Page 1
555-230-704
Issue 4
September, 1995
Table of
Contents
DEFINITY
Communications System Generic 3
Basic Call Management System
Operations
Graphics © AT&T 1988
Page 2
Contents
Table of Contents i
1 Introduction 1-1
■ Overview 1-1
■ Organization 1-1
■ Conventions Used in This Document 1-2
2 BCMS Description and Applications 2-1
■ Overview 2-1
■ BCMS Reports 2-1
Feature Capac ity Limits (Maxim ums) 2-3
Hardware Configuration 2-4
■ BCMS Applications 2-6
Interactions With External CMS 2-7
Interactions with VuStats 2-8
3 System Access 3-1
■ Logging In and Log ging Off 3-1
BCMS Login 3-2
Logging In 3-2
Logging In from a Local Terminal 3-2
Logging In from a Remote Terminal 3-3
Logging Off 3-4
■ How to Change the BCMS Password 3-5
Issue 4 September 1995 iii
Page 3

Contents
4 BCMS Report Generation 4-1
■ Overview 4-1
Acceptable Service Level 4-1
Percent within Service Level 4-1
Acceptable Service Level Administration 4-2
BCMS Commands 4-3
Online Help 4-5
■ Real-Time Reports 4-5
Monitor Command 4-6
■ BCMS Split Status Report 4-6
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-7
Displaying the BCMS Sp lit Status Report 4-10
Printing the BCMS Split Status Report 4-10
■ BCMS System Status Report 4-10
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-11
Displaying the BCMS System Status Report 4-14
Printing the BCMS System Status Report 4-14
■ BCMS VDN Status Report 4-14
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-15
Displaying the BCMS VDN Status Repo r t 4-17
Printing the BCMS VD N Status Report 4-17
■ Historical Reports 4-18
List Commands 4-18
■ BCMS Agent Report 4-19
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-21
Displaying the BCMS Agent R eport 4-23
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report 4-23
Displaying a Daily Report 4-23
Printing the BCMS Agent Report 4-24
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report 4-24
Printing a Daily Report 4-24
iv Issue 4 September 1995
Page 4

Contents
Scheduling the BCMS Agent Report to Print 4-25
Schedu lin g a n Hourly/ Hal f-Hourly
Interval Report to Print 4-25
Schedu li n g a Daily Report to Print 4-26
■ BCMS Agent Summary Report 4-28
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-29
Displaying the BCMS Agent S ummary Report 4-31
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report 4-31
Displaying a Daily Report 4-32
Printing the BCMS Agent Summary Report 4-32
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report 4-32
Printing a Daily Report 4-33
Scheduling the BCMS Agent Summary
Report to Print 4-33
Schedu lin g a n Hourly/ Hal f-Hourly
Interval Report to Print 4-33
Schedu li n g a Daily Report to Print 4-35
■ BCMS Spl it Report 4-37
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-39
Displaying the BCMS Split Report 4-43
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report 4-43
Displaying a Daily Report 4-44
Printing the BCMS Split Repo rt 4-44
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report 4-44
Printing a Daily Report 4-45
Scheduling the BCMS Split Repo rt to Print 4-45
Schedu lin g a n Hourly/ Hal f-Hourly
Interval Report to Print 4-45
Schedu li n g a Daily Report to Print 4-47
■ BCMS Spl it Summary Report 4-49
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-51
Displaying the BCMS Split Summary Report 4-55
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report 4-55
Issue 4 September 1995 v
Page 5

Contents
Displaying a Daily Report 4-56
Printing the BCMS Split Summary Report 4-56
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report 4-56
Printing a Daily Report 4-57
Scheduling the BCMS Split Summary
Report to Print 4-57
Schedu lin g a n Hourly/ Hal f-Hourly
Interval Report to Print 4-57
Scheduling a Daily Report to Print 4-59
■ BCMS Trunk Group Report 4-60
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-62
Displaying the BCMS Trunk Group Report 4-64
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report 4-64
Displaying a Daily Report 4-65
Printing the BCMS Trunk Group Report 4-65
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report 4-65
Printing a Daily Report 4-66
Scheduling the BCMS Trunk Group
Report to Print 4-66
Schedu lin g a n Hourly/ Hal f-Hourly
Interval Report to Print 4-66
Scheduling a Daily Report to Print 4-68
■ BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report 4-70
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-71
Displaying the BCMS Trunk Group
S umm ar y Report 4-73
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report 4-74
Displaying a Daily Report 4-74
Printing the BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report 4-75
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report 4-75
Printing a Daily Report 4-75
Scheduling the BCMS Trunk Group
Sum mar y Report to Print 4-76
Schedu lin g a n Hourly/ Hal f-Hourly
Interval Report to Print 4-76
Scheduling a Daily Report to Print 4-77
vi Issue 4 September 1995
Page 6

Contents
■ BCMS VDN Report 4-79
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-80
Displaying the BCMS VDN Report 4-83
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report 4-83
Displaying a Daily Report 4-83
Printing the BCMS VDN Report 4-84
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report 4-84
Printing a Daily Report 4-84
Scheduling the BCMS VDN Report to Print 4-85
Schedu lin g a n Hourly/ Hal f-Hourly
Interval Report to Print 4-85
Schedu li n g a Daily Report to Print 4-86
■ BCMS VDN Summary Report 4-88
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions 4-89
Displaying the BCMS VDN Summary Report 4-91
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report 4-91
Displaying a Daily Report 4-92
Printing the BCMS VD N Summary Report 4-92
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report 4-92
Printing a Daily Report 4-93
Scheduling the BCMS VDN Summary
Report to Print 4-93
Schedu lin g a n Hourly/ Hal f-Hourly
Interval Report to Print 4-93
Schedu li n g a Daily Report to Print 4-95
5 System Printer and Report Scheduler 5-1
■ System Printer 5-1
G3i System Printer Administration 5-1
G3r System Printer Administration 5-3
System Printer Data Link Operation
and Ma in tena nce 5-5
Issue 4 September 1995 vii
Page 7
Contents
■ Report Scheduler 5-6
Print Intervals 5-6
Adding a Report to the Report Scheduler 5-6
Summary of the Steps for Printing Reports
on the System Printer 5-9
Listing Scheduled Reports 5-10
Change Command 5-11
Remove Command 5-13
6 Use of BCMS Reports for ACD Planning 6-1
■ Planning/Engineering Object ives 6-1
BCMS System Status Report 6-2
BCMS Split Status Report 6-3
BCMS VDN Status Report 6-3
BCMS Trunk Group Report 6-4
BCMS Agent Report 6-4
BCMS Split or Skill Report 6-5
BCMS VDN Report 6-5
■ Engineering ACD Applications with
Data Obtained from the BCMS Reports 6-5
Agent Engineering/O ptimiz i ng Guidelines 6-6
Trunk Engineering Guidelines 6-34
A Error Messages A-1
B Data Module and Printer Options B-1
■ 7400A Data Module Switch Settings
for BCMS Terminals B-1
■ 7400A Da ta Module Swi tch Settings
for AT&T 475 Printer B-2
viii Issue 4 September 1995
Page 8

Contents
■ AT &T 61 5 Terminal Options B-3
■ AT&T 572 Printer B-3
■ AT&T 475 Printer B-5
C References C-1
■ Basic C-1
■ Call Center C-5
■ Networks C-6
■ Application Specific C-6
D BMCS/CMS Report Heading Comparison D-1
■ Summary of Differences D-1
ABB Abbreviations ABB-1
GL Glossary GL-1
IN Index IN1
Issue 4 September 1995 ix
Page 9

Contents
x Issue 4 September 1995
Page 10

Introduction
Overview
This document p rovides a comprehensive description of the Basic Call
Management System (BCMS) feature, which is available with the DEFINITY.
Communications System Generic 3 (G3). This document also describes the
Report Scheduler feature, which is often used with BCMS.
1
Although intended primarily for the BCMS administrator, this document may
prove useful to the system administrator, the Automatic Call Distribution ( ACD)
spl it supervisor, the ACD administrator, and ACD agents.
Organization
This guide is divided into the following chapters and appendices:
■ Chapter 1. " Introduction" is an introduction to this document.
■ Chapter 2. "BCMS Description and Applications" provides a brief
■ Chapter 3. "System Access" provides procedures on how to log in and
■ Chapter 4. "BCMS Report Generation" describes th e BC MS comman ds
overview of the BCMS feature and lists the reports, feature capacity lim its,
relevant hardware considerations, and typical applications of the BCMS
feature.
log off BCMS . This chapter also provides the procedures for changing the
BCMS password.
that are available to the BCMS administrator followed by a display and a
description of the various rep o rt s that the c ommands produce.
Issue 4 September 1995 1-1
Page 11
Introduction
■ Chapter 5. "System Printer and Report Scheduler" describes the
optional Report Scheduler feature. Also i n c luded in this chapter is a
description of the report scheduler commands and a display of the
reports.
■ Chapter 6. "Use of BCMS Reports for ACD Planning" desc ribes
desirable objectives and how the BCMS reports can be used to plan,
engineer, and optimize ACD splits and trunk group s.
■ Appendix A, "Error Messages" contains a list of possible error
messages that may be encountered if a command is entered incorrectly.
■ Appendix B, "Data Module and Printer Options" lists the required
switch settings for the 7400A Data Module, the AT& T 572 serial printer, the
AT&T 475 serial printer, and the 615 Data Terminal Equipment (DTE).
■ Appendix C, "References" lists other documents that may be used for
reference
■ Appendix D, "BMCS/CMS Report Heading Comparison" c o mpares
reports and report headings between BCMS and CMS
■ "Abbreviations" contains definitions for abbreviations and acronyms
used throughout the DEFINITY documentation.
■ "Glossary" contains a list of frequently used terms and their definitions.
■ ‘’Index’’ contains a cross-refere nced index.
Conventions Used in This Document
This manual uses the following conventions:
■ The names of c ommands are shown in the foll owi n g typefac e:
change system-parameters feature
■ Information you type is shown in the following typeface: EIA
■ Information displayed on the screen is shown in the following typeface:
login:
■ Keyboard keys are shown as follows: RETURN
■ Functi on keys are shown as follows: CANCEL
1-2 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 12

BCMS Description and Applic ations
Overview
In order to monitor the operations of an ACD application, which automatical ly`
distributes incoming calls to one or more groups of agents, AT&T offers the Call
Management S y stem (CMS ) software. T he CMS collects dat a r egarding the calls
on the switch and organizes the data into reports that help you manage ACD
facilities and personnel. These reports may be displayed on a video d isplay
terminal in real time, printed immediately, or scheduled for printing at a later time.
2
AT&T offers two types of CMS: External CMS and BCMS. Although both of these
options perform the same tasks, they are configured differently and have
different capacities. Th is chapter presents the capacities f o r B C MS G3vs, BCM S
G3s, BCMS G3i, and BCMS G3r.
In the External CMS arrangement, the CMS software resides in a computer
(usually referred to as an ‘‘adjunct’’) that is connected to the syst em via a data
link. In the BCMS arra ngement, the CMS software resides within the system. A
third arrangement exists in which both BCMS and External CMS report on a hunt
group. For R2 CMS, if external CMS or ‘‘BOTH’’ is requested, measured hunt
groups must begin with hunt group 1 and be consecutively assigned.
BCMS Reports
The BCMS fe ature provides the fol lowing reports:
1. Monitor Reports, which are real-time reports that present data on:
■ All splits, on a system basis, that have been administered for
internal measurements
Issue 4 September 1995 2-1
Page 13

BCMS Description and Applications
■ Individual splits that have been administered for internal or both
measurements
■ VDNs that are bein g measured by BCMS.
2. List Reports, which provide historical information and can be printed
immediately or scheduled for subsequent printing. These reports present
data on:
■ Individual agents or a group of agents, based on the time of day
■ Individual agents or a group of agents, based on the day of the
week
■ Individual splits or a group of splits, based on the time of day
■ Individual splits or a group of splits, based on the day of the week
■ Individual trunk groups or a group of trunk groups, based on the
time of day
■ Individual trunk groups or a group of trunk groups, based on the
day of the week
■ Individual Vector Directory Numbers (VDNs) based on the time of
day
■ Individual VDNs based on the day of the week
The examples of reports throughout this manual illustrate BCMS reports as they
appear in G3V4. If you have an earlier version of the switch, your reports may
differ from the examples.
NOTE:
Agents can be measured b y their physical extension (that is, the phone
extension they use), or they can be measured by their Login IDs when
either EAS or BCMS/VuStats Login IDs is optioned.
2-2 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 14

BCMS Reports
Feature Capacity Limits (Maximums)
The BCMS feature is designed to support ACD applications with requirements
that do not exceed the capac ity limits contained in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1. BCMS capacities for V3 and V4
G3vs/s V3G3iV3G3rV3G3vs/sV4G3iV4G3r
Item
V4
Measured A g ents
75 200 600 75 400 2,000
or Login IDs
Measured Splits 12/24* 99 99 12/24* 99 255
Measured Trunk
16/32* 32 32 16/32* 32 32
Groups
Measured VDNs NA/24 99 512 NA/24 99 512
Historical Data
Storage
Time Intervals 25 25 25 25 25 25
Daily Summaries 7 7 7 7 7 7
Historical (List)
16 16 16 16 16 16
Reports
Real-Time Reports 3 3 3 3 3 3
* Stands for PBP/ABP capacities.
NOTE:
In G3V3 and later releases, an agent can log into a maximum of four
measured splits at any one time.
The important point regarding these capacity limits is that the system will only
make internal measurements for parameters that are within these limits. If you
want to measure one or more ACD parameters that exceed the BCMS capacity
limits, you must use External CMS.
BCMS reports may be accessed fr o m a G 3 M an agem ent Terminal or on a dial-up
basis. When dial-up access is used, two constraints can affect the number of
terminals that can access BCMS data simultaneously:
■ The number of dial-up (Netcon) channels. The system provides f o ur
Netcon channels.
■ The number of Terminal User IDs (TUIs). A TUI is a switch resource used
by:
— A T&T T echnical Service Center (TSC) when logged in
Issue 4 September 1995
2-3
Page 15

BCMS Description and Applications
NOTE:
— The G3 Management Terminal when powered up
— A rem ote Management Terminal when logged in
— A BCMS terminal when logged in
— The system printer while printing
BCMS data is stored in volatile switch me mory; it cannot be saved to or
retrieved from tape. The switch preserves historical data if a Reset System
1, Reset System 2, or Reset System Interchange (i n a du p licated system)
occurs. Real-time data is preserved if a Reset System 1 or Reset System
Interchange occurs.
The switch loses all data (historical and real-time) during software
upgrades.
Hardware Configuration
Th e B C MS reports may be displaye d via t he G 3 M anagemen t Terminal or printed
on its associated printer. As a result, the BCMS feature does not require any new
or additional hardware. As an option, the BCMS reports may be scheduled via
the Report Schedu le r an d directed to its associated printer. The Report
Scheduler option i s preferred over the Management Terminal and its associated
slave printer. Scheduled reports cannot be sent to a CRT or associated slave
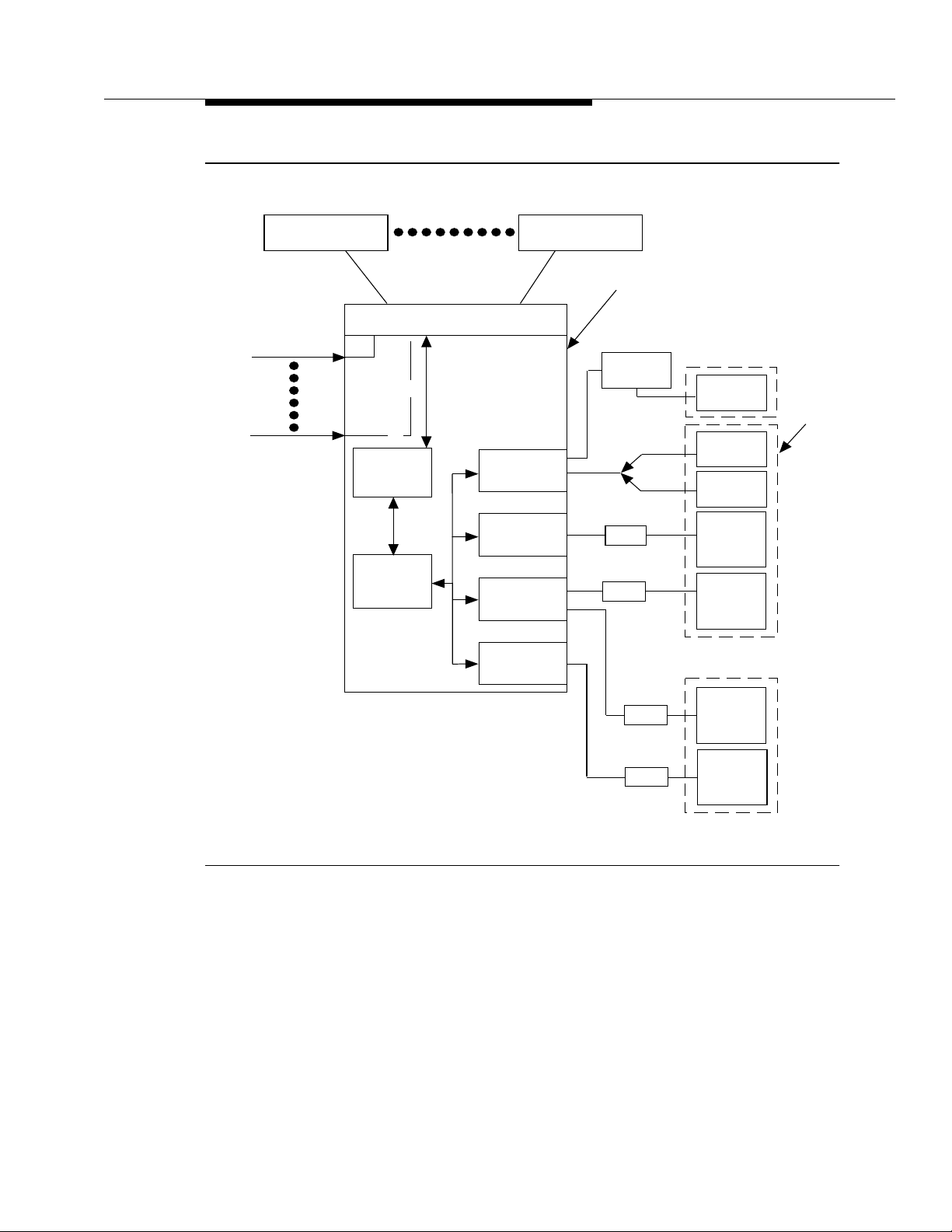
printer. Figure 2-1 shows a sample ACD/BCMS equipment configuration,
including arrangements for connecting the optional printer(s).
2-4 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 16
BCMS Reports
R
AGENT #1 AGENT #200
DEFINITY G3 SWITCH
TRUNK GROUP
#1
TRUNK GROUP
#99
(NOTE 1)
"ACD" FEATURE
"BCMS"
FEATURE
"REPORT
SCHEDULER"
FEATURE
(NOTE 2)
NOTES:
1. THE ACD AND BCMS FEATURES WILL
SUPPORT UP TO 400 TRUNKS (MAXIMUM) IN A
MAXIMUM OF 32 MEASURED TRUNK GROUPS.
2. ALTHOUGH THE "REPORT SCHEDULER"
FEATURE IS STANDARD WITH BCMS,
OPTIONAL HARDWARE IS REQUIRED
TO PRINT REPORTS.
TN773
PROCESSOR
TN726
DATA LINE
TN754
DIGITAL LINE
TN726
DATA LINE
EIA
MANAGER 1
TERMINAL
"OR"
ADU
7400A
7400B
ADU
PRINTER
CONFIGURATION
ARRANGEMENTS
PRINTER
PRINTER
PERSONAL
COMPUTER
PRINTER
OR
PERSONAL
COMPUTER
PRINTER
OR
PERSONAL
COMPUTER
SUPERVISOR
TERMINALS
615 WITH
513
EMULATION
615 WITH
513
EMULATION
SYSTEM
PRINTE
Figure 2-1. BCMS Sample Configuration
The Report Scheduler is enabled on the System-Parameters Customer-Options
form. Only an authorized AT&T representative can access and make changes to
the System-Parameter s Custome r-Options form. The parameters of the system
printer, which are used by the Report Scheduler feature, are administered on the
Feature-Related Sy stem Parameters form. If the parameters for the system printer
are not administered, scheduled reports cannot be printed. The system
administrator login may access this screen by entering the change
system-parameters features c ommand. This comma n d a n d the requirem ents
Issue 4 September 1995
2-5
Page 17

BCMS Description and Applications
NOTE:
for using the Feature-Related System Parameters for to set up the Report
Scheduler are covered in Chapter 5, "System Printer and Report Scheduler".
Th e R eport Scheduler should not be confused with and does not replace the
journal, Call Detail Records (CDR), or Property Manageme nt System (P MS)
dedicated printers. Consisting of virtually any asynchronous printer, the Report
Scheduler is intended to print all DEFINITY Generic 3 reports and the output of
virtually all list, display, and test commands. As an option, a personal computer
(PC) or host computer may be used to store the reports and provide additional
data manipulation capabilities. AT&T does not provide PC software for this
application.
The BCMS software resides completely on the switch and does not include
any special software or unique communications protocol for the PC/host
computer application. Although AT&T does propose the use of a PC to
collect, store, and p rint the reports, AT&T does not recommend an
applications software package for the PC. Since AT&T does not install,
administer, or control the PC application, AT&T does not guarantee correct
operation of this arrangement. Customers using a PC to collect report data
will need the following report output information for each report:
1. Begin with one-half page of line feeds.
2. Print a four-line banner containing th e following information:
■ Print job ID
■ Command
■ Time of day
■ User
3. Provide a form feed.
4. Begin report data using 80 characters p er line. Use spaces where there
are no data, and a newline character at the end of each line.
5. Provide a form feed after each page of data. (The page length is defined
in system parameters.)
6. Provide a form feed when the report is finished printing.
BCMS Applications
You can use the BCMS feature to support tho se service applications that use the
ACD f ea t ur e. The primary service applications that use the ACD feature are calls
and customer servic e centers.
2-6 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 18

