Page 1

NVIDIA RAID Installation Guide
1. NVIDIA BIOS RAID Installation Guide …………………….. 2
1.1 Introduction to RAID ……………………………………. 2
1.2 RAID Configurations Precautions …………………….. 3
1.3 Installing Windows 2000 / XP / XP 64-bit / Vista /
Vista 64-bit With RAID Functions ……………………... 5
1.3.1 Installing Windows 2000 / XP / XP 64-bit With
RAID Functions ……………………................. 5
1.3.2 Installing Windows Vista / Vista 64-bit With RAID
Functions ……………………............................... 6
1.4 Create Disk Array ……………………………………….. 8
2. NVIDIA Windows RAID Installation Guide ………………… 11
2.1 NVIDIA Windows RAID Installation Guide for Windows
2000 / XP / XP 64-bit Users ……………………………. 11
2.2 NVIDIA Windows RAID Installation Guide for Windows
Vista / Vista 64-bit Users ……………………………….. 21
1
Page 2

1. NVIDIA BIOS RAID Installation Guide
NVIDIA BIOS RAID Installation Guide is an instruction for you to configure RAID
functions by using NVIDIA RAID Utility under BIOS environment. After you make a
SATA / SATAII driver diskette, press <F2> to enter BIOS setup to set the option to
RAID mode by following the detailed instruction of the “User Manual” in our support CD
or “Quick Installation Guide”, you can start to use NVIDIA RAID Utility to configure
RAID.
This section includes examples of using NVRAID RAID Utility for creating RAID arrays.
If your motherboard is equipped with two SATA / SATAII ports, you may choose to use
RAID 0, RAID 1, or JBOD function with your motherboard. If your motherboard is
equipped with four SATA / SATAII ports, you may choose to use RAID 0, RAID 1,
RAID 0+1, JBOD, or RAID 5 function with your motherboard according to the SATA /
SATAII HDDs amount you install. Please refer to the RAID functions your motherboard
provides in advance and follow the instruction in this section to create RAID arrays.
1.1 Introduction to RAID
The term “RAID” stands for “Redundant Array of Independent Disks”, which is a
method combining two or more hard disk drives into one logical unit. For optimal
performance, please install identical drives of the same model and capacity when
creating a RAID set.
RAID 0 (Data Striping)
RAID 0 is called data striping that optimizes two identical hard disk drives to read and
write data in parallel, interleaved stacks. It will improve data access and storage since
it will double the data transfer rate of a single disk alone while the two hard disks
perform the same work as a single drive but at a sustained data transfer rate.
WARNING!!
Although RAID 0 function can improve the access performance, it does not provide any fault
tolerance. Hot-Plug any HDDs of the RAID 0 Disk will cause data damage or data loss.
RAID 1 (Data Mirroring)
RAID 1 is called data mirroring that copies and maintains an identical image of data
from one drive to a second drive. It provides data protection and increases fault
tolerance to the entire system since the disk array management software will direct
all applications to the surviving drive as it contains a complete copy of the data in
the other drive if one drive fails.
2
Page 3

RAID 0+1 (Stripe Mirroring)
RAID 0 drives can be mirrored using RAID 1 techniques, resulting in a RAID 0+1
solution for improved performance plus resiliency. The controller combines the
performance of data striping (RAID 0) and the fault tolerance of disk mirroring
(RAID 1). Data is striped across multiple drives and duplicated on another set of
drives.
JBOD (Spanning)
A spanning disk array is equal to the sum of all drives. Spanning stores data onto a
drive until it is full then proceeds to store files onto the next drive in the array. When
any member disk fails, it will affect the entire array. JBOD is not really a RAID, and it
does not support fault tolerance.
RAID 5
RAID 5 stripes both data and parity information across three or more hard disk drives.
Among the advantages of RAID 5configuration include better HDD performance, fault
tolerance, and higher storage capacity. The RAID 5 configuration is best suited for
transaction processing, relational database applications, enterprise resource planning,
and other business systems. Use a minimum of three identical hard disk drives for this
setup.
1.2 RAID Configurations Precautions
1. Please use two new drives if you are creating a RAID 0 (striping) array for
performance. It is recommended to use two SATA drives of the same size. If
you use two drives of different sizes, the smaller capacity hard disk will be
the base storage size for each drive. For example, if one hard disk has an
80GB storage capacity and the other hard disk has 60GB, the maximum
storage capacity for the 80GB-drive becomes 60GB, and the total storage
capacity for this RAID 0 set is 120GB.
2. You may use two new drives, or use an existing drive and a new drive to
create a RAID 1 (mirroring) array for data protection (the new drive must be
of the same size or larger than the existing drive). If you use two drives of
different sizes, the smaller capacity hard disk will be the base storage size.
For example, if one hard disk has an 80GB storage capacity and the other
hard disk has 60GB, the maximum storage capacity for the RAID 1 set is
60GB.
3
Page 4

