Page 1

2345678901234567
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
2345678901234567
TM
The New Concept
CU8232
Remote Control Interface
for the
AR8000
Hand Portable Radio Receiver
- 1 -
Page 2

Index
Thank you for purchasing the CU8232 computer control interface for the AR8000
receiver.
Every effort has been made to make this manual correct and up to date. Due to
continuous development of the product and by error or omission anomalies may
be found and these are acknowledged.
Most apparent faults are usually due to accidental mis-operation of the product,
carefully read all of the manual and relevant sections in the AR8000 operating
manual before deciding to return the interface for repair.
This manual is protected by copyright AOR LTD 1994. No information contained
in this manual may be copied or transferred by any means without the prior written
consent of AOR LTD. AOR and the [AOR] logo are trade marks of AOR, LTD.
All other trade marks and names acknowledged. E&OE.
(C) 1994 AOR LTD. Japan.
Index
1 General ................................................................. 3
2 Supplied accessories ............................................ 3
3 AR8000/CU8232 connection & clone .................... 3,4,5,6
4 Connection for RS232 operation ........................... 6,7
5 Communication parameters ................................... 8
6 WINDOWS TERMINAL ......................................... 8,9,10,11,12
7 How to send a command ....................................... 12
8 List of commands ................................................... 13
9 Command index ...................................................... 14,15
10 Explanation of commands ....................................... 16 - end
- 2 -
Page 3