BCMS Applications
Determining the proper size for the ACD trunk groups and the number of agents
that should b e assigned to each split requires knowledge of the incoming call
volume with respect to the following factors:
■ Each type of service provided
■ Time of day
■ Day of the week
■ Skill level of the agent
Generally, ACD applications are not preplanned because the types of traffic
information that would be required are unavailable. Initially, ACD applications are
engineered based on an estimated calling volume. Subsequently, the BCMS
reports allow you to manage the hourly and/or daily operations of the ACD by:
■ Monitoring trunk group usage
■ Monitoring the calling volume for each split
■ Monitoring VDNs
■ Monitoring the work load of each agent
■ Comparing agents’ performances
Chapter 4, "BCMS Report Generation" describes each BCMS report in detail
while Chapter 6, "Use of B CMS R eports for ACD Planning" describes ho w t o plan
and maintain an ACD based on the information provided by these reports.
NOTE:
Most BCMS measurement data is collec t ed a t the end of a call, whereas
hunt group measurements count calls as soon as they begin. Therefore,
calls spanning across a time interval boundary will be co unted differentl y
by the two. If comparing the measurements from BCMS with those from the
hunt groups, there may be slight differences. However, both hunt group
and BCMS measurements should indicate the same trends.
Interactions With External CMS
From the administration perspective, the ACD parameters associated with trunks
groups, hunt groups, and VDNs are any of the following:
■ Not measured
■ Internally measured by BCMS
■ Externally measured by External CMS
■ Measured both internally and externally
Note that using BCMS in conjunction with External CMS increases the maximum
number of agents and trunk groups that can be measured for a particular ACD
Issue 4 September 1995
2-7
Page 19

BCMS Description and Applications
application. In other words, the capacities shown for BCMS are additive to those
of External CMS.
NOTE:
If both BCMS and External CMS are used simultaneously, switch
performance may be degraded.
Interactions with VuStats
G3V3 and later releases provide the VuStats feature, which enables agents and
supervisors with display terminal to view data about agents, splits, and VDNs.
Much of this information is the same as that provided by BCMS and external
CMS. Refer to the VuStats section in the
Generic 3 Version 4 Implementation
Vustats data items and BCMS report columns.
DE FINITY Communications System
manual, 555-230-655, for a comparison of
2-8 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 20

System Access
Logging In and Logging Off
BCMS p rovides one login ID and supports a maximum of five G3 Management
Terminals logged in simultaneously. (A BCMS terminal is considered to be a
remote Management Terminal. You can access BCMS reports either from a
Management Terminal (local) or on a dial-up (remote) basis. When dial-up
access is used, the following two constraints affect the number of terminals that
can access BCMS data simultaneously:
3
■ The number of dial-up (Netcon) channels. The system provides four
Netcon channels.
■ The number of Terminal User IDs (TUIs). A TUI is a switch resource used
by:
— TSC when logged in
— the Management Terminal when powered up
— a remote Management Terminal when logged in
— a BCMS terminal when logged in
— the system p rinter while printing
When the switch is configured with more than one Management Terminal, you
may use one of the following terminals to access the BCMS feature:
■ 4410
■ 4425
■ 513
■ 610
■ 615
Issue 4 September 1995 3-1
Page 21
System Access
Typically, one terminal i s dedic a ted to the administration and/or maintenance
tasks, while the others are used for the ACD/BCMS features.
BCMS Login
The switch provides several different categories of login names. The login name
identifies the user and his or her permitted capabilities to the system. Generally,
each category permits unique capabilities (and restrictions). The BCMS login
allows you to display, print, and schedule BCMS reports. The BCMS login is
simply bcms, and the password is bcmspw. Since more than one user will
typically log into the system with this same login, all the users must know the
password.
Logging In
■ 715 BCT
NOTE:
A BCMS terminal is considered to be a remote Management Terminal.
There are two types of terminal configurations for logging into BCMS: a remote
terminal and a local terminal. Although both configurations use the same types of
terminals, the remote terminal requires a data module for dialing up the system.
Logging In from a Local Terminal
To log into BCMS from a local terminal, perform the following steps:
1. Turn on the terminal (if required) and press
displayed).
— The screen displays the following prompt:
Login:
2. Enter bcms and press
— The screen displays the following prompt:
Password:
3. Enter your password and press
For security reasons, the password is not displayed as you type it. The
system verifies that the login and password you entered are valid.
— If you entered an invalid login or password, t h e system displays the
following message and prompt:
INCORRECT LOGIN
BREAK (if no prompt is
RETURN.
RETURN. The default password is bcmspw.
Login:
Repeat Steps 2 and 3.
3-2 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 22

Logging In and Logging Off
— If you entered the correct login and associated password, the
sc reen dis plays the following prompt:
Terminal Type (Enter 513, 4410, 4425): [513]
Proceed to Step 4.
4. Enter the appropriate terminal type:
■ If you are using a 4410 terminal, enter 4410 and press RETURN.
■ If you are using a 4425 terminal, enter 4425 and press RETURN.
■ If you are using a 513 terminal, just press RETURN. 513 (which is
displayed in brackets on the screen) is the default.
■ If you are using a 610 or 615 MT terminal that has a 513 emulation
cartridge, just press
■ If you are using a 610 or 615 MT that does not have the 513
emulation ca rtridge, enter 4410 and press
■ If you are using a 715 BCT terminal, just press RETURN.
After you enter the appropriate terminal type, the system displays the
following prompt :
RETURN.
RETURN.
enter command:
Th e sys t em is no w ready for you t o enter a command to generate a BCMS
report.
Logging In from a Remote Terminal
To log into BCMS from a remote terminal, perform the following steps:
1. Turn on the terminal (if required) and press
displayed).
— The screen displays the following prompt:
Dial:
2. Enter the hunt group extension number for th e N etcon channel s a nd press
RETURN.
— The screen displays the following prompt:
Login:
3. Enter bcms and press
— The screen displays the following prompt:
Password:
4. Enter your password and press
BREAK (if no prompt is
RETURN.
RETURN. The default password is bcmspw.
For security reasons, the password is not displayed as you type it. The
system verifies that the login and password you entered are valid.
Issue 4 September 1995
3-3
Page 23

System Access
— If you entered an invalid login or password, t h e system displays the
following message and prompt:
INCORRECT LOGIN
"Login:
Repeat Steps 3 and 4.
— If you entered the correct login and associated password, the
sc re e n dis pla y s the following prompt:
Terminal Type (Enter 513, 4410, 4425): [513]
Proceed to Step 5.
5. Enter the appropriate terminal type:
■ If you are using a 4410 terminal, enter 4410 and press RETURN.
■ If you are using a 4425 terminal, enter 4425 and press RETURN.
■ If you are using a 513 terminal, just press RETURN. 513 (which is
displayed in brackets on the screen) is the default.
■ If you are using a 610 or 615 MT terminal that has a 513 emulation
cartridge, just press
RETURN.
Logging Off
Whenever you are not using the terminal, log off the system. To log off the
system, perform the following steps:
The switch automatically disconnects the terminal.
■ If you are using a 610 or 615 MT that does not have the 513
emulation ca rtridge, enter 4410 and press
■ If you are using a 715 BCT, just press RETURN.
RETURN.
After you enter the appropriate terminal type, the system displays the
following prompt :
enter command:
The system is now ready fo r you to enter a command to generate a BCMS
report.
1. Type logoff.
2. Press
RETURN.
3-4 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 24
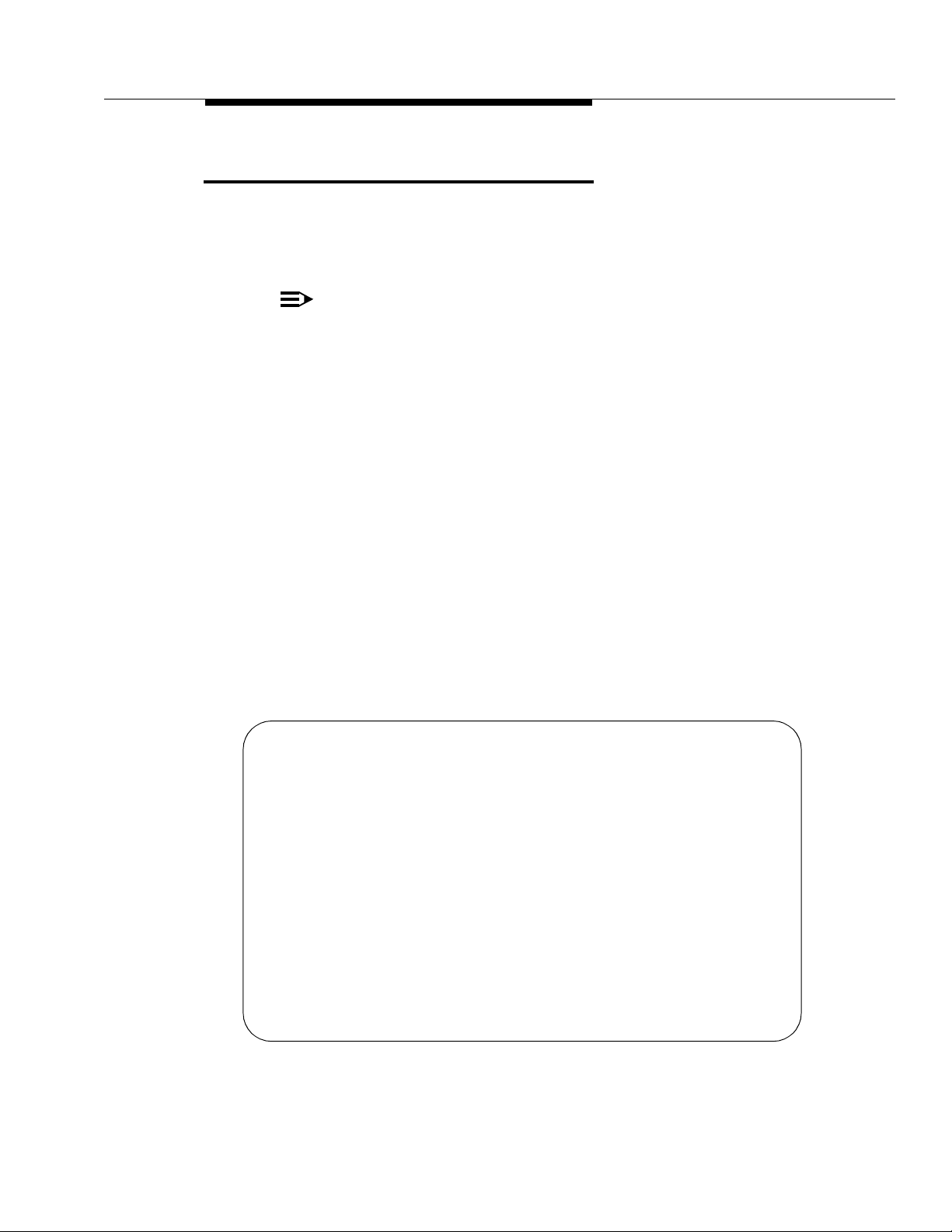
How to Change the BCMS Password
change password bcms Page 1 of 1
PASSWORD CHANGE
Change Password For Login Name: bcms
Your Current Password: _______
New Password For Login Name: _______
New Password (enter again): _______
How to Change the BC MS Password
To maintain the security of the system, the System Manager (or any user with
special privileges) can change the password asso ciated with the BCMS login.
The BCMS login cannot be administered and does not change. Only the
passwo rd for the BCMS login can change.
NOTE:
The BCMS login does not have the privilege to change the BCMS
password.
The password should be changed:
■ When the system is installed (change the password from the default
bcmspw)
■ Each time a new person takes over the associated login name
■ If an unauthorized person has discovered the password
Once the password is assigned, keep the followi n g t hings in mind:
■ Do not give the password to anyone
■ Keep the written p a s sword in a locked place
To chan ge a password, perform the following steps:
1. At the enter command: prompt, enter change password bcms and
RETURN.
press
— The system displays the Password Chang e screen (Screen 3-1).
The cursor is positioned on the Your Current Password: field.
Screen 3-1. Password Change Screen
Issue 4 September 1995
3-5
Page 25

System Access
NOTE:
2. Enter your current password and press RETURN.
— The cursor is positioned on the New Password For Login
Name: field.
3. Enter your new password and press
RETURN.
Valid passwords contain four to seven alphabetic or numeric
characters, or a combination of alphabetic and numeric characters.
— Th e cursor is positioned on t he Ne w Password (enter again):
field.
4. Re-enter your new password and press
— The system displays the followin g prompt:
command completed successfully
enter command:
RETURN.
3-6 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 26

BCMS Report Generation
Overview
This chapter helps you understand the Acceptable Service Level and the
Percent Within Service Level, and it provid e s inf ormati on on generating BCMS
reports. It also provides descriptions of each of the reports.
4
Acceptable Service Level
Before using BCMS, you must understand the concept of Acceptable S e rvice
Level and then set the acceptable service level field on various forms.
Acceptable Service Level is the desired time to answer for a given VDN or hunt
group. Timing for a call begins when the call encounters a VDN or enters a hunt
group queue. If the number of seconds to an swer the call is equal to or less than
the administered a cceptable service level for the VDN or hunt group, the call is
recorded as acc eptable.
Percent within Service Level
A service level can be administered for each hunt group or VDN, if t he customer
option has been set to
The service level is the amount of time (number of seconds) all owed t he switch to
answer calls.
To calcul ate the perc entage of calls within the acceptable service level, BCMS
divides the number of acceptable calls by the calls offered.
y
and if the hunt group or V DN is administered by BCMS.
Issue 4 September 1995 4-1
Page 27

BCMS Report Generati on
For hunt groups, BCMS calculates the Percent Within Service Level as follows:
% IN SERV LEVL =
where
accepted — Is the number of calls answered for which the queue time was less
than or equal to the administered service level for the split
dequeued — Is the n umber of calls t hat encou ntered t h e s plit’s queu e, but w er e
NOT answered, abandoned, or outflowed. This occurs with multiple split
queuing.
For VDNs, BCMS calculates the Percent Within Service Level as follows:
where
_ ________________________________________
ACDcalls + abandons + out f lows + dequeued
% IN SERV LEVL =
accepted * 100
accepted * 100
_ _____________
calls o ff ered
accepted — Is the number of answered calls (
time was less than or equal to the administered service level for the VDN.
here refers to the data item on the form of the same name.
ans
calls offered — Is the total number of ended cal ls t h at access ed th e VDN during
the current interval.
Acceptable Service Level Administration
The
Acceptable Service Level
Customer-Options, VDN, and Hunt Group forms. On the System-Parameters
Customer-Options form (only changeable by an AT&T technician) set the field
BCMS Service Level to y to activate BCMS.
On the Hunt Group Form (user changeable) set the field BCMS Acceptable
Service Level to a number between 0 and 9999. Set the Measured field to either
internal or both.
On the Vector Directory Number form set the field BCMS Acceptable Service
Level to a number between 0 and 9999. Set the Measured field to either
internal or both
NOTE:
The column % IN SERV LEVL may be blank for one or more of the
following reasons:
field i s administered on the System-Parameters
num ans
) for which the answer
num
■ T he BCMS Service Level field on the Customer Options form is set to n.
4-2 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 28

Overview
■ No service level is defined for the split or VDN (it cannot be set if BCMS
Service Level is set to n).
■ No call ended in the interval.
BCMS Commands
After you log into BCMS, the system prompts you to enter a command. BCMS
commands consist of the following three components:
1. The ACTION to be taken
2. The OBJECT for the specified action
3. The QUALIFIER(S) for the specified object
Issue 4 September 1995
4-3
Page 29

BCMS Report Generati on
Table 4-1 lists all of the commands you can perform with the BCMS login.
Table 4-1. Permitted BCMS Administration Commands
BCMS Administration Commands
Action Object Qualifiers
monitor bcms split split number [print] (Note 1)
bcms system [split number] [print] (Note 2)
bcms vdn extension [print] (Note 2)
list bcms agent ext.|loginID [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule] (Notes
2, 3, 4)
bcms agent ext.|loginID [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule] (Notes
2, 4)
bcms summary agent ext.|loginID [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule] (Notes
2, 4)
bcms summary agent ext.|loginID [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule] (Notes
2,4)
bcms split split number [time] [s tart time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
bcms split split number [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
bcms summary split split number [time] [start time] [print|schedule] (Note 2)
bcms summary split split number [day] [start day] [print|schedule] ( Note 2)
bcms trunk group number [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
bcms trunk group number [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
bcms summary trunk g r oup number [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
(Note 2)
bcms summary trunk group number [day] [start day] [stop day] [print | s chedul e] (N ot e
2)
bcms vdn extension [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
bcms vdn extension [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
bcms summar y vdn extension [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule] (Note 2)
bcms summary vdn extension [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule] (Note 2)
NOTES
1. Items de picted within brackets, such as [print], are optional.
2. You may enter a single number, a list of numbers, or a range of numbers
(for example 100-200).
4-4 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 30

Real-Time Reports
3. Whenever the command line qualifier [ schedule] is initially executed, the
4. If "BCMS/VuStats Login IDs" is enabled on the System-Parameters
Online Help
If you are unsure of a command, press HELP to obtain the list of permissib le
commands. For exam ple, suppose, you wanted to generate a BCMS Split
Report. The command to generate this report is monitor bcms split #. However,
you only know the beginning of the command (in this case, monitor bcms). To
find out the rest of the command, you would perform the following steps:
system defaults the report for im mediate printi ng (unless a day/time of day
is scheduled) and ge n erates a Job Id. The Job Id is required by the
Report Scheduler feature for updating and deleting the schedule of
reports. T he Report Scheduler (described in Chapter 6, "Use of BCMS
Reports for ACD Planning") is used to administer a time/day schedule for
each desired report.
Customer-Options form, then you must enter an agent’s login ID or a
range of login IDs in place of the physical extension or range of
extensions.
1. At the com man d promp t , e nter monitor bcms
2. Press
HELP.
— The system displays the followin g list of secondary commands for
the monitor command:
split
system
vdn
Real-Time Reports
BCMS provides three real-time reports:
■ BCMS Split Status Report
■ BCMS System Status Report
■ BCMS VDN Status Report
The BCMS Split Status Report provides the current (real-time) status and
cumulative measurement data for thos e agents ass igned to the split you specify.
The BCMS System Status Report provides current (real-time) status information
for either all BCMS splits or selected splits. The BCMS VDN S tatus Report
provides the current (real-time) status and cumulative measurement data for
VDNs monitored by BCMS.
You may gener ate t hese reports using the monitor command, which is discussed
below.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-5
Page 31