3. Please verify the status of your hard disks before you set up your new RAID
array.
WARNING!!
Please backup your data first before you create RAID functions. In the process you
create RAID, the system will ask if you want to “Clear Disk Data” or not. It is
recommended to select “Yes”, and then your future data building will operate under a
clean environment.
4
Page 5

1.3 Installing Windows® 2000 / XP / XP 64-bit / Vista
TM
/ VistaTM 64-bit With RAID Functions
If you want to install Windows® 2000, Windows® XP, Windows® XP 64-bit, Windows
VistaTM or Windows® VistaTM 64-bit on your SATA / SATAII HDDs with RAID functions,
please follow below procedures according to the OS you install.
Before installing Windows® 2000 to your system, your Windows® 2000 optical
disk is supposed to include SP4. If there is no SP4 included in your disk, please
visit the below website for proper procedures of making a SP4 disk:
http://www.microsoft.com/Windows2000/downloads/servicepacks/sp4/spdeploy.
htm#the_integrated_installation_fmay
1.3.1 Installing Windows® 2000 / XP / XP 64-bit With RAID
Functions
If you want to install Windows® 2000 / Windows® XP / Windows® XP 64-bit on your SA T A
/ SATAII HDDs with RAID functions, please follow below steps.
STEP 1: Set Up BIOS.
A. Enter BIOS SETUP UTILITY Advanced screen IDE Configuration.
B. Set the “SATA Operation Mode” option to [RAID].
STEP 2: Make a SATA / SATAII driver diskette.
A. Insert the ASRock Support CD into your optical drive to boot your system.
B. During POST at the beginning of system boot-up, press <F1 1> key, and
then a window for boot devices selection appears. Please select CD-ROM
as the boot device.
C. When you see the message on the screen, “Generate Serial ATA driver
diskette [YN]?”, press <Y>.
D. Then you will see these messages,
Plea se choose:
1. Generate AHCI Driver diskette for Windows2000/XP/XP64
2. Generate RAID Driver diskette for Windows2000/XP
3. Generate RAID Driver diskette for WindowsXP64
4. Exit
Reboot system now
Press any key to continue
Please in sert a floppy diskette into the floppy drive. Select your required
item on the list according to the mode you choose and the OS you install.
Then press any key.
E. The system will start to format the floppy diskette and copy SATA / SATAII
drivers into the floppy diskette.
If you want to enable Hot Plug function on eSATAII ports but you install OS
on IDE HDD, please skip step 2.
®
5
Page 6