General : Accessories : Connection & clone
(1) General
The CU8232 interface allows computer control via the RS232 serial port of a
computer. An additional piece of software will usually be required in order to
address the computer’s serial port with the correct set of parameters. If using
an IBM-PC or clone (with 80386 processor or higher) Microsoft WINDOWS
“TERMINAL” may be used to address the computer’s serial port, configuration
of “TERMINAL” is covered later in this manual.
In order to gain the greatest flexibility, a specialist software package is desirable.
It is planned to later introduce a Microsoft WINDOWS package to support the
AR8000 receiver.
The CU8232 interface also enables data to be copied between two AR8000
receiver when simultaneously connected to the CU8232. Memory, search and all
data may be transferred enabling full CLONE of one receiver onto another. This
may be accomplished without the use of a host computer and the interface is
powered from the AR8000 receiver.
(2) Supplied Accessories
Please check that the following items are included in the package:
Description Quantity
CU8232 remote control interface box One
Flat cable Two
RS232C 9-pin to 25-pin adaptor One
RS232C 9-pin male-Female adaptor One
English language operating manual (this booklet) One
(3)
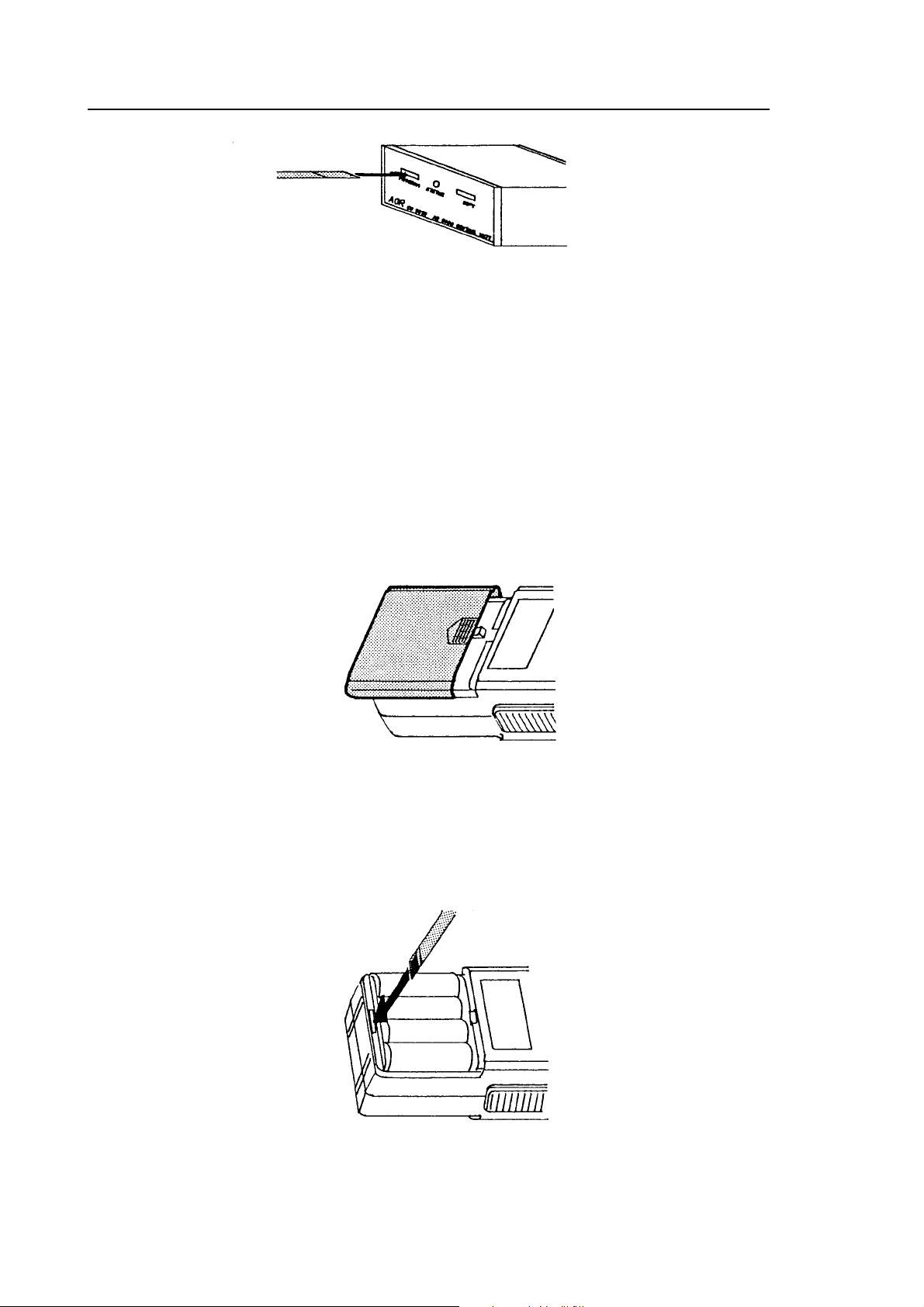
1. A ribbon cable is used to connect the AR8000 to the CU8232. One end of the
AR8000/CU8232 connection & clone
ribbon cable has a reinforced plate, this is used at the AR8000 end of the
connection. Insert one flat cable (they are both identical) into the CU8232
[PROGRAM] socket contact (metal) side downward.
- 3 -
Page 4
Connection & clone
Figure 1
The [PROGRAM] socket is the primary receiver connection used for computer
control. This port also takes power from the receiver (when the AR8000 is
switched On).
Should you wish to CLONE data between two AR8000 receivers, connect the
second ribbon cable to the socket labelled [COPY].
2. Remove the battery compartment lid of the AR8000 using a downward sliding
motion.
Figure 2
Locate the remote control socket which is located at the bottom edge of the
battery compartment. Insert the ribbon cable (with the reinforced plate) contact
(metal) side downward.
Figure 3
- 4 -
Page 5
Connection & clone
It may be difficult to insert the flat cable into the CU8232 socket for the first time
as they are necessarily quite tight. If this is the case, try inserting with a little
upward pressure, it should become easier the next time. DO NOT APPLY
EXCESSIVE STRESS TO THE FLAT CABLE UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES.
A DC voltage is fed to the CU8232 by the AR8000 connected to the [PROGRAM]
socket. When the receiver is switched On, the AR8000 DATA is routed to the
RS232 connector.
If a second receiver is connected to the [COPY] socket and switched On, the
CU8232 recognises it’s presence and routes data between receivers and not to
the RS232 socket.
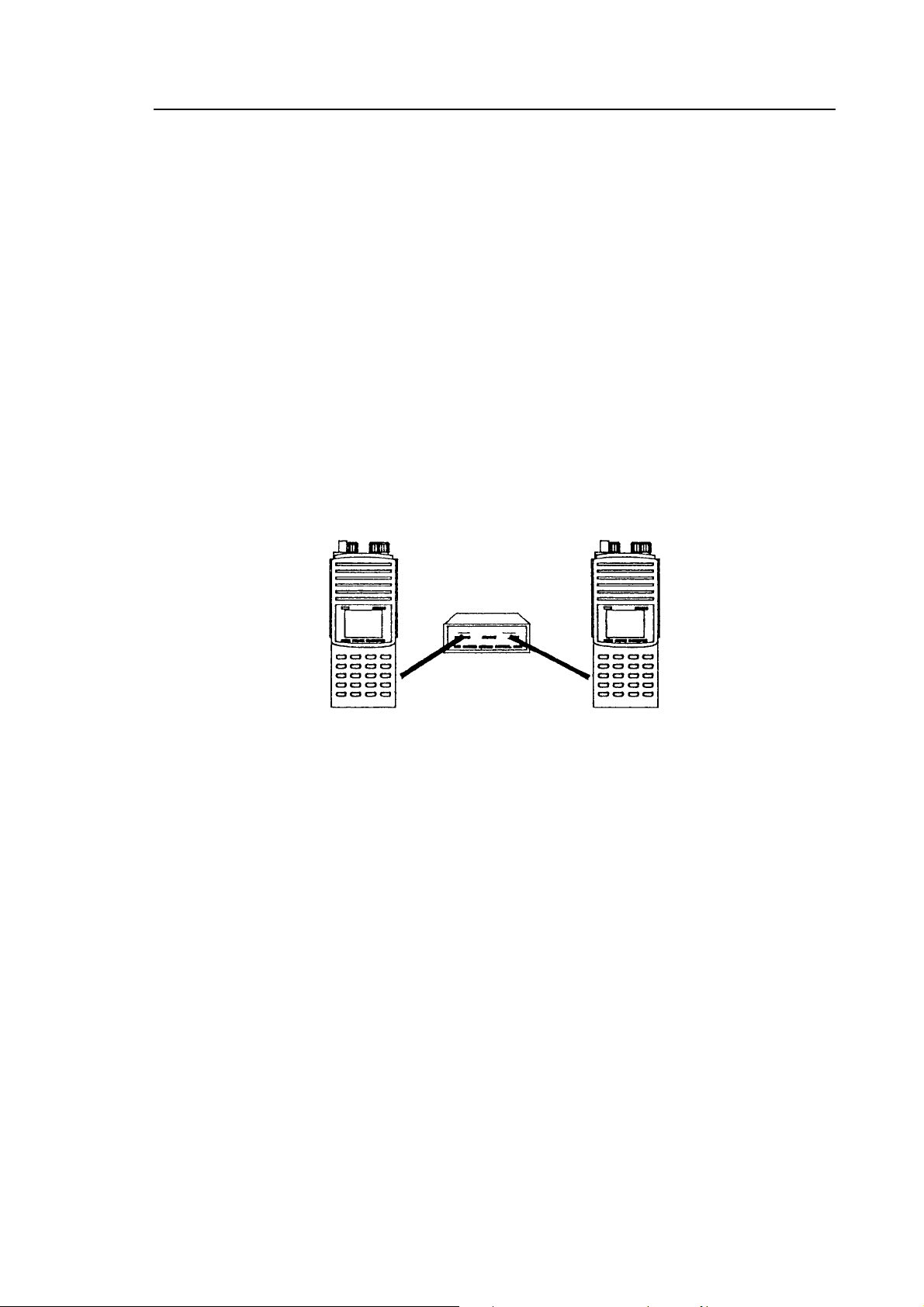
3. To CLONE data between two AR8000 receivers, connect each receiver to the
CU8232 using a ribbon cable as outlined above. Data may be transferred in
BOTH direction between the [PROGRAM] and [COPY] sockets.
Figure 4
4. Switch both receivers On and run the CLONE functions as detailed on page
102 section 19 of the English language operating manual.
Caution! Make sure that no low / flat batteries occur while the data clone is in
progress. Although no significant extra current is required for clone operations,
flat batteries may cause corrupted data transfer. It is advisable that the receivers
are both powered from their chargers (which were supplied with the receivers)
during clone operation.
5. If a data clone fails retry the procedures of clone operation after checking the
following:
¶ Make sure that all connections are correct and there is no loose contact.
¶ Ensure that one receiver is in TRANSMIT mode and the other is in
RECEIVE mode.
- 5 -
Page 6
Connection & clone : RS232
¶ Always press the [ENT] key of the AR8000 in RECEIVE mode first so that
it is ready to accept data.
¶ Press the [CLEAR] key of the receiver prior to the retry if the failure is
due to incorrect connections or an error in key sequence.
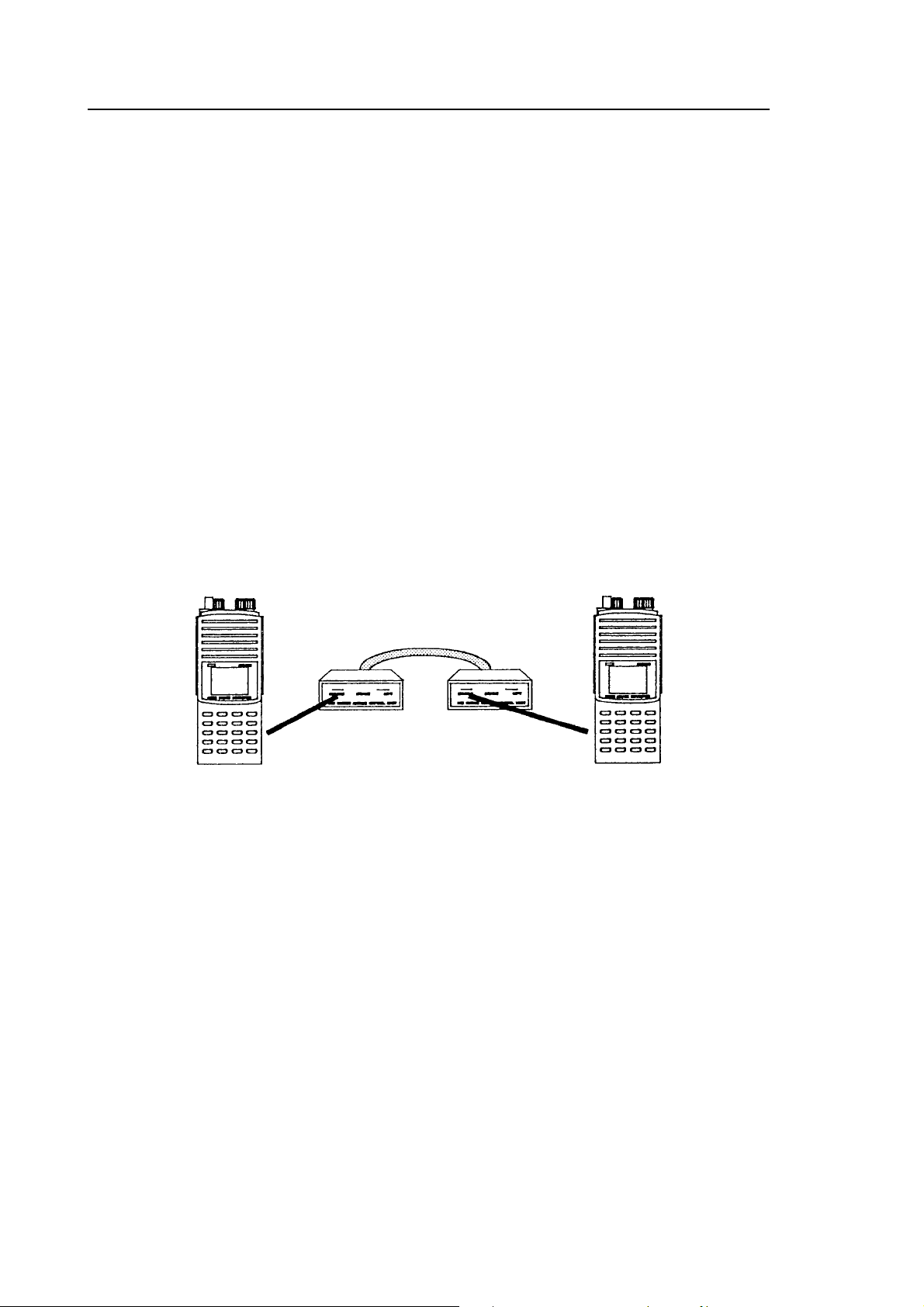
6. An alternative method may be used to connect two AR8000 receivers for data
CLONE. Two CU8232 interfaces may be employed with each AR8000
connected to the [PROGRAM] socket. The RS232 9-pin connectors are
linked using a three wire crossed cable:
CU8232 CU8232
Pin 2 Pin 3
Pin 3 Pin 2
Pin 5 Pin 5
No other pins are used.
Figure 5
(4) Connection for RS232 operation
The remote facility enables the AR8000 to be operated via a computer such as an
IBM-PC or similar, basic remote control terminal or dedicated software will be
required to address the AR8000 through the CU8232.
Switching the receiver On/Off, setting of volume and adjustment of squelch cannot
be achieved via the RS232 port.
Computers “always” generate RF noise which may interfere with the AR8000
reception if the standard helical rubber aerial is used. To reduce the effects of
noise, use of a remote aerial is highly recommended with good quality 50 OHM
coaxial cable employed.
- 6 -
Page 7
RS232 operation
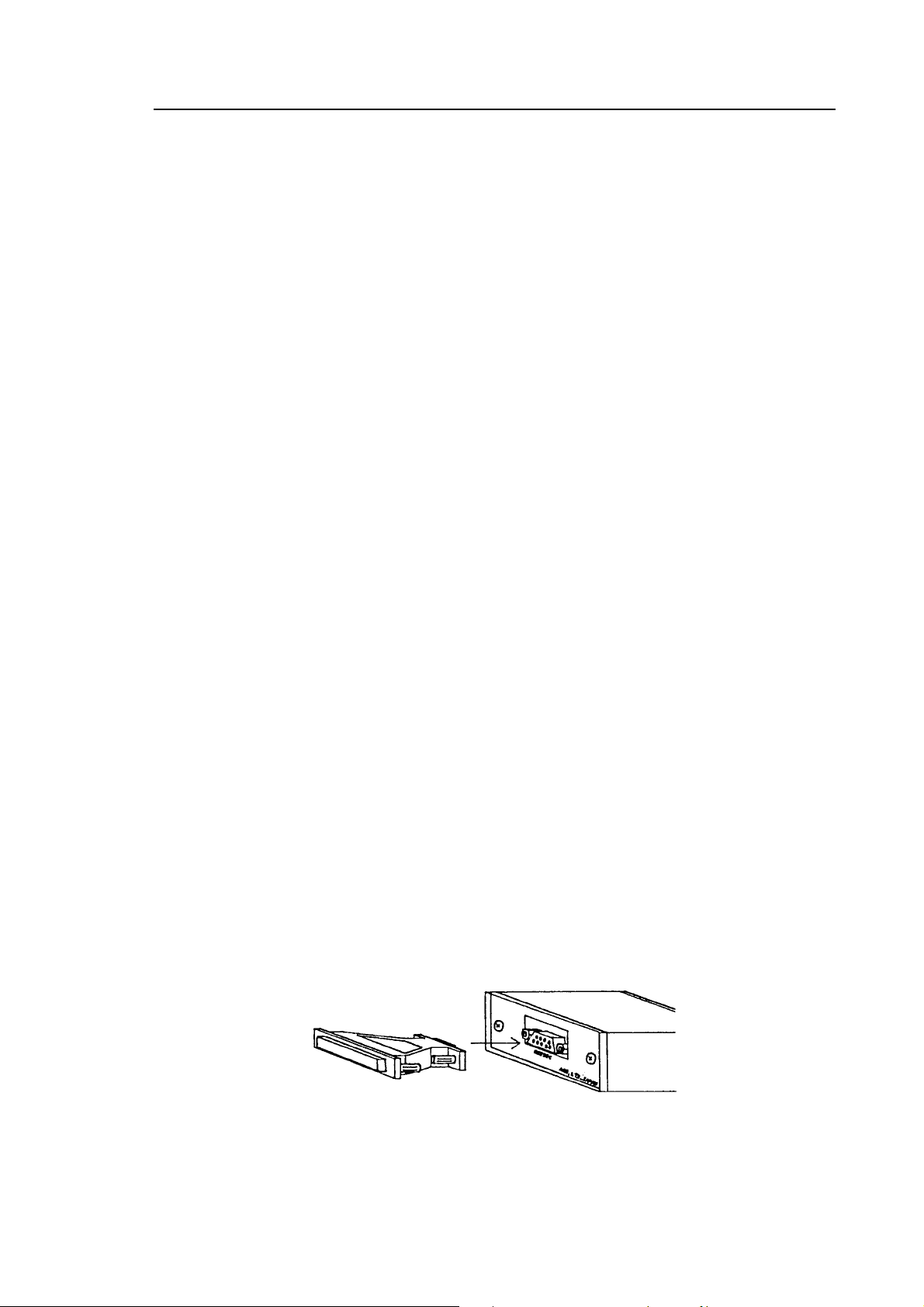
Connect the AR8000 to the [PROGRAM] socket of the CU8232 as outlined earlier
in section (3) and figure 1.
Connection to a computer is via the rear panel RS232C 9-pin “D” type female
socket. Should you require a male socket then a 9-pin gender changer is
supplied in the package. Should you prefer to use a 25-way “D” type female
socket, an adaptor is also supplied as standard.
Always use a straight RS232 cable (null modem is not to be used!). The RS232
cable should be of good quality and no more than 2m in length. As the CU8232 is
powered from the AR8000, excessive cable length may cause lost data between
the AR8000 and computer.
Connection for an IBM-PC or clone is as follows:
CU8232 9-PIN IBM-PC 9-PIN
22
33
5 5 (Ground)
All other pins not used but pins 4, 6 & 8 are linked together inside the CU8232.
Some software requires the linking of CTS/RTS at the computer end of the cable
(pins 7 & 8).
CU8232 9-PIN IBM-PC 25-PIN
23
32
5 7 (Ground)
All other pins not used but pins 4, 6 & 8 are linked together inside the CU8232.
Some software requires the linking of CTS/RTS at the computer end of the cable
(pins 4 & 5).
Figure 6
- 7 -
Page 8
Communication parameters : WINDOWS TERMINAL
(5) Communication parameters
Communication between the AR8000 and computer (via the CU8232) uses
semi-duplex. Refer to both the English language operating manual (page 101
section 18-1) and the computer handbook for correct settings.
Baud rate: 2400, 4800, 9600 selectable
Delimiter: CR or CR,LF selectable
Stop bit: 2 BIT
Parity check: None
The PC requires X-parameter flow control.
Both the computer and AR8000 must use the same parameters for correct
operation.
If data is regularly lost or corrupted, try using a slower speed such as 4800 or
2400 baud. Use of a slower baud rate should not greatly reduce overall
communications transfer rate since the processing time within the receiver and
PLL lock-time ultimately restricts the whole process.
Note: When changing BAUD rate, switch the AR8000 Off/On to
ensure the new speed is selected.
(6) Use of Microsoft WINDOWS “TERMINAL”
Assuming you have DOS and WINDOWS 3.1 (or later) loaded on an IBM-PC
compatible computer, WINDOWS “TERMINAL” may be used to address the
CU8232 and AR8000 receiver to enable basic remote operation.
Start WINDOWS by typing WIN at the DOS prompt. Locate the [TERMINAL]
ICON in the program manager ACCESSORIES group and double-click.
Figure 7
- 8 -
Page 9
WINDOWS TERMINAL
If the terminal program has not be configured an error message will appear
(depending upon the serial port / mouse configuration). Click on [OK] to continue.
Figure 8
TERMINAL will open and appear on the screen. You may re-size or maximise the
screen at this point.
Figure 9
Click on the Settings heading toward the top of the screen so that the
communications and terminal parameters may be configured. Click on
“TERMINAL EMULATION” then select “ANSI” then click on [OK].
Figure 10
- 9 -
Page 10
WINDOWS TERMINAL
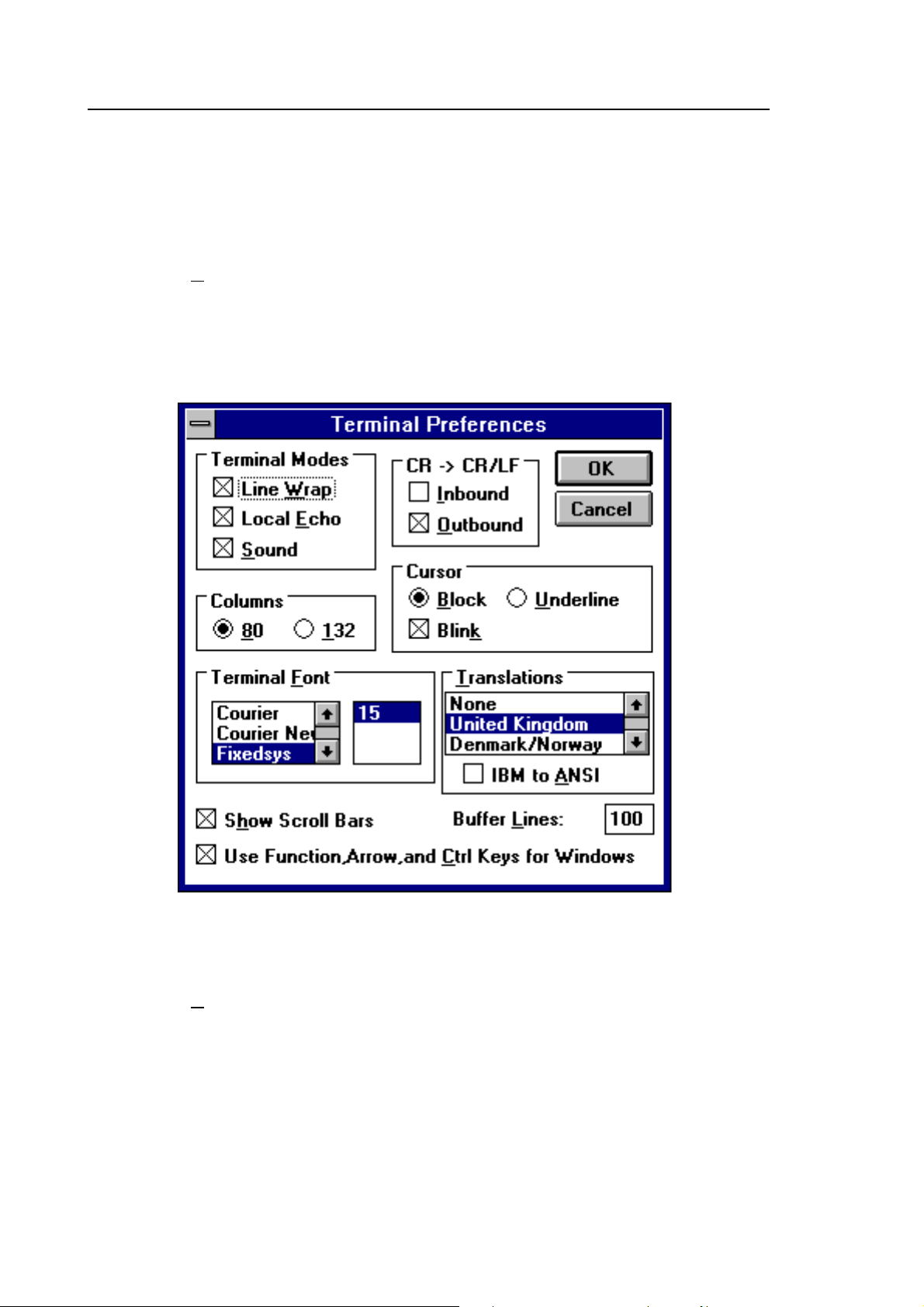
Click on the Settings heading toward the top of the screen so that the
communications and terminal parameters may be re-configured. Click on
“TERMINAL PREFERENCES” then select the options as shown in figure 11.
Finally click on [OK].
Figure 11
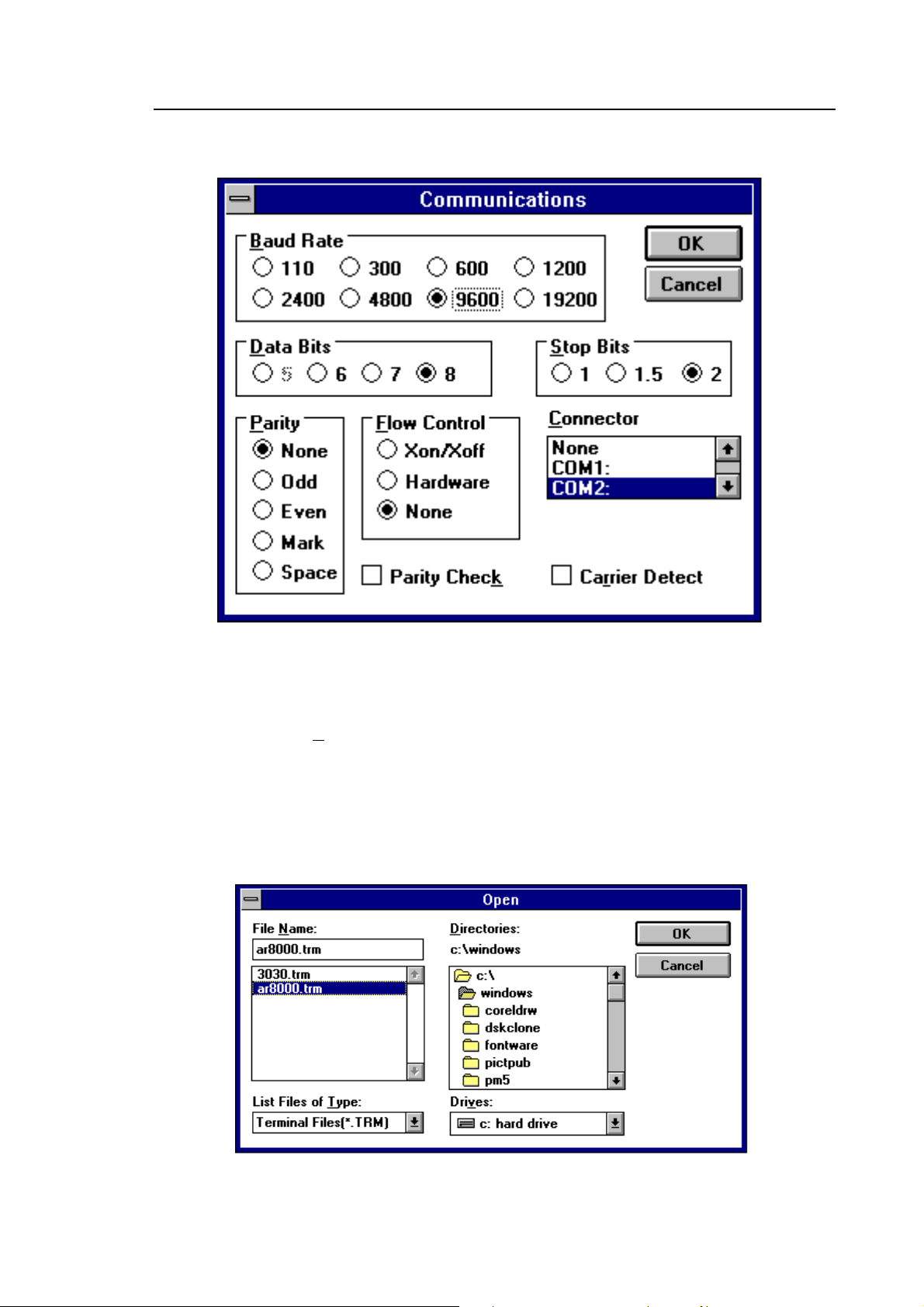
Click on the Settings heading toward the top of the screen so that the
communications and terminal parameters may be re-configured. Click on
“COMMUNICATIONS” then select the options as shown in figure 12. The choice
of COM port (COM1, COM2 etc) will depend upon your computer serial port and
mouse configuration. Finally click on [OK].
- 10 -
Page 11
WINDOWS TERMINAL
Figure 12
Finally click on the File heading toward the top of the screen and select
SAVE_AS. This will enable the chosen parameters to be saved in a file which
may be OPENED next time TERMINAL is selected so that the parameters will not
require future re-configuration. Figure 13 shows a file name of AR8000.TRM,
(.TRM being the default extension). The file is saved in the main WINDOWS sub
directory.
Figure 13
- 11 -
Page 12

