information using the Web interface:
1. Open the Automatic Provisioning page (Management tab > Automatic Update menu >
Automatic Provisioning).
Figure 9-20: Automatic Provisioning – Static URL
2. Configure the parameters using the table below as reference, and then click Submit.
Administrator's Manual 64 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 65

Administrator's Manual 9. Obtaining Firmware and Configuration Files
To configure static provisioning information using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Table 9-4: Static URL Automatic Provisioning Parameters
Parameter Description
Provisioning Method
[provisioning/method]
Firmware URL
[provisioning/firmware/url]
Configuration URL
[provisioning/configuration/url]
Defines the provisioning method:
[Disable] Disable - Automatic update is disabled. The phone
attempts to upgrade its firmware and configuration
[Dynamic] DHCP Options (Dynamic URL) (default) - Using
DHCP Option 160 and Options 66/67 for provisioning
[Static] Static URL - Using Static URL for provisioning
The static URL for checking the firmware file. The URL must be
entered using one of the following syntax options:
<protocol>://<server IP address or host name>
<protocol>://<server IP address or host name>/<firmware
file name>
Where<protocol> can be one of the following protocols: ftp,
tftp, http or https. For example:
tftp://192.168.2.1 – retrieved firmware file is440HD.img
ftp://192.168.2.1/Different_Firmware_Name.img - retrieved
firmware file is Different_Firmware_Name.img
Note: This parameter is applicable only when 'method' is
configured to Static.
The static URL for checking the configuration file. The URL
must be entered using one of the following syntax options:
<protocol>://<server IP address or host name>
<protocol>://<server IP address or host
name>/<configuration file name>
Where<protocol> can be one of the following protocols: "ftp",
"tftp", "http" or "https". For example:
http://192.168.2.1 - configuration file name is <MAC
Address>.cfg, for example, 001122334455.cfg
https://192.168.2.1/440HD_<MAC>_conf.cfg - retriev ed
configuration file name is 440HD_<MAC
Address>_conf.cfg, for example,
440HD_001122334455_conf.cfg
Note: This parameter is applicable only when 'method' is
configured to Static.
Version 2.2.16 65 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 66

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 66 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 67

Part III
Quick Setup
Page 68

Page 69

Administrator's Manual 10. Quick Setup
10 Quick Setup
The Web interface provides a Quick Setup page that lets you configure basic features to
quickly set up your phone to operational level.
Note: For Quick Setup parameters descriptions, see Part IV (Networking) and Part V
(VoIP Features).
To quickly set up your phone:
1. Open the Quick Setup page (Configuration tab >Quick Setup menu >Quick Setup).
Figure 10-1: Quick Setup
2. For descriptions of parameters on this page:
• See Section 13.1.2 for descriptions of parameters under the LAN Setup group
• See Section 16.2 for descriptions of parameters under the SIP Proxy and Registrar
group
• See Section 21 for descriptions of parameters under the Line Settings group
Version 2.2.16 69 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 70

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 70 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 71

Part IV
Networking
Page 72

Page 73

Administrator's Manual 11. Introduction
11 Introduction
Here's how to configure network settings manually, if required.
Note: By def ault, the network settings are set for automatic provisioning. However, if you
need to change them, you can do so manually, as described in this section.
Version 2.2.16 73 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 74

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 74 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 75

Administrator's Manual 12. Configuring Date and Time Manually
12 Configuring Date and Time Manually
Note: By default, date and time settings are automatically provisioned via the enterprise
DHCP server when the phone is connected to the Internet and to the power supply, but
you can manually change them if required. This section shows how.
The phone automatically retrieves date and time from a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server
when connected to the internet. To configure the NTP server for automatic provisioning of
date and time, see Section 12.2. NTP is a protocol for distributing Coordinated Universal
Time (UTC) by synchronizing the clocks of computer systems over packet-switched,
variable-latency data networks. Date/time can also be manually configured in the Web
interface.
To manually configure date and time using the Web interface:
1. Open the Date and Time page (Configuration tab > Advanced Applications menu > Date
and Time).
Figure 12-1: Date and Time
2. Configure the 'Set System Time' parameter.
3. Set the 'Time Display Format' to 24 Hours or 12 Hours
4. Set the 'Date Display Format' to European or American. See the table below.
5. Click Submit.
To configure date and time using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Parameter Description
Date Display Format
[system/ntp/date_display_format]
Table 12-1: Date Display Format
Select either:
EUROPEAN (default)
AMERICAN
The European date format is DDMMYYYY.
The American format is MMDDYYYY.
Version 2.2.16 75 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 76