STEP 3: Use “RAID Installation Guide” to set RAID configuration.
Before you start to configure RAID function, you need to check the RAID installation
guide in the Support CD for proper configuration. Please refer to the BIOS RAID
installation guide part of the document in the following path in the Support CD:
.. \ RAID Installation Guide
STEP 4: Install Windows® 2000 / XP / XP 64-bit OS on your system.
After step 1, 2, 3, you can start to install Windows® 2000 / Windows® XP / Windows
XP 64-bit OS on your system. At the beginning of Windows® setup, press F6 to install
a third-party RAID driver. When prompted, insert the SATA / SATAII driver diskette
containing the NVIDIA® RAID driver. After reading the floppy disk, the drivers will be
presented. Select the drivers to install. The drivers are as below:
A. NVIDIA RAID Driver (required)
B. NVIDIA nForce Storage Controller (required)
Please select A and B for Windows® 2000 / XP / XP 64-bit in RAID mode. (There are
two RAID drivers needed for RAID mode, you have to select them separately. Please
specify the first RAID driver and then specify again for the second one.)
NOTE. If you install Windows® 2000 / Windows® XP / Windows® XP 64-bit on IDE
HDDs and want to manage (create, convert, delete, or rebuild) RAID functions
on SATA / SATAII HDDs, you still need to set up “SATA Operation Mode” to [RAID]
in BIOS first. Then, please set the RAID configuration by using the Windows RAID
installation guide part of the document in the following path in the Support CD:
.. \ RAID Installation Guide
®
1.3.2 Installing Windows® VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit With RAID
Functions
If you want to install Windows® VistaTM / Windows® VistaTM 64-bit on your SATA / SA TAII
HDDs with RAID functions, please follow below steps.
STEP 1: Set Up BIOS.
A. Enter BIOS SETUP UTILITY Advanced screen IDE Configuration.
B. Set the “SATA Operation Mode” option to [RAID].
STEP 2: Use “RAID Installation Guide” to set RAID configuration.
Before you start to configure RAID function, you need to check the RAID installation
guide in the Support CD for proper configuration. Please refer to the BIOS RAID
installation guide part of the document in the following path in the Support CD:
.. \ RAID Installation Guide
STEP 3: Install Windows® VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit OS on your system.
Insert the Windows® VistaTM / Windows® VistaTM 64-bit optical disk into the optical
drive to boot your system, and follow the instruction to install Windows® VistaTM /
Windows® VistaTM 64-bit OS on your system. When you see “Where do you want to
6
Page 7