BCMS Report Generati on
Monitor Command
The monitor command is used to display real-time status reports for splits and
split agents. These reports display data accrued since the last inte rv al boundary.
The time intervals may be in one-hour or half-hour increments. (To select the
desired increment, ac ce ss the F eature-Related System Parameters screen and
enter hour or half-hour in the Measurement Interval field. Consult Chapter 6,
"Use of BCMS Reports for ACD Planning" for more information.)
There are three monitor commands, one to print each real-time report:
■ bcms split
■ bcms system
■ bcms vdn
The bcms split command generates the BCMS Split Status Report. The bcms
system command generates the BCMS System Status Report. The bcms vdn
command generates the BCMS VDN Status Report.
Whenever a status report is displayed on the G3 Management Terminal, it is
updated automatically approximately every 30 seconds. You can immediately
update the on-screen status report by pressing
command and return to the command prompt, press
consists of more than one page, press
pages and
PREVPAGE to display any p revious pages.
UPDATE. To cancel the monitor
CANCEL. If the status report
NEXTPAGE to display any subsequent
If you incorrectly enter the command, or if the qualifier is not applicable or cannot
be measured, a descriptive error message appear s o n t he message l ine , located
on the bottom of the screen. Usually, the error message descriptions provide
enough inform ation about the problem so that you will not need to research it.
However, if you require more information about the error message, press
Some examples of error messages are listed below:
■
?? invalid report type for spec i fied time or day
■ ?? number of BCM S measured agents exceeds maximum
■ Split not measured by BCMS
Appendix A lists all possible BCMS error messages.
BCMS Split Status Report
The BCMS Split Status Report provides the current (real-time) status and
cumulative measurement data for thos e agents ass igned to the split you specify.
This report displays data accrued since the last interval boundary. For example,
if the interval is set for hourly, and you issue the command to display the BCMS
Split Status Report at 11:10 a.m., the report displays the data accrued since
11:00 a.m. Although this report is updated approximately every 30 seconds, you
HELP.
4-6 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 32
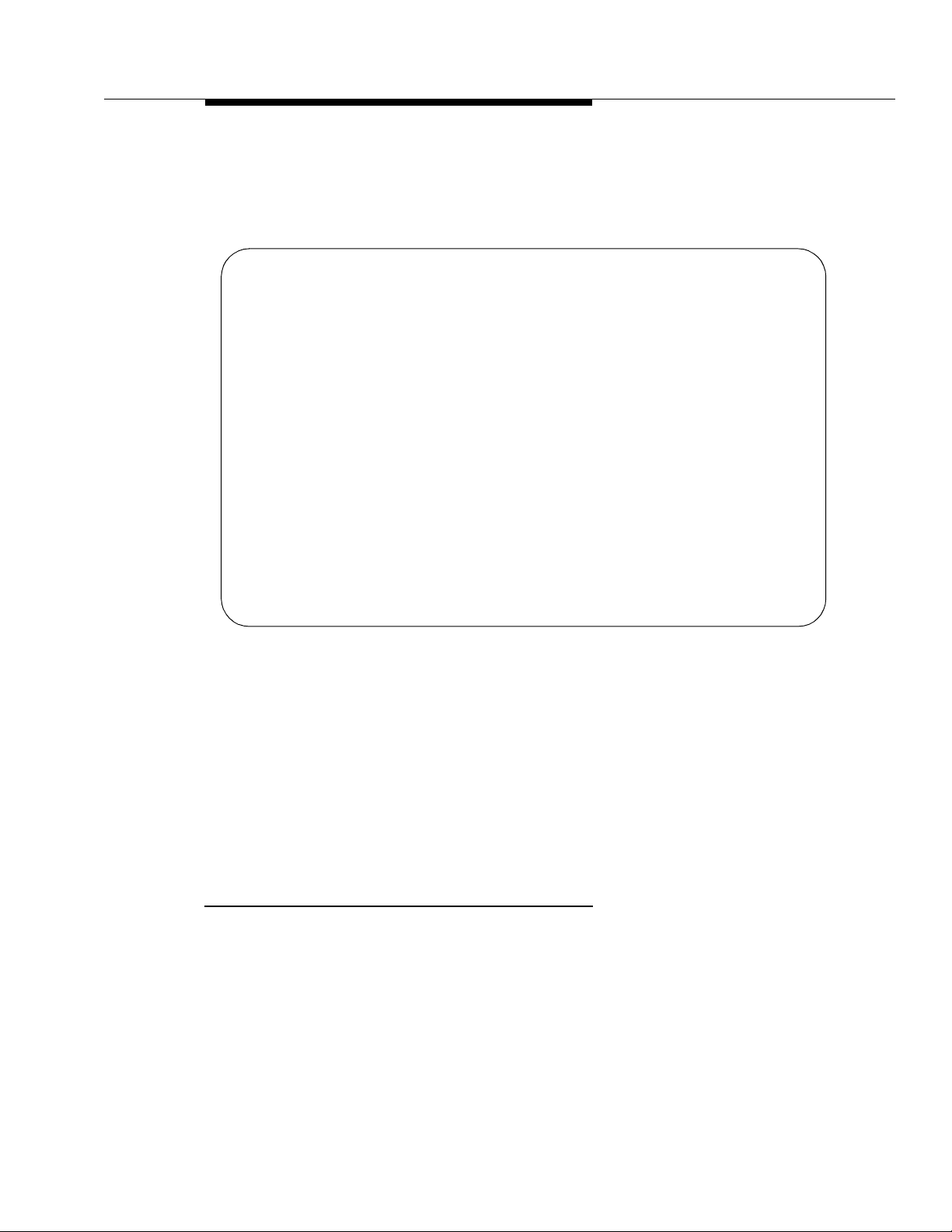
BCMS Split Status Report
can i m m e di a t e l y updat e the information on the screen by press ing UPDATE. At the
beginning of the next interval, the report resets. Screen 4-1 shows the BCMS
Split Status Report.
monitor bcms split 30
Split: 30 Date: 12:13 pm MON MAY 15, 1995
Split Name: headquarters
Calls Waiting: 5 Acceptable Service Level: xxx
Oldest Call: 1:39 % Within Service Level: xxx
Staffed: 7 Avail: 1 ACD: 1 ACW: 1 AUX: 1 Extn Calls: 2 Other: 1
AGENT NAME LOGIN ID EXT STATE TIME CALLS CALLS CALLS
Agent 1 32191 12345 Avail 12:00 0 0 0
Agent 2 32192 12346 ACD 12:04 1 0 0
Agent 3 32193 12347 ACW 12:12 3 0 0
Agent 4 32194 12348 AUX 11:30 0 0 0
Agent 5 32195 12349 Ext In 12:08 1 2 0
Agent 6 32196 12350 Ext Out 12:10 0 0 1
Agent 7 32197 12351 Other 11:58 0 0 0
$ 32198 12352 INIT 00:00 0 0 0
BCMS SPLIT (AGENT) STATUS
ACD EXT IN EXT OUT
Screen 4-1. BCMS Split Status Report Screen
* An asterisk precedes the
Call Waiting
Direct Agent calls.
& The
LOGIN ID
column is empty if the BCMS login system
parameter is set to
no.
$ If name is not adminis tered, this column is blank for the agent.
Split is displayed as "Skill" when EAS is optioned.
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions
The header information at the top o f each page includes the command entered
to generate the report, the page number and the total number of pages in the
report, the title of the report, and the time and date the report was generated. If
there are more than nine agents in the split, the remaining agent information
appears on subsequent pages.
Split — The split number specified with the command line.
field if any of the calls are
Issue 4 September 1995
4-7
Page 33

BCMS Report Generati on
NOTE:
NOTE:
With BCMS, splits do not have to be numbered from 1, and split numbers
do not have to be c o nsecutive.
Split Name — Th e admin istered name of the split. This name usually describes
the purpose or service of the split (for example, sales, service, or help line). If no
name exists, BCMS displays the split extension (for example, EXT 65222).
T he split name is limited to a maximum of 11 characters. If you enter more
than 11 characters, the additiona l char a cters are not printed on the System
Printer.
Calls Waiting — The number of calls currently queued and calls ringing at an
agent’s phone. If any of the calls in the queue are Direct Agent calls, an asterisk
appears before the value in this field. The Glossary describes the Direct Agent
feature.
Oldest Call — The number of minutes and seconds that the oldest call in queue
has been waiting to be answered. This includes calls ringing at an agent’s
phone.
Acceptable Service Level — The desir ed tim e to answer for a given hunt group
or VDN. Timing for a call begins when the call enters the hunt group queue.
% Within Service Level — The percentage of calls answered within th e
administered service level. This field is blank if no calls have been recorded for
this time interval or if there is no
Hunt Group form.
Staffed — The num ber of agents currently logged into the split.
Avail — The number of agents in this split c urrentl y available to receive an ACD
call. In order to b e counted as being available, agents must either be in the
Auto-In or Manual-In work mode. Refer to the Glossary for a description of work
modes. If the agent is on another split’s call or is performing After Call Work for
another split, the agent is not considered available and is not recorded here. If a
call is ringing at the agent’s phone or a call is on hold, the agent is not
considered available unless Multiple Call Handling is active and the agent
selects AI/MI with a call on hold.
ACD — Th e n umber of agents who are currently on an ACD call for this split. This
value also includes Direct Agent calls and those agents who are currently on
ACD calls that flowed in from another split.
ACW — The number of agents in this split who are currently in ACW mode for
this split. Refer to the G los sary for a description of A fte r Ca ll Work (ACW) mode. If
an agent is in ACW mode for another split, the agent is included in the Other
Acceptable Service Level
administered on the
4-8 Issue 4 S eptember 1995
Page 34

BCMS Split Status Report
state count for this split. Also, if an agent is on a call while in ACW mode, the
agent appears in the Extn state count, and not in the ACW state.
AUX — The number of agents in this split who are currently in the AUX work
mode for this split. If an agent is answering a call from another split or is in ACW
work mode for another split, that agent is not considered in AUX work mode for
this split and is not included in this number. The agent is included in th e Other
state count.
Extn — The number of agents in this split who are currently on non-ACD calls.
These non-ACD calls may be either incoming (direct to the extension) or
outgoing (direct from the extension). Those agents receiving or making extension
calls while in Avail, ACW, or AUX work mode is recorded as being on extension
calls.
Other — The number of agents in this split who:
■ Are on a call from another split
■ Are in AC W work mode for another split
■ Have placed a call on HOLD and made no other state selections
■ Have a call ringing at their voice terminals
■ Are dialing a number (to place a call or activate a feature)
All of the agents in the Other state are unavailable for ACD calls .
AGENT NAME — The name of the agent. Generally, this is the agent’s first or last
name. However, if no name is administered on the station form, this field is left
blank. When the field is blank, the data can be identified by th e extension.
LOGIN ID — The BCMS login ID(s) (taken from the BCMS Login ID f orm or EAS
Login form) for which you requested the report. This column does not appear if
BCMS logins are not optioned.
EXT — The 2-, 3-, 4-, or 5-digit extension number for the agent.
STATE — The current work state for the agent. Possible work states are Avail,
ACD, ACW, AUX, Extn, and Other. (The sum of the time the agent spends in the
possible work states is the agent’s
staffed
time.) Unstaffed agents do not appear
on the report. When the system t ime is changed, agents are in the INIT state.
Each agent remains in the INIT state until he or she takes a call or pushes a work
button.
NOTE:
Refer to the Glossary for a description of the term
work state.
TIME — The 24-hour clock time that the agent entered this work state.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-9
Page 35

BCMS Report Generati on
ACD CALLS — T he number of ACD calls that the agent has completed since the
beginni n g of the current interval. T his value includes any calls that flowed in from
other splits. (Calls in process are not cou nted until they are completed.)
EXT IN CALLS — The number of non-ACD calls that the agent has received
(incoming) since the beginning of the current interval. (Calls in process are not
counted until they are completed.) The maximum value is 255.
EXT OUT CALLS — The number of non-ACD calls that the agent has made
(outgoing) since the beginning of t he current interval . (Calls in process are not
counted until they are completed.) The maximum value is 255.
Displaying the BCMS Split Status Report
To display this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter monitor bcms split ## (where ## is the number of an
administered split that is measured by BCMS) and press
split number is o nly one digit (for example, split 5), just enter the single
digit.
RETURN. If the
— The BCMS Split Status Report appears on your screen.
2. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
3. If you want to immediately update the report data, press
4. To exit the BCMS Split Status report, press
— The enter command: prompt appears.
Printing the BCMS Split Status Report
To print the BCMS Split Status report, enter monitor bcms split ## print
(where ## is the number of an administered split that is m easured by BCMS) and
RETURN. If the split number is on ly one digit (for example, split 5), just enter
press
the single digit.
— The report immediately prints on the printer attached to your terminal, and
the system displays the enter comman d: pro mpt.
BCMS System Status Report
The BCMS System Status Report provides current (real-time) status information
for either all BCMS splits or selected BCMS splits. This report displays data
ac crued since the last interval boundary . For example, if the interval is set to
hour, and you issue the command to display the BCMS System Status Report at
11:10 a.m., the report displays the data accrued since 11:00 a.m. Although this
report is updated approximately every 30 s e conds, you can immediately update
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
UPDATE.
CANCEL.
4-10 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 36

BCMS System Status Report
NOTE:
the information on the screen by pressing UPDATE. Th is report is reset at the
beginning of the time interval (for example, hour or half-hour). Screen 4-2 shows
the BCMS System Status Repo rt.
When analyzing this report, keep the following things in mind:
■ All averages are for completed calls only.
■ A completed call may span more than one time interval. ACD calls that are
in process (have not terminated) are counted in the time interval in which
they terminate. For example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00 to 11:00
time in t er v a l, but terminates in the 11:00 to 12:00 time interval, the data for
this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00 time interval.
■ Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has been
exceeded .
monitor bcms system
BCMS SYSTEM STATUS
Date: 12:53 MON MAY 15, 1995
SPLIT NAME WAIT CALL ANS AGENT CALLS TIME CALLS TIME CALL LEVL
CALLS OLDEST SPEED AVAIL ABAND ABAND ACD TALK AFTER SERV
Service 3 1:03 :45 0 3 :30 20 2:30 1:25 85
EXT 4000 5 :33 :15 0 11 :45 36 1:32 :35 91
AVG AVG AVG AVG % IN
Screen 4-2. BCMS System Status Report Screen
& Split name is not administered (em default i s EXT xxxx, where xxxx
is the extension administered for the split.
SPLIT is displayed as "SKILL" when EAS is optioned.
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions
This report presents header infor m ation at the top of each page. This information
includes the command entered to generate the report, the page number and the
total number of pages in the report, the title of the report, and the time and date
the report was generated. If more than 14 splits are being measured by BCMS,
the remaining splits are displayed on multiple pages.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-11
Page 37

BCMS Report Generati on
SPLIT NAME — The name of th e split (for example, sales, service, or help line).
If no name exists, the split extension (for example, EXT 12345) is displayed.
CALLS WAIT — The number of calls in the split’s queue that are currently
waiting to be answered and calls ringing at an agent’s phone. If any of the calls in
the queue are Direct Agent calls, an asterisk appears before this field. Consult
the Glossary for a description of the Direct Agent feature.
OLDEST CALL — The number of minutes and seconds the oldest call in queue
has been waiting to be answered. This includes calls ringing at an agent’s
phone.
AVG SPEED ANS — The average amount of time it takes before the calls are
being answered. This value includes time waiting in th e queue and time ringing
at the agent’s voice terminal. The calculation is:
AVG SPEED ANS =
NOTE:
Keep the following things in mind :
Sum o f Each Completed Call′s Time In Queue + Time Ringing
_ ________________________________________________________
The Total Number o f ACD Calls Answered
■ Calls that flow in from other split(s) do not include
time in queue
from the other splits in this calculation. Also, the AVG SPEED ANS
does not include time spent listening to a forced first
announcement.
■ A completed call may span more than one time period. ACD calls
that are in process (have not terminated ) are counte d i n the time
period in which they terminate. For example, if an ACD call begins
in the 10:00 to 11:00 time period, but terminates in the 11:00 to
12:00 time period, the data for this call is counted in the 11:00 to
12:00 time period.
■ Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has
been exceeded .
AVAIL AGENT — The number of agents in this split who are currently available
to receive an AC D call directed to this sp lit.
ABAND CALLS — The total number of ACD calls that have hung up while
waiting to be answered. This includes those calls that have abandoned while in
queue or while ringing. Calls that are not queued (for example, because the
queue is full, the caller receives a forced first announcement and abandons
during the announcement, or no agents are staffed) are not counted as
abandoned for the hunt group.
4-12 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 38

BCMS System Status Report
_
AVG ABAND TIME — The average time before an ACD call abandons. This
does not include any time spent in another spli t’s que u e b e fore intraflowin g t o
this split. The calculation is:
AVG ABAND TIME =
NOTE:
This value does not include time spent listening to a forced first
announcement or ca ll s that
announcement.
ACD CALLS — The num ber of ACD calls completed during the current interval.
This number also includes those calls tha t flow in from other splits.
AVG TALK TIME — The average duration of ACD calls for each split . This
calculation includes the time each agent spent talking but does not inc l ude rin g
time at an agent’s voice terminal. The calculation is:
AVG TALK TIME =
_ ______________________________
Total Number o f Abandoned Calls
_ ________________________________
Total Number o f ACD Calls Answered
Total Abandon Time
abandon
while listening to a forced first
Total ACD Talk Time
AVG AFTER CALL — The average ACW time for call-relat ed ACW time
completed by agents in this split during this time interval. Call-related AC W is the
time that occurs immediately after an ACD call (that is, when an agent was in
Manual mode and an ACD call ended, or when the agent presses the ACW
button during an ACD call). AVG AFTER CALL does not include time spent on
direct incoming or outgoing calls while in ACW or time that immediately follows
an EXTN call. The calculation is:
Total Call Related ACW Time
AVG AFTER CALL =
NOTE:
The average is for A C W sessions , which may not correspond to the number
of ACD c a lls either because some ACD ca lls did not have ACW time or
because the call was recorded in another interval.
% IN SERV LEVL — The percentage of calls answered with in the administered
service level for this split. Calculation is based on the following:
% IN SERV LEVL =
where
_ _________________________________
Number o f Call Related ACW Sessions
_ _________________________________________
ACD calls + Abandons + Out f lows +dequeued
Accepted * 100
accepted is calls answered whose queue time was less than or equal to the
administered service level for the split.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-13
Page 39

BCMS Report Generati on
dequeued is a call that encountered the split’s queue, but which was NOT
answered, abandoned, or outflowed. This occurs with multiple split queuing.
Displaying the BCMS System Status Report
BCMS allows you to generate a BCMS System Status Report on all the BCMS
splits or selected BCMS splits. To generate a report on all the BCMS splits, enter
the monitor bcms system command. The report produced by this command
presents information on all BCMS splits that had agents staffed when you
entered the command. To generate a report on selected BCMS splits, you must
include t he split number(s) or split ranges at the end of the command. For
example, if y ou wanted to generate a BCMS S y stem Status Report on split 4, you
would enter: monitor bcms system 4. If you wanted to generate a BCMS
System Status Report on splits 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, you would enter: monitor bcms
system 1-5. BCMS also allows you to specify a range of splits and individual
splits in a command. For example, if you have 8 splits (numbered 1 through 8)
and wanted to generate a BCMS Sy stem St atus Report on splits 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and
8, you would enter: monitor bcms system 1-4 6 8.
To display the BCMS System Status Report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter monitor bcms system and press
— The BCMS System Status Report appears on your screen.
2. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
3. If you want to immediately update the report data, press
4. To exit the BCMS System Status report, press
— The enter command: prompt appears.
Printing the BCMS System Status Report
To print the BCMS System Status report, enter monitor bcms system print
and press
RETURN.
— The report is immediately printed on the printer atta ched to yo ur terminal,
and the system displays the enter command: prompt.
BCMS VDN Status Report
The V DN Status Report gives real-time status information for internally measured
VDNs. You can monitor up to 99 VDNs at one time, however; the report can
display up to 13 VDNs on a single page. Therefore, if you are monitoring 99
VDNs, the report is 6 pages long. You must specify the extensions of the VDNs
you want the system to monitor. You can specify the extension in a list or in a
range format. For example,
monitor bcms vdn 12345 12346 12350-12359.
RETURN.
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
UPDATE.
CANCEL.
4-14 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 40

BCMS VDN Status Report
monitor bcms vdn 12345-12349
BCMS VECTOR DIRECTORY NUMBER STATUS
AVG AVG AVG CALLS % IN
CALLS OLDEST ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK/ CONN FLOW BUSY/ SERV
VDN NAME WAIT CALL CALLS ANS CALLS TIME HOLD CALLS OUT DISC LEVL
knives 5 :25 50 :39 5 :45 2:30 0 0 24 91
EXT 12346 0 :00 0 :00 0 :00 :00 0 0 0 0
Date: 15:30 Mon May 15, 1995
Screen 4-3. BCMS VDN Status Report Screen
* Indic ates that the VDN name is not administered for the VDN;
default extension is as shown.
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions
Date — The current date and time (updated every 30 seconds or when the
update key is pressed).
VDN NAME — Th e n ame of the VDN being reported. If the VDN does not have a
name administered, this field displays
EXT XXXXX
where "
XXXX X
is the VDN’s
extension.
CALLS WAIT — The number of calls that encountered this VDN and have not
been answered, abandoned, outflowed, or forced busy/disc. Includes calls in
queues in vector processing, and ringing at an agent’s station.
OLDEST CALL — The time the oldest call currently waiting has waited in the
VDN. Timing starts when the call enters the VDN.
ACD CALLS — The number of completed ACD calls answered in a
BCMS-measured split. The split may have been reached via the queue-to-main,
check backup, route-to, messaging split, or adjunct rou ting commands. Includes
Direct Agent calls.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-15
Page 41

BCMS Report Generati on
_
_
_
AVG SPEED ANS — The ave r age speed of answer for ACD and connect calls
that have completed for this VDN during the current period. This includes the
time in vector processing, in a split’s queue, and time ringing. The calculation is:
AVG SPEED ANS =
NOTE:
Answer time for a ca ll i s r ecorded when the call ends. If a call originates in
interval x, is answered in interval y, and ends in interval z, the associated
answer and talk times are re corded in interval z.
ABAND CALLS — T he number of calls to this V DN that have abandoned before
being answered during the current period. This includes VDN calls that were
routed to an attendant, station, or announcement, and abandoned before being
answered.
AVG ABAND TIME — The average time abandoned c a l ls waited before
abandoning during the current period. The cal culation i s:
AVG ABAND TIME =
_ ____________________________________
Total Answer Time
Total ACD Calls + Total CONNect CALLS
Total Abandon Time
_ __________________
Total Calls Abandoned
AVG TALK/HOLD — T he average ta lk tim e f or ACD calls completed by t his V DN
during the current period. This does n ot i nclude ring ti m e , but i t does i nclude any
time the call e r s pent on Hold. The calculati on is:
Total Talk Time
AVG TALK / HOLD =
CONN CALLS — The number of calls that were routed to a station (agent or
non-ACD), attendant, or announcement, and were answered there.
FLOW OUT — T h e nu mber of calls th at wer e r ou ted to another VD N or to a trunk,
including su ccessful look-ahead attempts.
CALLS BUSY/DISC — The number of calls that encountered a busy or
disconnect step (and the announcement ends).
% IN SERV LEVL — The percent of calls offered that completed and were
answered within the acceptable service level defined on the VDN form. The
calculation is:
% SERV LEVL =
Offered
is defined as:
_ _____________
ACD Calls
Acceptable * 100
_ _______________
O ff ered
acdcalls + flowout calls + abandoned + connect + busy/disc
4-16 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 42