400HD Series IP Phones
[ENABLE] Enable
12.1 Configuring Daylight Saving Time
You can configure Daylight Saving Time using the Web interface or configuration file.
To configure Daylight Saving Time using the Web interface:
1. Open the Date and Time page (Configuration tab > Advanced Applications menu > Date
and Time) as described above.
2. Set the 'Active' parameter to Enable; the page shown below opens.
Figure 12-2: NTP & Time Settings
3. Set the 'Obtain Time Zone from DHCP' parameter to Disable; the Daylight Saving Time
page shown below opens:
Figure 12-3: Daylight Saving Time
4. Configure the settings using the table below as reference.
To configure Daylight Saving Time using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Table 12-2: Daylight Saving Time Parameters
Parameter Description
Active
[system/daylight_saving/activate]
Administrator's Manual 76 Document #: LTRT-11974
Determines whether the phone automatically
detects the Daylight Saving Time for the selected
Time Zone.
[DISABLE] Disable (default)
Page 77

Administrator's Manual 12. Configuring Date and Time Manually
Parameter Description
Start Time
[system/daylight_saving/start_date]
Start Time
[system/daylight_saving/start_date/month]
Start Time
[system/daylight_saving/start_date/day]
Start Time
[system/daylight_saving/start_date/hour]
Start Time
[system/daylight_saving/start_date/minute]
This subsection defines the starting day for the
daylight saving offset.
[month] - defines specific month in year
[day] - defines specific day in month
[hour] - defines specific hour in day
[minute] - defines specific minute in hour
Example: To configure the phone to start daylight
savings with a specific offset on February 22nd at
14:30, set the following:
system/daylight_saving/start_date/month=2
system/daylight_saving/start_date/day=22
system/daylight_saving/start_date/hour=14
system/daylight_saving/start_date/minute=30
The month in a year.
The valid range is 1 to 12.
The day in a month.
The valid range is 1 to 31.
The hour in the day.
The valid range is 0 to 23.
The minute in an hour.
The valid range is 0 to 59.
End Time
[system/daylight_saving/end_date]
End Time
[system/daylight_saving/end_date/month]
End Time
[system/daylight_saving/end_date/day]
End Time
[system/daylight_saving/end_date/hour]
This subsection defines the ending day for the
daylight saving offset.
[month] - defines the specific month in a year
[day] - defines the specific day in a month
[hour] - defines the specific hour in a day
[minute] - defines the specific minute in an
hour
For example: To configure the phone to end the
daylight savings on July 16th at 22:15, set the
following:
system/ntp/daylight_saving/end_date/month=7
system/ntp/daylight_saving/end_date/day=16
system/ntp/daylight_saving/end_date/hour=22
system/ntp/daylight_saving/end_date/minute=15
The month in a year.
The valid range is 1 to 12.
The day in a month.
The valid range is 1 to 31.
The hour in the day
The valid range is 0 to 23.
End Time
[system/daylight_saving/end_date/minute]
The minute in an hour.
The valid range is 0 to 59.
Version 2.2.16 77 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 78