Sending a command
¶ For further information regarding WINDOWS TERMINAL and configuration,
please refer to the operating manual supplied with Microsoft software and
the computer.
Click on “COMMUNICATIONS” then select the options as shown in figure 11.
The choice of COM port (COM1, COM2 etc) will depend upon your computer
serial port and mouse configuration. Finally click on [OK].
(7) How to send a command
Each command comprises of two upper case letters (header) along with options
as required. All commands use ASCII code which MUST BE IN UPPER CASE
(except for the “ARROW” é ê which uses the control code of ASCII).
A multiple command entry is only valid where specified. Where a multiple
command entry is allowed, each command MUST be separated with a space
“h20” (HEX DECIMAL).
Each command is completed with a [CR] or [CR],[LF] whichever is specified in the
AR8000 receiver configuration (page 101 section 18-1 of the English language
AR8000 operating manual), thereafter described as [ï].
Although there is no local echo, either [ï] or a specified response should come
back from the receiver after confirming the correct command.
A space is often shown as "_" in the following examples.
REMOTE indication
When the AR8000 has received a command via the RS232C port the receiver’s
LCD with alternate between the top line of data and the wired “REMOTE”. When
remote mode is engaged the receiver’s keypad becomes inoperative. To restore
operation to the receiver’s keypad press [LOCAL] - effectively remote operation is
cancelled. Remote mode is re-engaged when a new command is received via the
RS232C port.
The receiver always acknowledges the receipt of a command by sending [ï]
(as specified in the receiver configuration) or will respond with the requested data.
Only send a second command after the first command has gained a response.
If no response has been gained after a short while, the receiver has failed to
receive the command properly. Send a [ï] then re-send the command. Should
problems persist, check your serial / CU8232 connections and try reducing the
RS232 baud rate.
- 12 -
Page 13