install Windows?” page, please insert the ASRock Support CD into your optical drive,
and click the “Load Driver” button on the left on the bottom to load the NVIDIA® RAID
drivers. NVIDIA® RAID drivers are in the following path in our Support CD:
.. \ I386 \ Vista32_RAID (For Windows® Vista
.. \ AMD64 \ Vista64_RAID (For Windows® Vista
TM
OS)
TM
64-bit OS)
After that, please insert W indows® VistaTM / Windows® VistaTM 64-bit optical disk into
the optical drive again to continue the installation.
NOTE. If you install Windows® VistaTM / Windows® VistaTM 64-bit on IDE HDDs and want to
manage (create, convert, delete, or rebuild) RAID functions on SATA / SATAII HDDs,
you still need to set up “SATA Operation Mode” to [RAID] in BIOS first. Then, please set
the RAID configuration by using the Windows RAID installation guide in the following
path in the Support CD:
.. \ RAID Installation Guide
7
Page 8
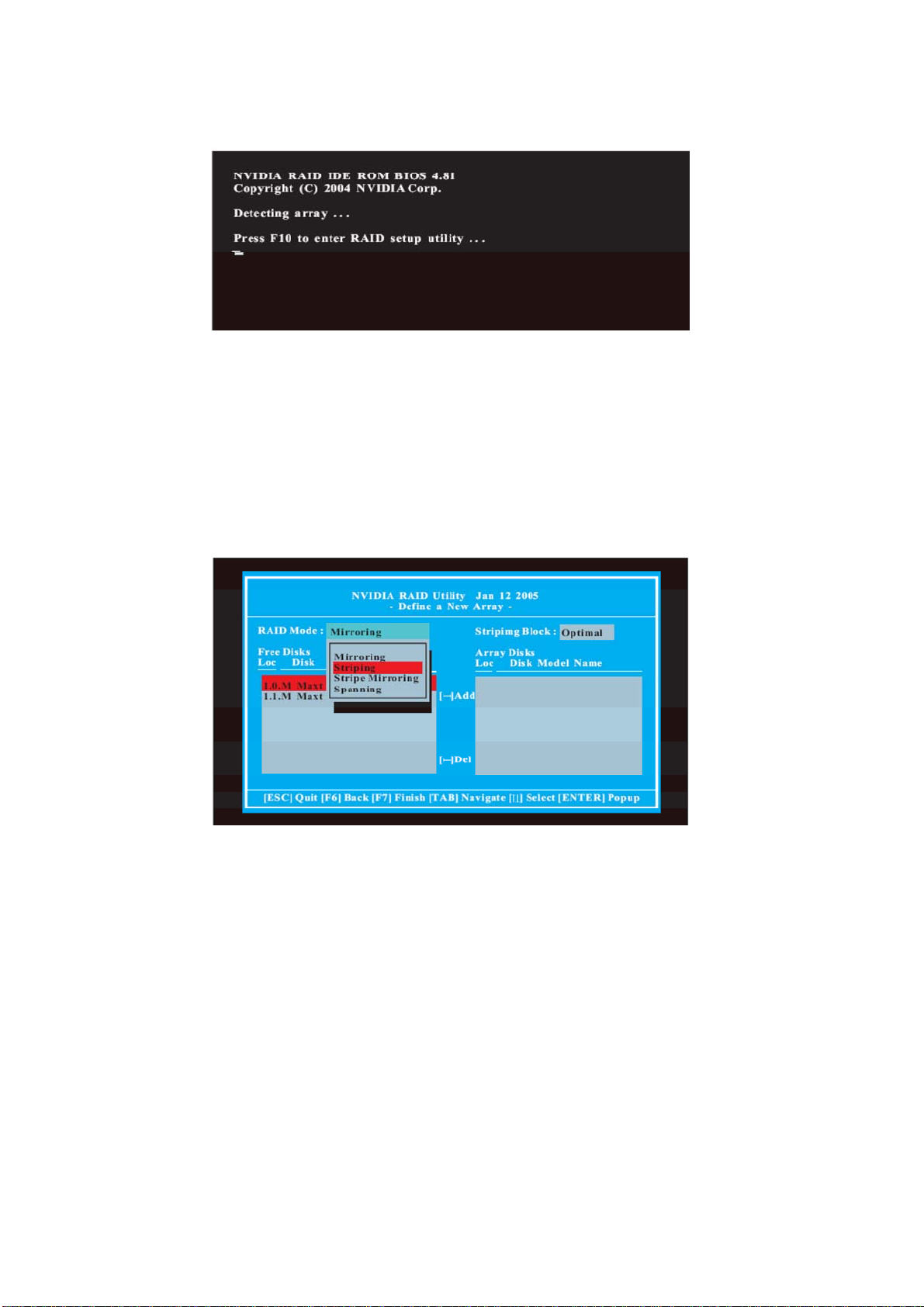
1.4 Create Disk Array
Power on your system. After adjusting the system BIOS to RAID mode, the below
window appears.
After rebooting your computer, wait until you see the RAID software prompting you to
press <F10>. The RAID prompt appears as a part of the system POST and boot
process prior to loading the OS. You have a few seconds to press <F10> before the
window disappears.
After you press <F10>, the NVIDIA RAID Utility - Define a New Array window
appears. By default, RAID Mode is set to Mirroring, but please set it to Striping if you
want to create RAID 0. And the Striping Block is set to Optimal as default. We take
RAID 0 for example to show you how to use NVRAID RAID Utility to create RAID 0
(Striping). If you plan to use NVRAID RAID Utility to create other RAID arrays, the
operation procedures are similar to the steps of creating RAID 0.
8
Page 9

Striping block size is given in kilobytes, and affect how data is arranged on the disk. It
is recommended to leave this value at the default Optimal, which is 64KB, but the
values can be between 8KB and 128KB (8, 16, 32, 64, and 128KB). Then, you have to
assign the disks. The disks that you enabled from the RAID Config BIOS setup page
appear in the Free Disks block. These are the drives that are available for use as RAID
array disk,
A. Tab to the Free Disks section. The first disk in the list is selected.
B. Move it from the Free Disks block to the Array Disks block by pressing the
right-arrow key.
C. Continue pressing the right-arrow key until all the disks that you want to use
as RAID array disks appear in the Array Disks block.
9
Page 10

After assigning your RAID array disks, press <F7> to save your changes of RAID array
disks.
Depending on the platform used, the system can have one or more channels. In a
typical system there is usually one adapter and multiple channels, and each channel
has a slave and a master. The adapter / channel / master / slave status of each hard
disk is given in the Loc (location) columns of the Free Disks and Array Disks lists. For
example:
1 . 0 . M
1: Channel - Typically, channel 0 is used for Parallel ATA drives while channel 1
is used for Serial ATA drives.
0: Controller
M: M means Master, S means Slave
Seri al ATA
1 . 0 . M Channel 1, controller 0, Master
1 . 1 . M Channel 1, controller 1, Master
Finally, the Array List window appears, where you can review the RAID arrays that
you have set up.
Healthy NVIDIA STRIPING 74.53G
10
Page 11