400HD Series IP Phones
Parameter Description
Offset
[system/daylight_saving/offset]
[system/daylight_saving/mode] Configures the daylight saving mode.
[system/daylight_saving/start_date/week] Relevant to 'Day of week' mode:
[system/daylight_saving/start_date/day_of_wee
k]
The offset value for the daylight saving.
The valid range is 0 to 180. The default offset is
60.
Valid values are
[FIXED]= Date is specified as: Month, Day of
month.
[DayOfWeek]= Date is specified as: Month,
Week of month, Day of week.
The week of month (values 1-5) for start of
daylight saving time.
Relevant to 'Day of week' mode:
The day of week for daylight saving time start
Valid values :
[SUNDAY]
[MONDAY]
[TUESDAY]
[WEDNESDAY]
[THURSDAY]
[FRIDAY]
[SATURDAY]
[system/daylight_saving/end_date/week] Relevant to 'Day of week' mode:
The week of month (values 1-5) for end of
daylight saving time.
[system/daylight_saving/end_date/day_of_wee
k]
Relevant to 'Day of week' mode:
The day of week for daylight saving time start
Valid values :
[SUNDAY]
[MONDAY]
[TUESDAY]
[WEDNESDAY]
[THURSDAY]
[FRIDAY]
[SATURDAY]
Administrator's Manual 78 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 79

Administrator's Manual 12. Configuring Date and Time Manually
12.2 Configuring the NTP Server
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) server can be configured using the Web interface or
configuration file. When activated, date and time are automatically obtained from the NTP
server.
To configure the NTP server using the Web interface:
1. Open the Date and Time page (Configuration tab > Advanced Applications menu > Date
and Time).
2. Configure the parameters using the table below as reference, and then click Submit.
Figure 12-4: NTP & Time Settings
To configure the NTP server using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Table 12-3: NTP Server Parameters
Parameter Description
Active
[system/ntp/enabled]
Primary Server
[system/ntp/primary_server_address]
Secondary Server
[system/ntp/secondary_server_address]
Update Interval
[system/ntp/sync_time]
Enables the NTP server from which the phone
automatically retrieves the date and time.
[0] Disable
[1] Enable – obtains the time information
automatically from a configured NTP server
(default)
Defines the address of the main NTP server (this can
be a domain name, for example, tick.nap.com.ar).
Defines the address of the secondary NTP server.
This sub-section defines how often the phone must
perform an update with the NTP server.
[days] -defines the number of days
[hours] - defines the number of hours
For example: To configure the phone to perform an
update with an NTP server every 1 day and 6 hours,
set the following:
system/ntp/sync_time/days=1
system/ntp/sync_time/hours=6
Version 2.2.16 79 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 80

400HD Series IP Phones
Parameter Description
Update Interval
[system/ntp/sync_time/days]
Update Interval
[system/ntp/sync_time/hours]
Time Display Format
[system/ntp/time_display_format]
The number of days.
The valid range is 0 to 7. The default of days is 0.
The number of hours.
The valid range is 0 to 24. The default is 12.
The format of the time displayed on the phone
screen.
[24Hour] (default)
[12Hour]
Administrator's Manual 80 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 81

Administrator's Manual 12. Configuring Date and Time Manually
12.3 Configuring NTP Server via DHCP
If the phone is set to obtain GMT offsets and NTP servers via DHCP (default), it receives the
following fields in the DHCP options:
Primary Server and Secondary Server – (Option 4 or 42).
Note: If both options (4 and 42) are received, priority is given to Option 42.
Time Zone – (Option 2)
The phone sends an NTP request to the Primary NTP server. If there is no response, the
NTP request is sent to the Secondary NTP server.
After obtaining the time from the server, it adds the GMT offset in Option 2. This is the
updated system time.
To manually configure NTP / GMT offset via DHCP using Web interface:
1. Open the Date and Time page (Configuration tab > Advanced Applications menu > Date
and Time).
2. From the 'Obtain Time Zone From DHCP' drop-down list, select Disable.
Figure 12-5: NTP and Time Settings
3. Configure the NTP and Time Settings according to the parameters in the table below,
and then click Submit.
Note: These values will have no affect if TimeZone is set to be obtained from DHCP. If
Time Zone and NTP server are manually set, the phone acts as described above but the
values are obtained from the configuration file and not from DHCP.
Version 2.2.16 81 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 82

400HD Series IP Phones
Table 12-4: NTP Server and GMT Parameters
Parameter Description
[system/ntp/gmt_offset] Default: 00:00
Enables the NTP server from which the phone
retrieves the date and time.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable – obtains the time information from
a configured NTP server
Administrator's Manual 82 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 83