List of commands
(8) List of commands
Application Command
VFO Freq Input RF VA VB
Receiver Function AT AU MC MD RX ST
SQ, S-Meter LC LM MG SG
Receive Mode DD MR MG MS SG SM SS VF
Search BN BQ BS SA SB SD SE SG SO SP SQ SR SS
Search Data Write AT AU MD SE SL SU ST TT
Pass Freq PD PR PS PW
Memo CH, Scan BM BN MA MG ML MP MQ MR MS XA XB XD XM
XO XP XQ
Memo CH Data Write AT AU MD MX RF ST TM
Select Scan GA GD GR SM
Others EX PA PI SC SI SN TI
é[UP] (1E) ê[DOWN] (1F) ( )= Hex Decimal
Arrow is a control code of ASCII.
No delimiter is required when sending Arrow.
Commands which have dual roles are duplicated in
this list.
- 13 -
Page 14

Command index
(9) Command index
AT Register the attenuator position ON/OFF.
AU Register the auto mode ON/OFF.
BM Register the scan bank link ON/OFF.
BN Change the search/scan bank.
BQ Register the search bank link function ON/OFF.
BS Register the search bank link ON/OFF.
DD Recall the VFO mode.
EX End the Remote mode (RS232C).
GA Register the select scan channel from Memory channel.
GD Delete the select scan channel from Memory channel.
GR Recall the select scan channel.
LC Respond with the received freq and S-level when SQ opens.
LM Respond with the S-level reading and SQ open/close.
MA Respond with the contents of the present bank or specified
bank.
MC Select the monitor switch position.
MD Select the receive mode.
MG Start the scan mode. Respond with receive freq and S-level
reading when SQ is open (as LC).
ML Register the scan bank link function ON/OFF.
MP Register the present memory channel as Pass channel.
MQ Delete the present bank or memory channel.
MR Switch to the memory read (M.RE) mode.
MS Switch to the scan (SCAN) mode.
MX Write data into memory channel.
PA Register the delay time of Power Save mode.
PD Delete the Search Pass Freq
PI Register the interval time of Power Save mode.
PR Recall the Search Pass Freq
PS Register the Search Pass Freq
PW Register the presently receiving freq as Pass Freq
RF Key in the Freq in VFO
RX Respond with the presently receiving data
SA Register the Audio Search ON/OFF.
SB Register the Level Search ON/OFF. Set the S-level.
SC Change the operating code of the option unit (when fitted - not
available in the UK).
SD Change-over HOLD/DELAY in Search mode. Register the delay
time.
- 14 -
Page 15

SE Register the Search data.
SG Start the Search mode. Respond with freq and S-level reading
when SQ is open.
SI Switch the option unit ON/OFF (when fitted - not available in the
UK).
SL Write the start freq of Search.
SM Start the Select Scan.
SN Write the Pass Word. Recall the Pass Word.
SO Recall the Search operating mode.
SP Register the Free Search ON/OFF and delay time.
SQ Check the SQ setting.
SR Recall the Search data.
SS Start the Search.
ST Register the step size in search mode.
SU Register the end freq of search mode.
TI Register the interval time of Priority channel.
TM Write the text for memory channel
TT Write the text for search bank
VA Initiate the AVFO mode.
VB Initiate the BVFO mode.
VF Initiate the 2VFO mode.
XA Register the Audio Scan ON/OFF.
XB Register the Level Scan ON/OFF.
XD Register the delay time in Scan mode.
XM Register the Mode Scan ON/OFF.
XO Recall the Free Scan operating mode.
XP Register the Free Scan ON/OFF and timing.
XQ Recall the SQ operating mode.
Arrow Mark
é[UP] ê[DOWN] similar to the receiver’s keyboard.
- 15 -
Page 16