BCMS VDN Status Report
Acceptable
is the number of ACD and CONNect calls that were answered within
the administered service level. This field is blank if no calls were recorded for thi s
time interval. This field is also bl an k if no
administered on the VDN form.
Displaying the BCMS VDN Status Report
BCMS allows you to generate a BCMS V D N S t atus R eport o n a ll the BCM S VDNs
or selected BCMS VDNs. To generate a report on all the BCMS VDNs, en ter the
monitor bcms vdn comma nd. The report produced by this command p resents
information on all BCMS VDNs that had agents staffed when you entered th e
command. You may include up to 30 VDNs at a time. To generate a report on
selected BCMS VDNs, you must include the VDN number(s) or VDN ranges at
the end of the command. For example, if you wanted to g enerate a BCMS
System Status Report on VDN 8250, you would enter: monitor bcms vdn
8250. If you wanted to generate a BCMS System Status Report on VDNs 8251,
8252, 8253, 8254, and 8255, you would enter: monitor bcms vdn
8251-8255. BCMS also allows you to specify a range of VDNs and individual
VDNs in a command. For example, if you have eight VDNs (numbered 51
through 58) and wanted to generate a BCMS VDN Status Report on these eight
VDNs, you would enter the following command: monitor bcms vdn 51-58.
To display the BCMS VDN Status Report, perform the following step s:
Acceptable Service Level
has been
1. Enter monitor bcms system and press
— The BCMS VDN Status Report appears on your screen.
2. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
3. If you want to immediately update the report data, press
4. To exit the BCMS VDN Status report, press
— The enter command: prompt appears.
Printing the BCMS VDN Status Report
To print the BCMS VDN Status report, enter monitor bcms vdn print and
RETURN.
press
— The report is immediately printed on the printer attached to y o ur terminal,
and the system displays the enter command: prompt.
RETURN.
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
UPDATE.
CANCEL.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-17
Page 43

BCMS Report Generati on
Historical Reports
BCMS provides eight historical reports. These reports give you information for an
interval of time. You can print the reports for a period time measured in minutes
or hours, or a period of time measured in days. The BCMS historical reports are:
■ Agent Report
■ Agent Summary Report
■ Split and Skill Report
■ Split and Skill Summary Report
■ Trunk Group Report
■ Trunk Group Summary Report
■ V DN Report
■ VD N Su mmary Report
You are able to print the historical reports using the list commands, which are
discussed below.
List Commands
The list commands are used to display historical information for agents, splits,
system, trunk groups, and VDNs. There are eight secondary list commands:
■ bcms agent
■ bcms summary agent
■ bcms split
■ bcms summary split
■ bcms trunk
■ bcms summary trunk
■ bcms vdn
■ bcms summary vdn
With these comman ds, y ou can specify:
■ Whether you want the data in the reports to be displayed in
■ The times or days for which you wish to see data
■ The system to immediately display the report on your terminal
■ The system to print the report. If you include print at the end of the
hourly/half-hourly or da i ly intervals
comman d , the system will immediately print the report to a slaved printer.
If you include schedule at the end of the command, the system will allow
4-18 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 44

BCMS Agent Report
NOTE:
NOTE:
you to schedule the report to print to the system printer immediately
(immediate), at a later time (deferred), or routinely at specified times
(scheduled).
Time interval data may be c ollected in half-hour or one-hour increments.
(To select the desired increment, access the Feature-Related System
Parameters screen and enter half-hour or hour in the Measurement
Interval: field. Consult Chapter 6, "Use of BCMS Reports for ACD Planning"
for more information.) The switch stores time interval data in a time
database which holds a maximum of 25 intervals. Data for the 26th interval
overwrites the first interval in the time database (and so on). Therefore, if
the half-hour option is selected, care should be exercised to ensure that
time interval reports are run while the data for the desired interval is still
available in the time database. For example, if you select the half-hour
option, print the report twice daily to ensure that you do not lose
information.
BCMS Agent Report
The BCMS Agent Report provides traffic information for the specified agent.
Depending on specifics from the command line, the information may be
time
nor
day
displayed as either a time interval or a daily summary. If neither
time
specified,
is the default. In this case, the report displays data accrued for
is
the previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour), including data from the most
recently completed time interval. To get information on the current time interval,
you must use a monitor bcms command. Screen 4-4 shows the BCMS Agent
Report — Hourly, and Screen 4-5 shows the BCMS Agent Report — Daily.
NOTE:
BCMS c an track agents based on their phone numbers, or based on login
IDs. If BCMS/VuStats Login IDs is optioned, BCMS tracks login IDs.
When analyzing this report, keep the following things in mind:
■ All averages are for completed calls only.
■ A completed call may span more than one time interval. ACD calls that are
in process (have not terminated) are counted in the time interval in which
they terminate. For example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00 to 11:00
time in t er v a l, but terminates in the 11:00 to 12:00 time interval, the data for
this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00 time interval.
■ Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has been
exceeded .
Issue 4 September 1995
4-19
Page 45

BCMS Report Generati on
list bcms agent 4222 8:00
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Agent: 4222
Agent Name: s-jones
BCMS AGENT REPORT
TIME CALLS TIME CALL TIME OTHER CALLS TIME STAFFED TIME
ACD TALK AFTER AVAIL AUX/ EXTN EXTN TIME HOLD
8:00- 9:00 10 1:15 7:30 25:00 10:40 1 4:00 60:00 :20
9:00-10:00 18 1:40 18:00 4:20 :00 2 3:20 60:00 1:00
10:00-11:00 10 1:20 8:20 16:10 :00 0 :00 38:00 :10
----------- ----- ------ ------- ------- ------- ----- ----- -------- -----SUMMARY 38 1:28 33:50 45:30 10:40 3 3:33 158:00 1:30
AVG TOTAL TOTAL TOTAL AVG TOTAL TOTAL
Screen 4-4. BCMS Agent Report — Hourly
NOTE:
4222 could be a login ID or an extension, depending on whether
BCMS/VuStats Login IDs is administered.
list bcms agent 4222 day 5/17
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Agent: 4222
Agent Name: s-jones
AVG TOTAL TOTAL TOTAL AVG TOTAL TOTAL
ACD TALK AFTER AVAIL AUX/ EXTN EXTN TIME HOLD
DAY CALLS TIME CALL TIME OTHER CALLS TIME STAFFED TIME
BCMS AGENT REPORT
5/14/95 200 1:30 100:00 35:00 80:00 10 2:00 540:00 5:00
5/13/95 38 1:28 34:12 45:30 10:40 3 3:33 158:00 1:30
----------- ----- ------ ------- ------- ------- ----- ----- -------- -----SUMMARY 238 1:30 134:12 80:30 90:40 13 2:22 698:00 6:30
Screen 4-5. BCMS Agent Report — Daily
NOTE:
4222 could be a login ID or an extension.
4-20 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 46

BCMS Agent Report
AVG TALK TIME =
Total Number o f ACD Calls Answered
Total ACD Talk Time
_ _________________________________
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions
This report presents header infor m ation at the top of each page. This information
includes the comman d entered to generate the report, the page number of the
report, the title of the report, and the time and date the report was generated. If
this is a time report and there are more than 11 time intervals, this report is
displayed on multiple pages. A daily summary report is displayed on the last
page of the report.
AGENT NAME — The name of the agent. If no name is administered, the agent’s
extension is displayed in the form
TIME/DAY — The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Time is always ex pressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are optional.
Reports always start at the earliest time interval (either hour or half-hour). If no
start time is given, the oldest time interval is the default. A stop time requires an
associated start time. If no stop time is given, the last completed time interval
(hour or half-hour) is the default. If no start time or stop time is given, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 24 t im e in tervals. If you specify
command and do not include a start day or stop day, the report displays data
accrued for the previous six days and data accrued through the most recently
completed interval (hour or half-hour).
EXT 65432.
day
in the
ACD CALLS — The number of ACD calls answered by this agent for all sp lits
during the reporting interval. This value includes calls that flowed in from other
splits and Direct Agent calls.
AVG TALK TIME — The average duration of ACD calls for all splits the agent
was logged into. This value includes time spent talking but does not include the
amount of time the agent was holding an ACD call or ring time at the agent’s
voice terminal. The calculation is:
TOTAL AFTER CALL — The total amount of time that the agent spent in
call-related or non-call-related ACW work states for all splits during the reporting
interval. This does not include time spent on direct incoming or outgoin g calls
while in ACW. If an agent entered ACW in one interval, but ended ACW in
another interval, the appropriate amount of ACW time is credited to each of the
intervals.
TOTAL AVAIL TIME — The sum of the time that the agent was available to
receive ACD calls during the current interval. During this time, the agent:
■ Was in Auto-In or Manual-In work modes for at least one split
■ Was not in ACW in any split
Issue 4 September 1995
4-21
Page 47

BCMS Report Generati on
AVG EXTN TIME =
Total Number o f Ext Calls
Total Ext Time
_ _______________________
■ Was not on any call or placing any call (unless MCH is active)
■ Did not have ringing calls
TOTAL AUX/OTHER — The sum of the time that the agent has the AUX button
pressed and is not doing any th i ng els e f o r a n y of th e o ther splits (that is, the sum
of the time that the agent is in AUX work mode for all splits). This value does not
include time the agent spent on an EXTN call or in Manual-In, Auto-In, or ACW
mode for another split. Note that if the agent was in Other for all logged-in splits
that time is reflected here. For example, ringing calls can cause several seconds
of AUX time to accrue.
For the agent report, any non-ACD call time is totaled in the AVG EXTN TIME
column. Two points of contrast are:
1. The measurement TOTAL AUX/OTHER is time-interval based, rather than
being call related. For example, assuming that the previously identified
stipulations are met, then if the agent is in AUX from 9:55 to 10:05, five
minutes is pegged in the 9:00 to 10:00 time interval and five minutes is
pegged in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval.
2. The measurement AVG EXTN TIME is call related. For example, if an agent
is on a non-ACD call from 9:55 to 10:05, the call and ten minutes of EXTN
time is pegged in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval.
Because the agent report includes some call-related items, the sum of all
items for a given hour may not exactly equal 60 minutes.
EXTN CALLS — The total number of non-ACD incoming and outgoin g calls for
this agent during the reporting interval. O nly those non-ACD calls that are
originated and/or received while the agent is logged into at least one split are
counted.
AVG EXTN TIME — The average amount of time that the agent spent on
non-ACD calls while logged into at least one split during the reporting interval.
This average does not inc lude time when the agent was holding the EXTN call.
The calcu lati on is:
TOTAL TIME STAFFED — The total time that the agent spe nt logged into at
least one split during the reporting interval. Staff time is clocked for an agent who
is in m ul t iple splits as long as the agent is logged i n to any split. Concurrent times
for each split are not totaled.
TOTAL HOLD TIME — The total time that the agent placed ACD calls on hold.
This time is the
c aller’s hold time
and is independent of the state of the agent.
TOTAL HOLD TIME does not include the hold time for non-ACD calls.
4-22 Issue 4 September 1995
SUMMARY — The total of each of the columns that do not contain averages.
Page 48

BCMS Agent Report
Columns that do contain averages are the total time divided b y the number of
calls.
Displaying the BCMS Agent Report
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly/half-hourly intervals or daily
intervals an d display the report on your terminal.
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To display this report, perform the following st eps:
1. Enter list bcms agent ext time xx:xx xx:xx (where "ext" is a
valid agent extension measured by BCMS). The first specified time is
referred to as the start time, while the second time is referred to as the
stop ti me. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format; however, the hours
may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number. Minutes are always
expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the report displays data
accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour).
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Agent Report appears on your screen.
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
Displaying a Daily Report
To display this report, perform the following st eps:
1. Enter list bcms agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx (where ## is a valid
agent extension or login ID measured by BCMS). Th e f irst specified day is
referred to as the start day, while the second day is referred to as the stop
day. If no start day is given, the report displays data accrued for the
previous six days and data accrue d through the most rece ntly completed
interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Agent Report appears on your screen.
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
PREVPAGE key to display previous
pages.
Issue 4 September 1995
NEXTPAGE key to
4-23
Page 49

BCMS Report Generati on
Printing the BCMS Agent Report
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly or half-hourly intervals and daily
intervals and to print the report. If you have a printer directly connected to your
terminal, you may print reports using the instructions provided below. If you do
not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, consult the instructions for
scheduling reports to print to the system printer.
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx print (where ## is
a valid agent extension or login ID measured by BCMS). T he first specified
time is referred to as the start time, while the second time is referred to a s
the stop time. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format; however, the
hours may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number. Minutes are
always expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or
half-hour).
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Agent Report prints on the printer attached to your
terminal.
Printing a Daily Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx print (where ## is a
valid agent extension or login ID measured by BCMS). The first specified
day is referred to as the start day, while the second day is referred to as
the stop day. If no start day is given, the report displays data a ccrued for
the pre vious six days and data accrued through the most recently
completed interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Agent Report prints on the printer attached to your
terminal.
4-24 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 50
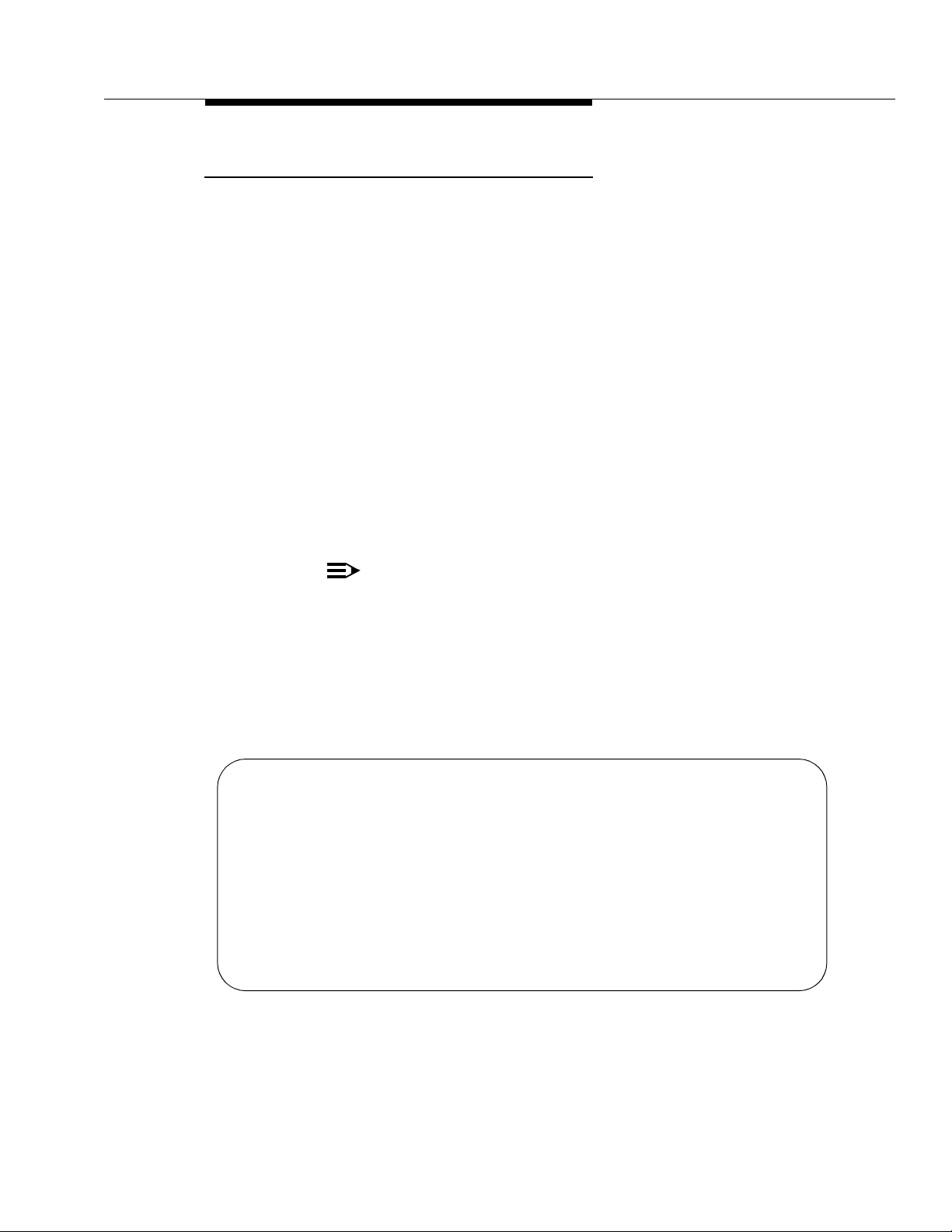
BCMS Agent Report
Scheduling the BCMS Agent Report to Print
Th e R eport Scheduler allows you to schedule the day or days for the system to
print the report. If you do not have a printer directly connected to your terminal,
you may use the Report Scheduler feature to print the report immediately to the
system printer. The data for this report can be collected in hourly/half-ho urly
intervals or daily interval s.
Scheduling an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report to Print
To schedule this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx schedule (where
## is a valid agent extension or login ID measured by BCMS). The first
specified time is referred to as the start time, while the second time is
referred to as the stop time. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format;
however, the hours may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number.
Minutes are always expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the
report displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or
half-hour).
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— Th e R eport Scheduler form appears on your sc reen. The cursor is
located in the Print Interval: field.
list bcms agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Print Interval: immediate
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-6. Report Scheduler Form
Issue 4 September 1995
4-25
Page 51
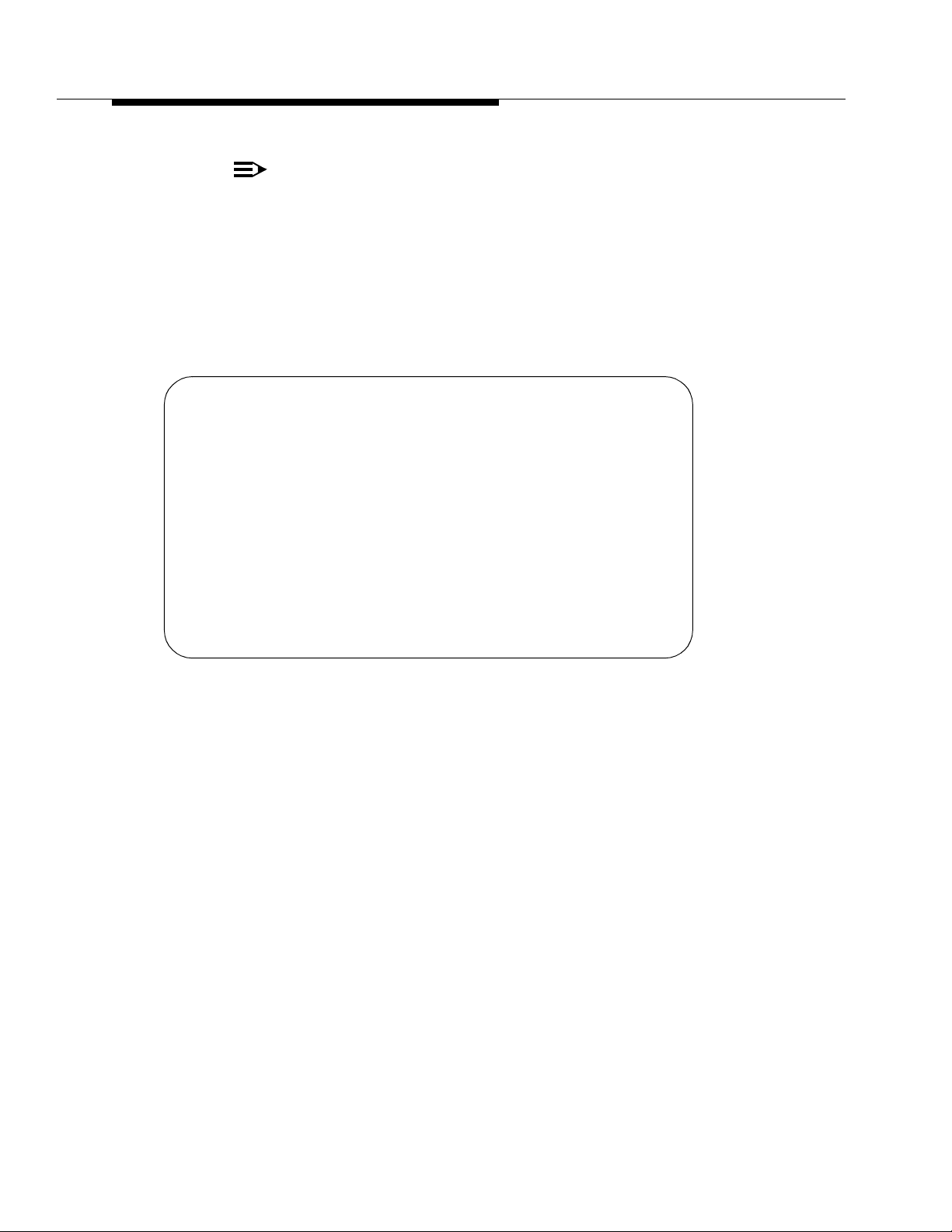
BCMS Report Generati on
NOTE:
If you do not have a printer direc t ly connected to your terminal, you
can immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing
ENTER.
3. Enter schedule and press
RETURN.
— T he Pr i n t T ime: fi e l d appears beneath the Print Interval: field, and
fields for each day of the week appear at the bottom of the form.
The cursor is located in the Print T ime: field.
list bcms agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-7. Report Scheduler Form with the Print Interval Set to
scheduled
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
— The cursor moves to the Sun: field.
5. Enter y for the day(s) you wa nt th e report prin ted. Us e
cursor to the next field.
6. When you are finished, press
— The report has been scheduled, and the system presents the enter
command: prompt.
Scheduling a Daily Report to Print
To schedule this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx schedule (where ##
is a valid agent extension or login ID measured by BCMS). The first
specified day is referred to as the start day, while the second day is
referred to as the stop day. If no start day is given, the report displays data
accrued for the previous six days and data a ccrued through the m ost
recently com pleted interval (hour or half-hour).
4-26 Issue 4 September 1995
RETURN to move the
ENTER.
Page 52
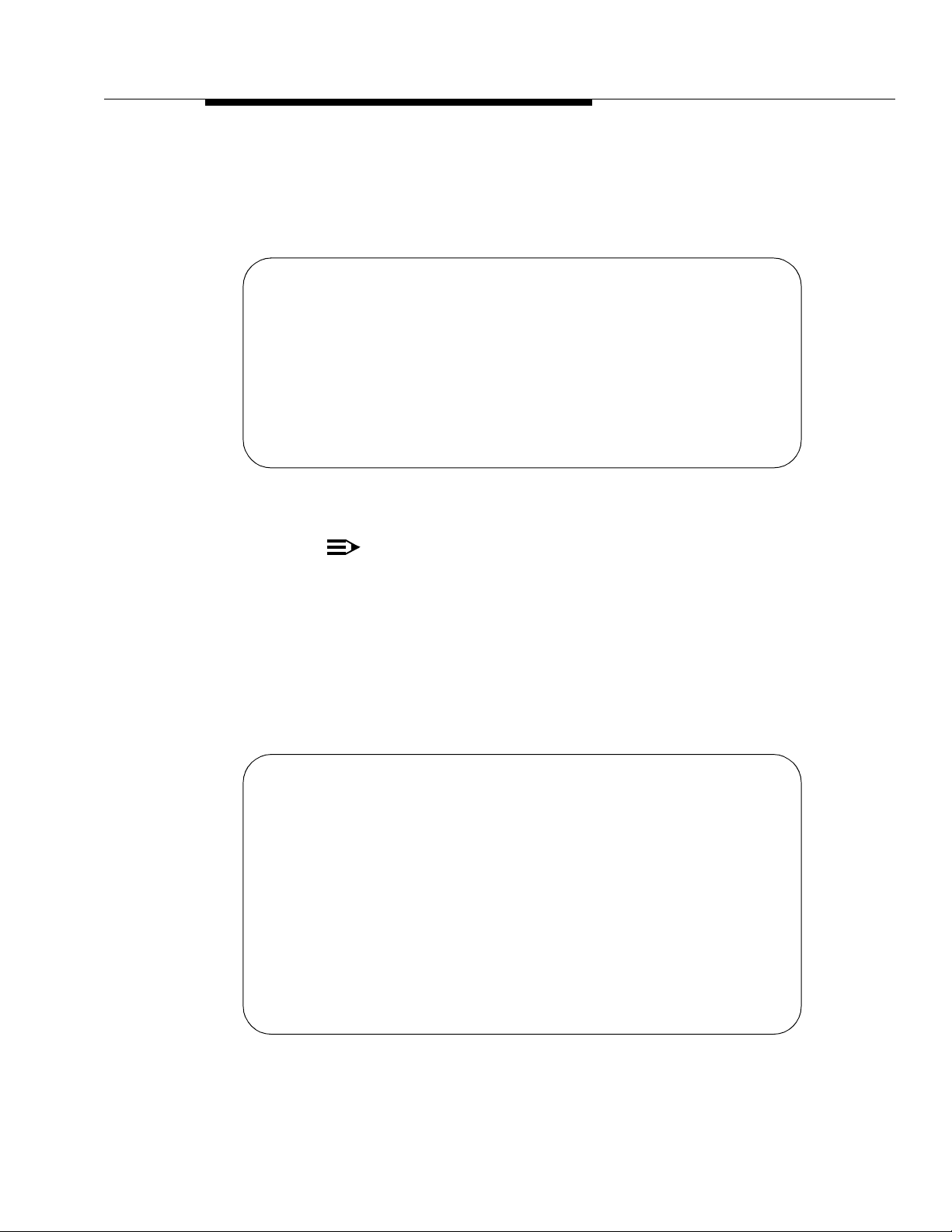
BCMS Agent Report
2. Press RETURN.
— Th e R eport Scheduler form appears on your sc reen. The cursor is
located in the Print Interval: field.
list bcms agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx
Print Interval: immediate
Screen 4-8. Report Scheduler Form
REPORT SCHEDULER
NOTE:
If you do not have a printer direc t ly connected to your terminal, you
can immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing
ENTER.
3. Enter schedule and press
RETURN.
— T he Pr i n t T ime: fi e l d appears beneath the Print Interval: field, and
fields for each day of the week appear at the bottom of the form.
The cursor is located in the Print Time: field.
list bcms agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms agent ##
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-9. Report Scheduler Form with the Print Interval Set to
Issue 4 September 1995
scheduled
4-27
Page 53