Administrator's Manual 13. Configuring IP Network Settings
13 Configuring IP Network Settings
The following section shows how to configure IP Network Settings including:
Static IP Address
Partial DHCP
13.1 Configuring Static IP Address
The static IP address can be configured using the following:
Phone screen
Web interface and configuration file
13.1.1 Configuring Static IP Address on the Phone
Here's how to configure Static IP Address on the phone on the phone. The LAN connection
interface can be manually defined (static IP address) or automatically provisioned using a
DHCP server from where the LAN IP address is obtained.
To configure the phone's LAN connection type:
1. Access and select the LAN Connection Type option (MENU key > Administration >
Network Settings).
2. Navigate to and select Static IP or Automatic IP (DHCP) IP addressing scheme.
3. If you select Static IP, continue with the next step (Step 4); else skip to Step 5.
4. Define a static IP addressing scheme:
c. Press the Edit softkey; the Static IP screen appears:
d. To configure each required network parameter, i.e., IP Address, Netmask,
Gateway, Primary DNS and Secondary DNS, navigate to and choose the
parameter, and then press the Edit softkey, for example, navigate to IP Address
and press the Edit softkey:
e. Enter the new address in dotted-decimal notation, using the following keys:
♦ Navigation control: moves the cursor left or right in the IP address
Version 2.2.16 83 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 84

400HD Series IP Phones
♦ Clear softkey: deletes the digit to the left of the cursor.
f. Press the Save and then Apply softkey.
5. Press the Save softkey.
13.1.2 Configuring IP Network Settings
Here's how to configure IP Network settings using the Web interface or configuration file.
The phone's LAN configuration includes defining the method for obtaining an IP address.
The phone's IP address can be static whereby the IP address is manually entered, or
automatic whereby the IP address is acquired from a DHCP server. For Automatic IP, you
can manually define some of the main parameters.
To define the phone's LAN settings using the Web interface:
1. Open the LAN Settings page (Configuration tab > Network Connections menu >
Network Settings).
Figure 13-1: Network Settings
2. Configure the LAN parameters using the table below as reference, and then click
Submit.
Administrator's Manual 84 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 85

Administrator's Manual 13. Configuring IP Network Settings
To define the phone's LAN settings using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Table 13-1: Network Settings Parameters
Parameter Description
IP Type
[network/lan_type]
network/lan/fixed_ip
IP Address
[network/lan/fixed_ip/ip_address]
Subnet Mask
[network/lan/fixed_ip/netmask]
Default Gateway Address
[network/lan/fixed_ip/gateway]
Domain Name
[network/lan/fixed_ip/domain_name]
Domain Name Server (DNS)
Primary DNS
[network/lan/fixed_ip/primary_dns]
Defines the IP addressing method:
[STATIC] Static IP (default)- Phone's IP address is
defined manually
[DHCP] Automatic IP DHCP - Phone's IP address is
acquired automatically from a DHCP server
This subsection defines the relevant parameters if
'lan_type' is configured to STATIC or the
corresponding 'network/lan/dhcp' parameter is set to 1.
The LAN IP address.
The subnet mask address.
The IP address of the default gateway.
The domain name.
The primary DNS server address.
Secondary DNS
[network/lan/fixed_ip/secondary_dns]
The secondary DNS server address. The phone
connects to this server if the primary DNS server is
unavailable.
Version 2.2.16 85 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 86