Explanation of commands : AT : AU
(10) Explanation of commands
AT
ATTENUATOR ON/OFF.
ATn[ï] n = 0 ATT OFF
n = 1 ATT ON
Multiple commands in conjunction with other commands are possible with a space
in between: AT, AU, MD, RF, ST, VA, VB.
Example: AU0_MD3_RF145.2_AT1[ï]
AT[ï] checks the current attenuator setting, the response being:
AT0 = ATT OFF
AT1 = ATT ON
Related commands MD MX RF SE VA VB
AU
AUTO MODE (and step) ON/OFF.
AUn[ï] n = 0 AUTO MODE OFF
n = 1 AUTO MODE ON
Multiple commands in conjunction with other commands are possible with a space
in between: AT, AU, MD, RF, ST, VA, VB.
Example: AU0_MD3_RF145.2[ï]
AU[ï] checks the current auto mode setting, this is not valid when “M.RE” or
“SCAN” is in use. The usual response to the AU request being:
AU0 = AUTO MODE OFF
AU1 = AUTO MODE ON - step size and receive mode set automatically.
Related commands MD MX RF SE ST VA VB
- 16 -
Page 17

BM
BM
SCAN BANK LINK ON/OFF (specifically).
BM[ï] checks the current status of linked scan banks.
If bank letters are specified then scan bank link is On (the specified banks will be
scanned as a group), if no letters are specified then the facility is Off.
First check the current status by typing BM[ï]
A typical response may be: BM -BC—GHIJa—e—h-j
To switch bank link Off type in the reported scan bank letters:
BM BCGHIJaehj (lower case input being accepted for the second group of
memory banks)
To activate a new scan bank link type in the required list of scan bank letters.
For example to link a few specified scan banks and turn the facility On:
Type BM followed by the bank letters and terminated with [ï]
BM ABDabcij [ï]
The BM command may be used to switch some banks On and others Off at the
same time. To make things easier a “-” character reverses the current status of
the specified bank, of course this may also be used to switch scan bank link Off.
Note: The SCAN BANK LINK facility can also be simply switched On/Off
using the ML command.
BS is the equivalent command for SEARCH bank link.
Related commands ML BN XA XB XD XM XO XP XQ
- 17 -
Page 18

BN : BQ : BS
BN
The BN command is used to change the starting point for SCAN and SEARCH
banks. In VFO mode, BN specifies the bank to use when SCAN or SEARCH
mode is entered (rather than the last used bank location).
In scan or search mode for format is BNx[ï] where x is a bank location A-J & a-j.
To review the current status of BN simply type BN[ï]
The response is split into SEARCH and SCAN banks, MXx for SCAN bank and
SRx for SEARCH bank. For example “SRD” indicates search bank D and MXj
indicated scan bank j.
Related commands BM BQ BS ML MQ
BQ
Switch search bank link On/Off (globally).
The BQ command provides a simple method of switching search bank link On/Off.
Type BQn[ï] to toggle the status n = 0 search bank link OFF
n = 1 search bank link ON
Related commands BN BS SA SB SD SG SO SP SS
BS
SEARCH BANK LINK ON/OFF (specifically).
BS[ï] checks the current status of linked search banks.
If bank letters are specified then search bank link is On (the specified banks will
be searched as a group), if no letters are specified then the facility is Off.
First check the current status by typing BS[ï]
A typical response may be: BS -BC—F-HIJa—e——j
To switch bank link Off type in the reported scan bank letters
BS BCFHIJaej (lower case input being accepted for the second group of memory
banks)
- 18 -
Page 19

BS : DD
To activate a new search bank link type in the required list of search bank letters.
For example to link a few specified search banks and turn the facility On:
Type BS followed by the bank letters and terminated with [ï]
BS ABDabcij [ï]
The BS command may be used to switch some banks On and others Off at the
same time. To make things easier a “-” character reverses the current status of
the specified bank, of course this may also be used to switch search bank link Off.
Note: The SEARCH BANK LINK facility can also be simply switched On/Off
using the BQ command.
BM is the equivalent command for SCAN bank link.
Related commands BQ SA SB SD SG SO SP SS
DD
Report the current VFO data.
Type DD[ï] to report the current VFO data.
Should a response be as follows:
RF0001134000_ST009000_AU1_MD2_AT0 the data breakdown is:
Receive frequency: 1.134 MHz
Step size: 9.0 kHz
Auto mode: ON
Receive mode: AM
Attenuator: OFF
Related commands MR MG MS RX SG SM SS VF [UP] [DOWN]
- 19 -
Page 20

EX : GA : GD
EX
End remote operation and restore keypad operation to AR8000.
To end RS232 remote operation type EX[ï]
This has the same effect as pressing the [LOCAL] key on the AR8000 receiver.
GA
Designate (“TAG”) memory channel for select scan.
The GA command is used to “tag” memory channels for select scan.
GAxnn[ï] where x is the bank letter A-J & a-j
where nn is the memory channel number 00-49
Related commands GD GR SM
GD
Deactivate (“UN-TAG”) memory channel for select scan.
The GD command is used to remove “tags” from memory channels and remove
the frequency from the select scan list.
GDnn[ï] where nn is the select scan channel number 00-49
For example, to clear select scan channel 03 type GD03[ï]
When a select scan channel has been deleted, the registered memory channel
number will automatically be updated. Use the GR command to check the
updated registered channel number.
To clear all select scan channels in one go type GD%%[ ï]
Related commands GA GR SM
- 20 -
Page 21

GR
GR
Recall select scan channels.
The GR command is used to recall the data from select channels specifically or as
a whole.
Select scan channels are assigned in order 00 - 99. When a select scan channel
is deleted the higher numeric channel “shuffle down” to fill the vacant allocation
(refer to page 69 section 11 of the English language operating manual for further
information).
To recall the data from a specific select scan channel use the format:
GRnn[ï] where nn is the channel number 00 - 99
To recall the data from all select scan channels type GR[ï]
The response for a specific channel may look like this:
GR01_MXB07_MP0_RF0126000000 ST025000_MD2_AT0_TMTEST123
The information reported being:
Select scan: Channel 01 (second registered channel)
Memory bank: B
Memory channel: 07
Memory pass: OFF
Receive Frequency: 126.00 MHz
Receive mode: AM
Attenuator: OFF
Displayed text: TEST123
Related commands GA GS GR SM
- 21 -
Page 22

LC : LM
LC
The LC command caused the receiver to supply FREQUENCY and S-METER
level only when the squelch is opened. A new response will be repeated
automatically when the squelch is closed and opened again.
The automatic data response will only be supplied when ALL squelch parameters
are met (level scan, audio scan etc).
To terminate the facility send another command.
LC[ï] will report the present receive frequency and S-meter. The S-meter report
is in 64 steps from hex decimal 00 to 3F.
A typical response may be: LC1B_RF0145300000
1VFO S-meter h1B Receive frequency 145.30 MHz
Another example: LC04_VA0128800000
2VFO VFOA S-meter h04 Receive frequency 128.80 MHz
Notes: S-meter reading and frequency are separated with a space. The S-meter
output is in 64 steps (hex decimal) 00 to 3F. “3F” may not be available on some
sets as he CPU processes the data and the MAXIMUM level may vary slightly
between sets.
Approximate relation of S-meter and LC report:
S-meter 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
“LC” 0 ~ 04 ~ 08 ~ 0C ~ 10 ~ 14 ~ 18 ~ 1C ~ 3F (16 hex)
Related commands LM MG SG
LM
S-meter reading and squelch status.
The LM command is used to report the S-meter level and squelch open / closed
status.
The S-meter reading is reported in 64 steps (hex) 00 ~ 3F. The squelch is
CLOSED when the response is 80 and above.
- 22 -
Page 23

A typical response to the LM[ï] command is: LM1D
00 ~ 3F Squelch is open
80 ~ BF Squelch is closed
Related commands LC MG SG [UP] [DOWN]
MA
Recall data from the current of specified memory bank.
The MR command recalls data from the current of specified memory bank.
MR[ï] recalls data from the current memory bank.
MRx[ï] recalls data from the specified memory bank where
x = A ~ j & a ~ j.
A typical response being:
LM : MA
MXA00_MP0_RF0000945000_ST009000_AU1_MD2_AT0_TMGEM AM
MXA01_MP0_RF0000693000_ST009000_AU1_MD1_AT0_TMRadio 5
SIMILAR FORMAT FOR ALL CHANNELS...
MXA49_MP0_RF0082520000_ST100000_AU1_MD1_AT0_TMJOAK-FM
The first memory channel data being:
Memory bank: A
Memory channel: 00
Memory pass: OFF
Receive frequency: 945 kHz (0.945 MHz)
Step increment: 9 kHz
Auto mode: ON
Receive mode: AM
Attenuator: OFF
Displayed text: GEM AM
If no data is available in the selected or current memory bank the response may
look like this:
MXD_— No memory data in this channel of bank “D”.
Related command MX
- 23 -
Page 24