2. NVIDIA Windows RAID Installation Guide
NVIDIA Windows RAID Installation Guide is an instruction for you to configure RAID
functions by using NVIDIAMAN under Windows environment. Please read this guide
carefully and follow the instructions below to configure and manage RAID functions.
For Windows 2000 / XP / XP 64-bit and Windows Vista / Vista 64-bit, there are different
installation procedures. Please follow the instructions below according to the OS you
install.
2.1 NVIDIA Windows RAID Installation Guide for Windows 2000 /
XP / XP 64-bit Users
A. Enter NVRAIDMAN
RAID driver is built in NVIDIA ALL in one driver provided in our support CD. After you
finish the driver installation, you can create, delete, or rebuild any RAID array. Please
enter NVRAIDMAN by clicking on Start → Programs → NVIDIA Corporation →
Mediashield → Mediashield. (There is also a “Mediashield” shortcut on the desktop.)
Then, the below screen appears.
11
Page 12

B. Creating RAID Arrays
This section includes examples of using NVRAIDMAN for creating RAID arrays. If your
motherboard is equipped with two SATA / SATAII ports, you may choose to use RAID
0, RAID 1, or JBOD function with your motherboard. If your motherboard is equipped
with four SATA / SATAII ports, you may choose to use RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1,
JBOD, or RAID 5 function with your motherboard according to the SATA / SATAII
HDDs amount you install. Please refer to the RAID functions your motherboard
provides in advance and follow the instruction in this section to create RAID arrays.
The RAID items which may be mentioned in this section are as below:
- RAID 0: Striping
- RAID 1: Mirroring
- RAID 0+1: Stripe Mirroring
- JBOD: Spanning
- RAID 5
NOTE:
Under Windows XP OS, the connector naming on our motherboard is different from NVIDIA utility naming. Please
refer to below table for detailed information.
SATAII_BLACK (PORT 1.0) --> Means SATA Primary Master.
SATAII_ORANGE (PORT 1.1) --> Means SATA Secondary Master.
SATAII_BLUE (PORT 2.0) --> Means SATA Primary Master.
SATAII_RED (PORT 2.1) --> Means SATA Secondary Master.
In this section, we take RAID 0 for example to show you how to use NVRAIDMAN to
create RAID 0 (Striping). If you plan to use NVRAIDMAN to create other RAID arrays,
12
Page 13

the operation procedures are similar to the steps of creating RAID 0. Please do the
following:
A. Go to the system BIOS and make sure that the drives that you want to use are
RAID enabled.
B. Boot to Windows and launch the NVRAIDMAN application.
C. Create Array and the following screen will appear.
D. Click Next and the following screen shot will appear.
13
Page 14

E. Click the RAID Mode list arrow and select Striping, and leave the “Stripe Size”
with its default value as shown in the following screen shot.
F. Click Next, and the following screen shot will appear.
G. Select the two disks that you want to include in the stripe set.
14
Page 15

To create a striped array with more disks, select additional disks from the list.
H. Click Next and the following screen shot will appear.
I. Click Finish and the following screen shot will appear.
The RAID 0 is created successfully.
C. Initializing NVRAID Array Disks
Now that the two-disk array has been created, it needs to be partitioned and formatted.
A. Click on Start → Settings → Control Panel.
15
Page 16

B. Double click on Administrative Tools.
C. Double click on Computer Management.
D. Click on Disk Management. The following screen is displayed.
E. The 153.38 GB is for the two disk striped array that was created earlier. To create
a partition on it, right click on the Unallocated partition and select New Partition.
F. Follow the Wizard for setting up and formatting the partition. Once that is done,
you can start using the newly created stripped array.
16
Page 17

D. Deleting a RAID Array
NVRAIDMAN can be used to delete an Array. To delete an Array, please do the
following.
A. Launch the NVRAIDMAN application and right click on the RAID array that you
want to delete (assuming that you have a RAID array already created) as shown
in the following screen shot.
The above screen shot shows that there is a Mirrored array that will be deleted. After
the “Delete Array...” has been selected, the following screen shot appear.
17
Page 18