400HD Series IP Phones
13.2 Configuring Partial DHCP
Partial DHCP can be configured with the following parameters:
Table 13-2: Partial DHCP Parameters
Parameter Description
Partial DHCP
network/lan/dhcp
This subsection defines the parameters to
configure if 'lan_type' is configured to DHCP.
Domain Name - Manual
[network/lan/dhcp/domain_name/enabled]
Enables setting the domain name manually.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Note: If enabled,
network/lan/fixed_ip/domain_name must be set.
IP Address - Manual
[network/lan/dhcp/ip_address/enabled]
Enables setting the IP address manually.
[0] Disable
[1] Enable (default)
Note: If enabled, network/lan/fixed_ip/ip_address
must be set.
Subnet Mask - Manual
[network/lan/dhcp/netmask/enabled]
Enables setting the network mask manually.
[0] Disable
[1] Enable (default)
Note: If enabled, network/lan/fixed_ip/netmask
must be set.
[network/lan/dhcp/gateway/enabled] Enables setting the default gateway manually.
[0] Disable
[1] Enable (default)
Note: If enabled, network/lan/fixed_ip/gateway
must be set.
Primary DNS - Manual
[network/lan/dhcp/primary_dns/enabled]
Enables setting the primary DNS manually.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Note: If enabled, network/lan/fixed_ip/primary_dns
must be set.
Secondary DNS - Manual
network/lan/dhcp/secondary_dns/enabled
Enables setting the secondary DNS manually.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Note:If enabled,
network/lan/fixed_ip/secondary_dns must be set.
Administrator's Manual 86 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 87

Administrator's Manual 13. Configuring IP Network Settings
Parameter Description
DHCP-Related Parameters
network/lan/dhcp/ntp/server_list/enabled
network/lan/dhcp/ntp/gmt_offset/enabled
Enables prioritization of the NTP server's
information received from the DHCP server
(Option fields 42 or 4), over the static configuration
(system/ntp/primary_server_address and
system/ntp/secondary_server_address).
[0] Disable
[1] Enable (default)
Enables prioritization of the NTP GMT offset
information received from the DHCP server
(Option field 2), over the static configuration
(system/ntp/gmt_offset).
[0] Disable
[1] Enable (default)
Version 2.2.16 87 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 88

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 88 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 89

Administrator's Manual 14. Configuring LAN and PC Port Settings
14 Configuring LAN and PC Port Settings
Port settings can be configured using the Web interface or configuration file.
Note: The optional values of the configuration file parameters are enclosed in square
brackets while its corresponding Web values are written outside the square brackets, for
example, [1] Enable.
To configure the phone's port settings using the Web interface:
1. Open the Network Settings page (Configuration tab > Network Connections menu >
Network Settings).
Figure 14-1: Network Settings - Port Mode
2. Configure the parameters using the table below as reference, and then click Submit.
To define the phone's port settings using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Parameter Description
LAN Port Mode
[network/lan/port_mode]
PC Port Mode
[network/pc/port_mode]
Table 14-1: Port Settings
Sets the LAN port mode.
Valid values are:
[AUTOMATIC] = Auto negotiation.
[FULL_10] = 10Mbps + full duplex
[FULL_100] = 100Mbps + half duplex
[HALF_10] = 10Mbps + full duplex
[HALF_100] = 100Mbps + half duplex
[FULL _ 1Gbps] = 1 Gbit/s port + full duplex
Sets the computer port mode.
Valid values are:
[AUTOMATIC] = Auto negotiation
[FULL_10] = 10Mbps + full duplex
[FULL_100] = 100Mbps + half duplex
[HALF_10] = 10Mbps + full duplex
[HALF_100] = 100Mbps + half duplex
[DISABLE] = Disables the PC port mode
Version 2.2.16 89 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 90

400HD Series IP Phones
This page is intentionally left blank.
Administrator's Manual 90 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 91

Administrator's Manual 15. Configuring VLAN Settings
15 Configuring VLAN Settings
You can configure VLAN settings using the Web interface or configuration file.
To configure the phone's VLAN settings using the Web interface:
1. In the Web interface access the Network Settings page (Configuration tab > Network
Connections menu > Network Settings).
Figure 15-1: Network Settings - VLAN Settings
2. Configure the settings using the table below as reference, and then click Submit.
To configure the phone's VLAN settings using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Parameter Description
VLAN Discovery Mode
[network/lan/vlan/mode]
Table 15-1: VLAN Settings
Determines how VLAN is assigned to your phone, i.e., manually or
automatically, and if automatically, according to which protocol.
Disable [Disable]
Manual Configuration of VLAN [Manual] - If selected, the screen
extends to also display 'VLAN ID' and 'VLAN Priority' (see these
settings below) for static configuration of VLAN ID and priority. See
Section 15.1 below for a detailed explanation.
Automatic Configuration of VLAN (CDP) [CDP] - VLAN discovery
mechanism based on Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP). See
Section 15.1 below for a detailed explanation.
Automatic Configuration of VLAN (LLDP) [LLDP] - VLAN discovery
mechanism based on LLDP. See Section 15.1 below for a detailed
explanation.
Automatic Configuration of VLAN (CDP+LLDP) [CDP_LLDP]
(default) - VLAN discovery mechanism based on LLDP and CDP.
LLDP is higher priority. See below for a detailed explanation.
Period
[network/lan/vlan/period]
Version 2.2.16 91 400HD Series IP Phones
The time period, in seconds, between discovery messages when
configured to CDP, LLDP or CDP+LLDP. The default value is 30.
Page 92