BCMS Report Generati on
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
— The cursor moves to the Sun: field.
5. Enter y for day(s) you want the report printed. Use
cursor to the next field.
6. When you are finished, press
— The report has been scheduled, and the system presents the enter
command: prompt.
BCMS Agent Summary Report
This report is similar to the BCMS Agent Report except that this report provides
one line of data for each agent. Yo u can specify one or more agents by entering
agent IDs or extensions. An agent does not appear on the report if there is no
data for that agent. If you specify that yo u wa nt the report to include more than
one time period, and the data exists for one or more, but not all of the specified
times, the system uses the available data to calculate and display the one-line
summary; the system does not identify which times are not included in the
calculations.
NOTE:
BCMS c an track agents based on their phone numbers, or based on login
IDs. If BCMS/VuStats Login IDs is optioned, BCMS tracks login IDs.
RETURN to move the
ENTER.
list bcms summary agent 4222-4224 4869 time 8:00-12:00
BCMS AGENT SUMMARY REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
AGENT NAME CALLS TIME CALL TIME OTHER CALLS TIME STAFFED TIME
s-jones 10 1:15 7:30 25:00 10:40 1 4:00 60:00 :20
t-anderson 18 1:40 18:00 4:20 :00 2 3:20 60:00 1:00
j-jacobsen 10 1:20 8:20 16:10 :00 0 :0 38:00 :10
----------- ----- ------ ------- ------- ------- ----- ----- -------- -----SUMMARY 38 1:28 33:50 45:30 10:40 3 3:33 158:00 1:30
Time: 8:00-12:00
AVG TOTAL TOTAL TOTAL AVG TOTAL TOTAL
ACD TALK AFTER AVAIL AUX/ EXTN EXTN TIME HOLD
Screen 4-10. BCMS Agent Summary Report — Hourly Summary
4-28 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 54

BCMS Agent Summary Report
NOTE:
4222-4224 in the command line could be a login ID or an extension,
depending on whether BCMS/VuStats Login IDs is administered.
list bcms sum agent 4222-4223 4869 day 5/14
BCMS AGENT SUMMARY REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
AGENT NAME CALLS TIME CALL TIME OTHER CALLS TIME STAFFED TIME
s-jones 10 1:15 7:30 25:00 10:40 1 4:00 60:00 :20
t-anderson 18 1:40 18:00 4:20 :00 2 3:20 60:00 1:00
j-jacobsen 10 1:20 8:20 16:10 :00 0 :0 38:00 :10
----------- ----- ------ ------- ------- ------- ----- ----- -------- -----SUMMARY 38 1:28 33:50 45:30 10:40 3 3:33 158:00 1:30
Day: 5/14
AVG TOTAL TOTAL TOTAL AVG TOTAL TOTAL
ACD TALK AFTER AVAIL AUX/ EXTN EXTN TIME HOLD
Screen 4-11. BCMS Agent Summary Report — Daily Summary
NOTE:
4222-4224 in the command line could be a login ID or an extension,
depending on whether BCMS/VuStats Login IDs is administered.
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions
This report presents header infor m ation at the top of each page. This information
includes the comman d entered to generate the report, the page number of the
report, the title of the report, and the time and date the report was generated. If
this is a time report and there are more than 11 time intervals, this report is
displayed on m ult iple pages. A s um ma ry ti me i s displa ye d on t he last page of the
report.
TIME/DAY — The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Time is always ex pressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are optional.
Reports always start at the earliest time interval (either hour or half-hour). If no
start time is given, the most recent time interval is the default. A stop time
requires an associated start time. If no stop time is g iven, onl y the start
interval/day is used. If no start time or stop time is given, the most current
day
interval/day is u sed. If you specify
in the command and do not include a start
day or stop day, th e report displays data for the current day accrued through the
most recently co m pleted interval (hour or half-hour).
Issue 4 September 1995
4-29
Page 55

BCMS Report Generati on
_
AGENT NAME — The name of the agent. If no name is administered, the agent’s
extension is displayed in the form
ACD CALLS — T he numb e r of ACD c alls answered by this agent for all splits
during the reporting interval. This value includes calls that flowed in from other
splits and Direct Agent calls.
AVG TALK TIME — The average duration of ACD calls for all splits the agent
was logged into. This value includes time spent t alking but does not include the
amount of time the agent was holding an ACD call or ring time at the agent’s
voice terminal. The calculation is:
AVG TALK TIME =
TOTAL AFTER CALL — The total amount of time that the agent spent in
call-related or non-call-related ACW work states for all splits during the re porting
interval. This does not include time spent on direct incoming or outgoing calls
while in ACW. If an agent entered ACW in one interval, but ended ACW in
another interval, the appropriate amount of ACW time is credited to each of the
intervals.
EXT 65432.
_ ________________________________
Total ACD Talk Time
Total Number o f ACD Calls Answered
TOTAL AVAIL TIME — The sum of the time that the agent was available to
receive ACD calls during the current interval. During this time, the agent:
■ Was in Auto-In or Manual-In work modes for at least one split
■ Was not in AC W in any split
■ Was not on any call or placing any call
■ Did not have ringing calls
TOTAL AUX/OTHER — The sum of the time that the agent has the AUX button
pressed and is not doing any th i ng els e f o r a n y of th e o ther splits (that is, the sum
of the time that the agent is in AUX work mode for all splits). This value does not
include time the agent spent on an EXTN call or in Manual-In, Auto-In, or ACW
mode for another split. Note that if the agent was in Other for all logged-in splits
that time is reflected here. For example, ringing calls can cause several seconds
of AUX time to accrue.
For the agent report, any non-ACD call time is totaled in the AVG EXTN TIME
column. Two points of contrast are:
1. The measurement TOTAL AUX/OTHER is time-interval based, rather than
being call related. For example, assuming that the previously identified
stipulations are met, then if the agent is in AUX from 9:55 to 10:05, five
minutes is pegged in the 9:00 to 10:00 time interval and five minutes is
pegged in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval.
4-30 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 56

BCMS Agent Summary Report
2. The measurement AVG EXTN TIME is call related. For example, if an agent
is on a non-ACD call from 9:55 to 10:05, the call and ten minutes of EXTN
time is pegged in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval.
Beca u se the agent report includes some call-related items, the su m of all
items for a given hour cannot exactly equal 60 minutes.
EXTN CALLS — The tota l nu mber of non-ACD incoming and outgoing calls for
this agent during the reporting interval. O nly those non-ACD calls that are
originated and/or received while the agent is logged into at least one split are
counted.
AVG EXTN TIME — The average amount of time that the agent spent on
non-ACD calls while logged into at least one split during the reporting interval.
This average does not inc lude time when the agent was holding the EXTN call.
The calcu lati on is:
AVG EXTN TIME =
TOTAL TIME STAFFED — The total time that the agent spent logged into at
least on e split during the reporting interval. Staff time is clocked for an agent who
is in multiple splits as long as the agent is logged int o any spl it. Concurrent times
for each split are not totaled.
Total Ext Time
_ _______________________
Total Number o f Ext Calls
TOTAL HOLD TIME — The total time that the agent placed ACD calls on hold.
This time is the
TOTAL HOLD TIME does not include the hold time for non-ACD calls.
SUMMARY — The total of each of the columns that do not contain averages.
Columns that do contain averages are the total time divide by the number of
calls.
c aller’s hold time
and is independent of the state of the agent.
Displaying the BCMS Agent Summary Report
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly/half-hourly intervals or daily
intervals an d display the report on your terminal.
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To display this report, perform the following st eps:
1. Enter list bcms summary agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx (where ##
is a valid agent extension or login ID measured by BCMS). The first
specified time is referred to as the start time, while the second time is
referred to as the stop time. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format;
however, the hours may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-31
Page 57

BCMS Report Generati on
NOTE:
Minutes are always expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the
report displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or
half-hour).
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS A gent Summary Report appears on your screen.
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
Displaying a Daily Report
To display this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx (where ##
is a valid agent extension or login ID measured by BCMS). The first
specified day is referred to as the start day, while the second day is
referred to as the stop day. If no start day is given, the report displays data
accrued for the previous six days and data a ccrued through the m ost
recently com pleted interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
RETURN.
— The BCMS A gent Summary Report appears on your screen.
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
Printing the BCMS Agent Summary Report
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly/half-hourly intervals or daily
intervals and print the report. If you have a printer directly connected to your
terminal, you may print reports using the instructions provided below. If you do
not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, consult the instructions for
scheduling reports to print to the system printer.
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx print
(where ## is a valid agent extension or login ID measured by BCMS). The
first specified time is referred to as the start time, while the second time is
referred to as the stop time. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format;
4-32 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 58

BCMS Agent Summary Report
NOTE:
however, the hours may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number.
Minutes are always expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the
report displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or
half-hour).
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCM S A gent Summary Report prints on the printer at tached to
your terminal.
Printing a Daily Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx print
(where ## is a valid agent extension or login ID measured by BCMS). The
first specified day is referred to as the start day, while the second day is
referred to as the stop day. If no s tart day is given, the report displays data
accrued for the previous six days and data accrued through the most
recently com pleted interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Agent Report Summary prints on the printer attached to
your terminal.
Scheduling the BCMS Agent Summary Report to Print
Th e R eport Scheduler allows you to schedule the day or days for the system to
print the report. If you do not have a printer directly connected to your terminal,
you may use the Report Scheduler feature to print the report immediately to the
system printer. The data for this report can be collected in hourly/half-ho urly
intervals or daily interval s.
Scheduling an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report to Print
To schedule this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
schedule (where ## is a valid agent exten sion or login ID measured by
BCMS). The first specified time is referred to as the start time, while the
second time is referred to as the stop time. Time must be displayed in
24-hour format; however, the hours may be indicated as either a 1- or
Issue 4 September 1995
4-33
Page 59
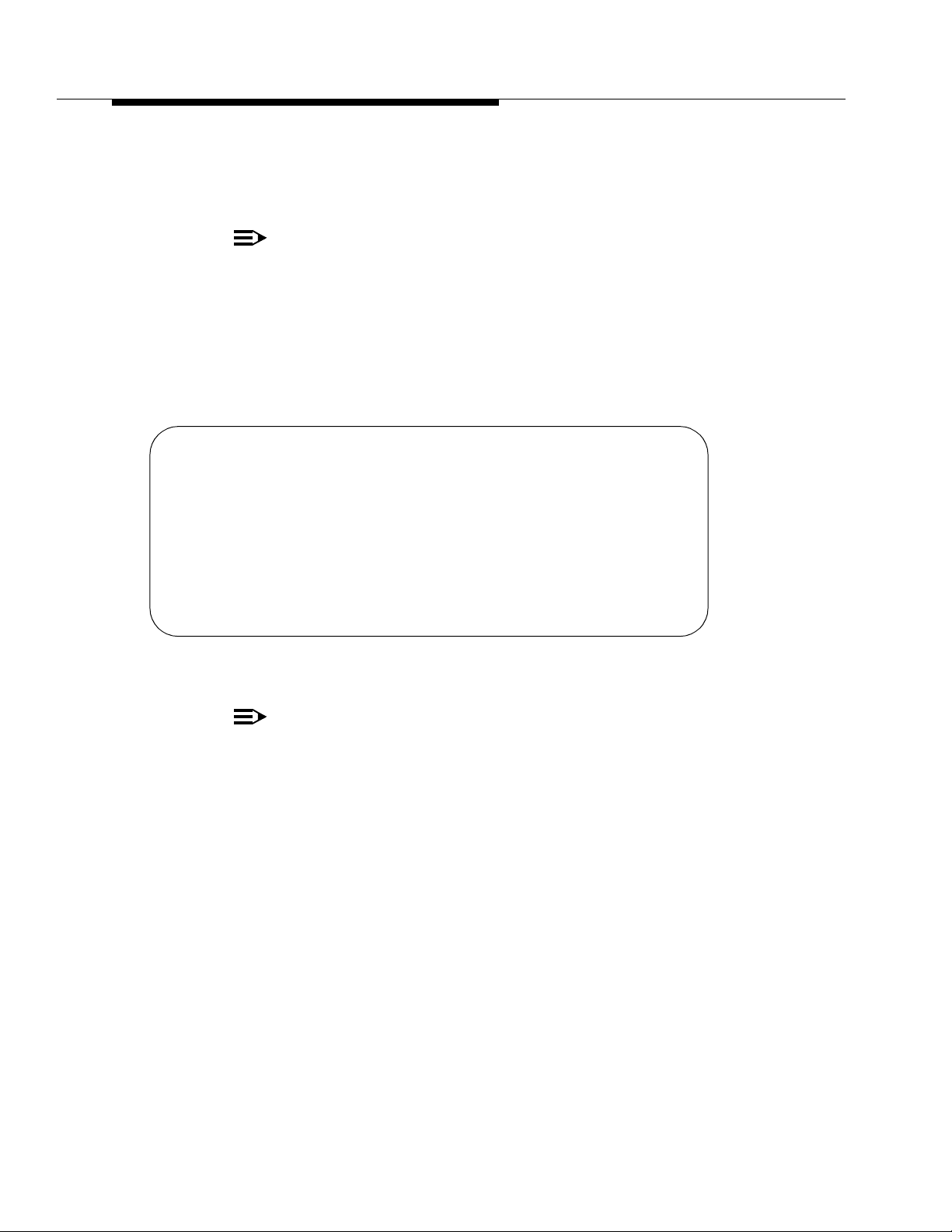
BCMS Report Generati on
NOTE:
2-digit number. Minutes are always expressed as two digits. If no start
time is given, the report displays data accrued for the previous 24 time
intervals (hour or half-hour).
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— Th e R eport Scheduler form appears on your scre en. The cursor is
located in the Print Interval: field.
list bcms summary agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms summary agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Print Interval: immediate
Screen 4-12. Report Scheduler Form
NOTE:
If you do not have a printer direc t ly connected to your terminal, you
can immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing
ENTER.
REPORT SCHEDULER
3. Enter schedule and press
— T he Pr i n t T ime: fi e l d appears beneath the Print Interval: field, and
fields for each day of the week appear at the bottom of the form.
The cursor is located in the Print T ime: field.
4-34 Issue 4 September 1995
RETURN.
Page 60

BCMS Agent Summary Report
list bcms summary agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms summary agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-13. Report Scheduler Form with the Print Interval Set to
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
— The cursor moves to the Sun: field.
5. Enter y for the day(s ) y o u w an t t h e r eport printed. Us e
cursor to the next field.
6. When you are finished, press
ENTER.
— The report has been scheduled, and the syst em presents the enter
command: prompt.
Scheduling a Daily Report to Print
To schedule this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx schedule
(where ## is a valid agent extension or login ID measured by BCMS). The
first specified day is referred to as the start day, while the second day is
referred to as the stop day. If no s tart day is given, the report displays data
accrued for the previous six days and data accrued through the most
recently com pleted interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
RETURN.
— Th e R eport Scheduler form appears on your sc reen. The cursor is
located in the Print Interval: field.
scheduled
RETURN to move the
Issue 4 September 1995
4-35
Page 61

BCMS Report Generati on
list bcms summary agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms summary agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx
Print Interval: immediate
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-14. Screen 4-14. Report Scheduler Form
NOTE:
If you do not have a printer direc t ly connected to your terminal, you
can immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing
ENTER.
3. Enter schedule and press
RETURN.
— T he Pr i n t T ime: fi e l d appears beneath the Print Interval: field, and
fields for each day of the week appear at the bottom of the form.
The cursor is located in the Print T ime: field.
list bcms summary agent ## day xx/xx xx/xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms summary agent
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-15. Report Scheduler Form with the Print Interval Set to
scheduled
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
— The cursor moves to the Sun: field.
4-36 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 62

BCMS Split Report
5. Enter y for day(s) you want the report printed. Use RETURN to move the
cursor to the next field.
6. When you are finished, press
— The report has been scheduled, and the syst em presents the enter
command: prompt.
BCMS Split Report
Th e B C MS Split Report provides traffic information for the specified split nu mber.
Depending on specifics from the command line, the information may be
displayed as either a time interval or a daily summary. If neither
time
specified,
the previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour), including data from the most
recently completed time interval. To get information on the current time interval,
you must use a monitor bcms command. Screen 4-16 shows the BCMS Split or
Skill Summary Report — Hourly, and Screen 4-17 shows the BCMS Split or Skill
Report — Daily.
NOTE:
When analyzing this report, keep the following things in mind:
■ All averages are for completed cal ls only.
■ A completed call may span more than one time interval. ACD calls that are
in process (have not terminated) are counted in the time interval in which
they terminate. For example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00 to 11:00
time in t er v a l, but terminates in the 11:00 to 12:00 time interval, the data for
this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00 time interval.
is the default. In this case, the report displays data accrued for
ENTER.
time
nor
day
is
■ Asterisks within a field indicate that the maximum for that field has been
exceeded .
Issue 4 September 1995
4-37
Page 63