MC : MD
MC
Select monitor switch position.
The monitor switch may be selected irrespective of squelch setting by use of the
MC command. This is particularly useful for weak or fluttery signal monitoring or
when listening to SSB transmissions. The MC command may also be used to
mute the audio completely.
MCn[ï] where n = 0 MUTE OFF (emit audio)
n = 1 MUTE ON (mute audio)
n = 2 MUTE AUTO (restore normal SQ operation)
MD
The MD command provides a quick method to report and change the current
receive mode without affecting other settings.
To report the current mode type:
MD[ï] where 0 = WFM
1 = NFM
2 = A M
3 = USB
4 = LSB
5 = C W
To change the current mode:
MDn[ï] where n equals 0 ~ 5 MD0[ï] WFM
MD1[ï] NFM
MD2[ï] A M
MD3[ï] USB
MD4[ï] LSB
MD5[ï] C W
Multiple command entry is of course possible: AT0_MD3_RF145.2[ï]
Related commands AU MX RF SE VA VB
- 24 -
Page 25

MG : ML
MG
Scan with frequency and S-meter then resume.
The MG commands causes an automatic response of receive frequency and
S-meter level (similar to LC command) AND places the receiver into memory scan
mode again.
MG[ï] will report the present receive frequency in Hz and S-meter. The S-meter
report is in 64 steps from hex decimal 00 to 3F.
A typical response may be: LC2B_RF0145300000
S-meter h2B Receive frequency 145.30 MHz
Related commands BM BN DD ML MP MQ MR MS MX SG SS VF XA VB XD XM
XO XP XQ é ê
ML
Scan bank link On/Off.
The ML command is used to switch the memory scan bank link facility ON / Off.
The command ML[ï] may be used to check the current status of scan bank link.
To change the status of scan bank link, the MLn[ï] command is used
where n = 0 Bank link OFF
n = 1 Bank link ON
Related commands BM BN XA XB XD XM XO XP XQ
- 25 -
Page 26

MP : MQ
MP
Register the present channel as PASS.
The MP command is used to register the current memory channel as PASS
(so that it will be skipped during scan). The command is generally used in
conjunction with the “MR” command.
To check the current status of PASS use the command MP[ï]
The response will be MP0 Memory PASS OFF
MP1 Memory PASS ON
It is possible to change the status of memory channel PASS using the command:
MPn[ï] where n = 0 Channel PASS OFF
n = 1 Channel PASS ON
Related commands BN MQ MR MG MS
MQ
Delete the current memory channel OR bank.
The MQ command can only be used in M.RE (memory read) mode. It is used
to delete memory channels or a whole memory bank in one go. The memory bank
must first be recalled as the active bank.
Note: One memory channels have been deleted the data is lost. They can not be
reinstated but new data has to be written to the channel if required.
The command MQ[ï] deleted the current memory channel.
The command MQnn[ï] deletes the specified memory channel from the current
bank were nn = 00 ~ 49
The command MQ%%[ï] deletes ALL memory channels from the current memory
bank.
Related commands BN MP MR MG MS
- 26 -
Page 27

MR
MR
Place the receiver in M.RE - memory read mode.
The MR command is used to place the receiver into memory read mode. The MR
command is also required before channels may be deleted using the MQ
command.
The MR[ï] command places the receiver in memory recall mode and the last
used channel data is reported.
It is possible to specify both the memory bank and channel number for recall:
MRxnn[ï] where x = memory bank A ~ J & a ~ j
nn = channel number 00 ~ 49
A typical response to the MR command may be:
MAC43_RF0435120000_ST20000_MD1_AT0_TMBANKC43
Memory bank: C
Memory channel: 43
Receive frequency: 435.12 MHz
Step size: 20 kHz
Receive mode: NFM
Attenuator: OFF
Text: BANKC43
A response of: MAD00_— indicates that the memory bank has no channels
programmed or they have been deleted.
Related command MA
- 27 -
Page 28

MS : MX
MS
Start memory scan.
The MS command places the receiver into memory scan mode.
MS[ï]
Commences memory scan from the current memory bank (or last one used if in
another operating mode).
MSx[ï]
Commences memory scan from a specified memory bank number
where x = A ~ J & a ~ j memory bank number
Related commands BM BN DD MG ML MP MQ MR MX SG SS VF XA VB XD XM
XO XP XQ é ê
MX
Write data into a memory channel.
The MX command is used to write a comprehensive set of data to a specified
memory bank / channel.
The format of the command is:
MXxnnRF[freq]_AU[auto mode]_ST[step size]_MD[mode]_AT[att]_TM[text] [ï]
For example: MXD12_RF124.8_AU1_AT0_TMAirband [ï]
This will set memory bank “D” channel “12” to 124.8 MHz, Auto mode ON,
Attenuator OFF and text “Airband”.
Always start with MX and end with TM followed by [ï]. Each command is
separated with a space _ .
MXxnn Memory location where x = A ~ J & a ~ j memory bank
nn = 00 ~ 49 memory channel
RFnnnnnnnnm0 (Hz) Frequency input frequency in Hz. The last but one
digit (tens of Hz) MUST be either “5” or “0”.
- 28 -
Page 29

MX
RFnnnn.nnnnm0 (MHz) Refer to the command “RF”.
AUn AUTO MODE where n = 0 OFF
n = 1 ON
* When AUTO MODE is ON, step size and mode is invalid.
STnnnnm0 (Hz) Step size input in MHz. The last but one digit (tens
of Hz) MUST be either “5” or “0”.
STnnn.nm0 (kHz) Refer to the command “ST”.
MDn Receive mode where n = 0 WFM
n = 1 NFM
n = 2 A M
n = 3 USB
n = 4 LSB
n = 5 C W
ATnAttenuator where n = 0 Attenuator OFF
n = 1 Attenuator ON
TMxxxxxxx Text write where xxxxxxx may be up to 7
characters in ASCII (refer to TM) or character
mode.
Absence of a command will cause the present or previous value to be
automatically entered.
Related commands MP MQ MR
- 29 -
Page 30

PA : PD
PA
Set delay time for power save mode.
The PA command is used to set the delay time and is used in conjunction with PI
which sets the interval time for the power save facility.
The command PA[ï] checks the current setting of power save delay time, the
response being PAnn where nn = 01 ~ 99 seconds
nn = 00 is power save OFF
To change the current setting, use the PA command followed by a two digit
numeric value between 00 ~ 99. The value is in seconds and “00” switched the
power save facility off (please refer to page 97 section 16 of the AR8000 English
language operating manual).
To set a delay of 12 seconds use the command PA12[ï]
Related command PI
PD
Delete PASS frequencies in search mode.
There are 50 PASS frequencies allocated per search bank, they may be deleted
on an individual basis or the whole bank may be deleted in one go.
The BN or SS commands must be used to choose the bank prior to using the PD
command.
PDnn[ï] deletes a specific PASS frequency from the chosen search bank
where nn is the PASS channel number 00 ~ 49.
When a PASS channel is deleted, the PASS frequency number will be
incremented upward.
PD%%[ï] deletes ALL PASS channels from the current search bank in one go.
Related commands BN PR PS PW SG SR SS
- 30 -
Page 31

PI : PR
PI
Set interval time for power save mode.
The PI command is used to set the interval time and is used in conjunction with PA
which sets the delay time for the power save facility.
The command PI[ï] checks the current setting of power save delay time, the
response being PIn where n = 1 ~ 9 seconds
To change the current setting, use the PI command followed by a single digit
numeric value between 1 ~ 9, the value is in seconds.
To set an interval of 5 seconds use the command PI5[ï]
(Please refer to page 97 section 16 of the AR8000 English language operating
manual).
Related command PA
PR
There are 50 PASS frequencies allocated per search bank, they may be recalled
on an individual basis for review using the PR command before being deleted
using the PD command.
The BN or SS commands must be used to choose the bank prior to using the PD
command.
PRnn[ï] recalls a specific PASS frequency from the chosen search bank
where nn is the PASS channel number 00 ~ 49.
When a PASS channel is deleted using the PD command, the PASS frequency
number will be incremented upward.
Related commands BN PD PS PW SG SR SS
- 31 -
Page 32

PS : PW
PS
Write search PASS frequency.
There are 50 PASS frequencies allocated per search bank, they may be entered
using the PS command. The BN or SS commands must be used to choose the
bank prior to using the PS command.
PSnnnnnnnn00[ï] (Hz) enter PASS frequency in Hz
PSnnnn.nnn[ï] (MHz) enter PASS frequency in MHz. If MHz entry is
used there is no need to enter the trailing digits
after the decimal point, they will be treated as “0”.
Examples of PASS frequency input:
150.2 MHz PS150.2[ï] or PS150200000[ï]
1134 kHz PS1.134[ï] or PS1134000[ï]
1691.0 MHz PS1691.[ï] or PS1691000000[ï]
Related commands BN PD PR PS SG SS
PW
Register current frequency as PASS.
The PW command is used to register the current receive frequency in the search
pass list. The BN or SS commands must be used to choose the bank prior to
using the PW command.
The command PW[ï] being used.
Related commands BN PD PR PS SG SS
- 32 -
Page 33

RF
Write and recall receive frequency to / from VFO.
The RF command is used to write a frequency to VFO. The input may be
specified in Hz or in MHz if the decimal point is used.
The format of the RF command being:
RFnnnnnnnnm0[ï] (Hz)
or
RFnnnn.nnnnm[ï] (MHz)
Note: "0" must always be used in the 1Hz place when using Hz input & "m" must
always be either 0 or 5 in the 10Hz position, any other number will be ignored.
Frequencies below 1.6 MHz (1600 kHz) are displayed as kHz.
RF
For example:
150.3 MHz input RF150.2[ï] or RF150200000[ï]
1134 kHz input RF1.134[ï] or RF1134000[ï]
1691.0 MHz input RF1691.[ï] or RF1691000000[ï]
To recall the receive frequency of the current VFO, the RF[ï] command is used.
The response may look like RF0001134000[ï]
Related commands VA VB
- 33 -
Page 34