400HD Series IP Phones
Parameter Description
VLAN ID
[network/lan/vlan/id]
VLAN Priority
[network/lan/vlan/priority]
PC Port VLAN Activate
[network/lan/vlan/pc_port_
tagging/enable]
The VLAN ID. The valid range is 0 to 4094. The default is 0.
The priority of traffic pertaining to this VLAN. The valid range is 0 to 7
(where 7 is the highest priority). The default is 0.
Default = Disable [0]. Change to Enable (1) for the traffic from the PC
to the network to be VLAN-tagged.
15.1 Configuring Manual or Automatic VLAN Assignment
You can configure the VLAN to be assigned manually or automatically to your phone. This
section shows when to configure what, and why.
15.1.1 Configuring Manual VLAN Assignment to the Phone
Configure manual assignment of the VLAN in order to set up two separate VLANs in your
enterprise, one for voice (your phone) and the other for data (your pc). Security
considerations may require this. If you configure manual assignment, the switch in your
enterprise will assign the VLAN to your phone. See Sections 13.1.1 and 13.1.2 for details.
15.1.2 Configuring Automatic VLAN Assignment to the Phone
Configure automatic assignment of VLAN if you do not need to separate voice from data, i.e.,
if there are no security considerations requiring it. In this case, configure either:
Automatic Configuration of VLAN (CDP) [CDP]
Automatic Configuration of VLAN (LLDP) [LLDP] -OR-
Automatic Configuration of VLAN (CDP+LLDP) [CDP_LLDP]
What you select depends on whether the switch deployed in your enterprise supports
Cisco-proprietary Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), or LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol)
which is a vendor-neutral protocol used by devices in an IEEE 802 LAN to advertise their
identity, capabilities, and neighbors. Not all switches support CDP. If You're unsure, select
CDP+LLDP. LLDP includes enhanced LLDP for Media Endpoint Devices, i.e., LLDP-MED,
to specifically address voice applications.
15.1.3 Configuring VLAN via DHCP Provisioning Path
VLAN can be configured using (1) Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) (2) Cisco Discovery
Protocol (CDP) and (3) manually.
If (1) is unsuccessful, (2) is attempted.
If (2) is unsuccessful, (3) is attempted.
If (3) is unsuccessful, (4) is attempted.
The capability provides an alternative VLAN configuration option. vi93303
Administrator's Manual 92 Document #: LTRT-11974
Page 93

Part V
VoIP Settings
B
Page 94

Page 95

Administrator's Manual 16. Configuring SIP Settings
16 Configuring SIP Settings
You can configure the following SIP settings using the Web interface or configuration file:
General
Proxy and Registration
SIP Timers
SIP QoS
16.1 Configuring General SIP Settings
The phone's General SIP settings can be configured using the Web interface or configuration
file.
To configure general SIP settings using the Web interface:
1. Open the Signaling Protocols page (Configuration tab > Voice Over IP menu >
Signaling Protocols).
Figure 16-1: Signaling Protocols- SIP General
2. Configure the SIP General parameters using Table 16-1 below as reference, and then
click Submit.
Version 2.2.16 95 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 96