B. Click Next and the following screen shot will appear.
C. Click Finish and the array will be deleted and the following screen shot will appear
showing all the free disks.
A similar process can be applied to delete any array created by NVIDIA RAID.
E. Rebuilding a RAID Array
Rebuilding is the process of restoring data to a hard drive from other drives in the array.
This applies only to fault tolerant arrays such as RAID 1, RAID 0+1, as well as a RAID
5. For example, assuming you have a three disk RAID 5 array, and one of the drives
fail, then you need to replace the failed drive with a new one, and rebuild the array to
re-generate the lost data on the newly added drive. After creating a mirrored array, you
can rebuild the array using the following steps:
A. Go to Windows and run the NVIDIA RAID Management utility.
B. Right-click on Mirroring. Then the popup menu appears.
C. From the popup menu, click Rebuild Array. The NVIDIA Rebuild Array Wizard
appears.
18
Page 19

D. Click Next. The Disk Selection page appears.
E. Select the drive that you want to rebuild by clicking it from the list, then click Next.
The Completing the NVIDIA Rebuild Array page appears.
19
Page 20

F. Click Finish.
F. More About Rebuilding Arrays
Rebuilding Occurs in the Background
The rebuilding process takes some time to complete, and occurs in the background so
as not to affect the performance of the system.
Rebuilding Applies Only to RAID 1, RAID 0+1, or RAID 5 Arrays
Rebuilding an array works only when using RAID 1, RAID 0+1, or RAID 5. Rebuilding
does not apply to RAID 0 and JBOD arrays.
Rebuilding applies to a degraded fault tolerant array
You can rebuild a degraded mirrored array using any available Free Disk or Dedicated
Disk.
G. Synchronizing a RAID Array
Synchronizing an array will force a rebuild of redundancy or parity. The operation is
applicable to any fault tolerant array such as RAID 1, 0+1 and RAID 5. For RAID1 and
RAID 0+1, “sync” results in copying the data to the redundancy disk. For RAID 5,
“sync” results in rebuilding the parity. To sync an array, do the following (This example
assumes you have already created a fault tolerant array such as RAID 1):
A. Right click on “Mirroring” and select “Synchronize Array”. Then the Synchronize
Array Wizard Welcome screen appears.
B. Click on “Next” and then click “Finish” at the Wizard Completion screen. The
20
Page 21

NVRAIDMAN window indicates that the array is synchronizing.
C. The synchronization process will start and it will be completed in a short period of
time.
2.2 NVIDIA Windows RAID Installation Guide for Windows Vista /
Vista 64-bit Users
A. Enter Storage
RAID driver is built in NVIDIA ALL in one driver provided in our support CD. After you
finish the driver installation, you can create, delete, or rebuild any RAID array. Please
enter Storage by clicking on Start → Programs → NVIDIA Corporation → Storage.
(There is also a “Storage” shortcut on the desktop.)
Then, the below screen appears.
21
Page 22

Click “Create array”. Then you can start to build up RAID.
B. Creating RAID Arrays
Click Next and the following screen shot will appear.
22
Page 23

Select a configuration that best suits your storage needs. It is recommended to select
“Custom”. Click Next.
Then, select the type of RAID array to create. You need to choose the RAID Mode first
and click Next. Here we take Striping (RAID 0) for example to show you how to use
Storage to create Striping (RAID 0). If you plan to use Storage to create other RAID
arrays, the operation procedures are similar to the steps of creating Striping (RAID 0).
23
Page 24

After you decide the RAID Mode, you are allowed to select the Stripe Size. The default
value of this item is 64K. Then click Next.
Select the disks to add to the new RAID array, and click Next.
Select the disk with data to preserve, and click Next.
24
Page 25

Click Next to confirm that you agree to use the default settings for RAID configurations.
Click Finish to complete the steps of creating RAID array.
C. Initializing NVRAID Array Disks
Now that the two-disk array has been created, it needs to be partitioned and formatted.
A. Click on Start → Settings → Control Panel.
B. Double click on Administrative Tools.
C. Double click on Computer Management.
D. Click on Disk Management. The following screen is displayed.
25
Page 26

Right-click on the unallocated partition and select New Simple Volume. Follow the
Wizard for setting up and formatting the partition. Once that is done, you can start
using the newly created stripped array.
26
 Loading...
Loading...