RX : SA
RX
Recall present operating condition and data.
The RX command is used to recall (generate a report) the current operating
condition of the receiver including VFO, SCAN, SEARCH etc along with receive
mode, frequency etc.
The format of the RX command is: RX[ï]
A two letter code reports the current operating condition with further details
(receiver frequency etc) following as appropriate. The meaning of the two letter
code is as follows:
DD. . VFO MODE
VF. . 2 VFO MODE
MR. . MEMO CH MODE
MS. . SCAN MODE
SM. . SELECT SCAN MODE
SS. . SEARCH MODE
Response examples are as follows:
VFO MODE DD_RF0126000000)ST025000_MD2_A T0
2VFO MODE VF_V A0128680000_ST025000_MD2_A T0
MEMO CH MODE (M.RE) MR_MXB07_MP0_RF0126000000_ST025000_MD2_A T0_TMTest123
SCAN MODE MS_MXB17_MP0_RF0197750000_ST025000_MD0_A T0_TMTV-8ch
SELECT SCAN MODE SM_MXA34_MP0_RF0028500000_ST000050_MD3_A T0_TM28m_HAM
SEARCH MODE SS_RF0128800000_ST025000_AU1_MD2_A T0_TT AIR.VHF
Related command BN
SA
Audio search ON/OFF.
The SA command is used to report the current setting of audio search and to
change the setting between On and Off.
To recall the current setting type SA[ï]
The response will be SAn where: n = 0 Audio search OFF
n = 1 Audio search ON
- 34 -
Page 35

SA : SB
To change the setting of audio search, use the command:
SA0[ï] Switch audio search OFF
SA1[ï] Switch audio search On
When audio search is ON, only signals with valid recognised audio will cause the
squelch to open.
Related commands BQ BS SD SG SO SP SQ
SB
Set level search and threshold.
The SB command is used to report the current setting of level search and to
change the setting between Off, On and seven levels.
To recall the current setting type SB[ï]
The response will be SBn where: n = 0 Level search OFF
n = 1 ~ 7 Audio search ON
The value of level search 1 ~ 7 represents the level of signal required before the
squelch will open, the higher the number then the greater the signal will need to
be. When level search is active, only signals above the preset level will open the
squelch.
To change the setting of level search, use the command:
SA0[ï] Switch level search OFF
SAn[ï] Switch audio search On where n = 1 ~ 7
this presets the level required to open the squelch
Related commands BQ BS SA SD SG SO SP SQ
- 35 -
Page 36

SC : SD
SC
Set operating code for option (not available in the UK).
The SC command is used to review and select the operating code if the option is
fitted to the AR8000. LSB is used to control the optional unit.
To review the current selection of code use the command SC[ ï]
The response will be in the format SCnn where nn = 00 ~ 7F (HEX DECIMAL)
Some units may only have four operating codes, in this case the lower end of 2BIT
is used. They are identical in operation: 01 05 09 0D 25 39 5D 79
To change the current code use the format SCnn[ï] where nn is the desired
operating code.
Related command SI
SD
Change HOLD / DELAY time in search mode.
The SD command is used to review and change the setting of HOLD / DELAY time
when in search mode.
To review the current setting use the command SD[ï]
The response will be in the format:
SDnn where nn = 01 ~ 99 DELAY in tenths of seconds (100mS)
nn = FF HOLD
nn = 00 DELAY OFF
Examples are: SD65 = DELAY of 6.5 seconds
SD52 = DELAY of 5.2 seconds
SDFF = HOLD ON
SD00 = DELAY OFF
To change the current setting of HOLD / DELAY in search mode use the format
SDnn[ï] where: nn = 01 ~ 99 DELAY in tenths of seconds (100mS)
nn = FF HOLD
nn = 00 DELAY OFF
Related commands BQ BS SA SB SG SO SP SQ
- 36 -
Page 37

SE
SE
The SE command is used to input data for search bands.
To write search data into the currently selected search bank, the format of the SE
command is:
SE_SL[LOWER FREQUENCY]_SU[HIGHER FREQUENCY]_AU[AUTOMODE]_
ST[STEP SIZE]_MD[MODE]_AT[A TTENUA TOR]_TT[TEXT][ï]
To write search date to a specific search bank, the following format is used:
SEx_SL[LOWER FREQUENCY]_SU[HIGHER FREQUENCY]_AU[AUTOMODE]_
ST[STEP SIZE]_MD[MODE]_AT[A TTENUA TOR]_TT[TEXT][ï]
Where:
SEx x = Search bank number A ~ J or a ~ j
SL Lower frequency limit nnnnnnnnm0 (Hz)
or nnnn.nnnnm (MHz)
m = "0" or "5" (tens of Hz position)
SU Upper frequency limit nnnnnnnnm0 (Hz)
or nnnn.nnnnm (MHz)
m = "0" or "5" (tens of Hz position)
AU Automode n = 0 Automode OFF
n = 1 Automode ON
When automode is ON, the receive mode and step
size is automatically set and any alternative input
of SE will be ignored. Refer to AU command.
ST Step size nnnnm0 (Hz)
or nnn.nm (kHz)
m = "0" or "5" (tens of Hz position)
MD Receive mode WFM 0
NFM 1
AM 2
USB 3
LSB 4
CW 5
AT Attenuator n = 0 Attenuator OFF
n = 1 Attenuator ON
TT Text comment - Up to 7 ASCII characters or
characters available in the list (see list under "TT"
command and further detail under TM command)
A typical input may look like:
SEC_SL0118500000_SU0135900000_AU1_(ST025000_MD2_)AT0_TTAIR.VHF[ï]
The input in brackets ( ) is ignored when automode is selected ON.
Related commands SR SG SS
- 37 -
Page 38

SG : SI
SG
Search with frequency and S-meter then resume.
The SG commands causes an automatic response of receive frequency and
S-meter level (similar to MG / LC command) AND places the receiver into search
mode again.
SG[ï] will report the present receive frequency in Hz and S-meter. The S-meter
report is in 64 steps from hex decimal 00 to 3F starting from the currently selected
search bank.
A typical response may be: LC2B_RF0145300000
S-meter h2B Receive frequency 145.30 MHz
The command SGx[ï] causes an automatic response and searching from the
specified bank where x = A ~ J & a ~ j.
Related commands LC MG SS é ê
SI
Set code for option ON / OFF (not available in the UK).
The SI command is used to review and select the optional code unit On / Off if the
option is fitted to the AR8000.
To review the current status use the command SI[ï]
The response will be in the format SIn
where
n = 0 Optional code unit OFF
n = 1 Optional code unit ON
To switch the code option ON / OFF use the format SIn[ï]
where
SI0[ï] = Optional code unit OFF
SI1[ï] = Optional code unit ON
Related command SC
- 38 -
Page 39

SL : SM : SN
SL
Set the lower frequency of a search bank.
This command cannot be used on its' own but must be used in conjunction with
the SE command, please refer to the section on SE.
SL Lower frequency limit nnnnnnnnm0 (Hz)
or
nnnn.nnnnm (MHz)
m = "0" or "5" (tens of Hz position), "0" must always be "0" any other entry will be
ignored. Input below 1.6 MHz is displayed in kHz.
Related commands SE SL SU TT
SM
Start memory scan.
The SM command is used to start a memory scan. The format of the command is
SM[ï]
Related commands GA GD GR é ê
SN
Select PASSWORD options.
The SN command is used to set or disable the PASSWORD protection of the
memory and search banks a ~ j.
To review the current password use the format SN[ï]
The response will be in the format SNnnnn where nnnn is the four digit
password. If the response is "0000" then the password facility is disabled.
To set a new password use the format SNnnnn[ï] where nnnn is a four digit
number comprising of digits 0 ~ 9 inclusive. To disable the password use the
command SN0000[ï]
- 39 -
Page 40

SO : SP
SO
Check the search options (delay, free & hold).
The SO command is used to check the current setting of search parameters.
Use the command SO[ï]
The response will be SO0 = DELAY MODE ON
SO1 = FREE MODE ON
SO2 = HOLD MODE ON
Related commands SA SB SD SP SQ BS BQ
SP
Free search mode On / Off.
The SP command is used to review and set the parameters of free search mode
including timing.
To review the current parameters use the format SP[ï]
The response will be SPnn where
nn = 01 ~ 99 seconds free search time
nn = 00 free search OFF
For example SP15 would represent free search ON and timing is 15 seconds.
To change the current setting of free search mode use the format SPnn[ï]
where
nn = 01 ~ 99 seconds free search time
nn = 00 free search OFF
For example SP52[ï] would switch free search mode ON with a timing of 52
seconds.
Related commands SA SB SD SO SQ BS BQ
- 40 -
Page 41

SQ : SR
SQ
Check the search options (level & audio).
The SO command is used to check the current setting of search parameters.
Use the command SQ[ï]
The response will be SQ0 = Not engaged
SQ1 = Level search ON
SQ2 = Audio search ON
SQ3 = BOTH level & audio search ON
Related commands SA SB SD SO SP BS BQ
SR
Recall search data.
The SR command is used to recall search data for a chosen bank.
To recall the search data from the currently selected search bank use the format
SR[ï]
To recall the search data from a specific bank use the format SRx[ï]
where
x = search bank A ~ J or a ~ j.
A typical response may be:
SRC_SL0118500000_SU0135900000_ST025000_AU1_MD2_AT0_TTAIR.VHF
This is a data breakdown of:
Search bank C
Lower (start) frequency 118.50 MHz
Upper (end) frequency 135.90 MHz
Automode ON (this means that mode & step are ignored so
do not have to be specified as will be taken
from the receivers preprogrammed data)
Attenuator OFF
Text AIR.VHF
Related command SE
- 41 -
Page 42