400HD Series IP Phones
Indicates the maximum time (in
terminated.
To configure General SIP parameters using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Table 16-1: SIP General Parameters
Parameter Description
SIP Transport Protocol
[voip/signalling/sip/transport_protocol]
TLS Port
[voip/signalling/sip/tls_port]
[voip/signalling/sip/enable_sips]
[voip/signalling/sip/subs_no_notify_timer]
SIP Local Port
[voip/signalling/sip/port]
Determines the transport layer for
outgoing SIP calls initiated by the
phone.
[UDP] UDP (default)
[TCP] TCP
[TLS] TLS
Defines the local TLS SIP port for SIP
messages.
The valid range is 1024 to 65535.
The default value is 5061.
Relevant for TLS only, if enabled, the
request URI prefix will be “sips:”
otherwise, the prefix will be “sip:”
milliseconds) that a subscription waits
from receiving 2xx response for a
SUBSCRIBE request, until receiving
the first NOTIFY request. If the timer
expires, the subscription will be
Defines the local SIP port (UDP or
TCP) for SIP messages.
The valid range is 1024 to 65535.
The default value is 5060.
Gateway Name
[voip/signalling/sip/proxy_gateway]
PRACK Mode
[voip/signalling/sip/prack/enabled]
Enable RPORT
[voip/signalling/sip/rport/enabled]
Administrator's Manual 96 Document #: LTRT-11974
Assigns a name to the phone. The
name is used as the host part of the
SIP URI in the From header.
Note:
Ensure that the name you choose
is the one with which the Proxy is
configured to identify the phone.
If not specified, the phone's IP
address is used (default).
Determines whether the phone
sends PRACK (Provisional
Acknowledgment) messages upon
receipt of 1xx SIP reliable responses.
[0] Disable
[1] Enable (default)
Determines whether the phone adds
the 'rport' parameter to the relevant
SIP message (in the SIP Via header).
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Page 97

Administrator's Manual 16. Configuring SIP Settings
Parameter Description
Include PTIME in SDP
[voip/signalling/sip/sdp_include_ptime]
Enable Keep Alive using OPTIONS
[voip/signalling/sip/keepalive_options/enabled]
Keep Alive Period
[voip/signalling/sip/keepalive_options/timeout]
Connect Media on 180 Response
[voip/signalling/sip/connect_media_on_180]
Determines whether the phone adds
the PTIME parameter to the SDP
message body.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Determines whether keep-alive is
performed using SIP OPTIONS
messages sent to the Proxy.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Defines the Proxy keep-alive time
interval (in seconds) between
Keep-Alive messages.
The valid range is 0 to 86400. The
default value is 300.
Determines whether the media is
connected upon receipt of SIP 180,
183, or 200 messages. When the
parameter is disabled, media is
connected upon receipt of 183 and
200 messages only.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Block Caller ID on Outgoing Calls
[voip/signalling/sip/block_callerid_on_outgoing_calls]
Can be configured only if the
BroadSoft BroadWorks application
server is used.
When enabled, the outgoing INVITE
message is sent with an anonymous
From header and
P-Asserted-Identityheader.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
For example:
FROMheader contains
anonymous URI:
From: "Anonymous"
sip:anonymous@anonymous.inv
alid
P-Asserted-Identityheader:
P-Asserted-Identity: "1001"
1115551001@proxy.net
Version 2.2.16 97 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 98

400HD Series IP Phones
compatibility (disabled by default)
Parameter Description
Incoming Anonymous Call Blocking
[voip/signalling/sip/anonymous_calls_blocking]
[voip/signalling/sip/auth_retries]
[voip/signalling/sip/display_name_in_registration_msg/ena
bled]
[voip/signalling/sip/semi_transfer_with_no_cancel/enabled]
Can be configured only if the
BroadSoft BroadWorks application
server is used.
When enabled, incoming INVITE
messages with anonymous From
header are rejected.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
For example:
From:"Anonymous"<sip:anonymous
@anonymous.invalid>
The phone responds with a SIP 403
"Forbidden" response.
Defines the number of times
authenticated register messages are
re-sent if 401 or 407 SIP responses
with a different "nonce" are received.
The valid range is 0 to 100. The
default value is 4.
Sets the Display Name in the 'To' and
'From' fields of the SIP REGISTER
message.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Determines whether semi-attendant
transfer is performed without sending
the SIP CANCEL message to the
remote side.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Note:
In this flow ("with_no_cancel"),
the Transferor's User Agent
continues the transfer as an
attended transfer even after the
Transferor hangs up. This is the
recommended flow defined by
http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-s
ipping-cc-transfer-03.
Existing / current behavior is
retained for backward
[voip/signalling/sip/PAI_On_Replay/enable]
Administrator's Manual 98 Document #: LTRT-11974
Enables the P-Asserted Identity
header to be added to “18x” and
“200” responses.
[0] (Default) PAI header is not
added to “18x” and “200”
responses
[1] PAI header is added to “18x”
and “200” responses
Page 99