BCMS Report Generati on
list bcms split 3 time 8:00-10:00
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Split: 03
Split Name: services Acceptable Service Level: 17
AVG AVG AVG TOTAL TOTAL % IN
ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK AFTER FLOW FLOW AUX/ AVG SERV
TIME CALLS ANS CALLS TIME TIME CALL IN OUT OTHER STAFF LEVL
8:00- 9:00 32 :25 4 :32 5:15 16:00 3 5 3:30 4.0 80*
9:00-10:0 8 :07 1 :03 3:20 :00 0 0 9:30 2.2 85
----------- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ------- ---- ---- ------ ----- --SUMMARY 40 :21 5 :26 4:52 :26 3 5 13:00 3.1 81
BCMS SPLIT REPORT
Screen 4-16. BCMS Split or Skill Report — Hourly
* Acceptable service level changed.
Split is displayed as "Skill" when EAS is optioned.
list bcms split 3 day 5/14/95
BCMS SPLIT REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Split: 03
Split Name: services Acceptable Service Level: 17
DAY CALLS ANS CALLS TIME TIME CALL IN OUT OTHER STAFF LEVL
5/14/95 40 :21 5 :26 4:52 17:20 3 5 13:00 3.1 81
-------- ----- ----- ---- ----- ----- ------- ---- ---- ------- ----- --SUMMARY 40 :21 5 :26 4:52 17:20 3 5 13:00 3.1 81
AVG AVG AVG TOTAL TOTAL % IN
ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK AFTER FLOW FLOW AUX/ AVG SERV
Screen 4-17. BCMS Split or Skill Report — Daily
Split is displayed as "Skill" when EAS is optioned.
NOTE:
Xs are used to show field size and are not dis played as p art of the form.
4-38 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 64
BCMS Split Report
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions
This report presents header infor m ation at the top of each page. This information
includes the comman d entered to generate the report, the page number of the
report, the title of the report, and the time and date the report was generated. If
this is a time report and there are more than 10 time intervals, this report is
displayed on multiple pages. A daily summary report is displayed on the last
page of the report.
SPLIT — The split number specified with the command line.
SPLIT NAME — Displays the name that is administered for this split number. If
no name exists, BCMS displays the split extension (for example, EXT 65432).
ACCEPTABLE SERVICE LEVEL — The desired time to answer for a given hunt
group. Timing for a call begins when the call enters the hun t group queue.
TIME/DAY — The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Time is always ex pressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are optional.
Reports always start at the earliest time interval (either hour or half-hour). If no
start time is given, the oldest time interval is the default. A stop time requires an
associated start time. If no stop time is given, the last completed time interval
(hour or half-hour) is the default. If no start or stop time is given, the report
day
displays data accrued for the previous 24 t im e in tervals. If you specify
in the
command and do not include a start day or stop day, the report displays data
accrued for the previous six days and data accrued through the most recently
completed interval (hour or half-hour).
ACD CALLS — The number of ACD calls completed for this split during the
current interval. This number also includes calls that flowed in from other splits
and Direct Agent calls.
AVG SPEED ANS — The average am ount of ti me answered ACD calls (split and
Direct Agent) spent in queue and ringing at an agent’s station before being
answered during the reporting interval. Calls that flowed in do not have queue
time from the previous split included in this average. Th is calculation is:
AVG SPEED ANS =
Sum o f Each Answered Call′s Time In Queue + Time Ringing at the Agent ′s Extension
_ _____________________________________________________________________________
Total Number o f ACD Calls Answered
NOTE:
Keep the following things in mind :
■ This value does not in c l ude time listening to a forc ed first
announcement.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-39
Page 65

BCMS Report Generati on
■ A completed call may span more than one time period. ACD calls
ABAND CALLS — The total number of ACD calls that have hung up while
waiting to be answered during this time interval. This value includes those calls
that have abandoned while in queue or while ringing. Calls that are not queued
(because the queue is full, the caller receives a forced first announcement and
abandons during the announcement, or no agents are staffed) are not counted
as abandoned. Also, calls that abandon while on hold are not counted as
abandoned.
AVG ABAND TIME — The average time before an ACD call abandons. This
value does not include any tim e s pent i n an o ther s plit’s queue before flowing into
this split. The calculation is:
AVG ABAND TIME =
that are in process (have not terminated ) are counte d i n the time
period in which they terminate. For example, if an ACD call begins
in the 10:00 to 11:00 time period, but terminates in the 11:00 to
12:00 time period, the data for this call is counted in the 11:00 to
12:00 time period.
_ ______________________________
Total Abandon Time
Total Number o f Abandoned Calls
NOTE:
T hi s va lu e does not i nclude tim e l is t en i ng to a forced first announcement or
calls that
abandon
while listening to a forced first announcement.
AVG TALK TIME — The average amount of time agents are active on ACD calls
(split and direct agent) for each split. This includes time spent talking. The
calculation does not include ring time at an agent’s voice terminal or time spent
on hold. The calculation is:
Total ACD Talk Time
AVG TALK TIME =
_________________________
Total Number o f ACD Calls
TOTAL AFTER CALL — The amount of time that the agents in this split spent in
call-related or n oncall-r elat ed ACW mode during the reporting interval. T his value
includes time spent on direct incoming or outgoing c a lls while in ACW. If an
agent entered ACW in one interval, but left ACW in an other interval, each interval
is credited with ACW time.
FLOW IN — The total number of completed calls that this split received as a
coverage point (intraflowed) from another BCMS-measured split, or are call
forwarded (interflowed) to this split during the reporting interval. This total does
not include calls that are interflowed from a remote switch by means of the Look
Ahead Interflow feature. FLOW INs are recorded when a call ends.
4-40 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 66
BCMS Split Report
FLOW OUT — The total number of calls queued to this split that were:
■ Successfully sent to the split’s coverage point after qu eui n g for the
■ Forwarded-out via c all forwarding
■ Forwarded-out via a route to station extension vector step
■ Answered via the Call Pickup feature
■ Forwarded-out via Look Ahead Interflow
■ First queued to this s plit and answered by the second or th ird split queued
■ Were redirected back to this split or its coverage path due to Redirect On
FLOW OUTs are recorded when a c all ends.
NOTE:
In a multiple split-queuing environment, inflows and outflows become a bit
more complicated. Consider the following scenarios:
specified
don’t answer
interval. (This does not include calls that went to
coverage based on any other criterion.)
to
No Answer timing.
■ If a multiply queued call is answered in a non primary split (that is, a
second or third split), an outflow is recorded to the statistics for the
first split, and an in f low and an answer are recorded t o th e s ta tistics
for the answering split. For example, suppose there are three splits
numbered 1 t hrough 3. A call comes in for split 1, but all agents ar e
busy on this split. The call then goes into queue for splits 2 and 3.
An agent on split 3 answers the call. In thi s example, an outflow is
recorded to the statistics for split 1, and an inflow and an answer
are recorded to the statistics for split 3. Th e st atistics for split 2 are
unaffected because the call was not answered in this split. This
scenario is shown in the following table.
Call Answered by Nonprimary Split
Split Pegging
Split 1 Split 2 Split 3
BCMS outflow dequeued inflow answer
If the call is answered in t he prima ry split, no inflows or outflows are
recorded t o the statistics for any split. Splits 2 and 3 record the call
as dequeued.
■ If a call is queued on three splits (for example, splits 1, 2, and 3,
with split 1 being the primary split), then encounters a route-to
command that sends the call to another VDN, that queues to
different splits (for example, splits 4 and 5), an outflow is recorded
to the statistics for split 1. If the call is answered in split 4, an
Issue 4 September 1995
4-41
Page 67
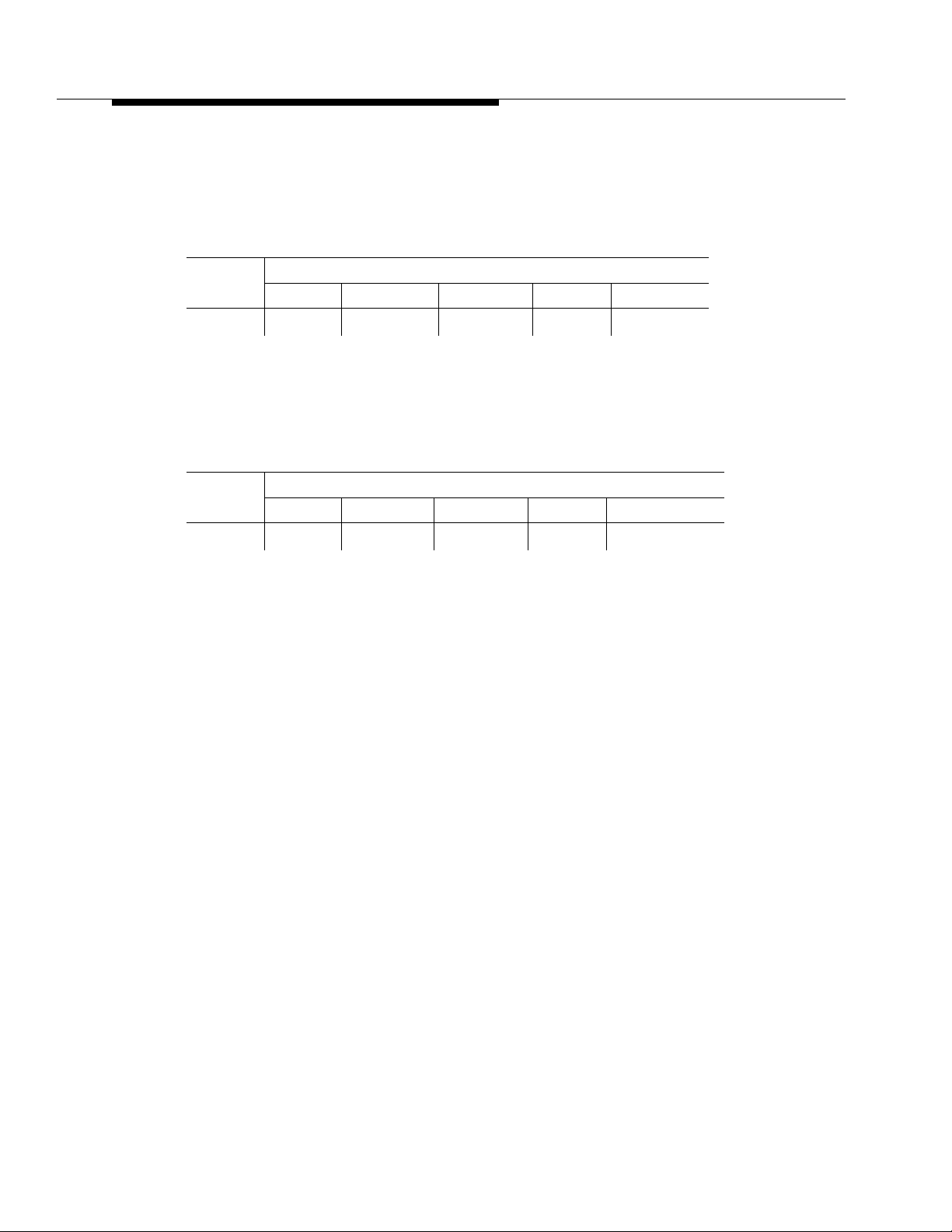
BCMS Report Generati on
Call Answered by Primary Split after a Route to VDN
BCMS outflow dequeued dequeued answer dequeued
Call Answered by Non-Primary Split after a Route to VDN
BCMS outflow dequeued dequeue d outflow inflow answer
answer is recorded t o the statistics for split 4. However, no inflow is
recorded to the statistics for split 4. This scenario is shown in the
following table.
Split Pegging
Split 1 Split 2 Split 3 Split 4 Split 5
If the call is answered on split 5, an outflow is recorded for the
statistics t o split 4, and both an inflow and an answer are recorded
to the statistics for split 5. This scenario is shown in the following
table.
Split Pegging
Split 1 Split 2 Split 3 S plit 4 Split 5
Similarly, if a multiply queued call routes to another split, an outflow
is recorded to the statistics f or the primary split, but no inflow is
recorded to the statistics for the routed-to split.
TOTAL AUX/OTHER — The total time that logged-in agents in this split were
unavai lable to receive calls during the reporting interval. T his value includes time
spent on non-ACD calls while in AUX for this split. This value does not in clude the
time agents spent on another split’s calls or in ACW for another split.
Note that a split totals AUX TIME whenever any agent logs into the split and :
■ Receives a EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
■ Makes a EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
■ Hits his/her AUX button
■ Other
Furthermore, the split report measurement AUX TIME is time-interval base d,
since it is not directly related to a ca l l. For example, if an agent is in AUX for any
of the previously identified reasons from 9:55 to 10:05, then five minutes is
pegged in the 9:00 to 10:00 time interval and five minutes is pegged in the 10:00
to 11:00 time interval.
If you perform these calculations for each agent with in a split and total them —
the calculated number should generally be the same as displayed on the split
report. However, because of differences in how the agent and split reports
handle EXTN calls you may (occasionally) see different numbers between the
two reports.
4-42 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 68

BCMS Split Report
_
AVG STAFF — The aver age number of agents who were logged into this split
(staffed) during the reporting interval.
% IN SERV LEVL — The percentage of calls answered within the administered
service l evel .
% IN SERV LEVL =
where
accepted is calls answered whose queue time was less than or equal to the
administered service level for the split
dequeued is a call that encountered the split’s queue, but that was NOT
answered, abandoned, or outflowed. This occurs with multiple split queuing.
Total Sta ff Time
AVG STAFF =
_ _________________________________________
ACD calls + abandons + out f lows + dequeued
_ _____________
Time Interval
Accepted *100
SUMMARY — For those columns that specify averages, the summary is an
average for the entire reporting interval. For the ACD CALLS, ABAND CALLS,
TOTAL AFTER CALL, FLOW IN, FLOW OUT, AUX TIME, and TOTAL HOLD TIME
columns, the summary is the sum of individual time intervals or specified days.
Displaying the BCMS Split Report
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly or half-hourly intervals and daily
intervals, and to display the report on your terminal.
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To display this report, perform the following st eps:
1. Enter list bcms split ## time xx:xx xx:xx (w here "##" is an
administered split measured by BCMS). If the split is only one digit (for
example, split 5), just enter the single digit. The first specified time is
referred to as the start time, while the second time is referred to as the
stop ti me. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format; however, the hours
may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number. Minutes are always
expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the report displays data
accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour).
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-43
Page 69
BCMS Report Generati on
2. Press RETURN.
— The BCMS Split Report appears on your screen.
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
Displaying a Daily Report
To display this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms split ## day xx/xx xx/xx (where ## is an
administered split measured by BCMS). If the split is only one digit (for
example, split 5), just enter the single digit. The first specified day is
referred to as the start day, whi l e the second day is referred to as the stop
day. If no start day is given, the report displays data accrued for the
previous six days plus data accrued through the most recently completed
interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Split Report appears on your screen.
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
Printing the BCMS Split Report
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly or half-hourly intervals and daily
intervals, and to print the report. If you have a printer directly connected to your
terminal, you may print reports using the instructions provided below. If you do
not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, consult the instructions in
the next section for scheduling reports to print to the system printer.
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms split ## time xx:xx xx:xx print (where ## is
an administered split measured by BCMS). If the split is only one digit (for
example, split 5), just enter the single digit. The first specified time is
referred to as the start time, while the second time is referred to as the
stop time. Time must be disp l ayed in 24-hour format; however, the hours
may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number. Minutes are always
expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the report displays data
accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour).
4-44 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 70
BCMS Split Report
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Split Report prints on the printer attached to your
terminal.
Printing a Daily Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms split ## day xx/xx xx/xx print (where ## is
an administered split measured by BCMS). If the split is only one digit (for
example, split 5), just enter the single digit. The first specified day is
referred to as the start day, while the second day is referred to as the stop
day. If no start day is given, the report displays data accrued for the
previous six days plus data accrued through the most recently completed
interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Split Report prints on the printer attached to your
terminal.
Scheduling the BCMS Split Report to Print
Th e R eport Scheduler allows you to schedule the day or days for the system to
print the report. If you do not have a printer directly connected to your terminal,
you may use the Report Scheduler feature to print the report immediately to the
system printer. The data for this report can be collected in hourly/half-ho urly
intervals or daily interval s.
Scheduling an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report to Print
To schedule this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms split ## time xx:xx xx:xx schedule (where
## is an administered split measured by BCMS). If the split is only one
digit (for example, split 5), just enter the single digit. The first specified
time is referred to as the start time, while the second time is referred to as
the stop time. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format; however, the
hours may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number. Min u tes are
always expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or
half-hour).
Issue 4 September 1995
4-45
Page 71

BCMS Report Generati on
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— Th e R eport Scheduler form appears on your scre en. The cursor is
located in the Print Interval: field.
list bcms split ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms split ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Print Interval: immediate
Screen 4-18. Report Scheduler Form
If you do not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, you can
immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing
3. Enter schedule and press
— T he Pr i n t T ime: fi e l d appears beneath the Print Interval: field, and
fields for each day of the week appear at the bottom of the form.
The cursor is located in the Print T ime: field.
REPORT SCHEDULER
ENTER.
RETURN.
4-46 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 72

BCMS Split Report
list bcms split ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms split ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-19. Report Scheduler Form with the Print Interval Set to
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
— The cursor moves to the Sun: field.
5. Enter y for the day(s ) y o u w an t t h e r eport printed. Us e
cursor to the next field.
6. When you are finished, press
ENTER.
— The report has been scheduled, and the syst em presents the enter
command: prompt.
Scheduling a Daily Report to Print
To schedule this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms split ## day xx/xx xx/xx schedule (where ##
is an administered split measured by BCMS). If the split is only one digit
(for example, split 5), just enter the single digit. The first specified day is
referred to as the start day, while the second day is referred to as the stop
day. If no start day is given, the report displays data accrued for the
previous six days plus data accrued through the most recently completed
interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
RETURN.
scheduled
RETURN to move the
— Th e R eport Scheduler form appears on your sc reen. The cursor is
located in the Print Interval: field.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-47
Page 73
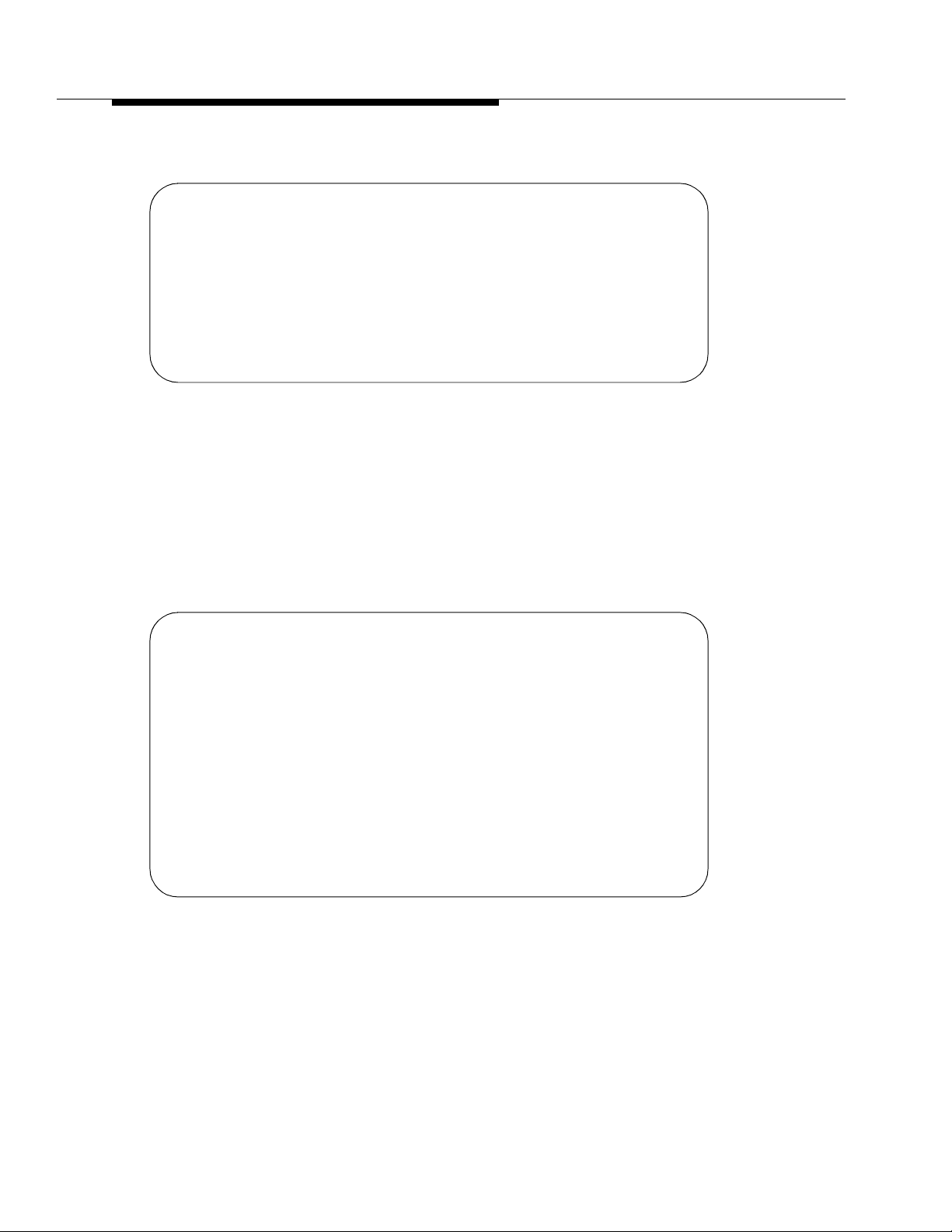
BCMS Report Generati on
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms split ## day xx/xx xx/xx schedule
Print Interval: immediate
Screen 4-20. Report Scheduler Form
If you do not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, you can
immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing
REPORT SCHEDULER
ENTER.
3. Enter schedule and press
RETURN.
— T he Pr i n t T ime: fi e l d appears beneath the Print Interval: field, and
fields for each day of the week appear at the bottom of the form.
The cursor is located in the Print T ime: field.
list bcms split ## day xx/xx xx/xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms split
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-21. Report Scheduler Form with the Print Interval Set to
scheduled
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
— The cursor moves to the Sun: field.
5. Enter y for the day(s) you wa nt th e report prin ted. Us e
cursor to the next field.
6. When you are finished, press
4-48 Issue 4 September 1995
RETURN to move the
ENTER.
Page 74