SS : ST
SS
Engage search mode - start search.
The SS command is used to start the search process from either the current or
specified search bank.
To start searching from the current search bank use the format SS[ï]
To start searching from a specified search bank use the format SSx[ï]
where
x = search bank A ~ J or a ~ j.
Related commands DD MR MS RX SG VF é ê
ST
Tuning step size.
The ST command is used in conjunction with several other commands to set the
tuning or search increment. Multiple command entry is possible with AT, AU, MD,
RF, ST, VA & VB (with a space separating each command).
The format of the command is ST nnnnm0[ï] (Hz)
or
ST nnn.nm[ï] (kHz)
m = "0" or "5" (tens of Hz position), "0" must always be zero - any other entry will
be ignored. Any step size is possible in multiples of 50 Hz up to 999.995 kHz.
Note: When step size is entered AUTOMODE is automatically switched OFF.
To view the current setting of step size use the command ST[ï]
A typical response may be ST020000 which would be 20 kHz.
A typical multiple command may be AU0_MD3_RF145.2_ST010.[ï]
Related commands AU MD MX RF SE VA VB
- 42 -
Page 43

SU : TI
SU
Set the upper frequency of a search bank.
This command cannot be used on its' own but must be used in conjunction with
the SE command, please refer to the section on SE.
SU Upper frequency limit nnnnnnnnm0 (Hz)
or
nnnn.nnnnm (MHz)
m = "0" or "5" (tens of Hz position), "0" must always be "0" any other entry will be
ignored. Input below 1.6 MHz is displayed in kHz.
Related commands SE SL TT
TI
Priority interval time.
The TI command is used to set the priority interval time (how long to wait between
checking the priority channel for activity).
To check the current setting use the format TI[ï]
The response will be TInn where nn = 01 ~ 19 seconds.
A typical response may look like TI13
To change the timing use the format TInn[ï] where nn = 01 ~ 19 seconds.
- 43 -
Page 44

TM : TT
TM
Write text in conjunction with memory channel.
The TM command cannot be used on its' own but is used in conjunction with the
MX command to write text comments into a memory channel. Up to 7 ASCII
characters or characters from the table (below) may be entered. Blank table
entries [ ] represent a blank space. Please refer to the MX command for full
details of use.
TMxxxxxxx Text write where xxxxxxx may be up to 7
characters in ASCII or character mode.
Entry is completed with a [ï]
Related commands MR MX
TT
Write text in conjunction with a search bank.
The TT command cannot be used on its' own but is used in conjunction with the
SE command to write text comments into a search bank. Up to 7 ASCII
- 44 -
Page 45

TT : VA : VB
characters or characters from the table (see TM) may be entered. Blank table
entries [ ] represent a blank space.
TTxxxxxxx Text write where xxxxxxx may be up to 7
characters in ASCII or character mode. Entry is
completed with a [ï]
Related commands SE SR
VA VB
Check and change the receive frequency of VFOA or VFOB.
The VB and VB commands may be used to read the current frequency from
VFOA or VFOB and to write a new receive frequency. Both commands are used
in the same manner , VA addressing VFOA and VB addressing VFOB.
To read the current receive frequency of VFO A use the format VA[ï]
A typical response may be:
VA0001134000_ST009000_AU1_MD2_AT0
2VFO MODE VFO A, receive frequency 1.134 MHz, channel step size 9 kHz,
automode ON, receive mode AM, attenuator OFF.
To read the current receive frequency of VFO B use the format VB[ï]
A typical response may be:
VB0145040000_ST020000_AU1_MD1_AT0
To write a new frequency to VFO A and switch to 2VFO mode use the format:
VAnnnnnnnnm0 (Hz)
VA nnnn.nnnnm (MHz)
where m = "0" or "5" in the 10Hz position. "0" in the Hz position is always "0", any
other value will be ignored. Frequencies below 1.6 MHz are displayed as kHz.
A typical input to write a new frequency of 433.250 MHz to VFO B would be:
VB433.25[ï]
Multiple command entry is possible (using AT, AU, MD, RF, ST) with a space
separating each command: AU0_MD3_VB433.2[ï]
Related commands AT AU MD RF ST VA VB
- 45 -
Page 46

VF : XA : XB
VF
Switch to 2VFO mode.
The VF command is used to place the receiver into 2VFO mode. The data from
the current VFO (A or B) is automatically reported.
Use the command VF[ï]
A typical response may be: VA0433040000_ST0200000_AU1_MD1_AT0
The date representing 2VFO mode, VFOA active, receive frequency 433.04 MHz,
20 kHz channel step, Automode ON, receive mode NFM, attenuator ON.
Another response may be (for VFOB):
Related commands DD MR MG MS SM SG SS VA VB
VB0145080000_ST020000_AU1_MD1_AT0
XA
Audio scan ON / OFF.
The XA command is used to check the current setting of audio scan mode and
change the status as required.
To check the current status use the format XA[ï]
The response will be XA0 = audio scan OFF
XA1 = audio scan ON
To change the status of audio scan ON / OFF use the format:
XAn[ï] where n = 0 audio scan OFF
n = 1 audio scan ON
Related commands BM ML XB XD XM XO XP XQ
XB
Level scan ON / OFF.
The XB command is used to check the current setting of level scan mode and
change the status as required.
- 46 -
Page 47

To check the current status use the format XB[ï]
The response will be XB0 = level scan OFF
XB1 ~ XB7 = level scan ON
To change the status of level scan ON / OFF use the format:
XBn[ï] where n = 0 level scan OFF
n = 1 ~ 7 level scan ON
for example SB3 means level scan set to
threshold 3
Related commands BM ML XA XD XM XO XP XQ
XD
XB : XD
Scan delay time.
The XD command is used to check and set the scan delay time.
To check the current setting use the format: XD[ï]
The response will be XDnn where nn = time incremented in tenths of seconds
(100mS), the value of nn is between 00 ~ 9.9 When nn = 00 scan delay is OFF.
For example a response of XD5.2 would indicate scan delay time is set to 5.2
seconds while a response of XD00 indicates that scan delay is OFF.
To change the setting of scan delay time use the format:
XDnn[ï] where nn = 00 ~ 9.9
The value being incremented in tenths of seconds (100mS) and 00 being scan
delay OFF.
Related commands BM ML XA XB XM XO XP XQ
- 47 -
Page 48

XM : XO
XM
Mode scan.
The XM command is used to check and set the options for MODE SCAN.
To check the current setting use the format: XM[ï]
The response will be: XM0 = WFM
XM1 = NFM
XM2 = A M
XM3 = USB
XM4 = LSB
XM5 = C W
XMF = ALL MODE (effectively scan mode off)
To change the setting of mode scan use the format: XMn[ï]
where:
n = 0 WFM
n = 1 NFM
n = 2 A M
n = 3 USB
n = 4 LSB
n = 5 C W
n = F OFF - ALL MODES will be scanned.
Related commands BM ML XA XB XD XO XP XQ
XO
Free scan ON / OFF.
The XO command is used to check the current setting of free scan mode.
To check the current status use the format XA[ï]
The response will be XO0 = free scan OFF
XO1 = free scan ON
Related commands BM ML XA XB XD XM XO XP XQ
- 48 -
Page 49

XP : XQ
XP
Change free scan time in scan mode.
The XP command is used to review and change the setting of free scan time when
in scan mode.
To review the current setting use the command XP[ï]
The response will be in the format:
XPnn where nn = 01 ~ 99 free scan time in seconds
nn = 00 free scan mode OFF
Examples are: XP52 = free scan time of 52 seconds
XP00 = free scan mode OFF
To change the current setting of free scan mode use the format XPnn[ï]
where: nn = 01 ~ 99 free scan time in seconds
nn = 00 free scan mode OFF
For example, an input of XP15[ï] would activate free scan mode with a delay
time of 15 seconds.
Related commands BM ML XA XB XD XM XO XQ
XQ
Check the scan options (level & audio).
The XQ command is used to check the current setting of scan parameters.
Use the command XQ[ï]
The response will be XQ0 = Not engaged
XQ1 = Level scan ON
XQ2 = Audio scan ON
SQ3 = BOTH level & audio scan ON
Related commands BM ML XA XB XD XM XO XP
- 49 -
Page 50

é ê
é ê
UP / DOWN arrows.
The é ê arrow commands have largely the same effect as the arrow keys
on the front panel of the AR8000 receiver. In VFO mode the frequency is
incremented upward or downward, in memory recall mode the next channel is
selected and in search/scan modes the direction of search/scan may be reversed.
The value for é is "h1E" (HEX DECIMAL) and the command may be sent
using the format é[ï]
The value for ê is "h1F" (HEX DECIMAL) and the command may be sent
using the format ê[ï]
Related commands DD MG MS SM SS VA VB VF
- 50 -
Page 51

Optional software
* IBM PC compatible specialist
software for the AR8000-
CU8232 & Microsoft WINDOWS
will be available soon
- 51 -
Page 52

TM
AOR, LTD
2-4-6 Misuji, Taito-ku, Tokyo 111, Japan
TEL (03) 3865 1681
© Copyright AOR, LTD 1994 9409
- 52 -
 Loading...
Loading...