Administrator's Manual 16. Configuring SIP Settings
16.2 Configuring Proxy and Registration
Here's how to configure Proxy and Registration settings using the Web interface or
configuration file.
To configure Proxy and Registration using the Web interface:
1. Open the Signaling Protocol page (Configuration tab > Voice Over IP menu > Signaling
Protocols).
Figure 16-2: SIP Proxy and Registrar
2. Configure Proxy and Registration parameters using the table below as reference, and
then click Submit.
To configure Proxy and Registration using the configuration file:
• Use the table below as reference.
Table 16-2: Proxy and Registrar Parameters
Parameter Description
Use SIP Proxy
[voip/signalling/sip/use_proxy]
[voip/signalling/sip/proxy_address]
Proxy Port
[voip/signalling/sip/proxy_port]
Determines whether to use a SIP Proxy
server.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
The IP address or host name of the SIP proxy
server. Default: 0.0.0.0
The UDP or TCP port of the SIP proxy server.
Range: 1024 to 65535. Default: 5060.
Version 2.2.16 99 400HD Series IP Phones
Page 100

400HD Series IP Phones
Parameter Description
Enable Registrar Keep Alive
[voip/signalling/sip/registrar_ka/enabled]
Registrar Keep Alive Period
[voip/signalling/sip/registrar_ka/timeout]
Maximum Number of Authentication Retries
[voip/signalling/sip/proxy_timeout]
Use SIP Proxy IP and Port for Registration
[voip/signalling/sip/use_proxy_ip_port_for_registra
r]
Determines whether to use the registration
keep-alive mechanism based on SIP OPTION
messages.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Note:
If there is no response from the server, the
timeout for re-registering is automatically
reduced to a user-defined value
(voip/signalling/sip/registration_failed_time
out)
When the phone re-registers, the
keep-alive messages are re-sent
periodically.
Defines the registration keep-alive time
interval (in seconds) between Keep-Alive
messages.
Range: 40 to 65536. Default: 60.
The SIP proxy server registration timeout (in
seconds).
Range: 0 to 86400. Default: 3600.
Determines whether to use the SIP proxy's IP
address and port for registration. When
enabled, there is no need to configure the
address of the registrar separately.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Use SIP Registrar
[voip/signalling/sip/sip_registrar/enabled]
Registrar IP Address or Host Name
[voip/signalling/sip/sip_registrar/addr]
Registrar Port
[voip/signalling/sip/sip_registrar/port]
Registration Failed Expires
[voip/signalling/sip/registration_failed_timeout]
Use SIP Outbound Proxy
[voip/signalling/sip/sip_outbound_proxy/enabled]
Determines whether the phone registers to a
separate SIP Registrar server.
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
[Only displayed if the 'Use SIP Registrar'
parameter is enabled.]
The IP address or host name of the Registrar
server. Default: 0.0.0.0
[Only displayed if the 'Use SIP Registrar'
parameter is enabled.] The UDP or TCP port
of the Registrar server.
Range: 1024 to 65535. Default: 5060.
If registration fails, this parameter determines
the interval between the register messages
periodically sent until successful registration.
Range: 1 to 86400. Default: 300.
Determines whether an outbound SIP proxy
server is used (all SIP messages are sent to
this server as the first hop).
[0] Disable (default)
[1] Enable
Administrator's Manual 100 Document #: LTRT-11974
 Loading...
Loading...