BCMS Split Summary Report
NOTE:
— The report has been scheduled, and the syst em presents the enter
command: prompt.
BCMS Split Summary Report
This report replaces (and enhances) the BCMS System Report. Customers
wi t h upgr a des from previous DEFINITY releases running BCMS will see that
their scheduled list bcms system command is changed automatically to
the list bcms summary split command to get this new report.
The BCMS Split Summary Report provides traffic measurement information for a
specified group of BCMS splits. Depending on specifics from the command line,
the information may be displayed as either a time interval or daily summary. If
time
nor
day
neither
displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour),
including data from the most recently completed ti m e interval. To get information
on the current time interval, you must use a monitor bcms c ommand. Screen
4-22 shows the BCMS Split or Skill Summary Report — Hourly Summary, a nd
Screen 4-23 shows the BCMS Split or Skill Summary Report — Daily Summary.
is specified,
time
is the defaul t. In this case, the report
This report is similar to the Split Report except tha t thi s r eport prov ides o ne l in e o f
data for each split, a nd that includes all data for the specif i ed times. A split does
not appear on the report if there is no data for that split. If you specify more than
one time period, and data exists for one or more, but not all, of the specified
times, the system uses the available data to calculate and display the one-line
summary; the system does not identify which agents are not included in the
calculations.
Time is always ex pressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are optional.
Reports always start at the earliest time interval (either hour or half-hour). If no
start time is given, the most recent time interval is the default. A stop time
requires an associated start time. If no stop time is g iven, then only the last
interval of data will be used to calculate the one-line display for each split. If you
day
specify
in the command and do not include a start day or stop day, the
report displays data for the current day accrued through the most recently
completed interval (hour or half-hour).
NOTE:
When analyzing this report, keep the following things in mind:
■ All averages are for completed cal ls only.
■ Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has been
exceeded .
Issue 4 September 1995
4-49
Page 75

BCMS Report Generati on
list bcms summary split 3 15 time 9:00-16:00
BCMS SPLIT SUMMARY REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
SPLIT NAME CALLS ANS CALLS TIME TIME CALL IN OUT OTHER STAFF LEVL
Service 8 :07 1 :03 3:20 :00 0 0 9:30 2.2 83*
-------- ----- ----- ---- ----- ----- ------- ---- ---- ------- ----- --SUMMARY 40 :21 5 :26 4:52 16:00 3 5 13:00 3.1 76
Time: 9:00-16:00
AVG AVG AVG TOTAL TOTAL % IN
ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK AFTER FLOW FLOW AUX/ AVG SERV
Sales 32 :25 4 :32 5:15 16:00 3 5 3:30 4.0 75
Screen 4-22. BCMS Split or Skill Summary Report — Hourly Summary
SPLIT is displayed as "SKILL" when EAS is optioned.
list bcms summary split 5 3 day
BCMS SPLIT SUMMARY REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Day: 5/15/95
AVG AVG AVG TOTAL TOTAL % IN
SPLIT NAME CALLS ANS CALLS TIME TIME CALL IN OUT OTHER STAFF LEVL
Sales 32 :25 4 :32 5:15 16:00 3 5 3:30 4.0 75
Service 8 :07 1 :03 3:20 :00 0 0 9:30 2.2 83*
-------- ----- ----- ---- ----- ----- ------- ---- ---- ------- ----- --SUMMARY 40 :21 5 :26 4:52 16:00 3 5 13:00 3.1 76
ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK AFTER FLOW FLOW AUX/ AVG SERV
Screen 4-23. BCMS Split or Skill Summary Report — Daily Summary
SPLIT is displayed as "SKILL" when EAS is optioned.
4-50 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 76

BCMS Split Summary Report
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions
This report presents header infor m ation at the top of each page. This information
includes the comman d entered to generate the report, the page number of the
report, the title of the report, and the time and date the report was generated. If
this is a time report and there are more than 10 time intervals, this report is
displayed on multiple pages. A daily summary report is displayed on the last
page of the report.
TIME/DAY — The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Time is always ex pressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are optional.
Reports always start at the earliest time interval (either hour or half-hour). If no
start time is given, the oldest time interval is the default. A stop time requires an
associated start time. If no stop time is given, the last completed time interval
(hour or half-hour) is the default. If no start or stop time is given, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 24 t im e in tervals. If you specify
command and do not include a start day or stop day, the report displays data
accrued for the previous six days and data accrued through the most recently
completed interval (hour or half-hour).
day
in the
SPLIT NAME — Displays the name that is administered for this split number. If
no name exists, the split extension (for example, EXT 65432) is di splayed.
ACD CALLS — The number of ACD calls completed for this split during the
current interval. This number also includes calls that flowed in from other splits
and Direct Agent calls.
AVG SPEED ANS — The average amount of ti me ACD calls (split and Direct
Agent) spent in queue and ringing at an agent’s station before being answered
during the re porting interval. Calls that flowed in do not have queue time from the
previous split included in this average. This calculation is:
AVG SPEED ANS =
Sum o f Each Completed Call′s Time In Queue + Time Ringing at the Agent ′s Extension
_ _____________________________________________________________________________
Total Number o f ACD Calls Answered
NOTE:
Keep the following things in mind :
■ This value does not in c l ude time listening to a forc ed first
announcement.
■ Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has
been exceeded .
ABAND CALLS — The total number of ACD calls that have hung up while
waiting to be answered during this time interval. This value includes those calls
Issue 4 September 1995
4-51
Page 77

BCMS Report Generati on
that have abandoned while in queue or while ringing. Calls that are not queued
(because the queue is full, the caller receives a forced first announcement and
abandons during the announcement, or no agents are staffed) are not counted
as abandoned. Also, calls that abandon while on hold are not counted as
abandoned.
AVG ABAND TIME — The average time before an ACD call abandons. This
value does not include any tim e s pent i n an o ther s plit’s queue before flowing into
this split. The calculation is:
AVG ABAND TIME =
NOTE:
T hi s va lu e does not i nclude tim e l is t en i ng to a forced first announcement or
calls that
AVG TALK TIME — The aver age duration of ACD calls (split and direct agent)
for each split . Th is includes time spent talking. The calculation does not include
ring time at an agent’s voice terminal or time spent on hold. The calculation is:
AVG TALK TIME =
abandon
_ ______________________________
Total Abandon Time
Total Number o f Abandoned Calls
while listening to a forced first announcement.
Total ACD Talk Time
_________________________
Total Number o f ACD Calls
TOTAL AFTER CALL — The amount of time that the agents in this split spent in
call-related or n oncall-r elat ed ACW mode during the reporting interval. T his value
includes time spent on direct incoming or outgoing c a lls while in ACW. If an
agent entered ACW in one interval, but left ACW in an other interval, each interval
is credited with ACW time.
FLOW IN — The total number of calls that this split received as a coverage point
(intraflowed) from another BCMS-measured split, or are call forwarded
(interflowe d) to this split during the repo rting interval. This total does not include
calls that are interflowed from a remote switch by means of the Look Ahead
Interflow feature. FLOW INs are recorded as they o ccur.
FLOW OUT — The total number of calls queued to this split that were:
■ Successfully sent to the split’s coverage point after queuing fo r the
specified
don’t answer
interval. (This does not include calls that went to
coverage based on any other criterion.)
■ Forwarded-out via call forwarding
■ Answered via the Call Pickup feature
■ Forwarded-out via Look Ahead Interflow
■ Forwarded-out via a "route to" station extension vector step
■ First queued to this split and answered by the second or third split queued
to
4-52 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 78

BCMS Split Summary Report
NOTE:
■ Were redirected back to this split or its coverage path due to Redirect On
No Answer timing.
FLOW OUTs are recorded when a c all ends.
In a vectoring environment, inflows and outflows become a bit more
complicated. Consider the following scenarios:
■ If a multiple queued call is answer ed in a nonprimary split (that is, a
second or third split), an outflow is recorded to the statistics for the
first split, and an in f low and an answer are recorded t o th e s ta tistics
for the answering split. For example, suppose there are three splits
numbered 1 t hrough 3. A call comes in for split 1, but all agents ar e
busy on this split. The call then goes into queue for splits 2 and 3.
An agent on split 3 answers the call. In thi s example, an outflow is
recorded to the statistics for split 1, and an inflow and an answer
are recorded to the statistics for split 3. Th e st atistics for split 2 are
unaffected because the call was not answered in this split. This
scenario is shown in the following table.
Call Answered by Nonprimary Split
Split Pegging
Split 1 Split 2 Split 3
BCMS outflow dequeued inflow answer
If the call is answered in t he prima ry split, no inflows or outflows are
recorded t o the statistics for any split. Splits 2 and 3 record the call
as not recorded.
■ If a call is queued on three splits (for example, splits 1, 2, and 3,
with split 1 being the primary split), then encounters a route-to
command that sends the call to another VDN, that queues to
different splits (for example, splits 4 and 5), an outflow is recorded
to the statistics for split 1. If the call is answered in split 4, an
answer is recorded t o the statistics for split 4. However, no inflow is
recorded to the statistics for split 4. This scenario is shown in the
following table.
Call Answered by Primary Split after a Route to VDN
Split Pegging
Split 1 Split 2 Split 3 Split 4 Split 5
BCMS outflow dequeued dequeued answer dequeued
Issue 4 September 1995
4-53
Page 79

BCMS Report Generati on
_
Call Answered by Non-Primary Split after a Route to VDN
BCMS outflow dequeued dequeued outflow inflow answer
TOTAL AUX/OTHER — The total time that logged-in agents in this split were
unavai lable to receive calls during the reporting interval. T his value includes time
spent on non-ACD calls while in AUX for this split. This value does not in clude the
time agents spent on another split’s calls or in ACW for another split.
If the call is answered on split 5, an outflow is recorded for the
statistics t o split 4, and both an inflow and an answer are recorded
to the statistics for split 5. This scenario is shown in the following
table.
Split Pegging
Split 1 Split 2 Split 3 Split 4 Split 5
Similarly, if a multiple queued call routes to another split, an outflow
is recorded to the statistics f or the primary split, but no inflow is
recorded to the statistics for the routed-to split.
A split totals AUX/OTHER TIME whenever any agent logs into the split and:
■ Receives a EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
■ Makes a EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
■ Hits his/her AUX button
■ Other
Furthermore, the split report measurement AUX TIME is time-interval base d,
since it is not directly related to a ca l l. For example, if an agent is in AUX for any
of the previously identified reasons from 9:55 to 10:05, then five minutes is
pegged in the 9:00 to 10:00 time interval and five minutes is pegged in the 10:00
to 11:00 time interval.
If you perform these calculations for each agent with in a split and total them —
the calculated number should generally be the same as displayed on the split
report. However, because of differences in how the agent and split reports
handle EXTN calls you may (occasionally) see different numbers between the
two reports.
AVG STAFF — The aver age number of agents who were logged into this split
(staffed) during the reporting interval.
Total Sta ff Time
AVG STAFF =
_ _____________
Time Interval
4-54 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 80

BCMS Split Summary Report
% IN SERV LEVL — The percentage of calls answered within the administered
service l evel .
% IN SERV LEVL =
_ _________________________________________
ACD calls + abandons + out f lows + dequeued
where
accepted is calls answered whose queue time was less than or equal to the
administered service level for the split
dequeued is a call that encountered the split’s queue, but that was NOT
answered, abandoned, or outflowed. This occurs with multiple split queuing.
SUMMARY — For those columns that specify averages, the summary is an
average for the entire reporting interval. For the ACD CALLS, ABAND CALLS,
TOTAL AFTER CALL, FLOW IN, FLOW OUT, AUX TIME, and TOTAL HOLD TIME
columns, the summary is the sum of individual time intervals or specified days.
Displaying the BCMS Split Summary Report
Accepted *100
BCMS allows you to collect data in ei ther hourly or half-hourly intervals and daily
intervals, and to display the report on your terminal.
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To display this report, perform the following st eps:
1. Enter list bcms summary split time xx:xx xx:xx. The first
specified time is referred to as the start time, while the second time is
referred to as the stop time. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format;
however, the hours may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number.
Minutes are always expressed as two digits. If no start time is given then
only the last interval of d a ta will be used to calcul ate the one-line display
for each split.
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
RETURN.
— The BCMS Split Summary Report appears on your screen.
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
Issue 4 September 1995
4-55
Page 81

BCMS Report Generati on
Displaying a Daily Report
To display this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary split day xx/xx xx/xx. The first
specified day is referred to as the start day, while the second day is
referred to as the stop day. If no start day is given then the data
accumulated for the last day (the current day) will be used to calculate the
one-line display for each split.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Split Summary Report appears on your screen.
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
Printing the BCMS Split Summary Report
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly/half-hourly intervals or daily
intervals and print the report. If you have a printer directly connected to your
terminal, you may print reports using the instructions provided below. If you do
not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, consult the instructions for
scheduling reports to print to the system printer.
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary split time xx:xx xx:xx print. The
first specified time is referred to as the start time, while the second time is
referred to as the stop time. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format;
however, the hours may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number.
Minutes are always expressed as two digits. If no start time is given then
only the last interval of d a ta will be used to calc ulate the one-line display
for each split.
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Split Summary Report prints on the printer attached to
your terminal.
4-56 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 82
BCMS Split Summary Report
Printing a Daily Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary split day xx/xx xx/xx print. The
first specified day is referred to as the start day, while the second day is
referred to as the stop day. If no start day is given then the data
accumulated for the last day (the current day) will be used to calculate the
one-line display for each split.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Split Summary Report prints on the printer attached t o
your terminal.
Scheduling the BCMS Split Summary Report to Print
Th e R eport Scheduler allows you to schedule the day or days for the system to
print the report. If you do not have a printer directly connected to your terminal,
you may use the Report Scheduler feature to print the report immediately to the
system printer. The data for this report can be collected in hourly/half-ho urly
intervals or daily interval s.
Scheduling an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report to Print
To schedule this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary split time xx:xx xx:xx schedule.
The first specified time is referred to as the start time, while the second
time is referred to as the stop time. Time must be displayed in 24-hour
format; however, the hours may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit
number. Minutes are always expressed as two digits. If no start time is
given then only the last interval of da ta wil l b e used to calculate the
one-line display for each split.
2. Press
— Th e R eport Scheduler form appears on your sc reen. The cursor is
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
RETURN.
located in the Print Interval: field.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-57
Page 83
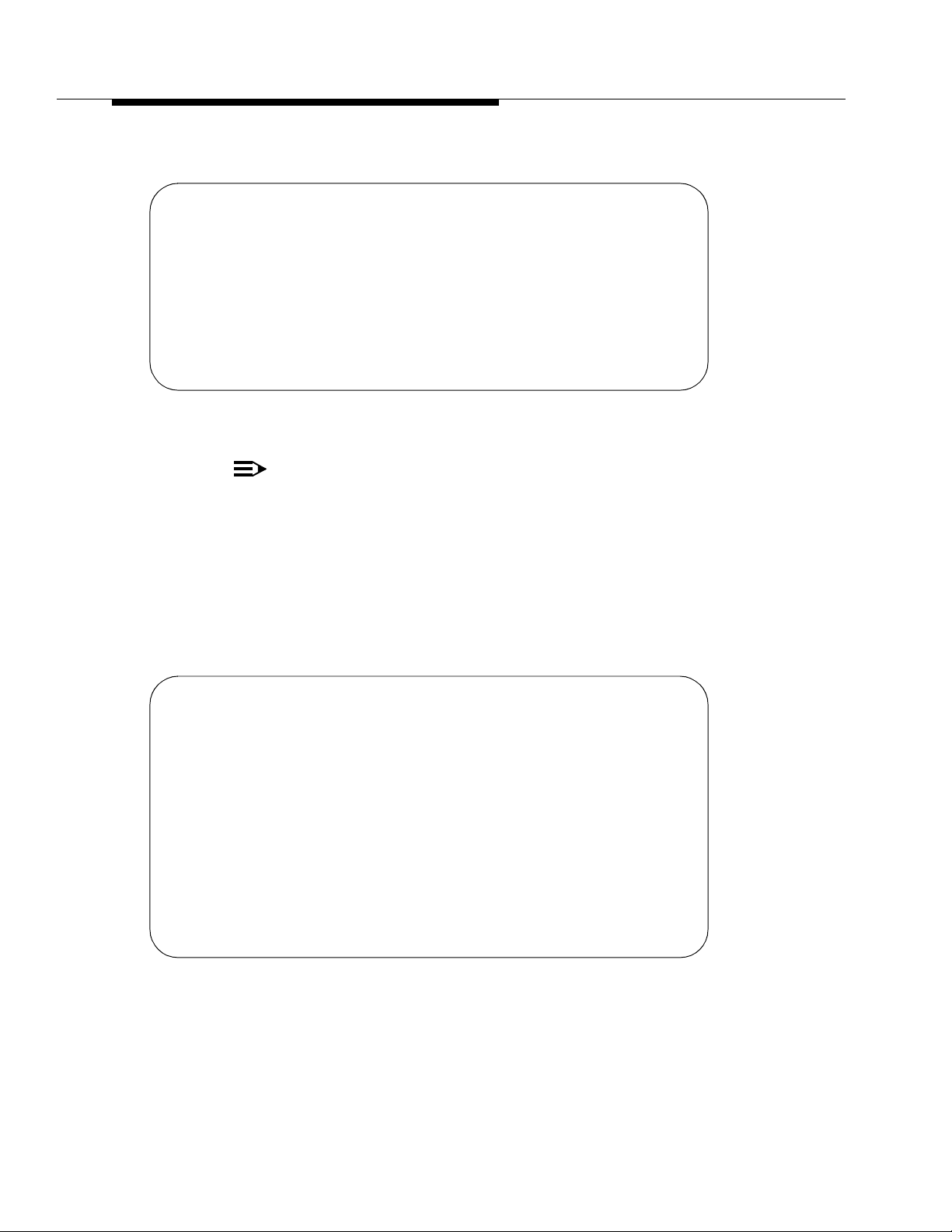
BCMS Report Generati on
list bcms summary split time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms summary split time xx:xx xx:xx schedule
Print Interval: immediate
Screen 4-24. Report Scheduler Form
NOTE:
If you do not have a printer direc t ly connected to your terminal, you
can immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing
ENTER.
REPORT SCHEDULER
3. Enter schedule and press
RETURN.
— T he Pr i n t T ime: fi e l d appears beneath the Print Interval: field, and
fields for each day of the week appear at the bottom of the form.
The cursor is located in the Print T ime: field.
list bcms summary split time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms summary split time xx:xx xx:xx schedule
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-25. Report Scheduler Form with the Print Interval Set to
scheduled
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
— The cursor moves to the Sun: field.
4-58 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 84

BCMS Split Summary Report
5. Enter y for the day( s) yo u w an t th e report prin ted. Us e RETURN to move the
cursor to the next field.
6. When you are finished, press
— The report has been scheduled and the system presents the enter
command: prompt.
Scheduling a Daily Report to Print
To schedule this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary split day xx/xx xx/xx schedule.
T he fi rst specified da y is referred to as the start day, while the second day
is referred to as the stop day. If no start day is given then the data
accumulated for the last day (the current day) will be used to calculate the
one-line display for each split.
2. Press
list bcms summary split day xx/xx xx/xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms summary split day xx/xx xx/xx schedule
Print Interval: immediate
RETURN.
— Th e R eport Scheduler form appears on your sc reen. The cursor is
located in the Print Interval: field.
ENTER.
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-26. Report Scheduler Form
NOTE:
If you do not have a printer direc t ly connected to your terminal, you
can immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing
ENTER.
3. Enter schedule and press
— T he Pr i n t T ime: fi e l d appears beneath the Print Interval: field, and
fields for each day of the week appear at the bottom of the form.
The cursor is located in the Print Time: field.
RETURN.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-59
Page 85
BCMS Report Generati on
list bcms summary split day xx/xx xx/xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms summary split day xx/xx xx/xx schedule
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-27. Report Scheduler Form with the Print Interval Set to
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
— The cursor moves to the Sun: field.
5. Enter y for the day(s) you wa nt th e report prin ted. Us e
cursor to the next field.
6. When you are finished, press
ENTER.
— The report has been scheduled, and the system presents the enter
command: prompt.
BCMS Trunk Group Report
The BCMs Trunk Group Report gives statistical information for all BCMS trunk
groups. The BCM S Trunk Group Report may be used by the ACD administrator
and/or manager to monitor use of the trunk group and to determine the optimal
number o f trunks for the trunk group. Depending on specific s f r o m t h e com m a nd
line, the information may be displayed as either a time interval or a daily
time
nor
day
summary. If neither
is specifi e d,
report displays dat a a ccrued for the previous 24 time interv als (hour or half-hour),
including data from the most recently completed time interval. Screen 4-28
shows the BCMS Trunk Group Time Interval Report, and Screen 4-29 shows the
BCMS Trunk Group Daily Report.
time
is the default. In this case, the
scheduled
RETURN to move the
NOTE:
When analyzing this report, keep the following things in mind:
■ All averages are for completed cal ls only.
4-60 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 86
BCMS Trunk Group Report
■ A completed call may span more than one time interval. ACD calls
that are in process (have no t terminated) are counted in the time
interval in which they terminate. For example, if an ACD call begins
in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval, but terminates in the 11:00 to
12:00 time interval, the data for this call is counted in the 11:00 to
12:00 time interval.
■ Asterisks in a field indicate that the maximum for that field has been
exceeded.
■ A single asterisk at the end of a time or date field indicates that
during the interval, trunk group administration o ccurred which
changed the number of trunks.
list bcms trunk 1 time 8:00 11:00
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 12:59 pm THU APR 20, 1995
Group: 1
Group Name: TG 1 Number of Trunks: 11
| INCOMING | OUTGOING |%ALL %TIME
TIME |CALLS ABAND TIME CCS | CALLS COMP TIME CCS|BUSY MAINT
8:00- 9:00* 23 2 2:15 31.02 1 1 1:36 .96 0 0
9:00-10:00 35 2 1:48 35.74 4 4 1:42 4.08 0 0
10:00-11:00 24 1 1:40 22.93 0 0 :00 .00 0 0
----------- ----- ---- ------ -------- ----- ---- ------ ------ --- --SUMMARY 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
BCMS TRUNK GROUP REPORT
Screen 4-28. BCMS Trunk Group Time Interval Report
NOTE:
Xs are used to show field size and are not dis played as p art of the form.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-61
Page 87

BCMS Report Generati on
list bcms trunk 1 day 4/17
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 12:59 pm THU APR 20, 1995
Group: 1
Group Name: TG 1 Number of Trunks: 11
| INCOMING | OUTGOING |%ALL %TIME
DAY |CALLS ABAND TIME CCS | CALLS COMP TIME CCS|BUSY MAINT
4/17/95* 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
----------- ----- ---- ------ -------- ----- ---- ------ ------ --- -- SUMMARY 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
BCMS TRUNK GROUP REPORT
Screen 4-29. BCMS Trunk Group Daily Report
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions
This report presents header infor m ation at the top of each page. This information
includes the comman d entered to generate the report, the page number of the
report, the title of the report, and the time and date the report was generated. If
this is a time inter val report and there are more than 11 time intervals, this report
is displayed on multiple pages. A daily summary report is displayed on one
page.
Trunk Group — The trunk group number specified with the command line.
Trunk Group Name — The name that is administered for this trunk group. If no
name is administered, then this field is displayed as blank.
Number of Trunks — The number of individual trunks in the trunk group at the
end of the first interval being reported.
TIME/DAY — The ti me or day i nterval specified i n the command line.
Time is always expressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are optional.
Reports always start at the top of the time interval (either hour or half-hour). If no
start time is given, the report displays data a ccrued for the previous 24 time
intervals. A stop time requires an associated start time. If no stop time is given,
the last completed tim e i nt er val (hour or half-hour) is the default. If no start time or
stop time is given, the report displays data ac crued for the previous 24 time
intervals. If you specify
stop day, the report displays data accrued for the previous six days and data
accrued through the most recently completed interval (hour or half-hour).
4-62 Issue 4 September 1995
day
in the command and do not include a start day or
Page 88

BCMS Trunk Group Report
_
If switch administration causes the number of trunks in a BCMS-measured trunk
group to change during a day or a time interval, an asterisk appears in the
DAY/TIME
INCOMING CALLS — The total number of inc oming calls carried by this trunk
group.
INCOMING ABAND — The number of i ncoming calls that queued to ACD splits,
then abandoned (without being answered by a staffed agent within this split)
during the reporting interval. Calls that cannot queue (for example, queue full, or
calls that receive a busy signal from the Central Office b e cause there aren’t any
available trunks) are not included in the INCOMING ABAND number. Also
included are calls directly to staffed ACD agents that are un answered.
INCOMING TIME — The average holding time for incoming calls to this trunk
group during the specified reporting interval. Holding time is defined as the
length of time in minutes and seconds that a facility is used during a call. The
calculation for incoming time is:
INCOMING TIME =
field.
Total Holding Time for all Incoming Calls
_ ___________________________________
Total Number o f Incoming Calls
INCOMING CCS — The total holding time (usage) for incoming calls to the trunk
group during the specified reporting interval. T he units are expressed in h undred
call seconds (CCS). Refer to the Glossary for a description of the term CCS.
OUTGOING CALLS — Th e total number of outgoing calls for this trunk group
during the specified reporting interval.
OUTGOING COMP — The total number of outgoing calls that were placed over
this trunk group and answered during the specified reporting interval.
NOTE:
Completi on i s deter min ed by either return of network answer superv is io n, o r
a call that lasts longer than the answer supervision t ime-out parameter;
whichever occurs first.
OUTGOING TIME — The average holding time for outgoing calls during the
specified reporting interval. The calculation is:
Total Holding Time for Outgoing Calls
OUTGOING TIME =
OUTGOING CCS — The total holding time for outgoing calls from this trunk
group. The units are expressed in CCS.
_ _________________________________
Total Number o f Outgoing Calls
Issue 4 September 1995
4-63
Page 89

BCMS Report Generati on
_
% ALL BUSY — The percentage of time that all the trunks in this trunk group
were busy . T his value includes trunks that are maintenance busy. The calculation
is:
% ALL BUSY =
where Busy Times is expressed in minutes and is the sum of all times when all
trunks were simultaneously busy.
% TIME MAINT — The percentage of time that one or more trunks have been
busied-out for maintenance purposes. The calculation is:
% TIME MAINT =
where:
■ Total Maintenance Busy Time is the sum of Maintenance Busy Time (in
minutes) for all trunks (individually) in this trunk group during this interval
Total o f all Busy Times
_ _____________________
Time Interval
Total Maintenance Busy Time × 100
_ _____________________________________
× ( 100 )
Time Interval × Number o f Trunks in Group
■ Time Interval is expressed in minutes (for example,
60
interval,
if using a one-hour interval, and
NOTE:
For reporting purposes, call data is stored during the time interval
(hour or half-hour) that the trunk goes idle, not when the station
releases. Also, changing the number of trunks in a trunk group can
cause unexpected results for that interval.
Displaying the BCMS Trunk Group Report
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly/half-hourly intervals or daily
intervals and display the report on your terminal.
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To display th is report, perfor m the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms trunk ## time xx:xx xx:xx (where ## is a valid
BCMS measured trunk group). If the trunk group is only one digit (for
example, trunk 5), just enter the single digit. The first specified time is
referred to as the start time, while the second time is referred to as the
stop time. Time must be disp l ayed in 24-hour format; however, the hours
may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number. Minutes are always
expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the report displays data
accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour).
30
if using a half-hour
1440
if using a daily summar y)
4-64 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 90

BCMS Trunk Group Report
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Trunk Grou p Report appears on your screen.
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
Displaying a Daily Report
To display this report, perform the following st eps:
1. Enter list bcms trunk ## day xx/xx xx/xx (where ## is a valid
BCMS measured trunk group). If the trunk group is only one digit (for
example, trunk 5), just enter the single digit. The first specified day is
referred to as the start day, while the second day is referred to as the stop
day. If no start day is given, the report displays data accrued for the
previous six days and data accrue d through the most rece ntly completed
interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
RETURN.
— The BCMS Trunk Grou p Report appears on your screen.
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
Printing the BCMS Trunk Group Report
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly/half-hourly intervals or daily
intervals and print the report. If you have a printer directly connected to your
terminal, you may print reports using the instructions provided below. If you do
not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, consult the instructions for
scheduling reports to print to the system printer.
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms trunk ## time xx:xx xx:xx print (where ## is
a valid BCMS measured trunk group). If the trunk g rou p i s o n ly one digit
(for example, trunk 5), just enter the single digit. The firs t s pecified time is
referred to as the start time, while the second time is referred to as the
stop ti me. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format; however, the hours
Issue 4 September 1995
4-65
Page 91

BCMS Report Generati on
NOTE:
may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number. Minutes are always
expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the report displays data
accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour).
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Trunk Group Report prints at the printer attached to your
terminal.
Printing a Daily Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms trunk ## day xx/xx xx/xx print (where ## is a
valid BCMS measured trunk group). If the trunk group is only one digit (fo r
example, trunk 5), just enter the single digit. The first specified day is
referred to as the start day, whi l e the second day is referred to as the stop
day. If no start day is given, the report displays data accrued for the
previous six days and data accrue d through the most rece ntly completed
interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Trunk Group Report prints at the printer attached to your
terminal.
Scheduling the BCMS Trunk Group Report to Print
The Report Scheduler allows you to schedule the day or days for the system to
print the report. If you do not have a printer directly connected to your terminal,
you may use the Report Scheduler feature to print the report immediately to the
system printer. The data for this report can be collected in hourly/half-hourly
intervals or daily i nterval s.
Scheduling an Hourly/Half-Hourly
Interval Report to Print
To schedule this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms trunk ## time xx:xx xx:xx schedule (where
## is a valid BCMS measured trunk group). If the trunk group is only one
digit (for example, trunk 5), just enter the single digit. The first specified
time is referred to as the start time, while the second time is referred to a s
the stop time. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format; however, the
hours may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number. Minutes are
4-66 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 92

BCMS Trunk Group Report
NOTE:
always expressed as two digits. If no start time is given, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or
half-hour).
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— Th e R eport Scheduler form appears on your sc reen. The cursor is
located in the Print Interval: field.
list bcms trunk ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms trunk ## time xx:xx xx:xx schedule
Print Interval: immediate
Screen 4-30. Report Scheduler Form
NOTE:
If you do not have a printer direc t ly connected to your terminal, you
can immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing
ENTER.
REPORT SCHEDULER
3. Enter schedule and press
— T he Pr i n t T ime: fi e l d appears beneath the Print Interval: field, and
fields for each day of the week appear at the bottom of the form.
The cursor is located in the Print Time: field.
RETURN.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-67
Page 93

BCMS Report Generati on
list bcms trunk ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms trunk ## time xx:xx xx:xx schedule
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-31. Report Scheduler Form with the Print Interval Set to
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
— The cursor moves to the Sun: field.
5. Enter y for the day(s) you wa nt th e report prin ted. Us e
cursor to the next field.
6. When you are finished, press
ENTER.
— The report has been scheduled, and the system presents the enter
command: prompt.
Scheduling a Daily Report to Print
To schedule this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms trunk ## day xx/xx xx/xx schedule (where ##
is a valid BCMS measured trunk group). If the trunk group is only one digit
(for example, trunk 5), just enter the single digit. Th e fi r s t specified day is
referred to as the start day, whi l e the second day is referred to as the stop
day. If no start day is given, the report displays data accrued for the
previous six days and data accrue d through the most rece ntly completed
interval (hour or half-hour).
2. Press
RETURN.
scheduled
RETURN to move the
— Th e R eport Scheduler form appears on your scre en. The cursor is
located in the Print Interval: field.
4-68 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 94
BCMS Trunk Group Report
list bcms trunk ## day xx/xx xx/xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms trunk ## day xx/xx xx/xx schedule
Print Interval: immediate
Screen 4-32. Report Scheduler Form
NOTE:
If you do not have a printer direc t ly connected to your terminal, you
can immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing
ENTER.
REPORT SCHEDULER
3. Enter schedule and press
RETURN.
— T he Pr i n t T ime: fi e l d appears beneath the Print Interval: field, and
fields for each day of the week appear at the bottom of the form.
The cursor is located in the Print Time: field.
list bcms trunk ## day xx/xx xx/xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms trunk ## day xx/xx xx/xx schedule
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
REPORT SCHEDULER
Screen 4-33. Report Scheduler Form with the Print Interval Set to
scheduled
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
— The cursor moves to the Sun: field.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-69
Page 95

BCMS Report Generati on
5. Enter y for the day(s) you want the report printed. Use R ETURN to move the
cursor to the next field.
6. When you are finished, press
ENTER.
— The report has been scheduled, and the system presents the enter
command: prompt.
BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report
The BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report provides information about
BCMS-measured trunk groups. You can sp ecify the trunk groups you want
included in the report. The BCMS Trunk Group Report can be used by the ACD
administrator and/or manager to monitor use of one or more trunk groups and to
determine the optimal number of trunks for the trunk groups. Note that this
applies only to trunk groups measured by BCMS.
Th is report is sim ila r to th e BCMS Tr unk Group Report except that the information
for a trunk appears on separate lines of the report, with totals of activity for all
trunks in the trunk group f o r th e specified time. You can print the report for a
certain time period spec ified in either hours or days (up to 7 days).
The report displays only the information that exists and does not identify absent
data. If data does not exist for a specified trunk group, the trunk group does not
appear on the report. Also, if information does not exist for a portion of the
specified time period, the report displays all existing information but does not
identify where there is no data. Screen 4-34 shows the BCMS Trunk Group
Summary Report for an interval of hours, and Screen 4-35 shows the BCMS
Trunk Group Summary Report for a daily interval.
NOTE:
When analyzing this report, keep the following things in mind:
■ All averages are for completed cal ls only.
■ Asterisks in a field indicate that the maximum for that field is
exceeded .
■ A single asterisk at the end of a time or date field indicates that
during the interval, trunk group administration occurred which
changed the number of trunks.
4-70 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 96

BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report
list bcms trunk sum 23-25 time 8:00
BCMS TRUNK GROUP SUMMARY REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 12:59 pm THU APR 20, 1995
GROUP NAME |CALLS ABAND TIME CCS | CALLS COMP TIME CCS|BUSY MAINT
IN-800 23 2 2:15 31.02 1 1 1:36 0.96 0 0
OUT-WATTS* 35 2 1:48 35.74 4 4 1:42 4.08 0 0
TIE-GROUP 24 1 1:40 22.93 0 0 :00 0.00 0 0
----------- ----- ---- ------ -------- ----- ----- ------ ------ --- --SUMMARY 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
Time: 8:00-13:00
| INCOMING | OUTGOING |%ALL %TIME
Screen 4-34. BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report — Hourly
list bcms trunk sum 23 day 5/17/92
BCMS TRUNK GROUP SUMMARY REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 12:59 pm THU APR 20, 1995
GROUP NAME |CALLS ABAND TIME CCS | CALLS COMP TIME CCS|BUSY MAINT
IN-800* 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
----------- ----- ---- ------ -------- ----- ----- ------ ------ --- --SUMMARY 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
Day: 5/17/95
| INCOMING | OUTGOING |%ALL %TIME
Screen 4-35. BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report — Daily
Report Headers, Abbreviations,
and Their Definitions
This report presents header infor m ation at the top of each page. This information
includes the comman d entered to generate the report, the page number of the
report, the title of the report , and the time and date the report was generated.
TIME/DAY — The time or day interval specified in the command line. Time is
always expressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are optional. Reports
always start at the top of the time interval (either hour or half-hour). If no start time
is given, the report displays data accrued for the p revious 24 time intervals. A
stop time requires an associa ted start t ime. If no stop time is given, the last
Issue 4 September 1995
4-71
Page 97

BCMS Report Generati on
_
completed time interval (hour or half-hour) is the default. If no start time or stop
time is given, the report displays data accrued for t he previous 24 time intervals.
If you specify
report displays data accrued for the previous six days and data accrued thro ugh
the most recently co m pleted interval (hour or half-hour).
If switch administration causes the number of trunks in a BCMS-measured trunk
group to change during a day or a time int erval, an asterisk appears in the
DAY/TIME
NAME — The name that is administered for this trunk group. If no name is
administered, this field is displayed as blank.
INCOMING CALLS — The total number of in coming ca lls carried by this trunk
group.
INCOMING ABAND — The number of i ncoming calls that queued to ACD splits,
then abandoned (without being answered by a staffed agent within this split)
during the reporting interval. Calls that cannot queue (for example, queue full, or
calls that receive a busy signal from the centra l office because there are no
available trunks) are not included in the INCOMING ABAND number. Also
included are calls directly to staffed ACD agents that are unanswered.
field.
day
in the command and do not i nclude a start day or stop day, the
INCOMING TIME — The average holding time for incoming calls to this trunk
group during the specified reporting interval. Holding time is defined as the
length of time in minutes and seconds that a facility is used during a call. The
cal culation for incoming tim e is:
Total Holding Time for all Incoming Calls
INCOMING TIME =
INCOMING CCS — The total holding time (usage) for incoming calls to the trunk
group during the specified reporting interval. The units are expressed i n hu ndred
call seconds (CCS). Refer to the Glossary for a description of the term CCS.
OUTGOING CALLS — The total number of outgoing c alls for this trunk group
during the specified reporting interval.
OUTGOING COMP — The total number of outgoing calls that were placed over
this trunk group and answered during the specified reporting interval.
NOTE:
Completi on i s deter min ed by either return of network answer superv is io n, o r
a call that lasts longer than the answer supervision time-out parameter;
whichever occurs first.
OUTGOING TIME — The average ho lding time for outgoing calls during the
specified reporting interval. The cal culation is:
_ ___________________________________
Total Number o f Incoming Calls
4-72 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 98

BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report
_
OUTGOING TIME =
OUTGOING CCS — The total holding time for outgoing calls from this trunk
group. The units are expressed in CCS.
% ALL BUSY — The percentage of time t hat all the trunks in this trunk group
were busy . T his value includes trunks that are maintenance busy. The calculation
is:
% ALL BUSY =
where
Busy Times is expressed in minutes and is the sum of all tim es when all trunks
were simultaneously busy.
% TIME MAINT — The percentage of time that one or more trunks have been
busied-out for maintenance purposes. The calculation is:
Total Holding Time for Outgoing Calls
_ _________________________________
Total Number o f Outgoing Calls
Total o f all Busy Times
_ _____________________
Time Interval
× ( 100 )
Total Maintenance Busy Time × 100
% TIME MAINT =
_ _____________________________________
Time Interval × Number o f Trunks in Group
where
■ Total Maintenance Busy Time is the sum of Maintenance Busy Time (in
minutes) for all trunks (individually) in this trunk group during this interval
■ Time Interval is expressed in minutes (for example,
60
interval,
if using a one-hour interval, and
NOTE:
For reporting p urp oses, call data is stored during the time interval
(hour or half-hour) that the trunk goes idle, not when the station
releases. Also, changing the number of trunks in a trunk group can
cause unexpected results for that interval.
Displaying the BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly/half-hourly intervals or daily
intervals an d display the report on your terminal.
30
if using a half-hour
1440
if using a daily summar y)
Issue 4 September 1995
4-73
Page 99

BCMS Report Generati on
Displaying an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To display this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary trunk ## time xx:xx xx:xx (where ##
is a valid BCMS measured trunk group). If the trunk group is only one digit
(for example, trunk 5), just enter the single digit. The firs t s pecified time is
referred to as the start time, while the second time is referred to as the
stop time. Time must be disp l ayed in 24-hour format; however, the hours
may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number. Minutes are always
expressed as two digits. If no start time is given then the last interval of
data will be used to calculate the one-line display for each trunk group.
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report appears on your screen.
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
Displaying a Daily Report
To display this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary trunk ## day xx/xx xx/xx (where ##
is a valid BCMS measured trunk group). If the trunk group is only one digit
(for example, trunk 5), just enter the single digit. Th e fi r s t specified day is
referred to as the start day, whi l e the second day is referred to as the stop
day. If no start day is given then the last day of data will be used to
calculate the one-line di splay for each trunk g roup.
2. Press
3. If the report consists of more than one page, press the
RETURN.
— The BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report appears on your screen.
display subsequent pages and the
pages.
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
NEXTPAGE key to
PREVPAGE key to display previous
4-74 Issue 4 September 1995
Page 100
BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report
Printing the BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report
BCMS allows you to collect data in either hourly/half-hourly intervals or daily
intervals and print the report. If you have a printer directly connected to your
terminal, you may print reports using the instructions provided below. If you do
not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, consult the instructions for
scheduling reports to print to the system printer.
Printing an Hourly/Half-Hourly Interval Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary trunk ## time xx:xx xx:xx print
(where ## is a valid BCMS measured trunk group). If the trunk group is
only one digit (for example, trunk 5), just enter the single digit. The first
specified time is referred to as the start time, while the second time is
referred to as the stop time. Time must be displayed in 24-hour format;
however, the hours may be indicated as either a 1- or 2-digit number.
Minutes are always expressed as two digits. If no start time is given then
the last interval of data will be used to calculate the one-line display for
each trunk group.
NOTE:
Whether the system collects the data in hourly or half- hourly intervals
depends on t h e M e asurement Interval setting in the Feature-Related
System Parameters screen.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report prints at the printer
attach e d to your terminal.
Printing a Daily Report
To print this report, perform the following steps:
1. Enter list bcms summary trunk ## day xx/xx xx/xx print
(where ## is a valid BCMS measured trunk group). If the trunk group is
only one digit (for example, trunk 5), just enter the single digit. The first
specified day is referred to as the start day, while the second day is
referred to as t he st op day. If no s tart day is given then the last day of data
will be used to calculate the one-line display for each trunk group.
2. Press
RETURN.
— The BCMS Trunk Group Summary Report prints at the printer
attach e d to your terminal.
Issue 4 September 1995
4-75
 Loading...
Loading...